How to Write a Great Essay in English! This lesson provides 100+ useful words, transition words and expressions used in writing an essay. Let’s take a look!
The secret to a successful essay doesn’t just lie in the clever things you talk about and the way you structure your points.
Overview of an Essay
Useful Phrases for Proficiency Essays
Developing the argument
- The first aspect to point out is that…
- Let us start by considering the facts.
- The novel portrays, deals with, revolves around…
- Central to the novel is…
- The character of xxx embodies/ epitomizes…
The other side of the argument
- It would also be interesting to see…
- One should, nevertheless, consider the problem from another angle.
- Equally relevant to the issue are the questions of…
Conclusion
- The arguments we have presented… suggest that…/ prove that…/ would indicate that…
- From these arguments one must…/ could…/ might… conclude that…
- All of this points to the conclusion that…
- To conclude…
Ordering elements
- Firstly,…/ Secondly,…/ Finally,… (note the comma after all these introductory words.)
- As a final point…
- On the one hand, …. on the other hand…
- If on the one hand it can be said that… the same is not true for…
- The first argument suggests that… whilst the second suggests that…
- There are at least xxx points to highlight.
Adding elements
- Furthermore, one should not forget that…
- In addition to…
- Moreover…
- It is important to add that…
Accepting other points of view
- Nevertheless, one should accept that…
- However, we also agree that…
Personal opinion
- We/I personally believe that…
- Our/My own point of view is that…
- It is my contention that…
- I am convinced that…
- My own opinion is…
Others’ opinions
- According to some critics…
Critics: - believe that
- say that
- suggest that
- are convinced that
- point out that
- emphasize that
- contend that
- go as far as to say that
- argue for this
Introducing examples
- For example…
- For instance…
- To illustrate this point…
Introducing facts
- It is… true that…/ clear that…/ noticeable that…
- One should note here that…
Saying what you think is true
- This leads us to believe that…
- It is very possible that…
- In view of these facts, it is quite likely that…
Certainty
- Doubtless,…
- One cannot deny that…
- It is (very) clear from these observations that…
Doubt
- All the same, it is possible that…
- It is difficult to believe that…
Accepting other points to a certain degree
- One can agree up to a certain point with…
- Certainly,… However,…
- It cannot be denied that…
Emphasizing particular points
- The last example highlights the fact that…
- Not only… but also…
- We would even go so far as to say that…
Moderating, agreeing, disagreeing
- By and large…
- Perhaps we should also point out the fact that…
- It would be unfair not to mention the fact that…
- One must admit that…
- We cannot ignore the fact that…
- One cannot possibly accept the fact that…
Consequences
- From these facts, one may conclude that…
- That is why, in our opinion, …
- Which seems to confirm the idea that…
- Thus,…/ Therefore,…
Comparison
- Some critics suggest…, whereas others…
- Compared to…
- On the one hand, there is the firm belief that… On the other hand, many people are convinced that…
How to Write a Great Essay | Image 1
How to Write a Great Essay | Image 2
Phrases For Balanced Arguments
Introduction
- It is often said that…
- It is undeniable that…
- It is a well-known fact that…
- One of the most striking features of this text is…
Thesis
- The first thing that needs to be said is…
- First of all, let us try to analyze…
- One argument in support of…
- We must distinguish carefully between…
- The second reason for…
- An important aspect of the text is…
- It is worth stating at this point that…
Antithesis
- On the other hand, we can observe that…
- The other side of the coin is, however, that…
- Another way of looking at this question is to…
Conclusion
- What conclusions can be drawn from all this?
- The most satisfactory conclusion that we can come to is…
- To sum up… we are convinced that…/ …we believe that…/ …we have to accept that…
How to Write a Great Essay | Image 3
To be truly brilliant, an essay needs to utilise the right language. You could make a great point, but if it’s not intelligently articulated, you almost needn’t have bothered.
Developing the language skills to build an argument and to write persuasively is crucial if you’re to write outstanding essays every time. In this article, we’re going to equip you with the words and phrases you need to write a top-notch essay, along with examples of how to utilise them.
