|
evgeniy_m Пользователь Сообщений: 109 |
#1 01.09.2014 23:36:22 Всем доброе время суток! Есть макрос, после обработки которого вылетает окно с сохранением (имя файла берется автоматически с ячейки «А31»
НО.. |
||
|
k61 Пользователь Сообщений: 2441 |
#2 02.09.2014 02:26:10 …
|
||
|
evgeniy_m Пользователь Сообщений: 109 |
|
|
socha Пользователь Сообщений: 13 |
Здравствуйте. |
|
Sanja Пользователь Сообщений: 14838 |
#5 05.10.2014 17:23:12 socha пишет:
Так это-ж ещё проще
Согласие есть продукт при полном непротивлении сторон. |
||||
|
socha Пользователь Сообщений: 13 |
В оригинале у меня место сохранения файла C:РаботаПродажаКлиентыА1″Папка клиента, имя которой совпадает с ячейкой А1. |
|
Sanja Пользователь Сообщений: 14838 |
#7 05.10.2014 17:37:42
а имя файла где указываете? Тоже в это-же ячейке (см пост #4)? Согласие есть продукт при полном непротивлении сторон. |
||
|
socha Пользователь Сообщений: 13 |
#8 05.10.2014 17:46:10 Вот по такому примеру нужно сделать макрос. Подставил свои параметры — все работает, только место сохранения, тоже должно быть переменное по указаной ячейке
Спасибо |
||
|
Sanja Пользователь Сообщений: 14838 |
#9 05.10.2014 17:51:45 Вы же практически все сделали
Согласие есть продукт при полном непротивлении сторон. |
||
|
socha Пользователь Сообщений: 13 |
Спасибо, все заработало. Просто не мог разобраться с синтаксисом |
|
vlasssov71 Пользователь Сообщений: 13 |
#11 05.10.2014 19:52:33 Еще символы надо убрать, которые в имени файла нежелательны
|
||
|
athe Пользователь Сообщений: 15 |
#12 19.06.2015 10:38:54 Добрый день.
К сожалению есть одно неудобство, данный код делает копию файла с указанным в ячейке названием и переходит в эту копию, закрывая изначальный файл. Может есть у кого код, который делал бы копию файла, не открывая его и не закрывал бы первичный файл? Изменено: athe — 19.06.2015 10:41:32 |
||
|
The_Prist Пользователь Сообщений: 14182 Профессиональная разработка приложений для MS Office |
#13 19.06.2015 10:49:13
Даже самый простой вопрос можно превратить в огромную проблему. Достаточно не уметь формулировать вопросы… |
||
|
athe Пользователь Сообщений: 15 |
The_Prist |
|
RNEtidi Пользователь Сообщений: 12 |
#15 12.04.2016 15:58:04
в цикле For..Next выдает ошибку: Имя файла NewName изменяется в цикле:
В чем причина может быть? (DoEvents — не помогает). Изменено: RNEtidi — 12.04.2016 16:37:05 |
||||||||
|
Юрий М Модератор Сообщений: 60575 Контакты см. в профиле |
RNEtidi, зачем цитируете всё подряд? Даже подпись. На чём хотели сделать акцент? Кнопка цитирования не для ответа. |
|
Hugo Пользователь Сообщений: 23251 |
#17 12.04.2016 16:36:25
— да хоть в том, что уже выше озвучивалось — в недопустимом имени файла. |
||
|
RNEtidi Пользователь Сообщений: 12 |
Hugo
, в моем случае в чем недопустимость имени файла? |
|
Юрий М Модератор Сообщений: 60575 Контакты см. в профиле |
Никто не видит, что у Вас в ячейке, из которой берётся имя файла )) Чему равна переменная х? |
|
RNEtidi Пользователь Сообщений: 12 |
#20 12.04.2016 17:00:09
x — изменяемый циклом параметр |
||
|
Hugo Пользователь Сообщений: 23251 |
#21 12.04.2016 17:17:29
|
||
|
RNEtidi Пользователь Сообщений: 12 |
ну для начала x = 1. Потом x = 2. И так далее до n. К примеру n = 5, тогда x изменяется от 1 до 5. Цикл For..Next так работает. |
|
Hugo Пользователь Сообщений: 23251 |
Сорри, подслеповат вероятно… |
|
RNEtidi Пользователь Сообщений: 12 |
запись в каталог не запрещена, но ошибка все равно выскакивает. |
|
Фродо Пользователь Сообщений: 348 |
#25 12.04.2016 19:16:43
уникальность имени? у меня простая версия Экселя, в ней нет кнопки «Прочитать мысли и сгенерировать файл пример» |
||
|
RNEtidi Пользователь Сообщений: 12 |
#26 12.04.2016 19:18:37
|
||
|
Фродо Пользователь Сообщений: 348 |
#27 12.04.2016 19:23:15 для начало попробуйте все убрать.
