Элемент управления пользовательской формы ComboBox для выбора и ввода информации в VBA Excel. Свойства поля с раскрывающимся списком, заполнение, извлечение данных, примеры кода.
UserForm.ComboBox – это элемент управления пользовательской формы, предназначенный для передачи в код VBA информации, выбранной пользователем из раскрывающегося списка или введенной с клавиатуры.
ComboBox представляет из себя комбинацию двух элементов управления: текстового поля (TextBox) и списка (ListBox), поэтому его еще называют «комбинированным списком» или «полем со списком». Также ComboBox сочетает в себе свойства этих двух элементов управления.
Изначально комбинированный список прорисовывается на форме в виде текстового поля с кнопкой для отображения раскрывающегося списка. Далее по тексту будем использовать слово «поле» в значении текстового поля в составе элемента управления ComboBox, а словосочетание «раскрывающийся список» – в значении списка в составе элемента управления ComboBox.
Поле со списком используется в тех случаях, когда необходимо добавить в форму информацию, которая заранее известна, а ее отдельные позиции можно сгруппировать в список, а также для ручного ввода с клавиатуры или вставки из буфера обмена, если необходимое значение в списке отсутствует.
Элемент управления ComboBox незаменим при больших списках. При списках из нескольких позиций его можно заменить на ListBox, который отображает позиции для выбора сразу после загрузки формы, не требуя дополнительных действий от пользователя.
Свойства поля со списком
| Свойство | Описание |
|---|---|
| AutoSize | Автоподбор размера комбинированного поля. True – размер автоматически подстраивается под длину выбранной или введенной строки. False – размер элемента управления определяется свойствами Width и Height. |
| AutoTab | Включение автоматической табуляции – передачи фокуса следующему элементу управления при достижении максимального числа символов при значениях свойства MaxLenght > 0. True – автоматическая табуляция включена, False – выключена. |
| ColumnCount | Указывает количество столбцов в раскрывающемся списке. Значение по умолчанию = 1. |
| ColumnHeads | Добавляет строку заголовков в раскрывающийся список. True – заголовки столбцов включены, False – заголовки столбцов выключены. Значение по умолчанию = False. |
| ColumnWidths | Ширина столбцов в раскрывающемся списке. Значения для нескольких столбцов указываются в одну строку через точку с запятой (;). |
| ControlSource | Ссылка на ячейку для ее привязки к элементу управления ComboBox. |
| ControlTipText | Текст всплывающей подсказки при наведении курсора на элемент управления. |
| Enabled | Доступ пользователя к полю и раскрывающемуся списку. True – доступ разрешен, False – доступ запрещен*. Значение по умолчанию = True. |
| Font | Шрифт, начертание и размер текста в поле. |
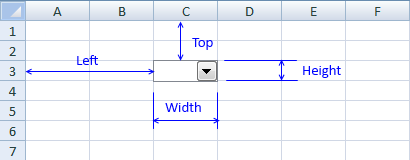
| Height | Высота элемента управления ComboBox. |
| Left | Расстояние от левого края внутренней границы пользовательской формы до левого края комбинированного списка. |
| List | Позволяет заполнить ComboBox данными из одномерного или двухмерного массива, а также обращаться к отдельным элементам раскрывающегося списка по индексам для записи и чтения. |
| ListIndex | Номер выбранной пользователем строки в раскрывающемся списке. Нумерация начинается с нуля. Если ничего не выбрано, ListIndex = -1. |
| ListRows | Количество видимых строк в раскрытом списке. Если общее количество строк больше ListRows, появляется полоса прокрутки. Значение по умолчанию = 8. |
| Locked | Запрет на отображение раскрывающегося списка, ввод и редактирование данных в поле. True – ввод и редактирование запрещены**, False – ввод и редактирование разрешены. Значение по умолчанию = False. |
| MatchRequired | Задает проверку вводимых в поле строк с элементами списка. True – проверка включена (допускается ввод только строк, совпадающих с элементами списка), False – проверка выключена (допускается ввод любых строк). Значение по умолчанию = False. |
| MaxLenght | Максимальная длина строки в поле. Значение по умолчанию = 0, что означает – ограничений нет. |
| RowSource | Источник строк для раскрывающегося списка (адрес диапазона на рабочем листе Excel). |
| TabIndex | Целое число, определяющее позицию элемента управления в очереди на получение фокуса при табуляции. Отсчет начинается с 0. |
| Text | Текстовое содержимое (значение) поля (=Value). |
| TextAlign | Выравнивание текста в поле: 1 (fmTextAlignLeft) – по левому краю, 2 (fmTextAlignCenter) – по центру, 3 (fmTextAlignRight) – по правому краю. |
| Top | Расстояние от верхнего края внутренней границы пользовательской формы до верхнего края комбинированного списка. |
| Value | Текстовое содержимое (значение) поля (=Text). |
| Visible | Видимость поля со списком. True – ComboBox отображается на пользовательской форме, False – ComboBox скрыт. |
| Width | Ширина элемента управления. |
* При Enabled в значении False пользователь не может раскрывать список, а также вводить или редактировать данные в поле.
** Для элемента управления ComboBox действие свойства Locked в значении True аналогично действию свойства Enabled в значении False.
В таблице перечислены только основные, часто используемые свойства поля со списком. Еще больше доступных свойств отображено в окне Properties элемента управления ComboBox, а все методы, события и свойства – в окне Object Browser.
Вызывается Object Browser нажатием клавиши «F2». Слева выберите объект ComboBox, а справа смотрите его методы, события и свойства.
Свойства BackColor, BackStyle, BorderColor, BorderStyle отвечают за внешнее оформление комбинированного списка и его границ. Попробуйте выбирать доступные значения этих свойств в окне Properties, наблюдая за изменениями внешнего вида элемента управления ComboBox на проекте пользовательской формы.
Способы заполнения ComboBox
Используйте метод AddItem для загрузки элементов в поле со списком по одному:
|
With UserForm1.ComboBox1 .AddItem «Элемент 1» .AddItem «Элемент 2» .AddItem «Элемент 3» End With |
Используйте свойство List, чтобы скопировать одномерный массив значений в элемент управления ComboBox:
|
UserForm1.ComboBox1.List = Array(«Строка 1», _ «Строка 2», «Строка 3», «Строка 4», «Строка 5») |
Вместо функции Array можно использовать переменные одномерных и двухмерных массивов. При загрузке значений из двухмерного массива, требуется предварительно указать количество столбцов в комбинированном списке.
Используйте свойство RowSource, чтобы загрузить в ComboBox значения из диапазона ячеек рабочего листа:
|
UserForm1.ComboBox1.RowSource = «Лист5!B1:B15» |
При загрузке данных из диапазона, содержащего более одного столбца, требуется предварительно указать количество столбцов в комбинированном списке:
|
With UserForm1.ComboBox1 ‘Указываем количество столбцов .ColumnCount = 5 .RowSource = «‘Таблица с данными’!A1:E20» End With |
В качестве имени листа используется имя ярлыка. Если имя листа содержит пробелы, оно заключается в одинарные кавычки.
Подробнее о заполнении элемента управления ComboBox вы можете ознакомиться в отдельной статье с наглядными примерами. И еще более подробно – в статье о заполнении ListBox, так как ListBox заполняется теми же способами, что и ComboBox.
Привязка поля со списком к ячейке
Чтобы привязать комбинированный список к ячейке на рабочем листе Excel, необходимо свойству ControlSource присвоить адрес ячейки. Это можно сделать непосредственно в окне Properties элемента управления ComboBox или в коде VBA:
UserForm1.ComboBox1.ControlSource = "Лист1!B2"
Имя листа для составного адреса ячейки берется из названия ярлыка. Если имя листа содержит пробелы, оно заключается в одинарные кавычки. При указании адреса без имени листа, ComboBox привязывается к ячейке на активном листе.
В результате привязки образуется взаимосвязь между свойством Value комбинированного списка и значением ячейки. Все изменения в поле ComboBox дублируются в привязанной ячейке и наоборот, изменения в ячейке приводят к изменению текста в поле.
Чтобы протестировать результаты привязки ячейки к полю со списком ComboBox1, разместите на пользовательской форме UserForm1 еще какой-нибудь элемент управления и запустите следующий код VBA Excel:
|
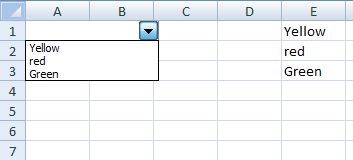
Sub Test() With UserForm1.ComboBox1 ‘Заполняем список ComboBox1 данными .List = Array(«Красный», «Оранжевый», «Желтый», _ «Зеленый», «Голубой», «Синий», «Фиолетовый») ‘Привязываем ComboBox1 к ячейке «A1» .ControlSource = «A1» ‘Открываем форму в немодальном окне End With UserForm1.Show 0 End Sub |
В результате работы кода пользовательская форма откроется в немодальном окне со значением в поле, скопированном из ячейки «A1» активного листа. Немодальное окно формы позволит редактировать ячейку «A1», не закрывая форму.
Меняйте значение ячейки «A1», нажимайте клавишу «Tab» или «Enter», поле комбинированного списка примет значение ячейки. Меняйте значение поля ComboBox1 с помощью клавиатуры или выбирайте из раскрывающегося списка, нажимайте клавишу «Tab» или «Enter», ячейка «A1» примет значение поля со списком.
Дополнительный элемент управления на форме нужен для передачи ему фокуса нажатием клавиши «Tab» или «Enter», чтобы завершить ввод значения в поле ComboBox1. Иначе новое значение поля будет передано в ячейку «A1» только при закрытии формы.
Значение ComboBox по умолчанию
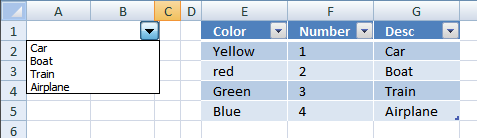
В раскрывающийся список элемента управления ComboBox1 загружены названия семи основных цветов:
|
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize() With Me.ComboBox1 .List = Array(«Красный», «Оранжевый», «Желтый», _ «Зеленый», «Голубой», «Синий», «Фиолетовый») ‘Сюда добавляем код вставки значения по умолчанию End With End Sub |
Есть несколько вариантов сделать так, чтобы при открытии пользовательской формы в поле ComboBox1 было отображено значение по умолчанию. Код следует вставлять перед строкой «End With».
|
‘Вариант 1 (произвольная строка) .Value = «Моя строка по умолчанию» ‘или .Value = «Синий» ‘Вариант 2 (произвольная строка) .ControlSource = «A1» Range(«A1») = «Моя строка по умолчанию» ‘или .ControlSource = «A1» Range(«A1») = «Желтый» ‘Вариант 3 (строка из списка) .ListIndex = 0 ‘Красный ‘или .ListIndex = 3 ‘Зеленый |
Кроме значения по умолчанию, в свойства комбинированного списка можно добавить текст всплывающей подсказки, который будет отображаться при наведении на ComboBox курсора:
UserForm1.ComboBox1.ControlTipText = "Выберите значение из списка"
Извлечение информации из ComboBox
Первоначально элемент управления ComboBox открывается с пустым полем или значением по умолчанию. Свойства Value и Text в этом случае возвращают пустую строку или текст по умолчанию.
Если пользователь выбрал новое значение из раскрывающегося списка или ввел его с клавиатуры, оно перезапишет значения свойств Value и Text. Из этих свойств мы с помощью кода VBA Excel извлекаем информацию, выбранную или введенную пользователем:
|
Dim myTxt As String myTxt = UserForm1.ComboBox1.Value ‘или myTxt = UserForm1.ComboBox1.Text |
Вторую строку кода можно записать myTxt = UserForm1.ComboBox1, так как Value является свойством поля со списком по умолчанию.
Если вас интересует, как извлечь значение из многостолбцового раскрывающегося списка, смотрите об этом в статье с описанием элемента управления ListBox. Извлечение данных из комбинированного поля аналогично извлечению данных из ListBox. Знакомясь со статьей, следует учесть, что у ComboBox отсутствует многострочный выбор.
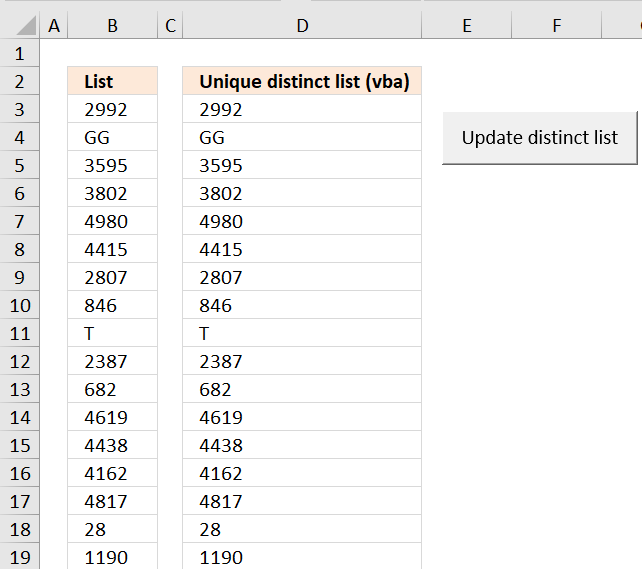
Иногда перед загрузкой в ComboBox требуется отобрать уникальные элементы из имеющегося списка. Смотрите, как это сделать с помощью объектов Collection и Dictionary.
If you’re dealing with Data Validation lists, you can use the Worksheet_Change event. Right click on the sheet with the data validation and choose View Code. Then type in this:
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
MsgBox Target.Value
End Sub
If you’re dealing with ActiveX comboboxes, it’s a little more complicated. You need to create a custom class module to hook up the events. First, create a class module named CComboEvent and put this code in it.
Public WithEvents Cbx As MSForms.ComboBox
Private Sub Cbx_Change()
MsgBox Cbx.Value
End Sub
Next, create another class module named CComboEvents. This will hold all of our CComboEvent instances and keep them in scope. Put this code in CComboEvents.
Private mcolComboEvents As Collection
Private Sub Class_Initialize()
Set mcolComboEvents = New Collection
End Sub
Private Sub Class_Terminate()
