I am using MS Excel 2010 and trying to get the current directory using the below code,
path = ActiveWorkbook.Path
But ActiveWorkbook.Path returns blank.
asked Nov 6, 2013 at 22:26
1
When one opens an Excel document D:dbtmptest1.xlsm:
-
CurDir()returnsC:Users[username]Documents -
ActiveWorkbook.PathreturnsD:dbtmp
So CurDir() has a system default and can be changed.
ActiveWorkbook.Path does not change for the same saved Workbook.
For example, CurDir() changes when you do «File/Save As» command, and select a random directory in the File/Directory selection dialog. Then click on Cancel to skip saving. But CurDir() has already changed to the last selected directory.
[ADD]
Resume VBA for different applications
Access D:dbtmptest1.accdb, like duckboy81 commented:
- CurDir() => C:Users[username]Documents
- Application.CurrentProject.Path => D:dbtmp
Excel D:dbtmptest1.xlsm:
- CurDir() => C:Users[username]Documents
- ActiveWorkbook.Path => D:dbtmp
- Application.DefaultFilePath => C:Users[username]Documents
Outlook:
- CurDir() => C:WINDOWSSystem32
- Application.Session.Stores(1).Filepath => D:programdataOutlookmyOutlookDocX.pst
PowerPoint D:dbtmptest1.ppt:
- CurDir() => C:Users[username]Documents
- ActivePresentation.Path => D:dbtmp
Word D:dbtmptest1.docx:
- CurDir() => C:Users[username]Documents
- Application.ActiveDocument.Path => D:dbtmp
- Application.ActiveDocument.FullName => D:dbtmptest1.docx
- Application.StartupPath => C:users[username]appdataroamingmicrosoftwordstartup
answered Nov 6, 2013 at 22:47
jacouhjacouh
8,3275 gold badges30 silver badges43 bronze badges
3
You have several options depending on what you’re looking for.
Workbook.Path returns the path of a saved workbook. Application.Path returns the path to the Excel executable. CurDir returns the current working path, this probably defaults to your My Documents folder or similar.
You can also use the windows scripting shell object’s .CurrentDirectory property.
Set wshell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
Debug.Print wshell.CurrentDirectory
But that should get the same result as just
Debug.Print CurDir
answered Nov 6, 2013 at 22:35
AndASMAndASM
9,0961 gold badge20 silver badges33 bronze badges
It would seem likely that the ActiveWorkbook has not been saved…
Try CurDir() instead.
answered Nov 6, 2013 at 22:35
Monty WildMonty Wild
3,9311 gold badge21 silver badges35 bronze badges
1
Your code: path = ActiveWorkbook.Path
returns blank because you haven’t saved your workbook yet.
To overcome your problem, go back to the Excel sheet, save your sheet, and run your code again.
This time it will not show blank, but will show you the path where it is located (current folder)
I hope that helped.
answered Jun 12, 2016 at 15:09
Use Application.ActiveWorkbook.Path for just the path itself (without the workbook name) or Application.ActiveWorkbook.FullName for the path with the workbook name.
answered Nov 9, 2015 at 8:06
This is the VBA that I use to open the current path in an Explorer window:
Shell Environ("windir") & "explorer.exe """ & CurDir() & "",vbNormalFocus
Microsoft Documentation:
CurDirFunctionEnvironFunctionShellFunction
answered Nov 18, 2018 at 7:55
ashleedawgashleedawg
20k8 gold badges73 silver badges104 bronze badges
If you really mean pure working Directory, this should suit for you.
Solution A:
Dim ParentPath As String: ParentPath = ""
Dim ThisWorkbookPath As String
Dim ThisWorkbookPathParts, Part As Variant
Dim Count, Parts As Long
ThisWorkbookPath = ThisWorkbook.Path
ThisWorkbookPathParts = Split(ThisWorkbookPath, _
Application.PathSeparator)
Parts = UBound(ThisWorkbookPathParts)
Count = 0
For Each Part In ThisWorkbookPathParts
If Count > 0 Then
ParentPath = ParentPath & Part & ""
End If
Count = Count + 1
If Count = Parts Then Exit For
Next
MsgBox "File-Drive = " & ThisWorkbookPathParts _
(LBound(ThisWorkbookPathParts))
MsgBox "Parent-Path = " & ParentPath
But if don’t, this should be enough.
