Examples of how to use the word “now” in a sentence. How to connect “now” with other words to make correct English sentences.
now (adv): at the present time, not in the past or future
Use “now” in a sentence
| We can either eat now or after the show – it’s up to you. |
| I’m feeling embarrassed right now. |
| The engine is running smoothly now. |
| What I want you to do now is to paint the fence. |
| It’s is no use trying to fix it now. |
| I have to leave now. |
| I’m in perfect health now. |
| We’re hiring now! |
| I’m so drunk now that I’m seeing two keyboards. |
| I am now very healthy, both physically and mentally. |
| Where are you living now? |
| What should I do now? |
| I’m afraid I have to go now.
Back to “3000 Most Common Words in English” |
Synonym: at once, immediately, presently, right away, today. Antonym: then. Similar words: bow, cow, how, know, low, new, no, nod. Meaning: [naʊ] n. the momentary present. adv. 1. at the present moment 2. in these times 3. in the historical present; at this point in the narration of a series of past events 4. (prefatory or transitional) indicates a change of subject or activity 5. used to preface a command or reproof or request 6. without delay or hesitation; with no time intervening 7. in the immediate past.
Random good picture Not show
1. The worse luck now, the better another time.
2. Now I shall go to sleep. Good night.
3. I now know that wars do not end wars.
4. Really, what we want now, is not laws, against crime, but a law a -gainst insaity.
5. I am not now that which I have been.(I am not what I used to be.).
6. When I was young, I admired clever people. Now that I am old, I admire kind people.
7. On the great clock of time there is but one word, «Now«.
8. All we can do now is wait and hope.
9. The minister preaches a sermon now and then.
10. The fur trade now exceeded timber in importance .
11. ‘I’m going now,’ she said, fastening her coat.
12. Very few students learn Latin now.
13. The coastline can now be monitored by radar.
14. ‘Where is he now?’ ‘I only wish I knew!’
15. Ever of lover, now the passers-by.
16. Things are frantic in the office right now.
17. These ideas have now been completely discarded.
18. The future looks pretty dismal right now.
19. His face has now broken out in pimples.
20. You must give in your examination papers now.
21. He is now in the laboratory.
22. I have a couple of things to do now.
23. They now live in relative comfort .
24. Convention now allows women to smoke in public.sentencedict .com
25. He is in his glory now.
26. The national railways have now been electrified.
27. I need a wax candle now.
28. Has the country got the bomb now?
29. After suffering an eclipse, she is now famous again.
30. With the extra resources, the scheme now seems feasible.
More similar words: bow, cow, how, know, low, new, no, nod, not, row, wow, dot, down, few, flow, fog, for, go, grow, jaw, Jew, job, joy, law, log, lot, mom, news, noon, norm.
Asked
7 years, 1 month ago
Viewed
1k times
Consider the following 2 sentences:-
- «Now the application is working fine».
- «The application is working fine now».
Which one is grammatically correct and why?
asked Feb 23, 2016 at 8:57
0
Both are correct. Adverbials, like «now» can assume a variety of syntactic positions, e.g. «now the application works fine» » the application now works fine.» » the application works fine now»
answered Feb 23, 2016 at 13:31
Do not use a comma after «now» at the start of a sentence to describe when something happens.
Do not use a comma after «now» at the start of a sentence to describe when something happens.
Now I need to go to the grocery store.
Add a comma after «now» when using it as a discourse marker (to organize your thoughts before adding the main part of the sentence).
Now, considering the circumstances, it was a good try.
Contents
- 1. Different Ways to Use ‘Now’
- 2. ‘Now’ as an Adverb of Time
- 3. ‘Now’ as the Subject of a Sentence
- 4. ‘Now’ as a Discourse Marker
1. Different Ways to Use ‘Now’
The word «now» is mainly used as:
- An adverb of time to mean «at present», «immediately», «nowadays», etc.
- The subject of a sentence (e.g., «Now is the time to act.»)
- A discourse marker to introduce a statement.
2. ‘Now’ as an Adverb of Time
At the beginning of a sentence, we do not commonly use a comma after single-word adverbs of time, such as «now«, «today», «yesterday», or «tomorrow».
Now we know that this is not true.
Now you are a celebrity, and everyone wants to be your friend.
Consequently, if «now» answers the question of when, then no comma.
Now I have to leave.
Now that Olivia is here, the meeting can begin.
We do not use a comma before or after «now» in mid-sentence unless the particular sentence structure requires it.
