Return to VBA Code Examples
In this Article
- IF…AND
- IF…OR
- IF NOT…
This article will demonstrate how to use the VBA If statement with And, Or and Not.
When we us an IF statement in Excel VBA, the statement will execute a line of code if the condition you are testing is true.
- We can use AND statement and OR statements in conjunction with IF statements to test for more than one condition and direct the code accordingly.
- We can also use a NOT statement with an IF statement to check if the condition is NOT true – it basically is the inverse of the IF statement when used alone.
IF…AND
We can use the IF…AND combination of logical operators when we wish to test for more than one condition where all the conditions need to be true for the next line of code to execute.
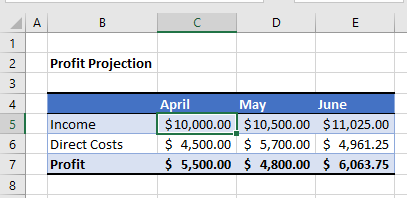
For example, consider the following sheet:
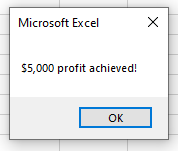
To check if the Profit is over $5,000, we can run the following macro:
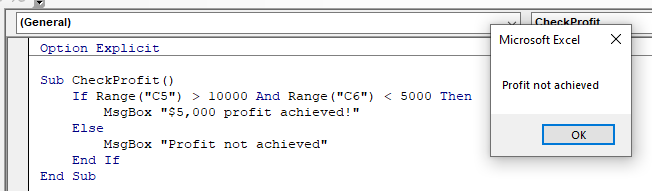
Sub CheckProfit()
If Range("C5") >= 10000 And Range("C6") < 5000 Then
MsgBox "$5,000 profit achieved!"
Else
Msgbox "Profit not achieved!"
End If
End SubThis macro will check that the cell C5 is greater or equal to $10,000 AND check that the cell B6 is less than $5,000. If these conditions are BOTH true, it will show the message box.
If we amend the macro to check if C5 is just greater than $10,000, then the profit would not be achieved!
IF…OR
We can use the IF…OR combination of logical operators when we wish to test for more than one condition where only one of the conditions needs to be true for the next line of code to execute.
The format for this is almost identical to the IF…AND example above.
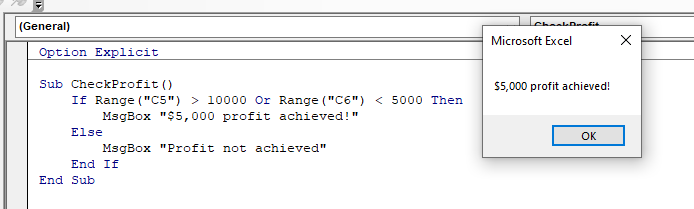
Sub CheckProfit()
If Range("C5") > 10000 Or Range("C6") < 5000 Then
MsgBox "$5,000 profit achieved!"
Else
Msgbox "Profit not achieved!"
End If
End SubHowever, with this macro, because we are using an IF …OR statement, only one of the conditions needs to be true.
IF NOT…
IF..NOT changes the IF statement around – it will check to see if the condition is NOT true rather than checking to see if the condition is true.
Sub CheckProfit()
If NOT Range("C5")< 10000 Or Range("C6") < 5000 Then
MsgBox "$5,000 profit achieved!"
Else
Msgbox "Profit not achieved!"
End If
End SubIn this example above, the IF statement is checking to see if the value in C5 is NOT smaller than 10000.
Therefore this line of code:
IF Range("C5") > 10000and this this line of code:
IF NOT Range("C5") < 10000are testing for the same thing!
In VBA, when you use the IF statement, it executes a line of code if the condition you have specified to test is TRUE. But when you use the NOT operator with IF, it checks if the condition you have specified is not TRUE and executes the code based on that. It’s like making the IF statement opposite, TRUE into FALSE and FALSE into TRUE.
Let’s say you want to test if A < B, and if this condition is true IF will return TRUE, right? But when you use IF NOT A < B, it will return FALSE.
Note: NOT is a logical operator.
