Macro codes can save you a ton of time.
You can automate small as well as heavy tasks with VBA codes.
And do you know?
With the help of macros…
…you can break all the limitations of Excel which you think Excel has.
And today, I have listed some of the useful codes examples to help you become more productive in your day to day work.
You can use these codes even if you haven’t used VBA before that.
But here’s the first thing to know:
What is a Macro Code?
In Excel, macro code is a programming code which is written in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) language.
The idea behind using a macro code is to automate an action which you perform manually in Excel, otherwise.
For example, you can use a code to print only a particular range of cells just with a single click instead of selecting the range -> File Tab -> Print -> Print Select -> OK Button.
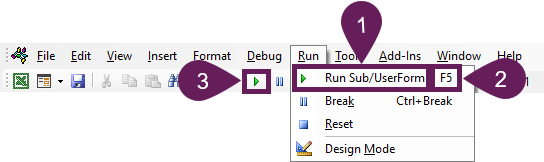
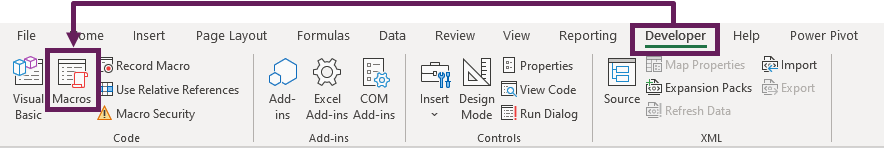
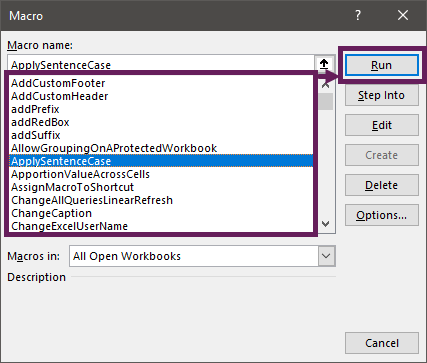
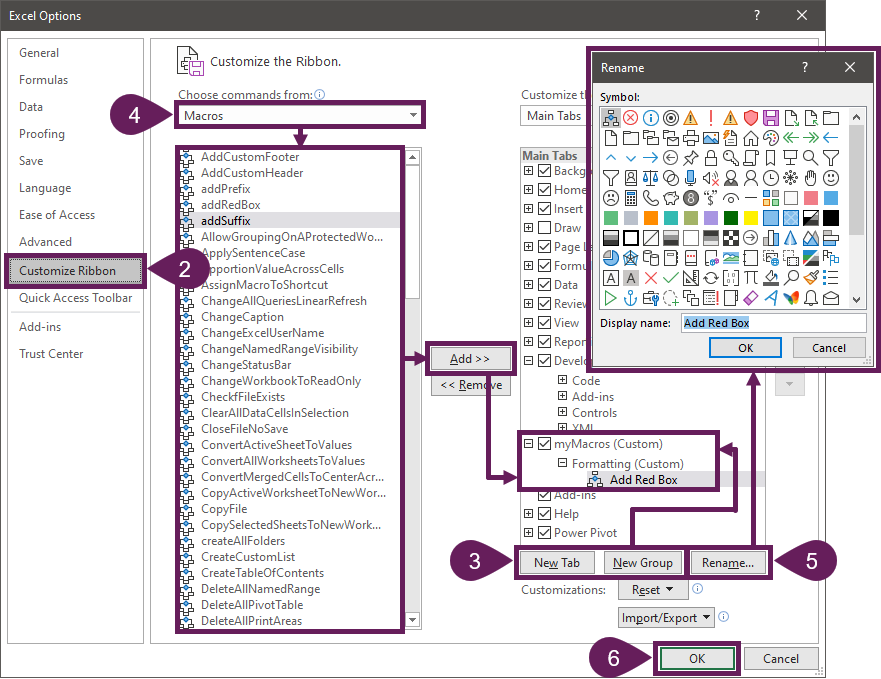
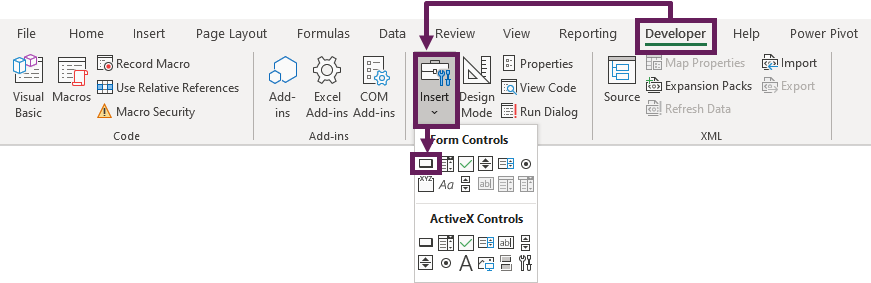
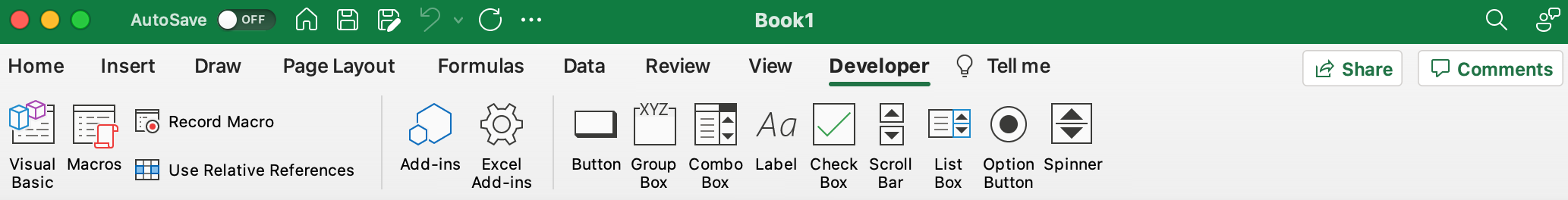
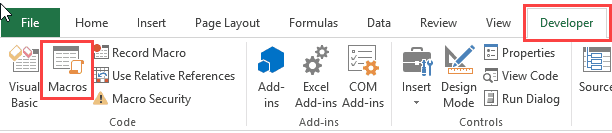
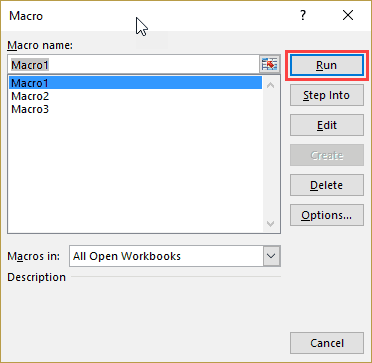
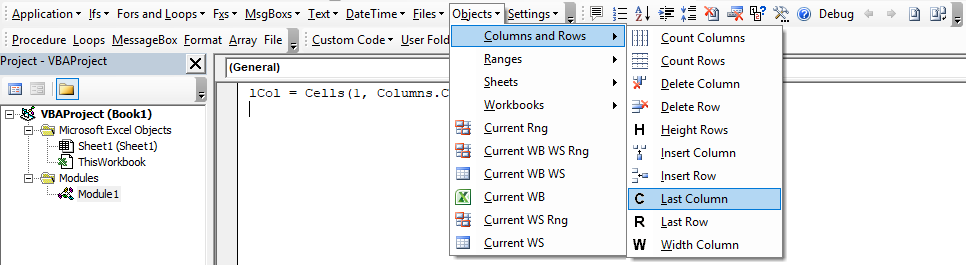
How to use a Macro Code in Excel
Before you use these codes, make sure you have your developer tab on your Excel ribbon to access VB editor. Once you activate developer tab you can use below steps to paste a VBA code into VB editor.
List of Top 100 macro Examples (CODES) for VBA beginners
I have added all the codes into specific categories so that you can find your favorite codes quickly. Just read the title and click on it to get the code.
- This is my Ultimate VBA Library which I update on monthly basis with new codes and Don’t forget to check the VBA Examples Sectionꜜ at the end of this list.
- VBA is one of the Advanced Excel Skills.
- To manage all of these codes make sure to read about Personal Macro Workbook to use these codes in all the workbooks.
- I have tested all of these codes in different versions of Excel (2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, and 2019). If you found any error in any of these codes, make sure to share with me.
Basic Codes
These VBA codes will help you to perform some basic tasks in a flash which you frequently do in your spreadsheets.
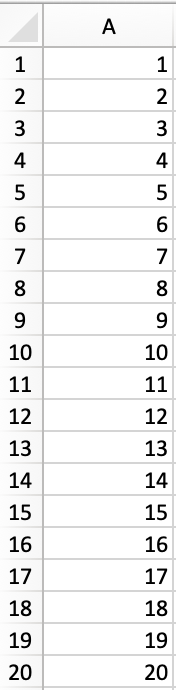
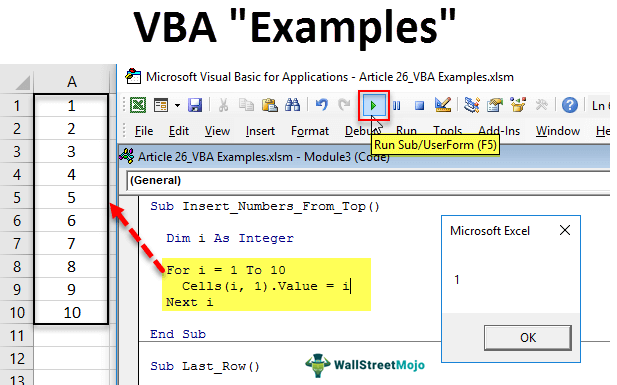
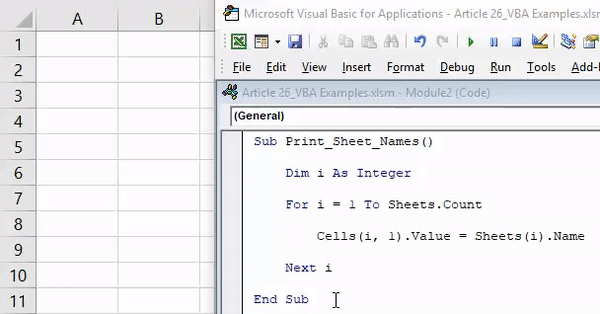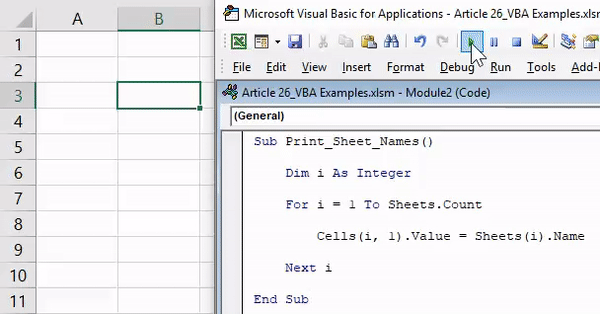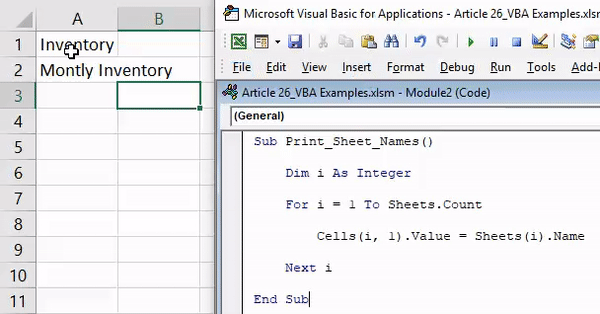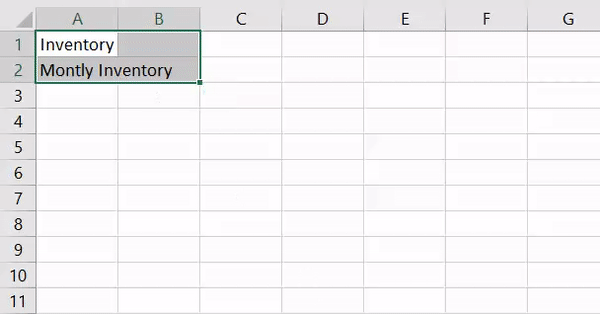
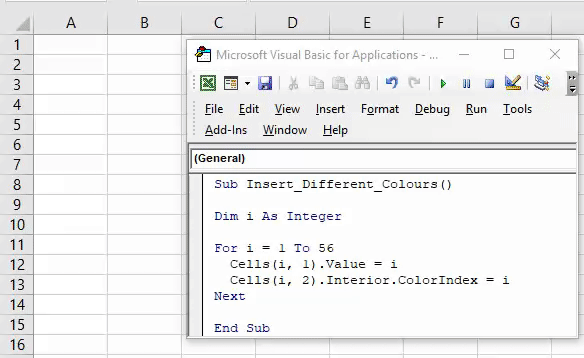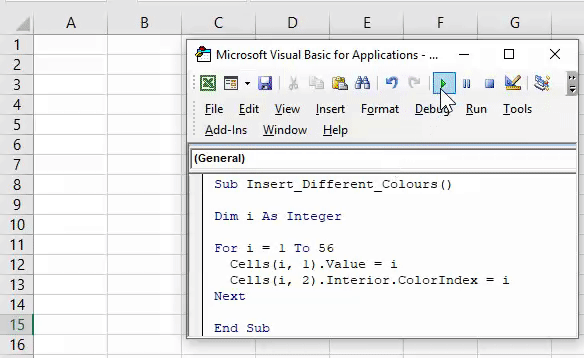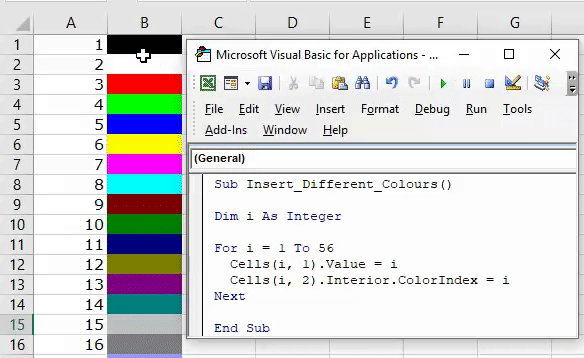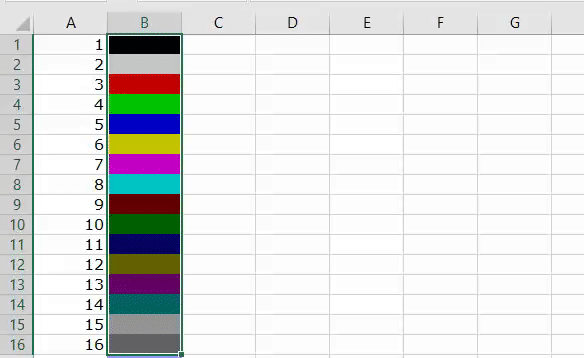
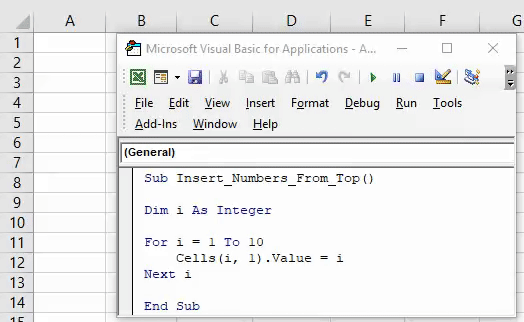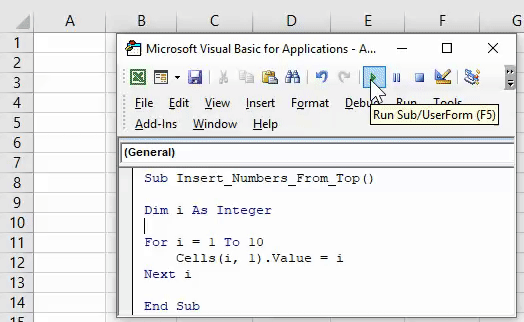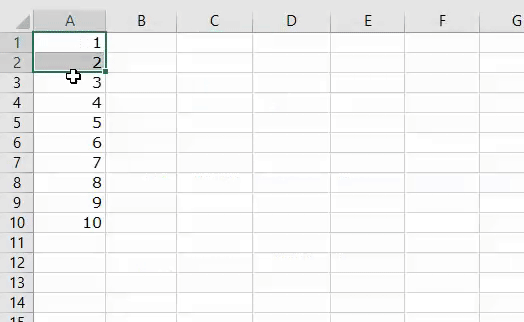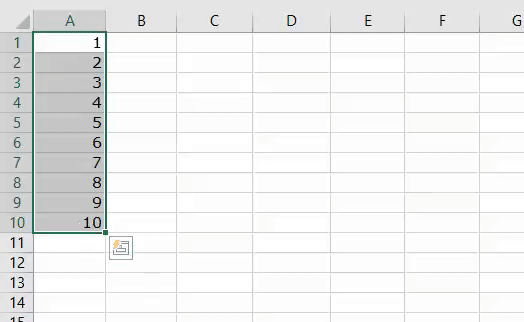
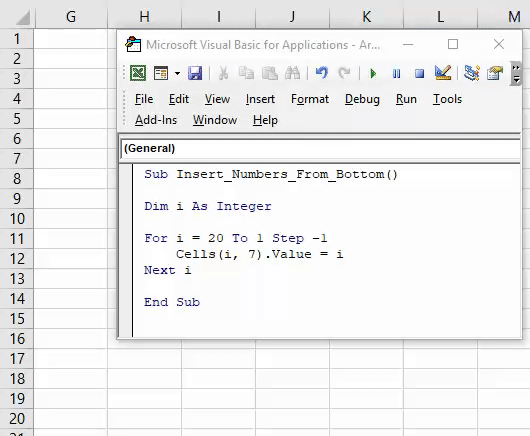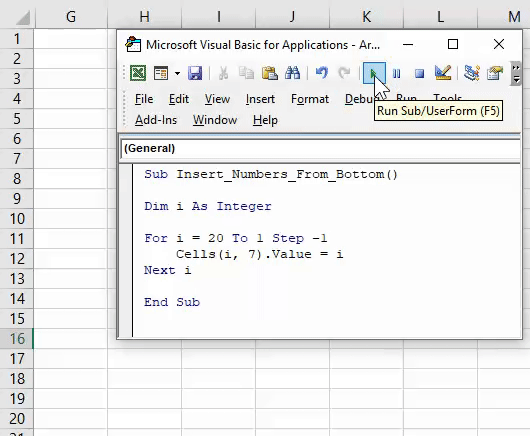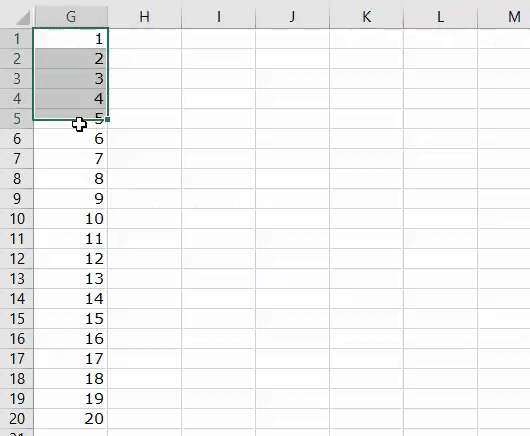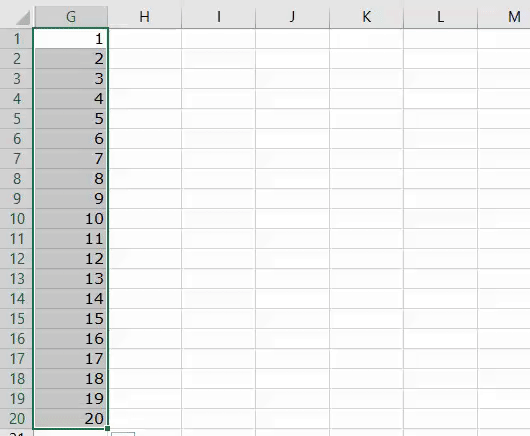
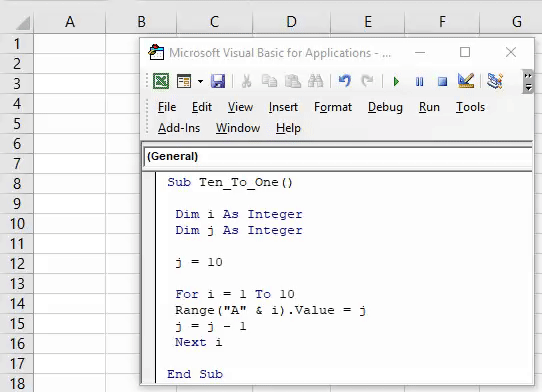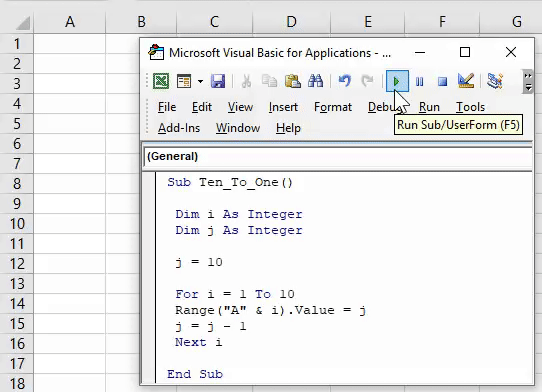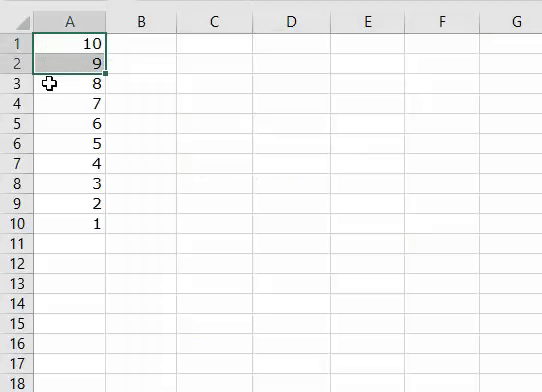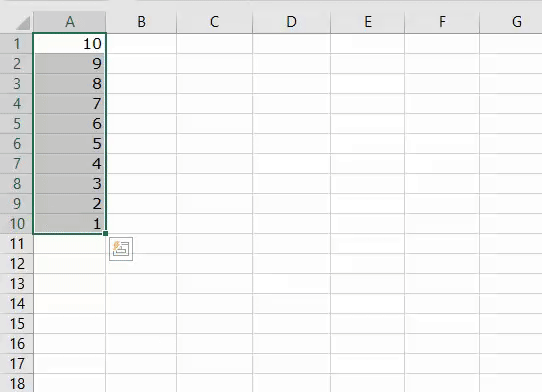
1. Add Serial Numbers
Sub AddSerialNumbers()
Dim i As Integer
On Error GoTo Last
i = InputBox("Enter Value", "Enter Serial Numbers")
For i = 1 To i
ActiveCell.Value = i
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Activate
Next i
Last:Exit Sub
End Sub
This macro code will help you to automatically add serial numbers in your Excel sheet which can be helpful for you if you work with large data.
To use this code you need to select the cell from where you want to start the serial numbers and when you run this it shows you a message box where you need to enter the highest number for the serial numbers and click OK. And once you click OK, it simply runs a loop and add a list of serial numbers to the cells downward.
2. Insert Multiple Columns
Sub InsertMultipleColumns()
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
ActiveCell.EntireColumn.Select
On Error GoTo Last
i = InputBox("Enter number of columns to insert", "Insert Columns")
For j = 1 To i
Selection.Insert Shift:=xlToRight, CopyOrigin:=xlFormatFromRightorAbove
Next j
Last: Exit Sub
End Sub
This code helps you to enter multiple columns in a single click. When you run this code it asks you the number columns you want to add and when you click OK, it adds entered number of columns after the selected cell. If you want to add columns before the selected cell, replace the xlToRight to xlToLeft in the code.
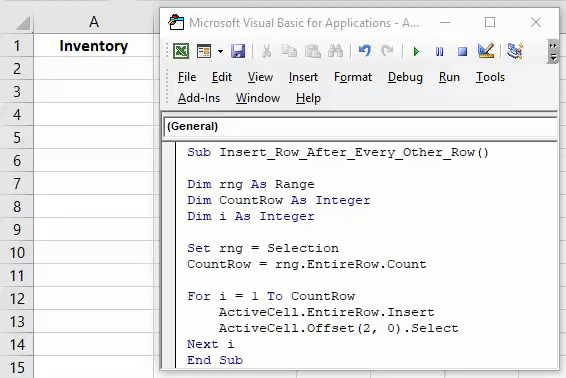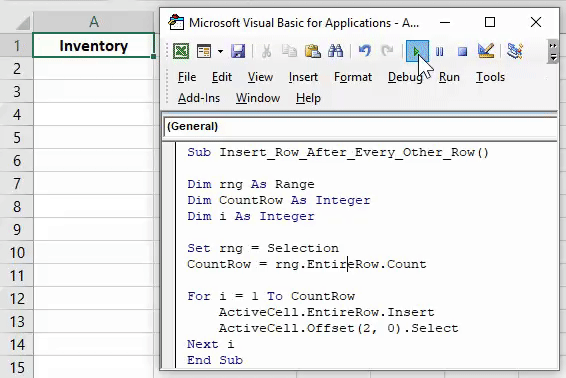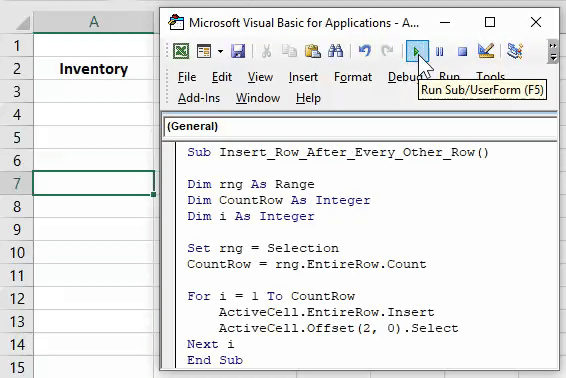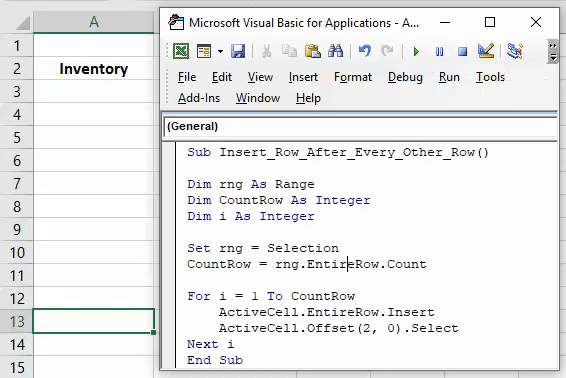
3. Insert Multiple Rows
Sub InsertMultipleRows()
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
ActiveCell.EntireRow.Select
On Error GoTo Last
i = InputBox("Enter number of columns to insert", "Insert Columns")
For j = 1 To i
Selection.Insert Shift:=xlToDown, CopyOrigin:=xlFormatFromRightorAbove
Next j
Last: Exit Sub
End Sub
With this code, you can enter multiple rows in the worksheet. When you run this code, you can enter the number of rows to insert and make sure to select the cell from where you want to insert the new rows. If you want to add rows before the selected cell, replace the xlToDown to xlToUp in the code.
4. Auto Fit Columns
Sub AutoFitColumns() Cells.Select Cells.EntireColumn.AutoFit End Sub
This code quickly auto fits all the columns in your worksheet. So when you run this code, it will select all the cells in your worksheet and instantly auto-fit all the columns.
5. Auto Fit Rows
Sub AutoFitRows() Cells.Select Cells.EntireRow.AutoFit End Sub
You can use this code to auto-fit all the rows in a worksheet. When you run this code it will select all the cells in your worksheet and instantly auto-fit all the row.
6. Remove Text Wrap
Sub RemoveTextWrap()
Range("A1").WrapText = False
End Sub
This code will help you to remove text wrap from the entire worksheet with a single click. It will first select all the columns and then remove text wrap and auto fit all the rows and columns. There’s also a shortcut that you can use (Alt + H +W) for but if you add this code to Quick Access Toolbar it’s convenient than a keyboard shortcut.
7. Unmerge Cells
Sub UnmergeCells() Selection.UnMerge End Sub
This code simply uses the unmerge options which you have on the HOME tab. The benefit of using this code is you can add it to the QAT and unmerge all the cell in the selection. And if you want to un-merge a specific range you can define that range in the code by replacing the word selection.
8. Open Calculator
Sub OpenCalculator() Application.ActivateMicrosoftApp Index:=0 End Sub
In Windows, there is a specific calculator and by using this macro code you can open that calculator directly from Excel. As I mentioned that it’s for windows and if you run this code in the MAC version of VBA you’ll get an error.
9. Add Header/Footer Date
Sub DateInHeader() With ActiveSheet.PageSetup .LeftHeader = "" .CenterHeader = "&D" .RightHeader = "" .LeftFooter = "" .CenterFooter = "" .RightFooter = "" End With End Sub
This macro adds a date to the header when you run it. It simply uses the tag «&D» for adding the date. You can also change it to the footer or change the side by replacing the «» with the date tag. And if you want to add a specific date instead of the current date you can replace the «&D» tag with that date from the code.
10. Custom Header/Footer
Sub CustomHeader()
Dim myText As String
myText = InputBox("Enter your text here", "Enter Text")
With ActiveSheet.PageSetup
.LeftHeader = ""
.CenterHeader = myText
.RightHeader = ""
.LeftFooter = ""
.CenterFooter = ""
.RightFooter = ""
End With
End Sub
When you run this code, it shows an input box that asks you to enter the text which you want to add as a header, and once you enter it click OK.
If you see this closely you have six different lines of code to choose the place for the header or footer. Let’s say if you want to add left-footer instead of center header simply replace the “myText” to that line of the code by replacing the «» from there.
Formatting Codes
These VBA codes will help you to format cells and ranges using some specific criteria and conditions.
11. Highlight Duplicates from Selection
Sub HighlightDuplicateValues() Dim myRange As Range Dim myCell As Range Set myRange = Selection For Each myCell In myRange If WorksheetFunction.CountIf(myRange, myCell.Value) > 1 Then myCell.Interior.ColorIndex = 36 End If Next myCell End Sub
This macro will check each cell of your selection and highlight the duplicate values. You can also change the color from the code.
12. Highlight the Active Row and Column
Private Sub Worksheet_BeforeDoubleClick(ByVal Target As Range, Cancel As Boolean) Dim strRange As String strRange = Target.Cells.Address & "," & _ Target.Cells.EntireColumn.Address & "," & _ Target.Cells.EntireRow.Address Range(strRange).Select End Sub
I really love to use this macro code whenever I have to analyze a data table. Here are the quick steps to apply this code.
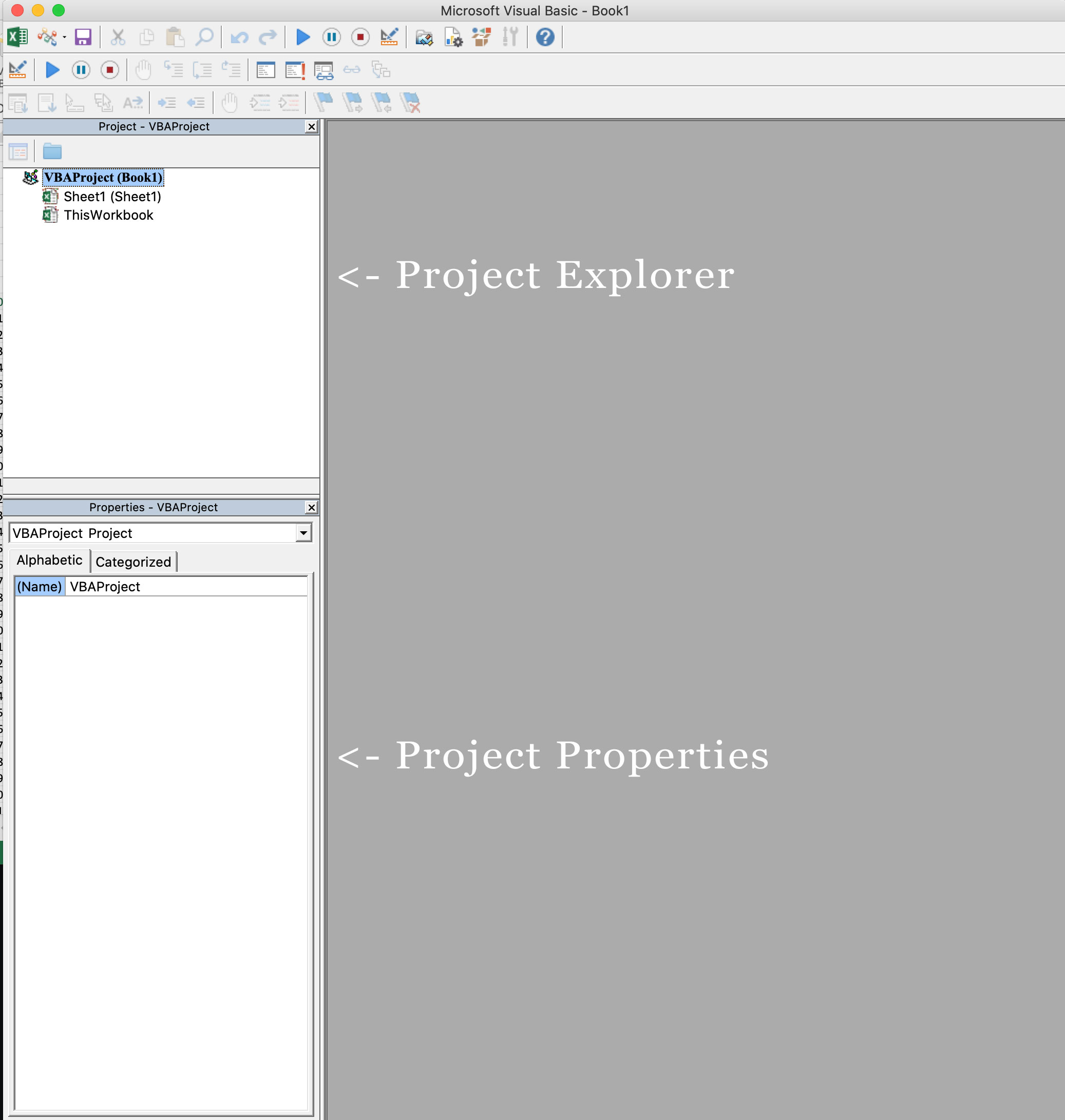
- Open VBE (ALT + F11).
- Go to Project Explorer (Ctrl + R, If hidden).
- Select your workbook & double click on the name of a particular worksheet in which you want to activate the macro.
- Paste the code into it and select the “BeforeDoubleClick” from event drop down menu.
- Close VBE and you are done.
Remember that, by applying this macro you will not able to edit the cell by double click.
13. Highlight Top 10 Values
Sub TopTen() Selection.FormatConditions.AddTop10 Selection.FormatConditions(Selection.FormatConditions.Count).S tFirstPriority With Selection.FormatConditions(1) .TopBottom = xlTop10Top .Rank = 10 .Percent = False End With With Selection.FormatConditions(1).Font .Color = -16752384 .TintAndShade = 0 End With With Selection.FormatConditions(1).Interior .PatternColorIndex = xlAutomatic .Color = 13561798 .TintAndShade = 0 End With Selection.FormatConditions(1).StopIfTrue = False End Sub
Just select a range and run this macro and it will highlight top 10 values with the green color.
14. Highlight Named Ranges
Sub HighlightRanges() Dim RangeName As Name Dim HighlightRange As Range On Error Resume Next For Each RangeName In ActiveWorkbook.Names Set HighlightRange = RangeName.RefersToRange HighlightRange.Interior.ColorIndex = 36 Next RangeName End Sub
If you are not sure about how many named ranges you have in your worksheet then you can use this code to highlight all of them.
