I am trying to select an entire row in a different sheet and then copy the row to the sheet I am currently in with a macro. The code works fine if the Rows() sub is passed integers hardcoded but when I put a variable I get the «Select method of Range class failed» error. here is the code I have:
Sheets("BOM").Select
Rows(copyFromRow & ":" & copyFromRow).Select
Selection.Copy
Sheets("Proposal").Select
Rows(copyToRow & ":" & copyToRow).Select
ActiveSheet.Paste
copyToRow = copyToRow + 1
Rows(copyToRow & ":" & copyToRow).Select
Application.CutCopyMode = False
Selection.Insert Shift:=xlDown, CopyOrigin:=xlFormatFromLeftOrAbove
if instead i used :
Rows("52:52").Select
Selection.Copy
it works fine, but when the variable is there, the error occurs.
Thanks
asked May 14, 2012 at 16:05
thebiglebowski11thebiglebowski11
1,44110 gold badges41 silver badges74 bronze badges
2
I just tested the code at the bottom and it prints 16384 twice (I’m on Excel 2010) and the first row gets selected. Your problem seems to be somewhere else.
Have you tried to get rid of the selects:
Sheets("BOM").Rows(copyFromRow).Copy
With Sheets("Proposal")
.Paste Destination:=.Rows(copyToRow)
copyToRow = copyToRow + 1
Application.CutCopyMode = False
.Rows(copyToRow).Insert Shift:=xlDown, CopyOrigin:=xlFormatFromLeftOrAbove
End With
Test code to get convinced that the problem does not seem to be what you think it is.
Sub test()
Dim r
Dim i As Long
i = 1
r = Rows(i & ":" & i)
Debug.Print UBound(r, 2)
r = Rows(i)
Debug.Print UBound(r, 2)
Rows(i).Select
End Sub
answered May 14, 2012 at 18:02
I solved the problem for me by addressing also the worksheet first:
ws.rows(x & ":" & y).Select
without the reference to the worksheet (ws) I got an error.
zx485
27.9k28 gold badges55 silver badges59 bronze badges
answered Aug 24, 2018 at 21:16
FelixFelix
311 bronze badge
Saw this answer on another site and it works for me as well!
Posted by Shawn on October 14, 2001 1:24 PM
var1 = 1
var2 = 5
Rows(var1 & ":" & var2).SelectThat worked for me, looks like you just have to keep the variables outside the quotes and add the and statement (&)
-Shawn
Wai Ha Lee
8,49379 gold badges60 silver badges91 bronze badges
answered Apr 8, 2015 at 17:33
The key is in the quotes around the colon and &, i.e. rows(variable & «:» & variable).select
Adapt this:
Rows(x & ":" & y).select
where x and y are your variables.
Some other examples that may help you understand
Rows(x & ":" & x).select
Or
Rows((x+1) & ":" (x*3)).select
Or
Rows((x+2) & ":" & (y-3)).select
Hopefully you get the idea.
answered Nov 10, 2016 at 17:58
You need to add quotes. VBA is translating
Rows(copyToRow & ":" & copyToRow).Select`
into
Rows(52:52).Select
Try changing
Rows(""" & copyToRow & ":" & copyToRow & """).Select
answered May 14, 2012 at 16:43
kirbskirbs
1681 silver badge8 bronze badges
1
One needs to make sure the space between the variables and ‘&’ sign.
Check the image. (Red one showing invalid commands)
The correct solution is
Dim copyToRow: copyToRow = 5
Rows(copyToRow & ":" & copyToRow).Select
answered Nov 23, 2020 at 16:30
Masood SalikMasood Salik
1191 gold badge1 silver badge10 bronze badges
mycell = ActiveCell
r = mycell.Row
c = mycell.Column
Range(Cells(r, c), Cells(r + 100, c)).Select
answered Dec 8, 2021 at 18:00
In this Article
- Select Entire Rows or Columns
- Select Single Row
- Select Single Column
- Select Multiple Rows or Columns
- Select ActiveCell Row or Column
- Select Rows and Columns on Other Worksheets
- Is Selecting Rows and Columns Necessary?
- Methods and Properties of Rows & Columns
- Delete Entire Rows or Columns
- Insert Rows or Columns
- Copy & Paste Entire Rows or Columns
- Hide / Unhide Rows and Columns
- Group / UnGroup Rows and Columns
- Set Row Height or Column Width
- Autofit Row Height / Column Width
- Rows and Columns on Other Worksheets or Workbooks
- Get Active Row or Column
This tutorial will demonstrate how to select and work with entire rows or columns in VBA.
First we will cover how to select entire rows and columns, then we will demonstrate how to manipulate rows and columns.
Select Entire Rows or Columns
Select Single Row
You can select an entire row with the Rows Object like this:
Rows(5).SelectOr you can use EntireRow along with the Range or Cells Objects:
Range("B5").EntireRow.Selector
Cells(5,1).EntireRow.SelectYou can also use the Range Object to refer specifically to a Row:
Range("5:5").SelectSelect Single Column
Instead of the Rows Object, use the Columns Object to select columns. Here you can reference the column number 3:
Columns(3).Selector letter “C”, surrounded by quotations:
Columns("C").SelectInstead of EntireRow, use EntireColumn along with the Range or Cells Objects to select entire columns:
