We use UBound and LBound functions to get the length of an Array in Excel VBA. In this article, we will discuss them in detail.
Syntax: UBound() function
UBound (arrayname, [ dimension ])
Parameters:
- arrayname: required. Array variable name
- dimension: optional
Returns: Return upper limit of an array dimension.
Syntax: LBound() Function
LBound (arrayname, [ dimension ])
Parameters:
- arrayname : required. Array variable name
- dimension : optional
Returns: Return lower limit of an array dimension
Sample Data:
VBA Code to get the length of Array (one-dimensional array):
Declare Variables:
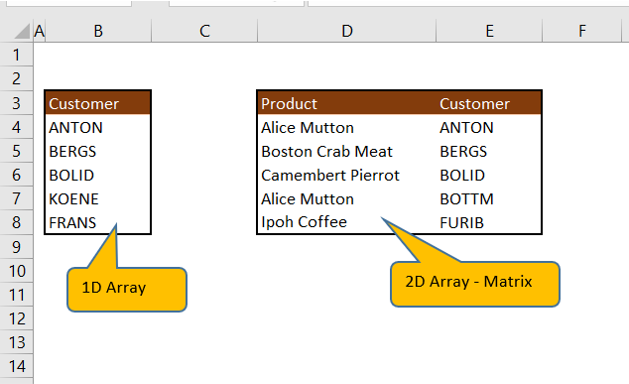
Declaring a customer array with the size of 10.
Sub oneDimArrayLength() ' Array variable Declaration Dim customer (1 To 10) As String
Assign values to array elements
customer(1) = "ANTON" customer(2) = "BERGS" customer(3) = "BOLID" customer(4) = "KOENE" customer(5) = "FRANS"
Use UBound function to get the size of an array and Message box to display the result
'Message box to popup length of 1D array MsgBox "Array has " & UBound(customer) & " element(s)." End Sub
To Run VBA Code
Press Alt+F8 to popup macro window. Select ” oneDimArrayLength” and Click Run button.
Output
VBA Code to get the length of Array (multi-dimensional array)
Declaring variables:
Declaring ProdAndCustomer multi-dimensional array size of 10 rows and 2 columns
Sub twoDimArrayLength() ' Array variable Declaration Dim ProdAndCustomer(1 To 10, 1 To 2) As String, noOfRow As Integer, noOfCol As Integer, noOfElements As Integer
Assign values to array elements
ProdAndCustomer(1, 1) = "Alice Mutton" ProdAndCustomer(2, 1) = "Boston Crab Meat" ProdAndCustomer(3, 1) = "Camembert Pierrot" ProdAndCustomer(4, 1) = "Alice Mutton" ProdAndCustomer(5, 1) = "Ipoh Coffee" ProdAndCustomer(1, 2) = "ANTON" ProdAndCustomer(2, 2) = "BERGS" ProdAndCustomer(3, 2) = "BOLID" ProdAndCustomer(4, 2) = "BOTTM" ProdAndCustomer(5, 2) = "FURIB"
Compute Number of Rows, Number of Columns using UBound and LBound function. Multiply by noOfRow and noOfCol variable to get Number of elements in multi-dimensional array.
noOfRow = UBound(ProdAndCustomer, 1) - LBound(ProdAndCustomer, 1) + 1 noOfCol = UBound(ProdAndCustomer, 2) - LBound(ProdAndCustomer, 2) + 1 noOfElements = noOfRow * noOfCol
Message box to popup result
'Message box to popup length of 1D array MsgBox "Array has " & noOfElements & " element(s)." End Sub
To Run VBA Code
Press Alt+F8 to popup macro window. Select ” twoDimArrayLength” and Click Run button.
Output:
Copy/Pasta Solution:
The most common answer is this:
UBound(myItems) - LBound(myItems) + 1
While it works +90% of the time, that other 10% fails with nasty unplanned errors when a client/user is running it. That is because there are a number of edge cases which this solution does not cover.