Set mcolComboEvents = Nothing
End Sub
Public Sub Add(clsComboEvent As CComboEvent)
mcolComboEvents.Add clsComboEvent, clsComboEvent.Cbx.Name
End Sub
Finally, create a standard module (not a class module). You’ll need code to put all of your comboboxes into the class modules. You might put this in an Auto_Open procedure so it happens whenever the workbook is opened, but that’s up to you.
You’ll need a Public variable to hold an instance of CComboEvents. Making it Public will kepp it, and all of its children, in scope. You need them in scope so that the events are triggered. In the procedure, loop through all of the comboboxes, creating a new CComboEvent instance for each one, and adding that to CComboEvents.
Public gclsComboEvents As CComboEvents
Public Sub AddCombox()
Dim oleo As OLEObject
Dim clsComboEvent As CComboEvent
Set gclsComboEvents = New CComboEvents
For Each oleo In Sheet1.OLEObjects
If TypeName(oleo.Object) = "ComboBox" Then
Set clsComboEvent = New CComboEvent
Set clsComboEvent.Cbx = oleo.Object
gclsComboEvents.Add clsComboEvent
End If
Next oleo
End Sub
Now, whenever a combobox is changed, the event will fire and, in this example, a message box will show.
You can see an example at https://www.dropbox.com/s/sfj4kyzolfy03qe/ComboboxEvents.xlsm
In this Article
- Create a ComboBox in Excel Worksheet
- Populate a ComboBox in VBA code
- Populate a ComboBox from a Cells Range
- Get a Selected Item of a ComboBox in VBA
- Clear a ComboBox
- Use a ComboBox in a Userform
This tutorial will demonstrate how to work with ComboBoxes in VBA.
ComboBoxes allow users to select an option from a drop-down menu list. ComboBoxes can be created in VBA UserForms or with an Excel worksheet. In this tutorial, you will learn how to create and manipulate ComboBoxes in VBA and in Excel worksheets.
If you want to learn how to create a Listbox, click here: VBA Listbox
If you want to learn how to create a Checkbox, click here: VBA Checkbox
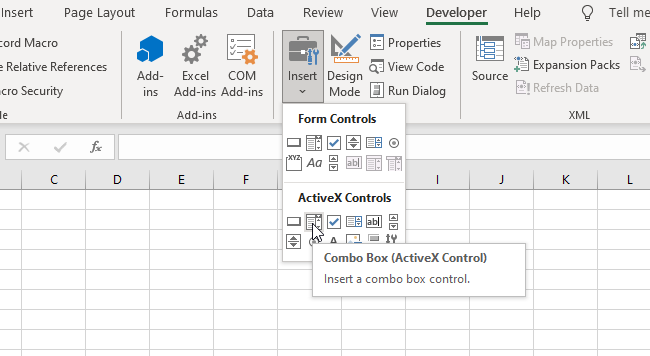
Create a ComboBox in Excel Worksheet
In order to insert a ComboBox in the Worksheet, you need to go to the Developer tab, click Insert and under ActiveX Controls choose Combo Box:
Image 1. Insert a ComboBox in the Worksheet
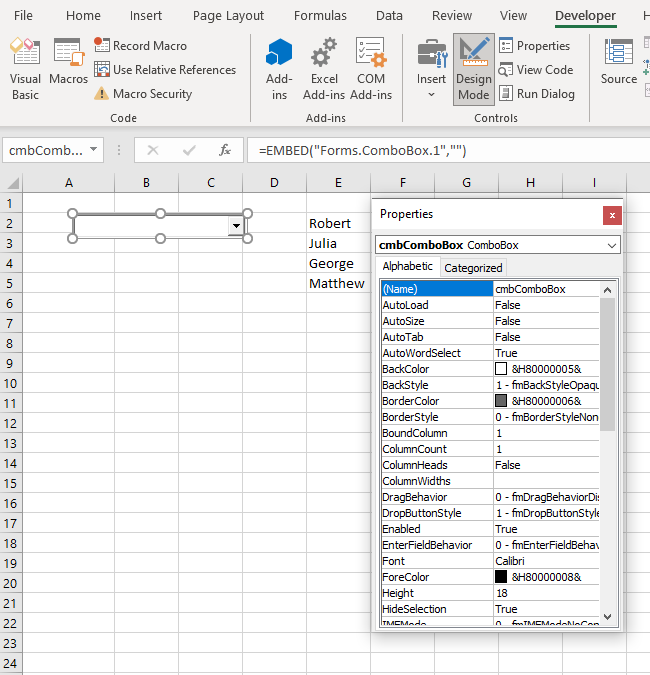
When you select the ComboBox which you inserted, you can click on Properties under the Developer tab:
Image 2. Change ComboBox Properties
Here you can set different properties of the ComboBox. To start, we changed the attribute Name to cmbComboBox. Now, we can use the ComboBox with this name in VBA code.
Populate a ComboBox in VBA code
First, we need to populate the ComboBox with values. In most cases, a ComboBox needs to be populated when the Workbook is opened. Because of this, we need to put a code for populating the ComboBox in object Workbook, procedure Open. This procedure is executed every time a user opens the Workbook. Here is the code:
With Sheet1.cmbComboBox
.AddItem "John"
.AddItem "Michael"
.AddItem "Jennifer"
.AddItem "Lilly"
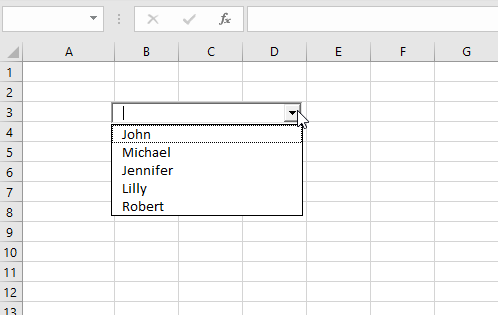
.AddItem "Robert"
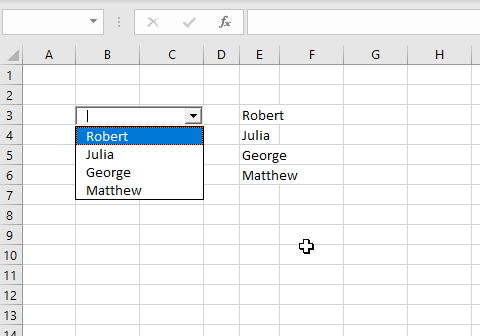
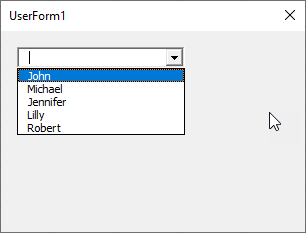
End WithWhen you click on the drop-down menu, you will get 5 names to choose from (John, Michael, Jennifer, Lilly and Robert):
Image 3. Populate the ComboBox in VBA
Populate a ComboBox from a Cells Range
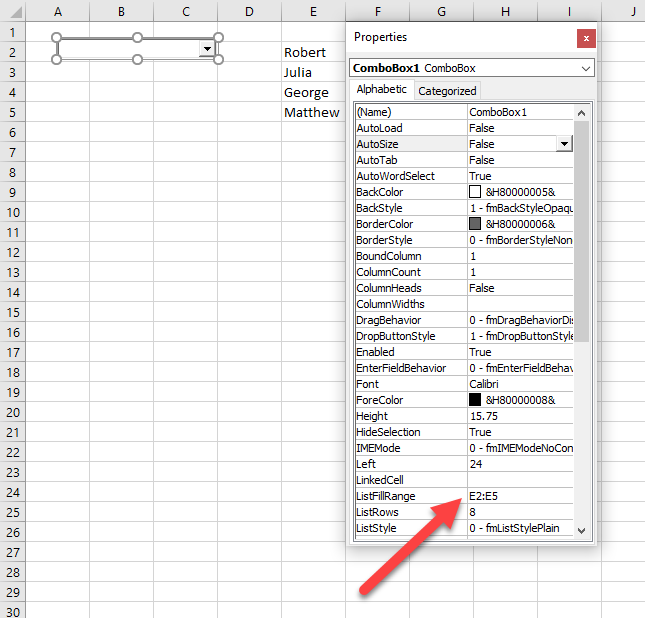
Another possible way to populate a ComboBox is to let a user do it. A ComboBox can be linked to the cells range. In this approach, every time a user enters a new value in the cells range, the ComboBox will update with that value.
If you want to enable this, you have to go to the Properties of the ComboBox and set the attribute ListFillRange to the cells range (in our case E2:E5):
Image 4. Populate the ComboBox from the cells range
We linked our ComboBox with the range E2:E5, where we put names we want (Nathan, Harry, George, Roberta). As a result, the ComboBox is now populated with these names:
Image 5. Populated ComboBox from the cells range
Get a Selected Item of a ComboBox in VBA
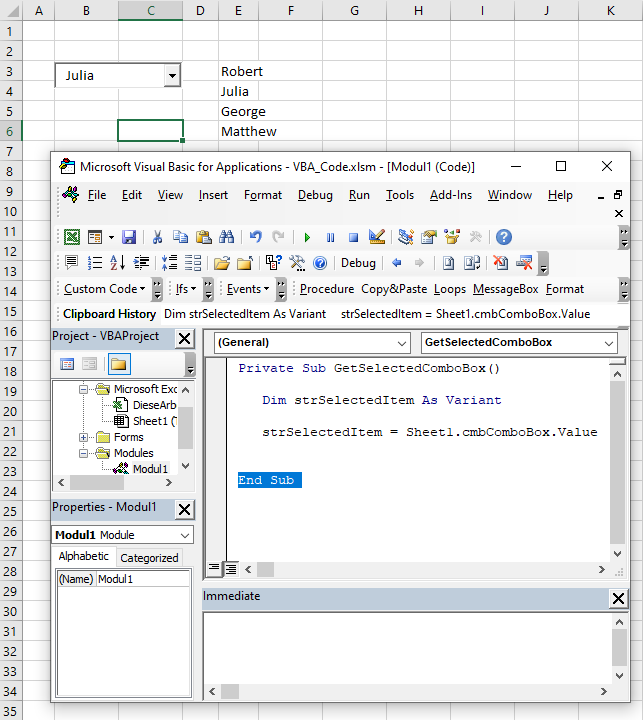
The purpose of a ComboBox is to get a users choice. In order to retrieve a users choice, you need to use this code:
Dim strSelectedItem As Variant
strSelectedItem = Sheet1.cmbComboBox.ValueThe users selection is in the attribute Value of Sheet1.cmbComboBox object. This value is assigned to the variable strSelectedItem:
Image 6. Get a selected value from the ComboBox in VBA
We selected Julia in the ComboBox and executed the procedure. As you can see in Image 5, the value of the strSelectedItem is Julia, which is the value we selected. Now you can process this variable further in the code.
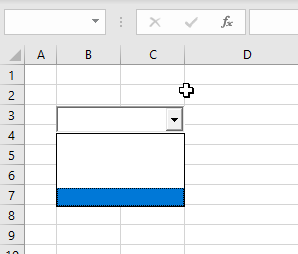
Clear a ComboBox
If you want to clear a ComboBox in VBA, you need to use Clear method of Sheet1.lstComboBox object. It will delete all the items from the ComboBox. Here is the code:
Sheet1.cmbComboBox.ClearNotice that the Clear method does not delete the attribute ListFillRange, so it must be removed from the properties of the ComboBox beforehand.
When we execute the code, we get the empty ComboBox:
Image 7. Clear the ComboBox
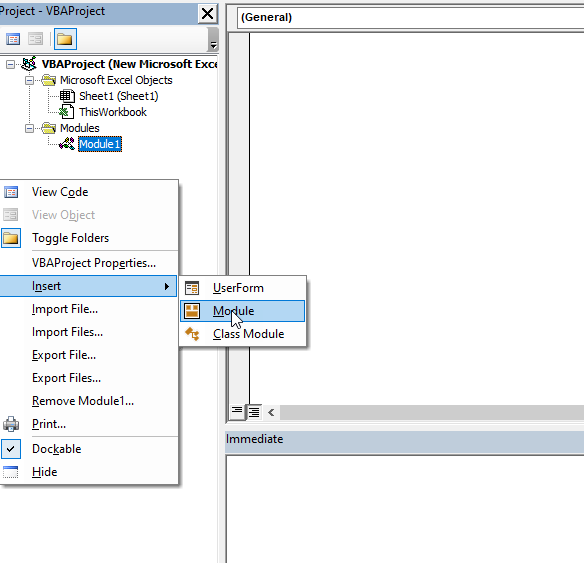
Use a ComboBox in a Userform
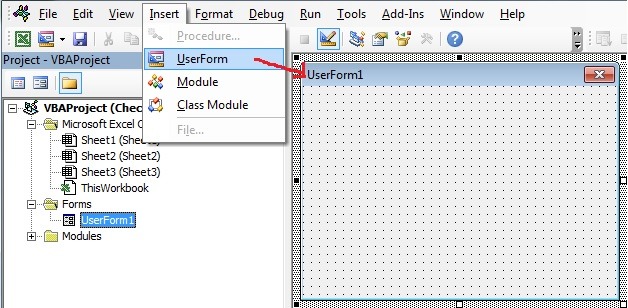
As we mentioned, Combobox is most often used in Userforms. To explain how you can do it, we will first insert an Userform. In VBA editor, right-click on Module name, click on Insert and choose UserForm:
Image 8. Insert a Userform
To display controls for inserting, you need to enable the Toolbox. To do this, click on the Toolbox icon in the toolbar. After that, you will get the windows with all the controls available. You can click on ComboBox to create it in the Userform.
Image 9. Insert a ComboBox in the Userform
We will name the ComboBox cmbComboBox. In order to populate it with values, we need to put the following code into the method Initialize of the object UserForm:
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
With UserForm1.cmbComboBox
.AddItem "John"
.AddItem "Michael"
.AddItem "Jennifer"
.AddItem "Lilly"
.AddItem "Robert"
End With
End SubThis code triggers every time a user runs the Userform and populates the Combobox with these 5 names:
Image 10. The ComboBox with values in the Userform
If you want to get selected value from the ComboBox, you need to use the same logic for the Combobox in a Worksheet, which is explained earlier in the article.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
Excel VBA UserForm ComboBox
ComboBox is one of the UserForm control. You can select and drag drop control on the UserForm. This control is used to store and display list of items to a list. This can be used on the UserForm. Please find more details about ComboBox Control in the following chapter. You can see how to load items to a Combo Box, how to get the value of combo box items, etc..,
- VBA ComboBox_Control on the UserForm
- Add Dynamic ComboBox_Control on the UserForm Using VBA
- Add Items to ComboBox_Control Using VBA
- Clear Items from the ComboBox_Control Using VBA
- Get the selected value of the ComboBox_Control using VBA
- VBA ComboBox default values in Excel
- Get the total count of ComboBox Items
- More details dbout the ComboBox_Control
VBA ComboBox_Control on the UserForm
Please find more details about VBA ActiveX Combo Box Control and how we are adding it on the UserForm.
-
- Go To Developer Tab and then click Visual Basic from the Code or Press Alt+F11.
- Go To Insert Menu, Click UserForm. Please find the screenshot for the same.
-
- Drag a ComboBox on the Userform from the Toolbox. Please find the screenshot for the same.
-
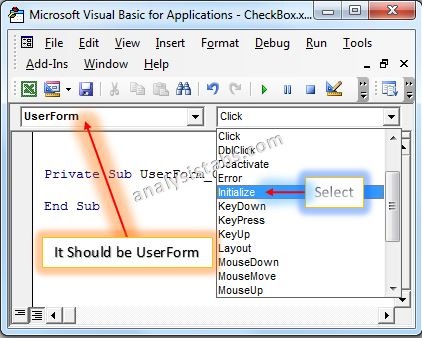
- Double Click on the UserForm, and select the Userform event as shown in the below screen shot.
-
- Now can see the following code in the module.
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize() End Sub
-
- Now, add the following code to the in between procedure.
Code:
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
ComboBox1.AddItem "MBA"
ComboBox1.AddItem "MCA"
ComboBox1.AddItem "MSC"
ComboBox1.AddItem "MECS"
ComboBox1.AddItem "CA"
End Sub
-
- Now, Press ‘F5’ to run the code. You can see the following Output. It is shown in the following Screen Shot.
Add dynamic ComboBox_Control on the UserForm using VBA
Please find the following steps and example code, it will show you how to add dynamic Combo Box control on the userform.
-
- Add command button on the userform from the toolbox.
- Right click on the command button, click properties
- Change the command button caption to ‘Create_ComboBox ’
- Double click on the command button
- Now, it shows following code.
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click() End Sub
-
- Call the below procedure named ‘Add_Dynamic_ComboBox ’ and find the below procedure to run.
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Call Add_Dynamic_ComboBox
End Sub
Procedure to call in the Command Button :
Sub Add_Dynamic_ComboBox()
'Add Dynamic Combo Box and assign it to object 'CmbBx'
Set CmbBx = UserForm3.Controls.Add("Forms.comboBox.1")
'Combo Box Position
CmbBx.Left = 20
CmbBx.Top = 10
End Sub
-
- Now, click F5 to run the macro, click ‘Create_ComboBox ’ button to see the result.
- You can see the created dynamic combo box in the following screen shot.
output:
Add Items to ComboBox_Control using VBA
Please find the following code, it will show you how to add list items to Combo Box.
Private Sub Insert _Items _To_ComboBox ()
ComboBox1.AddItem "Item 1"
ComboBox1.AddItem "Item 2"
ComboBox1.AddItem "Item 3"
ComboBox1.AddItem "Item 4"
ComboBox1.AddItem "Item 5"
End Sub
In the above code ComboBox1 is the name of the Combo Box. Where ‘additem’ is the property of Combo Box.
Clear Items from the ComboBox_Control using VBA
Please find the following code, it will show you how to clear the Combo Box items. The below code clears the ComboBox1 items on the UserForm1.
Sub Clr_CmbBx()
UserForm3.ComboBox1.Clear
End Sub
Get the selected value of the ComboBox using VBA
Please find the below code to know how to get the selected value of the Combo Box using VBA. In the below example value is the property of Combo box.
Sub Chk_Item_SelectOrNot()
MsgBox ComboBox1.Value
End Sub
VBA ComboBox Default Values in Excel
Here is the VBA Combo Box default values in Excel. After adding items to Combo Box by using any of the below code you can define the default value.
Code 1:
The below code is useful to select blank option in Combo Box . Where ‘-1’ is the index number.
Sub LstBx_Dflt_Val_Ex1()
UserForm3.ComboBox1.ListIndex = -1
End Sub
Code 2:
The below code is useful to select first item in the Combo Box from the available list. . Where ‘0’ is the index number.
Sub LstBx_Dflt_Val_Ex2()
UserForm3.ComboBox1.ListIndex = 0
End Sub
Code 3:
The below code is useful to select second item in the Combo Box from the available list. Where ‘1’ is the index number.
Sub LstBx_Dflt_Val_Ex3()
UserForm3.ComboBox1.ListIndex = 1
End Sub
Code 4:
The below code is useful to select the last item in the Combo Box from the available list. Where ‘1’ is the index number.
Sub LstBx_Dflt_Val_Ex4()
UserForm3.ComboBox1.ListIndex = UserForm3.ComboBox 1.Count - 1
End Sub
Get the total count of ComboBox Items
Here is the following example, it will show you how to get the total count of items in a Combo Box. In the below example ComboBox1 is the Combo Box name and ListCount is the property of Combo Box .
Sub Get_Ttl_Cnt()
MsgBox "Total Items in a ComboBox is " & UserForm3.ComboBox1.ListCount
End Sub
More Details About the ComboBox_Control
VBA ComboBox Excel Macros Examples Codes Adding Clearing Items
Please find more details about Remove Duplicates in Combo Box in Excel VBA.
Read More …
VBA Remove Duplicates in ComboBox
Please find the following link for more details about VBA Combo Box Excel Macros Examples and Codes Adding and Clearing Items.
Read More …
Excel VBA FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
Please find the most frequently asked questions and answers for your reference. These are explained more detailed way with examples.
Read More …
A Powerful & Multi-purpose Templates for project management. Now seamlessly manage your projects, tasks, meetings, presentations, teams, customers, stakeholders and time. This page describes all the amazing new features and options that come with our premium templates.
Save Up to 85% LIMITED TIME OFFER

