IMPORTANT: Ideas in Excel is now Analyze Data
To better represent how Ideas makes data analysis simpler, faster and more intuitive, the feature has been renamed to Analyze Data. The experience and functionality is the same and still aligns to the same privacy and licensing regulations. If you’re on Semi-Annual Enterprise Channel, you may still see «Ideas» until Excel has been updated.
Analyze Data in Excel empowers you to understand your data through natural language queries that allow you to ask questions about your data without having to write complicated formulas. In addition, Analyze Data provides high-level visual summaries, trends, and patterns.
Have a question? We can answer it!
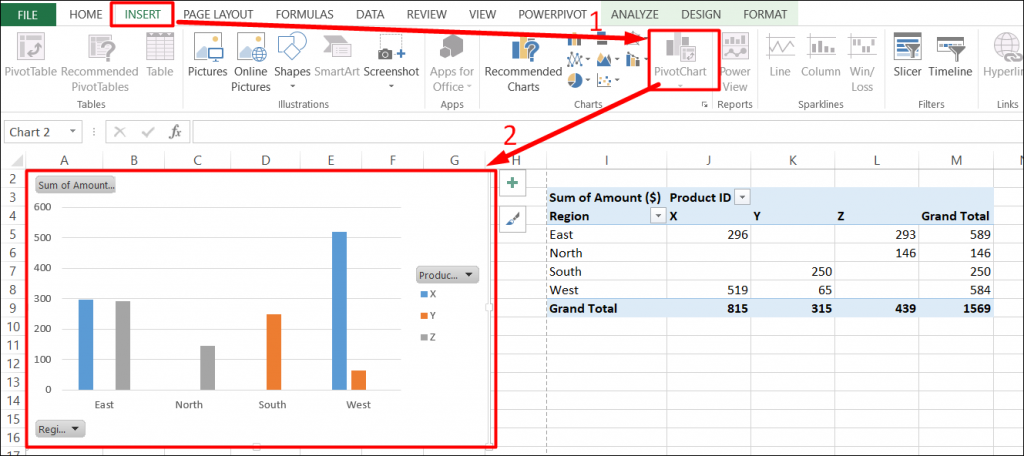
Simply select a cell in a data range > select the Analyze Data button on the Home tab. Analyze Data in Excel will analyze your data, and return interesting visuals about it in a task pane.
If you’re interested in more specific information, you can enter a question in the query box at the top of the pane, and press Enter. Analyze Data will provide answers with visuals such as tables, charts or PivotTables that can then be inserted into the workbook.
If you are interested in exploring your data, or just want to know what is possible, Analyze Data also provides personalized suggested questions which you can access by selecting on the query box.
Try Suggested Questions
Just ask your question
Select the text box at the top of the Analyze Data pane, and you’ll see a list of suggestions based on your data.

You can also enter a specific question about your data.

Notes:
-
Analyze Data is available to Microsoft 365 subscribers in English, French, Spanish, German, Simplified Chinese, and Japanese. If you are a Microsoft 365 subscriber, make sure you have the latest version of Office. To learn more about the different update channels for Office, see: Overview of update channels for Microsoft 365 apps.
-
The Natural Language Queries functionality in Analyze Data is being made available to customers on a gradual basis. It may not be available in all countries or regions at this time.
Get specific with Analyze Data
If you do not have a question in mind, in addition to Natural Language, Analyze Data analyzes and provides high-level visual summaries, trends, and patterns.
You can save time and get a more focused analysis by selecting only the fields you want to see. When you choose fields and how to summarize them, Analyze Data excludes other available data — speeding up the process and presenting fewer, more targeted suggestions. For example, you might only want to see the sum of sales by year. Or you could ask Analyze Data to display average sales by year.
Select Which fields interest you the most?
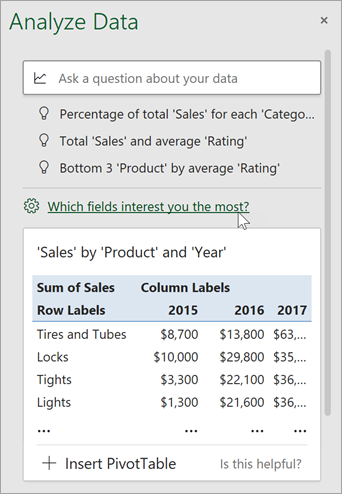
Select the fields and how to summarize their data.
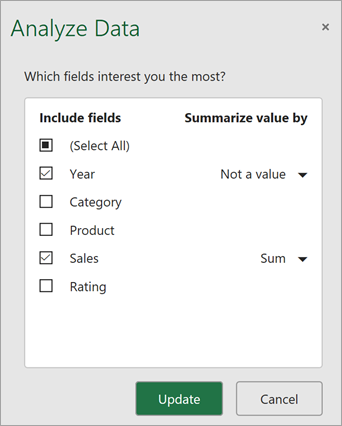
Analyze Data offers fewer, more targeted suggestions.
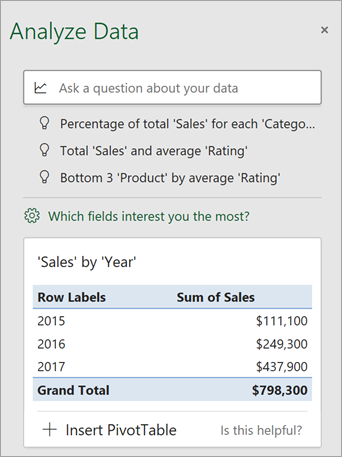
Note: The Not a value option in the field list refers to fields that are not normally summed or averaged. For example, you wouldn’t sum the years displayed, but you might sum the values of the years displayed. If used with another field that is summed or averaged, Not a value works like a row label, but if used by itself, Not a value counts unique values of the selected field.
Analyze Data works best with clean, tabular data.
Here are some tips for getting the most out of Analyze Data:
-
Analyze Data works best with data that’s formatted as an Excel table. To create an Excel table, click anywhere in your data and then press Ctrl+T.
-
Make sure you have good headers for the columns. Headers should be a single row of unique, non-blank labels for each column. Avoid double rows of headers, merged cells, etc.
-
If you have complicated, or nested data, you can use Power Query to convert tables with cross-tabs, or multiple rows of headers.
Didn’t get Analyze Data? It’s probably us, not you.
Here are some reasons why Analyze Data may not work on your data:
-
Analyze Data doesn’t currently support analyzing datasets over 1.5 million cells. There is currently no workaround for this. In the meantime, you can filter your data, then copy it to another location to run Analyze Data on it.
-
String dates like «2017-01-01» will be analyzed as if they are text strings. As a workaround, create a new column that uses the DATE or DATEVALUE functions, and format it as a date.
-
Analyze Data won’t work when Excel is in compatibility mode (i.e. when the file is in .xls format). In the meantime, save your file as an .xlsx, .xlsm, or .xlsb file.
-
Merged cells can also be hard to understand. If you’re trying to center data, like a report header, then as a workaround, remove all merged cells, then format the cells using Center Across Selection. Press Ctrl+1, then go to Alignment > Horizontal > Center Across Selection.
Analyze Data works best with clean, tabular data.

Here are some tips for getting the most out of Analyze Data:
-
Analyze Data works best with data that’s formatted as an Excel table. To create an Excel table, click anywhere in your data and then press
+T.
-
Make sure you have good headers for the columns. Headers should be a single row of unique, non-blank labels for each column. Avoid double rows of headers, merged cells, etc.
Didn’t get Analyze Data? It’s probably us, not you.
Here are some reasons why Analyze Data may not work on your data:
-
Analyze Data doesn’t currently support analyzing datasets over 1.5 million cells. There is currently no workaround for this. In the meantime, you can filter your data, then copy it to another location to run Analyze Data on it.
-
String dates like «2017-01-01» will be analyzed as if they are text strings. As a workaround, create a new column that uses the DATE or DATEVALUE functions, and format it as a date.
-
Analyze Data can’t analyze data when Excel is in compatibility mode (i.e. when the file is in .xls format). In the meantime, save your file as an .xlsx, .xlsm, or xslb file.
-
Merged cells can also be hard to understand. If you’re trying to center data, like a report header, then as a workaround, remove all merged cells, then format the cells using Center Across Selection. Press Ctrl+1, then go to Alignment > Horizontal > Center Across Selection.
Analyze Data works best with clean, tabular data.

Here are some tips for getting the most out of Analyze Data:
-
Analyze Data works best with data that’s formatted as an Excel table. To create an Excel table, click anywhere in your data and then click Home > Tables > Format as Table.
-
Make sure you have good headers for the columns. Headers should be a single row of unique, non-blank labels for each column. Avoid double rows of headers, merged cells, etc.
Didn’t get Analyze Data? It’s probably us, not you.
Here are some reasons why Analyze Data may not work on your data:
-
Analyze Data doesn’t currently support analyzing datasets over 1.5 million cells. There is currently no workaround for this. In the meantime, you can filter your data, then copy it to another location to run Analyze Data on it.
-
String dates like «2017-01-01» will be analyzed as if they are text strings. As a workaround, create a new column that uses the DATE or DATEVALUE functions, and format it as a date.
We’re always improving Analyze Data
Even if you don’t have any of the above conditions, we may not find a recommendation. That’s because we are looking for a specific set of insight classes, and the service doesn’t always find something. We are continually working to expand the analysis types that the service supports.
Here is the current list that is available:
-
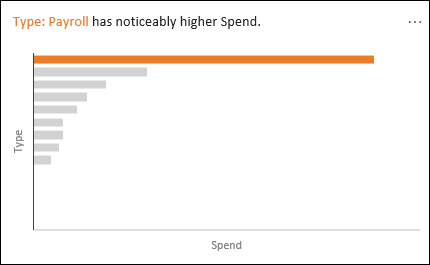
Rank: Ranks and highlights the item that is significantly larger than the rest of the items.
-
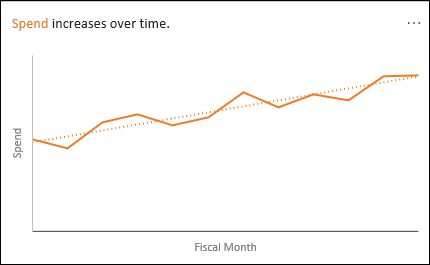
Trend: Highlights when there is a steady trend pattern over a time series of data.
-
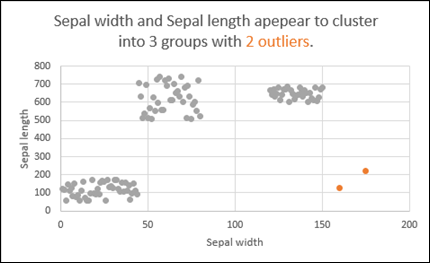
Outlier: Highlights outliers in time series.
-
Majority: Finds cases where a majority of a total value can be attributed to a single factor.
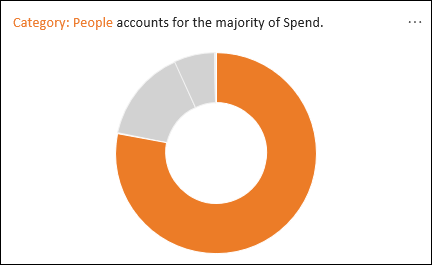
If you don’t get any results, please send us feedback by going to File > Feedback.
Because Analyze Data analyzes your data with artificial intelligence services, you might be concerned about your data security. You can read the Microsoft privacy statement for more details.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Data Analysis with Excel is a detailed lesson that gives readers a clear understanding of the newest and most sophisticated functions offered by Microsoft Excel. It describes in detail how to use MS-capabilities Excel to carry out various data analysis tasks. The guide includes a good amount of screenshots that step-by-step demonstrate how to use various features. One of the most used programs for data analysis is Microsoft Excel. You can simply import, browse, clean, analyze, and display your data using this all-in-one data management tool.
Types of Data Analysis
Charts
Any set of information may be graphically represented in a chart. A chart is a graphic representation of data that employs symbols to represent the data, such as bars in a bar chart or lines in a line chart. Excel has several different chart types available for you to choose from, or you can use the Excel Recommended Charts option to look at charts specifically made for your data and choose one of those.
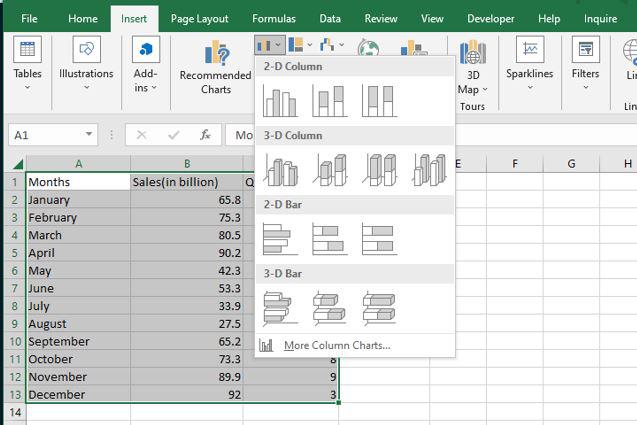
Step 1: Select a table. After that go to the Insert tab on the top of the ribbon then in the charts group select any chart. Here we are going to select a 3-D column chart.
