Копирование и перемещение файлов в VBA Excel с помощью методов CopyFile и MoveFile объекта FileSystemObject. Синтаксис, параметры, примеры.
Копирование файлов
Метод CopyFile
CopyFile – это метод объекта FileSystemObject, который копирует один или несколько файлов из одного расположения в другое.
Синтаксис
|
object.CopyFile source, destination, [overwrite] |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| object | Переменная, возвращающая объект FileSystemObject. Обязательный параметр. |
| source | Строковое выражение, задающее полное имя файла, который требуется скопировать в другое расположение. Для копирования нескольких файлов используются подстановочные знаки. Обязательный параметр. |
| destination | Строковое выражение, задающее конечное расположение, куда требуется скопировать файл (файлы) из элемента source. Подстановочные знаки не допускаются. Обязательный параметр. |
| overwrite | Логическое значение, которое указывает, требуется ли перезаписывать существующие файлы в конечном расположении. True – файлы будут перезаписаны, False – перезапись не выполняется. Необязательный параметр, по умолчанию – True. |
Если копируемый файл с полным именем source не существует, будет сгенерирована ошибка.
При копировании одного файла методом CopyFile допустимо в параметре destination указать другое собственное имя файла, тогда скопированный файл будет сохранен под новым именем. В том числе, можно изменить и расширение файла.
Примеры
Пример 1
Копирование одного файла в другое расположение с проверкой его существования:
|
Sub Primer1() Dim fso As Object ‘Присваиваем переменной fso ссылку ‘на новый экземпляр FileSystemObject Set fso = CreateObject(«Scripting.FileSystemObject») ‘Проверяем существование копируемого файла If Dir(«C:Папка 1test1.txt») <> «» Then ‘Если файл существует, копируем его в другую папку fso.CopyFile «C:Папка 1test1.txt», «C:Папка 2« End If End Sub |
Пример 2
Наглядный, но неправильный пример по копированию одного файла в другую папку со сменой собственного имени, включая расширение:
|
Sub Primer2() Dim fso As Object Set fso = CreateObject(«Scripting.FileSystemObject») If Dir(«C:Папка 1test1.txt») <> «» Then ‘Копируем файл в другую папку со сменой имени, включая расширение fso.CopyFile «C:Папка 1test1.txt», «C:Папка 2test2.xlsx» End If End Sub |
Пример назван неправильным, так как у скопированного файла меняется только расширение с .txt на .xlsx без конвертации в другой формат. На самом деле файл так и остается текстовым, и открыть его программой Excel невозможно.
Перемещение файлов
Метод MoveFile
MoveFile – это метод объекта FileSystemObject, который перемещает один или несколько файлов из одного расположения в другое.
Синтаксис
|
object.MoveFile source, destination |
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| object | Переменная, возвращающая объект FileSystemObject. Обязательный параметр. |
| source | Строковое выражение, задающее полное имя файла, который требуется переместить в другое расположение. Для перемещения нескольких файлов используются подстановочные знаки. Обязательный параметр. |
| destination | Строковое выражение, задающее конечное расположение, куда требуется переместить файл (файлы) из элемента source. Подстановочные знаки не допускаются. Обязательный параметр. |
Если перемещаемый файл с полным именем source не существует, будет сгенерирована ошибка. Ошибка произойдет и в том случае, если одноименный файл в расположении destination уже имеется.
Примеры
Пример 3
Перемещение одного файла без проверки его существования:
|
Sub Primer3() Dim fso As Object ‘Присваиваем переменной fso ссылку ‘на новый экземпляр FileSystemObject Set fso = CreateObject(«Scripting.FileSystemObject») ‘Завершаем программу, если произойдет ошибка On Error Resume Next ‘Перемещаем файл в другую папку fso.MoveFile «C:Папка 1Документ 1.docx», «C:Папка 2« End Sub |
Обработчик ошибок On Error Resume Next необходим для того, чтобы корректно завершить программу, если перемещаемый файл не существует, или он уже есть в папке назначения, в результате чего будет сгенерирована ошибка.
Пример 4
Перемещение нескольких файлов из одного расположения в другое:
|
Sub Primer4() Dim fso As Object Set fso = CreateObject(«Scripting.FileSystemObject») On Error Resume Next ‘Перемещаем файлы в другую папку fso.MoveFile «C:Папка 1Документ*», «C:Папка 2« End Sub |
В результате работы этого кода VBA Excel в новое расположение будут перемещены все файлы начинающиеся с подстроки «Документ».
Знаки подстановки
- Звездочка (*) – заменяет любое количество символов или ни одного.
- Вопросительный знак (?) – заменяет один символ или ни одного.
Знаки подстановки позволяют создать шаблон, по которому можно скопировать или переместить сразу несколько файлов.
Примеры
Примеры шаблонов с подстановочными знаками:
Все файлы Word, включая файлы с расширениями .doc и .dot:
"C:Папка 1*.do??"
Файлы Word, кроме файлов с расширениями .dot, .dotx и .dotm:
"C:Папка 1*.doc?"
Все файлы с подстрокой «01.2020» в собственном имени:
"C:Папка 1*01.2020*"
The FileSystemObject VBA CopyFile method copies one or more files from one a source to a destination location.
VBA FileSystemObject Methods
- BuildPath
- CopyFile
- CopyFolder
- CreateFolder
- CreateTextFile
- DeleteFile
- DeleteFolder
- DriveExists
- FileExists
- FolderExists
- GetAbsolutePathName
- GetBaseName
- GetDrive
- GetDriveName
- GetExtensionName
- GetFile
- GetFileName
- GetFolder
- GetParentFolderName
- GetSpecialFolder
- GetTempName
- MoveFile
- MoveFolder
- OpenTextFile
VBA CopyFile Syntax
fso.CopyFile source, destination, [ overwrite ]
source
The source location of the file or files. You can use wildcards such as *.* to specify more than a single file matching the pattern.
destination
The destination location (folder) where the source files are to be copied to.
overwrite
Optional. If True will overwrite files with same name in destination folder. If True it will omit files for which there is an existing filename in the destination folder.
VBA CopyFile Examples
Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
'Copy just the Hello.xlsx file
fso.CopyFile "c:SrcHello.xlsx", "c:Dest"
'Copy all files with XLSX extension to destination folder
fso.CopyFile "c:Src*.xlsx", "c:Dest"
'Copy all files to destination folder
fso.CopyFile "c:Src*.*", "c:Dest"
'Copy all files in subfolders of C:Src to destination folder
fso.CopyFile "C:Src**.*", "c:Dest"
In this Article
- Using the FileSystemObject (FSO) in Excel VBA
- Creating a FileSystemObject
- Using the ‘Exists’ Methods
- Using the ‘Get’ Methods
- GetAbsolutePathname
- GetBaseName
- GetDriveName
- GetExtensionName
- GetFile
- GetFolder
- GetParentFolderName
- Using the ‘Create’ Methods
- CreateFolder
- CreateTextFile
- Using the ‘Copy’ Methods
- CopyFile
- CopyFolder
- Using the ‘Move’ Methods
- MoveFile
- MoveFolder
- Using the ‘Delete’ Methods
- DeleteFile
- DeleteFolder
- Other Methods in the FSO
- OpenAsTextStream.
- BuildPath
- OpenTextFile
- Properties of the FSO
- Drives
- Name
- Path
- Size
- Type
Using the FileSystemObject (FSO) in Excel VBA
The FileSystemObject (FSO) gives you access to a whole range of functions for accessing your computer’s file system. Using this object, you can easily access files, folders, and drives, and also read and write to files.
Many of the FSO functions could be written by you in traditional VBA, but would require more coding, and would be more difficult for an incoming developer to maintain and understand. The FSO is a tried and tested API (Application Programming Interface) and is more reliable than your own code. It is easy to use and ready and available.
The FSO works to international standards and settings that you have on your computer. If you are distributing your Excel application globally then using the FSO will take care of any differences in settings between countries, which your own code would have trouble doing.
The FSO will allow you to do almost everything in VBA code that you could do in Windows File Explorer. It gives you complete access to the Windows file system.
Creating a FileSystemObject
The FileSytemObject is not part of Excel VBA. You can use the FSO by creating an object (late binding) in VBA:
Sub CreateFSO()
Set MyFSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
End Sub
Alternatively, you can add a reference into VBA for the FSO library. This is called early binding and it is faster than late binding, since the object does not have to be created when your code is run.
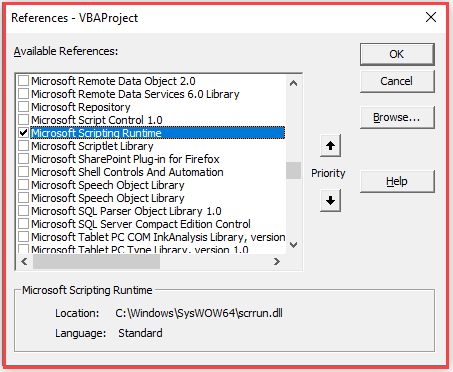
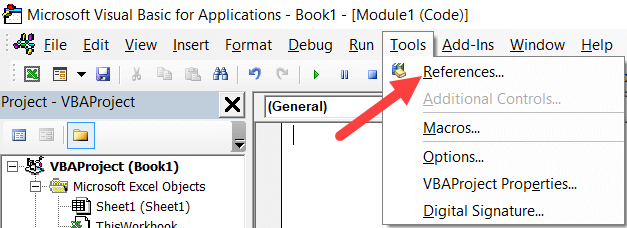
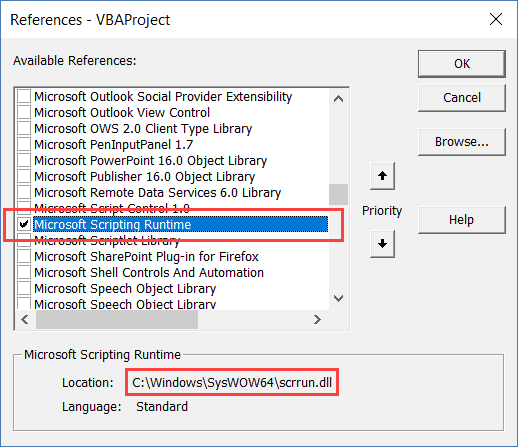
To add a reference, you need to press Alt-F11 to enter the Visual Basic Editor (VBE), and then use ‘Tools|References’ from the VBE menu. This will display a pop-up window for you to select the relevant reference (see below).
Scroll down the list of available references until you can see ‘Microsoft Scripting Runtime’. Tick the box and click on OK, and the library is now part of your application.
The location of the DLL library file is C:WindowsSysWOW64scrrun.dll
If you are distributing your application to other colleagues or locations, it is essential that they have this file in the correct location on their computer, otherwise your code will error.
It is worth putting an error trap on the ‘WorkbookOpen’ event using the Dir command to check that the file exists. If it is absent, then give a warning message and close the Excel file.
Once the reference has been added, you can use the following code to create the FSO:
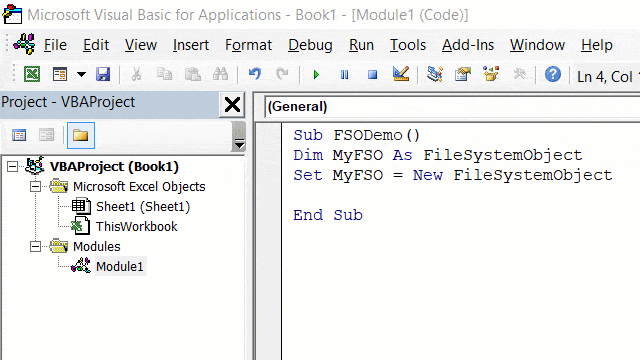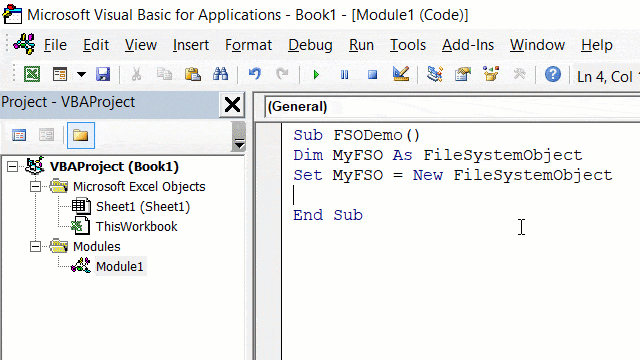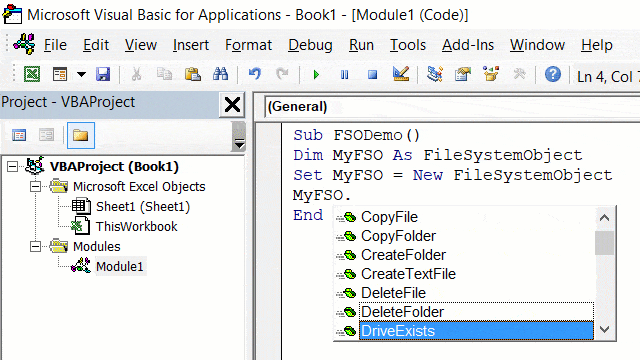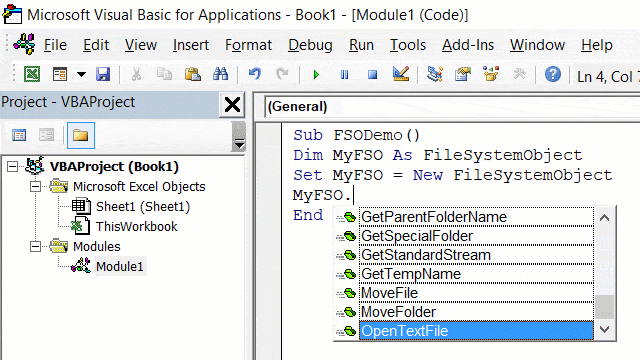
Sub TestFSO()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
End Sub
All the examples in this article will use this methodology to create the FSO.