15. Highlight Greater than Values
Sub HighlightGreaterThanValues()
Dim i As Integer
i = InputBox("Enter Greater Than Value", "Enter Value")
Selection.FormatConditions.Delete
Selection.FormatConditions.Add Type:=xlCellValue, _
Operator:=xlGreater, Formula1:=i
Selection.FormatConditions(Selection.FormatConditions.Count).S
tFirstPriority
With Selection.FormatConditions(1)
.Font.Color = RGB(0, 0, 0)
.Interior.Color = RGB(31, 218, 154)
End With
End Sub
Once you run this code it will ask you for the value from which you want to highlight all greater values.
16. Highlight Lower Than Values
Sub HighlightLowerThanValues()
Dim i As Integer
i = InputBox("Enter Lower Than Value", "Enter Value")
Selection.FormatConditions.Delete
Selection.FormatConditions.Add _
Type:=xlCellValue, _
Operator:=xlLower, _
Formula1:=i
Selection.FormatConditions(Selection.FormatConditions.Count).S
tFirstPriority
With Selection.FormatConditions(1)
.Font.Color = RGB(0, 0, 0)
.Interior.Color = RGB(217, 83, 79)
End With
End Sub
Once you run this code it will ask you for the value from which you want to highlight all lower values.
17. Highlight Negative Numbers
Sub highlightNegativeNumbers() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(Rng) Then If Rng.Value < 0 Then Rng.Font.Color= -16776961 End If End If Next End Sub
Select a range of cells and run this code. It will check each cell from the range and highlight all cells the where you have a negative number.
18. Highlight Specific Text
Sub highlightValue()
Dim myStr As String
Dim myRg As range
Dim myTxt As String
Dim myCell As range
Dim myChar As String
Dim I As Long
Dim J As Long
On Error Resume Next
If ActiveWindow.RangeSelection.Count > 1 Then
myTxt = ActiveWindow.RangeSelection.AddressLocal
Else
myTxt = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.AddressLocal
End If
LInput: Set myRg = _
Application.InputBox _
("please select the data range:", "Selection Required", myTxt, , , , , 8)
If myRg Is Nothing Then
Exit Sub
If myRg.Areas.Count > 1 Then
MsgBox "not support multiple columns"
GoTo LInput
End If
If myRg.Columns.Count <> 2 Then
MsgBox "the selected range can only contain two columns "
GoTo LInput
End If
For I = 0 To myRg.Rows.Count - 1
myStr = myRg.range("B1").Offset(I, 0).Value
With myRg.range("A1").Offset(I, 0)
.Font.ColorIndex = 1
For J = 1 To Len(.Text)
Mid(.Text, J, Len(myStr)) = myStrThen
.Characters(J, Len(myStr)).Font.ColorIndex = 3
Next
End With
Next I
End Sub
Suppose you have a large data set and you want to check for a particular value. For this, you can use this code. When you run it, you will get an input box to enter the value to search for.
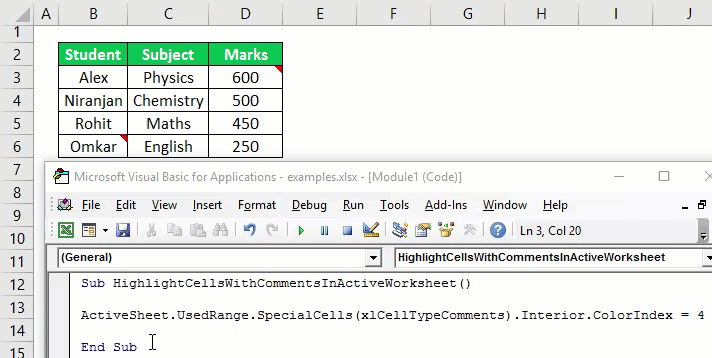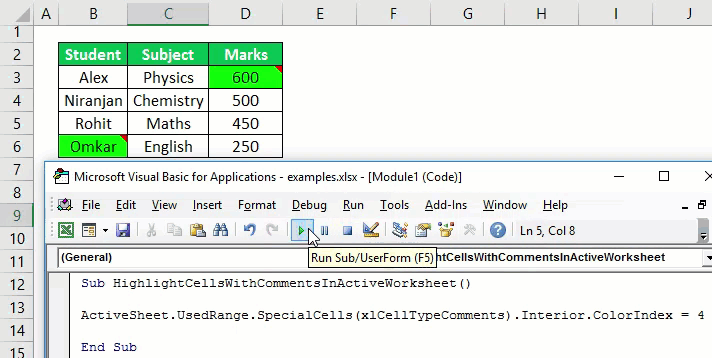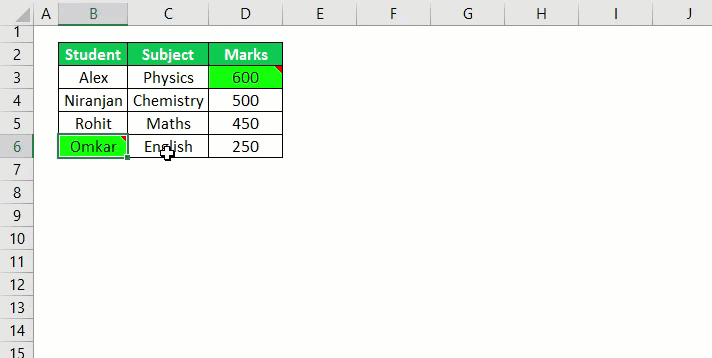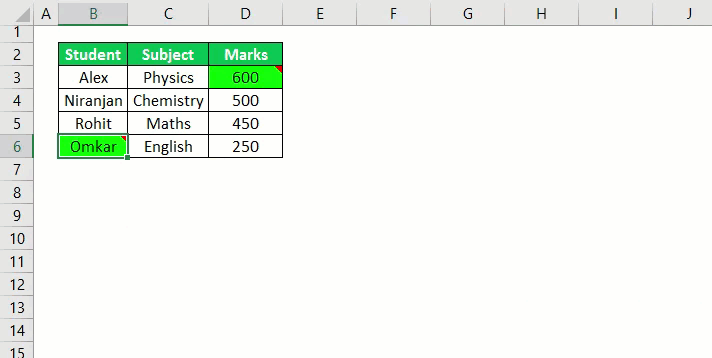
19. Highlight Cells with Comments
Sub highlightCommentCells() Selection.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeComments).Select Selection.Style= "Note" End Sub
To highlight all the cells with comments use this macro.
20. Highlight Alternate Rows in the Selection
Sub highlightAlternateRows() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection.Rows If rng.Row Mod 2 = 1 Then rng.Style = "20% -Accent1" rng.Value = rng ^ (1 / 3) Else End If Next rng End Sub
By highlighting alternate rows you can make your data easily readable, and for this, you can use below VBA code. It will simply highlight every alternate row in selected range.
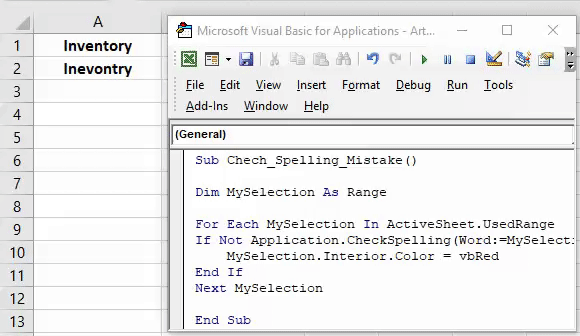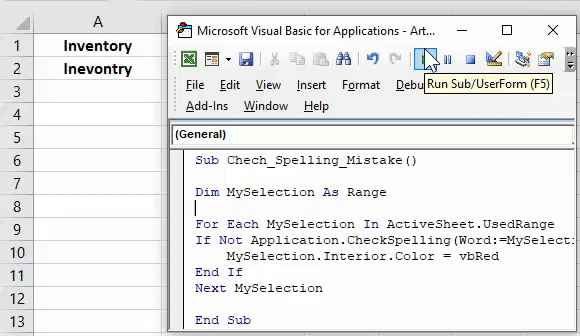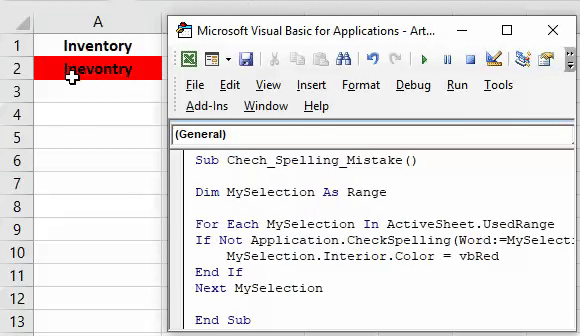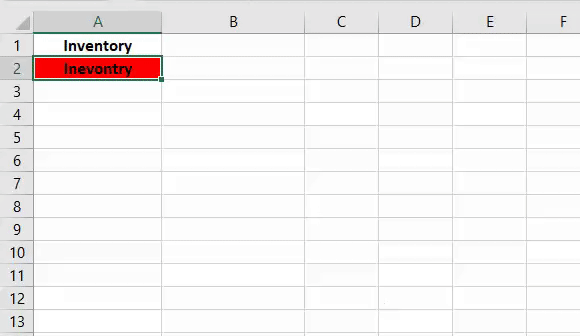
21. Highlight Cells with Misspelled Words
Sub HighlightMisspelledCells() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If Not Application.CheckSpelling(word:=rng.Text) Then rng.Style = "Bad" End If Next rng End Sub
If you find hard to check all the cells for spelling error then this code is for you. It will check each cell from the selection and highlight the cell where is a misspelled word.
22. Highlight Cells With Error in the Entire Worksheet
Sub highlightErrors() Dim rng As Range Dim i As Integer For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If WorksheetFunction.IsError(rng) Then i = i + 1 rng.Style = "bad" End If Next rng MsgBox _ "There are total " & i _ & " error(s) in this worksheet." End Sub
To highlight and count all the cells in which you have an error, this code will help you. Just run this code and it will return a message with the number error cells and highlight all the cells.
23. Highlight Cells with a Specific Text in Worksheet
Sub highlightSpecificValues()
Dim rng As range
Dim i As Integer
Dim c As Variant
c = InputBox("Enter Value To Highlight")
For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange
If rng = c Then
rng.Style = "Note"
i = i + 1
End If
Next rng
MsgBox "There are total " & i & " " & c & " in this worksheet."
End Sub
This code will help you to count the cells which have a specific value which you will mention and after that highlight all those cells.
24. Highlight all the Blank Cells Invisible Space
Sub blankWithSpace() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If rng.Value = " " Then rng.Style = "Note" End If Next rng End Sub
Sometimes there are some cells which are blank but they have a single space and due to this, it’s really hard to identify them. This code will check all the cell in the worksheet and highlight all the cells which have a single space.
25. Highlight Max Value In The Range
Sub highlightMaxValue() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection If rng = WorksheetFunction.Max(Selection) Then rng.Style = "Good" End If Next rng End Sub
It will check all the selected cells and highlight the cell with the maximum value.
26. Highlight Min Value In The Range
Sub Highlight_Min_Value() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection If rng = WorksheetFunction.Min(Selection) Then rng.Style = "Good" End If Next rng End Sub
It will check all the selected cells and highlight the cell with the Minimum value.
27. Highlight Unique Values
Sub highlightUniqueValues() Dim rng As Range Set rng = Selection rng.FormatConditions.Delete Dim uv As UniqueValues Set uv = rng.FormatConditions.AddUniqueValues uv.DupeUnique = xlUnique uv.Interior.Color = vbGreen End Sub
This codes will highlight all the cells from the selection which has a unique value.
28. Highlight Difference in Columns
Sub columnDifference()
Range("H7:H8,I7:I8").Select
Selection.ColumnDifferences(ActiveCell).Select
Selection.Style= "Bad"
End Sub
Using this code you can highlight the difference between two columns (corresponding cells).
29. Highlight Difference in Rows
Sub rowDifference()
Range("H7:H8,I7:I8").Select
Selection.RowDifferences(ActiveCell).Select
Selection.Style= "Bad"
End Sub
And by using this code you can highlight difference between two row (corresponding cells).
Printing Codes
These macro codes will help you to automate some printing tasks which can further save you a ton of time.
30. Print Comments
Sub printComments() With ActiveSheet.PageSetup .printComments = xlPrintSheetEnd End With End Sub
Use this macro to activate settings to print cell comments in the end of the page. Let’s say you have 10 pages to print, after using this code you will get all the comments on 11th last page.
31. Print Narrow Margin
Sub printNarrowMargin() With ActiveSheet.PageSetup .LeftMargin = Application .InchesToPoints (0.25) .RightMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.25) .TopMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.75) .BottomMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.75) .HeaderMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.3) .FooterMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.3) End With ActiveWindow.SelectedSheets.PrintOut _ Copies:=1, _ Collate:=True, _ IgnorePrintAreas:=False End Sub
Use this VBA code to take a print with a narrow margin. When you run this macro it will automatically change margins to narrow.
32. Print Selection
Sub printSelection() Selection.PrintOut Copies:=1, Collate:=True End Sub
This code will help you print selected range. You don’t need to go to printing options and set printing range. Just select a range and run this code.
33. Print Custom Pages
Sub printCustomSelection()
Dim startpage As Integer
Dim endpage As Integer
startpage = _
InputBox("Please Enter Start Page number.", "Enter Value")
If Not WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(startpage) Then
MsgBox _
"Invalid Start Page number. Please try again.", "Error"
Exit Sub
End If
endpage = _
InputBox("Please Enter End Page number.", "Enter Value")
If Not WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(endpage) Then
MsgBox _
"Invalid End Page number. Please try again.", "Error"
Exit Sub
End If
Selection.PrintOut From:=startpage, _
To:=endpage, Copies:=1, Collate:=True
End Sub
Instead of using the setting from print options you can use this code to print custom page range. Let’s say you want to print pages from 5 to 10. You just need to run this VBA code and enter start page and end page.
Worksheet Codes
These macro codes will help you to control and manage worksheets in an easy way and save your a lot of time.
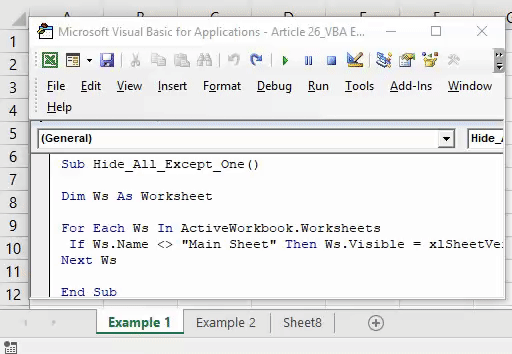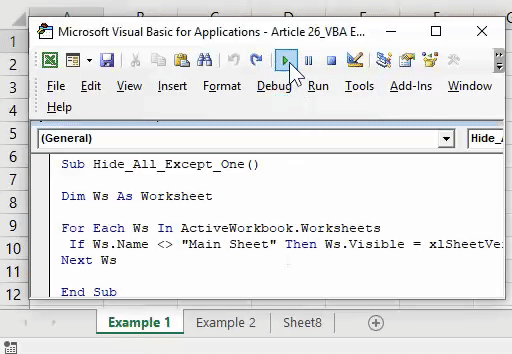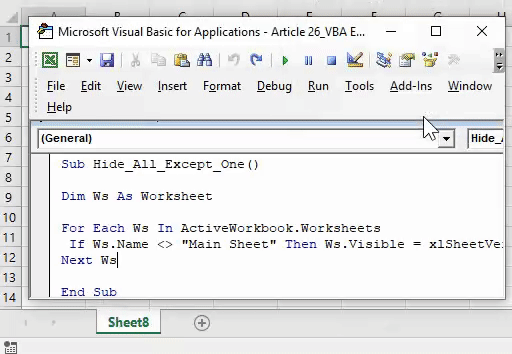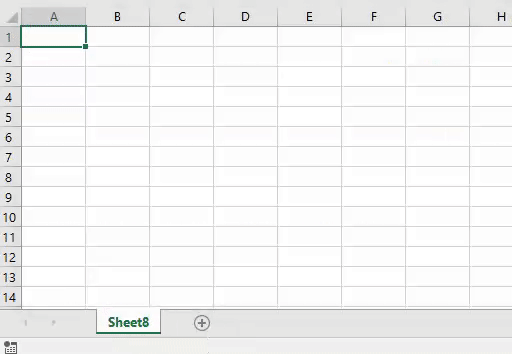
34. Hide all but the Active Worksheet
Sub HideWorksheet() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If ws.Name <> ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.Name Then ws.Visible = xlSheetHidden End If Next ws End Sub
Now, let’s say if you want to hide all the worksheets in your workbook other than the active worksheet. This macro code will do this for you.
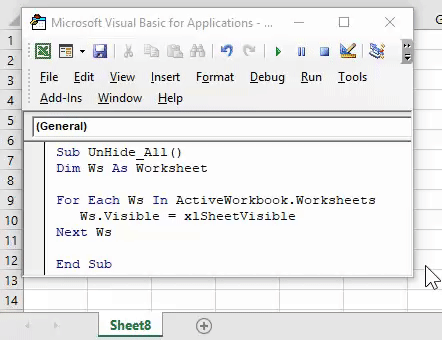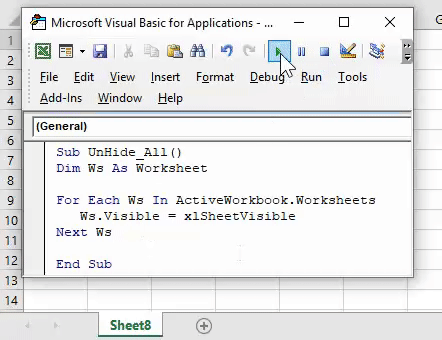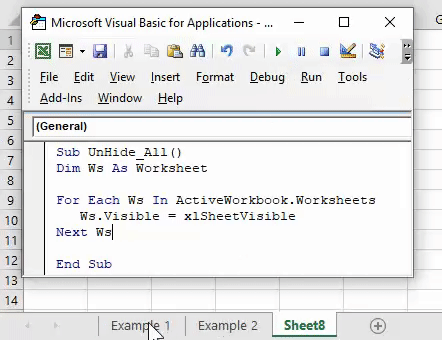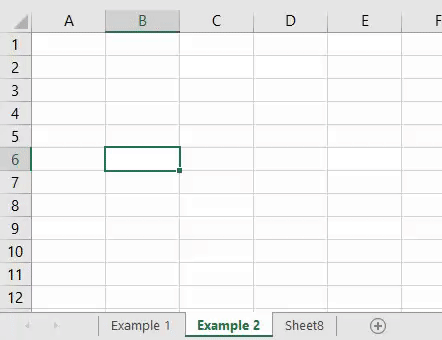
35. Unhide all Hidden Worksheets
Sub UnhideAllWorksheet() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible Next ws End Sub
And if you want to un-hide all the worksheets which you have hide with previous code, here is the code for that.
36. Delete all but the Active Worksheet
Sub DeleteWorksheets() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If ws.name <> ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.name Then Application.DisplayAlerts = False ws.Delete Application.DisplayAlerts = True End If Next ws End Sub
If you want to delete all the worksheets other than the active sheet, this macro is useful for you. When you run this macro it will compare the name of the active worksheet with other worksheets and then delete them.
37. Protect all Worksheets Instantly
Sub ProtectAllWorskeets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim ps As String
ps = InputBox("Enter a Password.", vbOKCancel)
For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets
ws.Protect Password:=ps
Next ws
End Sub
If you want to protect your all worksheets in one go here is a code for you. When you run this macro, you will get an input box to enter a password. Once you enter your password, click OK. And make sure to take care about CAPS.
38. Resize All Charts in a Worksheet
Sub Resize_Charts() Dim i As Integer For i = 1 To ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Count With ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(i) .Width = 300 .Height = 200 End With Next i End Sub
Make all chart same in size. This macro code will help you to make all the charts of the same size. You can change the height and width of charts by changing it in macro code.
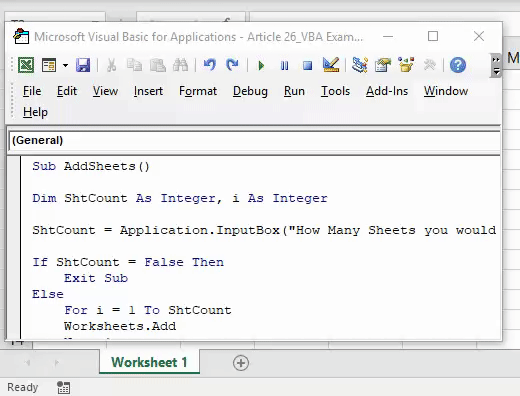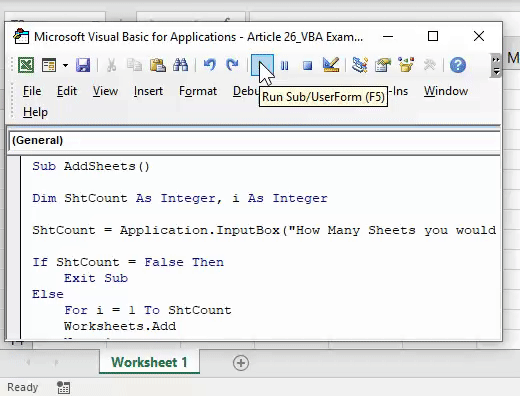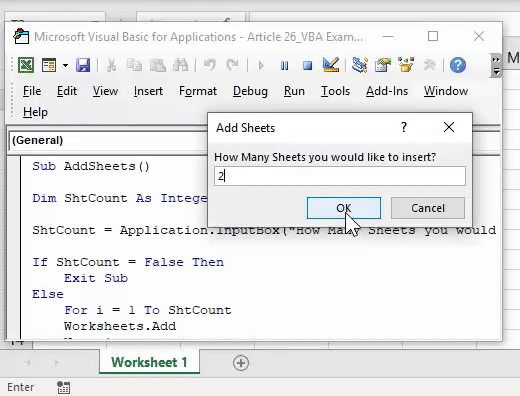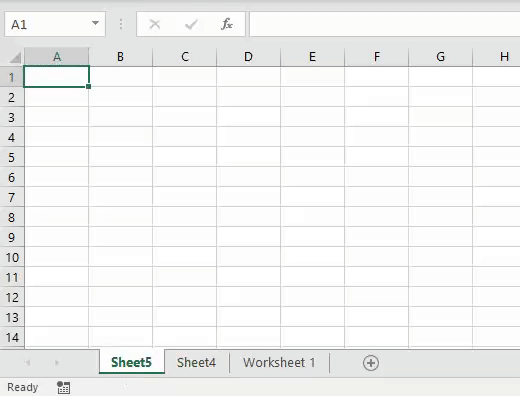
39. Insert Multiple Worksheets
Sub InsertMultipleSheets()
Dim i As Integer
i = _
InputBox("Enter number of sheets to insert.", _
"Enter Multiple Sheets")
Sheets.Add After:=ActiveSheet, Count:=i
End Sub
You can use this code if you want to add multiple worksheets in your workbook in a single shot. When you run this macro code you will get an input box to enter the total number of sheets you want to enter.
40. Protect Worksheet
Sub ProtectWS() ActiveSheet.Protect "mypassword", True, True End Sub
If you want to protect your worksheet you can use this macro code. All you have to do just mention your password in the code.
41. Un-Protect Worksheet
Sub UnprotectWS() ActiveSheet.Unprotect "mypassword" End Sub
If you want to unprotect your worksheet you can use this macro code. All you have to do just mention your password which you have used while protecting your worksheet.
42. Sort Worksheets
Sub SortWorksheets()
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
Dim iAnswer As VbMsgBoxResult
iAnswer = MsgBox("Sort Sheets in Ascending Order?" & Chr(10) _
& "Clicking No will sort in Descending Order", _
vbYesNoCancel + vbQuestion + vbDefaultButton1, "Sort Worksheets")
For i = 1 To Sheets.Count
For j = 1 To Sheets.Count - 1
If iAnswer = vbYes Then
If UCase$(Sheets(j).Name) > UCase$(Sheets(j + 1).Name) Then
Sheets(j).Move After:=Sheets(j + 1)
End If
ElseIf iAnswer = vbNo Then
If UCase$(Sheets(j).Name) < UCase$(Sheets(j + 1).Name) Then Sheets(j).Move After:=Sheets(j + 1)
End If
End If
Next j
Next i
End Sub
This code will help you to sort worksheets in your workbook according to their name.
43. Protect all the Cells With Formulas
Sub lockCellsWithFormulas() With ActiveSheet .Unprotect .Cells.Locked = False .Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeFormulas).Locked = True .Protect AllowDeletingRows:=True End With End Sub
To protect cell with formula with a single click you can use this code.
44. Delete all Blank Worksheets
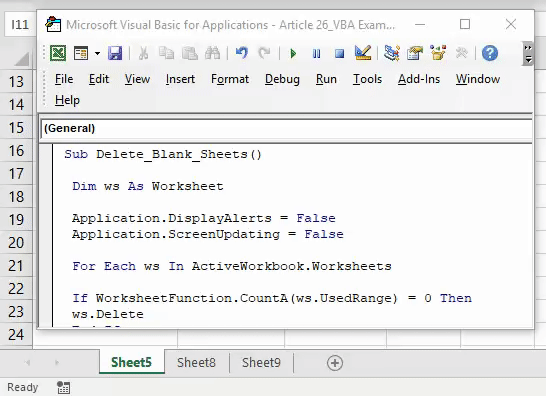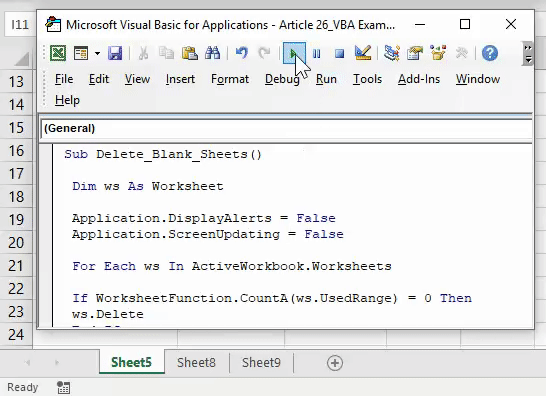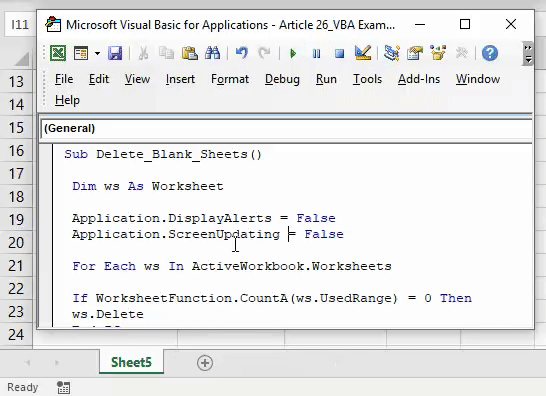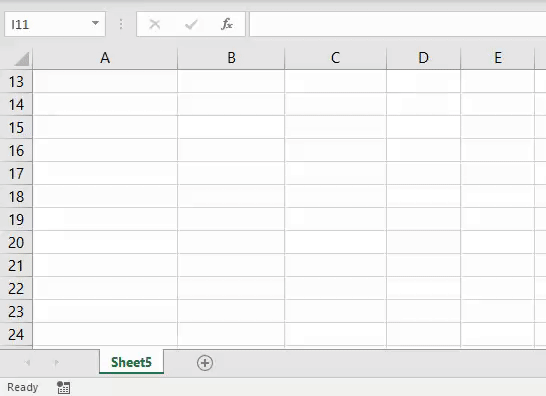
Sub deleteBlankWorksheets() Dim Ws As Worksheet On Error Resume Next Application.ScreenUpdating= False Application.DisplayAlerts= False For Each Ws In Application.Worksheets If Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(Ws.UsedRange) = 0 Then Ws.Delete End If Next Application.ScreenUpdating= True Application.DisplayAlerts= True End Sub
Run this code and it will check all the worksheets in the active workbook and delete if a worksheet is blank.
45. Unhide all Rows and Columns
Sub UnhideRowsColumns() Columns.EntireColumn.Hidden = False Rows.EntireRow.Hidden = False End Sub
Instead of unhiding rows and columns on by one manually you can use this code to do this in a single go.
46. Save Each Worksheet as a Single PDF
Sub SaveWorkshetAsPDF() Dimws As Worksheet For Each ws In Worksheets ws.ExportAsFixedFormat _ xlTypePDF, _ "ENTER-FOLDER-NAME-HERE" & _ ws.Name & ".pdf" Next ws End Sub
This code will simply save all the worksheets in a separate PDF file. You just need to change the folder name from the code.
47. Disable Page Breaks
Sub DisablePageBreaks() Dim wb As Workbook Dim wks As Worksheet Application.ScreenUpdating = False For Each wb In Application.Workbooks For Each Sht In wb.Worksheets Sht.DisplayPageBreaks = False Next Sht Next wb Application.ScreenUpdating = True End Sub
To disable page breaks use this code. It will simply disable page breaks from all the open workbooks.
Workbook Codes
These codes will help you to perform workbook level tasks in an easy way and with minimum efforts.
48. Create a Backup of a Current Workbook
Sub FileBackUp() ThisWorkbook.SaveCopyAs Filename:=ThisWorkbook.Path & _ "" & Format(Date, "mm-dd-yy") & " " & _ ThisWorkbook.name End Sub
This is one of the most useful macros which can help you to save a backup file of your current workbook.
It will save a backup file in the same directory where your current file is saved and it will also add the current date with the name of the file.
49. Close all Workbooks at Once
Sub CloseAllWorkbooks() Dim wbs As Workbook For Each wbs In Workbooks wbs.Close SaveChanges:=True Next wb End Sub
Use this macro code to close all open workbooks. This macro code will first check all the workbooks one by one and close them. If any of the worksheets is not saved, you’ll get a message to save it.
50. Copy Active Worksheet into a New Workbook
Sub CopyWorksheetToNewWorkbook() ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.Copy _ Before:=Workbooks.Add.Worksheets(1) End Sub
Let’s say if you want to copy your active worksheet in a new workbook, just run this macro code and it will do the same for you. It’s a super time saver.
51. Active Workbook in an Email
Sub Send_Mail()
Dim OutApp As Object
Dim OutMail As Object
Set OutApp = CreateObject("Outlook.Application")
Set OutMail = OutApp.CreateItem(0)
With OutMail
.to = "Sales@FrontLinePaper.com"
.Subject = "Growth Report"
.Body = "Hello Team, Please find attached Growth Report."
.Attachments.Add ActiveWorkbook.FullName
.display
End With
Set OutMail = Nothing
Set OutApp = Nothing
End Sub
Use this macro code to quickly send your active workbook in an e-mail. You can change the subject, email, and body text in code and if you want to send this mail directly, use «.Send» instead of «.Display».
52. Add Workbook to a Mail Attachment
Sub OpenWorkbookAsAttachment() Application.Dialogs(xlDialogSendMail).Show End Sub
Once you run this macro it will open your default mail client and attached active workbook with it as an attachment.
53. Welcome Message
Sub auto_open() MsgBox _ "Welcome To ExcelChamps & Thanks for downloading this file." End Sub
You can use auto_open to perform a task on opening a file and all you have to do just name your macro «auto_open».
54. Closing Message
Sub auto_close() MsgBox "Bye Bye! Don't forget to check other cool stuff on excelchamps.com" End Sub
You can use close_open to perform a task on opening a file and all you have to do just name your macro «close_open».
55. Count Open Unsaved Workbooks
Sub VisibleWorkbooks() Dim book As Workbook Dim i As Integer For Each book In Workbooks If book.Saved = False Then i = i + 1 End If Next book MsgBox i End Sub
Let’s you have 5-10 open workbooks, you can use this code to get the number of workbooks which are not saved yet.
Pivot Table Codes
These codes will help you to manage and make some changes in pivot tables in a flash.
56. Hide Pivot Table Subtotals
Sub HideSubtotals() Dim pt As PivotTable Dim pf As PivotField On Error Resume Next Set pt = ActiveSheet.PivotTables(ActiveCell.PivotTable.Name) If pt Is Nothing Then MsgBox "You must place your cursor inside of a PivotTable." Exit Sub End If For Each pf In pt.PivotFields pf.Subtotals(1) = True pf.Subtotals(1) = False Next pf End Sub
If you want to hide all the subtotals, just run this code. First of all, make sure to select a cell from your pivot table and then run this macro.
57. Refresh All Pivot Tables
Sub vba_referesh_all_pivots() Dim pt As PivotTable For Each pt In ActiveWorkbook.PivotTables pt.RefreshTable Next pt End Sub
A super quick method to refresh all pivot tables. Just run this code and all of your pivot tables in your workbook will be refresh in a single shot.
58. Create a Pivot Table
Follow this step by step guide to create a pivot table using VBA.
59. Auto Update Pivot Table Range
Sub UpdatePivotTableRange()
Dim Data_Sheet As Worksheet
Dim Pivot_Sheet As Worksheet
Dim StartPoint As Range
Dim DataRange As Range
Dim PivotName As String
Dim NewRange As String
Dim LastCol As Long
Dim lastRow As Long
'Set Pivot Table & Source Worksheet
Set Data_Sheet = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("PivotTableData3")
Set Pivot_Sheet = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Pivot3")
'Enter in Pivot Table Name
PivotName = "PivotTable2"
'Defining Staring Point & Dynamic Range
Data_Sheet.Activate
Set StartPoint = Data_Sheet.Range("A1")
LastCol = StartPoint.End(xlToRight).Column
DownCell = StartPoint.End(xlDown).Row
Set DataRange = Data_Sheet.Range(StartPoint, Cells(DownCell, LastCol))
NewRange = Data_Sheet.Name & "!" & DataRange.Address(ReferenceStyle:=xlR1C1)
'Change Pivot Table Data Source Range Address
Pivot_Sheet.PivotTables(PivotName). _
ChangePivotCache ActiveWorkbook. _
PivotCaches.Create(SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=NewRange)
'Ensure Pivot Table is Refreshed
Pivot_Sheet.PivotTables(PivotName).RefreshTable
'Complete Message
Pivot_Sheet.Activate
MsgBox "Your Pivot Table is now updated."
End Sub
If you are not using Excel tables then you can use this code to update pivot table range.
60. Disable/Enable Get Pivot Data
Sub activateGetPivotData() Application.GenerateGetPivotData = True End Sub Sub deactivateGetPivotData() Application.GenerateGetPivotData = False End Sub
To disable/enable GetPivotData function you need to use Excel option. But with this code you can do it in a single click.
Charts Codes
Use these VBA codes to manage charts in Excel and save your lot of time.
61. Change Chart Type
Sub ChangeChartType() ActiveChart.ChartType = xlColumnClustered End Sub
This code will help you to convert chart type without using chart options from the tab. All you have to do just specify to which type you want to convert.
Below code will convert selected chart to a clustered column chart. There are different codes for different types, you can find all those types from here.
62. Paste Chart as an Image
Sub ConvertChartToPicture()
ActiveChart.ChartArea.Copy
ActiveSheet.Range("A1").Select
ActiveSheet.Pictures.Paste.Select
End Sub
This code will help you to convert your chart into an image. You just need to select your chart and run this code.
63. Add Chart Title
Sub AddChartTitle()
Dim i As Variant
i = InputBox("Please enter your chart title", "Chart Title")
On Error GoTo Last
ActiveChart.SetElement (msoElementChartTitleAboveChart)
ActiveChart.ChartTitle.Text = i
Last:
Exit Sub
End Sub
First of all, you need to select your chart and the run this code. You will get an input box to enter chart title.
Advanced Codes
Some of the codes which you can use to preform advanced task in your spreadsheets.
