Я не могу предоставить пример с макросом, поскольку еще пишу скелет. Текстовый файл, тоже особо смылса кидать нет.
Ситауция следующая, имеется текстовый файл, в который периодически идет поток данных, необходимо в определенное время(об OnTime Now и TimeSerial я осведомлен)
проверять пришли ли данные. С этого этапа принципиально может быть 3 ситуации развития событий:
1) Данные пришли какие надо, следствие этого идем далее
2) Данные пришли но с ошибкой, следствие этого необходимо закомментировать строку
3) Данные не пришли., пока данные не пришли циклим ждем прихода….
у данных есть две характерных особенности у них есть порядковый номер, и у них есть скажем так
«характерный номер обратной связи»
который фактически является булевой переменной: Есть ошибка/нет ошибки.
Прошу прощения, что в принципе не правильно объявил тему, и что не задал сути вопроса в заглавном посте, до написания на форум, я был уверен в том что я ошибаюсь при работе с функцией .Find, и изначально предполагал, что тот нюанс который есть при работе с переменной у функции .Find который для более опытных товарищей очевиден, всплывет на поверхность.
Алгоритм такой :
1) открывай текстовый файл помещаем в переменную
2) в переменной ищем, наличие нового порядкового номера, если его нет закрываем файл, и открываем опять ( делаем это в цикле)
3) если он есть смотрим на
«характерный номер обратной связи»,
если ошибка есть комментим строку с ошибкой закрываем файл,
записываем ошибки в отдельный массив в Эксель ( грубо говоря в столбик)
Основное условие этого алгоритма пришли ли данные,
т.е. в итоге вопрос такой имеется
некая изначальная информация которую необходимо найти в текстовом файле, если использовать Instr
Это скелет в нем могут быть ошибки как грамматические в комментариях, так синтаксические в работе функции Instr,
так и алгоритмические.
| Код |
|---|
Sub Poisk_txt() Dim s, Poisk, Nashli, Nashli//DC, Poisk//DC As String Dim Count_mistake As Integer ' Счетчик ошибок Open "C:testfile.txt" For Input As #1 s = Input(LOF(1), 1) ' содержимое текстового файла в переменной строкового типа Poisk = "4//" ' какой порядковый номер ищем Poisk//DC = "4//DC//1//" ' порядковый номер и характерный номер обратной связи БЕЗ ОШИБКИ который ищем Nashli = Instr(s, Poisk, 1) ' Непосредственно ищем, могу неправильно набрать, функция Instr похожа на ПоискПоз 'Do If Nashli = Poisk Then ' If-1 Nashli//DC = Instr(s, Poisk//DC, 1) If Nashli//DC = Poisk//DC Then ' If - 2 ' 'это то что нужно, если значение IF = True то выходим из цикла Else: Cells(Count_mistake, 7) = Poisk ' If - 2 Count_mistake = Count_mistake + 1 s = Replace(s, "4//", "*;4//") Print #1, s Close #1 Open #1 End If ' If - 2 Else ' If -1 Close #1 Open #1 End If ' If- 1 'Loop End Sub |
Вопроса два если Instr или Find или Регулярные выражения ничего не найдут по заданному условию то будет ошибка
1) ошибку стоит проходить конструкцией On Error Resume Next? или другой?
2) и второй момент как оптимальнее зациклить, просто бесконечный цикл? или что то более функциональное?
Прошу меня извинить что в самом начале так все не расписал.
Благодарю еще раз всех Вас.
|
f1eshka 0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 30.05.2018 Сообщений: 1 |
||||
|
1 |
||||
|
01.06.2018, 10:05. Показов 5974. Ответов 2 Метки vba (Все метки)
Доброго времени суток. Допустим есть файл info.txt ( состоит из множества строк, например gsd = 797 …. dig = 7666 и т.д.) в корне в с экселевким(готова таблица) нужно сделать так, чтобы через vba ексель находил в этом файле определенные строки и выставлял в конкретные ячейки ексель при этом, чтобы взятая строка вставлялась в эксель с данными после знака равенства. Пока сам только научился делать простейший импорт данных из открытого файла.
