/ / Uncategorized
What is the Difference Between Began and Begun?
Contents
- 1 What is the Difference Between Began and Begun?
- 2 Using Began in a Sentence
- 3 Using Begun in a Sentence
- 4 Remembering Began vs. Begun
- 5 Outside Examples
- 6 Quiz: Begun vs. Began
- 7 Article Summary
Began and begun are both different forms of the same verb. Therefore, they have the same definition, but are appropriate in different tenses and grammatical contexts.
Began is the simple past tense form of begin, which means to start.
- It all began one day about ten years ago.
Begun is the past participle form of begin.
- We can’t stop this process once it has begun.
Now, let’s look at the specific ways to use these conjugations of begin, as well as how to avoid common mistakes.
Using Began in a Sentence
When to use began: Began is the simple past tense form of begin. It means to commence or to start.
For example,
- You’re late! Dinner began at 7 o’clock and it is now almost 8:30!
- The snow began falling early in the evening last night and had accumulated to over two feet by early this morning.
There are several idioms and expressions that use the word begin. A couple of these, which are listed below, can also occur in the simple past:
- a journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step: a big project starts with a small action
- The race to find a cure for the horrible disease began with a single step: the discovery of bacteria.
- to begin to see: to start to understand
- When my sister stole my money I began to see that she had become a criminal.
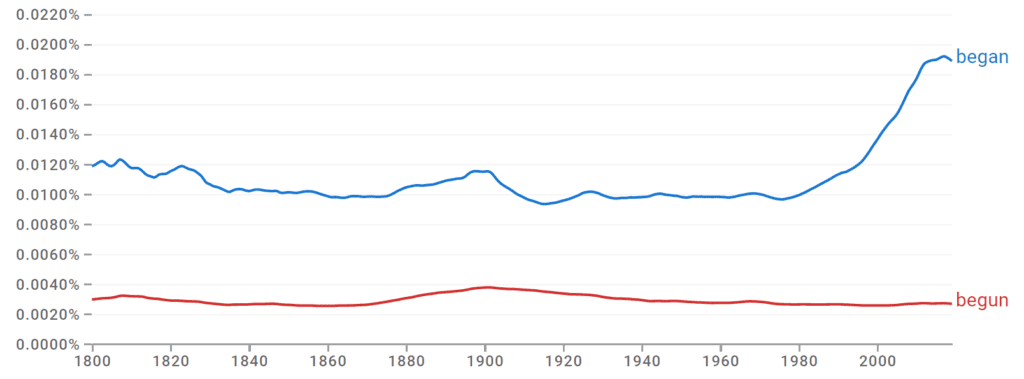
Began occurs more frequently than begun.
Using Begun in a Sentence
When to use Begun: Begun is the past participle form of begin. It appears after the helping verb have in the perfect tenses.
For example,
- You can’t stop the process now. It has already begun.
- By the time the racer realized he had forgotten his shoes, the race had begun.
- Have you begun your homework yet?
There is one proverb that uses begun:
- well begun is half done: if you get a good start to a project, completing the rest of it will be easy
- I know you’re worried about writing a ten-page essay, but you know what they say! Well begun is half done. You’ve already done the research and you’re an expert on the topic. Now all you have to do is write down what you already know.
Between the synonyms begin, start, and commence, start is the most common and commence is the most formal.
Remembering Began vs. Begun
It is possible to use the spelling of these words to remember the meanings.
These words are spelled exactly the same except for the a and the u difference. Usually, when students of English learn the three forms of irregular verbs, they learn in the order of base form, simple past tense form, and past participle form (like go, went, gone). Just as the past tense comes before the past participle form, a comes before u alphabetically.
Alternatively, there are many other irregular verbs that include a stem change from i to a to u from base form to past simple to past participle. Some examples of verbs in that order include swim, swam, swum; drink, drank, drunk; sing, sang, sung; and ring, rang, rung.