64. Save Selected Range as a PDF
Sub HideSubtotals() Dim pt As PivotTable Dim pf As PivotField On Error Resume Next Set pt = ActiveSheet.PivotTables(ActiveCell.PivotTable.name) If pt Is Nothing Then MsgBox "You must place your cursor inside of a PivotTable." Exit Sub End If For Each pf In pt.PivotFields pf.Subtotals(1) = True pf.Subtotals(1) = False Next pf End Sub
If you want to hide all the subtotals, just run this code. First of all, make sure to select a cell from your pivot table and then run this macro.
65. Create a Table of Content
Sub TableofContent()
Dim i As Long
On Error Resume Next
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Worksheets("Table of Content").Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
On Error GoTo 0
ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Add Before:=ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(1)
ActiveSheet.Name = "Table of Content"
For i = 1 To Sheets.Count
With ActiveSheet
.Hyperlinks.Add _
Anchor:=ActiveSheet.Cells(i, 1), _
Address:="", _
SubAddress:="'" & Sheets(i).Name & "'!A1", _
ScreenTip:=Sheets(i).Name, _
TextToDisplay:=Sheets(i).Name
End With
Next i
End Sub
Let’s say you have more than 100 worksheets in your workbook and it’s hard to navigate now.
Don’t worry this macro code will rescue everything. When you run this code it will create a new worksheet and create a index of worksheets with a hyperlink to them.
66. Convert Range into an Image
Sub PasteAsPicture() Application.CutCopyMode = False Selection.Copy ActiveSheet.Pictures.Paste.Select End Sub
Paste selected range as an image. You just have to select the range and once you run this code it will automatically insert a picture for that range.
67. Insert a Linked Picture
Sub LinkedPicture() Selection.Copy ActiveSheet.Pictures.Paste(Link:=True).Select End Sub
This VBA code will convert your selected range into a linked picture and you can use that image anywhere you want.
68. Use Text to Speech
Sub Speak() Selection.Speak End Sub
Just select a range and run this code. Excel will speak all the text what you have in that range, cell by cell.
69. Activate Data Entry Form
Sub DataForm() ActiveSheet.ShowDataForm End Sub
There is a default data entry form which you can use for data entry.
70. Use Goal Seek
Sub GoalSeekVBA()
Dim Target As Long
On Error GoTo Errorhandler
Target = InputBox("Enter the required value", "Enter Value")
Worksheets("Goal_Seek").Activate
With ActiveSheet.Range("C7")
.GoalSeek_ Goal:=Target, _
ChangingCell:=Range("C2")
End With
Exit Sub
Errorhandler: MsgBox ("Sorry, value is not valid.")
End Sub
Goal Seek can be super helpful for you to solve complex problems. Learn more about goal seek from here before you use this code.
71. VBA Code to Search on Google
Sub SearchWindow32()
Dim chromePath As String
Dim search_string As String
Dim query As String
query = InputBox("Enter here your search here", "Google Search")
search_string = query
search_string = Replace(search_string, " ", "+")
'Uncomment the following line for Windows 64 versions and comment out Windows 32 versions'
'chromePath = "C:Program FilesGoogleChromeApplicationchrome.exe"
'Uncomment the following line for Windows 32 versions and comment out Windows 64 versions
'chromePath = "C:Program Files (x86)GoogleChromeApplicationchrome.exe"
Shell (chromePath & " -url http://google.com/#q=" & search_string)
End Sub
Formula Codes
These codes will help you to calculate or get results which often you do with worksheet functions and formulas.
72. Convert all Formulas into Values
Sub convertToValues()
Dim MyRange As Range
Dim MyCell As Range
Select Case _
MsgBox("You Can't Undo This Action. " _
& "Save Workbook First?", vbYesNoCancel, _
"Alert")
Case Is = vbYes
ThisWorkbook.Save
Case Is = vbCancel
Exit Sub
End Select
Set MyRange = Selection
For Each MyCell In MyRange
If MyCell.HasFormula Then
MyCell.Formula = MyCell.Value
End If
Next MyCell
End Sub
Simply convert formulas into values. When you run this macro it will quickly change the formulas into absolute values.
73. Remove Spaces from Selected Cells
Sub RemoveSpaces()
Dim myRange As Range
Dim myCell As Range
Select Case MsgBox("You Can't Undo This Action. " _
& "Save Workbook First?", _
vbYesNoCancel, "Alert")
Case Is = vbYesThisWorkbook.Save
Case Is = vbCancel
Exit Sub
End Select
Set myRange = Selection
For Each myCell In myRange
If Not IsEmpty(myCell) Then
myCell = Trim(myCell)
End If
Next myCell
End Sub
One of the most useful macros from this list. It will check your selection and then remove all the extra spaces from that.
74. Remove Characters from a String
Public Function removeFirstC(rng As String, cnt As Long) removeFirstC = Right(rng, Len(rng) - cnt) End Function
Simply remove characters from the starting of a text string. All you need is to refer to a cell or insert a text into the function and number of characters to remove from the text string.
It has two arguments «rng» for the text string and «cnt» for the count of characters to remove. For Example: If you want to remove first characters from a cell, you need to enter 1 in cnt.
75. Add Insert Degree Symbol in Excel
Sub degreeSymbol( ) Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection rng.Select If ActiveCell <> "" Then If IsNumeric(ActiveCell.Value) Then ActiveCell.Value = ActiveCell.Value & "°" End If End If Next End Sub
Let’s say you have a list of numbers in a column and you want to add degree symbol with all of them.
76. Reverse Text
Public Function rvrse(ByVal cell As Range) As String rvrse = VBA.strReverse(cell.Value) End Function
All you have to do just enter «rvrse» function in a cell and refer to the cell in which you have text which you want to reverse.
77. Activate R1C1 Reference Style
Sub ActivateR1C1() If Application.ReferenceStyle = xlA1 Then Application.ReferenceStyle = xlR1C1 Else Application.ReferenceStyle = xlR1C1 End If End Sub
This macro code will help you to activate R1C1 reference style without using Excel options.
78. Activate A1 Reference Style
Sub ActivateA1() If Application.ReferenceStyle = xlR1C1 Then Application.ReferenceStyle = xlA1 Else Application.ReferenceStyle = xlA1 End If End Sub
This macro code will help you to activate A1 reference style without using Excel options.
79. Insert Time Range
Sub TimeStamp() Dim i As Integer For i = 1 To 24 ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = i & ":00" ActiveCell.NumberFormat = "[$-409]h:mm AM/PM;@" ActiveCell.Offset(RowOffset:=1, ColumnOffset:=0).Select Next i End Sub
With this code, you can insert a time range in sequence from 00:00 to 23:00.
80. Convert Date into Day
Sub date2day() Dim tempCell As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each tempCell In Selection If IsDate(tempCell) = True Then With tempCell .Value = Day(tempCell) .NumberFormat = "0" End With End If Next tempCell End Sub
If you have dates in your worksheet and you want to convert all those dates into days then this code is for you. Simply select the range of cells and run this macro.
81. Convert Date into Year
Sub date2year() Dim tempCell As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each tempCell In Selection If IsDate(tempCell) = True Then With tempCell .Value = Year(tempCell) .NumberFormat = "0" End With End If Next tempCell End Sub
This code will convert dates into years.
82. Remove Time from Date
Sub removeTime() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If IsDate(Rng) = True Then Rng.Value = VBA.Int(Rng.Value) End If Next Selection.NumberFormat = "dd-mmm-yy" End Sub
If you have time with the date and you want to remove it then you can use this code.
83. Remove Date from Date and Time
Sub removeDate() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If IsDate(Rng) = True Then Rng.Value = Rng.Value - VBA.Fix(Rng.Value) End If NextSelection.NumberFormat = "hh:mm:ss am/pm" End Sub
It will return only time from a date and time value.
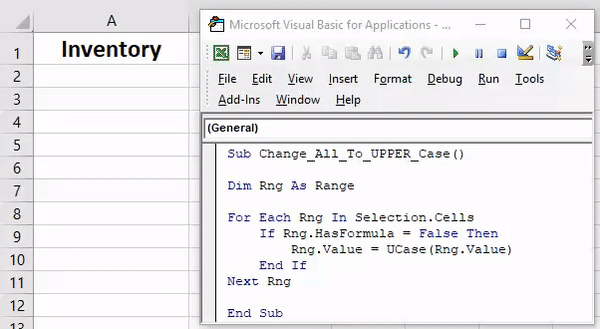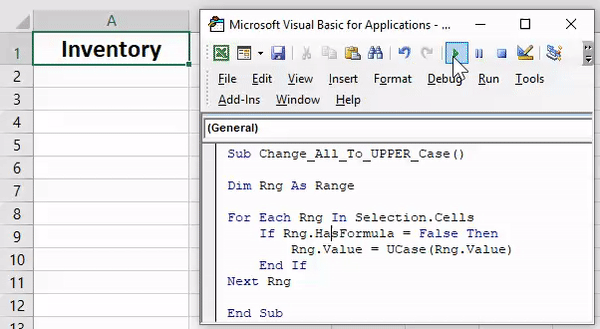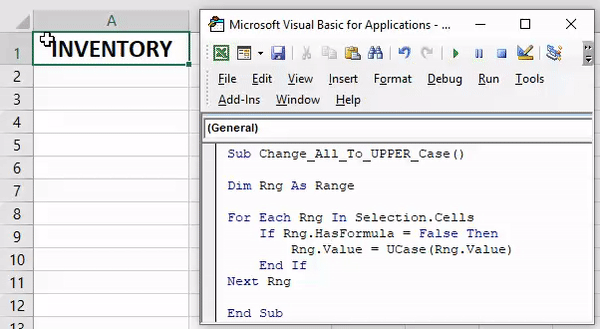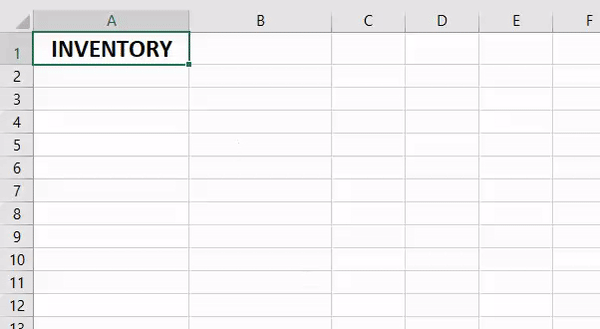
84. Convert to Upper Case
Sub convertUpperCase() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If Application.WorksheetFunction.IsText(Rng) Then Rng.Value = UCase(Rng) End If Next End Sub
Select the cells and run this code. It will check each and every cell of selected range and then convert it into upper case text.
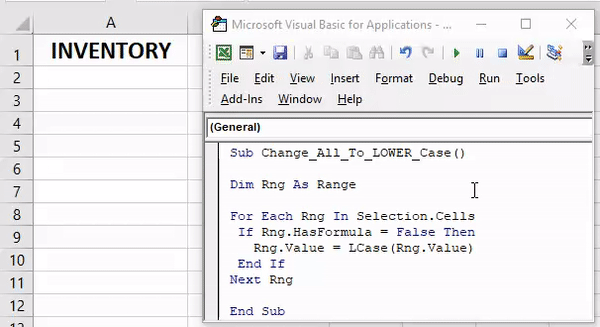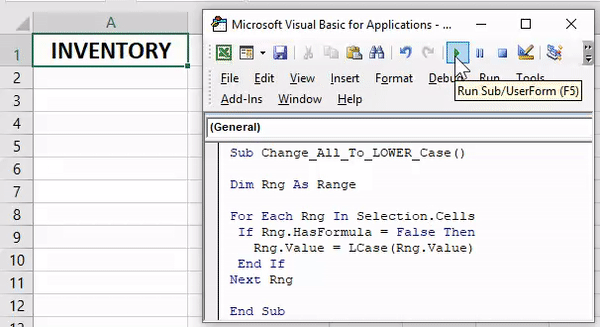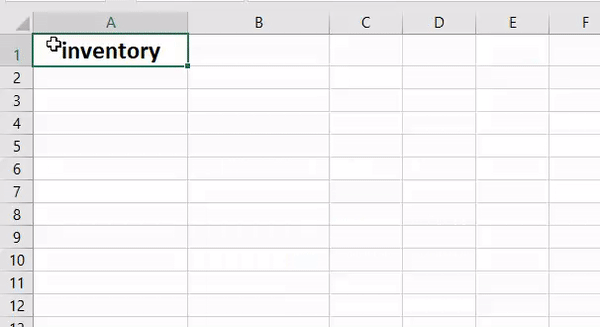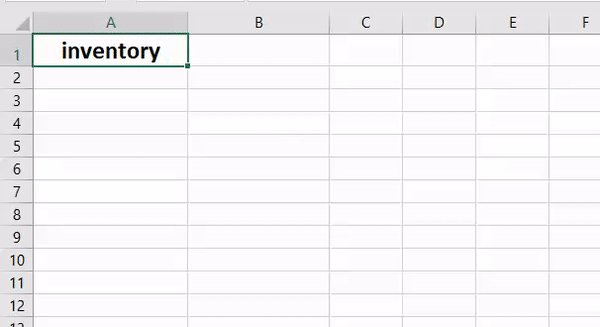
85. Convert to Lower Case
Sub convertLowerCase() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If Application.WorksheetFunction.IsText(Rng) Then Rng.Value= LCase(Rng) End If Next End Sub
This code will help you to convert selected text into lower case text. Just select a range of cells where you have text and run this code. If a cell has a number or any value other than text that value will remain same.
86. Convert to Proper Case
Sub convertProperCase() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsText(Rng) Then Rng.Value = WorksheetFunction.Proper(Rng.Value) End If Next End Sub
And this code will convert selected text into the proper case where you have the first letter in capital and rest in small.
87. Convert to Sentence Case
Sub convertTextCase() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsText(Rng) Then Rng.Value = UCase(Left(Rng, 1)) & LCase(Right(Rng, Len(Rng) - 1)) End If Next Rng End Sub
In text case, you have the first letter of the first word in capital and rest all in words in small for a single sentence and this code will help you convert normal text into sentence case.
88. Remove a Character from Selection
Sub removeChar()
Dim Rng As Range
Dim rc As String
rc = InputBox("Character(s) to Replace", "Enter Value")
For Each Rng In Selection
Selection.Replace What:=rc, Replacement:=""
Next
End Sub
To remove a particular character from a selected cell you can use this code. It will show you an input box to enter the character you want to remove.
89. Word Count from Entire Worksheet
Sub Word_Count_Worksheet() Dim WordCnt As Long Dim rng As Range Dim S As String Dim N As Long For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Cells S = Application.WorksheetFunction.Trim(rng.Text) N = 0 If S <> vbNullString Then N = Len(S) - Len(Replace(S, " ", "")) + 1 End If WordCnt = WordCnt + N Next rng MsgBox "There are total " _ & Format(WordCnt, "#,##0") & _ " words in the active worksheet" End Sub
It can help you to count all the words from a worksheet.
90. Remove the Apostrophe from a Number
Sub removeApostrophes() Selection.Value = Selection.Value End Sub
If you have numeric data where you have an apostrophe before each number, you run this code to remove it.
91. Remove Decimals from Numbers
Sub removeDecimals() Dim lnumber As Double Dim lResult As Long Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection rng.Value = Int(rng) rng.NumberFormat = "0" Next rng End Sub
This code will simply help you to remove all the decimals from the numbers from the selected range.
92. Multiply all the Values by a Number
Sub addNumber()
Dim rng As Range
Dim i As Integer
i = InputBox("Enter number to multiple", "Input Required")
For Each rng In Selection
If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(rng) Then
rng.Value = rng + i
Else
End If
Next rng
End Sub
Let’s you have a list of numbers and you want to multiply all the number with a particular. To use this code: Select that range of cells and run this code. It will first ask you for the number with whom you want to multiple and then instantly multiply all the numbers with it.
93. Add a Number in all the Numbers
Sub addNumber()
Dim rng As Range
Dim i As Integer
i = InputBox("Enter number to multiple", "Input Required")
For Each rng In Selection
If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(rng) Then
rng.Value = rng + i
Else
End If
Next rng
End Sub
Just like multiplying you can also add a number into a set of numbers.
94. Calculate the Square Root
Sub getSquareRoot() Dim rng As Range Dim i As Integer For Each rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(rng) Then rng.Value = Sqr(rng) Else End If Next rng End Sub
To calculate square root without applying a formula you can use this code. It will simply check all the selected cells and convert numbers to their square root.
95. Calculate the Cube Root
Sub getCubeRoot() Dim rng As Range Dimi As Integer For Each rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(rng) Then rng.Value = rng ^ (1 / 3) Else End If Nextrng End Sub
To calculate cube root without applying a formula you can use this code. It will simply check all the selected cells and convert numbers to their cube root.
96. Add A-Z Alphabets in a Range
Sub addsAlphabets1() Dim i As Integer For i = 65 To 90 ActiveCell.Value = Chr(i) ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select Next i End Sub
Sub addsAlphabets2() Dim i As Integer For i = 97 To 122 ActiveCell.Value = Chr(i) ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select Next i End Sub
Just like serial numbers you can also insert alphabets in your worksheet. Beloware the code which you can use.
97. Convert Roman Numbers into Arabic Numbers
Sub convertToNumbers() Dim rng As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each rng In Selection If Not WorksheetFunction.IsNonText(rng) Then rng.Value = WorksheetFunction.Arabic(rng) End If Next rng End Sub
Sometimes it’s really hard to understand Roman numbers as serial numbers. This code will help you to convert roman numbers into Arabic numbers.
98. Remove Negative Signs
Sub removeNegativeSign() Dim rng As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(rng) Then rng.Value = Abs(rng) End If Next rng
This code will simply check all the cell in the selection and convert all the negative numbers into positive. Just select a range and run this code.
99. Replace Blank Cells with Zeros
Sub replaceBlankWithZero() Dim rng As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each rng In Selection If rng = "" Or rng = " " Then rng.Value = "0" Else End If Next rng End Sub
For data where you have blank cells, you can use the below code to add zeros in all those cells. It makes easier to use those cells in further calculations.
More Codes
100. More VBA Examples and Tutorials
- User Defined Function [UDF] in Excel using VBA
- VBA Interview Questions
- Add a Comment in a VBA Code (Macro)
- Add a Line Break in a VBA Code (Single Line into Several Lines)
- Add a New Line (Carriage Return) in a String in VBA
- Personal Macro Workbook (personal.xlsb)
- Record a Macro in Excel
- VBA Exit Sub Statement
- VBA Immediate Window (Debug.Print)
- VBA Module
- VBA MSGBOX
- VBA Objects
- VBA With Statement
- Count Rows using VBA
- Excel VBA Font (Color, Size, Type, and Bold)
- Excel VBA Hide and Unhide a Column or a Row
- Excel VBA Range – Working with Range and Cells in VBA
- Apply Borders on a Cell using VBA in Excel
- Find Last Row, Column, and Cell using VBA in Excel
- Insert a Row using VBA in Excel
- Merge Cells in Excel using a VBA Code
- Select a Range/Cell using VBA in Excel
- How to SELECT ALL the Cells in a Worksheet using a VBA Code
- use ActiveCell in VBA in Excel
- How to use Special Cells Method in VBA in Excel
- How to use UsedRange Property in VBA in Excel
- VBA AutoFit (Rows, Column, or the Entire Worksheet)
- VBA ClearContents (from a Cell, Range, or Entire Worksheet)
- VBA Copy Range to Another Sheet + Workbook
- VBA Enter Value in a Cell (Set, Get and Change)
- VBA Insert Column (Single and Multiple)
- VBA Named Range
- VBA Range Offset
- VBA Sort Range | (Descending, Multiple Columns, Sort Orientation
- VBA Wrap Text (Cell, Range, and Entire Worksheet)
- How to CLEAR an Entire Sheet using VBA in Excel
- How to Copy and Move a Sheet in Excel using VBA
- How to COUNT Sheets using VBA in Excel
- How to DELETE a SHEET using VBA in Excel
- How to Hide & Unhide a Sheet using VBA in Excel
- How to PROTECT and UNPROTECT a Sheet using VBA in Excel
- RENAME a Sheet using VBA
- Write a VBA Code to Create a New Sheet
- VBA Worksheet Object
- Activate a Sheet using VBA
- Copy an Excel File (Workbook)
- VBA Activate Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Close Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Combine Workbooks (Excel Files)
- VBA Create New Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Delete Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Open Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Protect/Unprotect Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Rename Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Save Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA ThisWorkbook (Current Excel File)
- VBA Workbook
- Declare Global Variable (Public) in VBA
- Range or a Cell as a Variable in VBA
- Option Explicit Statement in VBA
- Variable in a Message Box
- VBA Constants
- VBA Dim Statement
- VBA Variables (Declare, Data Types, and Scope)
- VBA Add New Value to the Array
- VBA Array
- VBA Array Length (Size)
- VBA Array with Strings
- VBA Clear Array (Erase)
- VBA Dynamic Array
- VBA Loop Through an Array
- VBA Multi-Dimensional Array
- VBA Range to an Array
- VBA Search for a Value in an Array
- VBA Sort Array
- How to Average Values in Excel using VBA
- Get Today’s Date and Current Time using VBA
- Sum Values in Excel using VBA
- Match Function in VBA
- MOD in VBA
- Random Number
- VBA Calculate (Cell, Range, Row, & Workbook)
- VBA Concatenate
- VBA Worksheet Function (Use Excel Functions in a Macro)
- How to Check IF a Sheet Exists using VBA in Excel
- VBA Check IF a Cell is Empty + Multiple Cells
- VBA Check IF a Workbook Exists in a Folder (Excel File)
- VBA Check IF a Workbook is Open (Excel File)
- VBA Exit IF
- VBA IF – IF Then Else Statement
- VBA IF And (Test Multiple Conditions)
- VBA IF Not
- VBA IF OR (Test Multiple Conditions)
- VBA Nested IF
- VBA SELECT CASE Statement (Test Multiple Conditions)
- VBA Automation Error (Error 440)
- VBA Error 400
- VBA ERROR Handling
- VBA Invalid Procedure Call Or Argument Error (Error 5)
- VBA Object Doesn’t Support this Property or Method Error (Error 438)
- VBA Object Required Error (Error 424)
- VBA Out of Memory Error (Error 7)
- VBA Overflow Error (Error 6)
- VBA Runtime Error (Error 1004)
- VBA Subscript Out of Range Runtime Error (Error 9)
- VBA Type Mismatch Error (Error 13)
- Excel VBA Do While Loop and (Do Loop While)
- How to Loop Through All the Sheets using VBA
- Loop Through a Range using VBA
- VBA FOR LOOP
- VBA GoTo Statement
- Input Box in VBA
- VBA Create and Write to a Text File
- VBA ScreenUpdating
- VBA Status Bar
- VBA Wait and Sleep
About the Author
Puneet is using Excel since his college days. He helped thousands of people to understand the power of the spreadsheets and learn Microsoft Excel. You can find him online, tweeting about Excel, on a running track, or sometimes hiking up a mountain.
Время на прочтение
7 мин
Количество просмотров 312K
Приветствую всех.
В этом посте я расскажу, что такое VBA и как с ним работать в Microsoft Excel 2007/2010 (для более старых версий изменяется лишь интерфейс — код, скорее всего, будет таким же) для автоматизации различной рутины.

VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) — это упрощенная версия Visual Basic, встроенная в множество продуктов линейки Microsoft Office. Она позволяет писать программы прямо в файле конкретного документа. Вам не требуется устанавливать различные IDE — всё, включая отладчик, уже есть в Excel.
Еще при помощи Visual Studio Tools for Office можно писать макросы на C# и также встраивать их. Спасибо, FireStorm.
Сразу скажу — писать на других языках (C++/Delphi/PHP) также возможно, но требуется научится читать, изменять и писать файлы офиса — встраивать в документы не получится. А интерфейсы Microsoft работают через COM. Чтобы вы поняли весь ужас, вот Hello World с использованием COM.
Поэтому, увы, будем учить Visual Basic.
Чуть-чуть подготовки и постановка задачи
Итак, поехали. Открываем Excel.
Для начала давайте добавим в Ribbon панель «Разработчик». В ней находятся кнопки, текстовые поля и пр. элементы для конструирования форм.
Появилась вкладка.
Теперь давайте подумаем, на каком примере мы будем изучать VBA. Недавно мне потребовалось красиво оформить прайс-лист, выглядевший, как таблица. Идём в гугл, набираем «прайс-лист» и качаем любой, который оформлен примерно так (не сочтите за рекламу, пожалуйста):
То есть требуется, чтобы было как минимум две группы, по которым можно объединить товары (в нашем случае это будут Тип и Производитель — в таком порядке). Для того, чтобы предложенный мною алгоритм работал корректно, отсортируйте товары так, чтобы товары из одной группы стояли подряд (сначала по Типу, потом по Производителю).
Результат, которого хотим добиться, выглядит примерно так:
Разумеется, если смотреть прайс только на компьютере, то можно добавить фильтры и будет гораздо удобнее искать нужный товар. Однако мы хотим научится кодить и задача вполне подходящая, не так ли?
Кодим
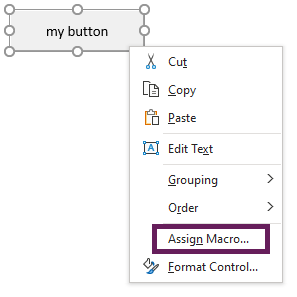
Для начала требуется создать кнопку, при нажатии на которую будет вызываться наша програма. Кнопки находятся в панели «Разработчик» и появляются по кнопке «Вставить». Вам нужен компонент формы «Кнопка». Нажали, поставили на любое место в листе. Далее, если не появилось окно назначения макроса, надо нажать правой кнопкой и выбрать пункт «Назначить макрос». Назовём его FormatPrice. Важно, чтобы перед именем макроса ничего не было — иначе он создастся в отдельном модуле, а не в пространстве имен книги. В этому случае вам будет недоступно быстрое обращение к выделенному листу. Нажимаем кнопку «Новый».
И вот мы в среде разработки VB. Также её можно вызвать из контекстного меню командой «Исходный текст»/«View code».
Перед вами окно с заглушкой процедуры. Можете его развернуть. Код должен выглядеть примерно так:
Sub FormatPrice()End Sub
Напишем Hello World:
Sub FormatPrice()
MsgBox "Hello World!"
End Sub
И запустим либо щелкнув по кнопке (предварительно сняв с неё выделение), либо клавишей F5 прямо из редактора.
Тут, пожалуй, следует отвлечься на небольшой ликбез по поводу синтаксиса VB. Кто его знает — может смело пропустить этот раздел до конца. Основное отличие Visual Basic от Pascal/C/Java в том, что команды разделяются не ;, а переносом строки или двоеточием (:), если очень хочется написать несколько команд в одну строку. Чтобы понять основные правила синтаксиса, приведу абстрактный код.
Примеры синтаксиса
' Процедура. Ничего не возвращает
' Перегрузка в VBA отсутствует
Sub foo(a As String, b As String)
' Exit Sub ' Это значит "выйти из процедуры"
MsgBox a + ";" + b
End Sub' Функция. Вовращает Integer
Function LengthSqr(x As Integer, y As Integer) As Integer
' Exit Function
LengthSqr = x * x + y * y
End FunctionSub FormatPrice()
Dim s1 As String, s2 As String
s1 = "str1"
s2 = "str2"
If s1 <> s2 Then
foo "123", "456" ' Скобки при вызове процедур запрещены
End IfDim res As sTRING ' Регистр в VB не важен. Впрочем, редактор Вас поправит
Dim i As Integer
' Цикл всегда состоит из нескольких строк
For i = 1 To 10
res = res + CStr(i) ' Конвертация чего угодно в String
If i = 5 Then Exit For
Next iDim x As Double
x = Val("1.234") ' Парсинг чисел
x = x + 10
MsgBox xOn Error Resume Next ' Обработка ошибок - игнорировать все ошибки
x = 5 / 0
MsgBox xOn Error GoTo Err ' При ошибке перейти к метке Err
x = 5 / 0
MsgBox "OK!"
GoTo ne
Err:
MsgBox
"Err!"
ne:
On Error GoTo 0 ' Отключаем обработку ошибок
' Циклы бывает, какие захотите
Do While True
Exit DoLoop 'While True
Do 'Until False
Exit Do
Loop Until False
' А вот при вызове функций, от которых хотим получить значение, скобки нужны.
' Val также умеет возвращать Integer
Select Case LengthSqr(Len("abc"), Val("4"))
Case 24
MsgBox "0"
Case 25
MsgBox "1"
Case 26
MsgBox "2"
End Select' Двухмерный массив.
' Можно также менять размеры командой ReDim (Preserve) - см. google
Dim arr(1 to 10, 5 to 6) As Integer
arr(1, 6) = 8Dim coll As New Collection
Dim coll2 As Collection
coll.Add "item", "key"
Set coll2 = coll ' Все присваивания объектов должны производится командой Set
MsgBox coll2("key")
Set coll2 = New Collection
MsgBox coll2.Count
End Sub
Грабли-1. При копировании кода из IDE (в английском Excel) есь текст конвертируется в 1252 Latin-1. Поэтому, если хотите сохранить русские комментарии — надо сохранить крокозябры как Latin-1, а потом открыть в 1251.
Грабли-2. Т.к. VB позволяет использовать необъявленные переменные, я всегда в начале кода (перед всеми процедурами) ставлю строчку Option Explicit. Эта директива запрещает интерпретатору заводить переменные самостоятельно.
Грабли-3. Глобальные переменные можно объявлять только до первой функции/процедуры. Локальные — в любом месте процедуры/функции.
Еще немного дополнительных функций, которые могут пригодится: InPos, Mid, Trim, LBound, UBound. Также ответы на все вопросы по поводу работы функций/их параметров можно получить в MSDN.
Надеюсь, что этого Вам хватит, чтобы не пугаться кода и самостоятельно написать какое-нибудь домашнее задание по информатике. По ходу поста я буду ненавязчиво знакомить Вас с новыми конструкциями.
Кодим много и под Excel
В этой части мы уже начнём кодить нечто, что умеет работать с нашими листами в Excel. Для начала создадим отдельный лист с именем result (лист с данными назовём data). Теперь, наверное, нужно этот лист очистить от того, что на нём есть. Также мы «выделим» лист с данными, чтобы каждый раз не писать длинное обращение к массиву с листами.
Sub FormatPrice()
Sheets("result").Cells.Clear
Sheets("data").Activate
End Sub
Работа с диапазонами ячеек
Вся работа в Excel VBA производится с диапазонами ячеек. Они создаются функцией Range и возвращают объект типа Range. У него есть всё необходимое для работы с данными и/или оформлением. Кстати сказать, свойство Cells листа — это тоже Range.
Примеры работы с Range
Sheets("result").Activate
Dim r As Range
Set r = Range("A1")
r.Value = "123"
Set r = Range("A3,A5")
r.Font.Color = vbRed
r.Value = "456"
Set r = Range("A6:A7")
r.Value = "=A1+A3"
Теперь давайте поймем алгоритм работы нашего кода. Итак, у каждой строчки листа data, начиная со второй, есть некоторые данные, которые нас не интересуют (ID, название и цена) и есть две вложенные группы, к которым она принадлежит (тип и производитель). Более того, эти строки отсортированы. Пока мы забудем про пропуски перед началом новой группы — так будет проще. Я предлагаю такой алгоритм:
- Считали группы из очередной строки.
- Пробегаемся по всем группам в порядке приоритета (вначале более крупные)
- Если текущая группа не совпадает, вызываем процедуру AddGroup(i, name), где i — номер группы (от номера текущей до максимума), name — её имя. Несколько вызовов необходимы, чтобы создать не только наш заголовок, но и всё более мелкие.
- После отрисовки всех необходимых заголовков делаем еще одну строку и заполняем её данными.
Для упрощения работы рекомендую определить следующие функции-сокращения:
Function GetCol(Col As Integer) As String
GetCol = Chr(Asc("A") + Col)
End FunctionFunction GetCellS(Sheet As String, Col As Integer, Row As Integer) As Range
Set GetCellS = Sheets(Sheet).Range(GetCol(Col) + CStr(Row))
End FunctionFunction GetCell(Col As Integer, Row As Integer) As Range
Set GetCell = Range(GetCol(Col) + CStr(Row))
End Function
Далее определим глобальную переменную «текущая строчка»: Dim CurRow As Integer. В начале процедуры её следует сделать равной единице. Еще нам потребуется переменная-«текущая строка в data», массив с именами групп текущей предыдущей строк. Потом можно написать цикл «пока первая ячейка в строке непуста».
Глобальные переменные
Option Explicit ' про эту строчку я уже рассказывал
Dim CurRow As Integer
Const GroupsCount As Integer = 2
Const DataCount As Integer = 3
FormatPrice
Sub FormatPrice()
Dim I As Integer ' строка в data
CurRow = 1
Dim Groups(1 To GroupsCount) As String
Dim PrGroups(1 To GroupsCount) As String
Sheets(
"data").Activate
I = 2
Do While True
If GetCell(0, I).Value = "" Then Exit Do
' ...
I = I + 1
Loop
End Sub
Теперь надо заполнить массив Groups:
На месте многоточия
Dim I2 As Integer
For I2 = 1 To GroupsCount
Groups(I2) = GetCell(I2, I)
Next I2
' ...
For I2 = 1 To GroupsCount ' VB не умеет копировать массивы
PrGroups(I2) = Groups(I2)
Next I2
I = I + 1
И создать заголовки:
На месте многоточия в предыдущем куске
For I2 = 1 To GroupsCount
If Groups(I2) <> PrGroups(I2) Then
Dim I3 As Integer
For I3 = I2 To GroupsCount
AddHeader I3, Groups(I3)
Next I3
Exit For
End If
Next I2
Не забудем про процедуру AddHeader:
Перед FormatPrice
Sub AddHeader(Ty As Integer, Name As String)
GetCellS("result", 1, CurRow).Value = Name
CurRow = CurRow + 1
End Sub
Теперь надо перенести всякую информацию в result
For I2 = 0 To DataCount - 1
GetCellS("result", I2, CurRow).Value = GetCell(I2, I)
Next I2
Подогнать столбцы по ширине и выбрать лист result для показа результата
После цикла в конце FormatPrice
Sheets("Result").Activate
Columns.AutoFit
Всё. Можно любоваться первой версией.
Некрасиво, но похоже. Давайте разбираться с форматированием. Сначала изменим процедуру AddHeader:
Sub AddHeader(Ty As Integer, Name As String)
Sheets("result").Range("A" + CStr(CurRow) + ":C" + CStr(CurRow)).Merge
' Чтобы не заводить переменную и не писать каждый раз длинный вызов
' можно воспользоваться блоком With
With GetCellS("result", 0, CurRow)
.Value = Name
.Font.Italic = True
.Font.Name = "Cambria"
Select Case Ty
Case 1 ' Тип
.Font.Bold = True
.Font.Size = 16
Case 2 ' Производитель
.Font.Size = 12
End Select
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
End With
CurRow = CurRow + 1
End Sub
Уже лучше:
Осталось только сделать границы. Тут уже нам требуется работать со всеми объединёнными ячейками, иначе бордюр будет только у одной:
Поэтому чуть-чуть меняем код с добавлением стиля границ:
Sub AddHeader(Ty As Integer, Name As String)
With Sheets("result").Range("A" + CStr(CurRow) + ":C" + CStr(CurRow))
.Merge
.Value = Name
.Font.Italic = True
.Font.Name = "Cambria"
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenterSelect Case Ty
Case 1 ' Тип
.Font.Bold = True
.Font.Size = 16
.Borders(xlTop).Weight = xlThick
Case 2 ' Производитель
.Font.Size = 12
.Borders(xlTop).Weight = xlMedium
End Select
.Borders(xlBottom).Weight = xlMedium ' По убыванию: xlThick, xlMedium, xlThin, xlHairline
End With
CurRow = CurRow + 1
End Sub
Осталось лишь добится пропусков перед началом новой группы. Это легко:
В начале FormatPrice
Dim I As Integer ' строка в data
CurRow = 0 ' чтобы не было пропуска в самом начале
Dim Groups(1 To GroupsCount) As String
В цикле расстановки заголовков
If Groups(I2) <> PrGroups(I2) Then
CurRow = CurRow + 1
Dim I3 As Integer
В точности то, что и хотели.