Generic Solution:
The solution below covers all the edge cases I have found thus far. And it eliminates all the run-time failures when a client/user is running it.
'Generic solution using Variant
Public Const SIZE_NOT_ARRAY As Long = -1
Public Const SIZE_EMPTY As Long = 0
'Return Value:
' -1 - Not an Array
' 0 - Empty
' > 0 - Defined
Public Function size( _
ByVal values As Variant _
, Optional ByVal dimensionOneBased As Long = 1 _
) As Long
Dim result As Long: result = SIZE_NOT_ARRAY 'Default to not an Array
Dim lowerBound As Long
Dim upperBound As Long
On Error GoTo NormalExit
If (IsArray(values) = True) Then
result = SIZE_EMPTY 'Move default to Empty
lowerBound = LBound(values, dimensionOneBased) 'Possibly generates error
upperBound = UBound(values, dimensionOneBased) 'Possibly generates error
If (lowerBound < upperBound) Then
result = upperBound - lowerBound + 1 'Size greater than 1
Else
If (lowerBound = upperBound) Then
result = 1 'Size equal to 1
End If
End If
End If
NormalExit:
size = result
End Function
Public Function isEmpty( _
ByVal values As Variant _
, Optional ByVal dimensionOneBased As Long = 1 _
) As Boolean
isEmpty = size(values, dimensionOneBased) = 0
End Function
Public Function isDefined( _
ByVal values As Variant _
, Optional ByVal dimensionOneBased As Long = 1 _
) As Boolean
isDefined = size(values, dimensionOneBased) > 0
End Function
Caveat:
While the above «Generic» solution works and is robust, it is not the most performant. IOW, if one knows one is working with Dim strings() As String, then a more specific solution can be many times faster.
Much Faster Solution:
The Array of String solution below is many times faster than the «Generic Solution» above. Why? Because the extra instructions (defaulting to SIZE_NOT_ARRAY, IsArray, IsEmpty, etc.) and the conversions around from Variant to Array appear to carry considerable cost. In my testing, the solution below can be over 10 times faster.
'Specifically Typed solution for String
Public Const SIZE_EMPTY As Long = 0
'Return Value:
' -1 - Not an Array
' 0 - Empty
' > 0 - Defined
Public Function size( _
ByRef r_values() As String _
, Optional ByVal dimensionOneBased As Long = 1 _
) As Long
Dim result As Long: result = SIZE_EMPTY 'Default to Empty
Dim lowerBound As Long
Dim upperBound As Long
On Error GoTo NormalExit
lowerBound = LBound(r_values, dimensionOneBased) 'Possibly generates error
upperBound = UBound(r_values, dimensionOneBased) 'Possibly generates error
If (lowerBound < upperBound) Then
result = upperBound - lowerBound + 1 'Size greater than 1
Else
If (lowerBound = upperBound) Then
result = 1 'Size equal to 1
End If
End If
NormalExit:
size = result
End Function
Public Function isEmpty( _
ByRef r_values() As String _
, Optional ByVal dimensionOneBased As Long = 1 _
) As Boolean
isEmpty = size(r_values, dimensionOneBased) = 0
End Function
Public Function isDefined( _
ByRef r_values() As String _
, Optional ByVal dimensionOneBased As Long = 1 _
) As Boolean
isDefined = size(r_values, dimensionOneBased) > 0
End Function
Return to VBA Code Examples
In this Article
- Get Array Length
- LBound and UBound Functions
- Get Array Length Function
- Get 2D Array Size
This tutorial will teach you how to get the length (size) of an Array in VBA.
Get Array Length
In order to get the length of an Array, you need to know the array’s start and end positions. You can do this with the VBA’s UBound and LBound Functions.
LBound and UBound Functions
This procedure demonstrates how to use the UBound and LBound Functions on a a single dimension array:
Sub UBoundLBound()
Dim exArr(1 To 4) As String
MsgBox UBound(exArr)
MsgBox LBound(exArr)
End SubSubtracting the two will give you the array length (UBound – LBound +1).