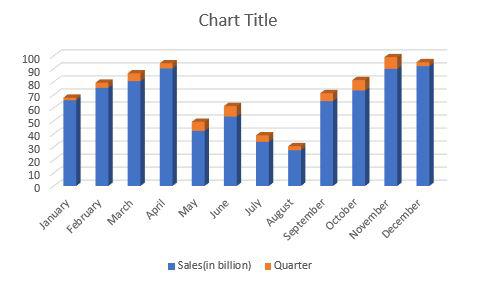
Step 2: As you can see, the excel table has been converted to a 3-D column chart.
Conditional Formatting
Patterns and trends in your data may be highlighted with the help of conditional formatting. To use it, write rules that determine the format of cells based on their values. In Excel for Windows, conditional formatting can be applied to a set of cells, an Excel table, and even a PivotTable report. To execute conditional formatting, adhere to the instructions listed below.
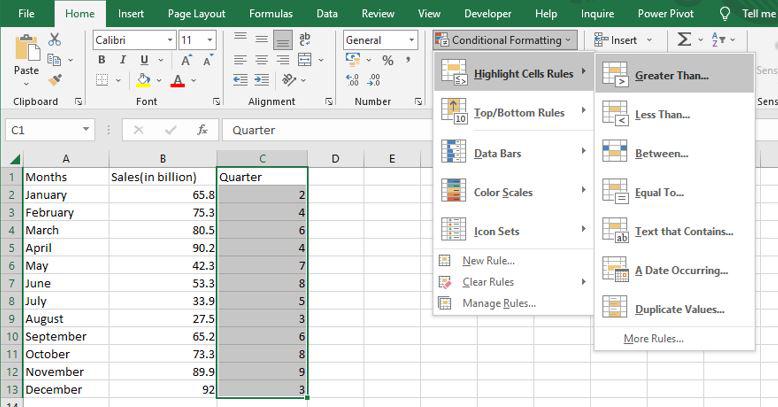
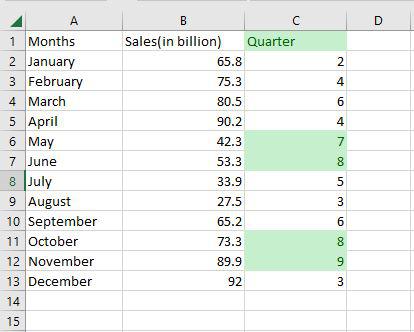
Step 1: Select any column from the table. Here we are going to select a Quarter column. After that go to the home tab on the top of the ribbon and then in the styles group select conditional formatting and then in the highlight cells rule select Greater than an option.
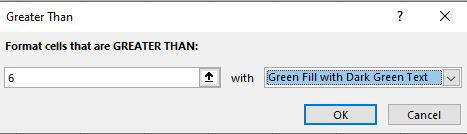
Step 2: Then a greater than dialog box appears. Here first write the quarter value and then select the color.
Step 3: As you can see in the excel table Quarter column change the color of the values that are greater than 6.
Sorting
Data analysis requires sorting the data. A list of names may be arranged alphabetically, a list of sales numbers can be arranged from highest to lowest, or rows can be sorted by colors or icons. Sorting data makes it easier to immediately view and comprehend your data, organize and locate the facts you need, and ultimately help you make better decisions. Both columns and rows can be used to sort. You’ll utilize column sorts for the majority of your sorting. By text, numbers, dates, and times, a custom list, format, including cell color, font color, or icon set, you may sort data in one or more columns.
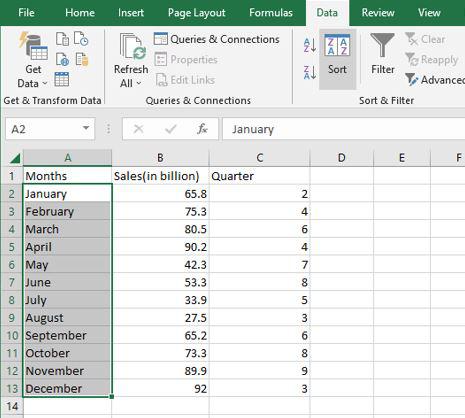
Step 1: Select any column from the table. Here we are going to select a Months column. After that go to the data tab on the top of the ribbon and then in the sort and filters group select sort.
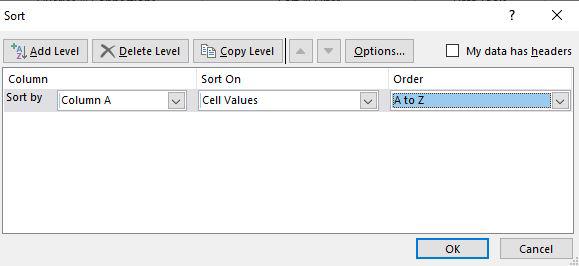
Step 2: Then a sort dialog box appears. Here first select the column, then select sort on, and then Order. After that click OK.
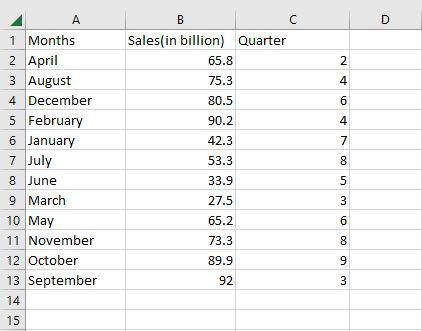
Step 3: Now as you can see the months column is now arranged alphabetically.
Filter
You may use filtering to pull information from a given Range or table that satisfies the specified criteria. This is a fast method of just showing the data you require. Data in a Range, table, or PivotTable may be filtered. You may use Selected Values to filter data. You may adjust your filtering options in the Custom AutoFilter dialogue box that displays when you click a Filter option or the Custom Filter link that is located at the end of the list of Filter options.
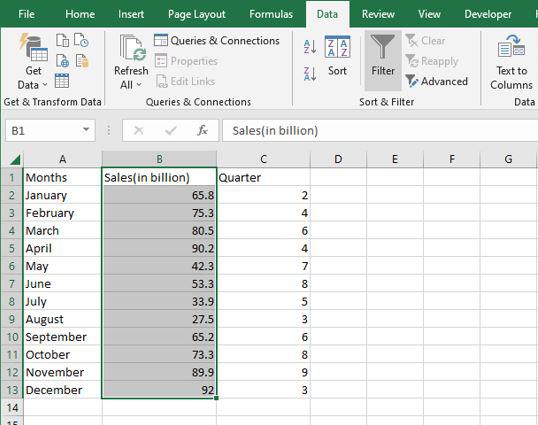
Step 1: Select any column from the table. Here we are going to select a Sales column. After that go to the data tab on the top of the ribbon and then in the sort and filters group select filter.
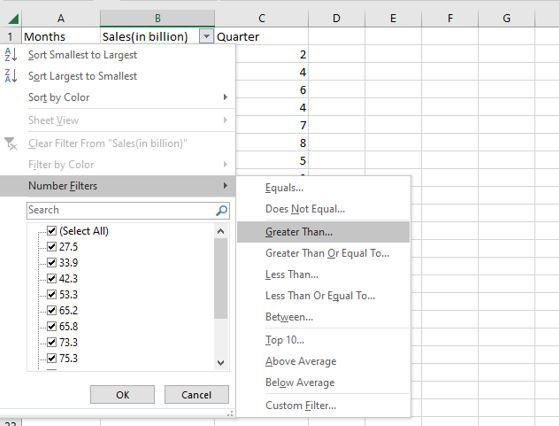
Step 2: The values in the sales column are then shown in a drop-down box. Here we are going to select a number of filters and then greater than.
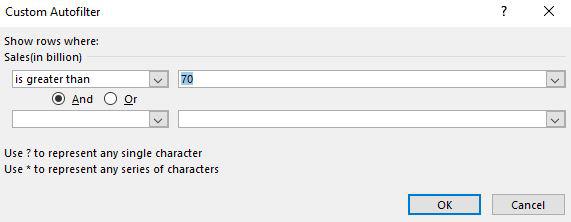
Step 3: Then a custom auto filler dialog box appears. Here we are going to apply sales greater than 70 and then click OK.
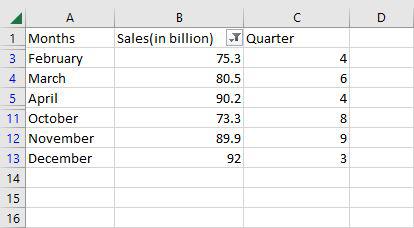
Step 4: Now as you can see only the rows greater than 70 are shown.
Method of Data Analysis
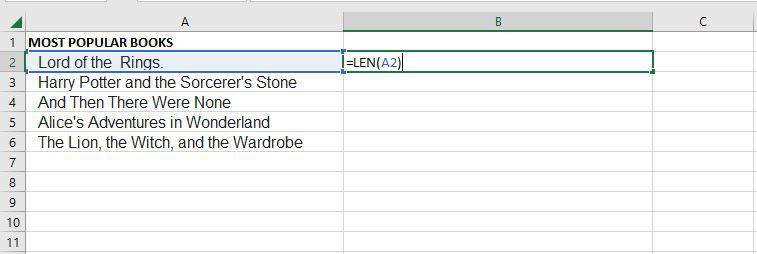
LEN
=LEN quickly returns the character count in a given cell. The =LEN formula may be used to calculate the number of characters needed in a cell to distinguish between two different kinds of product Stock Keeping Units, as seen in the example above. When trying to discern between different Unique Identifiers, which might occasionally be lengthy and out of order, LEN is very crucial.
=LEN(Select Cell)
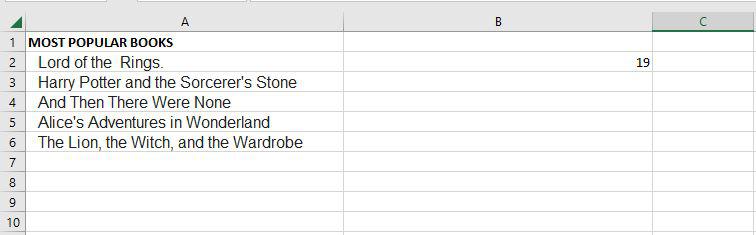
Step 1: If we want to see the length of cell A2, for that we need to write the function of length.
Step 2: Now as you can see it shows the length of the cell A2.
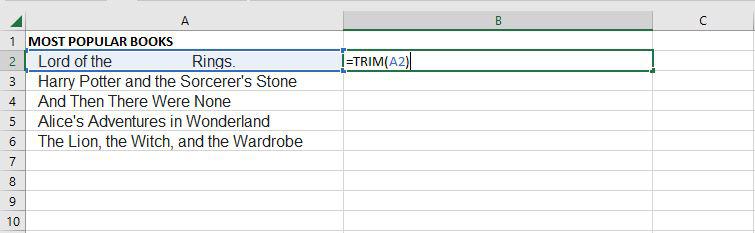
TRIM
=TRIM function will remove all spaces from a cell, with the exception of single spaces between words. The most frequent application of this function is to get rid of trailing spaces. When content is copied verbatim from another source or when users insert spaces at the end of the text, this is normal.
=TRIM(Select Cell)
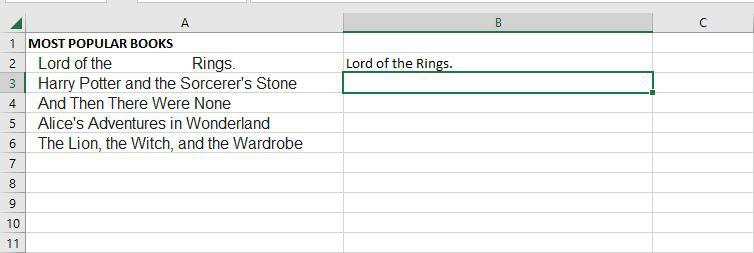
Step 1: If we want to remove all spaces from cell A2, for that we need to write the function of trim.
Step 2: Now as you can see after using the trim function, it removes all spaces.
