This was my first main automation in Excel VBA. I was working a lot on SAP data and modifying it in Excel on the daily basis. Almost every day tons of same routine for get the data. One day I thought to myself about automation. I knew that I can record my activity in Excel, but did not know at all how to connect to SAP using Excel VBA?

Open SAP application
Firstly, if we don’t want to open SAP manually, we need to provide its directory.
'Change for your file directory
Shell "C:Program Files (x86)SAPFrontEndSAPguisaplogon.exe", 4
Set WshShell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")Then just wait for the activation of application, because sometimes it can lasts longer than usually.
Do Until WshShell.AppActivate("SAP Logon ")
Application.Wait Now + TimeValue("0:00:01")
LoopSet SAP app as object
After that we should set some objects to handle SAP.
Set SapGui = GetObject("SAPGUI")
Set Appl = SapGui.GetScriptingEngine
Set Connection = Appl.Openconnection("paste name of module", True)
Set session = Connection.Children(0)In Connection object put the name of the module you want to connect (from the SAP Logon Module screen below). It is important to put proper name, in other case You won’t connect.
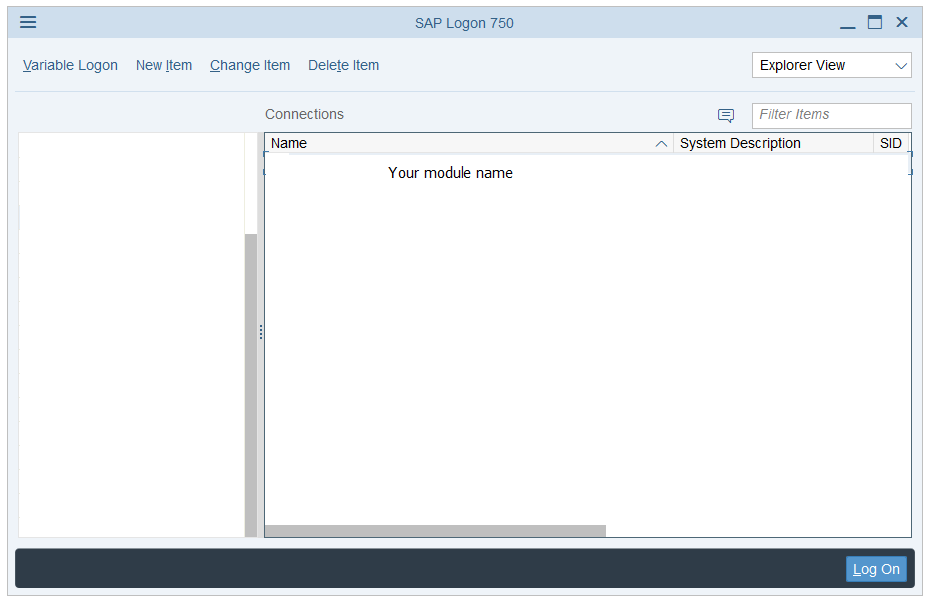
Log in with the data
In my case there was no need to login and write password, but if it is neccessary in your case I am also prepared for that.
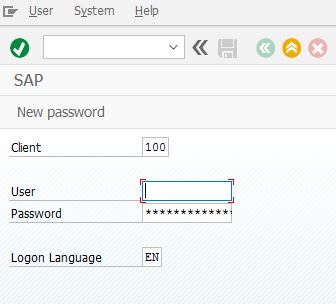
'if You need to pass username and password
session.findById("wnd[0]/usr/txtRSYST-MANDT").Text = "100"
session.findById("wnd[0]/usr/txtRSYST-BNAME").Text = "user"
session.findById("wnd[0]/usr/pwdRSYST-BCODE").Text = "password"
session.findById("wnd[0]/usr/txtRSYST-LANGU").Text = "EN"In first row there is unit number, in second put your user login, in third your password and in the last row choose language.
Check if it’s already opened
I also implemented to my SAP code check if it is already opened.
If session.Children.Count > 1 Then
answer = MsgBox("You've got opened SAP already," & _
"please leave and try again", vbOKOnly, "Opened SAP")
session.findById("wnd[1]/usr/radMULTI_LOGON_OPT3").Select
session.findById("wnd[1]/usr/radMULTI_LOGON_OPT3").SetFocus
session.findById("wnd[1]/tbar[0]/btn[0]").press
Exit Sub
End IfIn the end of connection, code is approving all the things from above and You are ready to do anything SAP.
session.findById("wnd[0]").maximize
session.findById("wnd[0]").sendVKey 0After that You can put your code, which is operating in SAP system. You can do this for example by script recording in Options.
Full code:
Sub SapConn()
Dim Appl As Object
Dim Connection As Object
Dim session As Object
Dim WshShell As Object
Dim SapGui As Object
'Of course change for your file directory
Shell "C:Program Files (x86)SAPFrontEndSAPguisaplogon.exe", 4
Set WshShell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
Do Until WshShell.AppActivate("SAP Logon ")
Application.Wait Now + TimeValue("0:00:01")
Loop
Set WshShell = Nothing
Set SapGui = GetObject("SAPGUI")
Set Appl = SapGui.GetScriptingEngine
Set Connection = Appl.Openconnection("paste name of module", _
True)
Set session = Connection.Children(0)
'if You need to pass username and password
session.findById("wnd[0]/usr/txtRSYST-MANDT").Text = "900"
session.findById("wnd[0]/usr/txtRSYST-BNAME").Text = "user"
session.findById("wnd[0]/usr/pwdRSYST-BCODE").Text = "password"
session.findById("wnd[0]/usr/txtRSYST-LANGU").Text = "EN"
If session.Children.Count > 1 Then
answer = MsgBox("You've got opened SAP already," & _
"please leave and try again", vbOKOnly, "Opened SAP")
session.findById("wnd[1]/usr/radMULTI_LOGON_OPT3").Select
session.findById("wnd[1]/usr/radMULTI_LOGON_OPT3").SetFocus
session.findById("wnd[1]/tbar[0]/btn[0]").press
Exit Sub
End If
session.findById("wnd[0]").maximize
session.findById("wnd[0]").sendVKey 0 'ENTER
'and there goes your code in SAP
End SubSummary
It took me couple of hours to find information in web how to connect to SAP via Excel VBA and finally set this up as code. After that I was only doing copy paste that to my next macros.
I just wanted to save your time, because I know how long and painful was that for me.
This code already helped one guy from StackOverflow – I hope it will help You too.
I also invite you to the next article in this series!
SAP session.findbyid – 10 code lines you can identify
I’m very advanced in VBA, Excel, also easily linking VBA with other Office applications (e.g. PowerPoint) and external applications (e.g. SAP). I take part also in RPA processes (WebQuery, DataCache, IBM Access Client Solutions) where I can also use my SQL basic skillset. I’m trying now to widen my knowledge into TypeScript/JavaScript direction.
