Изменение размера ячейки в VBA Excel. Высота строки, ширина столбца, автоподбор ширины ячейки. Свойства RowHeight и ColumnWidth объекта Range.
Размер ячейки
Размер ячейки по высоте и ширине определяется высотой строки и шириной столбца, на пересечении которых она находится. Если, в вашем случае, нежелательно изменять размеры всей строки или всего столбца, используйте объединенные ячейки нужной величины.
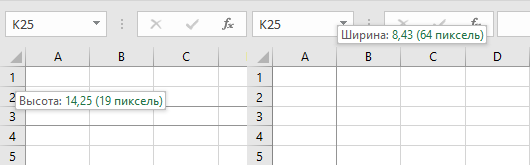
Обратите внимание, что высота строки задается в пунктах, а ширина столбца в символах, поэтому их числовые значения не соответствуют друг другу по фактическому размеру.
Высота строки и ширина столбца в Excel
Программно, без дополнительных макросов, можно изменять высоту строки только в пунктах, а ширину столбца только в символах.
На сайте поддержки офисных приложений Microsoft так написано об этих величинах:
- высота строки может принимать значение от 0 до 409 пунктов, причем 1 пункт приблизительно равен 1/72 дюйма или 0,035 см;
- ширина столбца может принимать значение от 0 до 255, причем это значение соответствует количеству символов, которые могут быть отображены в ячейке.
Смотрите, как сделать все ячейки рабочего листа квадратными.
Высота строки
Для изменения высоты строки используйте свойство RowHeight объекта Range. И не важно, будет объект Range представлять из себя выделенный произвольный диапазон, отдельную ячейку, целую строку или целый столбец — высота всех строк, пересекающихся с объектом Range будет изменена после присвоения свойству RowHeight этого объекта нового значения.
Примеры изменения высоты строк:
Пример 1
Изменение высоты отдельной ячейки:
|
ActiveCell.RowHeight = 10 |
в результате, строка, в которой находится активная ячейка, приобретает высоту, равную 10 пунктам.
Пример 2
Изменение высоты строки:
в результате, третья строка рабочего листа приобретает высоту, равную 30 пунктам.
Пример 3
Изменение высоты ячеек заданного диапазона:
|
Range(«A1:D6»).RowHeight = 20 |
в результате, каждой из первых шести строк рабочего листа будет задана высота, равная 20 пунктам.
Пример 4
Изменение высоты ячеек целого столбца:
|
Columns(5).RowHeight = 15 |
в результате, всем строкам рабочего листа будет назначена высота, равная 15 пунктам.
Ширина столбца
Для изменения ширины столбца используйте свойство ColumnWidth объекта Range. Как и в случае с высотой строки, не важно, будет объект Range представлять из себя выделенный произвольный диапазон, отдельную ячейку, целую строку или целый столбец — ширина всех столбцов, пересекающихся с объектом Range будет изменена после присвоения свойству ColumnWidth этого объекта нового значения.
Примеры изменения ширины столбцов:
Пример 1
Изменение ширины отдельной ячейки:
|
ActiveCell.ColumnWidth = 15 |
в результате, столбец, в котором находится активная ячейка, приобретает ширину, равную 15 символам.
Пример 2
Изменение ширины столбца:
|
Columns(3).ColumnWidth = 50 |
в результате, третий столбец рабочего листа (столбец «C») приобретает ширину, равную 50 символам.
Пример 3
Изменение ширины ячеек заданного диапазона:
|
Range(«A1:D6»).ColumnWidth = 25 |
в результате, каждому из первых четырех столбцов рабочего листа будет задана ширина, равная 25 символам.
Пример 4
Изменение ширины ячеек целой строки:
в результате, всем столбцам рабочего листа будет назначена ширина, равная 35 символам.
Автоподбор ширины
Для автоподбора ширины ячейки в соответствие с размером ее содержимого используйте следующий код:
|
‘запишем для примера в любую ячейку рабочего ‘листа какой-нибудь текст, например, такой: Cells(5, 5) = «Автоподбор ширины ячейки» ‘теперь подгоним ширину ячейки, а точнее ‘столбца, в котором эта ячейка находится: Cells(5, 5).EntireColumn.AutoFit |
Имейте в виду, что ширина столбца будет подогнана по расположенной в этом столбце ячейке с самым длинным содержимым. Например, если длина содержимого ячейки Cells(7, 5) будет превышать длину содержимого ячейки Cells(5, 5), то автоподбор ширины пятого столбца произойдет по содержимому ячейки Cells(7, 5), несмотря на то, что в строке кода указана другая ячейка.
Как осуществить автоподбор ширины объединенной ячейки, в которой метод AutoFit не работает, смотрите в следующей статье.
|
Trambulanga Пользователь Сообщений: 20 |
#1 18.02.2023 10:39:18 Доброго дня.
