This is a guest post by Vijay, our in-house VBA Expert.
Often I have thought, if I could have write “Select EmployeeName From Sheet Where EmployeeID=123” and use this on my excel sheet, my life would be simpler. So today we will learn how to do this.
People spend a lot of time thinking whether to use Excel as their database or not. Eventually they start using Access or SQL Server etc.
Today we will learn how to use Excel as a Database and how to use SQL statements to get what we want.
Excel as a Database – Demo
We will learn how to build this:
Before we begin:
- The entire sheet (where the raw data has been stored) will be referred as one single database table by Excel. This is very important to understand.
- This has nothing related with the in-built Table (2007 and greater) / List (2003 and previous) feature of Excel.
- If you know SQL (Structured Query Language) your task becomes much easier.
Setting up Excel as Database
We need some raw data and we will utilize Customer Service Dashboard sample database here.
Let’s get started.
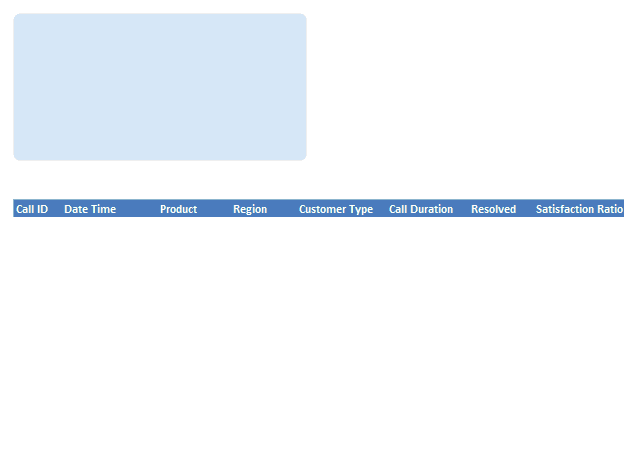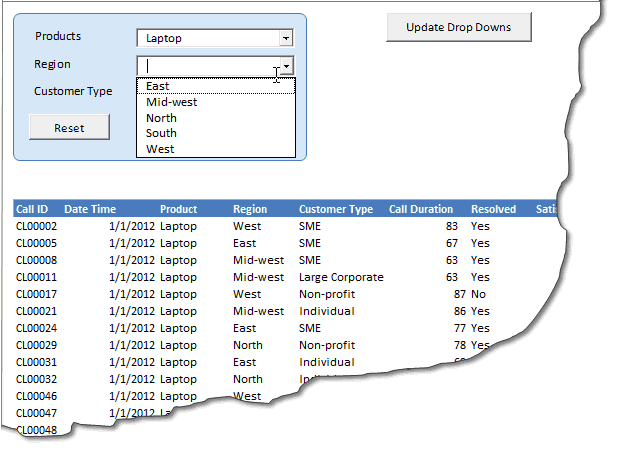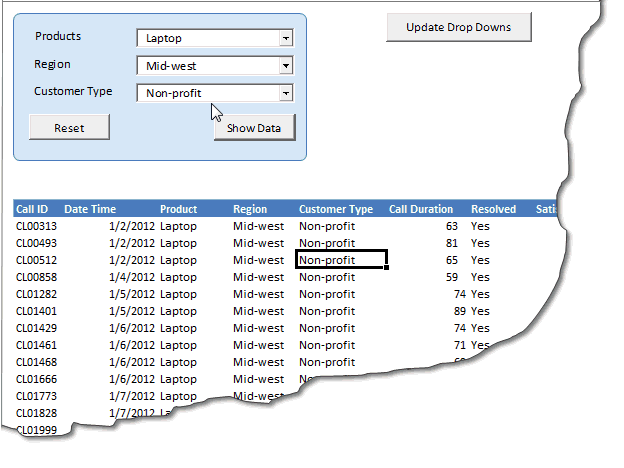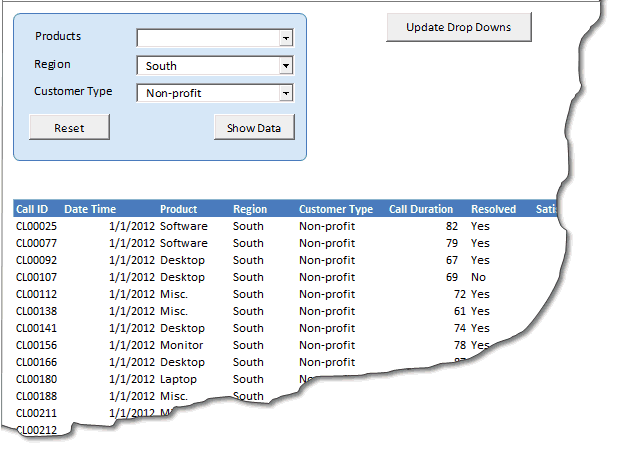
First we will design the structure of what all option we want to present for filtering the data, which you can see in the interface below.
Once the user clicks on Show Data we will use a SQL statement to filter-out the data as per the drop down options selected by the user and the put them in the table below.
We will also use another SQL statement to populate the top right hand side table for calls data when all the 3 drop downs have some options selected.
Adding Active-x data objects reference
We need to add a reference to the Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects Library to be able to use the worksheet as a database table. You can do this from Visual Basic Editor > Tools.
I usually select the most recent version, however if you are developing a product it will be best suited if you are familiar with the operating system and office version used by the end-user’s system and accordingly select the best version available.
Opening Excel as a Database
Once this is done we need to hit the road with some VBA code.
Public Sub OpenDB()
If cnn.State = adStateOpen Then cnn.Close
cnn.ConnectionString = "Driver={Microsoft Excel Driver (*.xls, *.xlsx, *.xlsm, *.xlsb)};DBQ=" & _
ActiveWorkbook.Path & Application.PathSeparator & ActiveWorkbook.Name
cnn.Open
End Sub
The above procedure is the heart of this post, this is where we define how to use the current Excel workbook as our database.
cnn.ConnectionString = "Driver={Microsoft Excel Driver (*.xls, *.xlsx, *.xlsm, *.xlsb)};DBQ=" & _
ActiveWorkbook.Path & Application.PathSeparator & ActiveWorkbook.Name
On this line, we define all the possible file extensions that we are allowed to create an Excel Workbook and then use as our database.
Let’s understand the code module
When you click on the Update Drop Downs button, the VBA code uses the “Data” worksheet as a table and then finds unique values for Products, Region and Customer Types and then populates them as ListItems for the ComboBox controls.
Example for Products drop down
strSQL = "Select Distinct [Product] From [data$] Order by [Product]"
closeRS
OpenDB
cmbProducts.Clear
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
cmbProducts.AddItem rs.Fields(0)
rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox "I was not able to find any unique Products.", vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Exit Sub
End If
What is important to notice here is how the Table and Fields have been identified using square brackets unlike traditional SQL where we just provide the name, also the table name has to be suffixed with a $ symbol at the end.
As I have suggested earlier, one entire sheet will be treated as one single table, so if you have multiple datasets that were currently organized within one sheet you may have to create multiple sheets to store that data to be able to use them as tables. This would also make maintenance of data easier.
Using Excel SQL to consolidate two sheets in to one
Many people ask, how to consolidate 2 or more sheets which have the similar data. Well I would have adopted this method and wrote a simple query as below.
SELECT ID, FirstName, MiddleName, LastName, Age, DOB From [Table1$]
UNION ALL
SELECT ID, FirstName, MiddleName, LastName, Age, DOB From [Table2$]
This would allow me to use both the sheets as one table and fetch all of my data into a new sheet.
Download Excel As Database Demo File
Click here to download the demo file & use it to understand this technique.
Do you use Excel as a database?
Do you also user Excel as your database? If yes please put in the comment below how do you use the same and what has been your experience. Leave a comment.
More on VBA & Macros
If you are new to VBA, Excel macros, go thru these links to learn more.
- What is VBA & Macros? Introduction
- Excel VBA Example Macros
- VBA tutorial videos
Join our VBA Classes
If you want to learn how to develop applications like these and more, please consider joining our VBA Classes. It is a step-by-step program designed to teach you all concepts of VBA so that you can automate & simplify your work.
Click here to learn more about VBA Classes & join us.
About Vijay
Vijay (many of you know him from VBA Classes), joined chandoo.org full-time this February. He will be writing more often on using VBA, data analysis on our blog. Also, Vijay will be helping us with consulting & training programs. You can email Vijay at sharma.vijay1 @ gmail.com. If you like this post, say thanks to Vijay.
Share this tip with your colleagues

Get FREE Excel + Power BI Tips
Simple, fun and useful emails, once per week.
Learn & be awesome.
-
218 Comments -
Ask a question or say something… -
Tagged under
advanced excel, database, downloads, Learn Excel, macros, screencasts, sql, VBA
-
Category:
Automation, Excel Howtos, VBA Macros

Welcome to Chandoo.org
Thank you so much for visiting. My aim is to make you awesome in Excel & Power BI. I do this by sharing videos, tips, examples and downloads on this website. There are more than 1,000 pages with all things Excel, Power BI, Dashboards & VBA here. Go ahead and spend few minutes to be AWESOME.
Read my story • FREE Excel tips book



Excel School made me great at work.
5/5

From simple to complex, there is a formula for every occasion. Check out the list now.

Calendars, invoices, trackers and much more. All free, fun and fantastic.

Power Query, Data model, DAX, Filters, Slicers, Conditional formats and beautiful charts. It’s all here.

Still on fence about Power BI? In this getting started guide, learn what is Power BI, how to get it and how to create your first report from scratch.
Related Tips
218 Responses to “Using Excel As Your Database”
-
Graham says:
Worst thing ever to do. Excel is as much a db as is Access.
Use excel as a spreadsheet and leave databases work to databases.
It’s bad enough seeing spreadsheets with multiple worksheets being used and screwed up by people without letting them think it’s a database.
Excel has a place in business just not as a db.
-
Ivo says:
In many companies DB people are usually overworked and everyone else is just stuck with large Excel data files that need to be manipulated. In such cases it’s unreasonable to expect people to wait until the DB person gets to their issue so managing the data in Excel is a good option.
-
Jeff «DrSynthetic» Wilson says:
Worst thing ever to do. Excel is as much a db as is Access.
Use excel as a spreadsheet and leave databases work to databases.
It’s bad enough seeing spreadsheets with multiple worksheets being used and screwed up by people without letting them think it’s a database.
Excel has a place in business just not as a db.>>>
I might have agreed with you thru Excel 2007 but since the advent of PowerPivot, Excel is as much a database as any other relational database. I suggest you read either Rob Collie’s book «DAX Formulas for PowerPivot or Bill Jelen’s Power Pivot for the DATA Analyst» (emphasis mine) This is a gamechanger-
arun says:
Hi.. i need to do a small project with two text boxes here i need to retrive and insert the data in database. here the database i need to use is Microsoft excel 2007…… can u explain me it by step by step procedure
-
-
Garouda Hanouman says:
I don’t like negative comments like that one, I must say!
If you like argue about the sex of angels, I would say that Access is not a bullet proof database either…
This is a great tutorial and it helps me a lot. I have two tables in Access, one with the provinces, districts and postal codes in Thailand. I added the second one with the tambon (subdistricts). The first has got 928 records, the second 7373 records. I want to keep only one table by writing the postal codes in the second table. This is a one shot action, so why should I modify my VB6/ADODB/SQL/MsJet programme for that purpose??? I am glad to use SQL instead of a ‘Find’ in VBA.
Thanks a lot Chandoo -
wXronXg says:
I totally disagree with you because I’ve been using Excel as a database for several years already. Access might be superior in handling and storing data, but, as in my case where my data are updated almost daily, and I need instant analyses (which are complex I should say) to monitor progress, Excel is the best way to go. Charts are also easier to create and update in Excel (my Access can’t even create a chart unless you copy paste it as an image!). I think it depends on the need or circumstances and nobody could conclude that a certain program should not be used for a certain task even if it has the capability. Also, this is an Excel and not an Access site…
Anyways, it is good to know that SQL could be used in Excel. I should really learn how to do it ASAP! As of now, I’m using the For… Next loop to search for a particular data in my macros which seem «UNawesome»! 🙂
-
Ben says:
I love that this is the first comment
No anyone reading this NEVER EVER EVER(!!!) USE EXCEL AS A ‘DATABASE’… EVER
-
Sam says:
Yea, tell that to my terrible IT dept, Graham.
I’m stuck using MS products. The company firewall uber restrictive and every request I’ve made for db server or server app has been denied.
I’m an engineer at a global company…my salary is in the low six figures. There is no way I’m gonna quit.
So…guess I’ll be making a ‘database’ with Excel while getting wildly overpaid for it.
-
-
Hey Chandoo is this taught at Excel School? Man, this is the awesomeness thing I had ever seen!
-
Excellent and thanks Vijay for providing such as an easy way to create DB using EXcel.
Ashwin
-
-
To save someone time, neither of these links work.
-
-
DaveG says:
Fantastic.
I use Excel as a ‘database’ but using more conventional (non-vba) methods so this is great.I agree with Graham, in so far as Excel is not designed to be a database and therefore you should keep its use to a minimum and make excel do what its best at, number and data manipulation, not data relationship management. However, on occasion it is very handy to use it in a minor way as a database instead of having to link different applications (which sometimes is not possible due to IT security policies) to achieve a result.
More articles like this are a must.
Thanks
Dave -
Great! What a coincidence? Only yesterday, I was searching for «database» in this site & did not get much information.
While I agree that Access is better used as a database, there are situations where we are forced to use Excel. Please write some more articles on databases. Thanks Vijay!
-
Thank you very much Vijay this is really creative work. I hope it will continue.
I have liked your teaching on vba class too. thanks again.
-
Gerard says:
I agree about the fact that Excel isn’t a database but I think it’s great. See practical use in a select numbers of situations. Use it wise I would like to say. Thanks for the information and I looking forward on more topics.
Regards
Gerard-
KHADIMHUSEN says:
I have seen excel file.
It seem it in nothing other than filter.
-
-
Jeff Weir says:
Good little demo. Note that the square brackets are only needed if your table or column name has a space in it. But I think its good practice to use them whether or not your table or column name has a space in it.
You can also use this character to do the same: `
For instance, you could remove the brackets from [data$] with and the query still works fine. But you could not remove the brackets from [Customer Type] because of the space, although you could use `Customer Type` in place of [Customer Type].
In regards of whether you should use Excel as a database, I don’t see why not. What’s worth pointing out is that you can also modify this approach to take data from just about any database and present it in Excel.
I’d be inclined to not hardcode the sheetname into this code. Instead i’d add this to both modules:
Dim sSheetName As String
sSheetName = «[» & Sheet2.Name & «$]»…and then replace all 11 instances of this:
[Data$]
…with this:
» & sSheetName & «
(including the quote marks) -
Uday says:
I have been using EXCEL as a front-end for managing data in Access DB. But could not find any easy way to manage the movement-between-records and other features that were available with VB6 «Data Control».
Is there anything equivalent available in EXCEL 2010?
Regards,
-
Vijay Sharma says:
@Uday,
The VB6 Data Control was built for such tasks and functionality. However there is nothing native within Excel to support this.
Could you specifiy what exactly you are after and maybe we can create something that would benefit everyone.
-
Uday says:
Thanks for the response Vijay. I have built a utility in EXCEL/Access for maintaining my Expense/Income as well as Investments in a consolidated form that always gives me up-to-date reports.
The data is obviously in Access and so is the «Master/Transaction Maintenance». What I have done is built the maintenance function using EXCEL VBA/Forms but you end up writing a huge code for all functions explicitly (add/modify/delete/view).
Wanted to know if there is anything available that can reduce this development time?Cheers,
-
Jeff Weir says:
Hi Uday. A very clever guy i’ve got to know called Craig Hatmaker has written a great Excel App to update an external database. It’s still a work in progress, but it’s very very clever, and there are some very good functions to allow you to modify the database that you could probably amend.
To quote from Craig’s own documentation:
There are times when Excel is perfect for manipulating data in databases. Examples include tariff/rate tables, journal entries, and employee time sheets. Excel also works well for maintaining simple lists like code files.Traditional approaches to leveraging Excel in data entry have end users key data into a formatted spreadsheet, save it to a shared directory, then run a server side program to check data, and if everything is okay, update the database. This approach has multiple objects on different platforms involved in a single task complicating development and maintenance. In addition, validation results are delivered well after entries have been made frustrating end users.
