Работа с внешними источниками данных
Материалы по работе с внешними источниками данных на примере Excel и SQL.
Рассмотрим способы передачи данных между Excel и внешней базой данной на SQL сервере с помощью ADO.
Задача первая. Подключаемся к внешней базе данных.
Для начала надо подключиться к внешней базе данных. Подключение возможно если на компьютере установлен драйвер. Список установленных драйверов для подключения к базам данных на компьютере под управлением Windows:
Панель управленияВсе элементы панели управленияАдминистрированиеИсточники данных (ODBC)
Проверить подключение к базе данных можно простым способом. Создаем пустой файл (например, «текстовый документ.txt»), затем изменяем имя и расширение на .udl (например, «connect.udl»). Двойной клик мышкой по новому файлу, далее приступаете к настройке и проверке подключения к базе данных. После того, как удалось настроить корректное подключение к базе данных, сохраняем файл «connect.udl». Открываем файл «connect.udl» обычным текстовым редактором (например, блокнотом), и видим в строке подключения все необходимые параметры. Про подключение к внешним базам данных можно посмотреть на ресурсе ConnectionStrings .
Теперь возвращаемся к нашему VBA для Excel. В редакторе VBA подключаем последнюю версию библиотеки:
Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects Library
Пример кода:
Sub TestConnection() Dim cn As ADODB.Connection Set cn = New ADODB.Connection cn.ConnectionString = "" 'Параметры строки подключения cn.Open 'Открываем подключение cn.Close 'Закрываем подключение Set cn = Nothing 'Стираем объект из памяти End Sub
Задача вторая. Загружаем данные из внешней базы данных на SQL сервере в Excel.
После того, как мы установили подключение к внешней базе данных можно приступать к чтению данных и выводу в Excel. Здесь потребуется знание языка запросов SQL. В результате выполнения SQL запроса к нам возвращается некая таблица с данными в объект RecordSet. Далее из объекта RecordSet можно выгружать данные непосредственно на лист или в сводную таблицу.
Пример кода простой процедуры:
Sub LoadData() Dim cn As ADODB.Connection Dim rst As ADODB.Recordset Set cn = New ADODB.Connection Set rst = New ADODB.Recordset cn.ConnectionString = "" 'Параметры строки подключения cn.Open rst.Open "SELECT TOP 10 * FROM <таблица>", cn 'SQL-запрос, подключение ActiveSheet.Range("A1").CopyFromRecordset rst 'Извлекаем данные на лист rst.Close cn.Close Set rst = Nothing Set cn = Nothing End Sub
Для удобства работы. Предлагаю создать собственный класс «tSQL» для работы с базой данных. У класса будет одно свойство:
Public ConnectionSring As String
Для чтения данных напишем метод SelectFrom с параметрами TableName и ws. TableName — это имя таблицы, откуда будем считывать данные и ws — лист Excel, куда будем записывать данные.
Public Sub SelectFrom(TableName As String, ws As Worksheet) Dim cn As ADODB.Connection Dim rst As ADODB.Recordset Dim SQLstring As String Dim i As Long Set cn = New ADODB.Connection Set rst = New ADODB.Recordset SQLstring = "SELECT * FROM " & TableName ws.Cells.Clear cn.ConnectionString = ConnectionSring cn.Open rst.Open SQLstring, cn For i = 1 To rst.Fields.Count ws.Cells(1, i) = rst.Fields(i - 1).Name Next i ws.Range("A2").CopyFromRecordset rst rst.Close cn.Close Set rst = Nothing Set cn = Nothing SQLstring = Empty i = Empty End Sub
Пример использования класса tSQL в процедуре
Sub mySQL() Dim ts As tSQL Set ts = New tSQL ts.ConnectionSring = '<Строка подключения> ts.SelectFrom "Название таблицы", ActiveSheet Set ts = Nothing End Sub
Задача третья. Загружаем данные из Excel во внешнюю базу данных.
Для записи данных напишем метод InsertInto с параметрами TableName. rHead и rData. TableName — это имя таблицы, куда будем добавлять данные; rHead — диапазон ячеек, с указанием полей; rData — диапазон ячеек с данными, которые будем добавлять.
Public Sub InsertInto(TableName As String, rHead As Range, rData As Range) Dim cn As ADODB.Connection Dim SQLstring As String Dim SQLstringH As String Dim SQLstringV As String Dim i As Long Dim j As Long Dim arrHead() Dim arrData() arrHead = rHead.Value arrData = rData.Value Set cn = New ADODB.Connection cn.ConnectionString = ConnectionSring cn.Open SQLstringH = "INSERT INTO " & TableName & "(" For j = LBound(arrHead, 2) To UBound(arrHead, 2) SQLstringH = SQLstringH & " " & arrHead(1, j) If j < UBound(arrHead, 2) Then SQLstringH = SQLstringH & "," Else SQLstringH = SQLstringH & ")" End If Next j SQLstringH = SQLstringH & " VALUES(" For i = LBound(arrData, 1) To UBound(arrData, 1) For j = LBound(arrData, 2) To UBound(arrData, 2) SQLstringV = SQLstringV & " " & arrData(i, j) If j < UBound(arrHead, 2) Then SQLstringV = SQLstringV & "," Else SQLstringV = SQLstringV & ") " End If Next j SQLstring = SQLstringH & SQLstringV SQLstringV = Empty cn.Execute SQLstring Next i cn.Close Set cn = Nothing SQLstring = Empty i = Empty j = Empty SQLstring = Empty SQLstringH = Empty SQLstringV = Empty Erase arrHead Erase arrData End Sub
Пример использования класса tSQL в процедуре
Sub mySQL() Dim ts As tSQL Set ts = New tSQL ts.ConnectionSring = '<Строка подключения> ts.InsertInto "Название таблицы", Range("B1:D1"), Range("B8:D300") Set ts = Nothing End Sub
Задача четвертая. Управляем внешней базой данных из Excel
Рекомендую использовать запросы в основном для чтения данных из внешней БД. Можно записывать данные в таблицы внешней БД.
Но крайне не желательно использовать Excel для управления внешней базой данных, лучше использовать стандартные средства разработки.
Полезные ссылки:
Data from Excel to SQL
http://www.excel-sql-server.com/excel-sql-server-import-export-using-vba.htm
При упоминании баз данных (БД) первым делом, конечно, в голову приходят всякие умные слова типа SQL, Oracle, 1С или хотя бы Access. Безусловно, это очень мощные (и недешевые в большинстве своем) программы, способные автоматизировать работу большой и сложной компании с кучей данных. Беда в том, что иногда такая мощь просто не нужна. Ваш бизнес может быть небольшим и с относительно несложными бизнес-процессами, но автоматизировать его тоже хочется. Причем именно для маленьких компаний это, зачастую, вопрос выживания.
Для начала давайте сформулируем ТЗ. В большинстве случаев база данных для учета, например, классических продаж должна уметь:
- хранить в таблицах информацию по товарам (прайс), совершенным сделкам и клиентам и связывать эти таблицы между собой
- иметь удобные формы ввода данных (с выпадающими списками и т.п.)
- автоматически заполнять этими данными какие-то печатные бланки (платежки, счета и т.д.)
- выдавать необходимые вам отчеты для контроля всего бизнес-процесса с точки зрения руководителя
Со всем этим вполне может справиться Microsoft Excel, если приложить немного усилий. Давайте попробуем это реализовать.
Шаг 1. Исходные данные в виде таблиц
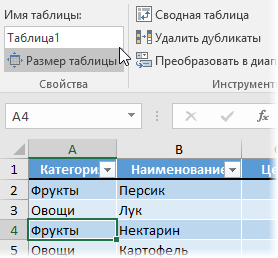
Информацию о товарах, продажах и клиентах будем хранить в трех таблицах (на одном листе или на разных — все равно). Принципиально важно, превратить их в «умные таблицы» с автоподстройкой размеров, чтобы не думать об этом в будущем. Это делается с помощью команды Форматировать как таблицу на вкладке Главная (Home — Format as Table). На появившейся затем вкладке Конструктор (Design) присвоим таблицам наглядные имена в поле Имя таблицы для последующего использования:
Итого у нас должны получиться три «умных таблицы»:
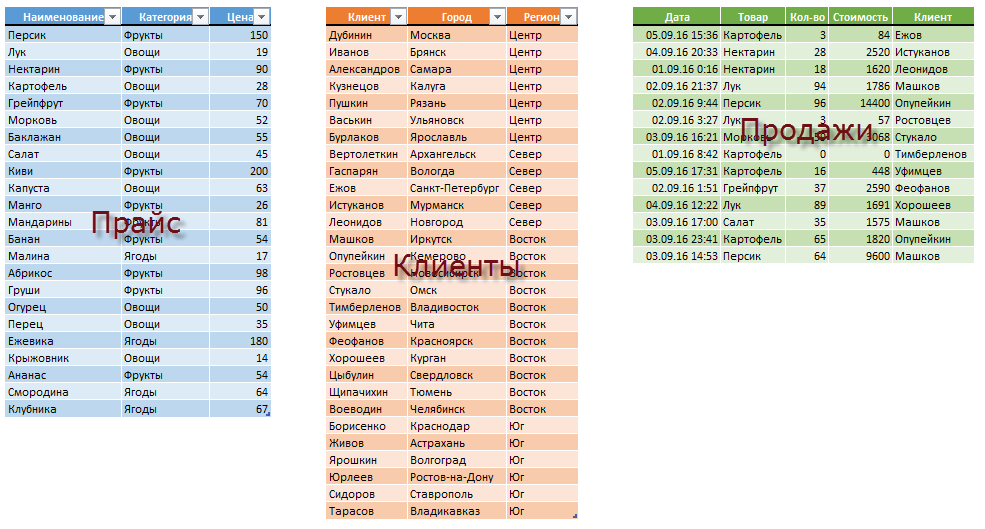
Обратите внимание, что таблицы могут содержать дополнительные уточняющие данные. Так, например, наш Прайс содержит дополнительно информацию о категории (товарной группе, упаковке, весу и т.п.) каждого товара, а таблица Клиенты — город и регион (адрес, ИНН, банковские реквизиты и т.п.) каждого из них.
Таблица Продажи будет использоваться нами впоследствии для занесения в нее совершенных сделок.
Шаг 2. Создаем форму для ввода данных
Само-собой, можно вводить данные о продажах непосредственно в зеленую таблицу Продажи, но это не всегда удобно и влечет за собой появление ошибок и опечаток из-за «человеческого фактора». Поэтому лучше будет на отдельном листе сделать специальную форму для ввода данных примерно такого вида:
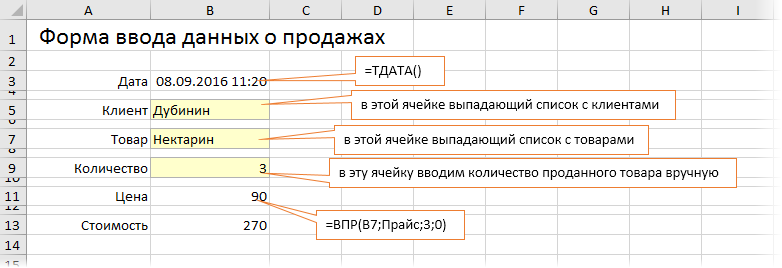
В ячейке B3 для получения обновляемой текущей даты-времени используем функцию ТДАТА (NOW). Если время не нужно, то вместо ТДАТА можно применить функцию СЕГОДНЯ (TODAY).
В ячейке B11 найдем цену выбранного товара в третьем столбце умной таблицы Прайс с помощью функции ВПР (VLOOKUP). Если раньше с ней не сталкивались, то сначала почитайте и посмотрите видео тут.
В ячейке B7 нам нужен выпадающий список с товарами из прайс-листа. Для этого можно использовать команду Данные — Проверка данных (Data — Validation), указать в качестве ограничения Список (List) и ввести затем в поле Источник (Source) ссылку на столбец Наименование из нашей умной таблицы Прайс:
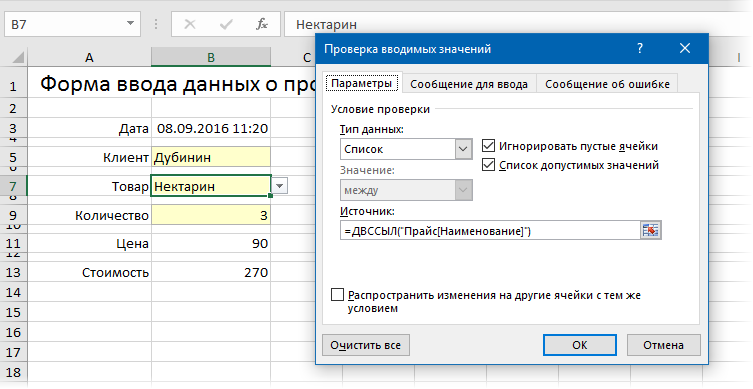
Аналогичным образом создается выпадающий список с клиентами, но источник будет уже:
=ДВССЫЛ(«Клиенты[Клиент]»)
Функция ДВССЫЛ (INDIRECT) нужна, в данном случае, потому что Excel, к сожалению, не понимает прямых ссылок на умные таблицы в поле Источник. Но та же ссылка «завернутая» в функцию ДВССЫЛ работает при этом «на ура» (подробнее об этом было в статье про создание выпадающих списков с наполнением).
Шаг 3. Добавляем макрос ввода продаж
После заполнения формы нужно введенные в нее данные добавить в конец таблицы Продажи. Сформируем при помощи простых ссылок строку для добавления прямо под формой:
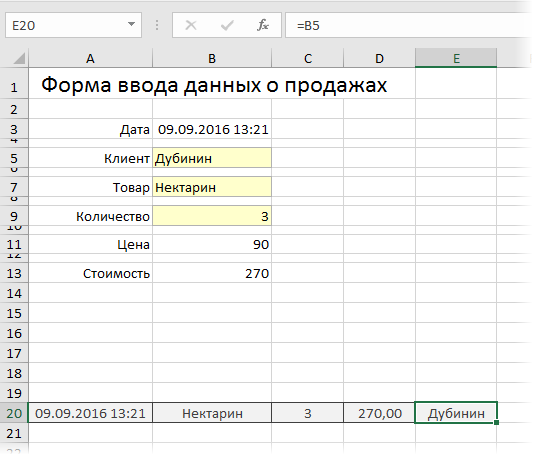
Т.е. в ячейке A20 будет ссылка =B3, в ячейке B20 ссылка на =B7 и т.д.
Теперь добавим элементарный макрос в 2 строчки, который копирует созданную строку и добавляет ее к таблице Продажи. Для этого жмем сочетание Alt+F11 или кнопку Visual Basic на вкладке Разработчик (Developer). Если эту вкладку не видно, то включите ее сначала в настройках Файл — Параметры — Настройка ленты (File — Options — Customize Ribbon). В открывшемся окне редактора Visual Basic вставляем новый пустой модуль через меню Insert — Module и вводим туда код нашего макроса:
Sub Add_Sell()
Worksheets("Форма ввода").Range("A20:E20").Copy 'копируем строчку с данными из формы
n = Worksheets("Продажи").Range("A100000").End(xlUp).Row 'определяем номер последней строки в табл. Продажи
Worksheets("Продажи").Cells(n + 1, 1).PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteValues 'вставляем в следующую пустую строку
Worksheets("Форма ввода").Range("B5,B7,B9").ClearContents 'очищаем форму
End Sub
Теперь можно добавить к нашей форме кнопку для запуска созданного макроса, используя выпадающий список Вставить на вкладке Разработчик (Developer — Insert — Button):
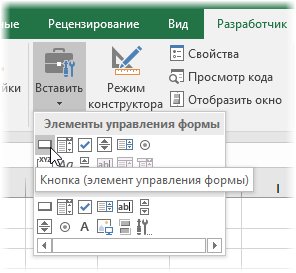
После того, как вы ее нарисуете, удерживая нажатой левую кнопку мыши, Excel сам спросит вас — какой именно макрос нужно на нее назначить — выбираем наш макрос Add_Sell. Текст на кнопке можно поменять, щелкнув по ней правой кнопкой мыши и выбрав команду Изменить текст.
Теперь после заполнения формы можно просто жать на нашу кнопку, и введенные данные будут автоматически добавляться к таблице Продажи, а затем форма очищается для ввода новой сделки.
Шаг 4. Связываем таблицы
Перед построением отчета свяжем наши таблицы между собой, чтобы потом можно было оперативно вычислять продажи по регионам, клиентам или категориям. В старых версиях Excel для этого потребовалось бы использовать несколько функций ВПР (VLOOKUP) для подстановки цен, категорий, клиентов, городов и т.д. в таблицу Продажи. Это требует времени и сил от нас, а также «кушает» немало ресурсов Excel. Начиная с Excel 2013 все можно реализовать существенно проще, просто настроив связи между таблицами.
Для этого на вкладке Данные (Data) нажмите кнопку Отношения (Relations). В появившемся окне нажмите кнопку Создать (New) и выберите из выпадающих списков таблицы и названия столбцов, по которым они должны быть связаны:
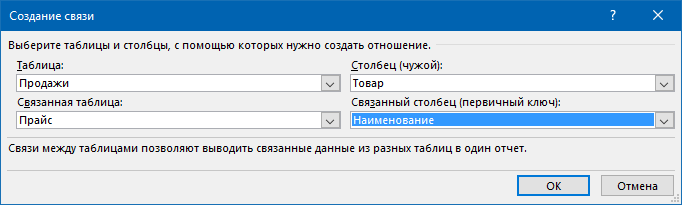
Важный момент: таблицы нужно задавать именно в таком порядке, т.е. связанная таблица (Прайс) не должна содержать в ключевом столбце (Наименование) повторяющихся товаров, как это происходит в таблице Продажи. Другими словами, связанная таблица должна быть той, в которой вы искали бы данные с помощью ВПР, если бы ее использовали.
Само-собой, аналогичным образом связываются и таблица Продажи с таблицей Клиенты по общему столбцу Клиент:
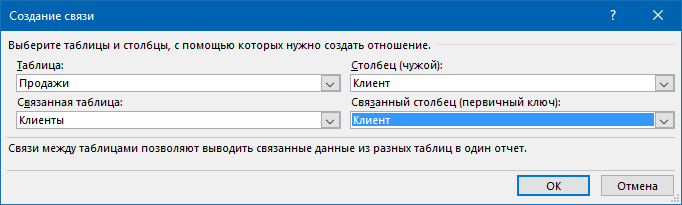
После настройки связей окно управления связями можно закрыть, повторять эту процедуру уже не придется.
Шаг 5. Строим отчеты с помощью сводной
Теперь для анализа продаж и отслеживания динамики процесса, сформируем для примера какой-нибудь отчет с помощью сводной таблицы. Установите активную ячейку в таблицу Продажи и выберите на ленте вкладку Вставка — Сводная таблица (Insert — Pivot Table). В открывшемся окне Excel спросит нас про источник данных (т.е. таблицу Продажи) и место для выгрузки отчета (лучше на новый лист):
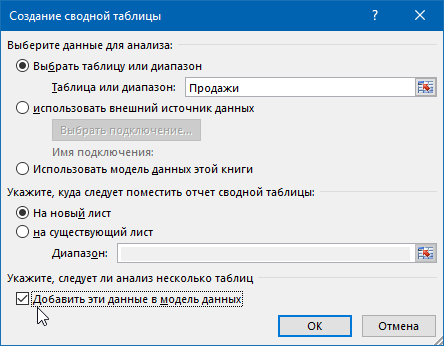
Жизненно важный момент состоит в том, что нужно обязательно включить флажок Добавить эти данные в модель данных (Add data to Data Model) в нижней части окна, чтобы Excel понял, что мы хотим строить отчет не только по текущей таблице, но и задействовать все связи.