Outside Examples
- Hundreds of fans began airing their complaints via social media that they had trouble streaming the pre-fight show via Showtime. –New York Post
- They had been waiting out the storm Saturday in Yeselia Castro’s home, but then the waters began pouring in. They tried putting the children on tables and on the bed to keep out of the water. Their brother-in-law, Jesus, even got on the roof. –LA Times
- Both Cabrera and Wilson have begun the appeals process, Ausmus said before Friday’s game against the Chicago White Sox. –USA Today
- The great eclipse migration has begun. And for those hitting the road late, maybe pack a lunch. Oh, and don’t forget some extra gas. You’re probably already too late for eclipse glasses or a place to stay. –Denver Post
Quiz: Begun vs. Began
Instructions: Fill in the blank with the correct word, either begun or began, in the correct form.
- I may not have __________ this fight, but I sure will finish it!
- The play has already _____________ so the theater won’t let the patrons enter.
- The whole rivalry _______________ about 100 years ago.
Article Summary
Should I use began or begun? These two words are both different forms of the past tense of begin. To know which one to use, you must know if you are using the simple past tense or the perfect tense.
- Began should occur in the simple past tense, for actions that completed in the past.
- Begun should occur in the perfect tenses, as the past participle.
Make sure you are aware of this difference when choosing which of these words to use.
Quiz Answers
- begun
- begun
- began
Use the word began in a sentence. The sentences below are ordered by length from shorter and easier to longer and more complex. They use began in a sentence, providing visitors a sentence for began.
- The service began. (8)
- The examination began. (8)
- The third day it began. (8)
- He began to take courage. (8)
- Miss Bertram began again. (4)
- He began to tell me at once. (9)
- She began to climb the stairs. (8)
- Her heart began the hammerthump. (10)
- She began to fear Willoughby again. (10)
- Then she began to read it once more. (9)
- I began to think you would never come. (4)
- March began to think so too, at times. (9)
- A cuckoo began calling from a thorn tree. (8)
- The breeze died away; midges began to bite. (8)
- In 1820, he began to compose systematically. (3)
- His stare wavered; he began to walk up and down. (8)
- He had hardly seen anything of her since it began. (8)
- Early in January he and his 500 men began to march. (19)
- He began marching about the room with great strides. (10)
- He looked at me hard, as if he began to scent heresy. (8)
- Mr. Cuthcott again began banging on the little table. (8)
- But if on this shock he began to drink, what might not happen? (8)
- It affected his imagination, and his heart began to beat sickeningly. (22)
- A little farther along the water courses began to flow to the eastward. (7)
- Thus passed three minutes, then she again began rubbing the soapy garment. (8)
- And, kneeling down, she began to disentangle a fly, imprisoned in a cobweb. (8)
- A little talking wind shivered along the houses; the dusk began creeping in. (8)
- His blood began to sing: O happy those within, to see her, and be about her! (10)
- Strolling out into the High Street he began observing the humours of the day. (8)
- The startled Jolyon set down his barley-water, and began crumbling his bread. (8)
- When any strange man began, she used to ask him what pattern caps grandmothers wore. (10)
- Lavender began to speak, had been looking at him with strange intensity, dropped his eyes. (8)
- Certain terms in the letters here and there, unsweet to ladies, began to trouble his mind. (10)
- Clementina began to feel her dignity infringed; she did not answer, and now Milray laughed. (9)
- Then term began, and Gyp sat down again to the long sharing of Summerhay with his other life. (8)
- It began that day at Lakelands; I fell in love with you the very first minute I set eyes on you! (10)
- Mrs. March began to try the Triscoes in this place and in that, to divine them and to class them. (9)
- Then, just as the real business of the season was beginning, she began to feel dull and restless. (8)
- I do not think the syndicate began with serials, and I do not think it is likely to end with them. (9)
- There is no certainty of when the smaller domestic houses of England began to use glazed windows. (17)
- And it was longer than usual, too, before a face peered down, and the tip-tap of the bast slippers began. (8)
- Holding him close with all her strength, as she might have held one desperately loved, she began to mount. (8)
- He crossed the wooded neck above the valley, and began descending, peering into gulfs of the twilight dusk. (10)
- He began to experience the fretful craving to see the antecedents of the torturing woman spread out before him. (22)
- I jumped up, and tried to take her in my arms, but she slipped away; then she turned, and began laughing softly. (8)
- Mrs. Pendyce looked after him; her fingers, from which he had torn his coat, began twining the one with the other. (8)