Examples to use VBA IF NOT
Here’s we will see a simple example to understand it:

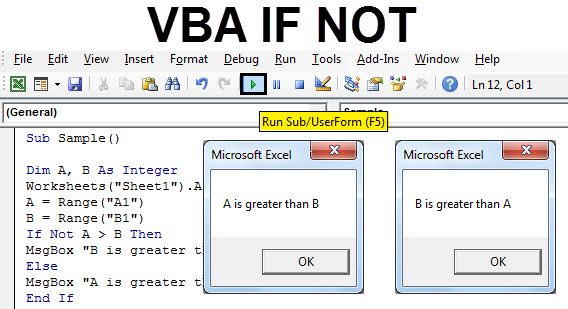
Sub myMacro()
Dim A As Range, B As Range
Set A = Range("A1")
Set B = Range("B1")
If Not A < B Then
MsgBox "A is not greater than B."
Else
MsgBox "B is not greater than A."
End If
End SubIn the above code, you have used the NOT operator to test whether B is not greater than the A.
If you look at the condition statement, you can understand the actual condition to test is if B is greater than A, but as we have used the NOT statement, it will return FALSE if the condition is TRUE.

Here’s another example that you can use to understand it.
Sub myMacro()
If Not ActiveSheet.Name = Sheets("Sheet1").Name Then
Sheets("Sheet1").Activate
End If
End SubNow, in this code, you have used NOT with IF to see if the active sheet is Sheet1 or not, and if it is not, the line of code that we have specified will activate the Sheet1.
VBA IF Not
In any programming language, we have logical operators AND OR and NOT. Every operator has a specific function to do. AND combines two or more statements and return values true if every one of the statements is true where is in OR operator if any one of the statements is true the value is true. The NOT operator is a different thing. NOT operator negates the given statement. We use these logical operators with IF statements in our day to day data analysis. If we use IF NOT statement in VBA consider this as an inverse function.
We have discussed above that we use the logical operators with if statements. In this article, we will use NOT operator with the if statement. I said earlier that IF NOT statement in VBA is also considered as an inverse function. Why is that because if the condition is true it returns false and if the condition is false it returns true. Have a look below,
IF A>B equals to IF NOT B>A
Both the if statements above are identical how? In the first statement if A is greater than B then the next statement is executed and in the next, if not statement means if B is not greater than A which in itself means A is greater than B.
The most simple way to understand IF NOT statement should be as follows:
If True Then If NOT false Then
Or we can say that
If False then IF NOT True then
Both the statements in Comparison 1 and Comparison 2 are identical to each other.
Let’s use IF NOT function in few examples which will make it more clearly for us.
Note: We need to keep in mind that in order to use VBA in excel we first have to enable our developer’s tab from the files tab and then from the options section.
How to Use Excel VBA IF Not?
We will learn how to use a VBA IF Not with few examples in excel.
You can download this VBA IF NOT Excel Template here – VBA IF NOT Excel Template
Example #1 – VBA IF Not
Follow the below steps to use IF NOT in Excel VBA.
For example, I have two values in sheet 1 in cell A1 and B1. Have a look at them below,
What I want to do is compare these two values which one is greater using IF NOT statement in VBA.
Step 1: Go to the developer’s tab and then click on Visual Basic to open the VB Editor.
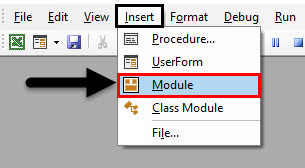
Step 2: Insert a module from the insert tab in the VB Editor. Double click on the module we just inserted to open another window where we are going to write our code.
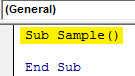
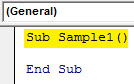
Step 3: Every VBA code starts with a sub-function as below,
Code:
Sub Sample() End Sub
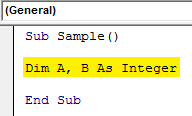
Step 4: Declare two variables as integers which will store our values from cell A1 and B1.
Code:
Sub Sample() Dim A, B As Integer End Sub
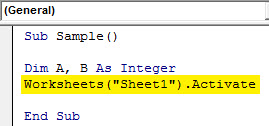
Step 5: To assign values to these variables we need to activate the worksheet first by the following code.
Code:
Sub Sample() Dim A, B As Integer Worksheets("Sheet1").Activate End Sub
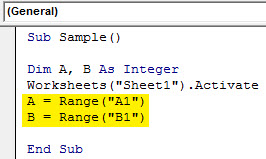
Step 6: Now we will assign these variables the values of A1 and B1.