0 |
|
Aleks777 95 / 91 / 16 Регистрация: 13.04.2015 Сообщений: 545 |
||||
|
05.06.2018, 23:56 |
2 |
|||
|
f1eshka,
0 |
|
6875 / 2807 / 533 Регистрация: 19.10.2012 Сообщений: 8,562 |
|
|
06.06.2018, 00:13 |
3 |
|
Обычно нужно вставлять не одно значение, а много, и разных. Поэтому есть смысл сперва прочитать весь файл в словарь (ну или в коллекцию), а затем циклом по листу всё собранное разложить по местам.
0 |
Поиск какого-либо значения в ячейках Excel довольно часто встречающаяся задача при программировании какого-либо макроса. Решить ее можно разными способами. Однако, в разных ситуациях использование того или иного способа может быть не оправданным. В данной статье я рассмотрю 2 наиболее распространенных способа.
Поиск перебором значений
Довольно простой в реализации способ. Например, найти в колонке «A» ячейку, содержащую «123» можно примерно так:
Sheets("Данные").Select
For y = 1 To Cells.SpecialCells(xlLastCell).Row
If Cells(y, 1) = "123" Then
Exit For
End If
Next y
MsgBox "Нашел в строке: " + CStr(y)
Минусами этого так сказать «классического» способа являются: медленная работа и громоздкость. А плюсом является его гибкость, т.к. таким способом можно реализовать сколь угодно сложные варианты поиска с различными вычислениями и т.п.
Поиск функцией Find
Гораздо быстрее обычного перебора и при этом довольно гибкий. В простейшем случае, чтобы найти в колонке A ячейку, содержащую «123» достаточно такого кода:
Sheets("Данные").Select
Set fcell = Columns("A:A").Find("123")
If Not fcell Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "Нашел в строке: " + CStr(fcell.Row)
End If
Вкратце опишу что делают строчки данного кода:
1-я строка: Выбираем в книге лист «Данные»;
2-я строка: Осуществляем поиск значения «123» в колонке «A», результат поиска будет в fcell;
3-я строка: Если удалось найти значение, то fcell будет содержать Range-объект, в противном случае — будет пустой, т.е. Nothing.
Полностью синтаксис оператора поиска выглядит так:
Find(What, After, LookIn, LookAt, SearchOrder, SearchDirection, MatchCase, MatchByte, SearchFormat)
What — Строка с текстом, который ищем или любой другой тип данных Excel
After — Ячейка, после которой начать поиск. Обратите внимание, что это должна быть именно единичная ячейка, а не диапазон. Поиск начинается после этой ячейки, а не с нее. Поиск в этой ячейке произойдет только когда весь диапазон будет просмотрен и поиск начнется с начала диапазона и до этой ячейки включительно.
LookIn — Тип искомых данных. Может принимать одно из значений: xlFormulas (формулы), xlValues (значения), или xlNotes (примечания).
LookAt — Одно из значений: xlWhole (полное совпадение) или xlPart (частичное совпадение).
SearchOrder — Одно из значений: xlByRows (просматривать по строкам) или xlByColumns (просматривать по столбцам)
SearchDirection — Одно из значений: xlNext (поиск вперед) или xlPrevious (поиск назад)
MatchCase — Одно из значений: True (поиск чувствительный к регистру) или False (поиск без учета регистра)
MatchByte — Применяется при использовании мультибайтных кодировок: True (найденный мультибайтный символ должен соответствовать только мультибайтному символу) или False (найденный мультибайтный символ может соответствовать однобайтному символу)
SearchFormat — Используется вместе с FindFormat. Сначала задается значение FindFormat (например, для поиска ячеек с курсивным шрифтом так: Application.FindFormat.Font.Italic = True), а потом при использовании метода Find указываем параметр SearchFormat = True. Если при поиске не нужно учитывать формат ячеек, то нужно указать SearchFormat = False.
Чтобы продолжить поиск, можно использовать FindNext (искать «далее») или FindPrevious (искать «назад»).
Примеры поиска функцией Find
Пример 1: Найти в диапазоне «A1:A50» все ячейки с текстом «asd» и поменять их все на «qwe»
With Worksheets(1).Range("A1:A50")
Set c = .Find("asd", LookIn:=xlValues)
Do While Not c Is Nothing
c.Value = "qwe"
Set c = .FindNext(c)
Loop
End With
Обратите внимание: Когда поиск достигнет конца диапазона, функция продолжит искать с начала диапазона. Таким образом, если значение найденной ячейки не менять, то приведенный выше пример зациклится в бесконечном цикле. Поэтому, чтобы этого избежать (зацикливания), можно сделать следующим образом:
Пример 2: Правильный поиск значения с использованием FindNext, не приводящий к зацикливанию.