После нажатия на ОК в правой половине окна появится панель Поля сводной таблицы, где нужно щелкнуть по ссылке Все, чтобы увидеть не только текущую, а сразу все «умные таблицы», которые есть в книге.А затем можно, как и в классической сводной таблице, просто перетащить мышью нужные нам поля из любых связанных таблиц в области Фильтра, Строк, Столбцов или Значений — и Excel моментально построит любой нужный нам отчет на листе:
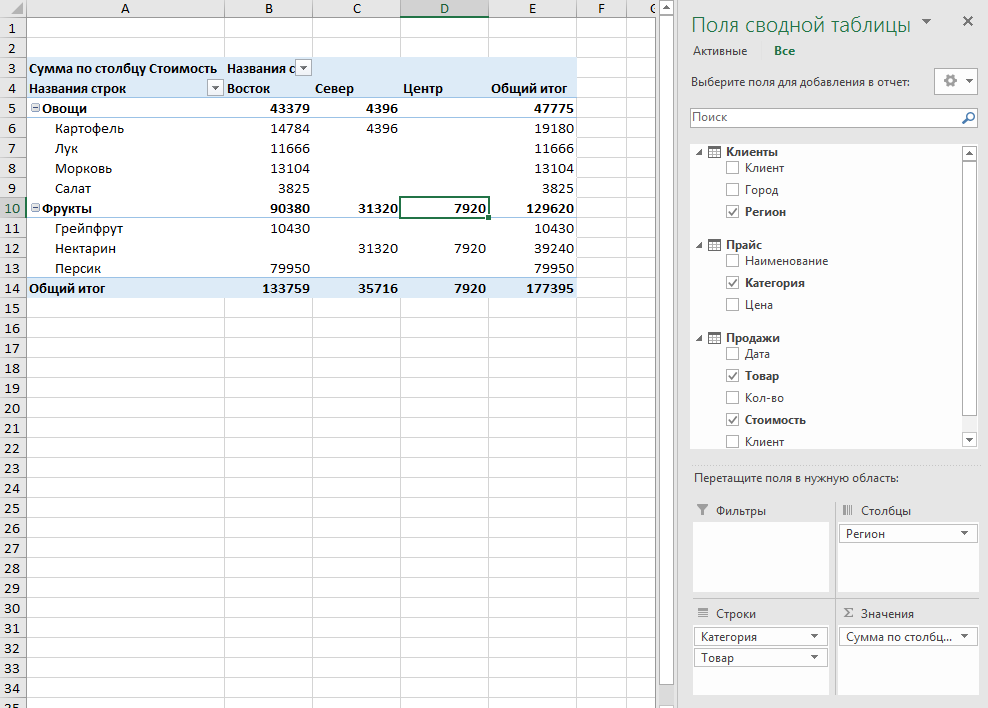
Не забудьте, что сводную таблицу нужно периодически (при изменении исходных данных) обновлять, щелкнув по ней правой кнопкой мыши и выбрав команду Обновить (Refresh), т.к. автоматически она этого делать не умеет.
Также, выделив любую ячейку в сводной и нажав кнопку Сводная диаграмма (Pivot Chart) на вкладке Анализ (Analysis) или Параметры (Options) можно быстро визуализировать посчитанные в ней результаты.
Шаг 6. Заполняем печатные формы
Еще одной типовой задачей любой БД является автоматическое заполнение различных печатных бланков и форм (накладные, счета, акты и т.п.). Про один из способов это сделать, я уже как-то писал. Здесь же реализуем, для примера, заполнение формы по номеру счета:

Предполагается, что в ячейку C2 пользователь будет вводить число (номер строки в таблице Продажи, по сути), а затем нужные нам данные подтягиваются с помощью уже знакомой функции ВПР (VLOOKUP) и функции ИНДЕКС (INDEX).
Ссылки по теме
- Как использовать функцию ВПР (VLOOKUP) для поиска и подстановки значений
- Как заменить ВПР функциями ИНДЕКС и ПОИСКПОЗ
- Автоматическое заполнение форм и бланков данными из таблицы
- Создание отчетов с помощью сводных таблиц
ADO in Excel VBA – Connecting to database using SQL
ADO Excel VBA – SQL Connecting to Database Example Macros helps to connect the different data sources from Excel VBA. Select, Delete,Update Records set.
In this Section:
- What is ADO?
- What is Database?
- What is SQL?
- adodb.connection VBA Reference
- Practical Learning: Using ADO and SQL with VBA
- Example File
What is ADO?
ADO Stands for ActiveX Data Objects, is Microsoft’s Client-Server technology to access the data between Client and Server. ADO can’t access the data source directly, it will take help of OLE DB Provider to communicate with the data source. Most of the times OLE DB providers are specific to a particular Data Source Type. However, we have an OLE DB provider for ODBC, it is a general purpose provider with help of this ADO can access any Data source which can understand ODBC.
What is Database?
Database (DB) is a collection of information organized in such a way that a computer program can easily understand and read the data. And the Database Management System (DBMS) are designed to understand and interact with other computer applications to perform the different operations on the data. MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Access, Oracle, and IBM DB2 are some of the well know DBMS.
Generally the information stored in the data in the form of tables, and a table is designed with set of records (rows) and fields (columns).
You can use Microsoft Excel to store some data, where an Excel workbook will act as a data source, worksheet will be a table and the rows and the columns of the worksheet will be records and the fields of the table.
What is SQL?
SQL Stands for Structured Query Language, ADO use SQL commands to communicate with the databases. Following are the most commonly used SQL commands to deal with the databases:
| SELECT command used to retrieve the data from a data source |
| INSERT command used to insert the records to a data source |
| UPDATE command used to modify the existing records of the data source |
| DELETE command used to delete the records from a data source |
adodb.connection VBA Reference
adodb.connection VBA Reference helps as to refer ADO in Excel VBA. We can use ADO in Excel VBA to connect the data base and perform data manipulating operations. We need add ‘Microsoft Activex Data Objects Library’ from References to reference the ADO in VBA. Here is the adodb.connection VBA Reference screen-shot.
ADO in Excel VBA – Practical Learning: Using ADO and SQL with VBA
To retrieve the data from any data source into Excel using ADO:
1. We have to Open the connection to the Data Source
2. We need to run the required SQL command
3. We have to copy the resulted record set into our worksheet
4. We have to close the record set and connection
We will consider the Excel workbook as data source and we will connect to the worksheet (table) to retrieve the data. In this example we will get the data from Sheet1 to Sheet2 using ADO.
Assuming you have an excel workbook with the following data in Sheet1, as shown below.
| EmpID | EmpName | EmpSalary |
|
1 |
Jo |
22000 |
|
2 |
Kelly |
28000 |
|
3 |
Ravi |
30000 |
Step 1:Add reference for Microsoft Activex Data Objects Library
1. Go to VBE (Alt+F11) and Select References.. from Tools Menu.
2. Then select ” Microsoft Activex Data Objects Library” from the list.
3. And Create sub procedure to write the code:
Sub sbADOExample() 'We will write the code here End Sub
Step 2: Create the Connection String with Provider and Data Source options
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim ReturnArray
Dim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.Recordset
Dim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
DBPath = ThisWorkbook.FullName 'Refering the sameworkbook as Data Source
'You can provide the full path of your external file as shown below
'DBPath ="C:InputData.xlsx"
sconnect = "Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=" & DBPath & ";HDR=Yes';"
'If any issue with MSDASQL Provider, Try the Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB:
'sconnect = "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" & DBPath _
& ";Extended Properties=""Excel 8.0;HDR=Yes;IMEX=1"";"
Step 3: Open the Connection to data source
Conn.Open sconnect
Step 4: Create SQL Command String
sSQLSting = "SELECT * From [Sheet1$]" ' Your SQL Statement (Table Name= Sheet Name=[Sheet1$])
Step 5: Get the records by Opening this Query with in the Connected data source
mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
Step 6: Copy the reords into our worksheet
Sheet2.Range("A2").CopyFromRecordset mrs
Step 7: Close the Record Set and Connection
'Close Recordset
mrs.Close
'Close Connection
Conn.Close
So, the final program should look like this:
Sub sbADOExample()
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim ReturnArray
Dim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.Recordset
Dim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
DBPath = ThisWorkbook.FullName
'You can provide the full path of your external file as shown below
'DBPath ="C:InputData.xlsx"
sconnect = "Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=" & DBPath & ";HDR=Yes';"
'If any issue with MSDASQL Provider, Try the Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB:
'sconnect = "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" & DBPath _
& ";Extended Properties=""Excel 8.0;HDR=Yes;IMEX=1"";"
Conn.Open sconnect
sSQLSting = "SELECT * From [Sheet1$]" ' Your SQL Statement (Table Name= Sheet Name=[Sheet1$])
mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
'=>Load the Data into an array
'ReturnArray = mrs.GetRows
''OR''
'=>Paste the data into a sheet
Sheet2.Range("A2").CopyFromRecordset mrs
'Close Recordset
mrs.Close
'Close Connection
Conn.Close
End Sub
Example File
You can download the example files here and explore it. Getting Data Using ADO (Using MSDASQL Provider)
Getting Data Using ADO (Using MSDASQL Provider)
Download the Example File: ANALYSIS TABS – Getting Data Using ADO (Using Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB Provider)
Getting Data Using ADO (Using Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB Provider)
A Powerful & Multi-purpose Templates for project management. Now seamlessly manage your projects, tasks, meetings, presentations, teams, customers, stakeholders and time. This page describes all the amazing new features and options that come with our premium templates.
Save Up to 85% LIMITED TIME OFFER

All-in-One Pack
120+ Project Management Templates
Essential Pack
50+ Project Management Templates
Excel Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
PowerPoint Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
MS Word Pack
25+ Word PM Templates
Ultimate Project Management Template
Ultimate Resource Management Template
Project Portfolio Management Templates
Related Posts
-
- What is ADO?
- What is Database?
- What is SQL?
- adodb.connection VBA Reference
- ADO in Excel VBA – Practical Learning: Using ADO and SQL with VBA
- Example File
VBA Reference
Effortlessly
Manage Your Projects
120+ Project Management Templates
Seamlessly manage your projects with our powerful & multi-purpose templates for project management.
120+ PM Templates Includes:
134 Comments
-
Vandana
August 7, 2013 at 4:49 PM — Reply -
lisa Pereira
February 12, 2014 at 7:33 AM — ReplyHI,
Nice one.. I am trying to pull multiple values from one parameter in excel, for example. I need to pull the parameter from Range(“a2”) separated by commas,
how can I do this? -
PNRao
February 25, 2014 at 11:58 PM — ReplyHi Lisa,
Assuming you have data at A1 as “1st,2nd,3rd,4th” and you want to separate it.
You can use Split function to separate the values. Please see the following code.
fullText=Range(“A1″).Value ‘i.e; fullText=”1,2,3,4″
arraySplitValues=Split(fullText,”,”)Now your array contains the comma delimited values:
arraySplitValues(0) contains 1st
arraySplitValues(1) contains 2nd
arraySplitValues(2) contains 3rd
arraySplitValues(3) contains 4thYou can print the values at any Range like:
Range(“B1”)=arraySplitValues(3)or you can loop the entire array to print all values:
For iCntr=0 to ubound(arraySplitValues,1)
Cells(iCntr+1,2)=arraySplitValues(iCntr) ‘ this will print all the values in the B Column
NextPlease explain your question in more detailed,so that I can help you in better way.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Hi – great article! 2 questions:
1. Do you have to install the ActiveX Object library 2.8 on every machine that uses this Excel file? I ask because I need to set up multiple files for multiple users who could benefit from this functinality (ADODB + SQL queries vs. Linked spreadsheets).
2. Do you know how to create an auto-install program for these MS library features? I ask because I don’t prefer to guide every user through the installation procedure.Thanks again!
Stephen -
PNRao
March 24, 2014 at 11:13 PM — ReplyHi Stephen,
Thanks for your comments! Please see my answers below:
1.You do not required to install ActiveX Object library in every machine, by default it is installed when user have installed in MS Office.
2.I think the above information answers this question too…To help you in understanding clearly: ActiveX Object Library is .DLL file which is installed with your office installation. You need to this reference this in your code, to use the ADO functionality in Excel VBA.
When you successfully write any code using ADO by referring ActiveX Object Library in your workbook. You can send the file to any one, it should work automatically in any system.
Hope this helps.
Thanks-PNRao! -
Lisa Pereira
June 18, 2014 at 5:00 AM — ReplyHi PN,
You are awesome , i love this site.have used your ideas and has helped me a lot. love it..
What i needed to know was that having pulled the record set into sheet :-
1) I want to use the values listed in rows in column A
2) transpose them into a cell and use these values to pull another query record-set with the IN statement.
is there a way to do this in one connection only or open another connection.?
let me know if this is possible.
Regards..
lisa -
PNRao
June 19, 2014 at 12:11 AM — ReplyHi Lisa,
How are you doing! Thanks for your feedback!
Yes, this can be done. Here is an example case:
To explain this, I have entered some data in ADO sheet of the example file (available at end of the article)
Step1: Entered 1 at Range A2, 2 at Range A3
The I concatenate these values at C1 using the below formul
-> =A2&”,”&A3
i.e; Now you can see ‘1,2’ at C1, I want to pass this in my SQL IN Operator, So – I changed the SQL Query string as follows:Step2: sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [DataSheet$] where Quarter IN (” & Range(“C1”) & “);”
i.e; it will form the query as ‘SELECT * From [DataSheet$] where Quarter IN (1,2);’Step3: Now executed and got the required values in the ADO sheet.
Hope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
Jon McNeil
July 1, 2014 at 9:58 PM — ReplyThanks PN,
This is working nicely. The only thing that I cannot appear to fix is that when one user has the source file open (from which the data comes from) the other user, who is using the destination file (where the data is pulled to), opens a read-only source file when they run the macro. Is there a way round this?
The source file is only supposed to be viewed by one person whereas the destination file is for multiple usersThanks in advance,
Jon
-
Shubhangi
July 1, 2014 at 11:24 PM — ReplyI used this code to connect to MS Access 2007 database but am getting a runtime error and an application error when I try to open the same. I used DSN as MS Access Database and Provider as Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0.
Please help. -
PNRao
July 2, 2014 at 3:35 PM — Reply -
Noz
July 3, 2014 at 3:24 PM — ReplyThis is very well explained, if this had been available when I was first learning it would have save me loads of time. Do you have something similar on how to insert into SQL tables from excel?
-
PNRao
July 4, 2014 at 12:48 AM — ReplyHi Noz, Thanks for your comments!
Yes, you can write insert query, you can download the example file and change the query string as follows:
sSQLSting = “INSERT INTO [DataSheet$](Quarter, Sales) Values(2,5000)”and comment the below line, as insert query will not return any values.
‘ActiveSheet.Range(“A2”).CopyFromRecordset mrsNow your ADO procedure should look like this:
Sub sbADO()
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim ReturnArrayDim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.RecordsetDim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
DBPath = ThisWorkbook.FullName
'You can provide the full path of your external file as shown below
'DBPath ="C:InputData.xlsx"sconnect = "Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=" & DBPath & ";HDR=Yes';"
Conn.Open sconnect
'sSQLSting = "SELECT * From [DataSheet$]" ' Your SQL Statemnt (Table Name= Sheet Name=[DataSheet$])
sSQLSting = "INSERT INTO [DataSheet$](Quarter, Sales) Values(2,5000)"
mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
'=>Load the Data into an array
'ReturnArray = mrs.GetRows
''OR''
'=>Paste the data into a sheet
'ActiveSheet.Range("A2").CopyFromRecordset mrs
'Close Recordset
mrs.Close'Close Connection
Conn.CloseEnd Sub
-
Jaishree Ramani
July 10, 2014 at 8:08 PM — Replyhello, this really helps when you have a simple query.. would you be kind enough to provide an example for a parameter query (multiple) i.e for dates say selct* from table data between fromDate and toDate?
-
PNRao
July 11, 2014 at 1:29 AM — ReplyHi,
Sure, you change the query to suits your requirement.
For example:
I have changed the query sting from sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [DataSheet$]” to sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [DataSheet$] Where Quarter Between 2 And 4” in the example file. And now it will pull the data if the quarter is between 2 and 4.For your requirement, sSQLSting will be something like below:
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [DataSheet$] Where YOUR_Date_Varibale Between ‘LowerDate’ And ‘UpperDate’”
If Dates creates any problems, try to use date values.
Hope this helps-Thanks-PNRao!
-
Jaishree Ramani
July 11, 2014 at 6:57 PM — ReplyHi Sir,
that works but I am having issue with the parameters dates as my query below
“O.DELIVERY_DATE BETWEEN :”From date” AND :”To Date” ) . how do i setup the parameters in vba to ensure that the record-set only pulls data in ‘DD-MMM-YYYY’ format. right now i have the dates converted to text(“dd-mmm-yyyy”) but when the data is returned its shows up in ‘mm/ddd/yyyy’ .note :i have the user to input the dates..
-
PNRao
July 12, 2014 at 1:05 PM — ReplyHi,
You can create the query string use as shown below:FromDate = 1 / 1 / 2010
ToDate = 12 / 30 / 2012
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [DataSheet$] Where O.DELIVERY_DATE Between ” & FromDate & ” And ” & ToDateAnd your excel, default date format is ‘mm/ddd/yyyy’, you can format the dates using either sql or VBA.
In VBA it is like this: Format(YourDate,”mm-dd-yyyy”)
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Jaishree Ramani
July 14, 2014 at 8:21 PM — ReplyHi Sir,
my code is
userInput (“Pls type FromDate”) ,FromDate
userInput (“Pls type ToDate”) ,ToDate
FromDate = format(FromDate,”dd-mmm-yyyy”)
ToDate = format(ToDate,”dd-mmm-yyyy”)“select…
…..”AND O276054.DELIVERY_DATE BETWEEN ” & FromDate & ” And ” & ToDate & _ ”i tried that but i keep getting error ‘saying missing expression..’
what am i doing wrong?? -
PNRao
July 15, 2014 at 10:56 AM — ReplyHi,
I could not find any issue in the code. As per the Error message, something wrong with the query string. Could you please provide me the complete query string.Or you can try this: You can use Debug.Print YourstrQery, now look into the Immediate Window to see the resulted query.
You can send me the file with some dummy data to our email id: info@analysistabs.com
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Nigel
July 18, 2014 at 7:29 PM — ReplyHello, very good site .. quick question do you have an example for record-sets and Pivot tables or cross-tabs.?
i have an issue which I am trying to merge two query’s into one record-set and Pivot them into a cross report?
something similar to what Discoverer does. but I am trying to combine aggregate data points with Detail data points into one sheet without errors..(that’s why the two query s)please direct in a right direction if this is doable???
-
PNRao
July 20, 2014 at 12:31 AM — ReplyHi Nigel,
Please look into the example below:
'Add reference for Microsoft Activex Data Objects LibrarySub sbADO()
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim ReturnArrayDim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.RecordsetDim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
DBPath = ThisWorkbook.FullName
'You can provide the full path of your external file as shown below
'DBPath ="C:InputData.xlsx"sconnect = "Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=" & DBPath & ";HDR=Yes';"
Conn.Open sconnect
sSQLSting = "SELECT * From [DataSheet$]"'***********> You can change this query as per your requirement (Join / Union)
mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
'Set record set as a pivot table data source
Set objPivotCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Add( _
SourceType:=xlExternal)
Set objPivotCache.Recordset = mrs
With objPivotCache
.CreatePivotTable TableDestination:=Range("G20"), _
TableName:="MyPivotTable1"
End With'Close Recordset
mrs.Close'Close Connection
Conn.CloseEnd Sub
Hope this helps! Thanks-PNRao!
-
Gavrav
July 24, 2014 at 1:59 PM — ReplyHi,
I would like to automate my daily process by using VBA and macro actually my doubt is there any solution for instead of copying and pasting the query statement to SSMS 2005 which is stored in excel.So by making that statements as link or by clicking some command buttons to pass that query to SSMS and thus the statement should be executed automatically by using ODBC conn or OLEDB data sources. Is it Possible ??? -
PNRao
July 24, 2014 at 2:53 PM — ReplyHi Gavrav,
Yes – we can do this. You can simply record a macro and fetch the data using tools in Data menu tab.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Ricky Dobriyal
July 26, 2014 at 9:39 PM — ReplyHi All,
I am very glad that I visited this website and would like thank you for giving such valuable info.
I have one question in VBA while using ADO and database as excel how we can use where condition and other query on excel sheet like below example of this website.sconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”
Conn.Open sconnect
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [DataSheet$] WHERE ” ‘ Your SQL Statemnt (Table Name= Sheet Name=[DataSheet$])mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
‘=>Load the Data into an array
‘ReturnArray = mrs.GetRows
”OR”
‘=>Paste the data into a sheet
ActiveSheet.Range(“A2”).CopyFromRecordset mrs
‘Close Recordset
mrs.CloseHere is only select condition used. Please help me how we can use different SQL condition.
Another question how we can connect to MYsql database using VBA?
Please help me in the above questions and thanks a ton in advannce.
Regards,
Ricky -
PNRao
July 26, 2014 at 9:49 PM — ReplyHi Ricky,
Thanks for your comments.
Please check the codes provided in the comments section, I have given the example queries which you have mentioned.
And regarding MySQL, you can use the following connection string:
sconnect = “DRIVER={MySQL ODBC 5.1 Driver};” & _ “SERVER=[Server];” & _ “DATABASE=[Database];” & _ “USER=[UserName];” & _ “PASSWORD=[Password];” & _ “Option=3”And replace [Server], [Database], [UserName] and [Password] with the respective original server name, database, User and Password.
