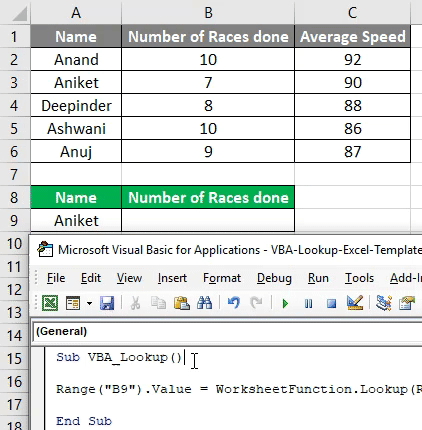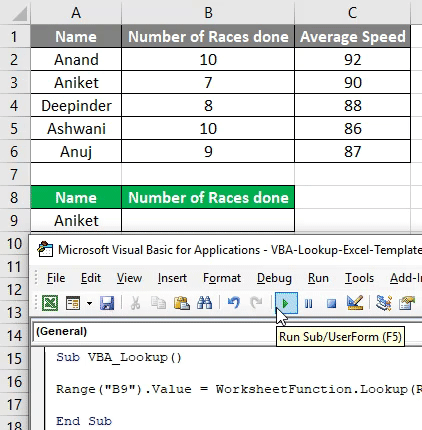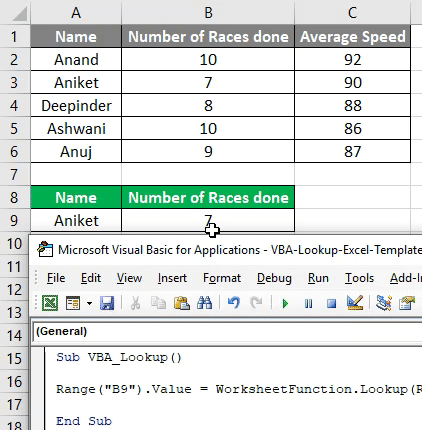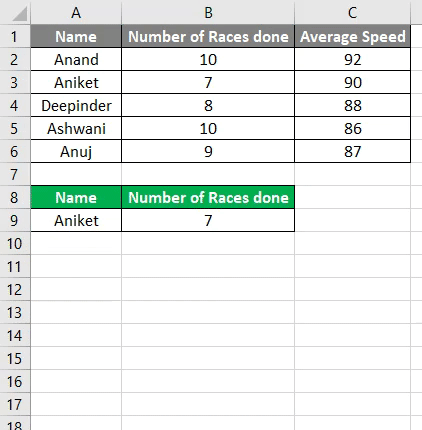
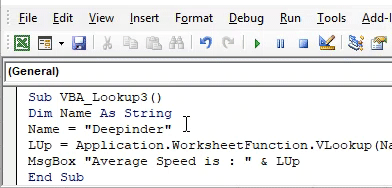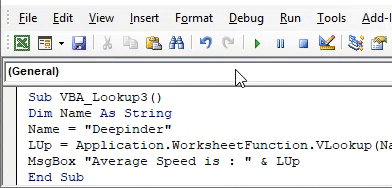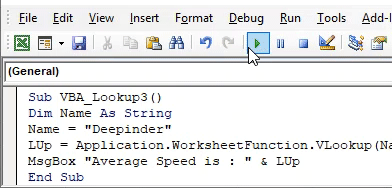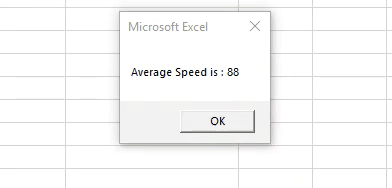
Я не могу предоставить пример с макросом, поскольку еще пишу скелет. Текстовый файл, тоже особо смылса кидать нет.
Ситауция следующая, имеется текстовый файл, в который периодически идет поток данных, необходимо в определенное время(об OnTime Now и TimeSerial я осведомлен)
проверять пришли ли данные. С этого этапа принципиально может быть 3 ситуации развития событий:
1) Данные пришли какие надо, следствие этого идем далее
2) Данные пришли но с ошибкой, следствие этого необходимо закомментировать строку
3) Данные не пришли., пока данные не пришли циклим ждем прихода….
у данных есть две характерных особенности у них есть порядковый номер, и у них есть скажем так
«характерный номер обратной связи»
который фактически является булевой переменной: Есть ошибка/нет ошибки.
Прошу прощения, что в принципе не правильно объявил тему, и что не задал сути вопроса в заглавном посте, до написания на форум, я был уверен в том что я ошибаюсь при работе с функцией .Find, и изначально предполагал, что тот нюанс который есть при работе с переменной у функции .Find который для более опытных товарищей очевиден, всплывет на поверхность.
Алгоритм такой :
1) открывай текстовый файл помещаем в переменную
2) в переменной ищем, наличие нового порядкового номера, если его нет закрываем файл, и открываем опять ( делаем это в цикле)
3) если он есть смотрим на
«характерный номер обратной связи»,
если ошибка есть комментим строку с ошибкой закрываем файл,
записываем ошибки в отдельный массив в Эксель ( грубо говоря в столбик)
Основное условие этого алгоритма пришли ли данные,
т.е. в итоге вопрос такой имеется
некая изначальная информация которую необходимо найти в текстовом файле, если использовать Instr
Это скелет в нем могут быть ошибки как грамматические в комментариях, так синтаксические в работе функции Instr,
так и алгоритмические.
| Код |
|---|
Sub Poisk_txt() Dim s, Poisk, Nashli, Nashli//DC, Poisk//DC As String Dim Count_mistake As Integer ' Счетчик ошибок Open "C:testfile.txt" For Input As #1 s = Input(LOF(1), 1) ' содержимое текстового файла в переменной строкового типа Poisk = "4//" ' какой порядковый номер ищем Poisk//DC = "4//DC//1//" ' порядковый номер и характерный номер обратной связи БЕЗ ОШИБКИ который ищем Nashli = Instr(s, Poisk, 1) ' Непосредственно ищем, могу неправильно набрать, функция Instr похожа на ПоискПоз 'Do If Nashli = Poisk Then ' If-1 Nashli//DC = Instr(s, Poisk//DC, 1) If Nashli//DC = Poisk//DC Then ' If - 2 ' 'это то что нужно, если значение IF = True то выходим из цикла Else: Cells(Count_mistake, 7) = Poisk ' If - 2 Count_mistake = Count_mistake + 1 s = Replace(s, "4//", "*;4//") Print #1, s Close #1 Open #1 End If ' If - 2 Else ' If -1 Close #1 Open #1 End If ' If- 1 'Loop End Sub |
Вопроса два если Instr или Find или Регулярные выражения ничего не найдут по заданному условию то будет ошибка
1) ошибку стоит проходить конструкцией On Error Resume Next? или другой?
2) и второй момент как оптимальнее зациклить, просто бесконечный цикл? или что то более функциональное?
Прошу меня извинить что в самом начале так все не расписал.
Благодарю еще раз всех Вас.

This VBA Find Tutorial is accompanied by an Excel workbook containing the data and macros I use in the examples below. You can get free access to this example workbook by clicking the button below.
Use the following Table of Contents to navigate to the Section you’re interested in.
Related Excel VBA and Macro Training Materials
The following VBA and Macro training materials may help you better understand and implement the contents below:
- Tutorials about general VBA constructs and structures:
- Tutorials for Beginners:
- Macros.
- VBA.
- Enable and disable macros.
- The Visual Basic Editor (VBE).
- Procedures:
- Sub procedures.
- Function procedures.
- Work with:
- Objects.
- Properties.
- Methods.
- Variables.
- Data types.
- R1C1-style references.
- Worksheet functions.
- Loops.
- Arrays.
- Refer to:
- Sheets and worksheets.
- Cell ranges.
- Tutorials for Beginners:
- Tutorials with practical VBA applications and macro examples:
- Find the last row or last column.
- Set or get a cell’s or cell range’s value.
- Check if a cell is empty.
- Use the VLookup function.
- The comprehensive and actionable Books at The Power Spreadsheets Library:
- Excel Macros for Beginners Book Series.
- VBA Fundamentals Book Series.
#1. Excel VBA Find (Cell with) Value in Cell Range
VBA Code to Find (Cell with) Value in Cell Range
To find a cell with a numeric value in a cell range, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
CellRangeObject.Find(What:=SearchedValue, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=XlSearchOrderConstant, SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
CellRangeObject
A Range object representing the cell range you search in.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the numeric value you search for) in a cell range (CellRangeObject).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=SearchedValue
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a cell range, set the What parameter to the numeric value you search for (SearchedValue).
After:=SingleCellRangeObject
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins. This must be a single cell in the cell range you search in (CellRangeObject).
If you omit specifying the After parameter, the search begins after the first cell (in the upper left corner) of the cell range you search in (CellRangeObject).
To find a cell with a numeric value in a cell range, set the After parameter to a Range object representing the cell after which the search begins.
LookIn:=xlValues
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a cell range, set the LookIn parameter to xlValues. xlValues refers to values.
LookAt:=xlWhole
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a cell range, set the LookAt parameter to xlWhole. xlWhole matches the data you are searching for against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=XlSearchOrderConstant
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (CellRangeObject) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a cell range, set the SearchOrder parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlByRows (SearchOrder:=xlByRows): To search by rows.
- xlByColumns (SearchOrder:=xlByColumns): To search by columns.
SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a cell range, set the SearchDirection parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlNext (SearchDirection:=xlNext): To search for the next match.
- xlPrevious (SearchDirection:=xlPrevious): To search for the previous match.
Macro Example to Find (Cell with) Value in Cell Range
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts two arguments:
- MyRange: The cell range you search in.
- MyValue: The numeric value you search for.
- Finds MyValue in MyRange.
- Returns a string containing the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the cell range (MyRange) where the numeric value (MyValue) is found.
Function FindValueInCellRange(MyRange As Range, MyValue As Variant) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 2 arguments: MyRange and MyValue
'(2) Finds a value passed as argument (MyValue) in a cell range passed as argument (MyRange)
'(3) Returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the cell range (MyRange) where the value (MyValue) is found
With MyRange
FindValueInCellRange = .Find(What:=MyValue, After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext).Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find (Cell with) Value in Cell Range
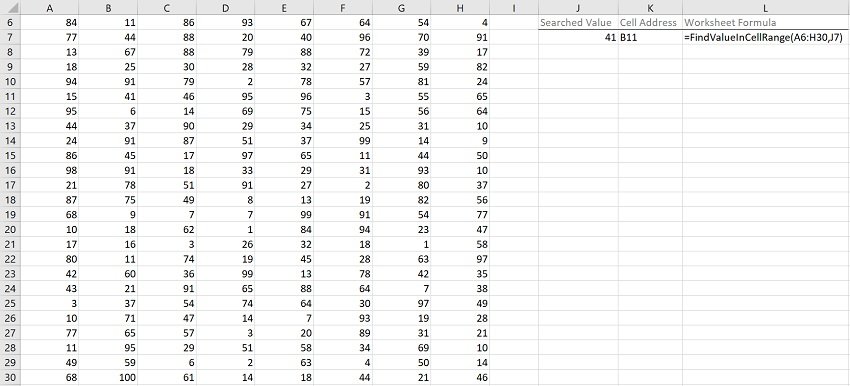
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H30) contain randomly generated values.
- Cell J7 contains the searched value (41).
- Cell K7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the cell range (MyRange) where the numeric value (MyValue) is found. This is cell B11.
- Cell L7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell K7 (=FindValueInCellRange(A6:H30,J7)).
- The cell range where the search is carried out contains cells A6 to H30 (A6:H30).
- The searched value is stored in cell J7 (J7).
#2. Excel VBA Find (Cell with) Value in Table
VBA Code to Find (Cell with) Value in Table
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
ListObjectObject.DataBodyRange.Find(What:=SearchedValue, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=XlSearchOrderConstant, SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
ListObjectObject
A ListObject object representing the Excel Table you search in.
DataBodyRange
The ListObject.DataBodyRange property returns a Range object representing the cell range containing an Excel Table’s values (excluding the headers).
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the numeric value you search for) in a cell range (containing the applicable Excel Table’s values).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=SearchedValue
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table, set the What parameter to the numeric value you search for (SearchedValue).
After:=SingleCellRangeObject
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins. This must be a single cell in the cell range you search in (containing the applicable Excel Table’s values).
If you omit specifying the After parameter, the search begins after the first cell (in the upper left corner) of the cell range you search in (containing the applicable Excel Table’s values).
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table, set the After parameter to a Range object representing the cell after which the search begins.
LookIn:=xlValues
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table, set the LookIn parameter to xlValues. xlValues refers to values.
LookAt:=xlWhole
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table, set the LookAt parameter to xlWhole. xlWhole matches the data you are searching for against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=XlSearchOrderConstant
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (containing the applicable Excel Table’s values) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table, set the SearchOrder parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlByRows (SearchOrder:=xlByRows): To search by rows.
- xlByColumns (SearchOrder:=xlByColumns): To search by columns.
SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table, set the SearchDirection parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlNext (SearchDirection:=xlNext): To search for the next match.
- xlPrevious (SearchDirection:=xlPrevious): To search for the previous match.
Macro Example to Find (Cell with) Value in Table
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts 3 arguments:
- MyWorksheetName: The name of the worksheet where the Excel Table you search in is stored.
- MyValue: The numeric value you search for.
- MyTableIndex: The index number of the Excel Table (stored in the worksheet named MyWorksheetName) you search in. MyTableIndex is an optional argument with a default value of 1.
- Finds MyValue in the applicable Excel Table’s values (excluding the headers).
- Returns a string containing the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the applicable Excel Table where the numeric value (MyValue) is found.
Function FindValueInTable(MyWorksheetName As String, MyValue As Variant, Optional MyTableIndex As Long = 1) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 3 arguments: MyWorksheetName, MyValue and MyTableIndex
'(2) Finds a value passed as argument (MyValue) in an Excel Table stored in a worksheet whose name is passed as argument (MyWorksheetName). The index number of the Excel Table is either:
'(1) Passed as an argument (MyTableIndex); or
'(2) Assumed to be 1 (if MyTableIndex is omitted)
'(3) Returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the Excel Table (stored in the MyWorksheetName worksheet and whose index is MyTableIndex) where the value (MyValue) is found
With ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(MyWorksheetName).ListObjects(MyTableIndex).DataBodyRange
FindValueInTable = .Find(What:=MyValue, After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext).Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find (Cell with) Value in Table
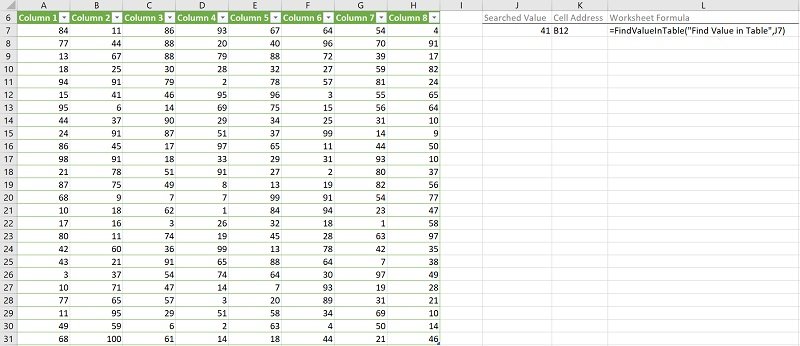
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H31) contain an Excel Table with randomly generated values.
- Cell J7 contains the searched value (41).
- Cell K7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the Excel Table where the numeric value (MyValue) is found. This is cell B12.
- Cell L7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell K7 (=FindValueInTable(“Find Value in Table”,J7)).
- The name of the worksheet where the Excel Table is stored is “Find Value in Table” (“Find Value in Table”).
- The searched value is stored in cell J7 (J7).
- The index number of the Excel Table is 1 (by default).
#3. Excel VBA Find (Cell with) Value in Column
VBA Code to Find (Cell with) Value in Column
To find a cell with a numeric value in a column, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
RangeObjectColumn.Find(What:=SearchedValue, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
RangeObjectColumn
A Range object representing the column you search in.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the numeric value you search for) in a cell range (RangeObjectColumn).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=SearchedValue
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a column, set the What parameter to the numeric value you search for (SearchedValue).
After:=SingleCellRangeObject
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins. This must be a single cell in the column you search in (RangeObjectColumn).
If you omit specifying the After parameter, the search begins after the first cell of the column you search in (RangeObjectColumn).
To find a cell with a numeric value in a column, set the After parameter to a Range object representing the cell after which the search begins.
LookIn:=xlValues
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a column, set the LookIn parameter to xlValues. xlValues refers to values.
LookAt:=xlWhole
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a column, set the LookAt parameter to xlWhole. xlWhole matches the data you are searching for against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=xlByRows
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable column (RangeObjectColumn) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a column, set the SearchOrder parameter to xlByRows. xlByRows results in the Range.Find method searching by rows.
SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a column, set the SearchDirection parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlNext (SearchDirection:=xlNext): To search for the next match.
- xlPrevious (SearchDirection:=xlPrevious): To search for the previous match.
Macro Example to Find (Cell with) Value in Column
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts two arguments:
- MyColumn: The column you search in.
- MyValue: The numeric value you search for.
- Finds MyValue in MyColumn.
- Returns a string containing the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the column (MyColumn) where the numeric value (MyValue) is found.
Function FindValueInColumn(MyColumn As Range, MyValue As Variant) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 2 arguments: MyColumn and MyValue
'(2) Finds a value passed as argument (MyValue) in a column passed as argument (MyColumn)
'(3) Returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the column (MyColumn) where the value (MyValue) is found
With MyColumn
FindValueInColumn = .Find(What:=MyValue, After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext).Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
End With
End Function
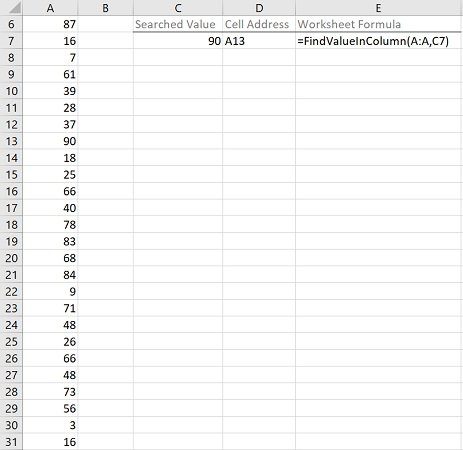
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find (Cell with) Value in Column
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Column A (cells A6 to A31) contains randomly generated values.
- Cell C7 contains the searched value (90).
- Cell D7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the column (MyColumn) where the numeric value (MyValue) is found. This is cell A13.
- Cell E7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell D7 (=FindValueInColumn(A:A,C7)).
- The column where the search is carried out is column A (A:A).
- The searched value is stored in cell C7 (C7).
#4. Excel VBA Find (Cell with) Value in Table Column
VBA Code to Find (Cell with) Value in Table Column
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table column, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
ListColumnObject.DataBodyRange.Find(What:=SearchedValue, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=XlSearchOrderConstant, SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
ListColumnObject
A ListColumn object representing the Excel Table column you search in.
DataBodyRange
The ListColumn.DataBodyRange property returns a Range object representing the cell range containing an Excel Table column’s values (excluding the header).
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the numeric value you search for) in a cell range (containing the applicable Excel Table column’s values).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=SearchedValue
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table column, set the What parameter to the numeric value you search for (SearchedValue).
After:=SingleCellRangeObject
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins. This must be a single cell in the cell range you search in (containing the applicable Excel Table column’s values).
If you omit specifying the After parameter, the search begins after the first cell of the cell range you search in (containing the applicable Excel Table column’s values).
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table column, set the After parameter to a Range object representing the cell after which the search begins.
LookIn:=xlValues
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table column, set the LookIn parameter to xlValues. xlValues refers to values.
LookAt:=xlWhole
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table column, set the LookAt parameter to xlWhole. xlWhole matches the data you are searching for against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=XlSearchOrderConstant
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (containing the applicable Excel Table column’s values) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table column, set the SearchOrder parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlByRows (SearchOrder:=xlByRows): To search by rows.
- xlByColumns (SearchOrder:=xlByColumns): To search by columns.
SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table column, set the SearchDirection parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlNext (SearchDirection:=xlNext): To search for the next match.
