Even Native English speakers mess up than and then because of their similar spelling and pronunciations. However, their meanings significantly vary.
This guide will show you nuanced differences between then vs. than. Learn when to use the two words in the sentence before the self-anointed grammar policemen point out your grammar error.
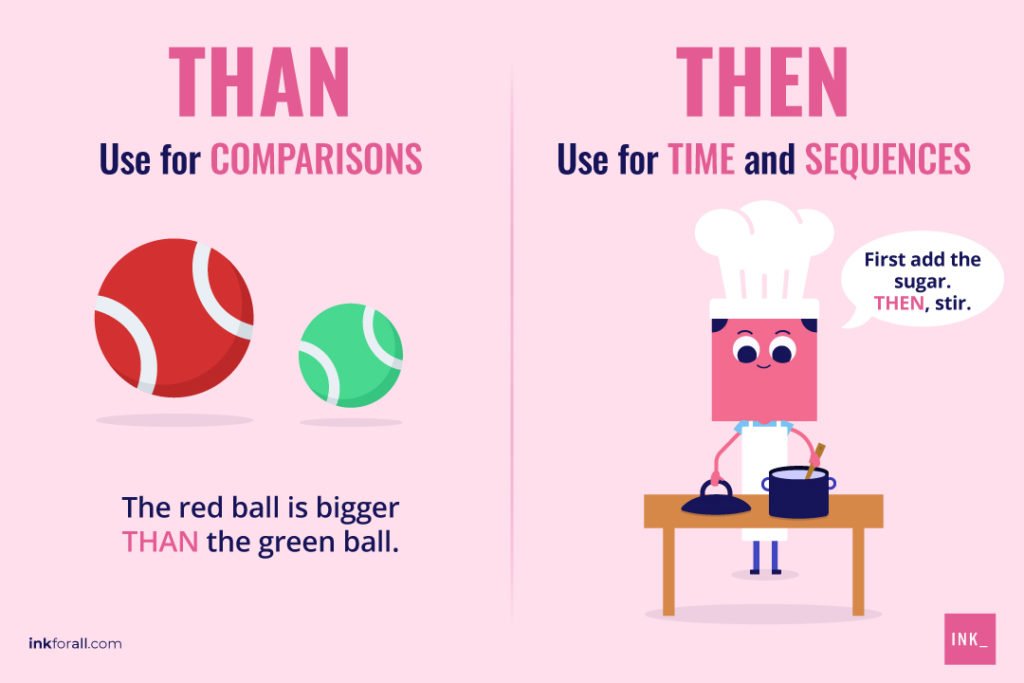
Then vs. Than: What’s The Difference?
Then is an adverb, noun, or adjective that indicates a previous time. Meanwhile, than is a conjunction used when comparing two items or people.
Use then in writing or events when there is an element of time. In the English language, then means at that time, at that point, or next. You’ll find it in phrases like since then and until then to show a reference of time.
Use than in common phrases like better than, further than, taller than, or broader than. You’ll find this word after terms like other, less, more, and rather.
In Middle English, then and than used to be the same word used for all their meanings. People used them to show relationships with time and for comparison purposes. However, modern writing now treats them differently.
That’s why the two words are now homophones people get confused with. Homophones are words that show an essential difference in spelling but similarities in sound.
When to Use Then
You can use then as an adverb to replace at that time in question to make grammatical sense. This adverb helps you place events in time in order, such as when relating to a future time.
Examples:
- But by then, Shannon might be tired.
- Let’s buy ice cream and then watch a movie.
Here’s a longer, multilayered example of then relating to the future.
My first subject is Chemistry, then French, then Science. Then, I’ll have lunch, go to Math class, and go home.
Then can also mean previous or former. Some English speakers use the term if they can’t recall the exact time of an event in the past. Here are some sentences that use then relating to a previous time.
Examples:
- The then president visited our small town.
- We lived in San Diego then.
Aside from using then in terms of time, you can also use it to show consequence or mean in that case.
Examples:
- If you had taken care of the cat, then we wouldn’t be in this situation.
- I slept late, so then I woke up dizzy.
When to Use Than
Making an unequal comparison requires using a particular word in the English language. Than is the conjunction that expresses a form of comparison in a sentence. Use it to introduce the second item or person to make direct comparisons.
For instance, when you say “truth is stranger than fiction,” it means that real events are more unnatural than imagination.
Examples:
- My mother told me that a curious person is better than a know-it-all.