Code:
Sub Sample() Dim A, B As Integer Worksheets("Sheet1").Activate A = Range("A1") B = Range("B1") End Sub
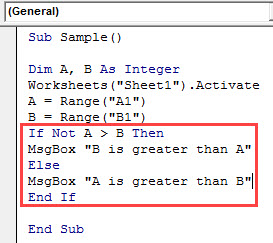
Step 7: Let us compare both the variables using IF NOT statement by the following code,
Code:
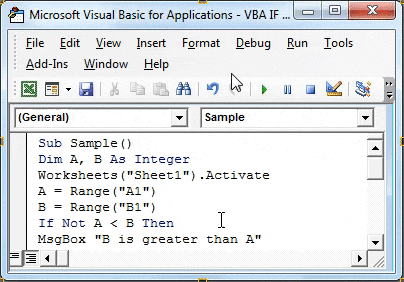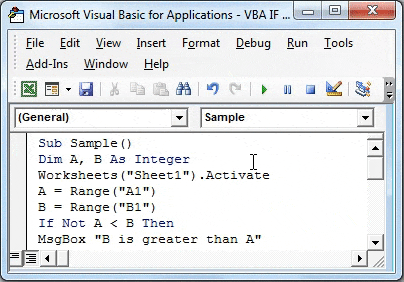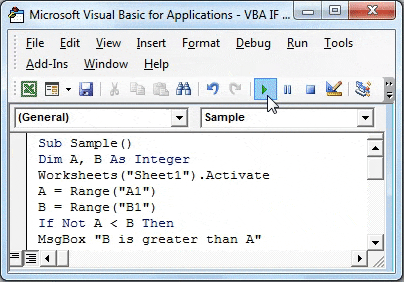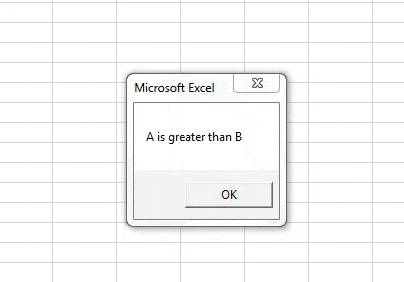
Sub Sample() Dim A, B As Integer Worksheets("Sheet1").Activate A = Range("A1") B = Range("B1") If Not A > B Then MsgBox "B is greater than A" Else MsgBox "A is greater than B" End If End Sub
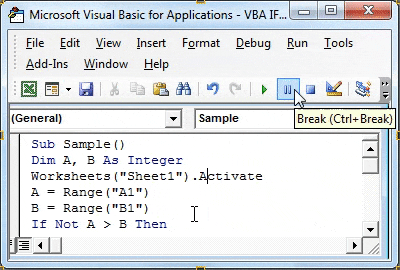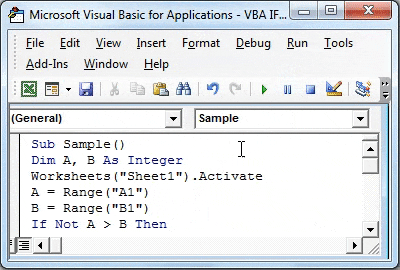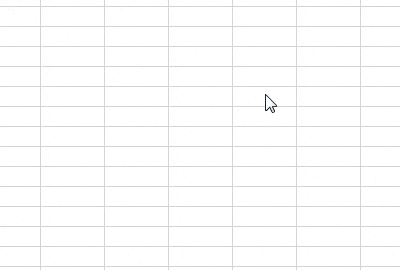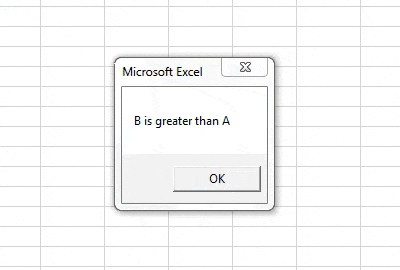
Step 8: Run the above code from the run button in VBA or we can press the F5 button to do the same. We will get the following result.
Step 9: Let us inverse the values of A and B and again run the code to see the following result.
In the first execution, A was greater than B but we compared IF NOT A>B, Initially, the condition was true so it displayed the result for False statement i.e. A is greater than B and vice versa for execution second.
Example #2 – VBA IF Not
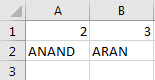
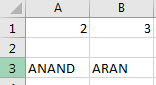
In the first example we compared integers, let us compare strings in this example with IF NOT statement in VBA. In the same sheet1, we have two strings in cell A3 and B3 as follows,
Let us compare both the strings using IF NOT Statement.