- Finally, all that dress-making in the house began to scare him with vague apprehensions in regard to his own dress. (9)
- He began to respect her, relishing her exquisite contempt, and he reflected that widows could be terrible creatures. (10)
- He began to hope wildly that this rumour about the horse was a falsity, for there was no commotion, no one declaiming. (22)
- And perceiving that the very basis of his faith was endangered, he threw off the bedclothes, and began to pace the room. (8)
- They crossed from Oswego on Lake Ontario to Kingston and York, and began at once felling trees and erecting rude cabins. (19)
- At last the trunks were all on the tender, and the bareheaded stewards began to run down the gangways with the hand-baggage. (9)
- The exertion made him hot, which may account for the rage he burst into when Mrs. Hawkshaw began flutteringly to apologize. (10)
- She began to cut down the expenses for his personal needs too, and he had to eke out his diet in restaurants and wine-rooms. (12)
- A year later, however, her son began to busy himself with matters that would certainly give some clue to her more recent envoys. (5)
- She found another shaving within reach of her parasol, and began poking that with it, and trying to follow it through its folds. (9)
- Mrs. MacAnder smiled at them; she knew everybody; and all these three, who had been admirably silent before, began to talk at once. (8)
- The woman here edged so close that he bolted across her in affright, and began to slant back towards the opposite side of the street. (8)
- Vittoria began to admit the existence of his likeness to her lover, though it seemed to her a guilty weakness that she should see it. (10)
- My most unexpected energy threw the whole table into a roar, at the conclusion of which Fin began his narrative of the mail-coach adventure. (6)
- Now we noticed that a soldier was stationed at every furlong of the shore, and we began to be anxious about finding a secluded camp-ground. (20)
- And gradually little pauses began to creep into their talk; then a big pause, and Nedda, who would never want to sleep again, was fast asleep. (8)
- How they could get through it all had often amazed Mrs. Allen; and, when Catherine saw what was necessary here, she began to be amazed herself. (4)
- The Greydons began the social season for the purpose of preparing society for the early announcement of the engagement between Roderick Barclugh and their daughter. (18)
Also see sentences for: beg, begat.
Definition of began:
- began, b-gan’, pa.t. of begin.(0)
Glad you visited this page with a sentence for began. Now that you’ve seen how to use began in a sentence hope you might explore the rest of this educational reference site Sentencefor.com to see many other example sentences which provide word usage information.
More Sentence Examples
Select First Letter
- Use the word began in a sentences
Sentence Examples
I began to realize how much I had denied myself forever.
The shrub soon stopped growing… and began to get ready to produce a flower.
In fact, Mademoiselle Sainsbury Seale was dead even before the investigations of this case began.
It began innocuously enough, when Wilkins started to investigate one of the chemicals found inside chromosomes.
When Meyerowitz first began photographing in the early 1960s, 5th Avenue was a happy hunting ground for some of the greatest names in contemporary photography.
The biggest change of all came when some photographers began to see the world in a weird new way, in colour.
Jerome began gardening in the lowlands of the Basalt area with the understand that it would be too difficult to grow near his home on Basalt Mountain due to the arid soils and difficulty in harnessing water but once I learned about permaculture
This is when we began the planting of this greenhouse last autumn, and this spring we had this much growth in there.
While you were frozen… we began a programme to clone you.
The next morning, the Turks began their attack.
The next morning, the general assault began.
Well we gathered that morning all probably an hour before actual service began upstairs.
And I don’t know how many minutes transpired before we all began, I believe, feeling a reaction the placebo in fact was a form of stimulant that would create a sensation.
In Switzerland the directors of Sandoz began to hear of the wide spread and uncontrolled abuse of their product.
As soon as the criminals were brought to shore, the storm began to rage again.
After that I began to love you.
…Jean began to realize he wasn’t the only one who loved Edith…
I began to meet it wherever I sailed:
I began to understand what it meant.
The «painful interrogation» preferably began with a «lighter» torture:
We had the same situation. Everything began with…
Everything began to spin before Mr. West’s eyes.
The electoral campaign began.
From the first light of day, Mallet began searching for Catherine.
The Weasel began Gudule’s education.
The shy young man suddenly began to talk without stopping.
As she introduced her friends, his heart began to sing.
