Операторы, использующиеся в VBA Excel для отрицания и сравнения логических выражений. Синтаксис, принимаемые значения, приоритет логических операторов.
Оператор «Not»
«Not» – это оператор логического отрицания (инверсия), который возвращает True, если условие является ложным, и, наоборот, возвращает False, если условие является истинным.
Синтаксис:
Таблица значений:
| Условие | Результат |
|---|---|
| True | False |
| False | True |
Оператор «And»
«And» – это оператор логического умножения (логическое И, конъюнкция), который возвращает значение True, если оба условия являются истинными.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Условие1 And Условие2 |
Таблица значений:
| Условие1 | Условие2 | Результат |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | False |
| False | False | False |
Оператор «Or»
«Or» – это оператор логического сложения (логическое ИЛИ, дизъюнкция), который возвращает значение True, если одно из двух условий является истинным, или оба условия являются истинными.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Условие1 Or Условие2 |
Таблица значений:
| Условие1 | Условие2 | Результат |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | True |
| False | True | True |
| False | False | False |
Оператор «Xor»
«Xor» – это оператор логического исключения (исключающая дизъюнкция), который возвращает значение True, если только одно из двух условий является истинным.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Условие1 Xor Условие2 |
Таблица значений:
| Условие1 | Условие2 | Результат |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | False |
| True | False | True |
| False | True | True |
| False | False | False |
Оператор «Eqv»
«Eqv» – это оператор логической эквивалентности (тождество, равенство), который возвращает True, если оба условия имеют одинаковое значение.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Условие1 Eqv Условие2 |
Таблица значений:
| Условие1 | Условие2 | Результат |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | False |
| False | False | True |
Оператор «Imp»
«Imp» – это оператор логической импликации, который возвращает значение False, если первое (левое) условие является истинным, а второе (правое) условие является ложным, в остальных случаях возвращает True.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Условие1 Imp Условие2 |
Таблица значений:
| Условие1 | Условие2 | Результат |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | True |
| False | False | True |
Приоритет логических операторов
Приоритет определяет очередность выполнения операторов в одном выражении. Очередность выполнения логических операторов в VBA Excel следующая:
- «Not» – логическое отрицание;
- «And» – логическое И;
- «Or» – логическое ИЛИ;
- «Xor» – логическое исключение;
- «Eqv» – логическая эквивалентность;
- «Imp» – логическая импликация.
In this Article
- Using the And Logical Operator
- Using the Or Logical Operator
- Using the Not Logical Operator
- Using the Xor Logical Operator
- Is Operator
- Like Operator
VBA allows you to use the logical operators And, Or, Not, Xor to compare values. The operators are considered “Boolean”, which means they return True or False as a result.
If you want to learn how to compare strings, click here: VBA Compare Strings – StrComp
If you want to learn how to use comparison operators, click here: VBA Comparison Operators – Not Equal to & More
Using the And Logical Operator
The And logical operator compares two or more conditions. If all the conditions are true, the operator will return True. If at least one of the conditions is not true, the operator will return False. Here is an example:
Dim intA As Integer
Dim intB As Integer
Dim blnResult As Boolean
intA = 5
intB = 5
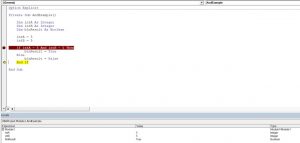
If intA = 5 And intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfIn this example, we want to check if both intA and intB are equal to 5. If this is true, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set values of intA and intB to 5:
intA = 5
intB = 5After that, we use the And operator in the If statement to check if the values are equal to 5:
If intA = 5 And intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfAs both variables are equal to 5, the blnResult returns True:
Image 1. Using the And logical operator in VBA
Using the Or Logical Operator
The Or logical operator compares two or more conditions. If at least one of the conditions is true, it will return True. If none of the conditions are true, the operator will return False. Here is the code for the example:
Dim intA As Integer
Dim intB As Integer
Dim blnResult As Boolean
intA = 5
intB = 10
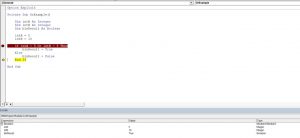