Step 1: To open VB Editor first click on Developer’s Tab and then click on Visual Basic.
Step 2: In the same module, we inserted above double click on it to start writing the second code.
Step 3: Declare a sub-function below the code we wrote first.
Code:
Sub Sample1() End Sub
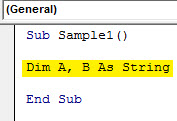
Step 4: Declare two variables as a string that will store our values from cell A3 and B3.
Code:
Sub Sample1() Dim A, B As String End Sub
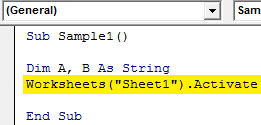
Step 5: To assign values to these variables we need to activate the worksheet first by the following code to use its properties.
Code:
Sub Sample1() Dim A, B As String Worksheets("Sheet1").Activate End Sub
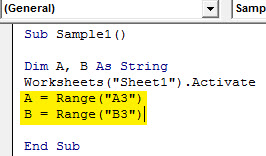
Step 6: Now we will assign these variables the values of A3 and B3.
Code:
Sub Sample1() Dim A, B As String Worksheets("Sheet1").Activate A = Range("A3") B = Range("B3") End Sub
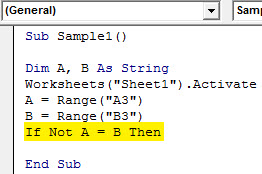
Step 7: Let us compare both the variables using IF NOT statement by the starting the if statement as follows,
Code:
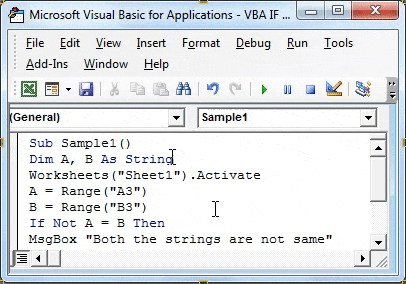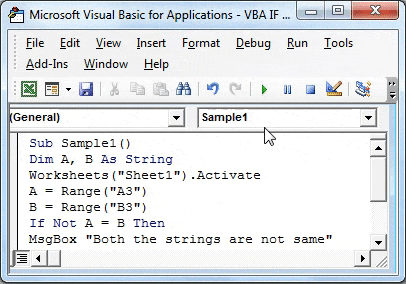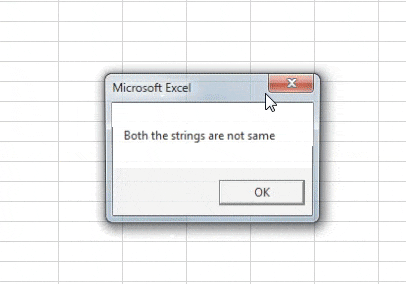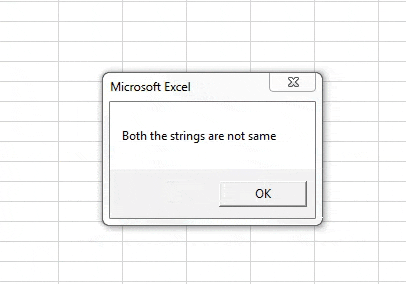
Sub Sample1() Dim A, B As String Worksheets("Sheet1").Activate A = Range("A3") B = Range("B3") If Not A = B Then End Sub
Step 8: If A = B condition is true then the above statement will negate it and return the value as false.