Solution B:
Dim ThisWorkbookPath As String
ThisWorkbookPath = ThisWorkbook.Path
MsgBox "Working-Directory = " & ThisWorkbookPath
answered Nov 27, 2018 at 4:45
NOTSermsakNOTSermsak
3561 gold badge8 silver badges8 bronze badges
Simple Example below:
Sub openPath()
Dim path As String
path = Application.ActivePresentation.path
Shell Environ("windir") & "explorer.exe """ & path & "", vbNormalFocus
End Sub
Amit Verma
8,5408 gold badges34 silver badges40 bronze badges
answered Feb 9, 2021 at 10:46
1
Use these codes and enjoy it.
Public Function GetDirectoryName(ByVal source As String) As String()
Dim fso, oFolder, oSubfolder, oFile, queue As Collection
Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set queue = New Collection
Dim source_file() As String
Dim i As Integer
queue.Add fso.GetFolder(source) 'obviously replace
Do While queue.Count > 0
Set oFolder = queue(1)
queue.Remove 1 'dequeue
'...insert any folder processing code here...
For Each oSubfolder In oFolder.SubFolders
queue.Add oSubfolder 'enqueue
Next oSubfolder
For Each oFile In oFolder.Files
'...insert any file processing code here...
'Debug.Print oFile
i = i + 1
ReDim Preserve source_file(i)
source_file(i) = oFile
Next oFile
Loop
GetDirectoryName = source_file
End Function
And here you can call function:
Sub test()
Dim s
For Each s In GetDirectoryName("C:New folder")
Debug.Print s
Next
End Sub
answered Dec 1, 2014 at 8:44
josefjosef
8449 silver badges8 bronze badges
Get current working directory using VBA in Excel explained with examples. We use CurDir VBA function to find current working directory or folder. It displays system default directory. It can be changed using ChDir function.
Table of Contents:
- Objective
- Macro to find current working directory using VBA CurDir Function
- Case study on Get current working directory
- Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code
- Other Useful Resources
Macro to find current working directory using Excel VBA
Here we see the VBA macro to get current working directory using VBA in Excel. In this example we are using ‘CurDir’ VBA function to find the working directory.
'Find Get current working directory using VBA
Sub Find_Get_current_working_directory_using_VBA()
'Variable declaration
Dim sDir As String
'Get current directory
sDir = CurDir
'Display output on the screen
MsgBox "Current Directory is " & sDir
End Sub
Here is the output screenshot for your reference.
Case study on Get current working directory
Let us see another example to Get current working directory in Excel VBA.
Please find the following two statements.
The first one is
'Get Active Workbook Path sWBPath = ActiveWorkbook.Path
Output: Active Workbook path is C:SomeswariVBAF1
The second one is
'Get current directory sDir = CurDir
Output: Current Directory is C:VBAF1
If you want to change current directory from C:VBAF1 to C:SomeswariVBAF1, you can use ChDir VBA function in the following way.
i.e ChDir ActiveWorkbook.Path or ChDir C:SomeswariVBAF1
Now the below mentioned two statements displays same output.
Statement 1: sWBPath = ActiveWorkbook.Path
Statement 2: sDir = CurDir
Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code or Procedure:
You can refer the following link for the step by step instructions.
Instructions to run VBA Macro Code
Other Useful Resources:
Click on the following links of the useful resources. These helps to learn and gain more knowledge.
VBA Tutorial VBA Functions List VBA Arrays VBA Text Files VBA Tables
VBA Editor Keyboard Shortcut Keys List VBA Interview Questions & Answers Blog
Содержание
- Vba excel моя директория
- Macro to find current working directory using Excel VBA
- Case study on Get current working directory
- Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code or Procedure:
- Other Useful Resources:
- Объект FileSystemObject
- Синтаксис
- Примечания
- Методы
- Свойства
- См. также
- Поддержка и обратная связь
- Функция Dir
- Синтаксис
- Параметры
- Примечания
- См. также
- Поддержка и обратная связь
- How to get current working directory using vba?