I now regret it.
Everything she has right now is circumstantial.
Arguing with you now is a waste of time.
Go now.
3. ‘Now’ as the Subject of a Sentence
«Now» can also be a noun as well as the subject of a sentence.
Now is the moment to take action.
With few exceptions, we should not use a comma to separate a subject from its verb.
Now is the time to teach your daughter healthy eating habits.
Now is just the right time to learn a new language.
4. ‘Now’ as a Discourse Marker
We can also use «now» as a discourse marker to introduce a new sentence.
Now, let me say that the protocol is being implemented by our team.
Discourse markers are words that help organize our thoughts, link sentences, or join ideas.
I already know that Alice is wrong. Now, are you going to help her or not?
Introductory words, such as «now«, «well», «yes», «hey», etc. should be preceded by a period or a semicolon and followed by a comma.
Yes, you are the best player of the soccer team. Now, can you help me with this?
By adding a comma after «now» we can change the meaning of a sentence.
Now I know this is a bad idea. («Now» indicates «when». I know something I didn’t know until recently.)
Now, I know this is a bad idea. («Now» simply is a discourse marker that helps us introduce a statement. It doesn’t really add meaning to the sentence.)
Recommended: Commas and conjunctive adverbs
Frequency adverbs in English
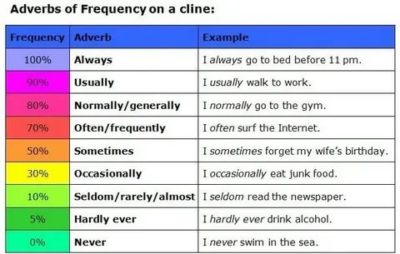
Adverbs play an important role in communication, they describe the way, character, image of the performed action. When we want to indicate how often a particular action is performed, we use an adverb that expresses frequency. What adverbs of frequency exist, how they differ and how to use them in speech — read further in this article.
The adverb of frequency indicates how often an action is performed (which is more often
everything is represented by a verb). There are 6 main adverbs of frequency: always — always, usually (or normally) — usually, often — often, sometimes — sometimes, rarely — rarely, never — never. They differ in the degree of frequency with which the action they describe is performed. What are the differences, see the table below.
In addition to rarely, seldom can be used, but it is gradually falling out of use in modern English.
The place of the adverb of frequency in the sentence
As you can see from the table above, the main place for the adverb of frequency in a sentence is
between the subject and the predicate, between the subject of the action and the action. Below are a few more examples:
- Sara always goes out on Saturday evenings. / Sarah always walks on Saturday nights.
- her boyfriend usually picks her up and they drive into the city center. / Her boyfriend usually picks her up by car and they drive to the city center.
- They often meet friends and have a drink together. / They often meet up with friends and go to a bar.
- In the winter they Sometimes go to the cinema. / In winter they sometimes go to the movies.
- They Rarely go in the summer because they prefer to stay outside. / In the summer they rarely go to the movies, as they prefer to stay in the fresh air.
- They never get home before midnight. / They never do not return home until midnight.
An exception to this rule is the verb to be (to be)… In sentences with this verb, the adverb of frequency comes after the verb, as in these examples:
- There are always lots of people in the city center on Saturday nights. / On Saturday evenings in the city center (available) always many people.
- It’s often difficult to find a place to park. / (This is) often difficult to find a parking place.
- But our friends are never on time so it doesn’t matter if we’re late. / But our friends (are) never [don’t come] on time, so it doesn’t matter if we’re late.
As is often the case in English, there are variations on this rule. For example,
you can put adverbs sometimes — sometimes and usually — usually at the beginning of a sentence:
- Sometimes she does her homework with friends. / Sometimes she is doing her homework with friends.
- Usually they study on their own. / Usually they do it on their own.
But, of course, the easiest way is to follow the basic rule and put all adverbs that express the frequency between the subject and the predicate, the subject of the action and the action.
Question form
To ask a question about how often an action is performed, it is usually used
How often design? — «How often?», For example:
- how often do you watch films? / How often do you watch movies
- how often does he play tennis? / How often he plays tennis?
- how often do the trains arrive late? / How often Are the trains late?
But you can simply use the desired adverb of frequency between the subject and the semantic verb:
- Do you often come here? / You often come here?
- does she always work so hard? / She always working so hard?
- do they ever pay on time? (For questions, use ‘ever’ instead of ‘never’)? / They at all someday (= as a synonym for «never») get paid on time?