Изменено: Trambulanga — 18.02.2023 11:19:04 |
||
|
Artem1977 Пользователь Сообщений: 163 |
#2 18.02.2023 12:07:18 Trambulanga, например для представленных строк так:
Изменено: Artem1977 — 18.02.2023 12:17:33 Microsoft Office 2010 64-bit, Windows 10 Professional 64-bit |
||
|
Настя_Nastya Пользователь Сообщений: 801 |
#3 18.02.2023 12:12:10 или так
|
||
|
Ігор Гончаренко Пользователь Сообщений: 13746 |
#4 18.02.2023 12:22:13
Программисты — это люди, решающие проблемы, о существовании которых Вы не подозревали, методами, которых Вы не понимаете! |
||
|
БМВ Модератор Сообщений: 21378 Excel 2013, 2016 |
#5 18.02.2023 13:25:12 в коллекцию
По вопросам из тем форума, личку не читаю. |
||
|
Всем большое спасибо за помощь! О таком количестве методов я и не подозревал))) |
|
|
Msi2102 Пользователь Сообщений: 3137 |
#7 18.02.2023 18:47:49
Вот ещё парочка, мне кажется это можно продолжать бесконечно
Изменено: Msi2102 — 18.02.2023 19:29:31 |
||||||
|
Апострофф Пользователь Сообщений: 720 |
#8 18.02.2023 20:37:25
|
||
|
nilske Пользователь Сообщений: 354 |
Апострофф, супер! Изменено: nilske — 18.02.2023 21:21:15 |
|
Апострофф Пользователь Сообщений: 720 |
nilske, если удосужитесь ручками набрать «20 13 5 10 15», угадайте, что будет вместо 3) |
|
БМВ Модератор Сообщений: 21378 Excel 2013, 2016 |
Апострофф, В чем смысл использовать Split(«20 13 5») вместо Array(20,13,5), та и тот я б вынес за цикл. По вопросам из тем форума, личку не читаю. |
|
Апострофф Пользователь Сообщений: 720 |
#12 19.02.2023 10:04:05 БМВ, ARRAY будет быстрее, но вынудит следить за его Bound`ами.
Изменено: Апострофф — 19.02.2023 10:28:06 |
||
|
Trambulanga Пользователь Сообщений: 20 |
#13 19.02.2023 16:23:34 Ну и в догонку тогда, да простят меня админы, если нужно было создать отдельную тему, но вопрос то капец близкий))
Но либо для меня не подходит, либо я не туда это прописываю… |
||
|
Ігор Гончаренко Пользователь Сообщений: 13746 |
#14 19.02.2023 16:31:21
начиная с какой? Программисты — это люди, решающие проблемы, о существовании которых Вы не подозревали, методами, которых Вы не понимаете! |
||
|
5, 14, 23, 32 строки. Остальные не нужны |
|
|
Ігор Гончаренко Пользователь Сообщений: 13746 |
#16 19.02.2023 17:31:38
каждая 4-я, говорите)) Программисты — это люди, решающие проблемы, о существовании которых Вы не подозревали, методами, которых Вы не понимаете! |
||||
|
Ну да, тупанул( упустил одну пустую строку в таблице, и посчитал, что в каждой таблице это будет 4-ая. Прошу прощения. Ну собственно да, именно те строки, что я указал выше… |
|
|
Ігор Гончаренко Пользователь Сообщений: 13746 |
#18 19.02.2023 17:58:34
Программисты — это люди, решающие проблемы, о существовании которых Вы не подозревали, методами, которых Вы не понимаете! |
||
|
Trambulanga Пользователь Сообщений: 20 |
#19 19.02.2023 18:16:01 Ігор Гончаренко, Благодарю за помощь! |
You can use the following methods to change the width of columns in Excel using VBA:
Method 1: Change Width of One Column
Sub ChangeColumnWidth()
Columns("B").ColumnWidth = 20
End Sub
This particular macro changes the width of column B to 20.
Note: The default width of columns in Excel is 8.29.
Method 2: Change Width of Multiple Columns
Sub ChangeColumnWidth()
Columns("B:D").ColumnWidth = 20
End Sub
This particular macro changes the width of all columns in the range from B to D to 20.
Method 3: Auto Adjust Width of Multiple Columns
Sub ChangeColumnWidth()
Columns("B:D").AutoFit
End Sub
This particular macro automatically adjusts the width of each column in the range from B to D to be as wide as necessary to display the longest cell in each column.
The following examples show how to use each of these methods in practice with the following dataset in Excel:
Example 1: Change Width of One Column
We can create the following macro to change the width of column B to 20:
Sub ChangeColumnWidth()
Columns("B").ColumnWidth = 20
End Sub
When we run this macro, we receive the following output:
Notice that only the width of column B (the “Points” column) has increased to 20 while the width of all other columns remained the same.
Example 2: Change Width of Multiple Columns
We can create the following macro to change the width of columns B through D to 20:
Sub ChangeColumnWidth()
Columns("B:D").ColumnWidth = 20
End Sub
When we run this macro, we receive the following output:
Notice that the width of each column from B to D has increased to 20 while the width of column A remained the same.
Example 3: Auto Adjust Width of Multiple Columns
We can create the following macro to automatically adjust the width of each column from A to D to be as wide as necessary to display the longest cell in each column.