With Worksheets(1).Range("A1:A50")
Set c = .Find("asd", lookin:=xlValues)
If Not c Is Nothing Then
firstResult = c.Address
Do
c.Font.Bold = True
Set c = .FindNext(c)
If c Is Nothing Then Exit Do
Loop While c.Address <> firstResult
End If
End With
В ниже следующем примере используется другой вариант продолжения поиска — с помощью той же функции Find с параметром After. Когда найдена очередная ячейка, следующий поиск будет осуществляться уже после нее. Однако, как и с FindNext, когда будет достигнут конец диапазона, Find продолжит поиск с его начала, поэтому, чтобы не произошло зацикливания, необходимо проверять совпадение с первым результатом поиска.
Пример 3: Продолжение поиска с использованием Find с параметром After.
With Worksheets(1).Range("A1:A50")
Set c = .Find("asd", lookin:=xlValues)
If Not c Is Nothing Then
firstResult = c.Address
Do
c.Font.Bold = True
Set c = .Find("asd", After:=c, lookin:=xlValues)
If c Is Nothing Then Exit Do
Loop While c.Address <> firstResult
End If
End With
Следующий пример демонстрирует применение SearchFormat для поиска по формату ячейки. Для указания формата необходимо задать свойство FindFormat.
Пример 4: Найти все ячейки с шрифтом «курсив» и поменять их формат на обычный (не «курсив»)
lLastRow = Cells.SpecialCells(xlLastCell).Row
lLastCol = Cells.SpecialCells(xlLastCell).Column
Application.FindFormat.Font.Italic = True
With Worksheets(1).Range(Cells(1, 1), Cells(lLastRow, lLastCol))
Set c = .Find("", SearchFormat:=True)
Do While Not c Is Nothing
c.Font.Italic = False
Set c = .Find("", After:=c, SearchFormat:=True)
Loop
End With
Примечание: В данном примере намеренно не используется FindNext для поиска следующей ячейки, т.к. он не учитывает формат (статья об этом: https://support.microsoft.com/ru-ru/kb/282151)
Коротко опишу алгоритм поиска Примера 4. Первые две строки определяют последнюю строку (lLastRow) на листе и последний столбец (lLastCol). 3-я строка задает формат поиска, в данном случае, будем искать ячейки с шрифтом Italic. 4-я строка определяет область ячеек с которой будет работать программа (с ячейки A1 и до последней строки и последнего столбца). 5-я строка осуществляет поиск с использованием SearchFormat. 6-я строка — цикл пока результат поиска не будет пустым. 7-я строка — меняем шрифт на обычный (не курсив), 8-я строка продолжаем поиск после найденной ячейки.
Хочу обратить внимание на то, что в этом примере я не стал использовать «защиту от зацикливания», как в Примерах 2 и 3, т.к. шрифт меняется и после «прохождения» по всем ячейкам, больше не останется ни одной ячейки с курсивом.
Свойство FindFormat можно задавать разными способами, например, так:
With Application.FindFormat.Font .Name = "Arial" .FontStyle = "Regular" .Size = 10 End With
Поиск последней заполненной ячейки с помощью Find
Следующий пример — применение функции Find для поиска последней ячейки с заполненными данными. Использованные в Примере 4 SpecialCells находит последнюю ячейку даже если она не содержит ничего, но отформатирована или в ней раньше были данные, но были удалены.
Пример 5: Найти последнюю колонку и столбец, заполненные данными
Set c = Worksheets(1).UsedRange.Find("*", SearchDirection:=xlPrevious)
If Not c Is Nothing Then
lLastRow = c.Row: lLastCol = c.Column
Else
lLastRow = 1: lLastCol = 1
End If
MsgBox "lLastRow=" & lLastRow & " lLastCol=" & lLastCol
В этом примере используется UsedRange, который так же как и SpecialCells возвращает все используемые ячейки, в т.ч. и те, что были использованы ранее, а сейчас пустые. Функция Find ищет ячейку с любым значением с конца диапазона.
Поиск по шаблону (маске)
При поиске можно так же использовать шаблоны, чтобы найти текст по маске, следующий пример это демонстрирует.