у меня простая версия Экселя, в ней нет кнопки «Прочитать мысли и сгенерировать файл пример» |
||
|
RNEtidi Пользователь Сообщений: 12 |
в этом то вся и прелесть: вне цикла все хорошо сохраняет. а в теле цикла при попытке сохранить выскакивает вышеназванная ошибка и excel напрочь зависает. |
|
Фродо Пользователь Сообщений: 348 |
#29 12.04.2016 20:02:38
а так попробуйте файл пример сделайте у меня простая версия Экселя, в ней нет кнопки «Прочитать мысли и сгенерировать файл пример» |
||
|
RNEtidi Пользователь Сообщений: 12 |
#30 12.04.2016 21:49:14 для чего писать true после имени файла? Прикрепленные файлы
Изменено: RNEtidi — 12.04.2016 22:35:42 |
In this Article
- Save Workbook – VBA
- Save a Specified Workbook
- Save the Active Workbook
- VBA Coding Made Easy
- Save the Workbook Where the Code is Stored
- Save all Open Workbooks
- Save all open workbooks that were not opened ReadOnly
- Save a workbook defined by a variable
- Save a workbook defined by a string variable
- Save a workbook defined by the order it was opened.
- Save a workbook based on a cell value
- Save As – VBA
- SaveAs Syntax:
- Save As Syntax Examples:
- Workbook Save As – Same Directory
- Workbook Save As – New Directory
- Workbook Save As – New Directory, Specify File Extension
- Workbook Save As – New Directory, Specify File Extension – Alt Method
- Workbook Save As – Add Password to Open File
- Workbook Save As – Add Password for Write Privileges
- Workbook Save As – Read-Only Recommended
- Other Save As Examples
- Create Save As Dialog Box
- Create Save As Dialog Box with Default File Name Provided
- Create Save As Dialog Box with Default File Name Provided
- Create & Save New Workbook
- Disable Save Alerts
This VBA Tutorial covers how to save a file using the Save and Save As commands in VBA.
Save Workbook – VBA
The VBA Save command saves an Excel file similarly to clicking the Save icon or using the Save Shortcut (CTRL + S).
Save a Specified Workbook
To save a workbook, reference the workbook object and use the Save command.
Workbooks("savefile.xlsm").SaveSave the Active Workbook
Note: This is the current active workbook from with in the VBA code, which is different from ThisWorkbook which contains the running code.
ActiveWorkbook.SaveVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro – A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
Save the Workbook Where the Code is Stored
ThisWorkbook.saveSave all Open Workbooks
This will loop through all open workbooks, saving each one.
Dim wb as workbook
For Each wb In Application.Workbooks
wb.Save
Next wbSave all open workbooks that were not opened ReadOnly
Note: opening a workbook in ReadOnly mode prevents the file from being saved.
To save the file you will need to use Save As and save the file with a different name.
Dim wb as workbook
For Each wb In Application.Workbooks
If not wb.ReadOnly then
wb.Save
End if
Next wbSave a workbook defined by a variable
This will save a workbook that was assigned to a workbook object variable.
Dim wb as workbook
set wb = workbooks("savefile.xlsm")
wb.saveSave a workbook defined by a string variable
This will save a workbook that’s name was saved to a string variable.
Dim wbstring as string
wbstring = "savefile.xlsm"
workbooks(wbstring).saveSave a workbook defined by the order it was opened.