View all posts by Tomasz Płociński
Accessing SAP Functions from Excel using Visual Basic Applications.
SAP has provided BAPIs which can be used to access SAP functions from Non SAP applications like Excel, VB, Java and C++.
Overview………………………………………………………………………………………………… 1
Call Standard SAP Function…………………………………………………………………………… 1
Whole Code………………………………………………………………………………………….. 3
Create Custom BAPIs………………………………………………………………………………….. 6
Catching Function Module Exception from VB……………………………………………………. 6
Creating table……………………………………………………………………………………….. 7
Create BAPI ZEMP_BAPI_INS_SMPL……………………………………………………………….. 7
Import Parameters…………………………………………………………………………………… 7
Exception…………………………………………………………………………………………….. 7
Function Module Code………………………………………………………………………………. 8
VB Code………………………………………………………………………………………………. 8
Catching Exception in VB…………………………………………………………………………… 9
Passing Table Parameters as Input………………………………………………………………….. 9
Create Structure…………………………………………………………………………………….. 9
Pass Table Parameter………………………………………………………………………………. 9
Function Module Code…………………………………………………………………………….. 10
VB Code…………………………………………………………………………………………….. 10
Overview
In this Blog, we will see how to call standard RFC enabled SAP function modules and custom Function Modules using VBA.
To access SAP from Excel, SAP GUI client must be installed on the pc.
Also only RFC (Remote Function Call) enabled functions can be called by External Applications.
The list of RFC enabled Function Modules in SAP can be obtained from the table TFDIR and set condition FMODE = ‘R’.
In this blog I have assumed the user is comfortable with Visual Basic and creating VBA macros in Excel.
Call Standard SAP Function
Example to get UserDetails.
In this example the BAPI BAPI_USER_GET_DETAIL is executed.
This BAPI can be executed on almost all SAP systems.
The parameters to this BAPI may change depending on the release number and type of system.
For ease the following constants are declared in VBA.
Public Const CNT_STR_USR As String = “MyId”
Public Const CNT_STR_PWD As String = “MYPWD” ‘It is better to make password in CAPITAL and less than 8 characters, because in some systems the password is case sensitive and password is send in CAPITAL to SAP system.
Public Const CNT_STR_APPLN_SRVR As String = “ides47”
Public Const CNT_STR_SYSTEM As String = “IDS”
Public Const CNT_STR_SYS_NUM As String = “00”
Public Const CNT_STR_CLIENT As String = “800”
Public Const CNT_STR_LOGON_LANG As String = “EN”
Public Const CNT_STR_LOG_FILE As String = “C:sap_vb.txt”
Public Const CNT_INT_LOG_LEVEL As Integer = 9
Const CNT_STR_BAPI_USER_DETAILS as String = “BAPI_USER_GET_DETAIL”
Create a macro in Excel called GetSAPUserDetails
Declaring the SAP Function control.
This ActiveX control is used to connect to SAP and call the Function Modules.
Either you can call this object at Runtime or at Design Time.
For calling this object at Design time, add a reference to the ActiveX Control “c:program filessapfrontendsapguiwdtfuncs.ocx”.
For getting the exact path of this ActiveX control, search in Windows registry for “SAP.Functions”
i.e. Dim obSAPFnCntrl as Object or
Dim obSAPFnCntrl as SAPFunctions
The advantage of calling object with Reference at runtime is that it is easy to change the code if you want to use it for VBScript.
Set obSAPFnCntrl = CreateObject (“SAP.Functions”)
Create a Connection Object to connect to SAP
Dim obSAPConn as Object
Set obSAPConn = obSAPFnCntrl.Connection
‘Set the Logfile and LogLevel Details
obSAPFnCntrl.LogLevel = CNT_INT_LOG_LEVEL
obSAPFnCntrl.LogFileName = CNT_STR_LOG_FILE
Set the properties for the connection control
With obSapConn
.ApplicationServer = CNT_STR_APPLN_SRVR
.SystemNumber = CNT_STR_SYS_NUM
.User = CNT_STR_USR
.Password = CNT_STR_PWD
.Language = CNT_STR_LOGON_LANG
.Client = CNT_STR_CLIENT
End With
Logging to SAP System
If obSapConn.Logon(0, True) = False Then
MsgBox “R/3 connection failed”
Exit Sub
End If
The Second Parameter True for the Logon method tells that it is a silent logon. If this parameter is set to False, then the LogonControl will be shown.
Create a BAPI Function Object.
Dim obSAPFnUserDetail as Object
‘Use the Add method of Function Control to attach Function.
Set obSAPFnUserDetail = obSapFnCntrl.Add(CNT_STR_BAPI_USER_DETAILS)
Declare the Export Parameter.
This is similar to Export Parameter while calling Function Modules.
The import parameter of Function Module is set as Export Parameter while calling the Function Module.
Here the only Export parameter is UserId
Call the Exports property of the function being called.
Dim obSAPExpUserName as Object
Set obSAPExpUserName = obSAPFnUserDetail.Exports(“USERNAME”)
Assign value for the Export Parameter
obSAPExpUserName.Value = CNT_STR_USR
Declare the Import Parameters
The import parameters can be set either before calling function or after calling Function
The import parameters to function are BAPI_USER_GET_DETAIL.
Here all Import Parameters are of type Structure
|
ParameterName |
Type |
AssociatedText |
ShortText |
|
LOGONDATA |
LIKE |
BAPILOGOND |
Structure with Logon Data |
|
DEFAULTS |
LIKE |
BAPIDEFAUL |
Structure with User Defaults |
|
ADDRESS |
LIKE |
BAPIADDR3 |
Address Data |
|
COMPANY |
LIKE |
BAPIUSCOMP |
Company for Company Address |
|
SNC |
LIKE |
BAPISNCU |
Secure Network Communication Data |
|
REF_USER |
LIKE |
BAPIREFUS |
User Name of the Reference User |
|
ALIAS |
LIKE |
BAPIALIAS |
User Name Alias |
Here we will use only the first 2 parameters logonData and Defaults
Declare objects for each parameter
Dim obSAPImpLogonData as Object ,obSAPImpDefaults as Object
Set obSAPImpLogonData = obSAPFnUserDetail.Imports(“LOGONDATA”)
Set obSAPImpDefaults = obSAPFnUserDetail.Imports(“DEFAULTS”)
The parameters can be of normal datatype like char or integer or structure.
The Set statement assigns the parameter type to the objects.
RETURN parameter.
The Return parameter can be of structure BAPIRET1 or BAPIRET2.
