Открытие книги Excel из кода VBA. Проверка существования книги. Создание новой книги, обращение к открытой книге и ее закрытие. Методы Open, Add и Close.
Открытие существующей книги
Существующая книга открывается из кода VBA Excel с помощью метода Open:
|
Workbooks.Open Filename:=«D:test1.xls» |
или
|
Workbooks.Open («D:test1.xls») |
В кавычках указывается полный путь к открываемому файлу Excel. Если такой файл не существует, произойдет ошибка.
Проверка существования файла
Проверить существование файла можно с помощью функции Dir. Проверка существования книги Excel:
|
If Dir(«D:test1.xls») = «» Then MsgBox «Файл не существует» Else MsgBox «Файл существует» End If |
Или, если файл (книга Excel) существует, можно сразу его открыть:
|
If Dir(«D:test1.xls») = «» Then MsgBox «Файл не существует» Else Workbooks.Open Filename:=«D:test1.xls» End If |
Создание новой книги
Новая рабочая книга Excel создается в VBA с помощью метода Add:
Созданную книгу, если она не будет использоваться как временная, лучше сразу сохранить:
|
Workbooks.Add ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=«D:test2.xls» |
В кавычках указывается полный путь сохраняемого файла Excel, включая присваиваемое имя, в примере — это «test2.xls».
Обращение к открытой книге
Обращение к активной книге:
Обращение к книге с выполняемым кодом:
Обращение к книге по имени:
|
Workbooks(«test1.xls») Workbooks(«test2.xls») |
Обратиться по имени можно только к уже открытой книге, а чтобы из кода VBA Excel книгу открыть, необходимо указать полный путь к файлу.
Открытая рабочая книга закрывается из кода VBA Excel с помощью метода Close:
|
Workbooks(«test1.xlsx»).Close |
Если закрываемая книга редактировалась, а внесенные изменения не были сохранены, тогда при ее закрытии Excel отобразит диалоговое окно с вопросом: Вы хотите сохранить изменения в файле test1.xlsx? Чтобы файл был закрыт без сохранения изменений и вывода диалогового окна, можно воспользоваться параметром метода Close — SaveChanges:
|
Workbooks(«test1.xlsx»).Close SaveChanges:=False |
или
|
Workbooks(«test1.xlsx»).Close (False) |
Закрыть книгу Excel из кода VBA с сохранением внесенных изменений можно также с помощью параметра SaveChanges:
|
Workbooks(«test1.xlsx»).Close SaveChanges:=True |
или
|
Workbooks(«test1.xlsx»).Close (True) |
Фразы для контекстного поиска: открыть книгу, открытие книги, создать книгу, создание книги, закрыть книгу, закрытие книги, открыть файл Excel, открытие файла Excel, существование книги, обратиться к открытой книге.
| title | keywords | f1_keywords | ms.prod | api_name | ms.assetid | ms.date | ms.localizationpriority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Workbooks.Open method (Excel) |
vbaxl10.chm203082 |
vbaxl10.chm203082 |
excel |
Excel.Workbooks.Open |
1d1c3fca-ae1a-0a91-65a2-6f3f0fb308a0 |
08/14/2019 |
medium |
Workbooks.Open method (Excel)
Opens a workbook.
[!includeAdd-ins note]
Syntax
expression.Open (FileName, UpdateLinks, ReadOnly, Format, Password, WriteResPassword, IgnoreReadOnlyRecommended, Origin, Delimiter, Editable, Notify, Converter, AddToMru, Local, CorruptLoad)
expression A variable that represents a Workbooks object.
Parameters
| Name | Required/Optional | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| FileName | Optional | Variant | String. The file name of the workbook to be opened. |
| UpdateLinks | Optional | Variant | Specifies the way external references (links) in the file, such as the reference to a range in the Budget.xls workbook in the following formula =SUM([Budget.xls]Annual!C10:C25), are updated. If this argument is omitted, the user is prompted to specify how links will be updated. For more information about the values used by this parameter, see the Remarks section.
If Microsoft Excel is opening a file in the WKS, WK1, or WK3 format and the UpdateLinks argument is 0, no charts are created; otherwise, Microsoft Excel generates charts from the graphs attached to the file. |
| ReadOnly | Optional | Variant | True to open the workbook in read-only mode. |
| Format | Optional | Variant | If Microsoft Excel opens a text file, this argument specifies the delimiter character. If this argument is omitted, the current delimiter is used. For more information about the values used by this parameter, see the Remarks section. |
| Password | Optional | Variant | A string that contains the password required to open a protected workbook. If this argument is omitted and the workbook requires a password, the user is prompted for the password. |
| WriteResPassword | Optional | Variant | A string that contains the password required to write to a write-reserved workbook. If this argument is omitted and the workbook requires a password, the user will be prompted for the password. |
| IgnoreReadOnlyRecommended | Optional | Variant | True to have Microsoft Excel not display the read-only recommended message (if the workbook was saved with the Read-Only Recommended option). |
| Origin | Optional | Variant | If the file is a text file, this argument indicates where it originated, so that code pages and Carriage Return/Line Feed (CR/LF) can be mapped correctly. Can be one of the following XlPlatform constants: xlMacintosh, xlWindows, or xlMSDOS. If this argument is omitted, the current operating system is used. |
| Delimiter | Optional | Variant | If the file is a text file and the Format argument is 6, this argument is a string that specifies the character to be used as the delimiter. For example, use Chr(9) for tabs, use «,» for commas, use «;» for semicolons, or use a custom character. Only the first character of the string is used. |
| Editable | Optional | Variant | If the file is a Microsoft Excel 4.0 add-in, this argument is True to open the add-in so that it is a visible window. If this argument is False or omitted, the add-in is opened as hidden, and it cannot be unhidden. This option does not apply to add-ins created in Microsoft Excel 5.0 or later.
If the file is an Excel template, True to open the specified template for editing. False to open a new workbook based on the specified template. The default value is False. |
| Notify | Optional | Variant | If the file cannot be opened in read/write mode, this argument is True to add the file to the file notification list. Microsoft Excel will open the file as read-only, poll the file notification list, and then notify the user when the file becomes available. If this argument is False or omitted, no notification is requested, and any attempts to open an unavailable file will fail. |
| Converter | Optional | Variant | The index of the first file converter to try when opening the file. The specified file converter is tried first; if this converter does not recognize the file, all other converters are tried. The converter index consists of the row numbers of the converters returned by the FileConverters property. |
| AddToMru | Optional | Variant | True to add this workbook to the list of recently used files. The default value is False. |
| Local | Optional | Variant | True saves files against the language of Microsoft Excel (including control panel settings). False (default) saves files against the language of Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) (which is typically United States English unless the VBA project where Workbooks.Open is run from is an old internationalized XL5/95 VBA project). |
| CorruptLoad | Optional | XlCorruptLoad | Can be one of the following constants: xlNormalLoad, xlRepairFile and xlExtractData. The default behavior if no value is specified is xlNormalLoad, and does not attempt recovery when initiated through the OM. |
Return value
A Workbook object that represents the opened workbook.