- xlPrevious (SearchDirection:=xlPrevious): To search for the previous match.
Macro Example to Find (Cell with) Value in Table Column
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts 4 arguments:
- MyWorksheetName: The name of the worksheet where the Excel Table (containing the column you search in) is stored.
- MyColumnIndex: The index/column number of the column you search in (in the applicable Excel Table).
- MyValue: The numeric value you search for.
- MyTableIndex: The index number of the Excel Table (stored in the worksheet named MyWorksheetName) containing the column you search in. MyTableIndex is an optional argument with a default value of 1.
- Finds MyValue in the applicable Excel Table column’s values (excluding the header).
- Returns a string containing the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the applicable Excel Table column where the numeric value (MyValue) is found.
Function FindValueInTableColumn(MyWorksheetName As String, MyColumnIndex As Long, MyValue As Variant, Optional MyTableIndex As Long = 1) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 4 arguments: MyWorksheetName, MyColumnIndex, MyValue and MyTableIndex
'(2) Finds a value passed as argument (MyValue) in an Excel Table column, where:
'(1) The table column's index is passed as argument (MyColumnIndex); and
'(2) The Excel Table is stored in a worksheet whose name is passed as argument (MyWorksheetName). The index number of the Excel Table is either:
'(1) Passed as an argument (MyTableIndex); or
'(2) Assumed to be 1 (if MyTableIndex is omitted)
'(3) Returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the applicable Excel Table column where the value (MyValue) is found
With ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(MyWorksheetName).ListObjects(MyTableIndex).ListColumns(MyColumnIndex).DataBodyRange
FindValueInTableColumn = .Find(What:=MyValue, After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext).Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
End With
End Function
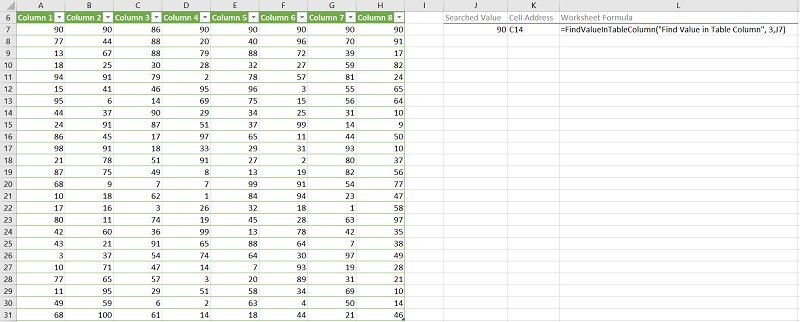
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find (Cell with) Value in Table Column
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H31) contain an Excel Table with randomly generated values. Cells in the first row (row 7) contain the searched value (90), except for the cell in the searched column (Column 3).
- Cell J7 contains the searched value (90).
- Cell K7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the applicable Excel Table column (Column 3) where the numeric value (MyValue) is found. This is cell C14.
- Cell L7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell K7 (=FindValueInTableColumn(“Find Value in Table Column”,3, J7)).
- The name of the worksheet where the Excel Table is stored is “Find Value in Table Column” (“Find Value in Table Column”).
- The index number of the Excel Table column is 3 (3).
- The searched value is stored in cell J7 (J7).
- The index number of the Excel Table is 1 (by default).
#5. Excel VBA Find Minimum Value in Cell Range
VBA Code to Find Minimum Value in Cell Range
To find the minimum value in a cell range, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
Application.Min(CellRangeObject)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
Application.Min
The WorksheetFunction.Min method returns the minimum value in a set of values.
CellRangeObject
The WorksheetFunction.Min method accepts up to thirty parameters (Arg1 to Arg30). These are the values for which you want to find the minimum value.
To find the minimum value in a cell range, pass a Range object (CellRangeObject) representing the cell range whose minimum value you want to find as method parameter.
Macro Example to Find Minimum Value in Cell Range
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts 1 argument (MyRange): The cell range whose minimum value you search for.
- Finds and returns the minimum value in the cell range (MyRange).
Function FindMinimumValueInCellRange(MyRange As Range) As Double
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 1 argument: MyRange
'(2) Finds the minimum value in the cell range passed as argument (MyRange)
FindMinimumValueInCellRange = Application.Min(MyRange)
End Function
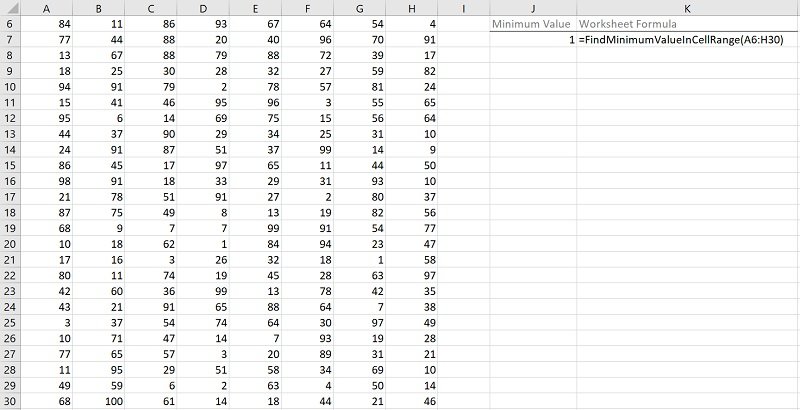
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Minimum Value in Cell Range
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H30) contain randomly generated values.
- Cell J7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the minimum value in the cell range (MyRange). This is the number 1.
- Cell K7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell J7 (=FindMinimumValueInCellRange(A6:H30)). The cell range where the search is carried out contains cells A6 to H30 (A6:H30).
#6. Excel VBA Find (Cell with) String (or Text) in Cell Range
VBA Code to Find (Cell with) String (or Text) in Cell Range
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a cell range, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
CellRangeObject.Find(What:=SearchedString, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=XlFindLookInConstant, LookAt:=XlLookAtConstant, SearchOrder:=XlSearchOrderConstant, SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant, MatchCase:=BooleanValue)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
CellRangeObject
A Range object representing the cell range you search in.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the string or text you search for) in a cell range (CellRangeObject).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=SearchedString
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a cell range, set the What parameter to the string (or text) you search for (SearchedString).
After:=SingleCellRangeObject
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins. This must be a single cell in the cell range you search in (CellRangeObject).
If you omit specifying the After parameter, the search begins after the first cell (in the upper left corner) of the cell range you search in (CellRangeObject).
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a cell range, set the After parameter to a Range object representing the cell after which the search begins.
LookIn:=XlFindLookInConstant
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a cell range, set the LookIn parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlFormulas (LookIn:=xlFormulas): To search in the applicable cell range’s formulas.
- xlValues (LookIn:=xlValues): To search in the applicable cell range’s values.
LookAt:=XlLookAtConstant
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a cell range, set the LookAt parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlWhole (LookAt:=xlWhole): To match against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
- xlPart (LookAt:=xlPart): To match against any part of the searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=XlSearchOrderConstant
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (CellRangeObject) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a cell range, set the SearchOrder parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlByRows (SearchOrder:=xlByRows): To search by rows.
- xlByColumns (SearchOrder:=xlByColumns): To search by columns.
SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a cell range, set the SearchDirection parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlNext (SearchDirection:=xlNext): To search for the next match.
- xlPrevious (SearchDirection:=xlPrevious): To search for the previous match.
MatchCase:=BooleanValue
The MatchCase parameter of the Range.Find method specifies whether the search is:
- Case-sensitive; or
- Case-insensitive.
The default value of the MatchCase parameter is False.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a cell range, set the MatchCase parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- True (MatchCase:=True): To carry out a case-sensitive search.
- False (MatchCase:=False): To carry out a case-insensitive search.
Macro Example to Find (Cell with) String (or Text) in Cell Range
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts two arguments:
- MyRange: The cell range you search in.
- MyString: The string (or text) you search for.
- Finds MyString in MyRange. The search is case-insensitive.
- Returns a string containing the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the cell range (MyRange) where the string or text (MyString) is found.
Function FindStringInCellRange(MyRange As Range, MyString As Variant) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 2 arguments: MyRange and MyString
'(2) Finds a string passed as argument (MyString) in a cell range passed as argument (MyRange). The search is case-insensitive
'(3) Returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the cell range (MyRange) where the string (MyString) is found
With MyRange
FindStringInCellRange = .Find(What:=MyString, After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext, MatchCase:=False).Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find (Cell with) String (or Text) in Cell Range
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H30) contain randomly generated words.
- Cell J7 contains the searched string or text (Excel).
- Cell K7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the cell range (MyRange) where the string or text (MyString) is found. This is cell F20.
- Cell L7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell K7 (=FindStringInCellRange(A6:H30,J7)).
- The cell range where the search is carried out contains cells A6 to H30 (A6:H30).
- The searched string or text is stored in cell J7 (J7).

#7. Excel VBA Find (Cell with) String (or Text) in Column
VBA Code to Find (Cell with) String (or Text) in Column
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a column, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
RangeObjectColumn.Find(What:=SearchedString, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=XlFindLookInConstant, LookAt:=XlLookAtConstant, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant, MatchCase:=BooleanValue)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
RangeObjectColumn
A Range object representing the column you search in.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the string or text you search for) in a cell range (RangeObjectColumn).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=SearchedString
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a column, set the What parameter to the string (or text) you search for (SearchedString).
After:=SingleCellRangeObject
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins. This must be a single cell in the column you search in (RangeObjectColumn).
If you omit specifying the After parameter, the search begins after the first cell of the column you search in (RangeObjectColumn).
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a column, set the After parameter to a Range object representing the cell after which the search begins.
LookIn:=XlFindLookInConstant
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a column, set the LookIn parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlFormulas (LookIn:=xlFormulas): To search in the applicable column’s formulas.
- xlValues (LookIn:=xlValues): To search in the applicable column’s values.
LookAt:=XlLookAtConstant
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a column, set the LookAt parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlWhole (LookAt:=xlWhole): To match against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
- xlPart (LookAt:=xlPart): To match against any part of the searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=xlByRows
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable column (RangeObjectColumn) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a column, set the SearchOrder parameter to xlByRows. xlByRows results in the Range.Find method searching by rows.
SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a column, set the SearchDirection parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlNext (SearchDirection:=xlNext): To search for the next match.
- xlPrevious (SearchDirection:=xlPrevious): To search for the previous match.
MatchCase:=BooleanValue
The MatchCase parameter of the Range.Find method specifies whether the search is:
- Case-sensitive; or
- Case-insensitive.
The default value of the MatchCase parameter is False.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a column, set the MatchCase parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- True (MatchCase:=True): To carry out a case-sensitive search.
- False (MatchCase:=False): To carry out a case-insensitive search.
Macro Example to Find (Cell with) String (or Text) in Column
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts two arguments:
- MyColumn: The column you search in.
- MyString: The string (or text) you search for.
- Finds MyString in MyColumn. The search is case-insensitive.
- Returns a string containing the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the column (MyColumn) where the string or text (MyString) is found.
Function FindStringInColumn(MyColumn As Range, MyString As Variant) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 2 arguments: MyColumn and MyString
'(2) Finds a string passed as argument (MyString) in a column passed as argument (MyColumn). The search is case-insensitive
'(3) Returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the column (MyColumn) where the string (MyString) is found
With MyColumn
FindStringInColumn = .Find(What:=MyString, After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext, MatchCase:=False).Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find (Cell with) String (or Text) in Column
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Column A (cells A6 to A30) contains randomly generated words.
- Cell C7 contains the searched string or text (Excel).
- Cell D7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the column (MyColumn) where the string or text (MyString) is found. This is cell A21.
- Cell E7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell D7 (=FindStringInColumn(A:A,C7)).
- The column where the search is carried out is column A (A:A).
- The searched string or text is stored in cell C7 (C7).

#8. Excel VBA Find String (or Text) in Cell
VBA Code to Find String (or Text) in Cell
To find a string (or text) in a cell, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
InStr(StartingPosition, SearchedCell.Value, SearchedString, VbCompareMethodConstant)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
InStr
The InStr function returns a number. This number specifies the position of the first occurrence of a string or text (SearchedString) in another string (the string stored in SearchedCell).
StartingPosition
The Start argument of the InStr function is:
- An optional argument.
- A numeric expression specifying the starting position for the string (or text) search.
If you omit specifying the Start argument, the search begins at the first character of the searched string (the string stored in SearchedCell).
To find a string (or text) in a cell, set the Start argument to the position (in the string stored in SearchedCell) where the string (or text) search starts.
SearchedCell.Value
The String1 argument of the InStr function represents the string expression the InStr function searches in.
To find a string (or text) in a cell, set the String1 argument to the value/string stored in the searched cell. For these purposes:
- “SearchedCell” is a Range object representing the searched cell.
- “Value” refers to the Range.Value property. The Range.Value property returns the value/string stored in the searched cell (SearchedCell).
SearchedString
The String2 argument of the InStr function represents the string expression (or text) the InStr function searches for.
To find a string (or text) in a cell, set the String2 argument to the string (or text) you search for.
VbCompareMethodConstant
The Compare argument of the InStr function:
- Is an optional argument.
- Specifies the type of string comparison carried out by the InStr function.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the vbCompareMethod enumeration.
If you omit specifying the Compare argument, the type of string comparison is determined by the Option Compare statement. The Option Compare statement declares the default string comparison method at a module level. The default string comparison method is binary (vbBinaryCompare).
To find a string (or text) in a cell, set the Compare argument to either of the following, as applicable:
- vbBinaryCompare: Performs a binary comparison. vbBinaryCompare:
- Results in a case-sensitive search.
- May be (slightly) faster than vbTextCompare.
- vbTextCompare: Performs a textual comparison. vbTextCompare:
- Results in a case-insensitive search.
- May be (slightly) slower than vbBinaryCompare.
- Is more prone to errors/bugs than vbBinaryCompare.
Macro Example to Find String (or Text) in Cell
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts three arguments:
- MyCell: The cell you search in.
- MyString: The string (or text) you search for.
- MyStartingPosition: The starting position for the string (or text) search. MyStartingPosition is an optional argument with a default value of 1.
- Finds MyString in the value/string stored in MyCell.
- Returns the following:
- If MyString is not found in the value/string stored in MyCell, the string “String not found in cell”.
- If MyString is found in the value/string stored in MyCell, the position of the first occurrence of MyString in the value/string stored in MyCell.
Function FindStringInCell(MyCell As Range, MyString As Variant, Optional MyStartingPosition As Variant = 1) As Variant
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts three arguments: MyCell, MyString and MyStartingPosition (optional argument with a default value of 1)
'(2) Finds a string passed as argument (MyString) in the value/string stored in a cell passed as argument (MyCell)
'(3) Returns the following (as applicable):
'If MyString is not found in the value/string stored in MyCell: The string "String not found in cell"
'If MyString is found in the value/string stored in MyCell: The position of the first occurrence of MyString in the value/string stored in MyCell
'Obtain position of first occurrence of MyString in the value/string stored in MyCell
FindStringInCell = InStr(MyStartingPosition, MyCell.Value, MyString, vbBinaryCompare)
'If MyString is not found in the value/string stored in MyCell, return the string "String not found in cell"
If FindStringInCell = 0 Then FindStringInCell = "String not found in cell"
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find String (or Text) in Cell
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Column A (cells A7 to A31) contains randomly generated words.
- Column B (cells B7 to B31) contains a 2-character string (ar).
- Column C (cells C7 to C31) contains worksheet formulas working with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. These worksheet formulas return either of the following (as applicable):
- The string “String not found in cell”, if the string (or text) specified in the applicable cell of column B is not found in the applicable cell of column A.
- The position of the first occurrence of the string (or text) specified in the applicable cell of column B in the applicable cell of column A, if the string (or text) specified in the applicable cell of column B is found in the applicable cell of column A.
- Column D (cells D7 to D31) displays the worksheet formulas used in column C (=FindStringInCell(CellInColumnA,CellInColumnB)).
- The cell where the search is carried out is in column A (CellInColumnA).
- The searched string or text is stored in column B (CellInColumnB).

#9. Excel VBA Find String (or Text) in String
VBA Code to Find String (or Text) in String
To find a string (or text) in a string, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
InStr(StartingPosition, SearchedString, SearchedText, VbCompareMethodConstant)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
InStr
The InStr function returns a number. This number specifies the position of the first occurrence of a string or text (SearchedText) in another string (SearchedString).
StartingPosition
The Start argument of the InStr function is:
- An optional argument.
- A numeric expression specifying the starting position for the string (or text) search.
If you omit specifying the Start argument, the search begins at the first character of the searched string (SearchedString).
To find a string (or text) in a string, set the Start argument to the position (in SearchedString) where the string (or text) search starts.
SearchedString
The String1 argument of the InStr function represents the string expression the InStr function searches in.
To find a string (or text) in a string, set the String1 argument to the searched string.
SearchedText
The String2 argument of the InStr function represents the string expression (or text) the InStr function searches for.
To find a string (or text) in a string, set the String2 argument to the string (or text) you search for.
VbCompareMethodConstant
The Compare argument of the InStr function:
- Is an optional argument.
- Specifies the type of string comparison carried out by the InStr function.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the vbCompareMethod enumeration.
If you omit specifying the Compare argument, the type of string comparison is determined by the Option Compare statement. The Option Compare statement declares the default string comparison method at a module level. The default string comparison method is binary (vbBinaryCompare).
To find a string (or text) in a string, set the Compare argument to either of the following, as applicable:
- vbBinaryCompare: Performs a binary comparison. vbBinaryCompare:
- Results in a case-sensitive search.
- May be (slightly) faster than vbTextCompare.
- vbTextCompare: Performs a textual comparison. vbTextCompare:
- Results in a case-insensitive search.
- May be (slightly) slower than vbBinaryCompare.
- Is more prone to errors/bugs than vbBinaryCompare.
Macro Example to Find String (or Text) in String
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts three arguments:
- MyString: The string you search in.
- MyText: The string (or text) you search for.
- MyStartingPosition: The starting position for the string (or text) search. MyStartingPosition is an optional argument with a default value of 1.
- Finds MyText in MyString.
- Returns the following:
- If MyText is not found in MyString, the string “Text not found in string”.
- If MyText is found in MyString, the position of the first occurrence of MyText in MyString.
Function FindTextInString(MyString As Variant, MyText As Variant, Optional MyStartingPosition As Variant = 1) As Variant
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts three arguments: MyString, MyText and MyStartingPosition (optional argument with a default value of 1)
'(2) Finds text (a string) passed as argument (MyText) in a string passed as argument (MyString)
'(3) Returns the following (as applicable):
'If MyText is not found in MyString: The string "Text not found in string"
'If MyText is found in MyString: The position of the first occurrence of MyText in MyString
'Obtain position of first occurrence of MyText in MyString
FindTextInString = InStr(MyStartingPosition, MyString, MyText, vbBinaryCompare)
'If MyText is not found in MyString, return the string "Text not found in string"
If FindTextInString = 0 Then FindTextInString = "Text not found in string"
End Function
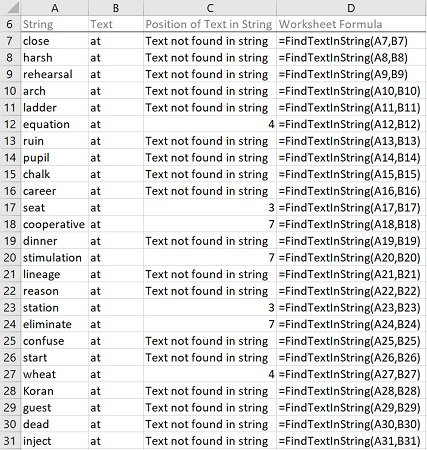
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find String (or Text) in String
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Column A (cells A7 to A31) contains randomly generated words.
- Column B (cells B7 to B31) contains text (at).
- Column C (cells C7 to C31) contains worksheet formulas working with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. These worksheet formulas return either of the following (as applicable):
- The string “Text not found in string”, if the string (or text) specified in the applicable cell of column B is not found in the string specified in the applicable cell of column A.
- The position of the first occurrence of the string (or text) specified in the applicable cell of column B in the string specified in the applicable cell of column A, if the string (or text) specified in the applicable cell of column B is found in the string specified in the applicable cell of column A.
- Column D (cells D7 to D31) displays the worksheet formulas used in column C (=FindTextInString(CellInColumnA,CellInColumnB)).