Надеюсь, что эта статья помогла вам немного освоится с программированием для Excel на VBA. Домашнее задание — добавить заголовки «ID, Название, Цена» в результат. Подсказка: CurRow = 0 CurRow = 1.
Файл можно скачать тут (min.us) или тут (Dropbox). Не забудьте разрешить исполнение макросов. Если кто-нибудь подскажет человеческих файлохостинг, залью туда.
Спасибо за внимание.
Буду рад конструктивной критике в комментариях.
UPD: Перезалил пример на Dropbox и min.us.
UPD2: На самом деле, при вызове процедуры с одним параметром скобки можно поставить. Либо использовать конструкцию Call Foo(«bar», 1, 2, 3) — тут скобки нужны постоянно.
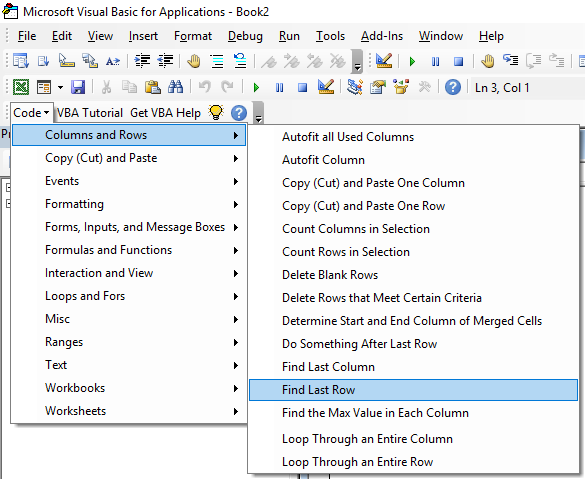
VBA Code Examples
AutoMacro: VBA Add-in with Hundreds of Ready-To-Use VBA Code Examples & much more!
Search the list below for free Excel VBA code examples complete with explanations.
Some include downloadable files as well. These Excel VBA Macros & Scripts are professionally developed and ready-to-use.
We hope you find this list useful!
Excel Macro Examples
Below you will find a list of basic macro examples for common Excel automation tasks.
Copy and Paste a Row from One Sheet to Another
This super simple macro will copy a row from one sheet to another.
Sub Paste_OneRow()
'Copy and Paste Row
Sheets("sheet1").Range("1:1").Copy Sheets("sheet2").Range("1:1")
Application.CutCopyMode = False
End SubSend Email
This useful macro will launch Outlook, draft an email, and attach the ActiveWorkbook.
Sub Send_Mail()
Dim OutApp As Object
Dim OutMail As Object
Set OutApp = CreateObject("Outlook.Application")
Set OutMail = OutApp.CreateItem(0)
With OutMail
.to = "test@test.com"
.Subject = "Test Email"
.Body = "Message Body"
.Attachments.Add ActiveWorkbook.FullName
.Display
End With
Set OutMail = Nothing
Set OutApp = Nothing
End SubList All Sheets in Workbook
This macro will list all sheets in a workbook.
Sub ListSheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim x As Integer
x = 1
ActiveSheet.Range("A:A").Clear
For Each ws In Worksheets
ActiveSheet.Cells(x, 1) = ws.Name
x = x + 1
Next ws
End SubUnhide All Worksheets
This macro will unhide all worksheets.
' Unhide All Worksheets
Sub UnhideAllWoksheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets
ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible
Next ws
End SubHide All Worksheets Except Active
This macro will hide all worksheets except the active worksheet.
' Hide All Sheets Except Active Sheet
Sub HideAllExceptActiveSheet()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If ws.Name <> ActiveSheet.Name Then ws.Visible = xlSheetHidden
Next ws
End SubUnprotect All Worksheets
This macro example will unprotect all worksheets in a workbook.
' UnProtect All Worksheets
Sub UnProtectAllSheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In Worksheets
ws.Unprotect "password"
Next ws
End SubProtect All Worksheets
This macro will protect all worksheets in a workbook.
' Protect All Worksheets
Sub ProtectAllSheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In Worksheets
ws.protect "password"
Next ws
End SubDelete All Shapes
This macro will delete all shapes in a worksheet.
Sub DeleteAllShapes()
Dim GetShape As Shape
For Each GetShape In ActiveSheet.Shapes
GetShape.Delete
Next
End SubDelete All Blank Rows in Worksheet
This example macro will delete all blank rows in a worksheet.
Sub DeleteBlankRows()
Dim x As Long
With ActiveSheet
For x = .Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell).Row To 1 Step -1
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(.Rows(x)) = 0 Then
ActiveSheet.Rows(x).Delete
End If
Next
End With
End SubHighlight Duplicate Values in Selection
Use this simple macro to highlight all duplicate values in a selection.
' Highlight Duplicate Values in Selection
Sub HighlightDuplicateValues()
Dim myRange As Range
Dim cell As Range
Set myRange = Selection
For Each cell In myRange
If WorksheetFunction.CountIf(myRange, cell.Value) > 1 Then
cell.Interior.ColorIndex = 36
End If
Next cell
End SubHighlight Negative Numbers
This macro automates the task of highlighting negative numbers.
' Highlight Negative Numbers
Sub HighlightNegativeNumbers()
Dim myRange As Range
Dim cell As Range
Set myRange = Selection
For Each cell In myRange
If cell.Value < 0 Then
cell.Interior.ColorIndex = 36
End If
Next cell
End SubHighlight Alternate Rows
This macro is useful to highlight alternate rows.
' Highlight Alternate Rows
Sub highlightAlternateRows()
Dim cell As Range
Dim myRange As Range
myRange = Selection
For Each cell In myRange.Rows
If cell.Row Mod 2 = 1 Then
cell.Interior.ColorIndex = 36
End If
Next cell
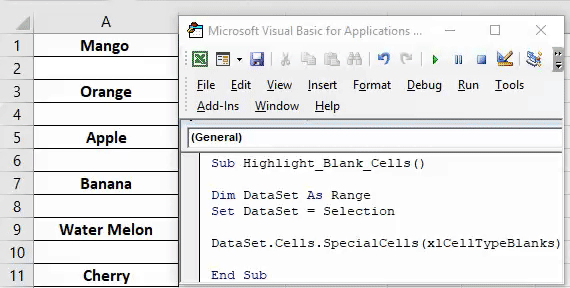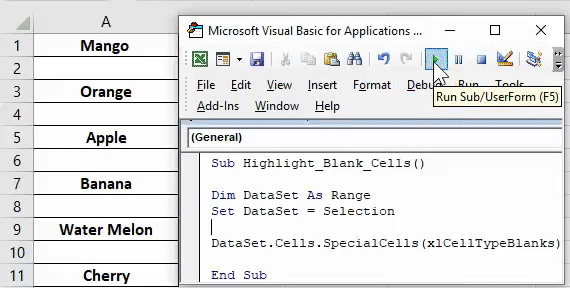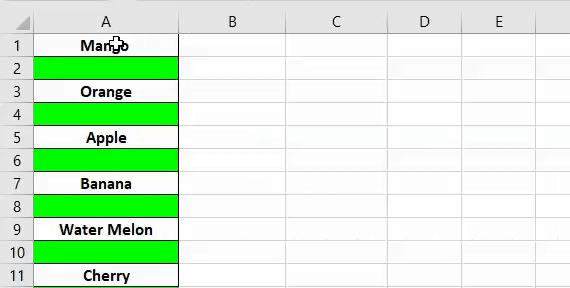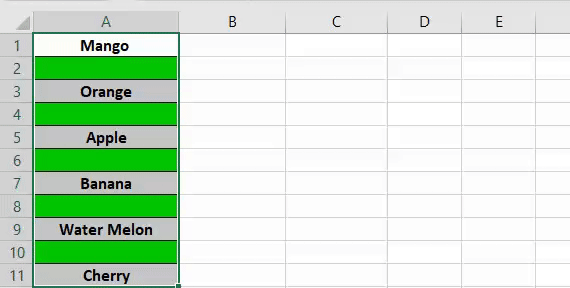
End SubHighlight Blank Cells in Selection
This basic macro highlights blank cells in a selection.
' Highlight all Blank Cells in Selection
Sub HighlightBlankCells()
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Selection
rng.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks).Interior.Color = vbCyan
End SubExcel VBA Macros Examples – Free Download
We’ve created a free VBA (Macros) Code Examples add-in. The add-in contains over 100 ready-to-use macro examples, including the macro examples above!
Download Page
Excel Macro / VBA FAQs
How to write VBA code (Macros) in Excel?
To write VBA code in Excel open up the VBA Editor (ALT + F11). Type “Sub HelloWorld”, Press Enter, and you’ve created a Macro! OR Copy and paste one of the procedures listed on this page into the code window.
What is Excel VBA?
VBA is the programming language used to automate Excel.
How to use VBA to automate Excel?
You use VBA to automate Excel by creating Macros. Macros are blocks of code that complete certain tasks.
Practice VBA
You can practice VBA with our interactive VBA tutorial.
With macros, we can automate Excel and save time; big tasks or small tasks, it doesn’t matter. All that matters is that we’ve become more efficient.
In this post, I share 30 of the most useful VBA codes for Excel that you can use today.
If you’ve never used VBA before, that’s fine. Part 1 contains instructions of how to use the codes and part 2 contains the code sample themselves.
Download the eBook

Get our FREE VBA eBook of the 30 most useful Excel VBA macros.
Claim your free eBook
PART ONE: How to use VBA Macros
What is VBA?
Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is the programming language created by Microsoft to control parts of their applications. Most things which you can do with the mouse or keyboard in the Microsoft Office suite, you can also do using VBA. For example, in Excel, you can create a chart; you can also create a chart using VBA, it is just another method of achieving the same thing.
Advantages of using VBA
Since VBA code can do the same things as we could with the mouse or keyboard, why bother to use VBA at all?
Saves time:
VBA code will operate at the speed your computer will allow, which is still significantly faster than you can operate. For example, if you have to open 10 workbooks, print the documents, then close the workbook, it might take you 2 minutes with a mouse and keyboard, but with VBA it could take seconds.
Reduces errors:
Do you ever click the wrong icons or type the wrong words? Me too, but VBA doesn’t. It will do the same task over and over again, without making any errors. Don’t get me wrong, you still have to program the VBA code correctly. If you tell it to do the wrong things 10 times, then it will. But if we can get it right, then it can remove the errors created by human interaction.
Completes repetitive actions without complaining:
Have you ever had to carry out the same action many times? Maybe creating 100 charts, or printing 100 documents, or changing the heading on 100 spreadsheets. That’s not fun, nobody wants to do that. But VBA is more than happy to do it for you. It can do the same thing in a repetitive way (without complaining). In fact, repetitive tasks is one of the things VBA does best.
Integration with other applications:
You can use VBA in Word, Access, Excel, Outlook and many other programs, including Windows itself. But it doesn’t end there, you can use VBA in Excel to control Word and PowerPoint, without even needing to open those applications.
What is programming?
Programming is simply writing words in a way which a computer can understand. However, computers are not particularly flexible, so we have to be very specific about what we want the computer to do, and how we tell it to do it. The skill of programming is learning how to convey the request to the computer as clearly, as simply and as efficiently as possible.
What is the difference between a Macro and VBA?
This is a common question which can be confusing. Put simply, VBA is the language used to write a macro – just in the same way as a paragraph might be written using the English language.
The terms ‘macro’ and ‘VBA’ are often used interchangeably.
The golden rule of learning VBA
If you are still learning to write VBA, there is one thing which will help you. While it may be common practice, to copy and paste code, it will not help you to learn VBA quickly. Here is the one rule I am going to ask you to stick to… type out the code yourself.
Why am I asking you to do this? Because it will help you learn the VBA language much faster.
Let’s get started
Now you know what VBA is, why you should use it, and the golden rule, so there is only one thing left to do… let’s get started!
Setting up Excel
Before you can get stuck in with using the code in this post, you must first have Excel set up correctly. This involves:
- Ensuring the correct macro security settings have been applied
- Enabling the Developer ribbon.
Macro security settings
Macros can be used for malicious purposes, such as installing a virus, recording key-strokes, etc. This can be blocked with the security settings. However, if the settings are set too high, you cannot run any macros, or too low, you will not be protected. Neither of these is a good option.
Let’s apply suitable settings which will give you the power to decide when to allow macros or not.
- In Excel, click File > Options
- In the Excel Options dialog box, click Trust Centre > Trust Centre Settings…
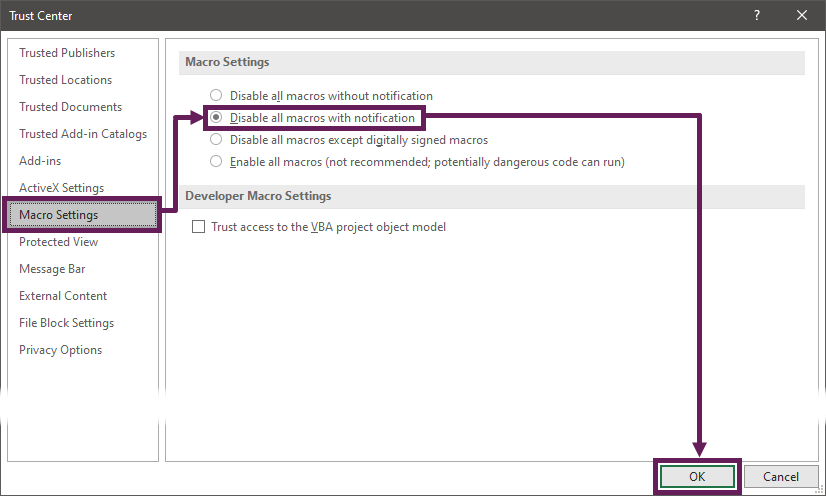
- In the Trust Centre dialog box, click Macro Settings > Disable all macros with notification.
- Click OK to close the Trust Centre, then OK again to close the Excel Options.
Workbooks containing macros will now be automatically disabled until you click the Enable Content button at the top of the screen.
Enable the Developer ribbon
The Developer ribbon is the place where all the VBA tools are kept. It is unlikely that this is already enabled, unless you or your IT department have already done so.
Look at the top of your Excel Window if you see the word ‘Developer’ in the menu options, then you are ready to go. You can skip straight ahead to the next part. However, if the ‘Developer’ ribbon is not there, just follow these instructions.
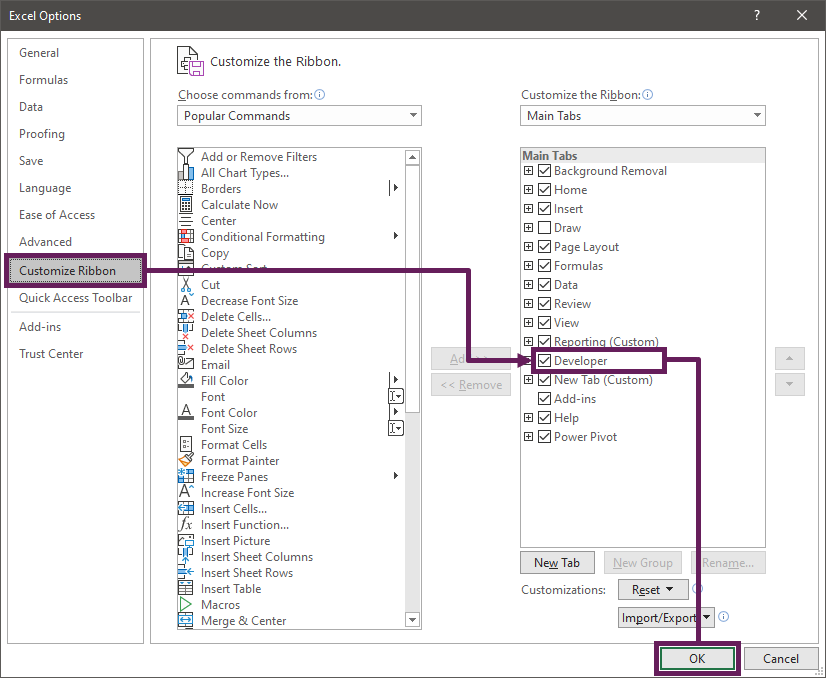
- In Excel, click File > Options
- In the Excel Options dialog box, click Customize Ribbon
- Ensure the Developer option is checked
- Click OK to close the Excel Options
The Developer ribbon should now be visible at the top of the Excel window.
File format for macro enabled files
To save a workbook containing a macro, the standard .xlsx format will not work.
Generally, the .xlsm (Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook) file format should be used for workbooks containing macros. However .xlam (Excel Add-in), .xlsb (Excel Binary Workbook) and .xltx (Excel Macro-Enabled Template) are scenario specific formats which can also contain macros.
The legacy .xls and .xla file formats can both contain macros. They were superseded in 2007, and should now be avoided.
The basic rule is… if you don’t know, go for .xlsm.
Personal macro workbook
If we want macros to be reusable for many workbooks, often the best place to save them is in the personal macro workbook.
A personal macro workbook is a hidden file which opens whenever the Excel application opens.
How to create a personal macro workbook?
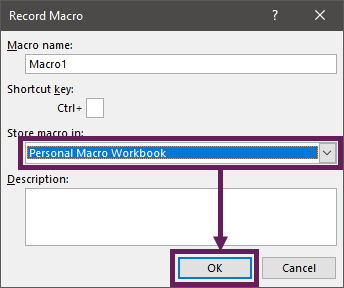
A personal macro workbook does not exist by default; we have to create it. There are many ways to do this, but the easiest is to let Excel do it for us.
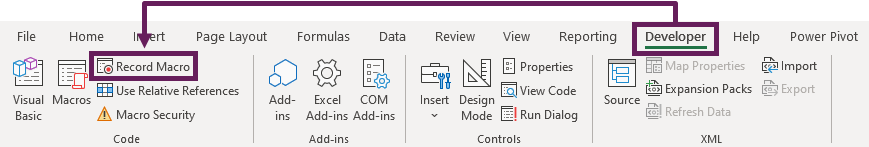
- In the ribbon, click Developer > Record Macro.
- In the Record Macro dialog box, select Personal Macro Workbook from the drop-down list.
- Click OK.
- Do anything in Excel, such as typing your name into cell A1.
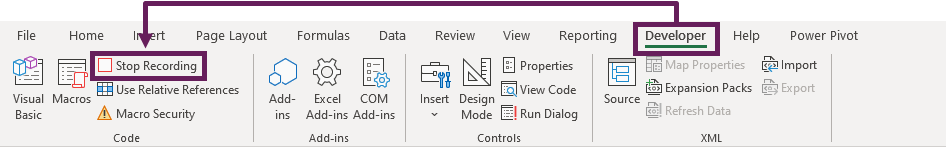
- Click Developer > Stop Recording
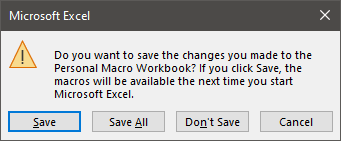
- Close all the open workbooks in Excel, this will force the personal macro workbook to be saved. A warning message will appear, click Save.
In the next part, we will learn how to use the Visual Basic Editor, which gives us access to the personal macro workbook.
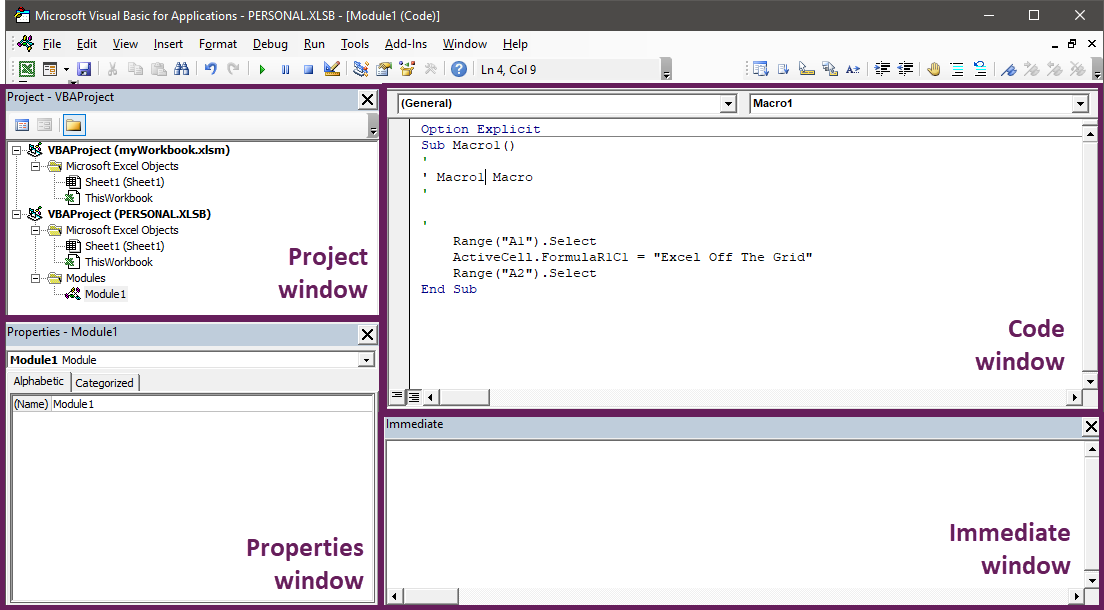
Using the Visual Basic Editor
The Visual Basic Editor (or VBE as it can be known) is the place where we enter or edit VBA code. The Visual Basic Editor is found within the Developer Ribbon
In Excel, click Developer > Visual Basic to open the VBE.
Alternatively, you could use the keyboard; press ALT+F11 (the + indicates that you should hold down the ALT key, press F11, then release the ALT key), which toggles between the Excel window and the VBE.
The Visual Basic Editor Window
The Visual Basic Editor contains four main sections.
Within the top left of the VBE, we will see a list of items which can contain VBA code (known as the project window)
Double-clicking any sheet name, workbook or module, will open the code window associated with that item. VBA code is entered into the code window.
Unless you have specific reasons, the best option is to enter the macro into a module. To create a module, click Insert > Module within the VBE.
Running a macro
There are many ways to run VBA code. This section is not exhaustive, but is intended to provide an overview of the most common methods.
Running a macro from within Visual Basic Editor
When testing VBA code, it is common to execute that code from the VBE.
Click anywhere within the code, between the Sub and End Sub lines, choose one of the following options:
- Click Run > Run Sub/UserForm from the menu at the top of the VBE
- Using the keyboard, you can press ALT+F5
- Click the play button at the top of the VBE
The code you entered will be executed.
Running a macro from within Excel
Once the code has been tested and in working order, it is common to execute it directly within Excel. There are lots of options for this too (including events, or user defined functions), however the three most common methods I will show you are:
Run from the Macro window
- Click View > Macros or Developer > Macros
- Select the macro from the list and click Run.
Create a custom ribbon
Having macros always available in the ribbon is a great time saver. Therefore, learning how to customize the ribbon is useful.
- In Excel, click File > Options
- In the Excel Options dialog box, click Customize Ribbon
- Click New Tab to create a new ribbon tab, then click New Group to create a section within the new tab.
- In the Choose commands from drop-down, select Macros. Select your macro and click
Add >> to move the macro it into your new group. - Use the Rename… button to give the tab, group or macro a more useful name.
- Click OK to close the window.
- The new ribbon menu will appear containing your macro. Click the button to run the macro.
Create a button/shape on a worksheet
Macros can be executed using buttons or shapes on the worksheet.
- To create a button, click Developer > Insert > Form Control > Button
- Draw a shape on the worksheet to show the location and size of the button
- The Assign Macro dialog will appear, select the macro and click OK.
- The button will appear. Clicking the button will run the macro
- Right-click on the button to change the description
To assign a different macro, right-click on the button and select Assign Macro… from the menu.
Alternatively, a macro can be assigned to a shape. After creating a shape, right-click on it and select Assign Macro… from the menu, then follow the same process as for a button.
Hide all selected sheets
What does it do?
Hides all the selected sheets.
VBA code
Sub HideAllSelectedSheets() 'Create variable to hold worksheets Dim ws As Worksheet 'Ignore error if trying to hide the last worksheet On Error Resume Next 'Loop through each worksheet in the active workbook For Each ws In ActiveWindow.SelectedSheets 'Hide each sheet ws.Visible = xlSheetHidden Next ws 'Allow errors to appear On Error GoTo 0 End Sub
Notes:
Excel requires at least one active worksheet. If all the visible sheets are selected, to avoid an error, the VBA code will not hide the last sheet.
For other examples of hiding worksheets check out these posts:
- Macro to hide all sheets except one
- Hide all sheets except one with Office Scripts
Unhide all sheets
What does it do?
Makes all worksheets visible.
VBA code
Sub UnhideAllWorksheets() 'Create variable to hold worksheets Dim ws As Worksheet 'Loop through each worksheet in the active workbook For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets 'Unhide each sheet ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible Next ws End Sub
Protect all selected worksheets
What does it do?
Protects all the selected worksheets with a password determined by the user.
VBA code
Sub ProtectSelectedWorksheets() Dim ws As Worksheet Dim sheetArray As Variant Dim myPassword As Variant 'Set the password myPassword = Application.InputBox(prompt:="Enter password", _ Title:="Password", Type:=2) 'The User clicked Cancel If myPassword = False Then Exit Sub 'Capture the selected sheets Set sheetArray = ActiveWindow.SelectedSheets 'Loop through each worksheet in the active workbook For Each ws In sheetArray On Error Resume Next 'Select the worksheet ws.Select 'Protect each worksheet ws.Protect Password:=myPassword On Error GoTo 0 Next ws sheetArray.Select End Sub
Unprotect all worksheets
What does it do?
Unprotects all worksheets with a password determined by the user.
VBA code
Sub UnprotectAllWorksheets() 'Create a variable to hold worksheets Dim ws As Worksheet 'Create a variable to hold the password Dim myPassword As Variant 'Set the password myPassword = Application.InputBox(prompt:="Enter password", _ Title:="Password", Type:=2) 'The User clicked Cancel If myPassword = False Then Exit Sub 'Loop through each worksheet in the active workbook For Each ws In ActiveWindow.SelectedSheets 'Protect each worksheet ws.Unprotect Password:=myPassword Next ws End Sub
Lock cells containing formulas
What does it do?
Password protects a single worksheet with cells containing formulas locked, all other cells are unlocked.
VBA code
Sub LockOnlyCellsWithFormulas() 'Create a variable to hold the password Dim myPassword As Variant 'If more than one worksheet selected exit the macro If ActiveWindow.SelectedSheets.Count > 1 Then 'Display error message and exit macro MsgBox "Select one worksheet and try again" Exit Sub End If 'Set the password myPassword = Application.InputBox(prompt:="Enter password", _ Title:="Password", Type:=2) 'The User clicked Cancel If myPassword = False Then Exit Sub 'All the following to apply to active sheet With ActiveSheet 'Ignore errors caused by incorrect passwords On Error Resume Next 'Unprotect the active sheet .Unprotect Password:=myPassword 'If error occured then exit macro If Err.Number <> 0 Then 'Display message then exit MsgBox "Incorrect password" Exit Sub End If 'Turn error checking back on On Error GoTo 0 'Remove lock setting from all cells .Cells.Locked = False 'Add lock setting to all cells .Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeFormulas).Locked = True 'Protect the active sheet .Protect Password:=myPassword End With End Sub
Hide formulas when protected
What does it do?
When the active sheet is protected, formulas will not be visible in the formula bar. Uses a predefined password of mypassword.
VBA code
Sub HideFormulasWhenProtected() 'Create a variable to hold the password Dim myPassword As String 'Set the password myPassword = "myPassword" 'All the following to apply to active sheet With ActiveSheet 'Unprotect the active sheet .Unprotect Password:=myPassword 'Hide formulas in all cells .Cells.FormulaHidden = True 'Protect the active sheet .Protect Password:=myPassword End With End Sub
Save time stamped backup file
What does it do?
Save a backup copy of the workbook with a time stamp.
VBA code
Sub SaveTimeStampedBackup() 'Create variable to hold the new file path Dim saveAsName As String 'Set the file path saveAsName = ActiveWorkbook.Path & "" & _ Format(Now, "yymmdd-hhmmss") & " " & ActiveWorkbook.Name 'Save the workbook ActiveWorkbook.SaveCopyAs Filename:=saveAsName End Sub
Prepare workbook for saving
What does it do?
The macro will, for each worksheet:
- Close all group outlining
- Set the view to the normal view
- Remove gridlines
- Hide all row numbers and column numbers
- Select cell A1
The first sheet is selected.
After running the macro, every worksheet in the workbook will be in a tidy state for the next use.
VBA code
Sub PrepareWorkbookForSaving() 'Declare the worksheet variable Dim ws As Worksheet 'Loop through each worksheet in the active workbook For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets 'Activate each sheet ws.Activate 'Close all of groups ws.Outline.ShowLevels RowLevels:=1, ColumnLevels:=1 'Set the view settings to normal ActiveWindow.View = xlNormalView 'Remove the gridlines ActiveWindow.DisplayGridlines = False 'Remove the headings on each of the worksheets ActiveWindow.DisplayHeadings = False 'Get worksheet to display top left ws.Cells(1, 1).Select Next ws 'Find the first visible worksheet and select it For Each ws In Worksheets If ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible Then 'Select the first visible worksheet ws.Select 'Once the first visible worksheet is found exit the sub Exit For End If Next ws End Sub
Convert merged cells to center across
What does it do?
Changes all single row merged cells into center across formatting.
VBA code
Sub ConvertMergedCellsToCenterAcross() Dim c As Range Dim mergedRange As Range 'Loop through all cells in Used range For Each c In ActiveSheet.UsedRange 'If merged and single row If c.MergeCells = True And c.MergeArea.Rows.Count = 1 Then 'Set variable for the merged range Set mergedRange = c.MergeArea 'Unmerge the cell and apply Centre Across Selection mergedRange.UnMerge mergedRange.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenterAcrossSelection End If Next End Sub
Fit selection to screen
What does it do?
Zoom the screen on the selected cells.
VBA code
Sub FitSelectionToScreen() 'To zoom to a specific area, then select the cells Range("A1:I15").Select 'Zoom to selection ActiveWindow.Zoom = True 'Select first cell on worksheet Range("A1").Select End Sub
Flip number signage on selected cells
What does it do?
Flips the number signage of all numeric values in the selected cells
VBA code
Sub FlipNumberSignage() 'Create variable to hold cells in the worksheet Dim c As Range 'Loop through each cell in selection For Each c In Selection 'Test if the cell contents is a number If IsNumeric(c) Then 'Convert signage for each cell c.Value = -c.Value End If Next c End Sub
Clear all data cells
What does it do?
Clears all cells in the selection which are constants (i.e. not formulas).
VBA code
Sub ClearAllDataCellsInSelection() 'Clear all hardcoded values in the selected range Selection.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeConstants).ClearContents End Sub
Add prefix to each cell in selection
What does it do?
Adds a prefix to each cell in the selected cells (excludes formulas and blanks).
VBA code
Sub AddPrefix() Dim c As Range Dim prefixValue As Variant 'Display inputbox to collect prefix text prefixValue = Application.InputBox(Prompt:="Enter prefix:", _ Title:="Prefix", Type:=2) 'The User clicked Cancel If prefixValue = False Then Exit Sub For Each c In Selection 'Add prefix where cell is not a formula or blank If Not c.HasFormula And c.Value <> "" Then c.Value = prefixValue & c.Value End If Next End Sub
Add suffix to each cell in selection
What does it do?
Adds a suffix to each value in the selected cells (excludes formulas and blanks).
VBA code
Sub AddSuffix() Dim c As Range Dim suffixValue As Variant 'Display inputbox to collect prefix text suffixValue = Application.InputBox(Prompt:="Enter Suffix:", _ Title:="Suffix", Type:=2) 'The User clicked Cancel If suffixValue = False Then Exit Sub 'Loop through each cellin selection For Each c In Selection 'Add Suffix where cell is not a formula or blank If Not c.HasFormula And c.Value <> "" Then c.Value = c.Value & suffixValue End If Next End Sub
Reverse row order
What does it do?
Reverses the order of all rows of data in the selection.
VBA code
Sub ReverseRows() 'Create variables Dim rng As Range Dim rngArray As Variant Dim tempRng As Variant Dim i As Long Dim j As Long Dim k As Long 'Record the selected range and it's contents Set rng = Selection rngArray = rng.Formula 'Loop through all cells and create a temporary array For j = 1 To UBound(rngArray, 2) k = UBound(rngArray, 1) For i = 1 To UBound(rngArray, 1) / 2 tempRng = rngArray(i, j) rngArray(i, j) = rngArray(k, j) rngArray(k, j) = tempRng k = k - 1 Next Next 'Apply the array rng.Formula = rngArray End Sub
Reverse column order
What does it do?
Reverses the order of all column data in the selection.
VBA code
Sub ReverseColumns() 'Create variables Dim rng As Range Dim rngArray As Variant Dim tempRng As Variant Dim i As Long Dim j As Long Dim k As Long 'Record the selected range and it's contents Set rng = Selection rngArray = rng.Formula 'Loop through all cells and create a temporary array For i = 1 To UBound(rngArray, 1) k = UBound(rngArray, 2) For j = 1 To UBound(rngArray, 2) / 2 tempRng = rngArray(i, j) rngArray(i, j) = rngArray(i, k) rngArray(i, k) = tempRng k = k - 1 Next Next 'Apply the array rng.Formula = rngArray End Sub
Transpose selection
What does it do?
Transposes the selected cells with a single click.
VBA code
Sub TransposeSelection() 'Create variables Dim rng As Range Dim rngArray As Variant Dim i As Long Dim j As Long Dim overflowRng As Range Dim msgAns As Long 'Record the selected range and it's contents Set rng = Selection rngArray = rng.Formula 'Test the range and identify if any cells will be overwritten If rng.Rows.Count > rng.Columns.Count Then Set overflowRng = rng.Cells(1, 1). _ Offset(0, rng.Columns.Count). _ Resize(rng.Columns.Count, _ rng.Rows.Count - rng.Columns.Count) ElseIf rng.Rows.Count < rng.Columns.Count Then Set overflowRng = rng.Cells(1, 1).Offset(rng.Rows.Count, 0). _ Resize(rng.Columns.Count - rng.Rows.Count, rng.Rows.Count) End If If rng.Rows.Count <> rng.Columns.Count Then If Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(overflowRng) > 0 Then msgAns = MsgBox("Worksheet data in " & overflowRng.Address & _ " will be overwritten." & vbNewLine & _ "Do you wish to continue?", vbYesNo) If msgAns = vbNo Then Exit Sub End If End If 'Clear the rnage rng.Clear 'Reapply the cells in transposted position For i = 1 To UBound(rngArray, 1) For j = 1 To UBound(rngArray, 2) rng.Cells(1, 1).Offset(j - 1, i - 1) = rngArray(i, j) Next Next End Sub
Create red box around selected areas
What does it do?
Draws a rectangle shape to fit around the selected cells.
VBA code
Sub AddRedBox() Dim redBox As Shape Dim selectedAreas As Range Dim i As Integer Dim tempShape As Shape 'Loop through each selected area in active sheet For Each selectedAreas In Selection.Areas 'Create a rectangle Set redBox = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeRectangle, _ selectedAreas.Left, selectedAreas.Top, _ selectedAreas.Width, selectedAreas.Height) 'Change attributes of shape created redBox.Line.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(255, 0, 0) redBox.Line.Weight = 2 redBox.Fill.Visible = msoFalse 'Loop to find a unique shape name Do i = i + 1 Set tempShape = Nothing On Error Resume Next Set tempShape = ActiveSheet.Shapes("RedBox_" & i) On Error GoTo 0 Loop Until tempShape Is Nothing 'Rename the shape redBox.Name = "RedBox_" & i Next End Sub
Delete all red boxes on active sheet
What does it do?