Remarks
By default, macros are enabled when opening files programmatically. Use the AutomationSecurity property to set the macro security mode used when opening files programmatically.
You can specify one of the following values in the UpdateLinks parameter to determine whether external references (links) are updated when the workbook is opened.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | External references (links) will not be updated when the workbook is opened. |
| 3 | External references (links) will be updated when the workbook is opened. |
You can specify one of the following values in the Format parameter to determine the delimiter character for the file.
| Value | Delimiter |
|---|---|
| 1 | Tabs |
| 2 | Commas |
| 3 | Spaces |
| 4 | Semicolons |
| 5 | Nothing |
| 6 | Custom character (see the Delimiter argument) |
Example
The following code example opens the workbook Analysis.xls and then runs its Auto_Open macro.
Workbooks.Open "ANALYSIS.XLS" ActiveWorkbook.RunAutoMacros xlAutoOpen
The following code example imports a sheet from another workbook onto a new sheet in the current workbook. Sheet1 in the current workbook must contain the path name of the workbook to import in cell D3, the file name in cell D4, and the worksheet name in cell D5. The imported worksheet is inserted after Sheet1 in the current workbook.
Sub ImportWorksheet() ' This macro will import a file into this workbook Sheets("Sheet1").Select PathName = Range("D3").Value Filename = Range("D4").Value TabName = Range("D5").Value ControlFile = ActiveWorkbook.Name Workbooks.Open Filename:=PathName & Filename ActiveSheet.Name = TabName Sheets(TabName).Copy After:=Workbooks(ControlFile).Sheets(1) Windows(Filename).Activate ActiveWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=False Windows(ControlFile).Activate End Sub
[!includeSupport and feedback]
In this Article
- Open a Workbook in VBA
- Open Workbook From Path
- Open Workbook – ActiveWorkbook
- Open Workbook and Assign to a Variable
- Workbook Open File Dialog
- Open New Workbook
- Open New Workbook To Variable
- Open Workbook Syntax
- Open Workbook Read-Only
- Open Password Protected Workbook
- Open Workbook Syntax Notes
- Close a Workbook in VBA
- Close Specific Workbook
- Close Active Workbook
- Close All Open Workbooks
- Close First Opened Workbook
- Close Without Saving
- Save and Close Without Prompt
- Other Workbook Open Examples
- Open Multiple New Workbooks
- Open All Excel Workbooks in a Folder
- Check if a Workbook is Open
- Workbook_Open Event
- Open Other Types of Files in VBA
- Open a Text file and Read its Contents
- Open a Text File and Append to it
- Opening a Word File and Writing to it
In this tutorial, you will learn how to use VBA to open and close Excel Workbooks and other types of Files in several ways.
VBA allows you to open or close files using the standard methods .Open and .Close.
If you want to learn how to check if a file exists before attempting to open the file, you can click on this link: VBA File Exists
Open a Workbook in VBA
Open Workbook From Path
If you know which file you want to open, you can specify its full path name in the function. Here is the code:
Workbooks.Open "C:VBA FolderSample file 1.xlsx"This line of the code opens “Sample file 1” file from the “VBA Folder”.
Open Workbook – ActiveWorkbook
When you open a workbook, it automatically becomes the ActiveWorkbook. You can reference the newly opened workbook like so:
ActiveWorkbook.SaveWhen you reference a sheet or range and omit the workbook name, VBA will assume you are referring to the ActiveWorkbook:
Sheets("Sheet1").Name = "Input"Open Workbook and Assign to a Variable
You can also open a workbook and assign it directly to an object variable. This procedure will open a workbook to the wb variable and then save the workbook.
Sub OpenWorkbookToVariable()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Open("C:VBA FolderSample file 1.xlsx")
wb.Save
End Sub
Assigning workbooks to variables when they open is the best way to keep track of your workbooks
Workbook Open File Dialog
You can also trigger the workbook Open File Dialog box. This allows the user to navigate to a file and open it:
Sub OpenWorkbook ()
Dim strFile As String
strFile = Application.GetOpenFilename()
Workbooks.Open (strFile)
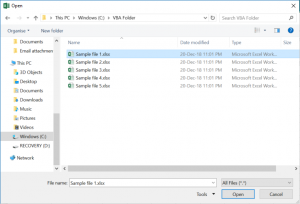
End SubAs you can see in Image 1, with this approach users can choose which file to open. The Open File Dialog Box can be heavily customized. You can default to a certain folder, choose which types of files are visible (ex. .xlsx only), and more. Read our tutorial on the Open File Dialog Box for detailed examples.
Open New Workbook
This line of code will open a new workbook:
Workbooks.AddVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Open New Workbook To Variable
This procedure will open a new workbook, assigning it to variable wb:
Sub OpenNewWorkbook()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Add
End SubOpen Workbook Syntax
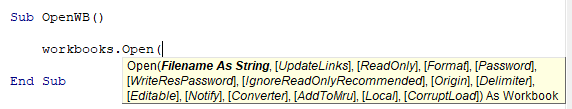
When you use Workbooks.Open you might notice that there are many options available when opening the workbook:
The Filename is required. All other arguments are optional – and you probably won’t need to know most of the other arguments. Here are the two most common:
Open Workbook Read-Only
When workbook is opened read-only, you can’t save over the original file. This prevents the file from being edited by the user.
Workbooks.Open "C:VBA FolderSample file 1.xlsx", , TrueVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Open Password Protected Workbook
A workbook might be password-protected. Use this code to open the password-protected workbook:
Workbooks.Open "C:VBA FolderSample file 1.xlsx", , , "password"Open Workbook Syntax Notes
Notice that in the image above, we included a parenthesis “(” to show the syntax. If you use parenthesis when working with Workbooks.Open, you must assign the workbook to a variable:
Sub OpenWB()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Open("C:VBA FolderSample file 1.xlsx", True, True)
End SubClose a Workbook in VBA
Close Specific Workbook
Similarly to opening a workbook, there are several ways to close a file. If you know which file you want to close, you can use the following code:
Workbooks.Close ("C:VBA FolderSample file 1.xlsx")This line of code closes the file “Sample file 1” if it’s opened. If not, it will return an error, so you should take care of error handling.