If your system is not insstalled MySQL, then you have to download and install MYSQL ODBC Driver: http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/odbc/5.1.html
Hope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
Nigel
July 29, 2014 at 8:32 PM — ReplyHi Pn,
Thanks your previous example works perfectly. would you be able to help with multiple record sets. I need to add the second query record-set in between the data of the first record set after exporting to sheet. -
Nigel
July 30, 2014 at 5:30 AM — ReplyHi PN, sorry hope if didn’t confuse you with my inquiry.. I will provide an example
I need to combine two record sets as I cannot put them in one query due to the data constraints.
query1= “select Total_DLV , AVAIL_DLV between date1 and date2 from Table1″ into Sheet1
query2=”select Sch_DLV , between date1 and date2 from Table2” into Sheet1
combine data from the two querys into sheet1 like
DLV_date—>aug1, Aug 2 ,aug3 (horizontal)
Total_DLV , ..
AVAIL_DLV
Sch_DLV
please let me know if this is possible.. -
Amir
August 1, 2014 at 4:08 PM — ReplyHi
Nice explanation!
Question: how can i get the data from different ‘sourcerange’ from within one sheet i.e multiple columns?code:
SourceRange = “C1:C6500 ,D1:D6500 ,AB1:AB6500,AG1:AG6500”
szSQL = “SELECT * FROM [” & SourceSheet$ & “$” & SourceRange$ & “];” -
Nigel
August 7, 2014 at 12:00 AM — ReplyHi PN ,
i fixed the issue.,, this was more to do with my query itself. i managed to fix this within the first query itself. no need for multiple queries.
however please provide an example for multiple record-sets if possible.. -
Ricky Dobriyal
August 17, 2014 at 12:54 AM — ReplyHello Team,
I have a sheet with thousand records and I want filter recordes based on Activsheet name
Query is working fine when I am putting directly the value in condition like below
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [Data$] where Country =’India’; ”
But I want to filter it based on Acrive sheet name.
I tried two methods but it is prompting same Run time error.
s = ActiveSheet.Name
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [Data$] where Country =s ”
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [Data$] where Country =Activeshet.name ”
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [Data$] where Country =’Activeshet.name’ ”Please cound you advise me how I can do this..
-
PNRao
August 17, 2014 at 11:15 AM — ReplyHi Amir,
You can mention the column names, instead of specifying multiple ranges, for example:
szSQL = “SELECT Column1, Column2 FROM [Sheet1$]”Thanks-PNRao!
-
PNRao
August 17, 2014 at 11:44 AM — ReplyHi Ricky,
Please change your code like this:s = ActiveSheet.Name
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [Data$] where Country = ‘” & s & “‘”Thanks-PNRao!
-
Graig
September 1, 2014 at 4:10 AM — ReplyI see you share interesting content here, you can earn some additional
cash, your blog has huge potential, for the
monetizing method, just search in google – K2 advices
how to monetize a website -
Yogesh
September 10, 2014 at 10:55 PM — Replyis there a way to send parameters(through InputBox/MsgBox) using Select statement and extracting user specific data into excel using ADO.
Thanks for all your help and support.
Yogesh -
Mandeep
September 11, 2014 at 9:56 AM — ReplyDear Pn rao,
Please let me know if you are pulling data from excel , is this code using sql while retrieving data ? because this is not connecting to server. waiting for your response. thanks in advance.
MAndeep -
Mandeep
September 11, 2014 at 9:59 AM — ReplyExplain me this line of code please ” sconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”
-
PNRao
September 11, 2014 at 8:19 PM — ReplyHi Mandeep,
We need to create a connection string to connect any data base using VBA.
sconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”Provider=MSDASQL.1 : This is OLEDB Provider, this helps excel to understand the data base query syntax.
DSN=Excel Files : Data Source Name, Excel Files is data source in the given example.
DBQ= &DBPath : Data base file path, this is the full path of Excel File to connect.
HDR=Yes’: Headers, Yes – if the first line of your data (in sheet or range) having headers, other wise No.Hope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
PNRao
September 11, 2014 at 8:22 PM — ReplyHi Mandeep,
Yes, we are pulling the data from Excel using ADO. You need to change the connection string if you are connecting any other DB.Thanks-PNRao!
-
PNRao
September 11, 2014 at 8:28 PM — ReplyHi Yogesh,
Yes, you can use Inputbox to enter some parameters and change the query accordingly.
Example:
x = InputBox(“Please enter field to select”, “Please Enter”)
‘You cna change the below query
‘sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [Sheet1$]
‘As shown below:
sSQLSting = “SELECT ” & x & ” From [Sheet1$]”
‘Your remaing code here, similarly you can keep a WHERE Condition—Thanks-PNRao!
-
Navneet Rao Ingle
September 15, 2014 at 2:35 PM — ReplyHi PN,
I am trying to copy the data from one workbook to another. Everything goes fine till the fetching of data from the source workbook but when I tried to paste the data in the destination workbook I am getting the following error:Run-time error ‘-2147467259 (80004005)’:
You cannont move a part of a PivotTable report, or insert worksheet
cells, rows, or columns inside a PivotTable report. To insert worksheet
cells, rows, or columns, first move the PivotTable report (with the
PivotTable report selected, on the Options tab, in the Actions group,
click Move PivotTable). To add, move, or remove cells within the
report, do one of the following:Code used is:
Dim DNameRecvd
Dim query As String
Dim ReturnArrayDNameRecvd = DName
Dim conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.RecordsetDim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
DBPath = ThisWorkbook.FullNamesconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”
conn.Open sconnect
query = “SELECT * from [Data$]”
mrs.Open query, connWorkbooks(“DestinationFile”).Activate
Sheets(“Sheet4”).ActivateSheet4.Range(“A2”).CopyFromRecordset mrs ‘—-Receiving error message at this line
mrs.Close
ActiveWorkbook.Save
MsgBox (“Done”)Please help. Thanks in Advance.
-
gayathiri
September 22, 2014 at 3:47 PM — ReplyDear Pn Rao
i have to go through entire spreadsheet/workbook to find current status of articles by adding received date to 20 and if it matches today’s date. change the color of that row. can i do it without ADO connection -
PNRao
September 22, 2014 at 7:56 PM — ReplyHi Gayathri,
Yes, we can open the workbook and do whatever we want without using VBA. Your code will be some thing like this:
You can open the required file:
set Wb=Workbooks.Open(“C:tempworkbook.xlsx”)
Assuming you have recieved date in Column A
iCntr=1
Do while Wb.Sheets(“SheetName”).Cells(iCntr,1)<>”
If Format(Wb.Sheets(“SheetName”).Cells(iCntr,1),”DD-MM-YYYY”)=Format(Now(),”DD-MM-YYYY”) then
‘Here you can change the cell/range color
End If
LoopHope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
gayathiri
September 23, 2014 at 11:14 AM — Replythanks a lot.. :)but where to put this code. either by keeping a button or create a macro module for this workbook. My requirement is Say if the article is received on september 10 i have to get that row say in green color on september 30
-
gayathiri
September 24, 2014 at 1:37 PM — ReplyMr.Rao thanks for your timely help:)
Customized ur code and it works well..
-
PNRao
September 26, 2014 at 9:31 PM — ReplyYou are most welcome!
Thanks-PNRao! -
Est228
October 10, 2014 at 9:45 PM — ReplyDear PnRao
I am using this code to connect to MS Access 2013 and used your previous comment to Shubhangi to structure the code. Everything seems to be working fine until I get to this part of the code:
sSQLSting = “SELECT * FROM [BD_X]” where BD_X is the name of my Access table
Here I keep getting an Error. I all ready have the required OLEDB and also tried using this code instead:
sSQLSting = “SELECT * FROM [BD_X$]”
I would appreciate some help. -
PNRao
October 12, 2014 at 10:06 AM — ReplyHi,
You can use the table name directly: sSQLSting = “SELECT * FROM BD_X”.If you want to refer Excel sheet as table then it will be like [BD_X$], if you connect any data base like MS Access, MS SQL Server, Oracle or Teradata you can use the table name.
Hope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
Philip
October 26, 2014 at 8:48 PM — ReplyGreetings PNRao,
I am in between developing a small project for the place I work at.
Currently I am helping out the call center gang with automating their reports.
There is a huge report that they spool off a web site at the end of each month…
They obtain it in the form of an excel file with 97 format, which means each sheet is limited to 65535 rows only.
So therefore the report spans to 4 sheets and could be more…
I have completely automated this report into various pivot format for them per their requirement using Excel VBA.
However the code is slow to about 10 seconds.
There are many data analysis involved like filtering out the blanks off 2 columns, unwanted rows from another and pivoting them to obtain 4 reports using different criteria each.
I am talking about 260000+ records analyzed to about 72000+ actual meaningful data for the report.Now, I thought maybe ADO could work out the trick more efficiently and faster.
I have worked with ADO before in access/excel and know how to on the basics of connection etc.Currently, I need to know 2 things at this point:
1) Is the ADO method faster than using excel automation via variant and/or range methods combined with loops?
2) How do I append data from 4 sheets into 1 recordset to later analyze it with various select statements? Do I have to use an append query to obtain data from each sheets? If so, let me know how the query would look.Note: What I am thinking of doing is to completely do the required data manipulations within ADODB recordset and insert the manipulated data into a new sheet in Excel 8 format. Also, to run queries and to obtain the reports required from these manipulated data and again insert sheets into excel form query object.
Could you kindly guide me into the various steps I need to be looking at to achieve these goals.
Thanks in advance,
Philip -
Suruchi
October 27, 2014 at 10:47 PM — ReplyHi PN ,
This is really helpful .
One thing that is not working at my end is changing HDR=No’; … this code is not giving me the header which is required.
I tried with for loop which is working in that case , just wanted to know if how would HDR would work.Thank you
-
Suruchi
October 28, 2014 at 11:55 AM — ReplyHi PN,
This code is working fine , but I am not able to get the header eve after making HDR =No .
Could you please help me on this .Thanks ,
Suruchi -
PNRao
October 29, 2014 at 10:34 PM — ReplyHi Philip,
PivotTable is better than ADO, if your customers use Excel 2010 or higher. And to combine the Data into one record set, you query all data into one record set using UNIONs.Hope this helps.
Thanks-PNRao! -
PNRao
October 29, 2014 at 10:38 PM — ReplyHi Suruchi,
The usage of HDR is to tell the ADO whether your data has headers or not.
HDR= Yes means: You have the data and the first row is having headers and data starts from the next row.
HDR= No means: Your data has no header row and and data the data starts from the first row.Hope this clarifies your query.
Thanks-PNRao! -
Mani
November 6, 2014 at 2:29 PM — ReplyHi PNRao,
This is a great & Nice Information!
Would you be kind enough to answer the following question too,Question: how can i get the data from Oracle Database, currently I use SQL Developer to query and store the result in excel and process it later, but since the number of individual sqls increased i’m looking for something like this and if you can help me in this regard, it would be great.
Thanks in advance
Mani -
Amjed
November 14, 2014 at 4:34 PM — ReplyHi,
i would like to connect to PL/SQL developer from MS Excel and fetch the records from it and copy to the excel sheet. The query i want to execute is ‘SELECT * FROM TABLE_NAME’. Please let me know the connection string to use.
Thanks in Advance. -
Satyarth Rao
November 19, 2014 at 11:54 PM — ReplyHi PN,
I am trying to pull data from SQL Server 2012 using excel VBA Code but it is showing that SQL Sever is not exit or access is denied. Please let me know how to do so. It will be a great help.
Thanks in Advance. -
Scott
November 28, 2014 at 4:08 AM — ReplyIs it possible to join 2 tables from separate databases in an SQL query within Excel VBA?
I am currently extracting data from a table in a Firebird database but need to access data from records form a table in another Firebird database. The results of the query are used as input to a case statement that totals and dumps data into a worksheet.
I can do this in Access since I link to the tables as required, can I have 2 connections open at once in Excel? -
Prasad Sakpal
December 2, 2014 at 12:40 PM — ReplyAmazing Website…………..Thank you for giving me proper information.
-
Prasad Sakpal
December 2, 2014 at 12:44 PM — ReplyWith help of this website, i have entered the insert query & it is properly working but on this “mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn” statement getting errors ‘Run-Time Error 3704’. Please help on this..I appreciated.
-
Prasad Sakpal
December 2, 2014 at 12:45 PM — ReplyRecord is properly inserted into SQL database but getting above error message. please check…
-
Sub sbADO()
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim ReturnArray
Dim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.Recordset
Dim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
sconnect = “Provider=SQLOLEDB.1;Data Source=******;Initial Catalog=******;User ID=*******;Password=*****;”
Conn.Open sconnect
sSQLSting = “INSERT INTO [tablename](code, fname,lname,process) Values(‘20202020′,’Prasad’,’Sakpal’,’PC001′)”
mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn ‘ Getting error message on this line, but record is properly inserted in to SQL database.
mrs.Close
Conn.Close
End SubError is = ‘Run-Time Error 3704′
Application Defined or Object Defined Error -
sandeep
December 5, 2014 at 4:49 PM — ReplyHi,
I have a query. While uploading data to SQL, if i try to download data from SQL using excal vba it is failing and throwing error.Do we have any wayt to handle mulitple calls in SQL using VBA….
An really confused shud it be done at vba end or SQL end? -
This thread has been very helpful in getting going. However, there is one problem. I am using an ODBC driver talking to Google big query but I imagine this problem I have could be relevant to any DBMS connection that has it’s own SQL variant. The key requirement for me is to be able to pass the NATIVE SQL code that the DBMS supports rather than being forced into submitting ANSI SQL which very limiting. I’m using a driver that is meant to supports both.
The following works as intended:
Dim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.Recordset
Conn.Open “DSN=bq”
SQLString = “SELECT count(*) as a from EVENTS.Game_20141205 ”
mrs.Open SQLString, Conn
Sheet2.Range(“A2”).CopyFromRecordset mrs
mrs.Close
Conn.CloseBut if I try and submit any non-ANSI SQL statement for example:
SQLString = “select a from (SELECT count(*) as a from EVENTS.Game_20141205) ”
(and this SQL runs perfectly well if you send it directly to Google bigquery directly from the google webconsole)The driver pops an error:
Run-time error ‘-2147217911 (80040e09)’:
[Simba][SQLEngine] (31480) syntax error near ‘select a from (SELECT count(*) as a from EVENTS.Game_20141205) <<>>
which I assume is because it’s not ANSI form SQL. Does anyone know how to submit the native SQL through vba (which should directly be passed through to the DBMS without any checking) -
Henning
December 15, 2014 at 8:06 PM — ReplyIn the file “remedy-export” there are no header and 5 rows of data
When I run the code, it only assigns data from row 2 to row 5 to the array. What am I doing wrong?
[code]
Sub Connect_to_Sheet()
Dim SQLString As String
Dim ReturnArray
Dim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim rsRecordset As New ADODB.Recordset
Dim DBPath As String, sConnect As StringDim Col_Idx, Row_Idx As Long
DBPath = ThisWorkbook.Path & “remedy-export.xlsx”
sConnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=NO’;”
Conn.Open sConnectSQLString = “SELECT * From [Ark2$]”
rsRecordset.Open SQLString, Conn, adOpenStatic, adLockReadOnly
Row_Idx = rsRecordset.RecordCount
ReturnArray = rsRecordset.GetRows
rsRecordset.CloseConn.Close
End Sub
[end code] -
saibabu
December 19, 2014 at 12:14 AM — ReplyHi All,
i want to copy only specific cells range.
KINDLY HELP ME.
-
kesav
December 30, 2014 at 1:12 PM — Replyhi pn
i am trying to connect ms access 2010 data base but its showing erroe
provider not recognized can to help me for over comming from this problem
thanks
kesav -
baha
January 6, 2015 at 11:14 PM — ReplyHo to delete table in existing access database? by using
-
PNRao
January 12, 2015 at 9:25 PM — ReplyHi Baha,
You can delete the table using TRUNCATE or Drop statement if have full permissions.
To delete only the data: TRUNCATE TABLE table_name;Warning: If you use the below statement, you will loss the entire table and you can not roll back.
To delete entire data: DROP TABLE table_name;Thanks-PNRao!
-
Haridas
January 25, 2015 at 12:37 AM — ReplyHi,
I need VBA & SQL learning material because i don’t have knowledge in VBA but i have knowledge in MS Office(Advance excel..).
Any one please send to my email. -
sachin
January 27, 2015 at 6:10 PM — ReplyI was creating a macro to remove exact row duplicate in excel using sql query,but it it giving me “Runtime error -2147217865(80040e37)”. Below isthe VBA code
Sub sbADOExample()
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim ReturnArrayDim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.RecordsetDim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
DBPath = ThisWorkbook.FullName
‘You can provide the full path of your external file as shown below
‘DBPath =”E:tempInputData.xlsx”sconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”
Conn.Open sconnect
sSQLSting = “select distinct column1, count(*) From [Sheet1$] group by column1 having count(*) >1″
‘ Your SQL Statement (Table Name= Sheet Name=[Sheet1$])
mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
‘=>Load the Data into an array
‘ReturnArray = mrs.GetRows
”OR”
‘=>Paste the data into a sheet
Sheet2.Range(“A2”).CopyFromRecordset mrs
‘Close Recordset
mrs.Close‘Close Connection
Conn.CloseEnd Sub
Note : Above code working perfectly fine for 2 column
-
PNRao
February 3, 2015 at 9:53 PM — ReplyHi Sachin,
I found no issues in your code. Please send your file with some dummy data. So that we can help you to solve your issue.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Manoj
February 23, 2015 at 5:40 PM — ReplyHi PN Rao – Thanks for the post really helpful
I am trying to use Sum( Case when ( condition) then 1 else 0 end ) in this concept and it keeps saying automation error
The same code is working perfectly in SQL server
Please adviseThanks
Manoj -
Hi Rao
I am also getting the same kind of error as Sachin is geeting
I am getting the error in this line “mrs.Open sSQLsting,conn”
error is “Runtime error -2147217865(80040e37)”
-
PNRao
March 2, 2015 at 7:05 PM — ReplyHi Richard and Sachin,
Please make sure that the field names are correct. I could not find any issue in the Sachin’s query.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Enrico
March 19, 2015 at 9:13 PM — ReplyDear analists
the code is working but I am retrieving in Sheets(1) just 54’816 lines on 575’000 present in Sheets(2).
do you know why?
I am using Excel 2010Thanks
Enrico -
Aswin
March 23, 2015 at 11:41 PM — ReplyHi PN ,
Read through the post great information you are sharing indeed.. I have a scenario where i would need to pull the values in a column in sheet say Sheet1 whose range may be dynamically changing into IN clause in SQL server query with values like ‘A’,’B’,’C’ etc
-
guys77
March 29, 2015 at 10:36 AM — ReplyHi experts..
How about Dbf files?what string/connection code?
Thanks -
KUMAR
May 4, 2015 at 1:07 PM — ReplyReally great. I could get what I could not even in Microsoft site
-
HONEY
May 8, 2015 at 12:23 PM — ReplyHi,
I want to access the info of memory usage of production database in my excel sheet.
can anyone help me with vba.
-
sheriff
May 14, 2015 at 9:54 PM — ReplyHi,
I want to get a notification automatically when a file is copied in a folder. Can this be done by VBA macro ?
Please help me.
Thanks,
Sheriff -
sheriff
May 14, 2015 at 9:58 PM — Reply -
Sam
May 22, 2015 at 8:04 AM — ReplyHi,
Thanks for sharing this info…
Very usefulregards
sam -
Anand Jo
May 29, 2015 at 9:19 PM — ReplyThanks for the code. It works with the user input when input command is used. But, it does not work when the user enters a value in the textfield in the userform created in excel VBA. Why does this happen? It just does not work with the userform text field input. Any help is appreciated. Here is the code:
Sub UForm()
Dim sSQLSting As String
Dim ReturnArrayDim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.Recordset
Dim DBPath As String, sconnect As StringDBPath = ThisWorkbook.FullName
sconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”
Conn.Open sconnect
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [Sheet1$] where Order_Number = ” & ordernotext1 ‘ Your SQL Statement (Table Name= Sheet Name=[Sheet1$])
mrs.Open sSQLSting, ConnSheets(“ReportsO”).Range(“A8”).CopyFromRecordset mrs
mrs.Close
Conn.Close
End Sub -
kishan Sanghani
June 5, 2015 at 4:18 AM — ReplyHi ,
I am able to execute query from VBA on my DB2. But sometime I need to abort query because of DB conjunction. Please suggest me way to abort query , if executed through VBA.
Thanks in advance.