All-in-One Pack
120+ Project Management Templates
Essential Pack
50+ Project Management Templates
Excel Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
PowerPoint Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
MS Word Pack
25+ Word PM Templates
Ultimate Project Management Template
Ultimate Resource Management Template
Project Portfolio Management Templates
-
-
- In this topic:
-
- VBA ComboBox_Control on the UserForm
- Add dynamic ComboBox_Control on the UserForm using VBA
-
- Procedure to call in the Command Button :
-
- Add Items to ComboBox_Control using VBA
- Clear Items from the ComboBox_Control using VBA
- Get the selected value of the ComboBox using VBA
- VBA ComboBox Default Values in Excel
-
- Code 1:
- Code 2:
- Code 3:
- Code 4:
-
- Get the total count of ComboBox Items
- More Details About the ComboBox_Control
-
- VBA ComboBox Excel Macros Examples Codes Adding Clearing Items
- VBA Remove Duplicates in ComboBox
- Excel VBA FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
-
VBA Reference
Effortlessly
Manage Your Projects
120+ Project Management Templates
Seamlessly manage your projects with our powerful & multi-purpose templates for project management.
120+ PM Templates Includes:
Effectively Manage Your
Projects and Resources
ANALYSISTABS.COM provides free and premium project management tools, templates and dashboards for effectively managing the projects and analyzing the data.
We’re a crew of professionals expertise in Excel VBA, Business Analysis, Project Management. We’re Sharing our map to Project success with innovative tools, templates, tutorials and tips.
Project Management
Excel VBA
Download Free Excel 2007, 2010, 2013 Add-in for Creating Innovative Dashboards, Tools for Data Mining, Analysis, Visualization. Learn VBA for MS Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Access, Outlook to develop applications for retail, insurance, banking, finance, telecom, healthcare domains.
Page load link