Пример 6: Выделить красным шрифтом ячейки, в которых текст начинается со слова из 4-х букв, первая и последняя буквы «т», при этом после этого слова может следовать любой текст.
With Worksheets(1).Cells
Set c = .Find("т??т*", LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole)
If Not c Is Nothing Then
firstResult = c.Address
Do
c.Font.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0)
Set c = .FindNext(c)
If c Is Nothing Then Exit Do
Loop While c.Address <> firstResult
End If
End With
Для поиска функцией Find по маске (шаблону) можно применять символы:
* — для обозначения любого количества любых символов;
? — для обозначения одного любого символа;
~ — для обозначения символов *, ? и ~. (т.е. чтобы искать в тексте вопросительный знак, нужно написать ~?, чтобы искать именно звездочку (*), нужно написать ~* и наконец, чтобы найти в тексте тильду, необходимо написать ~~)
Поиск в скрытых строках и столбцах
Для поиска в скрытых ячейках нужно учитывать лишь один нюанс: поиск нужно осуществлять в формулах, а не в значениях, т.е. нужно использовать LookIn:=xlFormulas
Поиск даты с помощью Find
Если необходимо найти текущую дату или какую-то другую дату на листе Excel или в диапазоне с помощью Find, необходимо учитывать несколько нюансов:
- Тип данных Date в VBA представляется в виде #[месяц]/[день]/[год]#, соответственно, если необходимо найти фиксированную дату, например, 01 марта 2018 года, необходимо искать #3/1/2018#, а не «01.03.2018»
- В зависимости от формата ячеек, дата может выглядеть по-разному, поэтому, чтобы искать дату независимо от формата, поиск нужно делать не в значениях, а в формулах, т.е. использовать LookIn:=xlFormulas
Приведу несколько примеров поиска даты.
Пример 7: Найти текущую дату на листе независимо от формата отображения даты.
d = Date Set c = Cells.Find(d, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlWhole) If Not c Is Nothing Then MsgBox "Нашел" Else MsgBox "Не нашел" End If
Пример 8: Найти 1 марта 2018 г.
d = #3/1/2018# Set c = Cells.Find(d, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlWhole) If Not c Is Nothing Then MsgBox "Нашел" Else MsgBox "Не нашел" End If
Искать часть даты — сложнее. Например, чтобы найти все ячейки, где месяц «март», недостаточно искать «03» или «3». Не работает с датами так же и поиск по шаблону. Единственный вариант, который я нашел — это выбрать формат в котором месяц прописью для ячеек с датами и искать слово «март» в xlValues.
Тем не менее, можно найти, например, 1 марта независимо от года.
Пример 9: Найти 1 марта любого года.
d = #3/1/1900# Set c = Cells.Find(Format(d, "m/d/"), LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart) If Not c Is Nothing Then MsgBox "Нашел" Else MsgBox "Не нашел" End If
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
I need to use Excel VBA to open a text file (easy enough), but then search the text file for a specific string. It looks like the TextorProperty/.FileSearch capacities would have taken care of this, but it was deprecated starting with Microsoft Office 2007.
I’ve tried several other ways, using «StreamReader» or making a new FileSystemObject, but my version of Excel won’t let me add any references, so neither of these worked. Any suggestions?
Answers
-
Try something like this:
Sub SearchTextFile()
Const strFileName = «C:MyFilesTextFile.txt»
Const strSearch = «Some Text»
Dim strLine As String
Dim f As Integer
Dim lngLine As Long
Dim blnFound As Boolean
f = FreeFile
Open strFileName For Input As #f
Do While Not EOF(f)
lngLine = lngLine + 1
Line Input #f, strLine
If InStr(1, strLine, strSearch, vbBinaryCompare) > 0 Then
MsgBox «Search string found in line » & lngLine, vbInformation
blnFound = True
Exit Do
End If
Loop
Close #f
If Not blnFound Then
MsgBox «Search string not found», vbInformation
End If
End Sub
Regards, Hans Vogelaar
-
Marked as answer by
Wednesday, July 3, 2013 1:31 PM
-
Marked as answer by
You will find everything you need to know on the Excel VBA Find function. The Range Find function allows you to find cells within your Excel worksheet (and workbook) that contain a certain text or value. In this post let us explore the many ways in which you can use the Find function.