Is it Earlier Than or Earlier Then?
Both phrases are correct but have different meanings. The more common phrase you might be looking for is earlier than. For example, you might arrive at school earlier than usual. However, you used to come earlier then.
Is it Later Then or Later Than?
The correct phrase is later than if you want to show a comparison between two late items, people, or events.
Is it Rather Then or Rather Than?
The correct term is rather than since rather is used to show preference in a specific matter. For instance, you might know someone who wants wine rather than a martini.
Is it Other Than or Other Then?
Other than is the appropriate phrase as it means apart from or except.
Is it Better Than or Better Then?
Better than is one of the most popular phrases with the word than. To be better than something or someone means you’re superior or more excellent.
Is it More Than or Then?
The appropriate phrase is more than, which indicates a bigger value or amount. It can also mean extremely, as in more than gratefulto be reading this post.
Is it Less Then or Less Than?
Use less than as a synonym for far from or certainly not.
It is Well Then or Well Than?
The correct phrase is well then to indicate that what someone said was unexpected or inappropriate. Well than is a wrong phrase because well is not in its comparative form.
Than Me or Than I?
The traditional rule is to use than I because the longer version of the sentence is typically than I am. However, it can lead to outdated-sounding language, especially if you use a different pronoun.
Example:
- He is smarter than she.
- He is smarter than I.
Can You Start a Sentence With Then?
You can start a sentence using then when showing a list of events or a chronology of events.
Example:
- I read a book last night. Then I got hungry and ordered food.
How Do You Use Than in a Sentence?
Here are plenty of examples of how you can use than in a sentence.
An asteroid wider than two football fields will zoom past Earth in the wee hours of Thursday (Aug. 4). The asteroid is set to pass at 12:23 a.m. (ET). [Live Science].
Indeed, it may have been no more than a coincidence that Tsai Chi-chang, deputy speaker of Taiwan’s legislature, appeared to respond to Pelosi’s suit by wearing a pink tie to meet her on Wednesday morning. [CNN].
She recalls one episode in which a former employer chastised her and two other assistants, each of whom made more than $150,000 a year, she says, for putting bananas in the refrigerator, instead of on the kitchen counter. [Wall Street Journal].
The arrests on Tuesday near Krugersdorp, a city northwest of Johannesburg, bring the total number of people detained since the attack to more than 120. [The Guardian].
How Do You Use Then in a Sentence?
Let’s take a look at these examples of then in sentences.
Shark! Man in New Jersey catches, then releases a 7-foot sand tiger shark. [Fox News].
Speaking to CNN, the congresswoman Carolyn Maloney said sorry for broaching the issue in a debate – but then said again she thought Biden would not run. [The Guradian].
No, because smartphones bring these three features into one product. Then why should organizations pay for three different products, when it is indeed possible to bring all these aspects into one smart product? [Forbes]
The Real Difference Between Than vs. Then
One of the writing issues that English speakers and writers face is the confusion between than vs. then. Using the two words interchangeably can be annoying for grammar perfectionists, even in informal writing. Remember:
- Use then in a sentence when referring to a sense of time, whether past or future. You can also use it to show consequences.
- Use than to feature comparisons between two unequal items, places, persons, or events.
Answer the worksheet below to test your knowledge of this homophone.
Main Than vs. Then Takeaways:
- Then and than are homophones. This means that they sound almost identical when spoken but have different meanings and spellings.
- When you think of then, think of time.
- When you think of than, think of comparisons.
- Sometimes, than can be used to indicate time, but it is still typically a comparison.
- Then can be an adverb, adjective, or noun.
- Than is a conjunction.
Like affect vs. effect and to vs. too, than vs. then cause a lot of confusion. While many use these homophones interchangeably, they are not the same. Choosing the wrong word may mean that you don’t communicate your message clearly or correctly. In fact, than and then have different functions and meanings. But, there are, of course, some exceptions. Here, we’ll make sure you have everything you need to keep them straight, once and for all.
Then vs. Than Rule
Here’s the best way to tell the difference between then vs. than: associate then with time and than with comparisons. For example, use then for clarifying a sequence of events like writing a recipe or retelling a story (“We went to the supermarket and then headed home.”). Try remembering that the “e” in “then” stands for “events.”
Conversely, use than when making a comparison (“We like going to the smaller shop nearby more than going to the supermarket.”).
You might see then in a comparison, but always about time (“Back then, we were less timid than we are now.”).