Sub ChangeColumnWidth()
Columns("A:D").AutoFit
End Sub
When we run this macro, we receive the following output:
Notice that the width of each column has automatically been adjusted to be as wide as necessary to display the longest cell in each column.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in VBA:
VBA: How to Count Number of Used Columns
VBA: How to Find Last Used Column
VBA: How to Delete Columns

This VBA Tutorial is accompanied by Excel workbooks containing the data and macros I use in the examples below. You can get immediate free access to these example workbooks by subscribing to the Power Spreadsheets Newsletter.
Use the following Table of Contents to navigate to the section you’re interested in.
Related VBA and Macro Tutorials
The following VBA and Macro Tutorials may help you better understand and implement the contents below:
- General VBA constructs and structures:
- Learn about using variables here.
- Learn about VBA data types here.
- Learn about R1C1 and A1 style references here.
- Practical VBA applications and macro examples:
- Learn how to work with worksheets here.
- Learn how to delete columns here.
- Learn how to hide or unhide rows and columns here.
You can find additional VBA and Macro Tutorials in the Archives.
#1: Set Column Width
VBA Code to Set Column Width
To set the width of a column with VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Worksheet.Range("A1CellReference").ColumnWidth = ColumnWidthUnits
Process Followed by VBA Code

VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Worksheet.
- VBA Construct: Workbook.Worksheets property.
- Description: Returns a Worksheet object representing the worksheet you work with.
- Item: Range(“A1CellReference”).
- VBA Construct: Worksheet.Range property.
- Description: Returns a Range object representing a cell within the column whose width you set. You specify the cell using an A1-style cell reference (A1CellReference) enclosed within quotations (“”).
- Item: ColumnWidth.
- VBA Construct: Range.ColumnWidth property.
- Description: Sets the width of the column containing the Range object returned by item #2 above.
- Item: ColumnWidthUnits.
- VBA Construct: New value of the Range.ColumnWidth property.
- Description: Specifies the width, in units, of the column containing the Range object returned by item #2 above.
- Column width isn’t measured in points, centimeters or inches. Excel measures column width units based on the size (width) of the font you use in the Normal style (for example, Calibri 11).
- Therefore, 1 unit of column width is equal to 1 character of the Normal style font. Consider the following:
- If your Normal style font is a fixed-width font, such as Courier New or Consolas, all characters have the same width.
- If your Normal style font is a proportional font, Excel considers the width of the character “0” (the number zero).
- If you explicitly declare a variable to represent ColumnWidthUnits, use a numeric data type that can handle the value you use to specify the column width in the appropriate units.
Macro Example
The following macro sets the width of column A of the worksheet named “Column width” to 15 units.
Sub columnWidth()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-column-width/
Worksheets("Column width").Range("A5").columnWidth = 15
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, VBA sets the width of column A to 15 units.
#2: Set Column Width for Multiple Contiguous Columns
VBA Code to Set Column Width for Multiple Contiguous Columns
To set the width of multiple contiguous columns with VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Worksheet.Range("FirstColumnLetter:LastColumnLetter").ColumnWidth = ColumnWidthUnits
Process Followed by VBA Code

VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Worksheet.
- VBA Construct: Workbook.Worksheets property.
- Description: Returns a Worksheet object representing the worksheet you work with.
- Item: Range(“FirstColumnLetter:LastColumnLetter”).
- VBA Construct: Worksheet.Range property.
- Description: Returns a Range object representing the columns whose width you set. Under this syntax:
- You identify columns by the letters of their headers (FirstColumnLetter and LastColumnLetter).
- The column letters are:
- Separated by a colon (:), which allows you to set up an array.
- Enclosed within quotations (“”).
- Item: ColumnWidth.
- VBA Construct: Range.ColumnWidth property.
- Description: Sets the width of the columns returned by item #2 above.
- Item: ColumnWidthUnits.
- VBA Construct: New value of the Range.ColumnWidth property.
- Description: Specifies the width, in units, of the columns returned by item #2 above.
- Column width isn’t measured in points, centimeters or inches. Excel measures column width units based on the size (width) of the font you use in the Normal style (for example, Calibri 11).
- Therefore, 1 unit of column width is equal to 1 character of the Normal style font. Consider the following:
- If your Normal style font is a fixed-width font, such as Courier New or Consolas, all characters have the same width.
- If your Normal style font is a proportional font, Excel considers the width of the character “0” (the number zero).
- If you explicitly declare a variable to represent ColumnWidthUnits, use a numeric data type that can handle the value you use to specify the column width in the appropriate units.
Macro Example
The following macro sets the width of columns C through E (C, D and E) of the worksheet named “Column width” to 10 units.
Sub columnWidthMultipleColumns()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-column-width/
Worksheets("Column width").Range("C:E").columnWidth = 10
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, VBA sets the width of columns C through E to 10 units.
#3: Set Column Width for Multiple Non-Contiguous Columns
VBA Code to Set Column Width for Multiple Non-Contiguous Columns
To set the width of multiple non-contiguous columns with VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Worksheet.Range("Column1Area1Letter:ColumnLastArea1Letter,Column1Area2Letter:ColumnLastArea2Letter, ... , Column1AreaLastLetter:ColumnLastAreaLastLetter").ColumnWidth = ColumnWidthUnits
Process Followed by VBA Code

VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Worksheet.