Declare the Table Parameters
Dim obSAPTblParameter as Object ,obSAPTblProfiles as Object , obSAPTblReturn as Object
‘Now Set the objects
Set obSAPTblParameter = obSAPFnUserDetail.Tables(“PARAMETER”)
Set obSAPTblProfiles = obSAPFnUserDetail.Tables(“PROFILES”)
Set obSAPTblReturn = obSAPFnUserDetail.Tables(“RETURN”)
Now Call the function.
If obSapFnUserDetail.Call = False Then
Msgbox “Function Call Error”
‘If there is any exception declared in code, it can be called as obSapFnUserDetail.Exception
EndIf
Now populate the structure details, 1 by 1.
At end remember to call the LogOff method of Connection object.
Whole Code
Public Sub GetUserDetails()
Dim obSAPFnCntrl As Object ‘Object for establishing Connection and Calling BAPI
Dim obSAPConn As Object ‘ SAP Connection Object
Dim obSAPFnUserDetail As Object ‘ Object used for calling BAPI function
Dim obSAPExpUserName As Object ‘ Export Parameter to hold the user Value
‘Import Parameters
Dim obSAPImpLogonData As Object, obSAPImpDefaults As Object, obSAPImpAddress As Object
Dim iColCnt As Integer, iIndex As Integer, iRowCount As Integer, iRowIndex As Integer, iColNameIndex As Integer
Dim obSAPTblActivitygroups As Object, obSAPTblAddtel As Object, obSAPTblAddfax As Object, obSAPTblAddttx As Object
Dim oColumn As Object
‘Table Parameters
Dim obSAPTblParameter As Object, obSAPTblProfiles As Object, obSAPTblReturn As Object
Set obSAPFnCntrl = CreateObject(“SAP.Functions”)
Set obSAPConn = obSAPFnCntrl.Connection
obSAPFnCntrl.LogLevel = CNT_INT_LOG_LEVEL
obSAPFnCntrl.LogFileName = CNT_STR_LOG_FILE
‘Set the properties for the connection control
With obSAPConn
.ApplicationServer = CNT_STR_APPLN_SRVR
.SystemNumber = CNT_STR_SYS_NUM
.User = CNT_STR_USR
.Password = CNT_STR_PWD
.Language = CNT_STR_LOGON_LANG
.Client = CNT_STR_CLIENT
End With
‘Logon to SAP in silent mode
If obSAPConn.Logon(0, True) = False Then
MsgBox “R/3 connection failed”
Exit Sub
End If
‘Use the Add method of Function Control to attach Function.
Set obSAPFnUserDetail = obSAPFnCntrl.Add(CNT_STR_BAPI_USER_DETAILS)
Set obSAPExpUserName = obSAPFnUserDetail.Exports(“USERNAME”)
obSAPExpUserName.Value = “BASIS” ‘Get Details of user BASIS
Set obSAPImpLogonData = obSAPFnUserDetail.Imports(“LOGONDATA”)
Set obSAPImpDefaults = obSAPFnUserDetail.Imports(“DEFAULTS”)
‘ Now Set the objects
Set obSAPTblParameter = obSAPFnUserDetail.Tables(“PARAMETER”)
Set obSAPTblProfiles = obSAPFnUserDetail.Tables(“PROFILES”)
Set obSAPTblReturn = obSAPFnUserDetail.Tables(“RETURN”)
‘Now Call the function.
If obSAPFnUserDetail.Call = False Then
MsgBox “Function Call Error”
Else
‘Function Call is Successfull
‘Now get the Imported Structure Details
‘Here we are calling the ColumnCount property of Structure object
‘This is because for this BAPI, all import parameters are Structures
iColCnt = obSAPImpLogonData.ColumnCount
For iIndex = 1 To iColCnt
‘Populate Contents into Excel Sheet
Sheet1.Cells(2, iIndex) = obSAPImpLogonData.ColumnName(iIndex)
Sheet1.Cells(3, iIndex).FormulaR1C1 = “‘” & obSAPImpLogonData.Value(iIndex)
Next
iColCnt = obSAPTblParameter.ColumnCount
iRowCount = obSAPTblParameter.RowCount
‘Now Get The Table Properties for Parameter
iColNameIndex = 1
iIndex = 0
For Each oColumn In obSAPTblParameter.Columns
iIndex = iIndex + 1
Sheet2.Cells(iColNameIndex, iIndex) = oColumn.Name
Next oColumn
For iRowIndex = 1 To iRowCount
For iIndex = 1 To iColCnt
Sheet2.Cells(iRowIndex + iColNameIndex, iIndex).FormulaR1C1 = obSAPTblParameter.Value(iRowIndex, iIndex)
Next
Next
‘If there is any exception decalred in code, it can be called as obSapFnUserDetail.Exception
End If
‘Get the whole tables Data
Dim oTables As Object ‘Use the Tables collection
Set oTables = obSAPFnUserDetail.Tables
Call GetColumnDetails(oTables)
Set oTables = Nothing
‘Get the Structure Details
Dim obImports As Object
Set obImports = obSAPFnUserDetail.Imports
Call GetImportDetails(obImports)
Set obImports = Nothing
obSAPFnCntrl.Remove (CNT_STR_BAPI_USER_DETAILS)
obSAPConn.LogOff
Set obSAPImpAddress = Nothing
Set obSAPImpLogonData = Nothing
Set obSAPImpDefaults = Nothing
Set obSAPTblParameter = Nothing
Set obSAPTblProfiles = Nothing
Set obSAPExpUserName = Nothing
Set obSAPTblReturn = Nothing
Set obSAPFnUserDetail = Nothing
Set obSAPConn = Nothing
Set obSAPFnCntrl = Nothing
End Sub
Private Sub GetColumnDetails(ByVal obTables As Object)
Dim iLoop As Integer, iColIndx As Integer, iColValuePos As Integer
Dim iTblCnt As Integer, iColCnt As Integer, iRowCnt As Integer, iRowIndx As Integer
Dim oTable As Object, oColumn As Object, iValuePosn As Integer
iTblCnt = obTables.Count
iValuePosn = 1
For iLoop = 1 To iTblCnt
Set oTable = obTables.Item(iLoop)
iColCnt = oTable.ColumnCount
iRowCnt = oTable.RowCount
iColValuePos = 1
‘Write the Table Name
Sheet3.Cells(iValuePosn, 1) = “The columns in table : ” & oTable.Name
‘Get ColumnNames
iValuePosn = iValuePosn + 1
For Each oColumn In oTable.Columns
Sheet3.Cells(iValuePosn, iColValuePos) = oColumn.Name
iColValuePos = iColValuePos + 1
Next oColumn
‘Enter the column Values
For iRowIndx = 1 To iRowCnt
iValuePosn = iValuePosn + 1
For iColIndx = 1 To iColCnt
Sheet3.Cells(iValuePosn, iColIndx) = oTable.Value(iRowIndx, iColIndx)
Next
Next
iValuePosn = iValuePosn + 2
Set oTable = Nothing
Next
End Sub
Private Sub GetImportDetails(ByVal obImpParameter As Object)
Dim iImpCnt As Integer, iLoop As Integer, iRowPosn As Integer
Dim iStrCols As Integer, iStrIndx As Integer
Dim obImpStructure As Object
iRowPosn = 1
iImpCnt = obImpParameter.Count
For iLoop = 1 To iImpCnt
‘Sheet3.Cells(iRowPosn, 1) = obImpParameter.Item(iLoop).Name
Set obImpStructure = obImpParameter.Item(iLoop)
If obImpStructure.IsStructure = True Then
Sheet4.Cells(iRowPosn, 1) = obImpStructure.Name & ” is a Structure”
iStrCols = obImpStructure.ColumnCount
‘Get Structure Names and Values
For iStrIndx = 1 To iStrCols
Sheet4.Cells(iRowPosn + 1, iStrIndx) = obImpStructure.ColumnName(iStrIndx)
Sheet4.Cells(iRowPosn + 2, iStrIndx) = obImpStructure.Value(iStrIndx)
Next
‘Now Get Columns of Structure
iRowPosn = iRowPosn + 4
End If
Set obImpStructure = Nothing
Next
End Sub
Create Custom BAPIs
Catching Function Module Exception from VB
For creating custom BAPIs, we will create a custom table ZEMP_DTLS with 4 columns.