The FSO has many methods and properties available. These are divided here into sections according to what they can do.
Using the ‘Exists’ Methods
You can use an FSO method to check whether a drive, a folder, or a file exists. These methods are easy to use and only require one parameter.
Sub CheckExistance()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
MsgBox MyFSO.DriveExists("C:")
MsgBox MyFSO.FolderExists("C:temp")
MsgBox MyFSO.FileExists("C:temptestfile.txt")
End Sub
These statements will all return ‘True’ assuming that your computer has a C: drive, a folder on it called ‘Temp’ and a file in the Temp folder called ‘testfile.txt’
The text strings in the parameters are not case-sensitive. You cannot use wildcards in any of these methods.
You also cannot use URLs (Uniform Resource Locators) to describe a folder or file location. The FSO works purely on the Windows Operating System and the file system thereon. For an external server location, you need to map a drive to this first of all, and then use the drive path itself.
Using the ‘Get’ Methods
The FSO has numerous methods to get information on the file and path, either splitting the path and file, or getting file or folder information such as date created or date modified.
GetAbsolutePathname
This will provide a complete path from the root of the specified drive.
Syntax is:
GetAbsolutePathName (pathspec)
Sub AbsolutePath()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject, Pth As String
Pth = "c:..."
MsgBox MyFSO.GetAbsolutePathName(Pth)
End Sub
This will return a string ‘C:UsersRichardDocuments’. This is because the path has been specified as C: followed by three dots. Each dot signifies a next level within the folder structure.
GetBaseName
This returns the name of a specified file or folder.
Syntax is:
GetBaseName (path)
Sub BaseName()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject, Pth As String
Pth = "C:temptestfile.txt"
MsgBox MyFSO.GetBaseName(Pth)
End Sub
This code will return ‘testfile’. The method returns the last section in the path name. If it is a file, then it does not return the file suffix.
If the path cannot be found then a blank string will be returned.
GetDrive
This allows you to use code to access drive information, based on the drive letter specified.
Syntax is:
GetDrive (drivespec)
Sub DriveInfo()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject, Pth As String, Dr As Drive
Pth = "C:"
Set Dr = MyFSO.GetDrive(Pth)
MsgBox Dr.FreeSpace
End Sub
This method returns a drive object based on the drive specified. You can use this object to access information about the drive, such as free space available.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
GetDriveName
This method will separate out the drive name from a path / filename string.
Syntax is:
GetDriveName (path)
Sub DriveName()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject, Pth As String
Pth = "C:temptestfile.txt"
MsgBox MyFSO.GetDriveName(Pth)
End Sub
This will return ‘C:’
GetExtensionName
This will return the file suffix in the path specified.
Syntax is:
GetExtensionName (path)
Sub ExtensionName()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject, Pth As String
Pth = "C:temptestfile.txt"
MsgBox MyFSO.GetExtensionName(Pth)
End Sub
This will return ‘txt’.
If no file is specified, then an empty string will be returned.
GetFile
This method returns a file object, which holds various information about the file itself.
Syntax is:
GetFile (filespec)
Sub FileInfo()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject, Pth As String, Fn As File
Pth = "C:temptestfile.txt"
Set Fn = MyFSO.GetFile(Pth)
MsgBox Fn.DateCreated
End Sub
This will return the date and time that the specified file was created. If no file is specified or the file does not exist, you will get a ‘file not found’ error.
Sub FileName()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject, Pth As String
Pth = "C:temptestfile.txt"
MsgBox MyFSO.GetFileName(Pth)
End Sub
This will return ‘testfile.txt’.
VBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
GetFolder
This creates a folder object for the base folder in the specified path. The path must only contain folder names. No filenames must be included otherwise an error will occur.
Syntax is:
GetFolder (folderspec)
Sub FolderInfo()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject, Pth As String, Fo As Folder
Pth = "C:temp"
Set Fo = MyFSO.GetFolder(Pth)
MsgBox Fo.DateCreated
End Sub
The folder object has various information in it which can be accessed. In this case, it returns the date that the folder was created.
You can also use this method to retrieve all the file names within a given folder:
Sub FileNames()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject, Pth As String, Fo As Folder, Fn As File
Pth = "C:temp"
Set Fo = MyFSO.GetFolder(Pth)
For Each Fn In Fo.Files
MsgBox Fn.Name
Next Fn
End Sub
This code will iterate through the ‘Temp’ folder and display each file name found.
GetParentFolderName
This method will return the folder name in the next level up in the folder hierarchy.
Syntax is:
GetParentFolderName (path)
Sub FolderName()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject, Pth As String, Fo As Folder
Pth = "C:usersrichard"
MsgBox MyFSO.GetParentFolderName(Pth)
End Sub
This will return ‘Users’ as this is the ‘parent’ for the folder ‘richard’.
Using the ‘Create’ Methods
With the FSO you can create a new folder and path and create a text file.
CreateFolder
You can specify a new folder path name to be created. A danger of this is that if the folder already exists, then an error will occur. You can use the method ‘FolderExists’ to ensure that this will not happen.
Syntax is:
CreateFolder (foldername)
Sub CreateNewFolder()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject, Pth As String
Pth = "C:tempMyFolder"
If MyFSO.FolderExists(Pth) = False Then
MyFSO.CreateFolder (Pth)
End If
End Sub
This code will create a new folder called ‘MyFolder’ under the existing path ‘C:temp’.
CreateTextFile
This method enables you to create a simple text file and to write directly into it.
Syntax is:
CreateTextFile (filename, [ overwrite, [ unicode ]])
Sub CreateTextFile()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject, Pth As String
Pth = "C:tempMyfile.txt"
Set Fn = MyFSO.CreateTextFile(Pth,True)
Fn.Write "Add my own text here" & vbLf & "This is the second line"
Fn.Close
End Sub
This code creates a text file called ‘Myfile.txt’ in the ‘Temp’ folder of the ‘C:’ drive and then writes two lines of text to it.
Note that a line feed character is concatenated into the string being written.
If the path that you are writing to does not exist then an error will occur. You can use the ‘FolderExists’ method to check this before creating the file.
There is an optional parameter to overwrite the existing file if required – this can be True or False. The default is True.
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Using the ‘Copy’ Methods
You can use these methods to copy a file or a folder to another location.
CopyFile
This method will copy a file from one folder location to another. Note that the copy will fail if the destination location has the read-only attribute set.
Syntax is:
CopyFile source, destination, [ overwrite ]
Sub CopyFile()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
MyFSO.CopyFile "C:temp*.txt", "C:tempmyfolder", True
End Sub
This code will make a copy of all the text (txt) files at ‘C:temp’ into ‘C:tempmyfolder’, overwriting the file where necessary. The default setting for Overwrite is True.
You can use an asterisk (*) wildcard for the filenames, but you cannot use a question mark (?) wildcard to represent single characters.
CopyFolder
You can use this method to copy an entire folder from one location to another.
Syntax is:
CopyFolder source, destination, [ overwrite ]
Sub CopyFolder()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
MyFSO.CopyFolder "C:temp*", "C:usersrichard"
End Sub
This code copies all the folders and files below ‘C:temp’ into ‘C:usersrichard’. The new folder created will be ‘C:usersrichardmyfolder’ as ‘C:temp’ had a folder within it called ‘myfolder’.
There are four possible outcomes when using this method:
- If the destination does not exist, then the source folder and contents is copied.
- If the destination already exists, then an error occurs.
- If the destination is a folder, then the source folder and its contents will be copied. An error will occur if Overwrite is set to False and there is already a copy of a file in the destination.
- If the destination is set to read only, an error will occur if overwrite is set to false.
This method stops at the first error that it encounters. There is no rollback of any actions that have succeeded before the error occurs.
Using the ‘Move’ Methods
These methods can be used to move files or folders to other locations. This is the same as cutting from one location and pasting into another location. Note that if the file to be moved is open, then the Move method will fail with an error.
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
MoveFile
This method is used to move a specific file to another location. Wildcards are allowed in the last path component of the source.
Syntax is:
MoveFile source, destination
Sub MoveAFile()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
MyFSO.MoveFile "C:temp*", "C:tempmyfolder"
End Sub
This code moves all the files found at ‘C:temp’ into ‘C:tempmyfolder’.
The source and destination folders must exist, as the destination folder does not automatically get created.
This method stops at the first error that it encounters. There is no rollback of any actions that have succeeded before the error occurs.
MoveFolder
This method moves a specific folder from one location to another.
Syntax is:
MoveFolder (source, destination)
Sub MoveAFolder()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
MyFSO.MoveFolder "C:tempmyfolder", "C:tempmydestination"
End Sub
This code moves the folder ‘myfolder’ and contents to the folder ‘mydestination’. ‘myfolder’ is effectively deleted and ‘mydestination’ is created, together with the contents from ‘myfolder’.
If the destination folder already exists then an error occurs.
Using the ‘Delete’ Methods
These methods are used to delete files or folders. They must be used with care as there is no rollback or undo methods if anything goes wrong.
DeleteFile
This deletes individual files or a group of files using wildcards.
Syntax is:
DeleteFile filespec, [ force ]
Sub DeleteFiles()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
MyFSO.DeleteFile "C:temp*"
End Sub
This code will delete all the files in the folder ‘C:temp’
The Force parameter is optional and is set to True or False. If it is set to True, then read-only files will be deleted. The default is False.
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
DeleteFolder
This method deletes a specified folder and its contents.
Syntax is:
DeleteFolder folderspec, [ force ]
Sub DeleteFolders()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
MyFSO.DeleteFolder "C:tempMyDestination"
End Sub
This code will delete the folder ‘MyDestination’ and all the files within that folder. The folder ‘temp’ will remain.
The Force parameter is optional and is set to True or False. If it is set to True, then read-only folders will be deleted. The default is False.
Wildcards can be used in the last component of the path. If the folder is not found then an error will occur.
This method stops at the first error that it encounters. There is no rollback of any actions that have succeeded before the error occurs.
Other Methods in the FSO
OpenAsTextStream.
This method opens a specified file as a Text Stream object and allows it to be read or written to. The advantage of this method is that it can open any file type and extract the available text.
Syntax is:
OpenAsTextStream ([ iomode, [ format ]])
The ‘iomode’ parameter allows read only (1), read/write (2), and appending (8). The read/write parameter overwrites the file.
The ‘format’ parameter is set to -2 for system default, -1 to open the file as Unicode, and 0 to open the file as ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange).
Sub TextStream()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
Set f = MyFSO.GetFile("C:tempmyfile.txt")
Set ts = f.OpenAsTextStream(2)
ts.Write "My new text"
ts.Close
Set ts = f.OpenAsTextStream(1)
s = ts.ReadLine
MsgBox s
ts.Close
End Sub
This code gets an existing text file and creates it as an object using the ‘GetFile’ method. It then opens the text stream as read / write (2) and writes a line of text. The file is then closed and re-opened as read (1) and a line is read from it, which is then displayed as a message box.
Note that the read line must be placed in a variable before it can be displayed in a message box.
BuildPath
This method will append a folder or file name to the end of an existing folder path. This only creates a text string and does not actually create the new folder.
Syntax is:
BuildPath (path, name)
Sub BuildPth()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
np = MyFSO.BuildPath("C:temp", "ANewFolder")
MsgBox np
End Sub
This will display ‘C:tempANewFolder’. However, if you want to actually use this folder, you need to use the ‘CreateFolder’ method.
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
OpenTextFile
This method allows files to be opened and read from or written to according to set parameters. It works in a similar way to the OpenAsTextStream method.
Syntax is:
OpenTextFile (filename, [ iomode, [ create, [ format ]]])
The ‘iomode’ parameter allows ForReading, ForWriting, and ForAppending. The ForWriting parameter overwrites the file.
The ‘create’ parameter is a Boolean value. True means that a new file will be created if the specified filename does not exist. False means that no file will be created if the filename is not found. The default is False.
The ‘format’ parameter can be set to TristateFalse, TristateMixed, TristateTrue, and TristateUseDefault depending on whether the file is ASCII or Unicode.