Code:
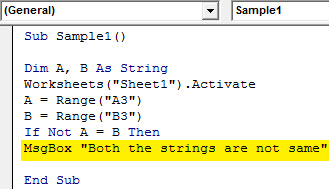
Sub Sample1() Dim A, B As String Worksheets("Sheet1").Activate A = Range("A3") B = Range("B3") If Not A = B Then MsgBox "Both the strings are not same" End Sub
Step 9: If both the strings are same i.e. if the result is returned as true display the following message,
Code:
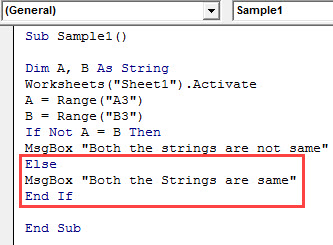
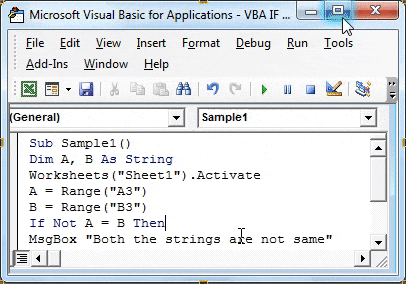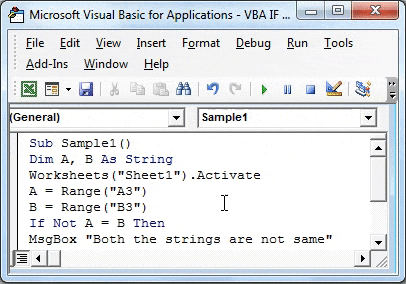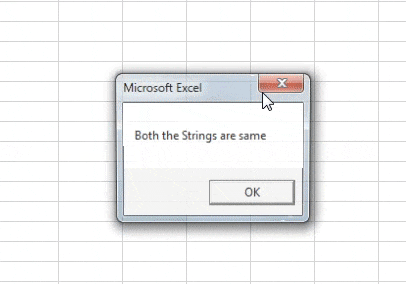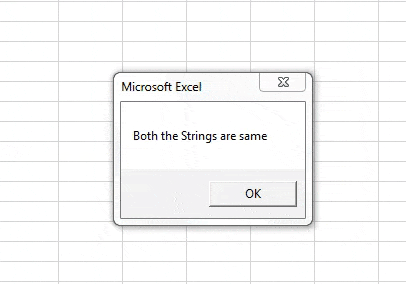
Sub Sample1() Dim A, B As String Worksheets("Sheet1").Activate A = Range("A3") B = Range("B3") If Not A = B Then MsgBox "Both the strings are not same" Else MsgBox "Both the Strings are same" End If End Sub
Step 10: Now let us run the above code by pressing the F5 button or from the run button given. Once we run the code we get the following result.
Step 11: Now let us make both the stings in A3 and B3 cell same to see the different result when we run the same code.
In the first execution A was not similar to B but we compared IF NOT A=B, Initially the condition was true so it displayed the result for false statement i.e. both the strings are not same and when both of the strings were same we get the different message as both the strings are same.
Things to Remember
- IF NOT is a comparison statement.
- IF NOT negates the value of the condition i.e. if a condition is true it returns false and vice versa.
- IF NOT statement is basically an inverse function.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to VBA If Not. Here we have discussed how to use Excel VBA If Not along with practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- VBA Active Cell
- VBA RGB
- VBA Transpose
- VBA Not
Logical functions are useful for calculations that require multiple conditions or criteria to test. In our earlier articles, we have seen “VBA IF,” “VBA OROr is a logical function in programming languages, and we have an OR function in VBA. The result given by this function is either true or false. It is used for two or many conditions together and provides true result when either of the conditions is returned true.read more,” and “VBA ANDVBA AND is an inbuilt logical function and a logical operator. Only when all of the conditions specified in this function are met , it returns the output as true. In contrast, if any of the conditions fails, the output is false.read more” conditions. This article will discuss the VBA NOT with the IF function in excelIF function in Excel evaluates whether a given condition is met and returns a value depending on whether the result is “true” or “false”. It is a conditional function of Excel, which returns the result based on the fulfillment or non-fulfillment of the given criteria.
read more. But, first, we need to look at the VBA NOT function to understand it.
Table of contents
- Excel VBA Not Function
- Examples
- Example #1
- Example #2 – NOT with IF Function
- Example #3 – Advanced NOT
- Recommended Articles
- Examples
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA Not Function (wallstreetmojo.com)
Examples
You can download this VBA Not Excel Template here – VBA Not Excel Template
Example #1
The NOT function is available with VBA too. It works the same as the Excel function. For example, look at the below set of VBA codesVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more.
Code:
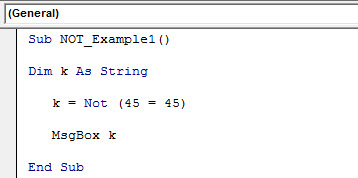
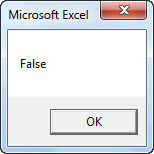
Sub NOT_Example1() Dim k As String k = Not (45 = 45) MsgBox k End Sub
We have declared the variable “k” as a string in the above code.
Dim k As String
Next, we have assigned the value through the NOT functionNOT Excel function is a logical function in Excel that is also known as a negation function and it negates the value returned by a function or the value returned by another logical function.read more. Does it NOT function to say whether the number 45 equals 45 or not?
k = Not (45 = 45)
Next, we have assigned the value returned by the NOT function to the variable “k” in the message box.