It’s by no means an exhaustive list, and there will often be other ways of using the words and phrases we describe that we won’t have room to include, but there should be more than enough below to help you make an instant improvement to your essay-writing skills.
This article is suitable for native English speakers and those who are learning English at Oxford Royale Academy and are just taking their first steps into essay writing.
General explaining
Let’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points.
1. In order to
Usage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument.
Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. In other words
Usage: Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point.
Example: “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. To put it another way
Usage: This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance.
Example: “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.”
4. That is to say
Usage: “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise.
Example: “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.”
5. To that end
Usage: Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”.
Example: “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.”
Adding additional information to support a point
Students often make the mistake of using synonyms of “and” each time they want to add further information in support of a point they’re making, or to build an argument. Here are some cleverer ways of doing this.
6. Moreover
Usage: Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making.
Example: “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”
7. Furthermore
Usage:This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information.
Example: “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
8. What’s more
Usage: This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”.
Example: “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.”
9. Likewise
Usage: Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned.
Example: “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.”
10. Similarly
Usage: Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”.
Example: “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.”
11. Another key thing to remember
Usage: Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”.
Example: “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.”
12. As well as
Usage: Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”.
Example: “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”
13. Not only… but also
Usage: This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information.
Example: “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.”
14. Coupled with
Usage: Used when considering two or more arguments at a time.
Example: “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…”
15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…
Usage: This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other.
Example: “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z.
16. Not to mention/to say nothing of
Usage: “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis.
Example: “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
Words and phrases for demonstrating contrast
When you’re developing an argument, you will often need to present contrasting or opposing opinions or evidence – “it could show this, but it could also show this”, or “X says this, but Y disagrees”. This section covers words you can use instead of the “but” in these examples, to make your writing sound more intelligent and interesting.
17. However
Usage: Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said.
Example: “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.”
18. On the other hand
Usage: Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion.
Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
19. Having said that
Usage: Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”.
Example: “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.”
20. By contrast/in comparison
Usage: Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence.
Example: “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.”
21. Then again
Usage: Use this to cast doubt on an assertion.
Example: “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.”
22. That said
Usage: This is used in the same way as “then again”.
Example: “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.”
23. Yet
Usage: Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea.
Example: “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.”
Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservations
Sometimes, you may need to acknowledge a shortfalling in a piece of evidence, or add a proviso. Here are some ways of doing so.
24. Despite this
Usage: Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence.
Example: “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.”
25. With this in mind
Usage: Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else.
Example: “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.”
26. Provided that
Usage: This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing.
Example: “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.”
27. In view of/in light of
Usage: These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else.
Example: “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…”
28. Nonetheless
Usage: This is similar to “despite this”.
Example: “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.”
29. Nevertheless
Usage: This is the same as “nonetheless”.
Example: “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.”
30. Notwithstanding
Usage: This is another way of saying “nonetheless”.
Example: “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.”
Giving examples
Good essays always back up points with examples, but it’s going to get boring if you use the expression “for example” every time. Here are a couple of other ways of saying the same thing.
31. For instance
Example: “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…”
32. To give an illustration
Example: “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…”
Signifying importance
When you want to demonstrate that a point is particularly important, there are several ways of highlighting it as such.
33. Significantly
Usage: Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent.
Example: “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.”
34. Notably
Usage: This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it).
Example: “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.”
35. Importantly
Usage: Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”.
Example: “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.”
Summarising
You’ve almost made it to the end of the essay, but your work isn’t over yet. You need to end by wrapping up everything you’ve talked about, showing that you’ve considered the arguments on both sides and reached the most likely conclusion. Here are some words and phrases to help you.
36. In conclusion
Usage: Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview.
Example: “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
37. Above all
Usage: Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay.
Example: “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…”
38. Persuasive
Usage: This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing.
Example: “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.”
39. Compelling
Usage: Use in the same way as “persuasive” above.
Example: “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.”
40. All things considered
Usage: This means “taking everything into account”. Example: “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…”
How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below, or get in touch here to find out more about courses that can help you with your essays.