Than vs. Then Exception: Comparisons About Time
There is one exception. Sometimes, than can appear in comparisons about time. But in these cases, there is still a comparison involved.
In this example, we’re dealing with time, but it’s secondary. The main function of than here remains the same: to make a comparison.
“He” is comparing his meeting time to 12 pm. He’ll be there no later than noon. In other words, other times are being compared to that one particular time-related target.
This may be confusing because we’re not drawing a 1:1 comparison between two individual things (he arrived earlier than I arrived); instead, we’re comparing one individual thing (12 pm) to a group (all times before 12 pm). Nevertheless, this is ultimately a comparison and as a result, should use then.
What Type of Word is Then?
Then usually refers to time and can function as three types of speech. First, then is usually an adverb (“If you leave, then turn off the lights”). Second, then can be an adjective (“Jackie Kennedy, then Jacqueline Onassis, studied literature“). Finally, it can be a noun (“See you then?” or “We’ll wait until then”). Conversely, than is a conjunction and is for making comparisons (“This cake is sweeter than that brownie”).
How is Then Used in a Sentence?
Then vs.than breaks down to time vs. comparisons. For instance, there are several ways to use then, and they all indicate time. Most often, then is an adverb to help clarify a sequence of events (“Wash then dry the dishes”). What’s more, then helps describe a condition and then a consequence (“If it rains, then we’ll eat inside”). Additionally, then can also be an adjective (“The then CEO”). Finally, then can be a noun (“I’ll see you then!”).
Then can function as several parts of speech. Most often, it’s found working as an adverb in sentences where time is involved, but can also be an adjective or noun. Use then to:
- Clarify a sequence or indicate the order in which certain actions occurred
- Illustrate the relationship between several actions or items
- Illustrate the consequences of a certain action
- Indicate a previously held position
Clarify a Sequence (Adverb)
Describe the Relationship Between a Condition and Consequence (Adverb)
You could also use then to tell the reader when something caused something else to happen. Those examples typically frame the second action as a consequence of the first. In that case, you’ll probably use an if/then construction, making it clear the connection between the two actions.
Indicate a Previously Held Position (Adjective)
Remember, then can be an adjective, an adverb, or a noun. It’s most often used in sentences that are discussing time. You might be demonstrating a series of events, indicating a relationship between several actions.
Refer to Past or Future Time (Noun)
How is Than Used in a Sentence?
Than is a conjunction used for comparisons (“She is taller than I am”).However, then is an adverb, adjective, or noun related to time. A point of overlap is that than can appear in comparisons about time (“Please arrive no later than 9 a.m.”).
Overall, than is important because it helps enrich the level of clarity and detail in your writing.
When the relationship between the nouns, verbs, and adjectives in a sentence isn’t equal, you can use than to indicate that one takes precedence. This helps clarify status, physical stature, order of operations, and other important information.
Like other conjunctions, than is used to connect two clauses or two words within the same clause. Unlike other conjunctions, than is specifically used to compare and contrast.
Than helps us understand which is bigger, better, louder, or simply more favored. For example, using “than” is a good way to paint a picture of how items contrast each other.
Here are easy examples of how to use than vs. then in a sentence:
Use the phrase “other than” when describing exceptions. You can replace other than with alternatives like except for and besides.
How to use Less Than and More Than
How to use More Than in a Sentence
How to Use Less Than in a Sentence
Common Expressions: Than vs. Then
Is it Other Than or Other Then?
The correct phrase is “other than” and not “other then.” Use “other than” to indicate an exception (“Other than cats, she’s not a fan of animals”). The item or situation that comes directly after “other than” is the only example mentioned that doesn’t fit into the described scenario. In this way, this structure compares the exception to the rule. Therefore, “other than” expresses a comparison. Since we use than for comparisons and then for time, “other then” doesn’t make sense here.
Is it Well Then or Well Than?
The correct phrase is “well then“, not “well than.” Use the phrase well then to switch topics. Similarly, use this phrase to start concluding a conversation or saying goodbye (Well then, I have to go. See you tomorrow!). Moreover, if a person says something strange or interesting, the response well then indicates that you’re surprised and unsure of what else to say. For this reason, some use it sarcastically.
For instance, say your friend has a history of jumping and hitting their head. You might ask them whether they think that’s a good idea. When they reluctantly say, No…, you could respond with, Well then….?! to suggest they should know better.
