In this Article
- Searching in a One-Dimensional Array
- Find values that match the Filter
- Find values that DO NOT match the Filter
- Case Sensitive Filters
- Option Compare Text
- Using a Loop to Search through an array
- Searching in a Multi-Dimensional Array
This tutorial will demonstrate how to Search for (Find) a Value in an Array in VBA
There are a number of ways you can search for a string in an array – depending on whether the array is a one dimensional or multi-dimensional.
Searching in a One-Dimensional Array
To search for a value in a one-dimensional array, you can use the Filter Function.
Dim z As Variant
'filter the original array
z = Filter(Array, String, True, vbCompareBinary)The Syntax of the Filter option is a follows
Filter(Source Array, Match as String, [Include as Boolean], [Compare as vbCompareMethod])
The Source Array and the Match as String are required while the Include as Boolean and the Compare as vbCompareMethod are optional. If these are not included they are set to True and vbCompareBinary respectively.
Find values that match the Filter
Sub FindBob()
'Create Array
Dim strName() As Variant
strName() = Array("Bob Smith", "John Davies", "Fred Jones", "Steve Jenkins", "Bob Williams")
'declare a variant to store the filter data in
Dim strSubNames As Variant
'filter the original array
strSubNames = Filter(strName, "Bob")
'if you UBound value is greater than -1, then the value has been found
If UBound(strSubNames ) > -1 Then MsgBox ("I found Bob")
End SubThe second array will hold the values found by the filter. If your UBound values are not -1, then the array has managed to find the value that you were searching for.
You can also see how many times the text appears in the original array.
Sub CountNames()
'Create array
Dim strName() As Variant
strName() = Array("Bob Smith", "John Davies", "Fred Jones", "Steve Jenkins", "Bob Williams")
'declare an array to store the filter data in
Dim strSubNames As Variant
'filter the original array
strSubNames = Filter(strName, "Bob")
'if you add 1 to the UBound value, we will get the number of times the text appears
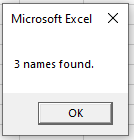
Msgbox UBound(strSubNames) + 1 & " names found."
End SubFind values that DO NOT match the Filter
The [Include as Boolean] option allows you to find how many values in your array which DO NOT match your filter
Sub CountExtraNames()
'create array
Dim strName() As Variant
strName() = Array("Bob Smith", "John Davies", "Fred Jones", "Steve Jenkins", "Bob Williams")
'declare an array to store the filter data in
Dim strSubNames As Variant
'filter the original array
strSubNames = Filter(strName, "Bob", False)
'if you add 1 to the UBound value, we will get the number of times the text appears
Msgbox UBound(strSubNames) + 1 & " names found."
End Subwe have therefore amended this line:
strSubNames = Filter(strName, "Bob")with this line:
strSubNames = Filter(strName, "Bob", False)Using this line in the code, would return all the names that do NOT match “Bob”.
Case Sensitive Filters
You will find that the filter is case sensitive by default. This is true for all VBA functions. If you want to search for text that is not case sensitive, you need to amend your code slightly.
z = Filter(strName, "bob",, vbTextCompare)Adding vbTextCompare to your filter line will enable your code to find “bob” or “Bob”. If this is omitted, VBA by default uses vbBinaryCompare which will only look for data that is an EXACT match. Notice in the example above, we have left out the [Include as Boolean] argument so True is assumed.
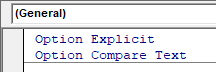
Option Compare Text
Alternatively, you can add the text Option Compare Text to the top of your module – this will make all the functions that you write in that particular module case insensitive.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Using a Loop to Search through an array
Using a loop is a little bit more complicated than using the Filter function. We can create a function that will loop through all the values in the array.
Sub LoopThroughArray()
'create array
Dim strName() As Variant
strName() = Array("Bob Smith", "John Davies", "Fred Jones", "Steve Jenkins", "Bob Williams")
Dim strFind as string
strFind = "Bob"
Dim i As Long
'loop through the array
For i = LBound(strName, 1) To UBound(strName, 1)
If InStr(strName(i), strFind) > 0 Then
MsgBox "Bob has been found!"