Range("C5").EntireColumn.Selector
Cells(5,3).EntireColumn.SelectYou can also use the Range Object to refer specifically to a column:
Range("B:B").SelectSelect Multiple Rows or Columns
Selecting multiple rows or columns works exactly the same when using EntireRow or EntireColumn:
Range("B5:D10").EntireRow.Selector
Range("B5:B10").EntireColumn.SelectHowever, when you use the Rows or Columns Objects, you must enter the row numbers or column letters in quotations:
Rows("1:3").Selector
Columns("B:C").SelectSelect ActiveCell Row or Column
To select the ActiveCell Row or Column, you can use one of these lines of code:
ActiveCell.EntireRow.Selector
ActiveCell.EntireColumn.SelectSelect Rows and Columns on Other Worksheets
In order to select Rows or Columns on other worksheets, you must first select the worksheet.
Sheets("Sheet2").Select
Rows(3).SelectThe same goes for when selecting rows or columns in other workbooks.
Workbooks("Book6.xlsm").Activate
Sheets("Sheet2").Select
Rows(3).SelectNote: You must Activate the desired workbook. Unlike the Sheets Object, the Workbook Object does not have a Select Method.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Is Selecting Rows and Columns Necessary?
However, it’s (almost?) never necessary to actually select Rows or Columns. You don’t need to select a Row or Column in order to interact with them. Instead, you can apply Methods or Properties directly to the Rows or Columns. The next several sections will demonstrate different Methods and Properties that can be applied.
You can use any method listed above to refer to Rows or Columns.
Methods and Properties of Rows & Columns
Delete Entire Rows or Columns
To delete rows or columns, use the Delete Method:
Rows("1:4").Deleteor:
Columns("A:D").DeleteVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Insert Rows or Columns
Use the Insert Method to insert rows or columns:
Rows("1:4").Insertor:
Columns("A:D").InsertCopy & Paste Entire Rows or Columns
Paste Into Existing Row or Column
When copying and pasting entire rows or columns you need to decide if you want to paste over an existing row / column or if you want to insert a new row / column to paste your data.
These first examples will copy and paste over an existing row or column:
Range("1:1").Copy Range("5:5")or
Range("C:C").Copy Range("E:E")Insert & Paste
These next examples will paste into a newly inserted row or column.
This will copy row 1 and insert it into row 5, shifting the existing rows down:
Range("1:1").Copy
Range("5:5").InsertThis will copy column C and insert it into column E, shifting the existing columns to the right:
Range("C:C").Copy
Range("E:E").InsertHide / Unhide Rows and Columns
To hide rows or columns set their Hidden Properties to True. Use False to hide the rows or columns:
'Hide Rows
Rows("2:3").EntireRow.Hidden = True
'Unhide Rows
Rows("2:3").EntireRow.Hidden = Falseor
'Hide Columns
Columns("B:C").EntireColumn.Hidden = True
'Unhide Columns
Columns("B:C").EntireColumn.Hidden = FalseGroup / UnGroup Rows and Columns
If you want to Group rows (or columns) use code like this:
'Group Rows
Rows("3:5").Group
'Group Columns
Columns("C:D").GroupTo remove the grouping use this code:
'Ungroup Rows
Rows("3:5").Ungroup
'Ungroup Columns
Columns("C:D").UngroupThis will expand all “grouped” outline levels:
ActiveSheet.Outline.ShowLevels RowLevels:=8, ColumnLevels:=8and this will collapse all outline levels:
ActiveSheet.Outline.ShowLevels RowLevels:=1, ColumnLevels:=1Set Row Height or Column Width
To set the column width use this line of code:
Columns("A:E").ColumnWidth = 30To set the row height use this line of code:
Rows("1:1").RowHeight = 30AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Autofit Row Height / Column Width
To Autofit a column:
Columns("A:B").AutofitTo Autofit a row:
Rows("1:2").AutofitRows and Columns on Other Worksheets or Workbooks
To interact with rows and columns on other worksheets, you must define the Sheets Object:
Sheets("Sheet2").Rows(3).InsertSimilarly, to interact with rows and columns in other workbooks, you must also define the Workbook Object:
Workbooks("book1.xlsm").Sheets("Sheet2").Rows(3).InsertGet Active Row or Column
To get the active row or column, you can use the Row and Column Properties of the ActiveCell Object.
MsgBox ActiveCell.Rowor
MsgBox ActiveCell.ColumnThis also works with the Range Object:
MsgBox Range("B3").ColumnVBA Select
It is very common to find the .Select methods in saved macro recorder code, next to a Range object.
.Select is used to select one or more elements of Excel (as can be done by using the mouse) allowing further manipulation of them.
Selecting cells with the mouse:

Selecting cells with VBA:
'Range([cell1],[cell2])
Range(Cells(1, 1), Cells(9, 5)).Select
Range("A1", "E9").Select
Range("A1:E9").Select
Each of the above lines select the range from «A1» to «E9».

VBA Select CurrentRegion
If a region is populated by data with no empty cells, an option for an automatic selection is the CurrentRegion property alongside the .Select method.
CurrentRegion.Select will select, starting from a Range, all the area populated with data.
Range("A1").CurrentRegion.Select

Make sure there are no gaps between values, as CurrentRegion will map the region through adjoining cells (horizontal, vertical and diagonal).
Range("A1").CurrentRegion.SelectWith all the adjacent data

Not all adjacent data

«C4» is not selected because it is not immediately adjacent to any filled cells.
VBA ActiveCell
The ActiveCell property brings up the active cell of the worksheet.
In the case of a selection, it is the only cell that stays white.
A worksheet has only one active cell.
Range("B2:C4").Select
ActiveCell.Value = "Active"

Usually the ActiveCell property is assigned to the first cell (top left) of a Range, although it can be different when the selection is made manually by the user (without macros).

The AtiveCell property can be used with other commands, such as Resize.
VBA Selection
After selecting the desired cells, we can use Selection to refer to it and thus make changes:
Range("A1:D7").Select
Selection = 7

Selection also accepts methods and properties (which vary according to what was selected).
Selection.ClearContents 'Deletes only the contents of the selection
Selection.Interior.Color = RGB(255, 255, 0) 'Adds background color to the selection

As in this case a cell range has been selected, the Selection will behave similarly to a Range. Therefore, Selection should also accept the .Interior.Color property.
RGB (Red Green Blue) is a color system used in a number of applications and languages. The input values for each color, in the example case, ranges from 0 to 255.
Selection FillDown
If there is a need to replicate a formula to an entire selection, you can use the .FillDown method
Selection.FillDown
Before the FillDown

After the FillDown

.FillDown is a method applicable to Range. Since the Selection was done in a range of cells (equivalent to a Range), the method will be accepted.
.FillDown replicates the Range/Selection formula of the first line, regardless of which ActiveCell is selected.
.FillDown can be used at intervals greater than one column (E.g. Range(«B1:C2»).FillDown will replicate the formulas of B1 and C1 to B2 and C2 respectively).
VBA EntireRow and EntireColumn
You can select one or multiple rows or columns with VBA.
Range("B2").EntireRow.Select
Range("C3:D3").EntireColumn.Select

The selection will always refer to the last command executed with Select.
To insert a row use the Insert method.
Range("A7").EntireRow.Insert
'In this case, the content of the seventh row will be shifted downward
To delete a row use the Delete method.
Range("A7").EntireRow.Delete
'In this case, the content of the eighth row will be moved to the seventh
VBA Rows and Columns
Just like with the EntireRow and EntireColumn property, you can use Rows and Columns to select a row or column.
Columns(5).Select
Rows(3).Select