Looking to search text within VBA strings instead? See the VBA InStr and VBA InStrRev functions
Before we show how to use VBA to search for text within an Excel spreadsheet let us first see how to do it Excel and explore the usually unknown features of the famous CTRL+F combo. See below where you can find it within the Home ribbon and Editing group.
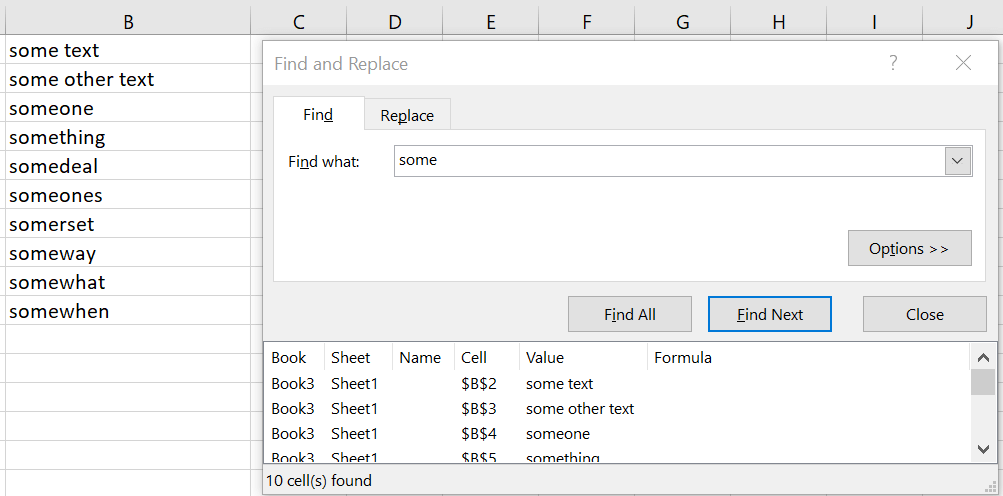
By clicking the above or simply using the key combo CTRL+F we can enter the Find & Replace modal window.
As you notice above Excel easily finds 10 matches for the cells on the left. However there are several more interesting search combinations you can use, including usage of wildcards you can use to get more specific patterns. See some examples below:
| Find | Matches |
|---|---|
| some*text |
|
| some ? |
|
| some*e*a |
|
As you might have already noticed I used 2 types of wildcards above:
- * – the asterisk symbol represents zero or many of any type of characters. It can be injected between characters to replace either no or any number of characters.
- ? – the question mark represents at least 1 character.
Now that we have a hand of the basic features of Excel in terms of word search let us move to how to use Excel VBA to find cells containing specific text.
VBA Range Find function
The VBA Find function is in fact a function of the Excel VBA Range object class. See Microsoft documentation for more details. A VBA Range represents any subset of cells within a spreadsheet – it can be a single cell, entire row or a patchwork of different cells and other Ranges. Executing the Find function in fact limits the search to only the cells within its Range object.
Below is the definition of the VBA Range Find function and its parameters:
.Find(What, [After] [LookIn], [LookAt], [SearchOrder],
[SearchDirection], [MatchCase], [MatchByte], [SearchFormat])
The Find function returns only the first match within the Range. To search for next items you need to follow it up with the FindNext function.
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| What | Required | The value you are searching for |
| After | Optional | The cell range from which you start your search from |
| LookIn | Optional | What to search in e.g. Formulas, Values or Comments – constants of XlFindLookIn: xlValues, xlFormulas, xlComments, xlCommentsThreaded |
| LookAt | Optional | Whether to search in a part of the string in a cell or whether it needs to match the entire cell string – constants of XlLookAt: xlWhole, xlPart |
| SearchOrder | Optional | The sequence of the search i.e. whether to search by rows or columns – constants of XlSearchOrder: xlByRows or xlByColumns |
| SearchDirection | Optional | Whether to search forward (next) or backwards (previous) – constants of XlSearchDirection: xlNext, xlPrevious |
| MatchCase | Optional | Case sensitive or not – True or False |
| MatchByte | Optional | Used for double byte languages. True to have double-byte characters match only double-byte characters – True or False |
| SearchFormat | Optional | Allow searching by format. See Application.FindFormat – True or False |
VBA Find – simple example
We will start with a very simple VBA Range Find function example – searching for a single cell within the entire Excel active spreadsheet:
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveSheet
Debug.Print ws.Cells.Find("some")
Output:
some text
As you can see it found the first match within the Activesheet (currently open and top spreadsheet) and returned the found value.