3 Realtime VBA Projects
with Source Code!
Go to Top
You’re VBA Combo Box Cheat Sheet
In this post I am going to share everything I know about using VBA with an Excel Form Control Combo Box (aka drop down). Most of the code is very self-explanatory so I will not write much of a description. However, some of the syntax can be a little tricky so pay close attention to how the code is structured. Please feel free to post comments if I missed an area or you have any questions! Enjoy 
Creating & Sizing/Positioning A Combo Box
Sub ComboBox_Create()
‘PURPOSE: Create a form control combo box and position/size it
Dim Cell As Range
Dim sht As Worksheet
Set sht = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(«Sheet1»)
‘Create
sht.DropDowns.Add(0, 0, 100, 15).Name = «Combo Box 1»
‘Create & Dimension to a Specific Cell
Set Cell = Range(«B5»)
With Cell
sht.DropDowns.Add(.Left, .Top, .Width, .Height).Name = «Combo Box 2»
End With
‘Create & Dimension to a Specific Cell Range
Set Cell = Range(«B8:D8»)
With Cell
sht.DropDowns.Add(.Left, .Top, .Width, .Height).Name = «Combo Box 3»
End With
End Sub
Deleting A Combo Box
Sub ComboBox_Delete()
‘PURPOSE: Delete a form control combo box
Dim sht As Worksheet
Set sht = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(«Sheet1»)
sht.Shapes(«Combo Box 1»).Delete
End Sub
Adding Values To A Combo Box
Sub ComboBox_InputRange()
‘PURPOSE: Add values to your drop down list
Dim Cell As Range
Dim sht As Worksheet
Dim myArray As Variant
Dim myDropDown As Shape
Set sht = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(«Sheet1»)
Set myDropDown = sht.Shapes(«Combo Box 1»)
myArray = Array(«Q1», «Q2», «Q3», «Q4»)
‘Based on data in a range (not linked)
MyDropDown.ControlFormat.List = sht.Range(«A1:A4»).Value
‘Linked to data in a range (automatically changes based on current cell values)
myDropDown.ControlFormat.ListFillRange = «A1:A4»
‘Based on Array values (written out)
MyDropDown.ControlFormat.List = _
Array(«Q1», «Q2», «Q3», «Q4»)
‘Based on Array values (variable)
myDropDown.OLEFormat.Object.List = myArray
‘Add one by one
With myDropDown.ControlFormat
.AddItem «Q1»
.AddItem «Q2»
.AddItem «Q3»
.AddItem «Q4»
End With
End Sub
Overriding Values In The Drop Down List
Sub ComboBox_ReplaceValue()
‘PURPOSE: Replace value of the third item in the drop down list
Worksheets(«Sheet1»).Shapes(«Combo Box 1»).ControlFormat.List(3) = «FY»
End Sub
Removing Values From The Drop Down List
Sub ComboBox_RemoveValues()
‘PURPOSE: Remove a value(s) from the drop down list
Dim Cell As Range
Dim sht As Worksheet
Set sht = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(«Sheet1»)
‘Remove A Single Item
sht.Shapes(«Combo Box 1»).ControlFormat.RemoveItem 2
‘Remove All Items
sht.Shapes(«Combo Box 1»).ControlFormat.RemoveAllItems
End Sub
Determine Current Selected Value From The Drop Down List
Sub ComboBox_GetSelection()
‘PURPOSE: Determine current selected value in ComboBox
Dim sht As Worksheet
Dim myDropDown As Shape
Set sht = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(«Sheet1»)
Set myDropDown = sht.Shapes(«Combo Box 1»)
With myDropDown.ControlFormat
MsgBox «Item Number: » & .Value & vbNewLine & «Item Name: » & .List(.Value)
End With
End Sub
Select A Value From The Drop Down List
Sub ComboBox_SelectValue()
‘PURPOSE: Automatically select a value from the drop down list
Dim Cell As Range
Dim sht As Worksheet
Dim Found As Boolean
Dim SetTo As String
Dim x As Long
Set sht = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(«Sheet1»)
‘Select First List Item
sht.Shapes(«Combo Box 1»).ControlFormat.ListIndex = 3
‘Select Item based on list Name/Value
SetTo = «Q2»
With sht.Shapes(«Combo Box 1»).ControlFormat
For x = 1 To .ListCount
If .List(x) = SetTo Then
Found = True
Exit For
Next x
If Found = True Then .ListIndex = x
End With
End Sub
Link User’s Selection To A Cell (Outputs Numerical List Position)
Sub ComboBox_CellLink()
‘PURPOSE: Output the selection’s list position to a specific cell
Dim sht As Worksheet
Set sht = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(«Sheet1»)
sht.Shapes(«Combo Box 1»).ControlFormat.LinkedCell = «$A$1»
End Sub
Adjust Drop Down Lines For A Combo Box
Sub ComboBox_DropDownLines()
‘PURPOSE: Set how many drop down lines are visible per scroll
Dim sht As Worksheet
Set sht = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(«Sheet1»)
sht.Shapes(«Combo Box 1»).ControlFormat.DropDownLines = 12
End Sub
Toggle On/Off 3D Shading
Sub ComboBox_3DShading()
‘PURPOSE: Turn 3D shading on or off
Dim sht As Worksheet
Set sht = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(«Sheet1»)
‘Turn 3D Shading On
sht.Shapes(«Combo Box 1»).OLEFormat.Object.Display3DShading = True
‘Turn 3D Shading Off
sht.Shapes(«Combo Box 1»).OLEFormat.Object.Display3DShading = False
End Sub
Assigning A Macro To A Combo Box
Sub ComboBox_AssignMacro()
‘PURPOSE: Assign a macro to be triggered when drop down is changed
Dim sht As Worksheet
Set sht = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(«Sheet1»)
sht.Shapes(«Combo Box 1»).OnAction = «Macro1»
End Sub
Any Others?
If I’ve missed any VBA functionalities please leave a comment in the comments section below so I can continue to grow this list of combo box code! I look forward to hearing your thoughts.
About The Author
Hey there! I’m Chris and I run TheSpreadsheetGuru website in my spare time. By day, I’m actually a finance professional who relies on Microsoft Excel quite heavily in the corporate world. I love taking the things I learn in the “real world” and sharing them with everyone here on this site so that you too can become a spreadsheet guru at your company.
Through my years in the corporate world, I’ve been able to pick up on opportunities to make working with Excel better and have built a variety of Excel add-ins, from inserting tickmark symbols to automating copy/pasting from Excel to PowerPoint. If you’d like to keep up to date with the latest Excel news and directly get emailed the most meaningful Excel tips I’ve learned over the years, you can sign up for my free newsletters. I hope I was able to provide you with some value today and I hope to see you back here soon!
— Chris
Founder, TheSpreadsheetGuru.com
There are three methods to read the selected values from a combobox in VBA. Please go through the following blog to know how you can do it.
Method 1:
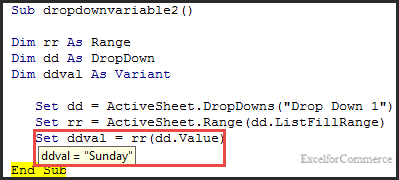
Consider, we have a dropdown list having days mentioned in it. The value selected in the dropdown is ‘Sunday’. Now, we will try to read the selected value from the dropdown list using Excel VBA.
To read the selected day from the dropdown list into a variable, we can use the following snippet.
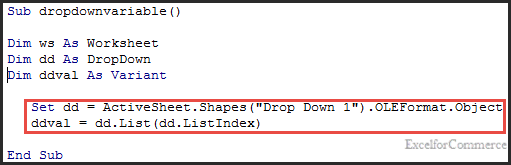
In the above code, we are creating an object reference for the dropdown “Drop Down 1”.
If you observe the code, we are using OLEFormat.Object. OLEFormat property is used when we are working with shapes (ComboBox, ListBox and so on) , inline shapes, or fields to return the OLEFormat object.
‘ddval’ is the variable that stores the value of the selected dropdown.
dd.List(dd.ListIndex)
Here, List returns an item from List index. List index is an expression that returns index of the objects in the list.
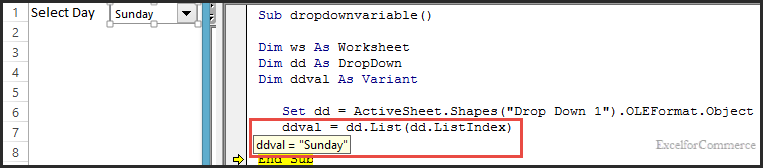
As we can see from the image above the variable ‘ddval’ has value ‘Sunday’.
Method 2:
In this method we will use ‘ListFillRange’. This property ‘ListFillRange’ reads the contents of every cell in the range designated for the list and inserts the cell values into the list box. Before fetching the selected dropdown value, we have to assign the range of dropdown values to property ‘ListFillRange’
Say, if the list of options are in Column Q starting from Q1 to Q10, then we define the listfillrange for the dropdown.
Once the ListFillRange is assigned, the selected dropdown value is fetched as below. ‘ddval’ is the variable that stores the dropdown value from the dropdown list.
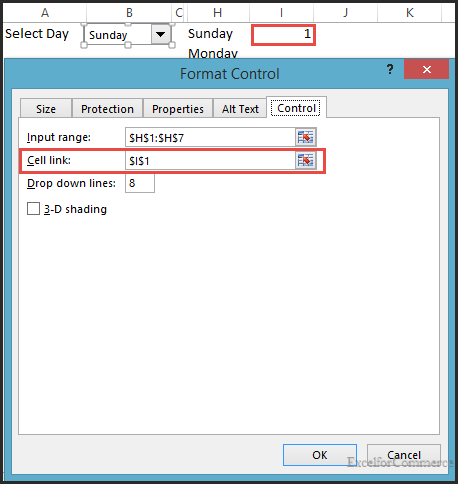
Method 3:
In this method, we will use cell link to read the dropdown value to the variable.
Based on the selection in the dropdown list the cell link value in ‘I1’ changes. The cell link value in ‘I1’ can be used to read the selected dropdown value.
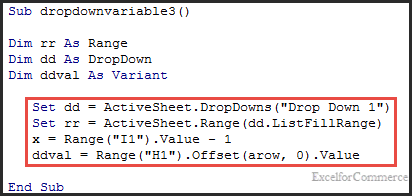
Offset method:
Here, we use ‘ListFillRange’ to identify the range and assign its value to the ‘rr’ variable. ‘x’ is the variable used to find the offset row location.
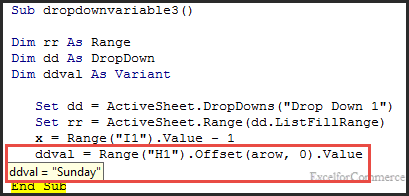
Based on ‘x’ value and by using offset function, the value of the dropdownlist is found as below
We are taking the dropdown value into the ‘ddval’ variable as shown in the image below.
This is how we get combobox selected value in VBA. If you have any queries then please contact our Excel Expert here.
This blog post demonstrates how to create, populate and change comboboxes (form control) programmatically.
Form controls are not as flexible as ActiveX controls but are compatible with earlier versions of Excel. You can find the controls on the developer tab.
Table of Contents
- Create a combobox using vba
- Assign a macro — Change event
- Add values to a combobox
- Remove values from a combo box
- Set the default value in a combo box
- Read selected value
- Link selected value
- Change combobox properties
- Populate combox with values from a dynamic named range
- Populate combox with values from a table
- Currently selected combobox
Watch this video about Combo Boxes
Create a combobox using vba
Sub CreateFormControl()
'Worksheets("Sheet1").DropDowns.Add(Left, Top, Width, Height)
Worksheets("Sheet1").DropDowns.Add(0, 0, 100, 15).Name = "Combo Box 1"
End Sub
Recommended article
Recommended articles
Back to top
Assign a macro — Change event
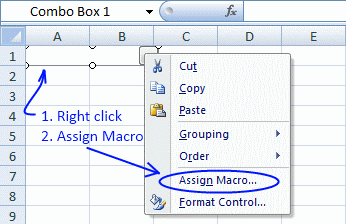
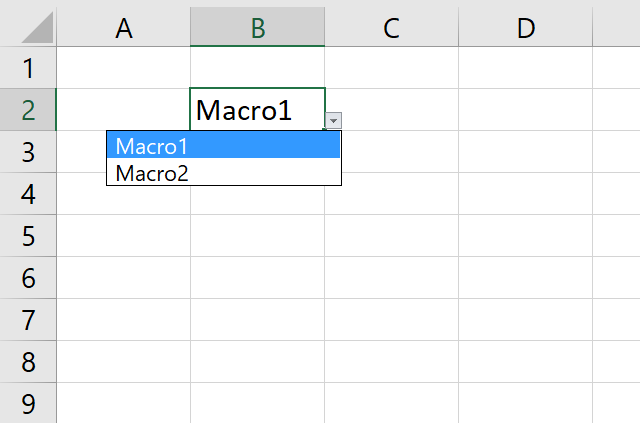
You can assign a macro to a combobox by press with right mouse button oning on the combobox and select «Assign Macro». Select a macro in the list and press ok!
This subroutine does the same thing, it assigns a macro named «Macro1» to «Combo box 1» on sheet 1. Macro1 is rund as soon as the selected value in the combo box is changed.
Sub AssignMacro()
Worksheets("Sheet1").Shapes("Combo Box 1").OnAction = "Macro1"
End Sub
Recommended article
Recommended articles
Back to top
Add values to a combo box
You can add an array of values to a combo box. The list method sets the text entries in a combo box, as an array of strings.
Sub PopulateCombobox1()
Worksheets("Sheet1").Shapes("Combo Box 1").ControlFormat.List = _
Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("E1:E3").Value
End Sub
The difference with the ListFillRange property is that the combo box is automatically updated as soon as a value changes in the assigned range. You don´t need to use events or named ranges to automatically refresh the combo box, except if the cell range also changes in size.
Sub PopulateCombobox2()
Worksheets("Sheet1").Shapes("Combo Box 1").ControlFormat.ListFillRange = _
"A1:A3"
End Sub
You can also add values one by one.
Sub PopulateCombobox3()
With Worksheets("Sheet1").Shapes("Combo Box 1").ControlFormat
.AddItem "Sun"
.AddItem "Moon"
.AddItem "Stars"
End Sub
Back to top
Recommended article
Recommended articles
Remove values from a combo box
RemoveAllItems is self-explanatory.
Sub RemoveAllItems()
Worksheets("Sheet1").Shapes("Combo Box 1").ControlFormat.RemoveAllItems
End Sub
The RemoveItem method removes a value using a index number.
Sub RemoveItem()
Worksheets("Sheet1").Shapes("Combo Box 1").ControlFormat.RemoveItem 1
End Sub
The first value in the array is removed.
Recommended article
Recommended articles
How to use DIALOG BOXES
A dialog box is an excellent alternative to a userform, they are built-in to VBA and can save you time […]
Back to top
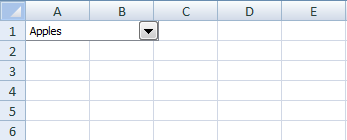
Set the default value in a combo box
The ListIndex property sets the currently selected item using an index number. ListIndex = 1 sets the first value in the array.
Sub ChangeSelectedValue()
With Worksheets("Sheet1").Shapes("Combo Box 1")
.List = Array("Apples", "Androids", "Windows")
.ListIndex = 1
End With
End Sub
Recommended article
Recommended articles
Back to top
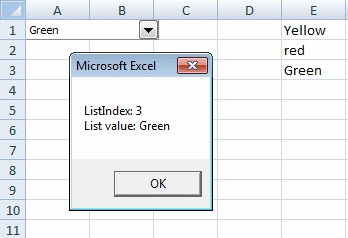
Read selected value
The ListIndex property can also return the index number of the currently selected item. The list method can also return a value from an array of values, in a combo box. List and Listindex combined returns the selected value.
Sub SelectedValue()
With Worksheets("Sheet1").Shapes("Combo Box 1").ControlFormat
MsgBox "ListIndex: " & .ListIndex & vbnewline & "List value:" .List(.ListIndex)
End With
End Sub
Recommended article
Recommended articles
Back to top
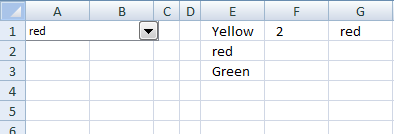
Link selected value
Cell F1 returns the index number of the selected value in combo box 1.
Sub LinkCell()
Worksheets("Sheet1").Shapes("Combo Box 1").ControlFormat.LinkedCell = "F1"
End Sub
Cell G1 returns the selected value in combo box 1.
Sub LinkCell2()
With Worksheets("Sheet1").Shapes("Combo Box 1").ControlFormat
Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("G1").Value = .List(.ListIndex)
End With
End Sub
Recommended article
Recommended articles
Back to top
Change combobox properties
Change the number of combo box drop down lines.
Sub ChangeProperties()
Worksheets("Sheet1").Shapes("Combo Box 1").ControlFormat.DropDownLines = 2
End Sub
Back to top
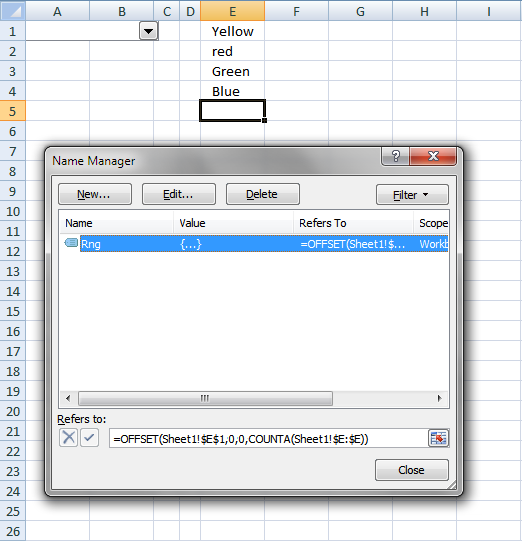
Populate combox with values from a dynamic named range
I created a dynamic named range Rng, the above picture shows how.
Sub PopulateFromDynamicNamedRange()
Worksheets("Sheet1").Shapes("Combo Box 1").ControlFormat.ListFillRange = "Rng"
End Sub
You can do the same thing as the subroutine accomplishes by press with right mouse button oning the combo box and then press with left mouse button on «Format Control…». Input Range: Rng
Back to top
Populate combox with values from a table
Sub PopulateFromTable()
Worksheets("Sheet1").Shapes("Combo Box 1").ControlFormat.List = _
[Table1[DESC]]
End Sub
Back to top
Currently selected combobox
It is quite useful to know which combo box the user is currently working with. The subroutine below is assigned to Combo Box 1 and is rund when a value is selected. Application.Caller returns the name of the current combo box.
Sub CurrentCombo() MsgBox Application.Caller End Sub
Back to top
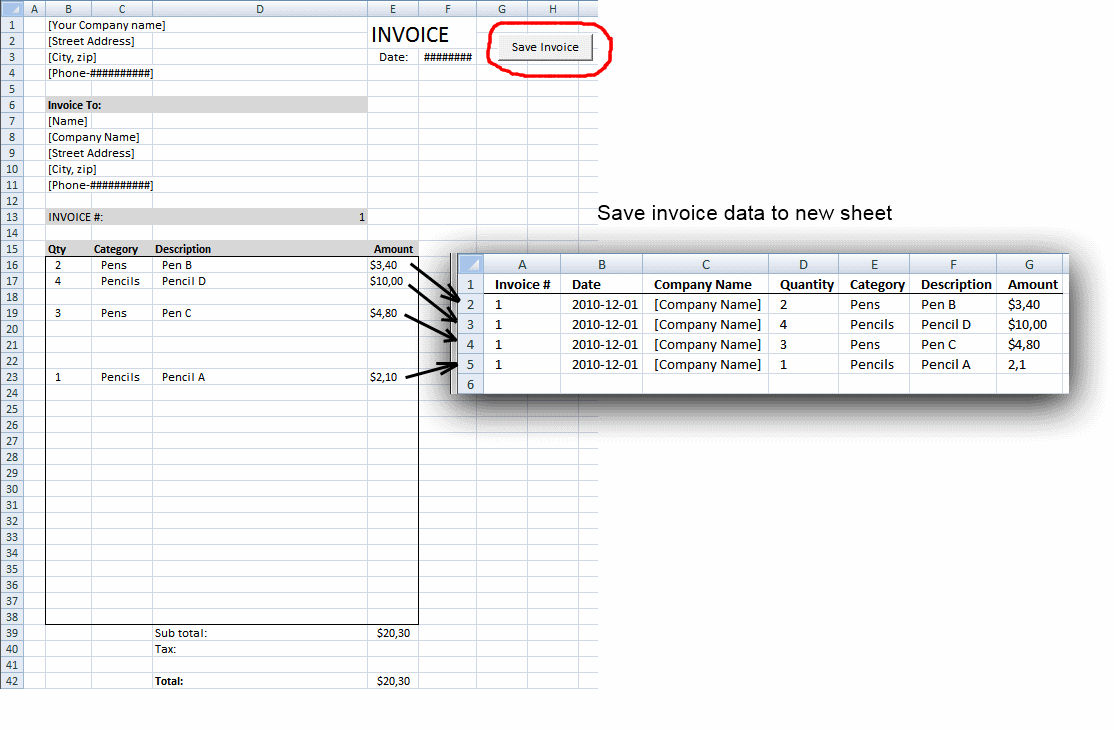
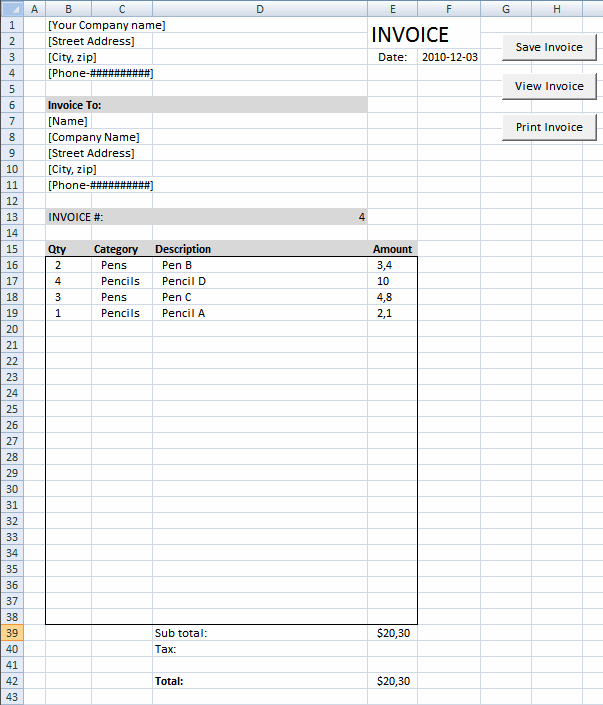
Save invoice data [VBA]
This article demonstrates a macro that copies values between sheets. I am using the invoice template workbook. This macro copies […]
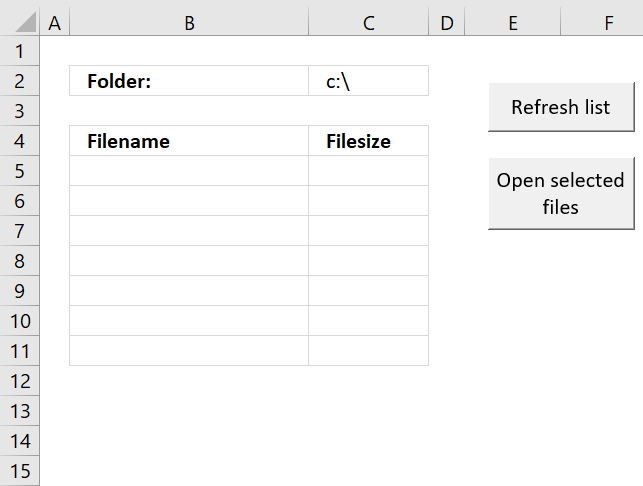
Open Excel files in a folder [VBA]
This tutorial shows you how to list excel files in a specific folder and create adjacent checkboxes, using VBA. The […]
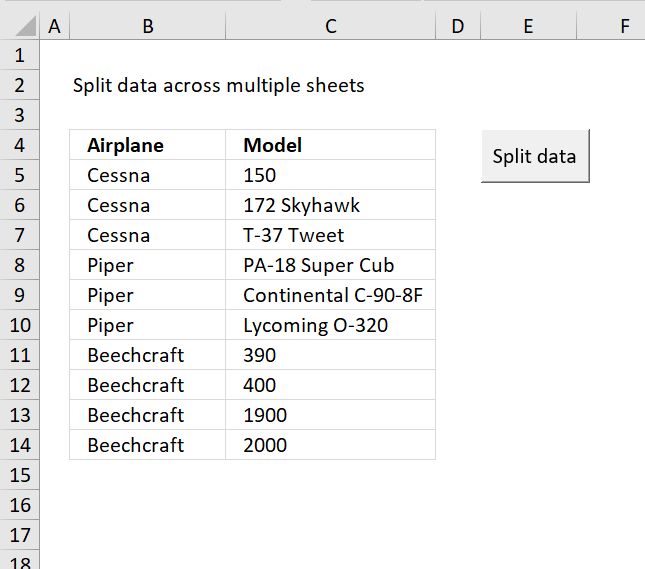
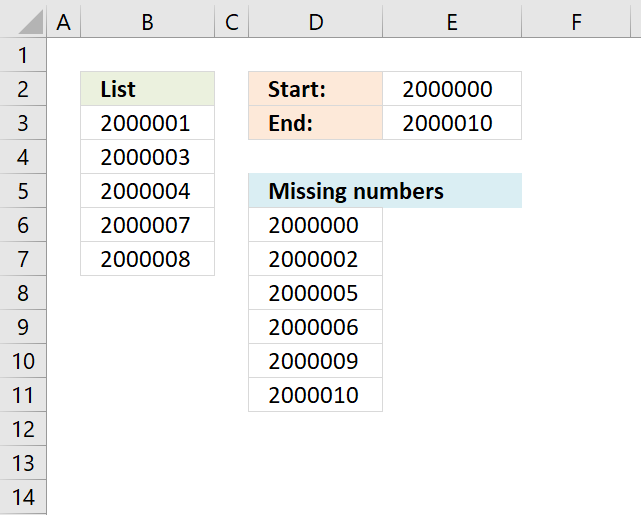
Identify missing numbers in a column
The image above shows an array formula in cell D6 that extracts missing numbers i cell range B3:B7, the lower […]