Regards,
Kishan Sanghani -
Krishna
June 10, 2015 at 9:00 PM — ReplyHi,
Am able to connect to excel data source using ADO connection. But my excel has 265000 rows and 118 columns. When I try to open record set, it struck and it taking more time.. Is that any way to use Ado connection and open record set in quick turnaround? Pls suggest.. Tnx
-
UDAY PRATAP
June 17, 2015 at 5:09 PM — ReplyNice Explanation…..Thanks.
If I want to save picture of employees in (the respective rows) a column. for example Emp_Photo
and if I run Select * from [Sheet1$] it is bringing all information but not the pictures
How to achieve it? -
UDAY PRATAP
June 17, 2015 at 5:12 PM — ReplyTry to connect in a blank New workbook and after connection is established then copy the original sheet into this new workseets.
-
Vic
June 30, 2015 at 7:37 PM — ReplyHi,
The code you gave worked! I am really kinda new to this old VBA stuff. My problem is it opens on a new sheet in a new workbook. How can I have the data displayed on an existing sheet with existing columns?
Thank you in advance for your help PN.
– V
-
Sameer
July 9, 2015 at 5:56 PM — ReplyHi PN – Your site has awesome content and I am hoping you can resolve my query.
I have a MySQL database and I have connect it to excel using VBA on the local machine. Now I want to give the same excel file as an input/output mechanism to all the users to interact with the database installed on my computer. All the users are in a network. Any help would be greatly appreciated.
-
PNRao
July 9, 2015 at 7:51 PM — ReplyHi Sameer,
Thanks for your feedback!
Here are the possible solutions and my preference order:
Solution 1: You can create new database in any server and export the local database into server and change the connection string. All your user need to have MySQL OLEDB Provider in their PCs.
Solution 2. You can export to MS Access database and change the connection string. For this your user do not required to install any additional Provider.
Hope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
Mahantesh
September 9, 2015 at 5:18 PM — ReplyStrSQL=”SELECT * FROM [Shee1$] MINUS SELECT * FROM [Sheet2$] is not getting executed.
Help required.
-
Dung Nguyen
September 14, 2015 at 8:58 PM — ReplyHi PNRao,
I would query to the first worksheet of selected workbook through navigate to the workbook location and user select it( I used worksheets(1) but can not successful), can you show me a sample how to assign this parameter of worksheets(1) to the vba query?
Regards/Dung
-
This paragraph ցives ϲlear idea in support οf the new users.
-
Sriram
October 7, 2015 at 12:48 PM — ReplyHi
Am trying to run sql Analysis query in excel macro . Can you please help me .Thanks in advance
-
Dan
October 21, 2015 at 7:20 AM — ReplyHi,
Very helpful page, thank you.
I have managed to use a select query to retreive data from a second sheet however I am wanting to update data in a sheet using this method. I have changed the sSQLSting to an update query which appears to run but the data does not update.
Could I please trouble you for a simple example of how to update a cell value?
Column A (Dealer) is unique and Column B (Value) is the cell that I am trying to update
Sheet name = DATA
Column A = Dealer
Column B = ValueThank you,
Dan
-
Dan
October 21, 2015 at 10:19 AM — ReplySorry for wasting your time with my first message, was a pretty simple mistake in the end.
I have it working however I am wanting to source the value that I am updating from a cell on the sheet. I have done this with:
Dim NewVal As String
NewVal = Sheets(“ADO”).Range(“N2”).Value
When I try to put this into the sSQLSting it errors. Can you please help me out.Thanks again.
Code:
‘Add reference for Microsoft Activex Data Objects Library
Sub sbADOUPDATE()
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim sSQLQry2 As String
Dim NewVal As StringDim ReturnArray
Dim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.RecordsetDim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
DBPath = “P:DocumentsSALESOrderwrite2015TestingBook2.xlsx”
NewVal = Sheets(“ADO”).Range(“N2″).Value‘You can provide the full path of your external file as shown below
‘DBPath =”C:InputData.xlsx”sconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”
Conn.Open sconnect
sSQLSting = “UPDATE [Data$] SET Content = ‘testing2’ WHERE Dealer = ‘Q325′”mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
sSQLSting2 = “UPDATE [Data$] SET Content = 1000 WHERE Dealer = ‘Q375′”mrs.Open sSQLSting2, Conn
‘Close Connection
Conn.CloseEnd Sub
-
Masaru
November 1, 2015 at 11:58 PM — ReplyQuestion: I have a header where it has been merge with under a 3 column, is it possible to call the sub column? Thanks!
-
Michael
November 10, 2015 at 8:37 PM — ReplyHi All
I have a spreadsheet with an Excel Table named Table1 with two Columns named Quarter and Sales.
The Table has say 4 rows of data beneath the header. Then there is more data in the rows below the table which is not part of the table.How do I copy only the data in the Table rows?
Using SqlQry = “SELECT [Quarter], [Sales] FROM [Sheet2$][Table1$]”
Copied all the data in the two columns including the data outside the Table.
Thanks. -
loes
November 25, 2015 at 7:52 PM — ReplyHello,
I am trying to set up a connection to MySQL and came across this example. I applied the code to my own file. But what i can not seem to figure out is why the file does not take the values you write in A1, A2 etc. where in the code do you tell the code to skip the first line?
-
Ray
November 26, 2015 at 10:35 AM — ReplyThis is precisely what i was searching for..Thanks a Ton.
One question please….Here we saw fetching data from a spreadsheet using ADO.
Can we write data from a User interface,like a form (in Spreadsheet A) to a Database (Spreadsheet B) using ADO ?
Please can you point me to where can I get more info on this.
All the best with your efforts. God bless !
-
mike
January 15, 2016 at 1:22 PM — ReplyHello,
I have made a connection with a dbf file with VBA this works great, but is it also possible to open multiple dbf files en join them in the SQL? Iám trying hard but can’t figure it out.
-
Shwetanjali Das
February 11, 2016 at 12:10 PM — ReplyHi,
I want to fetch records from a database. How to do that? I have read only access to that database.
-
srimeenakshi
March 22, 2016 at 6:01 PM — Replyhi friends,
i want a code to update a table in a database. when we click command button in vba?
anyone can help me -
Iris
March 29, 2016 at 3:21 PM — Replyhi, i couldn’t download the example file, seems the linkage was corrupted.
-
Akit
May 3, 2016 at 10:09 AM — ReplyHI ,
Really helpful blog, I am encountering an error when I tried to use Like operator in my sql statement.
exs
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim ReturnArray
Dim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.Recordset
Dim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
DBPath = ThisWorkbook.FullName
‘You can provide the full path of your external file as shown below
‘DBPath =”C:InputData.xlsx”
sconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”
Conn.Open sconnect
Debug.Print YourstrQery,1. SQLSting = “SELECT * From [Sheet1$] WHERE [URL] like ‘%POST /login.form HTTP/1.1%’ ”
2. SQLSting = “SELECT * From [Sheet1$] WHERE session in(Select Distinct session from [Sheet1$]) and [URL] like ‘%POST /login.form HTTP/1.1%’ ”
mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
-
ram
May 10, 2016 at 12:34 PM — ReplyThere are records in the sheet titled ‘Table2’, which have Cust_ID not present in column Cust_ID in the sheet titled ‘Table1’ (e.g. 110, 117). Can you write an Excel VBA program that transfers the data in these sheets to 2 separate tables in Access DB, runs the appropriate query and provides the list of unmatched records from ‘Table2’? Please use ADO method for database connectivity. The program should execute on clicking a button in Excel and output should comprise of unmatched records displayed in a new Excel sheet.
-
Guilherme
June 4, 2016 at 12:08 AM — ReplyI did’nt find the example file =(
Can you send me the link? -
PNRao
June 4, 2016 at 9:43 PM — ReplyThanks- We have fixed the download link.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Kamal Kroor
June 21, 2016 at 1:08 PM — ReplyDear All,
Any one can help me with using variables in update command? in the above example, update is used only with exact number which will not be the case for real time situation. We need a variable that takes values from the user form.
Thanks,Kamal Kroor
-
Célio Ávila
June 21, 2016 at 7:56 PM — ReplyDamn… I’ve been trying so hard to learn this, but nothing ever seems to work.
I finally downloaded the example file and not even that is working. I get the message, “System error &H8000FFFF (-2147418113). Catastrophic Failure.”
I activated the 2.8 library something, so I dont know what could be going wrong.Also, every source I look for to study gives me a completely different macro example, so I can’t even compare them to better understand the coding.
When I do find good content to learn SQL from, it doesnt seem to be related to excel vba, so it doesnt help me all that much.
I’m trying to learn how to filter data with ADO insteand of using autofilter. At first I saw someone posting this example:
Sub testConnection()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim c As WorkbookConnection
Dim sql As StringSet wb = ActiveWorkbook
Set c = wb.Connections.Item(1)
sql = c.ODBCConnection.CommandText
sql = Replace(sql, “WHERE (`’Sheet1$’`.k=10)”, _
“WHERE (`’Sheet1$’`.k=9) AND (`’Sheet1$’`.l=11) AND (`’Sheet1$’`.m=12) AND (`’Sheet1$’`.n=13) “)
c.ODBCConnection.CommandText = sql
c.RefreshEnd Sub
can anyone make sense of this?
-
Ankush
June 28, 2016 at 3:31 PM — ReplyHi
Could you let me know if we can connect a macro to the server and get the information from the log files.
And if yes , then could you let me know how we could connect to the server.
-
Stanley
July 1, 2016 at 1:25 PM — ReplyHi PNRao,
Your website is awesome!
Do you have experience to use RANK() OVER(PARTITION BY) function by ADODB connection?
I need to rank first and output them.
Any help would be greatly appreciated.Stanley
-
Stewart
July 15, 2016 at 2:27 PM — ReplyHI PNRao,
New to using VBA & ADO , I wish to use a similar code that uses an input-box to pull through the relevant input from a closed workbook to my current active workbook, is this possible?
Kind Regards,
Stewart
-
Sanjeev Sharma
August 6, 2016 at 12:54 AM — ReplyThanks!! for the valuable information!!
-
Pawan
August 30, 2016 at 10:49 AM — ReplyVery nice Article. I have one query in this that I have one column which has number as well as text and I found one thing that vb query that declare the fields type as Number and it will not show Text values. So is it possible to import all the fields with data type as a string because string can capture both number as well as text.
-
Tomi
August 30, 2016 at 11:58 PM — ReplyHi, I am new to VBA and application development. Please how can someone start with learning VBA and Database Application development? Thank you
-
Durgam Sasidhar
January 4, 2017 at 7:36 PM — ReplyWOW, This is what am searching for entire day, and this post Cleared My doubts and issues. Thx a lot
-
Sunil Sehgal
April 5, 2017 at 11:05 AM — ReplyHello sir,
While I run my code it is showing automation error. Can you please etell me why is it so occuring.. tell me the solutio n for the same. -
Hasan
May 4, 2017 at 9:05 PM — ReplyHi,
when the Excel file is opened read-only, the sql query (with both providers MSDASQL and Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB) does not return any results.
Any ideas how to overcome this, maybe using additional parameters?
-
Rakesh
May 17, 2017 at 2:43 PM — ReplyHi PNRao,
Information provided by you in your website is excellent.
I customised this code to postgresql,but getting an Run-Time error object required: 424.Can you please help me with this error.Thanks
Rakesh -
AK
July 19, 2017 at 7:57 PM — ReplyDear PN,
Really, this webpage is very useful, thanks for your efforts.
I have one question here:
Instead of figures (2 & 5000) at ‘Values(2,500)’ how can use variables or cells from active sheet?Thanks in advance & regards,
AK -
PNRao
July 19, 2017 at 8:51 PM — ReplyYou need to form the string as per your requirement. Replace the below statement: sSQLSting = “INSERT INTO [DataSheet$](Quarter, Sales) Values(2,5000)”. With: sSQLSting = “INSERT INTO [DataSheet$](Quarter, Sales) Values(" &Range("A1") &"," &Range("A2") &")”.The second statement will read the values from Range A1 and A2 of ActiveSheet. You can also specify the sheet name if it is not a active sheet, Sheets(“SheetName”).Range(“A1”)
Thanks!
-
YasserKhalil
July 20, 2017 at 10:59 PM — ReplyThat’s really awesome. Thank you very much
How to update closed workbook using ADO? -
Andi permana
November 30, 2017 at 4:36 PM — ReplyHow do I use where statement and group by??
-
Mayur raj
March 4, 2018 at 12:50 PM — ReplyHi recordset stores the result in array form, when using select a view/output is getting stored.but using insert there is no output, it will process the query and store data in mentioned table.
Add one more line, select * from [inserted_table]
Before msr.
Hope you get the logic.
Thanks -
Anil
April 19, 2018 at 6:10 PM — ReplyHi Sir,
I have insert code but show the error.
Option Explicit
Dim BlnVal As BooleanPrivate Sub Done_Click()
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim ReturnArray
Dim con As ADODB.Connection
Dim sqlstr As String, datasource As String
Set con = New ADODB.Connection
datasource = “D:TEST.xlsx” ‘change to suitDim sconnect As String
sconnect = “Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0;” & _
“Data Source=” & datasource & “;” & _
“Extended Properties=”Excel 12.0;HDR=YES”;”
With con
.Open sconnect
‘
sqlstr = “Insert Into [Sheet2$](Sno, Name, Amt) Values (GP.ComboBox1.Value, GP.TextBox1, GP.TextBox2)”
‘
.Execute sqlstr
.Close
End WithSet con = Nothing
End Sub
-
Anil
April 19, 2018 at 6:14 PM — ReplyI have insert data in offline Excel File & Same Update Data Combobox1 and TextBox1 only Number accept. not Text.
-
nalini raju
May 14, 2018 at 6:47 PM — Reply‘Iam not able to insert
‘Iam getting error–Automation error in runtime
‘Using MSDASQL Provider
‘sconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”‘Using Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB Provider – If you get an issue with Jet OLEDN Provider try MSDASQL Provider (above statement)
sconnect = “Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=” & DBPath _
& “;Extended Properties=”Excel 8.0;HDR=Yes;IMEX=1″;”Conn.Open sconnect
‘DeleteId = InputBox(“Name”)
” sSQLSting = “SELECT DISTINCT Date,SalesRep,Product,Discount,Units,Region,Net_Sales From [DataSheet$]”
‘ Your SQL Statemnt (Table Name= Sheet Name=[DataSheet$])
‘ sSQLSting = “UPDATE [DataSheet$] SET SalesRep=10,Product=10,Discount=10,Units=10,Region=10 WHERE Units=1”
sSQLSting = “INSERT INTO [RAMA$](Quarter, Sales) Values(” & Sheets(“RAMA”).Range(“A1”) & “,” & Sheets(“RAMA”).Range(“A2”) & “)”
‘ sSQLSting = “Select * from [DataSheet$]” ‘ where Date is not null”
mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn‘ Sheets(“RAMA”).Range(“A1”).CopyFromRecordset mrs
mrs.Close
‘Close Connection
Conn.Close
End Sub -
Taesoo
June 14, 2018 at 4:51 PM — ReplyHi,
I read date from db file but can not read full data.
Below is the data in db file
Date
4/16/2016 16:39
4/19/2016 12:50
4/22/2016 16:12
4/25/2016 10:28
4/27/2016 10:51This is what I read
Date
4/16/2016
4/19/2016
4/22/2016
4/25/2016
4/27/2016Sub db_query()
Dim conn As Object, rst As Object
Worksheets(“results”).Range(“A2:AI5001”).ClearContentsSet conn = CreateObject(“ADODB.Connection”)
Set rst = CreateObject(“ADODB.Recordset”)conn.Open “DRIVER=SQLite3 ODBC Driver;Database=D:backup.db;”
strSQL = “SELECT Date from Tb_Result_Summary”
rst.Open strSQL, conn, 1, 1Worksheets(“results”).Range(“A2”).CopyFromRecordset rst
rst.CloseSet rst = Nothing: Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
-
Baze
July 9, 2018 at 3:50 PM — ReplyHi PN, thank you for this material. it is very educative especially for a person who is beginner in VBA like me.
I am trying to make a connection from my excel file to a database and i tried your code but it resulted in a mistake :‘Sheet1$’ is not a valid name. Make sure that it does not include invalid characters or punctuation and that it is not too long
I am apologizing in advance, cause this question might seem very beginner for you, but I am in my first steps with VBA.
-
Deepak Bisht
October 2, 2018 at 6:45 PM — ReplyEach time i pull data the file opened in read only mode.. Please advise
-
Prabhu Murugan
December 20, 2018 at 9:42 AM — ReplyHi,
A column in an excel file consist of values only. But still select query for the field throws data type mismatch in criteria even after I changed all the cells to values.
select * from table where field < 0
It works only for
select * from table where field < ‘0’
-
Amber
July 18, 2019 at 5:58 AM — ReplyI want to get into an array all records brought by getRows but I can’t. When I try like this, the array stay empty anyway. I only get success by using getString but my goal is insert each record into a cell of a listbox. I hope you can understend my english!
-
anil
November 17, 2019 at 12:50 PM — Replythanks for efforts sir as a beginer easyly understand whole concept
-
Mon
February 9, 2020 at 1:15 PM — ReplyHi,
please advise how can I use the SQL command to delete the record
thank you
-
Dinesh
May 2, 2020 at 10:37 PM — Reply
Effectively Manage Your
Projects and Resources
ANALYSISTABS.COM provides free and premium project management tools, templates and dashboards for effectively managing the projects and analyzing the data.
We’re a crew of professionals expertise in Excel VBA, Business Analysis, Project Management. We’re Sharing our map to Project success with innovative tools, templates, tutorials and tips.
Project Management
Excel VBA
Download Free Excel 2007, 2010, 2013 Add-in for Creating Innovative Dashboards, Tools for Data Mining, Analysis, Visualization. Learn VBA for MS Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Access, Outlook to develop applications for retail, insurance, banking, finance, telecom, healthcare domains.
Page load link

3 Realtime VBA Projects
with Source Code!
Go to Top
ORM переводится, как object relational mapping (объектно-реляционное отображение). Это означает, что мы работаем с базой не на уровне SQL запросов, а на уровне объектов.
Давайте я покажу пример и как это будет работать в итоге.
Для начала скажу, что у меня есть база «SQL Server 2016» серьезная база для промышленной реализации, но не пугайтесь она так же доступна простым смертным. Где её скачать расскажу позже.
Каждый раз для использования нашей ORM необходимо объявить и инициализировать несколько переменных c типом DataBase, RecordSet, UnitOfWork. И соединить их с помощью метода Init.
Давайте объявим эти переменные.
Dim db As New DataBase Dim Rs As New ADODB.Recordset Dim uow As New unitOfWork uow.Init db, Rs
Давайте посмотрим, как получить данные.
Для этого объявим переменную с типом User. И реализуем цикл с помощью метода GetAll . Посмотрите, как удобно получать данные о пользователях. Всё что нам надо это просто вызвать метод GetAll в свойстве UserRepository. Точно такие же репозитории будут добавляться и для других типов данных, например, некие документы или накладные InvoiceRepository. После чего в самом цикле мы переберем всех пользователи из базы и выведем их в консоль.
В цикле можно перебрать любые данные. Использовать такие методы, как GetAll очень удобно. Мы не заморачиваемся с SQL запросами и получаем объект определенного типа, свойства и методы которого можно получить и увидеть через IntelliSence. Свойства полученного объекта в нашем примере это Id, Email, UserName объект пока не содержит методов только свойства.
Теперь давайте посмотрим, как добавить запись в базу
Фактически всё что нам нужно это создать объект и задать этому объекту новые значения.
Потом добавить объект через метод “Add”, который есть у любых коллекций и зафиксировать изменения в базе через метод “uow.Commit”.
Если мы запустим наш цикл, который выводил данные мы увидим нашу новую запись.
Та же самая запись сохранилась в базе. При этом Id добавился автоматически, т.е. Id это так называемый первичный ключ в базе, который сама база добавляет автоматически.
И в этом примере добавление данных выглядит крайне удобно и вполне естественно. Создаем объект пользователь, задаем ему значения свойств и добавляем в репозиторий. Всё!
Итак, теперь подробнее про саму реализацию ORM.
Для работы с этим примером нам потребуется несколько программ. Первая программа — это SQL Server 2016. Вы сможете найти её по адресу (https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/sql-server/application-development). Также для работы нам потребуется Management studio (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/ssms/download-sql-server-management-studio-ssms). Выберите и нажмите ссылку в зависимости от вашего языка.
В ООП есть специальные шаблоны проектирования, чтобы другие программисты, увидев их понимали, что мы написали и как работает наша программа.
В данном случае у нас есть шаблон проектирования – репозиторий его суть — это удобное переключение баз данных, получение данных в объектном стиле. В моем примере мы работаем с SQL Server 2016, но с шаблоном проектирования репозиторий мы можем поменять базу, например, на MySql или MS Access довольно просто. При этом наша основная логика не пострадает.
