Запись от po4emy4ka размещена 02.02.2014 в 01:05
Обновил(-а) po4emy4ka 02.02.2014 в 01:13
(Добавил архив с исходниками)
Шаг 1
Шаг 2 (можно в поиске набрать excel, чтобы было удобней)
Добавить в наш проект подключение типов и переменные.
Шаг 3
Для того, что бы при закрытии нашей программы в памяти не оставалось приложение Excel, мы его будем закрывать перед закрытием самой формы.
Шаг 4
Итак, откроем наш первый файл test_vb.xls в нашем приложении:
| VB.NET | ||
|
Изначально приложение Excel будет находится в невидимом состоянии (скрытый процесс) и если нам ничего никому показывать не нужно, то это даже очень удобно. А вот если нам нужно видеть, что же происходит то лучше отобразить приложение Excel. Для этого добавим на форму еще одну кнопку и напишем для нее обработчик.
| VB.NET | ||
|
ExApp.Visible = False — Скрытый режим
ExApp.Visible = True — Видимый режим
Excel_VBNET.rar
Всего комментариев
In this tutorial, I will teach you how to read an excel file in Visual basic.net (VB.Net).
This tutorial can be integrated to your personalized vb.net project.
What is Visual Basic’s purpose?
The third-generation programming language was created to aid developers in the creation of Windows applications. It has a programming environment that allows programmers to write code in.exe or executable files. They can also utilize it to create in-house front-end solutions for interacting with huge databases. Because the language allows for continuing changes, you can keep coding and revising your work as needed.
However, there are some limits to the Microsoft Visual Basic download. If you want to make applications that take a long time to process, this software isn’t for you. That implies you won’t be able to use VB to create games or large apps because the system’s graphic interface requires a lot of memory and space. Furthermore, the language is limited to Microsoft and does not support other operating systems.
So let’s get started:
Step How to Read an Excel file in Visual Basic.Net
- Step 1: First is open the Visual Basic, Select File on the menu, then click New and create a new project.
- Step 2: Then a New Project Dialog will appear. You can rename your project, depending on what you like to name it. After that click OK
- Step 3: Design your form like this just like what I’ve shown you below.
Add a 2 Textbox and a Button
- Step 4: After designing your form. Add a reference to Microsoft Excel 12.0 Object Library
In your project menu click on Project– Add Reference – go to COM tab
Add Microsoft Excel 12.0 Object Library
- Step 5: Then, go to the code page and add the following declarations:
Imports Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel Public Class Form1 Dim APP As New Excel.Application Dim worksheet As Excel.Worksheet Dim workbook As Excel.Workbook
- Step 6: Add this following code to Form_Load Event
Private Sub Form1_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
workbook = APP.Workbooks.Open("C:UsersCliveDocumentsVisual Studio 2008clive projectswriteandreadwriteandreadbinDebugsales.xlsx")
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets("sheet1")
End Sub
Step 7: To get the value from Excel cell to TextBox. Add this following code to the Button Click Event.
Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _ Handles Button1.Click TextBox1.Text = worksheet.Cells(1, 1).Value TextBox2.Text = worksheet.Cells(1, 2).Value End Sub
Step 8: Then finally, add this code to save the Excel file and closes it.
Private Sub Form1_FormClosed(ByVal sender As System.Object, _ ByVal e As System.Windows.Forms.FormClosedEventArgs) _ Handles MyBase.FormClosed workbook.Save() workbook.Close() App.Quit() End Sub
- Step 9: Click F5 to run the program.
Inquiries
If you have any questions or suggestions about How to Read an Excel file using Visual Basic.Net please contact me through our contact page or simply leave a comment below.
Download the Code Below
Download How to Read an Excel file using Visual Basic.Net Source code here.
Readers might read also:
- How to Export DataGridView Data to Excel using VB.Net
- How to Create an Excel File Using Visual Basic.Net
- Basic Calculator Using Visual Basic.Net
If you want to get started with a little bit of advance topic in VB.Net you may start your lesson here on how to connect access database to vb.net. Watch the video here below.
VB .NET Read & Create Excel Files (Code Example Tutorial)
Developers need a smooth and simple approach to accessing VB .NET Excel files. In this walkthrough, we’ll use IronXL to read VB dotnet Excel files and access all data for our project use. We’ll learn about creating spreadsheets in all formats ( .xls, .xlsx, .csv and .tsv ), as well as setting cell styles and inserting data using VB.NET Excel programming.