A better approach, in my opinion, is to put that same validation and update logic from the server program into the Excel entry sheet so there’s just one object to maintain. This has the additional benefit of providing end users with immediate feedback as to the validity of entries.
Though this App specifically updates the Employee 2003 table in Microsoft Access’ demo database, Northwind 2003.accdb, the template can be easily modified for use with any database.
Craig tells me he’s happy for me to share the file with you. Flick me a line at weir.jeff@gmail.com and I’ll send you a link to the documentation as well as the access table and excel app he uses.
Also, check out Craig’s blog at
http://itknowledgeexchange.techtarget.com/beyond-excel/forward/
-
-
-
-
NARAYAN says:
Hi Vijay ,
Thanks.
Narayan
-
AnalysisParalysis says:
I agree with most of the comments. Never use Excel as a DB.
Use Access or another DB to handle all your data then just set up an odbc and use Excel to make pretty the data.
-
ADITYA says:
hi,
i hace ado 2.6 . i use windows xp and office 2007.
how can i find version 6.0.
regards
Aditya-
-
Fahmi says:
hi vijay, why when i change the combobox to call the data by date, it’s always say «data type mismatch in criteria expression». can you help me to solve this problem?
i think its because the date format, maybe
-
-
-
Susan says:
Vijay —
Thank you for giving those of us without a copy of Access the opportunity to keep progressing with Excel. Very good information!
Best-
Susan -
Devnath says:
Thanks, Vijay for posting on the topic use excel as database. I hope this has helped many of excel users.
-
Dave Thornton says:
Hi Chandoo,
I understand describing this technique as «using Excel as your database», for a lack of a better term. But it could be misleading. Excel makes for a poor database, but your article is not really bastardising Excel in lieu of a proper database as some may interpret. The main concepts in your article are about using ADO and the Excel ODBC driver. This technique applies whether you’re using a text file, SQL Server tables, or spreadsheets. Therefore, I look at it more like using Excel as your «data source». I think it would be valuable if you could explain that a little more so that people understand the context. This is a powerful and time saving technique, great for anyone’s arsenal, so it’s sad to see people make blanket statements against it. Although I do agree in principle that databases make better sources the majority of the time, there are valid reasons for using ADO and Excel in this fashion.
In addition, I hope people understand that you can also use query tables and list objects to accomplish the same. The added benefit is that you can record macros to get generic VBA code, don’t have to worry about references, and can also use MS Query to fine-tune your SQL if you’re not fluent.
Lastly, people should understand that there are significant caveats like how data types are determined or issues with complex SQL statements. I can get into my experiences with this if anyone wants more details.
-
Palek says:
This is great. When I download the Excel database demo I keep getting error. Is the demo not working for others too?
Thanks
-
Dave says:
It worked for me. I first downloaded it using «open» instead of «save» and I got errors. I looked at the code and the ado connection was referencing the spreadsheet from http://img.chandoo.org/vba… rather than my computer. I then saved the file to my desktop and ran it from there with no problems.
-
deb says:
can you explain how to change the code….i’m getting the same errors
-
-
José Lôbo says:
Hi, I just want to add those lines for use in the case your database has one or more field’s date (column), and you need to select data from a interval.
I think this is useful because SQL has many sintaxe’s variation and this works with VBA:dvenc1 = Format(Sheets(«View»).Range(«G6»).Value, «dd/mm/yyyy»)
dvenc2 = Format(Sheets(«View»).Range(«H6»).Value, «dd/mm/yyyy»)
dpago1 = Format(Sheets(«View»).Range(«G7»).Value, «dd/mm/yyyy»)
dpago2 = Format(Sheets(«View»).Range(«H7»).Value, «dd/mm/yyyy»)strSQL = «SELECT * FROM [data$] WHERE ([vencimento]» & _
» between #» & dvenc1 & «# And #» & dvenc2 & «#)»strSQL = «SELECT * FROM [data$] WHERE ([pagamento]» & _
» between #» & dpago1 & «# And #» & dpago2 & «#)»-
Mohammad hassani says:
dear José Lôbo
very thanks for your operational cods 🙂
-
-
Jay says:
Hey, I like this. This also has a practical side where the data will «eventually» end up in a true DB.
However, I have a question: I downloaded the sample file, and was unable to run it because the ado library wasn’t activated.
If this file was shared with others, would they also have to enable the component in excel? Is there a way to make this happen automagically(tm)?
Thanks
-
José Lôbo says:
Jay, I found the code below, that can automatic load/unload the library, if it has been installed in your machine:
‘Put in the module «This workbook»
Private Sub Workbook_Open()
MsgBox «Oi, obrigado por carregar a Biblioteca», vbInformation, «JFLôbo»
‘Include Reference Library
‘Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects 2.8 Library
On Error Resume Next
ThisWorkbook.VBProject.References.AddFromFile «C:Program FilesCommon FilesSystemADOmsado15.dll»
End SubPrivate Sub Workbook_BeforeClose(Cancel As Boolean)
‘remove ADO reference
Dim x As Object
n = Application.VBE.ActiveVBProject.References.CountDo While Application.VBE.ActiveVBProject.References.Count > 0 And n > 0
On Error Resume Next
Set x = Application.VBE.ActiveVBProject.References.Item(n)
y = x.Name
If y = «ADODB» Then
Application.VBE.ActiveVBProject.References.Remove x
End If
n = n — 1
LoopEnd Sub
-
Jay says:
awesome, thanks.
I also found that I can enable all the «ADO» libraries back to some point, say 2.6, and order their «priority» and save the document. They will show as «missing» if you look in your references, however the code will still run. Seems the original attempted to load 6.0, which I didn’t have. Now, with the others specified, it eventually found one that worked. in other words, the reference was actually saved with the file and automatically loaded, I just didn’t have it.
-
Mick C says:
I’ve never seen a better way to use Excel as a database than via Laurent Longre’s Indirect.ext function. Set up multiple Excel spreadsheets, populate the data, then consolidate them without opening them — I’ve used it many times and it’s fool-proof…no need for VBA, just using your brain for the data analysis piece afterwards.
-
Daniel says:
I tried to modify the query to Select based on [Date Time] and encountered the following error when click on Show Data
[Microsoft][ODBC Excel Driver] Data type mismatch in criteria expression.This could be due to restriction where the value has to be a text value instead of Date Value.
Any suggestion how to overcome this?
Many thanks to Vijay for this fantastic post
-
José Lôbo says:
On a post above, dated (04/09), I gave an example of selecting dates into an interval. Dates are on their right format on the cell.
-
Ankita says:
HI Vijay ,
Thank for posting this thread. I used the excel sheet and ammended it according to my data. Now the problem I am facing is that when I run the Update drop down button I am getting error [MICROSOFT][ODBC Excel driver] Too few parameters. Expected 1 in the line rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic. can u please help me out on this .
-
Vijay Sharma says:
Hello Ankita,
Your SQL statement needs to be looked at. You may send me the file at sharma.vijay1@gmail.com to look at.
~VijaySharma
-
Ankita says:
I have mailed you the file. Please take a look. Thanks 🙂
-
Jim says:
I really am intrigued by this article, however I keep crashing the program when I save it. I tried the solution from Jose and am still getting the same errors. The errors are below:
Your changes could not be saved to ‘Excel_As Database-demo-v1.xlsm» because of a sharing violation. Try saving to a different file.
When I try to save it to another file, I get the message: «The file you are trying to open, ‘791CF000’,is in a different format than specified by the file extension. Verify that the file is not corrupted and is from a trusted source before opening the file. Do you want to open the file now?»
I saved it as a new workbook and the same errors appear.
Any thoughts would be greatly appreciated.
Thanks in advance for your help
-
Jurgen says:
Hello Jim and Vijay,
I have the same problem. I have downloaded the demo file. When i change something in the data sheet and just click on the update dropdown button. It’s not possible to save the file any more.
Its give me the same error Your changes could not be saved to ‘Excel_As Database-demo-v1.xlsm” because of a sharing violation. Try saving to a different file.
Is there already a sollution for this problem.
-
M Yudha Tristianto says:
try this
cnn.ConnectionString = «Driver={Microsoft Excel Driver (*.xls, *.xlsx, *.xlsm, *.xlsb)};DBQ=» & _
ActiveWorkbook.Path & Application.PathSeparator & ActiveWorkbook.Name & «;ReadOnly=false;»
-
-
-
Conrado Natac says:
Hi Vijay,
I was wondering if you can help me. I tried to use a variable on my sql statement and it keeps getting an error.
Can you help figure out the problem.
Dim xtype As String
‘this is the invoice type
xtype = «I»closeRS
OpenDBstrSQL = «SELECT * FROM [data$] WHERE [data$].[Type] = » & xtype _
& » and [data$].[Cust #]='» & cmbcustno.Text & «‘»closeRS
‘this is the connrection
OpenDB‘this is the error
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
Thanks a lot.
Conrad
-
Martin says:
strSQL = «SELECT * FROM [data$] WHERE [data$].[Type] = » & xtype _
& » and [data$].[Cust #]='» & cmbcustno.Text & «‘»you probably need to encase the xtype variable in single quotes
try….
WHERE [data$].[Type] = ‘» & xtype _
& «‘ and
-
-
-
-
Chris says:
Technically this provides database like query facilities. It’s not providing database capability in excel, as a spreadsheet is incapable of being a database. A spreadsheet has no concept (or ability to represent) tuples and relationships between data with primary indexes. But then most people at work don’t see any difference at all, and call a spreadsheet a database and vice-versa…happily introducing data anomalies along the way. It has been estimated that 95% of spreadsheets in workplaces contain errors…so treating a spreadsheet as a database is just one more problem of technology in hands of the litte trained.
I must say i’ve seen some doozy formulas and spreadsheets, both the WTF kind and the kind where an inordinate amount of time and money was spent to create a spreadsheet, where something else would be much better and way more efficient. spreadsheets are not scripting languages and herendous formulas get created when scripting language should be used instead. but never mind.
keep up the good work people, teaching the good stuff.-
Jay says:
Agreed,
However, you are assuming that, when a DB is needed, one is actually available to the user. Many times this is not the case, and the data for the spreadsheet is actually required to be contained in the spreadsheet itself. I happen to be in this boat. I would much rather use proper tools for the job, they just aren’t available. This is much better than just «well, can’t be done.» Even more so, this is more like using a Ball Peen hammer when what you really need is a framing hammer. Rather than say, using a pipe wrench. At least is’t in the same family. It won’t be as effective, but it’s not a complete hack (like many of the examples you cite)
-
-
Jeff Weir says:
People…check out Microsoft’s addin for Excel called «PowerPivot».
PowerPivot for Excel is an add-in to Excel 2010 that provides the foundation to import and combine source data from any location for massive data analysis on the desktop, including relational databases, multidimensional sources, cloud services, data feeds, Excel files, text files, and data from the Web.
The data that you add to the workbook is stored internally, as an embedded PowerPivot database inside the .xlsx file.
From a user perspective, key points are:It allows data people to quickly create mashups of disparate data source on the fly – including web data, text files, datawarehouse files, and excel tables – and serve it up as a pivottable.
It extends the capability of Excel 2010 so that users can crunch, filter, sort millions of records with very low overhead, as well as incorporate both relational and non-relational data sources easily into analysis, using an interface they are already familiar with.
It can be programmed with SQL or DAX, but users don’t need to write SQL or DAX queries in order to use it (although they can if they want). Behind the scenes, Powerpivot creates OLAP cubes, and draws heavily on components of SQL Server to do this, but no istall of SQL Server is required.
This addin extends the capability of Excel so much that it might well remove the organisational need for some of the other apps in some cases (such as SAS) and make their licencing costs disappear.
Given Excel would be most organisation’s most widely used/deployed tool, and that this free add-in is the most significant advancement in Excel in the last decade, I think this would raise the bar on what your average analyst could do, and lower the total cost of doing it.
Further benefits of the add-in listed at http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee210644.aspx-
Jay says:
Yes, I’ve been eyeing the PP plugin for some time now. Our corp won’t be migrating users to 2010 for some time though….sigh. At least it gets us time to req an sql server though. basically this technique will allow me to get much of the dev work framed before the sql server goes up, then eventually replace it with the pp plugin.
-
-
umesh says:
My computer doesn’t have Microsoft Activex Data ovjects 6.0 Library so how to get this
-
Vijay Sharma says:
Hello Umesh,
What is the operating system installed on your system. This version is available from Windows Vista onwards.
Vijay Sharma
-
-
Jay says:
Now, if I could just get an example of «filtering» data, without using a pivot table, that supports multi-select filters. Vijay? got a slick solution? right now I am copying filter settings via vba to multiple pivot table, and it’s crap, slow, and more crap. I did something with some named ranges and checked boxes…it was okish
-
Jeff Weir says:
Jay — can you elaborate a bit more about what you are trying to do? I’m developing an add-in so that users can very easily filter any existing pivottable QUICKLY based on a named range i.e. «Filter pivottable A based on all the entries in range B». I’m doing this because i’ve noticed that users spend significant amounts of time manualy filtering pivottables so that they match items in another data set.
One problem with filtering pivottables is there might be tens of thousands of pivotitems in any one field, so iterating through them can take significant time. That said, I’ve found a very smart way to iterate through them, plus am developing another approach where I don’t have to iterate through the collection at all.
However, for pivotfields with tens of thousands of items, filtering them with SQL will always be quicker.
-
@Jay
In addition to Jeff’s comments I often will do a pre-filter first using an Advanced Filter to get rid of the bulk of non-important data
Then run the Pivot table on the filtered data
-
-
Jay says:
yes, the problem is: I have a large set data sets (say that fast five times!) with about 8 common fields. The powers that be want to be able to filter on about 6 of those at any given time. MOST of the filters are restricted to about a dozen or so, however there are a few that number closer to 100. and of course, they want:Ability to multi-select, all pivot filters linked to a master filter. I’ve used a variety of vb and other techniques to link the filters, but of course copying those 100ish items to 6-10 other pivot tables ultimately is time consuming. I’d much rather use this sql technique, but I don’t know how to support the multi-select. I have done it in the past by using the pivot_change event, duping all the filter settings to a table, then using a formula in the data for each table to set «in scope». that filter setting is pre-set to «true» for all pivots, and hidden. its better, but not good. The most efficient i have done is to put the data for each of the «100ish» into separate tabs, use sum-ifs on the main page, and move «out of scope» tabs outside the sum-if tab range, again a kludge (but surprisingly the fastest method) I think I could apply this method using a tree-view control as the input(s) rather than a select box… In reality, we shouldn’t be using excel as our presentation layer, but alas, we are!
-
Jeff Weir says:
@Jay they want [the] ability to multi-select, all pivot filters linked to a master filter. If they have Excel 2010, then slicers are a damn easy way to do this — assuming all pivots run off the same cache. (That said, there’s a way around that that I want to try out). Otherwise, Debra has some code at http://blog.contextures.com/archives/2012/01/03/change-all-pivot-tables-with-one-selection/ that may help (although it might take significant time to iterate through each pivottable and each pivot field, and each pivotitem)
I don’t know how to support the multi-select Sound’s like a simple WHERE IN clause would do the trick.
Can you post a sample spreadsheet somewhere for me to have a look at?-
Jay says:
Yes, I’d love for them to move to 2010, then I’d go with the Power Pivot plugin and move the data to an sql server that we should be getting soonish. I have used the code you linked, or a variant. It’s slow, but works. I actually use a different «hack» I have found a little faster for large filter sets, but it’s not pretty. I have been looking at this method. I like it, since 2 of the large filters are interdependant (depending on what is set on 1, I can reduce the second filter choices significantly) I just need to figure out an elegant way to do multi-select. I think I have. I can, in theory use a TreeView control. The ListBox control with mulit-select also might work well, particularly for the «non-interdependent» filters. Then build up the SQL, probably with an «Apply» button. I’ll let you know if I get it to work well.
-
-
HI,
I am a novice on excel vba, i used to complete the task whatever assigned to me by searching google, on searching i found this link and it is very very useful. The query which i got was in the attachment attached in this post the product field got some product related information but if i put Date in its place it didn’t filtered out!!. can you please advice how can it be achieved?? and also advice us how can we proceed the above function with only one key say date field alone(in this tutorial u used 3 keys). -
Bee_Boo says:
Hi,
i am completely untouched by programming (if you dont count in some classes many years ago), and my goal is to create stock database. For filtering of what i have in stock (and movements) i can use yours tutorial to filter out data i need to see, but what about adding new rows to data sheet? It is possible to do it in some kind of dialogue box?