- 9 Answers 9
- [ADD] Resume VBA for different applications
Vba excel моя директория
Get current working directory using VBA in Excel explained with examples. We use CurDir VBA function to find current working directory or folder. It displays system default directory. It can be changed using ChDir function.
Macro to find current working directory using Excel VBA
Here we see the VBA macro to get current working directory using VBA in Excel. In this example we are using ‘CurDir’ VBA function to find the working directory.
Here is the output screenshot for your reference.

Case study on Get current working directory
Let us see another example to Get current working directory in Excel VBA.
Please find the following two statements.
The first one is
Output: Active Workbook path is C:SomeswariVBAF1
The second one is
Output: Current Directory is C:VBAF1
If you want to change current directory from C:VBAF1 to C:SomeswariVBAF1, you can use ChDir VBA function in the following way.
Now the below mentioned two statements displays same output.
Statement 1: sWBPath = ActiveWorkbook.Path
Statement 2: sDir = CurDir
Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code or Procedure:
You can refer the following link for the step by step instructions.
Other Useful Resources:
Click on the following links of the useful resources. These helps to learn and gain more knowledge.
Источник
Объект FileSystemObject
Предоставляет доступ к файловой системе компьютера.
Синтаксис
Scripting.FileSystemObject
Примечания
Приведенный ниже код иллюстрирует использование объекта FileSystemObject для возврата объекта TextStream, который можно читать, и в который можно записать данные.
- Функция CreateObject возвращает объект FileSystemObject ( fs ).
- Метод CreateTextFile создает файл в качестве объекта TextStream ( a ).
- Метод WriteLine записывает строку текста в созданный текстовый файл.
- Метод Close опустошает буфер и закрывает файл.
Методы
| Метод | Описание |
|---|---|
| BuildPath | Добавляет имя в существующий путь. |
| CopyFile | Копирует один или несколько файлов из одного расположения в другое. |
| CopyFolder | Копирует одну или несколько папок из одного расположения в другое. |
| CreateFolder | Создает новую папку. |
| CreateTextFile | Создает текстовый файл и возвращает объект TextStream, который можно использовать для чтения или записи в файл. |
| DeleteFile | Удаляет один или несколько указанных файлов. |
| DeleteFolder | Удаляет одну или несколько указанных папок. |
| DriveExists | Проверяет, существует ли указанный диск. |
| FileExists | Проверяет, существует ли указанный файл. |
| FolderExists | Проверяет, существует ли указанная папка. |
| GetAbsolutePathName | Возвращает полный путь из корневого каталога диска для указанного пути. |
| GetBaseName | Возвращает базовое имя указанного файла или папки. |
| GetDrive | Возвращает объект Drive, соответствующий диску в указанном пути. |
| GetDriveName | Возвращает имя диска указанного пути. |
| GetExtensionName | Возвращает имя расширения файла для последнего компонента в указанном пути. |
| GetFile | Возвращает объект файла для указанного пути. |
| GetFileName | Возвращает имя файла или папки для последнего компонента в указанном пути. |
| GetFolder | Возвращает объект Folder для указанного пути. |
| GetParentFolderName | Возвращает имя родительской папки последнего компонента в указанном пути. |
| GetSpecialFolder | Возвращает путь к некоторым специальным папкам Windows. |
| GetTempName | Возвращает созданный случайным образом временный файл или папку. |
| Move | Перемещает заданный файл или указанную папку из одного места в другое. |
| MoveFile | Перемещает один или несколько файлов из одного места в другое. |
| MoveFolder | Перемещает одну или несколько папок из одного места в другое. |
| OpenAsTextStream | Открывает указанный файл и возвращает объект TextStream, который можно использовать для считывания, записи и дополнения данных в файле. |
| OpenTextFile | Открывает файл и возвращает объект TextStream, который можно использовать для доступа к файлу. |
| WriteLine | Записывает заданную строку и символ новой строки в файл TextStream. |
Свойства
| Свойство | Описание |
|---|---|
| Drives | Возвращает коллекцию всех объектов Drive на компьютере. |
| Name | Устанавливает или возвращает имя указанного файла или заданной папки. |
| Path | Возвращает путь для указанного файла, диска или указанной папки. |
| Size | Для файлов возвращает размер указанного файла в байтах; для папок возвращает размер всех файлов и вложенных папок в байтах. |
| Type | Возвращает сведения о типе файла или папки (например, для файлов с расширением .TXT возвращается «Text Document»). |
См. также
Поддержка и обратная связь
Есть вопросы или отзывы, касающиеся Office VBA или этой статьи? Руководство по другим способам получения поддержки и отправки отзывов см. в статье Поддержка Office VBA и обратная связь.