Exit For
End If
Next i
End SubIn order to find a part of the text string ie “Bob” instead of “Bob Smith” or “Bob Williams”, we needed to use the Instr Function in the If Statement. This looked in the string returned by the loop from the Array to see if “Bob” was in the string, and as it was in the string, it would return a message box and then Exit the Loop.
Searching in a Multi-Dimensional Array
We also use the loop to search through a multi-dimensional array. Once again, we need to create a function than enables us to loop through all the values in the array, but this time, we also need to loop through each dimension of the array.
Function LoopThroughArray()
Dim varArray() As Variant
Dim strFind As String
strFind = "Doctor"
'declare the size of the array
ReDim varArray(1, 2)
'initialise the array
varArray(0, 0) = "Mel Smith"
varArray(0, 1) = "Fred Buckle"
varArray(0, 2) = "Jane Eyre"
varArray(1, 0) = "Accountant"
varArray(1, 1) = "Secretary"
varArray(1, 2) = "Doctor"
'declare variables for the loop
Dim i As Long, j As Long
'loop for the first dimension
For i = LBound(varArray, 1) To UBound(varArray, 1)
'loop for the second dimension
For j = LBound(varArray, 2) To UBound(varArray, 2)
'if we find the value, then msgbox to say that we have the value and exit the function
If varArray(i, j) = strFind Then
MsgBox "Doctor has been found!"
Exit Function
End If
Next j
Next i
End Function
В данной статье показаны 2 способа быстрого поиска значений в двумерных массивах.
Поскольку искомое значение может встретиться в нескольких строках обрабатываемого двумерного массива,
оба способа получают на выходе отфильтрованный двумерный массив.
Способы формирования отфильтрованных массивов — разные:
первый способ использует функцию ArrAutofilterEx
второй способ — функцию ArraySearchResults
Основные отличия и особенности этих 2 способов поиска:
- ArrAutofilterEx позволяет задавать несколько критериев поиска (фильтрации)
- ArrAutofilterEx ищет вхождение искомого текста в значения заданных столбцов (неточное совпадение)
-
ArrAutofilterEx при каждом вызове заново в цикле перебирает все элементы массива,
соответственно, при поиске 10 значений время работы кода увеличивается в 10 раз - ArraySearchResults позволяет использовать фильтрацию массива только по одному столбцу
- ArraySearchResults ищет совпадение искомого текста со значением столбца (точное совпадение)
-
ArraySearchResults производит поиск в заранее сформированной текстовой строке
Таким образом, перебираются все ячейки массива в цикле только один раз, и поиск 100 значений в массиве займёт ненамного больше времени, чем поиск 1 значения.
