Try it!
Use filters to temporarily hide some of the data in a table, so you can focus on the data you want to see.
Filter a range of data
-
Select any cell within the range.
-
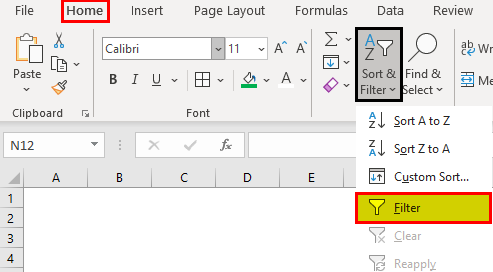
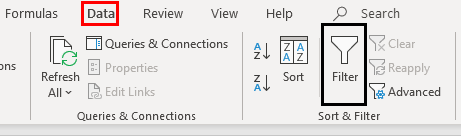
Select Data > Filter.
-
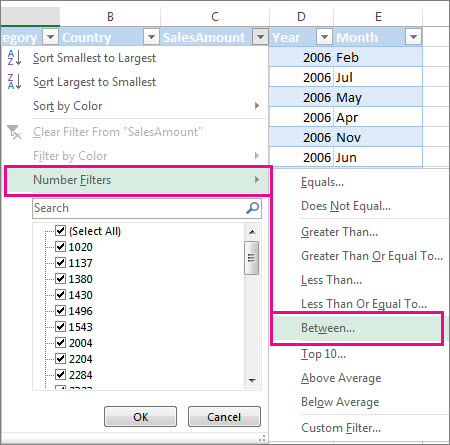
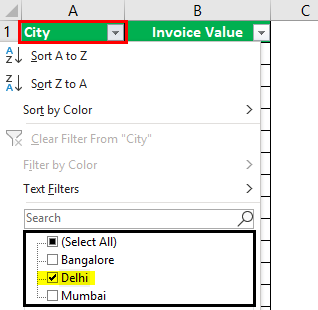
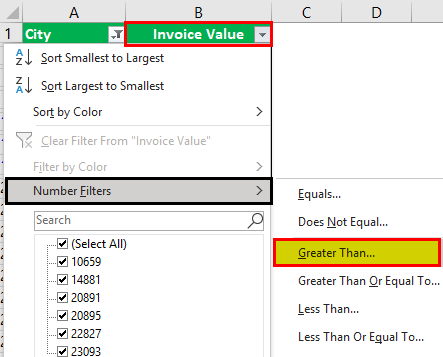
Select the column header arrow
.
-
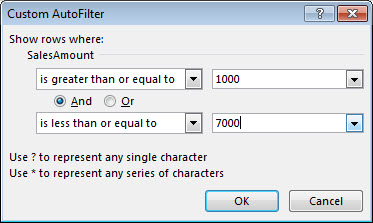
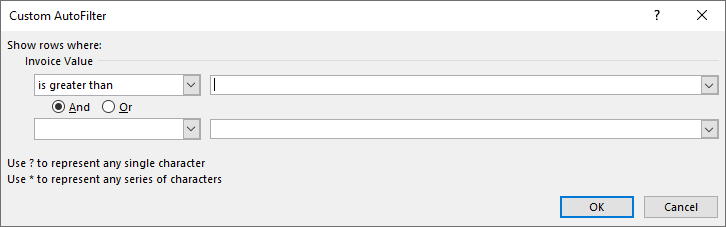
Select Text Filters or Number Filters, and then select a comparison, like Between.
-
Enter the filter criteria and select OK.
Filter data in a table
When you Create and format tables, filter controls are automatically added to the table headers.
-
Select the column header arrow
for the column you want to filter.
-
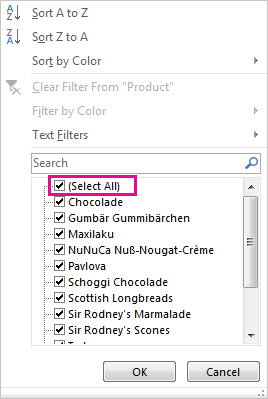
Uncheck (Select All) and select the boxes you want to show.
-
Click OK.
The column header arrow 