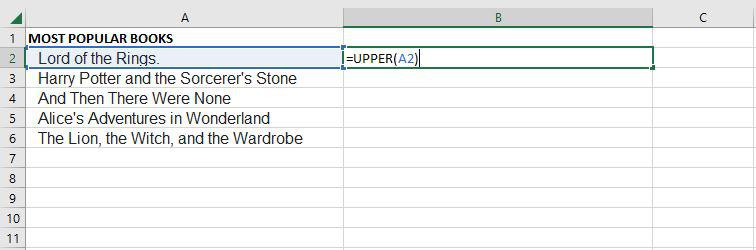
UPPER
The Excel Text function “UPPER Function” will change the text to all capital letters (UPPERCASE). As a result, the function changes all of the characters in a text string input to upper case.
=UPPER(Text)
Text (mandatory parameter): This is the text that we wish to change to uppercase. Text can relate to a cell or be a text string.
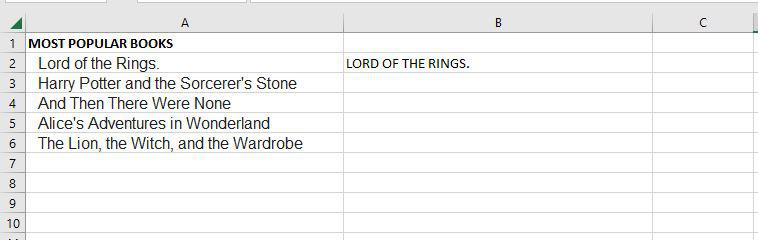
Step 1: If we want to convert the A2 cell to upper text, for that we need to write the upper function.
Step 2: Now as you can see after using the upper function, the text is changed to the upper text.
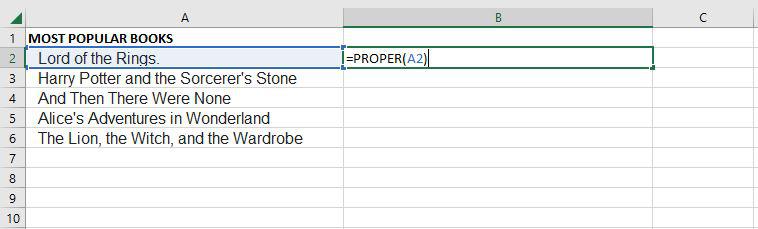
PROPER
Under Excel Text functions, the PROPER Function is listed. Any subsequent letters of text that come after a character other than a letter will also be capitalized by PROPER.
=PROPER(Text)
Text (mandatory parameter): A formula that returns text, a cell reference, or text in quote marks must surround the text you wish to partly capitalize.
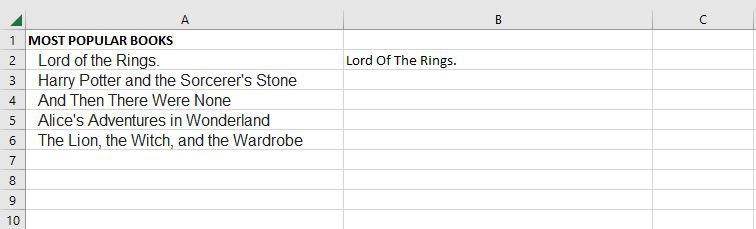
Step 1: If we want to convert the A2 cell to proper text, for that we need to write the proper function.
Step 2: Now as you can see after using the proper function, the text is changed to the proper form.
The PROPER function changes the initial letter of every word, letters that follow digits, and other punctuation to uppercase. It could be where we least expect it. The characters for numbers and punctuation remain unaffected.
COUNTIF
Excel has a built-in function called COUNTIF that counts the given cells. The COUNTIF function can be used in both straightforward and sophisticated applications. The fundamental application of counting particular numbers and words is covered in this.
=COUNTIF(range,criteria)
- Range: The size of the cell range to count.
- Criteria: The standards by which cells are selected for counting.
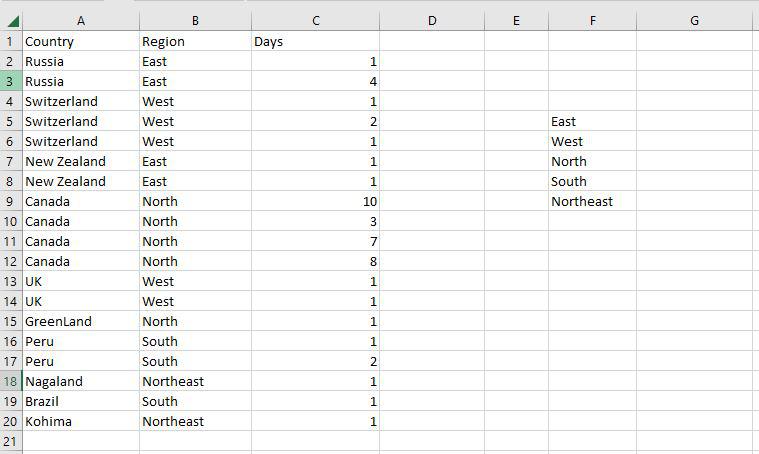
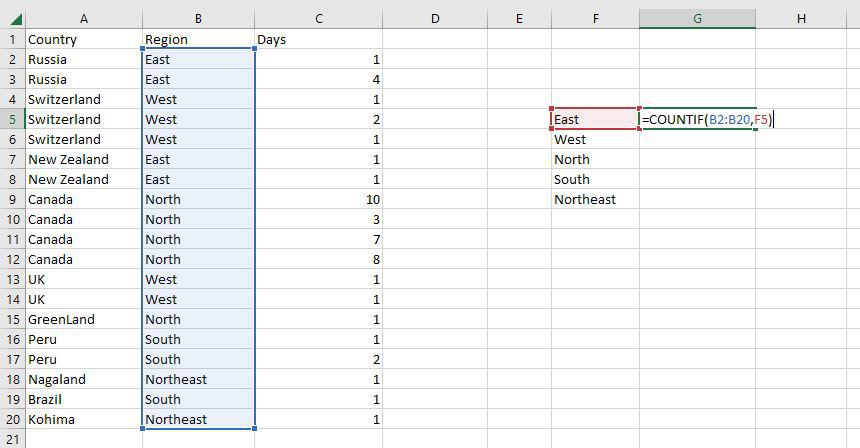
Step 1: Use the COUNTIF function on the range B2:B20 to get the number of regions we have of each type.
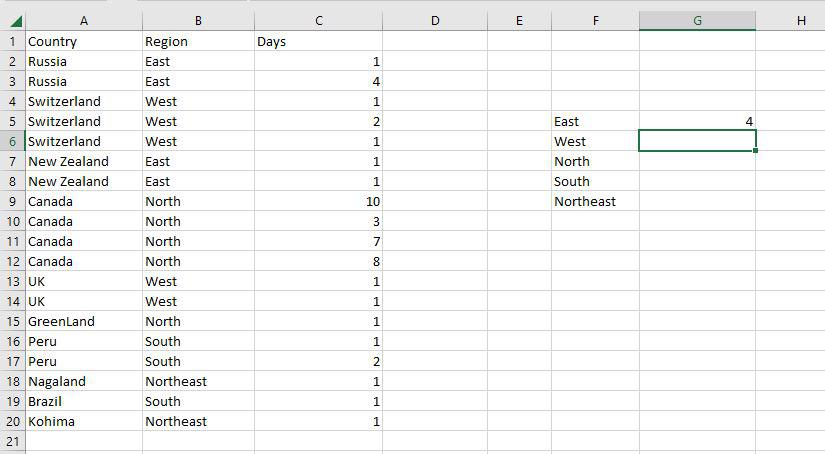
Step 2: The COUNTIF function will now be used to count the different sorts of Regions in the range F5:F9.
Step 3: Now as you can see the 4 East Region has been correctly enumerated using the COUNTIF function.
AVERAGEIF
An Excel built-in function called AVERAGEIF determines the average of a range depending on a true or false condition.
=AVERAGEIF(range, criteria, [average_range])
- Range: The size of the cell range to count.
- Criteria: The standards by which cells are selected for counting.
- Average Range: The range in which the function computes the average is known as the average range. But the average range is not required.
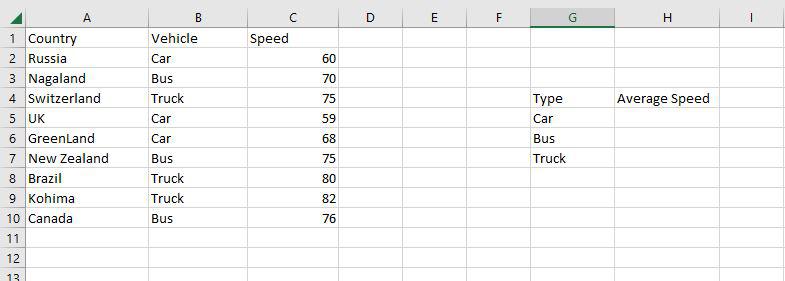
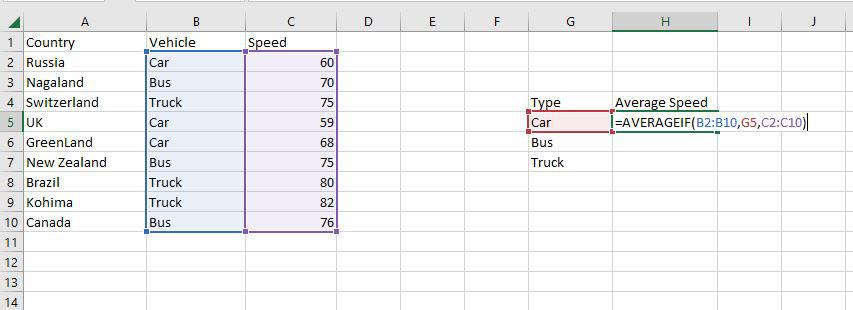
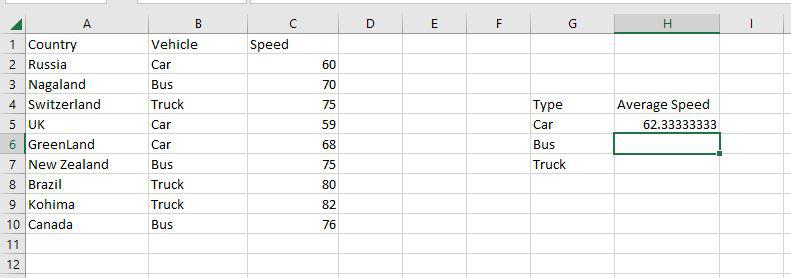
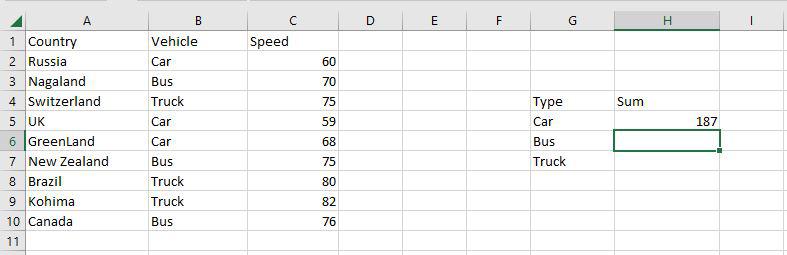
Step 1: Use the AVERAGEIF function on the range B2:B10 to get the average speed of vehicles.
Step 2: The AVERAGEIF function will now be used to find the average of Vehicles in the range H4:H7.
Step 3: Now as you can see the 62.333 Car average has been correctly enumerated using the AVERAGEIF function.
SUMIF
A built-in Excel function called SUMIF determines if a condition is true or false before adding the values in a range.
=SUMIF(range, criteria, [sum_range])
- Range: The size of the cell range to count.
- Criteria: The standards by which cells are selected for counting.
- Sum Range: The range that the function uses to calculate the total is known as the sum range.
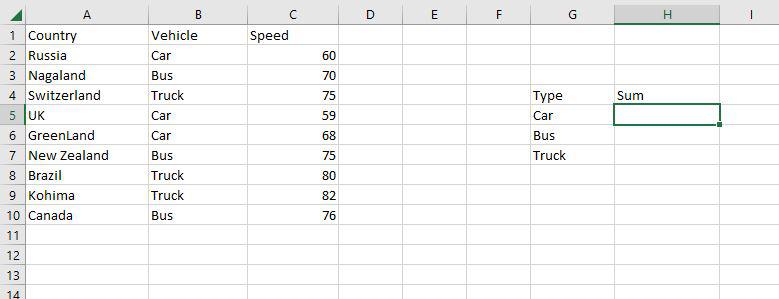
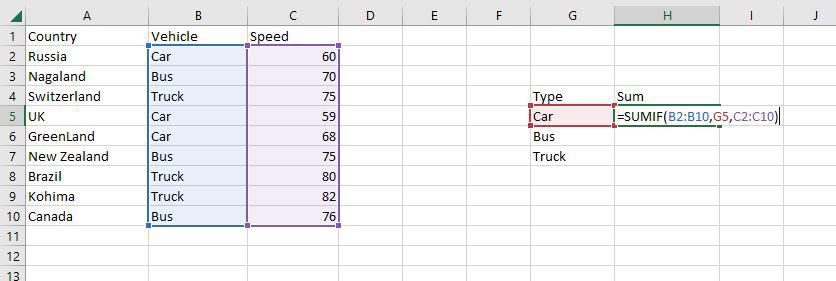
Step 1: Use the SUMIF function on the range B2:B10 to get the sum of the vehicle’s speed.