Sub OpenTxtFile()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
Set ts = MyFSO.OpenTextFile("C:tempmyfile.txt", ForReading, False, TristateUseDefault)
s = ts.ReadLine
MsgBox s
ts.Close
End Sub
This code will read a line from the text file ‘myfile.txt’.
An advantage which the OpenTextFile method has over the OpenAsTextStreamMethod is that it has drop downs for the parameters, which are more meaningful than trying to remember the appropriate numeric values for the various parameter options.
Properties of the FSO
Drives
This property holds a collection of available drives on your computer.
Sub Drv()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject, d As Drive
Set Dr = MyFSO.Drives
For Each d In Dr
MsgBox d.DriveLetter
Next d
End Sub
This code will return each drive letter available on your computer.
Name
This returns the name of a specified file or folder.
Sub NameExample()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
Set f = MyFSO.GetFile("C:tempmyfile.txt")
i = f.Name & " on Drive " & UCase(f.Drive) & vbCrLf
i = i & "Created: " & f.DateCreated & vbCrLf
i = i & "Last Accessed: " & f.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
i = i & "Last Modified: " & f.DateLastModified
MsgBox i
End Sub
This code will give the name of the file and information about it using the Drive property.
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Path
The Path property will separate the path out from a file specification.
Sub PathExample()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
Set f = MyFSO.GetFile("C:tempmyfile.txt")
i = f.Path & f.Name & " on Drive " & UCase(f.Drive) & vbCrLf
i = i & "Created: " & f.DateCreated & vbCrLf
i = i & "Last Accessed: " & f.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
i = i & "Last Modified: " & f.DateLastModified
MsgBox i
End Sub
This example works in the same way as the Name example, except that it now provides the path for the file.
Size
The Size property will give the size of a folder or a file.
Sub FSize()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
Set f = MyFSO.GetFolder("C:temp")
MsgBox f.Size
End Sub
This code above will return the size of the folder ‘C:temp’.
Sub FSize()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
Set f = MyFSO.GetFile("C:tempmyfile.txt")
MsgBox f.Size
End Sub
This code above will return the size of the file ‘myfile.txt’.
Type
The type property will return the text for the file or folder type.
Sub FType()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
Set f = MyFSO.GetFolder("C:temp")
MsgBox f.Type
End Sub
This code above will return the text ‘File folder’.
Sub FType()
Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject
Set f = MyFSO.GetFile("C:tempmyfile.txt")
MsgBox f.Type
End Sub
This code above will return the text ‘Text document’.
Note the use of ‘GetFolder’ and ‘GetFile’ in each example.
Содержание
- Объект FileSystemObject
- 1. Создание объекта
- 2. Свойства
- 2.1. Drives
- 3. Методы
- 3.1. CreateFolder
- 3.2. CopyFile
- 3.3. CopyFolder
- 3.4. MoveFile
- 3.5. MoveFolder
- 3.6. DeleteFile
- 3.7. DeleteFolder
- 3.8. BuildPath
- 3.9. GetAbsolutePathName
- 3.10. GetBaseName
- 3.11. GetExtensionName
- 3.12. GetFileName
- 3.13. GetParentFolderName
- 3.14. GetDriveName
- 3.15. DriveExists
- 3.16. FileExists
- 3.17. FolderExists
- 3.18. GetDrive
- 3.19. GetFile
- 3.20. GetFolder
- 3.21. GetSpecialFolder
- 3.22. GetTempName
- 3.23. CreateTextFile
- 3.24. OpenTextFile
- 3.25. GetStandardStream
- 3.26. GetFileVersion
- 4. Объект Drive
- 4.1. Создание объекта
- 4.2. Свойства
- 4.2.1. AvailableSpace
- 4.2.2. DriveLetter
- 4.2.3. DriveType
- 4.2.4. FileSystem
- 4.2.5. FreeSpace
- 4.2.6. IsReady
- 4.2.7. Path
- 4.2.8. RootFolder
- 4.2.9. SerialNumber
- 4.2.10. ShareName
- 4.2.11. TotalSize
- 4.2.12. VolumeName
- 5. Объект File
- 5.1. Создание объекта
- 5.2. Свойства
- 5.2.1. Attributes
- 5.2.2. DateCreated
- 5.2.3. DateLastAccessed
- 5.2.4. DateLastModified
- 5.2.5. Drive
- 5.2.6. Name
- 5.2.7. ParentFolder
- 5.2.8. Path
- 5.2.9. ShortName
- 5.2.10. ShortPath
- 5.2.11. Size
- 5.2.12. Type
- 5.3. Методы
- 5.3.1. Copy
- 5.3.2. Move
- 5.3.3. Delete
- 5.3.4. OpenAsTextStream
- 6. Объект Folder
- 6.1. Создание объекта
- 6.2. Свойства
- 6.2.1. Attributes
- 6.2.2. DateCreated
- 6.2.3. DateLastAccessed
- 6.2.4. DateLastModified
- 6.2.5. Drive
- 6.2.6. IsRootFolder
- 6.2.7. Name
- 6.2.8. ParentFolder
- 6.2.9. Path
- 6.2.10. ShortName
- 6.2.11. ShortPath
- 6.2.12. Size
- 6.2.13. Type
- 6.2.14. SubFolders
- 6.2.15. Files
- 6.3. Методы
- 6.3.1. Copy
- 6.3.2. Move
- 6.3.3. Delete
- 6.3.4. CreateTextFile
- 7. Объект TextStream
- 7.1. Создание объекта
- 7.2. Свойства
- 7.2.1. AtEndOfLine
- 7.2.2. AtEndOfStream
- 7.2.3. Column
- 7.2.4. Line
- 7.3. Методы
- 7.3.1. Close
- 7.3.2. Read
- 7.3.3. ReadAll
- 7.3.4. ReadLine
- 7.3.5. Skip
- 7.3.6. SkipLine
- 7.3.7. Write
- 7.3.8. WriteLine
- 7.3.9. WriteBlankLines
Объект FileSystemObject
Ниже приведен справочник по объекту FileSystemObject, который умеет работать с файлами, каталогами, файловыми потоками. Данный объект позволяет читать файлы, писать в файлы, получать информацию о файлах и др. Данный объект используется в ОС Windows, в некоторых скриптовых языках.
1. Создание объекта
2. Свойства
2.1. Drives
3. Методы
3.1. CreateFolder
3.2. CopyFile
3.3. CopyFolder
3.4. MoveFile
3.5. MoveFolder
3.6. DeleteFile
3.7. DeleteFolder
3.8. BuildPath
3.9. GetAbsolutePathName
3.10. GetBaseName
3.11. GetExtensionName
3.12. GetFileName
3.13. GetParentFolderName
3.14. GetDriveName
3.15. DriveExists
3.16. FileExists
3.17. FolderExists
3.18. GetDrive
3.19. GetFile
3.20. GetFolder
3.21. GetSpecialFolder
3.22. GetTempName
3.23. CreateTextFile
3.24. OpenTextFile
3.25. GetStandardStream
3.26. GetFileVersion
4. Объект Drive
4.1. Создание объекта
4.2. Свойства
4.2.1. AvailableSpace
4.2.2. DriveLetter
4.2.3. DriveType
4.2.4. FileSystem
4.2.5. FreeSpace
4.2.6. IsReady
4.2.7. Path
4.2.8. RootFolder
4.2.9. SerialNumber
4.2.10. ShareName
4.2.11. TotalSize
4.2.12. VolumeName
5. Объект File
5.1. Создание объекта
5.2. Свойства
5.2.1. Attributes
5.2.2. DateCreated
5.2.3. DateLastAccessed
5.2.4. DateLastModified
5.2.5. Drive
5.2.6. Name
5.2.7. ParentFolder
5.2.8. Path
5.2.9. ShortName
5.2.10. ShortPath
5.2.11. Size
5.2.12. Type
5.3. Методы
5.3.1. Copy
5.3.2. Move
5.3.3. Delete
5.3.4. OpenAsTextStream
6. Объект Folder
6.1. Создание объекта
6.2. Свойства
6.2.1. Attributes
6.2.2. DateCreated
6.2.3. DateLastAccessed
6.2.4. DateLastModified
6.2.5. Drive
6.2.6. IsRootFolder
6.2.7. Name
6.2.8. ParentFolder
6.2.9. Path
6.2.10. ShortName
6.2.11. ShortPath
6.2.12. Size
6.2.13. Type
6.2.14. SubFolders
6.2.15. Files
6.3. Методы
6.3.1. Copy
6.3.2. Move
6.3.3. Delete
6.3.4. CreateTextFile
7. Объект TextStream
7.1. Создание объекта
7.2. Свойства
7.2.1. AtEndOfLine
7.2.2. AtEndOfStream
7.2.3. Column
7.2.4. Line
7.3. Методы
7.3.1. Close
7.3.2. Read
7.3.3. ReadAll
7.3.4. ReadLine
7.3.5. Skip
7.3.6. SkipLine
7.3.7. Write
7.3.8. WriteLine
7.3.9. WriteBlankLines
1. Создание объекта
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
2. Свойства
2.1. Drives
Синтаксис:
Drives
Возвращаемое значение: объект-коллекция «Drives».
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
For Each Drive In FSO.Drives
MsgBox Drive.DriveLetter
Next
Другой пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Drives = FSO.Drives
MsgBox "Всего дисков - " & Drives.Count
Set DriveC = Drives.Item("C:")
MsgBox "Диск C: имеет метку " & DriveC.VolumeName
3. Методы
3.1. CreateFolder
Синтаксис:
CreateFolder(<Foldername>)
Назначение: создаёт каталог с указанным именем.
Параметры:
- <Foldername> — строка, путь к каталогу. Если такой каталог уже существует, произойдёт ошибка.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
FSO.CreateFolder "C:New Folder"
3.2. CopyFile
Синтаксис:
CopyFile(<Source>,<Destination>,<Overwrite>)
Назначение: копирует один или несколько файлов.
Параметры:
- <Source> — строка, путь к источнику копирования (что копировать). В последнем компоненте параметра можно использовать групповые символы «*» и «?».
- <Destination> — строка, путь назначения (куда копировать).
- <Overwrite> — необязательный, булево (число). Перезаписывать существующие файлы, или нет. По умолчанию — True (перезаписывать). Если файл, который нужно перезаписать, имеет атрибут read-only, возникнет ошибка (независимо от установки этого параметра).
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
FSO.CopyFile "C:*.bat", "A:", 0
3.3. CopyFolder
Синтаксис:
CopyFolder(<Source>,<Destination>,<Overwrite>)
Назначение: рекурсивно копирует каталог.
Параметры:
- <Source> — строка, путь к источнику копирования (что копировать). В последнем компоненте параметра можно использовать групповые символы «*» и «?».
- <Destination> — строка, путь назначения (куда копировать).
- <Overwrite> — необязательный, булево (число). Перезаписывать существующие файлы, или нет. По умолчанию — True (перезаписывать). Если файл, который нужно перезаписать, имеет атрибут read-only, возникнет ошибка (независимо от установки этого параметра).
Описание: процесс копирования прерывается после первой возникшей ошибки.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
FSO.CopyFolder "C:NewFolder*", "C:TEMP", 0
3.4. MoveFile
Синтаксис:
MoveFile(<Source>,<Destination>)
Назначение: перемещает один или несколько файлов.
Параметры:
- <Source> — строка, путь к источнику копирования (что копировать). В последнем компоненте параметра можно использовать групповые символы «*» и «?».
- <Destination> — строка, путь назначения (куда копировать).
Описание: процесс перемещения прерывается после первой возникшей ошибки. Если перемещаемый файл уже существует или является папкой в Destination, возникнет ошибка.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
FSO.MoveFile "C:*.txt", "A:"
3.5. MoveFolder
Синтаксис:
MoveFolder(<Source>,<Destination>)
Назначение: рекурсивно перемещает один или несколько каталогов.
Параметры:
- <Source> — строка, путь к источнику копирования (что копировать). В последнем компоненте параметра можно использовать групповые символы «*» и «?».
- <Destination> — строка, путь назначения (куда копировать).
Описание: процесс перемещения прерывается после первой возникшей ошибки. Если перемещаемый каталог уже существует или является файлом в Destination, возникнет ошибка.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
FSO.MoveFolder "C:New Folde*", "C:TEMP"
3.6. DeleteFile
Синтаксис:
DeleteFile(<Filespec>,<Force>)
Назначение: удаляет указанный файл.
Параметры:
- <Filespec> — строка, путь к файлу. В последнем компоненте параметра можно использовать групповые символы «*» и «?».
- <Force> — необязательный, булево (число). Определяет, удалять или нет файлы с атрибутом read-only. По умолчанию — False (не удалять).
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
FSO.DeleteFile "A:*", 0
3.7. DeleteFolder
Синтаксис:
DeleteFolder(<Folderspec>,<Force>)
Назначение: удаляет указанную папку.
Параметры:
- <Folderspec> — строка, путь к папке. В последнем компоненте параметра можно использовать групповые символы «*» и «?».