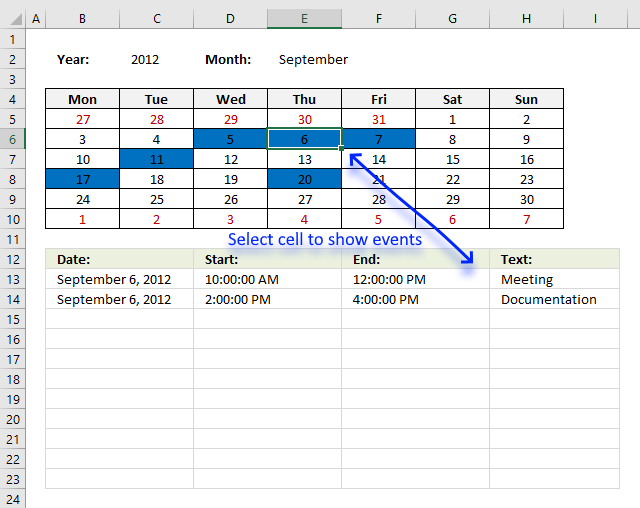
Excel calendar [VBA]
This workbook contains two worksheets, one worksheet shows a calendar and the other worksheet is used to store events. The […]

Working with FILES
In this blog article, I will demonstrate basic file copying techniques using VBA (Visual Basic for Applications). I will also […]
Auto resize columns as you type
Excel does not resize columns as you type by default as the image above demonstrates. You can easily resize all […]

Create a Print button [VBA]
This article describes how to create a button and place it on an Excel worksheet then assign a macro to […]
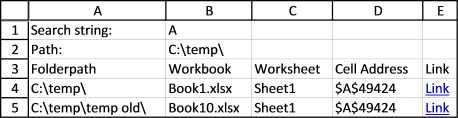
Search all workbooks in a folder
Today I’ll show you how to search all Excel workbooks with file extensions xls, xlsx and xlsm in a given folder for a […]

Save invoice data [VBA]
This article demonstrates a macro that copies values between sheets. I am using the invoice template workbook. This macro copies […]

Open Excel files in a folder [VBA]
This tutorial shows you how to list excel files in a specific folder and create adjacent checkboxes, using VBA. The […]
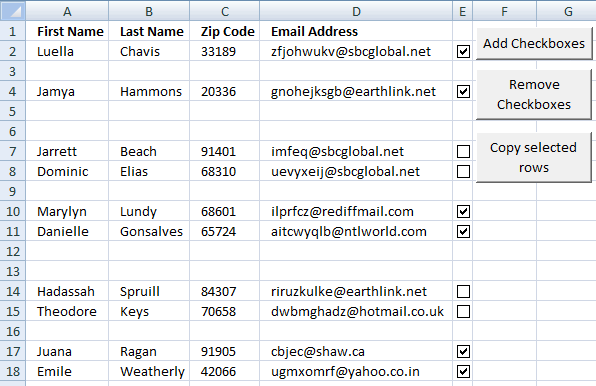
Copy selected rows (checkboxes) (2/2)
This article demonstrates a macro that copies selected rows based on enabled check boxes. The image above shows data on […]


Identify missing numbers in a column
The image above shows an array formula in cell D6 that extracts missing numbers i cell range B3:B7, the lower […]

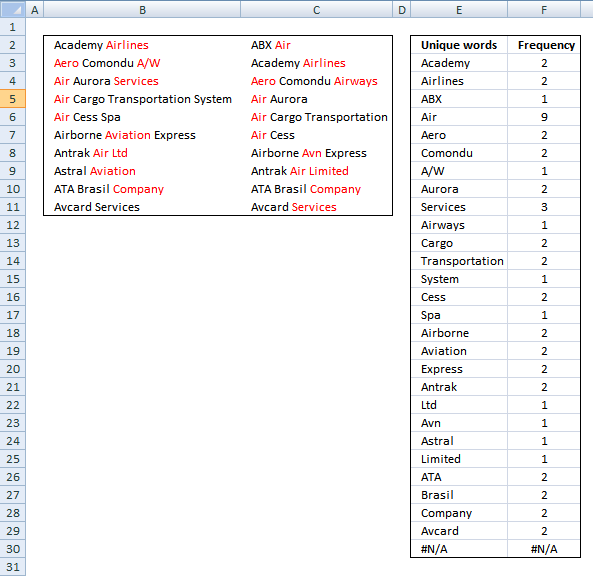
Analyze word frequency in a cell range
This article demonstrates two ways to calculate the number of times each word appears in a given range of cells. […]

Excel calendar [VBA]
This workbook contains two worksheets, one worksheet shows a calendar and the other worksheet is used to store events. The […]


Working with FILES
In this blog article, I will demonstrate basic file copying techniques using VBA (Visual Basic for Applications). I will also […]

Auto resize columns as you type
Excel does not resize columns as you type by default as the image above demonstrates. You can easily resize all […]

Create a Print button [VBA]
This article describes how to create a button and place it on an Excel worksheet then assign a macro to […]