How to Read Excel File in VB.NET
- Download VB.NET Read Excel C# Library
- Create Excel Files in VB.NET
- Insert Data into Worksheet
- Read Excel File in VB.NET
- Access Data From WorkSheet
- Perform Functions on Data
Step 1
1. Excel for VB.NET Library
Get the IronXL Excel for VB.NET Library using DLL Download or NuGet. IronXL is our Step 1 to quickly accessing Excel data in our VB.NET projects, and what we’ll be using for this tutorial (free for development).
PM > Install-Package IronXL.ExcelHow To Tutorial
2. Create Excel Files in VB.NET
IronXL provides the simplest approach to create an Excel (.xlsx format) file in a VB.NET project. After this, we can insert data and also set cell properties like font styles or borders.
2.1. Create Excel File
Let’s first create a WorkBook:
Dim wb As New WorkBookThe above code is for creating a new Excel file. By default, its extension is .xlsx.
2.2. Create XLS File
In the case that you want to create an .xls extension file, then you can use this code.
Dim wb As New WorkBook(ExcelFileFormat.XLS)Dim wb As New WorkBook(ExcelFileFormat.XLS)VB.NET
2.3. Create Worksheet
After creating the WorkBook, an Excel WorkSheet can be created as follows:
Dim ws1 As WorkSheet = wb.CreateWorkSheet("Sheet1")Dim ws1 As WorkSheet = wb.CreateWorkSheet("Sheet1")VB.NET
The above code will create new WorkSheet ws1 with name sheet1 in WorkBook wb.
2.4. Create Multiple Worksheets
Any number of WorkSheets can be created in the same way:
Dim ws2 As WorkSheet = wb.CreateWorkSheet("Sheet2")
Dim ws3 As WorkSheet = wb.CreateWorkSheet("Sheet3")Dim ws2 As WorkSheet = wb.CreateWorkSheet("Sheet2")
Dim ws3 As WorkSheet = wb.CreateWorkSheet("Sheet3")VB.NET
3. Insert Data into Worksheet
3.1. Insert Data into Cells
Now we can easily insert data into WorkSheet cells as follows:
worksheet("CellAddress").Value = "MyValue" worksheet("CellAddress").Value = "MyValue"VB.NET
For example, data in worksheet ws1 can be inserted as:
ws1("A1").Value = "Hello World"ws1("A1").Value = "Hello World"VB.NET
The above code will write Hello World in A1 cell of WorkSheet ws1.
3.2. Insert Data into Range
It is also possible to write data into many cells using the range function as follows:
ws1("A3:A8").Value = "NewValue"ws1("A3:A8").Value = "NewValue"VB.NET
The above code will write NewValue from cell A3 to A8 in worksheet ws1.
3.3. Create and Edit Worksheets Example
We will create a new Excel file Sample.xlsx and insert some data in it to showcase the code we learned above.
/**
Create and Edit Excel
anchor-create-and-edit-worksheets-example
**/
Imports IronXL
Sub Main()
Dim wb As New WorkBook(ExcelFileFormat.XLSX)
Dim ws1 As WorkSheet = wb.CreateWorkSheet("Sheet1")
ws1("A1").Value = "Hello"
ws1("A2").Value = "World"
ws1("B1:B8").Value = "RangeValue"
wb.SaveAs("Sample.xlsx")
End Sub/**
Create and Edit Excel
anchor-create-and-edit-worksheets-example
**/
Imports IronXL
Sub Main()
Dim wb As New WorkBook(ExcelFileFormat.XLSX)
Dim ws1 As WorkSheet = wb.CreateWorkSheet("Sheet1")
ws1("A1").Value = "Hello"
ws1("A2").Value = "World"
ws1("B1:B8").Value = "RangeValue"
wb.SaveAs("Sample.xlsx")
End SubVB.NET
Note: By default, new Excel file will create in bin>Debug folder of the project.If we want to create new file in custom path then: wb.SaveAs(@"E:IronXLSample.xlsx")
Here is the screenshot of our newly created Excel file sample.xlsx:
It is clear how simple it can be to create Excel files using IronXL in a VB.NET Application.
IronXl also provides a simple approach to read Excel (.xlsx) files in your VB dotnet project. For this purpose, simply get the Excel document, load it in your project, read its data, and use it as per your requirements.
Follow these steps:
4.1. Access Excel File in Project
WorkBook is the class of IronXL whose object provides full access to the Excel file and its functions. For example, if we want to access the Excel file, we simply use:
WorkBook wb = WorkBook.Load("sample.xlsx") 'Excel file pathWorkBook wb = WorkBook.Load("sample.xlsx") 'Excel file pathVB.NET
In the code above, WorkBook.Load() function load sample.xlsx in wb. Any type function can be performed on wb by accessing specific WorkSheet of Excel file.