- VBA Construct: Workbook.Worksheets property.
- Description: Returns a Worksheet object representing the worksheet you work with.
- Item: Range(“Column1Area1Letter:ColumnLastArea1Letter,Column1Area2Letter:ColumnLastArea2Letter, … , Column1AreaLastLetter:ColumnLastAreaLastLetter”).
- VBA Construct: Worksheet.Range property.
- Description: Returns a Range object representing the columns whose width you set. Under this syntax:
- You identify columns by the letters of their headers (Column1Area1Letter, ColumnLastArea1Letter, Column1Area2Letter, ColumnLastArea2Letter, … , Column1AreaLastLetter and ColumnLastAreaLastLetter”).
- The column letters identifying contiguous columns (within the same data area) are separated by a colon (:), which allows you to set up an array. If you’re only referring to a single column (for example, column B), include the letter reference twice and separate them with a colon (:) (for example “B:B”).
- The column letters identifying non-contiguous columns (in separate data areas) are separated by the union operator, a comma (,).
- The complete column reference is enclosed within quotations (“”).
- Item: ColumnWidth.
- VBA Construct: Range.ColumnWidth property.
- Description: Sets the width of the columns returned by item #2 above.
- Item: ColumnWidthUnits.
- VBA Construct: New value of the Range.ColumnWidth property.
- Description: Specifies the width, in units, of the columns returned by item #2 above.
- Column width isn’t measured in points, centimeters or inches. Excel measures column width units based on the size (width) of the font you use in the Normal style (for example, Calibri 11).
- Therefore, 1 unit of column width is equal to 1 character of the Normal style font. Consider the following:
- If your Normal style font is a fixed-width font, such as Courier New or Consolas, all characters have the same width.
- If your Normal style font is a proportional font, Excel considers the width of the character “0” (the number zero).
- If you explicitly declare a variable to represent ColumnWidthUnits, use a numeric data type that can handle the value you use to specify the column width in the appropriate units.
Macro Example
The following macro sets the width of columns B, F and H of the worksheet named “Column width” to 20 units.
Sub columnWidthMultipleNonAdjacentColumns()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-column-width/
Worksheets("Column width").Range("B:B,F:F,H:H").columnWidth = 20
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, VBA sets the width of columns B, F and H to 20 units.
#4: AutoFit Column Width Based on Entire Column
VBA Code to AutoFit Column Width Based on Entire Column
To autofit the width of a column with VBA, considering the contents of the entire column, use a statement with the following structure:
Worksheet.Range("A1CellReference").EntireColumn.AutoFit
Process Followed by VBA Code

VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Worksheet.
- VBA Construct: Workbook.Worksheets property.
- Description: Returns a Worksheet object representing the worksheet you work with.
- Item: Range(“A1CellReference”).
- VBA Construct: Worksheet.Range property.
- Description: Returns a Range object representing a cell within the column you autofit. You specify the cell using an A1-style cell reference (A1CellReference) enclosed within quotations (“”).
- Item: EntireColumn.
- VBA Construct: Range.EntireColumn property.
- Description: Returns a Range object representing the entire column containing the Range object returned by item #2 above.
- Item: AutoFit.
- VBA Construct: Range.AutoFit method.
- Description: Modifies the width of the column represented by the Range object returned by item #3 above to achieve the best fit (autofits).
Macro Example
The following macro autofits the width of column G of the worksheet named “Column width” based on the contents of all the cells in the entire column.
Sub columnWidthAutoFitEntireColumn()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-column-width/
Worksheets("Column width").Range("G5").EntireColumn.AutoFit
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, VBA autofits the width of column G based on the contents of all the cells in the entire column. Notice the contents in cell G10 (Autofit based on entire column), which are used as the basis for the autofitting operation.
#5: AutoFit Column Width Based on Specific Cell
VBA Code to AutoFit Column Width Based on Specific Cell
To autofit the width of a column with VBA, considering the contents of a specific cell or row, use a statement with the following structure:
Worksheet.Range("A1CellReference").Columns.AutoFit
Process Followed by VBA Code

VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Worksheet.
- VBA Construct: Workbook.Worksheets property.
- Description: Returns a Worksheet object representing the worksheet you work with.
- Item: Range(“A1CellReference”).
- VBA Construct: Worksheet.Range property.
- Description: Returns a Range object representing a cell.
- This cell:
- Is within the column you autofit.
- Is the cell whose contents Excel considers for purposes of achieving the best fit (autofitting).
- You specify the cell using an A1-style cell reference (A1CellReference) enclosed within quotations (“”).
- This cell:
- Item: Columns.
- VBA Construct: Range.Columns property.
- Description: Returns a Range object representing the column containing the Range object returned by item #2 above.
- Item: AutoFit.
- VBA Construct: Range.AutoFit method.
- Description: Modifies the width of the column represented by the Range object returned by item #3 above to achieve the best fit (autofits) based on the contents within the cell represented by the Range object returned by item #2 above.