Close Active Workbook
If you want to close the Workbook which is currently active, this line of code will enable you to do that:
ActiveWorkbook.CloseAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Close All Open Workbooks
To close all open Workbooks, you can simply use this code:
Workbooks.CloseClose First Opened Workbook
This will close the first opened/created workbook:
Workbooks(1).CloseReplace 1 with 2 to close the second opened / created workbook and so on.
Close Without Saving
This will close a Workbook without saving and without showing the save prompt:
ActiveWorkbook.Close savechanges:=FalseSave and Close Without Prompt
Similarly this will save and close a Workbook without showing the save prompt:
ActiveWorkbook.Close savechanges:=TrueNote: There are several other ways to indicate whether to save or not save a Workbook and also whether to show prompts or not. This is discussed in more detail here.
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Other Workbook Open Examples
Open Multiple New Workbooks
This procedure will open multiple new workbooks, assigning the new workbooks to an array:
Sub OpenMultipleNewWorkbooks()
Dim arrWb(3) As Workbook
Dim i As Integer
For i = 1 To 3
Set arrWb(i) = Workbooks.Add
Next i
End SubOpen All Excel Workbooks in a Folder
This procedure will open all Excel Workbooks in a folder, using the Open File Dialog picker.
Sub OpenMultipleWorkbooksInFolder()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim dlgFD As FileDialog
Dim strFolder As String
Dim strFileName As String
Set dlgFD = Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogFolderPicker)
If dlgFD.Show = -1 Then
strFolder = dlgFD.SelectedItems(1) & Application.PathSeparator
strFileName = Dir(strFolder & "*.xls*")
Do While strFileName <> ""
Set wb = Workbooks.Open(strFolder & strFileName)
strFileName = Dir
Loop
End If
End Sub
Check if a Workbook is Open
This procedure will test if a workbook is open:
Sub TestByWorkbookName()
Dim wb As Workbook
For Each wb In Workbooks
If wb.Name = "New Microsoft Excel Worksheet.xls" Then
MsgBox "Found it"
Exit Sub 'call code here, we'll just exit for now
End If
Next
End SubAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Workbook_Open Event
VBA Events are “triggers” that tell VBA to run certain code. You can set up workbook events for open, close, before save, after save and more.
Read our Workbook_Open Event tutorial to learn more about automatically running macros when a workbook is opened.
Open Other Types of Files in VBA
You can use the VBA to open other types of files with VBA – such as txt or Word files.
Open a Text file and Read its Contents
The VBA open method allows you to read or write to the file once you have opened it. To read the contents of a file, we can open the file for INPUT.
Sub OpenTextFile()
Dim strFile As String
Dim strBody As String
Dim intFile As Integer
strFile = "C:datatest.txt"
intFile = FreeFile
Open strFile For Input As intFile
strBody = Input(LOF(intFile), intFile)
'loop here through your text body and extract what you need
''some vba code here
Debug.Print strBody
Close intFile
End SubThe code above will open the text file “test.txt” and then it will read the entire contents of the file to the strBody variable. Once you have extracted the file data into the strBody variable, you can use it for what you require. Using the Debug.Print command above enables us to see the contents of the strBody variable in the Immediate window in the VBE.
Open a Text File and Append to it
We can also open a text file in VBA, and then append to the bottom of the file using the Append method.
Sub AppendToTextFile()
Dim strFile As String
Dim strBody As String
Dim intFile As Integer
strFile = "C:datatest.txt"
intFile = FreeFile
Open strFile For Append As intFile
'add two lines to the bottom
Print #intFile, "This is an extra line of text at the bottom"
Print #intFile, "and this is another one"
'close the file
Close intFile
End SubThe above code will open the text file and then append 2 lines of text to the bottom of the file using the #intFile variable (the # sign is the key!). The code then closes the file.
Opening a Word File and Writing to it
We can also use VBA in Excel to open a Word file.
Sub OpenWordFile()
Dim wApp As Object
Dim wDoc As Object
Set wApp = CreateObject("Word.Application")
Set wd = wApp.documents.Open("c:datatest.docx")
wApp.Visible = True
End SubThis code will open a copy of Word, and then open the document test.docx.
Excel VBA Workbook Open
The most common operations in day to day life is to open an excel Workbooks when you are working with Excel. You cannot work in Excel without opening the Excel Workbooks or Excel file. So in this article, we are going to cover how we can open an Excel Workbooks with the help of VBA.
Methods to Open Exel Workbooks in VBA
There are two methods to open excel Workbooks in VBA and we are going to cover both methods in this article.
You can download this VBA Workbook Open Excel Template here – VBA Workbook Open Excel Template
Method #1 – Excel VBA Workbooks.open Method
The first method in the VBA is to use the inbuilt function Workbooks.open. There are 15 optional arguments in the “Workbooks.open” function and to cover all the 15 arguments will take a lot of time. So we will just try to understand some basics of Workbooks.open and see how we can use this function in VBA to open the Workbooks.
So the first step in this method is you should know the file name of the Excel Workbooks. Below is the statement to open the Workbooks.”Workbooks.open “File_Name”
Or
Workbooks.Open Filename: =”File_Name”
The “File_Name” is the name of the Workbooks that you want to open. But you need to be careful here because you need to provide the full path where the file is saved and name of the file with the extension of the files (.XLS, .XLSX, .xlsm, etc). We can take the example of below macro to understand this function.
Example
Suppose you want to open an excel file with the name “Test File” which is saved in the D Drive of the computer. Create a Macro in an Excel macro-enabled workbook. Follow the below steps to use Excel VBA Workbooks.open method.
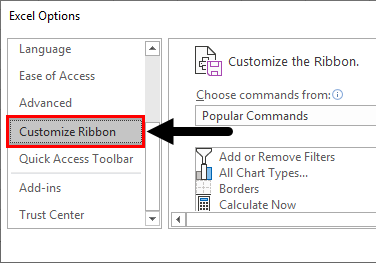
Step 1: Click on File.
Step 2: Click on Options.
Step 3: Click on Customize Ribbon.