Step 2: The SUMIF function will now be used to find the sum of Vehicles’ speed in the range H4:H7.
Step 3: Now as you can see the 187 Car sum has been correctly enumerated using the SUMIF function.
VLOOKUP
VLOOKUP is a built-in Excel function that permits searching across several columns.
=VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup])
- Lookup_value: Choose the cell that will be used to input the search criteria.
- Table_array: The whole table range, which includes each and every cell.
- Col_index_num: The information being searched for. The column’s number, starting from the left, is the input.
- Range_lookup: FALSE if text (0), TRUE if numbers (1).
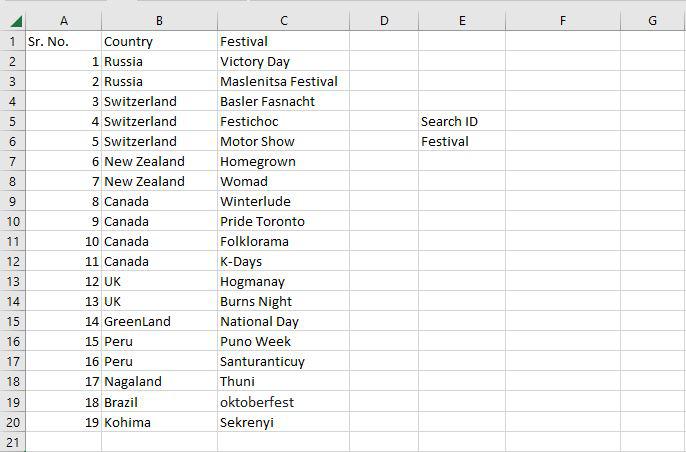
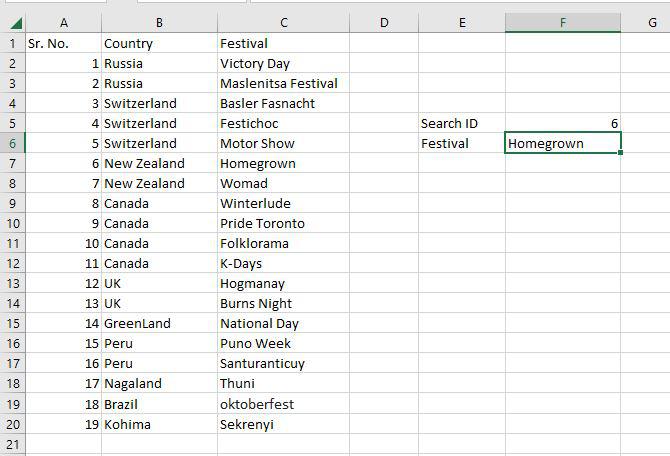
Step 1: To locate the Festival names depending on their search ID, use the VLOOKUP function. The Festival names in this instance are determined by their search ID.
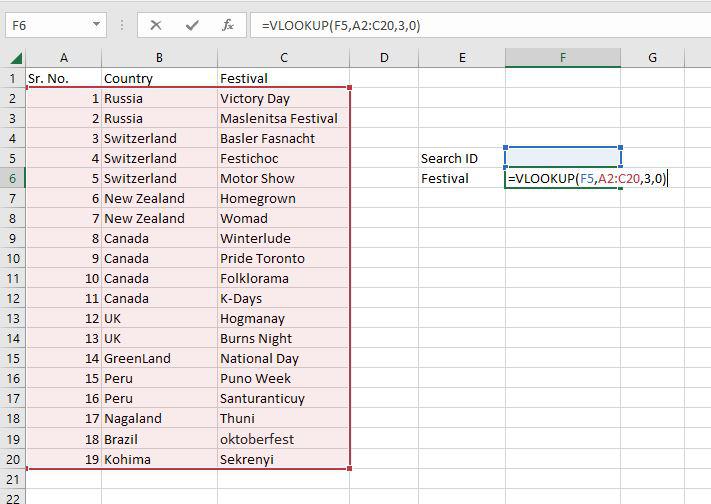
Step 2: F5 was chosen as the lookup value. The search query is typed in this cell. Table array, in this case, A2:C20, is designated as the table’s range. The col index number is set to 3, which is entered. The information being searched is in the third column from the left. Range lookup is entered as 0 (False).
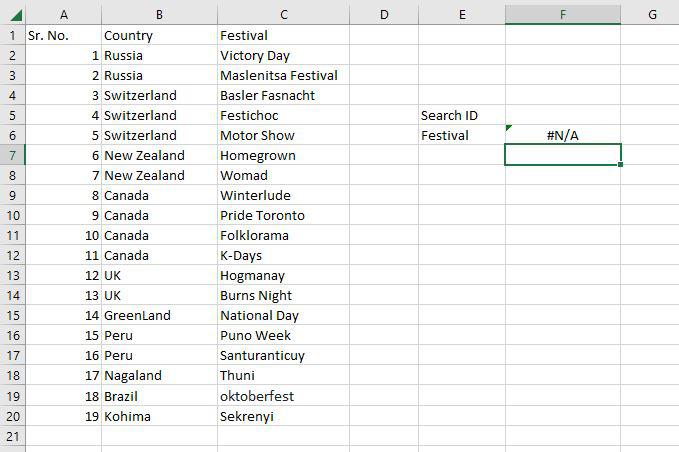
Step 3: The #N/A value is what the function returns. This is the result of the Search ID F5 having no value entered.
Step 4: The Homegrown Festival, which has Search ID 6, has been located through the VLOOKUP tool.
PIVOT TABLE
In order to create the required report, a pivot table is a statistics tool that condenses and reorganizes specific columns and rows of data in a spreadsheet or database table. The utility simply “pivots” or rotates the data to examine it from various angles rather than altering the spreadsheet or database itself.
Step 1: Select any cell and then go to the home tab and then select Pivot table.
Step 2: Create Pivot table dialog box appears here select the new worksheet and then click OK.
Step 3: Now you can see it creates a pivot table.
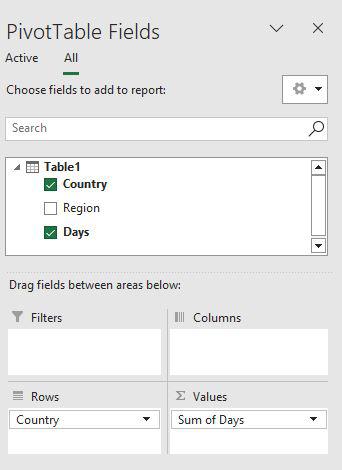
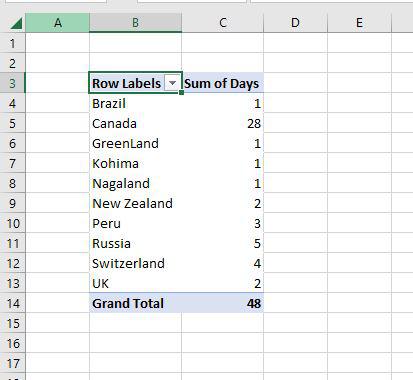
Step 4: Just drag the Country field to the row area and the Days field to the value area.
Step 5: Now you can see the proper pivot table with Country and days fields.
Анализ данных • 23 ноября 2022 • 5 мин чтения
4 инструмента быстрого и простого анализа данных в Microsoft Excel
Обычно аналитики работают со специфическими программами, но в некоторых случаях эффективнее использовать простой инструмент — Microsoft Excel.
Продакт-менеджер, эксперт бесплатного курса по Excel
- Настройка анализа данных в Excel
- Техники анализа данных в Microsoft Excel
- Совет эксперта
-
1. Сводные таблицы
-
2. Лист прогноза в Excel
-
3. Быстрый анализ в Excel
-
4. 3D-карты
Практически все инструменты для анализа данных уже встроены в Excel, и специально настраивать их не нужно. Эти инструменты находятся в главном меню программы в разделе «Данные».
Здесь лежат инструменты для сортировки, фильтрации, прогнозирования и других действий с данными таблицы
В других разделах они тоже встречаются — например, отображение географически привязанных данных на глобусе находится в разделе «Вставка → 3D-карта».
В Excel есть инструменты, которые нужно подключать отдельно. К таким относится анализ корреляций между значениями. Чтобы его использовать, нужно нажать «Файл → Параметры → Надстройки».
Затем в выпадающем списке «Управление» выбрать «Настройки Excel» и нажать «Перейти». Откроется список надстроек.
Нужно поставить галочку на «Пакет анализа» и нажать «ОК». После этого в разделе меню «Данные» появится пункт «Анализ данных» с доступными инструментами для анализа.
Инструменты для анализа данных в Excel простые в освоении, но плохо подходят для сложных задач. Тут аналитикам пригодится специальное ПО, аналитические базы данных и код на Python. Работать с этими инструментами учат на курсе «Аналитик данных».
Повышайте прибыль компании с помощью данных
Научитесь анализировать большие данные, строить гипотезы и соберите 13 проектов в портфолио за 6 месяцев, а не 1,5 года. Сделайте первый шаг к новой профессии в бесплатной вводной части курса «Аналитик данных».
Техники анализа данных в Microsoft Excel
Разберём несколько техник, которые позволят быстро изучить информацию, собранную в таблицу Excel.
Нужны для того, чтобы сводить данные, то есть смотреть, как соотносится информация в разных столбцах и строках исходной таблицы. Например, есть данные по профессиям и зарплатам разных специалистов. Сводная таблица покажет, сколько в среднем зарабатывает представитель каждой профессии или какая из профессий популярнее.
Чтобы создать сводную таблицу для анализа данных в Microsoft Excel, сначала нужно сделать простую. Затем выделить все данные для анализа и нажать «Вставка» → «Сводная таблица». Excel предложит опции.
В этом окне можно задать диапазон, а также указать, куда именно вставить новую сводную таблицу — на новый или на этот же лист.
Затем появится новый лист, пока ещё пустой. В окне справа нужно задать поля сводной таблицы.
Например, зададим поля «Профессия» и «Зарплата».
По умолчанию Excel выбирает для числовых данных «Сумму по полю», то есть показывает сумму всех значений. Это можно скорректировать в графе значения, нажав на строку «Сумма по полю» → «Параметры поля значений».
Здесь можно выбрать новое имя для колонки и задать нужную операцию, например вычисление среднего. Получится следующая таблица.
В таблицу можно добавлять дополнительные значения. Допустим, поставить галочку в графе «Возраст», чтобы узнать средний возраст представителей профессии.
Если перетащить графу «Возраст» из раздела «Значений» в «Строки», получится средняя зарплата по профессиям для каждого возраста.
Чтобы вычислить самую популярную профессию, нужно распределить все по столбцам и посчитать, сколько раз они встречаются в таблице.
Инструмент «Сводные таблицы» позволяет сопоставлять самые разные значения друг с другом и делать простые вычисления. Часто для базового анализа данных большего и не требуется.
С чем работает аналитик данных: 10 популярных инструментов
2. Лист прогноза в Excel
Это средство анализа данных в MS Excel позволяет взять набор изменяющихся данных и спрогнозировать, как они будут изменяться дальше. Для этого понадобится как можно больший набор данных за прошлые периоды, причём равные — неделю, месяц, год.
Для примера возьмём динамику зарплат за два года.
Посчитаем, какой примерно будет зарплата в течение следующего года. Для этого нужно выделить данные для анализа и нажать «Данные» → «Лист прогноза». Появится диалоговое окно.
В нём можно выставить конечную точку и сразу увидеть примерный график. После нажатия кнопки «Создать» Excel создаст отдельный лист с прогнозируемыми данными.
Также на листе будет график, на котором можно визуально отследить примерные изменения.
Чем больше значений для анализа, тем точнее будет прогноз. Разумеется, он построен на простом математическом анализе, а не на моделях машинного обучения, поэтому не может учитывать нюансы и сложные факторы. Однако для простых примерных прогнозов подойдёт.
3. Быстрый анализ в Excel
Этот набор инструментов отвечает на вопрос «Как сделать анализ данных в Excel быстро?». В Microsoft Office 365 он называется экспресс-анализом. Инструмент появляется в нижнем правом углу, если выделить диапазон данных. У быстрого анализа чуть меньший набор опций, однако он позволяет в пару кликов проводить большинство стандартных аналитических операций.