Note: The first workbook opened would have 1, the second 2, etc.
workbooks(1).saveVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Save a workbook based on a cell value
This will save a workbook that’s name is found in a cell value.
Dim wbstring as string
wbstring = activeworkbook.sheets("sheet1").range("wb_save").value
workbooks(wbstring).saveSave As – VBA
The VBA Save As command saves an Excel file as a new file, similar to clicking the Save As icon or using the Save As Shortcut (Alt > F > A).
Above, we identified all the ways to specify which workbook to save. You can use those exact same methods to identify workbooks when using Save As.
Save As behaves similarly to Save, except you also need to specify the name of the new file.
In fact, Save As has many potential variables to define:
SaveAs Syntax:
workbook object .SaveAs(FileName, FileFormat, Password, WriteResPassword, _
ReadOnlyRecommended, CreateBackup, AccessMode, ConflictResolution, _
AddToMru,TextCodepage, TextVisualLayout, Local)A full description of all of the SaveAs arguments is included below. For now we will focus on the most common examples.
Note: These arguments can be entered as string with parenthesis or as defined variables.
Save As Syntax Examples:
Workbook Save As – Same Directory
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "new"or
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs "new"or
Dim wbstring as string
wbstring = "new"
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= wbstringAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Workbook Save As – New Directory
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "C:new"or
Dim wbstring as string
wbstring = "C:new"
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= wbstring=Workbook Save As – New Directory, Specify File Extension
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "C:new.xlsx"or
Dim wbstring as string
wbstring = "C:new.xlsx"
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= wbstringWorkbook Save As – New Directory, Specify File Extension – Alt Method
You can also specify the file format in it’s own argument.
.xlsx = 51 '(52 for Mac)
.xlsm = 52 '(53 for Mac)
.xlsb = 50 '(51 for Mac)
.xls = 56 '(57 for Mac)ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "C:new", FileFormat:= 51Workbook Save As – Add Password to Open File
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "C:new.xlsx", Password:= "password"AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Workbook Save As – Add Password for Write Privileges
If correct password is not supplied then workbook opens as Read-Only
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "C:new.xlsx", WriteRes:= "password"Workbook Save As – Read-Only Recommended
TRUE to display a message box, recommending that the file is opened read-only.
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:= "C:new.xlsx", ReadOnlyRecommended:= TRUEOther Save As Examples
Create Save As Dialog Box
This Generates the Save As Dialog Box, prompting the user to Save the file.
Keep in mind that this simple code may not be appropriate in all cases.
Application.GetSaveAsFilenameAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Create Save As Dialog Box with Default File Name Provided
Application.GetSaveAsFilename InitialFilename:="test.xlsx"Create Save As Dialog Box with Default File Name Provided
Application.GetSaveAsFilename InitialFilename:="test.xlsx"Create & Save New Workbook
This will create a new workbook and immediately save it.
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Add
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
wb.SaveAs Filename:=”c:Test1.xlsx”
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
Disable Save Alerts
As you work with saving in VBA, you may come across various Save Warnings or Prompts. To disable warnings, add this line of code:
Application.DisplayAlerts=Falseand to re-able alerts:
Application.DisplayAlerts=TrueSave Workbook Using Excel VBA to Specific Folder
VBA save as Workbook Excel Macro code helps Save file to a specific Folder, its is a common task in automation process. Once you are done with actual calculations or task, at end of the procedure we generally call a procedure to export or Save the Output File to a Specific Folder or common drive. Or in other case you may not have the permissions to Save the File in a location, so that you can use SaveAs Option to store the revised or updated file.
VBA save as Workbook – Solution(s):
You can use SaveAs method to Save the File to a specific location. You can Save with the same File Name and Location. Or you can use different File Name and Location to Save the File. You can also set to an object and Save the File.
In other method, you use Save Dialog Box. So that user can choose a specific folder to save the Excel File.