Источник
Функция Dir
Возвращает значение типа String, определяющее имя файла, каталога или папки, которое соответствует указанному шаблону, атрибуту файла либо метке тома диска.
Синтаксис
Dir [ (pathname, [ attributes ] ) ]
Синтаксис функции Dir состоит из следующих элементов.
| Часть | Описание |
|---|---|
| pathname | Необязательный. Строковое выражение, указывающее имя файла; может включать каталог или папку, а также диск. Если файл, указанный параметром pathname, не найден, возвращается строка нулевой длины («»). |
| attributes | Необязательный. Константа или числовое выражение, определяющее атрибуты файла. Если этот параметр опущен, возвращаются файлы, которые соответствуют параметру pathname, но не имеют атрибутов. |
Параметры
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| vbNormal | 0 | (По умолчанию.) Определяет файлы без атрибутов. |
| vbReadOnly | 1 | В дополнение к файлам без атрибутов определяет файлы, доступные только для чтения. |
| vbHidden | 2 | Определяет скрытые файлы, а также файлы без атрибутов. |
| vbSystem | 4 | В дополнение к файлам без атрибутов определяет системные файлы. Недоступно в macOS. |
| vbVolume | 8 | Определяет метку тома; если указан какой-либо другой атрибут, параметр vbVolume игнорируется. Недоступно в macOS. |
| vbDirectory | 16 | В дополнение к файлам без атрибутов определяет каталоги (папки). |
| vbAlias | 64 | Указанное имя файла является псевдонимом. Доступно только в macOS. |
Эти константы определены в Visual Basic для приложений и могут использоваться в коде вместо фактических значений.
Примечания
В Microsoft Windows и macOS Dir поддерживает использование подстановочных знаков с несколькими символами (*) и одним символом (?) для указания нескольких файлов.
Так как macOS не поддерживает использование подстановочных знаков, для определения группы файлов используйте тип файла. Чтобы вместо имен файлов указать тип файла, воспользуйтесь функцией MacID. Например, следующий оператор возвращает имя первого текстового файла в текущей папке:
Чтобы вывести следующий файл в папке, укажите пустую строку:
Если функция MacID используется с функцией Dir в Microsoft Windows, возникает ошибка.
Любое значение атрибута, превышающее 256, считается значением MacID.
Значение pathname необходимо указать при первом вызове функции Dir, иначе произойдет ошибка. Если задаются атрибуты файла, значение pathname также должно быть указано.
Функция Dir возвращает первое имя файла, соответствующее значению pathname. Для получения дополнительных имен файлов, соответствующих значению pathname, вызовите функцию Dir повторно без аргументов. Если других соответствий найдено не будет, функция Dir возвратит пустую строку («»). После возврата строки нулевой длины в последующих вызовах необходимо указывать значение pathname, иначе произойдет ошибка.
Значение pathname можно изменить без получения всех имен файлов, соответствующих текущему значению pathname. Однако нельзя осуществить рекурсивный вызов функции Dir. С помощью функции Dir с атрибутом vbDirectory невозможно последовательно возвращать подкаталоги.