If intA = 5 Or intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfIn this example, we want to check if both intA is equal to 5. or intB is equal to 10. If any of these conditions is true, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set the value of intA to 5 and intB to 10:
intA = 5
intB = 10After that, we use the Or operator in the If statement to check if any of the values is equal to 5:
If intA = 5 Or intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfAs intA value is 5, the blnResult returns True:
Image 2. Using the Or logical operator in VBA
Using the Not Logical Operator
The Not logical operator checks one or more conditions. If the conditions are true, the operator returns False. Otherwise, it returns True. Here is the code for the example:
Dim intA As Integer
Dim blnResult As Boolean
intA = 5
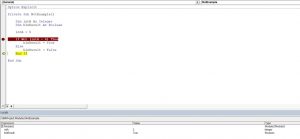
If Not (intA = 6) Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfIn this example, we want to check if the value of intA is not equal to 6. If intA is different than 6, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set the value of intA to 5:
intA = 5After that, we use the Not operator in the If statement to check if the value of intA is different than 6:
If Not (intA = 6) Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfAs intA value is 5, the blnResult returns True:
Image 3. Using the Not logical operator in VBA
Using the Xor Logical Operator
The Xor logical operator compares two or more conditions. If exactly one of the conditions is true, it will return True. If none of the conditions are true, or more than one are true, it will return False. Here is the code for the example:
Dim intA As Integer
Dim intB As Integer
Dim blnResult As Boolean
intA = 5
intB = 10
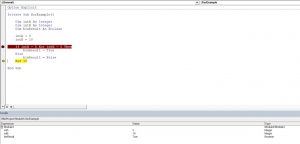
If intA = 5 Xor intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfIn this example, we want to check if exactly one of the values (intA or IntB) are equal to 5. If only one condition is true, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set the value of intA to 5 and intB to 10:
intA = 5
intB = 10After that, we use the Or operator in the If statement to check if any of the values is equal to 5:
If intA = 5 Xor intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfAs intA value is 5 and intB is 10, the blnResult returns True:
Image 4. Using the Xor logical operator in VBA
Is Operator
The Is Operator tests if two object variables store the same object.
Let’s look at an example. Here we will assign two worksheets to worksheet objects rng1 and rng2, testing if the two worksheet objects store the same worksheet:
Sub CompareObjects()
Dim ws1 As Worksheet, ws2 As Worksheet
Set ws1 = Sheets("Sheet1")
Set ws2 = Sheets("Sheet2")
If ws1 Is ws2 Then
MsgBox "Same WS"
Else
MsgBox "Different WSs"
End If
End SubOf course the worksheet objects are not the same, so “Different WSs” is returned.
Like Operator
The Like Operator can compare two strings for inexact matches. This example will test if a string starts with “Mr.”
Sub LikeDemo()
Dim strName As String
Dim blnResult As Boolean
strName = "Mr. Michael James"
If strName Like "Mr*" Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End If
End SubVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
Logical operators are used for performing logical and asthmatic operations on a set of values or variables. The table depicts all the different types of logical operators supported by Excel:
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
|
AND (LOGICAL AND) |
If both the conditions are True, then the Expression is true. Example: Assume variable A holds 10 and variable B holds 0, then a<>0 AND b<>0 is False |
|
OR ( Logical OR Operator) |
If any of the two conditions are True, then the condition is true. Example: Assume variable A holds 10 and variable B holds 0, then a<>0 OR b<>0 is true. |
|
NOT ( Logical NOT Operator) |
Reverse the result. If a condition is true, then the Logical NOT operator will make false. Example: Assume variable A holds 10 and variable B holds 0, then NOT(a<>0 OR b<>0) is false. |
|
XOR ( Logical XOR Operator) |
It is the combination of NOT and OR Operator. If one, and only one, of the expressions, evaluate to be True, the result is True. Example: Assume variable A holds 10 and variable B holds 0, then (a<>0 XOR b<>0) is true |
1. AND (LOGICAL AND)
If both the conditions are True, then the Expression is true.
Example:
Assume variable A holds 20 and variable B holds 0, then a<>0 AND b<>0 is False
Program:
Private Sub Demo_Loop()
Dim a As Integer //Declaring variable
a = 20
Dim b As Integer //Declaring variable
b = 0
If a <> 0 And b <> 0 Then
MsgBox ("AND LOGICAL Operator Result is : True")
Else
MsgBox ("AND LOGICAL Operator Result is : False")
End If
End Sub
Output:
AND LOGICAL Operator Result is : False
2. OR( Logical OR Operator)
If any of the two conditions are True, then the condition is true.