If someone makes a strong display of emotion or a comment that you find surprising, provocative, or offensive comment, you might respond with well then.
Notice that because “well” is an interjection in these examples, there’s often a comma between “well” and “then.”
Is it Rather Than or Rather Then?
The correct phrase is “rather than“, not “rather then.” This is because than is most commonly used in comparisons (“He’s taller than her”) while then is more for discussing time (“Sal went to the store then stopped by the post office”). Since “rather than” compares two actions or choices, it only makes sense to use “rather than” instead of “rather then.”
Is it Older Than or Older Then?
Both “older than” and “older then” are correct. But, they are not interchangeable because they mean different things. Usually, we use then for time and than for comparisons. However, this question is confusing because both “older than” and “older then” deal with time and comparisons, but in different ways. Use “older than” to compare the age of one person to that of another person (“My sister is older than I am”). On the other hand, we use “older then” to refer to a time other than the present (“See you then!” Let’s wait a week and buy it then”).
Technically both options are correct. Which one you choose to use depends on your message and the surrounding context.
Rather than accidentally making a mistake with then or than in the future, bookmark this page and review as needed. Happy writing!
Is it Better Than or Better Then?
The answer will depend on the context of your statement. If you’re comparing two things in your sentence, then the correct phrase is “better than.” However, if you are referring to a certain time in the past as better, then “better then” is the right phrase. See examples below:
Let’s see if Then and Than Still Confuse you
Then vs Than Question #1
A. The word “then” mostly functions as an adverb in a sentence.
B. Then can function as an adjective, adverb, or noun.
C. You can use “then” and “than” interchangeably in a sentence.
D. Then is often used in sentences that are discussing time.
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is C. “Then” suggests the order in which specific actions occurred, while “than” is used for comparison.
Then and Than Question #2
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is TRUE. Although both words sound alike, they have different meanings.
Than Question #3
Preposition
Conjunction
Both
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is BOTH. “Than” is a conjunction or preposition, depending on how it is used in a sentence.
Than or Then Question #4
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is THAN. “Than” is commonly used in comparisons.
Then or Than Question #5
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is THEN. “Then” is used to indicate time.
Then vs Than Question #6
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is THAN. “Rather than” compares two actions or choices, with the person in question opting for one over the other.
Than vs. Then Quiz Result
Expert!
Not bad!
Almost got it! Review the article and try again.
Read More: What’s The Difference Between Yea, Yeah, and Yay?
/ / Uncategorized
What’s the Difference Between Then and Than?
Contents
- 1 What’s the Difference Between Then and Than?
- 2 Using Then in a Sentence
- 3 Using Than in a Sentence
- 4 Remembering Then vs. Than
- 5 Outside Examples
- 6 Quiz: Than vs. Then
- 7 Article Summary
Then and than have similar pronunciations and spellings. In fact, one of the pronunciations of than is exactly the same as then. However, these words have no overlap, and they are also different parts of speech.
Then is usually an adverb, but it can also be an adjective or a noun. The most common definition for then is at that time.
- I’m not a dancer now, but I was when I was younger. Back then I danced all the time!
Than is a conjunction used most often in comparisons between two things.
- A giant is taller than a dwarf.
Now that you know the differences between these two words, let’s look at them in context to ensure you don’t confuse one for the other.
Using Then in a Sentence
When to use then: Then can act as an adverb, adjective, or noun. As an adverb, it can mean at that time, next, or consequently. As an adjective, it can describe someone or something as being a certain way at that time in the past, but not now. As a noun, it can mean that time.
For example,
- He played soccer then took a shower. (adverb meaning 2)
- If you aren’t going to study then you’ll fail the test. (adverb meaning 3)
- The then president embezzled a large amount of money. (adjective meaning)
Then also appears in some expressions:
- but then again: on the other hand
- No, thanks. I don’t want any ice cream. But then again, I did just finish my diet yesterday. I guess I will have some ice cream.
- right then and there: at exactly that time and place
- They couldn’t believe that that doctor started singing right then and there, in the middle of the surgery!
- and then some: and even more than that
- She added the amount of alcohol that the recipe noted, and then some!
- now and then: occasionally or at times
- The professor does have a drink at the bar now and then, but not very frequently.
- until then: goodbye until we meet again
- Yes, I’ll see you at the party on Saturday. Until then!
Then is more common than than and appears in both formal and informal speech.