Если нажать на кнопку с иконкой в виде молнии либо сочетание клавиш CTRL+Q, открывается большой набор инструментов для анализа и визуализации.
Например, если выбрать «Форматирование» → «Гистограмма», Excel прямо
внутри ячеек для сравнения наглядно отобразит, насколько одни значения больше других.
При выборе «Диаграмма» Excel отобразит предварительный результат.
Затем создаст отдельный лист с настраиваемой диаграммой, в которой можно задавать свои параметры.
Прямо здесь можно вычислить среднее с автоматическим добавлением строки с результатами.
Инструмент быстрого анализа позволяет составить сводную таблицу без перехода в отдельные пункты меню.
Этот инструмент позволяет с помощью MS Excel провести анализ данных, в которых есть указание города или страны. Работает только в последних версиях Excel старше 2019 года, без интернета недоступен.
Возьмём таблицу с профессиями и зарплатами и добавим в неё новую колонку — город проживания. Далее нужно выделить диапазон данных и нажать «Вставка» → «3D-карта». В отдельном окне откроется карта.
Слева можно выбрать параметры отображения. Например, задать высоту столбцов в зависимости от нужного показателя. Возьмём «Зарплату», выставим среднее значение и посмотрим, как это отобразится на 3D-карте.
Высота столбцов изменится в зависимости от средней зарплаты в регионе — Excel посчитает это самостоятельно. Можно задать категории, например «Профессию».
Excel раскрасит столбики в зависимости от того, сколько представителей каждой профессии живёт в конкретном городе.
При наведении на конкретный элемент столбика можно увидеть город, профессию и среднюю зарплату.
3D-карты пригодятся, когда в таблице очень много данных и их география имеет большое значение. Этот инструмент подойдёт как для анализа, так и для быстрой визуализации. Внутри инструмента можно изменить параметры отображения и быстро создать видео для презентации результатов анализа.
Совет эксперта
Настя Шушурина
Вышеописанные функции и лайфхаки — только часть инструментария Excel. Ими можно воспользоваться, когда нужно быстро провести агрегацию данных, найти ответ на вопрос или просто сравнить ряд данных и добавить пару классных визуализаций в презентацию. В Excel есть и множество других инструментов, которые позволяют делать интересные вещи и проводить быстрые манипуляции с данными без умения писать код.
Как пересечение и объединение множеств используются в анализе данных
С чем работает аналитик данных: 10 популярных инструментов
Excel is currently the most flexible tool used in business. It has been around since the 1980s and continues to be the most essential data structure and analysis tool. It is an indispensable resource for personnel in IT, Finance, HR, Marketing, and virtually every other department imaginable. Let us have a conversation about its usefulness for our esteemed marketers.
Excel was used as a tool for data storage and organization. Over time, it became a tool for doing modest data calculations. Today, after several upgrades, it is recognized as a gateway into the realm of analytics. Let us accept the strength of this instrument and plunge into the realm of Excel-based marketing analytics with this post. This article will help to demonstrate the power of Excel in data analytics.
What does Excel do?
It is true that huge organizations have abandoned spreadsheets for enormous data sets, yet spreadsheets are still utilized for everyday tasks. In its most fundamental form, each cell in Excel contains data points. To facilitate viewing and organizing, exports of raw data, sales dates, SKUs, and units sold are inserted (or imported) into a spreadsheet. An effective Excel spreadsheet will arrange unstructured data into a format that makes it simpler to extract insights that can be put into action. Excel allows you to define fields and functions that perform computations with more sophisticated data. Even with bigger data sets, segmented data may be examined and viewed more thoroughly without the need for additional tools. Determine hypothetical profit margins or budgets for departments. While it cannot create a complete data product on its own, it may provide easy-to-read graphics and precise computations. If you are considering a career as an analyst or need to work with data to create a report, analytics is not the simplest procedure to learn in a single sitting. Use data spreadsheets as a little representation of a bigger data endeavor.
- What is the intent? Overview? What insights do you require?
- Where does the data originate? What exports and imports are required?
- Does the data require translation?
- What obstacles exist? Limitations?
How do you get your conclusions? Which post-analysis choices must be made?
Excel is an excellent starting point for context, but a true big data project requires far more people, expertise, and degree of detail.
What benefits does Data Analysis provide for Sales and Marketing?
Information Analysis will provide additional insights used to boost advertising activities. Be it their budgetary allocations, their interest group, or geology. Let us consider the following scenario: a marketing administrator is arranging a paid assignment on Google. Based on keyword trends, reverberation rates on the landing page, and the number of leads that will be generated from these clicks, he will have a good idea of how many clicks the promotion will generate within a certain time frame. An exhaustive data analysis will reveal the average income/benefits that will be generated by this project, enabling him to easily determine ROI, adjust advertising budgets as necessary, and establish benchmarks for each project.
How to Conduct Data Analysis in Microsoft Excel
Let us discuss the well-known features and functions of Microsoft Excel that are commonly employed by business professionals for data analysis in Excel.
Turn Tables
Turn tables allow you to extract relevant information from a massive dataset. This is considered the most effective method for analyzing information. You may embed a Pivot Table and then move fields, sort, filter, or modify the summary calculation. You may also create a Two-Layer Pivot Table. Group Pivot Table Items, Multi-level Pivot Table, Frequency Distribution, Pivot Chart, Slicers, Update Pivot Table, Calculated Field/Item, and Get-Pivot-Data are useful capabilities.
What-if Evaluation
Consider the possibility that Analysis facilitates the exploration of many routes pertaining to a variety of scenarios involving values or equations. Excel’s What-if analysis is initiated by clicking on the What-if button. After entering details about the anticipated circumstance, click the Outline button. Under this capability, you may also explore Data Tables, Quadratic Equation, and Goal Seek.
Limiting Formatting
The Conditional Formatting feature lets highlight cells with a distinct color based on the value assigned to it. Contingent planning is useful for managing rules, information bars, color scales, symbol sets, observe copies, concealing substitute columns, examining two documents, conflicting rules, the agenda, and Marketing Professionals.
Diagrams
A chart is more useful than a sheet since it displays information in several ways and is extremely easy to create. You can create an outline, alter the graph type, adjust the line or segment, legend location, and information markings. Column Chart, Line Chart, Pie Chart, Bar Chart, Area Chart, Scatter Plot, Data Series, Axes, Chart Sheet Trendline, Error Bars, Sparklines, Combination Chart, Gauge Chart, Thermometer Chart, Gantt Chart, and Pareto Chart are some of the many types of outlines in Microsoft Excel.
Sort and Filter
Sorting and filtering are the most frequently used Excel functions. Within segments, it should be able to arrange in ascending or descending order. List arrangement should be feasible via shading, inversion, or randomization. Channels are utilized to display information that conforms to models. Number and Text Filters, Date Filters, an Advanced Filter, a Data Form, Remove Duplicates, Outlining Data, and Subtotal are all available.
Vlookup and Hlookup
Examiners rely on Vlookup and Hlookup to notice a value in a data collection and get other attributes linked to it. It is frequently used by information analysts to connect and consolidate vital data from several dominant Marketing Professionals.
Can Excel be Used for Complex Data Analysis?
Excel has the capability to do predictive analytics using plugins. For complex data analysis, the add-ons in Excel will centralize all your complex business formulas and calculations from multiple systems in one sheet, view, or graph. Having all your data in one centralized place and detailed, customizable dashboards enable you to easily compare, measure, and analyze complex data so that you can make informed business decisions.
A company may sell its products and services in multiple countries. It uses eCommerce platforms for its Online Stores. They have different marketing platforms, payment gateways, inventories, logistic channels, and target audiences in each country. Hence, businesses are bound to use several tools and applications for each job to be done.
For a simple calculation of profit, where
Profits/Losses = Sales – Expenses
The sales data will come from eCommerce sites, Expenses from the marketing costs on the platforms like Google AdWords, and Facebook Ads. There can be other expenses like purchasing stock which might come from inventory management platforms like Olabi, which further need to be added to all other expenses occurred that is usually present in accounting software like FreshBooks. Additionally, there will be different data silos for each country. Thus, you must pull all these data from multiple platforms for each country separately in Excel, and then analyze all this data together with the expense data and calculate profits. It involves a lot of working hours which cost money, and there is usually a time lag involved, which reduces the accuracy of the analysis and its effectiveness as the data is not analyzed in real-time. Thus, it becomes necessary to consolidate all the data in a data warehouse using a data pipeline.
Daton is a modern cloud data pipeline designed to replicate data to a cloud data warehouse with the utmost ease. Daton, our eCommerce-focused data pipeline, has built-in support for more than 100 applications, databases, files, cloud storage, analytics, CRM, Customer support, and many others. Analysts can replicate data from any source to any destination (BigQuery, Snowflake, Redshift), without writing a single line of code and in a matter of minutes.
Table of Contents
- Overview of Excel
- What is data analysis?
- Why Excel for data analysis?
- How to carry out data analysis with Excel
- Data collection
- Data cleaning
- Data exploration (using Pivot Table)
- Data visualization
- Advanced Tools for Data Analysis
- PowerPivot
- ToolPak
- End Note
Overview of Excel
Excel is basically a spreadsheet that Microsoft developed for the different operating systems such as Windows, macOS, Android and iOS. It comes equipped with diverse functionalities such as calculation, graphing tools, pivot tables and a macro programming language called Visual Basic for Applications. It forms a part of Microsoft Office.
In the actual application, the world of business has embraced Excel as it is smooth, effective and flexible in the way it can be used. Nearly all major businesses make use of Excel in one way or the other. It suits any and every kind of business processes whether it’s sales, marketing or anything else. It’s such an integral part of businesses because it can be customized and it can produce effective results quite quickly without any specific technical expertise.
Since data is imported into Excel most of the times, it’s interesting how Excel itself can be used to carry out data analysis.
But before we go to data analysis, let’s understand what it entails…
What is data analysis?
While data is of vital importance and the world has become data-driven, data in the raw form is not quite useful. In order to use data to derive actionable intelligence, it needs to be inspected, cleansed and transformed. This kind of a process is what is called Data Analysis.
There is no single way to accomplish this. There are a variety of ways to carry out data analysis. These diverse ways of data analysis are used in different fields such as business, science and even social sciences. In fact, data analysis is something that contemporary business world thrives on. Data analysis is leveraged in order to glean business intelligence to drive business growth.
Data mining is also an exercise of data analysis but it focuses on discovering new knowledge for predictive rather than descriptive purposes. As far as statistical applications are concerned, data analysis can be bifurcated into descriptive statistics, exploratory data analysis (EDA) and confirmatory data analysis (CDA).
While EDA is all about identifying new features in the data, CDA endeavours to confirm or prove the existing hypotheses wrong.
Predictive analytics is an exercise of applying statistical models for predictive forecasting or classification. In order to extract and classify information from textual sources, text analytics, on the other hand, makes use of statistical, linguistic and structural techniques.
These are all variations of data analysis. Data integration is something that is needed prior to data analysis. Data analysis is also connected with data visualization and data dissemination. Sometime, people use the terms data analysis and data modeling interchangeably.
Why Excel for data analysis?
You know how navigating through data could be a nightmare in itself.
It’s quite tricky to explore and process data when you are looking at large chunks of data. Analyzing it could very well be a unique challenge. However, Excel can come to your rescue.
Excel contains functions that can process a large amount of data quite effectively and easily. While different tasks of data analysis could be tricky, Excel functions are quite easy and anybody can use them and analyze the data.
It’s not necessary either to remember all the functions. You can simply Google it and find out the function you need for data analysis tasks.
For the sheer speed, simplicity and accuracy of it, Excel is not just useful but imperative for data analysis. It can save your valuable time and effectively enable the data analysis without any hassle as well.
How to carry out data analysis with Excel?
You might wonder how data analysis actually works. Here’s an overview of the step-wise process of data analysis for you:
Specifying Data Requirements
In order to carry out effective data analysis, it is imperative to specify the data requirements right at the outset. Let’s say that the data pertains to population. If that be so, the specific variables such as age, income etc., need to be specified and obtained. The data obtained could be in the form of numbers or categories.
Data Collection
Once the variables are specified, the information regarding the variables needs to be collected. It can be collected from various sources and made available for further process. This data may not contain any insights in the present form. Therefore, it needs to be processed and cleaned.
Data Processing
The data that is collected needs to be organized for further analysis. This would entail structuring the data in a particular way so that it becomes compatible for various analysis tools. For instance, you may need to place the data in rows and columns in a table for further analysis either in a Spreadsheet or Statistical Application. You may even need to create a data model as well.