4.2. Access Specific WorkSheet
To access a specific sheet in Excel, take the WorkSheet class, which can be used in the following different ways:
4.2.1. By Sheet Name
Dim ws As WorkSheet = WorkBook.GetWorkSheet("sheet1") 'by sheet nameDim ws As WorkSheet = WorkBook.GetWorkSheet("sheet1") 'by sheet nameVB.NET
wb is the WorkBook declared in the above section.
4.2.2. By Sheet Index
Dim ws As WorkSheet = WorkBook.WorkSheets(0) 'by sheet index Dim ws As WorkSheet = WorkBook.WorkSheets(0) 'by sheet indexVB.NET
4.2.3. Default Sheet
Dim ws As WorkSheet = workbook.DefaultWorkSheet() 'for the default sheet: Dim ws As WorkSheet = workbook.DefaultWorkSheet() 'for the default sheet: VB.NET
4.2.4. First Sheet
Dim sheet As WorkSheet = workbook.WorkSheets.FirstOrDefault() 'for the first sheet:Dim sheet As WorkSheet = workbook.WorkSheets.FirstOrDefault() 'for the first sheet:VB.NET
4.2.1. First or Default Sheet
Dim sheet As WorkSheet = workbook.WorkSheets.FirstOrDefault() 'for the first or default sheet:Dim sheet As WorkSheet = workbook.WorkSheets.FirstOrDefault() 'for the first or default sheet:VB.NET
After getting Excel sheet ws , you can get any type of data from the corresponding WorkSheet of the Excel file and perform all Excel functions.
5. Access Data From WorkSheet
Data can be accessed from the ExcelSheet ws in this way:
Dim int_Value As Integer = sheet("A2").IntValue 'for integer
Dim str_value As String = sheet("A2").ToString() 'for stringDim int_Value As Integer = sheet("A2").IntValue 'for integer
Dim str_value As String = sheet("A2").ToString() 'for stringVB.NET
5.1. Data from Specific Column
It is also possible to get data from many cells of specific column by the following way:
For Each cell In sheet("A2:A10")
Console.WriteLine("value is: {0}", cell.Text)
Next cellFor Each cell In sheet("A2:A10")
Console.WriteLine("value is: {0}", cell.Text)
Next cellVB.NET
It will display values from cell A2 to A10. A code example of above whole discussion is given below.
/**
Load and Edit Values
anchor-data-from-specific-column
**/
Imports IronXL
Sub Main()
Dim wb As WorkBook = WorkBook.Load("sample.xlsx")
Dim ws As WorkSheet = wb.WorkSheets.FirstOrDefault()
For Each cell In ws("A2:A10")
Console.WriteLine("value is: {0}", cell.Text)
Next
Console.ReadKey()
End Sub/**
Load and Edit Values
anchor-data-from-specific-column
**/
Imports IronXL
Sub Main()
Dim wb As WorkBook = WorkBook.Load("sample.xlsx")
Dim ws As WorkSheet = wb.WorkSheets.FirstOrDefault()
For Each cell In ws("A2:A10")
Console.WriteLine("value is: {0}", cell.Text)
Next
Console.ReadKey()
End SubVB.NET
This will display the following output:
And we can see a Screenshot of Excel file Sample.xlsx:
6. Perform Functions on Data
It is simple to access filtered data from an Excel WorkSheet by applying aggregate functions like Sum, Min or Max in the following way:
Dim sum As Decimal = ws("From:To").Sum()
Dim min As Decimal = ws("From:To").Min()
Dim max As Decimal = ws("From:To").Max()Dim sum As Decimal = ws("From:To").Sum()
Dim min As Decimal = ws("From:To").Min()
Dim max As Decimal = ws("From:To").Max()VB.NET
You can read more about Excel Aggregate Functions here.
/**
Apply Functions to Data
anchor-perform-functions-on-data
**/
Imports IronXL
Sub Main()
Dim wb As WorkBook = WorkBook.Load("sample.xlsx")
Dim ws As WorkSheet = wb.WorkSheets.FirstOrDefault()
Dim sum As Decimal = ws("G2:G10").Sum()
Dim min As Decimal = ws("G2:G10").Min()
Dim max As Decimal = ws("G2:G10").Max()
Console.WriteLine("Sum is: {0}", sum)
Console.WriteLine("Min is: {0}", min)
Console.WriteLine("Max is: {0}", max)
Console.ReadKey()
End Sub/**
Apply Functions to Data
anchor-perform-functions-on-data
**/
Imports IronXL
Sub Main()
Dim wb As WorkBook = WorkBook.Load("sample.xlsx")
Dim ws As WorkSheet = wb.WorkSheets.FirstOrDefault()
Dim sum As Decimal = ws("G2:G10").Sum()
Dim min As Decimal = ws("G2:G10").Min()
Dim max As Decimal = ws("G2:G10").Max()
Console.WriteLine("Sum is: {0}", sum)
Console.WriteLine("Min is: {0}", min)
Console.WriteLine("Max is: {0}", max)
Console.ReadKey()
End SubVB.NET
This code will give us this display:
And this Excel file Sample.xlsx:
You can learn more about how to read Excel in the linked article.