Thanks for help. -
Vrunda says:
Vijay Sir
Like jim said on 24-04-2012 I am also getting same errors repeatedly with some Alphanumeric Name generated excel file… Is this due to using excel as database??
2) Will the data be lost if we use this code & will there be any problem to our computer for same….
Why this type of errors are coming ?? Please Clarify-
Vijay Sharma says:
Hello Vrunda,
Kindly share your workbook with me at sharma.vijay1@gmail.com to look at and figure out what is going wrong.
~VijaySharma
-
Jurgen says:
I have the same problem. I have downloaded the demo file. When i change something in the data sheet and just click on the update dropdown button. It’s not possible to save the file any more.
Its give me the same error Your changes could not be saved to ‘Excel_As Database-demo-v1.xlsm” because of a sharing violation. Try saving to a different file.Also the problem when you change something in the data sheet. click reset and click update dropdown button. than choose products and show data. Its giving me the old data. The database is not been reset or reloaded.
I found a workaround: Update the data sheet with your query than save close the file open the file and than update drop down.
Now you have the full functionality
-
-
-
Binu says:
Hi Vijay,
Can you provide me the VBA code to read from multilpe excel files to a single excel sheet
Thanks,
Binu -
Luis says:
Hi Vijay,
Thanks for sharing this work with us novices.
I have modifed the combo box names to suit my data table but get run-time error, type mismatch when update dropdowns button is pressed.Private Sub cmdUpdateDropDowns_Click()
strSQL = «Select Distinct [Card] From [data$] Order by [Card]»
closeRS
OpenDB
cmbCard.Clear
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
cmbCard.AddItem rs.Fields(0)
rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox «I was not able to find any unique Card.», vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Exit Sub
End If -
bong25 says:
Dear Vijay,
Really helps me a lot with this.
Could you help me how to add code for Manipulating Headings of Data.
What I was trying to achieve is aside from the sample data$ (say sheet1), I need to display datas from sheet2. The content and headings are not exactly the same.
In shot I need code to manipulate Headings from data that I was trying to view.
-
Sebghatulbary says:
Thank You very very very very very very very very very very very very very Muchhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh
its really excellent -
Abdalla says:
You are the best. I get so much out of your examples and explanations. I plan on signing up for your training in the next few months. But first I need some help for I project I a m working on. I have data tables in different tabs within the same workbook. How do I use VBA or other tools to get them to export the tabs as Access tables without leaving Excel? Assume no Access tables exist and that I have two scenarios for storing the Access tables:
1) I do this every month and want to keep the monthly access tables seperate.
2) I do this every month and want to update the same table.Thanks.
-
Hi Jijay,
I have learn so much from your demo file- Excel as Datase. I have motified the vba code to fit my dataset for my work. However, I run to the problem when I try to save the file after clicking the «Show Data» button. Its give me the same error «Your changes could not be saved to ‘Excel_As Database-demo-v1.xlsm” because of a sharing violation. Try saving to a different file. » I have seen other viewers post the same issue but have not found a solution be posted yet. Please advise how I can fix the problem? Thank you.
-
Cho7tom says:
Hello everyone,
Thank you for this method!
Any answer regarding Louis’s issue (posted on Sept 9th 2012).
I encounter the same pb (run time error 13 — type mismatch).
Best regards
-
Vijay Sharma says:
@Cho07tom and Louis, Please look for blank records in the column that you are getting as a result of the SQL query, this is causing the issue. Please try the below code
strSQL = "Select Distinct [Product] From [data$] Order by [Product]"
closeRS
OpenDB
cmbProducts.Clear
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
If Not IsNull(rs.Fields(0)) Then cmbProducts.AddItem rs.Fields(0)
rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox "I was not able to find any unique Products.", vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Exit Sub
End IfLet me know if you need any further assistance.
~VijaySharma
-
Cho7tom says:
Hello Vijay,
It perfectly works!
Many thanks for your help.
Regards,
cho7tom
-
kshitiz says:
I keep getting the error ODBC does not support the requested parametes error -2147217887 at the line
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
-
-
-
Old Fogey says:
Am trying to use this method in my workbook.
The example book works fine.
When I change to my own book, however, I get a 446 when it is executing the cnn.ConnectionString line in the OPENDB sub.
I have selected the activeX library in the references.
Any ideas ?
-
Old Fogey says:
Please ignore the post I made — it is resolved now.
-
-
Old Fogey says:
Using SQL in Excel — how do I address the columns in a sheet without giving each column a name ?
For example, I need to select the 3rd and 4th columns of a sheet and do not want to give them a name ( as the sheets are from read-only work books which do not have named columns )
I have tried «Select c,d…» which does not work.
-
Vijay Sharma says:
@Old Fogey,
In that case the first row is treated as column headings.
~VijaySharma
-
-
I see a lot of people saying Excel shouldn’t be used as a DB yet they never say why. To me, it seems they just want to keep DB administration so complex that it becomes necessary to keep a DB admin on staff. Excel, is understood by a larger group of people and is more approachable.
Access sometimes creates unnecessary duplication with multiple references spread out on multiple tables whereas with Excel, a simple common reference allows for a leaner DB.
So, good on you Vijay to put forward that Excel can be used as a DB. As long as you can archive rarely used data and then have ability to retreive it, there shouldn’t be a problem. -
HEerten says:
Well, one reason to use Excel as a database is when your “user” bought a Home and Student version of Office. They don’t have Access to use as a database because it’s not included. I can’t tell someone to buy Access because they may not have the financial means to do so. So for a very, very simple and small database system (about 1500 records) Excel will do. It’s not as convenient as Access, but nevertheless useful….
-
gowrishankar says:
I am a non-computer background, am doing a research in medical(microbiology), i need a simple database with excel back end, can u send the details… my requirement is receiving sample and entering to the database with id number & date, oftenly i have to check with id number whether the id number received or not.
-
Jay says:
Sounds like you meant to say a simple database with excel Front End.
that said, if you have a small data set, you could just use an excel table (let’s call it TableMyMicrobeData to hold the data, and your charts or whatever (pivot tables?) would use as the source.Otherwise, since it sounds like you have office, you could use an access database and a data connection via MSQuery in excel. both have enough «visual» tools, you could complete your database-excel report without writing any code at all.
-
-
Sumit says:
Please Vijay,
can u be a little more step by step, as like in other tutorials on this site.
i am totally new to this SQL thing and whenever u try to make new database, as u did, or modify ur database, i am getting errors.jst need steps as how to modify basic names and if some1 want to add 1 more filter/search box
thank you.
-
Hi,
just to let you know Excel-to-database has become ‘Excel Database Task’s (EDT) and allows very easy Data Edit of a database Table from Excel.
Please see blog for new features:
http://leansoftware.net/forum/en-us/blog.aspx
Shortly to include drop down lists for relational data.
Thank you for the interest -
Bramley says:
Hi Chandoo,
I am new to totally new to VBA or any programming for that matter,
I am using Excel to do my Quotes and Invoices. In the same workbook, I want to start a database to show a history of quotes for the month/year, without losing any data. I would also like to possibly add a macro for when I print my quote, to only save the Quotation worksheet and not the whole file, but also update the database automatically.
The Database could also be used to pull information for invoicing purposes.
Would you require me to send through my workbook so you can get a better understanding of what I am talking about.
How would I go about doing this?
Your help will really be appreciated, Thanks. -
LAURA says:
Can i buy a template for this ss?
I have tried to create it, starting on the VBA and Macros stuff but couldnt even make a cell go red for some reason.
Thanks -
Zuber says:
Awesome Job. I have question.
in View sheet.
When it putts data on sheet starting from row 12.
What is the easiest way to Sort by column I then G.
Thanks a lot for sharing. -
afshin says:
Hi
My English is not my database. And therefore all its characters? Appear. What can I do? -
plz
help me….
My English is not my database. And therefore all its characters? Appear. What can I do? -
Bob Holmes says:
Is there any way to handle nulls within a SQL statement in Excel VBA ? It does not recognize the nz() function
-
Love this! In many of our systems and reports, we work with an OLAP database called Cognos TM1. Excel and TM1 Excel formulas are really the most common interface to that database.
Because of that and the fact that most of our work ends up being in Excel pages itself anyway, I can really see using this Excel as a Database functionality becoming really useful for so many posibilities. This also will finally allow us not to bring in yet a third application platform like Access or Oracle in our Excel Datamarts. -
kumar says:
I undersood the logic of connecting the sheets but i didnt understand how to build the second sheet i.e. view sheet…….
Please help me in building the second sheet…….. i have written the code as you said in this post but unable to get the file as u r showing in thi spost…
how to get the view part……. -
Garouda Hanouman says:
Thanks for this nice tutorial.
Hope you don’t mind if I make some remarks.I would highly recommend:
1. NO need of a module and above all NO PUBLIC variables, if there is another workbook with the same variables you’ll get an error!
Move your code from ‘module1’ to the sheet ‘View’ and declare the variable like this:
Option Explicit
Dim cnn As ADODB.Connection’ or Private…
Dim rs As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strSQL As String ‘ could be repeated at Procedure level…
2.Other changes:
Private Sub OpenDB()
Set cnn = New ADODB.ConnectionPrivate Sub cmdShowData_Click()
Set rs = New ADODB.RecordsetEach time you open a recordset, disconnect it. How many instances of the connection do you create???
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
Set cnn = Nothing ‘ disconnect the recordset and dispose the connectionAt each place where you exit a sub, dispose the recordset!
Set rs = Nothing ‘dispose the recordset
Exit SubStart using a discipline in programming that follows the OOP rules…
Hope it helps,Best Wishes,
Bernard
-
Garouda Hanouman says:
Another point:
You will see that the format is not the same, no $ sign after a few rows, different alignment…
This will help:
‘Now putting the data on the sheet
ActiveCell.CopyFromRecordset rs
‘Add this to have the same format
With Range(«dataSet»)
.Select
.Copy
End With
Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).PasteSpecial (xlPasteFormats)
Application.CutCopyMode = False’ clear the clipboard
Range(«dataSet»).SelectBest Wishes,
Garouda.
-
Garouda Hanouman says:
Well, I fear some people may get confused. I prefer to give the whole code here.
remark: remove module1Option Explicit
Dim cnn As ADODB.Connection
Dim rs As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strSQL As StringPrivate Sub OpenDB()
Set cnn = New ADODB.Connection
If cnn.State = adStateOpen Then cnn.Close
cnn.ConnectionString = "Driver={Microsoft Excel Driver (*.xls, *.xlsx, *.xlsm, *.xlsb)};DBQ=" & _
ActiveWorkbook.Path & Application.PathSeparator & ActiveWorkbook.Name
cnn.Open
End SubPrivate Sub cmdReset_Click()
'clear the data
cmbProducts.Clear
cmbCustomerType.Clear
cmbRegion.Clear
Sheets("View").Visible = True
Sheets("View").Select
Range("dataSet").Select
Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).ClearContents
End SubPrivate Sub cmdShowData_Click()
Set rs = New ADODB.Recordset
'populate data
strSQL = "SELECT * FROM [data$] WHERE "
If cmbProducts.Text "" Then
strSQL = strSQL & " [Product]='" & cmbProducts.Text & "'"
End IfIf cmbRegion.Text "" Then
If cmbProducts.Text "" Then
strSQL = strSQL & " AND [Region]='" & cmbRegion.Text & "'"
Else
strSQL = strSQL & " [Region]='" & cmbRegion.Text & "'"
End If
End IfIf cmbCustomerType.Text "" Then
If cmbProducts.Text "" Or cmbRegion.Text "" Then
strSQL = strSQL & " AND [Customer Type]='" & cmbCustomerType.Text & "'"
Else
strSQL = strSQL & " [Customer Type]='" & cmbCustomerType.Text & "'"
End If
End IfIf cmbProducts.Text "" Or cmbRegion.Text "" Or cmbCustomerType.Text "" Then
'now extract dataOpenDB
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
Set cnn = Nothing
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Sheets("View").Visible = True
Sheets("View").Select
Range("dataSet").Select
Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).ClearContents'Now putting the data on the sheet
ActiveCell.CopyFromRecordset rs
With Range("dataSet")
.Select
.Copy
End With
Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).PasteSpecial (xlPasteFormats)
Application.CutCopyMode = False
Range("dataSet").Select
Else
MsgBox "I was not able to find any matching records.", vbExclamation + vbOKOnly
Set rs = Nothing
Exit Sub
End If'Now getting the totals using Query
If cmbProducts.Text "" And cmbRegion.Text "" And cmbCustomerType.Text "" Then
strSQL = "SELECT Count([data$].[Call ID]) AS [CountOfCall ID], [data$].[Resolved] " & _
" FROM [Data$] WHERE ((([Data$].[Product]) = '" & cmbProducts.Text & "' ) And " & _
" (([Data$].[Region]) = '" & cmbRegion.Text & "' ) And (([Data$].[Customer Type]) = '" & cmbCustomerType.Text & "' )) " & _
" GROUP BY [data$].[Resolved];"OpenDB
rs.Close
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
Set cnn = Nothing
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Range("L6").CopyFromRecordset rs
Else
Range("L6:M7").Clear
MsgBox "There was some issue getting the totals.", vbExclamation + vbOKOnly
Set rs = Nothing
Exit Sub
End If
End If
End If
rs.Close
Set rs = Nothing
End SubPrivate Sub cmdUpdateDropDowns_Click()
strSQL = "Select Distinct [Product] From [data$] Order by [Product]"OpenDB
cmbProducts.Clear
Set rs = New ADODB.Recordsetrs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
Set cnn = Nothing
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
cmbProducts.AddItem rs.Fields(0)
rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox "I was not able to find any unique Products.", vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Set rs = Nothing
Exit Sub
End If'----------------------------
strSQL = "Select Distinct [Region] From [data$] Order by [Region]"OpenDB
cmbRegion.Clear
rs.Close
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
Set cnn = Nothing
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
cmbRegion.AddItem rs.Fields(0)
rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox "I was not able to find any unique Region(s).", vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Set rs = Nothing
Exit Sub
End If
'----------------------
strSQL = "Select Distinct [Customer Type] From [data$] Order by [Customer Type]"OpenDB
cmbCustomerType.Clear
rs.Close
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
Set cnn = Nothing
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
cmbCustomerType.AddItem rs.Fields(0)
rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox "I was not able to find any unique Customer Type(s).", vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Set rs = Nothing
Exit Sub
End If
rs.Close
Set rs = Nothing
End Sub
Best Wishes,Garouda
-
Garouda Hanouman says:
I noticed another potential issue.
The combo boxes are set as 0-fmStyleDropDownCombo.
Look at Properties, Style, in Design Mode…
This enables the user to add some item in the combo.
I would rewrite the Reset code like this:
Private Sub cmdReset_Click()
'clear the data
cmbProducts.Clear
cmbProducts.Text = vbNullString' in case a user wrote something
cmbCustomerType.Clear
cmbCustomerType.Text = vbNullString
cmbRegion.Clear
cmbRegion.Text = vbNullString
Sheets("View").Visible = True
Sheets("View").Select
Range("dataSet").Select
Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).ClearContents
Me.[C4].Select ' no visible selection
End SubBest Wishes,
Garouda
-
Deeksha Baluja says:
Hey Garouda Hanouman ,
Would you please please explain as to what is ME.[C4].SELECT
Thanks a lot in advance
-
-
Colin says:
Is there a way to solve the issue that prevents saving. I get a sharing violation if I try to save the file after making changes. Should I implement the database based on the comments from Garouda?
-
Colin says:
Garouda, your code worked and I can now save the file.
Thanks for posting it.
-
Garouda Hanouman says:
Hi Colin,
One possible reason is that the file is ‘read only’. What you have to do is to save it under another name.!One little change in the code: to avoid any problem, it would be better to replace
rs.close
by
If rs.State = adStateOpen Then rs.Close
at the end of the procedure
cmdShowData_ClickIndeed, if you do not select anything and click on the command button Show Data, it’ll generate an error.
Basically the program should have some safety features to prevent this.