Want more?
Filter data in a range or table
Filter data in a PivotTable
Need more help?
This post will guide you how to extracts matched values using FILTER function in Microsoft Excel 365. And also will introduce that how to use FILTER function with same examples in Excel 365.
Table of Contents
- Excel Filter Function
- Entering FILTER Formula in Excel
- Excel filtering by a single criteria
- Example 1: How to use a number as a filter
- Example 2: How to filter in Excel by a cell value
- Example 3: Using Excel’s text filter
- Example 4: Using NOT EQUAL TO as a FILTER condition in Excel
- Example 5: How to use the date filter in Excel
- Example 6: Filtering by date in Excel
- Example 7: Filtering based on two Conditions
- Example 8: Filtering Based on Two Conditions using OR Logic
- Example 9: Filter Data in Excel from Another Sheet
- Example 10: Providing Maximum Number of Rows of Filtered Data
- Conclusion
- Related Functions
The FILTER function “filters” a set of data according to the conditions specified. The outcome is an array of values that match those in the original range. Simply said, the FILTER function extracts matched records from a collection of data using one or more logical checks. The include argument specifies logical tests, which might encompass a wide variety of formula conditions. For instance, FILTER may match data from a given year or month, data containing specific content, or numbers above a specified threshold.
=FILTER(array,include,[if empty])
Three parameters are required for the FILTER function: array, include, and if empty.
Where:
- Array – This is required argument. The range or array to filter is specified by array.
- Include – This is required argument. Include one or more logical tests in the include These tests should return TRUE or FALSE depending on the array values evaluated.
- If_empty – This is option argument. The last input, if empty, specifies the value to return if FILTER does not discover any matching values. Typically, this is a message along the lines of “No records found,” although other values may also be returned. To show nothing, provide an empty string (“”).
Entering FILTER Formula in Excel
FILTER provides dynamic results. When the values in the source data change or the size of the source data array changes, the FILTER results are updated automatically. The results of FILTER will “leak” into numerous cells on the worksheet.
To filter data in Excel using the FILTER function, follow these steps:
Step1: To begin your filter formula, enter =FILTER(.
Step2: Enter the address for the range of cells containing the data you want to filter, for example, A2:C10.
Step3: Type a comma, followed by the filter's condition, such as B2:B20>3 (To specify a condition, type the address of the “criteria column,” such as C1:C, followed by an operator symbol such as greater than (>), and finally the criterion, such as the number 3.
Step4: Complete the parenthesis with a closing parenthesis and then hit enter on the keyboard. Your full formula will appear as follows: =FILTER(A2:C10, B2:B20>3)
I’ll begin with the fundamentals of utilizing the FILTER function, and then demonstrate some more advanced uses of the FILTER function. This article discusses the FILTER function as a formula entered into spreadsheet cells, not the filter command accessible from the toolbar and pop-up menus.
While using the FILTER function in Excel is almost identical to using it in Google Sheets, there are some subtle variations.
Excel filtering by a single criteria
To begin, let’s review how to use Excel’s FILTER function in its simplest version, with a single condition/criteria.
I’ll demonstrate how to filter data using a number, a cell value, a text string, or a date… and I’ll also demonstrate how to utilize a variety of “operators” in the filter condition (Less than, Equal to, etc…).
Example 1: How to use a number as a filter
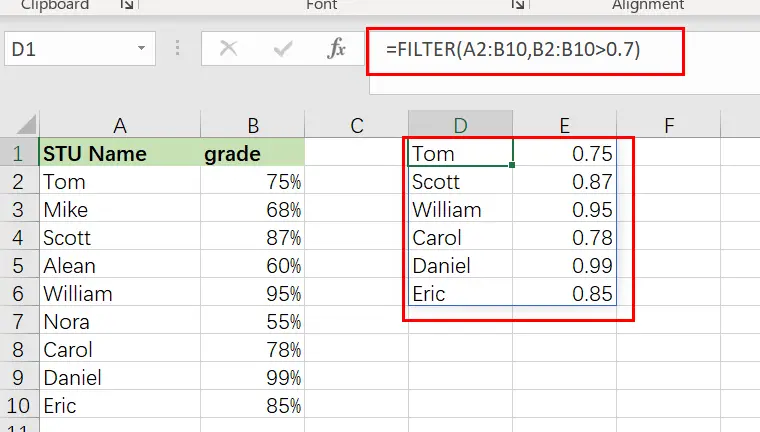
In this first demonstration of how to use the filter tool in Excel, we have a list of students and their grades and wish to create a filtered list of only students with flawless grades.
The assignment: Display a list of students and their grades, but only those who have earned an A.
The reasoning: Filter the range A2:B10 for values larger than 0.7 in the column B2:B10 (70 percent ). Then you can use the following FILTER formula,type:
=FILTER(A2:B10, B2:B10 >0.7)
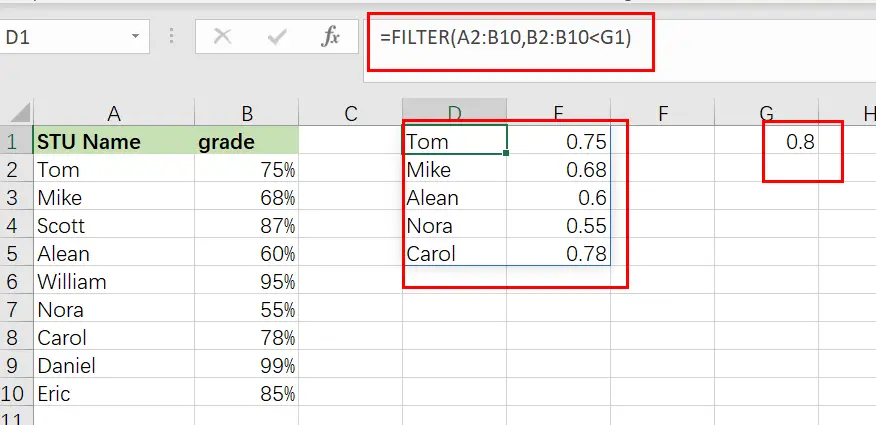
Example 2: How to filter in Excel by a cell value
In this excel filter function example, we want to do the same thing as stated before, but rather than inputting the condition straight into the formula, we’re going to use a cell reference.
When you filter in Excel by a cell value, your sheet is configured in such a way that you may alter the value in the cell at any moment, which updates the value to which the filter criterion is tied.
In this example, rather than explicitly entering the value “0.8” into the formula, the filter criterion is set to cell G1, which contains the “0.8” value.
The assignment: Display a list of students and their grades, but only those with a score of less than 80%.
The reasoning: Filter the range A2:B10 to the extent that B2:B10 is smaller than the value supplied in column G1 (0.8).
You can use the following FILTER formula, type:
=FILTER(A2:B10, B2:B10 <G1)
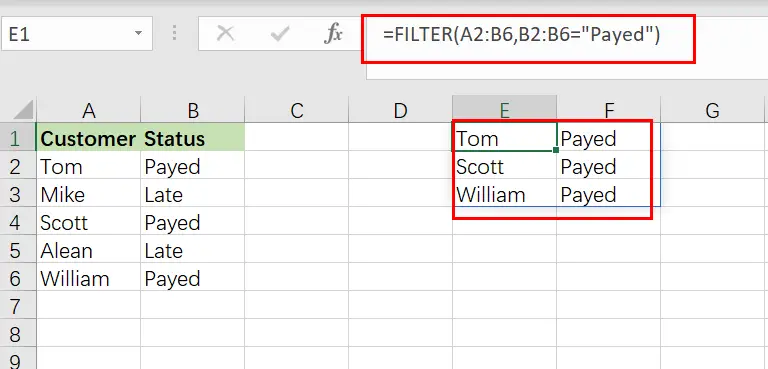
Example 3: Using Excel’s text filter
In this example, we’ll utilize a text string as the filter formula’s criterion. This is fairly similar to using a number, except that the text to filter must be enclosed in quote marks.
We are filtering a list of customers and their payment status in this instance, and we want to present just customers with a payment status of “Payed“.
The objective is to provide a list of clients that have paid on their payments.
The reasoning: Filter the range A2:B6 by substituting the string “ Payed ” for B2:B6.
The following formula: In this example, the formula below is typed in the cell (E1).
=FILTER(A3:B12, B2:B6=" Payed ")
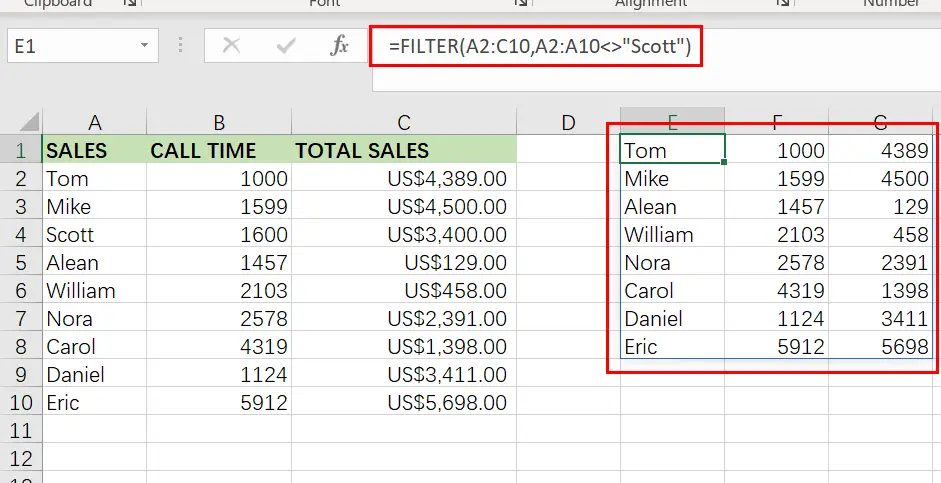
Example 4: Using NOT EQUAL TO as a FILTER condition in Excel
Now that you have a working knowledge of how to use the filter function in Excel, here is another example of filtering by a string of text, but this time we will use the “not equal” operator (<>) to demonstrate how to filter a range and return data that is NOT equal to the criteria you set.
Additionally, we will utilize a bigger data set in this example to show a more comprehensive usage of the FILTER function in the real world.
You may be surprised at how often a circumstance arises in which you need to filter data that is “not equal to” a certain number or piece of text.
In this example, we’ll use a report/spreadsheet to display data from sales calls that occur at your organization, and we’ll filter the data to exclude a certain sales person (Scott) from the result.
The assignment: Display sales call statistics for all sales representatives except ” Scott “.
The reasoning: Filter the range A2:C10 for values A2:A10 that DO NOT match the string “Scott “.
The following formula: In this example, the formula below is typed in the cell (E1).
=FILTER(A2:C10, A2:A10 <>"Scott")
Take note that the filtered data on the right side of the figure above does not include any of Scott ‘s rows/calls.
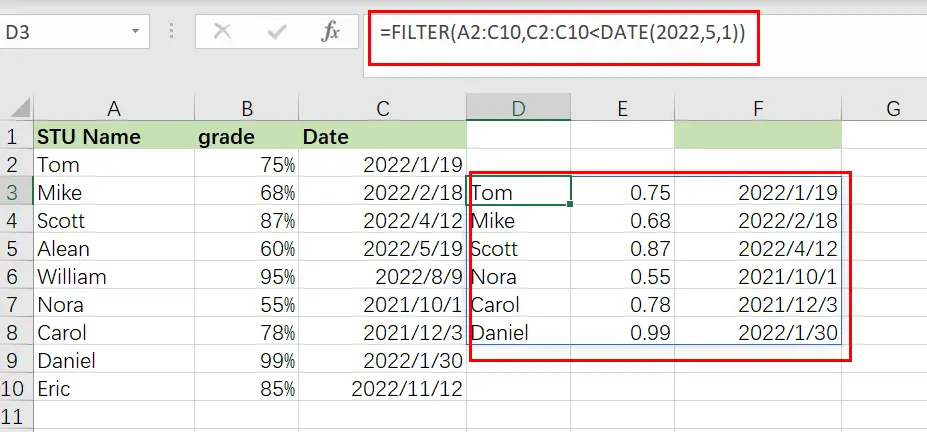
Example 5: How to use the date filter in Excel
Filtering in Excel by a date may be accomplished in a few different methods, which I will demonstrate below. If you attempt to put a date into the FILTER function in the same way that you would typically type into a cell, the formula will fail to operate properly.
Therefore, you may either enter the date you want to filter into a cell and then reference that cell in your formula… Alternatively, you may use the DATE function.
When filtering by date, the same operators (>, =, etc…) are available as they are in other FILTER function applications. Each individual day/date in Excel is merely a number that has been formatted differently. In Excel, for example, the date “01/30/2022” is just the serial number “44591” formatted as a date. Each time you add a day to the calendar, this number increases by one… For example, “44591” “44592” “44593”
Thus, if one date is farther in the future, it might be regarded “greater than” another. In contrast, if one date is farther in the past, it might be considered to be “less than” another.
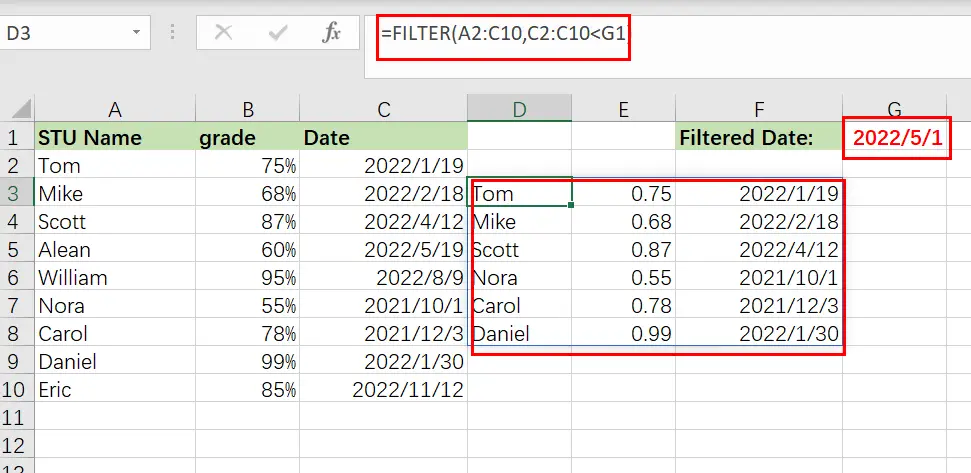
In this example, we’ll use a cell reference to filter on a date. This is identical to the example discussed in Example 2, except that we are dealing with dates instead of percentages.
Consider the following scenario: we want to filter a list of students, their exam results, and the dates on which the tests were administered… and we wish to display only tests conducted before to June (05/01/2022).
=FILTER(A2:C10, C2:C10 <G1)
Example 6: Filtering by date in Excel
In this example of date filtering in Excel, we’ll use the same data as in the previous one and attempt to obtain the same results… however, instead of referencing a cell, we’ll utilize the DATE function, which allows you to put the date straight into the FILTER function.
When using the DATE function to provide a date, you must first input the year, followed by the month and finally the day… each denoted with a comma (shown below).
The assignment: Display only exams given before to May
The reasoning: Filter the range A2:C10 so that C2:C10 is less than or equal to the date (05/01/2022).
The following formula: In this example, the formula below is typed in the cell (D3).
=FILTER(A2:C10,C2:C10<DATE(2022,5,1))
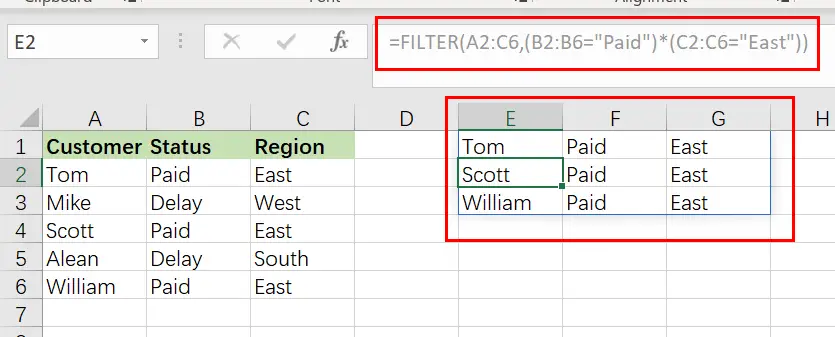
Example 7: Filtering based on two Conditions
When utilizing the Excel FILTER function, you may want to produce data that fits many criteria. I’ll demonstrate two methods for filtering by several criteria in Excel, depending on the scenario and the desired behavior of the calculation.
The conventional method of adding another condition to your filter function (as shown by the Excel formula syntax) allows you to provide a second condition, where both the first AND second conditions must be fulfilled in order for the filter output to be returned.
However, I will demonstrate how to make a little tweak to the function so that you may choose to return/display in the filter function’s output/destination a second condition where EITHER condition might be satisfied. (To utilize AND logic, separate the conditions with an asterisk, or use a plus symbol to separate the criteria.)
In this example, we’re going to filter a collection of data and show those rows that satisfy BOTH the first and second conditions.
To utilize a second condition in this manner (using AND logic), just insert it after the first condition in the formula, separated by an asterisk (*). Each condition must be included in a separate pair of parentheses.
When a filter formula is used with several conditions, the columns referenced in each condition must be distinct.
In this case, we’d want to filter a list of clients based on their payment status and region… and to display those customers who are both current members AND paid on their payment status.
The objective is to provide a list of customers who are paid on payments, but only those who are in East region.
The reasoning: Filter the range A2:C6 such that B2:B6 equals the text “Paid,” AND C2:C6 equals the text “East“.
The following formula: In this example, the formula below is typed in the blue cell (E1).
=FILTER(A2:C6,( B2:B6="Paid")*( C2:C6 ="East"))
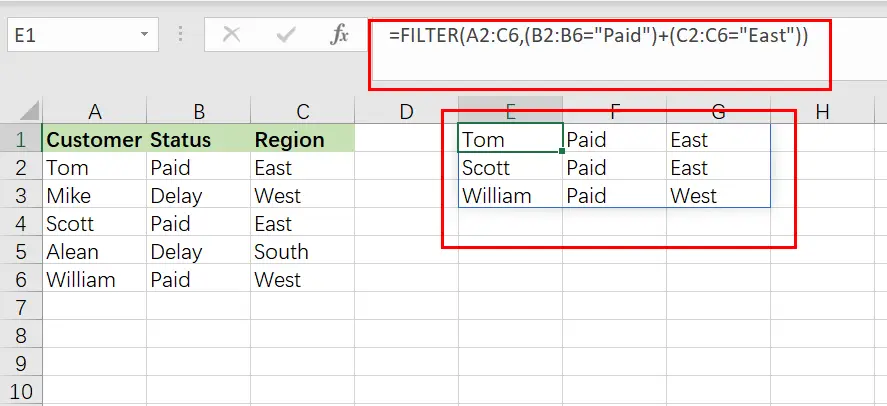
Example 8: Filtering Based on Two Conditions using OR Logic
In this example, we’re going to filter a collection of data and show those rows that satisfy either the first OR the second criterion.