MsgBox k
Run the code and see what the result is.
Example #2 – NOT with IF Function
As we said in one of the earlier articles, “IF with other logical functions are the best pairs in Excel.”
Similarly, NOT with IF is useful in many ways. For example, with IF, we can have our results instead of the default results of TRUE or FALSE.
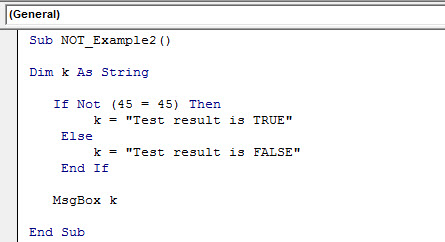
Take the same example code above. Again, we will apply NOT with the IF function.
Code:
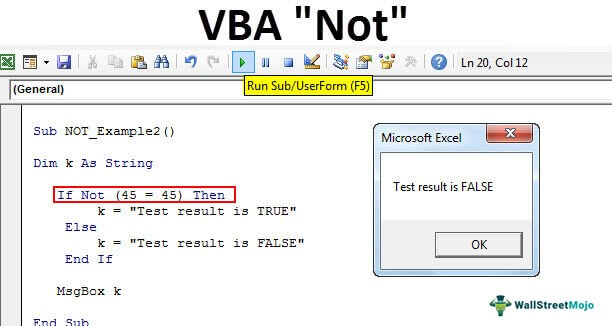
Sub NOT_Example2() Dim k As String If Not (45 = 45) Then k = "Test result is TRUE" Else k = "Test result is FALSE" End If MsgBox k End Sub
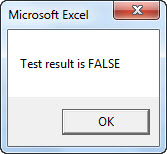
In the above code, we have altered the default results from “Test result is FALSE” and “Test result is TRUE.” If the supplied logical test is true, it will return “Test result is FALSE,” and if the supplied logical test is false, it will return. “Test result is TRUE.”
In the above code, we have a value of 45 = 45, so we will get the answer as follows.
Example #3 – Advanced NOT
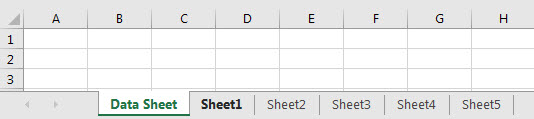
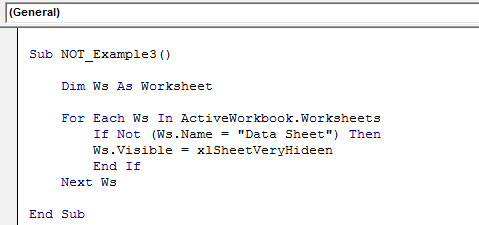
The NOT function is utilized best with the IF function. For example, we can use this function to hide all the sheets except one particular sheet.
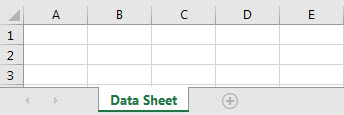
We have various sheets, as follows in our Excel.
Below is the sample code to hide all sheets except one particular sheet.
Code:
Sub NOT_Example3() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets If Not (Ws.Name = "Data Sheet") Then Ws.Visible = xlSheetVeryHideen End If Next Ws End Sub
The above code hides all the worksheets except the worksheet “Data Sheet.”
You can use this VBA code to hideVBA columns need to be hidden for the sheet to convey only the relevant information. To hide a column, simply set the property value to ‘TRUE’; to unhide the column, set the property value to ‘FALSE’.read more all the sheets except one particular sheet by changing the sheet name to your sheet name.
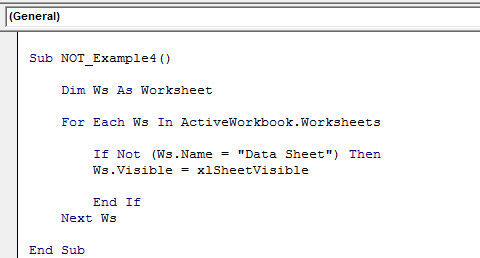
For how we can also unhide sheets in excelThere are different methods to Unhide Sheets in Excel as per the need to unhide all, all except one, multiple, or a particular worksheet. You can use Right Click, Excel Shortcut Key, or write a VBA code in Excel. read more. The below code will unhide all the sheets except the sheet name “Data Sheet.”