This is a great day! This is where all our dreams began.
Thus Heizaburo began a life of wandering.
He began to despair at his sorry state.
A while later… Heizaburo became the Rat’s bodyguard and began coming to the Yoshihogawa restaurant.
He began in 1915 at Gaumont and, in 1921, had his first international hit with «L’Atlantide» based on the novel by Pierre Beno├«t.
The ice on the Yukon began to break
And from crowded eastern cities, civilization began pouring the overflow into the trackless immensity of the West.
Old World blood began to fuse with Colonial strains … and «westward the course of empire takes its way».
And the next day, Boleslas Vorowski began the most painful stage of his ordeal
And here the bells began to ring …
Alraune began a new life together the one she loved.
Trains began to travel in Ukrainian steppes… And the zvenyhora-mountain and forests and rivers kept the old man’s secret.
That’s how George Manolescu’s life as a swindler began.
I began to think of the strangest things, like being out in the fields.
I began to wonder if I was all wrong.
Shrapnel began bursting all around him.
So the trip began, the barrow was full of fish in front of this treasure, Reynard remembered his kids… his beloved kids, so fond of trout, salmon, gudgeon.
As shot, Dracula’s following line originally began, quote:
This marriage crumbled, as she began a self-destructive spiral of drink, drugs and periodic commitment to sanitariums.
He was born in Halifax, Nova Scotia, in 1901, began a stage career in the 1920s, before switching to film.
AND SO began THE TRANSFORMATION
I began to realize how much I had denied myself forever.
The shrub soon stopped growing… and began to get ready to produce a flower.
In fact, Mademoiselle Sainsbury Seale was dead even before the investigations of this case began.
It began innocuously enough, when Wilkins started to investigate one of the chemicals found inside chromosomes.
When Meyerowitz first began photographing in the early 1960s, 5th Avenue was a happy hunting ground for some of the greatest names in contemporary photography.
The biggest change of all came when some photographers began to see the world in a weird new way, in colour.
Jerome began gardening in the lowlands of the Basalt area with the understand that it would be too difficult to grow near his home on Basalt Mountain due to the arid soils and difficulty in harnessing water but once I learned about permaculture
This is when we began the planting of this greenhouse last autumn, and this spring we had this much growth in there.
While you were frozen… we began a programme to clone you.
The next morning, the Turks began their attack.
The next morning, the general assault began.
Well we gathered that morning all probably an hour before actual service began upstairs.
And I don’t know how many minutes transpired before we all began, I believe, feeling a reaction the placebo in fact was a form of stimulant that would create a sensation.
In Switzerland the directors of Sandoz began to hear of the wide spread and uncontrolled abuse of their product.
As soon as the criminals were brought to shore, the storm began to rage again.
After that I began to love you.
…Jean began to realize he wasn’t the only one who loved Edith…
I began to meet it wherever I sailed:
I began to understand what it meant.
The «painful interrogation» preferably began with a «lighter» torture:
We had the same situation. Everything began with…
Everything began to spin before Mr. West’s eyes.
The electoral campaign began.
From the first light of day, Mallet began searching for Catherine.
The Weasel began Gudule’s education.
The shy young man suddenly began to talk without stopping.
As she introduced her friends, his heart began to sing.
This is a great day! This is where all our dreams began.
Thus Heizaburo began a life of wandering.
He began to despair at his sorry state.
A while later… Heizaburo became the Rat’s bodyguard and began coming to the Yoshihogawa restaurant.
He began in 1915 at Gaumont and, in 1921, had his first international hit with «L’Atlantide» based on the novel by Pierre Beno├«t.
The ice on the Yukon began to break
And from crowded eastern cities, civilization began pouring the overflow into the trackless immensity of the West.
Old World blood began to fuse with Colonial strains … and «westward the course of empire takes its way».
And the next day, Boleslas Vorowski began the most painful stage of his ordeal
And here the bells began to ring …
Alraune began a new life together the one she loved.
Trains began to travel in Ukrainian steppes… And the zvenyhora-mountain and forests and rivers kept the old man’s secret.
That’s how George Manolescu’s life as a swindler began.
I began to think of the strangest things, like being out in the fields.
I began to wonder if I was all wrong.
Shrapnel began bursting all around him.