Macro Example
The following macro autofits the width of column I of the worksheet named “Column width” based on the contents of cell I5.
Sub columnWidthAutoFitRow()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-column-width/
Worksheets("Column width").Range("I5").Columns.AutoFit
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, VBA sets autofits the width of column I based on the contents of cell I5. Notice the contents in cell I10 (Autofit based on specific cell), which aren’t used as the basis for the autofitting operation.
#6: Set Column Width in Points
VBA Code to Set Column Width in Points
To set the width of a column in points with VBA, use a macro with the following statement structure:
With Worksheet.Range("A1CellReference")
For Counter = 1 To 3
.ColumnWidth = ColumnWidthPoints * (.ColumnWidth / .Width)
Next Counter
End With
Process Followed by VBA Code

VBA Statement Explanation
Lines #1 and #5: With Worksheet.Range(“A1CellReference”) | End With
- Item: With… End With.
- VBA Construct: With… End With statement.
- Description: Statements within the With… End With statement (lines # through #4 below) are executed on the Range object returned by item #3 below.
- Item: Worksheet.
- VBA Construct: Workbook.Worksheets property.
- Description: Returns a Worksheet object representing the worksheet you work with.
- Item: Range(“A1CellReference”).
- VBA Construct: Worksheet.Range property.
- Description: Returns a Range object representing a cell within the column whose width you set. You specify the cell using an A1-style cell reference (A1CellReference) enclosed within quotations (“”).
Lines #2 and #4: For Counter = 1 To 3 | Next Counter
- Item: For… Next Counter.
- VBA Construct: For… Next statement.
- Description: Repeats the statement within the loop (line #3 below) 3 times, as required by item #3 below.
- Item: Counter.
- VBA Construct: Counter of For… Next statement.
- Description: Loop counter. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent the loop counter, use the Long data type.
- Item: 1 To 3.
- VBA Construct: Counter Start (1) and Counter End (3) of For… Next statement.
- Description: The statement within the loop (line #3 below) is executed 3 times (1 To 3).
- Theoretically, line #3 below should be enough to set the column width in points without requiring the loop specified by these lines #2 and #4. In practice, this may not be the case. Some tests suggest that repeating line #3 below (or similar) 3 times generally gets you the closest to the specified column width.
Line #3: .ColumnWidth = ColumnWidthPoints * (.ColumnWidth / .Width)
- Item: .ColumnWidth.
- VBA Construct: Range.ColumnWidth property.
- Description:
- Sets the width of the column containing the Range object within the opening statement of the With… End With block (line #1, item #3 above).
- .ColumnWidth is included twice in the statement. In this first mention, (.ColumnWidth = …), ColumnWidth is the property to which a value is assigned. The value assigned to the ColumnWidth property is the value returned by the other items within this statement.
- Item: ColumnWidthPoints.
- VBA Construct: Numeric (for example, Double) variable.
- Description: Specifies the width (in points) of the columns containing the Range object within the opening statement of the With… End With block (line #1, item #3 above).
- If you explicitly declare a variable to represent ColumnWidthPoints, use a numeric data type that can handle the value you use to specify the column width in points.
- Item: .ColumnWidth.
- VBA Construct: Range.ColumnWidth property.
- Description:
- Returns the width of the column containing the Range object within the opening statement of the With… End With block (line #1, item #3 above).
- .ColumnWidth is included twice in the statement. In this second mention, (.ColumnWidth), ColumnWidth returns the current value of the property.
- The ColumnWidth property returns the column width in units based on the size (width) of the font you use in the Normal style (for example, Calibri 11). Therefore, 1 unit of column width is equal to 1 character of the Normal style font. If your Normal style font is a proportional (not fixed-width) font, Excel considers the width of the character “0” (the number zero).
- Item: .Width.
- VBA Construct: Range.Width property.
- Description:
- Returns the width of the column containing the Range object within the opening statement of the With… End With block (line #1, item #3 above).
- The Width property returns the column width in points.
- Item: (.ColumnWidth / .Width).
- VBA Construct: Numeric expression.
- Description:
- Both ColumnWidth (item #3 above) and Width (item #4 above) return the width of the column containing the Range object within the opening statement of the With… End With block (line #1, item #3 above).
- The units in which ColumnWidth and Width return the column width differ.
- ColumnWidth expresses the column width in units based on the size (width) of the font you use in the Normal style.
- Width expresses the column width in points.
- ColumnWidth divided by Width (.ColumnWidth / .Width) returns the factor by which you must multiply the desired column width expressed in points (item #2 above) to obtain the appropriate column width in units based on the size (width) of the font you use in the Normal style. In other words, this expression converts ColumnWidthPoints from points to the units required by the ColumnWidth property.
Macro Example
The following macro sets the width of column J of the worksheet named “Column width” to 80 points.
Sub columnWidthPoints()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-column-width/
Dim iCounter As Long
With Worksheets("Column width").Range("J5")
For iCounter = 1 To 3
.columnWidth = 80 * (.columnWidth / .Width)
Next iCounter
End With
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, VBA sets the width of column J to 80 points.