Tutorial Quick Access
Documentation API Reference
Access the documentation API reference of IronXL and the simple ways to work with Excel in your VB.NET project. Find lists of features, functions, classes and more.
Documentation API Reference
Is there a way to just call Open() function with the file name and extension (xlApp.Workbooks.Open(“Test.xlsx”)) and have it search your whole computer for the file? I know you can open the file if it has a specified path like «c:docume~1(username)desktopTest.xlsx» but I was wondering if there’s a way to search your whole computer for the file without specifying the whole path.
asked Aug 15, 2012 at 22:21
Josh ValdiviesoJosh Valdivieso
1,1681 gold badge14 silver badges22 bronze badges
4
You could use:
string[] fileNames = Directory.GetFiles("C:\", "yourFile.xls",
SearchOption.AllDirectories);
or
var txtFiles = Directory.EnumerateFiles("C:\", "yourFiles.xls",
SearchOption.AllDirectories);
but you should read carefully the documentation (GetFiles) (EnumerateFiles) on MSDN because there are numerous facts to be prepared of. (Unauthorized Access Exceptions, Search times)
answered Aug 15, 2012 at 22:33
3
- Download source code — 10.6 KB
Introduction
This articles helps user to Insert, Update, Delete, and Select data in Excel files using the OLEDBDataProvider in VB.NET.
Here is the connection string to connect with Excel using OleDBDataProvider:
Private Const connstring As String = "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _ "Data Source=C:Test.xls;Extended Properties=""Excel 8.0;HDR=YES;"""
Here is the code on the button click event to select and insert data in an Excel file:
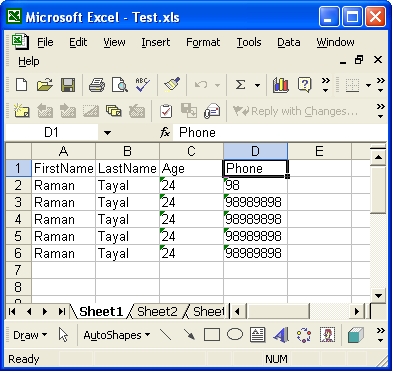
Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _ ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click Dim pram As OleDbParameter Dim dr As DataRow Dim olecon As OleDbConnection Dim olecomm As OleDbCommand Dim olecomm1 As OleDbCommand Dim oleadpt As OleDbDataAdapter Dim ds As DataSet Try olecon = New OleDbConnection olecon.ConnectionString = connstring olecomm = New OleDbCommand olecomm.CommandText = _ "Select FirstName, LastName, Age, Phone from [Sheet1$]" olecomm.Connection = olecon olecomm1 = New OleDbCommand olecomm1.CommandText = "Insert into [Sheet1$] " & _ "(FirstName, LastName, Age, Phone) values " & _ "(@FName, @LName, @Age, @Phone)" olecomm1.Connection = olecon pram = olecomm1.Parameters.Add("@FName", OleDbType.VarChar) pram.SourceColumn = "FirstName" pram = olecomm1.Parameters.Add("@LName", OleDbType.VarChar) pram.SourceColumn = "LastName" pram = olecomm1.Parameters.Add("@Age", OleDbType.VarChar) pram.SourceColumn = "Age" pram = olecomm1.Parameters.Add("@Phone", OleDbType.VarChar) pram.SourceColumn = "Phone" oleadpt = New OleDbDataAdapter(olecomm) ds = New DataSet olecon.Open() oleadpt.Fill(ds, "Sheet1") If IsNothing(ds) = False Then dr = ds.Tables(0).NewRow dr("FirstName") = "Raman" dr("LastName") = "Tayal" dr("Age") = 24 dr("Phone") = 98989898 ds.Tables(0).Rows.Add(dr) oleadpt = New OleDbDataAdapter oleadpt.InsertCommand = olecomm1 Dim i As Integer = oleadpt.Update(ds, "Sheet1") MessageBox.Show(i & " row affected") End If Catch ex As Exception MessageBox.Show(ex.Message) Finally olecon.Close() olecon = Nothing olecomm = Nothing oleadpt = Nothing ds = Nothing dr = Nothing pram = Nothing End Try End Sub
This member has not yet provided a Biography. Assume it’s interesting and varied, and probably something to do with programming.