Теперь, давайте посмотрим пример поподробнее. Для того, чтобы реализовать шаблон нам надо несколько классов сам репозиторий. В моем примере это – UserRepository. Класс, который объединяет репозитории это класс UnitOfWork. И классы, которые соответствуют таблицам в базе данных такие классы называют модели данных. Они же в идеале должны содержать большую часть логики (которые обычно реализуются через методы), так называемая, богатая модель. Если модель не содержит логики т.е. методов, то её принято называть ананимичная модель т.е. бедная. В моем простом примере нет пока логики, поэтому модель «User» пока можно отнести к ананимичной модели данных.
И так давайте посмотрим на модель User. В классе добавлено три псевдосвойства Id, Email, UserName. У меня есть отдельное видео рассказывающее про эти свойства. Те же самые поля у меня определенны в базе данных. В Management Studio я создал простую базу TestDb и добавил таблицу User. В исходниках у Вас будет SQL файл с запросом на создание этой таблицы. Просто запустите его в своей Management Studio.
Либо в Management Studio добавьте таблицу, нажав правую кнопку -> New -> Table. И добавьте поля Id, Email, UserName. Для Id добавьте тип данных bigint, для Email nvarchar(50), для UserName nvarchar(50).
Потом нажмите правую кнопку мышки по полю Id и выберите “Set primarity key” (добавить). Это тот самый первичный ключ, который автоматически увеличивается при каждом добавлении данных в базу.
Поэтому в свойствах поля проставьте инкремент полю Id, чтобы при каждом добавление записей в таблицу поле Id автоматически увеличивалось на единицу.
UnitOfWork
Давайте теперь посмотрим класс UnitOfWork
Данный класс в основном должен содержать только репозитории и метод Commit для сохранения данных в базе. И может содержать несколько вспомогательных членов.
В моем примере я добавил метод Init, чтобы через этот метод можно было внедрить объекты типа DataBase и Recordset. Т.к. в стандартном конструкторе на VBA нет возможности передать параметры. Такой механизм передачи объектов извне класса называется внедрение зависимостей.
Private pUserRepository As UserRepository Public Function Init(DataBase As DataBase, Recordset As ADODB.Recordset) Set pUserRepository = New UserRepository Set pUserRepository.DataBase = DataBase Set pUserRepository.Recordset = Recordset End Function
Давайте посмотрим класс DataBase. Сам класс DataBase еще проще всё что он делает это запускает соединение при каждой инициализации и открывает соединение.
Public Connection As New ADODB.Connection
Private pStr As String
Private Sub Class_Initialize()
pStr = "Driver={SQL Server Native Client 11.0};Server=localhost;Database=TestDb;Trusted_Connection=yes;"
Connection.ConnectionString = pStr
If Connection.State = 0 Then
Connection.Open
End If
End Sub
Друзья я еще не рассказывал, как работать с базами через библиотеку ADODB. Если вы хотите более подробный урок по этой теме просто напишите мне или пролайкайет видео.
Репозиторий (UserRepository)
Сам репозиторий довольно простой для начала я добавил три публичных свойства, чтобы был доступ к самой базе SQL Server через объект типа DataBase. Добавил свойство RecordSet для работы с ним внутри метода GetAll. В принципе сам класс UserRepositroy можно запускать независимо, но для реализации шаблона я инициализирую репозиторий в классе UnitOfWork.
Public LocalUsers As New Collection Public DataBase As DataBase Public Recordset As ADODB.Recordset
И далее два основных метода. Метод GetAll и метод Add. Метод GetAll просто получает все записи из базы данных и переводит их в объект коллекцию типа User c помощью встроенного объекта RecordSet. Внутри метода я запускаю SQL запрос на выборку нужных мне полей. А далее через объект RecorSet получаю их.
Public LocalUsers As New Collection Public DataBase As DataBase Public Recordset As ADODB.Recordset Public Function GetAll() As Collection Dim selectAllQuery As String: selectAllQuery = "Select Id, Email, UserName from [User]" If DataBase Is Nothing Then MsgBox "DataBase not found set it" If Recordset Is Nothing Then MsgBox "RecordSet not found set it" Recordset.Open selectAllQuery, DataBase.Connection Dim userCollection As New Collection Dim user As user With Recordset While (Not .EOF) Set user = New user user.Id = .Fields(0).Value user.Email = .Fields(1).Value user.UserName = .Fields(2).Value userCollection.Add user .MoveNext Wend End With Recordset.Close Set GetAll = userCollection End Function
Public Function Add(user As user) LocalUsers.Add user End Function
Метод Add добавляет объект типа User в глобальную переменную LocalUsers с ней мы будем работать через класс UnitOfWork, чтобы сохранить данные в базе.
Connecting to Microsoft Access Database from Excel VBA, using DAO Object Model
Microsoft Access: Data Access Objects Library (DAO), Connect with Access Databases from Excel using VBA.
Part 1 of 3
Microsoft Access: Data Access Objects Library (DAO), Connect with Access Databases from Excel using VBA
1. Connecting to Microsoft Access Database from Excel VBA, using DAO Object Model.
2. Microsoft Access DAO Object Model: Create an Index, Create Relationship between Fields, Create and Execute a Query.
3. Microsoft Access DAO Object Model: Import or Export Data from Access to Excel.
—————-
Also Read:
Microsoft Access: ActiveX Data Objects (ADO), Connect with Access Databases from Excel using VBA.
————————————————————————————
Contents:
Connect with Databases using DAO, RDO and ADO Objects
DAO Objects & Programming model
The DBEngine object & Workspace Object
DAO Databases
Tables of a DAO Database
Fields / Columns of a Table
Recordset & Records of a DAO Database Table
————————————————————————————
To connect with other databases, when working in VBA, you can use either DAO (Data Access Objects), RDO (Remote Data Objects) or ADO (ActiveX Data Objects). After connecting to a database, you can manipulate its data. DAO, RDO and ADO are data access interfaces ie. they are object and programming models used to access data. Earlier, DAO was used to interface with local databases (viz. MS Access), RDO was used to interface with large databases such as Oracle and SQL Server. ADO was their replacement to interface with all types of data sources. Both DAO and ADO are commonly used while connecting to Microsoft Access Database.
This section explains using the DAO Objects & Programming model to Connect with Access Databases from Microsoft Excel, the DBEngine object, Workspace Object & Workspaces Collection, DAO Databases, Tables of a DAO Database, Fields / Columns of a Table, Recordset & Records of a DAO Database Table, with practical examples.
Connect with Databases using DAO, RDO and ADO Objects
To connect with other databases, when working in VBA, you can use either DAO (Data Access Objects), RDO (Remote Data Objects) or ADO (ActiveX Data Objects). After connecting to a database, you can manipulate its data.
DAO, RDO and ADO are data access interfaces ie. they are object and programming models used to access data. Earlier, DAO was used to interface with local databases (viz. MS Access), RDO was used to interface with large databases such as Oracle and SQL Server. ADO was their replacement to interface with all types of data sources. Both DAO and ADO are commonly used while connecting to Microsoft Access Database. DAO is native to Access, the DAO object library is the default reference in Access 2007 and the library will be existing when you use Access (ADO object library was the default reference in Access 2000 and 2002, whereas DAO returned as the default object library with Access 2003 after being the default in Access 97 earlier). DAO integrates well with Access databases and provides faster access. ADO provides access to a wider variety of data sources than DAO, besides Access. ADO has succeeded DAO and is the latest data access technology, is simpler and more flexible, and interfaces with Microsoft’s powerful data access technology of OLE DB. In ADO the objects are less than in DAO, and it contains more properties, methods and events. ADO/OLE DB is recommended for new projects but it might not be worthwhile to convert DAO code to ADO for existing projects.
ADO creates a reference to the database using the Connection object, to connect to the data source. You use the Open and Close methods to open and close a Connection object. DAO creates a reference to the database using the database object, to connect to the data source.
In Microsoft Access, Recordset objects are used to access and manipulate data in a database. A Recordset object represents a set of records in a database table, or a set of records returned from running a query. Both DAO and ADO libraries have a Recordset object, though the methods, properties, and options of the respective object is different. A Record object is one row of data in a Recordset. A Recordset object has a Fields collection which contains all the Field objects, where each Field object represents a column in the Recordset. In other words, each record represents a row of data and contains many fields, and each field corresponds to a column in the database table.
In your VBA code, you should ideally precede the object name by its program ID (ProgID) prefix, which in ADO is «ADODB» and in DAO is «DAO». Many objects, for example the Recordset object, have similar names in both DAO and ADO and it is advisable to have explicit references in your project. This becomes a must if you have included references to both the DAO and ADO libraries in your VBA project, else the object library mentioned first in the References list will prevail, resulting in confusion in the vba code.
While instantiating the Recordset object, you should use:
Dim daoRecSet As DAO.Recordset
Dim adoRecSet As ADODB.Recordset
instead of:
Dim RecSet As Recordset
DAO Objects & Programming model
DAO (Data Access Objects) is an object-oriented data access interface, used to connect to and access databases. It was the first Objects & Programming model which used the Microsoft Jet database engine, and is optimized to work Microsoft Access files (.mdb). The objects and collections in the DAO object hierarchy are used to connect to a database, access and manipulate its data and database structure.
A database engine is the underlying software component of a database used to manipulate its data. DAO Object Model by default uses the Microsoft Jet database engine for data access. ODBCDirect (which came after ODBC) allowed DAO to access ODBC data sources directly without using the Jet database engine. In this section we will illustrate connecting to Microsoft Access Database using DAO with the Jet engine. Prior to Access 2007, Access used the Microsoft (JET) engine, but with Access 2007 the new and improved ACE engine has succeeded and replaced JET. The ACE engine is fully backward-compatible so that it can be used with the .accdb files (Access 2007) and the earlier .mdb files.
Automating Access from Excel: You can connect to and access a database using DAO, from external applications which support automation (viz. MS Excel, MS Word, etc.), and in this section we show how to do this from Microsoft Excel by using VBA. With automation you can control another application (MS Access) within your host application (MS Excel) without any manual intervention. Automation is used typically to run macros or queries from Excel to connect to or create or manipulate MS Access database and its structure, to access and manipulate MS Access data and reports, to import data from MS Access to Excel for creating charts and pivot tables and otherwise use the data for calculations and analysis.
ODBC (Open Database Connectivity):
ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) is an interface which enables an application to connect and access a relational database, using the SQL query syntax. An ODBC database is a DBMS (Database Management System) for which there is an appropriate ODBC driver (examples of DBMS include SQL Server, Oracle, AS/400, Foxpro, Microsoft Access). The ODBC Driver is a software that resides between the ODBC Client (which is the front-end application wherein the driver is loaded) and the DBMS (wherein the data is stored for access), and it translates the command into a format that is understood by the DBMS. DAO Object Model uses the Microsoft Jet database engine and is optimized to work Microsoft Access files (.mdb), but ODBC databases can also be accessed with DAO and the Microsoft Jet database engine. A database engine is the underlying software component of a database used to manipulate its data. Jet (Joint Engine Technology) is used by Microsoft Access as its database engine.
OLE DB and ODBC:
OLE DB was intended as a successor to improve on ODBC by providing an enhanced and faster interface for data access. OLE DB is not bound to the SQL language like ODBC and it supports all forms of data sources (ie. relational and non-relational data sources including mainframe and hierarchical databases, e-mail and file systems, text and graphical data, custom business objects, …) whereas ODBC was limited to relational databases. OLE DB was complex to be used directly with Visual Basic and Microsoft’s ADO (ActiveX Data Objects) Object Model was introduced which interfaces with an OLE DB provider and enables an application (viz. Excel) to access and manipulate data from a database (viz. MS Access).
ODBC vs DAO, ADO vs DAO:
When working with ODBC data sources, use ODBC. With ODBC you can access any data source for which there is an appropriate ODBC driver for the database you want to access. Examples of ODBC databases include Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Visual FoxPro, IBM DB2, Microsoft Access. When working with Microsoft Jet (.mdb) databases, using DAO will be more efficient. Examples of Microsoft Jet databases include Micorsoft Access, Microsoft SQL Server, Paradox. DAO Object Model uses the Microsoft Jet database engine and is optimized to work Microsoft Access files (.mdb), but ODBC databases can also be accessed with DAO and the Microsoft Jet database engine when you want the Jet database engine’s speed and DAO’s extra functionality. DAO precedes ADO and ODBC precedes OLE DB. ADO/OLE DB is recommended for new projects but it might not be worthwhile to convert DAO code to ADO for existing projects.
Add a reference to the DAO Object Library
To use DAO in your VBA project, you must add a reference to the DAO Object Library in Excel (your host application) by clicking Tools-References in VBE, and then choose an appropriate version (mostly, you should choose the highest version number), which is «Microsoft DAO 3.6 Object Library» for Access 2000 onwards.
The DBEngine object
The highest level object in the DAO object model is the DBEngine object, and it contains all objects in the hierarchy of DAO objects. There can only be one DBEngine object and there is no collection of which it is an element of. The DBEngine object has many properties and methods, and contains 2 collections — the Workspaces collection and the Errors collection. You can configure the database engine with properties and methods provided by the DBEngine object. A database engine is the underlying software component of a database used to manipulate its data. You can refer to DBEngine directly without explicitly declaring an object variable of type DBEngine.
Workspace Object & Workspaces Collection
Create a Workspace object to define a user session by name, in which a user performs all database operations by using the Microsoft Access database engine. The Workspace object allows you to open multiple databases or connections in a session, and you can open additional sessions with the Workspace object. A Workspace session starts on creation of a new Workspace object and ends when the Workspace object Close method is used. Multiple sessions (ie. workspace objects) are specifically useful when you want to perform operations as different users or when you want to manage separate and independent operations in each session. All active and unhidden workspace objects are called the Workspaces collection, which is contained in the DBEngine object. In DAO, when you open databases, they automatically exist within the default workspace which is the first workspace in the Workspaces collection. A default workspace, DBEngine.Workspaces(0), is automatically created when a Workspace object is first referred to or used, with the name as «#Default Workspace#», and if security is not enabled with username as «admin» (if security is implemented then username is set to the name of the user who logs on).
You can use the CreateWorkspace method to create a Workspace object. It is not necessary to append a Workspace object to the Wokspaces collection after creating it, and in this case you will need to refer it by the object variable used in the CreateWorkspace method. It will be required to append a Workspace object to the Wokspaces collection after creating it, if you want to refer to it from the Workspaces collection by its ordinal number or Name viz. DBEngine.Workspaces(0) or DBEngine.Workspaces(«WorkspaceObjectName») or DBEngine.Workspaces![WorkspaceObjectName]. All defined DAO Workspace objects appended to the collection comprise the Workspaces collection. There are 2 types of Workspace objects, as defined by WorkspaceTypeEnum Enumeration in the CreateWorkspace method — (i) Microsoft Jet Workspace objects (type — ‘dbUseJet’) which creates a Microsoft Access workspace; and (ii) ODBCDirect workspaces (type — ‘dbUseODBC’) which are not supported in Microsoft Office Access 2007. In this section we will discuss only the Microsoft Jet Workspace objects.
By default the DBEngine.DefaultUser Property is set to «Admin» and the DBEngine.DefaultPassword Property is set to a zero-length string («») and the default Workspace object’s user and password are defined accordingly. When you start Access or access an Access database with vba, all users automatically log-in with the default name «Admin» and the password of zero-length string («»), but to access a database in a secured system (ie. a secured Access Database) users must provide a username and a password (if a password has been assigned to the user). In a secured system, for the default workspace you set the DefaultUser and DefaultPassword properties (for the DBEngine object), and after the default session has been initialized, additional sessions can be created with user names and passwords. Note that password is case-sensitive but not the username. In this section we do not go into further details of accessing a secured Microsoft Access database.
DBEngine.CreateWorkspace Method
Use the DBEngine.CreateWorkspace Method to create a new Workspace object. Syntax: DBEngineObject.CreateWorkspace(Name, UserName, Password, UseType). All arguments, except UseType, are mandatory. In the Name argument, specify a unique Workspace name for a session. In the UserName argument, specify the name of the user for identification. In the Password argument, you are required to enter a password for the Workspace object with a maximum of 20 characters. The UseType argument specifies one of the WorkspaceTypeEnum values: (i) dbUseJet — (Microsoft Jet Workspace objects) which creates a Microsoft Access workspace, and is also the default; and (ii) dbUseODBC — for ODBCDirect workspaces which are not supported in Microsoft Office Access 2007.
In DAO, when you open databases, they automatically exist within the default workspace which is the first workspace in the Workspaces collection. You need to use the DBEngine.CreateWorkspace Method only to create a second workspace which is seldom required.
Example 1: DAO WorkSpace Object & Workspaces Collection.
1. Create a new Workspace object, using the CreateWorkspace method, and append to the Workspaces collection.
2. Access properties of all workspace objects (ie. default workspace and the newly created workspace).
Sub AccessDAO_CreateWorkspace_1()
‘Create a new Workspace object, using the CreateWorkspace method, and append to the Workspaces collection.
‘Access properties of all workspace objects (ie. default workspace and the newly created workspace).
‘To use DAO in your Excel VBA project, you must add a reference to the DAO Object Library in Excel (your host application) by clicking Tools-References in VBE.
Dim strMyPath As String, strDBName As String, strDB As String
Dim wrkSpace As DAO.Workspace, wrkSpaceNew As DAO.Workspace
Dim prpWrkSpace As DAO.Property
‘create a new Microsoft Jet Workspace, with the default type of dbUseJet:
Set wrkSpaceNew = DBEngine.CreateWorkspace(«newWS», «admin», «», dbUseJet)
‘append the new workspace to the Workspaces collection:
DBEngine.Workspaces.Append wrkSpaceNew
‘return the number of workspace objects in the Workspaces collection (returns 2 — default & new workspace):
MsgBox DBEngine.Workspaces.count
‘access properties of all workspace objects (ie. default workspace and the newly created workspace):
For Each wrkSpace In DBEngine.Workspaces
‘workspace name (returns «#Default Workspace#» & «newWS»):
MsgBox «Workspace Name: » & wrkSpace.Name
‘username property setting:
MsgBox wrkSpace.UserName
‘properties of workspace object:
For Each prpWrkSpace In wrkSpace.Properties
MsgBox «Property Name: » & prpWrkSpace.Name
Next prpWrkSpace
Next wrkSpace
‘returns the name of the default Workspace, ie. «#Default Workspace#»:
MsgBox DBEngine.Workspaces(0).Name
‘because the Workspace object has been appended to the Wokspaces collection after creating it, we can refer to it from the Workspaces collection by its ordinal number or Name (returns «newWS»):
MsgBox DBEngine.Workspaces(«newWS»).Name
‘if the Workspace object had not been appended to the Wokspaces collection after creating it, in this case you would have had to refer it by the object variable used in the CreateWorkspace method (returns «newWS»):
MsgBox wrkSpaceNew.Name
‘close the objects:
wrkSpaceNew.Close
‘destroy the variables:
Set wrkSpace = Nothing
Set wrkSpaceNew = Nothing
Set prpWrkSpace = Nothing
End Sub
DAO Workspace Object Methods
DAO Workspace Object Methods: The Close Method is used to close an open Workspace. CreateDatabase method is used to create a new database and the OpenDatabase method is used to open an existing database. To manage transaction processing during a session (ie. when a series of database changes made in a session are treated as one unit), you have three transaction methods of BeginTrans, CommitTrans and Rollback. The OpenConnection Method, available only in an ODBCDirect workspace, is used to open a connection to an ODBC data source. Note that Microsoft Office Access 2007 does not support ODBCDirect workspaces.
DAO Databases
DBEngine.OpenDatabase Method
Use the DBEngine.OpenDatabase Method to open a Database, as specified by its name/path. A reference to the Database object variable (to which the database is assigned) is returned by this method, and the database is not actually opened in the Microsoft Access window. If you open a database object without specifying a workspace, it will exist within the default workspace: DBEngine.Workspaces(0). Syntax: DBEngineObject.OpenDatabase(Name, Options, ReadOnly, Connect). Name argument is mandatory while all other arguments are optional. In the Name argument you will specify the database file name and full path, which you want to open. In the Options argument, you can specify False which is the Default and opens the database in shared mode while specifying True opens the database in exclusive mode. In the ReadOnly argument specifying False (default) will open the database with read-write access and specifying True will open in read-only. Connect argument is used to specify connection information (ex. password).