#7: Set Column Width in Inches
VBA Code to Set Column Width in Inches
To set the width of a column in inches with VBA, use a macro with the following statement structure:
With Worksheet.Range("A1CellReference")
For Counter = 1 To 3
.ColumnWidth = Application.InchesToPoints(ColumnWidthInches) * (.ColumnWidth / .Width)
Next Counter
End With
Process Followed by VBA Code

VBA Statement Explanation
Lines #1 and #5: With Worksheet.Range(“A1CellReference”) | End With
- Item: With… End With.
- VBA Construct: With… End With statement.
- Description: Statements within the With… End With statement (lines # through #4 below) are executed on the Range object returned by item #3 below.
- Item: Worksheet.
- VBA Construct: Workbook.Worksheets property.
- Description: Returns a Worksheet object representing the worksheet you work with.
- Item: Range(“A1CellReference”).
- VBA Construct: Worksheet.Range property.
- Description: Returns a Range object representing a cell within the column whose width you set. You specify the cell using an A1-style cell reference (A1CellReference) enclosed within quotations (“”).
Lines #2 and #4: For Counter = 1 To 3 | Next Counter
- Item: For… Next Counter.
- VBA Construct: For… Next statement.
- Description: Repeats the statement within the loop (line #3 below) 3 times, as required by item #3 below.
- Item: Counter.
- VBA Construct: Counter of For… Next statement.
- Description: Loop counter. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent the loop counter, use the Long data type.
- Item: 1 To 3.
- VBA Construct: Counter Start (1) and Counter End (3) of For… Next statement.
- Description: The statement within the loop (line #3 below) is executed 3 times (1 To 3).
- Theoretically, line #3 below should be enough to set the column width in inches without requiring the loop specified by these lines #2 and #4. In practice, this may not be the case. Some tests suggest that repeating line #3 below (or similar) 3 times generally gets you the closest to the specified column width.
Line #3: .ColumnWidth = Application.InchesToPoints(ColumnWidthInches) * (.ColumnWidth / .Width)
- Item: .ColumnWidth.
- VBA Construct: Range.ColumnWidth property.
- Description:
- Sets the width of the column containing the Range object within the opening statement of the With… End With block (line #1, item #3 above).
- .ColumnWidth is included twice in the statement. In this first mention, (.ColumnWidth = …), ColumnWidth is the property to which a value is assigned. The value assigned to the ColumnWidth property is the value returned by the other items within this statement.
- Item: Application.InchesToPoints.
- VBA Construct: Application.InchesToPoints method.
- Description: Converts the measurement specified by item #3 below from inches to points.
- Item: ColumnWidthInches.
- VBA Construct: Inches parameter of Application.InchesToPoints method.
- Description: Specifies the width (in inches) of the columns containing the Range object within the opening statement of the With… End With block (line #1, item #3 above).
- If you explicitly declare a variable to represent ColumnWidthInches, use a numeric data type that can handle the value you use to specify the column width in inches.
- Item: .ColumnWidth.
- VBA Construct: Range.ColumnWidth property.
- Description:
- Returns the width of the column containing the Range object within the opening statement of the With… End With block (line #1, item #3 above).
- .ColumnWidth is included twice in the statement. In this second mention, (.ColumnWidth), ColumnWidth returns the current value of the property.
- The ColumnWidth property returns the column width in units based on the size (width) of the font you use in the Normal style (for example, Calibri 11). Therefore, 1 unit of column width is equal to 1 character of the Normal style font. If your Normal style font is a proportional (not fixed-width) font, Excel considers the width of the character “0” (the number zero).
- Item: .Width.
- VBA Construct: Range.Width property.
- Description:
- Returns the width of the column containing the Range object within the opening statement of the With… End With block (line #1, item #3 above).
- The Width property returns the column width in points.
- Item: (.ColumnWidth / .Width).
- VBA Construct: Numeric expression.
- Description:
- Both ColumnWidth (item #4 above) and Width (item #5 above) return the width of the column containing the Range object within the opening statement of the With… End With block (line #1, item #3 above).
- The units in which ColumnWidth and Width return the column width differ.
- ColumnWidth expresses the column width in units based on the size (width) of the font you use in the Normal style.
- Width expresses the column width in points.
- ColumnWidth divided by Width (.ColumnWidth / .Width) returns the factor by which you must multiply the desired column width expressed in inches/points (items #2 and #3 above) to obtain the appropriate column width in units based on the size (width) of the font you use in the Normal style. In other words, this expression converts Application.InchesToPoints(ColumnWidthInches) from points to the units required by the ColumnWidth property.
Macro Example
The following macro sets the width of column K of the worksheet named “Column width” to 1 inch.
Sub columnWidthInches()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-column-width/
Dim iCounter As Long
With Worksheets("Column width").Range("K5")
For iCounter = 1 To 3
.columnWidth = Application.InchesToPoints(1) * (.columnWidth / .Width)
Next iCounter
End With
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, VBA sets the width of column K to 1 inch.