- The string where the search is carried out is stored in column A (CellInColumnA).
- The searched string (or text) is stored in column B (CellInColumnB).
#10. Excel VBA Find Character in String
VBA Code to Find Character in String
To find a character in a string, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
InStr(StartingPosition, SearchedString, SearchedCharacter, VbCompareMethodConstant)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
InStr
The InStr function returns a number. This number specifies the position of the first occurrence of a string or text (SearchedCharacter) in another string (SearchedString).
StartingPosition
The Start argument of the InStr function is:
- An optional argument.
- A numeric expression specifying the starting position for the character search.
If you omit specifying the Start argument, the search begins at the first character of the searched string (SearchedString).
To find a character in a string, set the Start argument to the position (in SearchedString) where the character search starts.
SearchedString
The String1 argument of the InStr function represents the string expression the InStr function searches in.
To find a character in a string, set the String1 argument to the searched string.
SearchedCharacter
The String2 argument of the InStr function represents the string expression (or text) the InStr function searches for.
To find a character in a string, set the String2 argument to the character you search for.
VbCompareMethodConstant
The Compare argument of the InStr function:
- Is an optional argument.
- Specifies the type of string comparison carried out by the InStr function.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the vbCompareMethod enumeration.
If you omit specifying the Compare argument, the type of string comparison is determined by the Option Compare statement. The Option Compare statement declares the default string comparison method at a module level. The default string comparison method is binary (vbBinaryCompare).
To find a character in a string, set the Compare argument to either of the following, as applicable:
- vbBinaryCompare: Performs a binary comparison. vbBinaryCompare:
- Results in a case-sensitive search.
- May be (slightly) faster than vbTextCompare.
- vbTextCompare: Performs a textual comparison. vbTextCompare:
- Results in a case-insensitive search.
- May be (slightly) slower than vbBinaryCompare.
- Is more prone to errors/bugs than vbBinaryCompare.
Macro Example to Find Character in String
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts three arguments:
- MyString: The string you search in.
- MyCharacter: The character you search for.
- MyStartingPosition: The starting position for the character search. MyStartingPosition is an optional argument with a default value of 1.
- Finds MyCharacter in MyString.
- Returns the following:
- If MyCharacter is not found in MyString, the string “Character not found in string”.
- If MyCharacter is found in MyString, the position of the first occurrence of MyCharacter in MyString.
Function FindCharacterInString(MyString As Variant, MyCharacter As Variant, Optional MyStartingPosition As Variant = 1) As Variant
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts three arguments: MyString, MyCharacter and MyStartingPosition (optional argument with a default value of 1)
'(2) Finds a character passed as argument (MyCharacter) in a string passed as argument (MyString)
'(3) Returns the following (as applicable):
'If MyCharacter is not found in MyString: The string "Character not found in string"
'If MyCharacter is found in MyString: The position of the first occurrence of MyCharacter in MyString
'Obtain position of first occurrence of MyCharacter in MyString
FindCharacterInString = InStr(MyStartingPosition, MyString, MyCharacter, vbBinaryCompare)
'If MyCharacter is not found in MyString, return the string "Character not found in string"
If FindCharacterInString = 0 Then FindCharacterInString = "Character not found in string"
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Character in String
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Column A (cells A7 to A31) contains randomly generated words.
- Column B (cells B7 to B31) contains a character (a).
- Column C (cells C7 to C31) contains worksheet formulas working with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. These worksheet formulas return either of the following (as applicable):
- The string “Character not found in string”, if the character specified in the applicable cell of column B is not found in the string specified in the applicable cell of column A.
- The position of the first occurrence of the character specified in the applicable cell of column B in the string specified in the applicable cell of column A, if the character specified in the applicable cell of column B is found in the string specified in the applicable cell of column A.
- Column D (cells D7 to D31) displays the worksheet formulas used in column C (=FindCharacterInString(CellInColumnA,CellInColumnB)).
- The string where the search is carried out is stored in column A (CellInColumnA).
- The searched character is stored in column B (CellInColumnB).

#11. Excel VBA Find Column with Specific Header
VBA Code to Find Column with Specific Header
To find a column with a specific header, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
HeaderRowRangeObject.Find(What:=SearchedHeader, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant, MatchCase:=BooleanValue)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
HeaderRowRangeObject
A Range object representing the cell range containing the headers you search in.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the header you search for) in a cell range (HeaderRowRangeObject).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=SearchedHeader
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find a column with a specific header, set the What parameter to the header you search for (SearchedHeader).
After:=SingleCellRangeObject
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins. This must be a single cell in the cell range containing the headers you search in (HeaderRowRangeObject).
If you omit specifying the After parameter, the search begins after the first cell of the cell range you search in (HeaderRowRangeObject).
To find a column with a specific header, set the After parameter to a Range object representing the cell after which the search begins.
LookIn:=xlValues
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find a column with a specific header, set the LookIn parameter to xlValues. xlValues refers to values.
LookAt:=xlWhole
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find a column with a specific header, set the LookAt parameter to xlWhole. xlWhole matches the data you are searching for against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=xlByColumns
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (HeaderRowRangeObject) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find a column with a specific header, set the SearchOrder parameter to xlByColumns. xlByColumns searches by columns.
SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find a column with a specific header, set the SearchDirection parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlNext (SearchDirection:=xlNext): To search for the next match.
- xlPrevious (SearchDirection:=xlPrevious): To search for the previous match.
MatchCase:=BooleanValue
The MatchCase parameter of the Range.Find method specifies whether the search is:
- Case-sensitive; or
- Case-insensitive.
The default value of the MatchCase parameter is False.
To find a column with a specific header, set the MatchCase parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- True (MatchCase:=True): To carry out a case-sensitive search.
- False (MatchCase:=False): To carry out a case-insensitive search.
Macro Example to Find Column with Specific Header
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts two arguments:
- MyRange: The cell range whose first row contains the headers you search in.
- MyHeader: The header you search for.
- Finds MyHeader in the first row of MyRange.
- Returns the number of the column containing the first cell in the header row where the header (MyHeader) is found.
Function FindColumnWithSpecificHeader(MyRange As Range, MyHeader As Variant) As Long
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 2 arguments: MyRange and MyHeader
'(2) Finds a header passed as argument (MyHeader) in the first row (the header row) of a cell range passed as argument (MyRange). The search is case-insensitive
'(3) Returns the number of the column containing the first cell in the header row where the header (MyHeader) is found
With MyRange.Rows(1)
FindColumnWithSpecificHeader = .Find(What:=MyHeader, After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, SearchDirection:=xlNext, MatchCase:=False).Column
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Column with Specific Header
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H31) contain data with the following characteristics:
- Headers in its first row (row 6).
- Randomly generated values.
- Cell J7 contains the searched header (Column 3).
- Cell K7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the column number of the first cell in the header row (cells A6 to H6) of the cell range (MyRange) where the header (MyHeader) is found. This is column 3 (C).
- Cell L7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell K7 (=FindColumnWithSpecificHeader(A6:H31,J7)).
- The cell range whose first row contains the headers where the search is carried out contains cells A6 to H31 (A6:H31).
- The searched header is stored in cell J7 (J7).

#12. Excel VBA Find Next or Find All
VBA Code to Find Next or Find All
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, use the following structure/template in the applicable procedure:
Dim FoundCell As Range
Dim FirstFoundCellAddress As String
Set FoundCell = SearchedRangeObject.Find(What:=SearchedData, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=XlFindLookInConstant, LookAt:=XlLookAtConstant, SearchOrder:=XlSearchDirectionConstant, SearchDirection:=xlNext, MatchCase:=BooleanValue)
If Not FoundCell Is Nothing Then
FirstFoundCellAddress = FoundCell.Address
Do
Statements
Set FoundCell = SearchedRangeObject.FindNext(After:=FoundCell)
Loop Until FoundCell.Address = FirstFoundCellAddress
End If
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
Lines #1 and #2: Dim FoundCell As Range | Dim FirstFoundCellAddress As String
Dim
The Dim statement:
- Declares variables.
- Allocates storage space.
FoundCell | FirstFoundCellAddress
The names of the variables declared with the Dim statement.
- FoundCell holds/represents the cell where the searched data is found.
- FirstFoundCellAddress holds/represents the address of the first cell where the searched data is found.
As Range | As String
The data type of the variables declared with the Dim statement.
- FoundCell is of the Range object data type. The Range object represents a cell or cell range.
- FirstFoundCellAddress is of the String data type. The String data type (generally) holds textual data.
Line #3: Set FoundCell = SearchedRangeObject.Find(What:=SearchedData, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=XlFindLookInConstant, LookAt:=XlLookAtConstant, SearchOrder:=XlSearchDirectionConstant, SearchDirection:=xlNext, MatchCase:=BooleanValue)
Set
The Set statement assigns an object reference to an object variable.
FoundCell
Object variable holding/representing the cell where the searched data is found.
=
The assignment operator assigns an object reference (returned by the Range.Find method) to an object variable (FoundCell).
SearchedRangeObject
A Range object representing the cell range you search in.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the data you search for) in a cell range (SearchedRangeObject).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=SearchedData
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, set the What parameter to the data you search for (SearchedData).
After:=SingleCellRangeObject
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins. This must be a single cell in the cell range you search in (SearchedRangeObject).
If you omit specifying the After parameter, the search begins after the first cell (in the upper left corner) of the cell range you search in (SearchedRangeObject).
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, set the After parameter to a Range object representing the cell after which the search begins.
LookIn:=XlFindLookInConstant
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, set the LookIn parameter to any of the following, as applicable:
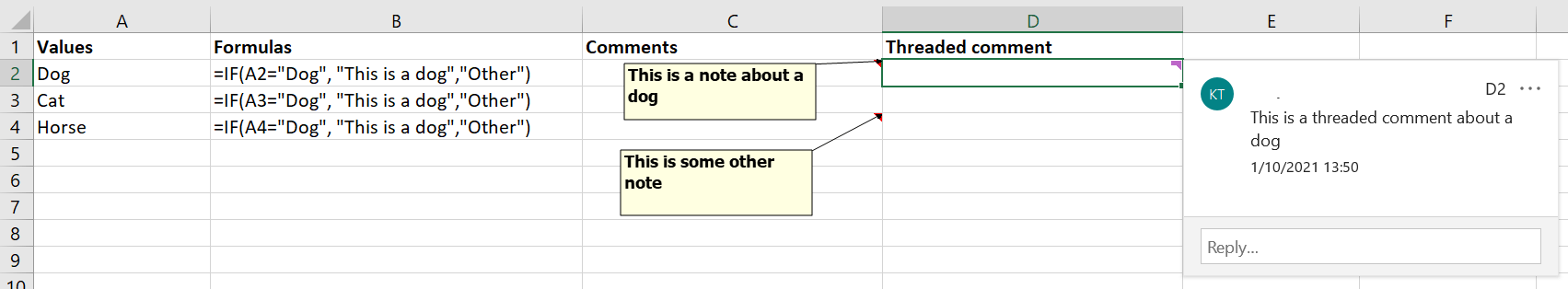
- xlCommentsThreaded (LookIn:=xlCommentsThreaded): To search in the applicable cell range’s threaded comments.
- xlValues (LookIn:=xlValues): To search in the applicable cell range’s values.
- xlComments (LookIn:=xlComments): To search in the applicable cell range’s comments/notes.
- xlFormulas (LookIn:=xlFormulas): To search in the applicable cell range’s formulas.
LookAt:=XlLookAtConstant
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, set the LookAt parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlWhole (LookAt:=xlWhole): To match against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
- xlPart (LookAt:=xlPart): To match against any part of the searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=XlSearchDirectionConstant
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (SearchedRangeObject) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, set the SearchOrder parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlByRows (SearchOrder:=xlByRows): To search by rows.
- xlByColumns (SearchOrder:=xlByColumns): To search by columns.
SearchDirection:=xlNext
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, set the SearchDirection parameter to xlNext. xlNext results in the Range.Find method searching for the next match.
MatchCase:=BooleanValue
The MatchCase parameter of the Range.Find method specifies whether the search is:
- Case-sensitive; or
- Case-insensitive.
The default value of the MatchCase parameter is False.
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, set the MatchCase parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- True (MatchCase:=True): To carry out a case-sensitive search.
- False (MatchCase:=False): To carry out a case-insensitive search.
Lines #4 and 10: If Not FoundCell Is Nothing Then | End If
If … Then | End If
The If… Then… Else statement:
- Conditionally executes a set of statements (lines #5 to #9);
- Depending on an expression’s value (Not FoundCell Is Nothing).
Not FoundCell Is Nothing
The condition of an If… Then… Else statement is an expression evaluating to True or False. If the expression returns True, the applicable set of statements (lines #5 to #9) is executed.
In this expression:
- Not FoundCell:
- The Not operator performs a logical negation on an expression.
- FoundCell is the object variable holding/representing the cell where the searched data is found.
- The Range.Find method (in line #3) returns Nothing if no match is found. Therefore:
- If the Range.Find method finds no match:
- FoundCell is Nothing.
- Not FoundCell is not Nothing.
- If the Range.Find method finds a match:
- FoundCell is not Nothing.
- Not FoundCell is Nothing.
- If the Range.Find method finds no match:
- Is: The Is operator is an object reference comparison operator.
- Nothing: Nothing allows you to disassociate a variable from the data it previously represented. The Range.Find method (in line #3) returns Nothing if no match is found.
Line #5: FirstFoundCellAddress = FoundCell.Address
FirstFoundCellAddress
Variable holding/representing the address of the first cell where the searched data is found.
=
The assignment operator assigns the result returned by an expression (FoundCell.Address) to a variable (FirstFoundCellAddress).
FoundCell
Object variable holding/representing the cell where the searched data is found.
At this point, FoundCell holds/represents the first cell where the searched data is found (by line #3).
Address
The Range.Address property returns a String representing the applicable cell range’s (FoundCell’s) reference.
Lines #6 and #9: Do | Loop Until FoundCell.Address = FirstFoundCellAddress
Do | Loop Until…
The Do… Loop Until statement repeats a set of statements until a condition becomes True.
FoundCell.Address = FirstFoundCellAddress
The condition of a Do… Loop Until statement is an expression evaluating to True or False. The applicable set of statements (lines #7 and #8) are:
- (Always) executed once, even if the condition is never met; and
- Repeatedly executed until the condition returns True.
In this expression:
- FoundCell.Address:
- FoundCell is an object variable holding/representing the cell where the searched data is found.
- The Range.Address property returns a String representing the applicable cell range’s (FoundCell’s) reference.
- =: The equal to comparison operator returns True or False as follows:
- True if both expressions (FoundCell.Address and FirstFoundCellAddress) are equal.
- False if the expressions (FoundCell.Address and FirstFoundCellAddress) are not equal.
- FirstFoundCellAddress: Variable holding/representing the address of the first cell where the searched data is found.
This condition is tested (only) after the procedure finds (and works with) the first cell where the searched data is found. Therefore, the condition (only) returns True after the Range.FindNext method (line #8) wraps around to the first cell where the searched data is found (after finding all other cells where the searched data is found).
Line #7: Statements
Set of statements to be repeatedly executed for each cell where the searched data is found.
Line #8: Set FoundCell = SearchedRangeObject.FindNext(After:=FoundCell)
Set
The Set statement assigns an object reference to an object variable.
FoundCell
Object variable holding/representing the cell where the searched data is found.
=
The assignment operator assigns an object reference (returned by the Range.FindNext method) to an object variable (FoundCell).
SearchedRangeObject
A Range object representing the cell range you search in.
FindNext
The Range.FindNext method:
- Continues the search that was begun by the Range.Find method (line #3).
- Finds the next cell matching the conditions specified by the Range.Find method (line #3).
- Returns a Range object representing the next cell where the information is found.
After:=FoundCell
The After parameter of the Range.FindNext method specifies the cell after which the search restarts.
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, set the After parameter to the object variable holding/representing the cell where the searched data is found.
Macro Example to Find Next or Find All
The following macro example does the following:
- Find:
- All cells whose value is 10;
- In the cell range containing cells A6 to H30 in the “Find Next All” worksheet in the workbook where the procedure is stored.
- Set the interior/fill color of all found cells to light green.
Sub FindNextAll()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This procedure:
'(1) Finds all cells whose value is 10 in cells A6 to H30 of the "Find Next All" worksheet in this workbook
'(2) Sets the found cells' interior/fill color to light green
'Declare variable to hold/represent searched value
Dim MyValue As Long
'Declare variable to hold/represent address of first cell where searched value is found
Dim FirstFoundCellAddress As String
'Declare object variable to hold/represent cell range where search takes place
Dim MyRange As Range
'Declare object variable to hold/represent cell where searched value is found
Dim FoundCell As Range
'Specify searched value
MyValue = 10
'Identify cell range where search takes place
Set MyRange = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Find Next All").Range("A6:H30")
'Find first cell where searched value is found
With MyRange
Set FoundCell = .Find(What:=MyValue, After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext)
End With
'Test whether searched value is found in cell range where search takes place
If Not FoundCell Is Nothing Then
'Store address of first cell where searched value is found
FirstFoundCellAddress = FoundCell.Address
Do
'Set interior/fill color of applicable cell where searched value is found to light green
FoundCell.Interior.Color = RGB(63, 189, 133)
'Find next cell where searched value is found
Set FoundCell = MyRange.FindNext(After:=FoundCell)
'Loop until address of current cell where searched value is found is equal to address of first cell where searched value was found
Loop Until FoundCell.Address = FirstFoundCellAddress
End If
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Next or Find All
The following image illustrates the effects of executing the macro example. In this example:
- Cells A6 to H30 contain randomly generated values.
- A text box (Find all cells where value = 10) executes the macro example when clicked.
After the macro is executed, Excel sets the interior/fill color of all cells whose value is 10 to light green.