Save Workbook to Specific Folder – Example Cases:
- Save Workbook to Specific Folder
- Set to an Object and Save it
- Save Workbook to Specific Folder using Save Dialog Box
- Save Workbook in the same location of the Macro (this) Workbook
- Save the Workbook
- Download: Example Macro Workbook
Save a Workbook to a Specific Folder
The following example show you how to save an Excel Workbook in Specific folder using SaveAs method:
Sub ExampleToSaveWorkbook() Workbooks.Add 'Saving the Workbook ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs "C:WorkbookName.xls" 'OR 'ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:="C:WorkbookName1.xls" End Sub
Set to an Object and Save it
Set to an Object and Save it, so that it is easy to refer to your workbook to do further tasks. If you are dealing with more than one workbook, you will need this method to access a specific Excel Workbook.
Sub ExampleToSaveWorkbookSet() Dim wkb As Workbook 'Adding New Workbook Set wkb = Workbooks.Add 'Saving the Workbook wkb.SaveAs "C:WorkbookName.xls" 'OR 'wkb.SaveAs Filename:="C:WorkbookName1.xls" End Sub
Save Workbook to Specific Folder using Save Dialog Box
You can Save the Workbook to Specific Folder by showing the Save Dialog Box to user. So that user can choose desired location to save the file.
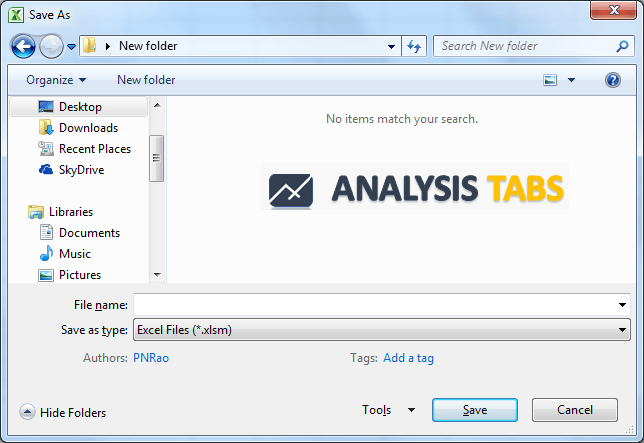
Sub sbSaveExcelDialog()
Dim IntialName As String
Dim sFileSaveName As Variant
IntialName = "Sample Output"
sFileSaveName = Application.GetSaveAsFilename(InitialFileName:=InitialName, fileFilter:="Excel Files (*.xlsm), *.xlsm")
If sFileSaveName <> False Then
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs sFileSaveName
End If
End Sub
Save Workbook in the same location of the Macro (this) Workbook
You can save the workbook in the same directory of the macro workbook using ThisWorkbook.Path property.
Sub ExampleToSaveWithSamePathDifferentName() Dim sFilename As String sFilename = "WorkbookName.xls" 'You can give a nem to save Workbooks.Add 'Saving the Workbook ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs ThisWorkbook.Path & "" & sFilename End Sub
Save the Workbook
You can simply save the file without changing its file name or path name using Save method.
Sub ExampleToSaveWithSameNameandPath() 'Saving the Workbook ActiveWorkbook.Save End Sub
Example Files
You can download the example file and explore it.
ANALYSISTABS – Save Workbook
Overwrite an Existing Workbook using VBA
While Saving the existing workbook or a new excel file with existing name, Excel will prompt a warning message. It will interrupt the procedure and ask user to press yes or no for overwriting a file.
Overwrite an Existing Workbook using VBA – Solution:
You can avoid this by disabling the alerts temporarily and save the workbook with the same name by setting the Application.DisplayAlerts=False property. Once you are done with the task, you should enable the application alerts by setting the property TRUE.
Overwrite an Existing Workbook using VBA – An Example
The following example will show you, how to overwrite a file by disabling the application alerts.
Code:
sub procedure to over write an excel file Sub ExampleToOverWriteExistingWorkbook() 'Declaration: Declaring the variable Dim wkb As Workbook 'Adding New Workbook using Workbook.Add method and setting to wkb Object Set wkb = Workbooks.Add 'Saving the Workbook 'Desable the application alerts before svaing the file Application.DisplayAlerts = False 'Now save the file wkb.SaveAs "C:WorkbookName.xls" ' change to existng file name 'OR 'wkb.SaveAs Filename:="C:WorkbookName1.xls"</span> 'Eanbling the Application Aletrts after saving the file Application.DisplayAlerts = True End Sub
Instructions:
- Open an excel workbook
- Press Alt+F11 to open VBA Editor
- Insert a Module for Insert Menu
- Copy the above code and Paste in the code window
- Save the file as macro enabled workbook
- Press F5 to execute itit
A Powerful & Multi-purpose Templates for project management. Now seamlessly manage your projects, tasks, meetings, presentations, teams, customers, stakeholders and time. This page describes all the amazing new features and options that come with our premium templates.