Code:
Sub NOT_Example4() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets If Not (Ws.Name = "Data Sheet") Then Ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible End If Next Ws End Sub
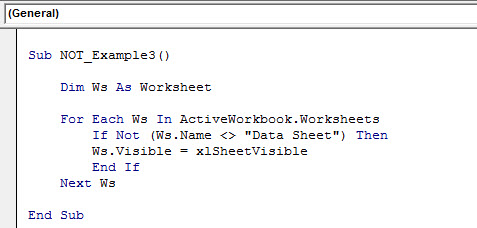
The below code will unhide only the sheet name “Data Sheet.”
Code:
Sub NOT_Example3() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets If Not (Ws.Name <> "Data Sheet") Then Ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible End If Next Ws End Sub
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA Not Function. Here, we discuss the working of the Not function, how to use it with the IF function, and practical examples and downloadable templates. Below are some useful articles related to VBA: –
- VBA If Else
- IF NOT in VBA
- For Each Loop in Excel VBA
- GoTo in VBA
VBA Logical Operators: AND, OR, NOT
Let’s say you want to process a customer order. For that, you want to first check to see if the ordered product exists or not. If it does, you also want to check if the quantity on hand is enough. Logical operators come in handy in such cases. Logical operators are used to evaluate more than one condition.
The main Excel VBA logical operators AND, OR, NOT are listed in the table below:
| S/N | Operator | Description | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AND | AND: This is used to combine more than one condition. If all the conditions are true, AND evaluates to true. If any of the condition is false, AND evaluates to false | If true = true AND false = true THEN | false |
| 2 | OR | OR: This is used to combine more than one condition. If any of the conditions evaluate to true, OR returns true. If all of them are false, OR returns false | If true = true OR true = false THEN | true |
| 3 | NOT | NOT: This one works like an inverse function. If the condition is true, it returns false, and if a condition is false, it returns true. | If NOT (true) Then | false |
VBA Logical Operators Example Source Code
For the sake of simplicity, we will be comparing hard coded numbers.
Add ActiveX buttons to the sheet from the “Insert option.”
Set the properties as shown in the image below
The following table shows the properties that you need to change and the values that you need to update too.
| S/N | Control | Property | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CommandButton1 | Name | btnAND |
| Caption | AND Operator (0 = 0) | ||
| 2 | CommandButton2 | Name | btnOR |
| Caption | OR Operator (1 = 1) Or (5 = 0) | ||
| 3 | CommandButton3 | Name | btnNOT |
| Caption | NOT Operator Not (0 = ) |
Add the following code to btnAND_Click
Private Sub btnAND_Click()
If (1 = 1) And (0 = 0) Then
MsgBox "AND evaluated to TRUE", vbOKOnly, "AND operator"
Else
MsgBox "AND evaluated to FALSE", vbOKOnly, "AND operator"
End If
End Sub
VBA If AND Operator
- “If (1 = 1) And (0 = 0) Then” the if statement uses the AND logical operator to combine two conditions (1 = 1) And (0 = 0). If both conditions are true, the code above ‘Else’ keyword is executed. If both conditions are not true, the code below ‘Else’ keyword is executed.
Add the following code to btnOR_Click
Private Sub btnOR_Click()
If (1 = 1) Or (5 = 0) Then
MsgBox "OR evaluated to TRUE", vbOKOnly, "OR operator"
Else
MsgBox "OR evaluated to FALSE", vbOKOnly, "OR operator"
End If
End Sub
VBA If OR Operator
- “If (1 = 1) Or (5 = 0) Then” the if statement uses the OR logical operator to combine two conditions (1 = 1) And (5 = 0). If any of the conditions is true, the code above Else keyword is executed. If both conditions are false, the code below Else keyword is executed.
Add the following code to btnNOT_Click
Private Sub btnNOT_Click()
If Not (0 = 0) Then
MsgBox "NOT evaluated to TRUE", vbOKOnly, "NOT operator"
Else
MsgBox "NOT evaluated to FALSE", vbOKOnly, "NOT operator"
End If
End Sub
VBA If NOT Operator
- “If Not (0 = 0) Then” the VBA If Not function uses the NOT logical operator to negate the result of the if statement condition. If the conditions is true, the code below ‘Else’ keyword is executed. If the condition is true, the code above Else keyword is executed.
Download Excel containing above code