To hide rows:
Range("A1:C3").Rows.Hidden = True

In the above example, rows 1 to 3 of the worksheet were hidden.
VBA Row and Column
Row and Column are properties that are often used to obtain the numerical address of the first row or first column of a selection or a specific cell.
Range("A3:H30").Row 'Referring to the row; returns 3
Range("B3").Column 'Referring to the column; returns 2
The results of Row and Column are often used in loops or resizing.
Consolidating Your Learning
Suggested Exercise
SuperExcelVBA.com is learning website. Examples might be simplified to improve reading and basic understanding. Tutorials, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content. All Rights Reserved.
Excel ® is a registered trademark of the Microsoft Corporation.
© 2023 SuperExcelVBA | ABOUT
Определение адреса выделенного диапазона ячеек на листе Excel с помощью кода VBA. Определение номера первой и последней строки. Программное выделение диапазона.
Адрес выделенного диапазона
Для определения адреса выделенного диапазона ячеек в VBA Excel используется свойство Address объекта Selection.
Объект Selection — это совокупность всех выделенных ячеек на листе Excel. Это может быть одна ячейка, смежный или несмежный диапазон ячеек, представляющий коллекцию смежных диапазонов. Если выделение состоит из несмежного диапазона, адреса смежных диапазонов, из которых он состоит, будут перечислены через запятую.
Смежный диапазон — прямоугольная область смежных (прилегающих друг к другу) ячеек.
Несмежный диапазон — совокупность (коллекция) смежных диапазонов (прямоугольных областей смежных ячеек).
Стоит отметить: несмотря на то, что в выделенном диапазоне может содержаться много ячеек, активной может быть только одна. Она представлена объектом ActiveCell. Для определения ее адреса в коде VBA Excel также используется свойство Address.
|
Sub Primer1() MsgBox «Адрес выделенного диапазона: « & Selection.Address & _ vbNewLine & «Адрес активной ячейки: « & ActiveCell.Address & _ vbNewLine & «Номер строки активной ячейки: « & ActiveCell.Row & _ vbNewLine & «Номер столбца активной ячейки: « & ActiveCell.Column End Sub |
Скопируйте и запустите код на выполнение. В результате получите что-то вроде этого, зависящее от того, какие диапазоны вы выберите:
Определение адресов выделенного диапазона и активной ячейки
Выделение ячеек и диапазонов
Выделить несмежный диапазон ячеек можно следующим образом:
|
Sub Primer2() Range(«B4:C7,E5:F7,D8»).Select End Sub |
Как видно из примера, в адресной строке объекта Range перечисляются адреса смежных диапазонов, составляющих общий несмежный диапазон, через запятую. Выделение осуществляется методом Select объекта Range.
Определение номеров первой и последней строки
Чтобы вычислить номера первой и последней строки выделенного диапазона, будем исходить из того, что первая ячейка смежного диапазона находится на первой строке, а последняя — на последней строке выделенного диапазона.
|
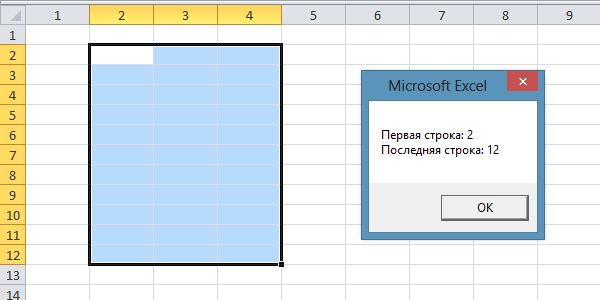
Sub Primer3() Dim i1 As Long, i2 As Long i1 = Selection.Cells(1).Row i2 = Selection.Cells(Selection.Cells.Count).Row MsgBox «Первая строка: « & i1 & _ vbNewLine & «Последняя строка: « & i2 End Sub |
Результат будет таким, зависит от выделенного диапазона:
Номера первой и последней строки выделенного смежного диапазона