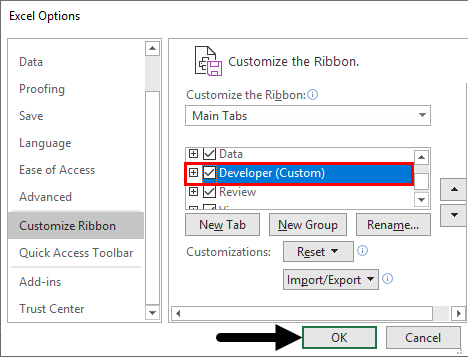
Step 4: Make sure the Developer field is marked as below and click ok.
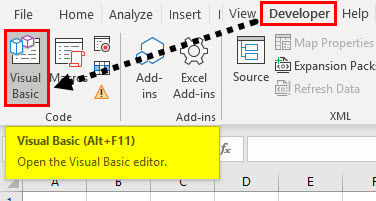
Step 5: Once you have the developer tab, click on Visual basic as shown in the below screenshot.
After you click on the Visual Basics, you need to start coding for your macro.
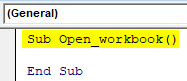
Step 6: Enter the below code in the VBA Module.
Code:
Sub Open_workbook() End Sub
This code provides the name for your workbook.
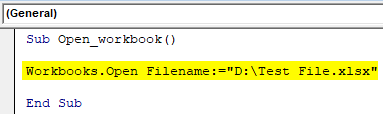
Step 7: Enter the code which can open the workbook saved in the D drive of the computer.
Code:
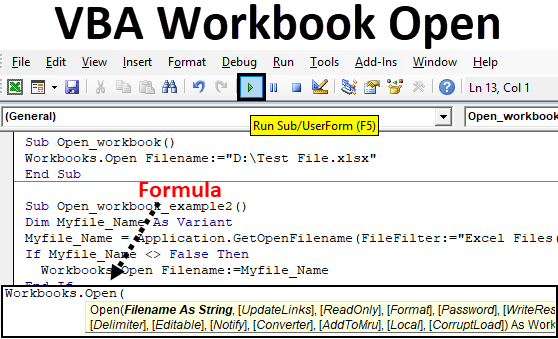
Sub Open_workbook() Workbooks.Open Filename:="D:Test File.xlsx" End Sub
Step 8: Run the code by pressing the F5 key or by clicking on Play Button. After running the macro, you will find the excel file is automatically opened. As you can see in the above code, the macro will open the Excel file with the name “Test File.xlsx” which is saved in the D drive of the computer. The path mentioned above is quite simple because there are no folders and subfolders to get the Workbooks.
This becomes challenging because many people don’t remember the path and if the Path of the file where it is saved changes a bit, the macro will not work. The macro will not work even if the Name of the file changes by a single letter. So if the Path/Name of the file changes you need to change the VBA code of the Macro. This makes the Job tedious and it is not error-free as well. So to make sure your macro runs perfectly without giving you an error, we will use the second method which is easy to handle and will not give you an error even when you don’t remember the pathname or even when the name of the file changes.
Method #2 – Get Open Filename
As you know the challenges we face in the First method of the change in path and the File name, this method avoids both of the challenges. This method gives the option to browse in your computer to the location where your file is saved and opens that particular Workbooks which you want to open.
This method actually works in two parts.
The first part of this method is Application.GetOpenFileName. This Part allows you to browse through your computer and select the path where your file is saved. The first part does not open the file which you want to open.
The second part is to open the file for which you still need to be dependent on the First Method (VBA Workbooks.open Method). There are 5 arguments in the Application.GetOpenFileName but will only look at the basics like we did it in the first method. Now let us try to understand this method with the help of an example.
Example
Suppose you want to open the “Test File” saved in the D drive of the computer then you just need to follow the below steps.
Step 1: Follow step 1 mentioned in the first example for opening the Visual Basic Editor or Open Visual Basic Editor from Developer Tab.
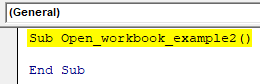
Step 2: Enter the below code which provides the name for your macro.
Code:
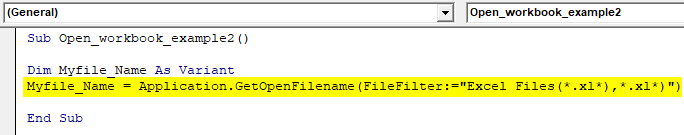
Sub Open_workbook_example2() End Sub
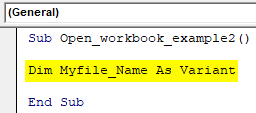
Step 3: Enter the below code. This statement declares the Filename as Variable because here we are not specifying any path or file name because it can change from time to time.
Code:
Sub Open_workbook_example2() Dim Myfile_Name As Variant End Sub
Step 4: Enter the below code. This statement opens the below dialog box and you can browse the folders to go to the path where the file is saved. Also, it will show the Excel file while browsing because we have put a filter for the Excel files.
Code:
Sub Open_workbook_example2() Dim Myfile_Name As Variant Myfile_Name = Application.GetOpenFilename(FileFilter:="Excel Files(*.xl*),*.xl*)") End Sub
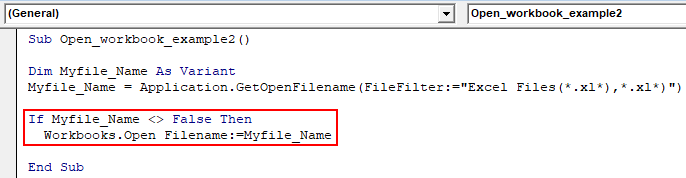
Step 5: Enter the below code. This statement is If Then statement which is used when the file .Name is not equal to false then open the selected Excel file.
Code:
Sub Open_workbook_example2() Dim Myfile_Name As Variant Myfile_Name = Application.GetOpenFilename(FileFilter:="Excel Files(*.xl*),*.xl*)") If Myfile_Name <> False Then Workbooks.Open Filename:=Myfile_Name End Sub
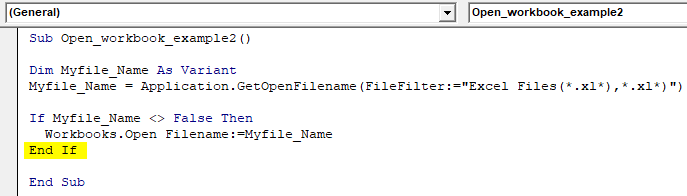
Step 6: Enter the below code. This statement closes the If then condition in the Macro.