So the trip began, the barrow was full of fish in front of this treasure, Reynard remembered his kids… his beloved kids, so fond of trout, salmon, gudgeon.
As shot, Dracula’s following line originally began, quote:
This marriage crumbled, as she began a self-destructive spiral of drink, drugs and periodic commitment to sanitariums.
He was born in Halifax, Nova Scotia, in 1901, began a stage career in the 1920s, before switching to film.
AND SO began THE TRANSFORMATION
What is the difference between began and begun?
Misusing the words began and begun is one of the most common mishaps in English grammar. Sure, the words look and sound similar enough, but there’s a right and wrong way to use them in a sentence.
The words began and begun are different forms of the irregular verb “to begin.” We use the verb “begin” for actions that ‘start,’ ‘initiate’ or ‘launch’ an activity or process. For example,
“Dinner begins with an appetizer.” (present tense)
“We began dinner with an appetizer.” (simple past tense)
“We’ve begun to eat dinner.” (present perfect tense)
As shown above, we use “began” for the past tense and “begun” as the past participle for all perfect tenses. Additional verb forms include begins (plural present) and beginning (present continuous/progressive).
”To begin” as an irregular verb…
There are several reasons why began and begun are commonly confused words, starting with the irregularities of the verb “begin.” Regular verbs consist of a simple past tense form with a present and past participle. Additionally, a regular verb’s simple past and past participle ends with -ed, such as “learned,” “passed,” or “separated.”
If “begin” were a regular verb, the past tense and past participle forms would look something like “begined”–– which is, clearly, not the case. Instead, the verb tense forms of begin look something like this:
- Simple past tense: began
- Present tense: begin/begins
- Future tense: begin
- Progressive tense: beginning
- Perfect tenses: begun
Beginner vs. beginning?
Another reason why it’s easy to confuse began vs. begun: similar, yet different words that start with “begin.” Do the nouns “beginner” or “beginning” ring a bell?
In addition to acting as the progressive tense form, the word “beginning” is also a noun. As explained by The American Heritage Dictionary, the noun “beginning” is ‘the time or place when something starts,’ ‘the earliest time of initiation,’ or ‘a source or cause.’ In this case, telling someone to “start at the beginning” is different from saying “something is beginning.”
Likewise, the noun (or adjective) “beginner” describes someone or something deemed ‘entry-level,’ ‘new,’ or ‘just starting to learn something.’ For example, if you’re taking an ESL class, you might be a “beginner-English student.” Or, if you start a new exercise class, you could enroll in a “beginner’s course” to get started.
What does begin mean?
The word begin is an irregular verb that means ‘to start,’ ‘arise,’ ‘perform,’ or ‘undergo the initial part of an action.’ Specific definitions and examples of “begin” include:
1. To initiate or ‘set about’ an activity or process. For example,
“She began writing after work.”
“Let’s begin with chapter 4.”
“The race begins at noon.”
“He’s in the beginning process of cleaning the garage.”
“They’ve already begun reading.”
2. To arise or originate in existence. For example,
“My life began in the early 90s.”
“A new day begins whether you like it or not.”
3. To establish or start an organization, process, or activity. For example,
“The book club began with only three members.”
“The private school was begun by local chapter members.”
Phrases with the verb begin:
As noted by Lexico, English speakers use the verb begin for several phrases, including:
- “Begin/began to do something:” to start at an initial task, time, or place.
- “Begin with:” to start with an initial element.
- “Begin on/upon:” to start working or stating something.
- “Begin at:” a minimum cost of something or to not have any likelihood of occurring.
- “To begin with:” to start with something first.
Synonyms
Actualize, appear, arise, commence, constitute, develop, embark, emerge, enter, establish, form, found, generate, inaugurate, initiate, innovate, institute, launch, materialize, open, originate, pioneer, start, surface, take-on, undertake.
Antonyms
Abolish, annihilate, annul, cease, close down, conclude, destroy, discontinue, end, expire, finish, halt, lay off, nullify, phrase out, shut up, stop, terminate, wrap up, quit.
Etymology of begin
According to The New Oxford American Dictionary, the word begin originated with Old English beginnan via early Germanic languages and is related to Dutch and German beginnen (“Begin” 150).