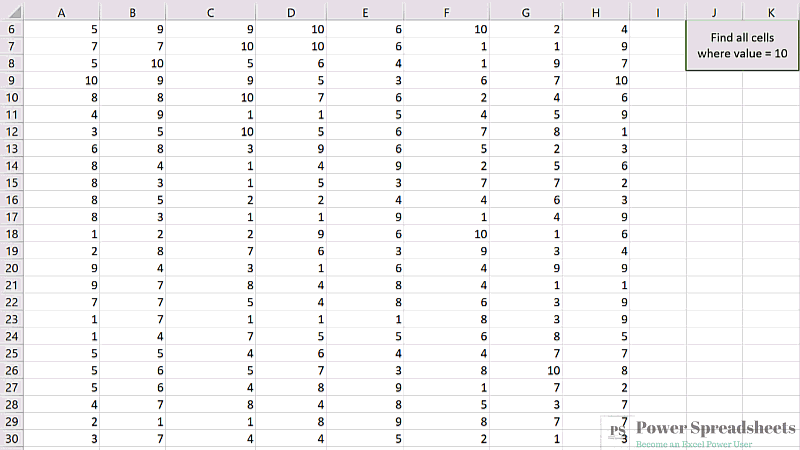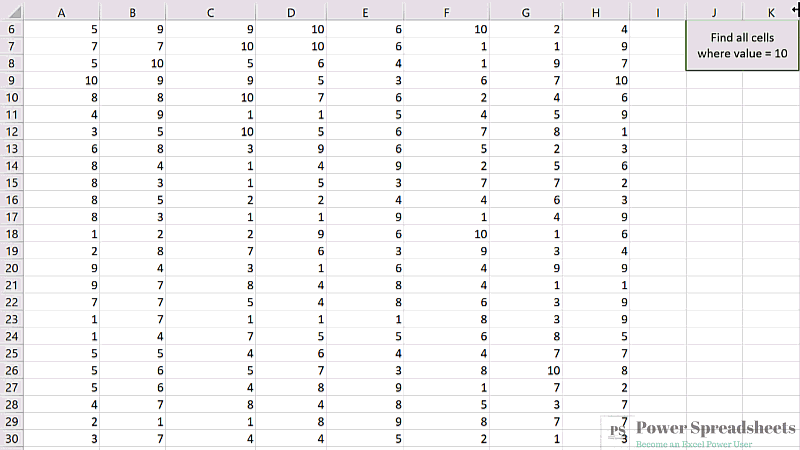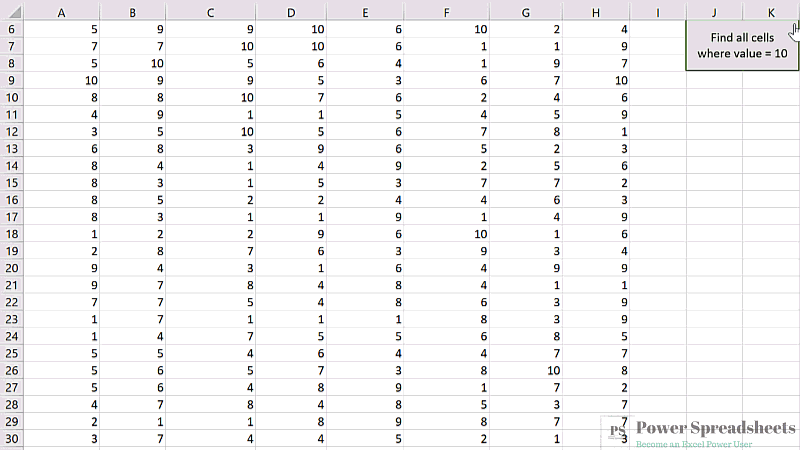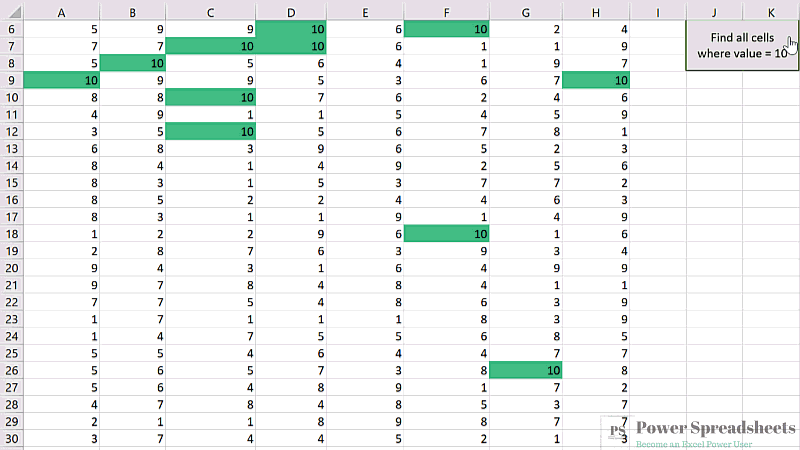
#13. Excel VBA Find Last Row with Data in Cell Range
VBA Code to Find Last Row with Data in Cell Range
To find the last row with data in a cell range, use the following structure/template in the applicable procedure:
If Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) = 0 Then
LastRowVariable = ValueIfCellRangeEmpty
Else
LastRowVariable = SearchedCellRangeObject.Find(What:="*", LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Row
End If
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
Lines #1, #3 and #5: If Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) = 0 Then | Else | End If
If… Then … Else… End If
The If… Then… Else statement:
- Conditionally executes a set of statements (line #2 or line #4);
- Depending on an expression’s value (Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) = 0).
Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) = 0
The condition of an If… Then… Else statement is an expression evaluating to True or False.
- If the expression returns True, a set of statements (line #2) is executed.
- If the expression returns False, a different set of statements (line #4) is executed.
In this expression:
- Application.CountA(…): The WorksheetFunction.CountA method counts the number of cells in a cell range (SearchedCellRangeObject) that are not empty.
- SearchedCellRangeObject: A Range object representing the cell range whose last row you search.
- =: The equal to comparison operator returns True or False as follows:
- True if both expressions (Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) and 0) are equal.
- False if the expressions (Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) and 0) are not equal.
- 0: The number 0. The WorksheetFunction.CountA method returns 0 if all cells in SearchedCellRangeObject are empty.
Line #2: LastRowVariable = ValueIfCellRangeEmpty
Assignment statement assigning:
- ValueIfCellRangeEmpty; to
- LastRowVariable.
In this expression:
- LastRowVariable: Variable of (usually) the Long data type holding/representing the number of the last row with data in the cell range whose last row you search (SearchedCellRangeObject).
- =: Assignment operator. Assigns a value (ValueIfCellRangeEmpty) to a variable (LastRowVariable).
- ValueIfCellRangeEmpty: Value assigned to LastRowVariable when SearchedCellRangeObject is empty and the WorksheetFunction.CountA method returns 0.
Line #4: LastRowVariable = SearchedCellRangeObject.Find(What:=”*”, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Row
LastRowVariable
Variable of (usually) the Long data type holding/representing the number of the last row with data in the cell range whose last row you search (SearchedCellRangeObject).
=
The assignment operator assigns a value (SearchedCellRangeObject.Find(What:=”*”, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Row) to a variable (LastRowVariable).
SearchedCellRangeObject
A Range object representing the cell range whose last row you search.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information in a cell range (SearchedCellRangeObject).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=”*”
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find the last row with data in a cell range, set the What parameter to any character sequence. The asterisk (*) acts as a wildcard and results in Range.Find searching for any character sequence.
LookIn:=xlFormulas
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find the last row with data in a cell range, set the LookIn parameter to xlFormulas. xlFormulas refers to formulas.
LookAt:=xlPart
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find the last row with data in a cell range, set the LookAt parameter to xlPart. xlPart matches the data you are searching for (any character sequence as specified by the What parameter) against any part of the searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=xlByRows
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (SearchedCellRangeObject) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find the last row with data in a cell range, set the SearchOrder parameter to xlByRows. xlByRows results in the Range.Find method searching by rows.
SearchDirection:=xlPrevious
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find the last row with data in a cell range, set the SearchDirection parameter to xlPrevious. xlPrevious results in the Range.Find method searching for the previous match.
Row
The Range.Row property returns the number of the first row of the first area in a cell range.
When searching for the last row with data in a cell range, the Range.Row property returns the row number of the cell represented by the Range object returned by the Range.Find method (Find(What:=”*”, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious)).
Macro Example to Find Last Row with Data in Cell Range
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts one argument (MyRange). This is the cell range whose last row you search.
- Tests whether MyRange is empty and proceeds accordingly:
- If MyRange is empty, returns the number 0 as the number of the last row with data in MyRange.
- If MyRange isn’t empty:
- Finds the last row with data in MyRange; and
- Returns the number of the last row with data in MyRange.
Function FindLastRow(MyRange As Range) As Long
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 1 argument: MyRange
'(2) Tests whether MyRange is empty
'(3) If MyRange is empty, returns 0 as the number of the last row with data in MyRange
'(4) If MyRange is not empty:
'(1) Finds the last row with data in MyRange by searching for the last cell with any character sequence
'(2) Returns the number of the last row with data in MyRange
'Test if MyRange is empty
If Application.CountA(MyRange) = 0 Then
'If MyRange is empty, assign 0 to FindLastRow
FindLastRow = 0
Else
'If MyRange isn't empty, find the last cell with any character sequence by:
'(1) Searching for the previous match;
'(2) Across rows
FindLastRow = MyRange.Find(What:="*", LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Row
End If
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Last Row with Data in Cell Range
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H30) contain data.
- Cell J7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the number of the last row with data in the cell range (MyRange). This is row 30.
- Cell K7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell J7 (=FindLastRow(A:H)). The cell range whose last row is searched contains columns A through H (A:H).
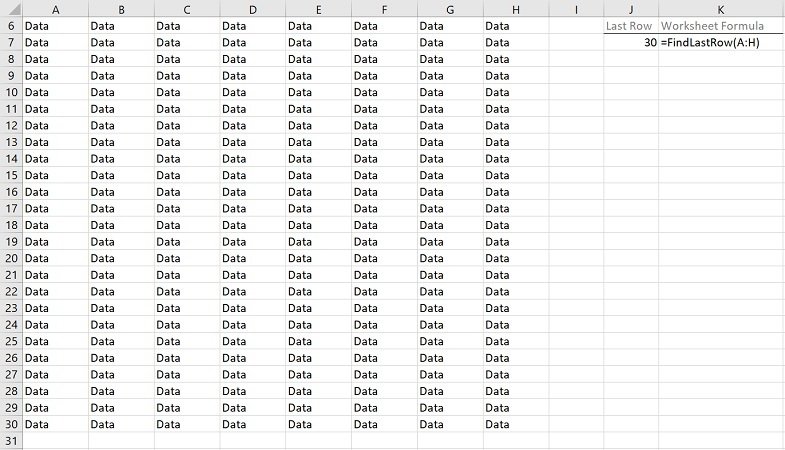
#14. Excel VBA Find Last Column with Data in Cell Range
VBA Code to Find Last Column with Data in Cell Range
To find the last column with data in a cell range, use the following structure/template in the applicable procedure:
If Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) = 0 Then
LastColumnVariable = ValueIfCellRangeEmpty
Else
LastColumnVariable = SearchedCellRangeObject.Find(What:="*", LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Column
End If
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
Lines #1, #3 and #5: If Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) = 0 Then | Else | End If
If… Then … Else… End If
The If… Then… Else statement:
- Conditionally executes a set of statements (line #2 or line #4);
- Depending on an expression’s value (Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) = 0).
Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) = 0
The condition of an If… Then… Else statement is an expression evaluating to True or False.
- If the expression returns True, a set of statements (line #2) is executed.
- If the expression returns False, a different set of statements (line #4) is executed.
In this expression:
- Application.CountA(…): The WorksheetFunction.CountA method counts the number of cells in a cell range (SearchedCellRangeObject) that are not empty.
- SearchedCellRangeObject: A Range object representing the cell range whose last column you search.
- =: The equal to comparison operator returns True or False as follows:
- True if both expressions (Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) and 0) are equal.
- False if the expressions (Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) and 0) are not equal.
- 0: The number 0. The WorksheetFunction.CountA method returns 0 if all cells in SearchedCellRangeObject are empty.
Line #2: LastColumnVariable = ValueIfCellRangeEmpty
Assignment statement assigning:
- ValueIfCellRangeEmpty; to
- LastColumnVariable.
In this expression:
- LastColumnVariable: Variable of (usually) the Long data type holding/representing the number of the last column with data in the cell range whose last column you search (SearchedCellRangeObject).
- =: Assignment operator. Assigns a value (ValueIfCellRangeEmpty) to a variable (LastColumnVariable).
- ValueIfCellRangeEmpty: Value assigned to LastColumnVariable when SearchedCellRangeObject is empty and the WorksheetFunction.CountA method returns 0.
Line #4: LastColumnVariable = SearchedCellRangeObject.Find(What:=”*”, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Column
LastColumnVariable
Variable of (usually) the Long data type holding/representing the number of the last column with data in the cell range whose last column you search (SearchedCellRangeObject).
=
The assignment operator assigns a value (SearchedCellRangeObject.Find(What:=”*”, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Column) to a variable (LastColumnVariable).
SearchedCellRangeObject
A Range object representing the cell range whose last column you search.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information in a cell range (SearchedCellRangeObject).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=”*”
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find the last column with data in a cell range, set the What parameter to any character sequence. The asterisk (*) acts as a wildcard and results in Range.Find searching for any character sequence.
LookIn:=xlFormulas
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find the last column with data in a cell range, set the LookIn parameter to xlFormulas. xlFormulas refers to formulas.
LookAt:=xlPart
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find the last column with data in a cell range, set the LookAt parameter to xlPart. xlPart matches the data you are searching for (any character sequence as specified by the What parameter) against any part of the searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=xlByColumns
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (SearchedCellRangeObject) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find the last column with data in a cell range, set the SearchOrder parameter to xlByColumns. xlByColumns results in the Range.Find method searching by columns.
SearchDirection:=xlPrevious
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find the last column with data in a cell range, set the SearchDirection parameter to xlPrevious. xlPrevious results in the Range.Find method searching for the previous match.
Column
The Range.Column property returns the number of the first column of the first area in a cell range.
When searching for the last column with data in a cell range, the Range.Column property returns the column number of the cell represented by the Range object returned by the Range.Find method (Find(What:=”*”, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious)).
Macro Example to Find Last Column with Data in Cell Range
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts one argument (MyWorksheetName). This is the name of the worksheet whose last column you search.
- Tests whether the worksheet named MyWorksheetName is empty and proceeds accordingly:
- If the worksheet named MyWorksheetName is empty, returns the number 0 as the number of the last column with data in the worksheet.
- If the worksheet named MyWorksheetName isn’t empty:
- Finds the last column with data in the worksheet; and
- Returns the number of the last column with data in the worksheet.
Function FindLastColumn(MyWorksheetName As String) As Long
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 1 argument: MyWorksheetName
'(2) Tests whether the worksheet named MyWorksheetName is empty
'(3) If the worksheet named MyWorksheetName is empty, returns 0 as the number of the last column with data in the worksheet
'(4) If the worksheet named MyWorksheetName is not empty:
'(1) Finds the last column with data in the worksheet by searching for the last cell with any character sequence
'(2) Returns the number of the last column with data in the worksheet
'Declare object variable to hold/represent all cells in the worksheet named MyWorksheetName
Dim MyRange As Range
'Identify all cells in the worksheet named MyWorksheetName
Set MyRange = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(MyWorksheetName).Cells
'Test if MyRange is empty
If Application.CountA(MyRange) = 0 Then
'If MyRange is empty, assign 0 to FindLastColumn
FindLastColumn = 0
Else
'If MyRange isn't empty, find the last cell with any character sequence by:
'(1) Searching for the previous match;
'(2) Across columns
FindLastColumn = MyRange.Find(What:="*", LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Column
End If
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Last Column with Data in Cell Range
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H30) in the worksheet named “Find Last Column Data” contain data.
- Columns A through H of the “Find Last Column Data” worksheet contain exactly the same data as that in the “Find Last Column Formula” worksheet (displayed in the image below).
- The “Find Last Column Data” worksheet contains no data in columns J or K whereas the “Find Last Column Formula” worksheet (displayed in the image below) does.
- Cell J7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the number of the last column with data in the worksheet (named “Find Last Column Data”). This is column H or 8.
- Cell K7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell J7 (=FindLastColumn(“Find Last Column Data”)). The name of the worksheet whose last column is searched is “Find Last Column Data”.
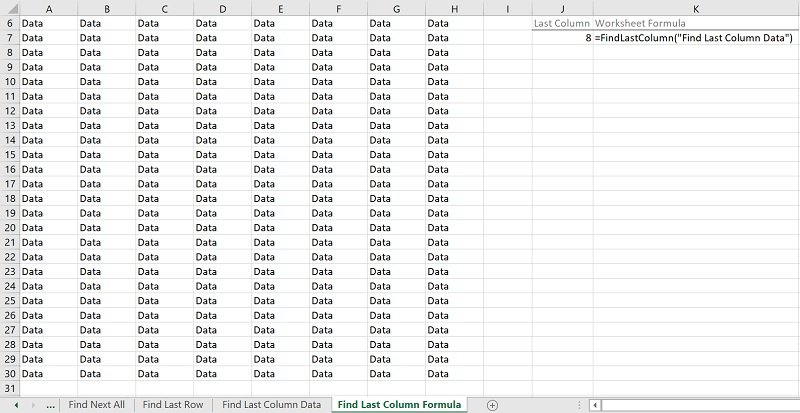
#15. Excel VBA Find Last Non Empty Cell in Column
VBA Code to Find Last Non Empty Cell in Column
To find the last non empty cell in a column, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
WorksheetObject.Range(ColumnLetter & WorksheetObject.Rows.Count).End(xlUp)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
WorksheetObject
A Worksheet object representing the worksheet containing the column whose last non empty cell you want to find.
Range
The Worksheet.Range property returns a Range object representing a cell or cell range.
ColumnLetter
The letter of the column whose last non empty cell you want to find.
&
The concatenation operator joins two strings and creates a new string.
WorksheetObject
A Worksheet object representing the worksheet containing the column whose last non empty cell you want to find.
Rows
The Worksheet.Rows property returns a Range object representing all rows in the applicable worksheet (containing the column whose last non empty cell you want to find).
Count
The Range.Count property returns the number of objects in a collection (the number of rows in the worksheet containing the column whose last non empty cell you want to find).
End(xlUp)
The Range.End property returns a Range object representing the cell at the end of the region containing the source range. In other words: The Range.End property is the rough equivalent of using the “Ctrl + Arrow Key” or “End, Arrow Key” keyboard shortcuts.
The Range.End property accepts one parameter: Direction. Direction:
- Specifies the direction in which to move.
- Can take the any of the built-in constants/values from the XlDirection enumeration.
To find the last non empty cell in a column, set the Direction parameter to xlUp. xlUp:
- Results in moving up, to the top of the data region.
- Is the rough equivalent of the “Ctrl + Up Arrow” or “End, Up Arrow” keyboard shortcuts.
Macro Example to Find Last Non Empty Cell in Column
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts one argument (MyColumn): The letter of the column (in the worksheet where the UDF is used) whose last non empty cell you want to find.
- Finds the last non empty cell in the applicable column.
- Returns a string containing the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the last non empty cell in the applicable column.
Function FindLastNonEmptyCellColumn(MyColumn As String) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 1 argument: MyColumn
'(2) Finds the last non empty cell in the column whose letter is passed as argument (MyColumn) in the worksheet where the UDF is used
'(3) Returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the last non empty cell found in the column whose letter is passed as argument (MyColumn) in the worksheet where the UDF is used
With Application.Caller.Parent
FindLastNonEmptyCellColumn = .Range(MyColumn & .Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Last Non Empty Cell in Column
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Column A (cells A6 to A30) contains data.
- Cell C7 contains the letter of the column whose last non empty cell is sought (A).
- Cell D7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the last non empty cell in column A (MyColumn). This is cell A30
- Cell E7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell D7 (=FindLastNonEmptyCellColumn(C7)). The letter of the column whose last non empty cell is sought is stored in cell C7 (C7).
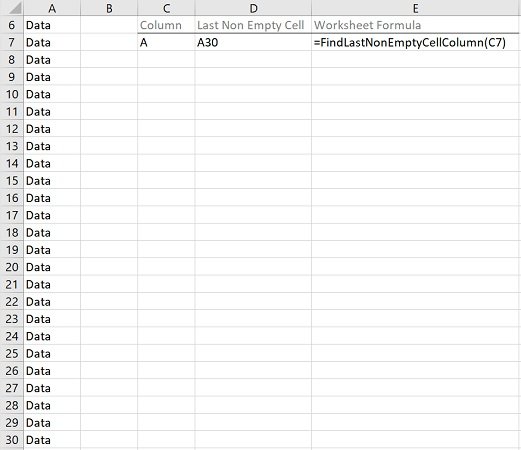
#16. Excel VBA Find Empty (or Blank) Cells
VBA Code to Find Empty (or Blank) Cells
To find all empty (or blank) cells in a cell range, use the following structure/template in the applicable procedure:
Dim BlankCellsObjectVariable As Range
On Error Resume Next
Set BlankCellsObjectVariable = RangeObjectWithBlankCells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks)
On Error GoTo 0
If Not BlankCellsObjectVariable Is Nothing Then
StatementsIfBlankCells
End If
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
Line #1: Dim BlankCellsObjectVariable As Range
Dim
The Dim statement:
- Declares variables.
- Allocates storage space.
BlankCellsObjectVariable
The name of the variable declared with the Dim statement.
BlankCellsObjectVariable holds/represents the empty (or blank) cells found.
As Range
The data type of the variable declared with the Dim statement.
BlankCellsObjectVariable is declared as of the Range object data type. The Range object represents a cell or cell range.
Line #2: On Error Resume Next
The On Error Resume Next statement specifies that, when a run-time error occurs, control passes to the statement immediately following that statement where the error occurred. Therefore, procedure execution continues.
Line #3 returns an error (Run time error ‘1004′: No cells were found) if the cell range where you search for empty (or blank) cells doesn’t contain any empty (or blank) cells.
Line #3: Set BlankCellsObjectVariable = RangeObjectWithBlankCells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks)
Set
The Set statement assigns an object reference to an object variable.
BlankCellsObjectVariable
Object variable holding/representing the empty (or blank) cells found.
=
The assignment operator assigns an object reference (returned by the Range.SpecialCells method) to an object variable (BlankCellsObjectVariable).
RangeObjectWithBlankCells
A Range object representing the cell range you search in for empty (or blank) cells.
SpecialCells
The Range.SpecialCells method returns a Range object representing all cells matching a specified:
- Type; and
- Value.
xlCellTypeBlanks
The Type parameter of the Range.SpecialCells method:
- Specifies the cells to include in the Range object returned by the Range.SpecialCells method.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlCellType enumeration.