At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a number of summer school courses for young people who are keen to improve their essay writing skills. Click here to apply for one of our courses today, including law, politics, business, medicine and engineering.
These useful academic expressions, words, vocabulary and phrases will help you to write a top-notch essay. Writing an essay can be a challenging task. However it becomes simpler if it is divided into manageable pieces. There are three main parts in an essay: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. You can easily overcome your essay writing task with these academic phrases and vocabulary for essay writing.
Phrases to Finish an Introduction Paragraph
In this essay, I will look at some of the arguments for
This essay will discuss different ways of …
This essay outline some of the reasons why…
Let us examine both views before reaching a concrete decision.
The following essay takes a look at both sides of the argument.
Vocabulary for Opinion Essay
In my opinion,
I strongly agree with the idea that …
I strongly disagree with the idea that …
I strongly opine that…
I strongly believe that…
In my view…
As far as I am concerned…
It seems to me that…
However, I strongly believe that…
I oppose the view and my reasons will be explained in the following paragraphs.
I will support this view with arguments in the following paragraphs.
I personally believe that…
Thus the advantages far outweigh the disadvantages…
Useful Expressions For Listing Your Ideas
First…
First of all…
Firstly…
First and foremost…
Initially…
To begin with…
To start with…
In the first place…
On the one hand…
Second(ly)… (do not use ‘Second of all’)
Third(ly)…
Then…
Next…
After that…
And…
Again…
Also…
Besides…
Likewise…
In addition…
Consequently…
What’s more…
Furthermore…
Moreover…
Apart from that…
Finally…
Last but not the least…
Check Also:
Vocabulary for Starting Your Essay
How to Write The Best Essay Ever!
Phrases to Show a Comparison in Your Essay
In the same way…
Likewise…
Similarly…
Like the previous point…
Similar to…
Also…
At the same time…
Just as…
Useful Vocabulary and Phrases to Show Contrast
On the other hand…
On the contrary…
However…
Nevertheless…/ Nonetheless…
But…
Nonetheless/ Nevertheless…
Oppositely…
Alternatively…
Unlike…
While…
Whilst…
Although…
Though…
Even though…
Despite… / In spite of…
In spite of the fact that…
Alternatively…
In contrast to this…
Then again…
On the other hand…
Despite the fact that…
Even so…
Yet…
Meanwhile…
Vocabulary For Expressing Condition
If…
Provided that…
Because of that…
For this reason…
Unless…
Providing that…
So that…
In case…
Whether…
Phrases for Expressing Certainty in Your Essay
Certainly…
Definitely…
No doubt…
Of course…
Doubtlessly…
Without any doubt…
Undoubtedly…
Vocabulary for Adding Further Information
In addition…
And…
Moreover…
Similarly…
Furthermore…
Also…
As well as…
Besides…
Even…
Too…
What’s more…
Again…
In a similar fashion…
Likewise…
Expressions for Agreement & Disagreement in Your Essay
While writing your essay, as a writer you are required to show whether you agree & disagree or partially agree with a given statement or opinion.
Vocabulary for Expressing Agreement
I strongly agree…
I completely agree that…
I totally agree with the given idea that…
I agree with the opinion that…
I am quite inclined to the opinion that…
I accept that…
I accept the fact that…
I am in agreement…
I consent that…
Vocabulary for Expressing Disagreement
I disagree with the opinion that…
I strongly disagree…
I completely disagree with…
I totally disagree with the given idea that…
I disagree with the statement…
I quite oppose the opinion that…
I disapprove that…
I totally do not accept the fact that…
My own opinion contradicts…
I disagree with the group of people…
However, my opinion is different from…
Vocabulary for Expressing Partial Agreement
To some extent…
In a way…
I agree with the given statement to some extent…
Up to a point, I agree…
More or less…
So to speak…
Essay Expression PDF – (download)
General explaining
Let’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points.
1. In order to
Usage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument.
Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. In other words
Usage: Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point.
Example: “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. To put it another way
Usage: This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance.
Example: “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.”
4. That is to say
Usage: “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise.