If there is a modal verb in the sentence, the adverb of frequency is placed between it and the semantic (main) verb:
- you must always try your best. / You should (you should) always try my best.
- We can usually find a seat on our train. / We can usually find a seat on our train.
- They should never be rude to customers. / They can not never be rude to customers.
The same rule applies to auxiliary verbs: the adverb of frequency comes between
auxiliary and main (semantic) verbs:
- I have never visited Turkey. / I AM never have not been to Turkey.
- He’s always taking things from my desk. It’s really annoying. / He all time takes things from my desk. This is very annoying.
- you had rarely arrived late at work until yesterday. / You rarely was late for work until yesterday.
Now you have learned what frequency adverbs are and how to use them.
Reinforce your new knowledge by answering the questions below using adverbs of frequency:
- What do you usually do on Saturday nights? / What do you usually do on Saturday night?
- How often do you see your best friend? / How often do you see your best friend / girlfriend?
- Do you ever go to the theater? / Do you often go to the theater?
- How often do you play sport or go to the gym? / How often do you exercise or go to the gym?
- Do you ever watch films or TV programs in English? / Do you ever watch movies or TV programs in English?
- What time do you usually go to bed? / When do you usually go to bed?
- How often do you eat at a restaurant? / How often do you go to a restaurant?
- Are you sometimes late for work or school? / Are you sometimes late for work or school?
Source: https://www.wallstreetenglish.ru/blog/adverbs-of-frequency/
Adverbs in English: rules of education and place in a sentence with tables and translation
An adverb is a part of speech that answers the question «How?» and characterizes a verb, adjective or other adverb. There are different types of adverbs — manner of action (how), place (where), time (when), degree (to what extent), frequency (how often), opinions. Consider the rules for using adverbs in English.
Formation of adverbs in English
How are adverbs formed? By structure, adverbs can be divided into the following groups:
| Simple | Derivatives | Composite | Composite |
| long (long) | slowly | anyhow (in any way) | at once (immediately) |
| enough (enough) | wise (similarly) | sometimes (sometimes) | at last (finally) |
| then (then) | forward | nowhere (nowhere) | so far (so far) |
The most common way to form adverbs is by adding the -ly suffix to the adjective. Such adverbs usually have a similar meaning to them.
| Adjective | Adverb |
| bad | badly (poorly) |
| Beautiful | beautifully (beautiful) |
| carefully | Carefully (attentively) |
| quick | quickly (quickly) |
| quiet | quietly (quiet) |
| soft | gently (soft) |
Consider the spelling change when adding the -ly suffix:
- le changing to ly (gentle — gently)
- y changing to ily (easy — easily)
- ic changing to ically (automatic — automatically)
- ue changing to uly (true — truly)
- ll changing to eye (full — fully)
Other examples of suffixes: -ward (s), -long, -wise
- clockwise
- forward
- headlong
Adverbs are exceptions
Some adverbs can be both adjectives and adverbs in different situations without adding suffixes:
- It was a fast train. The train went fast.
- He returned from a long journey. Will you stay here long?
- The price is very low. The plane flew very low.
- We have very little time. He reads very little.
Other examples of exceptions are hard, high, deep, last, late, near, wide, early, far, straight, right, wrong.
Most common exception: good — well.
Some adverbs have two forms — one without -ly and one with it. These forms have different meanings. Examples: hard / hardly, last / lastly, late / lately, near / nearly, high / highly.
| Adjective | Adverb without -ly | Adverb with -ly |
| He is a hard worker | He works hard | I could hardly understand him (I could hardly understand him) |
| He returned in late autumn (He returned in late autumn) | I went to bed late yesterday (I went to bed late yesterday) | I haven’t seen him lately (I haven’t seen him lately) |
| He is studying the history of the Near East | He lives quite near | It is nearly 5 o’clock (Now almost 5 o’clock) |
| The house is very high | The plane flew very high | It is a highly developed state |
Place and order of adverbs in a sentence
Where is the adverb in English? The position in the sentence depends on the type of adverb (read below), their number and other factors.
| — before adjectives, other adverbs and participles | The task was surprisingly simple.He walked very fast.We are extremely interested in their offer. |
| — usually after verbs | He speaks slowly |
| — at the beginning of a sentence for emphasis | Slowly, he entered the room. Now I understand what you mean |
| — when there are two or more adverbs in a sentence, they go in the following order: manner — place — time | She spoke very well here last time |
| — if the sentence contains a verb of movement (go, come, leave etc.), the adverbs go in this order: place — manner — time | She arrived here by train yesterday |
Types of adverbs in English with lists
The following classification of adverbs is distinguished — the adverbs of the mode of action, time, frequency, place and direction, degree and opinion. Let’s consider all these groups in more detail.