How to use began vs. begun in a sentence?
Now that we understand the definition and irregularities of the verb ‘to begin,’ it’s time to learn how to craft “began” and “begun” into a sentence. As a partial recap, let’s look at which verb tenses we use for all verb forms of begin.
Begin:
- Present tense: begin/begins
- Future tense: will begin
Began:
- Simple past tense: began
Begun:
- Future perfect tense: will have begun
- Present perfect tense: have/has begun
- Past perfect tense: had begun
Beginning:
- Present continuous tense: am/are beginning
- Past continuous tense: was/were beginning
- Future continuous tense: will be beginning
- Present perfect continuous tense: have/has been beginning
- Past perfect continuous tense: had been beginning
- Future perfect continuous tense: have been beginning
When to use began vs. begun
As shown through prior verb lists, the only time we use “began” is for the simple past tense. For example,
“I began reading Jane Austin novels.”
“He began every text message with an emoji.”
“They began dancing and singing.”
Meanwhile, the word “begun” only occurs for the past, present, and future perfect tenses. Example sentences include,
“By Friday, every resident will have begun the voting process.” (future perfect)
“The city has begun decorating for fall.” (present perfect)
“We had begun celebrating by then.” (past perfect)
Writing tips for begun vs. began
The second lesson for using “begun” and “began” involves grammar and context:
Use “began” to reference a former title
If you’re looking to reference someone’s former or initial role, “began” is the best word choice. For example:
- Correct: “She began as the assistant.”
- Incorrect: “She begun as the assistant.”
Using “began” with inanimate subjects?
If you use “began” with an inanimate object or thing, the verb may imply that something originated or materialized into existence. For example,
“Crater Lake began as a natural disaster.”
“The post office began their deliveries at 5 a.m.”
“The floor began to shake.”
Only use “to” before “begin”
Whenever you read the word “to” before a verb, that’s because it’s written in the infinitive form (e.g., ‘to begin’). The infinitive form of a verb only contains the root word, so it’s incorrect to use other tense forms.
- Use: “to begin.”
- Don’t use: “to began,” “to begun,” “to beginning,” etc.
One last note: If you choose to use the infinitive phrase, beware of using “with” afterward. According to Garner’s Modern English Usage, “to begin” is an introductory phrase that we use to enumerate a reason. Therefore, writing the phrase “to begin with” can imply a chronological order, whether it’s intended or not (Garner 102).
To illustrate, compare the implied meaning of each example sentence:
- “We are going to begin with reading.” vs. “We are going to begin reading.”
- “She’s to begin with Spanish 101.” vs. “She’s to begin Spanish 101.”
Can you tell the difference? The examples above all convey a command, but using “with” appears more demanding because it implies a negated option. Let’s look at one more:
- “I don’t know what to begin with.” vs. “I don’t know what to begin.”
For the final example, the appearance of “with” nearly changes the entire meaning of the sentence. The first example implies there are several options ‘to start,’ but the second example can imply that someone is confused or unaware of a task at hand.
Avoid using auxiliary verbs with “began”
One of the trickier rules for “began” involves auxiliary verbs or ‘helping verbs.’ Most English speakers are aware of other auxiliary verbs like “to have,” “to do,” or “to be” because they allow other verbs to express their tense forms. But in the case of ‘begin,’ we don’t use auxiliary verbs for its past participle form.
As noted by GMEU, linguists have made examples of phrases like ‘has began’ as “careless speech” and “writing” since 1951–– a writer’s worst nightmare, if you ask us (Garner 102). To avoid these embarrassing call-outs, avoid pairing auxiliary verbs with “began” at all costs!
Correct:
- “He will begin.”
- “She has begun.”
- “We have begun.”
- “I will have begun.”
Incorrect:
- “He will began.”
- “She has began.”
- “We have began.”
- “I will have began.”
Want to learn more about verbs?
If you enjoyed learning about began vs. begun, check out our recent posts on verbs like:
- Inquire vs. enquire?
- Is vs. are?
- Lets vs. let’s?
- Into vs. in to?
- Chose vs. choose?
Test Yourself!
Confusing words like began and begun have a bad rap for a reason. See how well you understand their differences with the following multiple-choice questions.