Примеры поиска в огромных массивах:
Поиск с использованием ArrAutofilterEx
Sub ПримерМедленногоПоискаВМассиве() t = Timer ИскомоеЗначение$ = 560 СтолбецДляПоиска& = 3 ' загружаем массив с листа arr = [a1:d30000].Value ' укорачиваем массив Arr, оставляя лишь те строки, ' где в заданном столбце есть искомое значение On Error Resume Next: Err.Clear resArr = ArrAutofilterEx(arr, СтолбецДляПоиска& & "=" & ИскомоеЗначение$) ' проверяем возвращеное функцией значение на наличие результатов поиска If Err Then Debug.Print "Такие строки в массиве не найдены": Exit Sub ' выводим из отфильтрованных строк значения первого столбца For i = LBound(resArr) To UBound(resArr) Debug.Print "Результат - строка " & i & " из " & UBound(resArr) & ": ", resArr(i, 1) Next i Debug.Print "Время: " & Timer - t & " сек." End Sub
Поиск с использованием ArraySearchResults
Sub ПримерБыстрогоПоискаВМассиве() t = Timer ИскомоеЗначение$ = 560 СтолбецДляПоиска& = 3 ' загружаем массив с листа arr = [a1:d30000].Value ' формируем строку поиска ss$ = SearchString(arr, СтолбецДляПоиска&) ' укорачиваем массив Arr, оставляя лишь те строки, ' где в заданном столбце есть искомое значение resArr = ArraySearchResults(arr, ss$, ИскомоеЗначение$) ' проверяем возвращеное функцией значение на наличие результатов поиска If Not IsArray(resArr) Then Debug.Print "Такие строки в массиве не найдены": Exit Sub ' выводим из отфильтрованных строк значения первого столбца For i = LBound(resArr) To UBound(resArr) Debug.Print "Результат - строка " & i & " из " & UBound(resArr) & ": ", resArr(i, 1) Next i Debug.Print "Время: " & Timer - t & " сек." End Sub
Код функции ArraySearchResults:
Function ArraySearchResults(ByRef arr, ByRef searchStr As String, ByVal txt As String, _ Optional ByVal Sep As String = "%$%") As Variant ' функция получает в качестве параметров массив Arr, ' и заранее сформированную строку SearchString из значений ячеек нужного столбца массива ' По этой строке SearchString функция ищет строки массива, в которые встречается значение txt, ' и возвращает усечённый массив, содержащий только подходящие строки ' Поиск ведётся по ТОЧНОМУ совпадению значений ro& = 0: spl = Split(searchStr, Sep & txt & Sep) If UBound(spl) = 0 Then Exit Function ' нет в массиве нужных строк ' перебираем результаты поиска, вычисляя номера строк в исходном массиве For i = LBound(spl) To UBound(spl) - 1 txt = spl(i): ro& = ro& + 1 + (Len(spl(i)) - Len(Replace(spl(i), Sep, ""))) / Len(Sep) 2 spl(i) = ro& Next i ' подготавливаем массив для результатов: ' по ширине - как исходный, по высоте - содержащий столько строк, сколько найдено совпадений ReDim resArr(1 To UBound(spl), LBound(arr, 2) To UBound(arr, 2)) ' заполняем новый массив For i = LBound(spl) To UBound(spl) - 1 For j = LBound(arr, 2) To UBound(arr, 2) resArr(i + 1, j) = arr(spl(i), j) Next j Next i ArraySearchResults = resArr End Function Function SearchString(ByRef arr, ByVal ArrayColumn As Long, _ Optional ByVal Sep As String = "%$%") As String ' Объединяет все значения из столбца ArrayColumn массива Arr в одну текстовую строку, ' в качестве разделителя элементов используя строку Sep ' Для ускорения конкатенации длинных строк используются ' промежуточные переменные buffer$ и buffer2$ buffer$ = "": buffer2$ = "": Sep2$ = Sep$ & Sep$: Const BufferLen& = 6000 On Error Resume Next: Err.Clear: SearchString = Sep2$ If ArrayColumn > UBound(arr, 2) Or ArrayColumn < LBound(arr, 2) Then Exit Function For i = LBound(arr) To UBound(arr) buffer$ = buffer$ & Trim$(arr(i, ArrayColumn)) & Sep2$ If Len(buffer$) > BufferLen& Then buffer2$ = buffer2$ & buffer$: buffer$ = "" If Len(buffer2$) > BufferLen& * 20 Then _ SearchString = SearchString & buffer2$: buffer2$ = "" End If Next i SearchString = SearchString & buffer2$ & buffer$ End Function
При поиске только одного значения время работы обоих макросов поиска не сильно отличается — но обычно функция ArraySearchResults оказывается немного быстрее.
Completing remark to Jimmy Pena’s accepted answer
As SeanC points out, this must be a 1-D array.