To find all empty (or blank) cells in a cell range, set the Type parameter to xlCellTypeBlanks. xlCellTypeBlanks results in the Range.SpecialCells method including blank/empty cells in the Range object it returns.
Line #4: On Error GoTo 0
The On Error GoTo 0 statement disables error handling (originally enabled by line #2).
Line #5 and #7: If Not BlankCellsObjectVariable Is Nothing Then | End If
If… Then | End If
The If… Then… Else statement:
- Conditionally executes a set of statements (line #6);
- Depending on an expression’s value (Not BlankCellsObjectVariable Is Nothing).
Not BlankCellsObjectVariable Is Nothing
The condition of an If… Then… Else statement is an expression evaluating to True or False. If the expression returns True, the applicable set of statements (line #6) is executed.
In this expression:
- Not BlankCellsObjectVariable:
- The Not operator performs a logical negation on an expression.
- BlankCellsObjectVariable is the object variable holding/representing the empty (or blank) cells found.
- BlankCellsObjectVariable holds/represents Nothing if no empty (or blank) cells are found. Therefore:
- If the Range.SpecialCells method finds no empty (or blank) cells:
- BlankCellsObjectVariable is Nothing.
- Not BlankCellsObjectVariable is not Nothing.
- If the Range.SpecialCells method finds empty (or blank) cells:
- BlankCellsObjectVariable is not Nothing.
- Not BlankCellsObjectVariable is Nothing.
- If the Range.SpecialCells method finds no empty (or blank) cells:
- Is: The Is operator is an object reference comparison operator.
- Nothing: Nothing allows you to disassociate a variable from the data it previously represented. BlankCellsObjectVariable holds/represents Nothing if no empty (or blank) cells are found.
Line #6: StatementsIfBlankCells
Statements conditionally executed by the If… Then… Else statement if the applicable condition (Not BlankCellsObjectVariable Is Nothing) returns True (the Range.SpecialCells method finds empty or blank cells).
Macro Example to Find Empty (or Blank) Cells
The following macro example does the following:
- Find all empty (or blank) cells in the cell range containing cells A6 to H30 in the “Find Blank Cells” worksheet in the workbook where the procedure is stored.
- Set the interior/fill color of all found empty (or blank) cells to light green.
Sub FindBlankCells()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This procedure:
'(1) Finds all blank cells in cells A6 to H30 of the "Find Blank Cells" worksheet in this workbook
'(2) Sets the found cells' interior/fill color to light green
'Declare object variable to hold/represent blank cells
Dim MyBlankCells As Range
'Enable error-handling
On Error Resume Next
'Identify blank cells in searched cell range
Set MyBlankCells = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Find Blank Cells").Range("A6:H30").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks)
'Disable error-handling
On Error GoTo 0
'Test whether blank cells were found in searched cell range
If Not MyBlankCells Is Nothing Then
'Set interior/fill color of blank cells found to light green
MyBlankCells.Interior.Color = RGB(63, 189, 133)
End If
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Empty (or Blank) Cells
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H30) contain:
- Data; and
- A few empty cells (with light green interior/fill).
- A text box (Find all blank cells) executes the macro example when clicked.
After the macro is executed, Excel sets the interior/fill color of all empty (or blank) cells to light green.

#17. Excel VBA Find First Empty (or Blank) Cell in Cell Range
VBA Code to Find First Empty (or Blank) Cell in Cell Range
To find the first empty (or blank) cell in a cell range, use the following structure/template in the applicable procedure:
For Each iCell In CellRangeObject
If IsEmpty(iCell) Then
StatementsForFirstEmptyCell
Exit For
End If
Next iCell
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
Lines #1 and #6: For Each iCell In CellRangeObject | Next iCell
For Each … In … | Next …
The For Each… Next statement repeats a series of statements for each element (iCell, an individual cell) in a collection (CellRangeObject).
iCell
Object variable (of the Range data type) used to iterate/loop through each element of the collection (CellRangeObject).
CellRangeObject
A Range object representing the cell range you search in.
The series of statements repeated by the For Each… Next statement are repeated for each individual element (iCell) in CellRangeObject.
Lines #2 and #5: If IsEmpty(iCell) Then | End If
If… Then | End If
The If… Then Else statement:
- Conditionally executes a set of statements (lines #3 and #4);
- Depending on an expression’s value (IsEmpty(iCell)).
IsEmpty(iCell)
The condition of an If… Then… Else statement is an expression evaluating to True or False. If the expression returns True, the applicable set of statements (lines #3 and #4) are executed.
In this expression:
- As a general rule, the IsEmpty function returns a Boolean value (True or False) indicating whether a variable is initialized. You can (also) use the IsEmpty function to test whether a cell is empty (or blank).
- iCell is an object variable representing the individual cell the For Each… Next statement is currently working with (iterating through).
- IsEmpty(iCell) returns True or False as follows:
- True if the cell (currently) represented by iCell is empty (or blank).
- False if the cell (currently) represented by iCell isn’t empty. A cell isn’t considered to be empty if, for example, it contains a worksheet formula returning a zero-length string (“”).
Line #3: StatementsForFirstEmptyCell
Statements conditionally executed by the If… Then… Else statement if the applicable condition (IsEmpty(iCell)) returns True (the cell currently represented by iCell is empty or blank).
Line #4: Exit For
The Exit For statement:
- Exits a For Each… Next loop.
- Transfers control to the statement following the Next statement (line #6).
Macro Example to Find First Empty (or Blank) Cell in Cell Range
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts one argument (MyRange): The cell range whose first empty cell you search for.
- Loops through each individual cell in the cell range (MyRange) and tests whether the applicable cell is empty (or blank).
- Returns the following:
- If MyRange contains empty cells, the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first empty cell in the cell range (MyRange).
- If MyRange doesn’t contain empty cells, the string “No empty cells found in cell range”.
Function FindNextEmptyCellRange(MyRange As Range) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 1 argument: MyRange
'(2) Loops through each individual cell in the cell range (MyRange) and tests whether the applicable cell is empty
'(3) Returns the following (as applicable):
'If there are empty cells in MyRange: The address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first empty cell
'If there are no empty cells in MyRange: The string "No empty cells found in cell range"
'Declare object variable to iterate/loop through all cells in the cell range (MyRange)
Dim iCell As Range
'Loop through each cell in the cell range (MyRange)
For Each iCell In MyRange
'If the current cell is empty:
'(1) Return the current cell's address (as an A1-style relative reference)
'(2) Exit the For Each... Next loop
If IsEmpty(iCell) Then
FindNextEmptyCellRange = iCell.Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
Exit For
End If
Next iCell
'If no empty cells are found in the cell range (MyRange), return the string "No empty cells found in cell range"
If FindNextEmptyCellRange = "" Then FindNextEmptyCellRange = "No empty cells found in cell range"
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find First Empty (or Blank) Cell in Cell Range
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H30) contain:
- Data; and
- A few empty cells (with light green interior/fill).
- Cell J7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first empty cell in the cell range (MyRange). This is cell B7.
- Cell K7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell J7 (=FindNextEmptyCellRange(A6:H30)). The cell range where the search is carried out contains cells A6 to H30 (A6:H30).
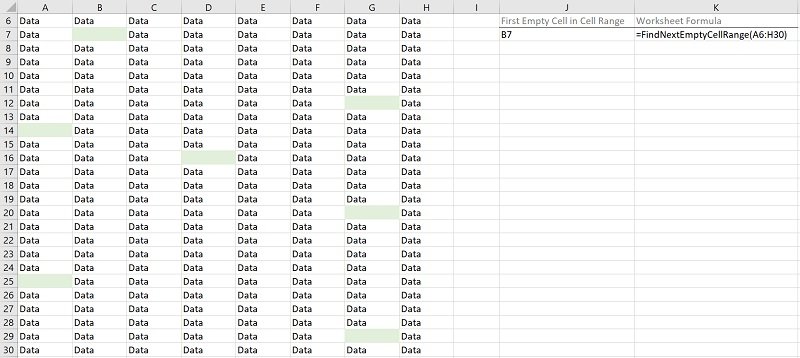
#18. Excel VBA Find First Empty (or Blank) Cell in Column
VBA Code to Find First Empty (or Blank) Cell in Column
To find the first empty (or blank) cell in a column, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
ColumnRangeObject.Find(What:="", After:=ColumnRangeObject.Cells(ColumnRangeObject.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
ColumnRangeObject
A Range object representing the column whose first empty (or blank) cell you search for.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the first empty or blank cell) in a cell range (ColumnRangeObject).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=””
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find the first empty (or blank) cell in a column, set the What parameter to a zero-length string (“”).
After:=ColumnRangeObject.Cells(ColumnRangeObject.Cells.Count)
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins.
To find the first empty (or blank) cell in a column, set the After parameter to “ColumnRangeObject.Cells(ColumnRangeObject.Cells.Count)”. For these purposes:
- “ColumnRangeObject” is a Range object representing the column whose first empty (or blank) cell you search for.
- The Range.Cells property (Cells) returns a Range object representing all cells in the column whose first empty (or blank) cell you search for.
- The Range.Item property returns a Range object representing the last cell in the column whose first empty (or blank) cell you search for. For these purposes, the RowIndex parameter of the Range.Item property is set to the value returned by the Range.Count property (Count).
- The Range.Count property (Count) returns the number of cells in the Range object returned by the Range.Cells property (ColumnRangeObject.Cells).
LookIn:=xlFormulas
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find the first empty (or blank) cell in a column, set the LookIn parameter to xlFormulas. xlFormulas refers to formulas.
LookAt:=xlWhole
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- The LookAt parameter can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find the first empty (or blank) cell in a column, set the LookAt parameter to xlWhole. xlWhole matches the data you are searching for against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=xlByRows
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (ColumnRangeObject) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find the first empty (or blank) cell in a column, set the SearchOrder parameter to xlByRows. xlByRows searches by rows.
SearchDirection:=xlNext
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find the first empty (or blank) cell in a column, set the SearchDirection parameter to xlNext. xlNext searches for the next match.
Macro Example to Find First Empty (or Blank) Cell in Column
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts one argument (MyColumn): The letter of the column (in the worksheet where the UDF is used) whose first empty (or blank) cell you search for.
- Finds the first empty (or blank) cell in the applicable column.
- Returns a string containing the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first empty (or blank) cell in the applicable column.
Function FindFirstEmptyCellColumn(MyColumn As String) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 1 argument: MyColumn
'(2) Finds the first empty (blank) cell in the column whose letter is passed as argument (MyColumn) in the worksheet where the UDF is used
'(3) Returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first empty (blank) cell in the column whose letter is passed as argument (MyColumn) in the worksheet where the UDF is used
With Application.Caller.Parent.Columns(MyColumn)
FindFirstEmptyCellColumn = .Find(What:="", After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext).Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find First Empty (or Blank) Cell in Column
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Column I (cells I1 to I25) contains:
- Data; and
- A few empty cells (with light green interior/fill).
- Cell A7 contains the letter of the column whose first empty (or blank) cell is sought (I).
- Cell B7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first empty (or blank) cell in column I (MyColumn). This is cell I10.
- Cell C7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell B7 (=FindFirstEmptyCellColumn(A7)). The letter of the column whose first empty (or blank) cell is sought is stored in cell A7 (A7).
#19. Excel VBA Find Next Empty (or Blank) Cell in Column
VBA Code to Find Next Empty (or Blank) Cell in Column
To find the next empty (or blank) cell in a column, use the following structure/template in the applicable procedure:
If IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell) Then
RangeObjectSourceCell.ActionForNextEmptyCell
ElseIf IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell.Offset(1, 0)) Then
RangeObjectSourceCell.Offset(1, 0).ActionForNextEmptyCell
Else
RangeObjectSourceCell.End(xlDown).Offset(1, 0).ActionForNextEmptyCell
End If
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
Lines #1, #3, #5 and #7: If IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell) Then | ElseIf IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell.Offset(1, 0)) Then | Else | End If
If… Then | ElseIf… Then | Else | End If
The If… Then… Else statement:
- Conditionally executes a set of statements (lines #2, #4 or #6);
- Depending on an expression’s value (IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell) or IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell.Offset(1, 0))).
IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell)
The condition of an If… Then… Else statement is an expression evaluating to True or False. If the expression returns True, the applicable set of statements (line #2) is executed.
In this expression:
- As a general rule, the IsEmpty function returns a Boolean value (True or False) indicating whether a variable is initialized. You can (also) use the IsEmpty function to test whether a cell is empty (or blank).
- RangeObjectSourceCell is a Range object representing the cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins.
- IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell) returns True or False as follows:
- True if the cell represented by RangeObjectSourceCell is empty (or blank).
- False if the cell represented by RangeObjectSourceCell isn’t empty. A cell isn’t considered to be empty if, for example, it contains a worksheet formula returning a zero-length string (“”).
IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell.Offset(1, 0))
The condition of an If… Then… Else statement is an expression evaluating to True or False. If the expression returns True, the applicable set of statements (line #4) is executed.
In this expression:
- As a general rule, the IsEmpty function returns a Boolean value (True or False) indicating whether a variable is initialized. You can (also) use the IsEmpty function to test whether a cell is empty (or blank).
- RangeObjectSourceCell is a Range object representing the cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins.
- The Range.Offset property (Offset(1, 0)) returns a Range object representing a cell range at an offset from the source cell range. In this expression:
- The source cell range is the cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins (RangeObjectSourceCell).
- The offset from the source cell range is as follows:
- 1 row downwards, as specified by the RowOffset parameter of the Range.Offset property (1).
- No column offsetting, as specified by the ColumnOffset parameter of the Range.Offset property (0).
- IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell.Offset(1, 0)) returns True or False as follows:
- True if the cell represented by the Range object returned by the Range.Offset property is empty.
- False if the cell represented by the Range object returned by the Range.Offset property isn’t empty. A cell isn’t considered to be empty if, for example, it contains a worksheet formula returning a zero-length string (“”).
Line #2: RangeObjectSourceCell.ActionForNextEmptyCell
Statement conditionally executed by the If… Then… Else statement if the applicable condition (IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell)) returns True.
RangeObjectSourceCell
A Range object representing the cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins.
ActionForNextEmptyCell
VBA construct (usually a property or method) working with the applicable cell (represented by RangeObjectSourceCell).
Line #4: RangeObjectSourceCell.Offset(1, 0).ActionForNextEmptyCell
Statement conditionally executed by the If… Then… Else statement if the applicable condition (IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell.Offset(1, 0))) returns True.
RangeObjectSourceCell
A Range object representing the cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins.
Offset(1, 0)
The Range.Offset property (Offset(1, 0)) returns a Range object representing a cell range at an offset from the source cell range. For these purposes:
- The source cell range is the cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins (RangeObjectSourceCell).
- The offset from the source cell range is as follows:
- 1 row downwards, as specified by the RowOffset parameter of the Range.Offset property (1).
- No column offsetting, as specified by the ColumnOffset parameter of the Range.Offset property (0).
ActionForNextEmptyCell
VBA construct (usually a property or method) working with the applicable cell (returned by the Range.Offset property).
Line #6: RangeObjectSourceCell.End(xlDown).Offset(1, 0).ActionForNextEmptyCell
Statement conditionally executed by the If… Then… Else statement if no previous condition (in lines #1 or #3) returns True.
RangeObjectSourceCell
A Range object representing the cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins.
End(xlDown)
The Range.End property returns a Range object representing the cell at the end of the region containing the source range. In other words: The Range.End property is the rough equivalent of using the “Ctrl + Arrow Key” or “End, Arrow Key” keyboard shortcuts.
The Range.End property accepts one parameter: Direction. Direction:
- Specifies the direction in which to move.
- Can take the any of the built-in constants/values from the XlDirection enumeration.
To find the next empty (or blank) cell in a column, set the Direction parameter to xlDown. xlDown:
- Results in moving down, to the bottom of the data region.
- Is the rough equivalent of the “Ctrl + Down Arrow” or “End, Down Arrow” keyboard shortcuts.
Offset(1, 0)
The Range.Offset property (Offset(1, 0)) returns a Range object representing a cell range at an offset from the source cell range. For these purposes:
- The source cell range is the cell represented by the Range object returned by the Range.End property (End(xlDown)).
- The offset from the source cell range is as follows:
- 1 row downwards, as specified by the RowOffset parameter of the Range.Offset property (1).
- No column offsetting, as specified by the ColumnOffset parameter of the Range.Offset property (0).
ActionForNextEmptyCell
VBA construct (usually a property or method) working with the applicable cell (returned by the Range.Offset property).
Macro Example to Find Next Empty (or Blank) Cell in Column
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts one argument (MySourceCell): The cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins.
- Finds the next empty (or blank) cell in the applicable column after MySourceCell.
- Returns a string containing the address (as an R1C1-style absolute reference) of the next empty (or blank) cell in the applicable column.
Function FindNextEmptyCellColumn(MySourceCell As Range) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 1 argument: MySourceCell
'(2) Finds the next empty/blank cell in the applicable column and after the cell passed as argument (MySourceCell)
'(3) Returns the address (as an R1C1-style absolute reference) of the next empty/blank cell in the applicable column and after the cell passed as argument (MySourceCell)
With MySourceCell(1)
'If first cell in cell range passed as argument (MySourceCell) is empty, obtain/return that cell's address
If IsEmpty(MySourceCell(1)) Then
FindNextEmptyCellColumn = .Address(ReferenceStyle:=xlR1C1)
'If cell below first cell in cell range passed as argument (MySourceCell) is empty, obtain/return that cell's address
ElseIf IsEmpty(.Offset(1, 0)) Then
FindNextEmptyCellColumn = .Offset(1, 0).Address(ReferenceStyle:=xlR1C1)
'Otherwise:
'(1) Find the next empty/blank cell in the applicable column and after the first cell in cell range passed as argument (MySourceCell)
'(2) Obtain/return the applicable cell's address
Else
FindNextEmptyCellColumn = .End(xlDown).Offset(1, 0).Address(ReferenceStyle:=xlR1C1)
End If
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Next Empty (or Blank) Cell in Column
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Column A (cells A6 to A30) contains:
- Data; and
- A few empty cells.
- Cell C7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an R1C1-style absolute reference) of the next empty (or blank) cell in column A after cell A13 (MySourceCell). This cell R21C1 (or A21 as an A1-style relative reference).
- Cell D7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell C7 (=FindNextEmptyCellColumn(A13)). The cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins is A13 (A13).
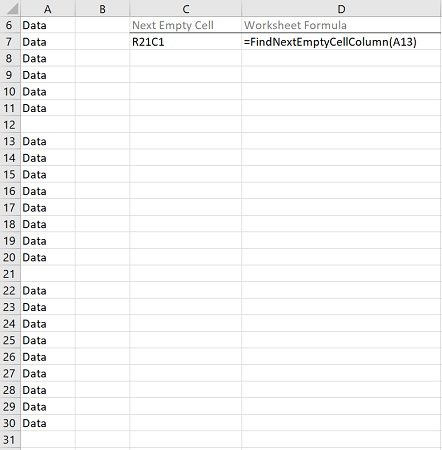
#20. Excel VBA Find Value in Array
VBA Code to Find Value in Array
To find a numeric value in a one-dimensional array, use the following structure/template in the applicable procedure:
Dim PositionOfValueInArray As Variant
Dim LoopCounter As Long
PositionOfValueInArray = OutputIfValueNotInArray
For LoopCounter = LBound(SearchedArray) To UBound(SearchedArray)
If SearchedArray(LoopCounter) = SearchedValue Then
PositionOfValueInArray = LoopCounter
Exit For
End If
Next LoopCounter
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
Lines #1 and #2: Dim PositionOfValueInArray As Variant | Dim LoopCounter As Long
The Dim statement:
- Declares variables.
- Allocates storage space.
PositionOfValueInArray | LoopCounter
The names of the variables declared with the Dim statement.
- PositionOfValueInArray holds/represents:
- The position of the searched numeric value in the array, if the searched numeric value is found in the array.
- The default/fallback output/data, if the searched numeric value isn’t found in the array.
- LoopCounter represents the loop counter used in the For… Next loop in lines #4 to #9.
As Variant | As Long
The data type of the variables declared with the Dim statement.