DAO Workspace.OpenDatabase Method
Use the DAO Workspace.OpenDatabase Method to open a Database, as specified by its name/path, in the specified Workspace object. A reference to the Database object variable (to which the database is assigned) is returned by this method, and the database is not actually opened in the Microsoft Access window. Syntax: WorkspaceObject.OpenDatabase(Name, Options, ReadOnly, Connect). The arguments are similar to as in the DBEngine.OpenDatabase Method, explained above.
DAO DBEngine.CreateDatabase Method
Use the DAO DBEngine.CreateDatabase Method to create, open and save a new Database. A reference to the Database object variable (to which the new database is assigned) is returned by this method. Note that this method creates a new empty database, which you will need to structure and enter content thereafter. If you create a database object without specifying a workspace, it will exist within the default workspace: DBEngine.Workspaces(0). Syntax: DBEngineObject.CreateDatabase(Name, Locale, Option). Name and Locale arguments are mandatory. In the Name argument (max 255 characters) you will specify the file name and full path of the database which is being created. The Locale argument specifies a collating order for the database (this is equated with the Database.CollatingOrder Property which specifies the database sort order sequence) ie. the character set to be used to determine how database values will be sorted. Specifying the constant «dbLangGeneral» for this argument means creating a database which will support sorting for «English, German, French, Portuguese, Italian, and Modern Spanish». A password for the new Database can also be created in concatenation with the constant specified in the Locale argument viz. dbLangGeneral & «;pwd=123», where password is «123». The Option argument specifies a constant to determine the version for the data format and if the database should be encrypted, and not specifying a constant will create an un-encrypted database.
DAO Workspace.CreateDatabase Method
Use the DAO Workspace.CreateDatabase Method to create, open and save a new Database. A reference to the Database object variable (to which the new database is assigned) is returned by this method. Note that this method creates a new empty database, which you will need to structure and enter content thereafter. This method creates a new Database and opens it in the specified workspace object. Syntax: Workspace.CreateDatabase(Name, Locale, Option). The arguments are similar to as in the DBEngine.CreateDatabase Method, explained above.
Example 2: Open an existing Database, Create a new Database.
1. Open an existing Database using the DAO OpenDatabase Method.
2. Create a new Database using the DAO CreateDatabase Method.
3. Return Databases and enumerate their properties in a Workspace.
Sub AccessDAO_OpenDatabaseCreateNewDatabase_2()
‘Create a New Microsoft Jet Workspace; Open an existing Database using the DAO OpenDatabase Method; Create a new Database using the DAO CreateDatabase Method; Return Databases and enumerate their Properties in a Workspace;
‘To use DAO in your Excel VBA project, you must add a reference to the DAO Object Library in Excel (your host application) by clicking Tools-References in VBE.
Dim strMyPath As String, strDBName As String, strDB As String, strDBNameNew As String, strDBNew As String
Dim daoDB As DAO.Database, daoDBNew As DAO.Database, daoDBS As DAO.Database
Dim wrkSpaceNew As DAO.Workspace
Dim prpDB As DAO.Property
‘—————
‘SET DATABASE NAMES (EXISTING & NEW):
‘your data source with which to establish connection — ENTER the existing MS Access Database Name:
strDBName = «SalesReport.accdb»
‘get path / location of the database, presumed to be in the same location as the host workbook:
strMyPath = ThisWorkbook.Path
‘set the string variable to the Database:
strDB = strMyPath & «» & strDBName
‘name of the new MS Access Database being created:
strDBNameNew = «SalesReportNew.accdb»
‘set the string variable to the new Database:
strDBNew = strMyPath & «» & strDBNameNew
‘—————
‘CREATE A NEW MICROSOFT JET WORKSPACE:
‘create a new Microsoft Jet Workspace, with the default type of dbUseJet:
Set wrkSpaceNew = DBEngine.CreateWorkspace(«newWS», «admin», «», dbUseJet)
‘append the new workspace to the Workspaces collection:
DBEngine.Workspaces.Append wrkSpaceNew
‘—————
‘OPEN AN EXISTING DATABASE:
‘open the database in the default workspace:
‘Set daoDB = DBEngine.Workspaces(0).OpenDatabase(strDB)
‘If you open a database object without specifying a workspace, it will exist within the default workspace:
‘Set daoDB = DBEngine.OpenDatabase(strDB)
‘If you open a database by specifying a workspace object, it will exist within the specified workspace:
Set daoDB = wrkSpaceNew.OpenDatabase(strDB, True)
‘alternatively:
‘Set daoDB = DBEngine.Workspaces(«newWS»).
OpenDatabase(strDB, False)
‘—————
‘CREATE A NEW DATABASE:
‘If you create a database object without specifying a workspace, it will exist within the default workspace:
Set daoDBNew = DBEngine.CreateDatabase(strDBNew, dbLangGeneral)
‘alternatively, to create a new database and open in the new Workspace object:
‘Set daoDBNew = wrkSpaceNew.CreateDatabase(strDBNew, dbLangGeneral)
‘—————
‘ACCESS DATABASES IN EACH WORKSPACE (DEFAULT AND NEW WORKSPACE):
‘return the number of database objects in the new Workspace:
MsgBox «No of database objects in the new Workspace: » & wrkSpaceNew.Databases.count
‘access databases in the new workspace:
For Each daoDBS In wrkSpaceNew.Databases
MsgBox daoDBS.Name
For Each prpDB In daoDBS.Properties
MsgBox «Property Name: » & prpDB.Name
Next prpDB
Next daoDBS
‘return the number of database objects in the default Workspace:
MsgBox «No of database objects in the default Workspace: » & DBEngine.Workspaces(0).Databases.count
‘access databases in the default workspace:
For Each daoDBS In DBEngine.Workspaces(0).Databases
MsgBox daoDBS.Name
For Each prpDB In daoDBS.Properties
MsgBox «Property Name: » & prpDB.Name
Next prpDB
Next daoDBS
‘—————
‘close the objects:
daoDB.Close
daoDBNew.Close
wrkSpaceNew.Close
‘destroy the variables:
Set daoDB = Nothing
Set daoDBNew = Nothing
Set daoDBS = Nothing
Set wrkSpaceNew = Nothing
Set prpDB = Nothing
End Sub
Return a Reference to the Current Database — CurrentDb Method
Use the CurrentDb Method to return a reference to the database which is currently open in the Microsoft Access window, from vba code. The method returns a database object, without the need to specfy the database name. You can use other DAO objects with the database object variable returned by this method. A reference to the current database is provided by the first member of the Databases collection. The reference pointed to the current database by using the syntax DBEngine(0)(0) can also be used but this syntax refers to the open copy of the current database, whereas with the CurrentDb method you can create ‘multiple database object variables’ referring to the current database because this method creates a new instance of the current database making it amenable for multi users. However, it is much slower to use CurrentDb than using DBEngine(0)(0). Note that another Database can be opened and worked upon simultaneously, using the OpenDatabase method, while the current database is already open in the Microsoft Access window.
Example 3: CurrentDb Method — return a reference to the currently open database.
Sub AccessDAO_ReferCurrentDatabase_3()
‘CurrentDb Method — return a reference to the currently open database.
‘To use DAO in your Excel VBA project, you must add a reference to the DAO Object Library in Excel (your host application) by clicking Tools-References in VBE.
Dim strMyPath As String, strDBName As String, strDB As String
Dim daoCDB1 As DAO.Database, daoCDB2 As DAO.Database, daoDB As DAO.Database
Dim recSet As DAO.Recordset
‘—————
‘RETURN MULTIPLE INSTANCES OF THE DATABASE CURRENTLY OPEN IN THE MICROSOFT ACCESS WINDOW:
‘assign current database reference to multiple object variables of type Database:
Set daoCDB1 = CurrentDb
Set daoCDB2 = CurrentDb
MsgBox daoCDB1.Name
MsgBox daoCDB2.Name
‘refer DAO TableDef Object in current database — you need to first assign the current database reference to an object variable (ex. daoCDB2):
Dim daoTblDef As DAO.TableDef
Dim fld As DAO.Field
Set daoTblDef = daoCDB2.TableDefs(«SalesManager»)
For Each fld In daoTblDef.Fields
MsgBox fld.Name
Next fld
‘—-
‘USE CurrentDb DIRECTLY WITH A RECORDSET OBJECT:
‘CurrentDb can be used directly with a Recordset object, while in most other DAO objects you need to first assign the current database reference to an object variable as above.
Set recSet = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset(«SalesManager», dbOpenDynaset)
‘displays first 3 fields of the first record:
MsgBox recSet.Fields(0)
MsgBox recSet.Fields(1)
MsgBox recSet.Fields(2)
‘—————
‘OPEN ANOTHER DATABASE USING THE OpenDatabase METHOD, TO WORK ON SIMULTANEOUSLY, WHILE THE CURRENT DATABASE IS ALREADY OPEN IN THE MICROSOFT ACCESS WINDOW:
‘your data source with which to establish connection — ENTER the MS Access Database Name:
strDBName = «SalesReport.accdb»
‘get path / location of the database, presumed to be in the same location as the host workbook:
strMyPath = ThisWorkbook.Path
‘set the string variable to the Database:
strDB = strMyPath & «» & strDBName
‘open the database in the default workspace:
Set daoDB = DBEngine.OpenDatabase(strDB)
MsgBox daoDB.Name
‘—————
‘close the objects:
recSet.Close
daoCDB1.Close
daoCDB2.Close
daoDB.Close
‘destroy the variables:
Set daoCDB1 = Nothing
Set daoCDB2 = Nothing
Set daoDB = Nothing
Set daoTblDef = Nothing
Set fld = Nothing
Set recSet = Nothing
End Sub
Tables of a DAO Database
TableDef Object and TableDefs collection
A TableDef object, with its properties and methods, is used to manipulate a table definition. With a TableDef object you can: create a new table (Database.CreateTableDef Method); create or add a new Field in a table (TableDef.CreateField Method); create a new Index (TableDef.CreateIndex Method); create a new Recordset and append it to the Recordsets collection (TableDef.OpenRecordset Method); update a linked table’s connection information (TableDef.RefreshLink Method); set or return information about a linked table (TableDef.Connect Property); set or return the name of a linked table (ableDef.SourceTableName Property); set or return validation value/rule for a field’s data (TableDef.ValidationRule Property); set or return the text message displayed when the field value does not conform to the ValidationRule (TableDef.ValidationText Property); and so on.
All stored TableDef objects in a database are referred to as the TableDefs collection. You create a new TableDef object using the Database.CreateTableDef Method. It is required to append a TableDef object to the TableDefs collection after creating it, using the DAO TableDefs.Append Method. You can refer to a TableDef object in the TableDefs collection by its ordinal number or Name viz. TableDefs(0) or TableDefs(«TableDefObjectName») or TableDefs![TableDefObjectName].
Database.CreateTableDef Method
Use the Database.CreateTableDef Method to create a new TableDef object. Syntax: DatabaseObject.CreateTableDef(Name, Attributes, SourceTableName, Connect). All arguments are optional to specify. The Name argument sets the name of the TableDef object, which can be a maximum of 64 characters. The Attributes argument sets a value indicating characteristic(s) of the TableDef object. The Attributes Property is read/write for a TableDef object till it is appended to its collection. The SourceTableName argument specifies the name of a linked or the base table that is the original data source in an external database. The Connect argument is a String value, which provides information of a TableDef object’s linked table or an open database source, consisting of a database type specifier and a database path.
Note that it is required to define one Field atleast before you can append a TableDef object to the TableDefs collection. Use the TableDefs.Delete Method to delete a TableDef object from the TableDefs collection.
Fields / Columns of a Table
A Field object corresponds to a column of data of similar data type and properties. The Index, QueryDef, Relation and TableDef objects all have a Fields collection, which represents all stored Field objects as specified in the respective object. The Recordset object also has a Fields collection, which represents all stored Field objects in a record or a row of data. A field object has its own properties & methods by which it is manipulated.
Create a new Field
TableDef.CreateField Method
Use the TableDef.CreateField Method to create a new Field object. Syntax: TableDefObject.CreateField(Name, Type, Size). All arguments are optional to specify. The Name argument specifies a name for the new Field. The Type argument sets the data type of the Field, as indicated by a constant. The Size argument determines the maximum size of a Field. For a Field with character data (except Memo), size determines the maximum number of characters; for numeric fields, it is the maximum size in bytes (of storage). Text fields can be set upto a maximum of 255 characters for a Microsoft Access database, whereas for non-Text fields the size is automatically determined by their Type property. Not specifying the Size will default the Field size to as permissible by the database. For Memo or Long Binary Fields use the Field.FieldSize Property to determine the size in the number of bytes used in the database, whereas use the Size property for all other Field data types.
You can use the CreateField method to add a new field to an Index or Relation object. To add a field to an Index object, use the DAO Index.CreateField Method, Syntax: IndexObject.CreateField(Name, Type, Size). The type and size arguments are not supported for an Index object, and are ignored in this case. To add a field to a Relation object, use the DAO Relation.CreateField Method, Syntax: RelationObject.CreateField(Name, Type, Size). The type and size arguments are not supported for a Relation object, and are ignored in this case.
Fields Collection Properties & Methods
Count the number of Fields
The Count property of the fields collection determines the number of fields in a collection, wherein numbering for members of a collection begins with zero. If you have seven fields in a Recordset, using RecordsetObject.Fields.count will return 7, and RecordsetObject.Fields(0) will return the value of the first field [OrdinalPosition of the first field is 0].
Access Fields by their ordinal position or Name property
You can Access Fields by their ordinal position or Name property viz. Recordset.Fields.(Name/OrdinalPosition). Recordset.Fields(0).Name returns the Name of the first field, and Recordset.Fields(0).Value returns the content in the first field. The Value property of the Field object is its Default property viz Recordset.Fields(0) is the same as Recordset.Fields(0).Value and will return the first fields’s value.
Examples: To reference a field named «FirstName», which is the second field in the table, you can use any of the following:-
RecordsetObject.Fields(«FirstName»)
RecordsetObject.Fields(1)
RecordsetObject![FirstName]
DAO Fields.Append Method
To add or append a new field to the Fields Collection of a TableDef or an Index object, use the DAO Fields.Append Method. To add a field to a table, use the Syntax: TableDefObject.Append(FieldObject). To add a field to an Index, use the Syntax: IndexObject.Append(FieldObject). The FieldObject argument mentions the Field Object variable which is being appended and is necessary to specify.
DAO Fields.Delete Method
To delete a field from the Fields Collection, use the DAO Fields.Delete Method. To delete a field from a table, use the Syntax: TableDefObject.Fields.Delete(Name). The Name argument mentions the name of the Field which is being deleted and is necessary to specify. Note that once an index referencing a field has been created, that Field cannot be deleted from a Fields collection of a TableDef object.
DAO Fields.Refresh Method
The relative position of a Field object within the Fields collection is usually the order in which the field has been appended in the collection, the first appended field at first position will have an OrdinalPosition of 0 (zero), the second appended field at second position will have an OrdinalPosition of 1, and so on, and this position can be changed (or returned) by using the DAO Field.OrdinalPosition Property. A change in the ordinal position of a Field may not change the order of the Fields in the collection unless the DAO Fields. Refresh Method is used. The Refresh method is particularly required to be used in a multi-user environment wherein different users might be making changes in the database, in which case only those objects are contained when you have referred to the collection initially without reflecting any subsequent changes made by other users, and the collection will get updated only on using the Refresh method.
Field Object Properties
Field properties are used to determine or return the name, size, type and characteristics of a Field. Some of these properties are elaborated below.
DAO Field.Name Property
Use the DAO Field.Name Property to set or return a Field’s name. It is a String value not exceeding 64 characters. The property is read-only after the Field object is appended to the Fields collection, before which it is read/write.
DAO Field.Value Property
Use the Field.Value Property to return, enter or edit the data in a Field. This is the default property of a Field object viz. you can refer to a field object without specifying the value property. For example, entering «Lisa» in the field named «FirstName» can be done either as RecordSetObject.Fields(«FirstName») = «Lisa» or as RecordSetObject.Fields(«FirstName»).Value = «Lisa».
DAO Field.OrdinalPosition Property
The relative position of a Field object within the Fields collection is usually the order in which the field has been appended in the collection, the first appended field at first position will have an OrdinalPosition of 0 (zero), the second appended field at second position will have an OrdinalPosition of 1, and so on, and this position can be changed (or returned) by using the DAO Field.OrdinalPosition Property. Note that this property uses «relative postion» so that if you have 3 fields and you change the OrdinalPosition property of these to 10, 12 & 15, then the field with OrdinalPosition value of 12 will be returned in an order relative to the others, ie. between the fields whose values have been set as 10 and 15.
The property is read-write for a Field object before it is appended to a Fields collection. After a Field object is appended, for Fields contained within a TableDef object it is read-write, and for fields contained within Recordset or QueryDef objects it is read-only, but the property is not supported for fields contained within Index & Relation objects.
DAO Field.Size Property
The Field.Size Property determines the maximum size of a Field. For a Field with character data (except Memo), size determines the maximum number of characters; for numeric fields, it is the maximum size in bytes (of storage). For Text fields you must set the Size property which can be set upto a maximum of 255 characters for a Microsoft Access database, whereas for non-Text fields the size is automatically determined by their Type property. Not specifying the Size will default the Field size to as permissible by the database. For Memo or Long Binary Fields use the Field.FieldSize Property to determine the size in the number of bytes used in the database, whereas use the Size property for all other Field data types.
The property is read-write for a Field object before it is appended to a Fields collection. After a Field object is appended, the property is supported for Fields contained within a TableDef object, Recordset object or QueryDef object, wherein it is read-only, but the property is not supported for fields contained within Index & Relation objects.
DAO Field.Type Property
Use the Type property to set or return the operational or data type of a Field. The value returned by this property is a constant which indicates the data type of a field. The property is read-only after the Field object is appended to the Fields collection or to any object, before which it is read/write.
Examples of data type constants that are supported by DAO, for the Type property, include:
dbBoolean (Boolean Value — Yes/No); dbChar (Char); dbCurrency (Currency); dbDate (Date); dbDouble (Double); dbGUID (GUID); dbInteger (Integer); dbBigInt (Big Integer); dbSingle (Single); dbLong (Long); dbMemo (Memo); dbText (Text); ….
DAO Field.Attributes Property
Use the DAO Field.Attributes Property to set (or return) the Field characteristics. The Field characteristic(s) is specified by a value or constant, which can be: dbAutoIncrField (to automatically increment the Field value to a unique Long integer); dbDescending (to sort Field values in a descending order — default sort order for a Field is Ascending if this attribute is not specified — this attribute is applicable only to an index field ie. to Fields collection of an Index); dbFixedField (dbFixedField specifies that the field has a fixed size — numeric fields have a Fixed field size by default — maps to ADO column attribute adColFixed); dbVariableField (valid only for text fields, it specifies a Variable Field size ie. the Text data type Field can store variable text lengths); dbUpdatableField (when the Field value can be updated or changed); dbHyperlinkField (hyperlink field, valid only for Memo field types); dbSystemField (these fields cannot be deleted).
To create an auto-increment field, set data type of field to Long and set Attributes property to dbAutoIncrField. An auto-increment field (also referred to as AutoNumber field) by default starts at 1 and increments sequentially and can be used aptly as a primary key field to automatically insert unique numbers in a field.
Set multiple attributes — sum the respective constants (using the plus «+» sign) to set multiple attributes, wherein any non-meaningful values get ignored without giving an error.
This property is read/write for a field before being appended to a collection. For a Field object after it is appended to a collection: for Fields contained within a TableDef object, the property is read/write; for Fields contained within an Index object, this property remains read-write until the TableDef object which contains the Index object is appended to a Database and then read-only thereafter; for Fields contained within a Recordset object or QueryDef object, the property is read-only; for Fields contained within a Relation object this property is not supported.
DAO Field.DefaultValue Property
Use the Field.DefaultValue Property to specify the default value to be entered in a Field automatically on creation of a new record. A text or an expression of String data type upto a maximum of 255 characters, can be specified as the default value. For AutoNumber and Long Binary fields, this property is not applicable.
The property is read-write for a Field object before it is appended to a Fields collection. After a Field object is appended, for Fields contained within a TableDef object it is read-write, and for fields contained within Recordset or QueryDef objects it is read-only, but the property is not supported for fields contained within Index & Relation objects.
DAO Field.Required Property
The Field.Required Property determines whether a field can accept null values. Setting the Property to False will allow null values in the field. Between an Index object and a Field object, set the Required property for the Field object because its validation for the Field object precedes that of an Index object.
The property is read-write for a Field object before it is appended to a Fields collection. After a Field object is appended, for Fields contained within a TableDef object it is read-write, and for fields contained within Recordset or QueryDef objects it is read-only, but the property is not supported for fields contained within Index & Relation objects.