#8: Set Column Width in Centimeters
VBA Code to Set Column Width in Centimeters
To set the width of a column in centimeters with VBA, use a macro with the following statement structure:
With Worksheet.Range("A1CellReference")
For Counter = 1 To 3
.ColumnWidth = Application.CentimetersToPoints(ColumnWidthCentimeters) * (.ColumnWidth / .Width)
Next Counter
End With
Process Followed by VBA Code

VBA Statement Explanation
Lines #1 and #5: With Worksheet.Range(“A1CellReference”) | End With
- Item: With… End With.
- VBA Construct: With… End With statement.
- Description: Statements within the With… End With statement (lines # through #4 below) are executed on the Range object returned by item #3 below.
- Item: Worksheet.
- VBA Construct: Workbook.Worksheets property.
- Description: Returns a Worksheet object representing the worksheet you work with.
- Item: Range(“A1CellReference”).
- VBA Construct: Worksheet.Range property.
- Description: Returns a Range object representing a cell within the column whose width you set. You specify the cell using an A1-style cell reference (A1CellReference) enclosed within quotations (“”).
Lines #2 and #4: For Counter = 1 To 3 | Next Counter
- Item: For… Next Counter.
- VBA Construct: For… Next statement.
- Description: Repeats the statement within the loop (line #3 below) 3 times, as required by item #3 below.
- Item: Counter.
- VBA Construct: Counter of For… Next statement.
- Description: Loop counter. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent the loop counter, use the Long data type.
- Item: 1 To 3.
- VBA Construct: Counter Start (1) and Counter End (3) of For… Next statement.
- Description: The statement within the loop (line #3 below) is executed 3 times (1 To 3).
- Theoretically, line #3 below should be enough to set the column width in centimeters without requiring the loop specified by these lines #2 and #4. In practice, this may not be the case. Some tests suggest that repeating line #3 below (or similar) 3 times generally gets you the closest to the specified column width.
Line #3: .ColumnWidth = Application.CentimetersToPoints(ColumnWidthCentimeters) * (.ColumnWidth / .Width)
- Item: .ColumnWidth.
- VBA Construct: Range.ColumnWidth property.
- Description:
- Sets the width of the column containing the Range object within the opening statement of the With… End With block (line #1, item #3 above).
- .ColumnWidth is included twice in the statement. In this first mention, (.ColumnWidth = …), ColumnWidth is the property to which a value is assigned. The value assigned to the ColumnWidth property is the value returned by the other items within this statement.
- Item: Application.CentimetersToPoints.
- VBA Construct: Application.CentimetersToPoints method.
- Description: Converts the measurement specified by item #3 below from centimeters to points.
- Item: ColumnWidthCentimeters.
- VBA Construct: Centimeters parameter of Application.CentimetersToPoints method.
- Description: Specifies the width (in centimeters) of the columns containing the Range object within the opening statement of the With… End With block (line #1, item #3 above).
- If you explicitly declare a variable to represent ColumnWidthCentimeters, use a numeric data type that can handle the value you use to specify the column width in centimeters.
- Item: .ColumnWidth.
- VBA Construct: Range.ColumnWidth property.
- Description:
- Returns the width of the column containing the Range object within the opening statement of the With… End With block (line #1, item #3 above).
- .ColumnWidth is included twice in the statement. In this second mention, (.ColumnWidth), ColumnWidth returns the current value of the property.
- The ColumnWidth property returns the column width in units based on the size (width) of the font you use in the Normal style (for example, Calibri 11). Therefore, 1 unit of column width is equal to 1 character of the Normal style font. If your Normal style font is a proportional (not fixed-width) font, Excel considers the width of the character “0” (the number zero).
- Item: .Width.
- VBA Construct: Range.Width property.
- Description:
- Returns the width of the column containing the Range object within the opening statement of the With… End With block (line #1, item #3 above).
- The Width property returns the column width in points.
- Item: (.ColumnWidth / .Width).
- VBA Construct: Numeric expression.
- Description:
- Both ColumnWidth (item #4 above) and Width (item #5 above) return the width of the column containing the Range object within the opening statement of the With… End With block (line #1, item #3 above).
- The units in which ColumnWidth and Width return the column width differ.
- ColumnWidth expresses the column width in units based on the size (width) of the font you use in the Normal style.
- Width expresses the column width in points.
- ColumnWidth divided by Width (.ColumnWidth / .Width) returns the factor by which you must multiply the desired column width expressed in centimeters/points (items #2 and #3 above) to obtain the appropriate column width in units based on the size (width) of the font you use in the Normal style. In other words, this expression converts Application.CentimetersToPoints(ColumnWidthCentimeters) from points to the units required by the ColumnWidth property.
Macro Example
The following macro sets the width of column L of the worksheet named “Column width” to 1 centimeter.
Sub columnWidthCentimeters()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-column-width/
Dim iCounter As Long
With Worksheets("Column width").Range("L5")
For iCounter = 1 To 3
.columnWidth = Application.CentimetersToPoints(1) * (.columnWidth / .Width)
Next iCounter
End With
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, VBA sets the width of column L to 1 centimeter.