Code:
Sub Open_workbook_example2() Dim Myfile_Name As Variant Myfile_Name = Application.GetOpenFilename(FileFilter:="Excel Files(*.xl*),*.xl*)") If Myfile_Name <> False Then Workbooks.Open Filename:=Myfile_Name End If End Sub
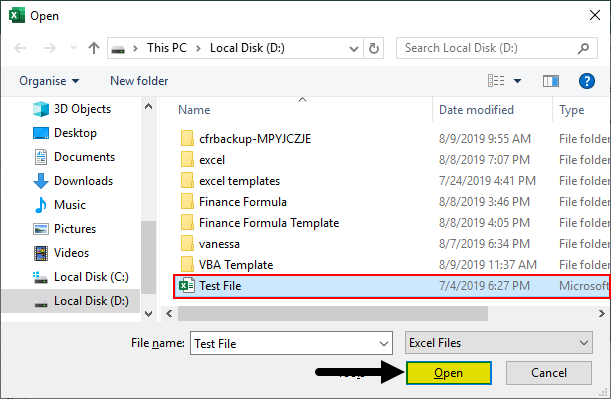
Step 7: Now run the code by pressing the F5 key or by clicking on the Play Button. You will see the dialog box to browse the file will open. Browse to the desktop where your file is saved. Now you will be able to see the file in the D Drive. Select the file and click open.
Now as we just saw in our example, we don’t need to worry about the file name and the path name where the file is saved. We can easily navigate to the folder where our file is saved and select the file which we want to open. So we can easily conclude that this method is much more efficient compared to the first method.
Things to Remember
- Make sure the pathname & the file name is correct while using the first method. The macro will not work when there is a change by letter or space in path or File Name.
- Make sure the filters mentioned in the code in the 2nd method is correct. There are many formats of Excel which may not be visible because of a filter.
- Make sure the declaration and the code used in the VBA are right to avoid errors.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to VBA Workbook Open. Here we discuss two different methods to open workbook using Excel VBA code along with practical examples and downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –
- VBA Workbook
- VBA Get Cell Value
- VBA FileDialog
- VBA Save Workbook
Содержание
- Ссылка на книгу с помощью VBA
- Создание нового объекта книги
- Откройте книгу с помощью VBA
- Сохранение книги
- Сохранение всех открытых книг
- Сохранение и закрытие всех книг
- Сохранить копию книги (с отметкой времени)
- Создайте новую книгу для каждого рабочего листа
- Назначьте объект книги переменной
- Цикл через открытые книги
- Ошибка при работе с объектом книги (ошибка времени выполнения «9»)
- Получить список всех открытых книг
- Откройте указанную книгу, дважды щелкнув ячейку
- Куда поместить код VBA
В этом руководстве я расскажу, как работать с книгами в Excel с помощью VBA.
В Excel «Рабочая книга» — это объект, который является частью коллекции «Рабочие книги». В книге у вас есть различные объекты, такие как рабочие листы, листы диаграмм, ячейки и диапазоны, объекты диаграмм, фигуры и т. Д.
С помощью VBA вы можете выполнять множество операций с объектом книги, например открывать конкретную книгу, сохранять и закрывать книги, создавать новые книги, изменять свойства книги и т. Д.
Итак, приступим.
Все коды, которые я упоминаю в этом руководстве, необходимо поместить в редактор Visual Basic. Перейдите в раздел «Где разместить код VBA», чтобы узнать, как это работает.
Если вы заинтересованы в изучении VBA простым способом, ознакомьтесь с моими Онлайн-обучение по Excel VBA.
Есть разные способы ссылаться на объект Workbook в VBA. Выбранный вами метод будет зависеть от того, что вы хотите сделать. В этом разделе я расскажу о различных способах обращения к книге вместе с некоторыми примерами кодов.
Использование имен книг
Если у вас есть точное имя книги, к которой вы хотите обратиться, вы можете использовать это имя в коде.
Начнем с простого примера.
Если у вас открыты две книги и вы хотите активировать книгу с именем — Examples.xlsx, вы можете использовать следующий код:
Sub ActivateWorkbook () Workbooks ("Examples.xlsx"). Активировать End Sub
Обратите внимание, что вам нужно использовать имя файла вместе с расширением, если файл был сохранен. Если оно не было сохранено, вы можете использовать имя без расширения файла.
Если вы не знаете, какое имя использовать, обратитесь за помощью в Project Explorer.
Если вы хотите активировать книгу и выбрать определенную ячейку на листе в этой книге, вам необходимо указать полный адрес ячейки (включая книгу и имя рабочего листа).
Sub ActivateWorkbook () Рабочие книги ("Examples.xlsx"). Рабочие листы ("Sheet1"). Активировать диапазон ("A1"). Выберите End Sub
Приведенный выше код сначала активирует Sheet1 в книге Examples.xlsx, а затем выбирает ячейку A1 на листе.
Вы часто будете видеть код, в котором ссылка на рабочий лист или ячейку / диапазон делается без ссылки на книгу. Это происходит, когда вы ссылаетесь на лист / диапазоны в той же книге, в которой есть код и которая также является активной книгой. Однако в некоторых случаях вам необходимо указать книгу, чтобы убедиться, что код работает (подробнее об этом в разделе ThisWorkbook).
Использование порядковых номеров
Вы также можете ссылаться на книги по их порядковому номеру.
Например, если у вас открыто три книги, следующий код покажет вам имена трех книг в окне сообщения (по одному).
Sub WorkbookName () MsgBox Workbooks (1) .Name MsgBox Workbooks (2) .Name MsgBox Workbooks (3) .Name End Sub
В приведенном выше коде используется MsgBox — функция, отображающая окно сообщения с указанным текстом / значением (в данном случае это имя книги).
Одна из проблем, с которыми я часто сталкиваюсь при использовании порядковых номеров с рабочими книгами, заключается в том, что вы никогда не знаете, какая из них первая книга, а какая вторая и так далее. Конечно, вам нужно будет запустить код, как показано выше, или что-то подобное, чтобы просмотреть открытые книги и узнать их порядковый номер.
Excel обрабатывает книгу, открытую первой, так, чтобы она имела номер индекса как 1, а следующая — как 2 и так далее.
Несмотря на этот недостаток, использование индексных номеров может оказаться полезным. Например, если вы хотите перебрать все открытые книги и сохранить все, вы можете использовать номера индексов. В этом случае, поскольку вы хотите, чтобы это произошло со всеми книгами, вас не беспокоят их индивидуальные порядковые номера.