Example: “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.”
5. To that end
Usage: Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”.
Example: “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.”
Adding additional information to support a point
Students often make the mistake of using synonyms of “and” each time they want to add further information in support of a point they’re making, or to build an argument. Here are some cleverer ways of doing this.
6. Moreover
Usage: Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making.
Example: “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”
7. Furthermore
Usage:This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information.
Example: “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
8. What’s more
Usage: This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”.
Example: “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.”
9. Likewise
Usage: Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned.
Example: “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.”
10. Similarly
Usage: Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”.
Example: “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.”
11. Another key thing to remember
Usage: Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”.
Example: “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.”
12. As well as
Usage: Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”.
Example: “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”
13. Not only… but also
Usage: This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information.
Example: “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.”
14. Coupled with
Usage: Used when considering two or more arguments at a time.
Example: “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…”
15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…
Usage: This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other.
Example: “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z.
16. Not to mention/to say nothing of
Usage: “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis.
Example: “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
Words and phrases for demonstrating contrast
When you’re developing an argument, you will often need to present contrasting or opposing opinions or evidence – “it could show this, but it could also show this”, or “X says this, but Y disagrees”. This section covers words you can use instead of the “but” in these examples, to make your writing sound more intelligent and interesting.
17. However
Usage: Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said.
Example: “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.”
18. On the other hand
Usage: Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion.
Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
19. Having said that
Usage: Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”.
Example: “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.”
20. By contrast/in comparison
Usage: Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence.
Example: “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.”
21. Then again
Usage: Use this to cast doubt on an assertion.
Example: “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.”
22. That said
Usage: This is used in the same way as “then again”.
Example: “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.”
23. Yet
Usage: Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea.
Example: “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.”
Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservations
Sometimes, you may need to acknowledge a shortfalling in a piece of evidence, or add a proviso. Here are some ways of doing so.
24. Despite this
Usage: Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence.
Example: “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.”
25. With this in mind
Usage: Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else.
Example: “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.”
26. Provided that
Usage: This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing.
Example: “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.”
27. In view of/in light of
Usage: These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else.
Example: “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…”
28. Nonetheless
Usage: This is similar to “despite this”.
Example: “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.”
29. Nevertheless
Usage: This is the same as “nonetheless”.
Example: “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.”
30. Notwithstanding
Usage: This is another way of saying “nonetheless”.
Example: “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.”
Giving examples
Good essays always back up points with examples, but it’s going to get boring if you use the expression “for example” every time. Here are a couple of other ways of saying the same thing.
31. For instance
Example: “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…”
32. To give an illustration
Example: “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…”
Signifying importance
When you want to demonstrate that a point is particularly important, there are several ways of highlighting it as such.
33. Significantly
Usage: Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent.
Example: “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.”
34. Notably
Usage: This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it).
Example: “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.”
35. Importantly
Usage: Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”.
Example: “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.”
Summarising
You’ve almost made it to the end of the essay, but your work isn’t over yet. You need to end by wrapping up everything you’ve talked about, showing that you’ve considered the arguments on both sides and reached the most likely conclusion. Here are some words and phrases to help you.
36. In conclusion
Usage: Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview.
Example: “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
37. Above all
Usage: Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay.
Example: “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…”
38. Persuasive
Usage: This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing.
Example: “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.”
39. Compelling
Usage: Use in the same way as “persuasive” above.
Example: “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.”
40. All things considered
Usage: This means “taking everything into account”.
Example: “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…”
How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below!
Additional Information ( more examples)
+20 Examples of Important Transition Words
Additional Information
There are many linking words which can lead us into additional information and while it is useful to vary your vocabulary beyond ‘and,’ these words are not mere replacements for ‘and.’ They have nuanced differences, thus, by these particular meanings, we can offer a more delicate illustration of the relationships between our ideas.
- ‘Furthermore’ is used to add information that expands upon the previous point. It precedes information that expands upon that already given. It usually occurs at the beginning of an independent clause.
- ‘Moreover’ and ‘More so’ are both similar to ‘furthermore’ while giving special emphasis to the greater importance of the following clause.