- PositionOfValueInArray is of the Variant data type. The Variant data type can (generally) contain any type of data, except for fixed-length Strings.
- LoopCounter is of the Long data type. The Long data type can contain integers between -2,147,483,648 and 2,147,483,647.
Line #3: PositionOfValueInArray = OutputIfValueNotInArray
PositionOfValueInArray
Variable holding/representing:
- The position of the searched numeric value in the array, if the searched numeric value is found in the array.
- The default/fallback output/data, if the searched numeric value isn’t found in the array.
=
The assignment operator assigns the result returned by an expression (OutputIfValueNotInArray) to a variable (PositionOfValueInArray).
OutputIfValueNotInArray
Expression specifying the default/fallback output/data to be assigned to the PositionOfValueInArray variable if the searched numeric value isn’t found in the array.
Lines #4 and #9: For LoopCounter = LBound(SearchedArray) To UBound(SearchedArray) | Next LoopCounter
For… = … To … | Next…
The For… Next statement repeats a series of statements a specific number of times.
LoopCounter
Variable holding/representing the loop counter.
LBound(…) | UBound(…)
The LBound/UBound functions return the lower/upper bound of an array’s dimension. The LBound/UBound functions accept two arguments:
- ArrayName: The name of the array whose lower/upper bound you want to obtain.
- Dimension:
- An optional argument.
- The dimension (of the applicable array) whose lower/upper bound you want to obtain.
If you omit specifying the Dimension argument, the LBound/UBound functions return the lower/upper bound of the array’s first dimension.
The initial/final values of LoopCounter are set to the following:
- Initial value (Start) of LoopCounter: The output returned by the LBound function (LBound(SearchedArray)).
- Final value (End) of LoopCounter: The output returned by the UBound function (UBound(SearchedArray)).
SearchedArray
The array you search in.
SearchedArray is passed as the ArrayName argument of the LBound/UBound functions.
Lines #5 and #8: If SearchedArray(LoopCounter) = SearchedValue Then | End If
If… Then… End If
The If… Then… Else statement:
- Conditionally executes a set of statements (lines #6 and #7);
- Depending on an expression’s value (SearchedArray(LoopCounter) = SearchedValue).
SearchedArray(LoopCounter) = SearchedValue
The condition of an If… Then… Else statement is an expression evaluating to True or False.
- If the expression returns True, a set of statements (lines #6 and #7) is executed.
- If the expression returns False:
- No statements are executed.
- Execution continues with the statement following End If (line #8).
In this expression:
- SearchedArray: The array you search in.
- LoopCounter: Variable holding/representing the loop counter.
- SearchedArray(LoopCounter): Array element whose index number is LoopCounter.
- =: The equal to comparison operator returns True or False as follows:
- True if both expressions (SearchedArray(LoopCounter) and SearchedValue) are equal.
- False if the expressions (SearchedArray(LoopCounter) and SearchedValue) are not equal.
- SearchedValue: Numeric value you search for in the array (SearchedArray).
Line #6: PositionOfValueInArray = LoopCounter
PositionOfValueInArray
Variable holding/representing:
- The position of the searched numeric value in the array, if the searched numeric value is found in the array.
- The default/fallback output/data, if the searched numeric value isn’t found in the array.
=
The assignment operator assigns the result returned by an expression (LoopCounter) to a variable (PositionOfValueInArray).
LoopCounter
Variable holding/representing the loop counter.
Line #7: Exit For
The Exit For statement:
- Exits a For… Next loop.
- Transfers control to the statement following the Next statement (line #8).
Macro Example to Find Value in Array
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts two arguments:
- MyArray: The array you search in.
- MyValue: The numeric value you search for.
- Loops through each element in MyArray and tests whether the applicable element is equal to MyValue.
- Returns the following:
- If MyValue is not found in MyArray, the string “Value not found in array”.
- If MyValue is found in MyArray, the position/index number of MyValue in MyArray.
Function FindValueInArray(MyArray As Variant, MyValue As Variant) As Variant
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 2 arguments: MyArray and MyValue
'(2) Loops through each element in the array (MyArray) and tests whether the applicable element is equal to the searched value (MyValue)
'(3) Returns the following (as applicable):
'If MyValue is not found in MyArray: The string "Value not found in array"
'If MyValue is found in MyArray: The position (index number) of MyValue in MyArray
'Declare variable to represent loop counter
Dim iCounter As Long
'Specify default/fallback value/string to be returned ("Value not found in array") if MyValue is not found in MyArray
FindValueInArray = "Value not found in array"
'Loop through each element in the array (MyArray)
For iCounter = LBound(MyArray) To UBound(MyArray)
'Test if the current array element is equal to MyValue
If MyArray(iCounter) = MyValue Then
'If the current array element is equal to MyValue:
'(1) Return the position (index number) of the current array element
'(2) Exit the For... Next loop
FindValueInArray = iCounter
Exit For
End If
Next iCounter
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Value in Array
To illustrate the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example, I use the following macro. The following macro does the following:
- Declare an array (MySearchedArray).
- Fill the array with values (0, 10, 20, …, 90).
- Call the FindValueInArray macro (User-Defined Function) example to find the number “50” in the array.
- Display a message box with the value/string returned by the FindValueInArray macro (User-Defined Function) example.
Sub FindValueInArrayCaller()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This procedure:
'(1) Declares an array and fills it with values (0, 10, 20, ..., 90)
'(2) Calls the FindValueInArray UDF to find the number "50" in the array
'(3) Displays a message box with the value/string returned by the FindValueInArray UDF
'Declare a zero-based array with 10 elements of the Long data type
Dim MySearchedArray(0 To 9) As Long
'Assign values to array elements
MySearchedArray(0) = 0
MySearchedArray(1) = 10
MySearchedArray(2) = 20
MySearchedArray(3) = 30
MySearchedArray(4) = 40
MySearchedArray(5) = 50
MySearchedArray(6) = 60
MySearchedArray(7) = 70
MySearchedArray(8) = 80
MySearchedArray(9) = 90
'Do the following:
'(1) Call the FindValueInArray UDF and search for the number "50" in MySearchedArray
'(2) Display a message box with the value/string returned by the FindValueInArray UDF
MsgBox FindValueInArray(MySearchedArray, 50)
End Sub
The following GIF illustrates the effects of using the macro above to call the macro (User-Defined Function) example.
As expected, this results in Excel displaying a message box with the number 5. This is the position of the searched numeric value (50) in the array.

Learn More About Excel VBA Find
Workbook Example Used in this Excel VBA Find Tutorial
This VBA Find Tutorial is accompanied by an Excel workbook containing the data and macros I use in the examples above. You can get free access to this example workbook by clicking the button below.
The Power Spreadsheets Library
The Books at The Power Spreadsheets Library are comprehensive and actionable guides for professionals who want to:
- Automate Excel;
- Save time for the things that really matter; and
- Open new career opportunities.
Learn more about The Power Spreadsheets Library here.
Содержание
- Vba excel аналог поиск
- VBA Lookup — Как реализовать и применить функцию поиска в Excel VBA?
- Функция поиска в Excel VBA
- Как использовать функцию поиска в Excel VBA?
- VBA Lookup — пример № 1
- VBA Lookup — пример № 2
- VBA Lookup — пример № 3
- Плюсы Excel VBA Функция поиска
- То, что нужно запомнить
- Рекомендуемые статьи
- VBA Excel. Метод WorksheetFunction.Match (поиск позиции)
- Метод WorksheetFunction.Match
- Синтаксис
- Параметры
- Примеры
- Пример 1
Vba excel аналог поиск
ВПР = Application.WorksheetFunction.VLook up
ГПР = Application.WorksheetFunction.HLook up
ПОИСКПОЗ = Application.WorksheetFunction.Match
Пройдите по этой ссылке,
пролистайте страницу до конца вниз, и скачайте Справочник по функциям MS Excel от Microsoft Office.
Вот прямая ссылка на скачивание файла
В этом файле описаны аналоги встроенных функций Excel для работы из VBA
Во-вторых что значит Like, и чем он отличается от простого равно?
Выражение c.Value Like «*MS*» будет истинно, если c.Value содержит текст MS
(например, 123MSasd, Mspoi, и т.д.)
Выражение c.Value = «*MS*» будет истинно, только если c.Value состоит из 4-х указанных символов *MS*
И ещё: на сайте http://msoffice.nm.ru/faq/macros.htm есть много полезной информации по работе с VBA Excel
А самой полной и полезной литературой по VBA является файл справки:
C:Program FilesMicrosoft OfficeOFFICE111049VBAXL10.CHM
——— готовое решение для замены формулы ВПР (VLOOKUP) —————
Надстройка LOOKUP предназначена для сравнения и подстановки значений в таблицах Excel.
Если вам надо сравнить 2 таблицы (по одному столбцу, или по нескольким),
и для совпадающих строк скопировать значения выбранных столбцов из одной таблицы в другую,
надстройка «Lookup» поможет сделать это нажатием одной кнопки.
В настройках программы можно задать:
- где искать сравниваемые файлы (использовать уже открытый файл, загружать файл по заданному пути, или же выводить диалоговое окно выбора файла)
- с каких листов брать данные (варианты: активный лист, лист с заданным номером или названием)
- какие столбцы сравнивать (можно задать несколько столбцов)
- значения каких столбцов надо копировать в найденные строки (также можно указать несколько столбцов)
Скачать надстройку для сравнения таблиц Excel и копирования данных из одинаковых строк
Источник
VBA Lookup — Как реализовать и применить функцию поиска в Excel VBA?
Функция поиска в Excel VBA
В Excel мы использовали VLookup много раз. Это есть в функции вставки, которая используется для извлечения или сопоставления любых значений, которые мы хотим. Аналогично, в VBA у нас есть приложение Lookup, которое работает так же, как Excel Vlookup. VBA Lookup имеет гибкую структуру данных, так как его можно использовать для сопоставления значений любого типа из любого вида массива таблиц. Это означает, что если мы применим Excel Vlookup, то мы не сможем сопоставить данные правого столбца с данными левого столбца в одном синтаксисе. В то время как в VBA Lookup нет правильной структуры отображения. Нам просто нужно следовать синтаксису VBA Lookup. Если синтаксис удовлетворен и правильно оформлен, то мы можем извлечь значения из правой или левой части таблицы.
Синтаксис функции поиска VBA:
- Arg1 = значение, которое мы хотим найти .
- Arg2 = диапазон столбцов или таблицы, откуда мы хотим искать.
- Arg3 = Результат в виде логического значения или вектора.
Как использовать функцию поиска в Excel VBA?
Мы узнаем, как использовать функцию поиска в Excel, используя код VBA.
Вы можете скачать этот шаблон Excel VBA Lookup здесь — Шаблон Excel VBA Lookup
VBA Lookup — пример № 1
Существует много способов написания кода поиска VBA. В этом примере мы увидим простой способ написания VBA Lookup. Для этого у нас есть набор данных, как показано ниже. В этой таблице указано количество гонок и средняя скорость гонщиков. Теперь мы будем использовать эти данные для применения VBA Lookup в таблице ниже с синими заголовками от A8 до B8. Для этого выполните следующие шаги:
Шаг 1. Откройте модуль на вкладке меню «Вставка», как показано ниже.
Шаг 2: Запишите подпроцедуру для выполненной работы в этом модуле. Здесь мы выбрали имя VBA Lookup.
Код:
Шаг 3: Выберите выходную ячейку, где нам нужно увидеть значение поиска. Здесь эта ячейка — B9, где мы будем искать значение со значением «Aniket», которое является нашим значением поиска.
Код:
Шаг 4: Теперь мы будем использовать функцию «Рабочий лист» и выбрать встроенную функцию « Поиск» в списке, как показано ниже.
Код:
Шаг 5: Как только мы выберем функцию Lookup, мы увидим Arg1, Arg2 и Arg3 в ее синтаксисе. Для этого мы сначала поместим наш диапазон значений Lookup, который является ячейкой A9 вместо Arg1.
Код:
Шаг 6: Теперь для Arg2 выберите диапазон поиска из ячейки A2: A5.
Код:
Шаг 7: Наконец, выберите диапазоны значений поиска от B2 до B5 вместо Arg3.
Код:
Шаг 8: Запустите код, нажав клавишу F5 или нажав кнопку воспроизведения, расположенную под лентой меню. Мы увидим, что согласно Lookup, количество гонок под именем «Аникет» равно 7.
VBA Lookup — пример № 2
Есть другой способ применить функцию Lookup в Excel VBA. Для этого мы будем использовать те же данные, которые мы видели в примере-1. Для этого выполните следующие шаги:
Шаг 1: Запишите подпроцедуру для VBA Lookup, как показано ниже.
Код:
Шаг 2: Определите переменную как String, которая будет использоваться для сопоставления столбца Name.
Код:
Шаг 3: В определенной переменной Name мы будем применять приложение Vlookup, как показано ниже.
Код:
Шаг 4: Допустим, наша поисковая ценность называется «Ashwani» из таблицы.
Код:
Шаг 5: И диапазон от А1 до С6 от Лист1.
Код:
Шаг 6: Теперь, если мы хотим увидеть здесь среднюю скорость гонщика «Ашвани», нам нужно отобразить ячейку в синтаксисе «Уточняющий запрос», которая находится на 3- м месте.
Код:
Шаг 7: Теперь, чтобы увидеть среднюю скорость гонщика «Ashwani», мы можем использовать MsgBox и Debug Print. Но использование Debug Print намного лучше, чем MsgBox. Так что назначьте Debug Print с определенной переменной Name.
Код:
Шаг 8: Теперь откройте Immediate Window, которое находится на вкладке меню View, чтобы увидеть результат.
Шаг 9: Скомпилируйте код и запустите его. Мы увидим, Lookup работал со скоростью Ashwani и извлек это в окно Immediate как 86 .
Код:
VBA Lookup — пример № 3
Для использования функции поиска в Excel VBA выполните следующие действия:
Шаг 1: Запишите подпроцедуру для VBA Lookup, как показано ниже.
Код:
Шаг 2: Объявите переменную для Name как String, как показано ниже.
Код:
Шаг 3: Теперь назначьте имя, которое хотите найти, определенной переменной Name, как показано ниже.
Код:
Шаг 4: Теперь используйте любое слово для определения и используйте Lookup, скажем, LUp . И в этом используйте функцию рабочего листа с Vlookup, как показано ниже.
Код:
Шаг 5: Теперь используйте тот же синтаксис Vlookup, который мы используем в Excel. В Arg1 поместите переменную Name, затем выберите матрицу диапазона и найдите значение up, которое мы хотим получить. Здесь этот столбец 3, как показано ниже.
Код:
Шаг 6: Теперь используйте MsgBox, чтобы увидеть результат.
Код:
Шаг 7: Скомпилируйте и запустите код. Мы увидим, что для имени «Deepinder» средняя скорость равна 88. Принимая во внимание то же значение для имени Deepinder в таблице.
Код:
Плюсы Excel VBA Функция поиска
- Он так же прост в использовании и применении, как и обычные формулы Excel Vlookup в Excel.
- Мы можем использовать любой вид диапазона и матрицы в VBA Lookup.
- При применении VBA Lookup очень мало или совсем нет ограничений.
То, что нужно запомнить
- Мы можем использовать Lookup вместо Vlookup в любой ситуации.
- Диапазон для вектора подстановки и вектора результата должен быть одинаковым.
- После завершения приложения сохраните файл в формате Macro Enable, чтобы сохранить код.
- Нет обязательного требования ставить столбец результата каждый раз, когда он находится справа от значения поиска.
Рекомендуемые статьи
Это руководство к функции поиска VBA. Здесь мы обсудим, как использовать функцию Lookup в Excel VBA вместе с практическими примерами и загружаемым шаблоном Excel. Вы также можете просмотреть наши другие предлагаемые статьи —
- Коллекция VBA (Примеры)
- VBA IF Заявления | Шаблоны Excel
- Как использовать функцию сортировки Excel VBA?
- VBA While Loop (Примеры с шаблоном Excel)
- VBA Environ
Источник
VBA Excel. Метод WorksheetFunction.Match (поиск позиции)
Поиск относительного положения элемента в массиве (диапазоне) с помощью метода VBA Excel WorksheetFunction.Match. Синтаксис, параметры, примеры.
Метод WorksheetFunction.Match
Обратите внимание на то, что
- поиск позиции в массиве возможен, если он одномерный или двумерный, но с набором элементов только по одному измерению, например: myArray(8, 0) или myArray(1 To 1, 1 To 20);
- поиск позиции в диапазоне рабочего листа возможен, если он содержит только одну строку или один столбец;
- нумерация относительного положения элемента в массиве начинается с единицы, независимо от заданной индексации массива.
Синтаксис
Синтаксис метода WorksheetFunction.Match в VBA Excel:
Параметры
Описание параметров метода WorksheetFunction.Match:
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| Arg1 | Обязательный параметр. Значение элемента массива, по которому будет произведен поиск относительного положения элемента в массиве. |
| Arg2 | Обязательный параметр. Непрерывный диапазон ячеек или массив, в котором будет произведен поиск позиции элемента, значение которого совпадет со значением параметра Arg1. |
| Arg3 | Необязательный параметр. Задает тип сопоставления значения Arg1 со значениями в массиве Arg2. |
В параметре Arg1 можно использовать знаки подстановки для шаблонов, те же, что и для методов Find и Replace.
Значения параметра Arg3, задающие тип сопоставления:
| Значение | Тип сопоставления |
|---|---|
| -1 | Метод WorksheetFunction.Match находит наименьшее значение элемента в Arg2, большее или равное Arg1. Значения элементов Arg2 должны быть расположены в убывающем порядке: [m, … 2, 1, 0, -1, -2, … -n], [z – a], [True, False] и т. д. |
| 0 | Метод WorksheetFunction.Match находит в Arg2 первое значение, равное Arg1. Значения элементов Arg2 могут быть расположены в любом порядке. |
| 1 | Значение по умолчанию. Метод WorksheetFunction.Match находит наибольшее значение элемента в Arg2, меньшее или равное Arg1. Значения элементов Arg2 должны быть расположены в возрастающем порядке: [-n, … -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, … m], [a – z], [False, True] и т. д. |
При сопоставлении строк регистр не учитывается.
Примеры
Пример 1
Поиск относительного положения элемента в массиве, индексация которого начинается с нуля:
Источник
Метод Find объекта Range для поиска ячейки по ее данным в VBA Excel. Синтаксис и компоненты. Знаки подстановки для поисковой фразы. Простые примеры.
Метод Find объекта Range предназначен для поиска ячейки и сведений о ней в заданном диапазоне по ее значению, формуле и примечанию. Чаще всего этот метод используется для поиска в таблице ячейки по слову, части слова или фразе, входящей в ее значение.
Синтаксис метода Range.Find
|
Expression.Find(What, After, LookIn, LookAt, SearchOrder, SearchDirection, MatchCase, MatchByte, SearchFormat) |
Expression – это переменная или выражение, возвращающее объект Range, в котором будет осуществляться поиск.
В скобках перечислены параметры метода, среди них только What является обязательным.
Метод Range.Find возвращает объект Range, представляющий из себя первую ячейку, в которой найдена поисковая фраза (параметр What). Если совпадение не найдено, возвращается значение Nothing.
Если необходимо найти следующие ячейки, содержащие поисковую фразу, используется метод Range.FindNext.
Параметры метода Range.Find
| Наименование | Описание |
|---|---|
| Обязательный параметр | |
| What | Данные для поиска, которые могут быть представлены строкой или другим типом данных Excel. Тип данных параметра — Variant. |
| Необязательные параметры | |
| After | Ячейка, после которой следует начать поиск. |
| LookIn | Уточняет область поиска. Список констант xlFindLookIn:
|
| LookAt | Поиск частичного или полного совпадения. Список констант xlLookAt:
|
| SearchOrder | Определяет способ поиска. Список констант xlSearchOrder:
|
| SearchDirection | Определяет направление поиска. Список констант xlSearchDirection:
|
| MatchCase | Определяет учет регистра:
|
| MatchByte | Условия поиска при использовании двухбайтовых кодировок:
|
| SearchFormat | Формат поиска – используется вместе со свойством Application.FindFormat. |
* Примечания имеют две константы с одним значением. Проверяется очень просто: MsgBox xlComments и MsgBox xlNotes.