- True or false: “began” and “begun” are different forms of the verb “begin.”
a. True
b. False - The word ____________ is the past participle form of begin.
a. Began
b. Begin
c. Begun
d. Beginning - The word ____________ is the simple past tense form of begin.
a. Began
b. Beginning
c. Begun
d. Begin - Forms of the irregular verb “begin” don’t include _____________.
a. Begins
b. Beginner
c. Beginner
d. Began - The future tense of the verb “begin” is _____________.
a. Beginning
b. Began
c. Begun
d. Begin
Answers
- A
- C
- A
- B
- D
Sources
- “Begin.” Garner’s Modern American Usage, 3rd ed., Oxford University Press, 2009, pp. 102.
- “Begin.” Lexico, Oxford University Press, 2020.
- “Begin.” The Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary, Merriam-Webster Inc., 2020.
- “Begin.” The New Oxford American Dictionary, 3rd ed., Oxford University Press, 2010, pp. 150.
- “Beginner.” The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, 5th ed., Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company, 2020.
- “Beginning.” The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, 5th ed., Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company, 2020.
- “Irregular verbs: overview and list.” OWL at Purdue, Purdue University, 2020.
- “To begin.” Reverso Conjugation, Reverso-Softissimo, 2020.
Is it began or begun? That’s a good question and one I hear all the time. Both words are correct forms of the verb begin, which means their definition is the same. But they have a massive difference in terms of usage. Learn the difference between begun and began in this guide with writing tips.
Begun vs. Began
Both began and begun are correct. No word is incorrectly spelled. However, their usage differs.
Both begun and began are the past tense forms of an irregular action verb begin. An irregular verb is a verb that does not follow the typical pattern of its past form. That means it does not end in -d or -ed, as in begined.
Begin means to start, undergo, or perform.
- Began is a simple past tense of begin. It does not need a helping verb.
Example: I began drinking coffee at 7 AM.
- Begun is the past participle of begin. We use it with helping verbs like have, has, or had to form perfect tenses. Sometimes, we use it as an adjective for modifying a noun or pronoun.
Example: We’ve only just begun eating dinner.
Do not use began in perfect tenses. For example:
- Incorrect: We had began eating when Joey arrived.
- Correct: We had begun eating when Joey arrived.
Do not use begun in the simple past tense. For example:
- Incorrect: She begun watching TV ten minutes ago.
- Correct: She began watching TV ten minutes ago.
Using Began in a Sentence
- I began reading the novel a few weeks ago.
- The crowd began to clap after the band’s memorable performance.
- It began to rain the minute the event ended.
- Excerpts of residents’ panicked conversation began to circulate on social media, along with videos of the emergency response. They showed fire crews struggling to get around barriers to approach the building. (Wall Street Journal)
- A World Cup that began in controversy and uncertainty will end with history being made, though exactly what kind of history remains to be seen. Perennial favorites Germany, Belgium, England, Spain, and now Brazil are out. Morocco, France, Croatia, and Argentina remain. (LA Times)
Using Begun in a Sentence
- I will have begun law school after graduating with my first degree.
- The game had already begun by the time we found our seats in the arena.
- We have begun searching for the lost puppy.
- A probe into the firefighting operation linked to the death of a full-time Singapore Civil Defence Force (SCDF) national serviceman has begun and the findings will be made public in time. (Strait Times)
- WNBA star Brittney Griner has begun serving her nine-year sentence for drug possession at a Russian penal colony, her lawyers and agent said Thursday. (AP News)
How to Remember the Difference
It can be challenging to remember the differences between began and begun.
But just remember: Began is in past tense and requires no helping verb, while begun is in past participle form with a helping verb.
Is Began Past Tense?
Yes, began is the past tense of begin. For example:
- We began planning the project yesterday.
Is It Has Begun or Has Began?
The correct verb phrase is has begun. It’s the present perfect form of begin if the subject is singular. The present perfect tense is formed using has or have plus the past participle form of a verb. For example:
- The teacher has begun checking our assignments.
Final Word on Began or Begun
Began and begun are not alternative spellings of each other so don’t fall prey to common mistakes like this in your writing. To know which word you should use, remember:
- Began is the simple past conjugation.
- Began is the past participle form that is used with a helping verb.