Creating table
Create BAPI ZEMP_BAPI_INS_SMPL
While creating BAPI ensure that in Attributes tab, the Remote Enabled Module is checked.
Import Parameters
In Import Parameter insure that the Passby Value is ticked.
Exception
Function Module Code
FUNCTION ZEMP_BAPI_INS_SMPL.
data:
wa_emp type ZEMP_DTLS. “Declare Work area for the table
wa_emp-empid = EMPID. “Populate the Work Area
wa_emp-doj = DOJ.
if doj<‘19010101’.
raise INVALID_DATE_OF_JOIN.
endif.
insert into ZEMP_DTLS values wa_emp.
ENDFUNCTION.
VB Code
Public Sub InsertBapiEmp()
Dim obSAPFnCntrl As Object ‘Object for establishing Connection and Calling BAPI
Dim obSAPConn As Object ‘ SAP Connection Object
Dim obSAPFnEmpIns As Object ‘ Object used for calling BAPI function
Dim obSAPExpEmpId As Object ‘ Export Parameter to hold the user Value
Dim obSAPExpDOJ As Object
Set obSAPFnCntrl = CreateObject(“SAP.Functions”)
Set obSAPConn = obSAPFnCntrl.Connection
obSAPFnCntrl.LogLevel = CNT_INT_LOG_LEVEL
obSAPFnCntrl.LogFileName = CNT_STR_LOG_FILE
‘Set the properties for the connection control
With obSAPConn
.ApplicationServer = CNT_STR_APPLN_SRVR
.SystemNumber = CNT_STR_SYS_NUM
.User = CNT_STR_USR
.Password = CNT_STR_PWD
.Language = CNT_STR_LOGON_LANG
.Client = CNT_STR_CLIENT
End With
‘Logon to SAP in silent mode
If obSAPConn.Logon(0, True) = False Then
MsgBox “R/3 connection failed”
Exit Sub
End If
‘Use the Add method of Function Control to attach Function.
Set obSAPFnEmpIns = obSAPFnCntrl.Add(CNT_STR_BAPI_EMP_INS)
Set obSAPExpEmpId = obSAPFnEmpIns.Exports(“EMPID”)
obSAPExpEmpId.Value = “K10021”
Set obSAPExpDOJ = obSAPFnEmpIns.Exports(“DOJ”)
obSAPExpDOJ.Value = “18980506”
If obSAPFnEmpIns.Call = False Then
MsgBox “Function Call Error, Exception is ” & obSAPFnEmpIns.Exception
End If
obSAPFnCntrl.Remove (CNT_STR_BAPI_EMP_INS)
Set obSAPExpDOJ = Nothing
Set obSAPExpEmpId = Nothing
Set obSAPFnEmpIns = Nothing
obSAPConn.LogOff
Set obSAPConn = Nothing
Set obSAPFnCntrl = Nothing
End Sub
Catching Exception in VB
The Macro will throw exception from SAP side
Now in the Macro, change value of DOJ parameter to “20070202”.
Single record will be inserted to Database Tables.
Passing Table Parameters as Input
Now we will pass a Table as an Input Parameter.
TO pass tables, it is required to create a structure first.
Create Structure
Using T-code SE11, create a structure ZEMP_STR
Now create a function ZEMP_BAPI_INS_TBL using T-code se37.
While creating function ensure that the Remote Function enabled radio button is clicked.
Pass Table Parameter
In Tables parameter add a parameter as shown below.
Function Module Code
The source code for function is below
FUNCTION zemp_bapi_ins_tbl.
DATA:
wa_emp TYPE zemp_dtls.
*Insert data
clear wa_emp.
LOOP AT zemp_tbl INTO wa_emp.
wa_emp-mandt = sy-mandt.
INSERT INTO zemp_dtls VALUES wa_emp.
CLEAR wa_emp.
ENDLOOP.
ENDFUNCTION.
Now in Excel create a Macro BapiInsertWithTable for calling this Function.
VB Code
Public Sub BapiInsertWithTable()
Dim obSapFn As Object
Dim obSapCon As Object
Dim obEmpFn As Object, obTblEmp As Object
Dim iSLoop As Long, iSRows As Long ‘Variables for looping through Excel Sheet
Set obSapFn = CreateObject(“SAP.Functions”)
obSapFn.LogLevel = CNT_INT_LOG_LEVEL
obSapFn.LogFileName = CNT_STR_LOG_FILE
Set obSapCon = obSapFn.Connection
With obSapCon
.ApplicationServer = CNT_STR_APPLN_SRVR
.System = CNT_STR_SYSTEM
.SystemNumber = CNT_STR_SYS_NUM
.User = CNT_STR_USR
.Password = CNT_STR_PWD
.Language = CNT_STR_LOGON_LANG
.Client = CNT_STR_CLIENT
‘ .AbapDebug = True
.Tracelevel = True
‘ .RfcWithDialog = True
.HostName = CNT_STR_APPLN_SRVR
.LowSpeedConnection = False
.MessageServer = CNT_STR_APPLN_SRVR
End With
‘Check For Connection
If obSapCon.Logon(0, True) = False Then
MsgBox “R/3 connection failed”
Exit Sub
End If
Set obEmpFn = obSapFn.Add(“ZEMP_BAPI_INS_TBL”)
Set obTblEmp = obEmpFn.Tables(“ZEMP_TBL”) ‘This creates the Table Type Object
obTblEmp.FreeTable
iSRows = 8 ‘ Number of rows to be looped
‘Assign values for each column of the table.