Приведенный ниже код будет перебирать все открытые книги и закрывать все, кроме книги с этим кодом VBA.
Sub CloseWorkbooks () Dim WbCount как целое число WbCount = Workbooks.Count For i = WbCount To 1 Step -1 Если Workbooks (i) .Name ThisWorkbook.Name Then Workbooks (i) .Close End If Next i End Sub
Приведенный выше код подсчитывает количество открытых книг, а затем просматривает все книги, используя цикл For Each.
Он использует условие IF, чтобы проверить, совпадает ли имя книги с именем книги, в которой выполняется код.
Если совпадений нет, рабочая книга закрывается и переходит к следующей.
Обратите внимание, что мы выполнили цикл от WbCount до 1 с шагом -1. Это делается по мере того, как с каждым циклом количество открытых книг уменьшается.
ThisWorkbook подробно рассматривается в следующем разделе.
Использование ActiveWorkbook
ActiveWorkbook, как следует из названия, относится к активной книге.
Приведенный ниже код покажет вам имя активной книги.
Sub ActiveWorkbookName () MsgBox ActiveWorkbook.Name End Sub
Когда вы используете VBA для активации другой книги, часть ActiveWorkbook в VBA после этого начнет ссылаться на активированную книгу.
Вот пример этого.
Если у вас есть активная книга, и вы вставляете в нее следующий код и запускаете ее, сначала будет показано имя книги с кодом, а затем имя Examples.xlsx (которое активируется кодом).
Sub ActiveWorkbookName () MsgBox ActiveWorkbook.Name Workbooks («Examples.xlsx»). Активировать MsgBox ActiveWorkbook.Name End Sub
Обратите внимание, что когда вы создаете новую книгу с помощью VBA, эта вновь созданная книга автоматически становится активной.
Использование ThisWorkbook
ThisWorkbook относится к книге, в которой выполняется код.
Каждая книга будет иметь объект ThisWorkbook как часть (видимый в Project Explorer).
ThisWorkbook может хранить обычные макросы (аналогичные тем, которые мы добавляем в модули), а также процедуры обработки событий. Процедура события — это то, что запускается на основе события, например двойного щелчка по ячейке, сохранения книги или активации листа.
Любая процедура события, которую вы сохраняете в этой «ThisWorkbook», будет доступна во всей книге по сравнению с событиями уровня листа, которые ограничены только определенными листами.
Например, если вы дважды щелкните объект ThisWorkbook в проводнике проекта и скопируйте и вставьте в него приведенный ниже код, он будет отображать адрес ячейки всякий раз, когда вы дважды щелкаете любую из ячеек во всей книге.
Private Sub Workbook_SheetBeforeDoubleClick (ByVal Sh As Object, ByVal Target As Range, Cancel As Boolean) MsgBox Target.Address End Sub
Хотя основная роль ThisWorkbook заключается в хранении процедуры события, вы также можете использовать ее для ссылки на книгу, в которой выполняется код.
Приведенный ниже код вернет имя книги, в которой выполняется код.
Sub ThisWorkbookName () MsgBox ThisWorkbook.Name End Sub
Преимущество использования ThisWorkbook (над ActiveWorkbook) заключается в том, что он будет ссылаться на одну и ту же книгу (ту, в которой есть код) во всех случаях. Поэтому, если вы используете код VBA для добавления новой книги, ActiveWorkbook изменится, но ThisWorkbook по-прежнему будет относиться к той, которая имеет код.
Создание нового объекта книги
Следующий код создаст новую книгу.
Sub CreateNewWorkbook () Workbooks.Add End Sub
Когда вы добавляете новую книгу, она становится активной.
Следующий код добавит новую книгу, а затем покажет вам имя этой книги (которое будет именем типа Book1 по умолчанию).
Sub CreateNewWorkbook () Workbooks.Add MsgBox ActiveWorkbook.Name End Sub
Откройте книгу с помощью VBA
Вы можете использовать VBA для открытия определенной книги, если знаете путь к файлу книги.
Приведенный ниже код откроет книгу — Examples.xlsx, которая находится в папке Documents в моей системе.
Sub OpenWorkbook () Workbooks.Open ("C: Users sumit Documents Examples.xlsx") End Sub
Если файл существует в папке по умолчанию, которая является папкой, в которой VBA сохраняет новые файлы по умолчанию, вы можете просто указать имя книги — без полного пути.
Sub OpenWorkbook () Workbooks.Open ("Examples.xlsx") End Sub
Если книга, которую вы пытаетесь открыть, не существует, вы увидите сообщение об ошибке.
Чтобы избежать этой ошибки, вы можете добавить несколько строк в свой код, чтобы сначала проверить, существует ли файл или нет, и, если он существует, попробуйте его открыть.
Приведенный ниже код проверит местоположение файла и, если он не существует, отобразит настраиваемое сообщение (не сообщение об ошибке):
Sub OpenWorkbook () If Dir ("C: Users sumit Documents Examples.xlsx") "" Then Workbooks.Open ("C: Users sumit Documents Examples.xlsx") Else MsgBox "Файл не "не существует" Конец Если Конец Подп.
Вы также можете использовать диалоговое окно «Открыть», чтобы выбрать файл, который хотите открыть.
Sub OpenWorkbook () При ошибке Возобновить следующий Dim FilePath As String FilePath = Application.GetOpenFilename Workbooks.Open (FilePath) End Sub
Приведенный выше код открывает диалоговое окно Открыть. Когда вы выбираете файл, который хотите открыть, он назначает путь к файлу переменной FilePath. Workbooks.Open затем использует путь к файлу для открытия файла.
Если пользователь не открывает файл и нажимает кнопку «Отмена», FilePath принимает значение False. Чтобы избежать появления ошибки в этом случае, мы использовали оператор «On Error Resume Next».
Связанный: Узнать все об обработке ошибок в Excel VBA
Сохранение книги
Чтобы сохранить активную книгу, используйте приведенный ниже код:
Подложка SaveWorkbook () ActiveWorkbook.Save End Sub
Этот код работает с книгами, которые уже были сохранены ранее. Кроме того, поскольку книга содержит указанный выше макрос, если он не был сохранен как файл .xlsm (или .xls), вы потеряете макрос, когда откроете его в следующий раз.
Если вы сохраняете книгу в первый раз, она покажет вам подсказку, как показано ниже:
При первом сохранении лучше использовать опцию «Сохранить».