Save Up to 85% LIMITED TIME OFFER

All-in-One Pack
120+ Project Management Templates
Essential Pack
50+ Project Management Templates
Excel Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
PowerPoint Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
MS Word Pack
25+ Word PM Templates
Ultimate Project Management Template
Ultimate Resource Management Template
Project Portfolio Management Templates
Related Posts
- VBA save as Workbook – Solution(s):
- Save Workbook to Specific Folder – Example Cases:
- Overwrite an Existing Workbook using VBA
- Overwrite an Existing Workbook using VBA – Solution:
VBA Reference
Effortlessly
Manage Your Projects
120+ Project Management Templates
Seamlessly manage your projects with our powerful & multi-purpose templates for project management.
120+ PM Templates Includes:
28 Comments
-
Katharina
February 3, 2014 at 9:22 AM — ReplyYour means of describing all in this paragraph is really good,
every one be able to easily understand it, Thanks a
lot. -
PNRao
February 3, 2014 at 9:54 AM — Reply -
Rob
October 15, 2014 at 5:30 AM — ReplyHaving trouble using the below code. Any ideas?
SaveFile = Application.GetSaveAsFilename( _
FileFilter:=”Excel Files (*.xlsx), *.xlsx”)
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs SaveFileAfter the file is saved it appears as an Excel file in the indicated location, but when you try to open it a dialogue box says: “Excel cannot open the file because the file format or file extension is not valid. Verify that the file has not been corrupted and that the file extension matches the format of the file.”
-
PNRao
October 18, 2014 at 1:57 PM — ReplyHi Rob,
I found no issues in your code, you may be using Excel 2003. If your Excel is not 2007 or higher, you can change the “Excel Files (*.xlsx), *.xlsx” as “Excel Files (*.xls), *.xls”i.e; xls, instead of xlsx
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Hi. This is great help thanks! But I am trying to combine two codes but I cannot do it! I would like the macro to save the workbook as a file name taken from a cell and also save in in a certain folder location.! Please can you help?!!
-
PNRao
November 29, 2014 at 7:44 PM — ReplyHi Jason,
Assuming you have the Folder path at Range A1 of sheet1, and File name at Range A2:wkb.SaveAs Filename:=Sheets(“Sheet1”).Range(“A1″) &” &Sheets(“Sheet1”).Range(“A2″) &”.xlsx”
Hope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
Chris
January 7, 2015 at 3:02 AM — ReplyHi,
Can I use a macro to save the excel file in a specific location based off of a specific cell within the document? Also, Could I have the macro change the name of the document based off of a different cell within the same document? -
PNRao
January 12, 2015 at 9:38 PM — ReplyHi Chris,
Yes, you can use SaveAs method of workbook to save the file with different name. Assuming you have the file name in the Cell A1.
The below code will save the active workbook in the same path with name specified at A1.
Dim strFilename As String strFilename = ActiveWorkbook.Path & " & Range("A1") & ".xlsm" ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=strFilename, FileFormat:=52The below code will save the active workbook in the given path with file name mentioned with the full path at A1.
Dim strFilename As String strFilename =Range("A1") & ".xlsm" ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=strFilename, FileFormat:=52Thanks-PNRao!
-
mo
March 25, 2015 at 6:04 PM — Replyhi,
i am trying to use this code but having some issues,
i am using excel 2010 but the extension .xlsm nor .xlsx is working
this code:
”
If sFileSaveName False Then
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs sFileSaveName
End If
”is saving a copy of the file but closes the original document to reopen the saved copy.
please help
-
PNRao
April 1, 2015 at 7:06 PM — ReplyHi,
SaveAs will save the file with the changes in the specified location. It will not neither close the old file nor open new file.
when you open the file, it will always stores in the temporary memory, when you Save the file, this will just save the changes to the existing file – SaveAs will save the file in the specified location.Hope this clarifies your query.