Change Row Height and Column Width using Excel VBA
Description:
Some times we may enter the data into cells more than it’s width. In this case we can not able to see entire text. So we can change row height and Column width using excel using VBA. So that we can see entire data in that cell. When you have more lengthy data in cells, you can Auto Adjust Column Width or Row Height in Excel VBA to show the entire data. So that users can see the entire data in the cells. We will see with Examples.
Changing Row Height in Excel VBA
We can change row height in Excel using RowHeight Property of a Row in VBA. See the following example to do it.
Examples
The following example will change the height of the 3rd Row to 25.
Sub sbChangeRowHeight() 'Changing the 3rd row Height Rows(3).RowHeight = 25 End Sub
We can also set the height for multiple rows, the following example will change the height of the 3rd to 20th row height to 25.
Sub sbChangeRowHeightMulti()
'Changing the 3rd-25the row Height
Rows("3:25").RowHeight = 25
End Sub
Instructions:
- Open an excel workbook
- Press Alt+F11 to open VBA Editor
- Insert a Module for Insert Menu
- Copy the above code and Paste in the code window
- Save the file as macro enabled workbook
- Press F5 to execute itit
Changing Column Width in Excel VBA
We can change column width in Excel using ColumnWidth Property of a Column in VBA. See the following example to do it.
In this Example I am changing the Column B width to 25.
Sub sbChangeColumnWidth()
Columns("B").ColumnWidth = 25
End Sub
Examples
We can also set the column width for multiple columns at a time, see this Example I am changing the Column B to E width to 25.
Sub sbChangeColumnWidthMulti()
Columns("B:E").ColumnWidth = 25
End Sub
Instructions:
- Open an excel workbook
- Press Alt+F11 to open VBA Editor
- Insert a Module for Insert Menu
- Copy the above code and Paste in the code window
- Save the file as macro enabled workbook
- Press F5 to execute it
Auto Adjust Column Width and Row Height using Excel VBA
We can use AutoFit method of Columns and Rows in Excel using VBA to Auto Adjust the rows and Columns.
Examples
Code to Auto Adjust Column Width
Following are the example to show you how to do this.
Sub sbAutoAdjustColumnWidth()
Columns(2).AutoFit
End Sub
Code to Auto fit Row Height
Following are the example to show you how to do this.
Sub sbAutoAdjustRowHight() Rows(2).AutoFit End Sub
Instructions:
Follow the instructions below to test the codes above.
- Open an excel workbook
- Press Alt+F11 to open VBA Editor
- Insert a Module for Insert Menu
- Copy the above code and Paste in the code window
- Save the file as macro enabled workbook
- Press F5 to execute it
A Powerful & Multi-purpose Templates for project management. Now seamlessly manage your projects, tasks, meetings, presentations, teams, customers, stakeholders and time. This page describes all the amazing new features and options that come with our premium templates.
Save Up to 85% LIMITED TIME OFFER

All-in-One Pack
120+ Project Management Templates
Essential Pack
50+ Project Management Templates
Excel Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
PowerPoint Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
MS Word Pack
25+ Word PM Templates
Ultimate Project Management Template
Ultimate Resource Management Template
Project Portfolio Management Templates
Related Posts
-
- Description:
- Changing Row Height in Excel VBA
- Examples
- Changing Column Width in Excel VBA
- Examples
- Auto Adjust Column Width and Row Height using Excel VBA
- Examples
VBA Reference
Effortlessly
Manage Your Projects
120+ Project Management Templates
Seamlessly manage your projects with our powerful & multi-purpose templates for project management.
120+ PM Templates Includes:
4 Comments
-
Koert penne
March 29, 2016 at 2:35 PM — ReplyI wanted the row height for content of one column, regardsless what was in the other columns. I did it as follows:
Sub rowheight_one_column()
Column = InputBox(“Hoeveelste kolom?”) + 0
Rows(20).Delete
For x = 4 To 13
Cells(20, Column) = Cells(x, Column)
Rows(20).AutoFit
hoogte = Cells(20, Column).RowHeight
Rows(x).RowHeight = hoogte
Next xRows(20).Delete
End Sub
-
Sathish
October 26, 2016 at 11:39 AM — ReplyPlease help me for auto fit the entire sheet1
-
Jack
February 21, 2017 at 7:43 PM — Replywhere have you declared your Variables, It does confuse people when your code is not neat and is exposed on the Internet where everybody does search and get stuck.
-
dskar
April 13, 2017 at 7:10 AM — Replythe difference between writing the code in code window and a module?
Effectively Manage Your
Projects and Resources
ANALYSISTABS.COM provides free and premium project management tools, templates and dashboards for effectively managing the projects and analyzing the data.
We’re a crew of professionals expertise in Excel VBA, Business Analysis, Project Management. We’re Sharing our map to Project success with innovative tools, templates, tutorials and tips.
Project Management
Excel VBA
Download Free Excel 2007, 2010, 2013 Add-in for Creating Innovative Dashboards, Tools for Data Mining, Analysis, Visualization. Learn VBA for MS Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Access, Outlook to develop applications for retail, insurance, banking, finance, telecom, healthcare domains.
Page load link

3 Realtime VBA Projects
with Source Code!
Go to Top