Data Cleaning
While the data may get organized, it may, however, be incomplete. It could still contain duplicate items. A few errors may also creep in. Data Cleaning is the way to correct these errors and make the data accurate. There are different ways to clean the data. Suppose it contains financial data, it will surely have totals. These totals can then be compared against authentic published data or some other parameters. In this way, the data can be cleaned.
Data Analysis
Once data passes through various phases such as processing and cleaning, it would be ready for data analysis. There are numerous techniques available for data analysis. Data visualization can also be used in order to project the data in a graphic format. Correlation or Regression Analysis which are well-known statistical models can also be used for data analysis.
Communication
While data analysis may seem like the last step of the process, the findings of data analysis need to be communicated in a structured way to the end users. The end users may want the findings in a particular format. This is where some of the techniques of data visualization such as table and charts can prove quite useful as they can communicate the message quite succinctly. Colour coding and other tools can help you simplify it and enable you to communicate the findings more effectively.
Process of Data Analysis with Excel:
When it comes to data analysis with Excel, here’s how you go about it:
- Data collection
- Data Cleaning
- Data Exploration (using Pivot Table)
- Data Visualization
Let’s get started…
Data Collection:
- In order to get started with data analysis, the first step is to collect information on the variables in a systematic way. This kind of a process will help us find answers to the important questions and assess the results.
- Data collection part is vital because it ensures the accuracy of the data so that decisions related to the data turn out to be valid.
- Data collection is also useful because you have a baseline with which you can measure and you also get a target where you aim at reaching.
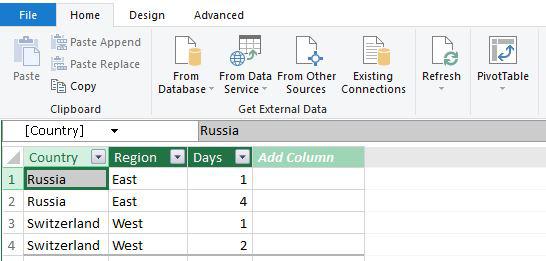
- As regards Excel, it is possible for you to collect and import data from a diversity of data sources. Your data sources could be:
- Web Page
- Microsoft Access database
- Let’s look at the practical example as mentioned below to see how we can collect data from various sources:
1. Extracting Data from Web Page
- It is possible that you would need the data that is refreshed on a website.
- For doing so, you can effectively use different Excel features. For instance, you can import data from a table on a website into Excel using a feature called Excel Web Query.
Step-by-Step Process to Extract Data From Web Pages:
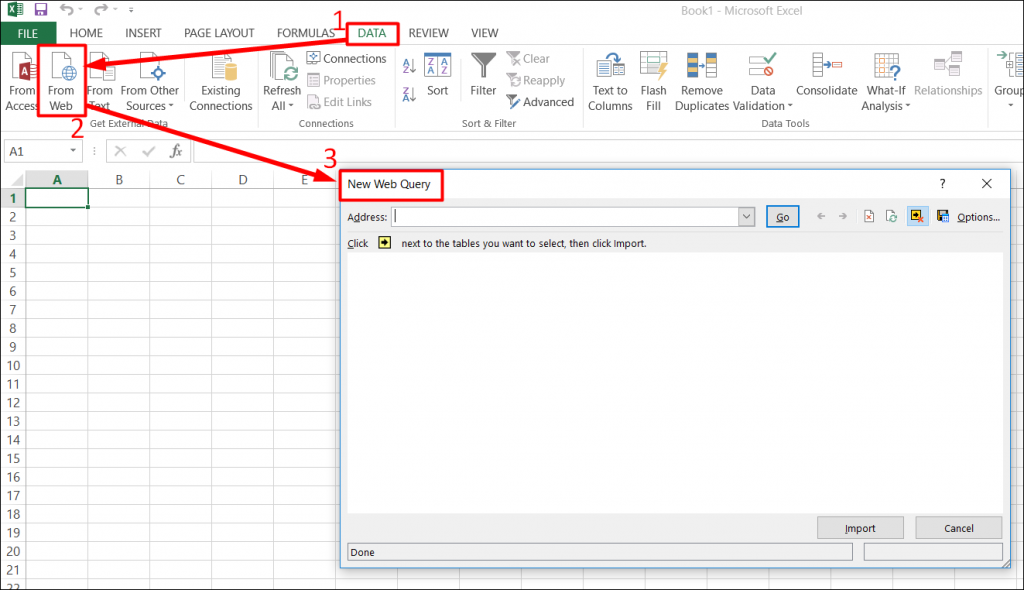
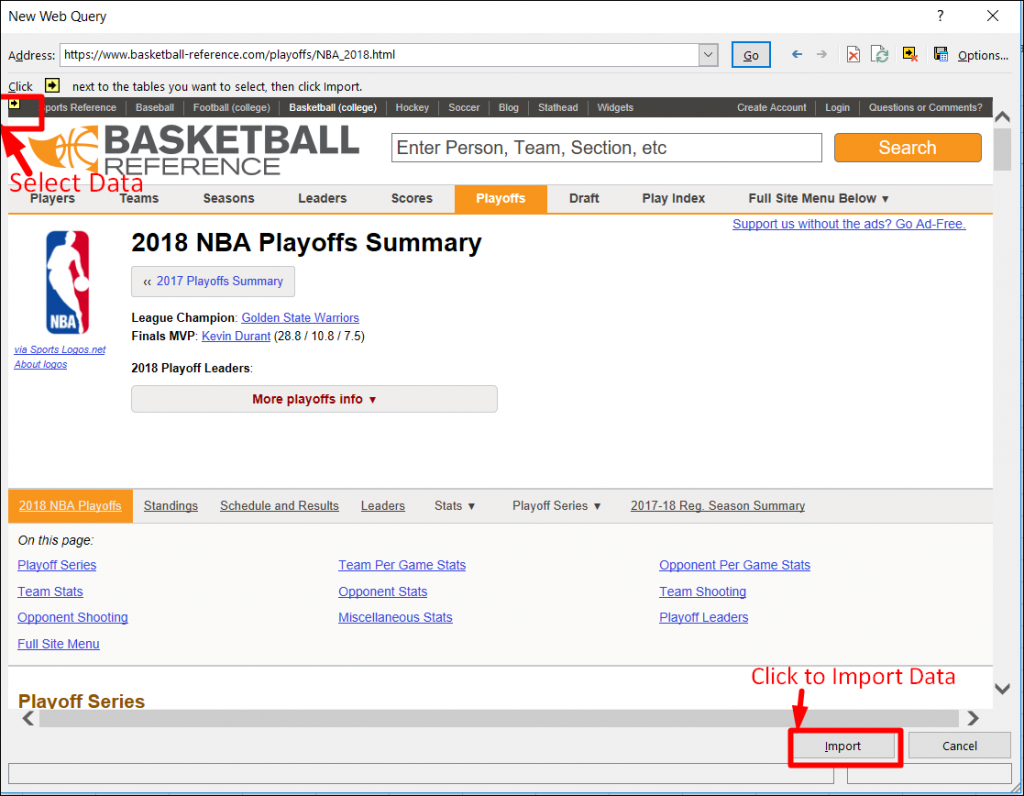
Step 1: Open a workbook with a blank worksheet in Excel.
Now, go to DATA tab on the Ribbon -> Click on From Web. You would be returned to the New Web Query dialog box as illustrated in screenshot given below.
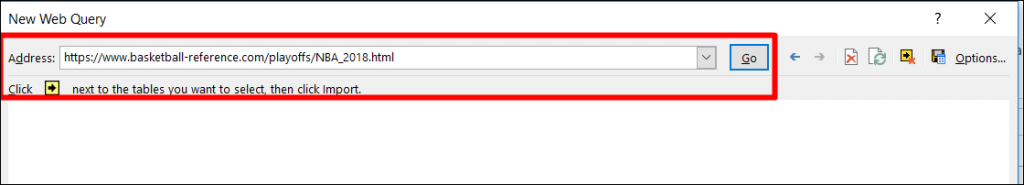
Step 2: Enter the URL of the website from where you want to import data, in the box next to Address and click Go.
In this example, we will extract data from the URL given below:
https://www.basketball-reference.com/playoffs/NBA_2018.html
Step 3: Click the yellow icons to select the data you want to import. Having done that, click the Import button after you have selected what you want.
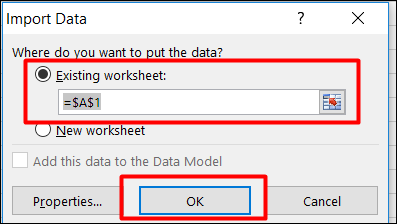
Step 4: Click Import data, specify where you want to put the data and click Ok. Arrange the data for further analysis and/or presentation.
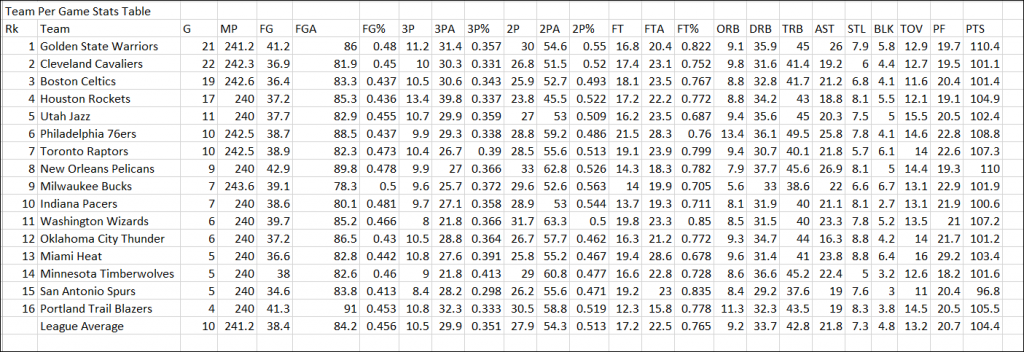
Output:
You can also collect data from other sources such as the following:
- From Microsoft Access Database
- From Files like csv, txt and xml
- From SQL server
Data Cleaning
- Data cleaning is all about finding out and correcting the errors in the dataset. It also includes replacing the incomplete or inaccurate parts with the correct ones.
- In Excel, you can clean data by using the techniques given below:
- Removing duplicate values
- Removing spaces
- Merging and splitting columns
- Reconciling table data by joining or matching
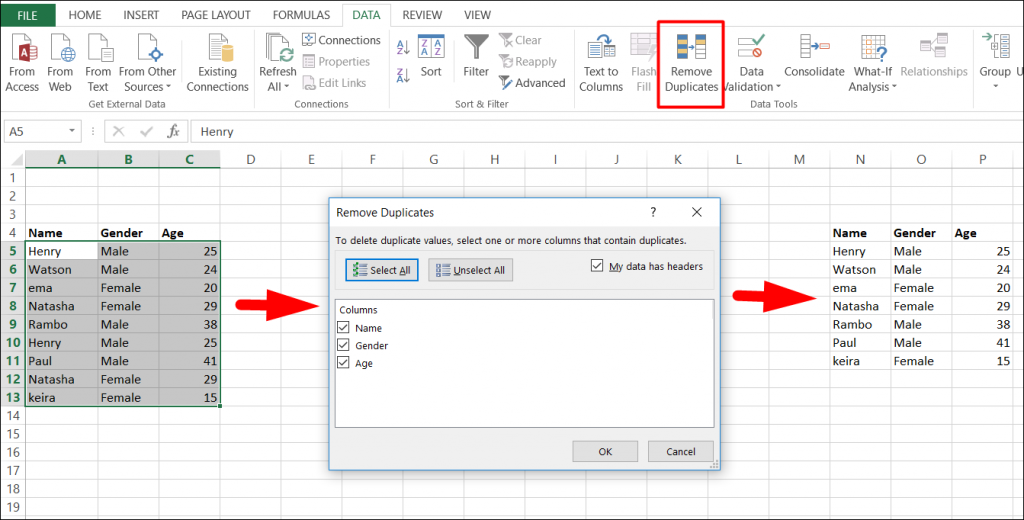
1. Removing duplicate rows:
- When you have large chunks of data, it is possible to have some duplicate rows. It would be advisable to filter for unique values first in order to confirm that the results are what you want before you remove duplicate values.
- Fortunately, Excel comes with an in-built feature to remove duplicate values from a table. With it, you can remove the duplicate values from a given table based on selected columns.
Let’s understand by an example:
Step 1:
Follow these steps to remove duplicate values: Select data –> Go to Data ribbon –> Remove Duplicates
2. Removing Spaces:
- It is possible that the data you have in Excel may contain leading, trailing, or multiple embedded space characters. These characters can sometimes cause unexpected results when you sort, filter, or search.
- However, you can use the Trim function in Microsoft Excel in order to remove all spaces from text except for single spaces between words.