I’ll made some changes in order to take that into account…
Another remark, I never declare variables at module level if I can avoid it. Declare them at procedure level each time you can. You will see that I send the connection to the OpenDB procedure By Reference ByRef.
There are two possibilities: ByVal or ByRef, ByRef is the default value in VBA and VB6, not in VB.Net anymore. In this case, only ByRef is possible. ByVal sends a copy of the variable to a procedure or a function where ByRef works like a pointer in C or C++. ByRef tells the programme where to find the object in the computer memory…
I’m going to copy the whole modified code again in a next post.
Try to click on ‘Show Data’ in my previous code, without selecting anything, and try it with the new code.Cheers,
Garouda
-
Garouda Hanouman says:
Here the modified code, more bullet proof…
Cheers,
Garouda
Do not forget to remove Module1 and replace the code in the sheet ‘View’ with this one:
Option Explicit
Dim niFlag As IntegerPrivate Sub OpenDB(ByRef cnn As ADODB.Connection)
'note the change between brackets ByRef cnn As...
cnn.ConnectionString = "Driver={Microsoft Excel Driver (*.xls, *.xlsx, *.xlsm, *.xlsb)};DBQ=" & _
ActiveWorkbook.Path & Application.PathSeparator & ActiveWorkbook.Name
cnn.Open
End SubPrivate Sub cmdReset_Click()
'clear the data
cmbProducts.Clear
cmbProducts.Text = vbNullString
cmbCustomerType.Clear
cmbCustomerType.Text = vbNullString
cmbRegion.Clear
cmbRegion.Text = vbNullString
Sheets("View").Visible = True
Sheets("View").Select
Range("dataSet").Select
Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).ClearContents
Me.[C4].Select ' more professional: the active cell is hidden...
niFlag = 0
End SubPrivate Sub cmdShowData_Click()
'it's always better to declare such variables at procedure level
Dim strSQL As String
Dim cnn As ADODB.Connection
Dim rs As ADODB.Recordset
If niFlag = 0 Then
MsgBox "Please populate the lists first - click on Update Drop Downs!", vbOKOnly + vbExclamation, "Excel and ADODB"
Exit Sub
End If
If cmbProducts.Text = vbNullString And cmbCustomerType.Text = vbNullString And cmbRegion = vbNullString Then
MsgBox "Select at least one item!", vbOKOnly + vbExclamation, "Excel and ADODB"
Exit Sub
End If
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
'create a new instance of the recordset
Set rs = New ADODB.Recordset
'populate data
strSQL = "SELECT * FROM [data$] WHERE "
If cmbProducts.Text "" Then
strSQL = strSQL & " [Product]='" & cmbProducts.Text & "'"
End IfIf cmbRegion.Text "" Then
If cmbProducts.Text "" Then
strSQL = strSQL & " AND [Region]='" & cmbRegion.Text & "'"
Else
strSQL = strSQL & " [Region]='" & cmbRegion.Text & "'"
End If
End IfIf cmbCustomerType.Text "" Then
If cmbProducts.Text "" Or cmbRegion.Text "" Then
strSQL = strSQL & " AND [Customer Type]='" & cmbCustomerType.Text & "'"
Else
strSQL = strSQL & " [Customer Type]='" & cmbCustomerType.Text & "'"
End If
End IfIf cmbProducts.Text "" Or cmbRegion.Text "" Or cmbCustomerType.Text "" Then
'now extract data
'create a new instance of the connection
Set cnn = New ADODB.Connection
'note that we have to add cnn
OpenDB cnn
'create the recordset
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
'dispose the connection and disconnect the recordset
Set cnn = Nothing
'DO NOT close the connection here as it'll close the recordset as well
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Sheets("View").Visible = True
Sheets("View").Select
Range("dataSet").Select
Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).ClearContents'Now putting the data on the sheet
ActiveCell.CopyFromRecordset rs
With Range("dataSet")
.Select
.Copy
End With
Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).PasteSpecial (xlPasteFormats)
Application.CutCopyMode = False
Me.[C4].Select
Else
MsgBox "I was not able to find any matching records.", vbExclamation + vbOKOnly
Set rs = Nothing
Exit Sub
End If'Now getting the totals using Query
If cmbProducts.Text "" And cmbRegion.Text "" And cmbCustomerType.Text "" Then
strSQL = "SELECT Count([data$].[Call ID]) AS [CountOfCall ID], [data$].[Resolved] " & _
" FROM [Data$] WHERE ((([Data$].[Product]) = '" & cmbProducts.Text & "' ) And " & _
" (([Data$].[Region]) = '" & cmbRegion.Text & "' ) And (([Data$].[Customer Type]) = '" & cmbCustomerType.Text & "' )) " & _
" GROUP BY [data$].[Resolved];"Set cnn = New ADODB.Connection
OpenDB cnn
rs.Close
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
Set cnn = Nothing
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Range("L6").CopyFromRecordset rs
Else
Range("L6:M7").Clear
MsgBox "There was some issue getting the totals.", vbExclamation + vbOKOnly
Set rs = Nothing
Exit Sub
End If
End If
End If
rs.Close
Set rs = Nothing
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End SubPrivate Sub cmdUpdateDropDowns_Click()
Dim strSQL As String
Dim cnn As ADODB.Connection
Dim rs As ADODB.Recordset
niFlag = 1
strSQL = "Select Distinct [Product] From [data$] Order by [Product]"
Set cnn = New ADODB.Connection
OpenDB cnn
cmbProducts.Clear
Set rs = New ADODB.Recordset
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
Set cnn = Nothing
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
cmbProducts.AddItem rs.Fields(0)
rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox "I was not able to find any unique Products.", vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Set rs = Nothing
Exit Sub
End IfstrSQL = "Select Distinct [Region] From [data$] Order by [Region]"
Set cnn = New ADODB.Connection
OpenDB cnn
cmbRegion.Clear
rs.Close
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
Set cnn = Nothing
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
cmbRegion.AddItem rs.Fields(0)
rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox "I was not able to find any unique Region(s).", vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Set rs = Nothing
Exit Sub
End If
'----------------------
strSQL = "Select Distinct [Customer Type] From [data$] Order by [Customer Type]"Set cnn = New ADODB.Connection
OpenDB cnn
cmbCustomerType.Clear
rs.Close
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
Set cnn = Nothing
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
cmbCustomerType.AddItem rs.Fields(0)
rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox "I was not able to find any unique Customer Type(s).", vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Set rs = Nothing
Exit Sub
End If
If rs.State = adStateOpen Then rs.Close
Set rs = Nothing
End Sub-
Michael says:
Garouda, Vijay, et al…
Funtionality with «bullet proof» code mod works great with updating multiple combo boxes with independent criteria. Unfortunately, I’m having a bit of dificulty trying to use the base code to sequentially update the combo boxes using criteria from the previously updated box.
My code:
‘————————————————
Option Explicit
Dim niFlag As IntegerPrivate Sub OpenDB(ByRef cnn As ADODB.Connection)
cnn.ConnectionString = «Driver={Microsoft Excel Driver (*.xls, *.xlsx, *.xlsm, *.xlsb)};DBQ=» & _
ActiveWorkbook.Path & Application.PathSeparator & ActiveWorkbook.Name
cnn.Open
End SubPrivate Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
End Sub
Private Sub Worksheet_Activate()
Dim strSQL As String
Dim cnn As ADODB.Connection
Dim rs As ADODB.Recordset
niFlag = 1
strSQL = «Select Distinct [CMD] From [data$] Order by [CMD]»
Set cnn = New ADODB.Connection
OpenDB cnn
Me.Cmb_CMD.Clear
Set rs = New ADODB.Recordset
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
Set cnn = Nothing
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
Me.Cmb_CMD.AddItem rs.Fields(0)
rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox «I was not able to identify Regional Medical Commands.», vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Set rs = Nothing
Exit Sub
End IfEnd Sub
Private Sub Cmb_CMD_Change()
Dim strSQL As String
Dim cnn As ADODB.Connection
Dim rs As ADODB.Recordset
niFlag = 1
strSQL = «Select Distinct [MTF] From [data$] Where [CMD] = ‘» & Cmb_CMD.Text & «‘ Order by [MTF]»
Set cnn = New ADODB.Connection
OpenDB cnn
Me.Cmb_MTF.Clear
Set rs = New ADODB.Recordset
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
Set cnn = Nothing
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
Me.Cmb_MTF.AddItem rs.Fields(0)
rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox «I was not able to identify Parent MTF(s).», vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Set rs = Nothing
Exit Sub
End IfEnd Sub
‘——————————————-The «Private Sub Worksheet_Activate()» operation is flawless. When I make a selection in the «Cmb_CMD» box, the «Private Sub Cmb_CMD_Change()» operation errors out with a «Run-time error ‘-2147217887 (80040e21)’: ODBC driver does not support the requested properties.» on the «rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic» line.
¿Qué pasa con eso?
-
Amit P says:
Michael did you got any solution to this code/Run-time error, if yes could you pls share it to me.
-
vicky says:
Hi Amit,
I am stuck in combine two tables » TableA and TableB»
I am trying select * from [TableA$] A,[TableB] B where A.id=B.id
Is this a right way..?
-
-
-
-
exceler says:
Needs to make littlle correction in source in case if you need to see all data: strSQL = «SELECT * FROM [data$] WHERE » instead use
strSQL = «SELECT * FROM [data$]» and move where to if statement
change.Plus it adds no value to excel filter.
This may be used when OR,Join functionality is needed from database.but MSquery muchmore dynamic and less cumbersome.-
Antonio says:
Exactly what part of the if statement does the WHERE go.
-
-
Marc says:
This is a great article as always and I think it could really help with a regular report I need to setup in work. Could you help by telling me how I could add a second table and link both using a unique identifier?
-
Mohammad hassani says:
hi Chandoo,
Many thanks for your efforts.
i use this cods in my project but i got a error when want to update combo boxes value Type mismatch as below:
Private Sub cmdUpdate_Click()
‘—————————-Updating Consignee Filds
strSQL = «Select Distinct [Client] From [data$] Order by [Client]»
closeRS
OpenDB
cmbConsignee.Clearrs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
cmbConsignee.AddItem rs.Fields(0) ==> type mismatche
rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox «I was not able to find any unique Consignee.», vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Exit Sub
End If
.
.
. -
Mohammad hassani says:
dear Garouda Hanouman ,
your last Cod don’t work i got error for line:
If cmbProducts.Text «» Then»
compiler error
syntax errorpls advise…
-
NairB says:
Fantastic tutorial
@Garouda Hanouman
I also have the same error with your alternative code when populating data:If cmbProducts.Text «» Then
-
NairB says:
I fixed it….
Code was missing operators. It should read….
If cmbProducts.Text “” Then
-
Tony says:
I still have an error when populating data:
If cmbProducts.Text “” Then
-
-
-
-
Mohammad hassani says:
again me!!
i just received below error can anyone help me to sorted it out?
[Microsoft][ODBC Excel Drive] the connection for viewing your linked Microsoft Excel worksheet was lost.
thanks.
-
Mohammad hassani says:
hi guys
all my last problem was sorted out now just have a question:
how we could show some of data on dataset on sheet view not all of data?
-
Deeksha Baluja says:
Hey Mohammad ,
could you please tell me , how did you manage to solve the Update dropdown problem ?
-
-
[…] ignorant when it comes to VBA so can someone point me at the right direction. Here’s the tutorial Using Excel As Your Database | Chandoo.org — Learn Microsoft Excel Online . What I need to apply it to my spreadsheet is a way to not only select from the dynamic lists, […]
-
Mohammad hassani says:
HI ALL
please help me how i could chose data between 2 date or after a date or before a date ?
thanks
-
Salim Talal says:
strSQL = «SELECT * FROM [data$] WHERE [Date Time] BETWEEN DateValue(‘» & sDate1 & «‘)» & » AND DateValue(‘» & sDate2 & «‘) AND [Product]='» & Me.cmbProducts.Text & «‘ AND [Region]='» & Me.cmbRegion.Text & «‘» AND [Customer Type]='» & Me.cmbCustomerType.Text & «‘;»
-
-
Frost says:
Hi,
I still find no difference between this demo of filtering and the normal filtering in excel, DATA > Filter. you get the same results, just in a different worksheet.
Can somone explain this to me please? -
SUMIT GUPTA says:
anybody can resolve my problem. i have a sheet and use filter on 6 rows out of 15 rows. in column a use some formula. but when i open the filter A cells amount will change .
my query is how to copy the filterd cell data and paste in same cells.
column A formula used subtotal(3,b$2:b2)
A B C
no. id count if
1 IN-1000048 1
2 IN-1000055 1
IN-1000056 3
IN-1000056 2
5 IN-1000056 1
IN-1000057 2
7 IN-1000057 1
8 IN-1000103 1
IN-1000157 3
IN-1000157 2
11 IN-1000157 1
IN-1000164 3
IN-1000164 2
14 IN-1000164 1
IN-1000182 2
16 IN-1000182 1
IN-1000215 2
18 IN-1000215 1
IN-1000240 2
20 IN-1000240 1AFTER FILTER
A B C
no. id count if
1 IN-1000048 1
2 IN-1000055 1
3 IN-1000056 1
4 IN-1000057 1
5 IN-1000103 1
6 IN-1000157 1
7 IN-1000164 1
8 IN-1000182 1
9 IN-1000215 1
10 IN-1000240 1PLEASE RESOLVE MY QUERY THANKS
-
Tope says:
Hi.
I’m having some problems with the code, I think it’s because i’m sitting on a Windows Server (2003). When i’m trying to update the Drop Down list i get this Error code (Can’t find project or library)
I also found out that i’m missig the:
Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects 6.0 Library, the latest version i have is
Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects 2.7 Library.is it possible to make the code work?
-
Tope says:
I solved it.
i forgot to uncheck the:
MISSING: Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects 6.0 Library
before i checked the
Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects 2.7 Library.
-
-
Vanessa Lambert says:
When I open the document to play around, it says that there is an error and needs to be de-bugged. Anyone know why the link is not working or what could be done to fix it?
Thanks!
-
afshin160 says:
HI.
how is ADOB , Delet ,update , insert support ? -
Dick Byrne says:
Vijay,
Just ran across your article and found it interesting. A few months back I had a situation that forced me to «learn by trying» the same basic technique. I have data in spreadsheets (very large — on the order of 90,000 rows). Needed to do some data conversions on some of the columns via a separate lookup spreadsheet (e.g. lookup ‘Business Unit’ in the big spreadsheet and create a column called ‘Dashboard Org’ based on a lookup table).Because the source data has so many rows, using an excel formula (actually several as there were multiple lookup tables involved) caused the spreadsheet recalc time to go through the roof.
Solved the problem using the ODBC Excel driver and some basic SQL. Yes, you can use SQL against an Excel workbook. In fact, you can do all kinds of good things via the ODBC driver — outer joins against multiple workbooks, using SQL’s scalar functions, etc.