Having created the red boxes in the macro above. This code removes all the red boxes on the active sheet with a single click.
VBA code
Sub DeleteRedBox() Dim shp As Shape 'Loop through each shape on active sheet For Each shp In ActiveSheet.Shapes 'Find shapes with a name starting with "RedBox_" If Left(shp.Name, 7) = "RedBox_" Then 'Delete the shape shp.Delete End If Next shp End Sub
Save selected chart as an image
What does it do?
Saves the selected chart as a picture to the file location contained in the macro.
VBA code
Sub ExportSingleChartAsImage() 'Create a variable to hold the path and name of image Dim imagePath As String Dim cht As Chart imagePath = "C:UsersmarksDocumentsmyImage.png" Set cht = ActiveChart 'Export the chart cht.Export (imagePath) End Sub
Resize all charts to same as active chart
What does it do?
Select the chart with the dimensions you wish to use, then run the macro. All the charts will resize to the same dimensions.
VBA code
Sub ResizeAllCharts() 'Create variables to hold chart dimensions Dim chtHeight As Long Dim chtWidth As Long 'Create variable to loop through chart objects Dim chtObj As ChartObject 'Get the size of the first selected chart chtHeight = ActiveChart.Parent.Height chtWidth = ActiveChart.Parent.Width For Each chtObj In ActiveSheet.ChartObjects chtObj.Height = chtHeight chtObj.Width = chtWidth Next chtObj End Sub
Refresh all Pivot Tables in workbook
What does it do?
Refresh all the Pivot Tables in the active workbook.
VBA code
Sub RefreshAllPivotTables() 'Refresh all pivot tables ActiveWorkbook.RefreshAll End Sub
Turn off auto fit columns on all Pivot Tables
What does it do?
By default, PivotTables resize columns to fit the contents. This macro changes the setting for every PivotTable in the active workbook, so that column widths set by the user are maintained.
VBA code
Sub TurnOffAutofitColumns() 'Create a variable to hold worksheets Dim ws As Worksheet 'Create a variable to hold pivot tables Dim pvt As PivotTable 'Loop through each sheet in the activeworkbook For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets 'Loop through each pivot table in the worksheet For Each pvt In ws.PivotTables 'Turn off auto fit columns on PivotTable pvt.HasAutoFormat = False Next pvt Next ws End Sub
Get color code from cell fill color
What does it do?
Returns the RGB and Hex for the active cell’s fill color.
VBA code
Sub GetColorCodeFromCellFill() 'Create variables hold the color data Dim fillColor As Long Dim R As Integer Dim G As Integer Dim B As Integer Dim Hex As String 'Get the fill color fillColor = ActiveCell.Interior.Color 'Convert fill color to RGB R = (fillColor Mod 256) G = (fillColor 256) Mod 256 B = (fillColor 65536) Mod 256 'Convert fill color to Hex Hex = "#" & Application.WorksheetFunction.Dec2Hex(fillColor) 'Display fill color codes MsgBox "Color codes for active cell" & vbNewLine & _ "R:" & R & ", G:" & G & ", B:" & B & vbNewLine & _ "Hex: " & Hex, Title:="Color Codes" End Sub
Create a table of contents
What does it do?
Creates or refreshes a hyperlinked table of contents on a worksheet called “TOC”, which is placed at the start of a workbook.
VBA code
Sub CreateTableOfContents() Dim i As Long Dim TOCName As String 'Name of the Table of contents TOCName = "TOC" 'Delete the existing Table of Contents sheet if it exists On Error Resume Next Application.DisplayAlerts = False ActiveWorkbook.Sheets(TOCName).Delete Application.DisplayAlerts = True On Error GoTo 0 'Create a new worksheet ActiveWorkbook.Sheets.Add before:=ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(1) ActiveSheet.Name = TOCName 'Loop through the worksheets For i = 1 To Sheets.Count 'Create the table of contents ActiveSheet.Hyperlinks.Add _ Anchor:=ActiveSheet.Cells(i, 1), _ Address:="", _ SubAddress:="'" & Sheets(i).Name & "'!A1", _ ScreenTip:=Sheets(i).Name, _ TextToDisplay:=Sheets(i).Name Next i End Sub
Excel to speak the cell contents
What does it do?
Excel speaks back the contents of the selected cells
VBA code
Sub SpeakCellContents() 'Speak the selected cells Selection.Speak End Sub
Fix the range of cells which can be scrolled
What does it do?
Fixes the scroll range to the selected cell range. It prevents a user from scrolling into other parts of the worksheet.
If a single cell is selected, the scroll range is reset.
VBA code
Sub FixScrollRange() If Selection.Cells.Count = 1 Then 'If one cell selected, then reset ActiveSheet.ScrollArea = "" Else 'Set the scroll area to the selected cells ActiveSheet.ScrollArea = Selection.Address End If End Sub
Invert the sheet selection
What does it do?
Select some worksheet tabs, then run the macro to reverse the selection.
VBA code
Sub InvertSheetSelection() 'Create variable to hold list of selected worksheet Dim selectedList As String 'Create variable to hold worksheets Dim ws As Worksheet 'Create variable to switch after the first sheet selected Dim firstSheet As Boolean 'Convert selected sheest to a text string For Each ws In ActiveWindow.SelectedSheets selectedList = selectedList & ws.Name & "[|]" Next ws 'Set the toggle of first sheet firstSheet = True 'Loop through each worksheet in the active workbook For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Sheets 'Check if the worksheet was not previously selected If InStr(selectedList, ws.Name & "[|]") = 0 Then 'Check the worksheet is visible If ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible Then 'Select the sheet ws.Select firstSheet 'First worksheet has been found, toggle to false firstSheet = False End If End If Next ws End Sub
Assign a macro to a shortcut key
What does it do?
Assigns a macro to a shortcut key.
VBA code
Sub AssignMacroToShortcut() '+ = Ctrl '^ = Shift '{T} = the shortcut letter Application.OnKey "+^{T}", "nameOfMacro" 'Reset shortcut to default - repeat without the name of the macro 'Application.OnKey "+%{T}" End Sub
Apply single accounting underline to selection
What does it do?
Single accounting underline is a formatting style which is not available in the ribbon. The macro below applies single accounting underline to the selected cells.
VBA code
Sub SingleAccountingUnderline() 'Apply single accounting underline to selected cells Selection.Font.Underline = xlUnderlineStyleSingleAccounting End Sub
About the author
Hey, I’m Mark, and I run Excel Off The Grid.
My parents tell me that at the age of 7 I declared I was going to become a qualified accountant. I was either psychic or had no imagination, as that is exactly what happened. However, it wasn’t until I was 35 that my journey really began.
In 2015, I started a new job, for which I was regularly working after 10pm. As a result, I rarely saw my children during the week. So, I started searching for the secrets to automating Excel. I discovered that by building a small number of simple tools, I could combine them together in different ways to automate nearly all my regular tasks. This meant I could work less hours (and I got pay raises!). Today, I teach these techniques to other professionals in our training program so they too can spend less time at work (and more time with their children and doing the things they love).
Do you need help adapting this post to your needs?
I’m guessing the examples in this post don’t exactly match your situation. We all use Excel differently, so it’s impossible to write a post that will meet everybody’s needs. By taking the time to understand the techniques and principles in this post (and elsewhere on this site), you should be able to adapt it to your needs.
But, if you’re still struggling you should:
- Read other blogs, or watch YouTube videos on the same topic. You will benefit much more by discovering your own solutions.
- Ask the ‘Excel Ninja’ in your office. It’s amazing what things other people know.
- Ask a question in a forum like Mr Excel, or the Microsoft Answers Community. Remember, the people on these forums are generally giving their time for free. So take care to craft your question, make sure it’s clear and concise. List all the things you’ve tried, and provide screenshots, code segments and example workbooks.
- Use Excel Rescue, who are my consultancy partner. They help by providing solutions to smaller Excel problems.
What next?
Don’t go yet, there is plenty more to learn on Excel Off The Grid. Check out the latest posts:
Introduction
This is a tutorial about writing code in Excel spreadsheets using Visual Basic for Applications (VBA).
Excel is one of Microsoft’s most popular products. In 2016, the CEO of Microsoft said «Think about a world without Excel. That’s just impossible for me.” Well, maybe the world can’t think without Excel.
- In 1996, there were over 30 million users of Microsoft Excel (source).
- Today, there are an estimated 750 million users of Microsoft Excel. That’s a little more than the population of Europe and 25x more users than there were in 1996.
We’re one big happy family!
In this tutorial, you’ll learn about VBA and how to write code in an Excel spreadsheet using Visual Basic.
Prerequisites
You don’t need any prior programming experience to understand this tutorial. However, you will need:
- Basic to intermediate familiarity with Microsoft Excel
- If you want to follow along with the VBA examples in this article, you will need access to Microsoft Excel, preferably the latest version (2019) but Excel 2016 and Excel 2013 will work just fine.
- A willingness to try new things
Learning Objectives
Over the course of this article, you will learn:
- What VBA is
- Why you would use VBA
- How to get set up in Excel to write VBA
- How to solve some real-world problems with VBA
Important Concepts
Here are some important concepts that you should be familiar with to fully understand this tutorial.
Objects: Excel is object-oriented, which means everything is an object — the Excel window, the workbook, a sheet, a chart, a cell. VBA allows users to manipulate and perform actions with objects in Excel.
If you don’t have any experience with object-oriented programming and this is a brand new concept, take a second to let that sink in!
Procedures: a procedure is a chunk of VBA code, written in the Visual Basic Editor, that accomplishes a task. Sometimes, this is also referred to as a macro (more on macros below). There are two types of procedures:
- Subroutines: a group of VBA statements that performs one or more actions
- Functions: a group of VBA statements that performs one or more actions and returns one or more values
Note: you can have functions operating inside of subroutines. You’ll see later.
Macros: If you’ve spent any time learning more advanced Excel functionality, you’ve probably encountered the concept of a “macro.” Excel users can record macros, consisting of user commands/keystrokes/clicks, and play them back at lightning speed to accomplish repetitive tasks. Recorded macros generate VBA code, which you can then examine. It’s actually quite fun to record a simple macro and then look at the VBA code.
Please keep in mind that sometimes it may be easier and faster to record a macro rather than hand-code a VBA procedure.
For example, maybe you work in project management. Once a week, you have to turn a raw exported report from your project management system into a beautifully formatted, clean report for leadership. You need to format the names of the over-budget projects in bold red text. You could record the formatting changes as a macro and run that whenever you need to make the change.
What is VBA?
Visual Basic for Applications is a programming language developed by Microsoft. Each software program in the Microsoft Office suite is bundled with the VBA language at no extra cost. VBA allows Microsoft Office users to create small programs that operate within Microsoft Office software programs.
Think of VBA like a pizza oven within a restaurant. Excel is the restaurant. The kitchen comes with standard commercial appliances, like large refrigerators, stoves, and regular ole’ ovens — those are all of Excel’s standard features.
But what if you want to make wood-fired pizza? Can’t do that in a standard commercial baking oven. VBA is the pizza oven.
Yum.
Why use VBA in Excel?
Because wood-fired pizza is the best!
But seriously.
A lot of people spend a lot of time in Excel as a part of their jobs. Time in Excel moves differently, too. Depending on the circumstances, 10 minutes in Excel can feel like eternity if you’re not able to do what you need, or 10 hours can go by very quickly if everything is going great. Which is when you should ask yourself, why on earth am I spending 10 hours in Excel?
Sometimes, those days are inevitable. But if you’re spending 8-10 hours everyday in Excel doing repetitive tasks, repeating a lot of the same processes, trying to clean up after other users of the file, or even updating other files after changes are made to the Excel file, a VBA procedure just might be the solution for you.
You should consider using VBA if you need to:
- Automate repetitive tasks
- Create easy ways for users to interact with your spreadsheets
- Manipulate large amounts of data
Getting Set Up to Write VBA in Excel
Developer Tab
To write VBA, you’ll need to add the Developer tab to the ribbon, so you’ll see the ribbon like this.
To add the Developer tab to the ribbon:
- On the File tab, go to Options > Customize Ribbon.
- Under Customize the Ribbon and under Main Tabs, select the Developer check box.
After you show the tab, the Developer tab stays visible, unless you clear the check box or have to reinstall Excel. For more information, see Microsoft help documentation.
VBA Editor
Navigate to the Developer Tab, and click the Visual Basic button. A new window will pop up — this is the Visual Basic Editor. For the purposes of this tutorial, you just need to be familiar with the Project Explorer pane and the Property Properties pane.
Excel VBA Examples
First, let’s create a file for us to play around in.
- Open a new Excel file
- Save it as a macro-enabled workbook (. xlsm)
- Select the Developer tab
- Open the VBA Editor
Let’s rock and roll with some easy examples to get you writing code in a spreadsheet using Visual Basic.
Example #1: Display a Message when Users Open the Excel Workbook
In the VBA Editor, select Insert -> New Module
Write this code in the Module window (don’t paste!):
Sub Auto_Open()
MsgBox («Welcome to the XYZ Workbook.»)
End Sub
Save, close the workbook, and reopen the workbook. This dialog should display.
Ta da!
How is it doing that?
Depending on your familiarity with programming, you may have some guesses. It’s not particularly complex, but there’s quite a lot going on:
- Sub (short for “Subroutine): remember from the beginning, “a group of VBA statements that performs one or more actions.”
- Auto_Open: this is the specific subroutine. It automatically runs your code when the Excel file opens — this is the event that triggers the procedure. Auto_Open will only run when the workbook is opened manually; it will not run if the workbook is opened via code from another workbook (Workbook_Open will do that, learn more about the difference between the two).
- By default, a subroutine’s access is public. This means any other module can use this subroutine. All examples in this tutorial will be public subroutines. If needed, you can declare subroutines as private. This may be needed in some situations. Learn more about subroutine access modifiers.
- msgBox: this is a function — a group of VBA statements that performs one or more actions and returns a value. The returned value is the message “Welcome to the XYZ Workbook.”
In short, this is a simple subroutine that contains a function.
When could I use this?
Maybe you have a very important file that is accessed infrequently (say, once a quarter), but automatically updated daily by another VBA procedure. When it is accessed, it’s by many people in multiple departments, all across the company.
- Problem: Most of the time when users access the file, they are confused about the purpose of this file (why it exists), how it is updated so often, who maintains it, and how they should interact with it. New hires always have tons of questions, and you have to field these questions over and over and over again.
- Solution: create a user message that contains a concise answer to each of these frequently answered questions.
Real World Examples
- Use the MsgBox function to display a message when there is any event: user closes an Excel workbook, user prints, a new sheet is added to the workbook, etc.
- Use the MsgBox function to display a message when a user needs to fulfill a condition before closing an Excel workbook
- Use the InputBox function to get information from the user
Example #2: Allow User to Execute another Procedure
In the VBA Editor, select Insert -> New Module
Write this code in the Module window (don’t paste!):
Sub UserReportQuery()
Dim UserInput As Long
Dim Answer As Integer
UserInput = vbYesNo
Answer = MsgBox(«Process the XYZ Report?», UserInput)
If Answer = vbYes Then ProcessReport
End Sub
Sub ProcessReport()
MsgBox («Thanks for processing the XYZ Report.»)
End Sub
Save and navigate back to the Developer tab of Excel and select the “Button” option. Click on a cell and assign the UserReportQuery macro to the button.
Now click the button. This message should display:
Click “yes” or hit Enter.
Once again, tada!
Please note that the secondary subroutine, ProcessReport, could be anything. I’ll demonstrate more possibilities in example #3. But first…
How is it doing that?
This example builds on the previous example and has quite a few new elements. Let’s go over the new stuff:
- Dim UserInput As Long: Dim is short for “dimension” and allows you to declare variable names. In this case, UserInput is the variable name and Long is the data type. In plain English, this line means “Here’s a variable called “UserInput”, and it’s a Long variable type.”
- Dim Answer As Integer: declares another variable called “Answer,” with a data type of Integer. Learn more about data types here.
- UserInput = vbYesNo: assigns a value to the variable. In this case, vbYesNo, which displays Yes and No buttons. There are many button types, learn more here.
- Answer = MsgBox(“Process the XYZ Report?”, UserInput): assigns the value of the variable Answer to be a MsgBox function and the UserInput variable. Yes, a variable within a variable.
- If Answer = vbYes Then ProcessReport: this is an “If statement,” a conditional statement, which allows us to say if x is true, then do y. In this case, if the user has selected “Yes,” then execute the ProcessReport subroutine.
When could I use this?
This could be used in many, many ways. The value and versatility of this functionality is more so defined by what the secondary subroutine does.
For example, maybe you have a file that is used to generate 3 different weekly reports. These reports are formatted in dramatically different ways.
- Problem: Each time one of these reports needs to be generated, a user opens the file and changes formatting and charts; so on and so forth. This file is being edited extensively at least 3 times per week, and it takes at least 30 minutes each time it’s edited.
- Solution: create 1 button per report type, which automatically reformats the necessary components of the reports and generates the necessary charts.
Real World Examples
- Create a dialog box for user to automatically populate certain information across multiple sheets
- Use the InputBox function to get information from the user, which is then populated across multiple sheets
Example #3: Add Numbers to a Range with a For-Next Loop
For loops are very useful if you need to perform repetitive tasks on a specific range of values — arrays or cell ranges. In plain English, a loop says “for each x, do y.”
In the VBA Editor, select Insert -> New Module
Write this code in the Module window (don’t paste!):
Sub LoopExample()
Dim X As Integer
For X = 1 To 100
Range(«A» & X).Value = X
Next X
End Sub
Save and navigate back to the Developer tab of Excel and select the Macros button. Run the LoopExample macro.
This should happen:
Etc, until the 100th row.
How is it doing that?
- Dim X As Integer: declares the variable X as a data type of Integer.
- For X = 1 To 100: this is the start of the For loop. Simply put, it tells the loop to keep repeating until X = 100. X is the counter. The loop will keep executing until X = 100, execute one last time, and then stop.
- Range(«A» & X).Value = X: this declares the range of the loop and what to put in that range. Since X = 1 initially, the first cell will be A1, at which point the loop will put X into that cell.
- Next X: this tells the loop to run again
When could I use this?
The For-Next loop is one of the most powerful functionalities of VBA; there are numerous potential use cases. This is a more complex example that would require multiple layers of logic, but it communicates the world of possibilities in For-Next loops.
Maybe you have a list of all products sold at your bakery in Column A, the type of product in Column B (cakes, donuts, or muffins), the cost of ingredients in Column C, and the market average cost of each product type in another sheet.
You need to figure out what should be the retail price of each product. You’re thinking it should be the cost of ingredients plus 20%, but also 1.2% under market average if possible. A For-Next loop would allow you to do this type of calculation.
Real World Examples
- Use a loop with a nested if statement to add specific values to a separate array only if they meet certain conditions
- Perform mathematical calculations on each value in a range, e.g. calculate additional charges and add them to the value
- Loop through each character in a string and extract all numbers
- Randomly select a number of values from an array
Conclusion
Now that we’ve talked about pizza and muffins and oh-yeah, how to write VBA code in Excel spreadsheets, let’s do a learning check. See if you can answer these questions.
- What is VBA?
- How do I get set up to start using VBA in Excel?
- Why and when would you use VBA?
- What are some problems I could solve with VBA?
If you have a fair idea of how to you could answer these questions, then this was successful.
Whether you’re an occasional user or a power user, I hope this tutorial provided useful information about what can be accomplished with just a bit of code in your Excel spreadsheets.
Happy coding!
Learning Resources
- Excel VBA Programming for Dummies, John Walkenbach
- Get Started with VBA, Microsoft Documentation
- Learning VBA in Excel, Lynda
A bit about me
I’m Chloe Tucker, an artist and developer in Portland, Oregon. As a former educator, I’m continuously searching for the intersection of learning and teaching, or technology and art. Reach out to me on Twitter @_chloetucker and check out my website at chloe.dev.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
VBA Code Excel Macro Examples Useful 100+ How Tos for Basic and Advanced Users
VBA Code Excel Macro Examples – Useful Macros, Codes, 100+ How To explained for Basic Beginners to Advanced VBA users. Tutorials to learn Excel 2003, 2007, 2010, 2013 Macros and Mastering in VBA. Selected examples to deal with different objects, methods and properties in Excel. Numerous free most useful VBA codes and tips will help you to deal with various Excel Objects like Cell, Range, Worksheets, Workbooks, Application, Charts, Pivot Tables, Hyperlinks, functions, User Forms, MsgBox, ListBox, ComboBox. Also provided free example codes to deal with MS Word, PowerPoint, Outlook, Access, Other Applications and File Handling. If you think that I missed any useful code, please feel free to write us. We will respond with a solution with in couple of days and publish here to make it available for all VBA Users.
100+ Excel VBA макросов коды Примеры | excel VBA makro kod örnekleri | Excel的VBA宏代码范例 | Excel-VBA-Makros Codes Beispiele | excel VBA Macro Codes Contoh | एक्सेल VBA मैक्रो कोड्स उदाहरण.
The Most Useful VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros! Learning Path
Learn VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros and do almost everything! We have explained verity of examples to cover most frequently used codes. Start learning …!
Cells and Range Objects : VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
Reading data from a Cell was my first exciting VBA Code when I stared learning Excel VBA. Then I successfully write data to Excel Cells. That was my first happy moment which motivated me to engage with VBA from last 10 years.
Here are the common VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros to deal with Cell and Range Objects of Worksheet.
You can find examples on reading and writing the data, selecting, copying and pasting the data.
Clearing, changing font color, font to bold, background color of cells or range. We can also see the examples on merging cells, adding comments and changing the font case to lower or upper using Excel VBA.
- Write Data to Worksheet Cell in Excel VBA
- Writing and Reading Excel Worksheet Cells Ranges in VBA
- Read or Get Data from Worksheet Cell to VBA in Excel
- Select Cell Range in Excel VBA
- Copy Data from One Range to Another in Excel VBA
- Clear Cells in Excel Range Worksheet using VBA
- Change Font Color in Excel VBA
- Change Font to Bold in Excel VBA
- Change Text Case – Upper Lower in Excel VBA
- Change Background Color of Cell Range in Excel VBA
- Merge UnMerge Cell Range in Excel VBA
- Add Clear Comments in Excel VBA
Top
Rows and Columns Objects: VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
Cell and Range objects helps to reading and writing the data from worksheet. Now we will look into Rows and Columns of the Worksheet, helps to show or hide the data. Here you can find the VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros on delete rows, columns, change row height, column width. Hiding or un-hiding columns or rows. Inserting or deleting Rows or Columns. And finding the Last row, or columns in the worksheet in different situations.
- Change Row Height and Column Width using Excel VBA
- Delete Rows and Columns in Excel VBA
- Hide UnHide Columns in Excel Worksheet using VBA
- Hide UnHide Rows in Excel Worksheet using VBA
- Finding last used Column with data in particular Row
- Finding last used Row with data in particular Column
- Inserting Columns in Excel Worksheet using VBA
- Inserting Rows in Excel Worksheet using VBA
- Find Last Column with data in Worksheet using Excel VBA
- Finding last used Row with data in Excel Worksheet using VBA
Top
Worksheet and Workbook Objects: VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
Now we will see the VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros on Worksheet and Workbook Objects. Here you can find creating new workbook, opening, closing and saving workbook. And example to show running a macro on opening or staring the workbook. We will also see how to protecting or unprotecting Excel workbooks or worksheets, Copying the data from one worksheet to another worksheet.
Hiding and unhiding worksheets. Changing the tab color of worksheet. Activating workbooks or worksheet, etc.
- Create New Workbook in Excel VBA
- Run a Macro Automatically on Opening Excel Workbook
- Open and Close Excel Workbook using VBA
- Save Workbook Using Excel VBA to Specific Folder
- Protect and Unprotect Excel Workbook using VBA
- Protect and UnProtect Worksheets in Excel VBA
- Hide UnHide Worksheets in Excel VBA
- Delete Worksheet in Excel VBA
- Copy Data from one Worksheet to another in Excel VBA
- Change the Color of Sheet Tabs in Excel VBA
- Activate Workbook Or Worksheet in Excel VBA
- Get Active Workbook or Worksheet Name Path FullName in Excel VBA
Top
Hyperlink: VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
Hyperlinks are most widely used concepts in Excel. We generally use hyperlinks to navigate or open a file, link or folder. But we can do many other things using Hyperlinks. Examples in this topic will show you the power of Hyperlinks in Excel VBA. We have covered the following examples in this tutorial:
- Add Create Hyperlinks in Excel VBA
- Removing Hyperlinks in Excel VBA
- VBA Open File Folder Website Using FollowHyperlink method in Excel
- VBA Create Send Emails Using FollowHyperlink Method – Send Keys in Excel
Hyperlinks in Excel VBA – Explained with Examples!
Charts : VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
Another powerful tool in Excel is charting. You can create rich visualized dashboards using Excel Charts and VBA. We have covered most commonly used Charting VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros. In this topic will show you how to deal with different chart objects to automate the charting process using VBA. Examples on creating charts, changing chart types. Changing chart axes titles, chart title, axis format, primary and secondary axes. We have provided more than 33 example to cover A-z of Excel Chart VBA.
- Example tutorials on Creating Charts using Excel VBA
- Example tutorials on Chart Type using Excel VBA
- Example Tutorials on Formatting Chart Objects using Excel VBA
- Example Tutorials on Chart Collection in Excel VBA
- Other useful Examples and tutorials on Excel VBA Charting
- Excel VBA Charting Constants and Enumeration
Excel Chart VBA Examples and Tutorials
Tables: VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
Tables in Excel help to manage our data in Excel and give the more control over the data. In this example we will see the different VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros like creating tables, sorting tables data and applying filters in the data. We have provided following example to deal with Tables using Excel VBA.
- Create Tables in Excel VBA
- Sorting Tables in Excel VBA
- Filtering Tables in Excel VBA
- Clear Toggle Table Filters in Excel VBA
Tables in Excel VBA – Explained with Examples!
Top
Pivot Tables: VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
Pivot tables help us to summarize the data and analyze it. VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros provided for creating pivot tables, pivot charts, adding calculated, changing row fields, column fields, value field fields in pivot tables using VBA. We have provided the following example to deal with pivot tables using Excel VBA, we will add some more examples to do more tasks using pivot tables.
- Creating Pivot Tables in Excel VBA
- Create Pivot Chart using Excel VBA
- Create Pivot Column Chart using Excel VBA
- Create Calculated Pivot Field in Excel VBA
Pivot Tables in Excel VBA – Explained with Examples!
Names: VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
Names are another time saving feature in the Excel. We can define the names to Cells, Ranges and Tables and use them across the worksheets in the workbook. Her we will see how to add or remove the Names using VBA. Hiding and un-hiding names from the users. Follwing examples covered in this topic to deal with Names using Excel VBA.
- Adding Names in Excel VBA
- Deleting Names in Excel VBA
- Hide UnHide Names in Excel VBA
Names in Excel VBA – Explained with Examples!
Top
Other Applications: VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
VBA is powerful, it can interact with the other applications like MS Word, PowerPoint, Access, Outlook, Internet Explorer, VBScript etc. Here are examples to deal with other application from Excel. Below examples are covered in this tutorial:
- Interact with PowerPoint from Excel VBA
- Dealing with MS Word From Excel VBA
- Interact with MS Access from Excel VBA
- Interact with Outlook from Excel VBA
- Dealing with Internet Explorer
- Dealing with Other Applications from Excel VBA – Calculator
- Run VBScript from Excel VBA
- VBA to Attach Send An Excel Chart to Outlook Email
Excel VBA to Interact with Other Applications
Application Object: Excel VBA Codes Examples Macros
Mastering the Application Objects Examples help you to fasten your VBA programs and writing optimized code in Excel VBA. Examples for stopping or displaying application alerts, stopping or enabling screen updating, stopping or enabling application events. The following example procedures and functions are covered in this topic to fasten and speed up VBA code processing.
- Stop Screen Updating
- Stop Events in Excel VBA – Disable Enable
- Stop Application Alerts in Excel VBA – Disable Enable
- Display Progress on Statusbar in VBA Excel
- Set Windows State in Excel VBA – Minimize Maximize Normal
- Toggle Full Screen in Excel VBA
- Get User Name in VBA Excel
- Stop Calculations in Excel VBA – Manual Automatic
- Open Visual Basic Editor (VBE) – Open Module with VBA
- VBA to Exit from Procedure or Function
Fasten VBA Code – Application Objects Explained with Examples
File Handling: Excel VBA Examples Macros Codes
File handling examples are provided to creating deleting files, folders. Copying Files and Folders and Moving from one location to another location. And displaying file or folder dialog boxes to browse the files or folders. And check if files exists in a folder using VBA.
- Check if Folder Exists using Excel VBA
- Opening Folders using VBA Excel
- Creating Folders in Excel VBA
- Copying Folders From One Location to Another in Excel VBA
- Move Folder From One Location to Another in Excel VBA
- Deleting Folders in VBA Excel
- Make File Read Only in VBA Excel
- Copy all Excel Files One Folder to Another in VBA Excel
- Opening Files Using File Dialog Box in Excel VBA
- Customize File or Folder Dialog Box in VBA Excel
- Excel VBA File Dialog Box – Displaying Vanilla Dialog Box to Pick Files
Folders and File Handling in Excel VBA
Some more VBA examples are added to deal with Files and Folders using Excel VBA:
- Delete Files Using VBA
- Copy Files from One Location to Another folder or directory in Excel VBA
Top
Miscellaneous Excel VBA Examples Macros Codes
- Remove Alpha Special characters from Range using Excel VBA
A Powerful & Multi-purpose Templates for project management. Now seamlessly manage your projects, tasks, meetings, presentations, teams, customers, stakeholders and time. This page describes all the amazing new features and options that come with our premium templates.
Save Up to 85% LIMITED TIME OFFER

All-in-One Pack
120+ Project Management Templates
Essential Pack
50+ Project Management Templates
Excel Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
PowerPoint Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
MS Word Pack
25+ Word PM Templates
Ultimate Project Management Template
Ultimate Resource Management Template
Project Portfolio Management Templates
Related Posts
- The Most Useful VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros! Learning Path
- Cells and Range Objects : VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
- Rows and Columns Objects: VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
- Worksheet and Workbook Objects: VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
- Hyperlink: VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
- Charts : VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
- Tables: VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
- Pivot Tables: VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
- Names: VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
- Other Applications: VBA Codes Excel Examples Macros
- Application Object: Excel VBA Codes Examples Macros
- File Handling: Excel VBA Examples Macros Codes
- Miscellaneous Excel VBA Examples Macros Codes
VBA Reference
Effortlessly
Manage Your Projects
120+ Project Management Templates
Seamlessly manage your projects with our powerful & multi-purpose templates for project management.
120+ PM Templates Includes:
183 Comments
-
Chitanya
March 3, 2013 at 8:23 PM — ReplyHi,
How to add excel chart to email body?
Thanks,
Chitanya -
PNRao
March 3, 2013 at 10:23 PM — Reply -
Chitanya
March 5, 2013 at 12:22 PM — Reply -
PNRao
March 6, 2013 at 12:19 AM — Reply -
Spoorthi M
May 2, 2013 at 9:35 AM — ReplyHi Team,
A very intersting site to learn VB. The thing which i liked here most is user friendly & explanation of each n every concepts very precisely. Applause for the whole team. Great JOB!!!
Regards
Spoorthi M -
PNRao
May 2, 2013 at 8:07 PM — Reply -
Lody
August 28, 2013 at 7:44 AM — ReplyHi PNRao,
It’s very interesting site to learn step by step VBA in easy way. Please allow me to copy your lesson learning. thank you -
PNRao
August 30, 2013 at 9:55 AM — ReplyHi Lody,
Thanks for visiting us. Unfortunately you should not copy the content from our site as it is against our terms and policies. We are a team working in day and night to build this. You can feel free to use our site as a reference for your queries our for learning purpose. We don’t allow the people to copy and duplicate our content.For more details, please read our terms and conditions:
Privacy Policy | Terms of Use
Thanks-PNRao
-
Amrut Parab
October 23, 2013 at 6:39 PM — ReplyCan we get 100+ Examples for Basic and Advanced Users in PDF format So that we can work or Refer while offline
-
Amrut Parab
October 23, 2013 at 6:43 PM — ReplyOk I got it, I read last comment Just now, Thanks for Good Effort,This website is best for all freshers who want to learn VBA programing, you are Amazing Guys.
May god Bless you. -
PNRao
October 23, 2013 at 11:13 PM — ReplyHi Amrut,
Thanks for visiting our site.
Yes, I am working on 100+ Excel VBA Examples and providing to my blog readers as soon as possible (with in a month).
Thanks
PNRao -
Mahendra
October 25, 2013 at 8:53 PM — ReplyHi,
I would like to know about the matrix multiplication,transpose and inverse of a matrix (mXn). Kindly help me on this.
Thanks
Maahendra -
PNRao
October 27, 2013 at 12:39 AM — ReplyHi Mahendra,
I will post the example programs ASAP.
Thanks-PNRao
-
Vivek
November 13, 2013 at 3:44 PM — ReplyHi ,
I am new to Excel VBA and my need is to create multiple worksheets on the same workbook based on the values from a range of cells(Text) from the Index Sheet and also i have to give hyperlink to the corresponding sheets.
For Eg:
cell A1 contains “Name”, a work sheets should be created on this name and Cell A1 should have hyper link to the created worksheet.
cell A1 will be in Index or 1st page.Thanks
-
Vivek
November 13, 2013 at 3:58 PM — ReplyHi,
I am very new to Excel VBA. I want to add multiple worksheets in the same workbook and i have to rename it with the values from a range of cells from the Index page. And also each sheet should be hyper linked to the corresponding Cell in the range.
For Eg:
Cell A1 has “Name”, i have to create a worksheet with that name and that created sheet has to be hyper linked with Cell A1.Thanks
-
Jaimin
November 13, 2013 at 9:37 PM — ReplyHow to write vba macro to copy data from one sheet to another without using “copy” command ?
-
PNRao
November 14, 2013 at 1:37 PM — ReplyHi Jaimin,
You can use for loop to get the data from one sheet to another sheet. For instance, if you want to get the data of cells A1:A20 from Sheet2 to cells B1:B20 of sheet1.
For iCntr=1 to 20
Sheets1.Cells(iCntr,2).value=Sheets2.Cells(iCntr,1)
Next
Its depending up on your requirement. If you want to copy only few cells. you can do it without using for loop.
However Copy command [Sheets2.Range(“A1:A10”).Copy Destination:=Sheets1.Range(“B1)] works more faster, you can copy the data including formats.
Hope this helps!
Thanks – PNRao! -
PNRao
November 14, 2013 at 2:32 PM — ReplyHi Vivek,
Here is the example program for your requirement.
[code language=”vb”]
Sub sbCreateTOCSheetHyperLinks()iCntr = 5 ‘ worksheets names starts from 5th row
‘loop until the cell is blank
Do While Sheets(«Index»).Range(«A» & iCntr) <> «»‘If you want to add new worksheets from last worksheet
Sheets.Add After:=Sheets(ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets.Count)
ActiveSheet.Name = Sheets(«Index»).Range(«A» & iCntr)Sheets(«Index»).Activate
‘delete if any existing hyperlink
Range(«A» & iCntr).Hyperlinks.Delete‘add hyperlinks
Sheets(«Index»).Hyperlinks.Add Anchor:=Range(«A» & iCntr), Address:=»», _
SubAddress:=»’» & Sheets(«Index»).Range(«A» & iCntr).Value & «’!A1», _
TextToDisplay:=Sheets(«Index»).Range(«A» & iCntr).ValueiCntr = iCntr + 1
LoopEnd Sub
[/code]You can download the example file form our downloads page: Download Now
You can use our add-in to create better TOC in easy way.
Hope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Jagadesh.K
November 17, 2013 at 5:37 PM — ReplyHi Team,
I want to Split data into multiple worksheets based on column(this column will contain numbers)
with VBA code. It will be more helpful if you would help on this.