The following example call demonstrates that the IsInArray() function cannot be called only for 1-dim arrays,
but also for «flat» 2-dim arrays:
Sub TestIsInArray()
Const SearchItem As String = "ghi"
Debug.Print "SearchItem = '" & SearchItem & "'"
'----
'a) Test 1-dim array
Dim Arr As Variant
Arr = Split("abc,def,ghi,jkl", ",")
Debug.Print "a) 1-dim array " & vbNewLine & " " & Join(Arr, "|") & " ~~> " & IsInArray(SearchItem, Arr)
'----
'//quick tool to create a 2-dim 1-based array
Dim v As Variant, vals As Variant
v = Array(Array("abc", "def", "dummy", "jkl", 5), _
Array("mno", "pqr", "stu", "ghi", "vwx"))
v = Application.Index(v, 0, 0) ' create 2-dim array (2 rows, 5 cols)
'b) Test "flat" 2-dim arrays
Debug.Print "b) ""flat"" 2-dim arrays "
Dim i As Long
For i = LBound(v) To UBound(v)
'slice "flat" 2-dim arrays of one row each
vals = Application.Index(v, i, 0)
'check for findings
Debug.Print Format(i, " 0"), Join(vals, "|") & " ~~> " & IsInArray(SearchItem, vals)
Next i
End Sub
Function IsInArray(stringToBeFound As String, Arr As Variant) As Boolean
'Site: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/10951687/how-to-search-for-string-in-an-array/10952705
'Note: needs a "flat" array, not necessarily a 1-dimensioned array
IsInArray = (UBound(Filter(Arr, stringToBeFound)) > -1)
End Function
Results in VB Editor’s immediate window
SearchItem = 'ghi'
a) 1-dim array
abc|def|ghi|jkl ~~> True
b) "flat" 2-dim arrays
1 abc|def|dummy|jkl|5 False
2 mno|pqr|stu|ghi|vwx True
Поиск относительного положения элемента в массиве (диапазоне) с помощью метода VBA Excel WorksheetFunction.Match. Синтаксис, параметры, примеры.
WorksheetFunction.Match – это метод VBA Excel, который возвращает относительное положение элемента в массиве (диапазоне), соответствующее его порядковому номеру в массиве (диапазоне). Метод соответствует функции рабочего листа =ПОИСКПОЗ (поиск позиции).
Обратите внимание на то, что
- поиск позиции в массиве возможен, если он одномерный или двумерный, но с набором элементов только по одному измерению, например: myArray(8, 0) или myArray(1 To 1, 1 To 20);
- поиск позиции в диапазоне рабочего листа возможен, если он содержит только одну строку или один столбец;
- нумерация относительного положения элемента в массиве начинается с единицы, независимо от заданной индексации массива.
Синтаксис
Синтаксис метода WorksheetFunction.Match в VBA Excel:
|
WorksheetFunction.Match (Arg1, Arg2, [Arg3]) |
Параметры
Описание параметров метода WorksheetFunction.Match:
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| Arg1 | Обязательный параметр. Значение элемента массива, по которому будет произведен поиск относительного положения элемента в массиве. |
| Arg2 | Обязательный параметр. Непрерывный диапазон ячеек или массив, в котором будет произведен поиск позиции элемента, значение которого совпадет со значением параметра Arg1. |
| Arg3 | Необязательный параметр. Задает тип сопоставления значения Arg1 со значениями в массиве Arg2. |
В параметре Arg1 можно использовать знаки подстановки для шаблонов, те же, что и для методов Find и Replace.
Значения параметра Arg3, задающие тип сопоставления:
| Значение | Тип сопоставления |
|---|---|
| -1 | Метод WorksheetFunction.Match находит наименьшее значение элемента в Arg2, большее или равное Arg1. Значения элементов Arg2 должны быть расположены в убывающем порядке: [m, … 2, 1, 0, -1, -2, … -n], [z – a], [True, False] и т. д. |
| 0 | Метод WorksheetFunction.Match находит в Arg2 первое значение, равное Arg1. Значения элементов Arg2 могут быть расположены в любом порядке. |
| 1 | Значение по умолчанию. Метод WorksheetFunction.Match находит наибольшее значение элемента в Arg2, меньшее или равное Arg1. Значения элементов Arg2 должны быть расположены в возрастающем порядке: [-n, … -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, … m], [a – z], [False, True] и т. д. |
При сопоставлении строк регистр не учитывается.