Adverbs of manner
Such adverbs tell us how something is happening: well, badly, slowly, and so on.
- How did John behave? He behaved badly.
- Did you sleep well?
- He came very quickly
We do not use adverbs after linking verbs to be, become, feel, get, look, seem. We use adjectives after them.
- Sue felt happy
- Nobody seemed amused
- I am not sure
Mode adverbs appear before the main verb, after auxiliary verbs, or at the end of a sentence
- They quickly returned
- He was anxiously waiting for their reply
- She smiled kindly
Adverbs of time
List of adverbs of the time: When (when), now (now), then (then, then) before (before, before) after (then, after), afterwards (subsequently), once (once), fair (just now, just), still (still), already / yet (already), yet (yet, yet), since (since), early (early), lately / recently (recently), suddenly (suddenly), soon (soon), long (for a long time), August (ago), today (today), Tomorrow (tomorrow), yesterday (yesterday) etc.
Tense adverbs usually appear at the end of a sentence. They can be placed in the first place for emphasis, in other words, to give the desired stylistic coloring:
- I saw her yesterday
- Still I can’t understand what happened then (still ahead for dramatic coloring)
Some monosyllabic adverbs of the tense (soon, now, then) come before the main verbs and after the auxiliary verbs:
- I now understand what he means
- She will soon come back home
Remarks:
- We say tonight (tonight / night), tomorrow night, last night (not “yesterday night”)
- Already and yet can mean already. At the same time, already is used only in statements, and yet in questions and negations.
- The preposition for can mean “during” and is used with adverbs of time: for a long time, for 10 years.
Adverbs of frequency
They answer the question «How often?» The most common ones are: always (always), generally, normally, normally (usually), frequently, frequently (often), seldom, rarely (rarely), Sometimes (sometimes), from time to time, occasionally (occasionally), never (never).
Where to put such adverbs? Frequency adverbs come after auxiliary verbs, but before the main semantic ones:
- He has never visited us.
- Paul is often barks.
- He Sometimes comes here.
Generally, usually, normally, often, frequently, sometimes can be at the beginning of a sentence to give a stylistic coloring:
- I usually go to work by metro. — Usually, I go to work by metro.
Adverbs of place and direction
List of the main adverbs of place and direction: here (here), there (there, there), Where (where, where), somewhere, anywhere (somewhere, somewhere) nowhere (nowhere, nowhere) elsewhere (somewhere else) far away (far), near (close), inside (inside), outside (outside), above (above, above), below (below, below).
Such adverbs are usually placed at the end of a sentence:
- How long are they going to stay here?
Somewhere, anywhere, nowhere
Source: https://dundeeclub.ru/grammar/narechiya-v-anglijskom-yazyke-s-perevodom-tablitsami-i-primerami-adverbs.html
Adverbs in English. Determining the place in sentences
Pre-Intermediate
Setting principle adverbs to a specific place in a sentence is based on two points:
- The adverb is placed either BEFORE or AFTER the verb.
- Adverbs of different categories (mode of action, time, place, etc.) occupy different places in the sentence.
Therefore, there are several possible options for setting each category of adverbs in a sentence.
1. Before the verb
- Adverbs always, often, seldom, ever, never, just, already, yet, usually, generally, sometimes, still, soon, once… But!!! These adverbs are placed AFTER THE VERB TO BE.
- Mode of action adverbs, if the verb is followed by an infinitive.
- All adverbs are placed before have to + infinitive and used to
2. After the verb
- Mode of action adverbs.
- All adverbs are placed after an auxiliary verb, after a modal verb, or after the first verb (if the verb construction is complex).
- The adverb «yet «to mean» yet «.
- The adverb «enough».
3. At the end of the sentence
- The adverb «yet«In the meaning» already «.
- Adverbs before, lately, recently.
- Adverbs too, either.
4. At the beginning or end of a sentence
- Sometimes can stand anywhere.
- Adverbs tomorrow, today, yesterday.
5. additional information
- Adverb enough is placed after an adverb or definition. It can also define a noun and stand both before and after it.