Example:
Assume variable A holds 20 and variable B holds 0, then a<>0 OR b<>0 is true.
Program:
Private Sub Demo_Loop()
Dim a As Integer //Declaring variable
a = 20
Dim b As Integer //Declaring variable
b = 0
If a <> 0 Or b <> 0 Then
MsgBox ("OR LOGICAL Operator Result is : True")
Else
MsgBox ("OR LOGICAL Operator Result is : False")
End If
End Sub
Output:
OR LOGICAL Operator Result is : True
3. NOT( Logical NOT Operator)
Reverse the result. If a condition is true, then the Logical NOT operator will make false.
Example:
Assume variable A holds 20 and variable B holds 0, then NOT(a<>0 OR b<>0) is false.
Program:
Private Sub Demo_Loop()
Dim a As Integer //Declaring variable
a = 20
Dim b As Integer //Declaring variable
b = 0
If a <> 0 Not b <> 0 Then
MsgBox ("NOT LOGICAL Operator Result is : True")
Else
MsgBox ("NOT LOGICAL Operator Result is : False")
End If
End Sub
Output:
NOT LOGICAL Operator Result is : False
4. XOR( Logical XOR Operator)
It is the combination of NOT and OR Operator. If one, and only one, of the expressions, evaluate to be True, the result is True.
Example:
Assume variable A holds 20 and variable B holds 0, then (a<>0 XOR b<>0) is true.
Program:
Private Sub Demo_Loop()
Dim a As Integer //Declaring variable
a = 20
Dim b As Integer //Declaring variable
b = 0
If a <> 0 Xor b <> 0 Then
MsgBox ("XOR LOGICAL Operator Result is : True")
Else
MsgBox ("XOR LOGICAL Operator Result is : False")
End If
End Sub
Output:
XOR LOGICAL Operator Result is : True
A Sample Program showing all the Operators is included below along with the outputs:
Program:
Private Sub Demo_Loop()
Dim a As Integer //Declaring variable
a = 20
Dim b As Integer //Declaring variable
b = 0
If a <> 0 And b <> 0 Then
MsgBox ("AND LOGICAL Operator Result is : True")
Else
MsgBox ("AND LOGICAL Operator Result is : False")
End If
If a <> 0 Or b <> 0 Then
MsgBox ("OR LOGICAL Operator Result is : True")
Else
MsgBox ("OR LOGICAL Operator Result is : False")
End If
If Not (a <> 0 Or b <> 0) Then
MsgBox ("NOT LOGICAL Operator Result is : True")
Else
MsgBox ("NOT LOGICAL Operator Result is : False")
End If
If (a <> 0 Xor b <> 0) Then
MsgBox ("XOR LOGICAL Operator Result is : True")
Else
MsgBox ("XOR LOGICAL Operator Result is : False")
End If
End Sub
Output:
AND LOGICAL Operator Result is : False OR LOGICAL Operator Result is : True NOT LOGICAL Operator Result is : False XOR LOGICAL Operator Result is : True
This Excel tutorial explains how to use the Excel OR function (in VBA) with syntax and examples.
Description
The Microsoft Excel OR function returns TRUE if any of the conditions are TRUE. Otherwise, it returns FALSE.
The OR function is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as a Logical Function. It can be used as a VBA function (VBA) in Excel. As a VBA function, you can use this function in macro code that is entered through the Microsoft Visual Basic Editor.
Please read our OR function (WS) page if you are looking for the worksheet version of the OR function as it has a very different syntax.
Syntax
The syntax for the OR function in Microsoft Excel is:
condition1 Or condition2 [... Or condition_n] )
Parameters or Arguments
- condition1, condition2, … condition_n
- Expressions that you want to test that can either be TRUE or FALSE.
Returns
The OR function returns TRUE if any of the conditions are TRUE.
The OR function returns FALSE if all conditions are FALSE.
Applies To
- Excel for Office 365, Excel 2019, Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2011 for Mac, Excel 2010, Excel 2007, Excel 2003, Excel XP, Excel 2000
Type of Function
- VBA function (VBA)
Example (as VBA Function)
The OR function with this syntax can only be used in VBA code in Microsoft Excel.
Let’s look at some Excel OR function examples and explore how to use the OR function in Excel VBA code.