Так как имена файлов возвращаются в порядке без учета регистра для Windows и с учетом регистра для macOS, их можно сохранить в массиве и затем отсортировать массив.
См. также
Поддержка и обратная связь
Есть вопросы или отзывы, касающиеся Office VBA или этой статьи? Руководство по другим способам получения поддержки и отправки отзывов см. в статье Поддержка Office VBA и обратная связь.
Источник
How to get current working directory using vba?
I am using MS Excel 2010 and trying to get the current directory using the below code,
But ActiveWorkbook.Path returns blank.
9 Answers 9
When one opens an Excel document D:dbtmptest1.xlsm :
CurDir() returns C:Users[username]Documents
ActiveWorkbook.Path returns D:dbtmp
So CurDir() has a system default and can be changed.
ActiveWorkbook.Path does not change for the same saved Workbook.
For example, CurDir() changes when you do «File/Save As» command, and select a random directory in the File/Directory selection dialog. Then click on Cancel to skip saving. But CurDir() has already changed to the last selected directory.
[ADD] Resume VBA for different applications
Access D:dbtmptest1.accdb, like duckboy81 commented:
- CurDir() => C:Users[username]Documents
- Application.CurrentProject.Path => D:dbtmp
Excel D:dbtmptest1.xlsm:
- CurDir() => C:Users[username]Documents
- ActiveWorkbook.Path => D:dbtmp
- Application.DefaultFilePath => C:Users[username]Documents
Outlook:
- CurDir() => C:WINDOWSSystem32
- Application.Session.Stores(1).Filepath => D:programdataOutlookmyOutlookDocX.pst
PowerPoint D:dbtmptest1.ppt:
- CurDir() => C:Users[username]Documents
- ActivePresentation.Path => D:dbtmp
Word D:dbtmptest1.docx:
Источник
VBA has some useful functions that can take your automation in Excel to the next level.
One such function is the VBA DIR function.
While by itself, it may seem like a simple function that does one specific thing.
But when you combine it with some other useful elements of the VBA coding language, you can create powerful stuff (covered in the examples later in this tutorial).
What Does VBA Dir Function Do?
Use VBA DIR function when you want to get the name of the file or a folder, using their path name.
To give you an example, if you have an Excel file in a folder, you can use the VBA DIR function to get the name of that Excel file (or any other type of file).
What if I want to get the names of all the Excel files in the folder (or all the files – be it Excel file or not)?
You can do that too!
When you use DIR function once, it returns the first file name in a folder. Now if you want to get the names of the second, third, fourth files as well, you can use the DIR function again (covered later as an example).
Dir returns the first file name that matches the pathname. To get any additional file names that match pathname, call Dir again with no arguments. When no more file names match, Dir returns a zero-length string (“”). Covered in Example 3 and 4 later in this tutorial.
Syntax of VBA DIR Function
Dir [ (pathname [ ,attributes ] ) ]
- pathname: This is an optional argument. This can be the file name, folder name, or directory name. If pathname is not found, VBA DIR function returns a zero-length string (“”)
- attributes: This is an optional argument. You can use this argument to specify some attributes and DIR function will return the file names based on those attributes. For example, if you want a list of all hidden files or read-only files (along with files with no attributes), you need to specify that in this argument.
Attributes available to use in VBA DIR function (you can use one or more of these):
| Constant | Value | Description |
| vbNormal | 0 | (Default) Specifies files with no attributes. |
| vbReadOnly | 1 | Specifies read-only files in addition to files with no attributes. |
| vbHidden | 2 | Specifies hidden files in addition to files with no attributes. |
| VbSystem | 4 | Specifies system files in addition to files with no attributes. Not available on the Macintosh. |
| vbVolume | 8 | Specifies volume label; if any other attributed is specified, vbVolume is ignored. Not available on the Macintosh. |
| vbDirectory | 16 | Specifies directories or folders in addition to files with no attributes. |
| vbAlias | 64 | Specified file name is an alias. Available only on the Macintosh. |
Using Wildcard Characters with DIR Function
If you’re working with Windows, you can also use the wildcard characters in the DIR function.