VBA Find All
Finding all matches is a little more complicated in VBA than in Excel. We will need to use Do While loop to run via all matches:
Dim searchRange As Range, found As Range, firstFind As Range
'Set the search range to the entire worksheet
Set searchRange = ActiveSheet.Cells
'Search for the first match
Set found = searchRange.Find("some")
'Save the first found cell to check later whether we have completed the search
Set firstFind = found
'Loop through all items using FindNext Range function
Do
If Not (found Is Nothing) Then
Debug.Print found.Value
Set found = searchRange.FindNext(found)
End If
Loop While Not (found = firstFind)
Output:
some text some other text someone something somedeal someones somerset someway somewhat somewhen
I highlighted above 2 key functions that were used the Range Find Function and the Range FindNext Function. As I mentioned above the Find function will only return the first match. To get next matches you need to run FindNext on the original range. This is I am executing FindNext on the searchRange variable and not the found variable.
Another interesting point to notice is the Do While…loop. Notice I am comparing the found variable to the firstFind variable. This is because when running FindNext it will at some point move to the first match once again and thus never end… it will just keep going in a cirle! Thus the loop is set to end once the FindNext function returns the same first cell.
Find using Wildcards
As mentioned above you can use 2 types of wildcards the asterisk * (zero or more characters) and the question mark ? (at least 1 character) to match slightly more complicates cases.
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveSheet
Debug.Print ws.Cells.Find("some ?")
'Output: some text
Debug.Print ws.Cells.Find("some*w")
'Output: someway
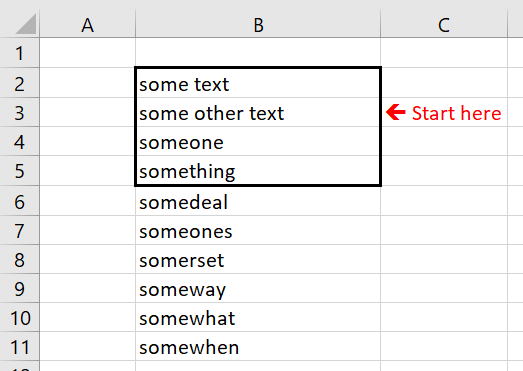
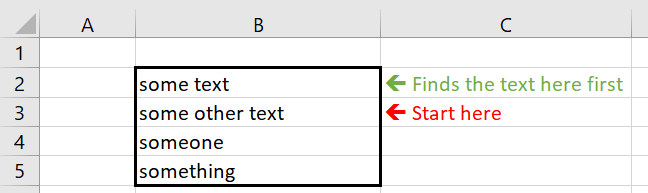
VBA Find with After
To remind the After parameter of the Excel VBA Range Find function defines where you will start your search. It is useful when you don’t want to redefine your range just for the purpose of the search activity. See the example below:
Debug.Print Range("B2:B5").Find("some ?", After:=Range("B3"))
Output:
someone
As you can see below the Find function starts searching for the “some” string just after cell B3 i.e. it will start at B4 where it finds the first matching string.
Find After – avoid wrap around
Even if we specify that the VBA Range Find function should start searching for the string after a specified cell, it might wrap around back to the beginning of the Range we specified if it does not find a match when going down. See example below to understand:
Debug.Print Range("B2:B5").Find("some*text", After:=Range("B3"))
Output:
some text
As you see the search started at B4 however once the search pattern “some*text” was not found until B5 the function resumed search on the remaining cells B2:B3 to find “some text”.
Find After Avoid wrapping using VBA Find
What to do to avoid this wrapping? We can check whether the found text is not within the preceding range using the Application.Intersect function.