В справке Microsoft тип данных всех параметров, кроме SearchDirection, указан как Variant.
Знаки подстановки для поисковой фразы
Условные знаки в шаблоне поисковой фразы:
- ? – знак вопроса обозначает любой отдельный символ;
- * – звездочка обозначает любое количество любых символов, в том числе ноль символов;
- ~ – тильда ставится перед ?, * и ~, чтобы они обозначали сами себя (например, чтобы тильда в шаблоне обозначала сама себя, записать ее нужно дважды: ~~).
Простые примеры
При использовании метода Range.Find в VBA Excel необходимо учитывать следующие нюансы:
- Так как этот метод возвращает объект Range (в виде одной ячейки), присвоить его можно только объектной переменной, объявленной как Variant, Object или Range, при помощи оператора Set.
- Если поисковая фраза в заданном диапазоне найдена не будет, метод Range.Find возвратит значение Nothing. Обращение к свойствам несуществующей ячейки будет генерировать ошибки. Поэтому, перед использованием результатов поиска, необходимо проверить объектную переменную на содержание в ней значения Nothing.
В примерах используются переменные:
- myPhrase – переменная для записи поисковой фразы;
- myCell – переменная, которой присваивается первая найденная ячейка, содержащая поисковую фразу, или значение Nothing, если поисковая фраза не найдена.
Пример 1
|
Sub primer1() Dim myPhrase As Variant, myCell As Range myPhrase = «стакан» Set myCell = Range(«A1:L30»).Find(myPhrase) If Not myCell Is Nothing Then MsgBox «Значение найденной ячейки: « & myCell MsgBox «Строка найденной ячейки: « & myCell.Row MsgBox «Столбец найденной ячейки: « & myCell.Column MsgBox «Адрес найденной ячейки: « & myCell.Address Else MsgBox «Искомая фраза не найдена» End If End Sub |
В этом примере мы присваиваем переменной myPhrase значение для поиска – "стакан". Затем проводим поиск этой фразы в диапазоне "A1:L30" с присвоением результата поиска переменной myCell. Далее проверяем переменную myCell, не содержит ли она значение Nothing, и выводим соответствующие сообщения.
Ознакомьтесь с работой кода VBA в случаях, когда в диапазоне "A1:L30" есть ячейка со строкой, содержащей подстроку "стакан", и когда такой ячейки нет.
Пример 2
Теперь посмотрим, как метод Range.Find отреагирует на поиск числа. В качестве диапазона поиска будем использовать первую строку активного листа Excel.
|
Sub primer2() Dim myPhrase As Variant, myCell As Range myPhrase = 526.15 Set myCell = Rows(1).Find(myPhrase) If Not myCell Is Nothing Then MsgBox «Значение найденной ячейки: « & myCell Else: MsgBox «Искомая фраза не найдена» End If End Sub |
Несмотря на то, что мы присвоили переменной числовое значение, метод Range.Find найдет ячейку со значением и 526,15, и 129526,15, и 526,15254. То есть, как и в предыдущем примере, поиск идет по подстроке.
Чтобы найти ячейку с точным соответствием значения поисковой фразе, используйте константу xlWhole параметра LookAt:
|
Set myCell = Rows(1).Find(myPhrase, , , xlWhole) |
Аналогично используются и другие необязательные параметры. Количество «лишних» запятых перед необязательным параметром должно соответствовать количеству пропущенных компонентов, предусмотренных синтаксисом метода Range.Find, кроме случаев указания необязательного параметра по имени, например: LookIn:=xlValues. Тогда используется одна запятая, независимо от того, сколько компонентов пропущено.
Пример 3
Допустим, у нас есть многострочная база данных в Excel. В первой колонке находятся даты. Нам необходимо создать отчет за какой-то период. Найти номер начальной строки для обработки можно с помощью следующего кода:
|
Sub primer3() Dim myPhrase As Variant, myCell As Range myPhrase = «01.02.2019» myPhrase = CDate(myPhrase) Set myCell = Range(«A:A»).Find(myPhrase) If Not myCell Is Nothing Then MsgBox «Номер начальной строки: « & myCell.Row Else: MsgBox «Даты « & myPhrase & » в таблице нет» End If End Sub |
Несмотря на то, что в ячейке дата отображается в виде текста, ее значение хранится в ячейке в виде числа. Поэтому текстовый формат необходимо перед поиском преобразовать в формат даты.
You will find everything you need to know on the Excel VBA Find function. The Range Find function allows you to find cells within your Excel worksheet (and workbook) that contain a certain text or value. In this post let us explore the many ways in which you can use the Find function.
Looking to search text within VBA strings instead? See the VBA InStr and VBA InStrRev functions
Before we show how to use VBA to search for text within an Excel spreadsheet let us first see how to do it Excel and explore the usually unknown features of the famous CTRL+F combo. See below where you can find it within the Home ribbon and Editing group.
By clicking the above or simply using the key combo CTRL+F we can enter the Find & Replace modal window.
As you notice above Excel easily finds 10 matches for the cells on the left. However there are several more interesting search combinations you can use, including usage of wildcards you can use to get more specific patterns. See some examples below:
| Find | Matches |
|---|---|
| some*text |
|
| some ? |
|
| some*e*a |
|
As you might have already noticed I used 2 types of wildcards above:
- * – the asterisk symbol represents zero or many of any type of characters. It can be injected between characters to replace either no or any number of characters.
- ? – the question mark represents at least 1 character.
Now that we have a hand of the basic features of Excel in terms of word search let us move to how to use Excel VBA to find cells containing specific text.
VBA Range Find function
The VBA Find function is in fact a function of the Excel VBA Range object class. See Microsoft documentation for more details. A VBA Range represents any subset of cells within a spreadsheet – it can be a single cell, entire row or a patchwork of different cells and other Ranges. Executing the Find function in fact limits the search to only the cells within its Range object.
Below is the definition of the VBA Range Find function and its parameters:
.Find(What, [After] [LookIn], [LookAt], [SearchOrder],
[SearchDirection], [MatchCase], [MatchByte], [SearchFormat])
The Find function returns only the first match within the Range. To search for next items you need to follow it up with the FindNext function.
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| What | Required | The value you are searching for |
| After | Optional | The cell range from which you start your search from |
| LookIn | Optional | What to search in e.g. Formulas, Values or Comments – constants of XlFindLookIn: xlValues, xlFormulas, xlComments, xlCommentsThreaded |
| LookAt | Optional | Whether to search in a part of the string in a cell or whether it needs to match the entire cell string – constants of XlLookAt: xlWhole, xlPart |
| SearchOrder | Optional | The sequence of the search i.e. whether to search by rows or columns – constants of XlSearchOrder: xlByRows or xlByColumns |
| SearchDirection | Optional | Whether to search forward (next) or backwards (previous) – constants of XlSearchDirection: xlNext, xlPrevious |
| MatchCase | Optional | Case sensitive or not – True or False |
| MatchByte | Optional | Used for double byte languages. True to have double-byte characters match only double-byte characters – True or False |
| SearchFormat | Optional | Allow searching by format. See Application.FindFormat – True or False |
VBA Find – simple example
We will start with a very simple VBA Range Find function example – searching for a single cell within the entire Excel active spreadsheet:
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveSheet
Debug.Print ws.Cells.Find("some")
Output:
some text
As you can see it found the first match within the Activesheet (currently open and top spreadsheet) and returned the found value.
VBA Find All
Finding all matches is a little more complicated in VBA than in Excel. We will need to use Do While loop to run via all matches:
Dim searchRange As Range, found As Range, firstFind As Range
'Set the search range to the entire worksheet
Set searchRange = ActiveSheet.Cells
'Search for the first match
Set found = searchRange.Find("some")
'Save the first found cell to check later whether we have completed the search
Set firstFind = found
'Loop through all items using FindNext Range function
Do
If Not (found Is Nothing) Then
Debug.Print found.Value
Set found = searchRange.FindNext(found)
End If
Loop While Not (found = firstFind)
Output:
some text some other text someone something somedeal someones somerset someway somewhat somewhen
I highlighted above 2 key functions that were used the Range Find Function and the Range FindNext Function. As I mentioned above the Find function will only return the first match. To get next matches you need to run FindNext on the original range. This is I am executing FindNext on the searchRange variable and not the found variable.
Another interesting point to notice is the Do While…loop. Notice I am comparing the found variable to the firstFind variable. This is because when running FindNext it will at some point move to the first match once again and thus never end… it will just keep going in a cirle! Thus the loop is set to end once the FindNext function returns the same first cell.
Find using Wildcards
As mentioned above you can use 2 types of wildcards the asterisk * (zero or more characters) and the question mark ? (at least 1 character) to match slightly more complicates cases.
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveSheet
Debug.Print ws.Cells.Find("some ?")
'Output: some text
Debug.Print ws.Cells.Find("some*w")
'Output: someway
VBA Find with After
To remind the After parameter of the Excel VBA Range Find function defines where you will start your search. It is useful when you don’t want to redefine your range just for the purpose of the search activity. See the example below:
Debug.Print Range("B2:B5").Find("some ?", After:=Range("B3"))
Output:
someone
As you can see below the Find function starts searching for the “some” string just after cell B3 i.e. it will start at B4 where it finds the first matching string.
Find After – avoid wrap around
Even if we specify that the VBA Range Find function should start searching for the string after a specified cell, it might wrap around back to the beginning of the Range we specified if it does not find a match when going down. See example below to understand:
Debug.Print Range("B2:B5").Find("some*text", After:=Range("B3"))
Output:
some text
As you see the search started at B4 however once the search pattern “some*text” was not found until B5 the function resumed search on the remaining cells B2:B3 to find “some text”.
Find After Avoid wrapping using VBA Find
What to do to avoid this wrapping? We can check whether the found text is not within the preceding range using the Application.Intersect function.
If the found cell is before our After cell then we can handle it as such:
Set found = Range("B2:B5").Find("some*text", After:=Range("B3"))
If Intersect(Range("B2:B3"), found) Is Nothing Then
Debug.Print "Found text: " & found.Value
Else
Debug.Print "Text found is within excluded range"
End If
Output:
Text found is within excluded range
However if the found cell is only After the cell we specified then it will show like this:
Set found = Range("B2:B5").Find("some", After:=Range("B3"))
If Intersect(Range("B2:B3"), found) Is Nothing Then
Debug.Print "Found text: " & found.Value
Else
Debug.Print "Text found is within excluded range"
End If
Output:
Found text: someone
Find in Values, Formulas, Comments
The VBA Range Find function allows you not only to search within Values (the evalution of your Excel formulas). It can also search instead (or including) within Formulas, Comments and even Excel Threaded Comments.
Let us explore how to use the LookIn parameter to look into specific attributes of a cell.
In the code below we will search for the word dog within Values, Formulas, Notes and Threaded Comments (just the first one). We will return the address first. Notice that for Formulas the result was the same – this is because the Value and Formula is the same in this case.
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("dog", LookIn:=xlValues).AddressLocal
'Output: $A$2
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("dog", LookIn:=xlFormulas).AddressLocal
'Output: $A$2 - as the formula and value for "dog" are the same in this case
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("This is a dog", LookIn:=xlFormulas).AddressLocal
'Output: $B$2
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("dog", LookIn:=xlNotes).AddressLocal
'Output: $C$2
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("dog", LookIn:=xlCommentsThreaded).AddressLocal
'Output: $D$2
The same code but this time returning the actual Value, Formula, Note or Comment:
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("dog", LookIn:=xlValues).Value
'Output: dog
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("dog", LookIn:=xlFormulas).Formula2Local
'Output: dog
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("This is a dog", LookIn:=xlFormulas).Formula2Local
'Output: =IF(A2="Dog", "This is a Dog","Other")
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("dog", LookIn:=xlNotes).NoteText
'Output: This is a note about a dog
Debug.Print Range("A1:D4").Find("dog", LookIn:=xlCommentsThreaded).CommentThreaded.Text
'Output: This is a threaded comment about a dog
Find After – avoid wrap around
Complex patterns for Find
In some cases the pattern you want to find might be more complicated such as e.g. looking for cells with any sequence of numbers, emails, addresses, phone numbers etc. In this case the VBA Range Find function will be too limited. However, there is a solution with the help of so call VBA Regular Expressions. Regular Expressions help define almost any search pattern and are widely used in other programming languages.
If you want to learn more read my VBA Regex Tutorial otherwise a very simple example below.
In below code snippet we would like to find only phone numbers – so we will create a simple expression that finds any sequence of digits.
'Define the Regular Expression
Dim regex As Object
Set regex = CreateObject("VBScript.RegExp")
With regex
'We will look only for sequences of at least 1 digit
.Pattern = "[0-9]+"
End With
'Search in all cells within the Range
Dim r As Range
For Each r In Range("A1:D4")
If regex.Test(r.Value) Then
Debug.Print "Found a match: " & r.AddressLocal
End If
Next r
Found a match: $A$3
Sub Excel_SEARCH_Function()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«SEARCH»)
ws.Range(«E5») = Application.WorksheetFunction.Search(ws.Range(«C5»), ws.Range(«B5»))
ws.Range(«E6») = Application.WorksheetFunction.Search(ws.Range(«C6»), ws.Range(«B6»), ws.Range(«D6»))
ws.Range(«E7») = Application.WorksheetFunction.Search(ws.Range(«C7»), ws.Range(«B7»), ws.Range(«D7»))
End Sub
OBJECTS
Worksheets: The Worksheets object represents all of the worksheets in a workbook, excluding chart sheets.
Range: The Range object is a representation of a single cell or a range of cells in a worksheet.
PREREQUISITES
Worksheet Name: Have a worksheet named SEARCH.
String Range: Have the range of strings that you want to search within captured in range («B4:B7»).
Search sub-string: Have the sub-string that you want to search for in range («C5:C7»).
Start Position: In this example the start position only applies to the bottom two examples. Therefore, if using the exact same VBA code ensure that the start position value is captured in range («D6:D7»).
ADJUSTABLE PARAMETERS
Output Range: Select the output range by changing the cell references («E5»), («E6») and («E7») in the VBA code to any cell in the worksheet, that doesn’t conflict with formula.
String Range: Select the range of strings that you want to search within by changing the range («B5:B7») in the VBA code to any cell in the worksheet, that doesn’t conflict with formula.
Search sub-string: Select the sub-string that you want to search for by changing the cell references («C5»), («C6») and («C7») to any range in the worksheet, that doesn’t conflict with the formula.
Start Position: Select the start position value by changing the range («D6:D7») to any range in the worksheet, that doesn’t conflict with the formula.
In this Article
- VBA Find
- Find VBA Example
- VBA Find without Optional Parameters
- Simple Find Example
- Find Method Notes
- Nothing Found
- Find Parameters
- After Parameter and Find Multiple Values
- LookIn Parameter
- Using the LookAt Parameter
- SearchOrder Parameter
- SearchDirection Parameter
- MatchByte Parameter
- SearchFormat Parameter
- Using Multiple Parameters
- Replace in Excel VBA
- Replace Without Optional Parameters
- Using VBA to Find or Replace Text Within a VBA Text String
- INSTR – Start
- VBA Replace Function
This tutorial will demonstrate how to use the Find and Replace methods in Excel VBA.
VBA Find
Excel has excellent built-in Find and Find & Replace tools.
They can be activated with the shortcuts CTRL + F (Find) or CTRL + H (Replace) or through the Ribbon: Home > Editing > Find & Select.
By clicking Options, you can see advanced search options:
You can easily access these methods using VBA.
Find VBA Example
To demonstrate the Find functionality, we created the following data set in Sheet1.
If you’d like to follow along, enter the data into your own workbook.
VBA Find without Optional Parameters
When using the VBA Find method, there are many optional parameters that you can set.
We strongly recommend defining all parameters whenever using the Find Method!
If you don’t define the optional parameters, VBA will use the currently selected parameters in Excel’s Find window. This means, you may not know what search parameters are being used when the code is ran. Find could be ran on the entire workbook or a sheet. It could search for formulas or values. There’s no way to know, unless you manually check what’s currently selected in Excel’s Find Window.
For simplicity, we will start with an example with no optional parameters defined.
Simple Find Example
Let’s look at a simple Find example:
Sub TestFind()
Dim MyRange As Range
Set MyRange = Sheets("Sheet1").UsedRange.Find("employee")
MsgBox MyRange.Address
MsgBox MyRange.Column
MsgBox MyRange.Row
End Sub
This code searches for “employee” in the Used Range of Sheet1. If it finds “employee”, it will assign the first found range to range variable MyRange.
Next, Message Boxes will display with the address, column, and row of the found text.
In this example, the default Find settings are used (assuming they have not been changed in Excel’s Find Window):
- The search text is partially matched to the cell value (an exact cell match is not required)
- The search is not case sensitive.
- Find only searches a single worksheet
These settings can be changed with various optional parameters (discussed below).
Find Method Notes
- Find does not select the cell where the text is found. It only identifies the found range, which you can manipulate in your code.
- The Find method will only locate the first instance found.
- You can use wildcards (*) e.g. search for ‘E*’
Nothing Found
If the search text does not exist, then the range object will remain empty. This causes a major problem when your code tries to display the location values because they do not exist. This will result in an error message which you do not want.
Fortunately, you can test for an empty range object within VBA using the Is Operator:
If Not MyRange Is Nothing ThenAdding the code to our previous example:
Sub TestFind()
Dim MyRange As Range
Set MyRange = Sheets("Sheet1").UsedRange.Find("employee")
If Not MyRange Is Nothing Then
MsgBox MyRange.Address
MsgBox MyRange.Column
MsgBox MyRange.Row
Else
MsgBox "Not found"
End If
End Sub VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Find Parameters
So far, we have only looked at a basic example of using the Find method. However, there are a number of optional parameters available to help you refine your search
| Parameter | Type | Description | Values |
| What | Required | The value to search for | Any data type such as a string or numeric |
| After | Optional | Single cell reference to begin your search | Cell address |
| LookIn | Optional | Use Formulas, Values, Comments for search | xlValues, xlFormulas, xlComments |
| LookAt | Optional | Match part or whole of a cell | xlWhole, xlPart |
| SearchOrder | Optional | The Order to search in – rows or columns | xlByRows, xlByColummns |
| SearchDirection | Optional | Direction for search to go in – forward or backward | xlNext, xlPrevious |
| MatchCase | Optional | Search is case sensitive or not | True or False |
| MatchByte | Optional | Used only if you have installed double byte language support e.g. Chinese language | True or False |
| SearchFormat | Optional | Allow searching by format of cell | True or False |
After Parameter and Find Multiple Values
You use the After parameter to specify the starting cell for your search. This is useful where there is more than one instance of the value that you are searching for.
If a search has already found one value and you know that there will be more values found, then you use the Find method with the ‘After’ parameter to record the first instance and then use that cell as the starting point for the next search.
You can use this to find multiple instances of your search text:
Sub TestMultipleFinds()
Dim MyRange As Range, OldRange As Range, FindStr As String
'Look for first instance of "‘Light & Heat"
Set MyRange = Sheets("Sheet1").UsedRange.Find("Light & Heat")
'If not found then exit
If MyRange Is Nothing Then Exit Sub
'Display first address found
MsgBox MyRange.Address
'Make a copy of the range object
Set OldRange = MyRange
'Add the address to the string delimiting with a "|" character
FindStr = FindStr & "|" & MyRange.Address
'Iterate through the range looking for other instances
Do
'Search for ‘Light & Heat’ using the previous found address as the After parameter
Set MyRange = Sheets("Sheet1").UsedRange.Find("Light & Heat", After:=Range(OldRange.Address))
'If the address has already been found then exit the do loop – this stops continuous looping
If InStr(FindStr, MyRange.Address) Then Exit Do
'Display latest found address
MsgBox MyRange.Address
'Add the latest address to the string of addresses
FindStr = FindStr & "|" & MyRange.Address
'make a copy of the current range
Set OldRange = MyRange
Loop
End Sub
This code will iterate through the used range, and will display the address every time it finds an instance of ‘Light & Heat’
Note that the code will keep looping until a duplicate address is found in FindStr, in which case it will exit the Do loop.
LookIn Parameter
You can use the LookIn parameter to specify which component of the cell you want to search in. You can specify values, formulas, or comments in a cell.