Using Than in a Sentence
When to use than: Than is a conjunction. It appears with comparative adjectives including, but not limited to, better, worse, and faster. It can also appear in sentences that express no choice except for one.
Additionally, than can show preference between two things.
- She doesn’t even study and she’s still smarter than me. (first definition)
- I wanted to get here earlier, but because my car broke down I had no choice other than to walk. (second definition)
- I’d rather exercise by lifting weights than by running. (third definition)
Than also appears in some expressions:
- actions speak louder than words: Doing something shows more commitment than saying something.
- You keep saying that you’ll work harder, but you never actually do work harder. Actions speak louder than words!
- better late than never: Doing something late is better than never doing it at all.
- I’m sorry I sent you this thank-you card so late, but better late than never, I suppose.
- better safe than sorry: It is better to be safe than it is to take a risk and have a horrible accident occur.
- Doctor’s recommend that most people get a yearly checkup to make sure they are healthy. It’s likely that nothing will be wrong, but it’s better to be safe than sorry.
- more than meets the eye: someone or something has more importance or depth than is apparent at first glance
- You should try dating him. I know he seems boring at first, but he’s actually very sweet and interesting. There’s more to him than meets the eye.
- no sooner said than done: the action will occur directly after stating that the action is desired
- If you want me to buy you a cake for your birthday, just let me know. It’s no sooner said than done.
Just like then, than has been an English word since before the year 900.
Remembering Then vs. Than
The spelling of then and than can act as a mnemonic device to help you to remember which word is which.
Then is spelled with an e, and has no a, just like the words time and moment. This fact can help you remember that then usually refers to a specific point in time.
Than contains an a but not an e, just like the word comparison. This can help you remember that than mostly appears with comparative adjectives.
Outside Examples
- They’d work out at the Gold’s Gym in Rockville, Maryland then go out to eat afterward, usually at the Dunkin’ Donuts or Silver Diner. –Chicago Tribune
- One way to do this is to turn your back to the sun, make the pound sign with your fingers and then look at your shadow. –LA Times
- According to Tesla and SpaceX CEO Elon Musk, concerns over artificial intelligence safety carry “more risk” than the potential for a nuclear war with North Korea. –USA Today
- Although data from the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development show digitalization reduces demand for mid-level routine tasks — such as running assembly lines — while boosting demand for low- and high-skilled jobs, that trend has been less pronounced in Japan than in the U.S. –Houston Chronicle
Quiz: Than vs. Then
Instructions: Fill in the blank with the correct word, either than or then, in the correct form.
- Run to the grocery store __________ pick up the laundry.
- I’d rather sleep in late ___________ wake up early.
- If you don’t clean ________ our parents will yell at us both.
See answers below.
Article Summary
Should I use then or than? These words sound similar. However, their definitions have no overlap.
- Then is usually an adverb, but it can also be an adjective or noun. It means at that time.
- Than is a conjunction that primarily connects the two nouns being compared with an adjective.
Despite the similar spellings, these words should not be interchanged for each other.
Answers
- then
- than
- then
Download Article
Download Article
People often misuse the words than and then. It’s a common mistake, in part because the words are pronounced similarly or in some cases because you simply don’t know the difference. However, it is important to know in which situations you would use each word, especially for academic or business writing. As a general rule, use than to indicate comparison and then to indicate time. Practice both usage and pronunciation, and then you’ll be using these words better than anyone you know.
Grammar Help
-
1
Remember that then is a word that indicates time or sequence. In all of its uses, then is used when you want to talk about a point in time or sequence of events. If someone is asking when something happened, then is the appropriate word for your response.[1]
- For example, if your teacher asks you where you were at noon yesterday, you could respond, “I was at lunch then.”
- If someone asks when something will be ready, you could let them know to, “Come back tomorrow afternoon. I will have everything ready by then.”
EXPERT TIP
Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014.
Christopher Taylor, Adjunct Assistant Professor of English, notes: «Than» is generally used to compare two things (e.g., bigger than a quarter), whereas «then» helps you establish a sequence of events (e.g., first this, then that).»
-
2
Connect a series of events using then. Another common use for then is to indicate sequential items. Use then to tell someone what comes next in time, space, or order. Some examples of these uses include:[2]
- We are going to leave at 9, and then we stop for lunch around 11.
- First, you line up part A and part B. Then, you screw them together.
- The inner planets go Mercury, Venus, Earth, and then Mars.