Thanks-PNRao! -
Saputro
July 18, 2015 at 6:19 PM — ReplyHi
How to keep text format when save as to *.csv or at least to show “keep using that format” question dialog with VBAThanks
-
November 27, 2015 at 4:56 PM — Replysave file as .xls…. for that first go to the “save as type”.. then choose “.xls” extension file… ur file automatically will b saved as “filename.xls”…
-
DLoughry
December 17, 2015 at 8:01 PM — ReplyWhat code do I use so that the file saves to a folder in a users My Documents. Now, the folder might not exist the first time they are saving the file, so I would need to incorporate that as well into the code.
Example path: C:UsersDocumentsWorkbook1.xlsx
Thanks in advance!
-
DLoughry
December 17, 2015 at 8:02 PM — ReplyWhat code do I use so that the file saves to a folder in a users My Documents. Now, the folder might not exist the first time they are saving the file, so I would need to incorporate that as well into the code.
Example path: C:UsersDocumentsWorkbook1.xlsx
Thanks in advance
-
DLoughry
December 17, 2015 at 8:05 PM — ReplyThe example path did not show correctly in my initial comment. Between Users and Documents it should show ” and between Documents and the file name it should show “.
C:Users”Documents”Workbook1.xlsx
-
DLoughry
December 17, 2015 at 8:07 PM — ReplyArgh…Ok. Where the quotes are should be username and New Folder respectively.
Sorry for all the extra comments.
-
Guz
January 2, 2016 at 2:39 AM — ReplyGreat, it really helped me!!
-
T.Lajos
April 12, 2016 at 11:09 PM — ReplyHi,
I tried several code to save my excxel file. All attemts including your “Save Workbook in the same location of the Macro (this) Workbook” results the same: I get a new but empty file (with your code workbookname.xls) in the same directory where workbook using ThisWorkbook.There is data in cells of original workbook but the saved one is empty…(excel 2007)..
Could you Have please some idea what couses this curious phenomena? -
MK
July 27, 2016 at 4:26 PM — ReplyI have the same problem. Maybe sone ideas?
-
Patrick Mahoney
August 26, 2016 at 2:41 AM — ReplyHi to all,
I am using Excel 2011 for Mac. In a macro file (.xlsm) triggered from my database, with an AutoOpen macro, I import data from my database, format the spreadsheet and then save it as a .xlsx file. My problem is that when the macro does a SaveAs, there is a dialog box telling me that the macros will be removed in the .xlsx file and then required that I click on the save button. How can I bypass that dialog and finish the save process without user intervention?My code:
ThisFile = Range(“B2”).Value
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=ThisFile, FileFormat:=xlOpenXMLWorkbook, CreateBackup:=True
Range(“A1”).Select
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
Application.Quit -
Sub
December 29, 2016 at 7:20 PM — ReplyI am passing a password through the variable “f” and trying to protect the workbook but it is not working.
Can you tell me how?
ActiveWorkbook.Protect Password:=f, Structure:=True, Windows:=False -
Shane
June 16, 2017 at 8:21 PM — ReplyHi All,
I am trying to add in code to save the below to a shared drive with a date in the name of the file ie “abc 16.06.2017” Would also love to send a print screen in the body of the mail too – can anyone help with that?
Thanks a mill
Sub Mail_ControlSheet()
Dim FileExtStr As String
Dim FileFormatNum As Long
Dim Sourcewb As Workbook
Dim Destwb As Workbook
Dim TempFilePath As String
Dim TempFileName As String
Dim OutApp As Object
Dim OutMail As ObjectWith Application
.ScreenUpdating = False
.EnableEvents = False
End WithSet Sourcewb = ActiveWorkbook
ActiveSheet.Copy
Set Destwb = ActiveWorkbookWith Destwb
Select Case Sourcewb.FileFormat
Case 51: FileExtStr = “.xlsx”: FileFormatNum = 51End Select
End With
Set OutApp = CreateObject(“Outlook.Application”)
Set OutMail = OutApp.CreateItem(0)With Destwb
With OutMail
.to = “xx@abc.com”
.CC = ”
.BCC = ”
.Subject = “XX ” & Format(Date, “dd-mm-yyyy”)
.Body = “Hi All,” & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & “XX.” & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & “Many Thanks” & vbCrLf & “Shane”
.Attachments.Add “hbeu.adroot.hsbcgb001Redir GB USERS LAPTOP43960692DocumentsShanehello.xlsm.”