For iSLoop = 2 To iSRows
obTblEmp.Rows.Add ‘Use the Rows.Add method to add row to table
‘obTblEmp.Value(obTblEmp.RowCount, “MANDT”) = CNT_STR_CLIENT
obTblEmp.Value(obTblEmp.RowCount, “EMPID”) = Sheet1.Cells(iSLoop, 1)
obTblEmp.Value(obTblEmp.RowCount, “DOJ”) = CDate(Sheet1.Cells(iSLoop, 2))
obTblEmp.Value(obTblEmp.RowCount, “LOCN”) = Sheet1.Cells(iSLoop, 3)
Next
If obEmpFn.Call = False Then
MsgBox “Error in calling Sap Fn “
End If
obTblEmp.FreeTable ‘After calling function free the internal table object
obSapFn.RemoveAll ‘ Remove function from the object
Set obTblEmp = Nothing
Set obEmpFn = Nothing
obSapCon.LogOff
Set obSapCon = Nothing
Set obSapFn = Nothing
End Sub
The Excel data is shown below.
After executing the Macro, 8 records will be inserted into the table ZEMP_DTLS.
Reference:
http://help.sap.com/printdocu/core/Print46c/en/data/pdf/BCFESDE5/BCFESDE5.pdf
I am trying to log on to SAP. The Excel VBA code gives me a popup window confirming my information however when I submit the form it does not take me to a new SAP window.
Additionally is there a way to automate all the popup boxes asking for confirmation on my information? I want this code eventually to run at certain times of the day, and I might not be available to input any data.
Sub login1()
Dim sap As Object
Dim conn As Object
Set sap = CreateObject("SAP.Functions")
Set conn = sap.Connection
conn.System = "System Test Environment"
conn.client = "100"
conn.user = "user"
conn.Password = "password"
conn.Language = "EN"
If conn.logon(0, False) <> True Then
MsgBox "Logon to the SAP system is not possible", vbOKOnly, "Comment"
Else
End If
End Sub
asked Nov 6, 2017 at 18:58
1
This Macro will never open a SAP Window — it will create an SAP-Object within VBA where you can work with SAP-RFC-Functions. (Reading Data from SAP, Writing Data into SAP)
In your version the SAP connection will be unaccessible after «End Sub». You have to declair the Object outside the sub.
This works silent (without dialog) for me:
Dim sap As Object
Public Function login1() As Boolean
Set sap = CreateObject("SAP.Functions")
sap.Connection.System = "System Test Environment"
sap.Connection.client = "100"
sap.Connection.user = "user"
sap.Connection.Password = "password"
sap.Connection.Language = "EN"
If sap.Connection.logon(0, False) <> True Then
sap.RemoveAll
MsgBox "Logon to the SAP system is not possible", vbOKOnly, "Comment"
Else
login1 = true
End If
End Function
Public Function SAPLogoff()
On Error Resume Next
sap.RemoveAll
sap.Connection.logoff
LoggedOn = False
Set sap = Nothing
'Set conn = Nothing
End Function
answered Nov 11, 2017 at 22:34
2
Since you want to «open a new SAP Window» you have to make a different approach!
At First try to open the new instance of SAP from the DOS Commandline with «sapshcut»:
C:Program Files (x86)SAPFrontEndSAPguisapshcut.exe -system="System Test Environment" -client="100" -user="user" -password="password" -language="EN"
If your SystemName has no Spaces (and I belive so!) then you can write it also like:
C:Program Files (x86)SAPFrontEndSAPguisapshcut.exe -system=SystemTestEnvironment -client=100 -user=user -password=password -language=EN
When this call works with your credentials, then you can transfer it to Excel like this:
Sub login1()
Call Shell("C:Program Files (x86)SAPFrontEndSAPguisapshcut.exe -system=SystemTestEnvironment -client=100 -user=user -password=password -language=EN",vbNormalFocus)
End Sub
You could also add a transaction by adding «-command=your_tcode» to the String.
If your have spaces in the parameters and you could only start it with -system=»System Test Environment» from the Commanline, you will have to escape this in Excel with -system=»»»System Test Environment»»» (!)
answered Nov 14, 2017 at 22:41
Содержание
- Interactive and dynamic Excel VBA template – SAP GUI Scripting –
- Best Practices for VBA in SAP BI Analysis for MS Excel
- How to access SAP using Excel VBA?
- 2 Answers 2
- SAP Intelligent RPA: Reading Data from Excel using VBA Excel reference properties
- What will you learn in this blog:
- Brief on Excel VBA reference that would be used to get all the Values without any Loops:
- Steps to follow:
- Prerequisites:
- Instructions:
- 1. Create a project
- 2. Create a new workflow
- 3.Import Excel Library Scripts
- 4. Designing Workflow with Custom Scripts
- 5. Display Range address and Random Cell Value
- Conclusion
Interactive and dynamic Excel VBA template – SAP GUI Scripting –
SAP GUI Scripting can be used for many small and intermediate batches for mass maintenance tasks (P-/Q- and D-Systems) and quality testing (Q-Systems) in SAP.
To reduce development workload or modify a lot of code for different SAP GUI recordings I saw a need for having an Excel VBA template which can cover a lot of requirements.
- Easy to use (One-Button-Solution).
- Excel functions and options can be used for data preparation and consolidation in front of starting update procedure.
- During initialization all existing and non-busy SAP sessions got displayed (UI-Listbox). So we are able to select a specific session for Excel VBA adoption.
- Data from SAP can easily imported into Excel worksheet (Data from ALV-list, fields, result list, status messages, error messages,… and so on).
- Only SAP GUI Scripting recording code need to integrate into VBA module ‘SAP_1_PROCESS’.
- More columns as data source or destination for field data can be added. Last two columns are reserved for procedure usage. This is achieved by using a data-array which got ‘Redim’ during process according to used rows and columns.
- Log-function is integrated (for SAP messages like statusbar Messages or free-text).
Prepare Excel VBA template:
- Step: Create folder on your desktop (or somewhere else) => folder name is up to you.