Приведенный ниже код сохранит активную книгу как файл .xlsm в расположении по умолчанию (которое является папкой документов в моей системе).
Sub SaveWorkbook () ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Имя файла: = "Test.xlsm", FileFormat: = xlOpenXMLWorkbookMacroEnabled End Sub
Если вы хотите, чтобы файл был сохранен в определенном месте, вам необходимо указать это в значении Filename. Приведенный ниже код сохраняет файл на моем рабочем столе.
Sub SaveWorkbook () ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Имя файла: = "C: Users sumit Desktop Test.xlsm", FileFormat: = xlOpenXMLWorkbookMacroEnabled End Sub
Если вы хотите, чтобы пользователь мог выбрать место для сохранения файла, вы можете использовать диалоговое окно «Сохранить как». Приведенный ниже код показывает диалоговое окно «Сохранить как» и позволяет пользователю выбрать место для сохранения файла.
Sub SaveWorkbook () Dim FilePath As String FilePath = Application.GetSaveAsFilename ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename: = FilePath & ".xlsm", FileFormat: = xlOpenXMLWorkbookMacroEnabled End Sub
Обратите внимание, что вместо использования FileFormat: = xlOpenXMLWorkbookMacroEnabled можно также использовать FileFormat: = 52, где 52 — это код xlOpenXMLWorkbookMacroEnabled.
Сохранение всех открытых книг
Если у вас открыто несколько книг и вы хотите сохранить все книги, вы можете использовать приведенный ниже код:
Sub SaveAllWorkbooks () Dim wb As Workbook for each wb In Workbooks wb.Save Next wb End Sub
Приведенное выше сохраняет все книги, включая те, которые никогда не сохранялись. Книги, которые не были сохранены ранее, будут сохранены в расположении по умолчанию.
Если вы хотите сохранить только те книги, которые были ранее сохранены, вы можете использовать следующий код:
Sub SaveAllWorkbooks () Dim wb As Workbook For each wb In Workbooks If wb.Path "" Then wb.Save End If Next wb End Sub
Сохранение и закрытие всех книг
Если вы хотите закрыть все книги, кроме книги, в которой есть текущий код, вы можете использовать приведенный ниже код:
Sub CloseandSaveWorkbooks () Dim wb As Workbook для каждого wb в рабочих книгах Если wb.Name ThisWorkbook.Name Then wb.Close SaveChanges: = True End If Next wb End Sub
Приведенный выше код закроет все книги (кроме книги с кодом — ThisWorkbook). Если в этих книгах есть изменения, они будут сохранены. Если есть книга, которая никогда не сохранялась, отобразится диалоговое окно «Сохранить как».
Сохранить копию книги (с отметкой времени)
Когда я работаю со сложными данными и панелью мониторинга в книгах Excel, я часто создаю разные версии своих книг. Это полезно на случай, если с моей текущей книгой что-то пойдет не так. По крайней мере, у меня была бы его копия, сохраненная под другим именем (и я потеряю только ту работу, которую проделал после создания копии).
Вот код VBA, который создаст копию вашей книги и сохранит ее в указанном месте.
Sub CreateaCopyofWorkbook () ThisWorkbook.SaveCopyAs Имя файла: = "C: Users sumit Desktop BackupCopy.xlsm" End Sub
Приведенный выше код будет сохранять копию вашей книги каждый раз, когда вы запускаете этот макрос.
Хотя это отлично работает, мне было бы удобнее, если бы я сохранял разные копии при каждом запуске этого кода. Причина, по которой это важно, заключается в том, что если я сделаю непреднамеренную ошибку и запущу этот макрос, он сохранит работу с ошибками. И у меня не будет доступа к работе, пока я не совершу ошибку.
Чтобы справиться с такими ситуациями, вы можете использовать приведенный ниже код, который сохраняет новую копию работы каждый раз, когда вы ее сохраняете. И он также добавляет дату и метку времени как часть имени книги. Это может помочь вам отследить любую допущенную вами ошибку, поскольку вы никогда не потеряете ни одну из ранее созданных резервных копий.
Private Sub Workbook_BeforeSave (ByVal SaveAsUI As Boolean, Cancel As Boolean) ThisWorkbook.SaveCopyAs Имя файла: = "C: Users sumit Desktop BackupCopy" & Format (Now (), "dd-mm-yy-hh-mm-ss -AMPM ") &" .xlsm "End Sub
Приведенный выше код будет создавать копию при каждом запуске этого макроса и добавлять метку даты / времени к имени книги.
Создайте новую книгу для каждого рабочего листа
В некоторых случаях у вас может быть книга с несколькими листами, и вы хотите создать книгу для каждого листа.
Это может быть в том случае, если у вас есть ежемесячные / ежеквартальные отчеты в одной книге, и вы хотите разделить их на одну книгу для каждого листа.
Или, если у вас есть отчеты по отделам, и вы хотите разделить их на отдельные книги, чтобы можно было отправлять эти отдельные книги руководителям отделов.
Вот код, который создаст книгу для каждого рабочего листа, присвоит ему то же имя, что и рабочий лист, и сохранит его в указанной папке.
Sub CreateWorkbookforWorksheets () Dim ws As Worksheet Dim wb As Workbook For each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets Установить wb = Workbooks.Add ws.Copy Before: = wb.Sheets (1) Application.DisplayAlerts = False wb.Sheets (2) .Delete Application.DisplayAlerts = True wb.SaveAs "C: Users sumit Desktop Test " & ws.Name & ".xlsx" wb.Close Next ws End Sub
В приведенном выше коде мы использовали две переменные «ws» и «wb».
Код просматривает каждый рабочий лист (используя цикл For Each Next) и создает для него книгу. Он также использует метод копирования объекта рабочего листа для создания копии рабочего листа в новой книге.
Обратите внимание, что я использовал оператор SET для присвоения переменной «wb» любой новой книге, созданной с помощью кода.
Вы можете использовать этот метод, чтобы назначить объект книги переменной. Это рассматривается в следующем разделе.
Назначьте объект книги переменной
В VBA вы можете назначить объект переменной, а затем использовать переменную для ссылки на этот объект.
Например, в приведенном ниже коде я использую VBA для добавления новой книги, а затем назначаю эту книгу переменной wb. Для этого мне нужно использовать инструкцию SET.
После того, как я назначил книгу переменной, все свойства книги также становятся доступными для переменной.