- <Force> — необязательный, булево (число). Определяет, удалять или нет файлы с атрибутом read-only. По умолчанию — False (не удалять).
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
FSO.DeleteFolder "A:*", 0
3.8. BuildPath
Синтаксис:
BuildPath(<Path>,<Name>)
Назначение: добавляет к заданному пути новое имя. Если необходимо, вставляется «».
Параметры:
- <Path> — строка, путь.
- <Name> — строка, имя файла.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Path = FSO.BuildPath("C:Program Files", "New Folder")
MsgBox Path
Path = FSO.BuildPath("C:Program Files", "New Folder")
MsgBox Path
3.9. GetAbsolutePathName
Синтаксис:
GetAbsolutePathName(<Pathspec>)
Назначение: возвращает полный путь для заданного относительного пути (из текущего каталога).
Параметры:
- <Pathspec> — строка, относительный путь.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Path = FSO.GetAbsolutePathName("..")
MsgBox Path
Path = FSO.GetAbsolutePathName(".aaabbbccc.txt")
MsgBox Path
3.10. GetBaseName
Синтаксис:
GetBaseName(<Path>)
Назначение: возвращает имя (без расширения) последнего компонента в заданном пути.
Параметры:
- <Path> — строка, путь.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Name = FSO.GetBaseName("Q:aaabredMySuperFile.txt")
MsgBox Name
3.11. GetExtensionName
Синтаксис:
GetExtensionName(<Path>)
Назначение: возвращает расширение последнего компонента в заданном пути.
Параметры:
- <Path> — строка, путь.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Name = FSO.GetExtensionName("Q:aaabredMySuperFile.txt")
MsgBox Name
3.12. GetFileName
Синтаксис:
GetFileName(<Path>)
Назначение: возвращает имя (с расширением) последнего компонента в заданном пути.
Параметры:
- <Path> — строка, путь.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Name = FSO.GetFileName("Q:aaabredMySuperFile.txt")
MsgBox Name
3.13. GetParentFolderName
Синтаксис:
GetParentFolderName(<Path>)
Назначение: возвращает путь к последнему компоненту в заданном пути (его каталог).
Параметры:
- <Path> — строка, путь.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Name = FSO.GetParentFolderName("Q:aaabredMySuperFile.txt")
MsgBox Name
3.14. GetDriveName
Синтаксис:
GetDriveName(<Path>)
Назначение: возвращает имя диска в заданном пути.
Параметры:
- <Path> — строка, путь.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Name = FSO.GetDriveName("X:aaabredMySuperFile.txt")
MsgBox Name
3.15. DriveExists
Синтаксис:
DriveExists(<Drivespec>)
Назначение: возвращает True, если указанный диск сущесвтвует, и False в противном случае.
Параметры:
- <Drivespec> — строка, путь.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Disk = "A:"
MsgBox "Диск " & Disk & " существует = " & FSO.DriveExists(Disk)
Disk = "Q:"
MsgBox "Диск " & Disk & " существует = " & FSO.DriveExists(Disk)
3.16. FileExists
Синтаксис:
FileExists(<Filespec>)
Назначение: возвращает True, если указанный файл сущесвтвует, и False в противном случае.
Параметры:
- <Filespec> — строка, путь.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
File = "C:Program Files1Cv77BIN1cv7s.exe"
MsgBox "Файл " & File & " существует = " & FSO.FileExists(File)
File = "С:1.txt"
MsgBox "Файл " & File & " существует = " & FSO.FileExists(File)
3.17. FolderExists
Синтаксис:
FolderExists(<Folderspec>)
Назначение: возвращает True, если указанный каталог сущесвтвует, и False в противном случае.
Параметры:
- <Folderspec> — строка, путь.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Folder = "C:Program Files"
MsgBox "Каталог " & Folder & " существует = " & FSO.FolderExists(Folder)
Folder = "С:ProgramFiles"
MsgBox "Каталог " & Folder & " существует = " & FSO.FolderExists(Folder)
3.18. GetDrive
Синтаксис:
GetDrive(<Folderspec>)
Назначение: возвращает объект «Drive» по указанному имени или пути.
Параметры:
- <Folderspec> — строка, имя диска или путь к корневому каталогу диска, возможно UNC-путь.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Drive = FSO.GetDrive("C:")
MsgBox Drive.FileSystem
Set Drive = FSO.GetDrive("C:")
MsgBox Drive.FileSystem
Set Drive = FSO.GetDrive("\Server1C_Predpr")
MsgBox Drive.FileSystem
3.19. GetFile
Синтаксис:
GetFile(<Filespec>)
Назначение: возвращает объект «File» по указанному пути.
Параметры:
- <Filespec> — строка, путь.
Описание: если файл не существует, произойдёт ошибка.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
MsgBox File.Size
3.20. GetFolder
Синтаксис:
GetFolder(<Folderspec>)
Назначение: возвращает объект «Folder» по указанному пути.
Параметры:
- <Folderspec> — строка, путь.
Описание: если каталог не существует, произойдёт ошибка.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
MsgBox Folder.ShortName
3.21. GetSpecialFolder
Синтаксис:
GetSpecialFolder(<Folderspec>)
Назначение: возвращает объект «Folder» для некоторых специальных папок Windows.
Параметры:
- <Folderspec> — число, определяет специальную папку. Возможные значения:
- 0 — Каталог Windows.
- 1 — Системный каталог библиотек и драйверов.
- 2 — Каталог временных файлов, путь к которому хранится в переменной среды «TMP».
Описание: если каталог не существует, произойдёт ошибка.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
For i=0 To 2
Set Folder = FSO.GetSpecialFolder(i)
MsgBox Folder.Path
Next
3.22. GetTempName
Синтаксис:
GetTempName()
Назначение: возвращает случайным образом сгенерированное имя файла, которое может быть использовано для создания временного файла.
Параметры: нет.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
MsgBox FSO.GetTempName()
3.23. CreateTextFile
Синтаксис:
CreateTextFile(<Filename>,<Overwrite>,<Unicode>)
Назначение: создаёт новый текстовый файл и возвращает объект «TextStream», указывающий на него.
Параметры:
- <Filename> — строка, путь к файлу.
- <Overwrite> — необязательный, булево (число). Перезаписывать файл, если он существует (True), или нет (False). По умолчанию — False. Если указано False и файл существует — произойдёт ошибка.
- <Unicode> — необязательный, булево (число). Файл в формате Unicode (True), или ASCII (False). По умолчанию — False.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set TextStream = FSO.CreateTextFile("C:Test.txt")
3.24. OpenTextFile
Синтаксис:
OpenTextFile(<Filename>,<Iomode>,<Create>,<Format>)
Назначение: открывает текстовый файл и возвращает объект «TextStream», указывающий на него.
Параметры:
- <Filename> — строка, путь к файлу.
- <Iomode> — необязательный, число. Возможные значения:
- 1 — Открыть файл только для чтения.
- 2 — Открыть файл для записи. Если файл уже существовал, его содержимое теряется.
- 8 — Открыть файл для добавления. Если файл уже существовал, информация будет дописываться в конец файла.
- <Create> — необязательный, булево (число). Создавать файл, если он не существует (True), или нет (False). По умолчанию — False.
- <Format> — необязательный, число. Возможные значения:
- -2 — Открыть файл в формате, используемом системой по умолчанию.
- -1 — Открыть файл в формате Unicode.
- 0 — Открыть файл в формате ASCII (по умолчанию).
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set TextStream = FSO.OpenTextFile("C:Test.txt", 2, True)
3.25. GetStandardStream
Синтаксис:
GetStandardStream(<StandardStreamType>,<Unicode>)
Назначение: возвращает объект «TextStream», ассоциированный с потоком «StdIn», «StdOut» или «StdErr».
Параметры:
- <StandardStreamType> — число, определяет поток. Возможные значения:
- 0 — StdIn.
- 1 — StdOut.
- 2 — StdErr.
- <Unicode> — необязательный, булево (число). True — формат Unicode, False — ASCII. По умолчанию — False.
Описание: метод применим при запуске административного скрипта в консоли с помощью CScript.exe.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set stdout = fso.GetStandardStream(1)
stdout.WriteLine "Hello, VBScript."
3.26. GetFileVersion
Синтаксис:
GetFileVersion(<Path>)
Назначение: возвращает номер версии исполняемого файла (строка).
Параметры:
- <Path> — строка, путь к файлу.
Описание: метод возвращает информацию, которую можно просмотреть на вкладке «Версия» палитры свойств файла в проводнике.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
MsgBox FSO.GetFileVersion("C:Program Files1Cv77BIN1cv7s.exe")
MsgBox FSO.GetFileVersion("C:Program Files1cv8bin1cv8.exe")
4. Объект Drive
4.1. Создание объекта
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set DriveC = FSO.Drives.Item("C:")
4.2. Свойства
4.2.1. AvailableSpace
Синтаксис:
AvailableSpace
Возвращаемое значение: число — количество доступного для пользователя места на диске в байтах.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set DriveC = FSO.GetDrive("C:")
Str = "Диск C:" & vbCrLf & _
"AvailableSpace: " & DriveC.AvailableSpace & vbCrLf & _
"DriveLetter: " & DriveC.DriveLetter & vbCrLf & _
"DriveType: " & DriveC.DriveType & vbCrLf & _
"FileSystem: " & DriveC.FileSystem & vbCrLf & _
"FreeSpace: " & DriveC.FreeSpace & vbCrLf & _
"IsReady: " & DriveC.IsReady & vbCrLf & _
"Path: " & DriveC.Path & vbCrLf & _
"RootFolder (Path): " & DriveC.RootFolder.Path & vbCrLf & _
"SerialNumber: " & DriveC.SerialNumber & vbCrLf & _
"ShareName: " & DriveC.ShareName & vbCrLf & _
"TotalSize: " & DriveC.TotalSize & vbCrLf & _
"VolumeName: " & DriveC.VolumeName
MsgBox Str
4.2.2. DriveLetter
Синтаксис:
DriveLetter
Возвращаемое значение: строка — буква, ассоциированная с ресурсом.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set DriveC = FSO.GetDrive("C:")
Str = "Диск C:" & vbCrLf & _
"AvailableSpace: " & DriveC.AvailableSpace & vbCrLf & _
"DriveLetter: " & DriveC.DriveLetter & vbCrLf & _
"DriveType: " & DriveC.DriveType & vbCrLf & _
"FileSystem: " & DriveC.FileSystem & vbCrLf & _
"FreeSpace: " & DriveC.FreeSpace & vbCrLf & _
"IsReady: " & DriveC.IsReady & vbCrLf & _
"Path: " & DriveC.Path & vbCrLf & _
"RootFolder (Path): " & DriveC.RootFolder.Path & vbCrLf & _
"SerialNumber: " & DriveC.SerialNumber & vbCrLf & _
"ShareName: " & DriveC.ShareName & vbCrLf & _
"TotalSize: " & DriveC.TotalSize & vbCrLf & _
"VolumeName: " & DriveC.VolumeName
MsgBox Str
4.2.3. DriveType
Синтаксис:
DriveType
Возвращаемое значение: число — определяет тип ресурса. Возможные значения:
- 0 — неизвестное устройство.
- 1 — устройство со сменным носителем.
- 2 — жёсткий диск.
- 3 — сетевой диск.
- 4 — CD-ROM.
- 5 — RAM-диск.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set DriveC = FSO.GetDrive("C:")
Str = "Диск C:" & vbCrLf & _
"AvailableSpace: " & DriveC.AvailableSpace & vbCrLf & _
"DriveLetter: " & DriveC.DriveLetter & vbCrLf & _
"DriveType: " & DriveC.DriveType & vbCrLf & _
"FileSystem: " & DriveC.FileSystem & vbCrLf & _
"FreeSpace: " & DriveC.FreeSpace & vbCrLf & _
"IsReady: " & DriveC.IsReady & vbCrLf & _
"Path: " & DriveC.Path & vbCrLf & _
"RootFolder (Path): " & DriveC.RootFolder.Path & vbCrLf & _
"SerialNumber: " & DriveC.SerialNumber & vbCrLf & _
"ShareName: " & DriveC.ShareName & vbCrLf & _
"TotalSize: " & DriveC.TotalSize & vbCrLf & _
"VolumeName: " & DriveC.VolumeName
MsgBox Str
4.2.4. FileSystem
Синтаксис:
FileSystem
Возвращаемое значение: cтрока — тип файловой системы (FAT, NTFS или CDFS).