Таким же образом можно вычислить номера первого и последнего столбцов выделенного диапазона, которые можно использовать для обработки информации по столбцам.
Обратите внимание, что для несмежных диапазонов этот пример не работает.
На практике я использовал определение номеров первой и последней строк по выделенному диапазону для формирования файла загрузки данных держателей дисконтных карт на сервис отправки СМС-сообщений. Оказалось, что базу данных клиентов заполнять в таблице Excel намного удобнее, чем на портале сервиса, а для загрузки в сервис достаточно сформировать несложный файл. Заполнил новые строки, выделил их по любому столбцу, нажал кнопку и файл готов.
|
0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 23.06.2008 Сообщений: 36 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
25.06.2008, 02:16. Показов 26306. Ответов 2
как выделить всю текущую строку? Excel. если извесно, что в строке 5 ячеек? спасибо
0 |
|
Programming Эксперт 94731 / 64177 / 26122 Регистрация: 12.04.2006 Сообщений: 116,782 |
25.06.2008, 02:16 |
|
2 |
|
Victory |
|
|
25.06.2008, 12:30 |
2 |
|
Если хочешь выделить всю строку пиши Rows(Activecell.row).select. |
|
TurboDuck 50 / 49 / 13 Регистрация: 23.11.2015 Сообщений: 401 |
||||
|
20.07.2016, 07:30 |
3 |
|||
0 |
! Знаю ячейку, а как выделить всю строку?
- GAL
- Обычный пользователь
-
- Сообщения: 69
- Зарегистрирован: 05.11.2004 (Пт) 15:57
! Знаю ячейку, а как выделить всю строку?
Привет!
Люди, подскажите, пожалуйста..
Как выделить строку если я знаю ячейку в этой строке?
Заранее большое спасибо.
- uhm
- Продвинутый гуру
-
- Сообщения: 1597
- Зарегистрирован: 02.12.2004 (Чт) 15:21
uhm » 06.04.2005 (Ср) 10:38
Rows(номер_строки).Select
Если в строке есть ячейки, объединенные с другими строками, выделится несколько строк.
- GAL
- Обычный пользователь
-
- Сообщения: 69
- Зарегистрирован: 05.11.2004 (Пт) 15:57
GAL » 06.04.2005 (Ср) 10:49
Я не знаю номер строки.
Я немогу явно указать номер этой строки.
У меня в макросе запускается поиск, нахожу ячейку с таким-то содержимым и мне нужно выделить строку содержащую эту ячейку.
Есть такая возможность?
- GAL
- Обычный пользователь
-
- Сообщения: 69
- Зарегистрирован: 05.11.2004 (Пт) 15:57
GAL » 06.04.2005 (Ср) 10:52
Я незнаю номер строки.
Я немогу указать его явно.
У меня макрос ищет ячейку с таким-то содержимым и когда найдет мне нужно выделить строку содержащую эту ячейку.
Есть такая возможность?
- uhm
- Продвинутый гуру
-
- Сообщения: 1597
- Зарегистрирован: 02.12.2004 (Чт) 15:21
uhm » 06.04.2005 (Ср) 10:53
Да, если x — это твоя найденная ячейка, то она содержится в столбце x.Column и в строке x.Row. Соответственно, можешь выделить строку так:
Rows(x.Row).Select
- GAL
- Обычный пользователь
-
- Сообщения: 69
- Зарегистрирован: 05.11.2004 (Пт) 15:57
GAL » 06.04.2005 (Ср) 11:03
Да, так получилось.
Спасибо uhm!
- GSerg
- Шаман
- Сообщения: 14286
- Зарегистрирован: 14.12.2002 (Сб) 5:25
- Откуда: Магадан
GSerg » 06.04.2005 (Ср) 12:51
x.entirerow.select
Как только вы переберёте все варианты решения и не найдёте нужного, тут же обнаружится решение, простое и очевидное для всех, кроме вас
Вернуться в VBA
Кто сейчас на конференции
Сейчас этот форум просматривают: Yandex-бот и гости: 2
Download Article
Download Article