- Step: Store below text-files into this folder: Please be aware that text-file ‘Modules_All.txt’ need to split into four text-files named ‘SAP_1_Process’, ‘SAP_2_Functions’. SAP_3_Public_Subs’ and ‘Module1’! Start and end of module specific coding is marked and must removed before saving of single text-file. First line in this files must be Attribute VB_Name = “SAP_1_Process”, Attribute VB_Name = “SAP_2_Functions” and Attribute VB_Name = “SAP_3_Public_Subs”. As I can´t upload more than three files you Need to split Modules_All.txt on your own and save files in folder.
- SAP_1_Process.txt
- SAP_2_Functions.txt
- SAP_3_Public_Subs.txt
- Userform1_frm.txt
- Userform1_frx.txt
- Module1.txt
- Step: Create a new Excel workbook and store this in same folder as text-files. You can choice every name you want. My suggestion is ‘Prepare_WB.xlsx’.
- Step: Now go into VBE of Excel ( ALT + F11) => insert Module => open text-file ‘Module1.txt’ => Select all and copy => paste into new module from Excel workbook.
- Step: Execute macro ‘prepare_worksheet’ (Reference to sapfewse.oxs will done utomatically. This require Folder-structure ENVIRON(“PROGRAMFILES”) & “SAPFRONTENDSAPguisapfewse.oxs”). If you have an different Destination please add manual.
- Step: Remove ‘Module1’ from macro-enabled workbook and save.
- Done
Usage of Excel VBA template (MM03_VBA_SAP_SCRIPTING_V1.xlsm):
This Excel template have for demonstration purposes SAP GUI Scripting integrated for getting MM03 data from ‘stor. loc. stck’-tab => ‘Qty. Unrestricted’ + “UoM’ + ‘Material description’ data.
- Step: Fillin ‘Materialnumber’ + ‘Company Code’ + ‘Storage location’ combination used in your system. As error handling is integrated for ‘Company Code’ + ‘Storage location’ combination you can test this as well.
- Step: Press button ‘Run macro ‘SAP_PROCESS’’
- Step: All open and Scripting-enabled SAP sessions got displayed in a Userform-Listbox
- Step: Select one session and press ‘Enter’ or Commandbutton
- Done: Script got executed and you will get data into Excel according to your input data combination (Materialnumber/CoCode/Storage location).
Important data structure information:
All data from Excel worksheet ‘SAP_PROCESS’ got stored into data-array ‘ arr_SAP_Data’ . This Array is defined with same number range as our used worksheet range. Starting from row ‘2’ up to last used row and all used columns (remember that last two columns are reserved for procedure process).
=> lngCounter is current executed row in worksheet. (lng_col +0) define column ‘1’
=> (lng_col +1) is second column
When you add or delete columns please save workbook immediately.
Feel free to use this template for your requirements by modify coding in ‘SAP_1_Process’-module. But be aware that I am not responsible for any issues, inconsistencies or other incidents which can cause by using this template. Feel free to ask if you Need any additional information. But do not expect any support for your purposes and requirements. Hope this will give you some lights how SAP GUI Scripting can make your daily tasks much smoother.
Источник
Best Practices for VBA in SAP BI Analysis for MS Excel
over the last year, I created some small applications in Analysis and thought it’s time to collect a few best practice ideas, which I experienced during development and test.
This document does not go too much into detail, since my idea is that also beginners of VBA in Analysis should be able to utilize some tips.
FYI: I worked only in 1.4.x versions so far. It might be that Analysis behaviour already changed in 2.x versions.
1) Always refresh, first!
The most important thing when doing anything in VBA related to Analysis is to refresh your datasource (DS) first … otherwise, nothing will work!
To prevent a refresh every time, you can check if the DS is already active
Dim lResult As Long
lResult = Application.Run(“SAPGetProperty”, “IsDataSourceActive“, “DS_1”)
If lResult = False Then
lResult = Application.Run(“SAPExecuteCommand”, “Refresh“, “DS_1”)
‘ Example: You can also skip the else
lResult = Application.Run(“SAPExecuteCommand”, “ShowPrompts“, “DS_1”)
2) Formulas and own columns upfront!
If you have the task to include your own Excel formula columns in your sheet, then always try to aviod putting it at the end of the Data source! Instead, put it at the beginning:
In that way you don’t have to take care about removing the columns when any drill-downs are happening and replacing them afterwards at the new end of the report. Of course you might need to adjust the formulas if they rely on certain key figure columns, but for “VLookups” it quite often saves work.
3) Find out the crosstab size
To find out the last column and row of your crosstab, you can use:
Dim lCols, lRows as Long
For this, also 1) applies! If your Datasource is not refreshed, you will not get the correct result. So if you need reliable variable contents you should store the previous “dimensions” of the crosstab in any cells on the sheet.
Especially if you “Remove Data Before Saving”. Then the crosstab is not existing and will cause you trouble if you execute a macro during Workbook initialization.
Therefore I try to avoid the checkbox “Remove Data Before Saving”.
4) Freeze the screen while macro runtime
To prevent a user is bothered with jumping through several thousand lines or several sheets, you always should freeze the screen before VBA execution and activate the screen update afterwards again. I prefer using:
‘At the very beginning
‘all the code in between…
‘At the very end
5) Fill the missing table headers for “Key and text” characteristics
Nothing more is annoying – when you want to create a PIVOT table on top of your datasource’s results – than the missing feature from the very first release: No headers on characteristics with “Key and text” display
For preventing problems 3) you should execute the macro only after 1):
Dim DS1_C, DS1_R, lResult As Long
Dim DS1 as String
DS1 = “your sheet name”
lResult = Application.Run(“SAPGetProperty”, “IsDataSourceActive”, “DS_1”)
If lResult = True Then
For i = 1 To DS1_C – 1
If Worksheets(DS1).Range(“A5”).Offset(0, i + 1) = “” Then
Worksheets(DS1).Range(“A5”).Offset(0, i + 1) = Worksheets(DS1).Range(“A5”).Offset(0, i) & “2”
In that way every blank header cell receives the text of the previous one including an attached “2”.
6) Actions after the Refresh of a Datasource: Register Callback
When you want a macro to execute everytime your datasource has been refreshed, e.g. by drill-down, execution of Variable prompt, etc. you can register a callback:
Step 1: Include this into “ThisWorkbook”
Public Sub Workbook_SAP_Initialize()
Call Application.Run(“SAPExecuteCommand”, “RegisterCallback”, “AfterRedisplay”, “Callback_AfterRedisplay”)
Step 2: In your VBA module you put all your coding between these lines:
Public Sub Callback_AfterRedisplay()
Attention: This coding is executed almost every time – even if you don’t really do anything, but just click “save”.
For that reason, you could read this note – there is a hint about improvements in your coding:
(I did not test it, yet. So I cannot give you any advice here)
7) Clear variable contents
Maybe you have the requirement to handover a long list of input characteristics to a query variable (like you would do it via the “copy from clipboard”-button), and refresh it. Unfortunately I did not found a “clear” method to remove the variable contents again.