To utilize a second condition in this manner (using OR logic), just insert it after the first condition in the formula, separated by a plus sign. Each condition must be included in a separate pair of parentheses (shown below).
When used in this manner, the FILTER formula allows you to choose criteria from the same or separate columns.
In this case, we’re filtering the same customer data as in the previous example, but this time we’re displaying a list of customers who either are in East region OR have paid on a payment. This will generate a list of clients to whom a payment notification have paid… whether they are current members or east region who have paid on their last payment.
The objective is to provide a list of customers who are in East region, as well as customers who have paid on payments regardless of whether they are in East region.
The following formula: In this example, the formula below is typed in the cell (E1).
=FILTER(A2:C6, (B2:B6="Paid ")+(C2:C6=" East ")
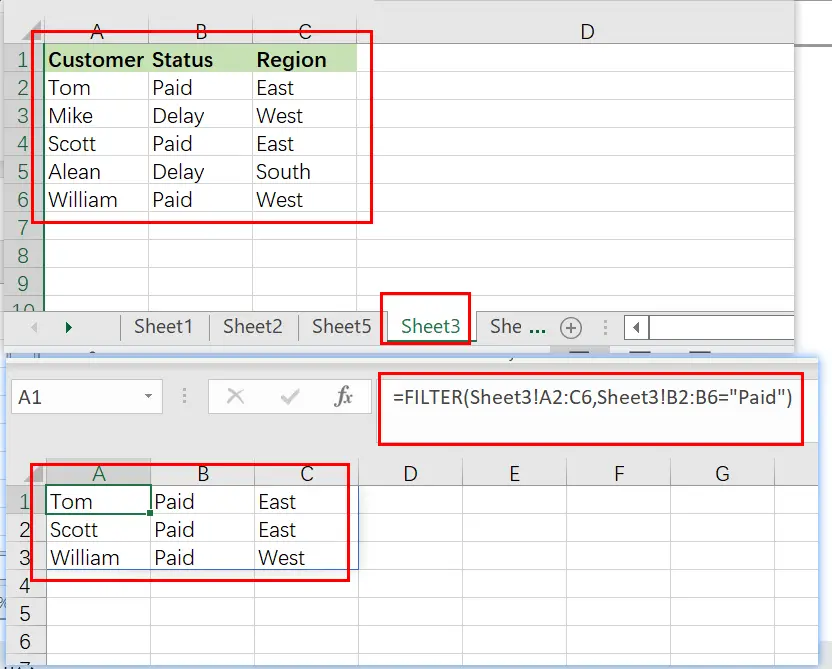
Example 9: Filter Data in Excel from Another Sheet
You may often encounter instances in Excel when you need to filter data from another sheet, where your raw unfiltered data is on one tab and your filter formula is on another sheet.
This may be accomplished by simply referring to a certain sheet’s name when providing the filter’s ranges. Thus, while you would typically give a range such as “A1:B4,” when referring another sheet when filtering, you indicate the sheet name by preceding the range with the sheet name and an exclamation mark, as in “SheetName!A1:B4“.
However, if the sheet name contains a space, an apostrophe must be used before and after the sheet name, as in "Sheet Name!" A1:B4.
The following is an example of how to filter data in Excel from a separate sheet, where the filter formula is located on a different sheet than the source range.
Consider the following scenario: On one sheet, you have a list of customers and their payment status, and you wish to present a filtered list of paid customer on another sheet.
The job is to filter the list of customers on the Sheet3 and to display a separate list of customer names with a pay status on another worksheet.
The reasoning: Filter the range using the Sheet3‘ command! A2:C6, where ‘ Sheet3′ is the range! B2:B6 corresponds to the phrase “Paid“.
The following formula: In this example, the formula below is typed in the cell (A3).
=FILTER(Sheet3! A2:C6, Sheet3!B2:B6="Paid")
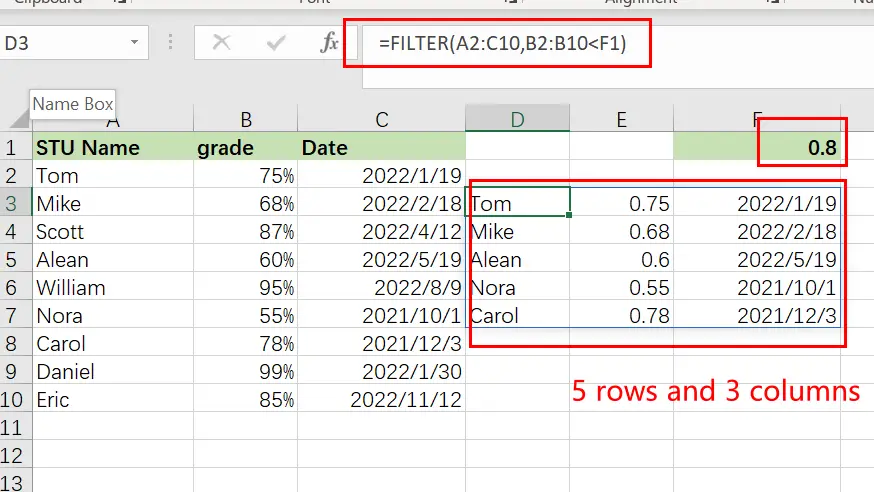
Example 10: Providing Maximum Number of Rows of Filtered Data
If your FILTER formula provides a large number of rows but your worksheet is restricted in space and you are unable to erase the data below, you may limit the amount of rows returned by the FILTER function.
Let us demonstrate how it works using a simple formula that filter data that grade is less than 0.7 from filter value in Cell F1:
=FILTER(A2:C10, B2:B10<F1)
The preceding formula produces all records that it discovers, in this instance five rows. However, imagine you only have room for two. To output just the first two rows discovered, follow these steps:
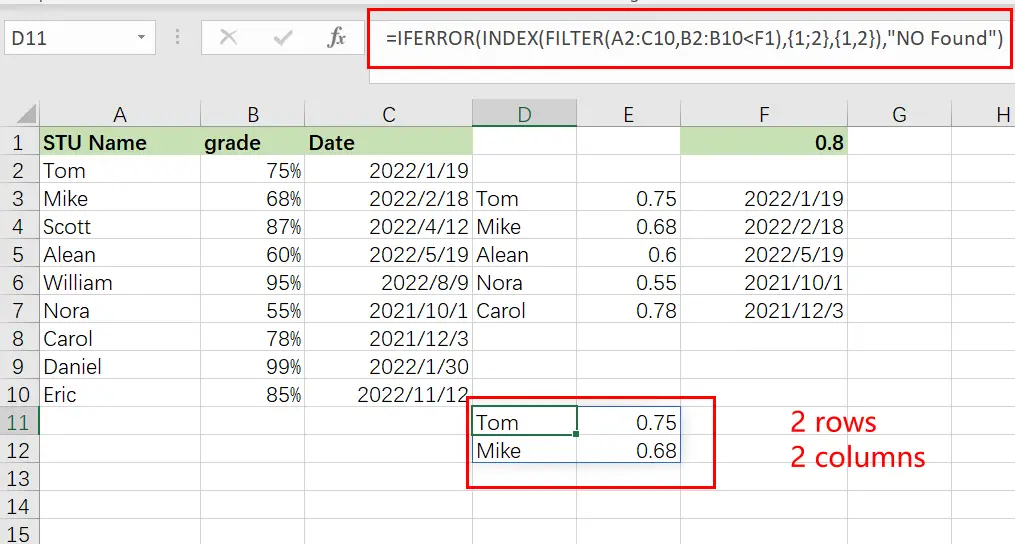
Step1: Incorporate the FILTER formula into the INDEX function’s array parameter
Step2: Use a vertical array constant such as 1;2 as the row num input to INDEX. It specifies the number of rows to return (2 in our case).
Step3: Use a horizontal array constant such as 1,2 for the column num parameter. It defines the columns that should be returned (the first 2 columns in this example).
Step4: To account for any mistakes caused by the absence of data meeting your criteria, you may wrap your calculation in the IFERROR function.
The entire excel filter formula is as follows:
=IFERROR(INDEX(FILTER(A2:C10, B2:B10<F1), {1;2},{1,2}), "No Found")
Conclusion
This section discusses the FILTER function and its many uses. In general, when it comes to time management, we need this feature for a variety of reasons. I demonstrated various techniques with accompanying examples, however there might be countless further iterations based on a variety of circumstances. If you know of another way to use this function, please share it with us.
- Excel IFERROR function
The Excel IFERROR function returns an alternate value you specify if a formula results in an error, or returns the result of the formula.The syntax of the IFERROR function is as below:= IFERROR (value, value_if_error)…. - Excel INDEX function
The Excel INDEX function returns a value from a table based on the index (row number and column number)The INDEX function is a build-in function in Microsoft Excel and it is categorized as a Lookup and Reference Function.The syntax of the INDEX function is as below:= INDEX (array, row_num,[column_num])…
What is Filter in Excel?
The filter in excel helps display relevant data by eliminating the irrelevant entries temporarily from the view. The data is filtered as per the given criteria. The purpose of filtering is to focus on the crucial areas of a dataset. For example, the city-wise sales data of an organization can be filtered by the location. Hence, the user can view the sales of selected cities at a given time.
A filter is necessarily required when working with a huge database. Being a widely used tool, the filter converts a comprehensive view into an easy-to-understand one. To apply filters, the dataset must contain a header row which specifies the name of every column.
Table of contents
- What is Filter in Excel?
- How to Filter in Excel?
- Method 1: With Filter Option Under the Home tab
- Method 2: With Filter Option Under the Data tab
- Method 3: With the Shortcut key
- How to Add Filters in Excel?
- Example #1–“Number Filters” Option
- Example #2–“Search Box” Option
- Option while you Drop Down the Filter Function
- The Techniques of Filtering in Excel
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Recommended Articles
- How to Filter in Excel?
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Filter in Excel (wallstreetmojo.com)
How to Filter in Excel?
You can download this Filter Column Excel Template here – Filter Column Excel Template
It is good to work with filters because they fit our needs the way we want to. In order to filter data, select the entries to be visible and deselect the rest of the items.
The three methods to add filters in excel are listed as follows:
- With filter option under the Home tab
- With filter option under the Data tab
- With the shortcut key
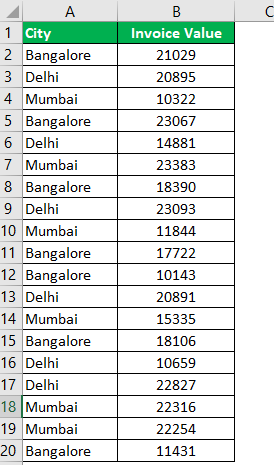
Let us consider a dataset to go through the three methods of adding filters.
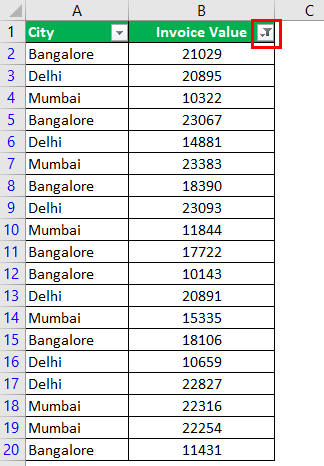
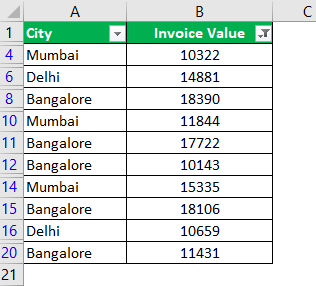
The following table shows the invoices issued to the buyers of different cities. We want to filter the data using different methods.
Method 1: With Filter Option Under the Home tab
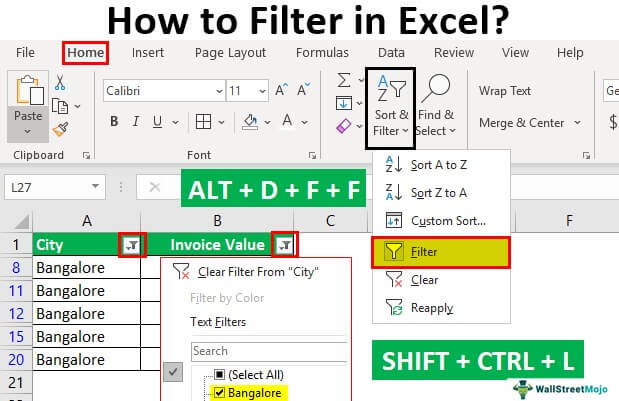
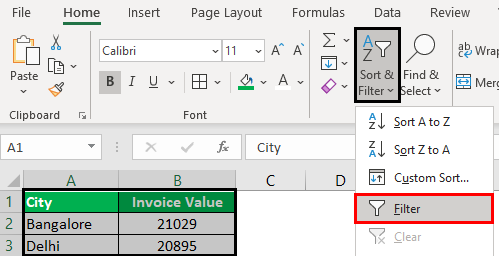
In the Home tab, there is a “filter” option under the “sort and filter” drop-down of the “editing” section, as shown in the following image.
Step 1: Select the data and click “filter” under the “sort and filter” drop-down.
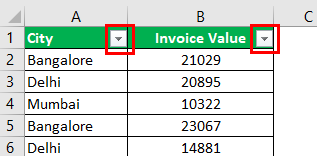
Step 2: The filters are added to the selected data range. The drop-down arrows, shown within the red boxes in the following image, are filters.
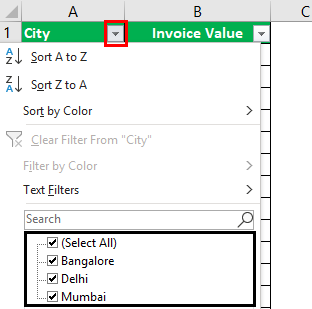
Step 3: Click the drop-down arrow of the column “city” to view the different names of the cities.
Step 4: To see the invoice values of “Delhi” only, select “Delhi” and uncheck all the remaining boxes.
Step 5: The data for the city “Delhi” is filtered and displayed in the following image.
Method 2: With Filter Option Under the Data tab
In the Data tab, there is a “filter” option under the “sort and filter” section, as shown in the following image.
Method 3: With the Shortcut key
The keyboard shortcutsAn Excel shortcut is a technique of performing a manual task in a quicker way.read more are a good way to speed up the daily tasks. Select the data and add the filter using either of the following shortcuts:
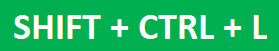
- Press the keys “Shift+Ctrl+L” together.
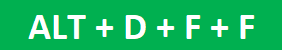
- Press the keys “Alt+D+F+F” together.
Note: The preceding shortcuts for adding filtersUsing sorting and filtering, we can see the data category wise. With filtering data quickly you can easily navigate through menus or clicking through a mouse in less time.read more are toggle keys. Repetitive pressing helps to turn on and turn off the filters.
How to Add Filters in Excel?
We can filter numbers using advanced techniques. Let us consider some examples to understand the working of filters in Excel.
Example #1–“Number Filters” Option
Working on the data under the preceding heading (methods of filtering in Excel), we want to apply the following filters:
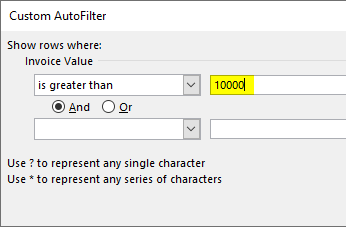
a. To filter column B (invoice value) for numbers greater than 10000
b. To filter column B for numbers greater than 10000 but less than 20000
Let us go through the two cases one by one.
a. Filter numbers greater than 10000
Step 1: Open the filter in column B (invoice value) by clicking on the filter symbol.
Step 2: In “number filters,” choose the “greater than” option, as shown in the following image.
Step 3: The “custom autofilter” box appears.
Step 4: Enter the number 10000 in the box to the right of “is greater than.”
Step 5: The output displays the invoice values greater than 10000. The symbol within the red box is the filter icon. It indicates that the filter has been applied to column B.
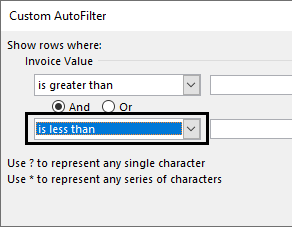
b. Filter numbers greater than 10000 but less than 20000
Step 1: In “number filters,” choose the “greater than” option.
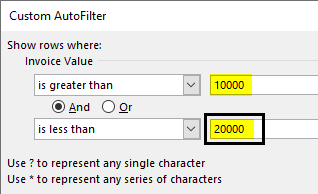
Step 2: In the “custom autofilter” box, select “is less than” in the second box to the left-hand side. This is shown in the following image.
Step 3: Enter the number 10000 in the box to the right of “is greater than.” Enter the number 20000 in the box to the right of “is less than.”
Step 4: The output displays the invoice values greater than 10000 but less than 20000.
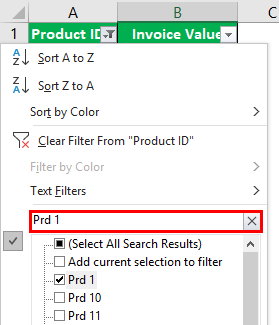
Example #2–“Search Box” Option
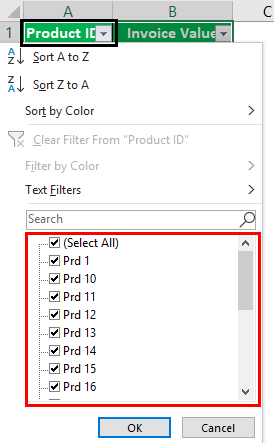
Working on the data under the preceding heading (methods of filtering in Excel), we have replaced the first column (city) with product IDs.
We want to filter the details of product ID “prd 1.”
The steps are listed as follows:
Step 1: Add filters to the columns “product ID” and “invoice value.”
Step 2: In the search boxA search box in Excel finds the needed data by typing into it, then filters the data and displays only that much info. When working with large datasheets, this simple tool may save a lot of time.read more, enter the value that is to be filtered. So, enter “prd 1.”
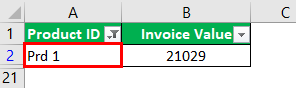
Step 3: The output displays only the filtered value from the list, as shown in the following image. Hence, we can see the invoice value of the product ID “prd 1.”
Option while you Drop Down the Filter Function
- Sort A to Z and Sort Z to A: If you wish to arrange your data ascending or descending order.
- Sort by Color: If you want to filter the data by color if a cell is filled by color.
- Text filter: When you want to filter a column with some exact text or number.
- Filter cells that begin with or end with an exact character or the text
- Filter cells that contain or do not contain a given character or word anywhere in the text.
- Filter cells that are exactly equal or not equal to a detailed character.
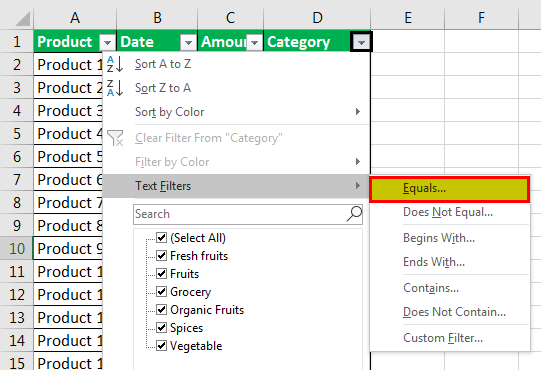
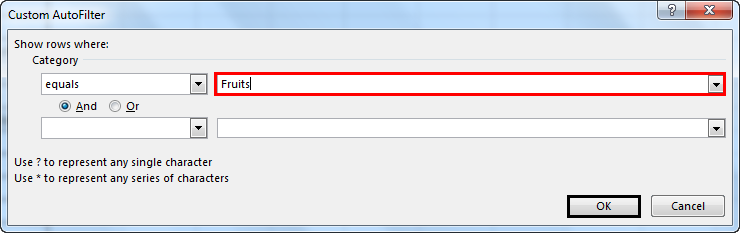
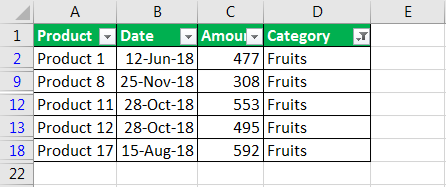
For example:
- Suppose you want to use the filter for a specific item. Click on to text filter and choose equals.
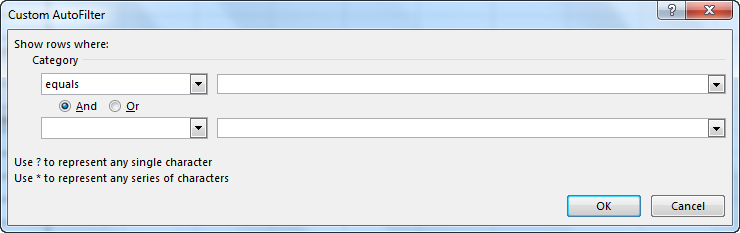
- It enables you the one dialogue, which includes a Custom Auto-Filter dialogue box.
- Enter fruits under category and click Ok.
- Now you will get the data of fruits category only as shown below.
The Techniques of Filtering in Excel
The following techniques must be followed while filtering data:
- If the dataset is large, type the value to be filtered. This filters all the possible matches.
- If numerical data has to be filtered by specifying the greater than or the less than number, use the “number filters” option.
- If data has to be filtered by the color of specific rows, use the “filter by color” option.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are filters and how to add them in Excel?
Filtering is a technique which displays the required information and removes the unwanted data from the view. It helps the user focus on the relevant data at a given time.
The steps to add filters in Excel are listed as follows:
• Ensure that a header row appears on top of the data, specifying the column labels.
• Select the data on which filters are to be added.
• Add filters by any of the three given methods.
o Click the “filter” option under the “sort and filter” (editing section) drop-down of the Home tab.
o Click the “filter” option under the “sort and filter” section of the Data tab.
o Press the keys “Shift+Ctrl+L” or “Alt+D+F+F.”
Note: As soon as the filters are added, a drop-down arrow appears on the particular column header.
2. How to apply filters to one or more columns?
The steps to apply filters to one or more columns are listed as follows:
• Click the drop-down arrow of the column to be filtered.
• Uncheck the “select all” option which helps deselect all data.
• Select the boxes to be displayed.
• Click “Ok.”
The drop-down arrow changes to the filter icon as soon as a filter is applied. When filters are applied to multiple columns, the filter icon appears on each one of them. Hovering over the filter icon shows the filters that have been applied.
Note: The drop-down arrow on a column header indicates a filter is added. The filter icon indicates a filter has been applied.
3. How to use filters in Excel?
The filters can be applied to numbers, text values, and dates. These cases are discussed as follows:
Filter numbers
• Click on the “number filters.”
• Select any of the options like “equals,” “does not equals,” “greater than,” “less than,” “between,” “above average,” and so on.
• Specify the required fields in the dialog box that appears. This box may or may not be displayed.
For instance, in “equals,” enter the number against which the values should be compared. The filtered results show the matching numerical values.
Filter text and date values
• To filter text and date values, select “text filters” and “date filters” from the respective drop-down arrows.
• The “text filters” allow filtering text strings which contain specific characters or words. The “date filters” allow filtering dates for a particular year, month, week, and so on.
Note: The “plus” and the “minus” sign of the date filters are used for expanding and collapsing the various levels respectively.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Filter in Excel. Here we discuss how to use/add filters in excel along with step by step examples and a downloadable template. You may learn more about Excel from the following articles –
- VBA FilterThe VBA Filter tool is used to sort out or fetch the desired data. However, this function accepts optional arguments, and the only required argument is an expression that covers the range, such as worksheets(«Sheet1»). Range(“A1”).read more
- How to Filter Pivot Table?By right-clicking on the pivot table, we can access the pivot table filter option. Another approach is to use the filter options available in the pivot table fields.read more
- Advanced Filter in ExcelThe advanced filter is different from the auto filter in Excel. This feature is not like a button that one can use with a single click of the mouse. To use an advanced filter, we have to define criteria for the auto filter and then click on the “Data” tab. Then, in the advanced section for the advanced filter, we will fill our criteria for the data.read more
- Types of Filters in Power BIThe filter function in Power BI is more commonly used to read data or reports based on multiple criteria. Visual level filters, page-level filters, report-level filters, drill-through filters, and so on are all available filters in Power Bi.read more
Watch Video – Excel Advanced Filter
Excel Advanced Filter is one of the most underrated and under-utilized features that I have come across.
If you work with Excel, I am sure you have used (or at least heard about the regular excel filter). It quickly filters a data set based on selection, specified text, number or other such criteria.
In this guide, I will show you some cool stuff you can do using the Excel advanced filter.
But First… What is Excel Advanced Filter?
Excel Advanced Filter – as the name suggests – is the advanced version of the regular filter. You can use this when you need to use more complex criteria to filter your data set.
Here are some differences between the regular filter and Advanced filter:
- While the regular data filter will filter the existing dataset, you can use Excel advanced filter to extract the data set to some other location as well.
- Excel Advanced Filter allows you to use complex criteria. For example, if you have sales data, you can filter data on a criterion where the sales rep is Bob and the region is either North or South (we will see how to do this in examples). Office support has some good explanation on this.
- You can use the Excel Advanced Filter to extract unique records from your data (more on this in a second).
EXCEL ADVANCED FILTER (Examples)
Now let’s have a look at some example on using the Advanced Filter in Excel.
Example 1 – Extracting a Unique list
You can use Excel Advanced Filter to quickly extract unique records from a data set (or in other words remove duplicates).
In Excel 2007 and later versions, there is an option to remove duplicates from a dataset. But that alters your existing data set. To keep the original data intact, you need to create a copy of the data and then use the Remove Duplicates option. Excel Advanced filter would allow you to select a location to get a unique list.
Let’s see how to use an advanced filters to get a unique list.
Suppose you have a dataset as shown below:
As you can see, there are duplicate records in this data set (highlighted in orange). These could be due to an error in data entry or result of data compilation.
In such a case, you can use Excel Advanced Filter tool to quickly get a list of all the unique records in a different location (so that your original data remains intact).
Here are the steps to get all the unique records:
This will instantly give you a list of all the unique records.
Caution: When you are using Advanced Filter to get the unique list, make sure you have also selected the header. If you don’t, it would consider the first cell as the header.
Example 2 – Using Criteria in Excel Advanced Filter
Getting unique records is one of the many things you can do with Excel advanced filter.
Its primary utility lies in its ability to allow using complex criteria for filtering data.
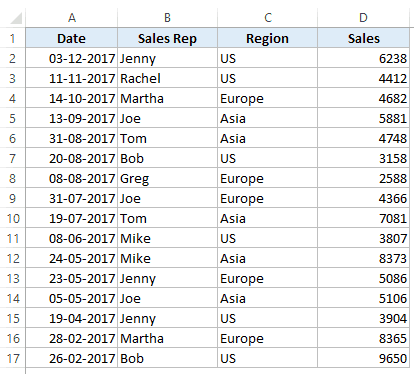
Here is what I mean by complex criteria. Suppose you have a dataset as shown below and you want to quickly get all the records where the sales are greater than 5000 and the region is the US.
Here is how you can use Excel Advanced Filter to filter the records based on the specified criteria:
This would instantly give you all the records where the region is the US and the sales are more than 5000.
The above example is a case where the filtering is done based on two criteria (US and sales greater than 5000).
Excel Advanced filter allows you to create many different combinations of criteria.
Here are some examples of how you can construct these filters.
Using the AND Criteria
When you want to use AND criteria, you need to specify it below the header.
For example:
Using the OR Criteria
When you want to use OR criteria, you need to specify the criteria in the same column.
For example:
By now, you must have realized that when we have the criteria in the same row, it is an AND criteria, and when we have it in different rows, it is an OR criteria.
Example 3 – Using WILDCARD Characters in Advanced Filter in Excel
Excel Advanced Filter also allows the usage of wildcard characters while constructing the criteria.
There are three wildcard characters in Excel:
- * (asterisk) – It represents any number of characters. For example, ex* could mean excel, excels, example, expert, etc.
- ? (question mark) – It represents one single character. For example, Tr?mp could mean Trump or Tramp.
- ~ (tilde) – It is used to identify a wildcard character (~, *, ?) in the text.
Now let’s see how we can use these wildcard characters to do some advanced filtering in Excel.
- To filter records where the sales rep name starts from J.
Note that * represent any number of characters. So any rep with the name starting with J would be filtered with these criteria.
Similarly, you can use the other two wildcard characters as well.
Note: In case you’re using Office 365, you should check out the FILTER function. It can do a lot of things that advanced filter can do with a simple formula.
NOTE:
- Remember, the headers in the criteria should be exactly the same as that in the data set.
- Advanced filtering cannot be undone when copied to other locations.
You May Also Like the Following Excel Tutorials:
- Dynamic Excel Filter – Extract Data as you Type.
- Filtering Cells with Bold Font Formatting.
- How to Filter Cells that have Duplicate Text Strings (Words) in it.
- How to Filter Data in a Pivot Table in Excel
- MS Guide for Advanced Filter in Excel.
- How to Compare Two Columns in Excel.
- Excel VBA Autofilter
- 20 Advanced Excel Functions and Formulas (for Excel Pros)
The FILTER function «filters» a range of data based on supplied criteria. The result is an array of matching values from the original range. In plain language, the FILTER function will extract matching records from a set of data by applying one or more logical tests. Logical tests are supplied as the include argument and can include many kinds of formula criteria. For example, FILTER can match data in a certain year or month, data that contains specific text, or values greater than a certain threshold.
The FILTER function takes three arguments: array, include, and if_empty. Array is the range or array to filter. The include argument should consist of one or more logical tests. These tests should return TRUE or FALSE based on the evaluation of values from array. The last argument, if_empty, is the result to return when FILTER finds no matching values. Typically this is a message like «No records found», but other values can be returned as well. Supply an empty string («») to display nothing.
The results from FILTER are dynamic. When values in the source data change, or the source data array is resized, the results from FILTER will update automatically. Results from FILTER will «spill» onto the worksheet into multiple cells.
Basic example
To extract values in A1:A10 that are greater than 100:
=FILTER(A1:A10,A1:A10>100)
To extract rows in A1:C5 where the value in A1:A5 is greater than 100:
=FILTER(A1:C5,A1:A5>100)
Notice the only difference in the above formulas is that the second formula provides a multi-column range for array. The logical test used for the include argument is the same.
Note: FILTER will return a #CALC! error if no matching data is found