Примеры
Пример 1
Поиск относительного положения элемента в массиве, индексация которого начинается с нуля:
|
Sub Primer1() Dim myArray As Variant, n As Long ‘заполнение массива значениями, нумерация элементов массива начинается с нуля myArray = Array(«Арка», 45, «Дуб», «Клуб», 85.37, «Литр», 103, «Небо», «Столб») ‘определяем относительное положение элемента в массиве, при чем ‘нумерация относительного положения начинается с единицы n = WorksheetFunction.Match(«Клуб», myArray) MsgBox n ‘Результат: 4 MsgBox myArray(n) ‘Результат: 85.37, так как нумерация массива начинается с нуля End Sub |
Пример 2
Определение индекса элемента в массиве по его относительному положению, возвращенному методом WorksheetFunction.Match:
|
Sub Primer2() Dim myArray(7 To 15) As Variant, i As Long, n As Long ‘заполнение элементов массива значениями For i = 7 To 15 myArray(i) = Choose(i, «», «», «», «», «», «», «Арка», 45, «Дуб», «Клуб», 85.37, «Литр», 103, «Небо», «Столб») Next n = WorksheetFunction.Match(«Клуб», myArray) MsgBox n ‘Результат: 4 ‘находим индекс элемента в массиве по его относительному положению n = n + LBound(myArray) — 1 MsgBox myArray(n) ‘Результат: Клуб End Sub |
Пример 3
Определение адреса ячейки на рабочем листе по найденному методом WorksheetFunction.Match относительному положению этой ячейки в заданном диапазоне:
|
Sub Primer3() Dim n As Long n = WorksheetFunction.Match(«Брелок», Range(«B1400:B1410»), 0) With Range(«B1400:B1410») MsgBox «Значение = « & .Cells(n) & vbNewLine & _ «Адрес = « & .Cells(n).Address & vbNewLine & _ «Строка = « & .Cells(n).Row & vbNewLine & _ «Столбец = « & .Cells(n).Column End With End Sub |
|
marker_mc Пользователь Сообщений: 228 |
Всем добрый день. есть 2 массива выбираю значение в combobox на userform, значения аналогичны значениям в массиве! на словах звучит так: Заранее спасибо! Изменено: marker_mc — 07.05.2013 14:58:12 |
|
LVL Пользователь Сообщений: 903 |
Перебор всех значений в цикле или словарь |
|
marker_mc Пользователь Сообщений: 228 |
я только к массивам добрался, а вы меня словарём сразу))))) |
|
marker_mc Пользователь Сообщений: 228 |
#4 07.05.2013 15:41:44 вопрос снят! LVL, спасибо за наводку. Сделал перебор значений в массиве через For Next Выглядит так:
|
||
|
Hugo Пользователь Сообщений: 23251 |
Комбобокс? Используйте индекс (т.е. номер выбранной записи). |
|
marker_mc Пользователь Сообщений: 228 |
Hugo, я правильно понял, что можно вернуть номер значения по счету из комбобокс? Если правильно понимаю, то вы предлагаете вернуть этот номер и найти значение по номеру в array Но все таки интересно на будущее, каким образом получить этот индекс? Насчет файла… признаю честно, специально не стал ложить сюда, чтоб не дали готового решения! Хотелось именно пару наводок, чтоб самому дойди… мне полезно, я учусь))))) Изменено: marker_mc — 07.05.2013 15:55:23 |
|
Hugo Пользователь Сообщений: 23251 |
#7 07.05.2013 15:58:52 Ну Вы же сказали, что в комбобоксе то, что и в массиве. Т.е. возможно массив является источником комбобокса… А примера нет…
Начало нумерации с 0. Изменено: Hugo — 07.05.2013 16:02:16 |
||
|
marker_mc Пользователь Сообщений: 228 |
#8 07.05.2013 16:05:57
)))) Да, в КБ тоже что и в Массиве и расположение тоже такое же, но КБ формируется не с массива, а с именованного диапазона EXCEL… но я немножко забегая на будущее… по принципу «а мало ли….» во избежании ошибки. Спасибо за подсказки! |