Note that you can not use these when working with VBA in Macintosh.
Using wildcards can be useful when:
- You want to get the file names of a particular file type (such as .XLSX or .PPTX)
- When you have a specific suffix/prefix in filenames and you want to get the names of these files/folders/directories. For example, if you want the names of all the files with the prefix 2019 in it, you can do that using wildcard characters.
There are three wildcard characters in Excel:
- * (asterisk) – It represents any number of characters. For example, 2019* would give you the names of all the files with the prefix 2019 in it.
- ? (question mark) – It represents one single character. For example, 2019? would give you the names of all the files that start with 2019 and has one more character in the name (such as 2019A, 2019B, 2019C, and so on)
Note: There is one more wildcard character – tilde (~). Since it’s not used a lot, I have skipped its explanation. You can read more about it here if interested.
VBA DIR Function – Examples
Now let’s dive in and see some examples of using the VBA DIR function.
Example 1 – Getting the File Name from its Path
When you have the path of a file, you can use the DIR function to get the name of the file from it.
For example, the below code returns the name of the file and shows it in a message box.
Sub GetFileNames()
Dim FileName As String
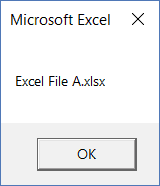
FileName = Dir("C:UserssumitDesktopTestExcel File A.xlsx")
MsgBox FileName
End Sub
The above code uses a variable ‘FileName’ to store the file name that is returned by the DIR function. It then uses a message box to display the file name (as shown below).
And what happens when the file doesn’t exist?
In that case, the DIR function would return an empty string.
The below code uses an If Then Else statement to check whether the file exists or not. If the file doesn’t exist, it shows a message box with a text “File Doesn’t Exist”, else it shows the file name.
Sub CheckFileExistence()
Dim FileName As String
FileName = Dir("C:UserssumitDesktopTestExcel File A.xlsx")
If FileName <> "" Then
MsgBox FileName
Else
MsgBox "File Doesn't Exist"
End If
End Sub
Example 2 – Check if a Directory Exists or Not (and create if it doesn’t)
The below code checks whether the folder ‘Test’ exists or not.
A message box is used to show a message in case the folder exists or when it doesn’t exist.
Sub CheckDirectory()
Dim PathName As String
Dim CheckDir As String
PathName = "C:UserssumitDesktopTest"
CheckDir = Dir(PathName, vbDirectory)
If CheckDir <> "" Then
MsgBox CheckDir & " exists"
Else
MsgBox "The directory doesn't exist"
End If
End Sub
You can refine this code further to check whether the folder exists or not, and if it doesn’t, then you can use VBA to create that folder.
Below is the code that uses the MkDir function to create a folder in case it doesn’t exist.
Sub CreateDirectory()
Dim PathName As String
Dim CheckDir As String
PathName = "C:UserssumitDesktopTest"
CheckDir = Dir(PathName, vbDirectory)
If CheckDir <> "" Then
MsgBox CheckDir & " folder exists"
Else
MkDir PathName
MsgBox "A folder has been created with the name" & CheckDir
End If
End Sub
Example 3 – Get the Names of All File and Folders in a Directory
If you want to get a list of all the file and folder names in a directory, you can use the DIR Function.
The below code lists all the files and folder names in the Test folder (which is located at the following path – C:UserssumitDesktopTest).
I am using Debug.Print to show the names in the Immediate window. You can also use this to list the names in a message box or in a column in Excel.
Sub GetAllFile&FolderNames()
Dim FileName As String
FileName = Dir("C:UserssumitDesktopTest", vbDirectory)
Do While FileName <> ""
Debug.Print FileName
FileName = Dir()
Loop
End Sub
The Do While loop in the above code continues till all the files and folders in the given path have been covered. When there are no more files/folders to cover, FileName becomes a null string and the loop stops.
Example 4 – Get the Names of All Files in a Folder
You can use the below code to get the names of all the files in a folder/directory (and not the names of the sub-folders).