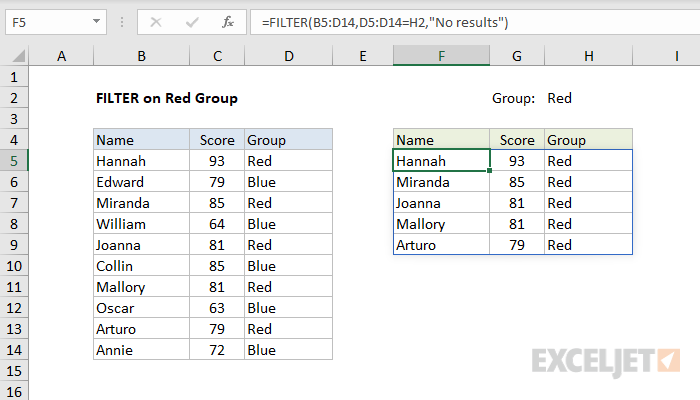
Filter for Red group
In the example shown above, the formula in F5 is:
=FILTER(B5:D14,D5:D14=H2,"No results")
Since the value in H2 is «red», the FILTER function extracts data from array where the Group column contains «red». All matching records are returned to the worksheet starting from cell F5, where the formula exists.
Values can be hardcoded as well. The formula below has the same result as above with «red» hardcoded into the criteria:
=FILTER(B5:D14,D5:D14="red","No results")
No matching data
The value for is_empty is returned when FILTER does not find matching results. If a value for if_empty is not provided, FILTER will return a #CALC! error if no matching data is found:
=FILTER(range,logic) // #CALC! error
Often, is_empty is configured to provide a text message to the user:
=FILTER(range,logic,"No results") // display message
To display nothing when no matching data is found, supply an empty string («») for if_empty:
=FILTER(range,logic,"") // display nothing
Values that contain text
To extract data based on a logical test for values that contain specific text, you can use a formula like this:
=FILTER(rng1,ISNUMBER(SEARCH("txt",rng2)))
In this formula, the SEARCH function is used to look for «txt» in rng2, which would typically be a column in rng1. The ISNUMBER function is used to convert the result from SEARCH into TRUE or FALSE. Read a full explanation here.
Filter by date
FILTER can be used with dates by constructing logical tests appropriate for Excel dates. For example, to extract records from rng1 where the date in rng2 is in July you can use a generic formula like this:
=FILTER(rng1,MONTH(rng2)=7,"No data")
This formula relies on the MONTH function to compare the month of dates in rng2 to 7. See full explanation here.
Multiple criteria
At first glance, it’s not obvious how to apply multiple criteria with the FILTER function. Unlike older functions like COUNTIFS and SUMIFS, which provide multiple arguments for entering multiple conditions, the FILTER function only provides a single argument, include, to target data. The trick is to create logical expressions that use Boolean algebra to target the data of interest and supply these expressions as the include argument. For example, to extract only data where one value is «A» and another is greater than 80, you can use a formula like this:
=FILTER(range,(range="A")*(range>80),"No data")
The math operation of addition (*) joins the two conditions with AND logic: both conditions must be TRUE in order for FILTER to retrieve the data. See a detailed explanation here.
Complex criteria
To filter and extract data based on multiple complex criteria, you can use the FILTER function with a chain of expressions that use boolean logic. For example, the generic formula below filters based on three separate conditions: account begins with «x» AND region is «east», and month is NOT April.
=FILTER(data,(LEFT(account)="x")*(region="east")*NOT(MONTH(date)=4))
See this page for a full explanation. Building criteria with logical expressions is an elegant and flexible approach that can be extended to handle many complex scenarios. See below for more examples.
Notes
- FILTER can work with both vertical and horizontal arrays.
- The include argument must have dimensions compatible with the array argument, otherwise FILTER will return #VALUE!
- If the include array includes any errors, FILTER will return an error.
#Руководства
- 5 авг 2022
-
0
Как из сотен строк отобразить только необходимые? Как отфильтровать таблицу сразу по нескольким условиям и столбцам? Разбираемся на примерах.
Иллюстрация: Meery Mary для Skillbox Media
Рассказывает просто о сложных вещах из мира бизнеса и управления. До редактуры — пять лет в банке и три — в оценке имущества. Разбирается в Excel, финансах и корпоративной жизни.
Фильтры в Excel — инструмент, с помощью которого из большого объёма информации выбирают и показывают только нужную в данный момент. После фильтрации в таблице отображаются данные, которые соответствуют условиям пользователя. Данные, которые им не соответствуют, скрыты.
В статье разберёмся:
- как установить фильтр по одному критерию;
- как установить несколько фильтров одновременно и отфильтровать таблицу по заданному условию;
- для чего нужен расширенный фильтр и как им пользоваться;
- как очистить фильтры.
Фильтрация данных хорошо знакома пользователям интернет-магазинов. В них не обязательно листать весь ассортимент, чтобы найти нужный товар. Можно заполнить критерии фильтра, и платформа скроет неподходящие позиции.
Фильтры в Excel работают по тому же принципу. Пользователь выбирает параметры данных, которые ему нужно отобразить, — и Excel убирает из таблицы всё лишнее.
Разберёмся, как это сделать.
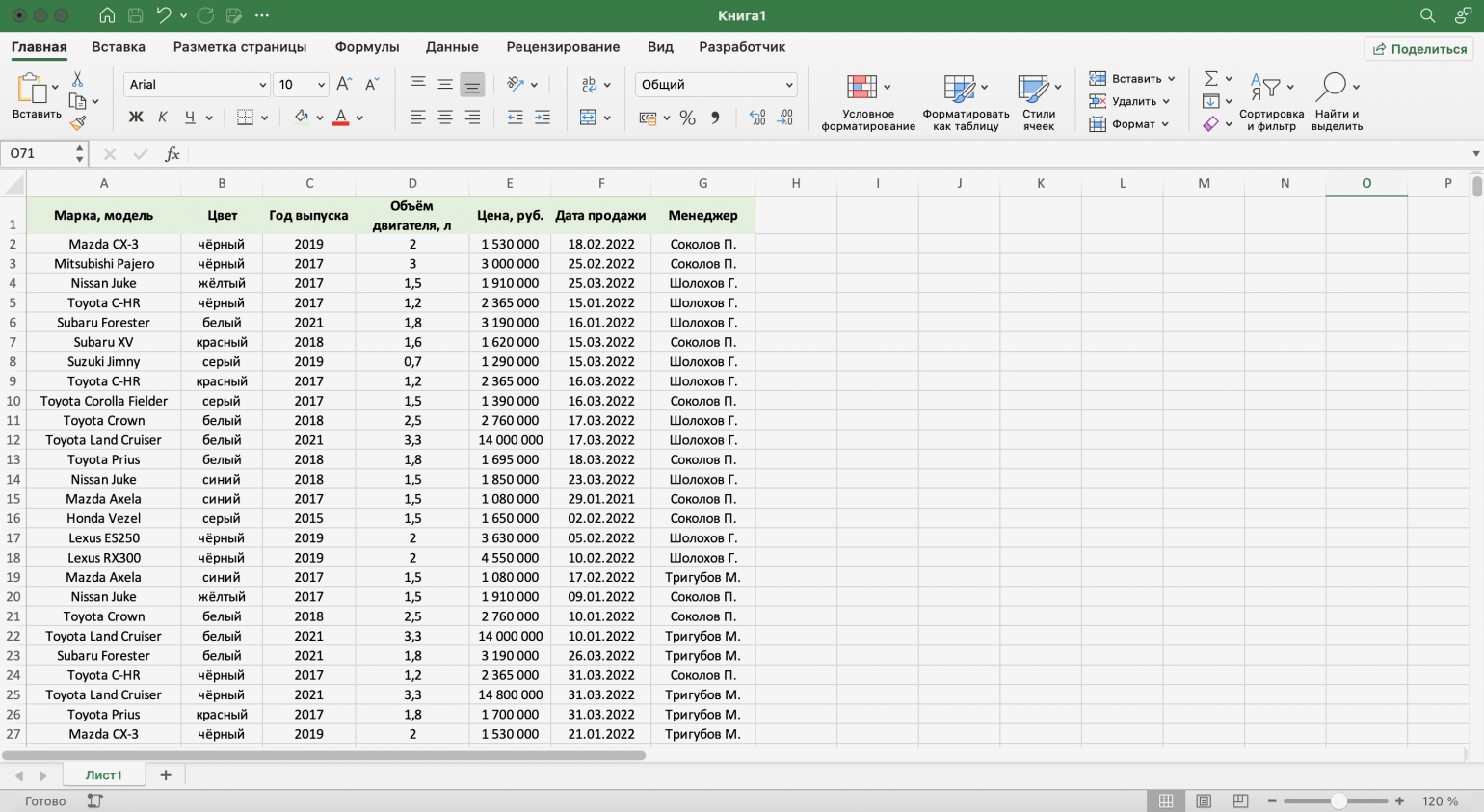
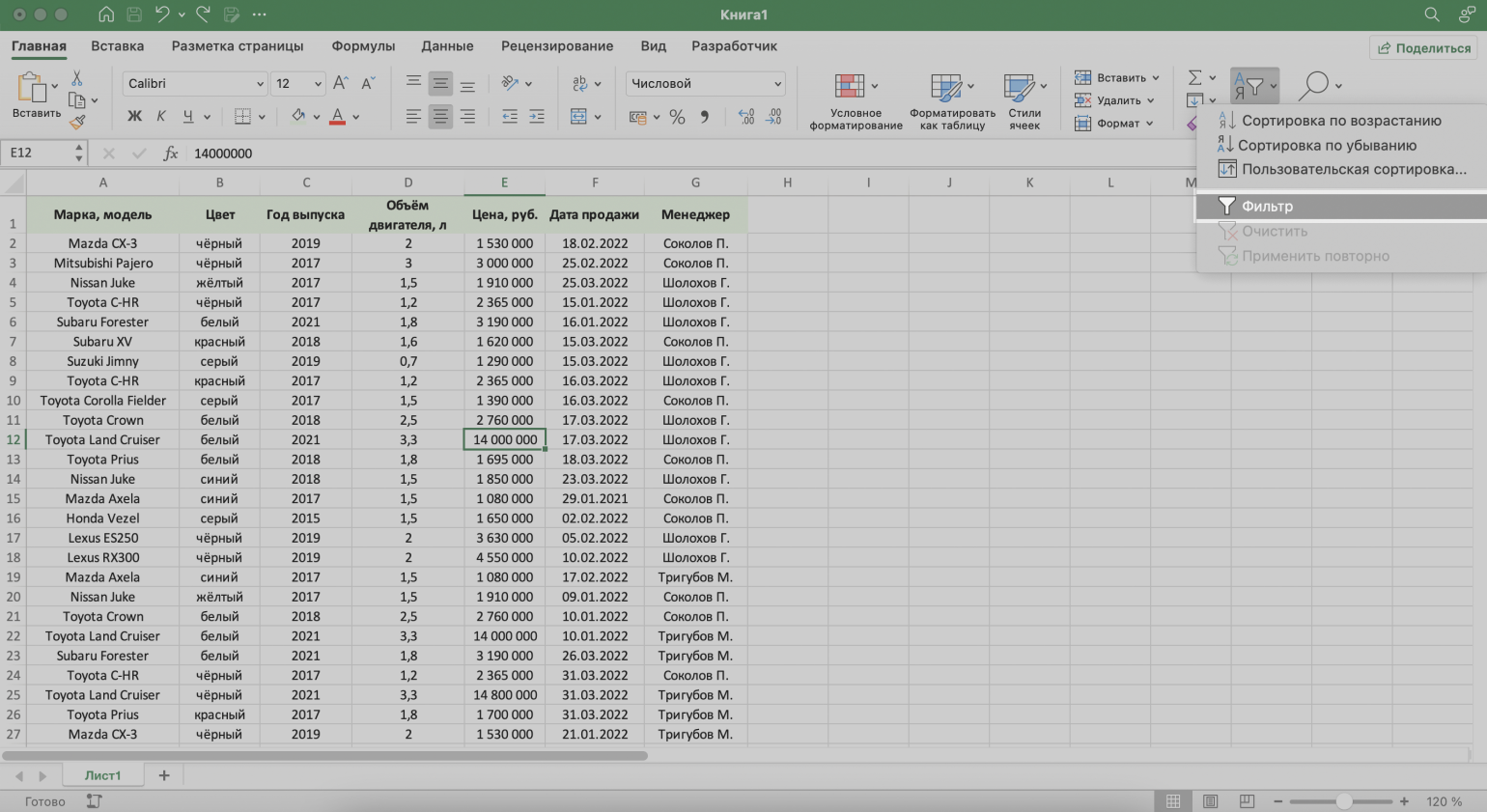
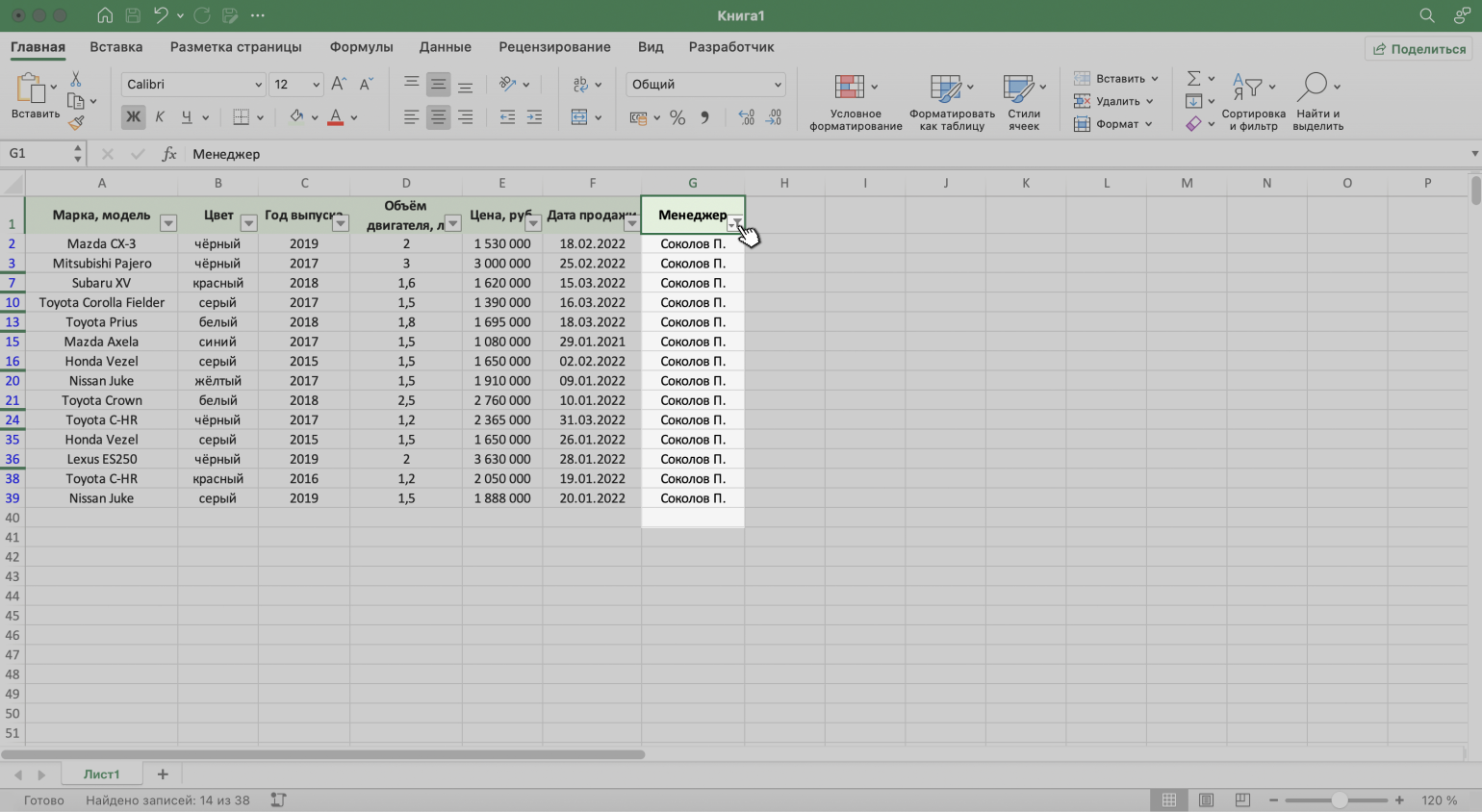
Для примера воспользуемся отчётностью небольшого автосалона. В таблице собрана информация о продажах: характеристики авто, цены, даты продажи и ответственные менеджеры.
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
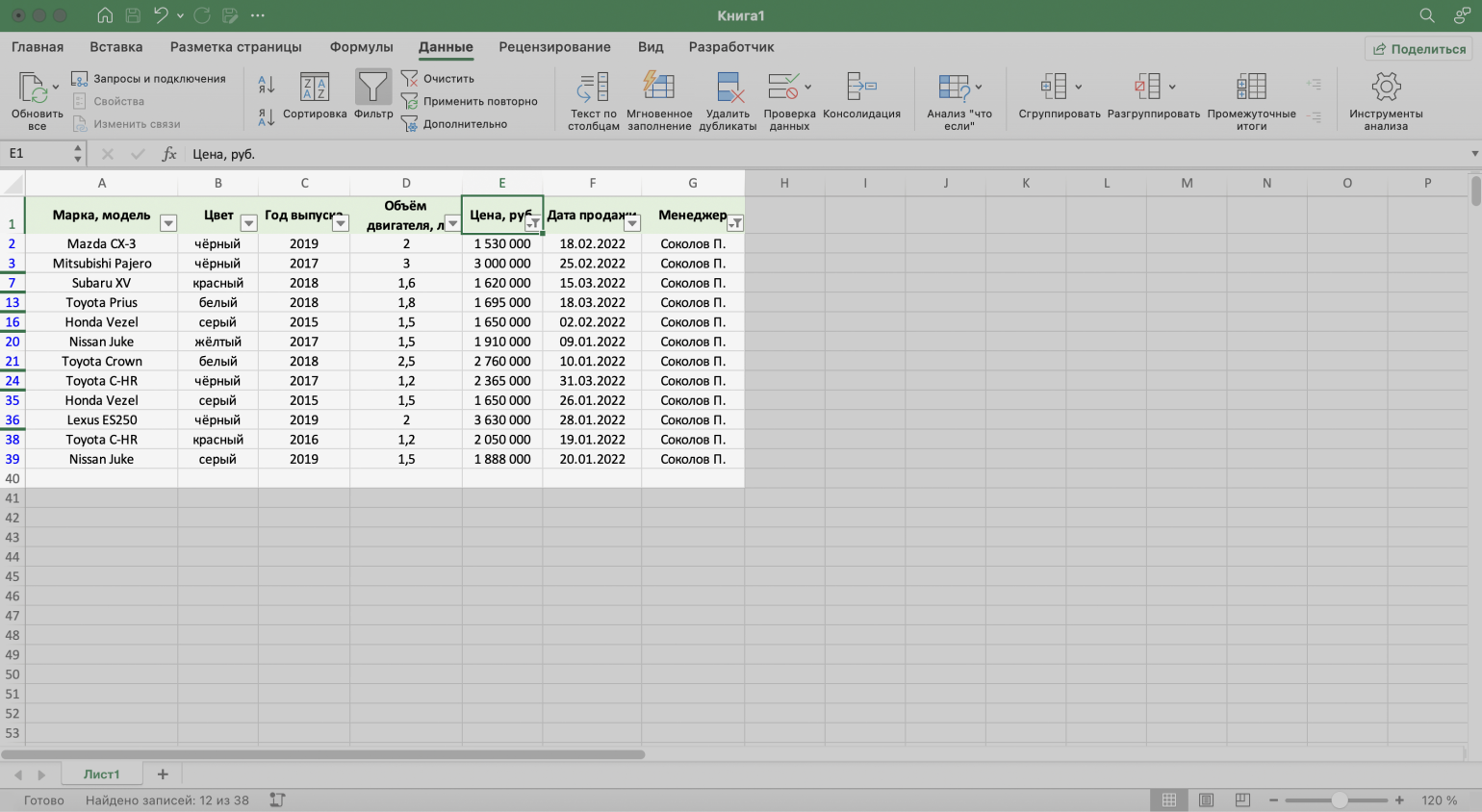
Допустим, нужно показать продажи только одного менеджера — Соколова П. Воспользуемся фильтрацией.
Шаг 1. Выделяем ячейку внутри таблицы — не обязательно ячейку столбца «Менеджер», любую.
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
Шаг 2. На вкладке «Главная» нажимаем кнопку «Сортировка и фильтр».
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
Шаг 3. В появившемся меню выбираем пункт «Фильтр».
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
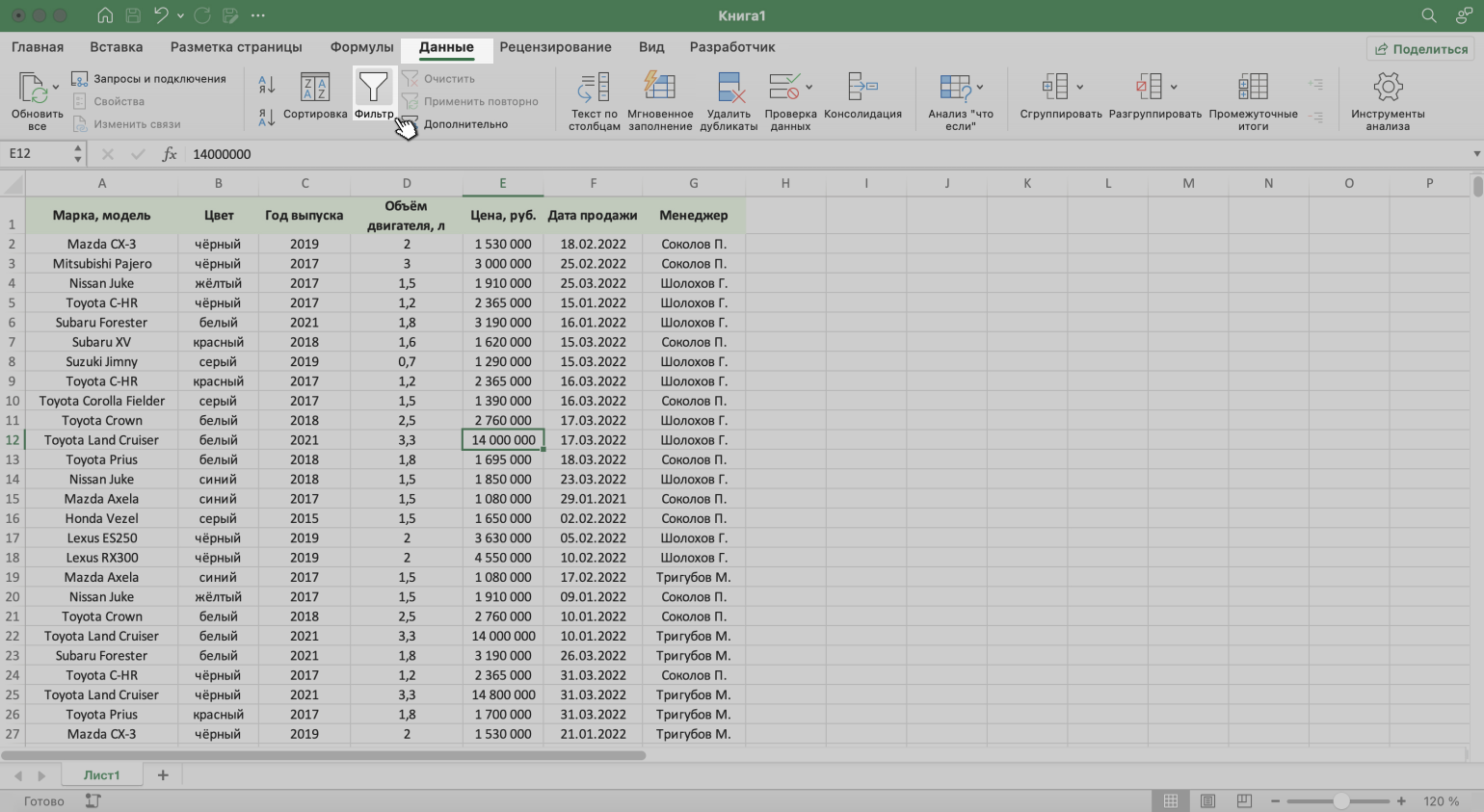
То же самое можно сделать через кнопку «Фильтр» на вкладке «Данные».
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
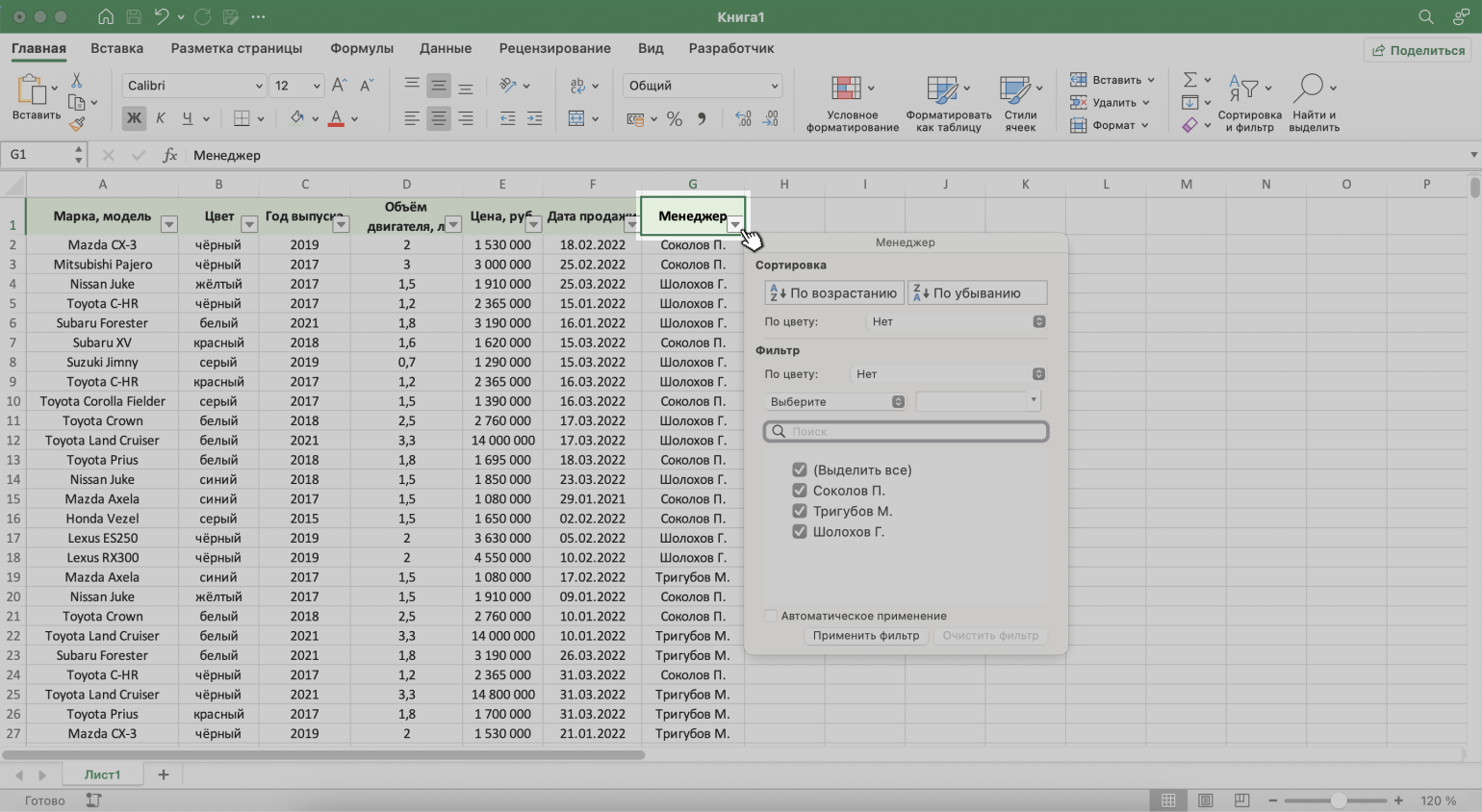
Шаг 4. В каждой ячейке шапки таблицы появились кнопки со стрелками — нажимаем на кнопку столбца, который нужно отфильтровать. В нашем случае это столбец «Менеджер».
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
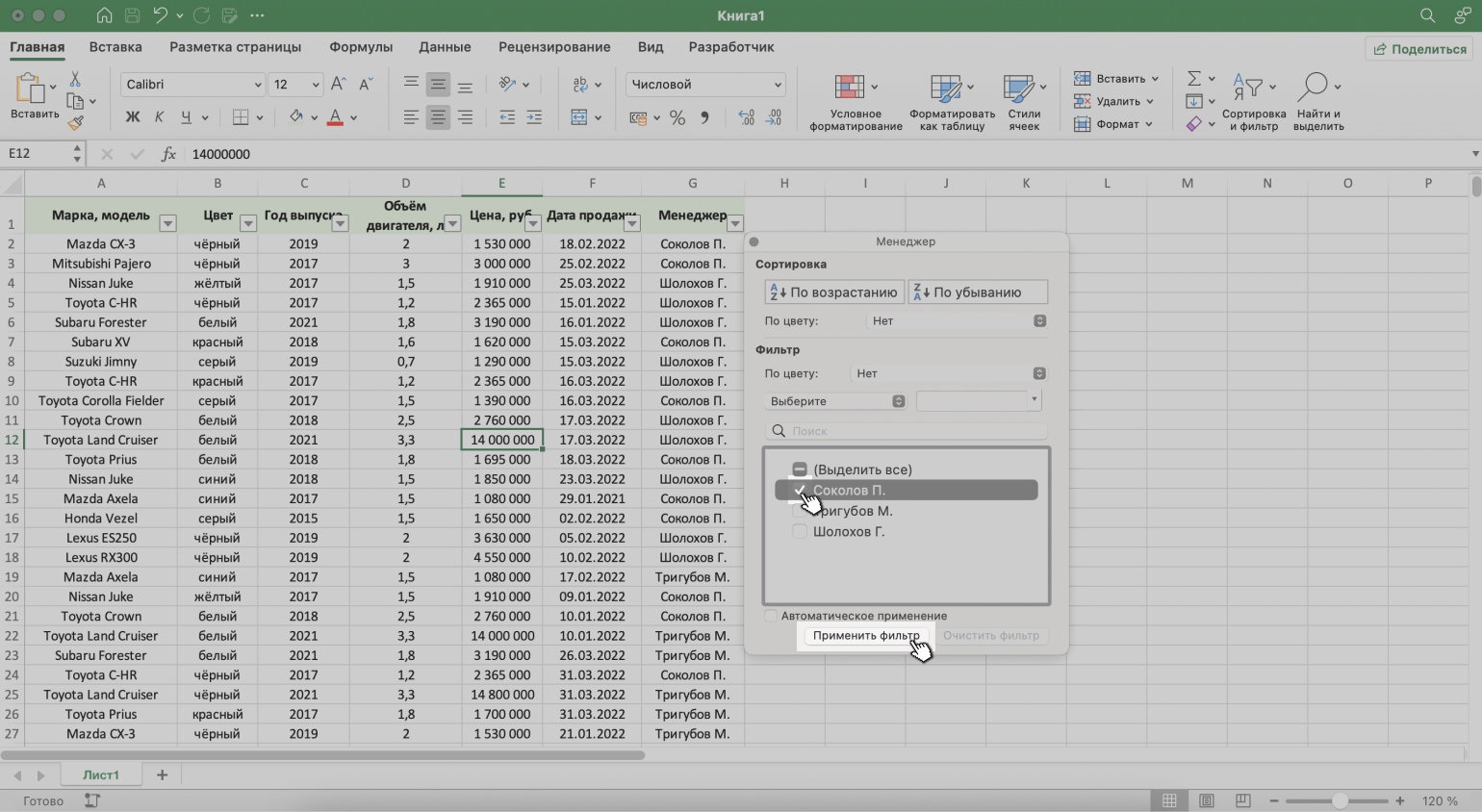
Шаг 5. В появившемся меню флажком выбираем данные, которые нужно оставить в таблице, — в нашем случае данные менеджера Соколова П., — и нажимаем кнопку «Применить фильтр».
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
Готово — таблица показывает данные о продажах только одного менеджера. На кнопке со стрелкой появился дополнительный значок. Он означает, что в этом столбце настроена фильтрация.
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
Чтобы ещё уменьшить количество отображаемых в таблице данных, можно применять несколько фильтров одновременно. При этом как фильтр можно задавать не только точное значение ячеек, но и условие, которому отфильтрованные ячейки должны соответствовать.
Разберём на примере.
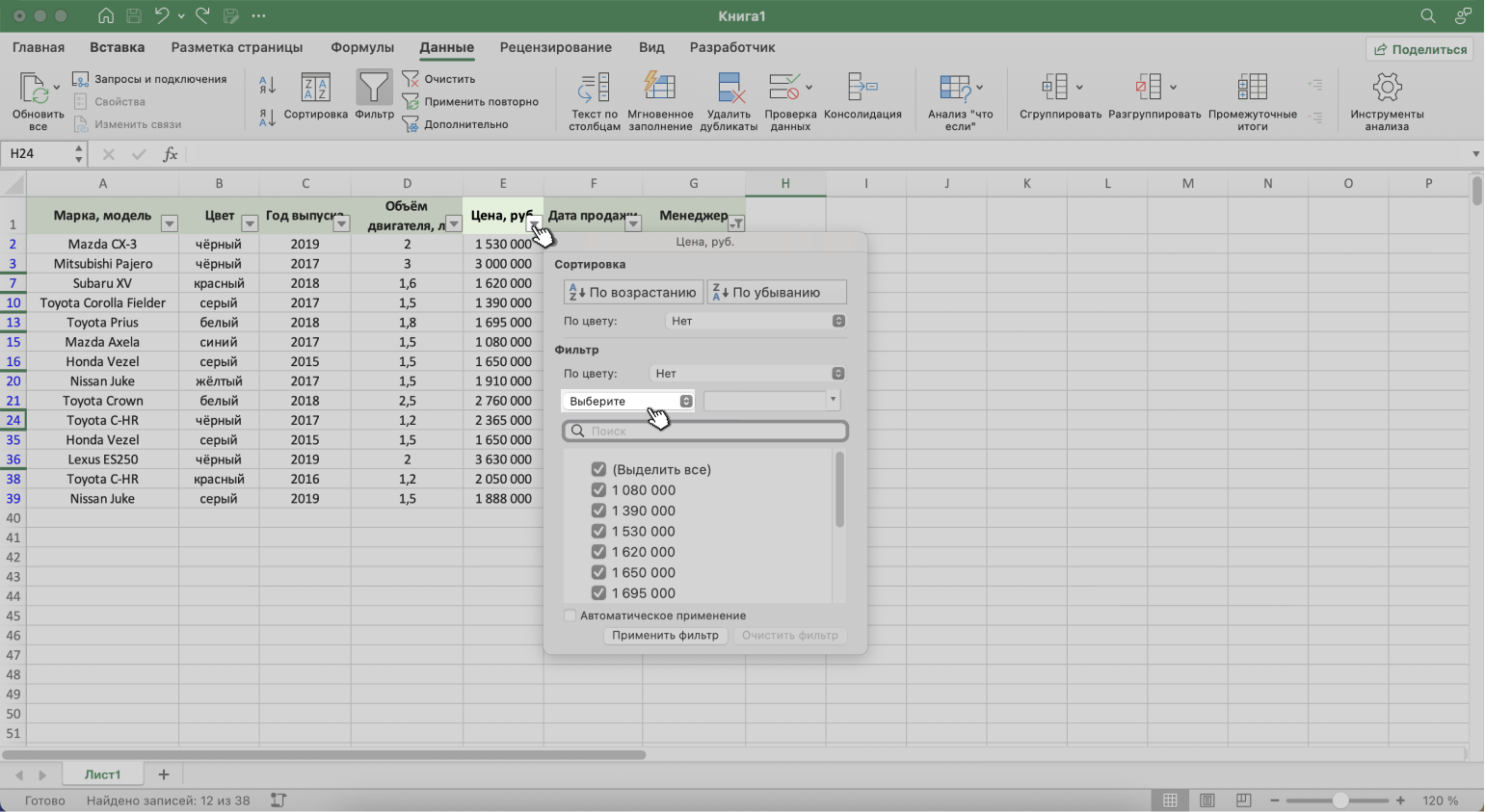
Выше мы уже отфильтровали таблицу по одному параметру — оставили в ней продажи только менеджера Соколова П. Добавим второй параметр — среди продаж Соколова П. покажем автомобили дороже 1,5 млн рублей.
Шаг 1. Открываем меню фильтра для столбца «Цена, руб.» и нажимаем на параметр «Выберите».
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
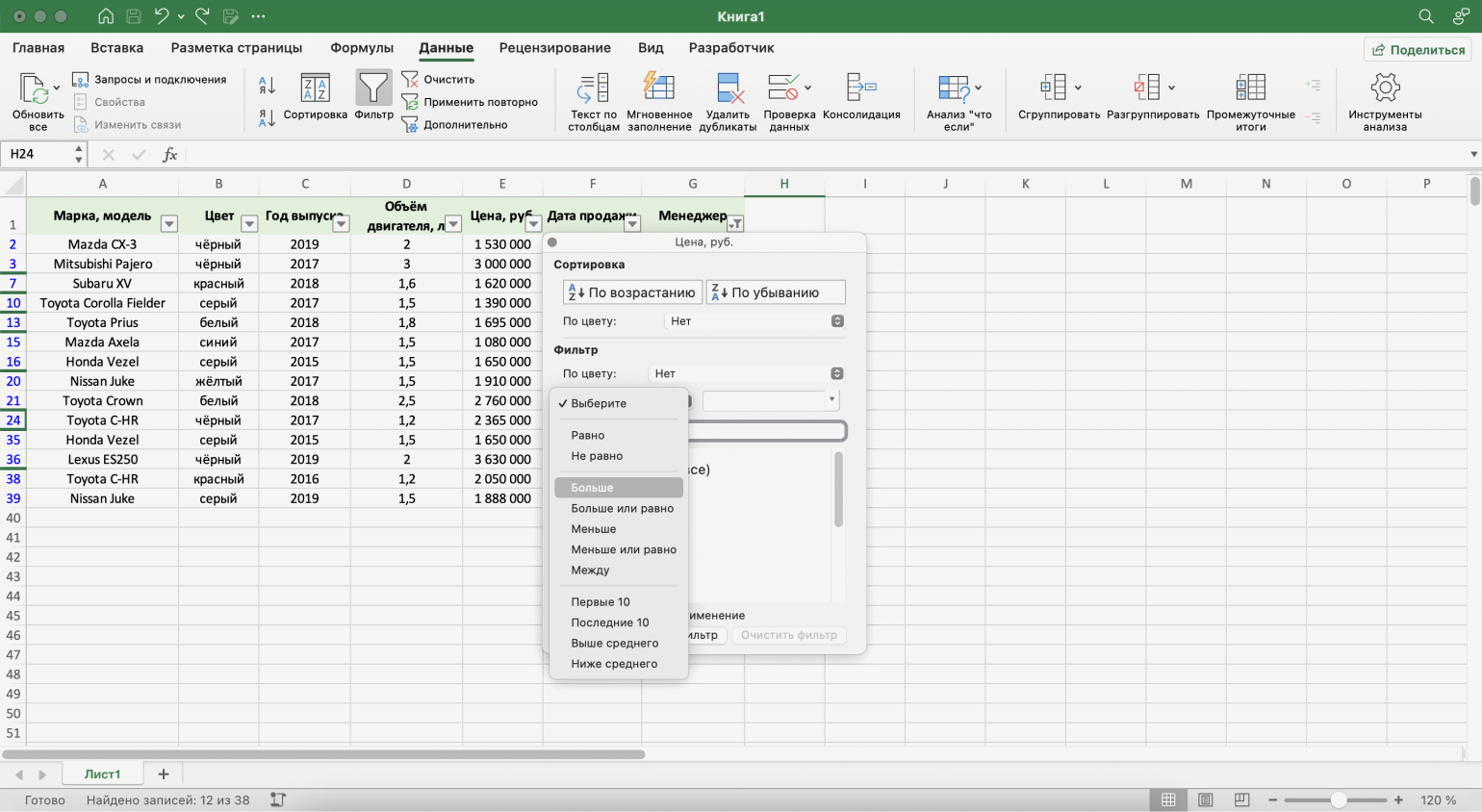
Шаг 2. Выбираем критерий, которому должны соответствовать отфильтрованные ячейки.
В нашем случае нужно показать автомобили дороже 1,5 млн рублей — выбираем критерий «Больше».
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
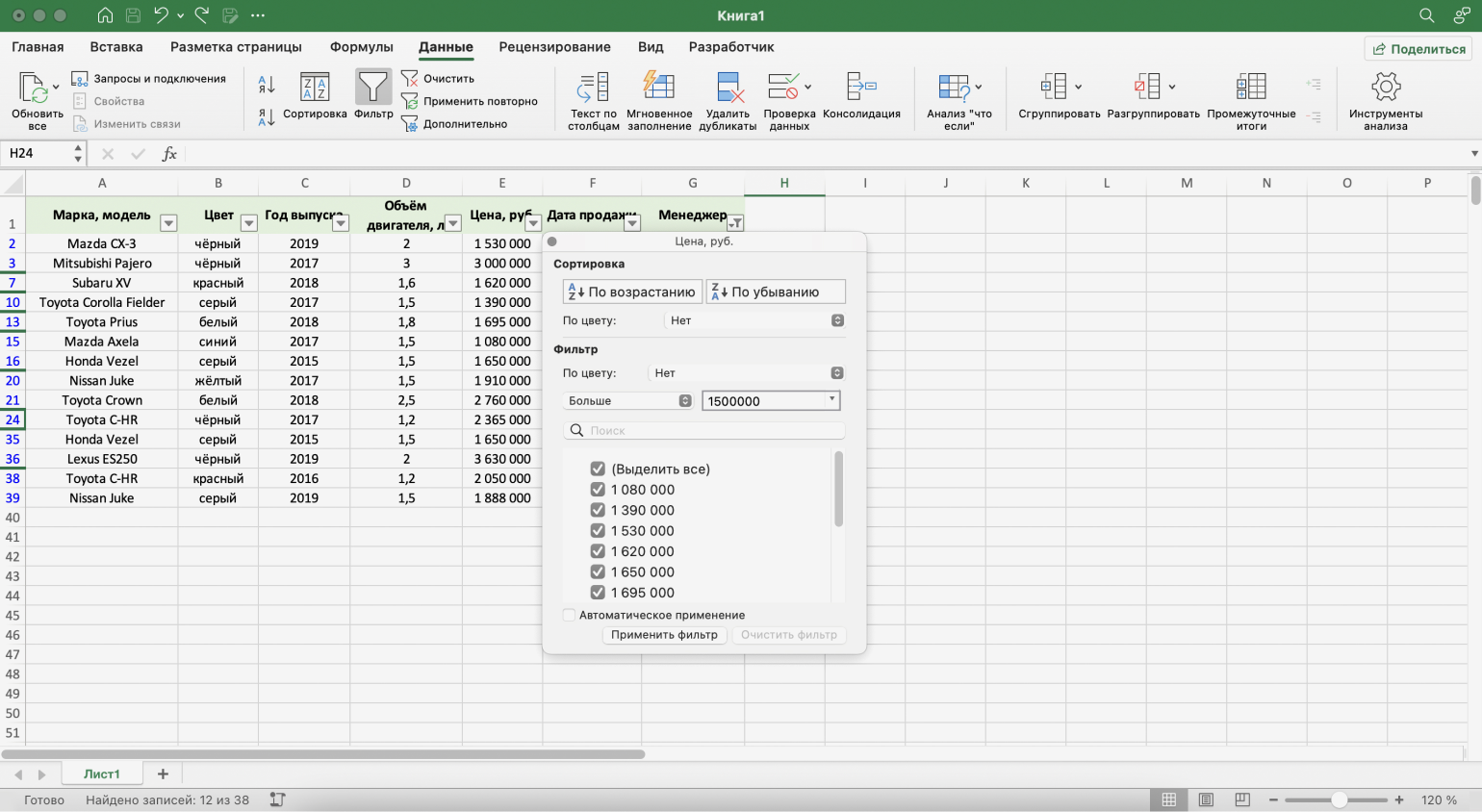
Шаг 3. Дополняем условие фильтрации — в нашем случае «Больше 1500000» — и нажимаем «Применить фильтр».
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
Готово — фильтрация сработала по двум параметрам. Теперь таблица показывает только те проданные менеджером авто, цена которых была выше 1,5 млн рублей.
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
Расширенный фильтр позволяет фильтровать таблицу по сложным критериям сразу в нескольких столбцах.
Это можно сделать способом, который мы описали выше: поочерёдно установить несколько стандартных фильтров или фильтров с условиями пользователя. Но в случае с объёмными таблицами этот способ может быть неудобным и трудозатратным. Для экономии времени применяют расширенный фильтр.
Принцип работы расширенного фильтра следующий:
- Копируют шапку исходной таблицы и создают отдельную таблицу для условий фильтрации.
- Вводят условия.
- Запускают фильтрацию.
Разберём на примере. Отфильтруем отчётность автосалона по трём критериям:
- менеджер — Шолохов Г.;
- год выпуска автомобиля — 2019-й или раньше;
- цена — до 2 млн рублей.
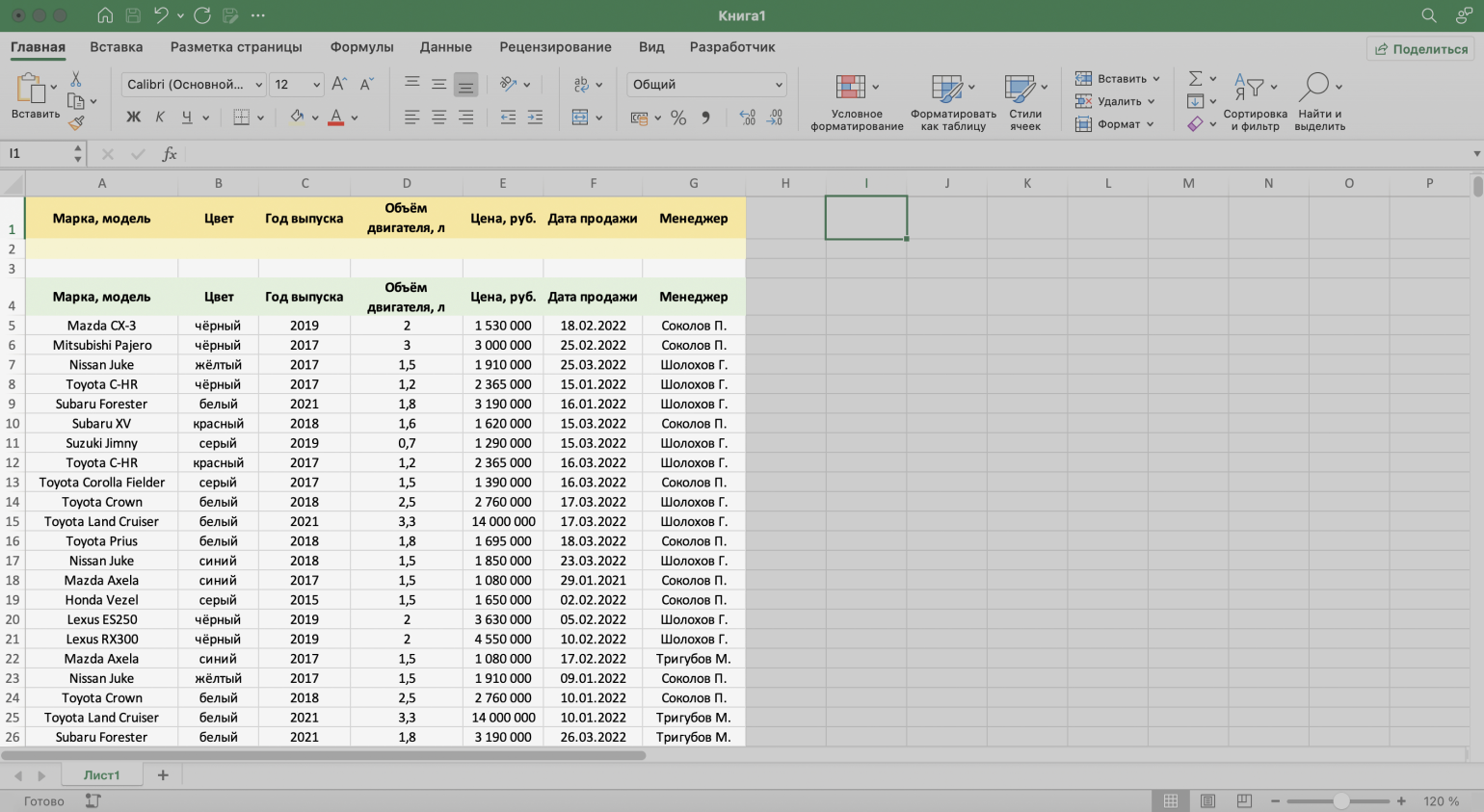
Шаг 1. Создаём таблицу для условий фильтрации — для этого копируем шапку исходной таблицы и вставляем её выше.
Важное условие — между таблицей с условиями и исходной таблицей обязательно должна быть пустая строка.
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
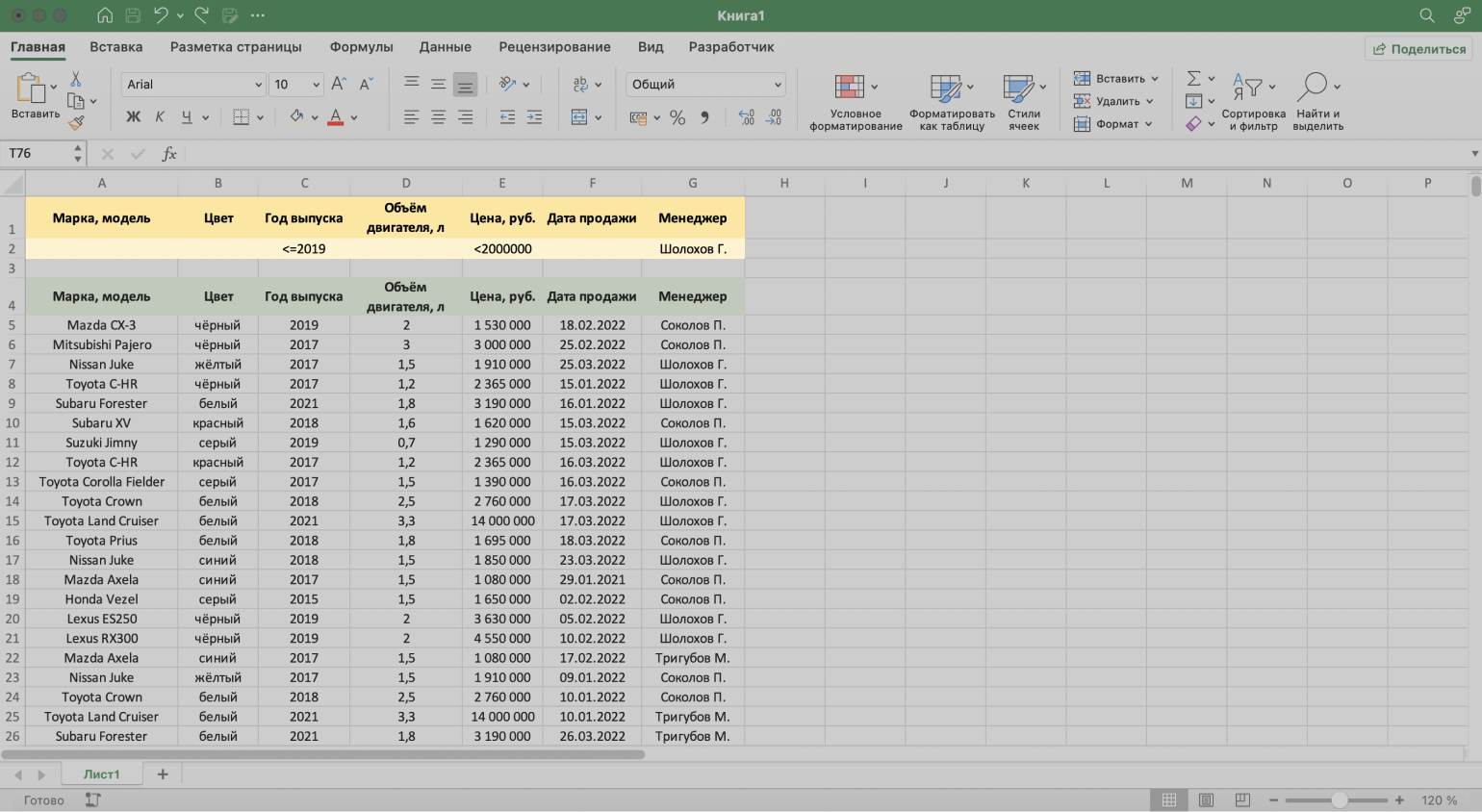
Шаг 2. В созданной таблице вводим критерии фильтрации:
- «Год выпуска» → <=2019.
- «Цена, руб.» → <2000000.
- «Менеджер» → Шолохов Г.
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
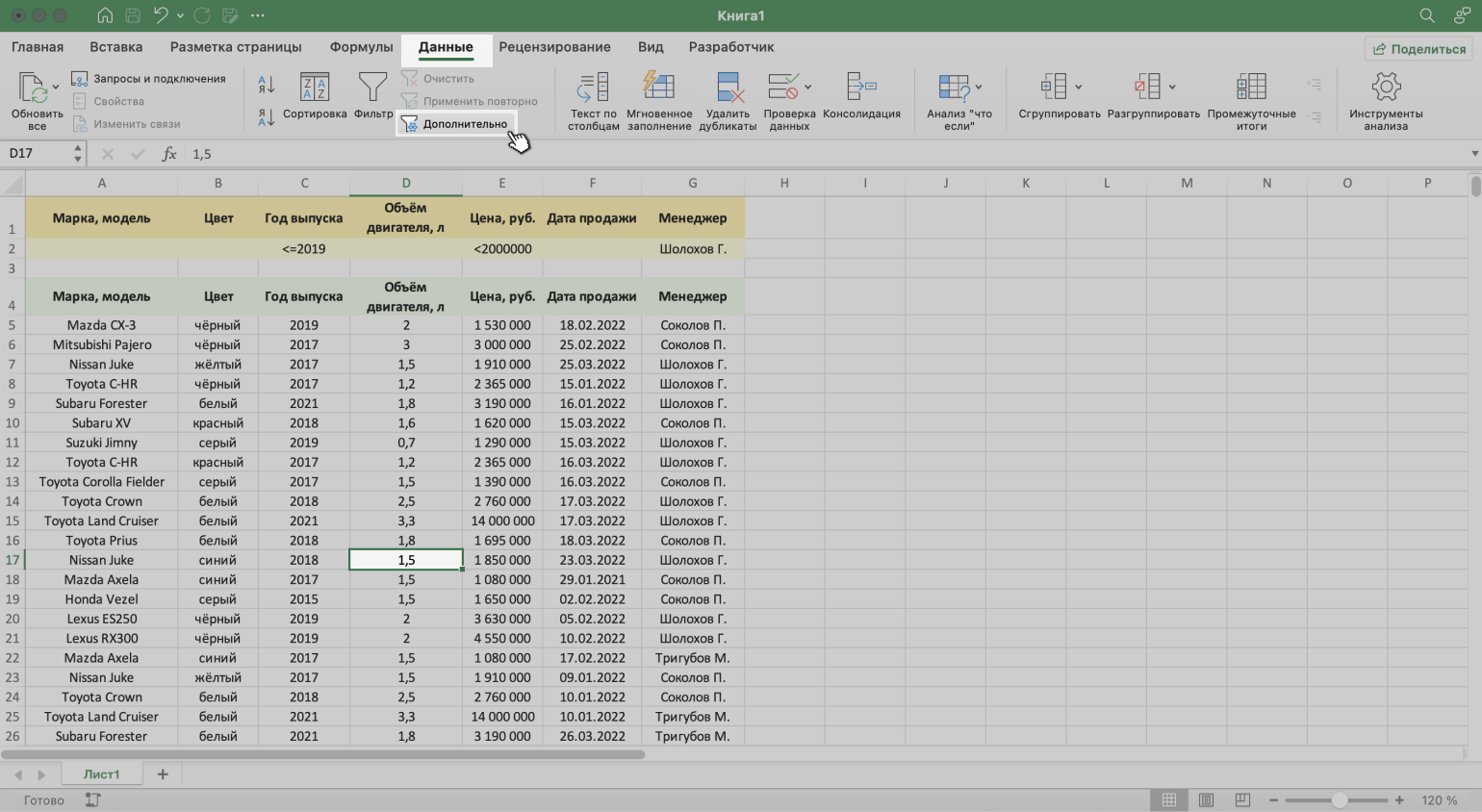
Шаг 3. Выделяем любую ячейку исходной таблицы и на вкладке «Данные» нажимаем кнопку «Дополнительно».
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
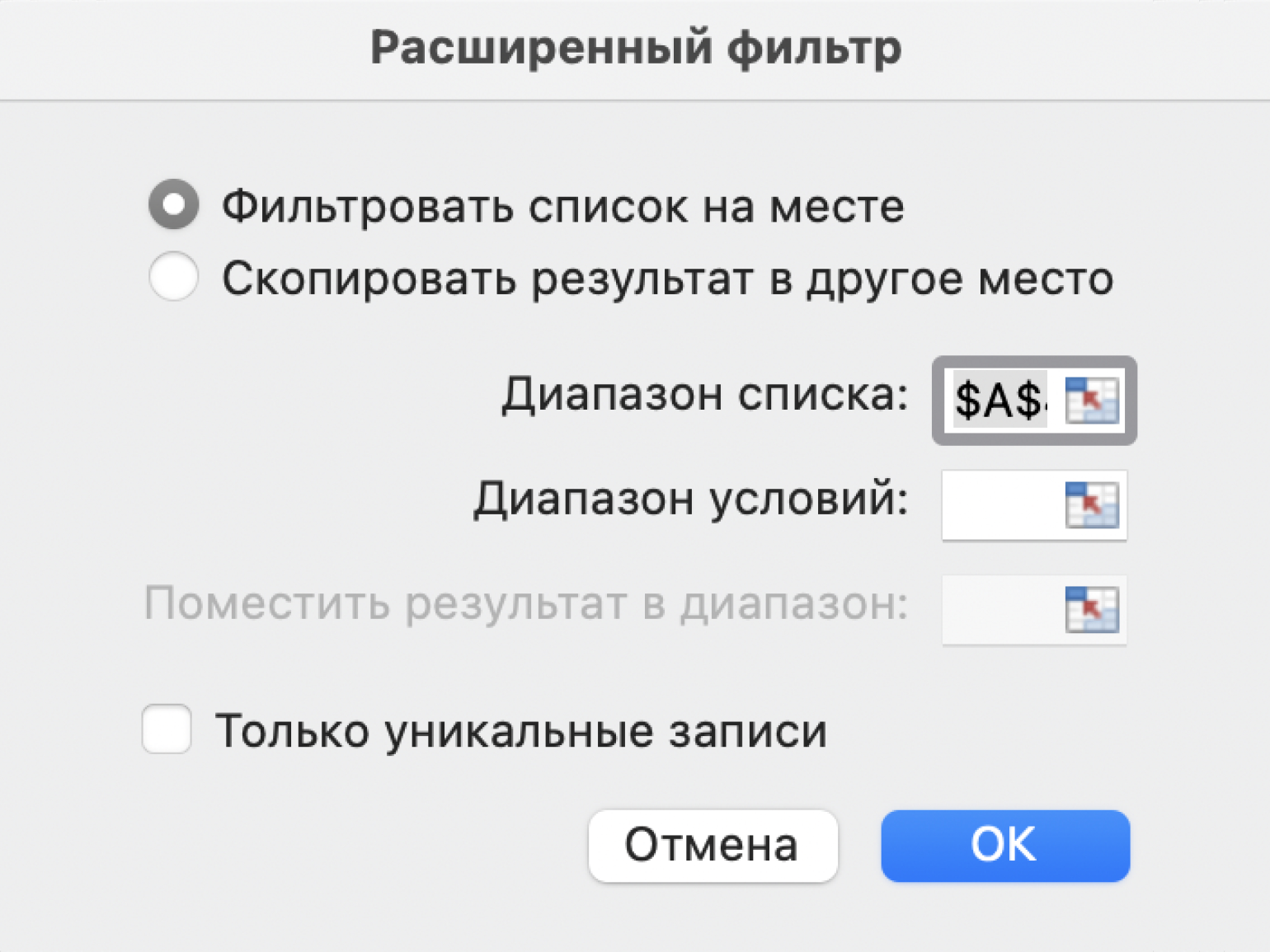
Шаг 4. В появившемся окне заполняем параметры расширенного фильтра:
- Выбираем, где отобразятся результаты фильтрации: в исходной таблице или в другом месте. В нашем случае выберем первый вариант — «Фильтровать список на месте».
- Диапазон списка — диапазон таблицы, для которой нужно применить фильтр. Он заполнен автоматически, для этого мы выделяли ячейку исходной таблицы перед тем, как вызвать меню.
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
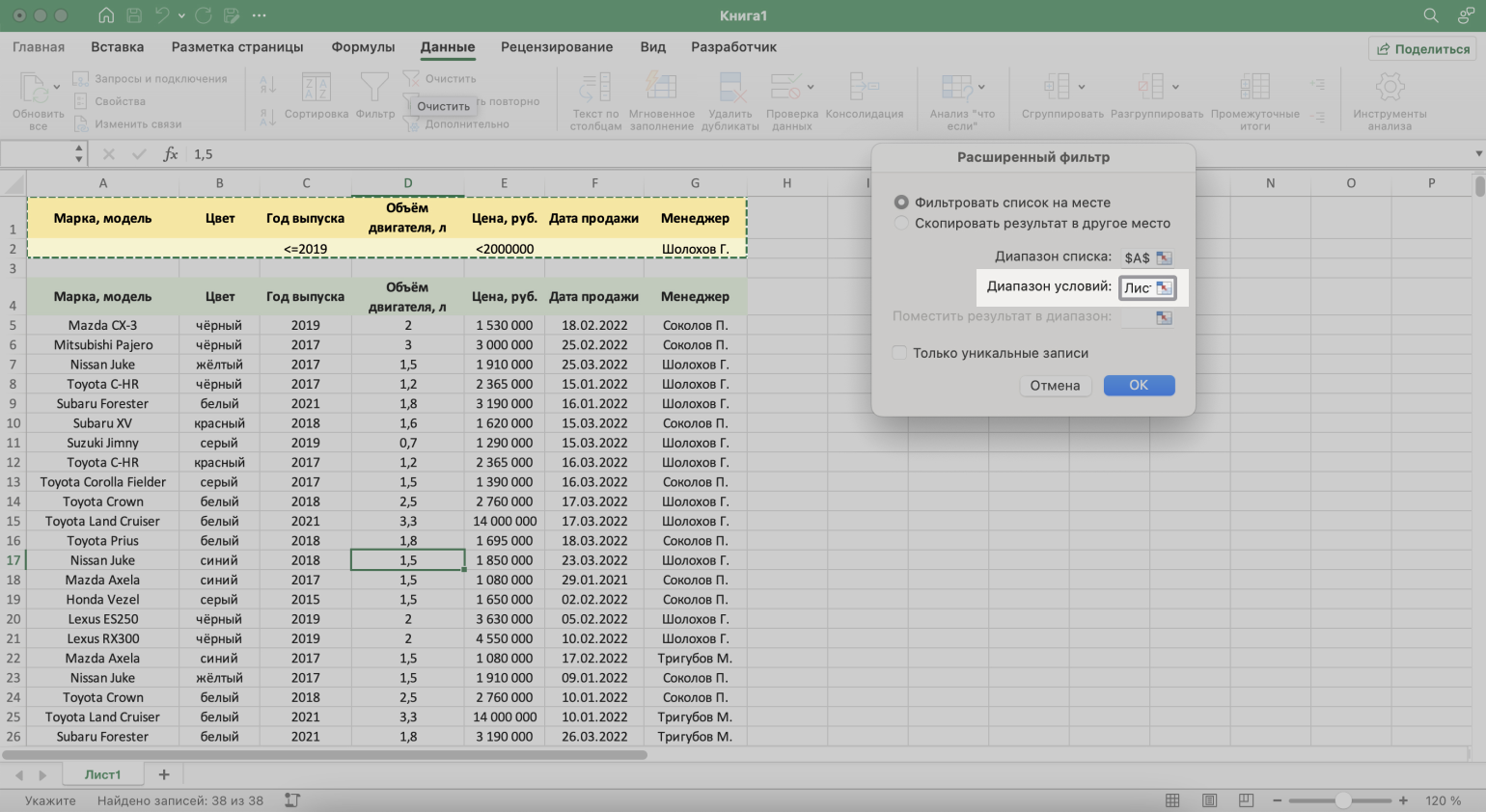
- Диапазон условий — диапазон таблицы с условиями фильтрации. Ставим курсор в пустое окно параметра и выделяем диапазон: шапку таблицы и строку с критериями. Данные диапазона автоматически появляются в окне параметров расширенного фильтра.
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
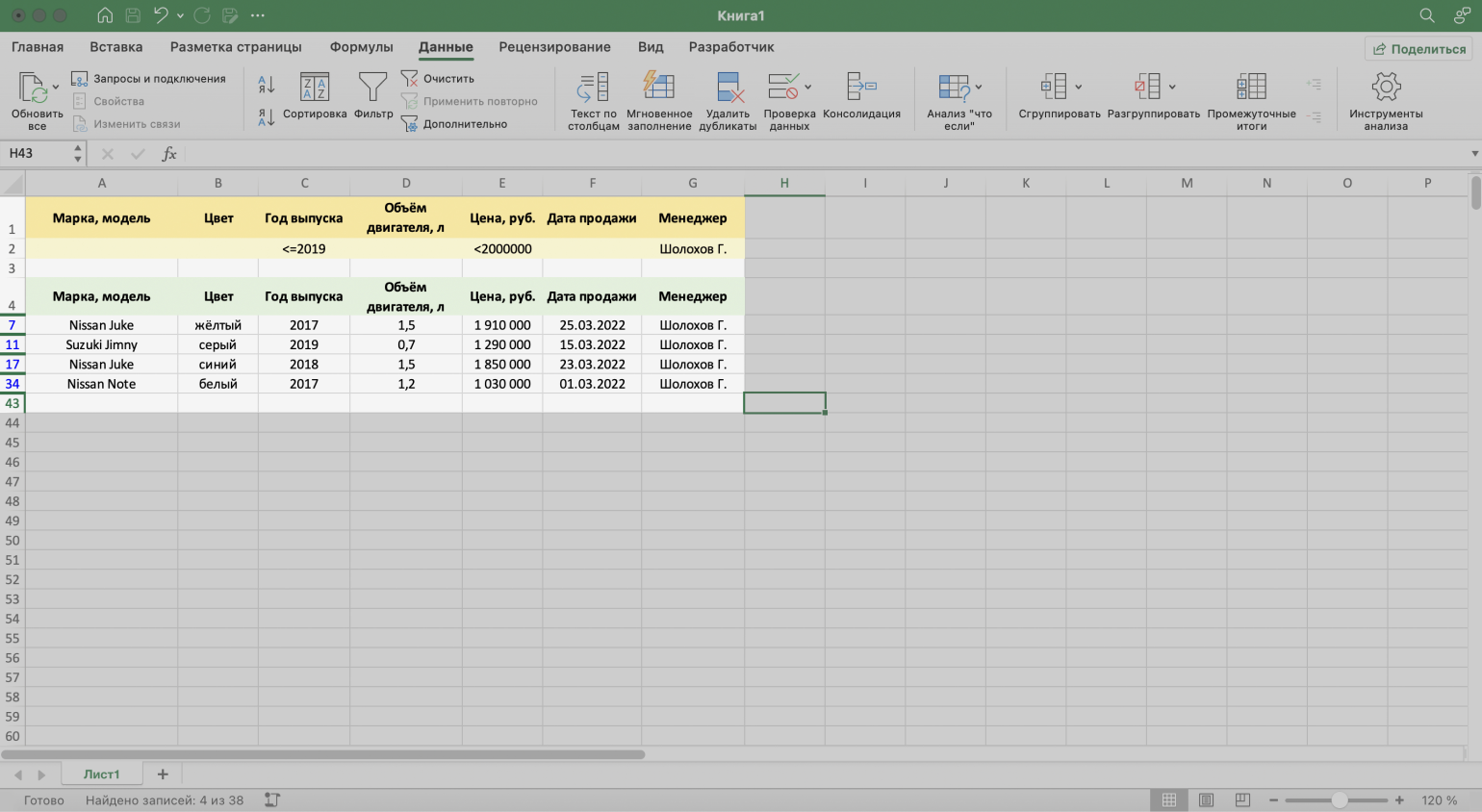
Шаг 5. Нажимаем «ОК» в меню расширенного фильтра.
Готово — исходная таблица отфильтрована по трём заданным параметрам.
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
Отменить фильтрацию можно тремя способами:
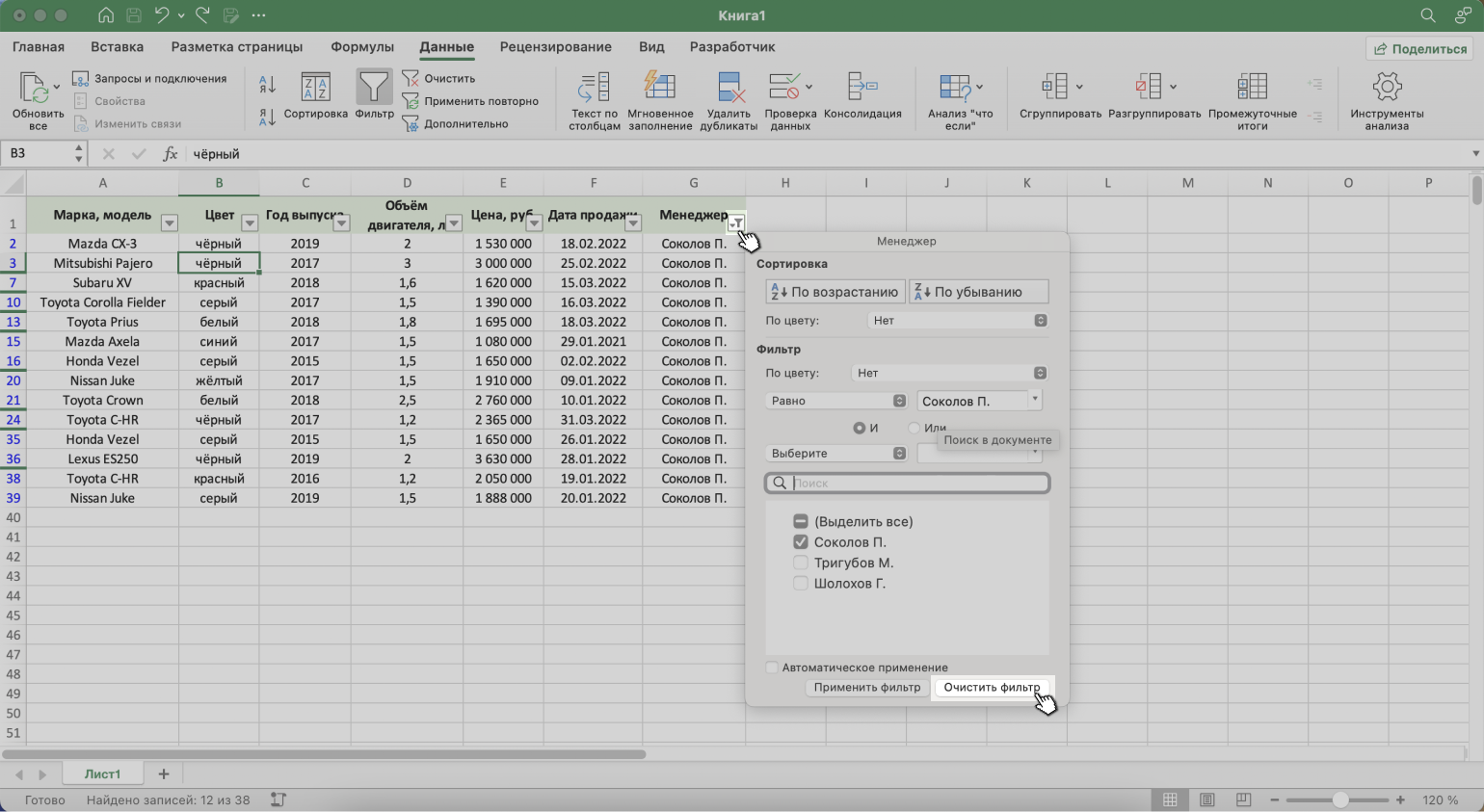
1. Вызвать меню отфильтрованного столбца и нажать на кнопку «Очистить фильтр».
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
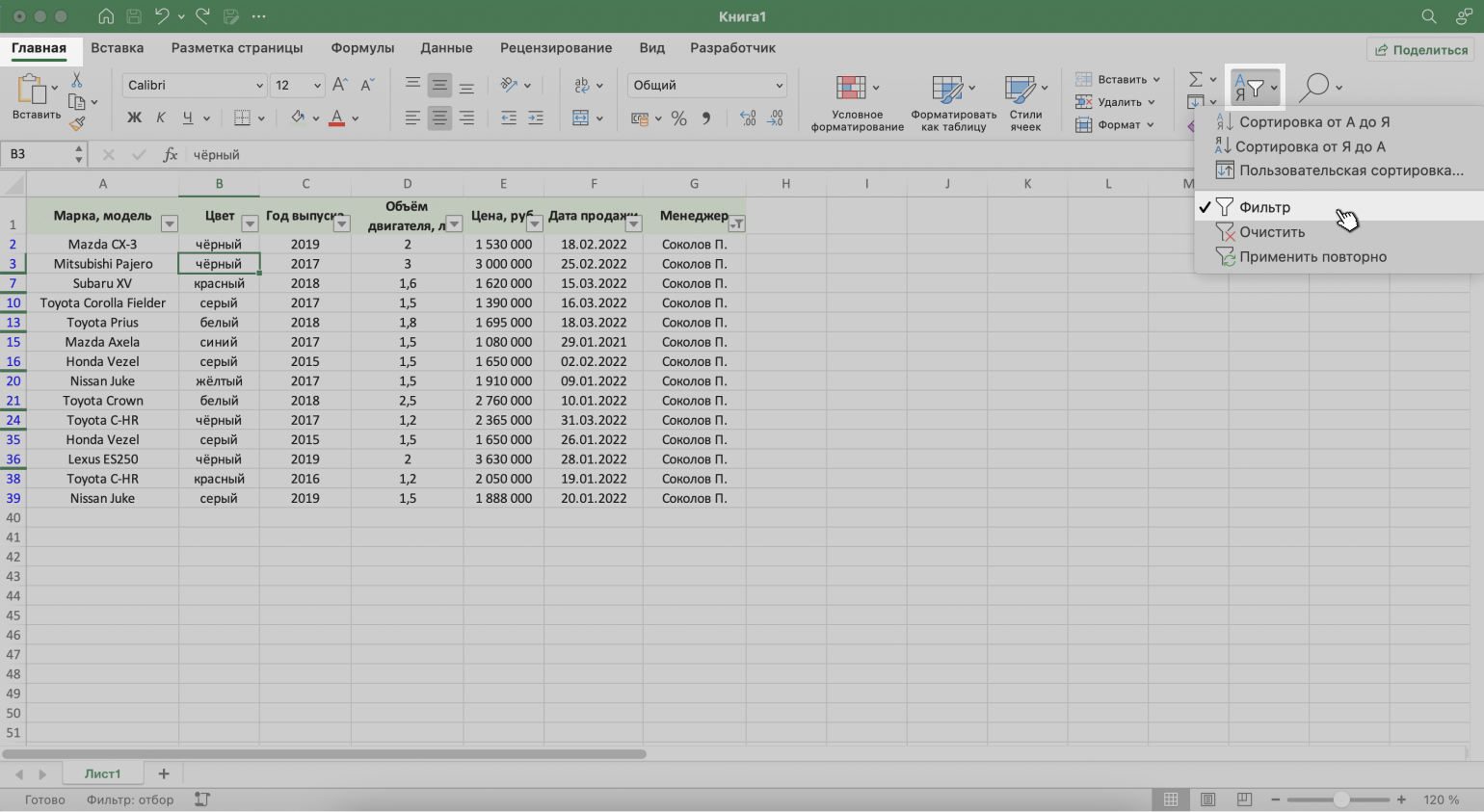
2. Нажать на кнопку «Сортировка и фильтр» на вкладке «Главная». Затем — либо снять галочку напротив пункта «Фильтр», либо нажать «Очистить фильтр».
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
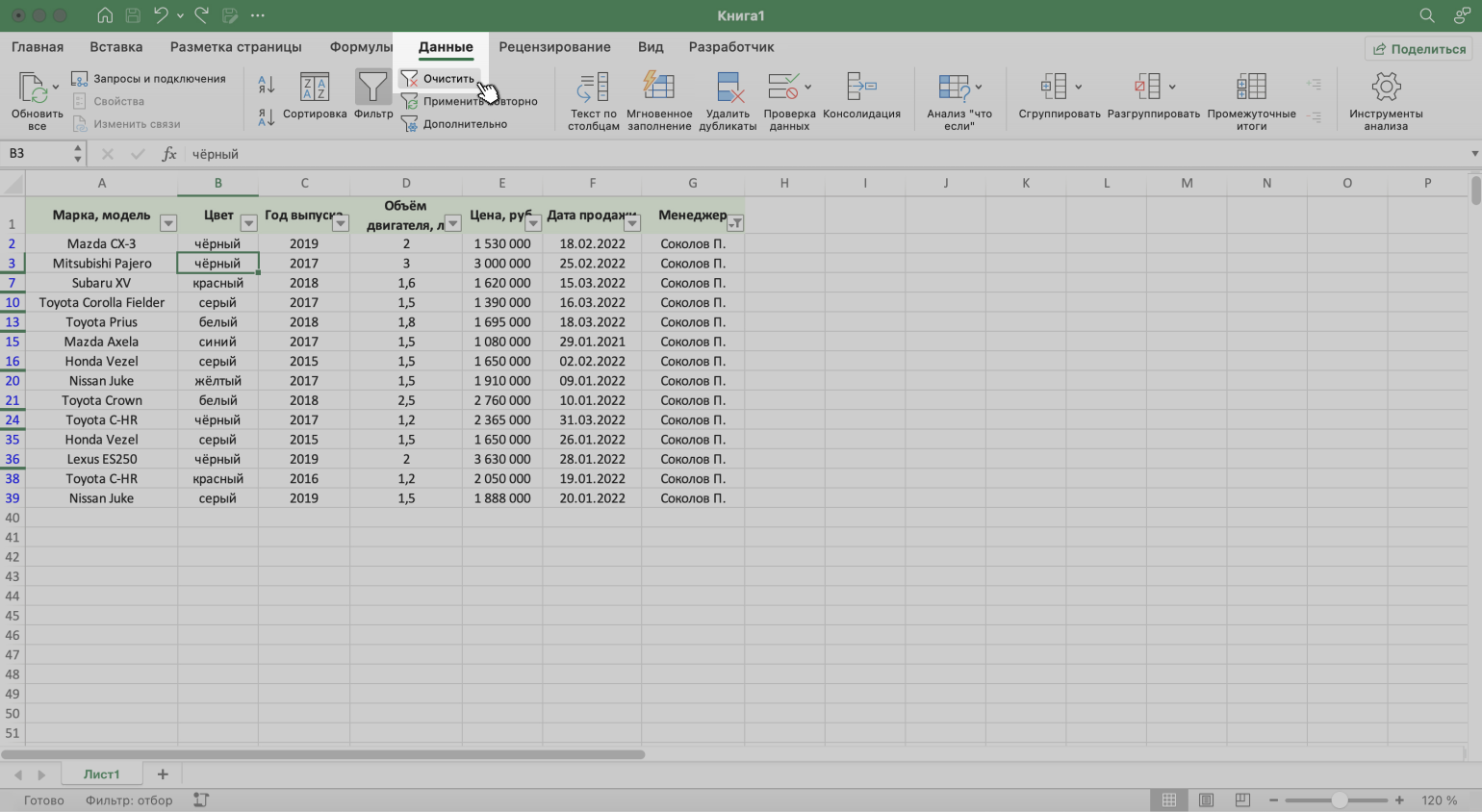
3. Нажать на кнопку «Очистить» на вкладке «Данные».
Скриншот: Excel / Skillbox Media
Научитесь: Excel + Google Таблицы с нуля до PRO
Узнать больше
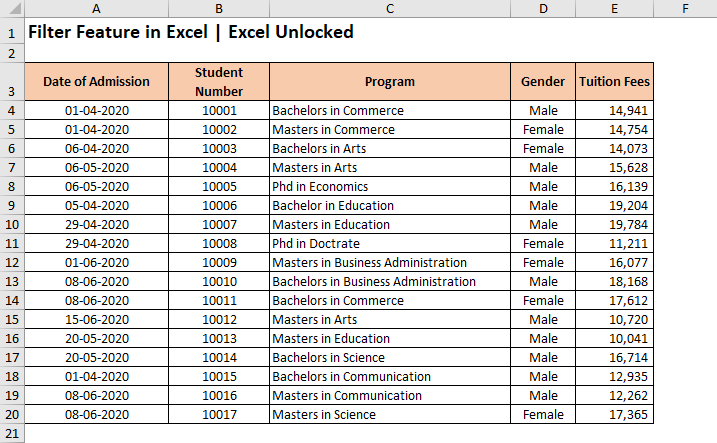
The Excel Filter Feature is a great tool that proves to be a lifesaver at the time when you are working with huge data in Excel. In this blog, we would unlock this filter feature in Excel. We would learn how to filter huge data in excel. We would also get into answering the following common questions – how to filter values, or numbers, or dates and time in Excel, how to use filter using wildcard characters in excel, how to filter using the search box, how to filter by text or cell color.
Sample Data – Download Sample File
In this blog, we would be using the below data. Kindly download and practice along with using the Download button.
Table of Contents
- Sample Data – Download Sample File
- What is the Purpose of Filter Feature in Excel?
- Adding Filter Option on Header Rows
- Simple Ways to Filter Your Data Set in Excel