- Adverb too in the meaning «too» is placed before the word that it defines.
- If the adverb of time and the adverb of place are next to each other, then the adverb of place comes first.
- An adverb defining an adjective or other adverb is placed before the word being defined.
Schematically, the principle of the arrangement of adverbs in a sentence can be depicted as follows:
TABLE.
| BEFORE VERB | AFTER VERB | AT THE END OF THE OFFER | AT THE BEGINNING OR END OF THE OFFER |
| always, often, seldom, ever, never, just, already, yet, usually, generally, sometimes, still, soon, once | Mode of action adverbs | «Yet» means «already» | Sometimes it can stand anywhere |
| Everything before have to + infinitive and used to | Everything after an auxiliary verb, after a modal verb, or after the first verb (if the verb construction is complex) | before, lately, recently | tomorrow, today, yesterday |
| Mode of action adverbs, if the verb is followed by an infinitive. | «Yet» means «yet»; enough | too, either | tomorrow, today, yesterday |
In conclusion, we recommend taking the test — choose the correct option:
Source: https://www.learnathome.ru/grammar/the-order-of-adverbs.html
Place of an adverb in a sentence in English: before a verb or after?
The place of an adverb in a sentence in English is not fixed in many cases. The same adverb can be used at the beginning, middle or end of a sentence. We will consider the basic patterns of the arrangement of adverbs in a sentence, the features of the use of individual adverbs.
Typically, an adverb occupies one of three positions in a sentence.
After the predicate and the complement, if any.
Let’s stay here… — Let’s stay here.
Before the subject.
Yesterday we had a good time. “We had a good time yesterday.
If the predicate consists of one verb, then “in the middle” is before the verb.
He Rarely talks to his neighbors. — He rarely talks to neighbors.
If the predicate has more than one word, then “in the middle” is after the auxiliary or modal verb.
You can never rely on him. — You never you can’t rely on him.
He is always late. — He always is late.
Some adverbs can appear before an auxiliary or modal verb.
He really is the person we were looking for. — He really and there is the person we were looking for.
He Surely can drive. — He definitely knows how to drive a car.
In an interrogative sentence, “middle” is between the subject and the main verb.
Do you often help people? — You often do you help people?
Consider in which cases the adverb is at the end of a sentence, at the beginning and in the middle.
Place of adverbs of mode of action
Mode of action adverbs such as slowly — slowly, fast, quickly — quickly, immediately — immediately, well — well, are at the end of the sentence.
You have done your work well. — You did the job good.
Hold the box carefully. — Keep the box carefully.
come back immediately. — Come back immediately.
Cats can sneak very slowly. — Cats are very good at sneaking slow.
Adverbs of place
Place adverbs such as here — here, there — there, also at the end of the sentence.
We will build a church here. — We will build here church.
His office is there. — His office there.
Place of adverbs of tense in a sentence
At the end of the sentence, adverbs indicating a specific time are used: now — now, now, tomorrow — tomorrow, yesterday — yesterday, etc. Do not confuse them with such adverbs as often — often, Rarely — rarely, always — always, never — never, indicating the frequency of action — they are also called adverbs of frequency (adverbs of frequency).
Don’t forget to return the books tomorrow. “Don’t forget to return the books tomorrow.
You will be safe now. — Now you will be safe.
The same adverbs, especially if you need to emphasize them, are often used at the beginning of a sentence:
tomorrow we will put an end to it. — Tomorrow we will put an end to this.
Now you will tell me the truth. — Now you will tell me the truth.
Place of adverbs of frequency (always, never, etc.)
Frequency adverbs are a type of time adverb that indicates how often an action takes place: often — often, Sometimes — sometimes, always, ever — always, never — never, Rarely — rarely, usually — usually. They are located in the middle of the sentence.
I usually take a bus to work. — I usually take the bus to work.
You can always use my tools. “You can always use my tools.
Usually sometimes found at the beginning of a sentence.
usually, we have lunch together. “We usually have lunch together.
Please note that if the adverb of frequency indicates not an indefinite frequency (always, rarely), but a specific one (every day, on Sundays), it is usually used at the end of a sentence:
We go to the swimming pool on Sundays… — We go to the pool on Sundays.
He reads in English every day. — He reads in English every day.
Place of adverbs of measure and degree
Adverbs of measure and degree include words such as: really — really, very, very — very, extremely — extremely, quite — enough, fair — just, just now, Almost — almost. They are in the middle of the sentence.