Sub AssigntoVariable () Dim wb As Workbook Set wb = Workbooks.Add wb.SaveAs Filename: = "C: Users sumit Desktop Examples.xlsx" End Sub
Обратите внимание, что первый шаг в коде — объявить «wb» как переменную типа книги. Это сообщает VBA, что эта переменная может содержать объект книги.
Следующий оператор использует SET для присвоения переменной новой книги, которую мы добавляем. Как только это назначение будет выполнено, мы можем использовать переменную wb для сохранения книги (или сделать с ней что-нибудь еще).
Цикл через открытые книги
Мы уже видели несколько примеров кода выше, в которых использовался цикл в коде.
В этом разделе я объясню различные способы перебора открытых книг с помощью VBA.
Предположим, вы хотите сохранить и закрыть все открытые книги, кроме той, в которой есть код, тогда вы можете использовать следующий код:
Sub CloseandSaveWorkbooks () Dim wb As Workbook для каждого wb в рабочих книгах Если wb.Name ThisWorkbook.Name Then wb.Close SaveChanges: = True End If Next wb End Sub
В приведенном выше коде цикл For Each используется для просмотра каждой книги в коллекции Workbooks. Для этого нам сначала нужно объявить «wb» в качестве переменной типа книги.
В каждом цикле цикла каждое имя книги анализируется, и если оно не соответствует имени книги с кодом, она закрывается после сохранения своего содержимого.
То же самое может быть достигнуто с помощью другого цикла, как показано ниже:
Sub CloseWorkbooks () Dim WbCount As Integer WbCount = Workbooks.Count For i = WbCount To 1 Step -1 Если Workbooks (i) .Name ThisWorkbook.Name Then Workbooks (i) .Close SaveChanges: = True End If Next i End Sub
В приведенном выше коде цикл For Next используется для закрытия всех книг, кроме той, в которой есть код. В этом случае нам не нужно объявлять переменную книги, но вместо этого нам нужно подсчитать общее количество открытых книг. Когда у нас есть счетчик, мы используем цикл For Next для просмотра каждой книги. Кроме того, в этом случае мы используем порядковый номер для ссылки на книги.
Обратите внимание, что в приведенном выше коде мы переходим от WbCount к 1 с шагом -1. Это необходимо, поскольку с каждым циклом книга закрывается, а количество книг уменьшается на 1.
Ошибка при работе с объектом книги (ошибка времени выполнения «9»)
Одна из наиболее частых ошибок, с которыми вы можете столкнуться при работе с книгами, — это ошибка времени выполнения «9» — индекс вне допустимого диапазона.
Как правило, ошибки VBA не очень информативны и часто оставляют вам задачу выяснить, что пошло не так.
Вот некоторые из возможных причин, которые могут привести к этой ошибке:
- Книга, к которой вы пытаетесь получить доступ, не существует. Например, если я пытаюсь получить доступ к пятой книге с помощью Workbooks (5), а открыты только 4 книги, я получу эту ошибку.
- Если вы используете неправильное имя для ссылки на книгу. Например, если имя вашей книги — Examples.xlsx, и вы используете Example.xlsx. тогда он покажет вам эту ошибку.
- Если вы не сохранили книгу и используете расширение, вы получите эту ошибку. Например, если имя вашей книги — Book1, и вы используете имя Book1.xlsx, не сохраняя его, вы получите эту ошибку.
- Книга, к которой вы пытаетесь получить доступ, закрыта.
Получить список всех открытых книг
Если вы хотите получить список всех открытых книг в текущей книге (книге, в которой вы запускаете код), вы можете использовать следующий код:
Sub GetWorkbookNames () Dim wbcount As Integer wbcount = Workbooks.Count ThisWorkbook.Worksheets.Add ActiveSheet.Range ("A1"). Активировать для i = 1 В диапазон wbcount ("A1"). Смещение (i - 1, 0). Значение = Workbooks (i). Name Next i End Sub
Приведенный выше код добавляет новый лист, а затем перечисляет имена всех открытых книг.
Если вы также хотите получить путь к их файлу, вы можете использовать приведенный ниже код:
Sub GetWorkbookNames () Dim wbcount As Integer wbcount = Workbooks.Count ThisWorkbook.Worksheets.Add ActiveSheet.Range ("A1"). Активировать для i = 1 В диапазон wbcount ("A1"). Смещение (i - 1, 0). Значение = Workbooks (i) .Path & "" & Workbooks (i) .Name Next i End Sub
Откройте указанную книгу, дважды щелкнув ячейку
Если у вас есть список путей к файлам для книг Excel, вы можете использовать приведенный ниже код, чтобы просто дважды щелкнуть ячейку с путем к файлу, и эта книга откроется.
Private Sub Workbook_SheetBeforeDoubleClick (ByVal Sh As Object, ByVal Target As Range, Cancel As Boolean) Workbooks.Open Target.Value End Sub
Этот код будет помещен в окно кода ThisWorkbook.
Сделать это:
- Дважды щелкните объект ThisWorkbook в проводнике проекта. Обратите внимание, что объект ThisWorkbook должен находиться в книге, где вам нужна эта функция.
- Скопируйте и вставьте приведенный выше код.
Теперь, если у вас есть точный путь к файлам, которые вы хотите открыть, вы можете сделать это, просто дважды щелкнув путь к файлу, и VBA мгновенно откроет эту книгу.
Куда поместить код VBA
Хотите знать, где находится код VBA в вашей книге Excel?
В Excel есть серверная часть VBA, называемая редактором VBA. Вам необходимо скопировать и вставить код в окно кода модуля VB Editor.
Вот как это сделать:
- Перейдите на вкладку Разработчик.
- Выберите вариант Visual Basic. Это откроет редактор VB в бэкэнде.
- На панели Project Explorer в редакторе VB щелкните правой кнопкой мыши любой объект книги, в которую вы хотите вставить код. Если вы не видите Project Explorer, перейдите на вкладку View и нажмите Project Explorer.
- Перейдите во вкладку «Вставить» и нажмите «Модуль». Это вставит объект модуля для вашей книги.
- Скопируйте и вставьте код в окно модуля.
Вам также могут понравиться следующие руководства по Excel VBA:
- Как записать макрос в Excel.
- Создание пользовательской функции в Excel.
- Как создать и использовать надстройку в Excel.
- Как возобновить макрос, поместив его в личную книгу макросов.
- Получите список имен файлов из папки в Excel (с VBA и без).
- Как использовать функцию Excel VBA InStr (с практическими примерами).
- Как отсортировать данные в Excel с помощью VBA (пошаговое руководство).