Latest updated articles.
More than 300 Excel functions with detailed information including syntax, arguments, return values, and examples for most of the functions used in Excel formulas.
More than 1300 formulas organized in subcategories.
Excel Tables simplifies your work with data, adding or removing data, filtering, totals, sorting, enhance readability using cell formatting, cell references, formulas, and more.
Allows you to filter data based on selected value , a given text, or other criteria. It also lets you filter existing data or move filtered values to a new location.
Lets you control what a user can type into a cell. It allows you to specifiy conditions and show a custom message if entered data is not valid.
Lets the user work more efficiently by showing a list that the user can select a value from. This lets you control what is shown in the list and is faster than typing into a cell.
Lets you name one or more cells, this makes it easier to find cells using the Name box, read and understand formulas containing names instead of cell references.
The Excel Solver is a free add-in that uses objective cells, constraints based on formulas on a worksheet to perform what-if analysis and other decision problems like permutations and combinations.
An Excel feature that lets you visualize data in a graph.
Format cells or cell values based a condition or criteria, there a multiple built-in Conditional Formatting tools you can use or use a custom-made conditional formatting formula.
Lets you quickly summarize vast amounts of data in a very user-friendly way. This powerful Excel feature lets you then analyze, organize and categorize important data efficiently.
VBA stands for Visual Basic for Applications and is a computer programming language developed by Microsoft, it allows you to automate time-consuming tasks and create custom functions.
A program or subroutine built in VBA that anyone can create. Use the macro-recorder to quickly create your own VBA macros.
UDF stands for User Defined Functions and is custom built functions anyone can create.
A list of all published articles.
UserForm Controls — ComboBox and ListBox
———————————————————-
Contents:
Difference between ListBox and ComboBox
Key Properties of ComboBox and ListBox
Add Items/Data to (Populate) a ListBox or ComboBox
Extract ListBox & ComboBox Items, with VBA
Delete ListBox rows using the RemoveItem Method
———————————————————-
UserForm acts as a container in which you add multiple ActiveX controls, each of which has a specific use and associated properties. By itself, a UserForm will not be of much use unless ActiveX controls are added to it which are the actual user-interactive objects. Using ActiveX Controls on a Worksheet have been illustrated in detail, in the separate section of «Excel VBA: ActiveX Controls, Form Controls & AutoShapes on a Worksheet».
An Excel VBA ListBox or ComboBox is a list of items from which a user can select. They facilitate in accepting data from users and making entries in an Excel worksheet.
Difference between ListBox and ComboBox:
1. The ComboBox is a drop-down list (the user-entered item or the list-selected item is visible in the text area, whereas list values are visible by using the drop-down), while a ListBox shows a certain number of values with or without a scroll bar. In a ComboBox, only one row of items is visible at a given time (without using the drop-down) whereas in a ListBox one or more can be visible at a time.
2. In a ComboBox you can select ony one option from the list, while in a ListBox you can select multiple options from the list.
3. The user can enter his own item (in text area) in a ComboBox if it is not included in the list, which is not possible to do in a ListBox. In this sense, ComboBox is a combination of TextBox and ListBox.
4. CheckBox can be used within ListBox, but not within ComboBox. ListBox allows you to display a check box next to each item in the list, to enable user to select items (this might be easier for the user than using the multiple selection methods). To use CheckBoxes in a ListBox, set ListStyle property (in Properties Window) to fmListStyleOption (vba code: ListBox1.ListStyle = fmListStyleOption). This setting is best used with a multiselect ListBox.
——————————————————————————————————————-
Key Properties of ComboBox and ListBox
Note1: All properties and methods given below are common to both ListBox and ComboBox, unless mentioned otherwise. Also refer «2. UserForm and Controls — Properties.» for properties common to the UserForm and most Controls.
Note 2: In below given examples, vba codes are required to be entered in the Code Module of the UserForm, unless specified otherwise.
AddItem Method:
Adds an item to the list, in a single-column ListBox or ComboBox. Adds a row to the list (ie. an item for each row), in a multi-column ListBox or ComboBox. Syntax: Control.AddItem(Item, Index). Item specifies the item or row to add. Index is an Integer which specifies the position where the new item or row is placed within the list, and if omitted, the item or row is added at the end. The item or row numbers begin with zero, and the first item or row is numbered 0, and so on. The value of Index cannot be greater than the total number of rows (ie. value of ListCount property). AddItem method will not work if ComboBox or ListBox is bound to data, hence RowSource data should be cleared before use. AddItem method can only be used with a macro or vba code. Note: AddItem method adds an item to the first column in a multi-column ListBox or ComboBox, and to add an item further to the first column, use the List or Column property specifying the item’s row and column number. More than one row can also be added at a time to a ListBox or ComboBox by using the List or Column properties (AddItem adds one row at a time). This means that you can copy a two-dimensional array of values to a ListBox or ComboBox, using List or Column properties rather than adding each individual element using the AddItem method. Note: Using the Column property to copy a two-dimensional array of values to a ListBox or ComboBox, transposes the array contents and equates myArray(iRow, iColumn) to ListBox1.Column(iCol, iRow). List property copies an array without transposing it and myArray(iRow, iColumn) equates to ListBox1.List(iRow, iColumn). Refer Image 13 for example.
BoundColumn Property:
Specifies the column from which value is to be stored in a multicolumn ComboBox or ListBox, when a row is selected by the user. First column has a BoundColumn value of 1, second column has a value of 2, and so on. Setting the BoundColumn value to 1 will assign the value from column 1 to the ComboBox or ListBox, and so on. BoundColumn property lets the user to store a different set of values per specified column while TextColumn property displays one set of values, viz. use the Text property to return the value from the first column (specified in the TextColumn property) containing the names and the BoundColumn property can specify another column containing height wherein on selecting a particular person’s name in the ListBox, his height will get returned or stored (refer Image 10). The ColumnWidths property of a column can be set to zero to not display it in the ListBox. Setting the BoundColumn value to 0 assigns the value of the ListIndex property (which is the number of the selected row) as the value of the control (ComboBox or ListBox). This setting is useful if you want to determine the row of the selected item in a ComboBox or ListBox. BoundColumn Property can be set in the Properties window and can also be used with a macro or vba code. Note: Where the ControlSource mentions =Sheet3!D2 (vba code: .ControlSource = «=Sheet3!D2»), the value in the BoundColumn of the selected row will get stored in cell D2, Sheet3.
Example 1: Setting the BoundColumn value to 0 assigns the value of the ListIndex property (which is the number of the selected row) as the value of the control (in a Single Selection ListBox) — refer Image 7
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ListBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ListBox1
.ColumnHeads = True
.ColumnCount = 2
‘ColumnWidths property of the second column is set to zero to not display it in the ListBox.
.ColumnWidths = «50;0»
.RowSource = «=Sheet3!A2:B6»
.MultiSelect = fmMultiSelectSingle
.BoundColumn = 0
End With
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
‘BoundColumn value is set as 0 which assigns the value of the ListIndex property (which is the number of the selected row) as the value of the control. Note: MultiSelect Property is set to fmMultiSelectSingle which allows only single selection.
If ListBox1.Value <> «» Then
TextBox1.Value = ListBox1.Value + 2
End If
End Sub
Clear Method:
Removes all items in a ComboBox or ListBox. Syntax: Control.Clear. Clear method will not work if ComboBox or ListBox is bound to data, hence RowSource data should be cleared before use. Clear method can only be used with a macro or vba code.
Column Property:
Refers to a specific column, or column and row combination, in a multiple-column ComboBox or ListBox. Syntax: Control.Column(iColumn, iRow). Column property can only be used with a macro or vba code and is not available at design time. iColumn specifies the column number wherein iColumn = 0 means the first column in the List. iRow specifies the row number wherein iRow = 0 means the first row in the List. Both iColumn and iRow are integer values ranging from 0 to number of columns and rows (respectively) in the list minus 1. Specifying both column and row numbers will refer to a specific item, and specifying only the column number will refer to a specific column in the current row viz. ListBox1.Column(1) refers the second column. You can copy a two-dimensional array of values to a ListBox or ComboBox, using Column (or List) property rather than adding each individual element using the AddItem method. Column property can be used to assign the contents of a ComboBox or ListBox to another control, viz. TextBox (refer Image 8). Note: Using the Column property to copy a two-dimensional array of values to a ListBox or ComboBox, transposes the array contents and equates myArray(iRow, iColumn) to ListBox1.Column(iCol, iRow). List property copies an array without transposing it and myArray(iRow, iColumn) equates to ListBox1.List(iRow, iColumn). Refer Image 13 for example.
Example 2: Load ListBox using AddItem method and List & Column properties; and use Column property to assign the contents of ListBox to TextBox — refer Image 8
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ListBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ListBox1
.ColumnCount = 3
.ColumnWidths = «50;50;50»
.ColumnHeads = False
.RowSource = «=Sheet2!A2:B6»
.MultiSelect = fmMultiSelectMulti
End With
‘clearing the TextBox if it is not empty
TextBox1 = «»
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
‘Add items in ListBox using AddItem method to add new rows; use List & Column properties to add items in columns beyond the first column; and use Column property to assign the contents of ListBox to TextBox
‘AddItem method will not work if ListBox is bound to data, hence RowSource is cleared if it had been set
ListBox1.RowSource = «»
‘Create a new row with AddItem
ListBox1.AddItem «banana»
‘add item in second column of this first row, using List property
ListBox1.List(0, 1) = «tuesday»
‘adding items in the 3 columns of the first row — this will become the second row in the end
ListBox1.List(0, 2) = «day 2»
ListBox1.AddItem «orange»
‘add item in second column of this second row, using Column property
ListBox1.Column(1, 1) = «wednesday»
‘adding items in the 3 columns of the second row — this will become the third row in the end
ListBox1.Column(2, 1) = «day 3»
‘Create a new row with AddItem and position as row number 1
ListBox1.AddItem «apple», 0
ListBox1.List(0, 1) = «monday»
‘adding items in the 3 columns and positioning this row as the first row — this will push down the above two rows
ListBox1.List(0, 2) = «day 1»
‘item in column number 3 and row number 2 of ListBox
TextBox1.Value = ListBox1.Column(2, 1)
End Sub
ColumnCount Property:
Specifies the number of columns to be displayed in a ComboBox or ListBox. A ColumnCount value of 0 does not display any column and a setting of -1 displays all columns. ColumnCount property can be set in the Properties window and can also be used with a macro or vba code.
ColumnHeads Property:
A Boolean value (True/False) which determines display of column headings (in a single row) for ComboBox or ListBox. ColumnHeads property can be set in the Properties window and can also be used with a macro or vba code. Column Headings can be displayed only if ColumnHeads is set to True in Properties window (VBA code: ListBox1.ColumnHeads = True) and if you bind the ListBox to a range (ie. set RowSource to a range that includes headings). Note: AddItem method will not work if ListBox or ComboBox is bound to data, hence RowSource property should be cleared for using AddItem.
List Property:
List Property is used in conjunction with the ListCount and ListIndex properties to return items in a ListBox or ComboBox control. Syntax -> Control.List(iRow,iCol). Each item in a list has a row number and a column number, wherein row and column numbers start with zero. iRow specifies the row number wherein iRow = 2 means the third row in the List. iColumn specifies the column number wherein iColumn = 0 means the first column in the List. Omitting to specify the iColumn will retrieve the first column. Specify iColumn only for a multi-column ListBox or ComboBox. List Property can only be used with a macro or vba code and is not available at design time. Note: To copy a two-dimensional array of values to a ListBox or ComboBox, use List or Column properties. To add a one-dimensional array or to add an individual element, use the AddItem method. Items can be removed from a List using the RemoveItem method. List property is available only by using a macro or VBA.
Example 3: Use Selected & List properties to display multiple-selected ListBox items (choose any column to display) in TextBox, and link a worksheet cell with TextBox using ControlSource property — refer Image 9.
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ListBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ListBox1
.ColumnHeads = True
.ColumnCount = 2
‘ColumnWidths property of the second column is set to zero to not display it in the ListBox.
.ColumnWidths = «50;0»
.RowSource = «=Sheet3!A2:B6»
.MultiSelect = fmMultiSelectMulti
.TextColumn = 1
End With
With TextBox1
.MultiLine = True
‘the text or value in the TextBox will get stored in the worksheet cell — Sheet3!F2
.ControlSource = «=Sheet3!F2»
‘if the cell Sheet3!F2 contains any text, this will not appear in the TextBox on initialization of UserForm
.Value = «»
End With
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
‘Use Selected & List properties to display multiple-selected ListBox items (choose any column to display) in TextBox, and link a worksheet cell with TextBox using ControlSource property
TextBox1.Value = «»
‘check all items in a ListBox
For n = 0 To ListBox1.ListCount — 1
‘if a ListBox item is selected, it will display in TextBox
If ListBox1.Selected(n) = True Then
If TextBox1.Value = «» Then
‘ListBox1.List(n, 0) or ListBox1.List(n)displays the first column in TextBox, ListBox1.List(n, 1) displays the second column and so on
‘alternate code which displays the second column in TextBox: TextBox1.Value = Range(ListBox1.RowSource).Offset(n, 1).Resize(1, 1).Value
TextBox1.Value = ListBox1.List(n, 1)
Else
‘alternate code which displays the second column in TextBox: TextBox1.Value = TextBox1.Value & vbCrLf & Range(ListBox1.RowSource).Offset(n, 1).Resize(1, 1).Value
TextBox1.Value = TextBox1.Value & vbCrLf & ListBox1.List(n, 1)
End If
End If
Next n
End Sub
ListCount Property:
Determines the total number of rows in a ListBox or ComboBox. This property can only be used with a macro or vba code and is not available at design time. Note: The column headings row is also counted, if ColumnHeads are displayed. The ListCount property can be used with the ListRows property to specify the number of rows to display in a ComboBox.
ListIndex Property:
Determines which item is selected in a ComboBox or ListBox. The first item in a list has a ListIndex value of 0, the second item has a value of 1, and so on. Hence, it is an integer value ranging from 0 to the total number of items in a ComboBox or ListBox minus 1. ListIndex returns -1 when no rows are selected. This property can only be used with a macro or vba code and is not available at design time. Note: In a Multiple Selection enabled ListBox, ListIndex returns the index of the row that has focus, irrespective of whether that row is selected or not. Hence the Selected property of the ListBox (and not the ListIndex property) shoud be used here to return and set a selection. In a Single Selection enabled ListBox (viz. MultiSelect property setting of fmMultiSelectSingle), ListIndex returns the index of the selected item and hence ListIndex property should be used here to return and set a selection.
ListRows Property:
Specifies the maximum number of rows which will display in the list box portion of a ComboBox. The default value is 8. Note: If the actual number of list items exceed this maximum value of the ListRows property, a vertical scroll bar will appear in the list box portion of the ComboBox (and the excess list items can be viewed by scrolling down). The ListCount property can be used with the ListRows property to specify the number of rows to display in a ComboBox. ListRows property can be set in the Properties window and can also be used with a macro or vba code. ListRows Property is valid for ComboBox and not for ListBox.
Example 4: Using the ListCount property with the ListRows property, to set number of rows to display in ComboBox
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘this macro sets the ListRow value, on initialization of the UserForm
With ComboBox1
If .ListCount > 5 Then
.ListRows = 5
Else
.ListRows = .ListCount
End If
End With
End Sub
MultiSelect Property:
Specifies whether multiple selections are allowed. There are 3 settings: (i) fmMultiSelectSingle (value 0), the default setting, wherein only a single item can be selected; (ii) fmMultiSelectMulti (value 1) which allows multiple selections wherein an item can be selected or deselected by clicking mouse or pressing SPACEBAR; and (iii) fmMultiSelectExtended (value 2) which allows multiple selections, wherein by pressing SHIFT and simultaneously moving the up or down arrows (or pressing SHIFT and clicking mouse) continues selection from the previously selected item to the current selection (ie. a continuous selection); this option also allows to select or deselect an item by pressing CTRL and clicking mouse. MultiSelect property can be set in the Properties window and can also be used with a macro or vba code. Note: MultiSelect Property is valid for ListBox and not for ComboBox. When multiple selections are made (viz. fmMultiSelectMulti or fmMultiSelectExtended), the selected items can be determined only by using the Selected property (Selected property is available by using macro) of the ListBox. The Selected property will have values ranging from 0 to ListCount minus 1 and will be True if the item is selected and False if not selected. The Selected property determines the items you chose, and the List property returns the items.
Example 5: Determining selected item in a Single Selection ListBox, in VBA:
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
‘determine and display selected item in a ListBox which allows only a single selection (viz. MultiSelect Property is set to fmMultiSelectSingle)
‘you can also determine selected item in a ListBox which allows only a single selection, by using the Selected Property (as used in a Multiple Selection enabled ListBox)
‘alternatively: If ListBox1.ListIndex >= 0 Then
If ListBox1.Value <> «» Then
MsgBox ListBox1.Value
End If
End Sub
RemoveItem Method:
A specified row is removed from the list in a ComboBox or ListBox. Syntax: Control.RemoveItem(Row_Index). Row_Index is the row number which is specified to be removed, wherein the first row is numbered 0, and so on. RemoveItem method will not work if ComboBox or ListBox is bound to data, hence RowSource data should be cleared before use. RemoveItem method can only be used with a macro or vba code.
RowSource Property:
Specifies the source of a list (which could be a worksheet range in Excel), for a ComboBox or ListBox. RowSource property can be set in the Properties window and can also be used with a macro or vba code. To set RowSource property in Properties window, enter without inverted commas: «=Sheet2!A2:A6» which populates ComboBox or ListBox with values in cells A2:A6 in Sheet2. VBA code for this is: ListBox1.RowSource = «=Sheet2!A2:A6». It is not necessary to use the equal mark in «=Sheet2!A2:A6» while setting the property and ListBox1.RowSource = «Sheet2!A2:A6» will have the same effect.
Selected Property:
Specifies whether an item is selected in a ListBox control. Syntax: Control.Selected(Item_Index). Returns True/False if the item is Selected/NotSelected; Set to True/False to select the item or remove selection [viz. Control.Selected(ItemIndex) = True/False]. Item_Index is an integer value ranging from 0 to number of items in the list minus 1, indicating its relative position in the list, viz. ListBox.Selected(2) = True selects the third item in the list. Selected property is particularly useful when working with multiple selections. Selected Property can only be used with a macro or vba code and is not available at design time. Note1: In a Multiple Selection enabled ListBox, ListIndex returns the index of the row that has focus, irrespective of whether that row is selected or not. Hence the Selected property of the ListBox (and not the ListIndex property) shoud be used here to return and set a selection. In a Single Selection enabled ListBox (viz. MultiSelect property setting of fmMultiSelectSingle), ListIndex returns the index of the selected item and hence ListIndex property should be used here to return and set a selection. Note2: Selected Property is valid for ListBox and not for ComboBox.
Example 6: Determining selected items in a multiple-selection enabled ListBox using Selected & List properties:
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
‘display all selected items in a ListBox using the Selected property (valid for a ListBox with MultiSelect Property setting of either single-selection or multiple-selection)
‘check all items in a ListBox
For n = 0 To ListBox1.ListCount — 1
‘if a ListBox item is selected, it will display in MsgBox
If ListBox1.Selected(n) = True Then
‘display a selected item
MsgBox ListBox1.List(n)
End If
Next n
End Sub
Style Property:
Valid for ComboBox only, not for ListBox. This property determines choosing or setting the value of ComboBox. There are 2 settings: (i) fmStyleDropDownCombo (value 0). The user has both options of typing a custom value in the text area or select from the drop-down list. This is the default value.; (ii) fmStyleDropDownList (value 2). The user can only select from the drop-down list, like in ListBox. Style Property can be set in the Properties window and can also be used with a macro or vba code.
TextColumn Property:
Specifies the column of data in a ListBox that supplies data for its Text property — the TextColumn property determines the column whose value the Text property will return whereas the BoundColumn property determines the column whose value the Value property returns. The Text property returns the same as Value property if the TextColumn property is not set. First column has a TextColumn value of 1, second column has a value of 2, and so on. Setting the TextColumn value to -1 indicates that the first column with a ColumnWidths value greater than 0 will be displayed. TextColumn property enables display of one set of values to the user but store a different set of values (per column specified in the BoundColumn property) viz. use the Text property to return the value from the first column (specified in the TextColumn property) containing the names and the BoundColumn property can specify another column containing height wherein on selecting a particular person’s name in the ListBox, his name & height will be returned. The ColumnWidths property of any column can be set to zero to not display it in the ListBox. Setting the TextColumn value to 0 displays the ListIndex value (which is the number of the selected row) in TextColumn Property — this setting is useful if you want to determine the row of the selected item. TextColumn property can be set in the Properties window and can also be used with a macro or vba code. Note: In a ComboBox, when a user selects an item, the column specified in the TextColumn property will be displayed in the ComboBox’s text box portion.
Example 7: Display first column in the List and use the TextColumn & BoundColumn Properties to return values from first & third columns (in a Single Selection ListBox) — refer Image 10
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ListBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ListBox1
.ColumnHeads = True
.ColumnCount = 3
‘set the ColumnWidths property of second & third columns to zero to not display them in the ListBox
.ColumnWidths = «40;0:0»
.RowSource = «=Sheet2!A2:C6»
.MultiSelect = fmMultiSelectSingle
‘specifies the column of data in a ListBox that supplies data for its Text property
.TextColumn = 1
.BoundColumn = 3
End With
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
‘TextColumn value is set as 1 and BoundColumn value is set as 3.
‘works only if MultiSelect Property of ListBox is set to fmMultiSelectSingle which allows single selection.
If ListBox1.Value <> «» Then
‘use the ListBox Text property to return the value from the column specified in the TextColumn column, whereas the ListBox Value property returns the value from the column specified in the BoundColumn property
TextBox1.Value = ListBox1.Text & » — » & ListBox1.Value & » cms»
End If
End Sub
———————————————————————————————————————
Add Items/Data to (Populate) a ListBox or ComboBox
1. Setting the RowSource property of a ListBox or ComboBox in a UserForm
VBA code — if the list is static:
Me.ListBox1.RowSource = «Sheet1!A1:B6»
or
Me.ListBox1.RowSource = «=Sheet1!A1:B6»
VBA code — if the list is dynamic:
Me.ListBox1.RowSource = «Sheet1!A1:B» & Sheet1.Cells(Rows.Count, «B»).End(xlUp).Row
Note: You can set the RowSource property of a ListBox or ComboBox in the Properties Window (without using vba code), by entering -> Sheet1!A1:B6
Example 8: Populate ComboBox by setting the RowSource property to a named list — refer Image 11
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘populate ComboBox by setting the RowSource property to a named list
With ComboBox1
.ColumnCount = 2
.ColumnWidths = «50;50»
.ColumnHeads = True
‘For a named list (viz. “HeightList” in Range A2:B6), the RowSource property can be set to Sheet1!HeightList
.RowSource = «Sheet1!HeightList»
End With
End Sub
2. Populate a ComboBox or ListBox from an Array:
VBA code — populate single column in ListBox:
ListBox1.List = Array(«RowOne», «RowTwo», «RowThree», «RowFour»)
VBA code — populate single column in ComboBox:
ComboBox1.List = Array(«Apples», «Bananas», «Oranges», «Pears»)
VBA code — populate ListBox from array named myArray:
Dim myArray As Variant
myArray = Array(«Adidas», «Nike», «Reebok»)
Me.ListBox1.List = myArray
VBA code — Populate single column ComboBox:
Dim i As Integer
Dim myArray As Variant
myArray = Array(«Adidas», «Nike», «Reebok», «Puma», «Polo»)
For i = LBound(myArray) To UBound(myArray)
Me.ComboBox1.AddItem myArray(i)
Next
Example 9 — Populate a multi-column Listbox directly with Worksheet Range — multiple rows added at one time using the List property:
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ListBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ListBox1
.ColumnCount = 3
.ColumnWidths = «50;50;50»
.ColumnHeads = False
End With
‘Load Worksheet Range directly to a ListBox
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Sheet1.Range(«A1:C6»)
Me.ListBox1.List = rng.Cells.Value
End Sub
Example 10 — Populate a multi-column Listbox directly with Worksheet Range — multiple rows added at one time using the List property:
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ListBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ListBox1
.ColumnCount = 3
.ColumnWidths = «50;50;50»
.ColumnHeads = False
End With
‘Load Worksheet Range directly to a ListBox:
Dim var As Variant
var = Sheet1.Range(«A1:C6»)
Me.ListBox1.List = var
End Sub
Example 11: Load Worksheet Range to a multi-column ListBox, after placing Range data in a 2-dimensional Array — refer Image 12
Option Base 1
——————————————
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘Load Worksheet Range to a ListBox, after placing data in an Array
Dim rng As Range
Dim cell As Range
Dim totalRows As Integer, totalColumns As Integer
Dim iRow As Integer, iCol As Integer
Dim myArray() As Variant
Set rng = Sheet1.Range(«A1:C6»)
totalRows = Sheet1.Range(«A1:C6»).Rows.Count
totalColumns = Sheet1.Range(«A1:C6»).Columns.Count
‘if Option Base 1 was not set, this line of code should be: ReDim myArray(1 To totalRows, 1 To totalColumns)
ReDim myArray(totalRows, totalColumns)
‘place worksheet range data in an Array:
For Each cell In rng
For iRow = 1 To totalRows
For iCol = 1 To totalColumns
myArray(iRow, iCol) = rng.Cells(iRow, iCol)
Next iCol
Next iRow
Next
‘set ListBox properties and load Array to ListBox
With ListBox1
.ColumnCount = 3
.ColumnWidths = «50;50;50»
.ColumnHeads = False
.List = myArray
End With
End Sub
Example 12: Load a 2-dimensional array to ListBox using the List property (copies an array without transposing it) and Column property (which transposes the contents of the array) — refer Image 13
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ListBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ListBox1
.ColumnCount = 3
.ColumnWidths = «50;50;50»
.ColumnHeads = False
End With
With ListBox2
.ColumnCount = 3
.ColumnWidths = «50;50;50»
.ColumnHeads = False
End With
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
‘create a 2-dimensional array and load to ListBox using the List property (copies an array without transposing it) and Column property (which transposes the contents of the array)
‘Declaring the array and its dimensions. The array has been named myArray, of size 3 by 3 (three rows by three columns). Note: When you populate an array with data, the array will start at zero, and if you include Option Base 1 the array will start at 1.
Dim myArray(3, 3)
‘populate column 1 of myArray, with numbers
For n = 0 To 2
myArray(n, 0) = n + 1
Next n
‘populate column 2 of myArray
myArray(0, 1) = «R1C2»
myArray(1, 1) = «R2C2»
myArray(2, 1) = «R3C2»
‘populate column 3 of myArray
myArray(0, 2) = «R1C3»
myArray(1, 2) = «R2C3»
myArray(2, 2) = «R3C3»
‘copy data to ListBox1 (using List property) and ListBox2 (using Column property):
‘copies an array without transposing it
ListBox1.List() = myArray
‘transposes the contents of the array
ListBox2.Column() = myArray
End Sub
3. Populate a ComboBox or ListBox with AddItem method
Example 13: Populate a single-column ListBox from worksheet range
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ListBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ListBox1
.ColumnCount = 1
.ColumnWidths = «50»
.ColumnHeads = False
‘AddItem method will not work if ListBox is bound to data, hence RowSource is cleared if it had been set
.RowSource = «»
End With
‘populating a single-column ListBox with AddItem method
Dim cell As Range
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Sheet1.Range(«A1:A6»)
For Each cell In rng.Cells
Me.ListBox1.AddItem cell.Value
Next cell
End Sub
Example 14: Populate a single-column ListBox with values from 1 to 500
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ListBox properties on activation of UserForm
With ListBox1
.ColumnCount = 1
.ColumnWidths = «50»
‘AddItem method will not work if ListBox is bound to data, hence RowSource is cleared if it had been set
.RowSource = «»
End With
‘populate a single-column ListBox with values from 1 to 500, and «N/A»
With ListBox1
.AddItem «N/A»
For i = 1 To 500
.AddItem i
Next i
End With
End Sub
Example 15: Create a new row with AddItem and specify its row number — refer Image 14
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ListBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ListBox1
.ColumnCount = 1
.ColumnWidths = «50»
.ColumnHeads = False
‘AddItem method will not work if ListBox is bound to data, hence RowSource is cleared if it had been set
.RowSource = «»
End With
‘using AddItem method to populate single-column ListBox:
ListBox1.AddItem «banana»
ListBox1.AddItem «orange»
‘Create a new row with AddItem and position as row number 1 — this will push down the above two rows
ListBox1.AddItem «apple», 0
‘Create a new row with AddItem and position as row number 2 — this will push down the above two rows to no. 3 and 4
ListBox1.AddItem «pears», 1
End Sub
Example 16: Populate a ComboBox with the 12 months in a year — Refer Image 15
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ComboBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ComboBox1
.ColumnCount = 1
.ColumnWidths = «50»
.ColumnHeads = False
‘AddItem method will not work if ComboBox is bound to data, hence RowSource is cleared if it had been set
.RowSource = «»
End With
‘populates ComboBox with the 12 months in a year
For n = 1 To 12
ComboBox1.AddItem Format(DateSerial(2011, n, 1), «mmmm»)
Next n
End Sub
4. Populate a multi-column ComboBox or ListBox using AddItem method and List & Column properties
Example 17: refer Image 16
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ComboBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ComboBox1
.ColumnCount = 3
.ColumnWidths = «50;50;50»
.ColumnHeads = False
‘AddItem method will not work if ComboBox is bound to data, hence RowSource is cleared if it had been set
.RowSource = «»
End With
‘Populating a multi-column ListBox using AddItem method and List & Column properties:
‘Create a new row with Additem
ComboBox1.AddItem «banana»
‘add item in second column of this first row, using List property
ComboBox1.List(0, 1) = «tuesday»
‘adding items in the 3 columns of the first row — this will become the second row in the end
ComboBox1.List(0, 2) = «day 2»
ComboBox1.AddItem «orange»
‘add item in second column of this second row, using Column property
ComboBox1.Column(1, 1) = «wednesday»
‘adding items in the 3 columns of the second row — this will become the third row in the end
ComboBox1.Column(2, 1) = «day 3»
‘Create a new row with Additem and position as row number 1
ComboBox1.AddItem «apple», 0
ComboBox1.List(0, 1) = «monday»
‘adding items in the 3 columns and positioning this row as the first row — this will push down the above two rows
ComboBox1.List(0, 2) = «day 1»
End Sub
5. Populate a multi-column ListBox from a worskheet range, using AddItem method and List property
Example 18: refer Image 17
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ListBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ListBox1
.ColumnCount = 3
.ColumnWidths = «50;50;50»
‘AddItem method will not work if ListBox is bound to data, hence RowSource is cleared if it had been set
.RowSource = «»
End With
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
‘populate a multi-column ListBox from a worskheet range, using AddItem method and List property
Dim counter As Long
Dim totalRows As Long
‘determine total number of rows in column A
totalRows = Sheet4.Cells(Rows.Count, «A»).End(xlUp).Row
counter = 0
‘ListBox gets populated with all rows in column A:
Do
With Me.ListBox1
counter = counter + 1
‘create a new row with Additem
.AddItem Sheet4.Cells(counter, 1).Value
‘add item in second column of a row
.List(.ListCount — 1, 1) = Sheet4.Cells(counter, 1).Offset(0, 1).Value
‘add item in third column of a row
.List(.ListCount — 1, 2) = Sheet4.Cells(counter, 1).Offset(0, 2).Value
End With
Loop Until counter = totalRows
End Sub
6. Add a new item/row to the list if ComboBox is bound to data in a worksheet.
Example 19: refer Images 18a & 18b
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ComboBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ComboBox1
.ColumnCount = 3
.ColumnWidths = «50;50;50»
.ColumnHeads = True
.BoundColumn = 1
‘a named-range (name: «cbRange») has been created in Sheet3 of the workbook, using the Name Manager: «=Sheet3!$A$2:$C$6»
.RowSource = «cbRange»
End With
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
‘add a new item/row to the list if ComboBox is bound to data in a worksheet
Dim colNo As Long
‘determine first column of the named-range «cbRange»
colNo = Range(«cbRange»).Column
‘create a new single-column named-range (name: «cbRangeTemp»), populated with only the first column of the named-range «cbRange».
Range(«cbRange»).Resize(Range(«cbRange»).Rows.Count, 1).Name = «cbRangeTemp»
‘checks if ComboBox1.Value is already existing in column 1 of named-range «cbRange»
If Application.CountIf(Range(«cbRangeTemp»), ComboBox1.Value) = 0 Then
‘resizing the named-range «cbRange», to add another worksheet row at the end, wherein the ComboBox1.Value will get posted:
Range(«cbRange»).Resize(Range(«cbRange»).Rows.Count + 1).Name = «cbRange»
ComboBox1.RowSource = «cbRange»
‘posting columns of the new row with values from ComboBox1, TextBox1 & TextBox2:
Sheet3.Cells(Range(«cbRange»).Rows.Count + 1, colNo) = ComboBox1.Value
Sheet3.Cells(Range(«cbRange»).Rows.Count + 1, colNo).Offset(0, 1) = TextBox1.Text
Sheet3.Cells(Range(«cbRange»).Rows.Count + 1, colNo).Offset(0, 2) = TextBox2.Text
Else
MsgBox «Item already in List»
End If
ComboBox1.Value = «»
TextBox1.Text = «»
TextBox2.Text = «»
End Sub
——————————————————————————————————————————————-
Extract ListBox & ComboBox Items, with VBA
VBA code — Display selected ComboBox item in TextBox:
‘the text area of ComboBox shows the item entered by user of his own choice or that selected from list items, and this item gets displayed in TextBox
TextBox1.Value = ComboBox1.Value
Note: VBA code-> TextBox1.Value = ListBox1.Value, or TextBox1.Text = ListBox1.Value, will work only in case MultiSelect property of ListBox is set to fmMultiSelectSingle, ie. in case of a single-selection enabled ListBox. It will copy the selected item (value in BoundColumn) from the list.
VBA code — Copy selected ComboBox item to a worksheet range:
‘the text area of ComboBox shows the item entered by user of his own choice or that selected from list items, and this item is copied to the worksheet range
Sheet1.Range(«G4»).Value = ComboBox1.Value
Note: VBA code-> Sheet4.Range(«G4»).Value = ListBox1.Value, will work only in case MultiSelect property of ListBox is set to fmMultiSelectSingle, ie. in case of a single-selection enabled ListBox. It will copy the selected item (value in BoundColumn) from the list.
VBA code — Copy ComboBox item determined by its position, to a worksheet range:
‘an existing ComboBox item, determined by its position (row 4, column 1), posted to a worksheet cell
Sheet1.Range(«F2»).Value = ComboBox1.List(3, 0)
Note: VBA code for ListBox -> Sheet1.Range(«F2»).Value = ListBox1.List(3, 0)
Example 20: Extracting ListBox items (of multi-column ListBox) to a worksheet range — refer Image 19
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ListBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ListBox1
.ColumnCount = 3
.ColumnWidths = «50;50;50»
.ColumnHeads = True
.RowSource = «Sheet2!A2:C6»
.MultiSelect = fmMultiSelectMulti
End With
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
‘Use Selected & List properties to copy multiple-selected ListBox items (of multi-column ListBox) to a worksheet range
‘check all items/rows in a ListBox
For r = 0 To ListBox1.ListCount — 1
‘if a ListBox row is selected, it will get copied to the worksheet range
If ListBox1.Selected(r) = True Then
‘copying multi-column ListBox rows to corresponding/matching worksheet rows & columns:
For c = 1 To ListBox1.ColumnCount
Sheet1.Cells(r + 1, c).Value = ListBox1.List(r, c — 1)
Next c
End If
Next r
End Sub
Example 21: Extract multiple items in a row from a single-selection enabled & multi-column ListBox, and copy to worksheet range — refer Image 20
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ListBoxBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ListBox1
.ColumnCount = 3
.ColumnWidths = «50;50;50»
.ColumnHeads = True
.BoundColumn = 1
.MultiSelect = fmMultiSelectSingle
.RowSource = «Sheet3!A2:C6»
End With
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
‘extract multiple items in a row from a single-selection enabled & multi-column ListBox, and copy to worksheet range
‘ListIndex property is used to return and set a selection in a single-selection ListBox, but not in a multi-selection ListBox
‘ListBox1.Value will work only in case of a single-selection ListBox. It will copy the selected item (value in BoundColumn) from the list.
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Sheet3.Cells(9, 1)
If ListBox1.Value <> «» Then
rng.Value = ListBox1.Value
rng.Offset(0, 1).Value = ListBox1.List(ListBox1.ListIndex, 1)
rng.Offset(0, 2).Value = ListBox1.List(ListBox1.ListIndex, 2)
End If
End Sub
Example 22: Select or enter name in ComboBox, and lookup its corresponding Grade in a worksheet range — refer Image 21
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set comboBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ComboBox1
.ColumnCount = 1
.ColumnWidths = «50»
.ColumnHeads = True
.RowSource = «Sheet3!A2:B6»
End With
‘disallow manual entry in TextBox
With TextBox1
.Enabled = False
End With
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
‘select or enter name in ComboBox, and lookup its corresponding Grade in a worksheet range — use ComboBox, TextBox & CheckBox properties and worksheet functions Vlookup and Countif
Dim totalRows As Long
‘determine total number of rows in column B
totalRows = Sheet3.Cells(Rows.Count, «B»).End(xlUp).Row
Me.ComboBox1.ControlTipText = «Select Name»
Me.CommandButton1.ControlTipText = «Click to get Grade»
‘Name selected in ComboBox is posted to TextBox
TextBox1.Text = ComboBox1.Value
‘Grade will be searched only if a name is selected and the CheckBox is selected:
If CheckBox1 = True And TextBox1.Text <> «» Then
‘check if name selected or entered in ComboBox is present in the lookup range:
If Application.CountIf(Sheet3.Range(«A1:A» & totalRows), TextBox1.Text) > 0 Then
‘lookup Grade of selected Name, in the worksheet range
Sheet3.Cells(1, 4).Value = TextBox1.Text & «‘s grade is » & Application.VLookup(TextBox1.Text, Sheet3.Range(«A1:B» & totalRows), 2, False)
Else
MsgBox «Name not found!»
End If
End If
End Sub
——————————————————————————————————————————————-
Delete ListBox rows using the RemoveItem Method