If the found cell is before our After cell then we can handle it as such:
Set found = Range("B2:B5").Find("some*text", After:=Range("B3"))
If Intersect(Range("B2:B3"), found) Is Nothing Then
Debug.Print "Found text: " & found.Value
Else
Debug.Print "Text found is within excluded range"
End If
Output:
Text found is within excluded range
However if the found cell is only After the cell we specified then it will show like this:
Set found = Range("B2:B5").Find("some", After:=Range("B3"))
If Intersect(Range("B2:B3"), found) Is Nothing Then
Debug.Print "Found text: " & found.Value
Else
Debug.Print "Text found is within excluded range"
End If
Output:
Found text: someone
Find in Values, Formulas, Comments
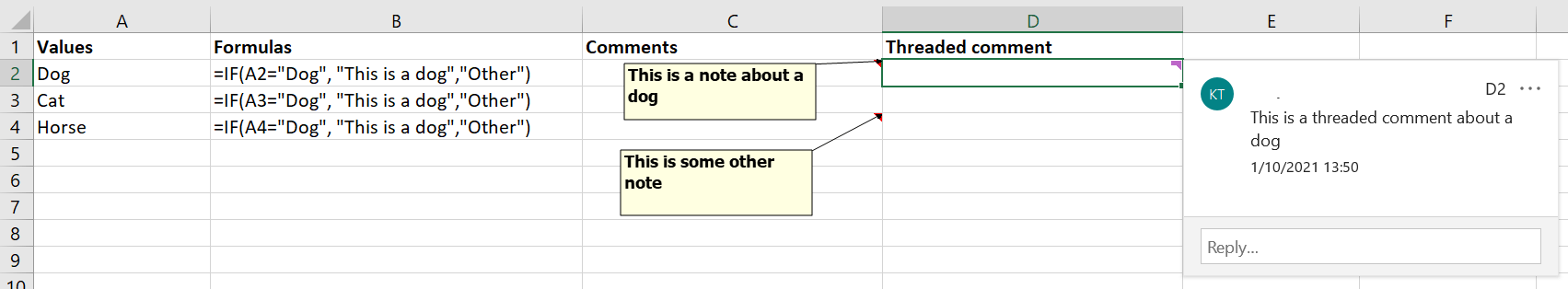
The VBA Range Find function allows you not only to search within Values (the evalution of your Excel formulas). It can also search instead (or including) within Formulas, Comments and even Excel Threaded Comments.
Let us explore how to use the LookIn parameter to look into specific attributes of a cell.
In the code below we will search for the word dog within Values, Formulas, Notes and Threaded Comments (just the first one). We will return the address first. Notice that for Formulas the result was the same – this is because the Value and Formula is the same in this case.
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("dog", LookIn:=xlValues).AddressLocal
'Output: $A$2
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("dog", LookIn:=xlFormulas).AddressLocal
'Output: $A$2 - as the formula and value for "dog" are the same in this case
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("This is a dog", LookIn:=xlFormulas).AddressLocal
'Output: $B$2
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("dog", LookIn:=xlNotes).AddressLocal
'Output: $C$2
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("dog", LookIn:=xlCommentsThreaded).AddressLocal
'Output: $D$2
The same code but this time returning the actual Value, Formula, Note or Comment:
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("dog", LookIn:=xlValues).Value
'Output: dog
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("dog", LookIn:=xlFormulas).Formula2Local
'Output: dog
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("This is a dog", LookIn:=xlFormulas).Formula2Local
'Output: =IF(A2="Dog", "This is a Dog","Other")
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("dog", LookIn:=xlNotes).NoteText
'Output: This is a note about a dog
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("dog", LookIn:=xlCommentsThreaded).CommentThreaded.Text
'Output: This is a threaded comment about a dog
Find After – avoid wrap around
Complex patterns for Find
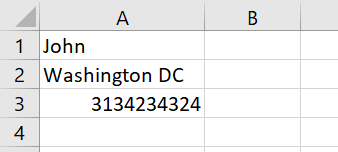
In some cases the pattern you want to find might be more complicated such as e.g. looking for cells with any sequence of numbers, emails, addresses, phone numbers etc. In this case the VBA Range Find function will be too limited. However, there is a solution with the help of so call VBA Regular Expressions. Regular Expressions help define almost any search pattern and are widely used in other programming languages.
If you want to learn more read my VBA Regex Tutorial otherwise a very simple example below.
In below code snippet we would like to find only phone numbers – so we will create a simple expression that finds any sequence of digits.
'Define the Regular Expression
Dim regex As Object
Set regex = CreateObject("VBScript.RegExp")
With regex
'We will look only for sequences of at least 1 digit
.Pattern = "[0-9]+"
End With
'Search in all cells within the Range
Dim r As Range
For Each r In Range("A1:D4")
If regex.Test(r.Value) Then
Debug.Print "Found a match: " & r.AddressLocal
End If
Next r
Found a match: $A$3