.Display
End With
On Error GoTo 0
.Close savechanges:=False
End WithEnd Sub
-
George
September 9, 2017 at 1:52 AM — ReplyI am trying to save file RENT.xls in different folders:
My Documents/Jan 17/ RENT.xls
My Documents/Feb/RENT.XLS
My Documents/Mar/RENT.xls
etc
etcCan someone help please?
-
PNRao
September 12, 2017 at 11:27 PM — ReplyHere is the Macro to save the file into required folders using VBA.
Sub sbSaveFileInToDifferentFolders() Set wb = Workbooks.Open("C:TempRENT.xls") MyFoldersArray = Array( _ "C:TempFolderA", _ "C:TempFolderB", _ "C:TempFolderC" _ ) For iCntr = 0 To UBound(MyFoldersArray, 1) wb.SaveAs MyFoldersArray(iCntr) & " & wb.Name Next End SubThanks!
-
hi,
After saving the workbook in a specific folder as shown below
Sub ExampleToSaveWorkbook()Workbooks. Add
‘Saving the Workbook
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs “G:LookupExercise.xlsx”
‘OR
‘ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=”G:LookupExercise.xlsx”End Sub
I am not able to see the content in the workbook why?. I am a little bit confused in the context can you explain please.
Thanks -
Aaron
February 14, 2019 at 11:48 PM — ReplyI need help with the following. I need to save a copy of a workbook with the File Name and the Date (A Save at that moment), and then open that saved Copy. Currently the below code will Save the file and rename the document correctly (except it will do .xlsm.xslm and I cant fix this…) but when you open the document, there is no information. Its completely blank…. so its not a save as, its just opening a new file and naming based on my file.
Can someone help me correct this code so that it saves all of my data, renames the file and opens it up once saved?
Sub snwb()
Dim thisWb As Workbook, d As IntegerSet thisWb = ActiveWorkbook
Workbooks.Add
d = InStrRev(thisWb.FullName, “.”)
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs filename:=Left(thisWb.FullName, d – 1) & Format(Now, ” yyyy.mm.dd”) & Mid(thisWb.FullName, d) & “.xlsm”, FileFormat:=52ActiveWorkbook.Close savechanges:=False
End Sub -
Aaron
February 15, 2019 at 4:36 AM — ReplyI have an updated code that seems to be working correct, however, I need this to work with Office 365. I need the file to save back to the same location on 365. Any ideas?
Sub SaveToRelativePath()
Dim relativePath As String
relativePath = ThisWorkbook.path & ” & ActiveWorkbook.Name
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs filename:=ThisWorkbook.Name & ” FINAL BID” & “.xlsm”, FileFormat:=xlOpenXMLWorkbookMacroEnabled
End Sub -
Sivaprakasam
October 28, 2019 at 12:57 PM — ReplyHi can u provide the below u r VBA including view list (file size, created date and modified date), due to i have confusing the new file or old file.
Save a Workbook to a Specific Folder
Sub ExampleToSaveWorkbook()
Workbooks.Add
‘Saving the Workbook
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs “C:WorkbookName.xls”
‘OR
‘ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=”C:WorkbookName1.xls”End Sub
Effectively Manage Your
Projects and Resources
ANALYSISTABS.COM provides free and premium project management tools, templates and dashboards for effectively managing the projects and analyzing the data.
We’re a crew of professionals expertise in Excel VBA, Business Analysis, Project Management. We’re Sharing our map to Project success with innovative tools, templates, tutorials and tips.