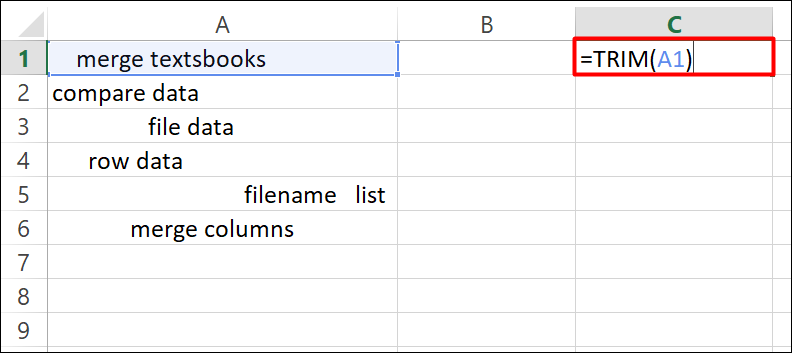
Step 1:
Enter the formula =TRIM (A1) in the adjacent cell C1 and press the Enter key.
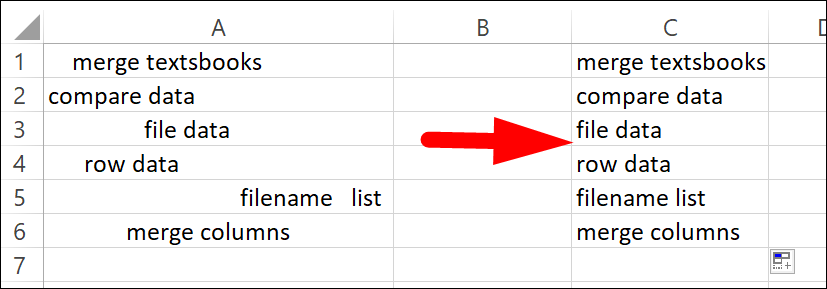
Step 2:
Select cell C1 and drag the fill handle down to the range cell that you want to remove the leading space. Then you can see all cell contents are extracted with all leading spaces removed. Please see the screenshot:
3. Merging and Splitting columns
- In Excel, it is common to merge or split two or more columns into one or split one column into two or more columns.
- For example, you may want to split a column that contains an address field into separate street, city, region, and postal code columns.
- For this task, we will make use of Table To Column Function.
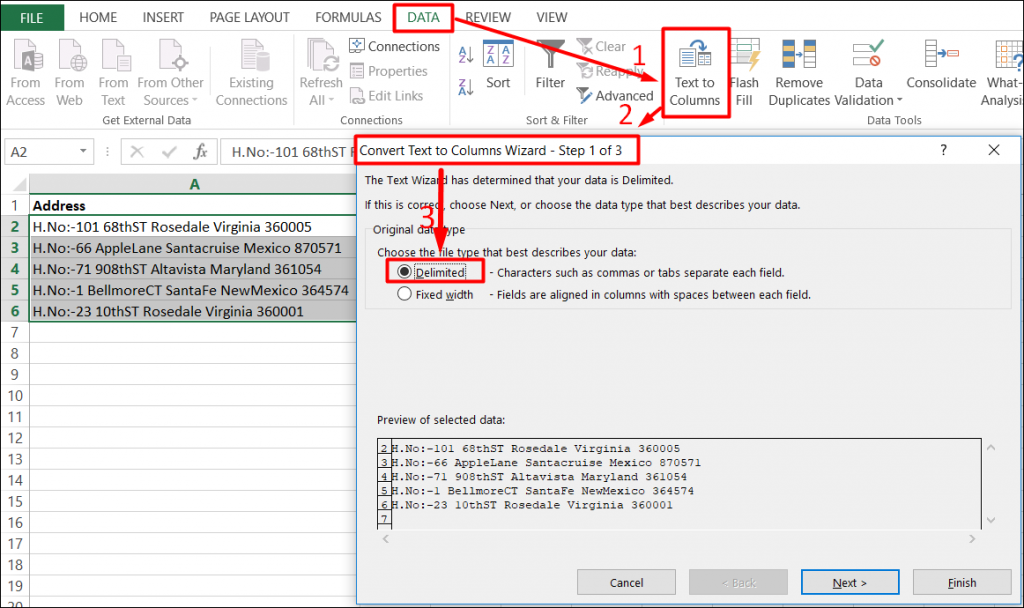
Step 1:
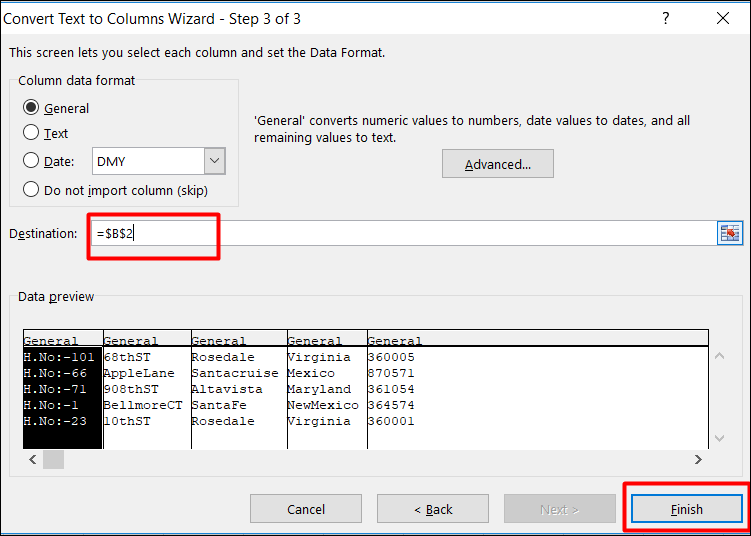
Go to Data tab, in Sort & Filter Group. Click on the Text to Columns.
Then choose radio button: Delimited (to split the address) and click on next button like the screenshot given below:
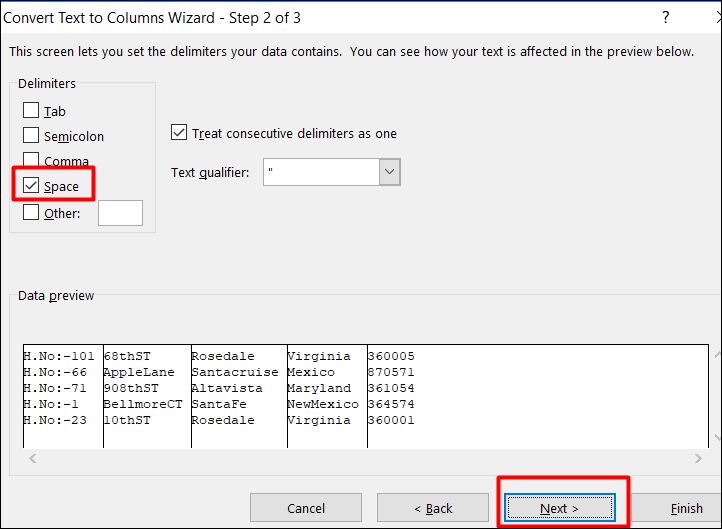
Step 2:
Click and put a tick on the “Space” check box because our data delimiter is “Space”. When you click on it, you will be able to see the data being separated in the data preview box.
Then Click on the Next button.
Step 3:
Click on destination to choose the location where you want to split the text and Click on the “Finish” button.
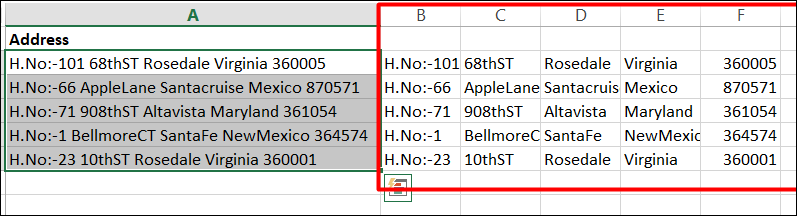
Step 4:
You can see that the text from one cell in column A has been split into the column B:F as shown below.
You can also use this feature for additional common values that may require merging into one column or splitting into multiple columns include product codes, file paths, and Internet Protocol (IP) addresses.
4. Reconciling table data by joining or matching
- Excel can also be used for finding and correcting matching errors when two or more tables are joined. This may entail reconciling two tables from different worksheets.
- For example, you can use it to see all records in both tables or to compare tables and find rows that don’t match.
- Here, function vlookup() would help to perform this task.
- Vlookup(): It searches for a value in the first column of a table array and returns a value in the same row from another column in the table array.
- Let’s look at the table below (order and Customer). In Order table, we want to map city name from the customer tables based on common key “Customer ID”.
- Here, function vlookup() will enable us to perform this task.
- Go to Formula tab -> in Function Library click on Lookup & Reference -> click on Vlookup.
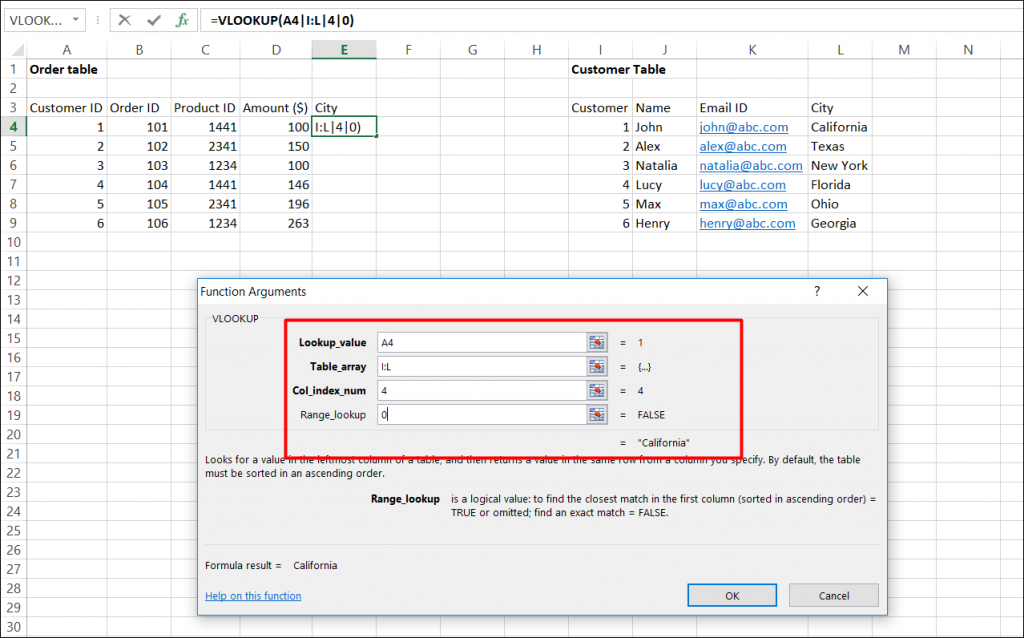
- Now, We´ll use the VLOOKUP function and type this formula into E3.
- Vlookup Syntax:
- Lookup_value : Key to lookup
- Table_array : Source_table
- Col_index_num : column of source table
- Range_lookup : are you ok with relative match?
- For our example:
- Lookup_value – A4
- Table_array – I : L
- Col_index_num – 4
- Range_lookup – 0
- This will return the city name for all the Customer id 1 and post that copy this formula for all Customer ids. Please see the screenshot given below:
Data Exploration Using Pivot Table
- Data Exploring is the vital process of performing initial investigations on data in order to find out patterns, to spot anomalies, to test hypothesis and to check assumptions with the help of summary statistics and graphical representations.
- Why it matters so much is that you can make use of exploring data and make sense of the data you have. You can then figure out what questions you want to ask and how to frame them, as well as how best to manipulate your available data sources to get the answers you need.
Pivot Table:
- Excel’s Pivot Table is a summary table that lets you count, average, sum, and perform other calculations according to the reference feature you have selected.