DAO Field.AllowZeroLength Property
Setting the Field.AllowZeroLength Property to True will allow value for Text or Memo data type Fields to be set to an empty or zero-length string («»). Zero Length string vs Null value: Note that in Access when you specify a Zero Length string it means that you actually specify a value, and when you set the Required porperty to be True it means that the Field can have a Null value which means that NO value needs to be entered — for the user there is no visible difference between the two.
The property is read-write for a Field object before it is appended to a Fields collection. After a Field object is appended, for Fields contained within a TableDef object it is read-write, and for fields contained within Recordset or QueryDef objects it is read-only, but the property is not supported for fields contained within Index & Relation objects.
DAO Field.ValidationRule Property
Use the Field.ValidationRule Property to validate a field’s data with a specified rule or condition. The property specifies a string value as a comparison like in a WHERE clause (as used in SQL statements) but does not use the WHERE word. If the field’s value does not conform to the specified rule or condition, the error message (a string value) as specified by the ValidationText property gets displayed. Only databases using the Microsoft Access database engine support validation.
The property is read-write for a Field object before it is appended to a Fields collection. After a Field object is appended, for Fields contained within a TableDef object it is read-write, and for fields contained within Recordset or QueryDef objects it is read-only, but the property is not supported for fields contained within Index & Relation objects.
DAO Field.ValidationText Property
Validation Text specifies the error message (a string value) which gets displayed if the field’s value does not conform to the specified rule or condition specified by the ValidationRule property.
The property is read-write for a Field object before it is appended to a Fields collection. After a Field object is appended, for Fields contained within a TableDef object it is read-write, and for fields contained within Recordset or QueryDef objects it is read-only, but the property is not supported for fields contained within Index & Relation objects.
Example 4a: Create Tables and Fields in a DAO Database.
Refer Image 4a as mentioned in the code.
1. Create a New Database;
2. Create & Append Tables (ie. TableDef objects);
3. Create & Append Fields;
4. Enumerate Tables in the Database and their Properties;
5. Enumerate Fields in a Table;
6. Delete Fields & Tables;
Sub AccessDAO_CreateTablesCreateFields_4a()
‘Create a New Database;
‘Create & Append Tables (ie. TableDef objects);
‘Create & Append Fields;
‘Enumerate Tables in the Database and their Properties;
‘Enumerate Fields in a Table;
‘Delete Fields & Tables;
‘To use DAO in your Excel VBA project, you must add a reference to the DAO Object Library in Excel (your host application) by clicking Tools-References in VBE.
Dim strMyPath As String, strDBName As String, strDB As String
Dim daoDB As DAO.Database
Dim daoTD As DAO.TableDef, daoTD1 As DAO.TableDef, daoTD2 As DAO.TableDef
Dim daoFld As DAO.Field
Dim daoPrp As DAO.Property
‘—————
‘get path / location of the database, presumed to be in the same location as the host workbook:
strMyPath = ThisWorkbook.Path
‘name of the new MS Access Database being created:
strDBName = «SalesReportNew.accdb»
‘set the string variable to the new Database:
strDB = strMyPath & «» & strDBName
‘—————
‘CREATE A NEW MS ACCESS DATATABASE, TABLES AND FIELDS:
‘Refer Image 4a to view Tables & Fields (in «SalesManager» Table) of the new Database («SalesReportNew.accdb») after running below code, before deleteing any table or field.
‘Create a New Database: If you create a database object without specifying a workspace, it will exist within the default workspace:
Set daoDB = DBEngine.CreateDatabase(strDB, dbLangGeneral)
‘Create Tables (ie. TableDef objects) named «SalesManager» and «Performance»:
Set daoTD1 = daoDB.CreateTableDef(«SalesManager»)
Set daoTD2 = daoDB.CreateTableDef(«Performance»)
‘Before you append the TableDef object to the TableDefs collection, you will create Fields and append them to the new TableDef object (Table named «SalesManager») created above:
With daoTD1
‘create a new auto increment field, and set attribute:
‘set data type of field to Long, set Attributes property to dbAutoIncrField. An auto-increment field (also referred to as AutoNumber field) by default starts at 1 and increments sequentially and can be used aptly as a primary key field to automatically insert unique numbers in a field.
.Fields.Append .CreateField(«EmployeeId», dbLong)
.Fields(«EmployeeId»).Attributes = dbAutoIncrField + dbFixedField
‘create a Text field, maximum 30 characters, and required.
Set daoFld = .CreateField(«FirstName», dbText, 30)
daoFld.Attributes = dbVariableField
daoFld.Required = True
.Fields.Append daoFld
‘Text field, allow zero length, and max 25 characters:
.Fields.Append .CreateField(«SurName», dbText, 25)
.Fields(«SurName»).Required = True
.Fields(«SurName»).AllowZeroLength = True
‘create a Date field with a validation rule and Validation Text:
Set daoFld = .CreateField(«JoinDate», dbDate)
‘specify a default value for the field:
daoFld.DefaultValue = «#04/01/2010#»
‘validate the field’s value, before it is set, with a specified rule or condition:
daoFld.ValidationRule = «>=#04/01/2010# and <=date()»
‘specify the error message which gets displayed if the field’s value does not conform to the specified rule or condition:
daoFld.ValidationText = «JoinDate should be on or after 04/01/2010 but within current date»
.Fields.Append daoFld
‘Currency Field and required:
.Fields.Append .CreateField(«Sales», dbCurrency)
.Fields(«Sales»).Required = True
‘create a Boolean (Yes/No) field:
.Fields.Append .CreateField(«NewJoinee?», dbBoolean)
‘create a Hyperlink field, and set the attribute:
Set daoFld = .CreateField(«WebProfile», dbMemo)
daoFld.Attributes = dbHyperlinkField + dbVariableField
.Fields.Append daoFld
End With
‘Before you append the TableDef object to the TableDefs collection, you will create Fields and append them to the new TableDef object (Table named «Performance») created above:
With daoTD2
.Fields.Append .CreateField(«FirstName», dbText)
End With
‘Save/Append the tables «SalesManager» & «Performance» to the TableDefs collection:
daoDB.TableDefs.Append daoTD1
daoDB.TableDefs.Append daoTD2
‘—————
‘ENUMERATE DATABASE TABLES AND PROPERTIES:
‘return number of Tables in database:
MsgBox daoDB.TableDefs.count
‘Enumerate Tables in the database and their properties:
For Each daoTD In daoDB.TableDefs
‘Use the Attributes property to ignore System and Hidden Tables. The Attributes argument returns or sets a value indicating characteristic(s) of the TableDef object. Note, that to check a specific attribute we have used the logical AND operator for comparison of: (i) the TableDef Attributes property and the dbSystemObject constant; and (ii) the TableDef Attributes property and the dbHiddenObject constant. You can alternatively do an equivalency test using numerical values of the constants.
If ((daoTD.Attributes And dbSystemObject) Or (daoTD.Attributes And dbHiddenObject)) Then
Else
For Each daoPrp In daoTD.Properties
MsgBox «Table Name: » & daoTD.Name & » — Property Name: » & daoPrp.Name & «, Property Type: » & daoPrp.Type & «, Property Value: » & daoPrp.Value
Next
End If
‘Alternate If statement to ignore System and Hidden Tables: dbSystemObject constant has a numerical value of -2147483646; dbHiddenObject constant has a numerical value of 1;
‘If daoTD.Attributes >= 0 And daoTD.Attributes <> 1 Then
‘MsgBox «Table Name: » & daoTD.Name
‘End If
Next
‘—————
‘ENUMERATE TABLE FIELDS:
‘return number of Fields in the Table named «SalesManager»:
MsgBox daoTD1.Fields.count
‘Enumerate Fields and return their name, type & size in the Table named «SalesManager»:
For Each daoFld In daoTD1.Fields
MsgBox daoFld.Name & «, » & daoFld.Type & «, » & daoFld.Size
Next
‘—————
‘DELETE FIELDS AND TABLES IN DATABASE:
‘Delete a field in the Table named «SalesManager»:
‘daoTD1.Fields.Delete «SurName»
‘Delete the Table (TableDef object) named «Performance» created above:
‘daoDB.TableDefs.Delete daoTD2.Name
‘or
daoDB.TableDefs.Delete «Performance»
‘—————
‘close the objects:
daoDB.Close
‘destroy the variables:
Set daoDB = Nothing
Set daoTD = Nothing
Set daoTD1 = Nothing
Set daoTD2 = Nothing
Set daoFld = Nothing
Set daoPrp = Nothing
End Sub
Recordset & Records of a DAO Database Table
After connecting to a database, you can manipulate its data. In Microsoft Access, Recordset objects are used to access and manipulate data in a database. A Recordset object represents a set of records in a database table, or a set of records returned from running a query. Both DAO and ADO libraries have a Recordset object, though the methods, properties, and options of the respective object is different. A Record object is one row of data in a Recordset. A Recordset object has a Fields collection which contains all the Field objects, where each Field object represents a column in the Recordset. In other words, each record represents a row of data and contains many fields, and each field corresponds to a column in the database table.
In your VBA code, you should ideally precede the object name by its program ID (ProgID) prefix, which in ADO is «ADODB» and in DAO is «DAO». Many objects, for example the Recordset object, have similar names in both DAO and ADO and it is advisable to have explicit references in your project. This becomes a must if you have included references to both the DAO and ADO libraries in your VBA project, else the object library mentioned first in the References list will prevail, resulting in confusion in the vba code.
While instantiating the Recordset object, you should use:
Dim daoRecSet As DAO.Recordset
Dim adoRecSet As ADODB.Recordset
instead of:
Dim RecSet As Recordset
DAO Recordset Types
There are five types of Recordsets:
1. A Table-type recordset is based on a Table and not on a query. A Table-type recordset is created only when working with a single non-linked table. Valid for Microsoft Access Jet workspaces only. You can use the Seek method (but not the Find Method) to search through this recordset (using a Table index), which is faster than using the Find method.
2. A Dynaset-Type recordset results from a query. The set of records can contain fields from one or more underlying tables or any linked table (ie. any table linked to the Access Database). The recordset gets dynamically updated and reflects any change made to the underlying records. After the recordset has been created it does not add any new record satisfying the criteria. This recordset type supports the Find method (but not the Seek method) to search through the recordset, which is however slower than the Seek method.
3. A Snapshot-type recordset shows the data as at the time when a snapshot is taken ie. when a recordset is created. The set of records can contain fields from one or more underlying tables or any linked table. This recordset type is a static copy of the records and does not get dynamically updated and does not reflect any change made to the underlying records. If a field value is changed in a record, it will not be updated dynamically like it gets done in a Dynaset-Type recordset and you will need to refresh the recordset to update. This recordset type is used to read data and searching through this recordset is very fast. This recordset type supports the Find method to search through the recordset.
4. A Forward-only-type recordset is identical to a snapshot-type wherein only scroll forward through records is possible.
5. A Dynamic-type recordset results from a query from one or more underlying tables. In this recordset you can add, change or delete records from a row-returning query. This recordset is similar to the Dynaset-Type except that after running a query the matching records added, deleted or edited in the underlying tables by other users also get automatically reflected in the recordset of this type. Valid for ODBCDirect workspaces only.
All active recordsets of a database are contained in the Recordsets collection, wherein a recordset gets appended to the collection when it is opened and gets removed from the collection when it is closed (using the Close method). Each recordset object contains a collection of the fields and a collection of the indexes in the underlying table.
DAO Recordset.Type Property
Use the Recordset.Type Property to set or return the type of Recordset, using the RecordsetTypeEnum constants or values. There are five settings: dbOpenTable (value-1, Table-type, for Microsoft Access workspaces only); dbOpenDynaset (value-2, Dynaset-type); dbOpenSnapshot (value-4, Snapshot-type); dbOpenForwardOnly (value-8, Forward-only type); dbOpenDynamic (value-16, Dynamic-type, for ODBCDirect workspaces only).
Create a new Recordset object
Create a Recordset object and append it to the Recordsets collection, using the OpenRecordset method. You can use the OpenRecordset method to open a Recordset that is based on a Table, SQL statement, stored or parameter query as detailed below. Arguments have the same meaning across the OpenRecordset methods.
DAO Database.OpenRecordset Method. Syntax: DatabaseObject.OpenRecordset(Name, Type, Options, LockEdit). In this method you pass the Table name to the method and use the Set operator to return the recordset.
Only the Name argument is mandatory to specify while other arguments are optional. The Name argument specifies the source of records and can be the name of a table or a query, or it can be an SQL statement. In the Type argument, specify one of the five types for the recordset by using the constants: dbOpenTable (Table-type); dbOpenDynaset (Dynaset-type); dbOpenSnapshot (Snapshot-type); dbOpenForwardOnly (Forward-only type); dbOpenDynamic (Dynamic-type). A Recordset created in a Microsoft Access local table without specifying the Type will default to Table-type. Executing the OpenRecordset method on a linked table or query, without specifying the Type, will default to Dynaset-type. In the Options argument you can specify one of the many constants representing the recordset’s characteristics viz. specifying dbReadOnly opens a recordset as read-only, and so on. The LockEdit argument specifies a constant which determines the type of record locking used when a recordset is opened.
DAO TableDef.OpenRecordset Method. Syntax: TableDefObject.OpenRecordset(Type, Options). In this method you first get a reference to the Table (TableDefObject) and then use the Set operator to return the recordset.
DAO Recordset.OpenRecordset Method. Syntax: RecordsetObject.OpenRecordset(Type, Options). In this method you first get a reference to a Recordset Object and then use the Set operator. Refer Example 7 wherein this method is used to Filter Records.
Creating a Recordset, based on a stored query or a parameter query, using the QueryDef.OpenRecordset Method. For details on this method, refer section «Create and Exceute a Query».
Create a new record in a Database Table — use the AddNew & Update methods
DAO Recordset.AddNew method
Create a new record for a Recordset object, using the Recordset.AddNew method. Syntax: RecordsetObject.AddNew. When you use this method, the field’s value is set to its default value and in the absence of a default value specification, it is set to Null. Ensure that after adding a new record using the AddNew method or after making any changes in a record using the Edit method, you must save the record and/or any changes to it by using the Update method BEFORE you perform any operation like move to another record or use the Edit or AddNew method again or close the recordset or set bookmark property for another record.
In DAO, after using the Update method, the current record will be the record which had focus before the AddNew method. Using the LastModified property (for a DAO recordset) returns a Bookmark pointing to the most recent added / modified record and setting the Bookmark property to this bookmark will make the new record as the current record.
When you add a record to a dynaset-type Recordset, using the AddNew method, the new record will appear at the end of the recordset disregrading the recordset’s sorting if any. In this case you can re-create the recordset or use the ReQuery method to have the new record appear in its sorted position. When a record is added to a table-type Recordset, the new record appears in accordance with the recordset’s index and in the absence of an index the new record will appear at the end of the recordset.
DAO Recordset.Update Method
Ensure that after adding a new record using the AddNew method or after making any changes in a record using the Edit method, you must save the record and/or any changes to it by using the Recordset.Update Method BEFORE you perform any operation like move to another record or use the Edit or AddNew method again or close the recordset or set bookmark property for another record. Syntax: RecordsetObject .Update(UpdateType, Force). Both arguments of UpdateType & Force are optional.
Recordset.LastModified Property
In Table-type or Dynaset-Type recordsets, a bookmark of the record which has most recently been added or changed, is returned by the Recordset.LastModified Property. Use this property to bookmark and move to the record which has last been added or modified. Syntax: RecordsetObject.LastModified. Refer Example 4b for using this property.
Recordset.Bookmark Property
Use the Recordset.Bookmark Property to uniquely identify the current record by setting or returning a bookmark. You can create any number of bookmarks in a recordset, by saving each bookmark and assigning its value to a variable and then return to that record by setting the Recordset’s Bookmark property to the variable. Refer Example 4b for using this property.
Edit Records in a Recordset
Use the DAO Recordset.Edit Method to make changes to fields of the current record in a Recordset object. Ensure that after making any changes in a record using the Edit method, you must save the changes to it by using the Update method. After editing the record, the current record to which changes are made remains current ie. the record with focus. Syntax: RecordsetObject.Edit.
Moving between Records in a Recordset
DAO Recordset.Move Method. Syntax: RecordsetObject.Move(Rows, StartBookmark). This method moves the position of the current record as per the specified number of rows (Rows argument) starting from a bookmarked record specified by the StartBookmark argument or from the current record if this argument is omitted. It is necessary to specify the Rows argument, and if this is more than 0 the current record moves forward towards end of recordset, and if less than 0 then the current record moves backwards. You can use this method with rows argument set to 0, to retrieve the current record’s underlying data.
MoveFirst, MoveLast, MoveNext, and MovePrevious Methods (DAO): MoveFirst method moves the current record to the first record. Remember that on opening a recordset, the first record is the current record. Using the MoveLast method moves the current record to the last record in the recordset. MoveNext method moves the current record one position forward and MovePrevious moves the current record one position backward. Note that the MoveFirst, MoveLast, and MovePrevious methods cannot be used on a Forward-only-type recordset. Syntax: RecordsetObject.MoveFirst, RecordsetObject.MoveLast, RecordsetObject.MoveNext, RecordsetObject.MovePrevious.
EOF Property (DAO) indicates whether the current record position is after the last record in the set of records, wherein its value will be TRUE. BOF Property (DAO) indicates whether the current record position is before the first record in the set of records, wherein its value will be TRUE. Both properties return a Boolean value and are used to determine if the current record is outside the limits of the Recordset object. There will be no current record if either the EOF Property or BOF Property is True, and if both properties are True on opening a recordset it will indicate that there are no records. Opening a Recordset having atleast one record makes the first record as the current record and in this case both the EOF Property and BOF Property will be False. Syntax: RecordsetObject .EOF, RecordsetObject .BOF.
Count the number of Records in a Recordset
Use the DAO Recordset.RecordCount Property to: (i) count the number of records which have been acceessed in a Dynaset-Type or Snapshot-type or Forward-only-type recordset, and after the last record is accessed (ie. after the recordset is populated) RecordCount indicates the total number of records contained in the recordset; or (ii) count the total number of records in a table-type Recordset or in a TableDef object, wherein RecordCount always returns the correct number. To forcibly access the last record in a Dynaset-Type or Snapshot-type or Forward-only-type recordset, use the Recordset.MoveLast method. Syntax: RecordsetObject.RecordCount.
Close DAO objects, using the Close Method
You should close an open Recordset by using the DAO Recordset.Close Method, which will free any associated system resources. Similarly, close an open Workspace object using the Workspace.Close Method and close an open Database using the Database.Close Method. Closing an object is not enough to remove it from memory, for which you need to set the object variable to Nothing, after closing the object.
To close a Recordset: RecordsetObject.Close
To destroy the Recordset variable: Set RecordsetObject = Nothing
Example 4b: Add / Edit Records and Enter Data, in Tables.
Refer Image 4b as mentioned in the code.
1. Add new records to a table using the AddNew method;
2. Edit records using the Edit method;
3. Use the Recordset.Bookmark Property to identify the current record;
4. Use Recordset.LastModified Property pointing to the most recent added / modified record.
Sub AccessDAO_AddRecordsEnterData_4b()
‘Add new records to a table using the AddNew method;
‘edit records using the Edit method;
‘Use the Recordset.Bookmark Property to identify the current record;
‘Use Recordset.LastModified Property pointing to the most recent added / modified record.
‘To use DAO in your Excel VBA project, you must add a reference to the DAO Object Library in Excel (your host application) by clicking Tools-References in VBE.
‘Refer Image 4b after running below code which adds & edits records in the database file created in example 4a above (note that the field «SurName» of «SalesManager» Table has not been deleted).
Dim strMyPath As String, strDBName As String, strDB As String, recBookMark As String
Dim daoDB As DAO.Database
Dim recSet As DAO.Recordset
‘—————
‘your data source with which to establish connection — ENTER the MS Access Database Name:
strDBName = «SalesReportNew.accdb»
‘get path / location of the database, presumed to be in the same location as the host workbook:
strMyPath = ThisWorkbook.Path
‘set the string variable to the Database:
strDB = strMyPath & «» & strDBName
‘If you open a database object without specifying a workspace, it will exist within the default workspace. First assign the database reference to an object variable:
Set daoDB = DBEngine.OpenDatabase(strDB)
‘Open a table-type recordset based on a MS Access Table named «SalesManager»:
Set recSet = daoDB.OpenRecordset(«SalesManager»)
‘—————-
‘add new records to a table, using the AddNew method (of the Recordset object):
With recSet
.AddNew
‘you need not enter a value for the auto-incrementing field of «EmployeeId»; the start value is 1. In DAO you cannot set the Seed of the auto-number, however you can start at a specific value in a new table by entering the specific value for the first record of an AutoNumber field and subsequent records will increment from this specific start value.