This first example combines the OR function with the IF Statement in VBA:
If LWebsite = "TechOnTheNet.com" Or LCount > 25 Then LResult = "Great" Else LResult = "Fair" End If
This would set the LResult variable to the string value «Great» if either LWebsite was «TechOnTheNet.com» or LCount > 25. Otherwise, it would set the LResult variable to the string value «Fair».
You can use the OR function with the AND function in VBA, for example:
If (LWebsite = "TechOnTheNet.com" Or LWebsite = "CheckYourMath.com") And LPages <= 10 Then LBandwidth = "Low" Else LBandwidth = "High" End If
This would set the LBandwidth variable to the string value «Low» if LWebsite was either «TechOnTheNet.com» or «CheckYourMath.com» and LPages <= 10. Otherwise, it would set the LBandwidth variable to the string value «High».
The OR function is a logical function in any of the programming languages. Similar to VBA, we have an OR function, as it is a logical function. The result given by this function is either “True” or “False.” This function is used for two or many conditions together. It gives us a “True” result when either of the conditions returns “True.”
What is OR Function in VBA?
In Excel, logical functions are the heart of daily formulas. Logical functions are there to conduct the logical test and result in Boolean data type, i.e., TRUE or FALSE. Some logical formulas in Excel are IF, IFERROR in excelThe IFERROR function in Excel checks a formula (or a cell) for errors and returns a specified value in place of the error.read more, ISERROR in excelISERROR is a logical function that determines whether or not the cells being referred to have an error. If an error is found, it returns TRUE; if no errors are found, it returns FALSE.read more, , AND, and OR Excel functions.
We hope you have used them quite often as a worksheet function. In VBA, too, we can use all of them, and in this article, we will explain the ways of using the “VBA OR” function.
What is the first thing that comes to mind when you think of the word “OR”?
In simple terms, “OR” means “either this or that.”
With the same idea, OR is a logical function that gives the result as TRUE if any of the logical tests is TRUE and gives FALSE if none of the logical tests are TRUE.
It works exactly the opposite of the VBA AND function. The AND function returns TRUE only if all the logical conditions are TRUE. If any of the conditions are not satisfied, we will get FALSE.
Table of contents
- What is OR Function in VBA?
- The formula of VBA OR Function
- Examples of Using OR Function in VBA
- VBA OR Function With IF Condition is Powerful
- Case Study to Solve
- Recommended Articles
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA OR Function (wallstreetmojo.com)
The formula of VBA OR Function
Let me frame a syntax for you to understand the function.
[Logical Test] OR [Logical Test] OR [Logical Test]
First, we need to mention the logical test, then mention the word “OR,” and then mention the second logical test. If you wish to conduct a more logical test, mention the word OR after a logical test.
Of all the logical tests you do, if any of the tests are satisfied or true, then we will get the result as TRUE if none or satisfied, then the result is FALSE.
Examples of Using OR Function in VBA
We will show you a simple example of using the OR function in VBA.
You can download this VBA OR Excel Template here – VBA OR Excel Template
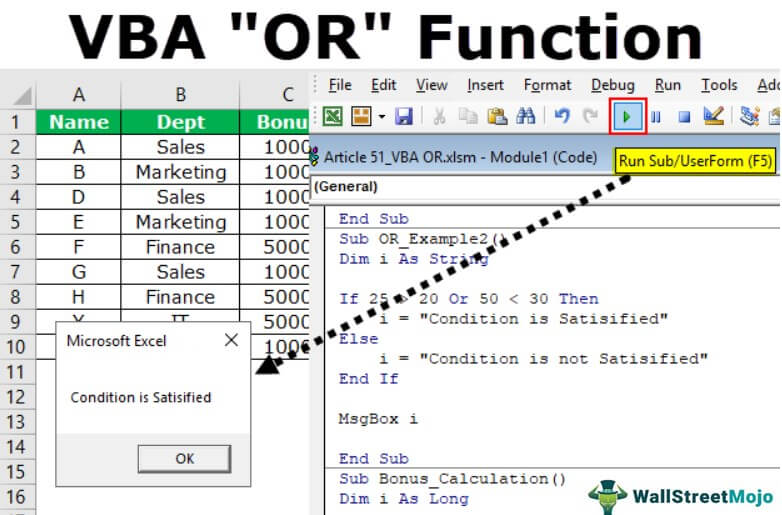
To understand the logical VBA function OR let us give you an example. Let us say we want to conduct the logical test of whether the number 25 is greater than 20 or the number 50 is less than 30.