Thanks
-
PNRao
November 17, 2013 at 5:47 PM — ReplyHi Jagadeesh,
Please check for the example (Copy Data from One Sheet to Different Sheets:) in the following page:
Excel VBA Downloads
Hope this help you to do your task.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Hi,
Really thanks for that, really that helps me a lot….
-
PNRao
November 22, 2013 at 11:59 PM — ReplyYou are most welcome!
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Mukund Joshi
December 21, 2013 at 1:12 AM — ReplyHi,
I am at a beginner level of learning VBA. So far it really helped me a lot at my workplace to drag my manager’s attention. I prefer referring your site and I really love the way you interpret useful info in the simplest way. Your work actually attracted me towards learning more & more of VB. Thank you for your hard work & knowledge sharing! -
PNRao
December 22, 2013 at 11:23 AM — ReplyHi Joshi,
Thank you for your comments, I am happy that our blog is helping and creating interest towards learning VBA.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
nitin chugh
December 31, 2013 at 8:46 PM — Replyhow to send email through excel using macro or without macro
-
PNRao
January 2, 2014 at 11:00 PM — Reply -
Mark Paull
January 5, 2014 at 8:12 PM — ReplyHi great site – i’m self learning VBA mostly through using the record macro function and analysing the coded output. Trying to make use of the text held within an object to drive an action based on the digit held within this object.
Fantastically built side in terms of content and style
-
PNRao
January 5, 2014 at 9:38 PM — ReplyThanks Paull! Enjoy learning VBA. -PNRao!
-
Patrizio
January 7, 2014 at 9:54 PM — ReplyHi,
first of all congrats for the amazing helpful website.
I am wondering if you could help me with this VBA issue:
1) Hypothesize we have in “sheet1” cell a1, a3, a5, a7 and so on with a gap of 2.
2) I would like a Macro that links (instead of copy if possible) cell b1, b2, b3, b4 and so on of “sheet2” to cell a1, a3, a5 … of “sheet1” (basically removing the Gap)Hope I was clear.
Thanks a lot for your help,
Patrizio
-
PNRao
January 8, 2014 at 12:18 AM — ReplyHi Patrizio,
Thanks for your comments. Here are VBA macros for your requirement.
[code language=”vb”]
Sub sbFill_OddRows()
‘Declaration
Dim iCntr, jCntr, lastRow As Long
‘iCntr to iterate Sheet2
‘jCntr to iterate Sheet1
‘lastRow for storeing last row with data in Sheet2lastRow = 25
‘Assuming you have data up to 25th row in Sheet2
‘If the last row is not fixed, then check
‘our most useful vba examples to find Last row
‘in different scenariosjCntr = 1
For iCntr = 1 To lastRow
Sheet1.Cells(jCntr, 1) = Sheet2.Cells(iCntr, 1)
jCntr = jCntr + 2 ‘increasing jCntr to skip one row
NextEnd Sub
‘*To fill even rows: Same as above with one change
Sub sbFill_EvenRows()
Dim iCntr, jCntr, lastRow As Long
lastRow = 25jCntr = 2 ‘ 1 to fill Odd rows, 2 to fill Even rows
For iCntr = 1 To lastRow
Sheet1.Cells(jCntr, 1) = Sheet2.Cells(iCntr, 1)
jCntr = jCntr + 2
NextEnd Sub
[/code]Hope this helps, let me know if you need more clarification.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
E Sivakuamr
February 7, 2014 at 2:39 PM — ReplyHi,
I want to insert multiple objeats using VBA,Please help me on this.Ex:Coulamn c is having the 100 objects names,I want to search in my system and i want to insert repect to that coulmn.
-
PNRao
February 9, 2014 at 6:33 PM — ReplyHi Sivakumar,
Thanks for writing us! Could you please specify your problem in more detailed.I understand that you will have your object names in C column of on of the sheet and you want to insert them just right to that respective cell. The thing I could not understand is Object: What are you referencing as object? is this a image?… please elaborate your question.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Ashish
February 12, 2014 at 9:39 PM — Replyhi this is my query, could you please help
i have these percentages
35%,40%,25% and then i have a value say 50,000
i have made a tab on which i click and it should calculate the percentages itselfwill the same macro run for multiple entries?
-
Anurag Mishra
February 21, 2014 at 3:50 PM — ReplyHi Team,
I want to extract data from MSSQL server between two date and this date must be insert by user in the text box of a vba form so give me an example where we take the date from text box n put it on SQL query and direct extract the data from the server.
Thankyou
-
sravan
February 21, 2014 at 5:17 PM — ReplyHi,
Can you please show me the code to insert alphabets from A to Z in Horizontally and vertically.
Thanks,
Sravan -
PNRao
February 22, 2014 at 11:18 AM — Reply -
PNRao
February 22, 2014 at 11:23 AM — ReplyHere you go…
Sub sbPrintAlphabetsVertically()For iCntr = 1 To 26
Cells(iCntr, 1) = Chr(64 + iCntr)
NextEnd Sub
Sub sbPrintAlphabetsHorizonatally()
For iCntr = 1 To 26
Cells(1, iCntr) = Chr(64 + iCntr)
NextEnd Sub
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Aslam
February 24, 2014 at 6:35 PM — ReplyHi
I am new to VBA can u please show me the code to search amount with negative sign in particular column and move it next/ before that column.
Thanks in advance,
Aslam
-
arc
February 25, 2014 at 7:39 AM — ReplySimilar to PNRao response. I want to selectively pick data out of a column (the picks will be stepped apart by 3) , select the picks and paste to another column in contiguous fashion (meaning continuous-no step). This works in manually recording a macro and running it but I cannot make it work with programmed VBA language. Excel 2003.
Thanks
arc -
PNRao
February 25, 2014 at 11:31 PM — ReplyHi Arc,
You can use STEP statement. Here is the example code:Assuming you have data in Column A: A1,A4,A7,…..
And you want to print in Column B: B1,B2,B3…
Sub sbPrintColumnAByStep3InColumnB()
Dim iCntr, jCntr, lastRow As Long
lastRow = 50 ' Last Row of Column A with data:You can change this
jCntr = 1 ' Counter for Column B
For iCntr = 1 To lastRow Step 3
Cells(jCntr, 2) = Cells(iCntr, 1)
jCntr = jCntr + 1
Next
End Sub
Thanks-PNRao! -
PNRao
February 25, 2014 at 11:37 PM — ReplyHi Aslam,
You can just check if the Column A value is <0 then print into Column B. Here is the Example:
Sub sbPrintNegativeColumnAValuesInToColumnB()
Dim iCntr, jCntr, lastRow As Long
lastRow = 50 ‘ Last Row of Column A with data:You can change this
For iCntr = 1 To lastRow
If Cells(iCntr, 1) < 0 Then Cells(iCntr, 2) = Cells(iCntr, 1)
Next
End Sub
-
PNRao
February 25, 2014 at 11:49 PM — ReplyHi Ashish,
I am assuming you have your Value at A1 and Percentages at B1,B2,B3 and you want to print the percentage of that values in C1,C2,C3.
for this you can use simple formula in C1=A1*B1/100 [Example, if you have 200 in A1 and 10 in B1, this will pront 20 in C1]
Sorry, your question is not clear, please provide more information. So that I can help you.
Thanks-PNRao! -
gc pathalla
March 3, 2014 at 12:43 AM — ReplyGreat Site!!
Very Helpful!!
Thanks a Lot!!
-
PNRao
March 3, 2014 at 10:49 PM — ReplyHi gcpathalla,
Thanks for your comments.
Thanks-PNRao! -
Satish Telgote
April 17, 2014 at 8:29 PM — ReplyHi, I am beginner, please advise me how to create tracker in VB using excel sheet. In a Excel sheet there are data in 5 column with titles, wanted to create Title on VB template. If I search with 1st Co data rest 4 columns data should be reflect e.g Column A Contain Dates, Column B contains Days, Column C Contains Activity etc
If the VB template if I input Dates Field all 4 Fields reflects relevant data
Regards
Satish Telgote -
PNRao
April 17, 2014 at 10:50 PM — ReplyHi Satish,
You can use Vlookup formula to achieve this. If you want to build your own function, you can loop through the each row and display the column data wherever its matching the given criteria.
The sample code looks like this:
Dim dtAVal as Date
Dim lastRow as Long
Dim blnFound as Boolean
blnFound =False
dtAVal = cdate(InputBox1.value) ' Your input date to find the respective data
lastRow=200 'Your last row in the worksheet'looping through all rows and trying to get match row number
For iCntr=1 to lastRow
If Cells(iCntr,1)=dtAVal then
blnFound =True
exit For
End if
Nextif blnFound =True then
'Fill the respective data into other columns
TextBox2.Value=Cells(iCntr,2) 'Column B
TextBox3.Value=Cells(iCntr,3) 'Column C
TextBox4.Value=Cells(iCntr,4) 'Column Dend if
Hope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
Gajanan Ashok Pujari
April 20, 2014 at 2:08 PM — ReplyHi, i heed an help, as i need coding , when some one click in txt box, then time should start, and when click on submit, should stop the time,
-
Malin Tedesund
April 24, 2014 at 7:24 PM — ReplyHi!
Also very much a beginner! I am trying to link excel to ppt using VBA, more precisely I want to be able to automize “moving” the value of one cell in excel to a specific location in my ppt presentation. Hoping this is possible and if so I could really use some help.
Thank you in advance,
Malin Tedesund -
PNRao
April 24, 2014 at 8:39 PM — ReplyHi Malin,
Thanks for visiting our blog. PPT automation is 100% possible with Excel VBA.
I am assuming, you want to export data/figures from Excel to particular slide in the PPT with required format. We can automate anything with PPT using Excel VBA, we can design a tool to do this task.
Please let us know your requirement, you can send the files and requirement to info@analysistabs.com.Thanks-PNRao!
-
PNRao
April 24, 2014 at 9:03 PM — ReplyHi Gajanan Ashok Pujari,
You can create two variables on module level variable 1 to capture the time on text box click. And the variable 2 is to capture the time on Submit button click. Now you can get the time difference of the variable 1 from variable 2.Hope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
Lailuma
April 26, 2014 at 12:09 PM — ReplyHi,
As I visit this website this is the best website for VBA developers.
I have a problem I have a folder with about 700 excel workbooks as telephone bills. I want to first divide all workbooks into proper folders. how can I move these files in to proper folder when I run the macro first it ask me about the Source Folder, second wants to select the files then it ask the Destination folder. if it is possible please help me in this regard.Thanks in advance,
Lailuma
-
PNRao
April 27, 2014 at 12:47 PM — ReplyHi Lailuma,
You can do this as explained below:
Create 3 buttons in Worksheet
Button1: Place at Range A3 – This is to select the Source Folder: Use the File dialog to pick the folder name and put the folder path into Range B3[vb]
Set fldFolder = Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogFolderPicker)
With fldFolder
.ButtonName = «Hello choose a Folder Now»
.Title = «Choose a Folder»
.Show
Range(«B3»)=.SelectedItems(1)
End With
[/vb]Button2: Place at Range A4 – This is to choose your files from the source folder: Use the File dialog to pick the multiple file names.
[vb]
Set fldFile = Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogFilePicker)
With fldFile
.ButtonName = «Hello choose your Files Now»
.Title = » Choose an Excel File»
.Show
For iCntr= 1 to .SelectedItems.Count
Range(«B» iCntr+4 )=.SelectedItems(iCntr)
Next
End With
[/vb]
Now you have your file names ready to move into a another folder.
Button3: Place at Range A5 – This is to choose your destination folder. use the the same method to choose a folder shown for Button1. And loop through the files in your worksheet and move the file.
See the file handling examples to move the files from one location to another location.Hope this helps.
Thanks-PNRao! -
Adam Sanderson
April 30, 2014 at 11:23 PM — ReplyThis website is really great! I am looking to compile cell A1 from 50 different tabs in 50 different spreadsheets that are all in one folder, into one column on one spreadsheet. Please help!!
-
Lailuma
May 3, 2014 at 5:45 PM — ReplyHi I have worked with the above code unfortunately it is not working an give “Run-time error ‘1004’: Method ‘Range’ of object ‘_Worksheet’ Message. if it is possible could you please write me the entire code.
Thanks,
Lailuma
-
PNRao
May 4, 2014 at 11:42 AM — ReplyHi Luiluma,
Could you please let us know the code which you have tried. And the Office Version which you have tried. So that we can help you to fix the issue.Thanks-PNRao!
-
PNRao
May 4, 2014 at 11:56 AM — ReplyHi Adam,
You can loop through all the files in the folder and then fetch the range A1 and put it in your destination sheet.
[vb]
Sub sbLoopThroughAllFilesInFolderGetData()
Dim StrFolder As String
StrFolder = Dir(«c:temp») ‘ Your folder name
iCntr = 0
Do While Len(StrFolder) > 0
iCntr = iCntr + 1
Set wb = Workbooks.Open(StrFolder) ‘open each file here
Cells(iCntr, 1) = StrFolder ‘ this your file name
Cells(iCntr, 2) = wb.Sheets(«Sheet1»).Range(«A1») ‘ this your data from Range A1
StrFolder = Dir
Loop
End Sub
[/vb]Thanks-PNRao!
-
Umesh Shinde
May 10, 2014 at 2:21 PM — ReplyI want to open text document in excel which is pipe saperator and last column as date and time i want date and time saperately while clicking command button
-
Rajeev
May 20, 2014 at 12:09 PM — ReplyHello,
I learnt many things from given Example.
Many Thanks
Thanks and Regards,
Rajeev -
PNRao
May 20, 2014 at 10:22 PM — ReplyHi Rajeev, Thanks for your comments – PNRao!
-
Lucia
June 6, 2014 at 8:17 PM — ReplySome other features of Microsoft Office 2010: microsoft
Publisher 2010 Access. There are several ways you can run your
brand new macro. Connecting your employees with specific information and expertise.Feel free to surf to my web site: Microsoft Office 365 serial number, Lucia,
-
Ary
June 14, 2014 at 2:15 AM — ReplyHey.. Thank you for your very helpful website. I am new to VBA and i am now stuck at this problem. I have a big data for temperature.
1. 21.40
2. 21.45
3. 21.38
4. 22.89
5. 23.27
……1000. 85.54and so on. And i put these data in Column A. So for each temperature, i want to assign their density and heat coeff. values in Column B (respective to the temperature). So i try this:
Dim Temp As Range, Density As Double
Set Temp = Range(“A1:A1000”)
Temp = Range(“A1:A1000”).Value
If Temp = 21 Then
Density = 998.08
ElseIf Temp=22 Then
Density = 997.86
ElseIf…(I do until the required Temp)
End If
Range(“B1:B1000”).Value = DensityAnd i got mismatch error. Could you please help me?
Thanks.Regards,
Ary -
PNRao
June 14, 2014 at 9:16 PM — ReplyHi Ary,
You can’t put everything in one-shot, use the for loop instead.
Sub temperature2HeatCoeff()
Dim iCntr As Long
Dim Temp As Double, Density As Double
For iCntr = 1 To 1000
Temp = Range("A" & iCntr)
If Temp = 21 Then
Density = 998.08
ElseIf Temp = 22 Then
Density = 997.86
'ElseIf…(I do until the required Temp)
' ----
End If
Range("B" & iCntr) = Density
Next
End Sub
-
Ary
June 17, 2014 at 3:04 AM — ReplyThank you very much. With your help now i can do it.
-
PNRao
June 17, 2014 at 10:58 PM — Reply -
Ary
June 25, 2014 at 4:33 AM — ReplyHi PNRao,
I need some help on this. Okay, as example i have data in excel and this is only a part of them:
Temp : (21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 29, 30, 26 25, 24, 23, 22), (24, 25, 26, 30, 27, 28, 29, 25, 21, 19), (20, 22, 23, 36,30, 34, 35, 30, 25, 23), (24, 26, 30, 34, 28, 25, 20)
These are temperature of a liquid. The temperature are increasing until the peak and then go down until certain temperature (one cycle). Then it is increasing and goes down again(next cycle). In these example there are 4 cycles. And it repeats until i have a few cycles.
For every each of the temperature, i can calculate its volume.
I try to write code to detect these cycles because i want to calculate the average volume for each cycle. But i don’t have idea how to start since i am new to VBA.Thank you
-
Charl
June 25, 2014 at 11:08 AM — ReplyHi, I’m trying to get part of a tag out of a cell into a new cell, the tag looks like this: “xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxxxxx” or some look like this: “xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxxxxx-xxxxxx”, I just want to get the last part of the tag (after the last “-“) into a new cell, I have +-35000 tags to do this with. can you tell met how to go about please.
-
PNRao
June 26, 2014 at 12:11 AM — ReplyHi Ary,
Here is the code, I am assuming your volume data in Column A (I pasted all your data in the column A from row 1 to Row 40)
Sub CycleAverage()
Dim lRow As LonglRow = Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
'Find
totSum = 0
totCount = 0
AvgVolCntr = 1
For iCntr = 1 To lRow
totSum = totSum + Range("A" & iCntr)
totCount = totCount + 1'If New Cycle Starts : When I find series of values some thing like this: 2-1-2 or 9-3-4 or a blank
If iCntr > 2 Then
If (Range("A" & iCntr) > Range("A" & iCntr - 1) And _
Range("A" & iCntr - 1) < Range("A" & iCntr - 2)) Or Range("A" & iCntr) = " Then'print Averages in Column D & E
Range("D" & AvgVolCntr) = "Cycle: " & AvgVolCntr
Range("E" & AvgVolCntr) = totSum / totCount'and set totals to zero
totSum = 0
totCount = 0'increase AvgVolCntr
AvgVolCntr = AvgVolCntr + 1
End If
End IfNext iCntr
End Sub
Hope this helps! Thanks — PNRao!
-
PNRao
June 26, 2014 at 12:27 AM — ReplyHi Charl,
You can find last sting using this VBA code:
Assuming that you have your data in Column A. And printing the last string in Column B
Sub find_Last_String()
Dim lrow As Long'find last row
lrow = Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row'process from first row to last row
For iCntr = 1 To lrow
MyString = Cells(iCntr, 1)
findLastHypen = Len(MyString) - InStr(1, StrReverse(MyString), "-")
finalString = Mid(MyString, findLastHypen + 2, Len(MyString) - findLastHypen)
'print in Column B
Cells(iCntr, 2) = finalString
Next
End SubHope this helps! Thanks – PNRao!
-
Ary
June 27, 2014 at 12:47 AM — ReplyThank you so much. This helps me a lot
-
Charl
June 27, 2014 at 12:14 PM — ReplyThanks PNRao, this is exactly what I needed.
-
Evan
June 28, 2014 at 6:49 AM — ReplyEverything is very open with a very clear description of the
challenges. It was definitely informative. Your website is
useful. Thank you for sharing! -
PNRao
June 28, 2014 at 10:47 PM — ReplyHi Evan, Thanks for your comments-PNRao!
-
Sumit
July 2, 2014 at 2:00 PM — ReplyI want a macro for replacing all the names same as in one cell say with a name in another cell.
-
PNRao
July 2, 2014 at 3:57 PM — ReplyHi Sumit,
Assuming Range A1 is having the name to find, Range B1 is having the Name to be replaced with.The following code will find the name mentioned at Range A1 and Replace with the name mentioned at Range B1:
Sub VBAToReplaceAString()
strToReplace = Range(“A1”).Value
strReplaceWith = Range(“B1”).ValueCells.Replace What:=strToReplace, Replacement:=strReplaceWith, LookAt:=xlPart, _
SearchOrder:=xlByRows, MatchCase:=False, SearchFormat:=False, _
ReplaceFormat:=False
Range(“A1”).Value = strToReplace
End SubHope this helps-Thanks-PNRao!
-
Deependu
July 7, 2014 at 2:15 AM — ReplyVery Nice website, Thankyou Mr Rao for your support & great efforts, its simply Great Effort…
-
PNRao
July 7, 2014 at 3:20 PM — ReplyThank you Mr. Deependu – We are very happy to receive such a sweet feedback from our reader.
Thanks-PNRao! -
Krishna M
July 12, 2014 at 3:35 PM — ReplyDear Sir,
I would like to register for the Aug 2014 course. Upon entering my e-mail id, i did not receive any mail from your site. Could you please let me know the procedure to register for the VBA macro course.Thanks,
Krishna M -
PNRao
July 12, 2014 at 7:00 PM — ReplyYou’r registration is successful, and I can send the discount detail before starting our online classes!
Thanks-PNRao!
-
kevin
August 7, 2014 at 3:12 PM — Replyhi i m new to VBA…could you please tell me how to do coding for BFS algorithm in excel?please reply ASAP..
-
Joey
August 8, 2014 at 7:33 AM — ReplyHi, I need some help:
Given:
– The stock price is 68.
– The risk-free rate is 0.05.
– The stock’s expected return is 0.15 when jumps are ignored.
– The stock’s volatility is 0.3.
– When jumps are ignored, stock prices are lognormally distributed.
– The annual number of jumps follows a Poisson distribution with l = 1.8.
– Jump magnitudes are lognormal with aj = -0.1 and sj = 0.3.Using control variate method to estimate the value of an European call option with 0.5 year to maturity and strike price of 70. Given 95% confidence interval as answer on the spreadsheet with proper statement and annotation.
Report on the estimate by (i) crude method (ii) control variate method and (iii) efficient of the control variate method over the crude method for 5000 simulations.
Thanks!
-
Brett
August 14, 2014 at 4:59 PM — ReplySay I have 18 files in a folder and I need to plot the 5th column of data each file onto the same graph. Any advice on this? Thanks so much!
-
PNRao
August 17, 2014 at 11:27 AM — ReplyHi Joey,
Could you please provide me sample file. So that it is easy to understand your problem to help you.Thanks-PNRao!
-
PNRao
August 17, 2014 at 11:36 AM — ReplyHi Brett,
You can do this using formulas, if your data ranges are always fixed. Other method is using VBA, you can write a simple macro to retrieve the data from all those file and plot a chart.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Roopert
September 12, 2014 at 9:33 PM — Replyhi,
I’m trying to sum a column/range within a column or row using VBA. I’d like to use the worksheetfunctions SUM, but I can’t seem to get it to work correctly. In fact I keep getting an error. Maybe I should be using something else? Please help.
Thanks – Roopert
-
allan
September 15, 2014 at 5:36 AM — ReplyHi PNRao,
I have an excel project that I am currently working on and I want to use VBA. I want to change the font color of all negative values, like for example column A, B and C. I update these values every month so the the value for let say, row 1 might be positive this month but negative next month. Just the negative values that i want the font color be changed into red and all the positive values remain black. Sorry, I am just new on VBA and macro.
Thanks in advance PNRao!
-
Hardeep Singh
September 24, 2014 at 8:21 PM — ReplyHello Sir,
Need your help?
I want to pull all the data from sheet1 to sheet2, using a commandbutton and two textbox in which i want to give the date range (such as 09/01/2014 to 09/25/2014) and will pull the complete information between that range from sheet1 (that is master sheet) to Sheet2 (that where I want the data between that date range).
Thanks -
PNRao
September 26, 2014 at 9:44 PM — ReplyHi Hardeep Singh,
Assuming that you have data in sheet1 in Column A and B and you want these records into sheet2 based on given date range.
If you have date in Column A:startDate = “09/01/2014”
endDate = “09/25/2014”
lRow = 100 ‘ This is thelast row in sheet1: please refer our 100+ codes if your last row is not fixed.
jCntr = 1
For iCntr = 1 To lRow
If Format(Sheets(“Sheet1”).Range(“A” & iCntr), “dd/mm/yyyy”) >= startDate And Format(Sheets(“Sheet1”).Range(“A” & iCntr), “dd/mm/yyyy”) <= endDate Then
Sheets(«Sheet2»).Range(«A» & jCntr) = Sheets(«Sheet1»).Range(«A» & iCntr)
jCntr = jCntr + 1
End If
NextHope this helps.
Thanks-PNRao! -
Kay
October 3, 2014 at 1:52 AM — ReplyHi Rao,
Help me with a script to add a comma after every 2words in a cell.
Eg: Column A (How to add a comma after every two words in excel); so the result in Column B(How to, Add a, comma after, every two, words in, excel)Also another script: Column A (How to split cell after every three words and result in four different column and the rest in last column)
so the result will be in Column B(How to split); Column C(Cell after every); Column D(three words and); Column E(result in four different column and the rest in last column) -
PNRao
October 3, 2014 at 9:10 PM — ReplyAnswer for your first query:
Sub sbUsage()
lRow = 20 ‘Last row with data in Cloumn A
For iCntr = 1 To lRow
Range(“B” & iCntr) = fnCommasEvery2TwoWords(Range(“A” & iCntr))
Next
End SubFunction fnCommasEvery2TwoWords(ByVal strText As String)
arrText = Split(strText)
If UBound(arrText, 1) >= 2 Then
strText = ”
For iCntr = 0 To UBound(arrText, 1) Step 2
If iCntr = 0 Then
strText = arrText(iCntr) & ” ” & arrText(iCntr + 1)
ElseIf iCntr + 1 <= UBound(arrText, 1) Then
strText = strText & «, » & arrText(iCntr) & » » & arrText(iCntr + 1)
Else
strText = strText & «, » & arrText(iCntr)
End If
Next
End If
fnCommasEvery2TwoWords = strText
End Function
I hope, now you can solve the second query yourself.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Kay
October 12, 2014 at 4:01 AM — ReplyHi Rao,
Thank you for your help but am getting error..
Compile Error: Syntax errors…and “Cannot execute in break mode” -
PNRao
October 12, 2014 at 10:08 AM — ReplyHi Kay,
Could you please post the VBA code which you are trying.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Kabanda James
October 18, 2014 at 9:49 PM — ReplyGreetings,
I am trying to develop a tax calculator using Excel VBA. I request you to assist me with a code for a separator for every three digits, for instance 1,000,000 and 234,456 etc.
I will be very grateful if my request is considered. -
Paudel
October 19, 2014 at 11:44 AM — Replyheloo
i am new in vba. i want to write a program that subtracts such that it can carry over from another cell in relative mode. eg, i want to subtract 2003 6 18 from 2014 10 19 such that it takes carryover a month that is adding up 12 in second cell and 30 days in another cell. all these number are in different cells.
thank you in advance. -
PNRao
October 20, 2014 at 6:52 PM — ReplyHi James,
You can use number formats:
Assuming that you have 1000000 in Range A1:
Sub GFormatNumbersWithCommas()MsgBox Format(Range(“A1”), “#,##0”)
‘OR
Range(“B1”) = Range(“A1”)
Range(“B1”).NumberFormat = “#,##0”End Sub
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Vasu
October 22, 2014 at 12:08 AM — ReplyIt’s Great place to learn excel programming… I am very new to this site.
I have a question, please help me on this.
From this place I learnt how to hide and unhide excel sheet via VBA. Now my question is I want to hide sheet in excel and should open by using activex button and close the sheet completely after review. Is it possible to do it in VBA please help me. -
Vasu
October 22, 2014 at 11:00 PM — ReplyHello,
I am beginner to VBA, and I am trying to do some automation in my project,… Please help me.I have around 20 to 25 tabs in my excel file and I want to hide all this only on pressing a button I need this tab to open then there should be close option which hides the file again.
could you please help me with code for this.
Regards,
Vasu -
Anandh
October 22, 2014 at 11:49 PM — ReplyI am looking for an code to send email automatically, when a range of cells are changed in an excel sheet(irrespective of Alphabets or numericals).
-
PNRao
October 23, 2014 at 5:31 PM — ReplyHi Vasu,
You can use the same method to hide the sheets.
Follow the below process for your requirement:
-> Enter 0 at some range (Example at Range A1000)
-> Add two activeX controls (Review Now, Complete)
-> when user press the Review Now, check if range A1000= 0 then un hide the sheet to review
-> when user press the ‘Complete’, enter 1 at A1000 and hide the sheetHope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
PNRao
October 23, 2014 at 5:39 PM — ReplyHi Vasu,
You can not hide all sheets at any particular time, at least one sheet should be opened. Follow the below approach.
-> Have a Home worksheet
-> here you can provide the environment to choose a sheet and provide button to open it
-> the below macro will help you to do this:
Sub sbHideAllExceptOne()
shtToShow = “SheetToShow” ‘Change this as per your requirement
Sheets(shtToShow).Visible = True
For Each sht In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If sht.Name shtToShow Then sht.Visible = False
Next
End SubThanks-PNRao!
-
vasu
October 31, 2014 at 11:43 PM — Reply -
PNRao
November 1, 2014 at 10:44 AM — Reply -
sravan
November 5, 2014 at 9:18 AM — ReplyReally it’s good website. Hope you are not updating on Facebook. Every day at-least post a tip or code which will make the blog or our forum & we all mutual friend have scope to have a chat
Even I have same query if i have a Excel sheet close I wish to copy the data & close the file need code in VBA. -
Vineet Dubey
November 7, 2014 at 3:59 AM — ReplyHi Mr. Rao,
It really feels good to see this site and these posts. Hats off to your efforts in developing programs and people with their skills so that they can earn bread and butter.My question is that how do i protect a folder from getting deleted. I want to protect the folder and the contents of the folder from being deleted. Is there a way out through VBA ?
My second question is that how do i add a specific content in all the worksheets in an excel file. there may be different tabs in excel and they might varry. we have to run a loop which will open all the existing tabs in an excel sheet and add that specific content. some times there are 12 tabs and some times there are 15 or 16 or 20 or even more than that. Could you please help me with a code to solve this thing.
-
PNRao
November 10, 2014 at 9:50 PM — ReplyHi sravan, Thanks for suggestions. Yes, I am thinking to Best ways to create a best VBA forum to discuss our ideas. I am working on it.
I am going to launch it soon. -
Shyam
November 26, 2014 at 10:31 AM — ReplyHi,
1) I want to know what will a vba vlookup function will return if the values in two columns in different sheets match.
2) Sample syntax to compare 2 columns present in two sheets. -
Kalim
December 5, 2014 at 4:17 PM — ReplyHi Mr Rao,
i am working in excel since 2005, i just wanted to learn VBA, please guide
Thanks,
Kalim -
lavanya
December 18, 2014 at 11:30 AM — Replyhello I am very new to VBA, i am developing a project in excel. the project is like validating a excel,
I have to compare two cells on some condition.
if the result cell is blank it should show some message or i should not able to save excel
I need the code for this. please help -
Hi Mr. Rao,
I need to move one excel sheet from one folder to another while the status box in one of the sheets changes to completed. The problem is, the excel sheet has got dataconnection from another sheet. I do not want that data connection to be affected, while moving it to the new folder. Could you please help me here.
-
Hi Mr. Rao,
I need to update the details of certain columns of a sharepoint list based on the changes in an excel sheet. Right now, I am doing it manually. Is it possible to automate it. Could you please help
-
Nick R
January 18, 2015 at 10:05 AM — ReplyI have a bunch of data on one sheet, I need a macro to sort all the data to separate sheets based on the data in Column “H” for example. Column “H” is item location, I need all items from Location A to be sorted to its respective sheet. I need a macro that is going to be efficient as there will be thousands of lines that need sorted. I am not very familiar with VBA so Any Help would be greatly appreciated.
-
Raghu Rao
January 20, 2015 at 9:17 AM — ReplyI have a list of all member information in one sheet and another sheet has list of all members who have paid their dues.
How do I generate a list of members who are yet to pay from these 2 sheets. I do not have much experience with VBA and any help would be appreciated. -
meena
January 21, 2015 at 4:48 PM — Replyiam very new to thisVB,can you explan me
-
PNRao
January 23, 2015 at 10:36 AM — ReplyHi Raghu,
Please check the below macro:
Sub HighlightUnMatchedCells() Dim lRowS1 As Long Dim blnMatched As Boolean 'Finding last row with data lRowS2 = Sheets("Sheet2").Range("A100000").End(xlUp).Row 'Sheet1 For iCntr = 1 To lRowS2 'Checking if Sheet2 names (in column A)are exitst in sheet1 (column A) If Sheets("Sheet2").Range("A" & iCntr) <> " Then 'check if it is not blank blnMatched = False On Error GoTo skipA If Application.WorksheetFunction.Match(Sheets("Sheet2").Range("A" & iCntr), Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A:A"), 0) > 0 Then blnMatched = True skipA: If blnMatched = True Then ' already paid Sheets("Sheet2").Range("A" & iCntr).Interior.ColorIndex = 4 Else 'not yet paid Sheets("Sheet2").Range("A" & iCntr).Interior.ColorIndex = 3 End If End If Next End SubHope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
PNRao
January 23, 2015 at 10:52 AM — Reply -
Hello Rao,
I am new to VB, need your help for the below mentioned problem.
I have temperature dependent Material properties like Yield strength for example in Excel sheet A.
The values are obtained for the required temperature by interpolating in that particular excel sheet A.
Right now I am working on New Excel sheet B, where the results are to be displayed when the temperature value is entered.
Problem is the the results are required for different temperature, which cant be done once you have linked to that sheet A, bcoz when you enter the required temperature value, old results are also getting modified, with respect to last entered value.
Required your help to write one marco which selects the particular material in that sheet A and displays the value (Yield Strength)in sheet B in first row and also when selected for different temperature the results previous should remain as it isand display the latest results in second row.
-
Adrian Sorinel
February 3, 2015 at 11:40 AM — ReplyHi PNRao,
Congretulations for your work.
Could you please help me with the following problem?Background:
I have an exel worksheet (36 columns and 13102 rows) which have to be distributed daily basis to other 4 people in order to bring them input and to be send back.
Action:
All these worksheets together must update a master worksheet from whrere a report will be issued.
Question:
Which macro do I need to get an automatically update from all worksheets into master worksheet (as final version).Thank you very much,
Adrian -
PNRao
February 3, 2015 at 10:17 PM — ReplyHi Shrikara,
Please provide a sample file.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
PNRao
February 3, 2015 at 10:24 PM — ReplyHi Adrian,
Thank you for your comments!
You can use ADO, to retrieve the the data and update into one worksheet. Please refer the below links:
http://analysistabs.com/excel-vba/ado-sql-macros-connecting-database/And some of these 100+ examples will help you to read and write the data in Excel.
Please feel free to ask if in case of any questions you have. You can post example files (with dummy data) to get the exact solution.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Hello Rao,
I tried sending the reference files to the info@analysistabs.com email id, which I am facing issues. Can I have some other Email-id for which I can send these files.
Regards
Shrikara Rao -
Hello Rao,
Please send me a email id for which I can send a sample presentation.
Because the email sent to ‘info@analysistabs.com’ is giving delivery failure message.Looking forward your email id for which all details can be sent.
Regards
Shrikara -
anne
February 24, 2015 at 4:31 PM — Replyhi. Im just a beginner in using macro. Hope you can help me with this. What are the codes that i need to run a macro using a button. The button is in sheet 1, once I click it ,the macro will perform in sheet 2. The macro that Im making is for formatting data. The data is in sheet2, and i want the sheet 1 to contain only the button. Is this workable? thanks for the help.
-
mamatha
February 26, 2015 at 3:40 PM — ReplyHello PNRao,
Im very new to VBA Excel programming could you help me with the following problem
I have the following code with a button to generate respective plots with data. now i have to write a small code to Change the Format of the plot which is Default (Black dotted line) i need a code like to add a check box for the data with a button to chnge the Format and colour of the line maually could you help me through this.
Im very thankful if you provide a code for me.