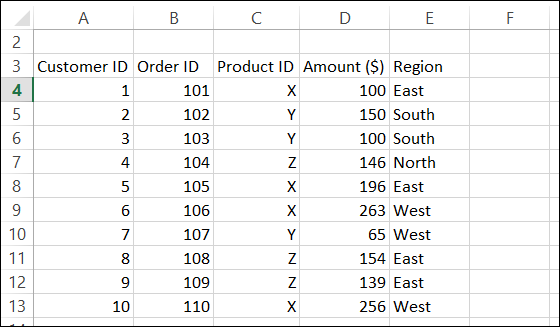
- Let’s Create Pivot Table for the table given below:
Step 1:
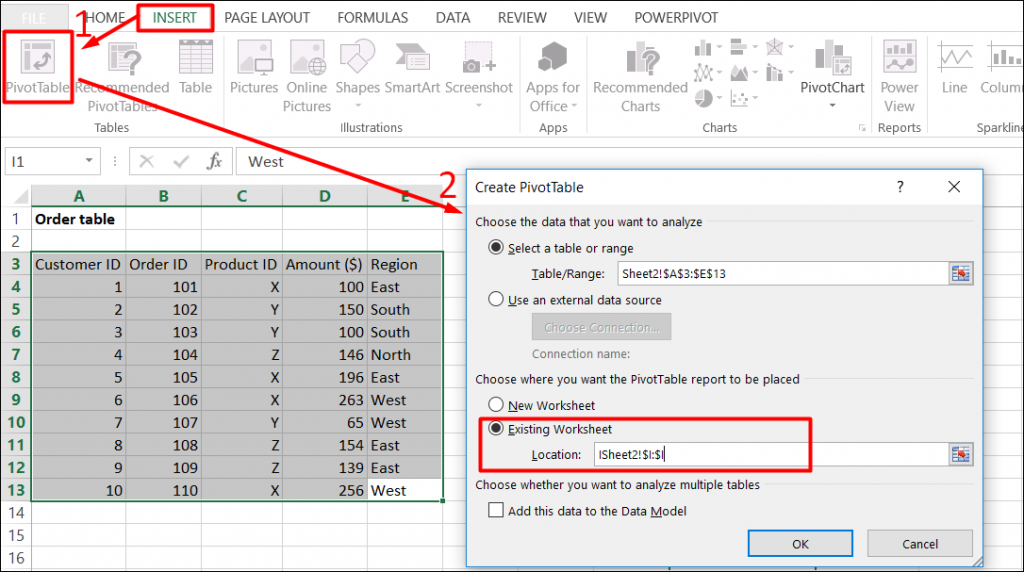
To show Region and Product wise sum of premium, we will create a pivot table as follows:
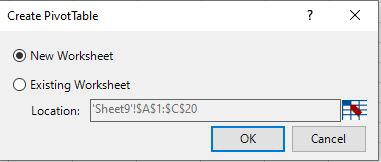
Select table (A3:E13) -> Go to Insert tab, in the tables group, Click on Pivot Table.
Then select Existing worksheet Location where you want the Pivot Table.
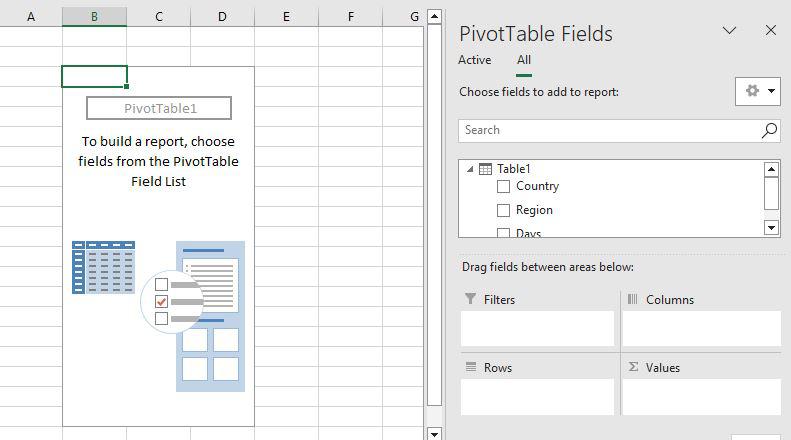
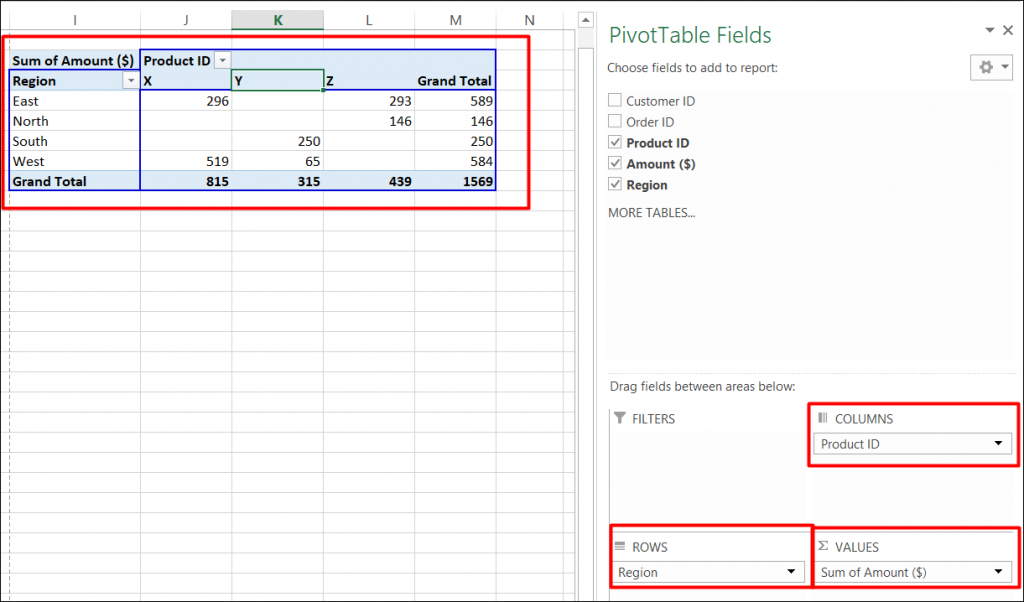
Step 2:
Now, you can see the Pivot Table Field List panel, which contains the fields from your list. All you need to do is to arrange them in the boxes at the foot of the panel. Once you have done that, the diagram on the left becomes your Pivot Table.
As shown in the screenshot, you can see that we have arranged “Region” in row, “Product id” in column and sum of “Premium” is taken as value. Now you are ready with pivot table which shows Region and Product wise sum of premium. You can also use count, average, min, max and other summary metric.
Data Visualization:
- As exploring data is quite important, data visualization as a technique through which we can explore data also becomes vital for us.
- Data visualization is the presentation of data in a pictorial or graphical format. The reason why such a graphical format matters is that it becomes easier for decision makers to see analytics presented visually. In other words, they can grasp difficult concepts or identify new patterns far more easily.
- In Excel, there are 2 features (Charts and Pivot Charts) which are most popular for data visualization.
Charts:
A simple chart in Excel can say a lot more than a sheet full of numbers. As you’ll see, creating charts is quite easy.
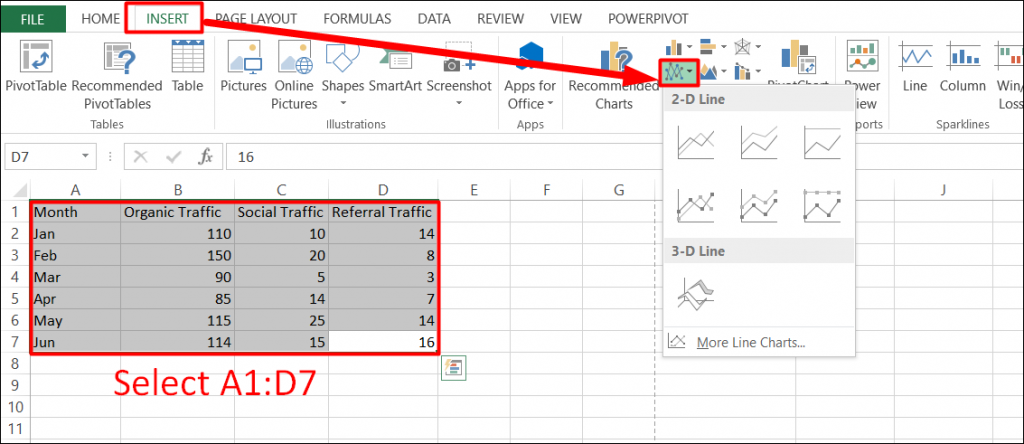
Let’s create Simple Line Chart by executing following steps:
Step 1:
Select the range A1:C11 -> On the Insert tab, in the Charts group, click the Line symbol.
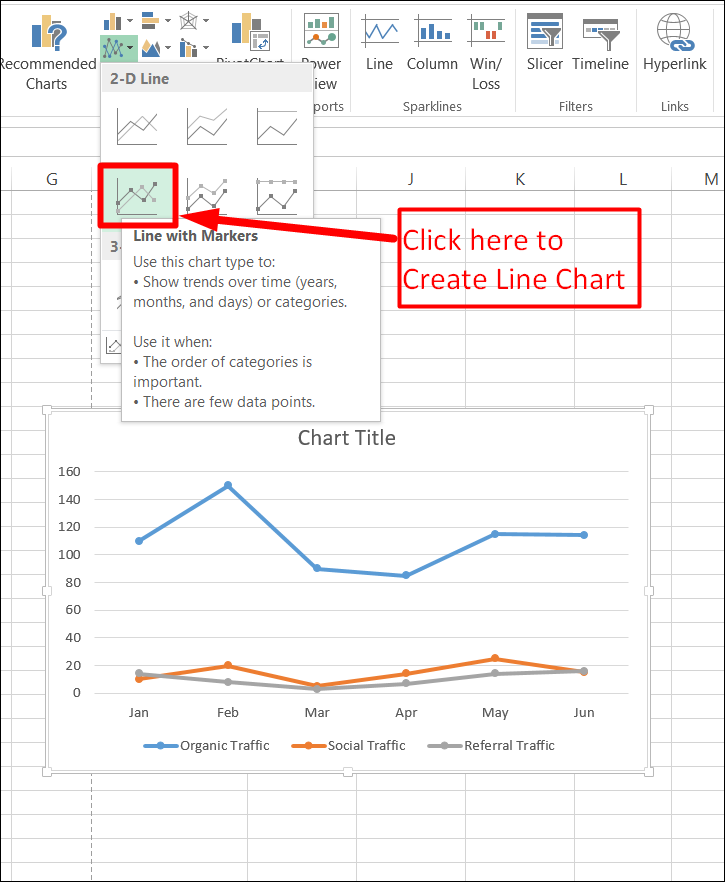
Step 2:
Now, to create Line Chart, click Line with Markers as shown in the screenshot.
Pivot chart:
A pivot chart is the visual representation of a pivot table in Excel. Pivot charts and pivot tables are connected with each other.
Go back to Pivot Tables to learn how to create this pivot table.
Let’s create a Pivot Chart:
Step 1:
Click any cell inside the pivot table -> On the Insert tab, in the Charts group, click Pivot Chart.
Then the Insert Chart dialog box appears. Click OK to create pivot Chart.
In the screenshot given below, you can find the pivot chart.
Once you have created the pivot chart, you can customize it to your particular needs to communicate your desired message by filtering chart attributes and changing chart types.
1. PowerPivot
Excel has limitations of 1048576 Rows which means you cannot analyze more than 1048576 rows of data.
And this is where Powerpivot comes in…
Power Pivot is an Excel Add-on that was first introduced in Excel 2010, and gives you a chance to import, merge and prepare data from more data sources at once.
You can import many tables from many different sources (SQL, Azure, Oracle, Excel, Access,…) into Power Pivot and then you can relate all this data to one another.
It means that you can build a Data Model containing multiple data sets from multiple different sources and by connecting them acquiring the ability to analyze them all in one Pivot Table.
Learn More about Power Pivot :
https://support.office.com/en-us/article/power-pivot-powerful-data-analysis-and-data-modeling-in-excel-a9c2c6e2-cc49-4976-a7d7-40896795d045
2. ToolPak
While developing complex statistical or engineering analyses, you can save steps and time by using the Analysis ToolPak.
All you need to do is to provide the data and parameters for each analysis, and the tool uses the appropriate statistical or engineering macro functions to calculate and display the results in an output table. Some tools generate charts in addition to output tables.
ToolPak Provides 19 various features (like Correlation, Covariance, Histogram, Regression and many more…) for data analysis.
Learn More about ToolPak:
https://support.office.com/en-us/article/use-the-analysis-toolpak-to-perform-complex-data-analysis-6c67ccf0-f4a9-487c-8dec-bdb5a2cefab6
End Note
It’s common knowledge how Excel is imperative for businesses in their day-to-day operations. However, not many businesses are aware of the potential of Excel for data analysis.
Since data analysis is crucial for businesses, it’s paramount that businesses leverage the power of Excel for data analysis. The more effectively you can use Excel, the more insights you can gain out of data analysis which you can utilize in enhancing your business.
There are other options such as Python, R Language or rapidminer that you can capitalize upon for data analysis as well. There are many tools that you can use for data analysis. However, each one will require a particular kind of expertise that you may or may not have. Therefore, data analysis with Excel is the simplest and yet one of the most effective data analysis solutions.
Do share your valuable feedback and comments regarding this blog.


 +T.
+T.