Step 1: Create a macro name.
Step 2: Define the variable as a string.
Code:
Sub OR_Example1() Dim i As String End Sub
Step 3: Now, we will assign the value through the OR logical test for this variable.
Code:
Sub OR_Example1() Dim i As String i = End Sub
Step 4: Our first logical test is 25 >20.
Code:
Sub OR_Example1() Dim i As String i = 25 > 20 End Sub
Step 5: Now, after the first logical test, mention the word OR and enter the second logical test.
Code:
Sub OR_Example1() Dim i As String i = 25 > 20 Or 50 < 30 End Sub
Step 6: Now, VBA OR function tests whether the logical tests are TRUE or FALSE. Now assign the result of the variable to the VBA message box.
Code:
Sub OR_Example1() Dim i As String i = 25 > 20 Or 50 < 30 MsgBox i End Sub
Step 7: Run the Macro and what the result is.
We got the result as TRUE because out of the two logical testsA logical test in Excel results in an analytical output, either true or false. The equals to operator, “=,” is the most commonly used logical test.read more we have provided, one test is TRUE, so the result is TRUE.
25 is greater than 20, and 50 is not less than 30. In this case, the first logical test is TRUE, but the second is FALSE. Because we have applied the VBA OR function, it needs any one of the conditions to be TRUE to get the result as TRUE.
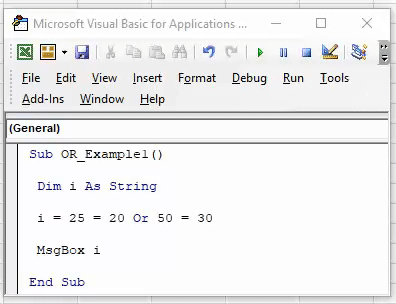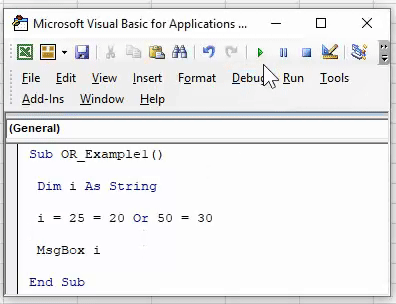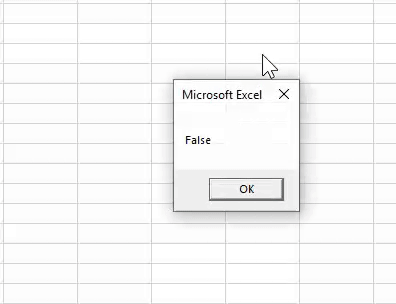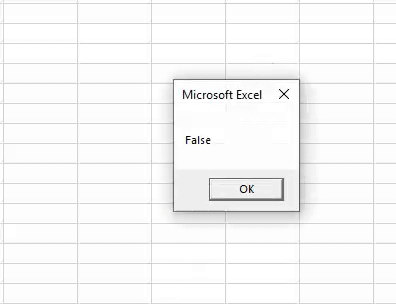
Now, look at the code below.
Code:
Sub OR_Example1() Dim i As String i = 25 = 20 Or 50 = 30 MsgBox i End Sub
We have changed the logical test equations from > and < to equal (=) sign. Therefore, it will return FALSE as the result because 25 is not equal to 20, and 50 is not equal to 30.
VBA OR Function With IF Condition is Powerful
As we said, the OR function can return either TRUE or FALSE as a result, but with the other logical function, “IF,” we can manipulate results as per our needs.
Take the same logical tests from above. Again, the OR function has returned only TRUE or FALSE, but let us combine this OR with IF.
Step 1: Before conducting any test, open the function IF.
Code:
Sub OR_Example2() Dim i As String IF End Sub
Step 2: Now, conduct tests using the OR function.
Code:
Sub OR_Example2() Dim i As String IF 25 = 20 Or 50 = 30 End Sub
Step 3: Put the word “Then” and write the result. If the condition is TRUE, assign the value to the variable as “Condition is Satisfied.”