This wikiHow teaches you how to start using Visual Basic procedures to select data in Microsoft Excel. As long as you’re familiar with basic VB scripting and using more advanced features of Excel, you’ll find the selection process pretty straight-forward.
-
1
Select one cell on the current worksheet. Let’s say you want to select cell E6 with Visual Basic. You can do this with either of the following options:[1]
ActiveSheet.Cells(6, 5).Select
ActiveSheet.Range("E6").Select
-
2
Select one cell on a different worksheet in the same workbook. Let’s say our example cell, E6, is on a sheet called Sheet2. You can use either of the following options to select it:
Application.Goto ActiveWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet2").Cells(6, 5)
Application.Goto (ActiveWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet2").Range("E6"))
Advertisement
-
3
Select one cell on a worksheet in a different workbook. Let’s say you want to select a cell from Sheet1 in a workbook called BOOK2.XLS. Either of these two options should do the trick:
Application.Goto Workbooks("BOOK2.XLS").Sheets("Sheet1").Cells(2,1)
Application.Goto Workbooks("BOOK2.XLS").Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A2")
-
4
Select a cell relative to another cell. You can use VB to select a cell based on its location relative to the active (or a different) cell. Just be sure the cell exists to avoid errors. Here’s how to use :
-
Select the cell three rows below and four columns to the left of the active cell:
ActiveCell.Offset(3, -4).Select
-
Select the cell five rows below and four columns to the right of cell C7:
ActiveSheet.Cells(7, 3).Offset(5, 4).Select
-
Select the cell three rows below and four columns to the left of the active cell:
Advertisement
-
1
Select a range of cells on the active worksheet. If you wanted to select cells C1:D6 on the current sheet, you can enter any of the following three examples:
ActiveSheet.Range(Cells(1, 3), Cells(6, 4)).Select
ActiveSheet.Range("C1:D6").Select
ActiveSheet.Range("C1", "D6").Select
-
2
Select a range from another worksheet in the same workbook. You could use either of these examples to select cells C3:E11 on a sheet called Sheet3:
Application.Goto ActiveWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet3").Range("C3:E11")
Application.Goto ActiveWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet3").Range("C3", "E11")
-
3
Select a range of cells from a worksheet in a different workbook. Both of these examples would select cells E12:F12 on Sheet1 of a workbook called BOOK2.XLS:
Application.Goto Workbooks("BOOK2.XLS").Sheets("Sheet1").Range("E12:F12")
Application.Goto Workbooks("BOOK2.XLS").Sheets("Sheet1").Range("E12", "F12")
-
4
Select a named range. If you’ve assigned a name to a range of cells, you’d use the same syntax as steps 4-6, but you’d replace the range address (e.g., «E12», «F12») with the range’s name (e.g., «Sales»). Here are some examples:
-
On the active sheet:
ActiveSheet.Range("Sales").Select
-
Different sheet of same workbook:
Application.Goto ActiveWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet3").Range("Sales")
-
Different workbook:
Application.Goto Workbooks("BOOK2.XLS").Sheets("Sheet1").Range("Sales")
-
On the active sheet:
-
5