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set DriveC = FSO.GetDrive("C:")
Str = "Диск C:" & vbCrLf & _
"AvailableSpace: " & DriveC.AvailableSpace & vbCrLf & _
"DriveLetter: " & DriveC.DriveLetter & vbCrLf & _
"DriveType: " & DriveC.DriveType & vbCrLf & _
"FileSystem: " & DriveC.FileSystem & vbCrLf & _
"FreeSpace: " & DriveC.FreeSpace & vbCrLf & _
"IsReady: " & DriveC.IsReady & vbCrLf & _
"Path: " & DriveC.Path & vbCrLf & _
"RootFolder (Path): " & DriveC.RootFolder.Path & vbCrLf & _
"SerialNumber: " & DriveC.SerialNumber & vbCrLf & _
"ShareName: " & DriveC.ShareName & vbCrLf & _
"TotalSize: " & DriveC.TotalSize & vbCrLf & _
"VolumeName: " & DriveC.VolumeName
MsgBox Str
4.2.5. FreeSpace
Синтаксис:
FreeSpace
Возвращаемое значение: число — количество свободного места на диске в байтах.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set DriveC = FSO.GetDrive("C:")
Str = "Диск C:" & vbCrLf & _
"AvailableSpace: " & DriveC.AvailableSpace & vbCrLf & _
"DriveLetter: " & DriveC.DriveLetter & vbCrLf & _
"DriveType: " & DriveC.DriveType & vbCrLf & _
"FileSystem: " & DriveC.FileSystem & vbCrLf & _
"FreeSpace: " & DriveC.FreeSpace & vbCrLf & _
"IsReady: " & DriveC.IsReady & vbCrLf & _
"Path: " & DriveC.Path & vbCrLf & _
"RootFolder (Path): " & DriveC.RootFolder.Path & vbCrLf & _
"SerialNumber: " & DriveC.SerialNumber & vbCrLf & _
"ShareName: " & DriveC.ShareName & vbCrLf & _
"TotalSize: " & DriveC.TotalSize & vbCrLf & _
"VolumeName: " & DriveC.VolumeName
MsgBox Str
4.2.6. IsReady
Синтаксис:
IsReady
Возвращаемое значение: булево (число) — True, если устройство готово, иначе — False. Актуально для устройства со сменным носителем или CD-ROM.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set DriveC = FSO.GetDrive("C:")
Str = "Диск C:" & vbCrLf & _
"AvailableSpace: " & DriveC.AvailableSpace & vbCrLf & _
"DriveLetter: " & DriveC.DriveLetter & vbCrLf & _
"DriveType: " & DriveC.DriveType & vbCrLf & _
"FileSystem: " & DriveC.FileSystem & vbCrLf & _
"FreeSpace: " & DriveC.FreeSpace & vbCrLf & _
"IsReady: " & DriveC.IsReady & vbCrLf & _
"Path: " & DriveC.Path & vbCrLf & _
"RootFolder (Path): " & DriveC.RootFolder.Path & vbCrLf & _
"SerialNumber: " & DriveC.SerialNumber & vbCrLf & _
"ShareName: " & DriveC.ShareName & vbCrLf & _
"TotalSize: " & DriveC.TotalSize & vbCrLf & _
"VolumeName: " & DriveC.VolumeName
MsgBox Str
4.2.7. Path
Синтаксис:
Path
Возвращаемое значение: строка — путь к диску (например, «C:», но не «C:»).
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set DriveC = FSO.GetDrive("C:")
Str = "Диск C:" & vbCrLf & _
"AvailableSpace: " & DriveC.AvailableSpace & vbCrLf & _
"DriveLetter: " & DriveC.DriveLetter & vbCrLf & _
"DriveType: " & DriveC.DriveType & vbCrLf & _
"FileSystem: " & DriveC.FileSystem & vbCrLf & _
"FreeSpace: " & DriveC.FreeSpace & vbCrLf & _
"IsReady: " & DriveC.IsReady & vbCrLf & _
"Path: " & DriveC.Path & vbCrLf & _
"RootFolder (Path): " & DriveC.RootFolder.Path & vbCrLf & _
"SerialNumber: " & DriveC.SerialNumber & vbCrLf & _
"ShareName: " & DriveC.ShareName & vbCrLf & _
"TotalSize: " & DriveC.TotalSize & vbCrLf & _
"VolumeName: " & DriveC.VolumeName
MsgBox Str
4.2.8. RootFolder
Синтаксис:
RootFolder
Возвращаемое значение: объект «Folder», соответствующий корневому каталогу диска.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set DriveC = FSO.GetDrive("C:")
Str = "Диск C:" & vbCrLf & _
"AvailableSpace: " & DriveC.AvailableSpace & vbCrLf & _
"DriveLetter: " & DriveC.DriveLetter & vbCrLf & _
"DriveType: " & DriveC.DriveType & vbCrLf & _
"FileSystem: " & DriveC.FileSystem & vbCrLf & _
"FreeSpace: " & DriveC.FreeSpace & vbCrLf & _
"IsReady: " & DriveC.IsReady & vbCrLf & _
"Path: " & DriveC.Path & vbCrLf & _
"RootFolder (Path): " & DriveC.RootFolder.Path & vbCrLf & _
"SerialNumber: " & DriveC.SerialNumber & vbCrLf & _
"ShareName: " & DriveC.ShareName & vbCrLf & _
"TotalSize: " & DriveC.TotalSize & vbCrLf & _
"VolumeName: " & DriveC.VolumeName
MsgBox Str
4.2.9. SerialNumber
Синтаксис:
SerialNumber
Возвращаемое значение: число — десятичный серийный номер диска.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set DriveC = FSO.GetDrive("C:")
Str = "Диск C:" & vbCrLf & _
"AvailableSpace: " & DriveC.AvailableSpace & vbCrLf & _
"DriveLetter: " & DriveC.DriveLetter & vbCrLf & _
"DriveType: " & DriveC.DriveType & vbCrLf & _
"FileSystem: " & DriveC.FileSystem & vbCrLf & _
"FreeSpace: " & DriveC.FreeSpace & vbCrLf & _
"IsReady: " & DriveC.IsReady & vbCrLf & _
"Path: " & DriveC.Path & vbCrLf & _
"RootFolder (Path): " & DriveC.RootFolder.Path & vbCrLf & _
"SerialNumber: " & DriveC.SerialNumber & vbCrLf & _
"ShareName: " & DriveC.ShareName & vbCrLf & _
"TotalSize: " & DriveC.TotalSize & vbCrLf & _
"VolumeName: " & DriveC.VolumeName
MsgBox Str
Синтаксис:
ShareName
Возвращаемое значение: строка — сетевое имя диска, если диск сетевой (иначе — пустая строка).
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set DriveC = FSO.GetDrive("C:")
Str = "Диск C:" & vbCrLf & _
"AvailableSpace: " & DriveC.AvailableSpace & vbCrLf & _
"DriveLetter: " & DriveC.DriveLetter & vbCrLf & _
"DriveType: " & DriveC.DriveType & vbCrLf & _
"FileSystem: " & DriveC.FileSystem & vbCrLf & _
"FreeSpace: " & DriveC.FreeSpace & vbCrLf & _
"IsReady: " & DriveC.IsReady & vbCrLf & _
"Path: " & DriveC.Path & vbCrLf & _
"RootFolder (Path): " & DriveC.RootFolder.Path & vbCrLf & _
"SerialNumber: " & DriveC.SerialNumber & vbCrLf & _
"ShareName: " & DriveC.ShareName & vbCrLf & _
"TotalSize: " & DriveC.TotalSize & vbCrLf & _
"VolumeName: " & DriveC.VolumeName
MsgBox Str
4.2.11. TotalSize
Синтаксис:
TotalSize
Возвращаемое значение: число — общий объём диска в байтах.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set DriveC = FSO.GetDrive("C:")
Str = "Диск C:" & vbCrLf & _
"AvailableSpace: " & DriveC.AvailableSpace & vbCrLf & _
"DriveLetter: " & DriveC.DriveLetter & vbCrLf & _
"DriveType: " & DriveC.DriveType & vbCrLf & _
"FileSystem: " & DriveC.FileSystem & vbCrLf & _
"FreeSpace: " & DriveC.FreeSpace & vbCrLf & _
"IsReady: " & DriveC.IsReady & vbCrLf & _
"Path: " & DriveC.Path & vbCrLf & _
"RootFolder (Path): " & DriveC.RootFolder.Path & vbCrLf & _
"SerialNumber: " & DriveC.SerialNumber & vbCrLf & _
"ShareName: " & DriveC.ShareName & vbCrLf & _
"TotalSize: " & DriveC.TotalSize & vbCrLf & _
"VolumeName: " & DriveC.VolumeName
MsgBox Str
4.2.12. VolumeName
Синтаксис:
VolumeName
Возвращаемое значение: строка — метка тома диска.
Замечание: чтение и запись.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set DriveC = FSO.GetDrive("C:")
Str = "Диск C:" & vbCrLf & _
"AvailableSpace: " & DriveC.AvailableSpace & vbCrLf & _
"DriveLetter: " & DriveC.DriveLetter & vbCrLf & _
"DriveType: " & DriveC.DriveType & vbCrLf & _
"FileSystem: " & DriveC.FileSystem & vbCrLf & _
"FreeSpace: " & DriveC.FreeSpace & vbCrLf & _
"IsReady: " & DriveC.IsReady & vbCrLf & _
"Path: " & DriveC.Path & vbCrLf & _
"RootFolder (Path): " & DriveC.RootFolder.Path & vbCrLf & _
"SerialNumber: " & DriveC.SerialNumber & vbCrLf & _
"ShareName: " & DriveC.ShareName & vbCrLf & _
"TotalSize: " & DriveC.TotalSize & vbCrLf & _
"VolumeName: " & DriveC.VolumeName
MsgBox Str
5. Объект File
5.1. Создание объекта
Пример №1:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
Пример №2:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:")
Set File = Folder.Files("autoexec.bat")
Пример №3:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:")
Set File = Folder.Files.Item("autoexec.bat")
5.2. Свойства
5.2.1. Attributes
Синтаксис:
Attributes
Возвращаемое значение: число, набор флагов атрибутов файла. Флаги:
- 0 — Normal. Обычный файл (нет атрибутов).
- 1 — ReadOnly. Файл только для чтения. Чтение и запись.
- 2 — Hidden. Скрытый. Чтение и запись.
- 4 — System. Системный. Чтение и запись.
- 8 — Volume. Диск. Только чтение.
- 16 — Directory. Папка или файл. Только чтение.
- 32 — Archive. Архивный. Чтение и запись.
- 1024 — Alias. Ссылка или ярлык. Только чтение.
- 2048 — Compressed. Сжатый. Только чтение.
Замечание: чтение и запись или только чтение, в зависимости от атрибута.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
Attrs = File.Attributes
Set Dict = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
Dict.Add "ReadOnly", 0
Dict.Add "Hidden", 0
Dict.Add "System", 0
Dict.Add "Volume", 0
Dict.Add "Directory", 0
Dict.Add "Archive", 0
Dict.Add "Alias", 0
Dict.Add "Compressed", 0
If Attrs And 2048 Then
Dict.Item("Compressed") = 1
End If
If Attrs And 1024 Then
Dict.Item("Alias") = 1
End If
If Attrs And 32 Then
Dict.Item("Archive") = 1
End If
If Attrs And 16 Then
Dict.Item("Directory") = 1
End If
If Attrs And 8 Then
Dict.Item("Volume") = 1
End If
If Attrs And 4 Then
Dict.Item("System") = 1
End If
If Attrs And 2 Then
Dict.Item("Hidden") = 1
End If
If Attrs And 1 Then
Dict.Item("ReadOnly") = 1
End If
Str = "Атрибуты файла """ & File.Path & """:" & vbCrLf
For Each Attr In Dict
Str = Str & Attr & " = " & Dict.Item(Attr) & vbCrLf
Next
MsgBox Str
5.2.2. DateCreated
Синтаксис:
DateCreated
Возвращаемое значение: дата создания файла.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & File.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & File.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & File.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & File.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & File.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & File.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & File.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & File.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & File.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & File.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип файла - " & File.Type
MsgBox Str
5.2.3. DateLastAccessed
Синтаксис:
DateLastAccessed
Возвращаемое значение: дата последнего доступа к файлу.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & File.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & File.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & File.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & File.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & File.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & File.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & File.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & File.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & File.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & File.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип файла - " & File.Type
MsgBox Str
5.2.4. DateLastModified
Синтаксис:
DateLastModified
Возвращаемое значение: дата последней модификации файла.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & File.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & File.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & File.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & File.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & File.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & File.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & File.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & File.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & File.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & File.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип файла - " & File.Type
MsgBox Str
5.2.5. Drive
Синтаксис:
Drive
Возвращаемое значение: объект «Drive» диска, на котором находится файл.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & File.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & File.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & File.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & File.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & File.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & File.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & File.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & File.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & File.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & File.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип файла - " & File.Type
MsgBox Str
5.2.6. Name
Синтаксис:
Name
Возвращаемое значение: имя файла.