- “Despite cutting back on other staff, her father gave her a position, furthermore, he gave her an enviable office while still not having a role for her.”
- Writers also sequence additional information. ‘Firstly,’ ‘secondly’ and ‘thirdly’ are obvious options used to achieve this, however, there are others. For example, we can look into the past with ‘previously,’ ‘until the present’ or ‘preceded by.’
- “Present growth in the company was *preceded by several quarters of stagnation”*
- ‘Meanwhile’ and ‘simultaneously’ talk about things which are happening at the same time as another, while ‘concurrently’ does this while emphasising that the two ideas have played out in conjunction with one another.
- Usually, ‘incidentally’ is used to add relevant information while downplaying its significance compared with that of other ideas.
- “The priority of the zoo had been to protect species’ from extinction. The panda breeding program was enjoying some rare success, while simultaneously, other programs to increase the numbers of endangered species were being trialled. Meanwhile, the zoo was being visited by an influx of tourists who were, incidentally, able to enjoy seeing the young animals.”
- ‘Subsequently’ and ‘afterward’ lead into information after the fact.
Compare and Contrast
When writers need to illustrate similarity they can employ words such as ‘in like manner,’‘comparatively,’ and ‘correspondingly.’ Whereas, when they wish to highlight difference they have phrases like ‘on the contrary,’ ‘however,’ ‘notwithstanding,’ ‘nevertheless’ and ‘on the other hand.’
Notwithstanding the vehement opposition to online education programs being made available to inmates, considerable improvements were made to the re-employment prospects of many offenders who benefited from the trial. On the contrary, prisoners who were not able to access education while incarcerated were found to be more likely to reoffend and return to prison.
Clarification
When it comes time to clarify an argument or point, some of the transitional phrases which are used are, ‘to reiterate,’ ‘specifically,’ or ‘inasmuch as.’
Consequence and Conclusion
When we have lead our reader through our flow of logic, there might be nothing more rewarding than driving our point home by showing consequence or concluding our arguments. There are a lot of strong phrases such as ‘accordingly,’ ‘hence,’ ‘thus’ and ‘thereupon’ which can do this.
I hope you will feel encouraged, by this article, to continue to further your understanding of how transitional words can work to guide your reader through your flow of logic. When used well, they add power and order to your argument and can add to the result you see from your work.
It’s not easy to write an academic essay.
Many students struggle to word their arguments in a logical and concise way.
To make matters worse, academic essays need to adhere to a certain level of formality, so we can’t always use the same word choices in essay writing that we would use in daily life.
If you’re struggling to choose the right words for your essay, don’t worry—you’ve come to the right place!
In this article, we’ve compiled a list of over 300 words and phrases to use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essay.
Words to Use in the Essay Introduction
The introduction is one of the hardest parts of an essay to write.
You have only one chance to make a first impression, and you want to hook your reader. If the introduction isn’t effective, the reader might not even bother to read the rest of the essay.
That’s why it’s important to be thoughtful and deliberate with the words you choose at the beginning of your essay.
Many students use a quote in the introductory paragraph to establish credibility and set the tone for the rest of the essay.
When you’re referencing another author or speaker, try using some of these phrases:
- To use the words of X
- According to X
- As X states
Example: To use the words of Hillary Clinton, “You cannot have maternal health without reproductive health.”
Near the end of the introduction, you should state the thesis to explain the central point of your paper.
If you’re not sure how to introduce your thesis, try using some of these phrases:
- In this essay, I will…
- The purpose of this essay…
- This essay discusses…
- In this paper, I put forward the claim that…
- There are three main arguments for…
Example: In this essay, I will explain why dress codes in public schools are detrimental to students.
After you’ve stated your thesis, it’s time to start presenting the arguments you’ll use to back up that central idea.
When you’re introducing the first of a series of arguments, you can use the following words:
- First
- First and foremost
- First of all
- To begin with
Example: First, consider the effects that this new social security policy would have on low-income taxpayers.
All these words and phrases will help you create a more successful introduction and convince your audience to read on.