||||
|
Hugo Пользователь Сообщений: 23251 |
Ну если с листа — то можно на листе формулой поискать. |
|
Юрий М Модератор Сообщений: 60575 Контакты см. в профиле |
на лист можно и Find натравить. |
|
marker_mc Пользователь Сообщений: 228 |
Ребята, поиск на листе это Вы уже не туда пошли… .find это я уже прошел и пользуюсь… стоял вопрос именно в массиве VBA array который с листом никак не связан, а вот КБ формируется именно с листа через созданное имя в диспетчере имен. |
|
Hugo Пользователь Сообщений: 23251 |
Да словарей тут вагон был… Хотя конечно на 8 значений нет смысла словарь привлекать (тем более что искать нужно только 1 значение при каждом запуске кода) — оставляйте перебор. Изменено: Hugo — 07.05.2013 23:27:13 |
|
Юрий М Модератор Сообщений: 60575 Контакты см. в профиле |
Куда-то мой пост подевался))) |
|
Hugo Пользователь Сообщений: 23251 |
Сапожник без сапог |
|
nerv Пользователь Сообщений: 3071 |
#15 07.05.2013 23:33:39
с ADO (sql) проще Чебурашка стал символом олимпийских игр. А чего достиг ты? |
||
|
Hugo Пользователь Сообщений: 23251 |
Но дольше |
|
nerv Пользователь Сообщений: 3071 |
#17 08.05.2013 00:38:24
не понял
ну, так зачем много раз одно и тоже набирать, если можно один раз сделать и потом использовать? Обычная практика. Всю лишнюю/скучную/глупую рутинную работу переложить на класс/функцию.
пример маневра Чебурашка стал символом олимпийских игр. А чего достиг ты? |
||||||
|
Hugo Пользователь Сообщений: 23251 |
Я как-то сравнивал скорость работы — словарь был быстрее. Можем ещё на какой задаче проверить. |
|
ambasad Пользователь Сообщений: 26 |
#19 08.05.2013 11:18:17
Может имеет смысл заполнить массив с того же листа? тогда всё будет совпадать |
||
|
Слэн Пользователь Сообщений: 5192 |
WorksheetFunction.Match() вам в помощь, но находит не индекс массива, а номер начиная с единицы. если индекс тоже с единицы, то все ок, иначе надо корректировать.. |
|
nerv Пользователь Сообщений: 3071 |
#21 08.05.2013 13:21:04
я почему то сомневаюсь )
все вышеописанное можно сделать с помощью ADO (SQL) Чебурашка стал символом олимпийских игр. А чего достиг ты? |
||||
|
ikki Пользователь Сообщений: 9709 |
#22 08.05.2013 13:31:32
а что мешает потестировать? фрилансер Excel, VBA — контакты в профиле |
||
|
marker_mc Пользователь Сообщений: 228 |
Раз уж тема крутится дальше… что то типа такого можно? b = Array([именованный диапазон]) |
|
LVL Пользователь Сообщений: 903 |
#24 08.05.2013 13:41:32
b — динамический массив типа Variant |
||
|
marker_mc Пользователь Сообщений: 228 |
LVL, это будет тогда не массив, а просто диапазон судя по записи |
|
Hugo Пользователь Сообщений: 23251 |
a = [именованный_диапазон].Value Но получите двумерный массив. |
|
marker_mc Пользователь Сообщений: 228 |
но а записать в переменную как |
|
LVL Пользователь Сообщений: 903 |
|
|
LVL Пользователь Сообщений: 903 |
в какую переменную? Массив и есть переменная |
|
marker_mc Пользователь Сообщений: 228 |
#30 08.05.2013 13:45:57 Ок, попробую ради интереса еще так переделать. Спасибо. Хотя через цикл уже давно работает)))) |
Home / VBA / Arrays / VBA Search for a Value in an Array
When you store values in an array, there could be a time when you need to search within an array. In that case, you need to know the methods that you can use. Now, look at the below code that can help you understand how to search for a value in an array.