Замечание: чтение и запись.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & File.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & File.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & File.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & File.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & File.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & File.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & File.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & File.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & File.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & File.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип файла - " & File.Type
MsgBox Str
5.2.7. ParentFolder
Синтаксис:
ParentFolder
Возвращаемое значение: объект «Folder» родительского каталога.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & File.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & File.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & File.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & File.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & File.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & File.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & File.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & File.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & File.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & File.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип файла - " & File.Type
MsgBox Str
5.2.8. Path
Синтаксис:
Path
Возвращаемое значение: полный путь к файлу.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & File.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & File.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & File.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & File.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & File.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & File.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & File.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & File.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & File.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & File.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип файла - " & File.Type
MsgBox Str
5.2.9. ShortName
Синтаксис:
ShortName
Возвращаемое значение: короткое имя файла в формате 8.3.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & File.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & File.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & File.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & File.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & File.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & File.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & File.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & File.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & File.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & File.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип файла - " & File.Type
MsgBox Str
5.2.10. ShortPath
Синтаксис:
ShortPath
Возвращаемое значение: короткий путь к файлу в формате 8.3.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & File.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & File.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & File.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & File.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & File.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & File.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & File.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & File.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & File.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & File.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип файла - " & File.Type
MsgBox Str
5.2.11. Size
Синтаксис:
Size
Возвращаемое значение: размер файла в байтах.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & File.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & File.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & File.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & File.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & File.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & File.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & File.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & File.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & File.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & File.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип файла - " & File.Type
MsgBox Str
5.2.12. Type
Синтаксис:
Type
Возвращаемое значение: тип файла. Информация, похожая на ту, которую можно увидеть в палитре свойств файла в проводнике.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & File.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & File.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & File.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & File.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & File.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & File.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & File.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & File.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & File.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & File.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип файла - " & File.Type
MsgBox Str
5.3. Методы
5.3.1. Copy
Синтаксис:
Copy(<Destination>,<Overwrite>)
Назначение: копирует файл в указанное место.
Параметры:
- <Destination> — строка, путь (куда копировать).
- <Overwrite> — необязательный, булево (число). Заменять файл, если он существует (True), или нет (False)
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
File.Copy "D:"
File.Copy "D:Copy of autoexec.bat"
5.3.2. Move
Синтаксис:
Move(<Destination>)
Назначение: перемещает файл в указанное место.
Параметры:
- <Destination> — строка, путь (куда перемещать).
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
File.Move "D:"
'File.Move "D:Copy of autoexec.bat"
5.3.3. Delete
Синтаксис:
Delete(<Force>)
Назначение: удаляет файл.
Параметры:
- <Force> — необязательный, булево (число). Удалять файл, если он имеет атрибут «только для чтения» (True), или нет (False).
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:Test.txt")
File.Delete
5.3.4. OpenAsTextStream
Синтаксис:
OpenAsTextStream(<Iomode>,<Format>)
Назначение: открывает текстовый файл и возвращает объект «TextStream», указывающий на него.
Параметры:
- <Iomode> — необязательный, число. Возможные значения:
- 1 — Открыть файл только для чтения.
- 2 — Открыть файл для записи. Если файл уже существовал, его содержимое теряется.
- 8 — Открыть файл для добавления. Если файл уже существовал, информация будет дописываться в конец файла.
- <Format> — необязательный, число. Возможные значения:
- -2 — Открыть файл в формате, используемом системой по умолчанию.
- -1 — Открыть файл в формате Unicode.
- 0 — Открыть файл в формате ASCII (по умолчанию).
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:boot.ini")
Set TextStream = File.OpenAsTextStream(1)
MsgBox TextStream.ReadAll()
TextStream.Close
6. Объект Folder
6.1. Создание объекта
Пример №1:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
Пример №2:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetSpecialFolder(0)
Пример №3:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set DriveC = FSO.GetDrive("C:")
Set Folder = DriveC.RootFolder
Пример №4:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
For Each SubFolder In Folder.SubFolders
WScript.Echo SubFolder.Name
Next
6.2. Свойства
6.2.1. Attributes
Синтаксис:
Attributes
Возвращаемое значение: число, набор флагов атрибутов папки. Флаги:
- 0 — Normal. Обычный файл (нет атрибутов).
- 1 — ReadOnly. Файл только для чтения. Чтение и запись.
- 2 — Hidden. Скрытый. Чтение и запись.
- 4 — System. Системный. Чтение и запись.
- 8 — Volume. Диск. Только чтение.
- 16 — Directory. Папка или файл. Только чтение.
- 32 — Archive. Архивный. Чтение и запись.
- 1024 — Alias. Ссылка или ярлык. Только чтение.
- 2048 — Compressed. Сжатый. Только чтение.
Замечание: чтение и запись или только чтение, в зависимости от атрибута.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
Attrs = Folder.Attributes
Set Dict = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
Dict.Add "ReadOnly", 0
Dict.Add "Hidden", 0
Dict.Add "System", 0
Dict.Add "Volume", 0
Dict.Add "Directory", 0
Dict.Add "Archive", 0
Dict.Add "Alias", 0
Dict.Add "Compressed", 0
If Attrs And 2048 Then
Dict.Item("Compressed") = 1
End If
If Attrs And 1024 Then
Dict.Item("Alias") = 1
End If
If Attrs And 32 Then
Dict.Item("Archive") = 1
End If
If Attrs And 16 Then
Dict.Item("Directory") = 1
End If
If Attrs And 8 Then
Dict.Item("Volume") = 1
End If
If Attrs And 4 Then
Dict.Item("System") = 1
End If
If Attrs And 2 Then
Dict.Item("Hidden") = 1
End If
If Attrs And 1 Then
Dict.Item("ReadOnly") = 1
End If
Str = "Атрибуты папки """ & Folder.Path & """:" & vbCrLf
For Each Attr In Dict
Str = Str & Attr & " = " & Dict.Item(Attr) & vbCrLf
Next
MsgBox Str
6.2.2. DateCreated
Синтаксис:
DateCreated
Возвращаемое значение: дата создания каталога.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & Folder.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & Folder.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & Folder.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & Folder.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Это корневой каталог - " & Folder.IsRootFolder & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & Folder.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & Folder.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & Folder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & Folder.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & Folder.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & Folder.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип каталога - " & Folder.Type & vbCrLf
MsgBox Str
6.2.3. DateLastAccessed
Синтаксис:
DateLastAccessed
Возвращаемое значение: дата последнего доступа к каталогу.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & Folder.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & Folder.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & Folder.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & Folder.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Это корневой каталог - " & Folder.IsRootFolder & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & Folder.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & Folder.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & Folder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & Folder.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & Folder.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & Folder.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип каталога - " & Folder.Type & vbCrLf
MsgBox Str
6.2.4. DateLastModified
Синтаксис:
DateLastModified
Возвращаемое значение: дата последней модификации каталога.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & Folder.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & Folder.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & Folder.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & Folder.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Это корневой каталог - " & Folder.IsRootFolder & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & Folder.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & Folder.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & Folder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & Folder.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & Folder.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & Folder.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип каталога - " & Folder.Type & vbCrLf
MsgBox Str
6.2.5. Drive
Синтаксис:
Drive
Возвращаемое значение: объект «Drive» диска, на котором находится каталог.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & Folder.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & Folder.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & Folder.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & Folder.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Это корневой каталог - " & Folder.IsRootFolder & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & Folder.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & Folder.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & Folder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & Folder.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & Folder.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & Folder.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип каталога - " & Folder.Type & vbCrLf
MsgBox Str
6.2.6. IsRootFolder
Синтаксис:
IsRootFolder
Возвращаемое значение: булево (число). Признак того, является ли каталог корневым.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & Folder.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & Folder.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & Folder.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & Folder.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Это корневой каталог - " & Folder.IsRootFolder & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & Folder.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & Folder.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & Folder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & Folder.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & Folder.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & Folder.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип каталога - " & Folder.Type & vbCrLf
MsgBox Str
6.2.7. Name
Синтаксис:
Name
Возвращаемое значение: имя каталога.
Замечание: чтение и запись.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & Folder.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & Folder.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & Folder.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & Folder.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Это корневой каталог - " & Folder.IsRootFolder & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & Folder.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & Folder.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & Folder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & Folder.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & Folder.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & Folder.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип каталога - " & Folder.Type & vbCrLf
MsgBox Str
6.2.8. ParentFolder
Синтаксис:
ParentFolder
Возвращаемое значение: объект «Folder» родительского каталога.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & Folder.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & Folder.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & Folder.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & Folder.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Это корневой каталог - " & Folder.IsRootFolder & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & Folder.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & Folder.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & Folder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & Folder.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & Folder.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & Folder.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип каталога - " & Folder.Type & vbCrLf
MsgBox Str
6.2.9. Path
Синтаксис:
Path
Возвращаемое значение: полный путь к каталогу.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & Folder.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & Folder.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & Folder.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & Folder.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Это корневой каталог - " & Folder.IsRootFolder & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & Folder.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & Folder.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & Folder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & Folder.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & Folder.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & Folder.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип каталога - " & Folder.Type & vbCrLf
MsgBox Str
6.2.10. ShortName
Синтаксис:
ShortName
Возвращаемое значение: короткое имя каталога в формате 8.3.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & Folder.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & Folder.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & Folder.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & Folder.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Это корневой каталог - " & Folder.IsRootFolder & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & Folder.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & Folder.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & Folder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & Folder.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & Folder.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & Folder.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип каталога - " & Folder.Type & vbCrLf
MsgBox Str
6.2.11. ShortPath
Синтаксис:
ShortPath
Возвращаемое значение: короткий путь к каталогу в формате 8.3.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & Folder.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & Folder.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & Folder.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & Folder.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Это корневой каталог - " & Folder.IsRootFolder & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & Folder.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & Folder.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & Folder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & Folder.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & Folder.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & Folder.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип каталога - " & Folder.Type & vbCrLf
MsgBox Str
6.2.12. Size
Синтаксис:
Size
Возвращаемое значение: размер всех файлов и подкаталогов, входящих в данный каталог, в байтах.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & Folder.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & Folder.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & Folder.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & Folder.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Это корневой каталог - " & Folder.IsRootFolder & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & Folder.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & Folder.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & Folder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & Folder.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & Folder.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & Folder.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип каталога - " & Folder.Type & vbCrLf
MsgBox Str
6.2.13. Type
Синтаксис:
Type
Возвращаемое значение: тип каталога. Информация, похожая на ту, которую можно увидеть в палитре свойств каталога в проводнике.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
Str = vbNullString
Str = Str & "Дата создания - " & Folder.DateCreated & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последнего доступа - " & Folder.DateLastAccessed & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Дата последней модификации - " & Folder.DateLastModified & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Диск - " & Folder.Drive.DriveLetter & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Это корневой каталог - " & Folder.IsRootFolder & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Имя - " & Folder.Name & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Родительский каталог - " & Folder.ParentFolder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь - " & Folder.Path & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Короткое имя - " & Folder.ShortName & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Путь в формате 8.3 - " & Folder.ShortPath & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Размер - " & Folder.Size & vbCrLf
Str = Str & "Тип каталога - " & Folder.Type & vbCrLf
MsgBox Str
6.2.14. SubFolders
Синтаксис:
SubFolders
Возвращаемое значение: объект-коллекция «Folders», содержащая все подкаталоги данного каталога, включая скрытые и системные.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:")
MsgBox Folder.SubFolders.Count
Set SubFolder = Folder.SubFolders.Item("Program Files")
MsgBox SubFolder.Path
Set SubFolder = Folder.SubFolders("Program Files")
MsgBox SubFolder.Path
Другой пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:Program Files")
For Each SubFolder In Folder.SubFolders
WScript.Echo SubFolder.Name
Next
Создание нового подкаталога:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:")
Set NewFolder = Folder.SubFolders.Add("New Folder")
6.2.15. Files
Синтаксис:
Files
Возвращаемое значение: объект-коллекция «Files», содержащая все файлы данного каталога, включая скрытые и системные.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:")
MsgBox Folder.Files.Count
Set File = Folder.Files.Item("AUTOEXEC.BAT")
MsgBox File.Path
Set File = Folder.Files("AUTOEXEC.BAT")
MsgBox File.Path
Другой пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:")
For Each File In Folder.Files
WScript.Echo File.Name
Next
6.3. Методы
6.3.1. Copy
Синтаксис:
Copy(<Destination>,<Overwrite>)
Назначение: копирует каталог в указанное место.
Параметры:
- <Destination> — строка, путь (куда копировать).
- <Overwrite> — необязательный, булево (число). Заменять каталог, если он существует (True), или нет (False).
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("D:JobSite")
Folder.Copy "D:"
6.3.2. Move
Синтаксис:
Move(<Destination>)
Назначение: перемещает каталог в указанное место.
Параметры:
- <Destination> — строка, путь (куда перемещать).
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("D:JobSite")
Folder.Move "D:"
6.3.3. Delete
Синтаксис:
Delete(<Force>)
Назначение: удаляет каталог со всем содержимым.
Параметры:
- <Force> — необязательный, булево (число). Удалять каталог, если он имеет атрибут «только для чтения» (True), или нет (False).
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:New Folder")
Folder.Delete
6.3.4. CreateTextFile
Синтаксис:
CreateTextFile(<Filename>,<Overwrite>,<Unicode>)
Назначение: создаёт новый текстовый файл и возвращает объект «TextStream», указывающий на него.
Параметры:
- <Filename> — строка, имя файла.