Here is an example of SQL that joins data from 5 different workbooks into a single worksheet:
SELECT IMDATA.*,
BU.[Dashboard Org],
BU.[New CU] AS «Customer Unit»,
BU.[New Business Unit] AS «Business Unit»,
AG.[Reporting Group]
FROM (( SELECT IM.*,
FORMAT(IM.[Create Date/Time], ‘YYYY-MM’) AS «Month Opened»,
FORMAT(IM.[Service Restored Date/Time], ‘YYYY-MM’) AS «Month Service Restored»,
IIF(IM.[Service Restored Date/Time] IS NULL, NULL,
DATEDIFF(‘s’, IM.[Create Date/Time], IM.[Service Restored Date/Time])/3600.0)
AS «Hrs To Service Restored»,
IIF(IM.[Service Restored Date/Time] IS NULL, NULL,
IM.[Total Duration Hours]-
IIF(IM.[Service Restored Hours] IS NULL, 0, IM.[Service Restored Hours])-
IIF(IM.[Suspend Hours] IS NULL, 0, IM.[Suspend Hours]))
AS «SLA Hours»,
LOCTBL.[New Business Unit] AS «Location BU»,
SEV1.BU AS «Sev 1 BU»,
SEV1.[Responsible Party],
SEV1.[Service Area],
SEV1.[WK Cause Code],
SEV1.[ProblemShortDescription],
IIF(SEV1.BU IS NULL,
IIF(IM.[CI BU] IS NULL,
IIF(LOCTBL.[New Business Unit] IS NULL,
‘Unknown’,
LOCTBL.[New Business Unit]),
IM.[CI BU]),
SEV1.BU)
AS «Selected BU»FROM (( `C:UsersDickByrneDocumentsITO Customer ServiceBU MetricsBU Reports2013-08Source DataIncidents — ODBC v2.xlsx`.`Incidents$` AS IM
LEFT OUTER JOIN `C:UsersDickByrneDocumentsITO Customer ServiceBU MetricsBU Reports2013-08Sev 1 3 year Trend Analysis.xlsm`.`Data$` AS SEV1
ON IM.[Incident ID] = SEV1.[Incident ID] )
LEFT OUTER JOIN `C:UsersDickByrneDocumentsITO Customer ServiceBU MetricsReferencesDiv-CU-BU-Loc Name Mapping for 2013.xlsx`.`’Dell Location Codes$’` AS LOCTBL
ON IM.Location = LOCTBL.[Location-Name-+] )
) AS IMDATALEFT OUTER JOIN `C:UsersDickByrneDocumentsITO Customer ServiceBU MetricsReferencesDiv-CU-BU-Loc Name Mapping for 2013.xlsx`.`’BU Lookup$’` AS BU
ON IMDATA.[Selected BU] = BU.[Original Business Unit] )
LEFT OUTER JOIN `C:UsersDickByrneDocumentsITO Customer ServiceBU MetricsReferencesAssignee Group Alignment.xlsx`.`’Assignee Group Mapping$’` AS AG
ON IMDATA.[Assignee Group] = AG.AssigneeGroupWHERE (IMDATA.[Affected Item Name] NOT LIKE ‘Update%’) AND (IMDATA.[Severity Number] <= 4)
Pretty cool stuff!
-
Anand says:
Hello Vijay,
Thanks for posting this article. After reading this article, I successfully developed an excel based tool using ADO to analyse customer issues. I very much appreciate your time and efforts in writing the article and more importantly sharing the code in the Excel file.
This site is great. Great work! keep it up!!Anand
-
[…] also has a great guest post by Vijay – Using Excel As Your Database – on this subject. Igrore all the naysayers in the comments who say “Excel […]
-
Msquared99 says:
After looking at this article I have pondered the idea of storing the data in Access as a table then using Excel to extract the data as selected instead of building queries and reports in Access.
I already have a macro that pulls data from Access and places it into Excel. All I would have to do is modify a little.
Thoughts, ideas?
-
Mohammad hassani says:
hi
I received below error:
Run-time error ‘-2 147217906 (80040e0e)’:
[Microsoft] [ODBC Excel Driver]Invalid bookmark
and below line be highlighted:
ActiveCell.CopyFromRecordset rs
pls anyone help me to fix it.
-
Deb says:
This is an awsome article. This has solved many problems with out using access.
Thanks a lot
-
Amar Ranjan Das says:
Hi, I have gone through your code and application, it is really a great help!
I am trying to develop a application using the sql query where I need to execute the update query, but I am unable to execute the query,
My query is like as below,
strSQL = «UPDATE location_details$ SET [location_details$].[SCANR_ID]='» & scanr_id & «‘, [location_details$].[SCAN_CAPACTY]='» & scanr_capacty & «‘ WHERE location_details$.[LOC_ID]='» & locId & «‘ AND location_details$.[REG_ID]='» & region & «‘»
But I am getting some error like,
a) syntax error in UPDATE statement
b) How I will execute the update or insert queryplease help me.
Thanks in Advance
-
chris says:
I tried this and am getting a (run time error) the below error on line
Range(«dataSet»).Select
not sure what i am missing. any help will be much apreciated
can one of you help me resolve this?Run-time error ‘1004’
method ‘Range’of object’_Worksheet’ failedCheers
Chris -
Jeff Slavin says:
I used your code, but modified the OpenDB function to read from a separate data file workbook. Code worked great BUT…..
After the code runs, i close the connections (by calling the cnn and rs Close() functions) and then set both variables to nothing.
After that, if I go to the data file and try to open it, i get the ‘File In Use’ message and it says i can only open s Read Only. It appears that Excel thinks the data file is still in use, even though I’ve closed the connections.
Any thoughts or help?
-
Jeff Slavin says:
can you give an example of writing to the database (eg. using UPDATE sql command)??
-
Amit P says:
I have question here is with two columns one is Product and another is region and as far as data in both columns is concerned is basically Region and Product. For e.g. In Product column i have country names like Accessories, Desktop, Laptop and Misc and against same Product names I have region as East in Region column.
What I want : In combo box I want to populate region names (which is already done and works fine) and in 2nd combo box I want to populate Product names on the basis of region selection. for e.g. If I select region as East in my Combo box then my 2 combo box should get populated with only Product .i.e Desktop, Laptop, Misc.
-
Chris says:
Dear Vijay,
I encountered some errors. When i click «Update Dropdown List», error message pops up saying: «[Microsoft][ODBC Excel Driver] Too few parameters. Expected 1» and highlighted (rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic). Please help me with this problem. Here is my code.
strSQL = «Select Distinct [Classification] From [BookDatabase$] Order by [Classification]»
closeRS
OpenDB
cboSearch.Clearrs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
cboSearch.AddItem rs.Fields(0)
rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox «Can’t find unique classification.», vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Exit Sub
End If -
Dean says:
I also had the sharing violation error on my Windows 7 64 bit, but I have solved it by changing the database reference from MSDASQL to Jet:
‘ NEW WAY to connect:
Public Sub open_db()close_db
Set cn = New ADODB.Connection
With cn
.Provider = «Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0»
.ConnectionString = «Data Source=» & ActiveWorkbook.FullName & «;Extended Properties=Excel 8.0;»
.Open
End With
End Sub‘ BELOW IS THE *OLD* WAY (which generated the sharing violation)
Dim cn as ADODB.Connection
Set cn = New ADODB.Connection
With cn
.Provider = «MSDASQL»
.ConnectionString = «Driver={Microsoft Excel Driver (*.xls)};» & _
«DBQ=C:MyFolderMyWorkbook.xls; ReadOnly=False;»
.Open
End With -
Raymond says:
Hello,
I am new in VB, I can understand your program perfectly. I could not understand this dataset, could you please explain it to me?
Range(«dataSet»).Select
Thank you,
Raymond -
[…] Beyond Excel: VBA and Database Manipulation blog. Chandoo also has a great guest post by Vijay — Using Excel As Your Database — on this subject. Ignore all the naysayers and unbelievers in the comments who say «Excel shalt […]
-
rene says:
Hi,
i work with this amazing feature now for a while. but to make things work even better i do bitwise searches on marked categories. however, i can not get this to work in excel..
the where part hangs:«WHERE CAST([group_desc$].[category_id1] as UNSIGNED INTEGER) & 1 0;»
Any idea anyone? or is it just excel that does not like this.
Regards,
Rene
-
rene says:
sorry,
missing the there.. -
Adam says:
Hi all,
Love the database. Was able to moody it to suit my needs, but the workbook bloated into 33MB file size and runs slow, any suggestions? -
Public cnn As New ADODB.Connection
-
Sakthi says:
You can use excel as front end application and as well as Database.
Inserting new records, updating existing new records and data query as done from an application is very well possible in excel with vba and sql combined commands.
I have created very good Data entry applications using excel as frontend and database
Regards
Sakthi -
Rod Ayers says:
I wonder if someone could help me.
I am using SQL to query an Excel table to produce another table. Everything is fine, except there are two columns that have data, but will always be empty in the result set. One of the columns is text, the other has a value from a Data Validation list. There are several other columns with these characteristics that are returned just fine in the record set.
Any help would be greatly appreciated.
Thank you,
Rod -
Conrado Natac says:
This is a perfect example. I will look at this sample. Thanks for a good work. This is what I have been looking for.
-
ajaj says:
I keep getting the error ODBC does not support the requested parametes error -2147217887 at the line excel
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
-
-
ajaj says:
I keep getting the error ODBC does not support the requested parametes error -2147217887 at line
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
the full code is
Private Sub cmdReset_Click()
‘clear the data
cmbProducts.Clear
cmbCustomerType.Clear
cmbRegion.Clear
Sheets(«View»).Visible = True
Sheets(«View»).Select
Range(«dataSet»).Select
Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).ClearContents
End SubPrivate Sub cmdShowData_Click()
‘populate data
strSQL = «SELECT * FROM [data$] WHERE «
If cmbProducts.Text «» Then
strSQL = strSQL & » [Product]='» & cmbProducts.Text & «‘»
End IfIf cmbRegion.Text «» Then
If cmbProducts.Text «» Then
strSQL = strSQL & » AND [Region]='» & cmbRegion.Text & «‘»
Else
strSQL = strSQL & » [Region]='» & cmbRegion.Text & «‘»
End If
End IfIf cmbCustomerType.Text «» Then
If cmbProducts.Text «» Or cmbRegion.Text «» Then
strSQL = strSQL & » AND [Customer Type]='» & cmbCustomerType.Text & «‘»
Else
strSQL = strSQL & » [Customer Type]='» & cmbCustomerType.Text & «‘»
End If
End IfIf cmbProducts.Text «» Or cmbRegion.Text «» Or cmbCustomerType.Text «» Then
‘now extract data
closeRSOpenDB
rs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Sheets(«View»).Visible = True
Sheets(«View»).Select
Range(«dataSet»).Select
Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).ClearContents‘Now putting the data on the sheet
ActiveCell.CopyFromRecordset rs
Else
MsgBox «I was not able to find any matching records.», vbExclamation + vbOKOnly
Exit Sub
End If‘Now getting the totals using Query
If cmbProducts.Text «» And cmbRegion.Text «» And cmbCustomerType.Text «» Then
strSQL = «SELECT Count([data$].[Call ID]) AS [CountOfCall ID], [data$].[Resolved] » & _
» FROM [Data$] WHERE ((([Data$].[Product]) = ‘» & cmbProducts.Text & «‘ ) And » & _
» (([Data$].[Region]) = ‘» & cmbRegion.Text & «‘ ) And (([Data$].[Customer Type]) = ‘» & cmbCustomerType.Text & «‘ )) » & _
» GROUP BY [data$].[Resolved];»closeRS
OpenDBrs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Range(«L6»).CopyFromRecordset rs
Else
Range(«L6:M7»).Clear
MsgBox «There was some issue getting the totals.», vbExclamation + vbOKOnly
Exit Sub
End If
End If
End If
End SubPrivate Sub cmdUpdateDropDowns_Click()
strSQL = «Select Distinct [Product] From [data$] Order by [Product]»
closeRS
OpenDB
cmbProducts.Clearrs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
If Not IsNull(rs.Fields(0)) Then cmbProducts.AddItem rs.Fields(0)rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox «I was not able to find any unique Products.», vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Exit Sub
End If‘—————————-
strSQL = «Select Distinct [Region] From [data$] Order by [Region]»
closeRS
OpenDB
cmbRegion.Clearrs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOFIf Not IsNull(rs.Fields(0)) Then cmbRegion.AddItem rs.Fields(0)
rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox «I was not able to find any unique Region(s).», vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Exit Sub
End If
‘———————-
strSQL = «Select Distinct [Customer Type] From [data$] Order by [Customer Type]»
closeRS
OpenDB
cmbCustomerType.Clearrs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
cmbCustomerType.AddItem rs.Fields(0)
rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox «I was not able to find any unique Customer Type(s).», vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Exit Sub
End If
End Sub -
John Paulsen says:
Hello! I Wonder if there is a posibility to make the comboboxes dependent of each other. If you choose from the combobox Products, only Regions related to Products would show up in the combobox Regions and so on?
-
James says:
Hi! I think i’m wondering about the same thing as John. Is there a way of making the drop down boxes dependent of each other? For instance, when i choose a Region in the drop Down, only Products related to that region will show in the Products drop Down. If anybody had any ideas on how to do this, please share.
Best regards, a vba novice
-
Lisa Pereira says:
Hi ,
this is awesome , i love this site.. lots of information.. mine is a very simple question , its probably answered , but I cannot find a direct resource..
I use Excel as a DB by creating query’s with ADO vba and pulling from the Dbase.
i am pretty new to access but familiar with EXCEL vba..
is there a way i can use the same query’s and transfer the data to a new database i want to create in ACESS. how do i go about it? can someone advise or forward somewhere i can refer this ? -
Saket says:
I have a column in excel with values as number as well as string. The SQL query is somehow not fetching all the distinct records.. Can you help?
Select Distinct [Model] From [QueryData$] WHERE [Model] IS NOT NULL Order by [Model]Thanks,
-
Cruiser says:
Thanks Vijay! I also want to use Excel as a database for users who do not have a separate database program available to them. Can you please read the following scenario and give me your thoughts? I want to write a COM Add-In which will be installed on each user’s machine and is used to read from and write to the single database workbook (which resides on the server). The add-in will contain a user form. When the user form is filled out, I click the «Add» button which invokes the code to copy the user form data, activate the database, add the record to the database, update my workbook from the database (adding my new record and all other changes since I last updated my workbook), and close the database. It should only take a few seconds, but what happens if two or more users try to add a record at the same time? Sharing is not an option. Can my add-in contain a contingency that tells it «if the database workbook is being accessed by another user, stop the process but keep trying to access it until it becomes available, then open it and continue the process»? Maybe replace the message box “Database.xlsx is locked for editing by another user” with “Updating Database”? In my scenario, the database workbook is the only element on the server. It will only be used for data storage and retrieval, with the results being displayed and manipulated in each user’s personal version of the workbook (residing on their own machine). Is this doable?
-
Cruiser says:
I guess I’m the only one. Well, in the future, if anyone else is trying to create an excel «database» on a shared drive, check out http://www.cpearson.com/excel/WaitForFileClose.htm
If someone else is accessing your «database» on the shared drive, this code keeps checking until the file to closed, then opens it, adds or retrieves data, saves and closes it. I found it very helpful.-
Cruiser says:
«…this code keeps checking until the file IS closed…»
-
-
-
Conrado Natac says:
Hello Vijay,
i cant get this line of code to work.
I love this article that you wrote and am testing it.
Option Explicit
Public cnn As New ADODB.Connection
Public rs As New ADODB.Recordset
Public strSQL As StringPublic Sub OpenDB()
If cnn.State = adStateOpen Then cnn.Close
cnn.ConnectionString = «Driver={Microsoft Excel Driver (*.xls, *.xlsx, *.xlsm, *.xlsb)};DBQ=» & _
ActiveWorkbook.Path & Application.PathSeparator & ActiveWorkbook.Name
cnn.Open
End SubPublic Sub closeRS()
If rs.State = adStateOpen Then rs.Close
rs.CursorLocation = adUseClientEnd Sub
Private Sub cmbtest_Click()
xcustno = Sheets(«View»).Range(«O14»).Value
closeRS
OpenDBstrSQL = «SELECT * FROM ([data$] WHERE [data$].[Cust #]).value = xcustno»
closeRS
‘this is the connrection
OpenDBrs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
‘dispose the connection
Set cnn = NothingIf rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Sheets(«View»).Visible = True
Sheets(«View»).Select
Range(«dataSet»).Select
Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).ClearContents‘Now putting the data on the sheet
ActiveCell.CopyFromRecordset rsEnd If
‘dispose the recordeset
Set rs = NothingEnd Sub
-
Rajesh says:
I am copying 28000 rows with 8 columns using copyfromrecordset option. But it is taking lot of time to copy the data into excel more than 1 hour. I am not sure why this is running for this much time. Any one have any idea
-
Andre Poorman says:
Vijay,
I am using Excel as a database as you excellently show, but I am also trying to use temporary tables within the SQL code. I get an error. One suggestion I got was to put «SET NOCOUNT ON» and «SET NOCOUNT OFF» in the SQL statement but I now get the error:
‘Run-time error ‘-2147217900 (80040e14)’:
‘[Microsoft][ODBC Excel Driver] Invalid SQL statement; expected ‘DELETE’, ‘INSERT’, ‘PROCEDURE’, ‘WELECT’, or ‘UPDATE’Any thoughts?
-
-
A simple way is to use the powerful inherent feature of Excel —
Advanced Filter. I have outlined a basic set of vba code below that can be used to query an excel list / database. You have to set up a criteria range on your spreadsheet and define YourRange (excel database) and YourCriteria (query criteria).Sub Filter()
Dim List as Range
Dim Criteria as range
Set List = Range(YourRange)
Set Criteria = Range(YourCriteria)
With List
.AdvancedFilter Action:=xlFilterInPlace, CriteriaRange:=Criteria, Unique:=False
End With
End Sub -
Hasan says:
Thanks Vijay for sharing, great stuff.