Advertisement
-
3
Add additional or conditional information using then. Then can also be used to mean «in addition,» «moreover,» or «in that case.» Use then when you need to add additional information to your sentence, or to modify outcomes based on conditions.[3]
- If you’re adding additional information you might say, “The dinner costs $20, and then you have to add the tip.”
- To express conditional information you may say, “If the weather is good, then we will go to the beach tomorrow.”
-
4
Use then when you are indicating something that was true at one time. In some special cases, then can be used as an adjective to indicate something that was true at the time, even if it isn’t so anymore. You may hear then used this way often with people like politicians who once held a position, but no longer do.[4]
- For example, “That program was instituted in 2010 by then President Barack Obama.”
- This use isn’t limited to just people, though. You could also say something like, “The historian wrote about the then thriving state of Rome.”
Advertisement
-
1
Use than as a conjunction in comparative contexts. A conjunction is a word used to connect 2 parts of a sentence. When you are talking about a noun (thing, person, place or concept) in relation to another noun, use than to introduce the second part of your comparison. Than is usually preceded by comparative words like better, worse, more, less, higher, lower, smaller, larger, etc. For example:
- There are more onions than scallions in your fridge.
- I can run faster now than I could last year.
- I like cloudy weather more than I like the sun.
-
2
Indicate a correlation between 2 events with than. Than can also be used with past tense verbs and some adverbial expressions. Adverbial expressions are multi-word expressions that function to modify or qualify a verb. In these cases, than is being used to indicate that one thing correlated with another.[5]
- For example, if it feels like your alarm goes off right after you fall asleep, you may say, “No sooner did I lay my head down than my clock started to ring.”
- This usage may seem similar to how then may be used sometimes, which can be confusing. The difference is that then would be used if there was a sequence, but than is not describing a sequence in this instance. It is showing correlation or relationship between 2 things, such as laying down your head and your alarm clock going off.
-
3
Use than when you can’t find a synonym for what you’re saying. If you’re trying to decide between than and then, try substituting the word. Than is a unique word with no synonyms. Then, however, can be substituted for works like “subsequently,” “next,” or “later.»[6]
- For example, it wouldn’t work to say “Jessica arrived later subsequently Joe.” Even though you’re talking about time, in this context you’re still comparing who was later. That is why this sentence needs to be, “Jessica arrived later than Joe.”
- However, it does make sense to say, “First and need to shower and next I have to catch the bus.” In this context, “next” can be substituted for then.
Advertisement
-
1
Test your usage. If you’re ever confused when you’re writing, test each word to see if it makes sense in the context of your sentence. Try asking yourself these questions as you write to find the correct word:[7]
- If I write the word «next» instead of «then,» will the sentence still make sense?
- «I will go to the store next» makes sense, so here we would say «I will go to the store then.»
- If I write the phrase «in comparison to» instead of the word «than,» will the sentence still make sense?
- «A used car costs less in comparison to a new car» makes sense, so you’d want to say «It costs less than a new car.»
- If I write the word «next» instead of «then,» will the sentence still make sense?
-
2
Practice writing with then and than frequently. The best way to get used to the different uses of then and than is to use them in context. Try writing a brief comparative essay to help you get used to than. Then, try writing out a set of instructions to practice your use of then. [8]
- Pay attention to your use of then and than in your everyday writing, too. Set aside a few extra minutes to proofread your essays, letters, school work, and documents so that you can check for the correct usage.
- You can even look for then and than quizzes and exercises online to help you test your usage.[9]
-
3
Pronounce the words differently. Phonetically speaking, native speakers of English use the schwa (ǝ, kind of like a soft «eh» sound) because it’s more efficient in daily conversations. Consequently, lots of «a»s and «e»s are not pronounced distinctly. However, taking the time to pronounce the words distinctly can help reinforce their use in your mind.[10]
- Try saying than with your mouth opened wide and the tongue pressed down toward your teeth. The vowel sounds from the back of the mouth and the throat is somewhat constricted.
- Say then with your mouth partially opened. The vowel rises from a relaxed throat and the tongue rests.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
What’s the difference between the words «than» and «then»?
Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014.
English Professor
Expert Answer
-
Question
How do you use the word «then» in a sentence?
Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014.
English Professor
Expert Answer
-
Question
When would you use «than» in a sentence?
Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014.
English Professor
Expert Answer
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
-
The simplest mnemonic is that «then» is a time word equivalent to «when,» so they are both spelled with an «e.»