For that reason I helped myself by setting one “default” value as key, which exists in the master data, and afterwards the user is able to simply remove it in the variable input screen:
Dim lResult As Long
lResult = Application.Run(“SAPExecuteCommand”, “Refresh”, “DS_1”)
lResult = Application.Run(“SAPExecuteCommand”, “ShowPrompts”, “DS_1”)

One more function is missing in my opinion… There is no SAPGetVariable() available.
That means if a user filled some variables in the prompt screen, you have to define an area in your workbook where you can get the list of all the variables, by using the formula:
Afterwards, you have to read the value of the respective cell with the right variable content:
Dim Input as Variant
Input = Sheets(“Your sheet”).Cells( , 2).Value
Finally you can use this Input to fill another variable in the second datasource, for example.
I think there are many ideas more, but for the moment it should be sufficient.
For the VBA-advanced readers, two more helpful links here:
Источник
How to access SAP using Excel VBA?
I am trying to log on to SAP. The Excel VBA code gives me a popup window confirming my information however when I submit the form it does not take me to a new SAP window.
Additionally is there a way to automate all the popup boxes asking for confirmation on my information? I want this code eventually to run at certain times of the day, and I might not be available to input any data.
2 Answers 2
This Macro will never open a SAP Window — it will create an SAP-Object within VBA where you can work with SAP-RFC-Functions. (Reading Data from SAP, Writing Data into SAP)
In your version the SAP connection will be unaccessible after «End Sub». You have to declair the Object outside the sub.
This works silent (without dialog) for me:
Since you want to «open a new SAP Window» you have to make a different approach!
At First try to open the new instance of SAP from the DOS Commandline with «sapshcut»:
If your SystemName has no Spaces (and I belive so!) then you can write it also like:
When this call works with your credentials, then you can transfer it to Excel like this:
You could also add a transaction by adding «-command=your_tcode» to the String.
If your have spaces in the parameters and you could only start it with -system=»System Test Environment» from the Commanline, you will have to escape this in Excel with -system=»»»System Test Environment»»» (!)
Источник
SAP Intelligent RPA: Reading Data from Excel using VBA Excel reference properties
This is to ease the reading of excel files which could have unknown number of rows to be read.
In this post I will show you how to read an Excel file with unknown number of rows using VBA Excel reference properties and custom scripts
What will you learn in this blog:
- Basics of excel reading
- Reading excel file using custom scripts
- VBA Excel reference properties that can make Excel reading simple
- Reading unknown number of rows without loops in workflow
Brief on Excel VBA reference that would be used to get all the Values without any Loops:
- Excel VBA Object model has Application object which refers to the entire Microsoft Excel application
- Application object has property ActiveSheet that returns the active Worksheet in the active excel
- WorkSheet object , in Excel VBA objects, which represents the Worksheet of the excel
- WorkSheet object has property UsedRange that returns the Range on the Worksheet that has been used or filled
- Range object represents one cell or block of cells
- Address property of Range, provides the representation of range as string
Steps to follow:
- Create a project;
- Create a new Workflow;
- Import Excel Library Scripts;
- Designing Workflow with Custom Scripts
- Display range address and random cell value
Prerequisites:
- Desktop Studio
- Microsoft office
Instructions:
1. Create a project
Open Desktop Studio and create a new project from File menu. Give it a name
2. Create a new workflow
Go to Workflow perspective , right click on Global and add new workflow give it a name.
3.Import Excel Library Scripts
Whenever you create a project, its framework includes most of the Libraries that would be useful for creating the workflows. Though you can drag and drop or use the Excel Lib function in your workflows, until you include the Excel Library workflow would run into errors during compilation and execution.
To include excel library,
go to edit project in the file menu, navigate to Libraries and select Excel integration
Or go to Scripts, right click on Global, click Include Library Script and select Excel Integration
4. Designing Workflow with Custom Scripts
- Add Activity of Initialize Excel which initializes the Excel library and mode parameters
- Mark the Initialization as start node with a right click and selecting Set as Start Node
- Next activity is to open the excel file, we add open existing Excel file ,from the activity list functions of Excel Lib. Filename must be a string and if path has been provided the separator would be \ between the folders.
- In case the workbook opened has multiple worksheets, we need to activate the sheet to be read, use Activate worksheet activity. If workbook has only one worksheet, it is optional activity. As the workbook used has multiple sheets, the following activating function has been added.
- Add Custom activity, to read the data from the sheet activated
- Once we generate the build for workflow created, we would be able to edit the custom activity to include the custom script. Click on the build to generate the script for the workflow.
- Go to Scripts -> workflow script -> Custom step to add the code to extract data using VBA properties
- Go to Scripts and right click to add custom library script
-
- Define the function getContents that has been used in Custom Step of the Workflow
- ctx.excel.application.getObject is available in Excel Library which fetches the Excel object. For more information refer to the documentation of the library.
- Application.ActiveSheet is Excel VBA property which fetches the active Worksheet
- UsedRange is the property of worksheet that returns the Range Object
- Address property of the Range provides the address of the range object as string . Ex: ‘$A$1:$B$3’
- ctx.excel.sheet.getValuesFromRangeDefinition takes the range definition as string. For more information refer to the documentation of the library
- Define the function getContents that has been used in Custom Step of the Workflow
5. Display Range address and Random Cell Value
- ctx.log has been used to write the property data to the logs for validation
- Log will be written with the Active sheet Name , Range Address and cell value at (1,1) position
Following file has been used,:
- File has two sheets with name ‘header’ and ‘item’.
- Active sheet would be ‘header’
- Range to be read would be “A1:H5”
- Cell Value at (1,1) position would be ‘A’
Following is the context log
As Excel VBA objects and properties used in Library of SAP IRPA, there would be warnings but the properties would be available during runtime.