Few years ago I had to create a portfolio selection interface, emulating Excel auto-filter. I used Advanced Filters with some code, but it was not as elegant as this (one sheet per dropdown + one control sheet).
It would be nice to have «communicating» dropdowns plus the (Select all) possibility (as in AutoFilter)
-
srinivas says:
Hi,I have one doubt in above example.If the records in which the sql query is fetching is having special characters,then what would be the output.
For example,
i have 10 records in the database sheet like abd’s,aws’q,xza’,qaws,étc….like that 10-15 records.
So,My question is how to fetch these records if i give same value(for ex:abd’s) in dropdown control.
Even if we try using regex/wildcard characters one record will not be displayed.
Try this and help me out guys……..
Thanks in Advance.-
Andrew says:
I had the same problem. First I used a data connection in Excel to run the SQL but found compatibility issues with Excel 2010.
I am now back to use ADO(DB) but changed the connection string to:
«Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0;» & _
«Extended Properties=’Excel 8.0′;» & _
«Data Source=» & ThisWorkbook.FullName & «;»
This does require ACE to be available.
Alternatively JET can be used instead of ACE but this cannot handle as much data.
-
-
yothin says:
if I add picture in each data (hyperlink or comment), how to show that data with picture??
-
Mike says:
Where I work the government will not allow us to use MS Access due to some security reasons. We have had our only other database software available for us to use without paying a developer removed…I won’t go into the reason as it upsets me.
Anyway, we have operator logs that are now filled out on a Word document, and then they save each individual document. Well with 3 shifts a day this is a lot of documents and if you want to go back through them to find something, or trend data you have a lot of $&!+ to sort through….SO, I have made the document save the data in an Excel workbook using ADODB in VBA. Then the data is in a spreadsheet for us to query and trend to our hearts delight. If i want to go back to see a particular log I can then retrieve the desired data and populate the Word document.
No this is not ideal, but is a work around as it takes this place years to get around to giving us new software, or we have to pay a third party developer a load of money.
The only issue I have is in the comment fields. The recordset fields won’t allow for more than 255 characters. I’ve tried changing the datatype using the ALTER TABLE method, but no luck…so far.
Anyway, I am for the most part successfully using Excel as a database, and once I sort out how to deal with the richtext type fields with more than 255 characters it will be good enough.
-
Al says:
Hi Chandoo,
Thanks for your excellent post. Just a question: I am working on exactly same thing with the exception of using text box instead of drop down boxes. Additionally I would like to have separate worksheet for adding data into the db. In total it would have three worksheet as data, add, view.
Could you help me for using text boxes?
Thanks a lot,
-
Deeksha Baluja says:
Dear Chandoo,
I’m very much naive at the technique if using Excel as your database, I saw the vba code after downloading the sample file , could you please please tell me where have the commands [data$] and product have come from and how have you designed combo boxes in this case.
Thanks a lot in advance
-
Helma says:
Hi. I’m using Excel as a database and populate the records in a multi colomn listbox in a userform in Word vba. I managed to do this.
I can even sort the different columns in the listbox.
But now I want to fill the textboxes in the userform with the values of the selected listbox item. The first column has an ID-no.
Can anyone tell me how to do that or is this a typical Word question?
Then I’m sorry I’ve put the question here.
Thank you.Helma
-
Madhu D N says:
Dear All,
I’m looking for VBA code for data import from website to excel!!
Requirement:- i have company website which we need to download data every time, need code for log-in website by credentials and download a data automatically by using VBA code.Thanks for your support!
Madhu D N (HR) -
Jose Lobo says:
Hi, Madhu,
I would suggest you to search the web. There are many websites about that. Take a look at:
http://www.wiseowl.co.uk/blog/s393/scraping-websites-vba.htm
I have a similar problem to get a table from a website that requires two dates and a click, but I did not solve the problem yet. -
Martin says:
VBA beginner here — How were the drop-down lists and buttons created in this database template? I’m having trouble figuring them out as there are no userforms shown in the VBA editor? Any help would be appreicated.
-
Pinder Singh says:
i do not know Nothing about VBA but still build this user form retrieve data from one worksheet to added into the other worksheet i think their gotta be a better way to do this if you could help i do not know where to Uoload my workbook so please let me know
-
Ren says:
as you are extracting data from the sheet I want it to be from a database.How is that possible?
-
Norman says:
Sadly, this no longer works on Office 2016 (Home and Student). I ran your example file without changing anything, and keep getting «microsoft excel is waiting for another application to complete an ole action». Do you have a solution to this? Would really appreciate if you could help. Thanks.
-
@Norman
It sure does work in Excel 2016
Did you add the reference to the Active X data Library?
Did you save the file to a local drive?
Did you click on Update Drop Downs? (This is important)If it still doesn’t work can you tell us what version of Excel and Windows you are using?
-
Norman says:
It doesn’t for me. I’ve uploaded a few screenshots to an album here: http://imgur.com/a/eDU6H
A reference to the ActiveX Data Library exists (as show in the screen shot).
The file is saved to a local dirve.
The error occurs after I click on the «Update Drop Downs» Button (included in the screen shot album)
One thing I’ve noticed, is that the Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects 6.0 Library references a «msado60.dll» in the example, whereas, it’s a «msado60.tlb» file in Excel 2016 (which I use).
Could this difference be causing the error?
-
-
-
shahbaz Nawaz says:
Dear Vijay & Garouda,
Dear both thanks a lot to produced this artical but i have one problem i need only specific range from «data» to show in view tab i dont want to show all.
Can you please help me.
Regards,
Shahbaz Nawaz
-
Collin says:
I tried this and am getting a (run time error) the below error on line
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Sheets(«View»).Visible = True
Sheets(«View»).Select
Range(«dataSet»).Select (this line)
Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).ClearContentsNot sure where it went wrong and any help will be much appreciated
It shows this error
Run-time error ‘1004’
method ‘Range’of object’_Worksheet’ failedCheers
Collin
-
@Collin
Is there a Named Range called dataSet already set up on the worksheet?
I’d recommend asking this in the Chandoo.org Forums
http://forum.chandoo.org/Attach a sample file with some data if you can
-
-
Santosh says:
Hi Vijay,
I need to update excel data using a Form not directly into sheet. Would appreciate if you can help, Since its a big excel designing a userform would be critical.
Regards
-
azuwan says:
thanks a gazillion dude. this can convert to MySQL!!!..the syntax was same. you are the MAN!!!!..
-
Mahesh says:
Hi,
I am using excel as database and unabl to use Insert Into query to updete records excel database for date and floating point columns.
I have tried all the options list useing # before and after, Using Clang funciton. Nothing works. Am I missing anything
Regards,
Mahesh-
Martin says:
This is how I update a «database» table(worksheet)
Sub ExpireOutOfDateContract()
If MsgBox(«This will expire all of the » & vbCrLf & «out of date contracts — AreYou Sure?», vbYesNo + vbQuestion, «Confirm Changes») = vbNo Then
Exit Sub
End IfDim s As Range, xRow As Long ‘reference range plus row number
Set s = ActiveSheet.Range(«A:A»)
xRow = 4 ‘start at row 4
Do While s.Cells(xRow, «a») «»
xRow = xRow + 1 ‘move on a row
If s.Cells(xRow, «a») = «» Then Exit Do ‘hit a blank and it must be the ‘end of data
If s.Cells(xRow, «x») = 1 Then
strSQL = «update [contract$] set [open] = ‘N’ where [contract] = ‘» & s.Cells(xRow, «d») & «‘»
cnn.Execute strSQL, , adExecuteNoRecords
End IfLoop
MsgBox «Contracts have been expired and will not appear on next refresh» & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & _
«If this was a mistake press the ‘Undo Contract Removal’ button» & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & «THIS IS THE ONLY CHANCE YOU HAVE TO UNDO YOUR CHANGES» & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & _
«After refresh, undo will not work», vbInformation + vbOKOnly, «Update Complete — You CAN change your mind»
Set cnn = Nothing
frmOptions.Hide
End Sub
-
-
Ash Rahman says:
Hi
Just downloaded the Demo Database example (THANKS!) Noticed though that it downlaods as ‘.xls’ which Excel (mine is 2010) then has a problem opening… Changed the extension to ‘.xlsm’ and all was well with the world.Thanks again
Ash -
HanShin says:
why doesn’t «call id» and «Date time» appear when i click «show data» ?
Help me please !!! 🙁-
Martin says:
Can you show example of what you are trying to do please?
-
-
Mohammad Affan says:
Best and very helpful. Keep sharing such article….
-
Kyle Franken says:
Hi,
I’ve downloaded the example template. I removed the data with my own data set and changed the headers/combo boxes in the view tab. I am able to pull all my data and the buttons all work; however, the last three columns of data are pulled in formatted as text. It is not formatted this way in the data tab so I am unsure why this continues to happen. *** I did add a few extra columns to the data tab in comparison to the original template. I’m not sure if that is the cause of the issue or how to go about resolving it. Any help would be appreciated!
Thanks!!!
-
I am crazeeeeeeee about this web site. Love it so much and I immediately described.
-
[…] Using Excel as your database: A nice tutorial from Chandoo. It includes animated GIFs to complement the text. This speeds up the process of learning, since the images are zoomed in, yet still moving, for a more engaging guide. It explains the code module too, which is an interesting take on the entire databasing process. Be warned that some of the images are from older Excel versions. […]
-
[…] Using Excel As Your Database | Chandoo.org — Learn. – Often I have thought, if I could have write «Select EmployeeName From Sheet Where EmployeeID=123» and use this on my excel sheet, my life would be simpler. So […]
-
Andi Permana says:
Very Good.
Inspiring me for explore more, please can give me an example another demo for excel database but with to another workbook. sorry for my bad english. thanks.
-
Albert says:
Hi,
It is a very good choice.
Thanks
-
Nino says:
Can anyone send me a simple database for me to use it in my service department in monitoring our medical equipments which we delivered and those units that are still in the warehouse. Including when it was installed and I need to have a preventive maintenance monitoring plus spare parts monitoring. Would somebody help me please.
Thank you.
Nino
-
KAMAL C. BHARAKHDA says:
I keep getting an error called, «External table is not in the expected format»
I’m using external workbook as a database.
-
Rajat says:
Hi,
I am trying to learn to use excel as database on my own. I have gone through your program, but unable understand how «cmbProducts» is coming from. Can you please elaborate?Thanks
Rajat -
Salim Talal says:
Chandoo, this is fantastic, you really saved my day…… absolutely unbelievable.
All of my years with Excel I never knew this was possible……
Really great!!!
-
Salim Talal says:
Hi Chandoo!
I wonder how the Excel sample file you provided executing SQL like charm, quite soo fast in retreiving records.
I tried implementing that in my application and found running sooo stubbornly slow, like 30 seconds just to retreive a record of 40 lines while yours has 14,000 records.
Is there a secret in making it execute fast just like your sample Excel file .
Regards,
Salim T. S. -
LamDT says:
I want to change the Product, Region, CustomerType to other name to fit with my purpose but when i change it on vba code, it always show error 424. Object required. Can someone help me ?
-
LamDT says:
Hi guys,
Recently i found Chandoo with so many good things can use for my daily works. Thank you so much for your goodness when sharing file for us. I am a newbie on Excel and VBA, i saw your demo file to use excel as database is very good with my work. I tried to change it to fit with mine but there are something cannot work:
Now i got issue when i insert my data to this file. It does not accept the data in merge format in Product, Region, Quotation columns and show error «Type mismatch», could you give me help ? -
Hi,
Thanks for sharing the feature. Have successfully modified the code and used it in many excel files at work. Can we connect another workbook to this database and extract/modify/update? records.
Regards
Rida Ali -
ahmimas says:
Thank you for your advises,
I downloaded the demo, was working fine.
but I noticed that if you format the data sheet (example: adding blank cells above the first row and changing the fill color) without any changes to the code. the software doesn’t run correctly anymore and it will start giving odbc error just right here:Private Sub cmdUpdateDropDowns_Click()
strSQL = «Select Distinct [Product] From [data$] Order by [Product]»
closeRS
OpenDB
cmbProducts.Clearrs.Open strSQL, cnn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
If rs.RecordCount > 0 Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
cmbProducts.AddItem rs.Fields(0)
rs.MoveNext
Loop
Else
MsgBox «I was not able to find any unique Products.», vbCritical + vbOKOnly
Exit Sub
End If -
Great and simple solution.
Thanks for sharing it.
Can I just suggest also one of the solutions that could people also use if the want to go further with the concept of Database in Excel, or maybe link Excel & MySQL (to store data in MySQL).
There is a simple tool that I have created for myself and now made it available to others. A tool called Virtual Forms for Excel that enables us to, without coding, create Data Entry Forms, Lookup Forms and also Master-Details forms for Excel. If you want to take a look, here is the link: https://www.virtual-forms.com
Davor -
Elvis says:
I have used Excel to create several database applications like POS (Point of Sale)application system for retail stores / supermarkets, Church / School administration/ management systems, financial house loans, savings and payments management systems without all the complications that I see described in various websites Including this.
I guess it all boils down to individual levels of understanding Excel but most importantly, how much Logical the individual can get. I’ve always told people, that your level of utilisation of Excel is largely dependent on much logic you can bring into your Excel problem solving solutions.
-
This is a 100% helpful article about the solution for common problems.
thanks -
You are such a very helpful teacher. thank you for this
-
Love this wonderful method of teaching. Thank you very much sir. Long life
-
Emirate says:
i have successfully modified the code and used it in many excel files at work. Can we connect another workbook to this database and extract/modify/update? records.
-
Novida says:
very happy. thanks, buddy for this helpful place. love
-
I just modified the code and used it in many excel files at work.
Leave a Reply
Do you need to create and use a database? This post is going to show you how to make a database in Microsoft Excel.
Excel is the most common data tool used in businesses and personal productivity across the world.
Since Excel is so widely used and available, it tends to get used frequently to store and manage data as a makeshift database. This is especially true with small businesses since there is no budget or expertise available for more suitable tools.
This post will show you what a database is and the best practices you should follow if you’re going to try and use Excel as a database.
Get the example files used in this post with the above link and follow along below!
What is a Database?
A database is a structured set of data that is often in an electronic format and is used to organize, store. and retrieve data.
For example, a database might be used to store customer names, addresses, orders, and product information.
Databases often have key features that make them an ideal place to store your data.
Database vs Excel
An Excel spreadsheet is not a database, but it does have a lot of great and easy-to-use features for working with data.
Here are some of the key features of a database and how they compare to an Excel file.
| Feature | Database | Excel |
|---|---|---|
| Create, read, update, and delete records | ✔️ | ✔️ Excel allows anyone to add or edit data. This can be viewed as a negative consideration. |
| Data types | ✔️ | ⚠️ Excel allows for simple data types such as text, numbers, dates, boolean, images, and error values. But lacks more complex data types such as date and timezones, files, or JSON. |
| Data validation | ✔️ | ⚠️ Excel has some data validation features, but you can only apply one rule at a time and these can easily be overridden on purpose or by accident. |
| Access and security | ✔️ | ❌ Excel doesn’t have any access or security controls. This is usually managed through your on-premise network or through SharePoint online. But anyone can access your Excel file if it’s downloaded and sent to them. |
| Version control | ✔️ | ❌ Excel has no version control. This can be managed through SharePoint. |
| Backups | ✔️ | ❌ Excel has no automated backups. These can be manually created or automated in SharePoint. |
| Extract and query data | ✔️ | ✔️ Excel allows you to extract and query data through Power Query which is easy to learn and use. |
| Perform calculations | ✔️ | ✔️ Excel has a large library of functions that can be used in calculated columns inside tables. Excel also has the DAX formula language for calculated columns in Power Pivot. |
| Aggregate and summarize data | ✔️ | ✔️ Excel can easily aggregate and summarize data with formulas, pivot tables, or power pivots. |
| Relationships | ✔️ | ✔️ Excel has many lookup functions such as XLOOKUP, as well as table merge functionality in Power Query, and 1 to many relationships in Power Pivot. |
| Scale with large amounts of data | ✔️ | ⚠️ Excel can hold up to 1,048,576 rows of data in a single sheet. Tools like Power Query and Power Pivot can help you deal with larger amounts of data but they will be constrained based on your hardware specifications. |
| User friendly | ❌ A database might not be user-friendly and may come with a steep learning curve that your intended users won’t be able to handle. | ✔️ Most people have some experience with using Excel. |
| Cost | ❌ Can be expensive to set up, run, and maintain a proper database tool. | ✔️ Your organization might already have access to and use Excel. |
This is not a comprehensive list of features that a database will have, but they are some of the major features that will usually make a proper database a more suitable option.