Project Management
Excel VBA
Download Free Excel 2007, 2010, 2013 Add-in for Creating Innovative Dashboards, Tools for Data Mining, Analysis, Visualization. Learn VBA for MS Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Access, Outlook to develop applications for retail, insurance, banking, finance, telecom, healthcare domains.
Page load link

3 Realtime VBA Projects
with Source Code!
Go to Top
I have created a sheet in vba Excel. I would like to save it the current directory, but not in absolute path, then, when this is executed somewhere else, there won’t be problem.
Can somebody help ?
0m3r
12.2k15 gold badges33 silver badges70 bronze badges
asked Dec 21, 2010 at 9:02
I am not clear exactly what your situation requires but the following may get you started. The key here is using ThisWorkbook.Path to get a relative file path:
Sub SaveToRelativePath()
Dim relativePath As String
relativePath = ThisWorkbook.Path & Application.PathSeparator & ActiveWorkbook.Name
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=relativePath
End Sub
answered Dec 21, 2010 at 11:53
Alex PAlex P
12.2k5 gold badges51 silver badges69 bronze badges
1
VBA has a CurDir keyword that will return the «current directory» as stored in Excel. I’m not sure all the things that affect the current directory, but definitely opening or saving a workbook will change it.
MyWorkbook.SaveAs CurDir & Application.PathSeparator & "MySavedWorkbook.xls"
This assumes that the sheet you want to save has never been saved and you want to define the file name in code.
answered Dec 21, 2010 at 15:24
Dick KusleikaDick Kusleika
32.5k4 gold badges51 silver badges73 bronze badges
2
If the Path is omitted the file will be saved automaticaly in the current directory.
Try something like this:
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs "Filename.xslx"
0m3r
12.2k15 gold badges33 silver badges70 bronze badges
answered Jun 10, 2015 at 14:26
0
Taking this one step further, to save a file to a relative directory, you can use the replace function. Say you have your workbook saved in: c:propertycaliforniasacramentoworkbook.xlsx, use this to move the property to berkley:
workBookPath = Replace(ActiveWorkBook.path, "sacramento", "berkley")
myWorkbook.SaveAs(workBookPath & "" & "newFileName.xlsx"
Only works if your file structure contains one instance of the text used to replace. YMMV.
answered Jul 18, 2014 at 15:36
0
Сохранение файла рабочей книги Excel, существующего или нового, с помощью кода VBA. Методы Save и SaveAs объекта Workbook, параметр SaveChanges метода Close.
Сохранение существующего файла
Сохранить существующий открытый файл рабочей книги Excel из кода VBA можно несколькими способами. В примерах используется выражение ActiveWorkbook, которое может быть заменено на ThisWorkbook, Workbooks(«ИмяКниги.xlsx»), Workbooks(myFile.Name), где myFile — объектная переменная с присвоенной ссылкой на рабочую книгу Excel.
Простое сохранение файла после внесенных кодом VBA Excel изменений:
Сохранение файла под другим именем (исходная рабочая книга будет автоматически закрыта без сохранения внесенных изменений):
|
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=«C:ТестоваяНоваяКнига.xlsx» |
Сохранить файл рабочей книги можно перед закрытием, используя параметр SaveChanges метода Close со значением True:
|
ActiveWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=True |
Чтобы закрыть файл без сохранения, используйте параметр SaveChanges метода Close со значением False:
|
ActiveWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=False |
Сохранение файла под другим именем при закрытии рабочей книги:
|
ActiveWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=True, Filename:=«C:ТестоваяНоваяКнига.xlsx» |
Если в примерах с методом Close параметр SaveChanges пропустить, будет открыто диалоговое окно с запросом о сохранении файла.
Новая книга сохраняется с указанием полного имени:
|
Workbooks.Add ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=«C:ТестоваяНоваяКнига.xlsx» |
После этого к новой книге можно обращаться по имени: Workbooks ("НоваяКнига.xlsx").
Если не указать полное имя для сохраняемого файла:
|
Workbooks.Add ActiveWorkbook.Save |
тогда новая книга будет сохранена с именем и в папке по умолчанию, например: Книга1.xlsx, Книга2.xlsx, Книга3.xlsx и т.д. в папке «Документы».