Adverbs of measure and degree can be used with an adjective or other adverb in front of them.
- Adverb before adjective:
The noise was too loud. — The noise was too loud.
It was extremely dangerous. — It was extremely dangerously.
- Adverb before another adverb:
They can also characterize the actions and states expressed by the verb. Let me remind you that if there is one verb in a sentence, then “in the middle of the sentence” — before this verb.
If there is an auxiliary or modal verb, then “in the middle of a sentence” is after the modal or auxiliary verb.
Some reinforcing adverbs such as really — really, surely, certainly — exactly, of course, definitely — definitely, can come before an auxiliary or modal verb.
Exceptions — adverb enough (enough), it comes after the word being defined.
Source: https://langformula.ru/english-grammar/adverb-position/
Enjoy learning English online with Puzzle English for free
An adverb is a part of speech that denotes a sign of an action and describes where, when and how this action is performed. Often, usually and always refer to adverbs of frequency and answer the question «How often?» Where often, usually and always are put in a sentence — we will consider below.
In English, adverbs of place, time, mode of action, measure and degree, adverbs of frequency of action and adverbs-interrogative words are distinguished. Often, usually and always refer to the adverbs of the frequency of action or otherwise the frequency — Adverbs of Frequency, but are not the only representatives of this group.
Examples of adverbs of frequency of action:
These are far from all the existing Adverbs of Frequency, there are a great many of them. They can be conditionally divided into adverbs of a certain frequency (definite frequency) and adverbs of an indefinite frequency (indefinite frequency). The adverbs of both groups answer the same question: «How often?»
Adverbs of a certain frequency of action:
- Daily — daily
- Annually — annually
- Every day / hour / month / year — every day / hour / month / year
- Once a week / month / year etc. — once a week / month / year, etc.
Let us dwell on the group of adverbs of an indefinite frequency of action, since often, usually and always represent this particular group. The most common adverbs of indefinite frequency are sometimes presented as a scale on which the difference between them is clearly visible. The frequency of the action is presented as a percentage.
When using these adverbs in speech, the speaker’s subjective opinion plays an important role: for some, «often» is three times a day, and for someone — three times a month.
Action frequency adverbs, including often, usually, and always, refer to Present Simple time markers. The simple present tense is associated with periodicity, regularity, or constancy. Accordingly, the meaning of its markers-adverbs of frequency is also similar.
Statement
As a general rule, if the predicate is expressed by a single semantic verb, then the adverb of frequency should be placed before the verb.
He often visited us. — He often visited us.
I usually drink tea in the morning. — I usually drink tea in the morning.
Question
In adverb matters, frequencies also take place in the middle of a sentence, after the subject.
Did he usually have tea for breakfast? — He always drank tea for breakfast?
Also, adverbs of indefinite frequency are used in short answers to questions before an auxiliary verb, when the speaker agrees or disagrees with what was said earlier.
Mary is depressed again. — Oh, she always is.
Mary is upset again. — She’s always like that.
Tom talks only about himself. — Yes, he always does.
Tom only talks about himself. — Yes, he always does that.
Source: https://puzzle-english.com/directory/often-usually-always
Frequency adverbs in English
Skip to content
In this article, we will analyze the adverbs of frequency in the English language.
These include adverbs of time, which provide the listener with additional information, showing the frequency of events.
These adverbs are important and should be part of the vocabulary of any English learner.
There are two types of frequency adverbs in English:
- certain adverbs of frequency that clearly indicate the frequency, time frame;
- indefinite adverbs of frequency that do not indicate specific terms.
Let’s take a closer look at them and learn how to use them.
Certain adverbs of frequency in English
Words that clearly describe the frequency with which events occur. Whether it’s week, month, time of day, day of the week:
- once — once, once;
- twice — twice;
- three, four times — three, four times;
- daily — daily;
- monthly — monthly;
- yearly / annually — annually.
Certain adverbs of frequency:
- change the meaning of the verb (characterize it);
- in most cases, they are placed at the beginning (separated by a comma) and at the end of a sentence;
- ending in «-ly»: used only at the end of a sentence; can act as adjectives — daily meetings, yearly report.
I drink beer daily… — Every day I drink beer.
They eat rice once a week… “They eat rice once a week.
They play football four teams a week… — They play football four times a week.