Sub GetAllFileNames()
Dim FileName As String
FileName = Dir("C:UserssumitDesktopTest")
Do While FileName <> ""
Debug.Print FileName
FileName = Dir()
Loop
End Sub
This code is just like the code used in Example 3, with one minor difference.
In this code, I have not specified vbDirectory in the DIR function. When you specify vbDirectory, it will give you the names of all the files as well as folders.
When you don’t specify vbDirectory, DIR function will only give you the names of the files.
Note: If you want to get the names of all the files in the main folder and the sub-folders, you can’t use the DIR function (as it’s not recursive). To do this, you can either use Power Query (no coding needed) or use the File System Object in VBA (with recursion).
Example 5 – Get the Names of All the Sub-Folders within a Folder
The below code would give you the names of all the sub-folders within the specified folder.
It uses the GetAtr function in VBA, which allows us to check whether the name returned by the DIR function is the name of a file or a folder/directory.
Sub GetSubFolderNames()
Dim FileName As String
Dim PathName As String
PathName = "C:UserssumitDesktopTest"
FileName = Dir(PathName, vbDirectory)
Do While FileName <> ""
If GetAttr(PathName & FileName) = vbDirectory Then
Debug.Print FileName
End If
FileName = Dir()
Loop
End Sub
Again, I am using Debug.Print to get the names in the immediate window. You can get these in a message box or in Excel (by modifying the code accordingly).
Example 6 – Get the First Excel File from a Folder
With DIR function, you can specify the file extension or any suffix/prefix that you want in the file name that is returned.
The below code would display the name of the first Excel file in the Test folder.
Sub GetFirstExcelFileName() Dim FileName As String Dim PathName As String PathName = "C:UserssumitDesktopTest" FileName = Dir(PathName & "*.xls*") MsgBox FileName End Sub
Note that I have used *.xls* (asterisk sign on both sides). This will ensure that all the versions of Excel files are checked (.xls, xlsx, .xlsm, .xlsb).
Example 7 – Get Names of All Excel File in a Folder
Use the below code to get the names of all the Excel files in the Test folder.
Sub GetAllFileNames()
Dim FolderName As String
Dim FileName As String
FolderName = "C:UserssumitDesktopTest"
FileName = Dir(FolderName & "*.xls*")
Do While FileName <> ""
Debug.Print FileName
FileName = Dir()
Loop
End Sub
While the DIR function returns the name of the first Excel file only, since we are calling it again in the loop, it goes through all the files and gives us the names of all the Excel files.
Hope you found this tutorial and the examples useful.
Let me know your thoughts in the comments section.
You May Also Like the Following Excel Tutorials:
- Excel VBA InStr Function.
- Excel VBA Split Function.
- Excel VBA TRIM Function
- VBA LCASE Function.
- VBA UCASE Function.
I have a macro-enabled WorkBook. I need to specify the current folder in which the macro-enabled file is present as the path. I tried setting
path = ActiveWorkbook.Path
and
path = CurDir()
but neither of these work for me. Any idea on this?
ashleedawg
20k8 gold badges73 silver badges104 bronze badges
asked Apr 18, 2012 at 18:27
9
If the path you want is the one to the workbook running the macro, and that workbook has been saved, then
ThisWorkbook.Path
is what you would use.
answered Apr 18, 2012 at 19:04
Tim WilliamsTim Williams
150k8 gold badges96 silver badges124 bronze badges
0
I thought I had misunderstood but I was right. In this scenario, it will be ActiveWorkbook.Path
But the main issue was not here. The problem was with these 2 lines of code
strFile = Dir(strPath & "*.csv")
Which should have written as
strFile = Dir(strPath & "*.csv")
and
With .QueryTables.Add(Connection:="TEXT;" & strPath & strFile, _
Which should have written as
With .QueryTables.Add(Connection:="TEXT;" & strPath & "" & strFile, _
answered Apr 18, 2012 at 20:14
Siddharth RoutSiddharth Rout
146k17 gold badges206 silver badges250 bronze badges