Words to Use in the Body of the Essay
The body of your essay is where you’ll explain your core arguments and present your evidence.
It’s important to choose words and phrases for the body of your essay that will help the reader understand your position and convince them you’ve done your research.
Let’s look at some different types of words and phrases that you can use in the body of your essay, as well as some examples of what these words look like in a sentence.
Transition Words and Phrases
Transitioning from one argument to another is crucial for a good essay.
It’s important to guide your reader from one idea to the next so they don’t get lost or feel like you’re jumping around at random.
Transition phrases and linking words show your reader you’re about to move from one argument to the next, smoothing out their reading experience. They also make your writing look more professional.
The simplest transition involves moving from one idea to a separate one that supports the same overall argument. Try using these phrases when you want to introduce a second correlating idea:
- Additionally
- In addition
- Also
- Secondly
- Furthermore
- Another key thing to remember
- In the same way
- Similarly
- Likewise
- Correspondingly
Example: Additionally, public parks increase property value because home buyers prefer houses that are located close to green, open spaces.
Another type of transition involves restating. It’s often useful to restate complex ideas in simpler terms to help the reader digest them. When you’re restating an idea, you can use the following words:
- In other words
- To put it another way
- That is to say
- To put it more simply
Example: “The research showed that 53% of students surveyed expressed a mild or strong preference for more on-campus housing. In other words, over half the students wanted more dormitory options.”
Often, you’ll need to provide examples to illustrate your point more clearly for the reader. When you’re about to give an example of something you just said, you can use the following words:
- For instance
- To give an illustration of
- To exemplify
- To demonstrate
- As evidence
Example: Humans have long tried to exert control over our natural environment. For instance, engineers reversed the Chicago River in 1900, causing it to permanently flow backward.
Sometimes, you’ll need to explain the impact or consequence of something you’ve just said.
When you’re drawing a conclusion from evidence you’ve presented, try using the following words:
- Thus
- As a result
- Hence
- Therefore
- Accordingly
- Due to
- As you can see
- This suggests that
- It follows that
- It can be seen that
- For this reason
- For all of those reasons
- Consequently
Example: “There wasn’t enough government funding to support the rest of the physics experiment. Thus, the team was forced to shut down their experiment in 1996.”
When introducing an idea that bolsters one you’ve already stated, or adds another important aspect to that same argument, you can use the following words:
- Moreover
- Further
- What’s more
- As well as
- Along with
- Besides
- Not only…but also
- Not to mention
- To say nothing of
- Another key point
Example: The volcanic eruption disrupted hundreds of thousands of people. Moreover, it impacted the local flora and fauna as well, causing nearly a hundred species to go extinct.
Often, you’ll want to present two sides of the same argument. When you need to compare and contrast ideas, you can use the following words:
- On the one hand / on the other hand
- Conversely
- However
- Alternatively
- In contrast to
- On the contrary
- Whereas
- By contrast
- In comparison
Example: On the one hand, the Black Death was undoubtedly a tragedy because it killed millions of Europeans. On the other hand, it created better living conditions for the peasants who survived.
Finally, when you’re introducing a new angle that contradicts your previous idea, you can use the following phrases:
- Having said that
- That said
- Even so
- Then again
- Differing from
- Granted
- Despite
- Yet
- In spite of
- While
- With this in mind
- Provided that
- Nevertheless
- Nonetheless
- Notwithstanding
- Admittedly
Example: Shakespearean plays are classic works of literature that have stood the test of time. Having said that, I would argue that Shakespeare isn’t the most accessible form of literature to teach students in the twenty-first century.
Good essays include multiple types of logic. You can use a combination of the transitions above to create a strong, clear structure throughout the body of your essay.
Strong Verbs for Academic Writing
Verbs are especially important for writing clear essays. Often, you can convey a nuanced meaning simply by choosing the right verb.
You should use strong verbs that are precise and dynamic. Whenever possible, you should use an unambiguous verb, rather than a generic verb.
For example, alter and fluctuate are stronger verbs than change, because they give the reader more descriptive detail.