Conclusion
Using Excel VBA Object properties in SAP Intelligent RPA would give the bot less time to read the whole data without using explicit loops. You can reuse the custom library to read the Excel for any dimensions
Источник
| Автор | Сообщение | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Заголовок сообщения: доступ к SAP из VBA (Excel)
|
|||
|
С обновлением SAP GUI с 6.4 Патч 23 до 7.01 Патч 15 перестал работать макрос загрузки данных из Excel в Z-таблицу SAP. Обнаружили, что коннект к БД НЕ проходит для такого макроса Code: Dim R3 As Object Если раскомментарить MsgBox, то пройдет: Code: Dim R3 As Object В чем может быть проблема?
|
||
| Вернуться к началу |
|
||
|
Deinis |
Заголовок сообщения: Re: доступ к SAP из VBA (Excel)
|
||
|
Вот так заработало Code: Dim R3 As Object Команда R3.Connection.Logon(0, True), с которой не работал коннект, взята с одной из тем форума. Есть какая-нибудь информация по ней?
|
||
| Вернуться к началу |
|
||
|
Besa |
Заголовок сообщения: Re: доступ к SAP из VBA (Excel)
|
|
|
а где Вы заполняете
|
| Вернуться к началу |
|
|
Deinis |
Заголовок сообщения: Re: доступ к SAP из VBA (Excel)
|
||
|
Besa написал: а где Вы заполняете Нигде. Насколько это важно? В окошке логона все поля (кроме пароля) почему-то сами по себе заполнены нужными значениями.
|
||
| Вернуться к началу |
|
||
|
pberezin |
Заголовок сообщения: Re: доступ к SAP из VBA (Excel)
|
||
|
в object browser’е в VBA-редаакторе посмотрите проперти к этому объекту — там интуитивно понятный интерфейс
|
||
| Вернуться к началу |
|
||
|
Deinis |
Заголовок сообщения: Re: доступ к SAP из VBA (Excel)
|
||
|
pberezin написал: в object browser’е в VBA-редаакторе посмотрите проперти к этому объекту — там интуитивно понятный интерфейс pberezin, можно чуть подробнее? Если это обычный Object browser, вызываемый в VBA-редакторе по клавише «F2», то в нем ничего про объект «SAP.Functions» нету. Тем более, про объект «R3».
|
||
| Вернуться к началу |
|
||
|
pberezin |
Заголовок сообщения: Re: доступ к SAP из VBA (Excel)
|
||
|
его не видно, потому что вы применяете позднее (динамическое) связывание через createobject. С саплогоном ставится ActiveX компонент SAP Remote function call control (файло wdtfuncs.ocx). Подключаете его в VBA через ToolsReferences, и вам станет доступен контрол SAPFunctions. Кидаете его на VBA-шную форму (очень удобно — в пропертях контрола Custom можно один раз настроить имена вызываемых из сапа RFC-ФМ, чтобы динамически через VBA их не присваивать). И в object browser’е будет всё видно. Единственное, с отладкой RFC-вызовов чудеса какието — если ставишь AbapDebug=true, он почемуто в отладку вываливается не прямо в вызываемом ФМ, а в какомто rfc_get_function_interface (видимо диспетчер какойто, х.з.)
|
||
| Вернуться к началу |
|
||
|
Deinis |
Заголовок сообщения: Re: доступ к SAP из VBA (Excel)
|
||
|
pberezin написал: С саплогоном ставится ActiveX компонент SAP Remote function call control (файло wdtfuncs.ocx). Подключаете его в VBA через ToolsReferences, и вам станет доступен контрол SAPFunctions. Спасибо, получилось! pberezin написал: Кидаете его на VBA-шную форму (очень удобно — в пропертях контрола Custom можно один раз настроить имена вызываемых из сапа RFC-ФМ, чтобы динамически через VBA их не присваивать). И в object browser’е будет всё видно. В object browser’е информация о составе SAPFunctions появилась, но до его подобъекта Connection. Что дальше — посмотреть не могу. Т.е. свойства SAPFunctions.Connection не вижу. Контекстное меню «Properties» светло-серое и невозможно для выбора. Как ни крутил. Кстати, контекстное меню «Properties» (щелк правой кнопкой мыши) и для SAPFunctions тоже недоступно для нажатия. Не подскажете, как посмотреть там подробнее об объекте SAPFunctions.Connection.Logon? Нужны ли вообще и какие именно нужны параметры при его вызове?
|
||
| Вернуться к началу |
|
||
|
pberezin |
Заголовок сообщения: Re: доступ к SAP из VBA (Excel)
|
||
|
У вас наверное настойки уровня безопасности макросов запрещают загрузку внешних activex. Потавьте в экселе самый низкий уровень безопасности. А по поводу именно объекта Connection — да он почемуто не типизирован, надо объявлять as Object и присваивать проперти динамически. Там можно в режиме VBA-отладчика глянуть все его проперти. Ну вот так например (здесь форма, с контролом SAPRfc и кнопкой btnGo) Private Sub btnGo_Click() With Me.SAPrfc OR3connection.RfcWithDialog = 1 ‘помоему без этого флажка gui будет не виден, соответственно abap-отладка тоже brc = OR3connection.Logon(0, True) .AboutBox End With
|
||
| Вернуться к началу |
|
||
|
Bully |
Заголовок сообщения: Re: доступ к SAP из VBA (Excel)
|
|
|
Ещё вариант: Code: ‘ Dim SAPFunctions As New SAPFunctionsOCX.SAPFunctions Set SAPConnection = SAPFunctions.Connection ‘ Параметры соединения по умолчанию: ‘ Подключаемся к SAP: ‘ Вызываем ФМ ‘BAPI_EMPLOYEE_GETDATA’ ‘ Заполняем параметры ‘ Собственно вызов: ‘ Обрабатываем результат: Dim i As Long End Sub
|
| Вернуться к началу |
|
|
pberezin |
Заголовок сообщения: Re: доступ к SAP из VBA (Excel)
|
||
|
Thanx. Про остальные два контрола я и не знал. Кстати, там ещё есть контрол SAP Bapi — тоже как вариант для rfc вызовов
|
||
| Вернуться к началу |
|
||
|
Deinis |
Заголовок сообщения: Re: доступ к SAP из VBA (Excel)
|
||
|
Хочу поблагодарить за помощь. Подключив все три файла Что интересно. С самого начала на это внимание обратил, но «забил».
|
||
| Вернуться к началу |
|
||
|
ilinvv |
Заголовок сообщения: Re: доступ к SAP из VBA (Excel)
|
||
|
Добрый день! Цитата: ‘ Собственно вызов: ошибка. пробовал с разными ФМ (с параметрами и без) — ошибка при SAPFunction.Call…
|
||
| Вернуться к началу |
|
||
|
ilinvv |
Заголовок сообщения: Re: доступ к SAP из VBA (Excel)
|
||
|
всё вопрос снят.
|
||
| Вернуться к началу |
|
||
|
raaleksandr |
Заголовок сообщения: Re: доступ к SAP из VBA (Excel)
|
|
|
Цитата: Что интересно. С самого начала на это внимание обратил, но «забил». Подозреваю, что лучше все-таки переписать программу на «позднее» связывание. Ранее связывание, конечно, удобно, но при изменении версии ActiveX компонента (видимо вызванном изменением версии SapGUI) действительно могут происходить такие эффекты, VBA теряет связь с контролом, тк привязывается к конкретной версии.
|
| Вернуться к началу |
|




