- <Overwrite> — необязательный, булево (число). Перезаписывать файл, если он существует (True), или нет (False). По умолчанию — False. Если указано False и файл существует — произойдёт ошибка.
- <Unicode> — необязательный, булево (число). Файл в формате Unicode (True), или ASCII (False). По умолчанию — False.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:")
Set TextStream = Folder.CreateTextFile("Test.txt")
7. Объект TextStream
7.1. Создание объекта
Пример №1:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set TextStream = FSO.CreateTextFile("C:Test.txt")
Пример №2:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Folder = FSO.GetFolder("C:")
Set TextStream = Folder.CreateTextFile("Test.txt")
Пример №3:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set TextStream = FSO.OpenTextFile("C:autoexec.bat")
Пример №4:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:autoexec.bat")
Set TextStream = File.OpenAsTextStream(1)
7.2. Свойства
7.2.1. AtEndOfLine
Синтаксис:
AtEndOfLine
Возвращаемое значение: содержит True, если указатель достиг конца строки и False в противном случае. Работает только если файл открыт для чтения.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:boot.ini")
Set TextStream = File.OpenAsTextStream(1)
Str = vbNullString
While Not TextStream.AtEndOfLine
Str = Str & TextStream.Read(1)
Wend
TextStream.Close
MsgBox Str
7.2.2. AtEndOfStream
Синтаксис:
AtEndOfStream
Возвращаемое значение: содержит True, если указатель достиг конца файла и False в противном случае. Работает только если файл открыт для чтения.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:boot.ini")
Set TextStream = File.OpenAsTextStream(1)
Str = vbNullString
While Not TextStream.AtEndOfStream
Str = Str & TextStream.ReadLine() & vbCrLf
Wend
TextStream.Close
MsgBox Str
7.2.3. Column
Синтаксис:
Column
Возвращаемое значение: содержит номер колонки текущего символа файла.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:boot.ini")
Set TextStream = File.OpenAsTextStream(1)
Str = vbNullString
While Not TextStream.AtEndOfLine
Str = Str & TextStream.Column & ": " & TextStream.Read(1) & vbCrLf
Wend
TextStream.Close
MsgBox Str
7.2.4. Line
Синтаксис:
Line
Возвращаемое значение: содержит номер текущей строки файла.
Замечание: только чтение.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:boot.ini")
Set TextStream = File.OpenAsTextStream(1)
Str = vbNullString
While Not TextStream.AtEndOfStream
Str = Str & TextStream.Line & ": " & TextStream.ReadLine() & vbCrLf
Wend
TextStream.Close
MsgBox Str
7.3. Методы
7.3.1. Close
Синтаксис:
Close
Назначение: закрывает открытый файл.
Параметры: нет.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:boot.ini")
Set TextStream = File.OpenAsTextStream(1)
MsgBox TextStream.ReadAll()
TextStream.Close
7.3.2. Read
Синтаксис:
Read(<Characters>)
Назначение: считывает из файла указанное количество символов и возвращает полученную строку.
Параметры:
- <Characters> — число, количество символов, которое нужно считать.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:boot.ini")
Set TextStream = File.OpenAsTextStream(1)
MsgBox TextStream.Read(13)
TextStream.Close
7.3.3. ReadAll
Синтаксис:
ReadAll
Назначение: считывает весь файл и возвращает полученную строку.
Параметры: нет.
Описание: для больших файлов использование этого метода потребует больших ресурсов памяти.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:boot.ini")
Set TextStream = File.OpenAsTextStream(1)
MsgBox TextStream.ReadAll()
TextStream.Close
7.3.4. ReadLine
Синтаксис:
ReadLine
Назначение: считывает строку из файла и возвращает полученную строку.
Параметры: нет.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:boot.ini")
Set TextStream = File.OpenAsTextStream(1)
Str = vbNullString
While Not TextStream.AtEndOfStream
Str = Str & TextStream.ReadLine() & vbCrLf
Wend
MsgBox Str
TextStream.Close
7.3.5. Skip
Синтаксис:
Skip(<Characters>)
Назначение: пропускает при чтении файла указанное количество символов.
Параметры:
- <Characters> — число, количество символов, которые нужно пропустить.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:boot.ini")
Set TextStream = File.OpenAsTextStream(1)
MsgBox TextStream.Read(13)
TextStream.Skip 10
MsgBox TextStream.Read(10)
TextStream.Close
7.3.6. SkipLine
Синтаксис:
SkipLine
Назначение: пропускает при чтении файла строку.
Параметры: нет.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set File = FSO.GetFile("C:boot.ini")
Set TextStream = File.OpenAsTextStream(1)
MsgBox TextStream.ReadLine()
TextStream.SkipLine
MsgBox TextStream.ReadLine()
TextStream.Close
7.3.7. Write
Синтаксис:
Write(<String>)
Назначение: записывает в файл указанную строку. Символы возврата каретки и новой строки в файл не записываются.
Параметры:
- <String> — строка для записи в файл.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set TextStream = FSO.CreateTextFile("C:Test.txt")
TextStream.Write("Text")
TextStream.Close
7.3.8. WriteLine
Синтаксис:
WriteLine(<String>)
Назначение: записывает в файл указанную строку. В файл записываются символы возврата каретки и новой строки.
Параметры:
- <String> — необязательный, строка для записи в файл. Если опущен, в файл записывается пустая строка.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set TextStream = FSO.CreateTextFile("C:Test.txt")
TextStream.WriteLine "Text"
TextStream.Close
7.3.9. WriteBlankLines
Синтаксис:
WriteBlankLines(<Lines>)
Назначение: записывает в файл указанное количество пустых строк (символы возврата каретки и новой строки).
Параметры:
- <Lines> — число, количество пустых строк, которое надо записать.
Пример:
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set TextStream = FSO.CreateTextFile("C:Test.txt")
TextStream.WriteBlankLines 5
TextStream.Close
This Access Excel VBA tutorial explains how to copy workbook or file.
You may also want to read:
FSO File Methods
Worksheets.Copy Method to copy worksheet
There are two common ways to copy workbook or file
- FSO.CopyFile Method
- FileCopy Function
I have explained how to use different FSO Methods in my previous post, click to see more details.
Using FSO.CopyFile Method to copy workbook
You should be able to run FSO in Excel 2013. If you fail to run FSO Object, open VBE (ALT+F11) > Tools > References > Check the box Microsoft Scripting Runtine
Syntax of FSO.CopyFile
object.CopyFile source, destination[, overwrite]
| object | Required. Always the name of a FileSystemObject. |
| source | Required. Character string file specification, which can include wildcard characters, for one or more files to be copied. |
| destination | Required. Character string destination where the file or files from source are to be copied. Wildcard characters are not allowed. |
| overwrite | Optional. Boolean value that indicates if existing files are to be overwritten. If True, files are overwritten; if False, they are not. The default is True. Note that CopyFile will fail if destination has the read-only attribute set, regardless of the value of overwrite. |
Example
The below Procedure copies a File from Desktop to C:test, overwriting existing File.
Public Sub cpyFile()
copyFromPath = "C:UsersWYMANDesktoptestDel.xlsx"
copyToPath = "C:testtestDel.xlsx"
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
If FSO.FileExists(copyFromPath) = True Then
FSO.copyfile copyFromPath, copyToPath, True
End If
End Sub
Using FileCopy Function to copy workbook
Note that this is FileCopy Function, while the above example demonstrates CopyFile Method. Click here to see the difference between Function and Method.
Syntax of FileCopy
FileCopy(Source As String, Destination As String)
| Source | Required. String expression that specifies the name of the file to be copied. Source may include the directory or folder, and drive, of the source file |
| Destination | Required. String expression that specifies the target file name. Destination may include the directory or folder, and drive, of the destination file. |
Example
Same as the above example, the below Macro copies a File from Desktop to C:test, overwriting existing File.
Note that FileCopy Function does not require FSO object, I declare FSO in order to use the FSO.FileExists Method.
Public Sub cpyFile2()
copyFromPath = "C:UsersWYMANDesktoptestDel.xlsx"
copyToPath = "C:testtestDel.xlsx"
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
If FSO.FileExists(copyFromPath) = True Then
FileCopy copyFromPath, copyToPath
End If
End Sub
In general when we write VBA scripts we either trying to automate an office application task like in Excel, Outlook, Word, or Access, or we are trying to implement a functionality to an existing program. One thing makes VBA versatile is its ability to work with Windows System API.
One of my favorite Window System API is the FileSystemObject (FSO).
The FileSystemObject gives you the ability to access a computer’s file system, that means you can manipulate files, folders, directory paths, as long as you have sufficient permission and privilege. If you are often having the need to organize files or folders, by knowing how to work with FileSystemObject, the skill will help you with your files and folders management tremendously.
The FileSystemObject has been around for a long long time, but even today, it is still pretty widely used on Windows. In this tutorial we will learn how to use the FileSystemObject’s methods by going through different examples together.
Example 1. BuildPath
Appends a name to an existing folder path.
Syntax
BuildPath(path, name)
Example 2. CopyFile
Copies one or more files from one location to another.
Syntax
CopyFile(source file path, destination folder path, [overwrite])
Example 3. CopyFolder
Copies one or more folders from one location to another.
Syntax
CopyFolder(source folder path, destination folder path, [overwrite])
Example 4. CreateFolder
Creates a new folder.
Syntax
CreateFolder(folder name)
Example 5. CreateTextFile
Creates a text file and returns as a TextStream object.
Syntax
CreateTextFile(file name, [overwrite], [unicode])
Example 6. DeleteFile
Deletes one or more files.
Syntax
DeleteFile(file path, [force])
Example 7. DeleteFolder
Deletes one or more folders.
Syntax
DeleteFolder(folder path, [force])
Example 8. DriveExists
Check if a specified drive exists.
Syntax
DriveExists(drive spec)
Example 9. FileExists
Check if a specified file exists.
Syntax
FileExists(file path)
Example 10. FolderExists
Check if a specified folder exists.
Syntax
FolderExists(folder path)
Example 11. GetAbsolutePathName
Returns the complete path from the root of the drive for the specified path.
Syntax
GetAbsolutePathName(path spec)
Example 12. GetBaseName
Returns the base name of a specified file or folder.
Syntax
GetBaseName(file or folder path)
Example 13. GetDriveName
Returns the drive name giving a specified file or folder path.
Syntax
GetDriveName(file or folder path)
Example 14. GetDrive
Returns a Drive object corresponding to the drive in a specified path.
Syntax
GetDrive(drive spec)
Example 15. GetExtensionName
Returns the file extension name.
Syntax
GetExtensionName(file path)
Example 16. GetFile
Returns a File object giving a specified file path.
Syntax
GetFile(file path)
Example 17. GetFileName
Returns the file name or folder name of the last component in a specified path.
Syntax
GetFileName(file path)
Example 18. GetFolder
Returns a Folder object giving a specified path.
Syntax
GetFolder(folder path)
Example 19. GetParentFolderName
Returns the name of the parent folder of the last component in a specified file or folder path.
Syntax
GetParentFolderName(folder name)
Example 20. GetSpecialFolder
Returns the Windows System paths
Syntax
GetSpecialFolder(folder spec)
Example 21. GetTempName
Returns a randomly generated temporary file name.
Syntax
GetTempName()
Example 22. MoveFile
Move one or more files from one location to another.
Syntax
MoveFile(source file path, destination folder path)
Example 23. MoveFolder
Move one or more folders from one location to another.
Syntax
MoveFolder(source folder path, destination folder path)
Example 24. OpenTextFile
Opens a file as a TextStream object.
Syntax
OpenTextFile(file name, [io mode], [create], [format]
io mode settings
[table id=3 /]
format settings
[table id=4 /]
When we use VBA in Excel, most of it is to automate our tasks.
This also means that most of the time, we work with cells and ranges, worksheets, workbooks, and other objects which are a part of the Excel application.
But VBA is a lot more powerful and can also be used to work with stuff outside of Excel.
In this tutorial, I will show you how to use VBA FileSystemObject (FSO) to work with files and folders on your system or network drives.
What is VBA FileSystemObject (FSO)?
FileSystemObject (FSO) allows you to access the file system of your computer. Using it, you can access and modify the files/folders/directories in your computer system.
For example, below are some of the things you can do by using FileSystemObject in Excel VBA:
- Check if a file or a folder exists.
- Create or rename folders/files.
- Get a list of all the file names (or sub-folder names) in a folder.
- Copy files from one folder to another.
I hope you get the idea.
I will cover all these above examples (plus more) later in this tutorial.
While some of the things mentioned above can also be done using traditional VBA functions (such as the DIR function) and methods, that would lead to longer and more complicated codes. FileSystemObject makes it easy to work with files and folders while keeping the code clean and short.
Note: FSO can only be used in Excel 2000 and later versions.
What All Objects Can You Access Through FileSystemObject?
As I mentioned above, you can access and modify files and folders using the FileSystemObject in VBA.