.Fields(«EmployeeId») = 55
.Fields(«FirstName») = «Lisa»
.Fields(«SurName») = «Randall»
‘enter a date/time value between # and #, or within double-quotes:
.Fields(«JoinDate») = «08/11/2012»
.Fields(«Sales») = «22456»
.Fields(«NewJoinee?») = True
‘for a hyperlink field, use both # and double-quotes:
.Fields(«WebProfile») = «#http://www.google.com#»
‘will save only after Update method is run:
.AddNew
‘note that «JoinDate» field is omitted, hence its default value will be entered
.Fields(«FirstName») = «Tracy» & » » & «Von»
.Fields(«SurName») = «Murray»
.Fields(«Sales») = «41098»
.Fields(«NewJoinee?») = False
.Fields(«WebProfile») = «#http://www.yahoo.com#»
.Update
‘second record — save position of current record:
.Bookmark = .LastModified
.AddNew
.Fields(«FirstName») = «John»
.Fields(«SurName») = «Mason»
.Fields(«JoinDate») = #9/2/2012#
.Fields(«Sales») = «31478»
.Fields(«NewJoinee?») = True
.Fields(«WebProfile») = «#http://www.msn.com#»
‘In DAO, after the Update, the current record will be the record which had focus before the AddNew. Using the LastModified property (for a DAO recordset — it does not work with an ADO recordset) returns a Bookmark pointing to the most recent added / modified record. This makes the new record as the current record.
.Bookmark = .LastModified
End With
‘returns «John»
MsgBox recSet.Fields(«FirstName»)
‘edit the new record, using the Edit method (of the Recordset object):
With recSet
‘Recordset.Edit Method is valid for a DAO recordset, it does not work with an ADO recordset:
.Edit
.Fields(«FirstName») = «Julia»
.Fields(«SurName») = «Willis»
‘will save only after Update method is run:
.Update
End With
‘returns «Julia»
MsgBox recSet.Fields(«FirstName»)
‘return the second record whose position was saved:
recSet.Bookmark = recBookMark
‘returns «Tracy Von»
MsgBox recSet.Fields(«FirstName»)
‘—————
‘close the objects:
daoDB.Close
‘destroy the variables:
Set daoDB = Nothing
End Sub
Example 5a: Open Recordset, Enumerate Recordset, Recordset Properties, Navigate through Records.
1. OpenRecordset method of the Database object — Open Recordset based on a Table; Open Recordset based on a SQL statement.
2. OpenRecordset method of the TableDef object — Open Recordset based on a Table.
3. Enumerate the Recordset; List all valid properties of Recordset.
4. Use the MoveFirst and MoveNext methods to navigate through records, together with EOF Property.
Sub AccessDAO_OpenRecordsetMoveThruRecords_5a()
‘OPEN RECORDSET; ENUMERATE RECORDSET; RECORDSET PROPERTIES; NAVIGATE THROUGH RECORDS:
‘OpenRecordset method of the Database object — Open Recordset based on a Table; Open Recordset based on a SQL statement.
‘OpenRecordset method of the TableDef object — Open Recordset based on a Table.
‘Enumerate the Recordset; List all valid properties of Recordset.
‘Use the MoveFirst and MoveNext methods to navigate through records, together with EOF Property.
‘To use DAO in your Excel VBA project, you must add a reference to the DAO Object Library in Excel (your host application) by clicking Tools-References in VBE.
Dim strMyPath As String, strDBName As String, strDB As String, strSQL As String
Dim daoDB As DAO.Database
Dim recSet As DAO.Recordset
Dim daoTblDef As DAO.TableDef
Dim daoFld As DAO.Field
Dim daoPrp As DAO.Property
Dim n As Long, i As Long
‘—————
‘your data source with which to establish connection — ENTER the MS Access Database Name:
strDBName = «SalesReport.accdb»
‘get path / location of the database, presumed to be in the same location as the host workbook:
strMyPath = ThisWorkbook.Path
‘set the string variable to the Database:
strDB = strMyPath & «» & strDBName
‘If you open a database object without specifying a workspace, it will exist within the default workspace. First assign the database reference to an object variable:
Set daoDB = DBEngine.OpenDatabase(strDB)
‘—————
‘OpenRecordset METHOD OF THE DATABASE OBJECT — OPEN RECORDSET BASED ON A TABLE:
‘Open table-type, read-only recordset based on a MS Access Table:
Set recSet = daoDB.OpenRecordset(«SalesManager», dbOpenTable, dbReadOnly)
‘return the first field (name & value) of each record of the Recordset:
‘while moving forward within a recordset, use EOF so as not to cross the last record. EOF Property indicates that the current record position is after the last record in the set of records.
Do While Not recSet.EOF
MsgBox recSet.Fields(0).Name & » — » & recSet.Fields(0).Value
‘MoveNext method moves the current record one position forward.
recSet.MoveNext
recSet.Close
Set recSet = Nothing
‘——
‘OpenRecordset METHOD OF THE DATABASE OBJECT — OPEN RECORDSET BASED ON AN SQL STATEMENT:
‘Open dynaset-type recordset based on a SQL statement:
strSQL = «SELECT * FROM SalesManager WHERE EmployeeId > 18″
Set recSet = daoDB.OpenRecordset(strSQL, dbOpenDynaset)
‘Enumerate the Recordset — all fields in each record of the Recordset:
fieldsCount = recSet.Fields.count
n = 1
‘navigate through records in a recordset:
With recSet
‘MoveFirst method moves the current record to the first record.
.MoveFirst
Do While Not .EOF
MsgBox «Record No. » & n
For i = 0 To fieldsCount — 1
MsgBox .Fields(i).Name & » — » & .Fields(i).Value
Next i
.MoveNext
n = n + 1
Loop
recSet.Close
Set recSet = Nothing
‘——
‘OpenRecordset METHOD OF THE TableDef OBJECT — OPEN RECORDSET BASED ON A TABLE:
‘refer to a TableDef object by its name: reference the table named SalesManager
Set daoTblDef = daoDB.TableDefs(«SalesManager»)
‘Open snapshot-type recordset based on a MS Access Table:
Set recSet = daoTblDef.OpenRecordset(dbOpenSnapshot, dbReadOnly)
‘List all fields of each record of the Recordset:
Do While Not recSet.EOF
For Each daoFld In recSet.Fields
MsgBox daoFld.Name & » — » & daoFld.Value
Next daoFld
recSet.MoveNext
‘List all valid properties of the Recordset object:
For Each daoPrp In recSet.Properties
‘skip invalid values with resume next statement
On Error Resume Next
MsgBox «Property Name: » & daoPrp.Name & «; Property Value: » & daoPrp.Value
Next daoPrp
‘—————
‘close the objects:
recSet.Close
daoDB.Close
‘destroy the variables:
Set daoDB = Nothing
Set recSet = Nothing
Set daoTblDef = Nothing
Set daoFld = Nothing
End Sub
Example 5b: Count the number of Records in a Recordset — DAO Recordset.RecordCount Property.
Refer Image 5 as mentioned in the code.
Sub AccessDAO_RecordCount_5b()
‘Count the number of Records in a Recordset — DAO Recordset.RecordCount Property
‘refer Image 5 to view the SalesManager Table in MS Access file «SalesReport.accdb», on which RecordCount is done in this code.
‘To use DAO in your Excel VBA project, you must add a reference to the DAO Object Library in Excel (your host application) by clicking Tools-References in VBE.
Dim strMyPath As String, strDBName As String, strDB As String, strSQL As String
Dim daoDB As DAO.Database
Dim recSet As DAO.Recordset
Dim daoTblDef As DAO.TableDef
Dim qryD As DAO.QueryDef
‘—————
‘your data source with which to establish connection — ENTER the MS Access Database Name:
strDBName = «SalesReport.accdb»
‘get path / location of the database, presumed to be in the same location as the host workbook:
strMyPath = ThisWorkbook.Path
‘set the string variable to the Database:
strDB = strMyPath & «» & strDBName
‘assign the database reference to an object variable:
Set daoDB = DBEngine.Workspaces(0).OpenDatabase(strDB)
‘—————
‘RecordCount in a TableDef object:
Set daoTblDef = daoDB.TableDefs(«SalesManager»)
‘returns 5, refer Image 5:
MsgBox «RecordsCount in a TableDef Object: » & daoTblDef.RecordCount
‘——
‘RecordCount in a Table-type recordset:
Set recSet = daoDB.OpenRecordset(«SalesManager», dbOpenTable)
‘returns 5, refer Image 5:
MsgBox «RecordsCount in Table-type recordset: » & recSet.RecordCount
recSet.Close
Set recSet = Nothing
‘——
‘RecordCount in a Dynaset-Type recordset:
strSQL = «SELECT * FROM SalesManager WHERE EmployeeId > 18″
Set qryD = daoDB.CreateQueryDef(«sqlQuery», strSQL)
Set recSet = qryD.OpenRecordset(dbOpenDynaset)
‘returns 1, refer Image 5:
MsgBox «RecordsCount in Dynaset-Type recordset BEFORE MoveLast: » & recSet.RecordCount
recSet.MoveLast
‘returns 3, refer Image 5:
MsgBox «RecordsCount in Dynaset-Type recordset AFTER MoveLast: » & recSet.RecordCount
daoDB.QueryDefs.Delete («sqlQuery»)
recSet.Close
Set recSet = Nothing
‘——
‘RecordCount in a Snapshot-type recordset:
Set recSet = daoDB.OpenRecordset(«SalesManager», dbOpenSnapshot)
‘returns 1, refer Image 5:
MsgBox «RecordsCount in Snapshot-type recordset BEFORE MoveLast: » & recSet.RecordCount
recSet.MoveLast
‘returns 5, refer Image 5:
MsgBox «RecordsCount in Snapshot-type recordset AFTER MoveLast: » & recSet.RecordCount
recSet.Close
Set recSet = Nothing
‘——
‘RecordCount in a Forward-only-type recordset:
Set recSet = daoDB.OpenRecordset(«SalesManager», dbOpenForwardOnly)
‘returns 1, refer Image 5:
MsgBox «RecordsCount in Forward-only-type recordset BEFORE MoveNext: » & recSet.RecordCount
recSet.MoveNext
‘returns 2, refer Image 5:
MsgBox «RecordsCount in Forward-only-type recordset AFTER first MoveNext: » & recSet.RecordCount
recSet.MoveNext
‘returns 3, refer Image 5:
MsgBox «RecordsCount in Forward-only-type recordset AFTER second MoveNext: » & recSet.RecordCount
‘——
‘close the objects:
recSet.Close
daoDB.Close
‘destroy the variables:
Set daoDB = Nothing
Set recSet = Nothing
Set daoTblDef = Nothing
End Sub
Example 6: Find Method (FindFirst & FindNext) in a Dynaset or Snapshot-type recordset; Edit / Delete Records.
Refer Images 6a, 6b & 6c as mentioned in the code.
1. Locate records matching specified criteria using the FindFirst and FindNext methods in a dynaset or snapshot-type recordset;
2. Edit a record using the Edit method;
3. Delete a record using the Delete method.
Sub AccessDAO_FindMethod_EditDeleteRecords_6()
‘Locate records matching specified criteria using the FindFirst and FindNext methods in a dynaset or snapshot-type recordset;
‘Edit a record using the Edit method;
‘Delete a record using the Delete method;
‘To use DAO in your Excel VBA project, you must add a reference to the DAO Object Library in Excel (your host application) by clicking Tools-References in VBE.
‘refer Image 6a to view the existing SalesManager Table in MS Access file «SalesReport.accdb».
Dim strMyPath As String, strDBName As String, strDB As String
Dim daoDB As DAO.Database
Dim recSet As DAO.Recordset
‘—————
‘your data source with which to establish connection — ENTER the MS Access Database Name:
strDBName = «SalesReport.accdb»
‘get path / location of the database, presumed to be in the same location as the host workbook:
strMyPath = ThisWorkbook.Path
‘set the string variable to the Database:
strDB = strMyPath & «» & strDBName
‘assign the database reference to an object variable:
Set daoDB = DBEngine.Workspaces(0).OpenDatabase(strDB)
‘Open a dynaset-type recordset based on a MS Access Table named «SalesManager»:
Set recSet = daoDB.OpenRecordset(«SalesManager», dbOpenDynaset)
‘—————-
‘USE FindFirst AND FindNext METHODS TO LOCATE ALL RECORDS THAT MATCH A SPECIFIED CRITERIA:
‘locate first record with matching criteria:
recSet.FindFirst «SurName LIKE ‘*A*'»
‘if a record with matching criteria is found:
If recSet.NoMatch = False Then
‘the NoMatch property is set to True, if no matched record is found:
Do While Not recSet.NoMatch
‘return record with matching criteria: returns Murray, Mason & Davis: refer Image 6a:
MsgBox recSet.Fields(«SurName»)
‘locate next record with matching criteria:
recSet.FindNext «SurName LIKE ‘*A*'»
Loop
Else
MsgBox «No Matching Record Found!»
‘———————
‘LOCATE RECORD TO EDIT, USING THE FindFirst METHOD:
‘refer Image 6b after running below code:
‘recSet.FindFirst «FirstName = ‘Jim'»
‘recSet.FindFirst «SurName = «»Murray»»»
recSet.FindFirst «EmployeeId=56»
‘the NoMatch property is set to True, if no matched record is found:
If Not recSet.NoMatch Then
‘modifying a DAO recordset — edit a record in a table, using the Edit method (of the Recordset object):
With recSet
.Edit
.Fields(«FirstName») = «James»
.Fields(«SurName») = «Bond»
‘will save only after Update method is run:
.Update
‘Using the LastModified property returns a Bookmark pointing to the most recent added / modified record. This makes the new record as the current record.
.Bookmark = .LastModified
End With
Else
MsgBox «No Matching Record Found!»
‘returns James, refer Image 6b after running this code:
MsgBox recSet.Fields(«FirstName»)
‘———————
‘FIND RECORD WHICH YOU WANT TO DELETE:
‘refer Image 6c after running below code:
recSet.FindFirst «EmployeeId=56»
‘modifying a DAO recordset — delete a record in a table, using the Delete method (of the Recordset object):
‘record with EmployeeId 56 is deleted, refer Image 6c:
If recSet.NoMatch = False Then
recSet.Delete
Else
MsgBox «Record Not Found»
End If
‘no current record after the Delete method is used, hence go to First Record:
recSet.MoveFirst
‘returns Tracy, refer Image 6c:
MsgBox recSet.Fields(«FirstName»)
‘go to the Last Record, then go back one record:
With recSet
.MoveLast
.Move -1
‘returns Jim, refer Image 6c:
MsgBox recSet.Fields(«FirstName»)
‘—————
‘close the objects:
recSet.Close
daoDB.Close
‘destroy the variables:
Set daoDB = Nothing
End Sub
Example 7: Use the DAO Recordset.Filter Property to Filter Records (applicable to dynaset–type, snapshot–type, or forward–only–type Recordsets).
Refer Images 7a & 7b, as mentioned in the code.
Sub AccessDAO_RecordsetFilter_7()
‘Filter Records: Use the DAO Recordset.Filter Property to determine inclusion of records in a Recordset opened thereafter. A Filter can be applied to dynaset–type, snapshot–type, or forward–only–type Recordsets.
‘To use DAO in your Excel VBA project, you must add a reference to the DAO Object Library in Excel (your host application) by clicking Tools-References in VBE.
Dim strMyPath As String, strDBName As String, strDB As String
Dim daoDB As DAO.Database
Dim recSet As DAO.Recordset, recSetF As DAO.Recordset
‘—————
‘your data source with which to establish connection — ENTER the MS Access Database Name:
strDBName = «SalesReport.accdb»
‘get path / location of the database, presumed to be in the same location as the host workbook:
strMyPath = ThisWorkbook.Path
‘set the string variable to the Database:
strDB = strMyPath & «» & strDBName
‘—————
‘assign the database reference to an object variable:
Set daoDB = DBEngine.Workspaces(0).OpenDatabase(strDB)
‘set values of all records in NewJoinee? field (Boolean) to False:
‘refer Image 7a to view the SalesManager Table in MS Access file «SalesReport.accdb», after running below code.
Set recSet = daoDB.OpenRecordset(«SalesManager»)
Do While Not recSet.EOF
recSet.Edit
recSet.Fields(«NewJoinee?»).Value = False
recSet.Update
recSet.MoveNext
recSet.Close
Set recSet = Nothing
‘—————
‘create a filtered Recordset (dynaset–type) with an SQL statement, returning records from SalesManager Table whose Employee Id is between 15 and 56, returning/sorting them in the order of JoinDate:
Set recSet = daoDB.OpenRecordset(«SELECT * FROM SalesManager WHERE EmployeeId BETWEEN 15 AND 56 ORDER BY JoinDate»)
‘refilter the recordset using the Filter property, returning records whose JoinDate is post «01/01/2011» and mark them as NewJoinee:
recSet.Filter = «JoinDate BETWEEN #01/01/2011# AND Now»
‘create another filtered Recordset (dynaset–type), using the DAO Recordset.OpenRecordset Method:
Set recSetF = recSet.OpenRecordset
‘return the EmployeeId & JoinDate fields of each record in the filtered Recordset:
‘refer Image 7b to view the SalesManager Table, after running below code.
Do While Not recSetF.EOF
MsgBox recSetF.Fields(«EmployeeId») & «, » & recSetF.Fields(«JoinDate»)
‘set values of filtered records in NewJoinee? field to True:
recSetF.Edit
recSetF.Fields(«NewJoinee?»).Value = True
recSetF.Update
recSetF.MoveNext
‘—————
‘close the objects:
recSet.Close
daoDB.Close
‘destroy the variables:
Set daoDB = Nothing
Set recSet = Nothing
End Sub


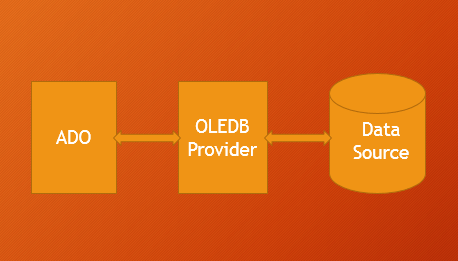
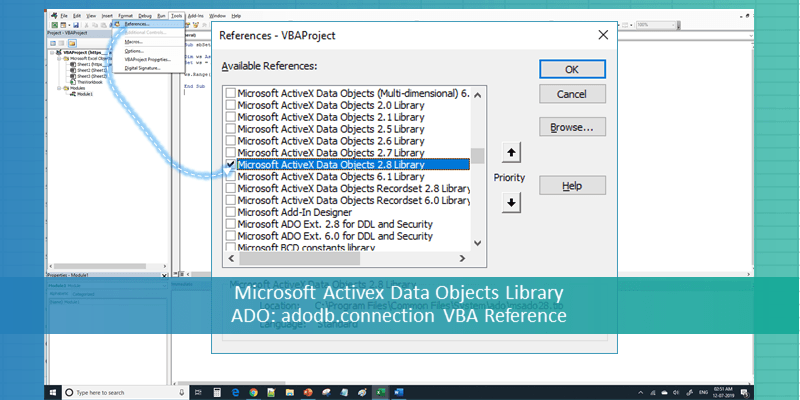
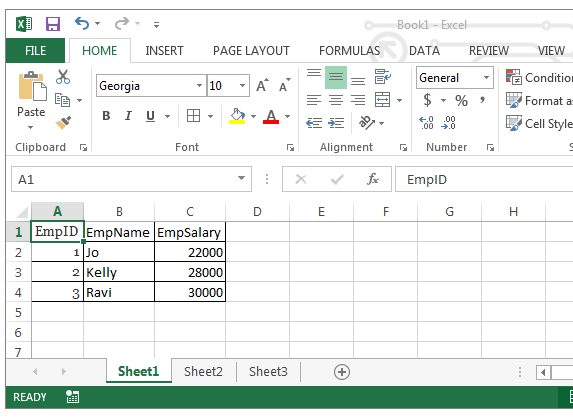
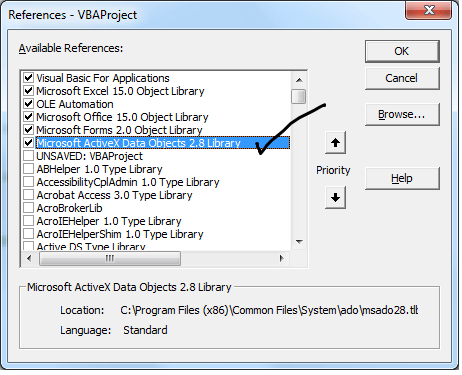
 Customized ur code and it works well..
Customized ur code and it works well..