- Applying Filter on Single Column
- Applying Filter on Multiple Columns
- Filter Data Using Filter Search Box in Excel
- Clearing Filter on Columns in Excel
- How to Filter Values or Text in Excel?
- Filter Values based on Two Criteria
- How to Filter Numbers in Excel?
- How to Filter Dates in Excel?
- How to Filter By Color in Excel?
- Quick Way to Filter By A Specific Cell’s Value, Font Color, Cell Color or Icon
- A Solution To – AutoFilter Does Not Work After Changing Data
- Copy and Paste only Filtered Data in Excel
- Copy and Paste Filtered Data Including Header Row
- Copy and Paste Filtered Data Excluding Header Row
- Removing Filter From Headers in Excel
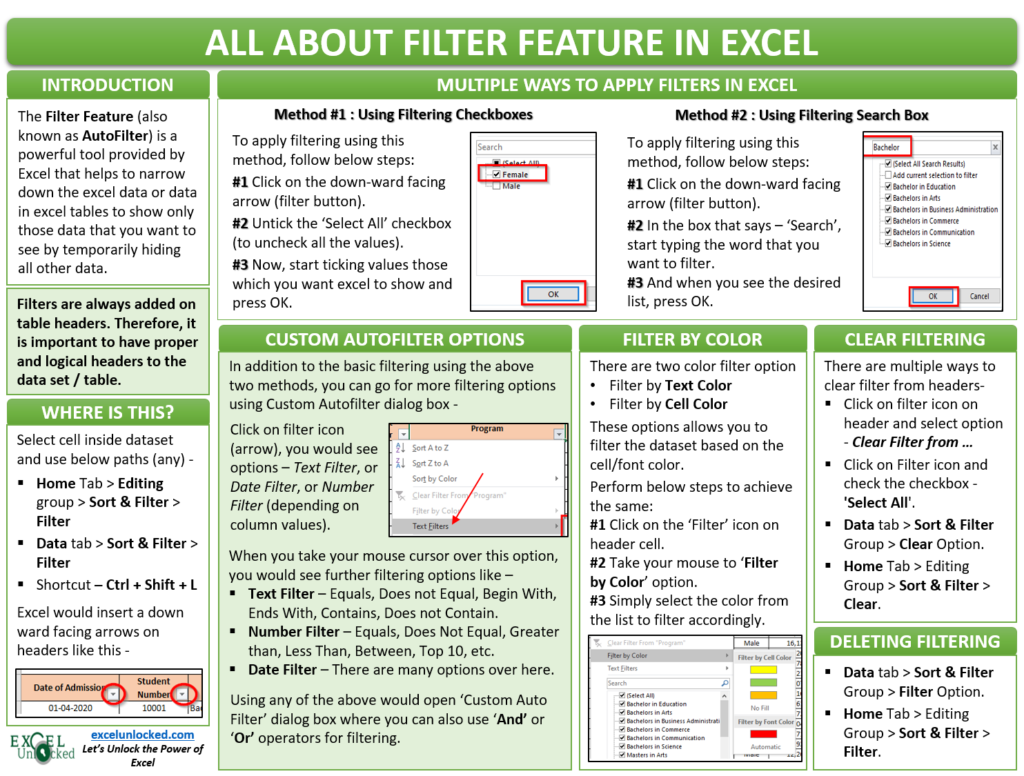
What is the Purpose of Filter Feature in Excel?
The Filter Feature (also known as AutoFilter) is a powerful tool provided by Excel that narrows down the excel data or data in excel tables to show only those data that you want to see by temporarily hiding all other data. In our sample data, for example, we can use this feature to condense the data such that it only shows the programs taken up by the ‘Female‘ applicants.
In a similar way, you can filter by dates, or values or by any other such criteria.
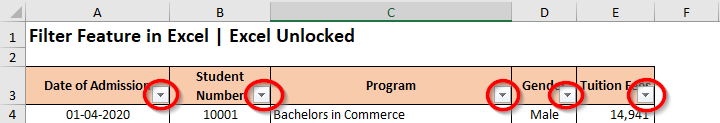
The filters are always added to the headers of the data set. Therefore, it is important that your excel data must contain a header row, with logical headings. In our example, row 3 is the header row with headings describing the column data.
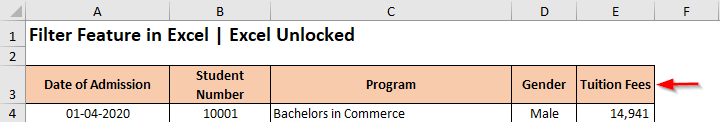
Once your dataset has proper headers, you are now good to insert the AutoFilter on these headers. To add AutoFilter on the header row, click on any of the cells inside the excel data set (like C7) and use any of the below-mentioned ways:
- Go to ‘Home‘ tab > ‘Editing‘ Group > ‘Sort & Filter‘ Option > ‘Filter‘ button.
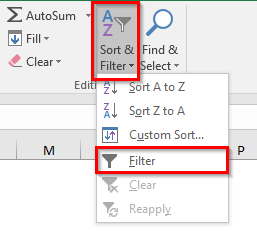
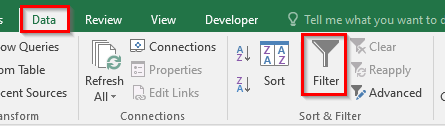
- Go to ‘Data‘ tab > ‘Sort & Filter‘ group > ‘Filter‘ Button.
- Keyboard Shortcut Method : Ctrl + Shift + L
As soon as you use any of the above methods, the excel would automatically detect the header row inside the table or data set and insert filter buttons on each of the header cells. These are the downward-facing arrows, like the way shown below:
Simple Ways to Filter Your Data Set in Excel
Once the filter option added to the headers, you are good to start filtering your data set.
With this feature, you can filter your data by a single column or by multiple columns.
Applying Filter on Single Column
To apply the filter on a single column, simply click on the filter button (downward-facing arrow) of the respective column. (Let us firstly apply the filter on the column ‘Program Name’). As a result, you would notice that all the checkboxes are checked by default.
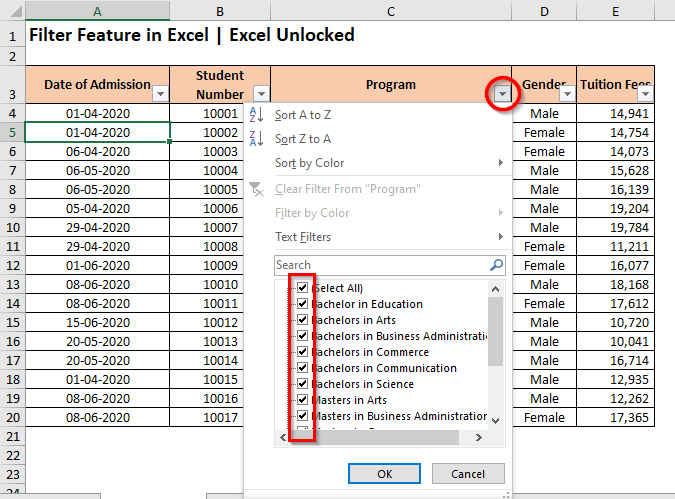
Uncheck the checkbox that says ‘Select All‘. This would remove the check boxes from all the values.
Now, start ticking the values that you wish to view and click on ‘OK’, like the way demonstrated in the below image.
Consequently, the excel would view or show only the selected values in the column, rest all are hidden. Don’t worry excel has not deleted them, they are still there in the backend.
Applying Filter on Multiple Columns
In a similar way, you can apply the filter on other columns in the Excel Data Table. There is no limitation on how many columns to which you can apply the filter.
Let us now apply another filter on the column having header – ‘Gender‘.
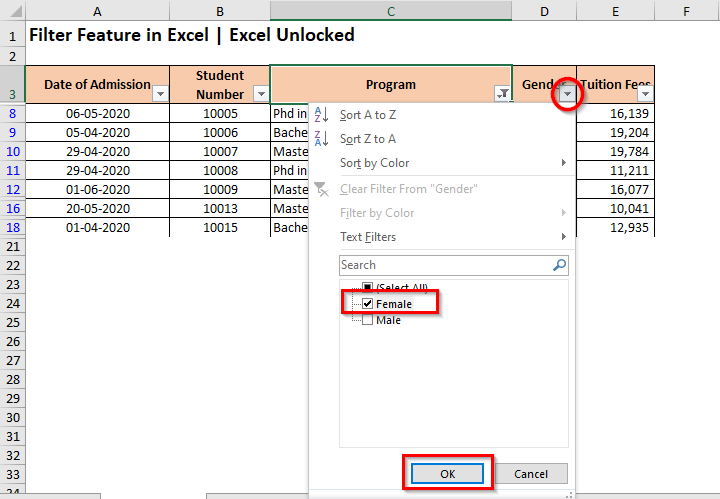
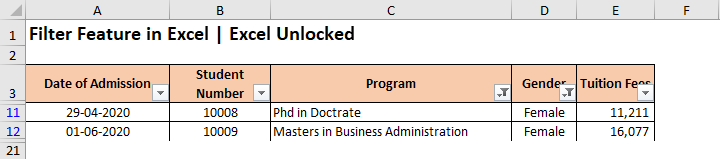
As a result, the excel would now only display the data set rows for selected ‘Program’ and for ‘Female’ candidates. All others are temporarily hidden (not removed).
Some Useful Points and Tips
Once a filter is applied on the header row-
- The Downward-facing arrow on the filtered column changes its icon which denotes that there is a filter applied to this column.
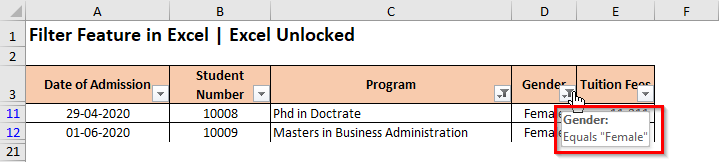
- When you take your mouse cursor over the filter button, it shows the filter values.
- To increase or decrease the width of the filter window, take your mouse cursor on the bottom-right corner of the filter window. Once the mouse cursor changes to a two-side facing arrow, click and drag right (to increase) or left (to decrease). See the below demonstration for more clarity.
Filter Data Using Filter Search Box in Excel
In the earlier section, we learned about how to filter your data set by selecting the checkboxes in the Filter window. There is yet another way to filter out a specific text or value or numbers or dates/time in Excel which is by using the ‘Filter’ search box. The Filter search box is placed just above the list of values in the Filter window.
To filter your data set using the ‘Filter’ search box, simply click on the ‘Filter’ drop-down icon on the header and type the search value in the search box. As a result, the excel would narrow down the list to show only the specified values. Finally, click on the ‘OK’ button to apply the filter.
To illustrate with an example, let us filter out the ‘Program’ column with the Bachelor’s degree.
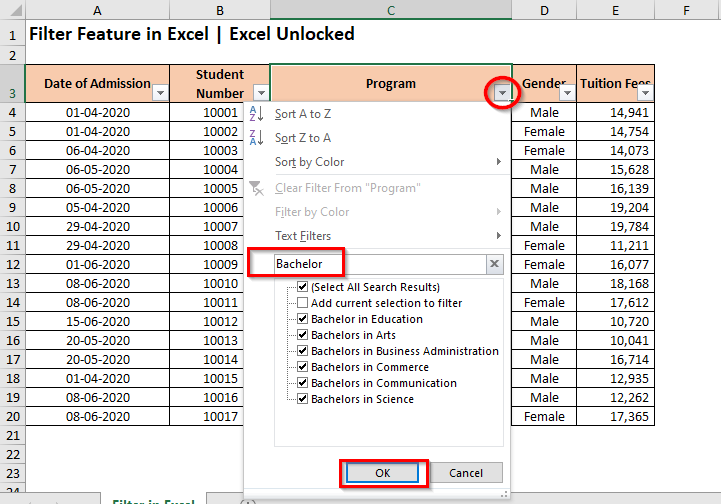
Not sure about the exact text to search, then use wildcard characters in the search box for a non-exact filter search in Excel. If you are unaware of what are wildcard characters in Excel and its usage, then please click here.
Clearing Filter on Columns in Excel
When you want to clear filter from selected or all the header columns in Excel, you can use any of the below-mentioned ways:
- Click on the ‘Filter‘ icon on the header of the column header, and click on the option that says – Clear Filter from <Column Header Name>
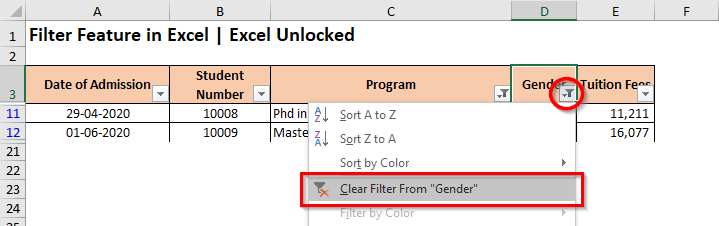
- Another way is to click on the ‘Filter‘ icon of the header, and check the checkbox – ‘Select All‘.
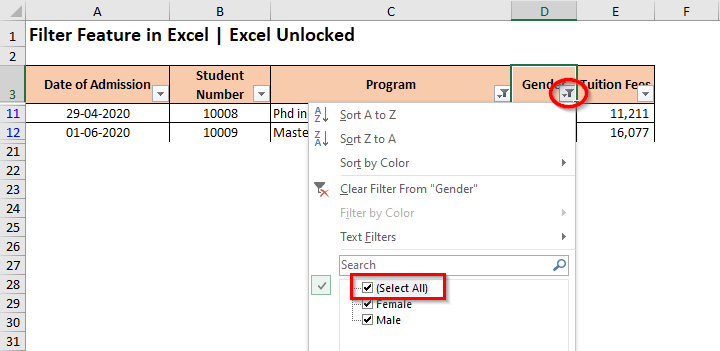
When you clear the filter from the column ‘Gender’, the data set would now only have a filter on the column header ‘Program’. It has only cleared filter from the row ‘Gender’ and has not touched any other filters.
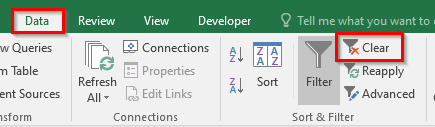
To clear multiple filter from all the headers cells, use any of the following way:
- Click on any of the cells in the dataset and navigate to the path – Data tab > Sort & Filter Group and there click on the option that says – Clear.
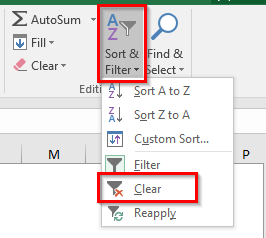
- Or you can even use this – Home Tab > Editing Group. Click the option Sort & Filter > Clear.
It is important to note that the above method only clears the filter from the header cell. It does not remove the filter icon from the header row. To learn how to remove the filter in Excel, wait until the end of this blog.
How to Filter Values or Text in Excel?
When you are working with text filters, there are many other text filter options available in addition to what we learned above. Below is the list of the same.
- You can filter the values or text which exactly Equals or which Does Not Equal to some text.
- Additionally, you can even filter for a non-exact match by using the Contains and Does Not Contain a text
- Or, you can even filter the values or text that starts or Begins With or Ends With a particular text.
These advanced filter options are available under the ‘Text Filter’ section of the Filter Window as shown in the image below:
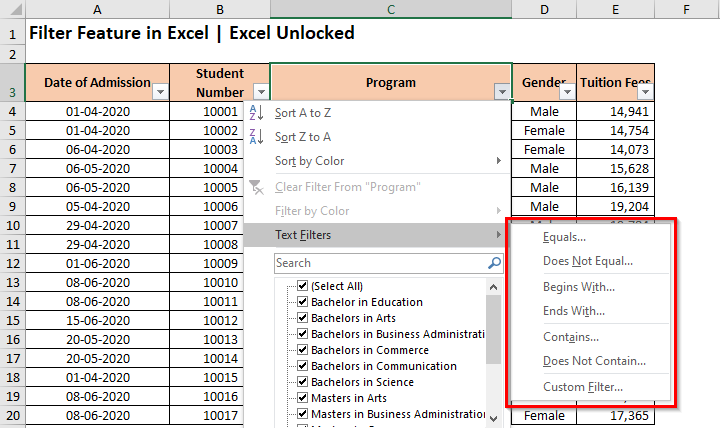
Let us understand this with the help of a small example: Let us, for example, get the program that contains the word ‘Business’ in it. To achieve it,
Click on the ‘Filter‘ icon on the column header – ‘Program’, and take your mouse cursor to the option – Text Filters.
In the list of options that come up, select the option that says – ‘Contains‘. As a result, the ‘Custom AutoFilter‘ dialog box would appear on your screen. In the input box besides the word ‘Contains’, write the text that you want to filter (in our case ‘Business’) and press OK.
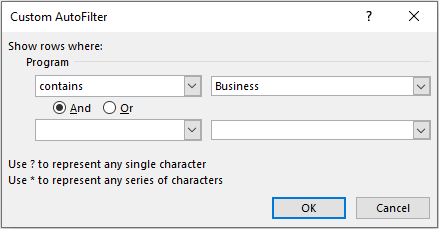
As soon as you press OK, excel would show all the values or text that contains the word ‘Business’ and will hide all other data rows.
Note that, just like Filter search box, this ‘Custom AutoFilter’ dialog box also accepts wildcard character search.
Filter Values based on Two Criteria
The Custom AutoFilter dialog box also allows us to filter out the data rows based on two criteria. Use the And and Or operator radio buttons based on how you wish to filter.
For example: Let us filter out all the programs for Commerce and Science. In this case, as we want both the values, we shall use Or operator, like this-
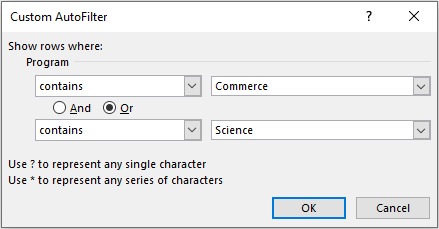
This would filter out those values which either contain the word ‘Commerce‘ or contain the word ‘Science‘.
How to Filter Numbers in Excel?
Similar to the text filter learned above, there are many additional filter options available carry Number Filters in Excel. Below is the list of the same:
- You can filter the exact number or amount by using Equals and Does Not Equal option under the ‘Number Filter’.
- Similarly, the Number Filter – Greater Than and Less Than allows us to get all values that are more or less than a specific value.
- Greater Than or Equal To and Less Than or Equal To works in a similar way.
- Between Number Filter allows you to filter out the values lies between two values (lower and upper values both inclusive)
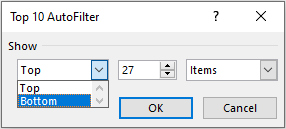
- Other options are – Top 10, Above Average, Below Average
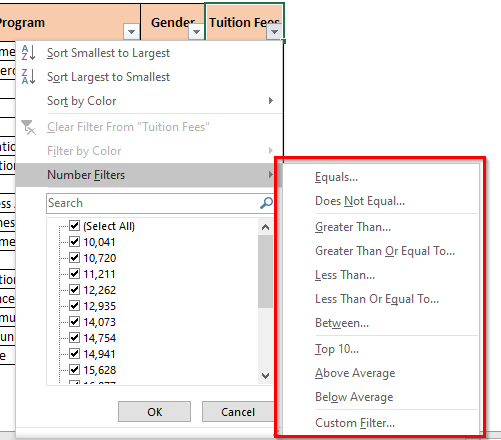
The filter option Top 10 does not exactly only mean Top 10 values. You can change it to any other value like Top 15, or Top 27 Values, and even Bottom 5 values and so on.
How to Filter Dates in Excel?
Unlike the Text and Number Filter, the Dates Filters option allows us with more advanced filtering options. The below image in itself is self-explanatory.
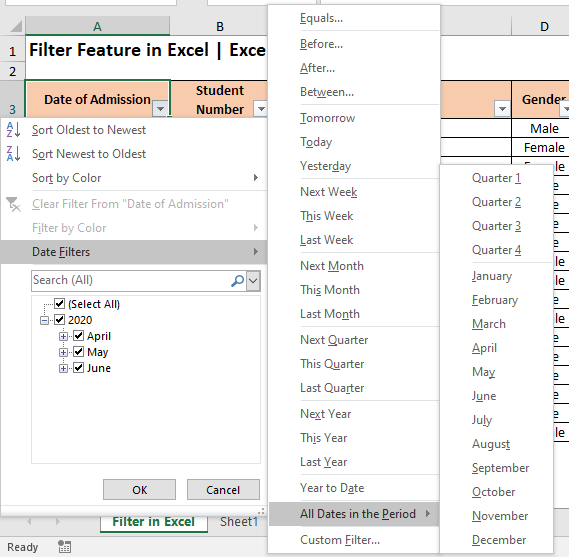
In a nutshell, below options are available for filtering dates in Excel –
- You can filter the dates which fall in the current month/week/quarter/year and even for previous and upcoming (i.e. next) month/week/quarter/year.
- Additionally, you can filter out by an exact date, or date that falls before or after a particular date, or between two dates.
- Excel provides with an option to filter all the dates in a particular month or quarter (regardless of the year in which it falls)
- You can create a custom date filter using the ‘Custom AutoFilter’ dialog box to which you are already aware of using.
Important to notice – Excel by default groups all the dates by year, months, and then the days. You can expand or collapse the groups (year, months, and days) to filter the dates and check/uncheck it to filter accordingly.
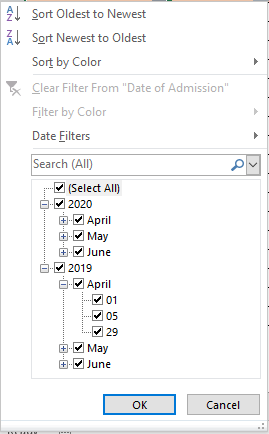
In the above image, you can see that all the dates are grouped by years first (2020 and 2019). Within the years there are months and then the days in the month. If you clear the checkbox for 2020, then the excel would only show the dates that lie in 2019.
How to Filter By Color in Excel?
When the data set contains any text with color or any cell with a background color, you can use the ‘Filter by Color‘ option in the ‘Filter’ Window to filter the dataset by a specific text or cell background color.
Let me explain this with a small example. I am changing the background color of different cells to yellow, orange, and green. Also, I have the font color in a few of the cells as ‘Red’.
To filter the values based on color, simply click on the ‘Filter’ drop-down arrow button on the header cell and take your mouse cursor over the option that says – ‘Filter by Color’.
As a result, you would see that excel lists all the cell and font color. You can choose the color that you want to filter with.