Frequency adverbs with «every»
Every:
- morning, evening, night — every morning (evening, night);
- weekend — every weekend;
- Saturday, Monday, ect. — every Saturday (Monday, etc.);
- minute, hour, day, week, year — every minute (hour, day, week, year).
every morning, I drink tea. — Every morning I drink tea.
Every year , my parents go to the theater. — Every year my parents go to the theater.
My mother cooks Cada dia… — My mom cooks every day.
All the family every week go fishing. — Every week the whole family goes fishing.
Every Friday, they play poker until the night. “They play poker until nightfall every Friday.
Always
Described Probability: 100%
They always go to the beach in the summer. — In the summer they always go to the beach.
My father is always very busy. — My father is always busy.
Usually
Described Probability: 90%
We usually get up at 10 am — We usually get up at 10 am.
Does Jane usually have lunch at home? «Does Jane usually have dinner at home?»
Normally
Translation: usually, as usual, usual
Described Probability: 80%
I Normally pay my rent. — I usually pay the rent.
He doesn’t Normally wear jeans. — He usually doesn’t wear jeans.
often, frequently
Described Probability: 60-70%
I often read before bed. — Before going to bed, I often read.
I Frequently exercise in the evenings. — I often exercise in the evenings.
Frequency adverbs in English describing events that occur from time to time
Source: https://englishboost.ru/narechiya-chastotnosti-v-anglijskom/
Adverbs in English sentences. Where do they belong?
Adverbs are words that describe verbs, adjectives, other adverbs, or phrases. They often answer the question «How?» (How?). For example:
She sings beautifully.
She sings beautifully. (How does she sing? Beautifully.)
He runs very Fast.
He runs very fast. (How fast does he run? Very fast.)
I occasionally practice speaking English.
From time to time I practice conversational English. (How often do I practice? From time to time.)
The place occupied by an adverb in an English sentence depends on what type this adverb belongs to. It is in this aspect that we will understand in today’s English lesson.
1. Do not put an adverb between the verb and the object of its action
In the next sentence painted is a verb and the house — an object. carefullyas you might have guessed — this is an adverb.
I Carefully painted the house. = Correctly
I painted the house Carefully. = Correctly
I painted Carefully the house. = Wrong
Here’s another example. In this sentence read Is a verb, a book Is the object of action, and Sometimes — adverb.
I Sometimes read a book before bed. = Correctly
Sometimes I read a book before bed. = Correctly
I read a book before bed Sometimes. = Acceptable, but only in informal situations
I read Sometimes a book before bed. = Wrong
Front position: at the beginning of a sentence
suddenly the phone rank.
Suddenly the phone rang.
fortunately, no one was injured.
Fortunately, no one was hurt.
Maybe I’ll go for a walk.
Maybe I’ll go for a walk.
Mid position: next to the main verb
I always exercise before work.
I always do my exercises before work.
They have Completely forgotten about our appointment.
They completely forgot about our meeting.
He was probably late for the interview.
He was probably late for the interview.
She slowly began to recover from her illness.
She slowly began to recover from her illness.
End position: at the end of a sentence
You speak English well.
You speak English well.
Please sit there.
Please sit here.
They ate dinner quietly.
They dined quietly.
Mode of action adverbs
quickly, slowly, easily, happily, well, * badly, seriously
The position in the middle of the sentence makes the adverb less expressive:
He quickly corrected his mistake.
He quickly corrected his mistake.
She easily passed the test.
She passed the test easily.
We happily
Source: https://english-bird.ru/position-of-adverbs/
Present Simple marker words: definition, rules and examples
“Time markers” are words that make it possible to determine that the sentence should use the present Simple temporal form. Let’s see how this works, taking the example of Present Simple marker words.
Present Simple time
One of the first topics when learning English grammar is Present Simple. This is the Simple Present Tense, which applies in the following cases:
- to indicate a state, habitual, repetitive action;
- to describe scientific facts, accepted statements, common truths, laws of nature;
- when listing the following one after another actions;
- practical guides, operating instructions, instructions;
- various schedules (trains, buses, cinema sessions, etc.);
- newspaper headlines;
The English language itself helps to understand all cases of using the temporary form of Present Simple. He may suggest special signals — time indicators.
What are time markers
The verbs in the sentence describe actions and events, and they unfold in time. Therefore, the verb itself is directly related to temporary circumstances: when the event took place, how long it lasted, by what moment it ended, etc.
Tense circumstances are not accidental in sentences: they serve as indicators for different verb forms. Such pointers are called temporary markers. For each time in the English language, its own set of indicators is allocated, including Present Simple markers.