Thank you
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Set nwsht = Sheets.Add(after:=Sheets(Worksheets.Count)) ‘add a new sheet
‘ nwsheet.Activate
ActiveSheet.Range(“B3:c4”).Select ‘basic formatting legende
With Selection
.MergeCells = True
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
.VerticalAlignment = xlCenter
.Value = “Legende”
.Font.Bold = True
.ColumnWidth = 5
End WithActiveSheet.Range(“B6:c7”).Select ‘basic formatting legende
With Selection
.MergeCells = True
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
.VerticalAlignment = xlCenter
.Value = “Akustik”
.Font.Bold = True
.ColumnWidth = 5
End WithActiveSheet.Range(“B9:c10”).Select ‘basic formatting legende
With Selection
.MergeCells = True
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
.VerticalAlignment = xlCenter
.Value = “Werte”
.Font.Bold = True
.ColumnWidth = 5
End WithActiveSheet.Range(“D1:d500”).ColumnWidth = 1 ‘basic formatting
ActiveSheet.Range(“G1:G500”).ColumnWidth = 1 ‘basic formatting
ActiveSheet.Range(“E3:F4”).Select ‘basic formatting legende cellWith Selection
.MergeCells = True
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
.VerticalAlignment = xlCenter
.ColumnWidth = 20
.Font.Bold = True
End WithActiveSheet.Range(“E5:G5”).RowHeight = 5 ‘basic formatting
ActiveSheet.Range(“E6:F7”).Select ‘basic formatting Ordnungen cell
With Selection
.MergeCells = True
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
.VerticalAlignment = xlCenter
.ColumnWidth = 20
.Font.Bold = True
‘ .Value = “Gesamt”
End With
ActiveSheet.Range(“E8:G8”).RowHeight = 5 ‘basic formattingActiveSheet.Range(“E9:F10”).Select ‘basic formatting Ordnungen werte cell
With Selection
.MergeCells = True
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
.VerticalAlignment = xlCenter
.ColumnWidth = 20
.Font.Bold = True
End With
ActiveSheet.Range(“E11:G11”).RowHeight = 5 ‘basic formattingActiveSheet.Range(“E12:E13”).Select ‘basic formatting drehzahl cell
With Selection
.MergeCells = True
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
.VerticalAlignment = xlCenter
.RowHeight = 20
.Value = “Drehzahl [rpm]”
.Font.Bold = True
End With
ActiveSheet.Range(“F12:F13”).Select ‘basic formatting drehzahl cell
With Selection
.MergeCells = True
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
.VerticalAlignment = xlCenter
.RowHeight = 20
.Value = “dB[A]/dB[lin]”
.Font.Bold = True
End With
ActiveSheet.Range(“E14:G14”).RowHeight = 2 ‘basic formattingActiveSheet.Range(“E6″).Select ‘data validation for Ordnungen
With Selection.Validation
.Delete
.Add Type:=xlValidateList, AlertStyle:=xlValidAlertStop, Operator:= _
xlBetween, Formula1:=”=moeglischplots”
.IgnoreBlank = True
.InCellDropdown = True
.InputTitle = ”
.ErrorTitle = ”
.InputMessage = ”
.ErrorMessage = ”
.ShowInput = True
.ShowError = True
End With
ActiveSheet.Range(“E6”).Value = “Gesamt”ActiveSheet.Range(“$Z$27”).Value = “Datei”
ActiveSheet.Range(“$Z$27”).Font.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0)ActiveSheet.Range(“$Z$28”).Value = “Gesamt”
ActiveSheet.Range(“$Z$29”).Value = “Ordnungen”
ActiveSheet.Range(“$Z$30”).Value = “Oktaven”ActiveSheet.Range(“$AA$28”).Value = “Ordnungen”
ActiveSheet.Range(“$AA$29”).Value = “Ordnungen”
ActiveSheet.Range(“$AA$30”).Value = “Oktaven”ActiveSheet.Range(“$AB$28”).Value = Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup(ActiveSheet.Range(“E6”), ActiveSheet.Range(“Z28:AA28”), 2, False) ‘ SVERWEIS(E6,$Z$28:$AA$30,2,FALSCH)] ‘vlookup für gesamt als ordnungen
ActiveSheet.Range(“E9″).Select ‘data validation for indirekt
With Selection.Validation
.Delete
.Add Type:=xlValidateList, AlertStyle:=xlValidAlertStop, Operator:= _
xlBetween, Formula1:=”=INDIRECT($E$6)”
.IgnoreBlank = True
.InCellDropdown = True
.InputTitle = ”
.ErrorTitle = ”
.InputMessage = ”
.ErrorMessage = “Kein Zugriff”
.ShowInput = True
.ShowError = True
End WithActiveSheet.Range(“I2:J7”).Select ‘space for button
Selection.Interior.ColorIndex = 2
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).Weight = xlThinActiveSheet.Range(“B3:f4”).Select ‘legend box
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).LineStyle = xlDash
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).LineStyle = xlDash
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).LineStyle = xlDash
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = xlDash
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).Weight = xlThinActiveSheet.Range(“B6:f7”).Select ‘akustik box
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).Weight = xlThinActiveSheet.Range(“B9:f10”).Select ‘werte box
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).Weight = xlThinActiveSheet.Range(“E15:f1000”).Select ‘zahlen box
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).Weight = xlThinActiveSheet.Range(“E12:f13”).Select ‘zahlen box
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).Weight = xlThinActiveSheet.Range(“A15:D15”).Select ‘copy hinweis
Selection.MergeCells = True
Selection.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
Selection.VerticalAlignment = xlCenter
Selection.Font.Bold = False
Selection.Font.Size = 7
Selection.Value = “datei ab hier kopierien”
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).Weight = xlThinActiveSheet.Range(“I12:K13”).Select
Selection.MergeCells = True
Selection.Value = “Lastenheft Datei”
Selection.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
Selection.VerticalAlignment = xlCenter
Selection.Font.Bold = True
Selection.Font.Size = 16
Selection.Font.Italic = True
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).LineStyle = xlDash
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).Weight = xlMedium
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).LineStyle = xlDash
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).Weight = xlMedium
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).LineStyle = xlDash
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).Weight = xlMedium
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = xlDash
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).Weight = xlMediumCall Lastenhefteingufen.CreateButton
End Sub
-
Jim Kevin Frazier
February 27, 2015 at 8:30 PM — ReplyI know nothing about VBA but I would like to know if I could write something that would tranpose data in rows to columns.
I have a list of names in rows, that have lost of data in the colums that repeat, for example below:
I need all the cities to appear in columns with just the one nameName City
John San Fran
John Cleveland
John Detroit
Can some one help, I have a big spreadsheet -
PNRao
March 2, 2015 at 7:41 PM — ReplyHi Anne,
It is possible, you can download the example files and explore the code.
Thanks-PNRao! -
valliappan
March 7, 2015 at 12:40 PM — Replyi dono how to insert the text box value to the tables weather can You provide the program for that?????
-
Rose
April 7, 2015 at 4:47 PM — ReplyJust want to ask how can I create a very simple accounting system using vbA where i can input data and generate then after.
-
Sven Holm
April 18, 2015 at 4:31 AM — ReplyHello
Is there code to bring data from another application into an excel file on a recurring time based interval.
Intervals are 5min,15min,30min and 1hour for about 40 sets of different data.Regards
Sven Holm -
Mathew
April 29, 2015 at 4:04 PM — ReplyHello,
i need a code to check a loop for multiple range name aa, ab, ac..for range e1:r24, s1:af24, ag2:at24 logically & give output range based on cell value, till the loop ends. In output i want to limit the worksheet size to 74 columns & then it should move to the next blank row.. -
nikolas
June 18, 2015 at 3:45 PM — Replyhi all , if enyone have ocupation in oil and gas geology, thy will anderstand me, i want do well constructions with VBA inputbox, means if i put options of oil wells, i want to do picture of construction, if anyone have idea wat i want, contact me i will show him exect wat i mean, thx a lots
-
Joey
July 11, 2015 at 1:00 AM — ReplyHello,
I am comparing a series of different materials across different year with varying amounts of dollars spent depending on the type of “contract”. These are then followed by 3 different teams, which each contain many people who “supply” the teams. I want to make these into a series of drop down menus. Meaning that once you click on one drop own menu, the next menu ill give you another choice.
For example
•Metal: Aluminum
•Forecasted Change in Year 17: 10%
•Type of Contract and it’s corresponding Spend 100,000 for fixed contracts, $50,000 for adjustable, etc.
•Team: 3 teams…each has roughly 60 suppliers who supply each team. Each supplier also has 4 sets of data to follow it (individual total spend, adjusted spend, and two more for anything that may come up).Is this possible? I know this is a pain, but I’m hoping anyone might be willing to help me. Thank you!
-
Ali
September 4, 2015 at 8:51 PM — ReplyHi there,
First off, thanks a lot for this fantastic page.
How can we find the last used row in a particular column within a specific range, lets say Range(“A3:E10”)? and likewise for the last used column in a row?
That would be really helpful.
Thanks.
-
mohsen
November 17, 2015 at 6:09 PM — Replyhi to all
i have a ?
How can disabled the click event in the worksheet in Excel 2007 ?
tanks for all user -
PNRao
November 17, 2015 at 9:55 PM — ReplyHi,
You can disable all the application events by Application.EnableEvents = False.
But worksheet events are user defined in the worksheet module or workbook modules. Please check and comment the codes to disable the worksheet events.Please provide the enough description of your requirement to understand better.
Thanks-PNRao! -
VSharp
November 27, 2015 at 3:07 AM — ReplyHi,
I am using Excel 2007, I have a drop down box so users can select ‘Yes’ or ‘No’. If ‘Yes’ is selected how do I create a pop up message asking the user to complete a particular question (i.e. now complete Question 2), but if the user selects ‘No’ from the drop down box the pop up message will ask the user to complete a different question (i.e. now complete Question 3), please help!
Many thanks VSharp -
PNRao
November 27, 2015 at 4:53 PM — ReplyHi VSharp,
Here is the code for the above question.
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize() ComboBox1.AddItem "Yes" ComboBox1.AddItem "No" End Sub Private Sub ComboBox1_Change() If ComboBox1.ListIndex = 0 Then MsgBox "Now complete Question 2", vbInformation Else MsgBox "Now complete Question 3", vbInformation End If End SubRegards-Valli
-
Lloyd
December 6, 2015 at 4:32 AM — ReplyI am trying to get a message box to appear if someone enters date in a cell that is not empty. I would like it to ask if they really want to change the value (yes, no) if Yes, allow change if No, end routine. If cell is empty then just allow input.
Is this possible.
Thanks in advance for any help you can offer. -
Lloyd
December 7, 2015 at 4:15 AM — ReplyThe above post should sat enters data in a cell not date
-
Jay
December 14, 2015 at 4:02 PM — ReplyHI,
We have 3 sheets.Sheet1:
Features John
a L1
b L2
c
d L4Sheet2:
w x y z
a 1
b 1
c 1
d 1Sheet3:
Area John
w L1
x
y
zHere a,b,c,d are features and w,x,y,z are areas. Sheet-2 is the mapping between feature and area. Suppose, in feature “a” John has L1 level. Now, we will check in Sheet2. In Sheet2 for “a” we need to check the nonblank cells, so here for “a” we have nonblank cell in “w” column. That means “a” has relation with “w”. So, in Sheet-3 “L1” value is stored in “w” row for John, like I have put “L1” in “w” row for John.
We have to design a button to fill the entire Sheet-3 on a single click.
Please help me.Thanks.
-
Uday
January 19, 2016 at 12:31 PM — ReplyHi,
I want to learn VBA(Macros) and need to know where i can get learning on coding from Basics.
**had good knowledge on Excel
Regards
Uday -
Rajashree
February 11, 2016 at 5:05 PM — ReplyHi, Thank you so much for the info it is really helping me out. but however, i am stuck with a situation where, i’am trying to merge few top and few bottom rows into one. For example,
Names Status
abc active
abc active
cbv closed
dfg closed
abc closedHere, how can i merge all those “abc” into one column without loosing any data?
any help in this would be appreciated. -
Ghie
February 15, 2016 at 1:16 PM — ReplyHelp
I have columns A-G
A = Either Arrival of Departure
B = military time (ex 1200, 2330, etc)
C = value if A=Arrival and B1200
E = value if A=Departure and B>1200
F = value if A=Departure and B<=1200I need a a column G which gives either the value C,D,E,F depending on A and B
-
balaviswanath
February 19, 2016 at 2:58 PM — ReplyHi Everyone,
I want to export comma(,) in to a text file using vba script using any function writeline and write .
Thanks,
Bala Viswanath. -
Limbani
February 21, 2016 at 9:50 PM — Replythanks for sharing the article i love to share with my buddies..
-
khirod kumar
March 29, 2016 at 10:59 AM — ReplyHello pn Raw,
I want to learn vba and I know very well advance excel and now I working as a mis executive .
I don’t know anything about vba so how to start vba can u give me basic vba book or any types of material that will help me my email I’d -
satvir
April 7, 2016 at 3:29 PM — ReplyHi,
Thank you for providing us helpful tricks.I am trying to run this VBA but it’s not working well.
I have got a table which is filtered. I want to multiply column b visible values only with 0 till the column b is blank.
I will appreciate your response.
Thanks
Satvir -
Kevin
April 12, 2016 at 7:58 PM — ReplyThank you very much for sharing this article!!
-
vishal jadhav
June 16, 2016 at 7:03 PM — ReplyHI,
I WANT TO KNOW About
i have one excel sheet in that 1 to 12400 rows
in rows written authorise to send and below that categorie1,……. categories 8
after that same as authorise to receive below that categorie 1,…….categories 8
in multiple time both written .
my scenario is need to delete only authorise to receive below that categorie 1,……..categories 8 but never want to delete categories of authorise to send. help me .and tell particular macro.
regards
vishal jadhav -
vishal jadhav
June 17, 2016 at 1:13 PM — ReplyHI,
i want to know aboutin my excel sheet have some data name location amt large data
i want add time from one application want to add automate time from application to my excel sheet.for each transaction -
Ajit
June 22, 2016 at 1:24 AM — ReplyHi
I am trying to use conditional formatting with VBA and a for or while loop. For example I have a worksheet which has dataset1 from ranges A1:Z3 which I want to use as the reference to be checked against. I have dataset2 which is from ranges A5:Z6 which I want to check against the first dataset1 in A1:Z3
I have the following code which I am using;
x = x + 1
With Range(Cells(x + 1, y + 1), Cells(x + 1, y + 1)).FormatConditions.Add( _
Type:=xlExpression, _
Formula1:=”=$I3$I7″)
.Interior.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0)
.Font.Color = RGB(255, 255, 0)End With
I would like to replace the cells which are in the line Formula1:=”=$I3$I7″) with something which can be incremented.
Please help.
Thanks
-
vee
June 23, 2016 at 12:40 PM — ReplyThank you very much. This is an excellent collection of useful VBA code!
-
ashu
June 29, 2016 at 2:42 PM — ReplyHiii, i m new to VBA…could you please tell me how to do coding for create a invoice template using buttons
i.e new, save ,delete ,update buttons
-
vishal
October 14, 2016 at 10:53 AM — Replyhi
i have a queri about vba
i have data sheet in data sheet i need to filter for date and need to add formula after 3 column .
for example ab column date filter then want formula in ad column equal to .need suggestion
regards
vishal jadhav -
ylnv prasadrao
October 28, 2016 at 6:50 AM — ReplyRespected Sir,
1.How to rounded off next rupee, if the value is 50 paise and above using excel vba?
1.How to rounded off lower rupee, if the value is 50 paise and below using excel vba?Thanking you sir,
Prasad
-
Mahendra
November 8, 2016 at 2:53 AM — ReplyHi how can I open only one instance at a time in excel 2010 using VBA code, any idea please?
-
Sharad Hardikar
November 12, 2016 at 7:54 PM — ReplyHi!
I passed an multidimensional array (7,9) to range A2:I10. The result however was the data got passed to column B to I and the last column was not passed. I changed the range to A2:J10 and all data got passed to columns B to J. On both occasions, The second row was blank and column A was blank. While I could not get a solution and had to move the data by deleting the row 2 and Column A cells throughcode, what is the reason for this phenomena? -
Nabi
November 15, 2016 at 3:17 PM — ReplyHi, I am Nabi, I have an excel macro VBA stock sheet but my Exit month wise item under report do not work when I click the Exit month button and try to see month wise report on that time report do not show and I got msg. box. The msg box has show report not available. So plz help me how can show my month wise (exit item report).
-
Vonjie
December 8, 2016 at 3:21 AM — ReplyHello,
Great effort in all of the comments that you have helped.
Hope you could help me too.
I want to create a Button that will gather all the data in the assigned cells and make it inserted in the existing table assigned per Person/borrower.
Table is Borrower’s logs of their individual payments as well as showing the remaining balance.
Example: Columns are Date, Payment Amount, Balance(this may not show, I just have to Subtract another cell with is Principal Amount versus its Payment.
Date Payment Amt Balance
1,000.00
12/1/16 300.00 700.00
12/3/16 50.00 650.00
13/6/16 275.00 375.00Best Regards,
Vonjie
-
Noufiya
December 19, 2016 at 8:23 PM — ReplyHi,
I am new to VBA. And i feel interesting to study VBA while gone through this site.
Now i try to modify my little projects in excel into in terms of VBA. My project is simple,
I have a set of standard values in a sheet. With reference to this standard values, my result after 1 production is analysed for each row. Each row contains different item so i need to set different formula. Fortunately i had done it well
. .
Now my aim is,
1) Copy each row into new sheet, (for eg: row1= A1:K1, row2= A2:K2…..row1=Ai: Ki). i need to copy only 1 row into new sheet…and each row contains formula. i need to copy this formula too. And the sheet name changes to item name( in first the column)2) Now i have 89 items (i.e.rows) to copy to different sheets. in the second sheet in my workbook is a commend box. where , if i click on a command box, its name is an item name, then corresponding sheet will activate. and i can edit it. all other sheets are on hide.
3) if I enter 90th row once, these above procedures must be followed.
So if i enter details in 90th row, and then click on command box in the same sheet, a new sheet with a copy of 90th row only generate. also this worksheet is saved under another command box on the second sheet.
hoping you will understand what i mean.
your earliest reply will be highly appreciated.
thank you very much
Noufi
-
vishal
December 20, 2016 at 6:29 PM — Replyhi
vishal here‘pre/post
Dim MyFile As String
Dim SORT_File As String
Dim LastRow As String
MyFile = Application.GetOpenFilename()
Workbooks.Open filename:=MyFile
MyFile = ActiveWorkbook.Name
Sheets(“Data”).Select
LastRow = Cells(Rows.Count, 2).End(xlUp).Row
For r1 = 2 To LastRow
Windows(MyFile).Activate
Sheets(“Data”).Select
If sheet2.Range(“AG” & r1).Value = “4:00 PM” Thensheet2.Range(“AN” & r1).Value = “=IF(P2<=$AN$1,»»Pre»»,»»Post»»)»
Else
sheet2.Range(«AN» & r1).Value = «=IF(P2<=$AO$1,»»Pre»»,»»Post»»)»
End If
Next
i have written this macro but tell me why not run this macro.need help anyoneregards
vishal jadhav -
vishal
December 21, 2016 at 1:50 PM — ReplyQUESTION:- RANGE A1 AND COLUMN 1 AUTOFILTER CRITERIA :- “04:00 PM”
IF RANGEA1&LASTROW.VALUE=”04:00 PM” THEN RANGE B2&LASTROW.VALUE= IBYB
IF RANGE A1&LASTROW.VALUE=”03:30 PM” THEN RANGE B2&LASTROW.VALUE=REMITTANCE
END IF END IFGIVE ME SOLUTION.
VISHAL -
gaurav gangh
December 21, 2016 at 2:11 PM — ReplyHi,
I have an excel file with xml mappings done which has links from another excel file, i need a code where the code automatically saves the file to a specified file name as soon as the xml mapped file receives any changes from the excel file.
regards
Gaurav Gangh -
subrahmanyam
January 7, 2017 at 11:48 AM — ReplyHi,
We are trying to build dashboard based on various types of data in excel sheets All these excel files will be located in specified path. All these files have commonly one unique field . Also , i have one more excel file which contains master list of that unique field.
For example :
I have 5 sheets in one specified folder.
all the files having one Project code as unique field.
However I need to create dashboard based on the portfolio under which the above projects are falling.
Like : for a project code “PPP” i have mapping of portfolio as “ABC”. This data will be stored in one excel file apart from the above mentioned 5 files.Now i need to generate data based on this mapping and rest 5 excel files and then have dashboards created on top of that.
Need help in having the code for this problem.
thank you.
-
Ordan
January 18, 2017 at 7:13 PM — ReplyHi there,
Is there anyway to add button that once you press it, will add the same pre-made data table?
Regards
Ordan Gilboa -
Blessy
February 10, 2017 at 1:47 PM — ReplyHi Suppose I have value 100, 101,105 in column A and column B has different values for eg 20,40,80,60 and I want to fetch the values only those are in front of 100 in Excel 2010.
Can you please advise how can it be done -
rajadurai
March 15, 2017 at 5:46 PM — ReplyOption Explicit
Dim binNew As Boolean
Dim TRows, THows, i As LongPrivate Sub UserForm_Click()
End Sub
Private Sub CmdClose_Click()
If CmdClose.Caption = “Close” Then
Unload Me
Else
CmdClose.Caption = “Close”
CmdNew.Enabled = True
CmdDelete.Enabled = True
End If
End SubPrivate Sub CmdNew_Click()
binNew = True
txtEmpNo.Text = ”
txtEmpName.Text = ”
txtAddr1.Text = ”
txtAddr2.Text = ”
txtAddr3.Text = ”CmdClose.Caption = “Cancel”
CmdNew.Enabled = False
CmdSave.Enabled = True
CmdDelete.Enabled = False
End SubPrivate Sub cmdSave_Click()
If Trim(txtEmpNo.Text) = ” Then
MsgBox “Enter Emp. No. “, vbCritical, “Save”
Exit Sub
End If
Call prSave
End SubPrivate Sub prSave()
If binNew = True Then
THows = Worksheets(“Data”).Range(“A1”).CurrentRegion.Rows.Count
With Worksheets(“Data”).Range(“A1″)
.Offset(THows, 0).Value = txtEmpNo.Text
.Offset(THows, 1).Value = txtEmpName.Text
.Offset(THows, 2).Value = txtAddr1.Text
.Offset(THows, 3).Value = txtAddr2.Text
.Offset(THows, 4).Value = txtAddr3.TextEnd With
txtEmpNo.Text = ”
txtEmpName.Text = ”
txtAddr1.Text = ”
txtAddr2.Text = ”
txtAddr3.Text = ”Call PrComboBoxFill
Else
For i = 2 To TRows
If Trim(Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 1).Value) = Trim(ComboBox1.Text) Then
Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 1).Value = txtEmpNo.Text
Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 2).Value = txtEmpName.Text
Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 3).Value = txtAddr1.Text
Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 4).Value = txtAddr2.Text
Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 5).Value = txtAddr3.TexttxtEmpNo.Text = ”
txtEmpName.Text = ”
txtAddr1.Text = ”
txtAddr2.Text = ”
txtAddr3.Text = ”Exit For
End If
Next i
End If
binNew = FalseEnd Sub
————————————-
Private Sub cmdDelete_Click()
TRows = Worksheets(“Data”).Range(“A1”).CurrentRegion.Rows.Count
Dim strDel
strDel = MagBox(“Delete ?”, vbYesNo, “Delete”)
If strDel = vbYes Then
For i = 2 To TRows
If Trims(Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 1).Value) = Trim(ComboBox1.Text) Then‘ sheet1.range(i & “:” & i).Delete
Worksheets(“Data”).Range(i & “:” & i).DeleteTxtEmpNo.Text = ”
txtEmpName.Text = ”
TxtempAddr1.Text = ”
TxtempAddr2.Text = ”
TxtempAddr3.Text = ”
TxtempAddr4.Text = ”
Call prCoboBoxFill
Exit For
End If
Next i
If Trim(ComboBox1.Text) = ” Then
cmdSave.Enabled = False
cmdDelete.Enabled = False
Else
cmdSave.Enabled = True
cmdDelete.Enabled = True
End If
End If
End Sub
——————————–
Private Sub CmdClose_Click()
If CmdClose.Caption = “Close” Then
Unload Me
Else
CmdClose.Caption = “Close”
CmdNew.Enabled = True
CmdDelete.Enabled = True
End If
End Sub
————————————-Private Sub PrComboBoxFill()
TRows = Worksheets(“Data”).Range(“A1”).CurrentRegion.Rows.Count
ComboBox1.Clear
For i = 2 To TRows
ComboBox1.AddItem Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 1).ValueNext i
End Sub
—————————————————–
Private Sub Userform_Initialize()
Call PrComboBoxFillCmdSave.Enabled = False
CmdDelete.Enabled = FalseEnd Sub
—————————————————–
Private Sub cmdsearch_Click()
binNew = False
txtEmpNo.Text = ”
txtEmpName.Text = ”
txtAddr1.Text = ”
txtAddr2.Text = ”
txtAddr3.Text = ”TRows = Worksheets(“Data”).Range(“A1”).CurrentRegion.Rows.Count
For i = 2 To TRows
If Val(Trim(Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 1).Value)) = Val(Trim(ComboBox1.Text)) ThentxtEmpNo.Text = Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 1).Value
txtEmpName.Text = Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 2).Value
txtAddr1.Text = Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 3).Value
txtAddr2.Text = Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 4).Value
txtAddr3.Text = Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 5).ValueExit For
End If
Next i
If txtEmpNo.Text = ” Then
Else
CmdSave.Enabled = True
CmdDelete.Enabled = True
End If
End Sub
————————————————-————————————————
-
rajadurai
March 15, 2017 at 6:32 PM — Reply -
ravi
March 16, 2017 at 4:29 PM — ReplyOption Explicit
Dim binNew As Boolean
Dim TRows, THows, i As LongPrivate Sub UserForm_Click()
End Sub
Private Sub CmdClose_Click()
If CmdClose.Caption = “Close” Then
Unload Me
Else
CmdClose.Caption = “Close”
CmdNew.Enabled = True
CmdDelete.Enabled = True
End If
End SubPrivate Sub CmdNew_Click()
binNew = True
txtEmpNo.Text = ”
txtEmpName.Text = ”
txtAddr1.Text = ”
txtAddr2.Text = ”
txtAddr3.Text = ”CmdClose.Caption = “Cancel”
CmdNew.Enabled = False
CmdSave.Enabled = True
CmdDelete.Enabled = False
End SubPrivate Sub cmdSave_Click()
If Trim(txtEmpNo.Text) = ” Then
MsgBox “Enter Emp. No. “, vbCritical, “Save”
Exit Sub
End If
Call prSave
End SubPrivate Sub prSave()
If binNew = True Then
THows = Worksheets(“Data”).Range(“A1”).CurrentRegion.Rows.Count
With Worksheets(“Data”).Range(“A1″)
.Offset(THows, 0).Value = txtEmpNo.Text
.Offset(THows, 1).Value = txtEmpName.Text
.Offset(THows, 2).Value = txtAddr1.Text
.Offset(THows, 3).Value = txtAddr2.Text
.Offset(THows, 4).Value = txtAddr3.TextEnd With
txtEmpNo.Text = ”
txtEmpName.Text = ”
txtAddr1.Text = ”
txtAddr2.Text = ”
txtAddr3.Text = ”Call PrComboBoxFill
Else
For i = 2 To TRows
If Trim(Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 1).Value) = Trim(ComboBox1.Text) Then
Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 1).Value = txtEmpNo.Text
Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 2).Value = txtEmpName.Text
Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 3).Value = txtAddr1.Text
Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 4).Value = txtAddr2.Text
Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 5).Value = txtAddr3.TexttxtEmpNo.Text = ”
txtEmpName.Text = ”
txtAddr1.Text = ”
txtAddr2.Text = ”
txtAddr3.Text = ”Exit For
End If
Next i
End If
binNew = FalseEnd Sub
————————————-
Private Sub cmdDelete_Click()
TRows = Worksheets(“Data”).Range(“A1”).CurrentRegion.Rows.Count
Dim strDel
strDel = MagBox(“Delete ?”, vbYesNo, “Delete”)
If strDel = vbYes Then
For i = 2 To TRows
If Trims(Worksheets(“Data”).Cells(i, 1).Value) = Trim(ComboBox1.Text) Then‘ sheet1.range(i & “:” & i).Delete
Worksheets(“Data”).Range(i & “:” & i).DeleteTxtEmpNo.Text = ”
txtEmpName.Text = ”
TxtempAddr1.Text = ”
TxtempAddr2.Text = ”
TxtempAddr3.Text = ”
TxtempAddr4.Text = ”
Call prCoboBoxFill
Exit For
End If
Next i
If Trim(ComboBox1.Text) = ” Then
cmdSave.Enabled = False
cmdDelete.Enabled = False
Else
cmdSave.Enabled = True
cmdDelete.Enabled = True
End If
End If
End Sub
——————————–
Private Sub CmdClose_Click()
If CmdClose.Caption = “Close” Then
Unload Me
Else
CmdClose.Caption = “Close”
CmdNew.Enabled = True
CmdDelete.Enabled = True
End If
End Sub
————————————-Private Sub PrComboBoxFill()
TRows = Worksheets(“Data”).Range(“A1”).CurrentRegion.Rows.Count
ComboBox1.Clear
For i = 2 To TRows -
raj
March 16, 2017 at 4:31 PM — Reply -
Subha
May 12, 2017 at 6:15 PM — ReplyHello,
I’m at the beginner level in VBA. I’m trying to automatically update the values entered in a table one sheet to a table in another sheet(on a monthly basis). It would be great if you could provide me with some references for this case. Thanks for the help. -
chris
June 7, 2017 at 12:52 AM — ReplyLooking for vba code to run a macro when I click on a cell
-
Jerry
June 25, 2017 at 6:53 PM — ReplyHi, I am very new to VBA programming and am basically trying to self-learn from using your website. Thank you so much for all of the helpful information.
I’m trying to create a macro that will look at all of the values in Colum F on Sheet 1 and if the value is > 0 then I want to copy that whole row to sheet 2. For instance, I have a table in sheet 1 that is 1000 rows long. In column F of that table, only 10 of those rows contain values that are greater than zero. I want to copy those 10 rows to Shwet 2 and I want them to be contiguous.
I tried writing this program myself and got it to work somewhat. The problem I’m having is that I cannot figure out how to make it contiguous on sheet 2. And also it’s copying rows from sheet 1 that have no data, but they do have some type of formatting. I don’t want it to copy those rows.
-
PNRao
July 17, 2017 at 2:44 PM — ReplyYou can use the worksheet events to to call your macros in respective worksheet module:
Private Sub Worksheet_BeforeDoubleClick(ByVal Target As Range, Cancel As Boolean) 'Call your Macro here MsgBox "Double Click" End Sub Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range) 'Call your Macro here MsgBox "When you Change the Selection" End Sub
-
Katherine Ingersoll
July 24, 2017 at 12:02 AM — ReplyHi there:
We have a business in Belize and import our inventory from the US. The cost of duty on the imports differs in percentage based upon a list of harmonized tariff codes. I have the list of tariff codes and the respective duty percentage for each.
I also have the manufacturer’s product list with the respective tariff codes. I need to be able to quickly create a new spreadsheet which will calculate the “landed cost” of the manufacture’s product given the currency conversion of BZD to USD plus the cost of the duty.
For example:
The tariff spreadsheet might have a description of “Oil” with a tariff code of XYZ with an import duty of 15%. The product list has a price of US$5.00 for an item with the tariff code of XYZ
I need to know how much that product costs me (cost plus duty) in Belize dollars for our POS system. The currency conversion is 1USD=2BZD.
So the cost of the product needs to be first converted to Belize dollars and then the duty percentage added to it based upon the corresponding tariff code. So in this example US$5.00 is BZ$10.00, plus duty of 15% equals a “landed cost” of $11.50.
There are a gazillion products and another gazillion tariff codes.
I’m not sure where/how to even begin to tackle this task. Your help would be immensely appreciated.
-
Yousaf
July 29, 2017 at 1:34 PM — ReplyHi Dear Sir/Madam.
How we decrease input value equal to zero. Thanks in advance. -
Fadi
September 22, 2017 at 8:03 PM — ReplyHi
I have an excel sheet with a list of 2500 motor names and some other specs.
I have a motor checklist where I should put the name of each motor and some other specs of each motor, I have to do it for all the motors I have.
I want to do it automatically and save each motor with it’s name so I can be able to print them afterwards.Your help would be immensely appreciated
-
Vasant Shetti
November 3, 2017 at 3:27 PM — ReplyHi,
I want help to write an output report in VBA thru the input data
Can you help with the code -
ABHISHEK CHITTILLA
November 20, 2017 at 10:12 AM — ReplyHello,
Our company wants to import all the data for the same part into a single spreadsheet, How can we insert all the spreadsheets into a single spreadsheet, is there any programming code for that -
Dilipkumar.H
January 2, 2018 at 9:49 AM — ReplyHi I have a data in Sheet 1. I need to copy the data’s in the range of dates & description.
ex : From Date : 1st Oct 2017, To Date : 31st Oct 2017, Description : Fruit. I need to copy this data from Sheet 1 to New Workbook using excel user form. -
Shibu
January 13, 2018 at 7:08 PM — ReplyFirst sheet
Date Sap code recvd qty
13 Jan 18. 101. 10
14 Jan 18. 102. 20
15 Jan 18. 103. 30Second sheet
Date Sap code. Issued qty
13 Jan 18. 101. 5
14 Jan 18. 102. 5
15 Jan 18. 103. 5I want the results to appear in below third sheet if I enter reciept and issues on daily basis as below
Master list to be updated
Sap code. Receipt. Issues
13jan 14jan 15jan 13jan 14jan 15jan
101. Xx. Xx. Xx. X. X. X
102. Xx. Xx. Xx. X. X. X
103. Xx. Xx. Xx. X. X. X
104
105
And so onI want the values in place of xx for reciept and x for issues.
How do I make a vba code for it or is there any other formula in excel.
I tried my best but could not do it. A pivot with external connection is not working because the master list contains many sap codes that may or may not be received or issued.Please help, thanks in advance.
-
Hello,
I need to take data stored in Excel files and populate (copy and paste ) the data into web forms, submit the form then loop through the enitre process until I have gone through the entire Excel file.
So the Excel file will have a many number of rows but always 4 colums of data per row.
I then need to:
1) login to the site (),
2) Navigate the site to get to the correct forms
3) Insert the data from Excel into the correct form field (column 1 and 2 data goes to Field 1 & 2, Field 3 to selected from drop down box based on column 3, Field 4 data pasted from column 4)
4) submit the data
5) do the process again and again to complete the entire rows
I want to create a macro for the above task. Hopefully the above points are helpful to understand my requirement.
Please help me
Thanks in advance. -
Suresh
February 10, 2019 at 5:20 PM — ReplyHi Team, I need the excel macro , which compare the 2 excel sheets/tabs (which is having data A to AZ and which is having many rows).
1. Compare the 2 excel sheet , highlight the new rows depending upon the multiple criteria
2. In last column there is comments which is added manually Jan2019 month , however in Feb209 number of rows will be increased and so highlight the new rows depending upon the multiple criterias .And copy those comments as well.in Feb2019 sheet.
3.Highlighted new rows last comment section will be blank.Could you please provide me the excel macro for above conditions.
Thanks in advance.
Regards
Suresh -
Satish
July 13, 2019 at 7:47 PM — ReplyHi VBA Expert,
I would like to append many workbooks by rows which consist of two sheets “sheet1” and “Sheet2” in to single Workbook without opening any excel sheets.
column length is fixed but rows length may vary.
Please help me to do this task using VBA macro.
Thanks in advance!!!
-
Suresh Dasari
September 6, 2019 at 3:12 PM — ReplyThanks for the detailed article.
Effectively Manage Your
Projects and Resources
ANALYSISTABS.COM provides free and premium project management tools, templates and dashboards for effectively managing the projects and analyzing the data.
We’re a crew of professionals expertise in Excel VBA, Business Analysis, Project Management. We’re Sharing our map to Project success with innovative tools, templates, tutorials and tips.
Project Management
Excel VBA
Download Free Excel 2007, 2010, 2013 Add-in for Creating Innovative Dashboards, Tools for Data Mining, Analysis, Visualization. Learn VBA for MS Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Access, Outlook to develop applications for retail, insurance, banking, finance, telecom, healthcare domains.