The features that a database has depends on what database it is. Not all databases have the same features and functionality.
You will need to decide what features are essential for your situation in order to decide if you should use Excel or some other database tool.
💡 Tip: If you have Excel for Microsoft 365, then consider using Dataverse for Teams as your database instead of Excel. Dataverse has many of the great database features mentioned above and it is included in your Microsoft 365 license at no additional cost.
Relational Database Design
A good deal of thought should happen about the structure of your database before you begin to build it. This can save you a lot of headaches later on.
Most databases have a relational design. This means the database contains many related tables instead of one table that contains all the data.
Suppose you want to track orders in your database.
One option is to create a single flat table that contains all the information about the order, the products, and the customer that created the order.
This isn’t very efficient as you end up creating multiple entries of the same customer information such as name, email, and address. You can see in the above data, column G, H, and I contains a lot of duplicate values.
A better option is to create separate tables to store the Order, Product, and Customer data.
The Order data can then reference a unique identifier in the Product and Customer data that will relate the tables and avoid unnecessary duplicate data entry.
This same example data might look like this when reorganized into multiple related tables.
- An Orders table that contains the Item and Customer ID field.
- A Products table that relates to the Item fields in the Orders table.
- A Customers table that relates to the Customer ID in the Orders table.
This avoids duplicated data entry in a flat single table structure and you can use the Item or Customer ID unique identifier to look up the related data in the respective Products or Customers tables.
Tabular Data Structure in Excel
If you’re going to use Excel as your database, then you’re going to need your data in tabular format. This refers to the way the data is structured.
The above example shows a product order dataset in tabular format. A tabular data format is best suited for Excel due to the row and column structure of a spreadsheet.
Here are a few rules your data should follow so that it’s in tabular format.
- 1st row should contain column headings. This is just a short and descriptive name for the data contained below.
- No blank column headings. Every column of data should have a name.
- No blank columns or blank rows. Blank values within a field are ok, but columns or rows that are entirely blank should be removed.
- No subtotals or grand totals within the data.
- One row should represent exactly one record of data.
- One column should contain exactly one type of data.
In the above orders example data, you can see B2:E2 contains the column headings of an Order ID, Customer ID, Order Date, Item, and Quantity.
The dataset has no blank rows or columns, and no subtotals are included.
Each row in the dataset represents an order for one type of product.
You’ll also notice each column contains one type of data. For example, the Item column only contains information on the name of the product and does not include other product information such as the price.
⚠️ Warning: If you don’t adhere to this type of structure for your data, then summarizing and analyzing your data will be more difficult later. Tools such as pivot tables require tabular data!
Use Excel Tables to Store Data
Excel has a feature that is specifically for storing your tabular data.
An Excel Table is a container for your tabular datasets. They help keep all the same data together in one object with many other benefits.
💡 Tip: Check out this post to learn more about all the amazing features of Excel Tables.
You will definitely want to use a table to store and organize any data table that will be a part of your dataset.
How to Create an Excel Table
Follow these steps to create a table from an existing set of data.
- Select any cell inside your dataset.
- Go to the Insert tab in the ribbon.
- Select the Table command.
This will open the Create Table menu where you will be able to select the range containing your data.
When you select a cell inside your data before using the Table command, Excel will guess the full range of your dataset.
You will see a green dash line surrounding your data which indicates the range selected in the Create Table menu. You can click on the selector button to the right of the range input to adjust this range if needed.
- Check the My table has headers option.
- Press the OK button.
📝 Note: The My table has headers option needs to be checked if the first row in your dataset contains column headings. Otherwise, Excel will create a table with generic column heading titles.
Your Excel data will now be inside a table! You will immediately see that it’s inside a table as Excel will apply some default format which will make the table range very obvious.
💡 Tip: You can choose from a variety of format options for your table from the Table Design tab in the Table Styles section.
The next thing you will want to do with your table is to give it a sensible name. The table name will be used to reference the table in formulas and other tools, so giving it a short descriptive name will help you later when reading formulas.
- Go to the Table Design tab.
- Click on the Table Name input box.
- Type your new table name.
- Press the Enter key to accept the new name.
Each table in your database will need to be in a separate table, so you will need to repeat the above process for each.
How to Add New Data to Your Table
You will likely need to add new records to your database. This means you will need to add new rows to your tables.
Adding rows to an Excel table is very easy and you can do it a few different ways.
You can add new rows to your table from the right-click menu.
- Select a cell inside your table.
- Right-click on the cell.
- Select Insert from the menu.
- Select Table Rows Above from the submenu.
This will insert a new blank row directly above the selected cells in your table.
You can add a blank row to the bottom of your table with the Tab key.
- Place the active cell cursor in the lower right cell of the table.
- Press the Tab key.
A new blank row will be added to the bottom of the table.
But the easiest way to add new data to a table is to type directly below the table. Data entered directly underneath the table is automatically absorbed into the table!
Excel Workbook Layout
If you are going to create an Excel database, then you should keep it simple.
Your Excel database file should contain only the data and nothing else. This means any reports, analysis, data visualization, or other work related to the data should be done in another Excel file.
Your Excel database file should only be used for adding, editing, or deleting the data stored in the file. This will help decrease the chance of accidentally changing your data, as the only reason to open the file will be to intentionally change the data.
Each table in the database should be stored in a separate worksheet and nothing else except the table should be in that sheet. You can then name the worksheet based on the table it contains so your file is easy to navigate.
💡 Tip: Place your table starting in cell A1 and then hide the remaining columns. This way it is clear the sheet should only contain the table and nothing else.
The only other sheet you might optionally include is a table of contents to help organize the file. This is where you can list each table along with the fields it contains and a description of what these fields are.
💡 Tip: You can hyperlink the table name listed in the table of contents to its associated sheet. Select the name and press Ctrl + K to create a hyperlink. This can help you navigate the workbook when you have a lot of tables in your database.
Use Data Validation to Prevent Invalid Data
Data validation is a very important feature for any database. This allows you to ensure only specific types of data are allowed in a column.
You might create data validation rules such as.
- Only positive whole numbers are entered in a quantity column.
- Only certain product names are allowed in the product column.
- A column can’t contain any duplicate values.
- Dates are between two given dates.
Excel’s data validation tools will help you ensure the data entered in your database follow such rules.
Follow these steps to add a data validation rule to any column in your table.
- Left-click on the column heading to select the entire column.
When you hover the mouse cursor over the top of your column heading in a table, the cursor will change to a black downward pointing arrow. Left-click and the entire column will be selected.
The data validation will automatically propagate to any new rows added to the table.
- Go to the Data tab.
- Click on the Data Validation command.
This will open up the Data Validation menu where you will be able to choose from various validation settings. If there is no active validation in the cell, you should see the Any values option selected in the Allow criteria.
Only Allow Positive Whole Number Values
Follow these steps from the Data Validation menu to allow only positive whole number values to be entered.
- Go to the Settings tab in the Data Validation menu.
- Select the Whole number option from the Allow dropdown.
- Select the greater than option from the Data dropdown.
- Enter 0 in the Minimum input box.
- Press the OK button.
💡 Tip: Keep the Ignore blank option checked if you want to allow blank cells in the column.
This will apply the validation rule to the column and when a user tries to enter any number other than 1, 2, 3, etc… they will be warned the data is invalid.
Only Allow Items from a List
Selecting items from a dropdown list is a great way to avoid incorrect text input such as customer or product names.
Follow these steps from the Data Validation menu to create a dropdown list for selecting text values in a column.
- Go to the Settings tab in the Data Validation menu.
- Select the List option from the Allow dropdown.
- Check the In-cell dropdown option.
- Add the list of items to the Source input.
- Press the OK button.
📝 Note: If you place the list of possible options inside an Excel Table and select the full column for the Source reference, then the range reference will update as you add items to the table.
Now when you select a cell in the column you will see a dropdown list handle on the right of the cell. Click on this and you will be able to choose a value from a list.
Only Allow Unique Values
Suppose you want to ensure the list of products in your Products table is unique. You can use the Custom option in the validation settings to achieve this.
- Go to the Settings tab in the Data Validation menu.
- Select the Custom option from the Allow dropdown.
=(COUNTIFS(INDIRECT("Products[Item]"),A2)=1)- Enter the above formula in the Formula input.
- Press the OK button.
The formula counts the number of times the current row’s value appears in the Products[Item] column using the COUNTIFS function.
It then determines if this count is equal to 1. Only values where the formula evaluates to 1 are allowed which means the product name can’t have been in the list already.
📝 Note: You need to reference the column by name using the INDIRECT function in order for the range to grow as you add items to your table!
Show Input Message when Cell is Selected
The data validation menu allows you to show a message to your users when a cell is selected. This means you can add instructions about what types of values are allowed in the column.
Follow these steps to add an input message in the Data Validation menu.
- Go to the Input Message tab in the Data Validation menu.
- Keep the Show input message when cell is selected option checked.
- Add some text to the Title section.
- Add some text to the Input message section.
- Press the OK button.
When you select a cell in the column which contains the data validation, a small yellow pop-up will appear with your Title and Input message text.
Prevent Invalid Data with Error Message
When you have a data validation rule in place, you will usually want to prevent invalid data from being entered.
This can be achieved using the error message feature in the Data Validation menu.
- Go to the Error Alert tab in the Data Validation menu.
- Keep the Show error alert after invalid data is entered option checked.
- Select the Stop option in the Style dropdown.
- Add some text to the Title section.
- Add some text to the Error message section.
- Press the OK button.
📝 Note: The Stop option is essential if you want to prevent the invalid data from being entered rather than only warning the user the data is invalid.
When you try to enter a repeated value in the column your custom error message will pop up and prevent the value from being entered in the cell.
Data Entry Form for Your Excel Database
Excel doesn’t have any fool-proof methods to ensure data is entered correctly, even when data validation techniques previously mentioned are used.
When a user copies and pastes or cuts and pastes values, this can override data validation in a column and cause incorrect data to enter into your database.
Using a data entry form can help to avoid data entry errors and there are a couple of different options available.
- Use a table for data entry.
- Use the quick access toolbar data entry form.
- Use Microsoft Forms for data entry.
- Use Microsoft Power Automate app for data entry.
- Use Microsoft Power Apps for data entry.
💡 Tip: Check out this post for more details on the various data entry form options for Excel.
Tools such as Microsoft Forms, Power Automate, and Power Apps will give you more data validation, access, and security controls over your data entry compared with the basic Excel options.
Access and Security for Your Excel Database
Excel isn’t a secure option for your data.
Whatever measures you set up in your Excel file to prevent users from changing data by accident or on purpose will not be foolproof.
Whoever has access to the file will be able to create, read, update, and delete data from your database if they are determined. There are also no options to assign certain privileges to certain users within an Excel file.
However, you can manage access and security to the file from SharePoint.
💡 Tip: Check out this post from Microsoft about recommendations for securing SharePoint files for more details.
When you store your Excel file in SharePoint you’ll also be able to see recent changes.
- Go to the Review tab.
- Click on the Show Changes command.
This will open up the Changes pane on the right-hand side of the Excel sheet.
It will show you a chronological list of all the recent changes in the workbook, who made those changes, when they made the change, and what the previous value was.
You can also right-click on a cell and select Show Changes. This will open the Changes pane filtered to only show the changes for that particular cell.
This is a great way to track down the cause of any potential errors in your data.
Query Your Excel Database with Power Query
Your Excel database file should only be used to add, edit, or delete records in your tables.
So how do you use the data for anything else such as creating reports, analysis, or dashboards?
This is the magic of Power Query! It will allow you to connect to your Excel database and query the data in a read-only manner. You can build all your reports, analysis, and dashboards in a separate file which can easily be refreshed with the latest data from your Excel database file.
Here’s how to use power query to quickly import your data into any Excel file.
- Go to the Data tab.
- Click on the Get Data command.
- Choose the From File option.
- Choose the From Excel Workbook option in the submenu.
This will open a file picker menu where you can navigate to your Excel database file.
- Select your Excel database file.
- Click on the Import button.
⚠️ Warning: Make sure your Excel database file is closed or the import process will show a warning that it’s unable to connect to the file because it’s in use!
Clicking on the Import button will then open the Navigator menu. This is where you can select what data to load and where to load it.
The Navigator menu will list all the tables and sheets in the Excel file. Your tables might be listed with a suffix on the name if you’ve named the sheets and tables the same.
- Check the option to Select multiple items if you want to load more than one table from your database.
- Select which tables to load.
- Click on the small arrow icon next to the Load button.
- Select the Load To option in the Load submenu.
This will open the Import Data menu where you can choose to import your data into a Table, PivotTable, PivotChart, or only create a Connection to the data without loading it.
- Select the Table option.
- Click on the OK button.
Your data is then loaded into an Excel Table in the new workbook.
The best part is you can always get the latest data from the source database file. Go to the Data tab and press the Refresh All button to refresh the power query connection and import the latest data.
💡 Tip: You can do a lot more than just load data with Power Query. You can also transform your data in just about any imaginable way using the Transform Data button in the Navigator menu. Check out this post on how to use Power Query for more details about this amazing tool.
Analyze and Summarize Your Excel Database with Power Pivot
Power Query isn’t the only database tool Excel has. The data model and Power Pivot add-in will help you slice and dice relational data inside your Excel pivot tables.
When you load your data with Power Quer, there is an option to Add this data to the Data Model in the Import Data menu.
This option will allow you to build relationships between the various tables in your database. This way you’ll be able to analyze your orders by category even though this field doesn’t appear in the Orders table.
You can build your table relationships from the Data tab.
- Go to the Data tab.
- Click on either the Relationships or Manage Data Model command.
Now you’ll be able to analyze multiple tables from your database inside a single pivot table!
Conclusions
Data is an essential part of any business or organization. If you need to track customers, sales, inventory, or any other information then you need a database.
If you need to create a database on a budget with the tools you have available then Microsoft Excel might be the best option and is a natural fit for any tabular data because of its row and column structure.
There are many things to consider when using Excel as a database such as who will have access to the files, what type of data will be stored, and how you will use the data.
Features such as Tables, data validation, power query, and power pivot are all essential to properly storing, managing, and accessing your data.
Do you use Excel as a database? Do you have any other tips for using Excel to manage your dataset? Let me know in the comments below!
About the Author
John is a Microsoft MVP and qualified actuary with over 15 years of experience. He has worked in a variety of industries, including insurance, ad tech, and most recently Power Platform consulting. He is a keen problem solver and has a passion for using technology to make businesses more efficient.

Creating a database in Excel for your invoices, to-do’s, project timesheets, and more is an excellent way to cut down on data entry time and gain new business insights. Data, particularly numerical data, can be used for everything from reviewing past sales to predicting future costs in your business.
Businesses from every sector use data in their day-to-day activities, and while data is an integral part of any organisation, it’s no use on its own. Without proper data management, your information will be pretty much useless.
Using Excel as a database or a similar data management tool will help categorise and segment your data, so it’s accessible and usable.
If you’re interested in learning more about using Excel in business as a database and how it compares to other Microsoft solutions like Access, this post is for you!
What Is A Database?
Before we dive into using Excel as a database, let’s define what a database is for those who haven’t created or used a database before.
A database is a broad term for a system that stores multiple records of data. Databases come in many different forms and allow users to store, search, filter data and review numerical information.
Databases can have a one-to-one relationship, one-to-many relationship or many-to-many relationship meaning that one record can have multiple other records or that other records can exist without a primary record.
These solutions can be offline or stored online using the Cloud. Databases come in a variety of styles and can be customised to suit your organisation’s unique requirements.
Relational databases, for example, allow data to be shared between several different computer systems, which gives users the ability to store, update and share data.
Databases can store a wide variety of information and can be split up into sections making searching for data and identifying patterns easier and less time-consuming. A database might also include user permissions, a drop-down menu, complex calculations and advanced filtering options.
What Programmes Can You Use To Create A Database?