Example 23: Use RemoveItem method to delete a ListBox row. The below code deletes the row from the ListBox and also deletes the row items (or rows) in the worksheet — refer Images 22a and 22b.
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ListBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ListBox1
.ColumnCount = 3
.ColumnWidths = «50;50;50»
.ColumnHeads = False
.MultiSelect = fmMultiSelectMulti
End With
Dim totalRows As Long
‘determine total number of rows in column A
totalRows = Sheet3.Cells(Rows.Count, «A»).End(xlUp).Row
‘load a dynamic worksheet range to a ListBox
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Sheet3.Range(«A2:C» & totalRows)
Me.ListBox1.List = rng.Cells.Value
‘removes all items in ListBox
‘ListBox1.Clear
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
‘use RemoveItem method to delete a ListBox row. The below code deletes the row from the ListBox and also deletes the row items (or rows) in the worksheet
Dim n As Long, i As Long
Dim var As Variant
‘deleting row from ListBox using RemoveItem method:
‘check all items in a ListBox; reverse order (Step -1) is used because rows are being deleted from ListBox.
For n = ListBox1.ListCount — 1 To 0 Step -1
If ListBox1.Selected(n) = True Then
‘item to be deleted is stored in the variable named var
var = ListBox1.List(n, 0)
ListBox1.RemoveItem (n)
‘determine row number in which items are to be deleted; Note: value of variable named var is derived from first column, hence Range(«A:A») is searched in the Match formula.
i = Application.Match(var, Sheet3.Range(«A:A»), 0)
‘delete all 3 columns of the determined row in the worksheet:
Sheet3.Cells(i, 1) = «»
Sheet3.Cells(i, 1).Offset(0, 1) = «»
Sheet3.Cells(i, 1).Offset(0, 2) = «»
‘use this code instead of the preceding 3-lines, to delete the determined row in the worksheet
‘Sheet3.Rows(i).Delete
End If
Next n
End Sub
Example 24: Delete all rows in ListBox, using RemoveItem method
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
‘set ListBoxBox properties on initialization of UserForm
With ListBox1
.ColumnCount = 3
.ColumnWidths = «50;50;50»
.BoundColumn = 1
.MultiSelect = fmMultiSelectMulti
‘RemoveItem method will not work if ListBox is bound to data, hence RowSource is cleared if it had been set
ListBox1.RowSource = «»
End With
For n = 2 To 6
With Me.ListBox1
‘create a new row with Additem
.AddItem Sheet3.Cells(n, 1).Value
‘add item in second column of a row
.List(.ListCount — 1, 1) = Sheet3.Cells(n, 1).Offset(0, 1).Value
‘add item in third column of a row
.List(.ListCount — 1, 2) = Sheet3.Cells(n, 1).Offset(0, 2).Value
End With
Next n
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
‘delete all rows in ListBox, using RemoveItem method
Dim n As Integer
For n = 1 To ListBox1.ListCount
‘Note: «ListBox1.RemoveItem 0» is the same as «ListBox1.RemoveItem (0)»
‘alternate code: ListBox1.RemoveItem 0
ListBox1.RemoveItem ListBox1.ListCount — 1
Next n
End Sub