Let us, for example, filter the programs by Red font color. The result of the filter would be as below.
Quick Way to Filter By A Specific Cell’s Value, Font Color, Cell Color or Icon
Instead of using the ‘Filter’ drop-down icon to filter, you can even filter the dataset based on a specific cell’s value, icon, or font and cell color. To do so, follow the undermentioned steps:
- Right-click on the cell that contains the color by which you want to filter. Let us, in this case, filter by yellow color. Therefore, I have right-clicked on C4 (as it has a yellow cell color).
- Take your mouse cursor to the option that says – ‘Filter‘, and click on the option – ‘Filter by Selected Cell’s Color‘.
As a result, excel would filter the dataset based on the cell color – Yellow, as demonstrated in the below image:
A Solution To – AutoFilter Does Not Work After Changing Data
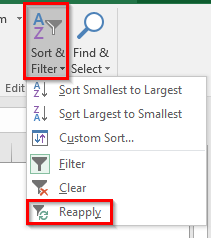
When you make any changes in the filtered data, you would notice that excel does not refresh the filter automatically. Yes, that is absolutely true. You need to reapply the filter in order to refresh the data and apply the filter on the changed data. There are a couple of ways to do the same, as listed below:
- Using Filter Window – After making changes in the filtered data, simply click on the ‘Filter’ drop-down arrow on the header cell and click ‘OK’ in there. However, there is are exceptions to this method. This would not work when you apply ‘filter by color’ or ‘Number Filter/Text Filter/Date Filter’. This technique only applies when you use the search box to filter out the data.
- Using Reapply Option – After making changes in the filtered data, simply navigate to the Data tab > Sort & Filter Group > Reapply Option. The keyboard shortcut key for the same is Ctrl + Alt + L.
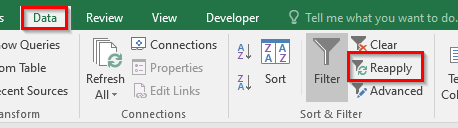
This option is also available in the Home Tab > Editing Group > Sort & Filter Option > Reapply.
Copy and Paste only Filtered Data in Excel
There are two possibilities to copy and paste only filtered data in Excel.
Copy and Paste Filtered Data Including Header Row
Simply, click on any of the cell in the filtered area, and press Ctrl + A to select the entire excel table or data set. As a result, you would notice that excel selects the entire table including both data rows as well as the header row. Now, press Ctrl + C to copy the selection and use Ctrl + V at the destination location to paste the filtered data cells.
Copy and Paste Filtered Data Excluding Header Row
To copy and paste only filtered data (without header row), select the top-left cell of the data (which in our case it is C4). Press keyboard keys Ctrl + Shift + Down_Arrow and then press Ctrl + Shift + Right_Arrow (instead you can even use Ctrl + Shift + End). Any of these ways would select the entire data set (excluding headers). Now, use Ctrl + C to copy the selection and then Ctrl + V to paste the filtered data set at the destination cell.
Usually, when you copy the filtered dataset using the above methods, excel does not include the hidden rows in the copy area. The hidden rows are excluded and it only takes the visible rows while copying. However, sometimes when your data is huge, it may not work in expected behavior. In those cases, to play safe, you can use the GoTo (F5) > Special > Visible Cells Only feature to select only the visible rows. The keyboard shortcut for the same is Alt + ; (semi-colon).
Finally, let us now learn how to remove filters from the excel header row. There are multiple ways using which you can remove filters, as listed below-
- The easiest way is to use the keyboard shortcut – Ctrl + Shift + L.
- Another way is to use ribbon path – Data Tab > Sort & Filter Group > Filter option OR Home Tab > Editing Group > Sort & Filter Option > Filter Option.
RELATED POSTS
-
How to Make A Table In Excel – A Hidden Functionality
-
How to Sort a Table or Data in Excel
-
Text and Number Filter in Pivot Table in Excel
-
Group and Ungroup Rows in Excel
-
FILTER Function in Excel – Dynamic Filtered Range
-
Applications – FILTER Function in Excel
How to Filter in Excel: Full Step-by-Step Guide (2023)
Working with large datasets in Excel can make it hard to find relevant information.
The filter tool offered by Microsoft Excel makes it easy for users to narrow down their data to find what’s relevant.
To learn more about the filter tool of Excel (both basic and advanced), jump right into the article below.
Also, as you scroll down, download our sample workbook for free here.
How to filter in Excel
The filter tool of Excel is a quick way to filter out the desired information only.
For example, the image below contains the sale data for some products.