Page load link

3 Realtime VBA Projects
with Source Code!
Go to Top
Excel VBA Examples for Beginners
Macros are your best friend when it comes to increasing productivity or saving time at your workplace. From small to big tasks, we can automate by using the VBA coding language. We know often you might have thought of some of the limitations Excel has but with VBA coding, you can eliminate all of those. If you struggled with VBA and are still a beginner in this article, we will give some useful examples of VBA Macro code in Excel.
Table of contents
- Excel VBA Examples for Beginners
- List of Top 19 Examples
- #1 – Print All Sheet Names
- #2 – Insert Different Color Index in VBA
- #3 – Insert Serial Number From Top
- #4 – Insert Serial Number From Bottom
- #5 – Insert Serial Number From 10 to 1
- #6 – Insert Worksheets as Much as You want
- #7 – Delete All Blank Worksheets From the Workbook
- #8 – Insert Blank Row After Every Other Row
- #9 – Highlight Spelling Mistake
- #10 – Change All To Upper Case Characters
- #11 – Change All To Lower Case Characters
- #12 – Highlight All the Commented Cells
- #13 – Highlight All the Blank Cells
- #14 – Hide All Sheets Except One Sheet
- #15 – Unhide All Sheets
- #16 – Delete All Files in the Folder
- #17 – Delete Entire Folder
- #18 – Find the Last Used Row in the Sheet
- #19 – Find the Last Used Column in the Sheet
- Recommended Articles
- List of Top 19 Examples
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA Examples (wallstreetmojo.com)
List of Top 19 Examples
- Print All Sheet Names
- Insert Different Color Index in VBA
- Insert Serial Number From Top
- Insert Serial Number From Bottom
- Insert Serial Number From 10 to 1
- Insert Worksheets as Much as You want
- Delete All Blank Worksheets From the Workbook
- Insert Blank Row After Every Other Row
- Highlight Spelling Mistake
- Change All To Upper Case Characters
- Change All To Lower Case Characters
- Highlight All the Commented Cells
- Highlight All the Blank Cells
- Hide All Sheets Except One Sheet
- Unhide All Sheets
- Delete All Files in the Folder
- Delete Entire Folder
- Find the Last Used Row in the Sheet
- Find the Last Used Column in the Sheet
Let’s see each of these examples in detail.
You can download this VBA Examples Excel Template here – VBA Examples Excel Template
#1 – Print All Sheet Names
Code:
Sub Print_Sheet_Names() Dim i As Integer For i = 1 To Sheets.Count Cells(i, 1).Value = Sheets(i).Name Next i End Sub
It will extract all the sheet names to the active sheet.
#2 – Insert Different Color Index in VBA
Code:
Sub Insert_Different_Colours() Dim i As Integer For i = 1 To 56 Cells(i, 1).Value = i Cells(i, 2).Interior.ColorIndex = i Next End Sub
It will insert numbers from 1 to 56 and their color index in the next column.
#3 – Insert Serial Number From Top
Code:
Sub Insert_Numbers_From_Top() Dim i As Integer For i = 1 To 10 Cells(i, 1).Value = i Next i End Sub
It will insert serial numbers from 1 to 10 from the top.
#4 – Insert Serial Number From Bottom
Code:
Sub Insert_Numbers_From_Bottom() Dim i As Integer For i = 20 To 1 Step -1 Cells(i, 7).Value = i Next i End Sub
It will insert serial numbers from 1 to 20 from the bottom.
#5 – Insert Serial Number From 10 to 1
Code:
Sub Ten_To_One() Dim i As Integer Dim j As Integer j = 10 For i = 1 To 10 Range("A" & i).Value = j j = j - 1 Next i End Sub
It will insert serial numbers from 10 to 1 from the top.
#6 – Insert Worksheets as Much as You want
Code:
Sub AddSheets() Dim ShtCount As Integer, i As Integer ShtCount = Application.InputBox("How Many Sheets you would like to insert?", "Add Sheets", , , , , , 1) If ShtCount = False Then Exit Sub Else For i = 1 To ShtCount Worksheets.Add Next i End If End Sub
It will ask you to enter the number of worksheets you would like to insert. Just specify the number in the input box and click on “OK.” It will insert those many sheets immediately.
#7 – Delete All Blank Worksheets From the Workbook
Code:
Sub Delete_Blank_Sheets() Dim ws As Worksheet Application.DisplayAlerts = False Application.ScreenUpdating = False For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets If WorksheetFunction.CountA(ws.UsedRange) = 0 Then ws.Delete End If Next ws Application.DisplayAlerts = True Application.ScreenUpdating = True End Sub
It will delete all the blank worksheets from the workbook we are working on.
#8 – Insert Blank Row After Every Other Row
Code:
Sub Insert_Row_After_Every_Other_Row() Dim rng As Range Dim CountRow As Integer Dim i As Integer Set rng = Selection CountRow = rng.EntireRow.Count For i = 1 To CountRow ActiveCell.EntireRow.Insert ActiveCell.Offset(2, 0).Select Next i End Sub
For this, first, you need to select the range where you would like to insert alternative blank rows.
#9 – Highlight Spelling Mistake
Code:
Sub Chech_Spelling_Mistake() Dim MySelection As Range For Each MySelection In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If Not Application.CheckSpelling(Word:=MySelection.Text) Then MySelection.Interior.Color = vbRed End If Next MySelection End Sub
First, select the data and run the VBA codeVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more. It will highlight the cells which have spelling mistakes.
#10 – Change All To Upper Case Characters
Code:
Sub Change_All_To_UPPER_Case() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection.Cells If Rng.HasFormula = False Then Rng.Value = UCase(Rng.Value) End If Next Rng End Sub
First, select the data and run the code. It will convert all the text values to upper case characters.
#11 – Change All To Lower Case Characters
Code:
Sub Change_All_To_LOWER_Case() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection.Cells If Rng.HasFormula = False Then Rng.Value = LCase(Rng.Value) End If Next Rng End Sub
First, select the data and run the code. It will convert all the text values to lower case characters in excelThere are six methods to change lowercase in excel — Using the lower function to change case in excel, Using the VBA command button, VBA shortcut key, Using Flash Fill, Enter text in lower case only, Using Microsoft word.
read more.
Code:
Sub HighlightCellsWithCommentsInActiveWorksheet() ActiveSheet.UsedRange.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeComments).Interior.ColorIndex = 4 End Sub
Result:
#13 – Highlight All the Blank Cells
Code:
Sub Highlight_Blank_Cells() Dim DataSet As Range Set DataSet = Selection DataSet.Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks).Interior.Color = vbGreen End Sub
First, select the data range and run the code. It will highlight all the blank cells with green color.
#14 – Hide All Sheets Except One Sheet
Code:
Sub Hide_All_Except_One() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets If Ws.Name <> "Main Sheet" Then Ws.Visible = xlSheetVeryHidden Next Ws End Sub
The above code hides all the sheets except the sheet named “Main Sheet.” You can change the worksheet name as per your wish.
#15 – Unhide All Sheets
Code:
Sub UnHide_All() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets Ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible Next Ws End Sub
It will unhide all the hidden sheets.
#16 – Delete All Files in the Folder
Code:
Sub Delete_All_Files() 'You can use this to delete all the files in the folder Test '' On Error Resume NextVBA On Error Resume Statement is an error-handling aspect used for ignoring the code line because of which the error occurred and continuing with the next line right after the code line with the error.read more Kill "C:UsersAdmin_2.Dell-PcDesktopDelete Folder*.*" On Error GoTo 0 End Sub
Change the folder path marked in red as per your folder deletion.
#17 – Delete Entire Folder
Code:
Sub Delete_Whole_Folder() 'You can use this to delete entire folder On Error Resume NextVBA On Error Resume Statement is an error-handling aspect used for ignoring the code line because of which the error occurred and continuing with the next line right after the code line with the error.read more Kill "C:UsersAdmin_2.Dell-PcDesktopDelete Folder*.*" 'Firstly it will delete all the files in the folder 'Then below code will delete the entire folder if it is empty RmDir "C:UsersAdmin_2.Dell-PcDesktopDelete Folder" 'Note: RmDir delete only a empty folder On Error GoTo 0 End Sub
Change the folder path marked in red as per your folder deletion.
#18 – Find the Last Used Row in the Sheet
Code:
Sub Last_Row() Dim LR As Long LR = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row MsgBox LR End Sub
Here, we find the last used row in the sheet.
#19 – Find the Last Used Column in the Sheet
Code:
Sub Last_Column() Dim LC As Long LC = Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column MsgBox LC End Sub
Here, we find the last used column in the sheet.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to VBA Examples. Here, we discuss the list of top 19 useful examples of VBA Macro code in Excel along with the downloadable template. Below are some useful articles related to Excel VBA: –
- VBA XLUP
- CDATE VBA Function
- VBA Tutorial
- VBA Randomize
In this article, I am going to show you some of the most amazing VBA Excel codes that you can use to optimize your work. VBA is a programming language, which can be used to extend the capabilities of MS Excel and other MS Office applications. It is extremely helpful for MS Excel users, because it can be used to automate your work and significantly improve your efficiency. This article will introduce you to VBA and show you some of the most useful, ready to use VBA codes out there. You can use these macro examples to create your own scripts that fit your own needs.
You do not need programming experience to take advantage of the information in this article, but you are expected to have basic knowledge of Excel. If you are a beginner user, I would recommend you to read the article 20 Excel Formulas You Should Start Using Now to learn more about Excel’s core functionalities.
I have prepared for you a number of ready to use VBA Excel Macro examples with great functionality that you can use to optimize your work. In order to use them, you need to “install” them in your Excel file. The next paragraph deals with Excel macro installation. Skip this part if you are already familiar with this.
Table of Contents
How to install a macro
In Excel, press the key combination alt + F11. This will take you to the VBA editor in MS Excel. Then, right-click on the Microsoft Excel Objects folder on the left and select Insert => Module. This is the place where the macros are stored. To make use of the macro, you need to save the Excel document as macro-enabled. From the tab file => save as, choose save as macro-enabled workbook (the .xlsm extension) Now, it’s time to write your first macro!
1. Copy data from one file to another.
Very useful macro, as it shows how to copy a range of data from inside vba and how to create and name a new workbook. You can easily upgrade it to fit your own requirements:
Sub CopyFiletoAnotherWorkbook() Sheets("Example 1").Range("B4:C15").Copy Workbooks.Add ActiveSheet.Paste Application.DisplayAlerts = False ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:="C:TempMyNewBook.xlsx" Application.DisplayAlerts = True End Sub
2. Show hidden rows
Occasionally, large Excel files contain hidden lines for better clarity. Here’s a macro that will unhide all rows from an active worksheet:
Sub ShowHiddenRows() Columns.EntireColumn.Hidden = False Rows.EntireRow.Hidden = False End Sub
3. Delete empty rows and columns
Blank rows in Excel are a problem with data processing. Here is how to get rid of them:
Sub DeleteEmptyRowsAndColumns() Dim MyRange As Range Dim iCounter As Long Set MyRange = ActiveSheet.UsedRange For iCounter = MyRange.Rows.Count To 1 Step -1 If Application.CountA(Rows(iCounter).EntireRow) = 0 Then Rows(iCounter).Delete End If Next iCounter For iCounter = MyRange.Columns.Count To 1 Step -1 If Application.CountA(Columns(iCounter).EntireColumn) = 0 Then Columns(iCounter).Delete End If Next iCounter End Sub
4. Find a blank cell
Sub FindEmptyCell() ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select Do While Not IsEmpty(ActiveCell) ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select Loop End Sub
5. Replace empty cells with a value.
As previously mentioned, blank cells interfere with data processing and the creation of pivot tables. Here is a code which replaces all blank cells with 0. This macro has a very large application because you can use it to find and replace N/A results, as well as other characters such as dots, commas or duplicate values:
Sub FindAndReplace() Dim MyRange As Range Dim MyCell As Range Select Case MsgBox("Can't Undo this action. " & _ "Save Workbook First?", vbYesNoCancel) Case Is = vbYes ThisWorkbook.Save Case Is = vbCancel Exit Sub End Select Set MyRange = Selection For Each MyCell In MyRange If Len(MyCell.Value) = 0 Then MyCell = 0 End If Next MyCell End Sub
6. Sort numbers
The following macro sorts in ascending order all numbers from the active cell’s column. Just double click any cell from a column you would like to sort.
NB: You need to put the code in Sheet 1 and not in a module to work:
Private Sub Worksheet_BeforeDoubleClick (ByVal Target as Range, Cancel As Boolean) Dim LastRow As Long LastRow = Cells (Rows.Count, 1) .End (xlUp) .Row Rows ("6:" & LastRow) .Sort _ Key1: = Cells (6, ActiveCell.Column), _ Order1: = xlAscending End Sub
7. Remove empty spaces
Occasionally, data in the workbook contains additional spaces (spaces) that can interfere with data analysis and to corrupt of formulas. Here’s a macro that will remove all the spaces from a preselected range of cells:
Sub TrimTheSpaces() Dim MyRange As Range Dim MyCell As Range Select Case MsgBox("Can't Undo this action. " & _ "Save Workbook First?", vbYesNoCancel) Case Is = vbYes ThisWorkbook.Save Case Is = vbCancel Exit Sub End Select Set MyRange = Selection For Each MyCell In MyRange If Not IsEmpty(MyCell) Then MyCell = Trim(MyCell) End If Next MyCell End Sub
8. Highlight dublicated values
Sometimes there are duplicate values in the several columns we would like to illuminate. Here’s a macro that does just that:
Sub HighlightDuplicates() Dim MyRange As Range Dim MyCell As Range Set MyRange = Selection For Each MyCell In MyRange If WorksheetFunction.CountIf(MyRange, MyCell.Value) > 1 Then MyCell.Interior.ColorIndex = 36 End If Next MyCell End Sub
9. Highlight top ten values
This code will highlight the top ten values from a selection of cells:
Sub TopTen() Selection.FormatConditions.AddTop10 Selection.FormatConditions(Selection.FormatConditions.Count).SetFirstPriority With Selection.FormatConditions(1) .TopBottom = xlTop10Top .Rank = 10 .Percent = False End With With Selection.FormatConditions(1).Font .Color = -16752384 .TintAndShade = 0 End With With Selection.FormatConditions(1).Interior .PatternColorIndex = xlAutomatic .Color = 13561798 .TintAndShade = 0 End With Selection.FormatConditions(1).StopIfTrue = False End Sub
You can easily tweak the code to highlight different number of values.
10. Highlight greater than values
When you run this code, a window will prompt. It will ask you the value you want to compare the cells you have selected.
Sub HighlightGreaterThanValues() Dim i As Integer i = InputBox("Enter Greater Than Value", "Enter Value") Selection.FormatConditions.Delete Selection.FormatConditions.Add Type:=xlCellValue, Operator:=xlGreater, Formula1:=i Selection.FormatConditions(Selection.FormatConditions.Count).SetFirstPriority With Selection.FormatConditions(1) .Font.Color = RGB(0, 0, 0) .Interior.Color = RGB(31, 218, 154) End With End Sub
You can tweak this code to highlight lower values as well.
A simple macro that highlights all the cells that contain comments:
Sub HighlightCommentCells() Selection.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeComments).Select Selection.Style= "Note" End Sub
12. Highlight Cells with Misspelled words
This is extremely useful when you work with functions that take strings, however, someone entered the string with a mistake and your formulas are not working. Here is how to fix this issue:
Sub ColorMispelledCells() For Each cl In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If Not Application.CheckSpelling(Word:=cl.Text) Then _ cl.Interior.ColorIndex = 28 Next cl End Sub
13. Create a pivot table
Here is how to create a pivot table from MS Excel (2007 version). Especially useful, when you are making a custom report every day. You can optimize the pivot table creation in the following way:
Sub PivotTableForExcel2007() Dim SourceRange As Range Set SourceRange = Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A3:N86") ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create( _ SourceType:=xlDatabase, _ SourceData:=SourceRange, _ Version:=xlPivotTableVersion12).CreatePivotTable _ TableDestination:="", _ TableName:="", _ DefaultVersion:=xlPivotTableVersion12 End Sub
14. Attach active workbook in an Email
My favorite VBA code. It lets you attach and send the file you’re working on with a predefined email address, message title, and message body! You first need to set reference to Microsoft Outlook (in your VBA editior, click on tools => references and choose Microsoft Outlook).
Sub SendFIleAsAttachment() Dim OLApp As Outlook.Application Dim OLMail As Object Set OLApp = New Outlook.Application Set OLMail = OLApp.CreateItem(0) OLApp.Session.Logon With OLMail .To = "admin@datapigtechnologies.com; mike@datapigtechnologies.com" .CC = "" .BCC = "" .Subject = "This is the Subject line" .Body = "Hi there" .Attachments.Add ActiveWorkbook.FullName .Display End With Set OLMail = Nothing Set OLApp = Nothing End Sub
15. Send all Excel charts to a PowerPoint presentation
A very handy macro that lets you add all your Excel charts in your Powerpoint presentation just with a single click:
Sub SendExcelFiguresToPowerPoint() Dim PP As PowerPoint.Application Dim PPPres As PowerPoint.Presentation Dim PPSlide As PowerPoint.Slide Dim i As Integer Sheets("Slide Data").Select If ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Count < 1 Then MsgBox "No charts existing the active sheet" Exit Sub End If Set PP = New PowerPoint.Application Set PPPres = PP.Presentations.Add PP.Visible = True For i = 1 To ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Count ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(i).Chart.CopyPicture _ Size:=xlScreen, Format:=xlPicture Application.Wait (Now + TimeValue("0:00:1")) ppSlideCount = PPPres.Slides.Count Set PPSlide = PPPres.Slides.Add(SlideCount + 1, ppLayoutBlank) PPSlide.Select PPSlide.Shapes.Paste.Select PP.ActiveWindow.Selection.ShapeRange.Align msoAlignCenters, True PP.ActiveWindow.Selection.ShapeRange.Align msoAlignMiddles, True Next i Set PPSlide = Nothing Set PPPres = Nothing Set PP = Nothing End Sub
16. Send Excel table in MS Word
Excel tables are usually put inside text documents. Here is an automated way of exporting your Excel table to MS Word:
Sub ExcelTableInWord() Dim MyRange As Excel.Range Dim wd As Word.Application Dim wdDoc As Word.Document Dim WdRange As Word.Range Sheets("Revenue Table").Range("B4:F10").Cop Set wd = New Word.Application Set wdDoc = wd.Documents.Open _ (ThisWorkbook.Path & "" & "PasteTable.docx") wd.Visible = True Set WdRange = wdDoc.Bookmarks("DataTableHere").Rangе On Error Resume Next WdRange.Tables(1).Delete WdRange.Paste WdRange.Tables(1).Columns.SetWidth _ (MyRange.Width / MyRange.Columns.Count), wdAdjustSameWidth wdDoc.Bookmarks.Add "DataTableHere", WdRange Set wd = Nothing Set wdDoc = Nothing Set WdRange = Nothing End Sub
We can use formulas if we want to extract certain number of symbols. But what if we want to extract only the second word from a sentence or a range of words in a cell? To do this, we can create a custom Excel function with VBA. This is one of the most iportant VBA functionalities, because it lets you create your own functions that are non-existent in MS Excel. Let’s go on and create two functions: findword() and findwordrev(). Here’s the vba code for this:
Function FindWord(Source As String, Position As Integer) As String On Error Resume Next FindWord = Split(WorksheetFunction.Trim(Source), " ")(Position - 1) On Error GoTo 0 End Function Function FindWordRev(Source As String, Position As Integer) As String Dim Arr() As String Arr = VBA.Split(WorksheetFunction.Trim(Source), " ") On Error Resume Next FindWordRev = Arr(UBound(Arr) - Position + 1) On Error GoTo 0 End Function
Very nice, we have created two cstom Excel functions. Now, try to use them in Excel. The function = FindWordRev (A1,1) takes the last word from cell A1. The function = FindWord (A1,3) takes the third word from cell A1, etc.
18. Protect your Workbook
Sometimes we want to protect the data in our file so that only we can change it. Here’s how to do this with VBA:
Sub ProtectSheets() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets ws.Protect Password:="1234" Next ws End Sub
Congratulations! Since you are still reading this, you are really keen on learning VBA. As you have already seen for yourself, the VBA programming language is extremely useful and can save us a lot of time. I hope you found this information helpful and use it to become a master in MS Excel, VBA and computer software in general.
© 2017 Atanas Yonkov
Literature:
1. ExcelChamps.com: Top 100 Useful Excel Macro [VBA] Codes Examples.
2. Michael Alexander, John Walkenbach (2012). 101 Ready-To-Use Excel Macros.
3. BG Excel.info: 14 ready-to-use Macros for Excel.
Using Excel Macros can speed up work and save you a lot of time.
One way of getting the VBA code is to record the macro and take the code it generates. However, that code by macro recorder is often full of code that is not really needed. Also macro recorder has some limitations.
So it pays to have a collection of useful VBA macro codes that you can have in your back pocket and use it when needed.
While writing an Excel VBA macro code may take some time initially, once it’s done, you can keep it available as a reference and use it whenever you need it next.
In this massive article, I am going to list some useful Excel macro examples that I need often and keep stashed away in my private vault.
I will keep updating this tutorial with more macro examples. If you think something should be on the list, just leave a comment.
You can bookmark this page for future reference.
Now before I get into the Macro Example and give you the VBA code, let me first show you how to use these example codes.
Using the Code from Excel Macro Examples
Here are the steps you need to follow to use the code from any of the examples:
- Open the Workbook in which you want to use the macro.
- Hold the ALT key and press F11. This opens the VB Editor.
- Right-click on any of the objects in the project explorer.
- Go to Insert –> Module.
- Copy and Paste the code in the Module Code Window.
In case the example says that you need to paste the code in the worksheet code window, double click on the worksheet object and copy paste the code in the code window.
Once you have inserted the code in a workbook, you need to save it with a .XLSM or .XLS extension.
How to Run the Macro
Once you have copied the code in the VB Editor, here are the steps to run the macro:
- Go to the Developer tab.
- Click on Macros.
- In the Macro dialog box, select the macro you want to run.
- Click on Run button.
In case you can’t find the developer tab in the ribbon, read this tutorial to learn how to get it.
Related Tutorial: Different ways to run a macro in Excel.
In case the code is pasted in the worksheet code window, you don’t need to worry about running the code. It will automatically run when the specified action occurs.
Now, let’s get into the useful macro examples that can help you automate work and save time.
Note: You will find many instances of an apostrophe (‘) followed by a line or two. These are comments that are ignored while running the code and are placed as notes for self/reader.
In case you find any error in the article or the code, please be awesome and let me know.
Excel Macro Examples
Below macro examples are covered in this article:
Unhide All Worksheets at One Go
If you are working in a workbook that has multiple hidden sheets, you need to unhide these sheets one by one. This could take some time in case there are many hidden sheets.
Here is the code that will unhide all the worksheets in the workbook.
'This code will unhide all sheets in the workbook Sub UnhideAllWoksheets() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible Next ws End Sub
The above code uses a VBA loop (For Each) to go through each worksheets in the workbook. It then changes the visible property of the worksheet to visible.
Here is a detailed tutorial on how to use various methods to unhide sheets in Excel.
Hide All Worksheets Except the Active Sheet
If you’re working on a report or dashboard and you want to hide all the worksheet except the one that has the report/dashboard, you can use this macro code.
'This macro will hide all the worksheet except the active sheet Sub HideAllExceptActiveSheet() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If ws.Name <> ActiveSheet.Name Then ws.Visible = xlSheetHidden Next ws End Sub
Sort Worksheets Alphabetically Using VBA
If you have a workbook with many worksheets and you want to sort these alphabetically, this macro code can come in really handy. This could be the case if you have sheet names as years or employee names or product names.
'This code will sort the worksheets alphabetically Sub SortSheetsTabName() Application.ScreenUpdating = False Dim ShCount As Integer, i As Integer, j As Integer ShCount = Sheets.Count For i = 1 To ShCount - 1 For j = i + 1 To ShCount If Sheets(j).Name < Sheets(i).Name Then Sheets(j).Move before:=Sheets(i) End If Next j Next i Application.ScreenUpdating = True End Sub
Protect All Worksheets At One Go
If you have a lot of worksheets in a workbook and you want to protect all the sheets, you can use this macro code.
It allows you to specify the password within the code. You will need this password to unprotect the worksheet.
'This code will protect all the sheets at one go Sub ProtectAllSheets() Dim ws As Worksheet Dim password As String password = "Test123" 'replace Test123 with the password you want For Each ws In Worksheets ws.Protect password:=password Next ws End Sub
Unprotect All Worksheets At One Go
If you have some or all of the worksheets protected, you can just use a slight modification of the code used to protect sheets to unprotect it.
'This code will protect all the sheets at one go Sub ProtectAllSheets() Dim ws As Worksheet Dim password As String password = "Test123" 'replace Test123 with the password you want For Each ws In Worksheets ws.Unprotect password:=password Next ws End Sub
Note that the password needs to the same that has been used to lock the worksheets. If it’s not, you will see an error.
Unhide All Rows and Columns
This macro code will unhide all the hidden rows and columns.
This could be really helpful if you get a file from someone else and want to be sure there are no hidden rows/columns.
'This code will unhide all the rows and columns in the Worksheet Sub UnhideRowsColumns() Columns.EntireColumn.Hidden = False Rows.EntireRow.Hidden = False End Sub
Unmerge All Merged Cells
It’s a common practice to merge cells to make it one. While it does the work, when cells are merged you will not be able to sort the data.
In case you are working with a worksheet with merged cells, use the code below to unmerge all the merged cells at one go.
'This code will unmerge all the merged cells Sub UnmergeAllCells() ActiveSheet.Cells.UnMerge End Sub
Note that instead of Merge and Center, I recommend using the Centre Across Selection option.
Save Workbook With TimeStamp in Its Name
A lot of time, you may need to create versions of your work. These are quite helpful in long projects where you work with a file over time.
A good practice is to save the file with timestamps.
Using timestamps will allow you to go back to a certain file to see what changes were made or what data was used.
Here is the code that will automatically save the workbook in the specified folder and add a timestamp whenever it’s saved.
'This code will Save the File With a Timestamp in its name Sub SaveWorkbookWithTimeStamp() Dim timestamp As String timestamp = Format(Date, "dd-mm-yyyy") & "_" & Format(Time, "hh-ss") ThisWorkbook.SaveAs "C:UsersUsernameDesktopWorkbookName" & timestamp End Sub
You need to specify the folder location and the file name.
In the above code, “C:UsersUsernameDesktop is the folder location I have used. You need to specify the folder location where you want to save the file. Also, I have used a generic name “WorkbookName” as the filename prefix. You can specify something related to your project or company.
Save Each Worksheet as a Separate PDF
If you work with data for different years or divisions or products, you may have the need to save different worksheets as PDF files.
While it could be a time-consuming process if done manually, VBA can really speed it up.
Here is a VBA code that will save each worksheet as a separate PDF.
'This code will save each worsheet as a separate PDF Sub SaveWorkshetAsPDF() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In Worksheets ws.ExportAsFixedFormat xlTypePDF, "C:UsersSumitDesktopTest" & ws.Name & ".pdf" Next ws End Sub
In the above code, I have specified the address of the folder location in which I want to save the PDFs. Also, each PDF will get the same name as that of the worksheet. You will have to modify this folder location (unless your name is also Sumit and you’re saving it in a test folder on the desktop).
Note that this code works for worksheets only (and not chart sheets).
Save Each Worksheet as a Separate PDF
Here is the code that will save your entire workbook as a PDF in the specified folder.
'This code will save the entire workbook as PDF Sub SaveWorkshetAsPDF() ThisWorkbook.ExportAsFixedFormat xlTypePDF, "C:UsersSumitDesktopTest" & ThisWorkbook.Name & ".pdf" End Sub
You will have to change the folder location to use this code.
Convert All Formulas into Values
Use this code when you have a worksheet that contains a lot of formulas and you want to convert these formulas to values.
'This code will convert all formulas into values Sub ConvertToValues() With ActiveSheet.UsedRange .Value = .Value End With End Sub
This code automatically identifies cells are used and convert it into values.
Protect/Lock Cells with Formulas
You may want to lock cells with formulas when you have a lot of calculations and you don’t want to accidentally delete it or change it.
Here is the code that will lock all the cells that have formulas, while all the other cells are not locked.
'This macro code will lock all the cells with formulas Sub LockCellsWithFormulas() With ActiveSheet .Unprotect .Cells.Locked = False .Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeFormulas).Locked = True .Protect AllowDeletingRows:=True End With End Sub
Related Tutorial: How to Lock Cells in Excel.
Protect All Worksheets in the Workbook
Use the below code to protect all the worksheets in a workbook at one go.
'This code will protect all sheets in the workbook Sub ProtectAllSheets() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In Worksheets ws.Protect Next ws End Sub
This code will go through all the worksheets one by one and protect it.
In case you want to unprotect all the worksheets, use ws.Unprotect instead of ws.Protect in the code.
Insert A Row After Every Other Row in the Selection
Use this code when you want to insert a blank row after every row in the selected range.
'This code will insert a row after every row in the selection Sub InsertAlternateRows() Dim rng As Range Dim CountRow As Integer Dim i As Integer Set rng = Selection CountRow = rng.EntireRow.Count For i = 1 To CountRow ActiveCell.EntireRow.Insert ActiveCell.Offset(2, 0).Select Next i End Sub
Similarly, you can modify this code to insert a blank column after every column in the selected range.
Automatically Insert Date & Timestamp in the Adjacent Cell
A timestamp is something you use when you want to track activities.
For example, you may want to track activities such as when was a particular expense incurred, what time did the sale invoice was created, when was the data entry done in a cell, when was the report last updated, etc.
Use this code to insert a date and time stamp in the adjacent cell when an entry is made or the existing contents are edited.
'This code will insert a timestamp in the adjacent cell Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range) On Error GoTo Handler If Target.Column = 1 And Target.Value <> "" Then Application.EnableEvents = False Target.Offset(0, 1) = Format(Now(), "dd-mm-yyyy hh:mm:ss") Application.EnableEvents = True End If Handler: End Sub
Note that you need to insert this code in the worksheet code window (and not the in module code window as we have done in other Excel macro examples so far). To do this, in the VB Editor, double click on the sheet name on which you want this functionality. Then copy and paste this code in that sheet’s code window.
Also, this code is made to work when the data entry is done in Column A (note that the code has the line Target.Column = 1). You can change this accordingly.
Highlight Alternate Rows in the Selection
Highlighting alternate rows can increase the readability of your data tremendously. This can be useful when you need to take a print out and go through the data.
Here is a code that will instantly highlight alternate rows in the selection.
'This code would highlight alternate rows in the selection Sub HighlightAlternateRows() Dim Myrange As Range Dim Myrow As Range Set Myrange = Selection For Each Myrow In Myrange.Rows If Myrow.Row Mod 2 = 1 Then Myrow.Interior.Color = vbCyan End If Next Myrow End Sub
Note that I have specified the color as vbCyan in the code. You can specify other colors as well (such as vbRed, vbGreen, vbBlue).
Highlight Cells with Misspelled Words
Excel doesn’t have a spell check as it has in Word or PowerPoint. While you can run the spell check by hitting the F7 key, there is no visual cue when there is a spelling mistake.
Use this code to instantly highlight all the cells that have a spelling mistake in it.
'This code will highlight the cells that have misspelled words Sub HighlightMisspelledCells() Dim cl As Range For Each cl In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If Not Application.CheckSpelling(word:=cl.Text) Then cl.Interior.Color = vbRed End If Next cl End Sub
Note that the cells that are highlighted are those that have text that Excel considers as a spelling error. In many cases, it would also highlight names or brand terms that it doesn’t understand.
Refresh All Pivot Tables in the Workbook
If you have more than one Pivot Table in the workbook, you can use this code to refresh all these Pivot tables at once.
'This code will refresh all the Pivot Table in the Workbook Sub RefreshAllPivotTables() Dim PT As PivotTable For Each PT In ActiveSheet.PivotTables PT.RefreshTable Next PT End Sub
You can read more about refreshing Pivot Tables here.
Change the Letter Case of Selected Cells to Upper Case
While Excel has the formulas to change the letter case of the text, it makes you do that in another set of cells.
Use this code to instantly change the letter case of the text in the selected text.
'This code will change the Selection to Upper Case Sub ChangeCase() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection.Cells If Rng.HasFormula = False Then Rng.Value = UCase(Rng.Value) End If Next Rng End Sub
Note that in this case, I have used UCase to make the text case Upper. You can use LCase for lower case.
Highlight All Cells With Comments
Use the below code to highlight all the cells that have comments in it.
'This code will highlight cells that have comments` Sub HighlightCellsWithComments() ActiveSheet.Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeComments).Interior.Color = vbBlue End Sub
In this case, I have used vbBlue to give a blue color to the cells. You can change this to other colors if you want.
Highlight Blank Cells With VBA
While you can highlight blank cell with conditional formatting or using the Go to Special dialog box, if you have to do it quite often, it’s better to use a macro.
Once created, you can have this macro in the Quick Access Toolbar or save it in your personal macro workbook.
Here is the VBA macro code:
'This code will highlight all the blank cells in the dataset Sub HighlightBlankCells() Dim Dataset as Range Set Dataset = Selection Dataset.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks).Interior.Color = vbRed End Sub
In this code, I have specified the blank cells to be highlighted in the red color. You can choose other colors such as blue, yellow, cyan, etc.
How to Sort Data by Single Column
You can use the below code to sort data by the specified column.
Sub SortDataHeader()
Range("DataRange").Sort Key1:=Range("A1"), Order1:=xlAscending, Header:=xlYes
End Sub
Note that the I have created a named range with the name ‘DataRange’ and have used it instead of the cell references.
Also there are three key parameters that are used here:
- Key1 – This is the on which you want to sort the data set. In the above example code, the data will be sorted based on the values in column A.
- Order- Here you need to specify whether you want to sort the data in ascending or descending order.
- Header – Here you need to specify whether your data has headers or not.
Read more on how to sort data in Excel using VBA.
How to Sort Data by Multiple Columns
Suppose you have a dataset as shown below:
Below is the code that will sort the data based on multiple columns:
Sub SortMultipleColumns()
With ActiveSheet.Sort
.SortFields.Add Key:=Range("A1"), Order:=xlAscending
.SortFields.Add Key:=Range("B1"), Order:=xlAscending
.SetRange Range("A1:C13")
.Header = xlYes
.Apply
End With
End Sub
Note that here I have specified to first sort based on column A and then based on column B.
The output would be something as shown below:
How to Get Only the Numeric Part from a String in Excel
If you want to extract only the numeric part or only the text part from a string, you can create a custom function in VBA.
You can then use this VBA function in the worksheet (just like regular Excel functions) and it will extract only the numeric or text part from the string.
Something as shown below:
Below is the VBA code that will create a function to extract numeric part from a string:
'This VBA code will create a function to get the numeric part from a string Function GetNumeric(CellRef As String) Dim StringLength As Integer StringLength = Len(CellRef) For i = 1 To StringLength If IsNumeric(Mid(CellRef, i, 1)) Then Result = Result & Mid(CellRef, i, 1) Next i GetNumeric = Result End Function
You need place in code in a module, and then you can use the function =GetNumeric in the worksheet.
This function will take only one argument, which is the cell reference of the cell from which you want to get the numeric part.
Similarly, below is the function that will get you only the text part from a string in Excel:
'This VBA code will create a function to get the text part from a string Function GetText(CellRef As String) Dim StringLength As Integer StringLength = Len(CellRef) For i = 1 To StringLength If Not (IsNumeric(Mid(CellRef, i, 1))) Then Result = Result & Mid(CellRef, i, 1) Next i GetText = Result End Function
So these are some of the useful Excel macro codes that you can use in your day-to-day work to automate tasks and be a lot more productive.
Other Excel tutorials you may like:
- How to Delete Macros in Excel
- How to Enable Macros in Excel?