Get Array Length Function
This function will calculate the size (length) of a single-dimensional Array:
Public Function GetArrLength(a As Variant) As Long
If IsEmpty(a) Then
GetArrLength = 0
Else
GetArrLength = UBound(a) - LBound(a) + 1
End If
End FunctionGet 2D Array Size
This function will calculate the number of positions in a two-dimensional array:
Sub testArrySize()
Dim arr2D(1 To 4, 1 To 4) As Long
MsgBox GetArrSize_2D(arr2D)
End Sub
Public Function GetArrSize_2D(a As Variant) As Long
Dim x As Long, y As Long
If IsEmpty(a) Then
GetArrSize_2D = 0
Else
x = UBound(a, 1) - LBound(a, 1) + 1
y = UBound(a, 2) - LBound(a, 2) + 1
GetArrSize_2D = x * y
End If
End FunctionVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
Home / VBA / Arrays / VBA Array Length (Size)
In VBA, to get the length of an array means to count the number of elements you have in that array. For this, you need to know the lowest element and the highest element. So, to get this you can use the UBOUND and LBOUND functions that return the upper bound and lower bound, respectively.
Apart from that, you can also use the COUNTA which is a worksheet function. And in this tutorial, we will see both of the methods so you can use any of them at your convenience.
Steps to Get the Size of an Array
Here we have an array that contains a list of months and sales quantity for each month.

- Make sure to have an array declared properly with rows and columns.
- After that, two more variables (as we have a two-dimensional array) to store the bounds of the array.
- Next, you need to use a formula where you have to use the Ubound function to get the upper bound and then Lbound to get the lower bound of the array.
- As you have a two-dimensional array you need to get bound for both of the dimensions and set that value to the variables.
- In the end, multiply lengths that you have got from the Ubound and Lbound as upper and lower bound.
Here’s the full code.
Dim yearSales(1 To 12, 1 To 2) As Integer
Dim iCount1 As Integer, iCount2 As Integer
iCount1 = UBound(yearSales, 1) - LBound(yearSales, 1) + 1
iCount2 = UBound(yearSales, 2) - LBound(yearSales, 2) + 1
MsgBox iCount1 * iCount2Note: You must be wondering that we have a total of 13 rows in the array that I shared with you at the start of the post.
But we have used an array with 13 rows because the first row was a heading. And here we have used an IF STATEMENT and ISEMPTY function to check if the declared array has zero elements.
Dim yearSales(1 To 12, 1 To 2) As Integer
Dim iCount1 As Integer, iCount2 As Integer
If IsEmpty(yearSales) = 0 Then
MsgBox "This array has zero elements."
Else
iCount1 = UBound(yearSales, 1) - LBound(yearSales, 1) + 1
iCount2 = UBound(yearSales, 2) - LBound(yearSales, 2) + 1
MsgBox "This array has " & iCount1 * iCount2 & " element(s)."Using COUNTA to get the Length of the Array
As you know that an array is a bunch of elements that are structured in a single or multi-dimensional way and you can use the COUNTA function (worksheet function) to count these elements in one go.
In the following code, you have used the same array that you have declared earlier and then used a variable to store the element count returned by the function.

And as you can see the result it has returned is 24 that’s the count of the total number of elements that we have in the array.
Dim yearSales(1 To 12, 1 To 2) As Integer
iCount = WorksheetFunction.CountA(yearSales)
MsgBox iCountThere’s one thing that you need to take care of that this method won’t be ideal to use in all situations, so it’s always good to use the method that we have discussed earlier.
You can also write a code to check first if the declared array is not blank.
Dim yearSales(1 To 12, 1 To 2) As Integer
If IsEmpty(yearSales) = 0 Then
MsgBox "This array has zero elements."