-
Pay attention to grammar check. If your word processor underlines or highlights the word «then» or «than,» you may have chosen the wrong word. Re-read your sentence to be sure.
-
People tend to misuse then more than than. Than mistakes may look strange or grossly incorrect; however, the then mistakes may seem more acceptable. Pay special attention to then and its uses.
Show More Tips
Advertisement
About This Article
Article SummaryX
To use the words than and then properly, remember that than is used when comparing things and then is used to indicate time. For example, if you were comparing how many oranges and apples you have, you would say «I have more oranges than apples.» But if you were explaining which fruit you bought first, you would say «I bought oranges and then I bought apples.» To learn helpful tricks for remembering the difference between than and then, keep reading!
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 3,704,757 times.
Did this article help you?
Than is used for comparisons and then for sequences.
Getty Images
Updated on January 21, 2020
Then and than are often confused in English; they are spelled alike and sound similar. However, they are used very differently. Here is an explanation of the two words with a follow-up quiz to help you practice, understand, and remember them.
Begin by reading the following sentences:
- She thinks soccer is more interesting than football.
- I’d like to first have lunch and then have a cup of coffee.
Using Than
In the first sentence, than is used to compare two items (…more interesting than…). Than is used in the comparative form in English. Here are some more examples:
- Living in the city is more exciting than living in the countryside.
- Tom has more responsibilities than Peter in this company.
- I think that painting is more beautiful than this one.
Than is also used to state a preference with the form would rather:
Subject + would rather + verb + (object) + than + verb + (object).
- I’d rather have Chinese food than eat Mexican food today.
- She’d rather stay home and watch a movie than go out on the town.
- Peter would rather do homework than have fun.
Other important expressions using than include expressions that refer to choices and differences between people, places, and things.
- other than: Other than Tom, I don’t know who wants to come.
- different than: You’ll find that learning Japanese is different than learning English.
- no one/nowhere/nothing else than: You should be nowhere else than here every day.
- anyone/anywhere/anything else than: I’d like to be anywhere else than here at the moment.
- better than: He can play tennis better than John.
Using Then
Then refers to the order in which things happen. In the second example sentence at the start of this article, I’d like to first have lunch and then have a cup of coffee, the person would first like to have lunch, and, after that (then), have a cup of coffee. It is a sequence of events, such as in:
- First, we’ll discuss last quarter’s business. Then, we’ll focus on the new marketing campaign.
- I usually begin my day with a shower, and then I have breakfast.
Then can also be used to refer to a logical result. For example:
- If you need to study, then go and study.
Then is also used as a time expression to speak about when something happens.
- I’ll see you then.
- I’ll be at the party.
- We can speak then.
Then vs. Than: Pronunciation
Then and than sound similar but are slightly different. Than has an a sound as in the word cat or tap. Then has an open e sound as in pet or let.
Read the sentence, concentrating on keeping the vowel a sound the same in each word.
- Pat grabbed the cat that was fatter than the bat.
Read the next sentence, focusing on keeping the e open in each word.
- Meg set a check on the desk and then met with Chet.
Then vs. Than Quiz
Do you understand the rules? Practice by using the form in these sentences:
1. Art class is easier _____ math for me.
Correct
Wrong
When comparing, use than.
2. Let’s study first and _____ go for a jog.
Correct
Wrong
Use then for a sequence of events.
3. I prefer to work hard in the morning and _____ take it easy during the rest of the day.
Correct
Wrong
Use then for a sequence of actions.
4. There’s nowhere else I’d rather be _____ here at home.
Correct
Wrong
Use than with the expression «nowhere else».
5. My brother is happier now _____ when he was 10 years younger.
Correct
Wrong
Use than when comparing time periods.
6. Jane gets up, has a shower, and has coffee. _____, she drives to work.
Correct
Wrong
Use then when discussing a sequence of actions.
7. Does this shirt look better on me _____ that shirt?
Correct
Wrong
Use than as in the expression better than to compare two things.
8. Other _____ Mary, I don’t anyone who is coming over tonight.
Correct
Wrong
Use than in the expression other than.
9. Study hard for the test and _____ pass it.
Correct
Wrong
Use then to show that something must be done first before something else can happen.
10. If you want to understand the issues, _____ you need to ask questions.
Correct
Wrong
Use then to show a logical result.
What’s the Difference Between Then and Than?
You got: % Correct.
Share Your Results
What’s the Difference Between Then and Than?
You got: % Correct.
Share Your Results