Select a range relative to a named range. The syntax varies depending on the named range’s location and whether you want to adjust the size of the new range.
- If the range you want to select is the same size as one called Test5 but is shifted four rows down and three columns to the right, you’d use:
ActiveSheet.Range("Test5").Offset(4, 3).Select
- If the range is on Sheet3 of the same workbook, activate that worksheet first, and then select the range like this:
Sheets("Sheet3").Activate ActiveSheet.Range("Test").Offset(4, 3).Select
- If the range you want to select is the same size as one called Test5 but is shifted four rows down and three columns to the right, you’d use:
-
6
Select a range and resize the selection. You can increase the size of a selected range if you need to. If you wanted to select a range called Database’ and then increase its size by 5 rows, you’d use this syntax:
Range("Database").Select Selection.Resize(Selection.Rows.Count + 5, _Selection.Columns.Count).Select
-
7
Select the union of two named ranges. If you have two overlapping named ranges, you can use VB to select the cells in that overlapping area (called the «union»). The limitation is that you can only do this on the active sheet. Let’s say you want to select the union of a range called Great and one called Terrible:
-
Application.Union(Range("Great"), Range("Terrible")).Select
- If you want to select the intersection of two named ranges instead of the overlapping area, just replace Application.Union with Application.Intersect.
-
Advertisement
-
1
Use this example data for the examples in this method. This chart full of example data, courtesy of Microsoft, will help you visualize how the examples behave:[2]
A1: Name B1: Sales C1: Quantity A2: a B2: $10 C2: 5 A3: b B3: C3: 10 A4: c B4: $10 C4: 5 A5: B5: C5: A6: Total B6: $20 C6: 20 -
2
Select the last cell at the bottom of a contiguous column. The following example will select cell A4:
ActiveSheet.Range("A1").End(xlDown).Select
-
3
Select the first blank cell below a column of contiguous cells. The following example will select A5 based on the chart above:
ActiveSheet.Range("A1").End(xlDown).Offset(1,0).Select
-
4
Select a range of continuous cells in a column. Both of the following examples will select the range A1:A4:
ActiveSheet.Range("A1", ActiveSheet.Range("a1").End(xlDown)).Select
ActiveSheet.Range("A1:" & ActiveSheet.Range("A1"). End(xlDown).Address).Select
-
5
Select a whole range of non-contiguous cells in a column. Using the data table at the top of this method, both of the following examples will select A1:A6:
ActiveSheet.Range("A1",ActiveSheet.Range("A65536").End(xlUp)).Select
ActiveSheet.Range("A1",ActiveSheet.Range("A65536").End(xlUp)).Select
Advertisement
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
-
The «ActiveSheet» and «ActiveWorkbook» properties can usually be omitted if the active sheet and/or workbook(s) are implied.
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Use ActiveSheet.Range(«E6»).Select to select E6 on the active sheet.
2. Use Application.Goto (ActiveWorkbook.Sheets(«Sheet2»).Range(«E6»)) to select E6 on Sheet2.
3. Add Workbooks(«BOOK2.XLS») to the last step to specify that the sheet is in BOOK2.XLS.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 167,714 times.