Databases can be made using a wide range of offline and online programmes. As well as creating a database in Excel, you can also use a selection of other solutions to create a database for your organisation.
Many of these tools are specialist database solutions, such as Knack and IBM Informix, which you can get subscriptions to and use to build databases.
Another Microsoft tool that can be used to create databases is Access. Both Access and Excel are part of the Microsoft Office 365 suite of products, meaning that they’re easily accessible to many business users.
Access is part of the Professional suite of tools, so users do need to pay extra to upgrade their licence to use it. However, it is a valuable tool similar to other Microsoft programs, making it user-friendly and useful for small-mid size businesses.
Creating a Database in Excel Vs Access
While Excel is a helpful tool for storing and managing your data there are many spreadsheet and database programmes to explore.
For example, Microsoft Access is specifically designed for creating and managing databases and storing data. Many businesses use it as their single database, so they have a master copy of their data set.
Some of the differences between Microsoft Excel and Access when it comes to data management include:
- Access is designed to manage databases and can act as your master database
- Excel is specifically created to allow data management and visual representation of information
- Excel is easier to use than Access for Microsoft novices
- Excel is non-relational as opposed to Access, which allows relational data
- Access has a greater capacity for data storage than Excel
Do you need Excel database help?
We are Excel Experts, so contact a member of our team today.
What Are The Benefits Of Using Excel?
Excel and Access are two unique tools, and each has its own benefits. While Access was designed to manage databases, Excel has many handy features to let you make calculations, automate data functions, generate reports, build a searchable database and more.
Some of the many benefits of using Excel to manage your data and create small databases are:
- Excel is already tabular, and it’s easy to view an Excel worksheet and access data
- Most business leaders have access to and know the basics of Excel
- Excel is perfect for numerical data, and making calculations, and it’s easy to enter data
- The rows and columns are easier to understand than some more complex database layouts
- VBA allows users to automate tasks and link Excel to other software programs
When To Use Excel As A Database
Excel can be used as a database when you’re only dealing with a small amount of information, or it’s not particularly business-critical.
An Excel database might also be used as a starter database for small business leaders who want to experiment or learn more about managing their data. For example, by creating a customer database or a database that only requires a simple database record.
As your business grows, you might want to explore more specific database software specifically designed to act as a database and deal with all the data your company collects.
Such a database will often have better security and can manage and store larger amounts of data.
Excel can handle just over a million records, but if you have more data records or regularly add new records to your data, it might struggle to deal with these volumes. In this case, you should consider using a specially-designed database program.
How Excel & Other Databases Can Work Together
While Excel might not be an ideal database if you’re dealing with over a million records, using a database in Excel is a useful tool for managing data. As such, you can still use Excel to manage your data and use the formulas to create unique predictions and insights.
You can then sync your Excel sheet with a larger database on a SQL server to transfer the data into a larger collection of information without entering the data again.
This approach will reduce your chances of corrupting your Excel files and spreadsheets, which aren’t designed to hold extremely large amounts of data.
It’ll also mean that you can still use Excel for small sections of your data and easily transfer it to a larger and more secure database tool.
Excel can be used in conjunction with most tools, both Microsoft’s own suite of products and third-party solutions. It has many functions and capabilities, including the ability to calculate averages and insert complex formulas easily.
So, if you’re struggling to perform these functions in another database program, you can combine its superior storage and security functions with Excel’s innovative capabilities.
How To Create A Database in Excel
Creating a database in Excel is surprisingly straightforward and can be done by almost anyone. The tool is intuitive and easy to use, so making a simple database is quick and easy.
Excel is a tabular tool, so the best layout is a database table. All you need to do is create the columns and rows, which will act as the database field and then enter data.
Once your data is in, you can search the database, review your information and even summarise data. You can also add formulas and use VBA, the programming language for Excel, to create instructions and automate the management of your database.
With Excel, you can also create multiple tabs and link them to input data to spread the content around and ensure that everything is clearly labelled.
However, Excel doesn’t allow the creation of a relational database, but you can still cross-reference and cross-link different tables and pull the data into a master table.

Learn how to create, analyse, import and export large amounts of data with the Excel 365 Bible.
Choose the Type of Database
The first step in creating a database is to decide which type of database you need. There are four basic types of databases:
1. Relational databases
A relational database is a type of database that stores and retrieves data by using tables. Tables are a collection of related data, and each table has a unique name. Tables are similar to folders in a file system, where each folder contains a collection of related files
2. Object-oriented databases
An object-oriented database is a type of database that stores and retrieves data by using objects. Objects are a collection of related data, and each object has a unique name. Objects are similar to files in a file system, where each file contains a collection of related data
3. Hierarchical databases
A hierarchical database is a type of database that stores and retrieves data by using a hierarchy. A hierarchy is a structure of connected nodes, where each node has a unique name. Nodes are similar to folders in a file system, where each folder represents a node in the hierarchy
4. Network databases
A network database is a type of database that stores and retrieves data by using a network. A network is a collection of connected nodes, where each node has a unique name. Nodes are similar to files in a file system, where each file represents a node in the network.
What Can You Use a Database For?
As Excel databases are easy to use and completely customisable, they can be made to suit the needs of a variety of organisations. There are many ways you can use them to save your company time and effort.
Some examples of what to use a database for in your business include:
- Listing customer or student data related to times/ appointments
- Calculating total sales figures over a set timeframe
- Tracking the productivity of team members
- Reviewing work orders
- Storing and managing data on stock
- Storing digital assets and marketing material
- Keeping supply chain management records and processes
- Storing customer details and order information
- Managing product information
- Automating data entry using Excel automation
Using databases for your business, and even for personal use, can bring a wealth of benefits. You can free up your time, increase your productivity and slice through information quickly.
It’s much easier to understand data when it’s organised in an Excel database compared with an unstructured list or via another type of cloud-based program.
Summary: Creating A Database In Excel
Ultimately, Excel is not technically a database but a spreadsheet and data management tool. That being said, Excel is a useful tool for business leaders who want to use it to create their first initial database and learn how to manage their information.
Whether you’re a small business or an organisation that wants to manage a small amount of data, Excel can be the perfect tool. The best thing about using Excel as a database is that it’s an easily accessible tool that can be used by almost everyone on your team.
For larger businesses, Microsoft Access could be a useful solution to help you to expand your database and manage more information. Excel can be used in conjunction with Access and other database solutions, even for larger organisations, as it has many innovative capabilities and data management functions.
If you’re planning on using Excel as a database, you need to understand the basics of using Excel and how it can interact with other Microsoft solutions, including Access.
About The Excel Experts
At The Excel Experts, we pride ourselves on helping businesses to learn more about the Microsoft suite of software solutions.
Check out our MS Office training and Excel training courses to find a solution that works for your business. Our team can create a custom training solution for your organisation and help you and your team make the most of Excel.
We also offer a range of Excel consultancy services, including creating custom Excel workbooks that can be used as databases for reporting data and much more.
If you’d like to learn more about our services and how we can help you use Excel to its full potential, then contact us today.
NEED HELP WITH AN EXCEL PROJECT, BIG OR SMALL?
The Excel Experts can help you or your business complete an unfinished project, integrate web applications, automate tasks, and much more.

Excel is the best tool to use for database analysis. It refers to a combination of rows and columns, and these rows and columns are used for storing our data as records. The excel rows and columns are further divided into smaller cells where the record data is inputted. Excel records can be converted into a table to form an excel database, and this makes the life of a regular excel user easier.
When creating an excel database, you need to carefully design the excel worksheet to have proper info in the database format.
1. Open the excel worksheet
Before accessing any feature on excel, you have to launch an excel application and create a new worksheet where you will add your data. Click on the excel option and tap the «New» button.
2. Entering the data
When entering the data in the worksheet, each cell is used to input each data of the database. Firstly, label the heading properly of your data.
After
the headers of the data table are clear, you can start entering data on the cells below the respective column headings. However, carefulness should be observed when entering data to ensure you don’t leave a single row empty. Similarly, you cannot have an empty column between the data. Therefore, fill in the data carefully.
3. Select the inputted data
Once all the data is inputted, highlight all the cells that contain the information to be converted to a database. Click the left mouse at the beginning of the data and then scroll down until all the required data are highlighted.
4. Click the «Insert» button
On the ribbon bar, locate and click on the insert button. Then, click the table button located on the leftmost side of the insert section. Alternatively, you can use excel’s shortcut to access the table feature. By selecting the data and then pressing Ctrl+T.
Here you need to make sure the header check box is checked and the data range shown selected properly. If the table header is not checked, you can activate it by clicking on the small box located on the left. Once everything is completely set, click the «ok» button.
5. Customize the database table
Since we’ve created a table, we have the database ready now, and it can be used for further references. When you enter the data after the last column, it will expand automatically. Excel is fitted with features that enable users to edit and make the table more appealing. These features are found under the table design tab. For example, if you wish to give your table a proper name, click the Table name tab on the Design tab, edit it and input the proper name of your table and then save by clicking anywhere on the worksheet screen.
Go ahead and click the excel tools button, and then click the save button to save your database.
Create Database in Excel
Before getting into database creation, Let’s first learn something about databases in excel.
You cannot at any instance enter data and leave a row between two entries empty. Here’s an illustration.
Some cells can be empty in a database and it is completely legal. Leaving a complete row empty, however, is illegal.
Furthermore, it is not a good practice when you leave a full column empty.
The reason you should never leave an empty row or column is that whenever Excel encounters such a gap, it treats the data after such rows or columns as a new set of database. Therefore, the functions you deploy would not be able to filter on the disconnected part.
Rows are called Records, while columns are known as Fields. Headings on the columns are known as Field names.
The following are steps to creating a database in Excel;
i). Start by creating a data spreadsheet in excel.
Ensure that the columns are properly headed. Columns are labeled alphabetically while rows are named numerically.
1. Open the Excel Sheet on your PC. Click on one cell to insert header names. The Tab button on your screen helps you to navigate from one row to a column. Once through, the cursor will take you to the next row or column.
2. Enter data or import from other sources. For instance, go to the Home tab, find the Cells segment and click on the Insert dropdown button. You cannot leave any row empty.
For data importation, look for the Data tab, look for Get Data and choose the destination of your data.
ii). Convert your data into a table.
Data should be converted into a table. Click on any cell with information and select Insert>Table. Ensure data is in the correct format. Once done, data will be directly incorporated, and click Ok on the pop-up table.
How to arrange data in your spreadsheet using excel.
1. Spreadsheet database using Simple Horizontal Gray cells.
For long, this method has been useful to excel users, and it is segmented into two forms. Horizontal and vertical modes.
The horizontal database on the spreadsheet is dated in one row. Dates on the column use monthly buckets. However, they could use any time required. The codes column uses general ledger accounts. Gray rows and columns are the most common features of simple cells.
2. Simple spreadsheet database vertical style.
One column of data is comprised of several fields. In this case, data is shown vertically.
Names are easy to allocate in this format. In a classic excel, select Insert, go to Name, and Create.
In a new excel, select formulas, proceed to Defined names, and create from the selection.
3. Excel tables
Typically, after setting tables, more columns and rows, are named automatically.
Look out for the following.
- Data Arranged
- Headers and Data
To confirm;
Select Insert
Go to Tables on the Create Table Dialog
Make sure that the table has headers and press OK
Excel will automatically name the tables i.e Table 1, Table 2 e.t.c
4. Tabular layout for pivot tables
Pivot tables have different benefits like exploring data that is relatable in excel. It returns sorted, sliced, and summarized data in spreadsheets.
Setting up a pivot database table to look like an excel table
Insert a pivot table using these simple steps:
- Go to the Data Set and click any single
- Go to Tables group, then Insert tab and click Pivot Table. Excel will select the data for you.
- Click OK on the pop-up table.
The pivot table Fields pane will appear that will show the total amount of exported data. Drag the following: product field to rows area, amount field to value area, and country field to filters area.
- Sort the table by accessing the cell inside the sum amount and clicking on it.
- Right-click on sort and sort from right to left.
Steps to create a database in Excel
- Create a data spreadsheet
- Add or import data
- Convert your data into a table
- Customize the table design and assign a name
- Interact with the data
Every business has numbers to crunch, but not every CEO is a math wiz. That’s why small business owners often outsource their accounting or let their bookkeeper deal with it.
However, there are many other ways you can process data to make operations more efficient. Plus, you probably want to avoid constantly running to someone else for help.
That’s where a basic knowledge of Excel databases comes in handy.
Excel is one of those tools that almost everyone has on their desktop, and you can enjoy its benefits without being a numbers wizard.
Excel databases provide a simple way to analyze data (such as sales numbers and forecasts), look at various calculations, and compare different data sets. Of course, there are advanced formulas and functions if you dive deeper and invest time in becoming a pro. But for many business owners, just knowing how to create a database in Excel will give them a lot of power.
Let’s take a step-by-step tour of using Excel to create a database.
Just so you know
Learn how to make the most of your data with Jotform’s detailed Microsoft Excel tutorial. You can even integrate Jotform with Excel to sync form data to your spreadsheets!
1. Create a data spreadsheet
Start by opening a new Excel sheet.
The Excel sheet is made up of vertical columns and horizontal rows, with each row representing a different line of data. Columns are labeled with letters, and rows are labeled with numbers.
The first row should display the names for each column. Click on a cell in the first row and begin typing to insert header names. The Tab button is a quick way to navigate the table; each time you press the Tab button, you’ll jump to the next column in a row. When you reach the end of a row, the cursor will jump to the first column of the next row, and so on.
2. Add or import data
You can add data in two ways: by entering it manually or importing data from other files, such as text or CSV files.
To add data manually, click on a cell and begin typing. To insert a new row or column, go to the Home tab and look for the Cells section. There you’ll find the Insert dropdown arrow. By clicking on the arrow, you can select the item you want to insert (i.e., column, row, etc.).
To import data from outside sources, click on the Data tab, go to the Get/Transform Data section, and select the source destination. In order to import data successfully, you must ensure that the data has the correct formatting, and formatting depends on the type of source file.
3. Convert your data into a table
To get the functionality of a database, you must convert the data into a table.
Click your mouse on any cell of the data you entered, and then click on Insert >Table. A popup box will appear, showing you the data fields to be included in the table. The table will automatically incorporate all the rows and columns in the block. It’s important not to leave any blank rows in your data block — these act as “breaks” and indicate to the software that they aren’t part of the table.
If the correct fields are shown in the dialog box and your headers are in order, click OK.
Remember, any blank rows are not automatically integrated into the table. To include newly entered data in the table, hover on the small triangle nestled in the bottom right corner of the current table and drag the table border down to include the new data rows.
4. Customize the table design and assign a name
There are several options for table design, but don’t spend a lot of time on this. Making your table easily viewable is the aim of the game.
Click the Design tab on the main menu. Change the table colors with a quick click on one of the predefined color themes. The default table design features banded rows, meaning every second row has a background fill. Many users like this style, as it makes the data easier to view. Uncheck the Banded Rows box if you prefer a clean, white table.
In the far left section of the Design toolbar, you can change the table name. Give it a name that is specific and easy to identify. This will help later down the road when you’re working with many Excel databases.
5. Interact with the data
Once your table is set up, it’s time to start interacting with it and getting the insights you need. Several formulas are predefined in Excel software, including Average, Count, and Sum, among others.
Click on the cell at the base of any data column you want to work with. The cell displays a clickable arrow that opens a dropdown menu of available formulas. Select the formula, and the calculation will automatically appear in the cell.
In the example below, we’re calculating the average number of units sold. The Average formula is an option in the dropdown menu.
The average number of units sold is calculated and appears in the cell.
There are so many ways you can use Excel to perform calculations and derive useful data for decision-making. Now that you’ve created a database in Excel, you can explore all the available features and functionality.
Go beyond Excel: Working with Jotform Tables
While Excel is a longstanding favorite for number crunching, tools like Jotform Tables can give you much more than a spreadsheet. Jotform Tables provides a full workspace for managing, tracking, and processing data, and integrating it into workflows and collaboration for smoother operations.
If you work with Excel databases, you can easily import them into Jotform Tables and continue your data management there. And as a free tool, Jotform Tables requires none of the investment and licenses you need with Excel.
For companies already using Jotform, Jotform Tables is the next step, as it enables you to build effective data-based strategies so your business can truly excel.
This article is originally published on Nov 10, 2020, and updated on Feb 24, 2023.