- In the first part of the code, you have variables that you need to use in the code further.
- After that, the next part generates random numbers by using RND to get you the ten values for the array.
- Next, an input box let you enter the value that you want to search within the array.
- After that, you have a line that uses the IF statement to check if the value you have entered in the input box is a number or not.
- In this part, you have a code for the string to use in the message box if the value you have entered is not found.
- This part of the code uses a For Loop (For Each) to loop through each item in the array and check if the value that you have entered is in the array or not.
- The last part of the code shows you a message about whether the value is found or not.
Option Base 1
Sub vba_array_search()
'this section declares an array and variables
'that you need to search within the array.
Dim myArray(10) As Integer
Dim i As Integer
Dim varUserNumber As Variant
Dim strMsg As String
'This part of the code adds 10 random numbers to
'the array and shows the result in the
'immediate window as well.
For i = 1 To 10
myArray(i) = Int(Rnd * 10)
Debug.Print myArray(i)
Next i
'it is an input box that asks
'you the number that you want to find
Loopback:
varUserNumber = InputBox _
("Enter a number between 1 and 10 to search for:", _
"Linear Search Demonstrator")
'it's an if statement that checks for the value that you
'have entered in the input box.
If varUserNumber = "" Then End
If Not IsNumeric(varUserNumber) Then GoTo Loopback
If varUserNumber < 1 Or varUserNumber > 10 Then GoTo Loopback
'message to show if the value doesn't found.
strMsg = "Your value, " & varUserNumber & _
", was not found in the array."
'loop through the array and match each value with the
'the value you have entered in the input box.
For i = 1 To UBound(myArray)
If myArray(i) = varUserNumber Then
strMsg = "Your value, " & varUserNumber & _
", was found at position " & i & " in the array."
Exit For
End If
Next i
'message box in the end
MsgBox _
strMsg, vbOKOnly + vbInformation, _
"Linear Search Result"
End Sub
-
#2
can’t find anything — are you looping the values in the array — what code are you using to find a match…
something like:
Code:
n = 0
test = 10
Do Until n > z
If varData(n) = test Then
MsgBox "Match in Row " & n + 2
Exit Sub
End If
n = n + 1
Loop(I had some code to create the array — z matches the number of values in the array)
-
#3
Yes, I’m using something very similar — just looping through the values and if I find a match I set a boolean variable to true and exit the loop. Its working fine — I was just wondering if there was a more efficient VBA function that does it in one line.
Anyway, thanks for the time…
Cheers,
Rajat
-
#4
Hi
If it’s a onedimensional array the Filter-Function could be used
dim z as variant
z = Filter(MyArray, Testvalue)
If UBound(z) < 0 Then MsgBox («empty»)
regards
Tommy
-
#5
Thanks Tommy, I wrote that out in one line (Ubound(filter….)), and now my code really does look slim. Great tip… thanks.
-
#6
Thanks for the tip Tommy.
However, I noticed that you need to be careful if passing a blank string as the search term.
Ordinarily, you’d expect a blank string to return false (that it does not exist in the array), unfortunately due to the way the filter function works, passing a blank string returns the entire array, which is then incorrectly reported as a successful search.