- xlValues – Searches cell values (the final value of a cell after it’s calculation)
- xlFormulas – Searches within the cell formula itself (whatever is entered into the cell)
- xlComments – Searches within cell notes
- xlCommentsThreaded – Searches within cell comments
Assuming that a formula has been entered on the worksheet, you could use this example code to find the first location of any formula:
Sub TestLookIn()
Dim MyRange As Range
Set MyRange = Sheets("Sheet1").UsedRange.Find("=", LookIn:=xlFormulas)
If Not MyRange Is Nothing Then
MsgBox MyRange.Address
Else
MsgBox "Not found"
End If
End Sub
If the ‘LookIn’ parameter was set to xlValues, the code would display a ‘Not Found’ message. In this example it will return B10.
VBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Using the LookAt Parameter
The LookAt parameter determines whether find will search for an exact cell match, or search for any cell containing the search value.
- xlWhole – Requires the entire cell to match the search value
- xlPart – Searches within a cell for the search string
This code example will locate the first cell containing the text “light”. With Lookat:=xlPart, it will return a match for “Light & Heat”.
Sub TestLookAt()
Dim MyRange As Range
Set MyRange = Sheets("Sheet1").UsedRange.Find("light", Lookat:=xlPart)
If Not MyRange Is Nothing Then
MsgBox MyRange.Address
Else
MsgBox "Not found"
End If
End Sub
If xlWhole was set, a match would only return if the cell value was “light”.
SearchOrder Parameter
The SearchOrder parameter dictates how the search will be carried out throughout the range.
- xlRows – Search is done row by row
- xlColumns – Search is done column by column
Sub TestSearchOrder()
Dim MyRange As Range
Set MyRange = Sheets("Sheet1").UsedRange.Find("employee", SearchOrder:=xlColumns)
If Not MyRange Is Nothing Then
MsgBox MyRange.Address
Else
MsgBox "Not found"
End If
End Sub
This influences which match will be found first.
Using the test data entered into the worksheet earlier, when the search order is columns, the located cell is A5. When the search order parameter is changed to xlRows, the located cell is C4
This is important if you have duplicate values within the search range and you want to find the first instance under a particular column name.
SearchDirection Parameter
The SearchDirection parameter dictates which direction the search will go in – effectively forward or backwards.
- xlNext – Search for next matching value in range
- xlPrevious – Search for previous matching value in range
Again, if there are duplicate values within the search range, it can have an effect on which one is found first.
Sub TestSearchDirection()
Dim MyRange As Range
Set MyRange = Sheets("Sheet1").UsedRange.Find("heat", SearchDirection:=xlPrevious)
If Not MyRange Is Nothing Then
MsgBox MyRange.Address
Else
MsgBox "Not found"
End If
End Sub
Using this code on the test data, a search direction of xlPrevious will return a location of C9. Using the xlNext parameter will return a location of A4.
The Next parameter means that the search will begin in the top left-hand corner of the search range and work downwards. The Previous parameter means that the search will start in the bottom right-hand corner of the search range and work upwards.
MatchByte Parameter
The MatchBye parameter is only used for languages which use a double byte to represent each character, such as Chinese, Russian, and Japanese.
If this parameter is set to ‘True’ then Find will only match double-byte characters with double-byte characters. If the parameter is set to ‘False’, then a double-byte character will match with single or double-byte characters.
SearchFormat Parameter
The SearchFormat parameter enables you to search for matching cell formats. This could be a particular font being used, or a bold font, or a text color. Before you use this parameter, you must set the format required for the search using the Application.FindFormat property.
Here is an example of how to use it:
Sub TestSearchFormat()
Dim MyRange As Range
Application.FindFormat.Clear
Application.FindFormat.Font.Bold = True
Set MyRange = Sheets("Sheet1").UsedRange.Find("heat", Searchformat:=True)
If Not MyRange Is Nothing Then
MsgBox MyRange.Address
Else
MsgBox "Not found"
End If
Application.FindFormat.Clear
End Sub
In this example, the FindFormat property is set to look for a bold font. The Find statement then searches for the word ‘heat’ setting the SearchFormat parameter to True so that it will only return an instance of that text if the font is bold.
In the sample worksheet data shown earlier, this will return A9, which is the only cell containing the word ‘heat’ in a bold font.
Make sure that the FindFormat property is cleared at the end of the code. If you do not your next search will still take this into account and return incorrect results.
Where you use a SearchFormat parameter, you can also use a wildcard (*) as the search value. In this case it will search for any value with a bold font:
Set MyRange = Sheets("Sheet1").UsedRange.Find("*", Searchformat:=True)AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Using Multiple Parameters
All the search parameters discussed here can be used in combination with each other if required.
For example, you could combine the ‘LookIn’ parameter with the ‘MatchCase’ parameter so that you look at the whole of the cell text, but it is case-sensitive
Sub TestMultipleParameters()
Dim MyRange As Range
Set MyRange = Sheets("Sheet1").UsedRange.Find("Light & Heat", LookAt:=xlWhole, MatchCase:=True)
If Not MyRange Is Nothing Then
MsgBox MyRange.Address
Else
MsgBox "Not found"
End If
End Sub
In this example, the code will return A4, but if we only used a part of the text e.g. ‘heat’, nothing would be found because we are matching on the whole of the cell value. Also, it would fail due to the case not matching.
Set MyRange = Sheets("Sheet1").UsedRange.Find("heat", LookAt:=xlWhole, MatchCase:=True)Replace in Excel VBA
There is, as you may expect, a Replace function in Excel VBA, which works in a very similar way to ‘Find’ but replaces the values at the cell location found with a new value.
These are the parameters that you can use in a Replace method statement. These operate in exactly the same way as for the Find method statement. The only difference to ‘Find’ is that you need to specify a Replacement parameter.
| Name | Type | Description | Values |
| What | Required | The value to search for | Any data type such as a string or numeric |
| Replacement | Required | The replacement string. | Any data type such as a string or numeric |
| LookAt | Optional | Match part or the whole of a cell | xlPart or xlWhole |
| SearchOrder | Optional | The order to search in – Rows or Columns | xlByRows or xlByColumns |
| MatchCase | Optional | Search is case sensitive or not | True or False |
| MatchByte | Optional | Used only if you have installed double byte language support | True or False |
| SearchFormat | Optional | Allow searching by format of cell | True or False |
| ReplaceFormat | Optional | The replace format for the method. | True or False |
The Replace Format parameter searches for a cell with a particular format e.g. bold in the same way the SearchFormat parameter operates in the Find method. You need to set the Application.FindFormat property first, as shown in the Find example code shown earlier
Replace Without Optional Parameters
At its simplest, you only need to specify what you are searching for and what you want to replace it with.
Sub TestReplace()
Sheets("Sheet1").UsedRange.Replace What:="Light & Heat", Replacement:="L & H"
End Sub
Note that the Find method will only return the first instance of the matched value, whereas the Replace method works through the entire range specified and replaces everything that it finds a match on.
The replacement code shown here will replace every instance of ‘Light & Heat’ with ‘L & H’ through the entire range of cells defined by the UsedRange object
Using VBA to Find or Replace Text Within a VBA Text String
The above examples work great when using VBA to interact with Excel data. However, to interact with VBA strings, you can use built-in VBA Functions like INSTR and REPLACE.
You can use the INSTR Function to locate a string of text within a longer string.
Sub TestInstr()
MsgBox InStr("This is MyText string", "MyText")
End Sub
This example code will return the value of 9, which is the number position where ‘MyText’ is found in the string to be searched.
Note that it is case sensitive. If ‘MyText’ is all lower case, then a value of 0 will be returned which means that the search string was not found. Below we will discuss how to disable case-sensitivity.
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
INSTR – Start
There are two further optional parameters available. You can specify the start point for the search:
MsgBox InStr(9, "This is MyText string", "MyText")The start point is specified as 9 so it will still return 9. If the start point was 10, then it would return 0 (no match) as the start point would be too far forward.
INSTR – Case Sensitivity
You can also set a Compare parameter to vbBinaryCompare or vbTextCompare. If you set this parameter, the statement must have a start parameter value.
- vbBinaryCompare – Case-sensitive (Default)
- vbTextCompare – Not Case-sensitive
MsgBox InStr(1, "This is MyText string", "mytext", vbTextCompare)This statement will still return 9, even though the search text is in lower case.
To disable case-sensitivity you can also declare Option Compare Text at the top of your code module.
VBA Replace Function
If you wish to replace characters in a string with different text within your code, then the Replace method is ideal for this:
Sub TestReplace()
MsgBox Replace("This is MyText string", "MyText", "My Text")
End Sub
This code replaces ‘MyText’ with ‘My Text’. Note that the search string is case sensitive as a binary compare is the default.
You can also add other optional parameters:
- Start – defines position in the initial string that the replacement has to start from. Unlike in the Find method, it returns a truncated string starting from the character number defined by the Start parameter.
- Count – defines the number of replacements to be made. By default, Replace will change every instance of the search text found, but you can limit this to a single replacement by setting the Count parameter to 1
- Compare – as in the Find method you can specify a binary search or a text search using vbBinaryCompare or vbTextCompare. Binary is case sensitive and text is non case sensitive
MsgBox Replace("This is MyText string (mytext)", "MyText", "My Text", 9, 1, vbTextCompare)This code returns ‘My Text string (mytext)’. This is because the start point given is 9, so the new returned string starts at character 9. Only the first ‘MyText’ has been changed because the Count parameter is set to 1.
The Replace method is ideal for solving problems like peoples’ names containing apostrophes e.g. O’Flynn. If you are using single quotes to define a string value and there is an apostrophe, this will cause an error because the code will interpret the apostrophe as the end of the string and will not recognize the remainder of the string.
You can use the Replace method to replace the apostrophe with nothing, removing it completely.
Поиск какого-либо значения в ячейках Excel довольно часто встречающаяся задача при программировании какого-либо макроса. Решить ее можно разными способами. Однако, в разных ситуациях использование того или иного способа может быть не оправданным. В данной статье я рассмотрю 2 наиболее распространенных способа.
Поиск перебором значений
Довольно простой в реализации способ. Например, найти в колонке «A» ячейку, содержащую «123» можно примерно так:
Sheets("Данные").Select
For y = 1 To Cells.SpecialCells(xlLastCell).Row
If Cells(y, 1) = "123" Then
Exit For
End If
Next y
MsgBox "Нашел в строке: " + CStr(y)
Минусами этого так сказать «классического» способа являются: медленная работа и громоздкость. А плюсом является его гибкость, т.к. таким способом можно реализовать сколь угодно сложные варианты поиска с различными вычислениями и т.п.
Поиск функцией Find
Гораздо быстрее обычного перебора и при этом довольно гибкий. В простейшем случае, чтобы найти в колонке A ячейку, содержащую «123» достаточно такого кода:
Sheets("Данные").Select
Set fcell = Columns("A:A").Find("123")
If Not fcell Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "Нашел в строке: " + CStr(fcell.Row)
End If
Вкратце опишу что делают строчки данного кода:
1-я строка: Выбираем в книге лист «Данные»;
2-я строка: Осуществляем поиск значения «123» в колонке «A», результат поиска будет в fcell;
3-я строка: Если удалось найти значение, то fcell будет содержать Range-объект, в противном случае — будет пустой, т.е. Nothing.
Полностью синтаксис оператора поиска выглядит так:
Find(What, After, LookIn, LookAt, SearchOrder, SearchDirection, MatchCase, MatchByte, SearchFormat)
What — Строка с текстом, который ищем или любой другой тип данных Excel
After — Ячейка, после которой начать поиск. Обратите внимание, что это должна быть именно единичная ячейка, а не диапазон. Поиск начинается после этой ячейки, а не с нее. Поиск в этой ячейке произойдет только когда весь диапазон будет просмотрен и поиск начнется с начала диапазона и до этой ячейки включительно.
LookIn — Тип искомых данных. Может принимать одно из значений: xlFormulas (формулы), xlValues (значения), или xlNotes (примечания).
LookAt — Одно из значений: xlWhole (полное совпадение) или xlPart (частичное совпадение).
SearchOrder — Одно из значений: xlByRows (просматривать по строкам) или xlByColumns (просматривать по столбцам)
SearchDirection — Одно из значений: xlNext (поиск вперед) или xlPrevious (поиск назад)
MatchCase — Одно из значений: True (поиск чувствительный к регистру) или False (поиск без учета регистра)
MatchByte — Применяется при использовании мультибайтных кодировок: True (найденный мультибайтный символ должен соответствовать только мультибайтному символу) или False (найденный мультибайтный символ может соответствовать однобайтному символу)
SearchFormat — Используется вместе с FindFormat. Сначала задается значение FindFormat (например, для поиска ячеек с курсивным шрифтом так: Application.FindFormat.Font.Italic = True), а потом при использовании метода Find указываем параметр SearchFormat = True. Если при поиске не нужно учитывать формат ячеек, то нужно указать SearchFormat = False.
Чтобы продолжить поиск, можно использовать FindNext (искать «далее») или FindPrevious (искать «назад»).
Примеры поиска функцией Find
Пример 1: Найти в диапазоне «A1:A50» все ячейки с текстом «asd» и поменять их все на «qwe»
With Worksheets(1).Range("A1:A50")
Set c = .Find("asd", LookIn:=xlValues)
Do While Not c Is Nothing
c.Value = "qwe"
Set c = .FindNext(c)
Loop
End With
Обратите внимание: Когда поиск достигнет конца диапазона, функция продолжит искать с начала диапазона. Таким образом, если значение найденной ячейки не менять, то приведенный выше пример зациклится в бесконечном цикле. Поэтому, чтобы этого избежать (зацикливания), можно сделать следующим образом:
Пример 2: Правильный поиск значения с использованием FindNext, не приводящий к зацикливанию.
With Worksheets(1).Range("A1:A50")
Set c = .Find("asd", lookin:=xlValues)
If Not c Is Nothing Then
firstResult = c.Address
Do
c.Font.Bold = True
Set c = .FindNext(c)
If c Is Nothing Then Exit Do
Loop While c.Address <> firstResult
End If
End With
В ниже следующем примере используется другой вариант продолжения поиска — с помощью той же функции Find с параметром After. Когда найдена очередная ячейка, следующий поиск будет осуществляться уже после нее. Однако, как и с FindNext, когда будет достигнут конец диапазона, Find продолжит поиск с его начала, поэтому, чтобы не произошло зацикливания, необходимо проверять совпадение с первым результатом поиска.
Пример 3: Продолжение поиска с использованием Find с параметром After.
With Worksheets(1).Range("A1:A50")
Set c = .Find("asd", lookin:=xlValues)
If Not c Is Nothing Then
firstResult = c.Address
Do
c.Font.Bold = True
Set c = .Find("asd", After:=c, lookin:=xlValues)
If c Is Nothing Then Exit Do
Loop While c.Address <> firstResult
End If
End With
Следующий пример демонстрирует применение SearchFormat для поиска по формату ячейки. Для указания формата необходимо задать свойство FindFormat.
Пример 4: Найти все ячейки с шрифтом «курсив» и поменять их формат на обычный (не «курсив»)
lLastRow = Cells.SpecialCells(xlLastCell).Row
lLastCol = Cells.SpecialCells(xlLastCell).Column
Application.FindFormat.Font.Italic = True
With Worksheets(1).Range(Cells(1, 1), Cells(lLastRow, lLastCol))
Set c = .Find("", SearchFormat:=True)
Do While Not c Is Nothing
c.Font.Italic = False
Set c = .Find("", After:=c, SearchFormat:=True)
Loop
End With
Примечание: В данном примере намеренно не используется FindNext для поиска следующей ячейки, т.к. он не учитывает формат (статья об этом: https://support.microsoft.com/ru-ru/kb/282151)
Коротко опишу алгоритм поиска Примера 4. Первые две строки определяют последнюю строку (lLastRow) на листе и последний столбец (lLastCol). 3-я строка задает формат поиска, в данном случае, будем искать ячейки с шрифтом Italic. 4-я строка определяет область ячеек с которой будет работать программа (с ячейки A1 и до последней строки и последнего столбца). 5-я строка осуществляет поиск с использованием SearchFormat. 6-я строка — цикл пока результат поиска не будет пустым. 7-я строка — меняем шрифт на обычный (не курсив), 8-я строка продолжаем поиск после найденной ячейки.
Хочу обратить внимание на то, что в этом примере я не стал использовать «защиту от зацикливания», как в Примерах 2 и 3, т.к. шрифт меняется и после «прохождения» по всем ячейкам, больше не останется ни одной ячейки с курсивом.
Свойство FindFormat можно задавать разными способами, например, так:
With Application.FindFormat.Font .Name = "Arial" .FontStyle = "Regular" .Size = 10 End With
Поиск последней заполненной ячейки с помощью Find
Следующий пример — применение функции Find для поиска последней ячейки с заполненными данными. Использованные в Примере 4 SpecialCells находит последнюю ячейку даже если она не содержит ничего, но отформатирована или в ней раньше были данные, но были удалены.
Пример 5: Найти последнюю колонку и столбец, заполненные данными
Set c = Worksheets(1).UsedRange.Find("*", SearchDirection:=xlPrevious)
If Not c Is Nothing Then
lLastRow = c.Row: lLastCol = c.Column
Else
lLastRow = 1: lLastCol = 1
End If
MsgBox "lLastRow=" & lLastRow & " lLastCol=" & lLastCol
В этом примере используется UsedRange, который так же как и SpecialCells возвращает все используемые ячейки, в т.ч. и те, что были использованы ранее, а сейчас пустые. Функция Find ищет ячейку с любым значением с конца диапазона.
Поиск по шаблону (маске)
При поиске можно так же использовать шаблоны, чтобы найти текст по маске, следующий пример это демонстрирует.
Пример 6: Выделить красным шрифтом ячейки, в которых текст начинается со слова из 4-х букв, первая и последняя буквы «т», при этом после этого слова может следовать любой текст.
With Worksheets(1).Cells
Set c = .Find("т??т*", LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole)
If Not c Is Nothing Then
firstResult = c.Address
Do
c.Font.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0)
Set c = .FindNext(c)
If c Is Nothing Then Exit Do
Loop While c.Address <> firstResult
End If
End With
Для поиска функцией Find по маске (шаблону) можно применять символы:
* — для обозначения любого количества любых символов;
? — для обозначения одного любого символа;
~ — для обозначения символов *, ? и ~. (т.е. чтобы искать в тексте вопросительный знак, нужно написать ~?, чтобы искать именно звездочку (*), нужно написать ~* и наконец, чтобы найти в тексте тильду, необходимо написать ~~)
Поиск в скрытых строках и столбцах
Для поиска в скрытых ячейках нужно учитывать лишь один нюанс: поиск нужно осуществлять в формулах, а не в значениях, т.е. нужно использовать LookIn:=xlFormulas
Поиск даты с помощью Find
Если необходимо найти текущую дату или какую-то другую дату на листе Excel или в диапазоне с помощью Find, необходимо учитывать несколько нюансов:
- Тип данных Date в VBA представляется в виде #[месяц]/[день]/[год]#, соответственно, если необходимо найти фиксированную дату, например, 01 марта 2018 года, необходимо искать #3/1/2018#, а не «01.03.2018»
- В зависимости от формата ячеек, дата может выглядеть по-разному, поэтому, чтобы искать дату независимо от формата, поиск нужно делать не в значениях, а в формулах, т.е. использовать LookIn:=xlFormulas
Приведу несколько примеров поиска даты.
Пример 7: Найти текущую дату на листе независимо от формата отображения даты.
d = Date Set c = Cells.Find(d, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlWhole) If Not c Is Nothing Then MsgBox "Нашел" Else MsgBox "Не нашел" End If
Пример 8: Найти 1 марта 2018 г.
d = #3/1/2018# Set c = Cells.Find(d, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlWhole) If Not c Is Nothing Then MsgBox "Нашел" Else MsgBox "Не нашел" End If
Искать часть даты — сложнее. Например, чтобы найти все ячейки, где месяц «март», недостаточно искать «03» или «3». Не работает с датами так же и поиск по шаблону. Единственный вариант, который я нашел — это выбрать формат в котором месяц прописью для ячеек с датами и искать слово «март» в xlValues.
Тем не менее, можно найти, например, 1 марта независимо от года.
Пример 9: Найти 1 марта любого года.
d = #3/1/1900# Set c = Cells.Find(Format(d, "m/d/"), LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart) If Not c Is Nothing Then MsgBox "Нашел" Else MsgBox "Не нашел" End If