Code:
Sub OR_Example2() Dim i As String If 25 = 20 Or 50 = 30 Then i = "Condition is Satisfied" End Sub
Step 4: If the condition is FALSE, then we need a different result, so put the word “ELSE” and, in the next line, assign the value to the variable “what should be the result if the condition or logical test is FALSE.”
Code:
Sub OR_Example2() Dim i As String If 25 = 20 Or 50 = 30 Then i = "Condition is Satisfied" Else i = "Condition is not Satisfied" End Sub
Step 5: End the IF function with “End If.”
Code:
Sub OR_Example2() Dim i As String If 25 = 20 Or 50 = 30 Then i = "Condition is Satisfied" Else i = "Condition is not Satisfied" End If End Sub
Step 6: Assign the value of the variable result to the message box.
Code:
Sub OR_Example2() Dim i As String If 25 = 20 Or 50 = 30 Then i = "Condition is Satisfied" Else i = "Condition is not Satisfied" End If MsgBox i End Sub
Run the Macro. If the logical test is TRUE, we will get the result as “Condition is Satisfied,” or else we will get “Condition is not Satisfied.”
We got the result “Condition is not Satisfied” because both the logical tests are FALSE.
Now, we will change the logical tests.
Code:
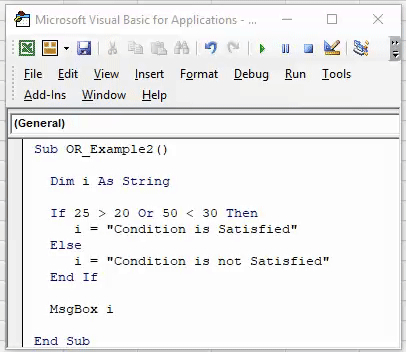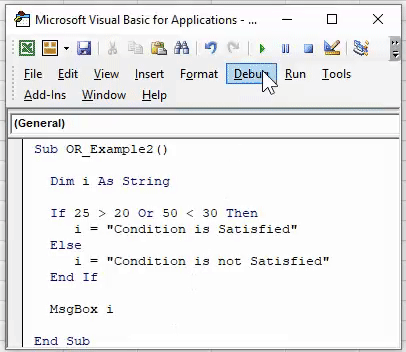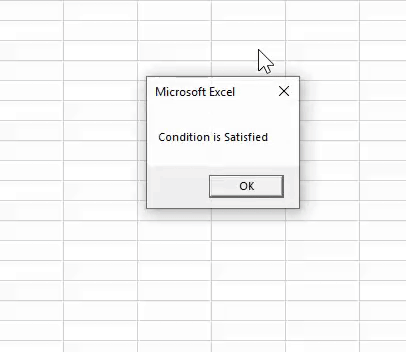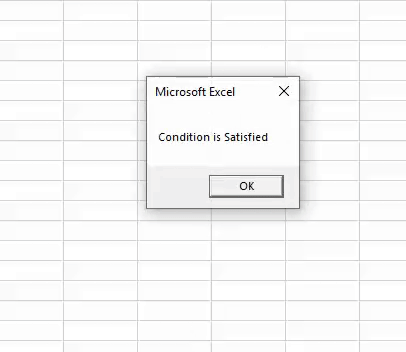
Sub OR_Example2() Dim i As String If 25 > 20 Or 50 < 30 Then i = "Condition is Satisfied" Else i = "Condition is not Satisfied" End If MsgBox i End Sub
We will run the macro and see what the result is.
Like this, we can use one logical function with other logical functions to arrive at the results.
Solve the below case study to get used to logical functions.
Case Study to Solve
We have employee names and their respective departments.
If you have tried and not found the result, then you can refer below code to understand the logic.
Code:
Sub Bonus_Calculation() Dim i As Long For i = 2 To 10 If Cells(i, 2).Value = "Finance" Or Cells(i, 2).Value = "IT" Then Cells(i, 3).Value = 5000 Else Cells(i, 3).Value = 1000 End If Next i End Sub
If the employee is from “Finance” or “IT,” then they should get the bonus of “5000.” For other department employees, the bonus is “1000.”
Conduct the logical test and arrive at the results.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA OR Function. Here, we learn how to use OR Logical Operator in VBA along with some practical examples and a downloadable Excel template. Below are some useful Excel articles related to VBA: –
- IFERROR in VBA
- Excel VBA On Error Statement
- Excel OR Function
- VBA Month Function