Instead consider the slight alteration:
Code:
[COLOR=Green] 'Initialise Array[/COLOR]
[COLOR=RoyalBlue]Dim [/COLOR]myArray(2) [COLOR=RoyalBlue]As String[/COLOR]
myArray(0) = "Value1"
myArray(1) = "Value2"
myArray(2) = "Value3"
[COLOR=SeaGreen] 'Initialise Search Term[/COLOR]
[COLOR=RoyalBlue]Dim [/COLOR]searchTerm [COLOR=RoyalBlue]As String[/COLOR]
searchTerm = "Value2"
[COLOR=SeaGreen]'Check if a value exists in the Array[/COLOR]
[COLOR=RoyalBlue]If UBound[/COLOR](Filter(myArray, searchTerm)) >= 0 [COLOR=RoyalBlue]And [/COLOR]searchTerm <> ""[COLOR=RoyalBlue] Then[/COLOR]
MsgBox ("Search Term SUCCESSFULLY located in the Array")
[COLOR=RoyalBlue]Else[/COLOR]
MsgBox ("Search Term could NOT be located in the Array")
[COLOR=RoyalBlue]End If[/COLOR]This works and corrects the issue of passing a blank string (this may be necessary if, for example, you are comparing the value a user typed into a cell against an array of valid values, within a manual validation function).
However, be aware that the Filter function also accepts partial matches.
For example, typing «Value» as the search term in the above example (with no number on the end) reports a valid match, even though no element in the array exactly matches this string.
Nevertheless, still should be a good one line alternative to using a loop and manually comparing each value in the array, assuming you can handle partial matches.
Last edited: Jun 26, 2011
-
#7
Here is a non-looping method that avoids the partial match problem that the Filter function opens one up to…
Code:
Dim C As String, FindMe As String, myArray() As Variant
Dim ItemFound As Boolean, MatchCase As Boolean
' Load dynamic Variant array in a single line of code
myArray = Array("Value1", "Value2", "Value3")
' Initialize search options
FindMe = "value2"
MatchCase = False
' Perform search
C = Chr$(1)
ItemFound = InStr(1, C & Join(myArray, C) & C, C & FindMe & C, 1 + MatchCase)
' Display result
If ItemFound Then
MsgBox "Found it!"
Else
MsgBox "Could NOT find it."
End IfThe above code only finds whole array element matches; that is, if you searched for «Val», it would not match any elements in the array (the Filter function method would produce a match). I also provided a MatchCase Boolean variable to control whether the letter casing must be exact or not when performing the search.
-
#8
Simple Application.Match(value, array, 0) won’t help? That is if the array element you are searching for is exactly same — eg. looking for «john» will find «john» but not «john doe».
Don’t use WorkSheetFunction.Match, because when it doesn’t find a match, it will throw runtime error.
-
#9
Here is a non-looping method that avoids the partial match problem that the Filter function opens one up to…
Code:
Dim C As String, FindMe As String, myArray() As Variant Dim ItemFound As Boolean, MatchCase As Boolean ' Load dynamic Variant array in a single line of code myArray = Array("Value1", "Value2", "Value3") ' Initialize search options FindMe = "value2" MatchCase = False ' Perform search C = Chr$(1) ItemFound = InStr(1, C & Join(myArray, C) & C, C & FindMe & C, 1 + MatchCase) ' Display result If ItemFound Then MsgBox "Found it!" Else MsgBox "Could NOT find it." End IfThe above code only finds whole array element matches; that is, if you searched for «Val», it would not match any elements in the array (the Filter function method would produce a match). I also provided a MatchCase Boolean variable to control whether the letter casing must be exact or not when performing the search.
Isn’t calling it ‘non-looping’ misleading?
If InStr loop as I’d expect, ‘letter by letter’, then it’s actually a less efficient solution than the original. In the original you loop for as many elements as there are in the array, with InStr you are effectively loop for as many letters as there are in all of the elements combined.
It would be interesting to time this on an appropriately large data-set.
-
#10
Hello,
I have a problem in a macro. I have a function and function input is an array. I used another function in the function whhich I prepared before and input of this function coming from the main function. I code is given below. I don’t know how to pass input of one function to anaother function. Could you please help me.
Function G_TP(ParamArray Comp() As Variant) As Variant
G_TP = H_TP(Comp()) — Comp(0) * S_TP(Comp())
End Function
Comp() in the function H_TP() must be an array. But in this form only first term of the Comp() ig cominh to H_TP() other terms are not coming how can I solve it. Please help me.