Here are some useful verbs that will help make your essay shine.
Verbs that show change:
- Alter
- Accommodate
- Evolve
- Fluctuate
- Generate
- Transform
- Transition
- Vary
Verbs that relate to causing or impacting something:
- Constrain
- Control
- Govern
- Ignite
- Impact
- Influence
- Inhibit
- Initiate
- Instigate
- Introduce
- Promote
- Provoke
- Stimulate
- Trigger
Verbs that show increase:
- Advance
- Develop
- Enlarge
- Exceed
- Extend
- Facilitate
- Improve
- Implement
- Maximize
Verbs that show decrease:
- Alleviate
- Cease
- Decline
- Depress
- Descent
- Deteriorate
- Minimize
- Subside
- Reduce
Verbs that relate to parts of a whole:
- Comprises of
- Is composed of
- Constitutes
- Encompasses
- Includes
-
Incorporates
Verbs that show a negative stance:
-
Caution
- Challenge
- Contend
- Contradict
- Deny
- Disagree
- Dismiss
- Dispute
- Disregard
- Invalidate
- Misconstrue
- Negate
- Refute
- Reject
- Question
Verbs that show a positive stance:
- Admit
- Advocate
- Affirm
- Assert
- Complement
- Emphasize
- Endorse
- Highlight
- Declare
- Maintain
- Substantiate
- Suggest
- Support
- Underscore
- Uphold
- Validate
- Verify
Verbs that relate to drawing conclusions from evidence:
- Allude
- Attest
- Confirm
- Convey
- Corroborate
- Demonstrate
- Document
- Entail
- Establish
- Hint
- Imply
- Indicate
- Present
- Reveal
- Signify
- Summarize
- Surface
- Unearth
- Yield
Verbs that relate to thinking and analysis:
- Analyze
- Appraise
- Assess
- Believe
- Clarify
- Concede
- Contend
- Consider
- Contemplate
- Define
- Derive
- Determine
- Diagnose
- Discuss
- Dissect
- Evaluate
- Examine
- Explore
- Hypothesize
- Identify
- Ignore
- Infer
- Interpret
- Investigate
- Observe
- Perceive
- Postulate
- Presume
- Recognize
- Refer
- Scrutinize
- Speculate
- Surmise
- Theorize
Verbs that relate to showing information in a visual format:
- Denote
- Depict
- Describe
- Display
- Illustrate
- Portray
- Represent
- Typify
Useful Adjectives and Adverbs for Academic Essays
You should use adjectives and adverbs more sparingly than verbs when writing essays, since they sometimes add unnecessary fluff to sentences.
However, choosing the right adjectives and adverbs can help add detail and sophistication to your essay.
Sometimes you’ll need to use an adjective to show that a finding or argument is useful and should be taken seriously. Here are some adjectives that create positive emphasis:
- Beneficial
- Clear
- Effective
- Important
- Invaluable
- Main
- Major
- Persuasive
- Relevant
- Significant
- Strong
- Successful
- Unbiased
- Useful
- Valid
- Valuable
Other times, you’ll need to use an adjective to show that a finding or argument is harmful or ineffective. Here are some adjectives that create a negative emphasis:
- Biased
- Controversial
- False
- Flawed
- Insignificant
- Invalid
- Irrelevant
- Limited
- Minor
- Questionable
- Unnecessary
- Unrealistic
Finally, you might need to use an adverb to lend nuance to a sentence, or to express a specific degree of certainty. Here are some examples of adverbs that are often used in essays:
- Accordingly
- Adequately
- Barely
- Briefly
- Certainly
- Completely
- Comprehensively
- Consequently
- Entirely
- Exhaustively
- Extensively
- Generally
- Hardly
- Initially
- Nearly
- Possibly
- Presumably
- Probably
- Regularly
- Respectively
- Scarcely
- Surprisingly
- Thoroughly
- Typically
Using these words will help you successfully convey the key points you want to express. Once you’ve nailed the body of your essay, it’s time to move on to the conclusion.