1. Apply filters to this data by selecting the header of the column where the filter is to be applied.
2. For example, if you want to filter sales based on product name, select the header for products.

3. Go to the Data Tab > Sort & Filter > Filter.

Pro Tip!
There are two alternate shortcuts that you can use to apply filters to your data.
- Go to Home > Editing Group > Sort & Filter > Filter
- Use the keyboard shortcut to add filters – Control Key + Shift + L
4. This adds drop-down arrows to the selected column header (Products in this case).

5. The filter is already applied, and you can now use it to filter our information as desired.

Must note that to apply filters, your data must have a proper column header where the filter is to be applied.
Using the filter tool, you can apply filters based on numeric or text values, format, or by criteria.
How to filter by text
Can you quickly filter out the sales of Apples made during the period❓
Simple. From the list of products, filter out the text ‘Apples’. The sales of Apples would be automatically filtered.
1. Apply filters to the column of products as explained above.

2. Click on the drop-down menu to launch the filter options.
3. The filter tool shows all the items that appear in the selected column.

4. From these items, uncheck all others, except for ‘Apples’.

5. Click Okay, and you’re good to go!👍
6. Excel filters out the sales of ‘Apples’ only

Quickly applying the SUM function to this sale tells that the total sales for Apples were $2940.
To save time that goes into checking and unchecking items, type the desired text (Apples) in the Search bar above and press Enter.
How to filter by numbers
Next is filtering in Excel using numbers.
The AutoFilter tool of Excel allows you to filter data based on numbers in a variety of ways.
Check out the variety of options in the image below.

You can set up any parameter. Like filtering numbers that equal to say $1000 or are less / more than $1000 or whatever.
Alternatively, you can simply sort numbers in descending or ascending order.
In the above example, let’s apply a filter based on numbers. For instance, let’s filter out the sales that are equal to or less than $400.
1. Select the column for Total Sales and apply the filter tool to it.
2. Launch the filter tool by clicking on the drop-down arrow.
3. Go to Number Filters.

4. To filter out the sales that are equal to or less than $400, choose an appropriate parameter.

5. This launches the Custom AutoFilter dialog box.

6. Against the ‘Less than or Equal to’ tab, input the number ‘400.

7. Click Okay.
8. Excel filters the sales as follows.

Excel has filtered out sales that were only equal to or less than $400.
Multiple filters simultaneously
Can you apply filters to multiple columns simultaneously?
For example, for the above data set, what if we want to filter out sales for Apples that are greater than $800?
This takes two filters:
- Text filters to filter out sales for the Product ‘Apples’.
- Number filters to filter out sales of Apples that exceed $800.
No worries. It’s still a piece of cake. See below.
1. Apply filters to the Product column.
2. From the filter drop-down menu, select ‘Apples’ to filter out sales for ‘Apples’ only.

3. Click ‘Okay’ and Excel filters out the sales of ‘Apples’ only

4. Next, apply filters to the column ‘Total Sales.’
5. Launch the filter tool by clicking on the drop-down arrow against the column heading ‘Total Sales”.
6. Go to Number Filters.

7. To filter out the sales that are more than $800, choose an appropriate parameter.

8. This launches the Custom AutoFilter dialog box. Against the ‘Greater than’ tab, input the number 800.

9. Click Okay, and Excel filters the sales as follows.

There you go! The AutoFilter tool filters out the sales of Apples that exceed $800.
You can apply as many filters as desired at any given time.
Pro Tip!
How do you know which columns of your data have the filter applied?🙋♂️
Look out for the filter (funnel) icon in place of the drop-down arrow. All the column headers that have this icon have the filter applied.
How to clear filters in Excel
There’s an undo to everything you do in Excel.
After you’ve applied filters to data, the drop-down menu for that column header takes a filter shape.

In this example, we have applied the filter to the column ‘Products’ to filter out the sales for ‘Apples’ only.
1. To remove this filter, go to the filter icon of the relevant column.
2. Launch the AutoFilter tool.
3. Select the option “Remove Filters.”

4. Alternatively, Go to Data > Sort & Filter > Clear.

5. This removes the filter “Apples” applied to Products.

Excel now shows all the products (apples, oranges, and kiwi).
Also, note how the filter icon is now again replaced by the drop-down arrow.
How to remove filters entirely
In the above section, we’ve seen how to remove filters from a particular filter column.
But what if you want to remove filters from your data set entirely?
1. Select the data from where you want to remove filters.
2. Go to Data > Sort & Filter > Click Filter Button again.

This removes the AutoFilter from the data.
3. No more drop-down arrows.

Remember the shortcut to Apply Filters? Control Key + Shift + L.
Press these three keys together to apply filters. Press them again together to remove the filters.
Filter by color in Excel
You can also use the AutoFilter Tool of Excel to filter out specific cells based on their color.
For example, the image below shows the marks of different students.

There’s also a key to the right side that tells how the coloring is done.
Let’s filter out the students who’ve passed.
1. Apply filters to the column that has the highlighted cells.

2. Launch the filter tool. Go to ‘Filter By Color’ and select the color blue.
We have selected the color blue as the key shows that the students who’ve passed are highlighted in blue.

And there you go! Excel only filters the cells that are highlighted in blue.

Advanced Filter in Excel
As the name suggests, advanced filters go a step beyond AutoFilters.
Using the advanced filters tool of Excel, you can apply multiple filters to your data at once.
1. Taking the data below for sales of different products as an example.

2. Let’s filter out sales for Oranges where the Quantity sold was 5 or more.
3. This involves two filters: Oranges and Qty of 5 or more.
4. To apply the Advanced filter, copy and paste the relevant headers of your data to separate cells. Relevant headers in this case are “Products” and “Quantity”

5. Under each header, mention the filter criteria as shown below.

Under the Product header, we have mentioned ‘Oranges’.
Under the Quantity header, we have mentioned the criterion “>=5”
6. Go to Data > Sort & Filter > Advanced.

7. Against the List Range, select the data to be filtered.
8. Against the Criteria Range, select the formatted cells where the criterion is mentioned.

9. Hit Okay. Excel filters the data to show sales of Oranges of 5 or more units only.

Advanced filters allow you to apply many filters at the same time. It further allows you to filter data in its place or create a copy of filtered data to another destined place.
That’s it – Now what?
If you didn’t know about the filter tool of Excel yet, this guide is your savior.
We learned about filtering data based on text and numbers and colors in Excel using the Auto Filter tool. We also took a glance at the advanced filtering tool of Excel.
The filter and advanced filter tool of Excel will help you narrow down your data and pick out the relevant stats in an instant.
Especially, when used to assist other major functions like the VLOOKUP, SUMIF, and IF functions, it eases your Excel jobs by a thousand times.
Don’t know much about these functions? No worries.
Click here to sign up for my free 30-minute email course to help yourself learn these and many more amazing functions of Excel.
Other resources
If you enjoyed learning about AutoFilter and Advanced Filter in Excel, we bet you’d love to know more about the filter function and tools in Excel.
Check out our articles on data validation and creating data tables in Excel.
Kasper Langmann2023-01-19T12:15:20+00:00
Page load link


 .
.