If you master the verbal indicators, it is much easier to detect the use of this or that tense. Present Simple pointers will prompt you that in such a context it is the simple present that is used, and not, for example, Present Continuous.
But you should always be careful. Some markers can refer to multiple times. The choice in such cases comes only from the context and understanding of the essence of the situation. And there may be sentences in which there are no circumstances of the tense at all and an indication of the verb form. Therefore, in order to use Present Simple correctly and correctly interpret the indicator hints, it is necessary to master the values of the present simple.
List of time markers
There are often more difficult situations. Sometimes we talk about events inherent in Present Simple. Sometimes we use Present Continuous and other times. It can be difficult to figure it out here, and temporary pointers make our life very much easier.
Basic temp pointers for Present Simple Tense (simple present tense)
| always | always |
| often | often |
| usually | usually |
| sometimes | sometimes |
| never | never |
Without these pointers, nowhere. You definitely need to know them. Often we are also asked the question: «How often do you do it?» (How often do you do this?)
And here there are often variations — twice a week, three times a week, every day, etc. How to say it?
Temporary pointer table for Present Simple Tense (simple present tense)
| every day | Cada dia |
| every week | every week |
| every month | every month |
| Every year | every year |
| two times a week | twice a week |
| three times per week | three times a week |
| four times a month | four times a month |
| on weekends | at weekends |
| on Mondays | on Mondays |
| on Sundays | on Sundays |
| rarely | seldom |
| Rarely |
This is a more extensive list of temporary pointers. Very often students forget how to say the word «rarely» in English. Not everyone knows the words seldom and rarely. In this case, you can say sometimes and everything will be clear.
It is also important to pay attention to the differences between British and American English when we talk about temporary pointers. How do you say “on weekends” in English? UK version — at weekends. The American version is on weekends. That is, a different pretext is put.
So, for each time in the English language there are auxiliary words — clues that show what kind of temporary form we have in front of us. Present Simple is no exception, and has its own list of auxiliary words.
Examples of time markers
Sample sentences with adverbs of frequency in Present Simple:
- He always gets up at 7 am — He always gets up at 7 am.
- They are usually at home in the evening. “They’re usually at home in the evening.
- Miranda and Greg often visit their grandmother. — Miranda and Greg often visit their grandmother.
- She rarely meets her friends. — She rarely meets with friends.
- We are hardly ever late for work. — We are almost never late for work.
- I never borrow money from my friends. — I never borrow money from friends.
Usually adverbs of frequency are placed before the main verb of the sentence, in particular:
- I sometimes have a shower in the morning. — I sometimes take a shower in the morning.
- Mark doesn’t always give his girlfriend flowers. — Mark does not always give flowers to his girlfriend.
However, there is one situation where this order of words is violated — when there is a verb to be in a sentence, adverbs of frequency are established after it, for example:
- She is hardly ever worried. — She almost never worries.
- Helen and Mike aren’t usually at work at this time. — Helen and Mike are usually not at work at this time.
As a rule, adverbs of frequency are placed before the main verb of a sentence, in particular:
- I sometimes have a shower in the morning. — I sometimes take a shower in the morning.
- Mark doesn’t always give his girlfriend flowers. — Mark does not always give flowers to his girlfriend.
However, there is one situation where this order of words is violated — when there is a verb to be in a sentence, adverbs of frequency are placed after it, in particular:
- She is hardly ever worried. — She almost never worries.
- Helen and Mike aren’t usually at work at this time. — Helen and Mike are usually not at work at this time.
Phrases expressing frequency — they are usually placed at the end of a sentence.
Phrases formed by the word every:
- every + day / week / month / year
- I go shopping every day. — I go shopping every day.
- Scarlett watches a new film every week. — Scarlett watches a fresh movie every week.
- She visits her mother-in-law every month. — She visits her mother-in-law every month.
- Molly goes on holiday every year. — Molly goes on vacation every year.
Phrases formed using the words once and twice:
- once + a week / month / year and twice + a week / month / year
- We see each other once a month. — We see each other once a month.
- Ivan has English lessons twice a week. — Ivan studies English twice a week.
Starting from 3 times or more, we use the word times: three times a month, four times a year
Charlotte’s daughter usually comes to see her about ten times a year. “Charlotte’s daughter usually visits her about ten times a year.
Source: https://englishfull.ru/grammatika/slova-markery-present-simple.html