Else
iCount = WorksheetFunction.CountA(yearSales)
MsgBox "This array has " & iCount & " element(s)."|
Здравствуйте всем. |
|
|
Так надо было? Sub test() |
|
|
R Dmitry Пользователь Сообщений: 3103 Excel,MSSQL,Oracle,Qlik |
#3 11.05.2011 22:07:35 {quote}{login=Михаил С.}{date=11.05.2011 09:54}{thema=Возможно ли определить размерность массива в VBA?}{post}Здравствуйте всем. Sub test()
|
|
|
Нет, это мы определим «длину» каждой размерности. А я хотел узнать, сколько всего этих размерностей. |
|
|
Пока сочинял для EducatedFool, появилось решение от R Dmitry. |
|
|
R Dmitry Пользователь Сообщений: 3103 Excel,MSSQL,Oracle,Qlik |
#6 11.05.2011 22:14:18 Sub test() Михаил так правильней , а то дописал код в форум не проверив
|
|
|
Не, Дим, попробовал ради интереса — ничего не выдает. |
|
|
Да, второй вариант то что надо. Спасибо! |
|
|
R Dmitry Пользователь Сообщений: 3103 Excel,MSSQL,Oracle,Qlik |
#9 11.05.2011 22:20:34 {quote}{login=Михаил С.}{date=11.05.2011 10:16}{thema=}{post}Не, Дим, попробовал ради интереса — ничего не выдает. Михаил, я исправил ошибку, у меня работает. Просто писал прямо в форум.
|
|
|
Правда чуть изменить пришлось |
|
|
Serge Пользователь Сообщений: 11308 |
{quote}{login=Михаил С.}{date=11.05.2011 10:16}{thema=}{post}Не, Дим, попробовал ради интереса — ничего не выдает. Планета становиться VB-образной |
|
kim Пользователь Сообщений: 3139 Игорь |
И это логично |
|
vikttur Пользователь Сообщений: 47199 |
Не обижать «Запорожец»! |
|
ЗапорожецЪ — моя любимая машина. Я себе в 1985 новый сделал, 965 модели («горбатый»). |
|
|
ran Пользователь Сообщений: 7091 |
{quote}{login=Михаил С.}{date=12.05.2011 12:13}{thema=}{post} |
|
слэн Пользователь Сообщений: 5192 |
вот вам мерседец Declare Function VarPtrArray Lib «msvbvm60.dll» Alias «VarPtr» (Var() As Any) As Long Sub t() msgbox «вы объявили «& p «измерений» |
|
слэн Пользователь Сообщений: 5192 |
а точнее( а главное безопаснее): Option Explicit Sub t() |
|
{quote}{login=слэн}{date=12.05.2011 03:47}{thema=}{post}а точнее( а главное безопаснее): Option Explicit Sub t() А вот как определить размерность 2-мерного массива ? |
|
|
{quote}{login=}{date=09.09.2011 06:40}{thema=Re: }{post} |
|
|
{quote}{login=Михаил С.}{date=11.05.2011 09:54}{thema=Возможно ли определить размерность массива в VBA?}{post}Здравствуйте всем. |
|
|
Bagir Пользователь Сообщений: 12 |
Ни разу не пришлось заморачиваться над определением мерности массива так сказать. Вот потребовалось. Полез искать волшебное слово, которое вернет мне количество измерений. А не тут то было. |
|
слэн Пользователь Сообщений: 5192 |
вообще-то верхняя граница может быть любой…( в том числе и отрицательной) Function RazmerArray(A) As Long Sub t() а в мерседеце просто непосредственно берется значение размерности из соответствующей структуры — без всяких циклов.. |
|
Alex_ST Пользователь Сообщений: 2746 На лицо ужасный, добрый внутри |
#23 16.01.2012 14:08:01 Private Function nDx%(Arr) ‘возвращает количество измерений массива Arr С уважением, Алексей (ИМХО: Excel-2003 — THE BEST!!!) |