Below is a table that shows the most important objects that you can access and modify using FSO:
| Object | Description |
| Drive | Drive Object allows you to get information about the drive such as whether it exists or not, it’s path name, drive type (removable or fixed), it’s size, etc. |
| Folder | Folder object allows you to create or modify folders in your system. For example, you can create, delete, rename, copy folders using this object. |
| File | File Object allows you to work with files in your system. For example, you can create, open, copy, move, and delete files using this object. |
| TextStream | TextStream object allows you to create or read text files. |
Each of the above objects has methods that you can use to work with these.
To give you an example, if you want to delete a folder, you will use the DeleteFolder method of the Folder object. Similarly, if you want to copy a file, you will use the CopyFile method of the File object.
Don’t worry if this seems overwhelming or hard to understand. You will get a much better understanding when you go through the examples that I have covered in this tutorial.
Just for the reference purpose, I have covered all the FileSystemObject methods (for each object) at the end of this tutorial.
Enabling FileSystemObject in Excel VBA
FileSystemObject is not available by default in the Excel VBA.
Since we are dealing with files and folders that are outside of the Excel application, we need to first create a reference to the library that holds these objects (drives, files, folders).
Now there are two ways you can start using FileSystemObject in Excel VBA:
- Setting the reference to the Microsoft Scripting Runtime Library (Scrrun.dll)
- Creating an object to refer to the library from the code itself
While both these methods work (and I’ll show you how to do this next), I recommend using the first method.
Note: When you enable FileSystemObject, you can access all the objects in it. This includes the FileSystemObject, Drive, Files, Folders, etc. I will be focussing majorly on the FileSystemObject in this tutorial.
Setting the Reference to the Microsoft Scripting Runtime Library
When you create a reference to the Scripting Runtime Library, you allow Excel VBA the access to all the properties and methods of files and folder. Once this is done, you can refer to the files/folders/drives object from within the Excel VBA (just like you can refer the cells, worksheets or workbooks).
Below are the steps to create a reference to the Microsoft Scripting Runtime Library:
- In the VB Editor, click on Tools.
- Click on References.
- In the References dialog box that opens, scroll through the available references and check the ‘Microsoft Scripting Runtime’ option.
- Click OK.
The above steps would now allow you to refer to the FSO objects from Excel VBA.
Creating an Instance of FileSystemObject in the Code
Once you have set the reference to the Scripting FileSystemObject library, you need to create an instance of the FSO object in your code.
Once this is created, you can use it in VBA.
Below is the code that will set the object variable MyFSO as a FileSystemObject object:
Sub CreatingFSO() Dim MyFSO As FileSystemObject Set MyFSO = New FileSystemObject End Sub
In this code, first I have declared the variable MyFSO as a FileSystemObject type object. This is possible only because I have created a reference to the Microsoft Scripting Runtime Library. If the reference is not created, this is going to give you an error (as Excel wouldn’t recognize what FileSystemObject means).
In the second line, two things happen:
- The NEW keyword creates an instance of the FileSystemObject. This means that now I can use all the methods of FileSystemObject to work with files and folders. If you don’t create this instance, you’ll not be able to access the methods of FSO.
- The SET keyword sets the object MyFSO to this new instance of FileSystemObject. This allows me to use this object to access files and folders. For example, if I need to create a folder, I can use MyFSO.CreateFolder method.
If you want, you can also combine the above two statements into one as shown below:
Sub CreatingFSO() Dim MyFSO As New FileSystemObject End Sub
A big benefit of using this method (which is to set the reference to the Microsoft Scripting Runtime Library) is that when you use the FSO objects in your code, you will be able to use the IntelliSense feature that shows the methods and properties associated with an object (as shown below).
This is not possible when you create the reference from within the code (covered next).
Creating an Object from the Code
Another way to create a reference to FSO is by doing it from the code. In this method, you don’t need to create any reference (as done in the previous method).
When you are writing the code, you can create an object from within the code and refer to the Scripting.FileSystemObject.
The below code creates an object FSO and then makes this a FileSystemObject type.
Sub FSODemo()
Dim FSO As Object
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
End Sub
While this may seem more convenient, a big downside of using this method is that it would not show an IntelliSense when you work with objects in FSO. For me, this is a huge negative and I always recommend using the previous method of enabling FSO (which is by setting the reference to the ‘Microsoft Scripting Runtime’)
VBA FileSystemObject Examples
Now let’s dive in and have a look at some practical examples of using FileSystemObject in Excel.
Example 1: Check if a File or Folder Exists
The following code will check whether the folder with the name ‘Test’ exists or not (in the specified location).
If the folder exists, the IF condition is True and it shows a message – ‘The Folder Exists’ in a message box. And if it doesn’t exist, it shows a message – The Folder Does Not Exist’.
Sub CheckFolderExist()
Dim MyFSO As FileSystemObject
Set MyFSO = New FileSystemObject
If MyFSO.FolderExists("C:UserssumitDesktopTest") Then
MsgBox "The Folder Exists"
Else
MsgBox "The Folder Does Not Exist"
End If
End Sub
Similarly, you can also check if a file exists or not.
The below code checks whether there is a file with the name Test.xlsx in the specified folder or not.
Sub CheckFileExist()
Dim MyFSO As FileSystemObject
Set MyFSO = New FileSystemObject
If MyFSO.FileExists("C:UserssumitDesktopTestTest.xlsx") Then
MsgBox "The File Exists"
Else
MsgBox "The File Does Not Exist"
End If
End Sub
Example 2: Create a New Folder in the Specified Location
The below code would create a folder with the name ‘Test’ in the C drive of my system (you will have to specify the path on your system where you want to create the folder).
Sub CreateFolder()
Dim MyFSO As FileSystemObject
Set MyFSO = New FileSystemObject
MyFSO.CreateFolder ("C:UserssumitDesktopTest")
End Sub
While this code works fine, it would show an error in case the folder already exists.
The below code checks whether the folder already exists and creates a folder if it doesn’t. In case the folder already exists, it shows a message. To check whether the folder exists, I have used the FolderExists method of the FSO.
Sub CreateFolder()
Dim MyFSO As FileSystemObject
Set MyFSO = New FileSystemObject
If MyFSO.FolderExists("C:UserssumitDesktopTest") Then
MsgBox "The Folder Already Exist"
Else
MyFSO.CreateFolder ("C:UserssumitDesktopTest")
End If
End Sub
Example 3: Get a List of All Files in a Folder
The below code would show the names of all the files in the specified folder.
Sub GetFileNames()
Dim MyFSO As FileSystemObject
Dim MyFile As File
Dim MyFolder As Folder
Set MyFSO = New Scripting.FileSystemObject
Set MyFolder = MyFSO.GetFolder("C:UserssumitDesktopTest")
For Each MyFile In MyFolder.Files
Debug.Print MyFile.Name
Next MyFile
End Sub
This code is a little more complex that the ones we have already seen.
As I mentioned above in this tutorial, when you reference the ‘Microsoft Scripting Runtime Library’, you can use FileSystemObject as well as all other objects (such as Files and Folders).
In the above code, I use three objects – FileSystemObject, File, and Folder. This allows me to go through each file in the specified folder. I then use the name property to get the list of all file names.
Note that I am using Debug.Print to get the names of all the files. These names will be listed in the immediate window in the VB Editor.
Example 4: Get the List of All Sub-folders in a Folder
The below code will give the names of all the sub-folders in the specified folder. The logic is exactly the same as covered in the above example. Instead of files, in this code, we have used sub-folders.
Sub GetSubFolderNames()
Dim MyFSO As FileSystemObject
Dim MyFile As File
Dim MyFolder As Folder
Dim MySubFolder As Folder
Set MyFSO = New Scripting.FileSystemObject
Set MyFolder = MyFSO.GetFolder("C:UserssumitDesktopTest")
For Each MySubFolder In MyFolder.SubFolders
Debug.Print MySubFolder.Name
Next MySubFolder
End Sub
Example 5: Copy a File from One Place to Another
The below code will copy the file from ‘Source’ folder and copy it to the ‘Destination’ folder.
Sub CopyFile() Dim MyFSO As FileSystemObject Dim SourceFile As String Dim DestinationFolder As String Set MyFSO = New Scripting.FileSystemObject SourceFile = "C:UserssumitDesktopSourceSampleFile.xlsx" DestinationFolder = "C:UserssumitDesktopDestination" MyFSO.CopyFile Source:=SourceFile, Destination:=DestinationFolder & "SampleFileCopy.xlsx" End Sub
In the above code, I have used two variables – SourceFile and DestinationFolder.
Source File holds the address of the file I want to copy and the DestinationFolder variable holds the address to the folder I want the file to be copied to.
Note that it’s not sufficient to give the destination folder name when you’re copying a file. You also need to specify the file name. You can use the same file name or can also change it. In the above example, I copied the file and named it SampleFileCopy.xlsx
Example 6: Copy All Files From One Folder to Another
The below code will copy all the files from the Source folder to the destination folder.
Sub CopyAllFiles()
Dim MyFSO As FileSystemObject
Dim MyFile As File
Dim SourceFolder As String
Dim DestinationFolder As String
Dim MyFolder As Folder
Dim MySubFolder As Folder
SourceFolder = "C:UserssumitDesktopSource"
DestinationFolder = "C:UserssumitDesktopDestination"
Set MyFSO = New Scripting.FileSystemObject
Set MyFolder = MyFSO.GetFolder(SourceFolder)
For Each MyFile In MyFolder.Files
MyFSO.CopyFile Source:=MyFSO.GetFile(MyFile), _
Destination:=DestinationFolder & "" & MyFile.Name, Overwritefiles:=False
Next MyFile
End Sub
The above code will copy all the files from the Source folder to the Destination Folder.
Note that in the MyFSO.CopyFile method, I have specified the ‘Overwritefiles’ property to be False (this is True by default). This makes sure that in case you already have the file in the folder, it’s not copied (and you will see an error). If you remove ‘Overwritefiles’ or set this to True, in case there are files in the destination folder with the same name, these would be overwritten.
Pro Tip: When copying files, there is always a chance of overwriting files. A good idea, in this case, is to add the timestamp along with the name. This will ensure that the names are always different and you can easily track which files were copied at what time.
If you want to copy the files of a certain extension only, you can do that by using an IF Then statement to check whether the extension is xlsx or not.
Sub CopyExcelFilesOnly()
Dim MyFSO As FileSystemObject
Dim MyFile As File
Dim SourceFolder As String
Dim DestinationFolder As String
Dim MyFolder As Folder
Dim MySubFolder As Folder
SourceFolder = "C:UserssumitDesktopSource"
DestinationFolder = "C:UserssumitDesktopDestination"
Set MyFSO = New Scripting.FileSystemObject
Set MyFolder = MyFSO.GetFolder(SourceFolder)
For Each MyFile In MyFolder.Files
If MyFSO.GetExtensionName(MyFile) = "xlsx" Then
MyFSO.CopyFile Source:=MyFSO.GetFile(MyFile), _
Destination:=DestinationFolder & "" & MyFile.Name, Overwritefiles:=False
End If
Next MyFile
End Sub
FileSystemObject (FSO) Methods
Here are the methods that you can use for each object. This is just for reference purpose and doesn’t worry about it too much. The usage of some of these has been shown in the examples covered above.
| FSO Methods | For Object | Description |
| DriveExists | Drive | Checks whether the drive exists or not |
| GetDrive | Drive | Returns an instance of the drive object based on the specified path |
| GetDriveName | Drive | Reruns the drive name |
| BuildPath | File/Folder | Generate a path from an existing path and a name |
| CopyFile | File/Folder | Copies a file |
| GetAbsolutePathName | File/Folder | Return the canonical representation of the path |
| GetBaseName | File/Folder | Return base name from a path. For example, “D:TestFolderTestFile.xlsm” will return TextFile.xlsm |
| GetTempName | File/Folder | Generate name that can be used to name a temporary file |
| CopyFolder | Folder | Copies a folder from one location to other |
| CreateFolder | Folder | Creates a new folder |
| DeleteFolder | Folder | Deletes the specified folder |
| FolderExists | Folder | Checks whether the Folder exists or not |
| GetFolder | Folder | Returns an instance of the folder object based on the specified path |
| GetParentFolderName | Folder | Retruns the name of the parent folder based on the specified path |
| GetSpecialFolder | Folder | Get the location of various system folders. |
| MoveFolder | Folder | Moves a folder from one location to other |
| DeleteFile | File | Deletes a file |
| FileExists | File | Checks if a file exists or not |
| GetExtensionName | File | Returns the file extension |
| GetFile | File | Returns the instance of a file object based on the specified path |
| GetFileName | File | Returns the file name |
| GetFileVersion | File | Returns the file version |
| MoveFile | File | Moves a file |
| CreateTextFile | File | Creates a text file |
| GetStandardStream | File | Retrieve the standard input, output or error stream |
| OpenTextFile | File | Open a file as a TextStream |
You May Also Like the Following Excel Tutorials:
- Get a List of File Names from Folders & Sub-folders (using Power Query).
- Get the List of File Names from a Folder in Excel (with and without VBA).
- Understanding Excel VBA Data Types (Variables and Constants).
- Creating a User Defined Function (UDF) in Excel VBA.