Words to Use in Your Essay Conclusion
The conclusion of your paper is important for synthesizing the arguments you’ve laid out and restating your thesis.
In your concluding paragraph, try using some of these essay words:
- In conclusion
- To summarize
- To sum up
- In summary
- In a nutshell
- In brief
- In short
- In essence
- All in all
- Given the above
- As described
- All things considered
- Finally
- Lastly
Example: In conclusion, it’s imperative that we take action to address climate change before we lose our coral reefs forever.
In addition to simply summarizing the key points from the body of your essay, you should also add some final takeaways. Give the reader your final opinion and a bit of a food for thought.
To place emphasis on a certain point or a key fact, use these essay words:
- Unquestionably
- Undoubtedly
- Particularly
- Especially
- Importantly
- Singularly
- Chiefly
- Namely
- Conclusively
- It should be noted
- Above all
- Ultimately
- On the whole
Example: Ada Lovelace is unquestionably a powerful role model for young girls around the world, and more of our public school curricula should include her as a historical figure.
These concluding phrases will help you finish writing your essay in a strong, confident way.
How to Improve Your Essay Writing Vocabulary
There are many useful essay words out there that we didn’t include in this article, because they are specific to certain topics.
If you’re writing about biology, for example, you will need to use different terminology than if you’re writing about literature.
So how do you improve your vocabulary skills?
The vocabulary you use in your academic writing is a toolkit you can build up over time, as long as you take the time to learn new words.
One way to increase your vocabulary is by looking up words you don’t know when you’re reading.
Try reading more books and academic articles in the field you’re writing about and jotting down all the new words you find. You can use these words to bolster your own essays.
You can also consult a dictionary or a thesaurus. When you’re using a word you’re not confident about, researching its meaning and common synonyms can help you make sure it belongs in your essay.
Don’t be afraid of using simpler words. Good essay writing boils down to choosing the best word to convey what you need to say, not the fanciest word possible.
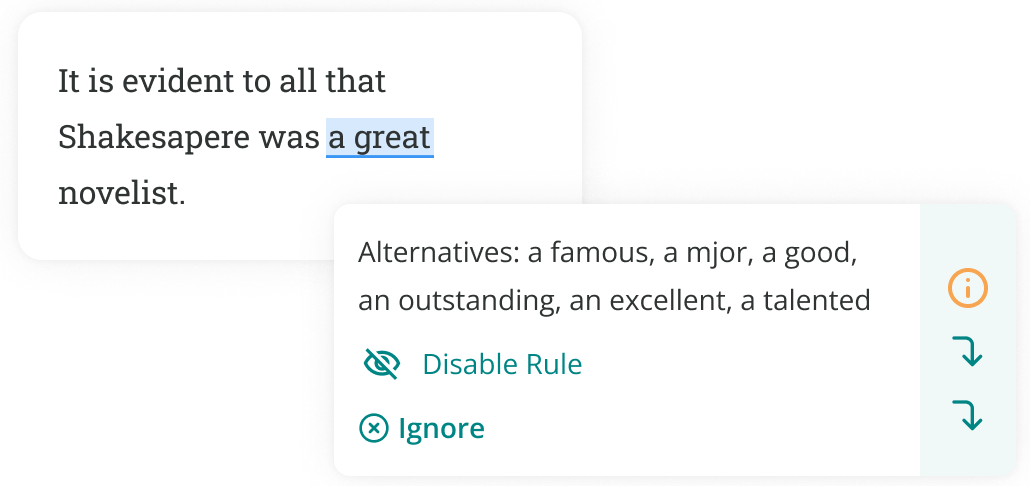
Finally, you can use ProWritingAid’s synonym tool or essay checker to find more precise and sophisticated vocabulary. Click on weak words in your essay to find stronger alternatives.
There you have it: our compilation of the best words and phrases to use in your next essay. Good luck!
Take your writing to the next level:
20 Editing Tips From Professional Writers
Whether you are writing a novel, essay, article, or email, good writing is an essential part of communicating your ideas.
This guide contains the 20 most important writing tips and techniques from a wide range of professional writers.