Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel 2021 Excel 2019 Excel 2016 Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 More…Less
In Excel, formatting worksheet (or sheet) data is easier than ever. You can use several fast and simple ways to create professional-looking worksheets that display your data effectively. For example, you can use document themes for a uniform look throughout all of your Excel spreadsheets, styles to apply predefined formats, and other manual formatting features to highlight important data.
A document theme is a predefined set of colors, fonts, and effects (such as line styles and fill effects) that will be available when you format your worksheet data or other items, such as tables, PivotTables, or charts. For a uniform and professional look, a document theme can be applied to all of your Excel workbooks and other Office release documents.
Your company may provide a corporate document theme that you can use, or you can choose from a variety of predefined document themes that are available in Excel. If needed, you can also create your own document theme by changing any or all of the theme colors, fonts, or effects that a document theme is based on.
Before you format the data on your worksheet, you may want to apply the document theme that you want to use, so that the formatting that you apply to your worksheet data can use the colors, fonts, and effects that are determined by that document theme.
For information on how to work with document themes, see Apply or customize a document theme.
A style is a predefined, often theme-based format that you can apply to change the look of data, tables, charts, PivotTables, shapes, or diagrams. If predefined styles don’t meet your needs, you can customize a style. For charts, you can customize a chart style and save it as a chart template that you can use again.
Depending on the data that you want to format, you can use the following styles in Excel:
-
Cell styles To apply several formats in one step, and to ensure that cells have consistent formatting, you can use a cell style. A cell style is a defined set of formatting characteristics, such as fonts and font sizes, number formats, cell borders, and cell shading. To prevent anyone from making changes to specific cells, you can also use a cell style that locks cells.
Excel has several predefined cell styles that you can apply. If needed, you can modify a predefined cell style to create a custom cell style.
Some cell styles are based on the document theme that is applied to the entire workbook. When you switch to another document theme, these cell styles are updated to match the new document theme.
For information on how to work with cell styles, see Apply, create, or remove a cell style.
-
Table styles To quickly add designer-quality, professional formatting to an Excel table, you can apply a predefined or custom table style. When you choose one of the predefined alternate-row styles, Excel maintains the alternating row pattern when you filter, hide, or rearrange rows.
For information on how to work with table styles, see Format an Excel table.
-
PivotTable styles To format a PivotTable, you can quickly apply a predefined or custom PivotTable style. Just like with Excel tables, you can choose a predefined alternate-row style that retains the alternate row pattern when you filter, hide, or rearrange rows.
For information on how to work with PivotTable styles, see Design the layout and format of a PivotTable report.
-
Chart styles You apply a predefined style to your chart. Excel provides a variety of useful predefined chart styles that you can choose from, and you can customize a style further if needed by manually changing the style of individual chart elements. You cannot save a custom chart style, but you can save the entire chart as a chart template that you can use to create a similar chart.
For information on how to work with chart styles, see Change the layout or style of a chart.
To make specific data (such as text or numbers) stand out, you can format the data manually. Manual formatting is not based on the document theme of your workbook unless you choose a theme font or use theme colors — manual formatting stays the same when you change the document theme. You can manually format all of the data in a cell or range at the same time, but you can also use this method to format individual characters.
For information on how to format data manually, see Format text in cells.
To distinguish between different types of information on a worksheet and to make a worksheet easier to scan, you can add borders around cells or ranges. For enhanced visibility and to draw attention to specific data, you can also shade the cells with a solid background color or a specific color pattern.
If you want to add a colorful background to all of your worksheet data, you can also use a picture as a sheet background. However, a sheet background cannot be printed — a background only enhances the onscreen display of your worksheet.
For information on how to use borders and colors, see:
Apply or remove cell borders on a worksheet
Apply or remove cell shading
Add or remove a sheet background
For the optimal display of the data on your worksheet, you may want to reposition the text within a cell. You can change the alignment of the cell contents, use indentation for better spacing, or display the data at a different angle by rotating it.
Rotating data is especially useful when column headings are wider than the data in the column. Instead of creating unnecessarily wide columns or abbreviated labels, you can rotate the column heading text.
For information on how to change the alignment or orientation of data, see Reposition the data in a cell.
If you have already formatted some cells on a worksheet the way that you want, there are several ways to copy just those formats to other cells or ranges.
Clipboard commands
-
Home > Paste > Paste Special > Paste Formatting.
-
Home > Format Painter
.
Right click command
-
Point your mouse at the edge of selected cells until the pointer changes to a crosshair.
-
Right click and hold, drag the selection to a range, and then release.
-
Select Copy Here as Formats Only.
Tip If you’re using a single-button mouse or trackpad on a Mac, use Control+Click instead of right click.
Range Extension
Data range formats are automatically extended to additional rows when you enter rows at the end of a data range that you have already formatted, and the formats appear in at least three of five preceding rows. The option to extend data range formats and formulas is on by default, but you can turn it on or off by:
-
Newer versions Selecting File > Options > Advanced > Extend date range and formulas (under Editing options).
-
Excel 2007 Selecting Microsoft Office Button
> Excel Options > Advanced > Extend date range and formulas (under Editing options)).
Need more help?
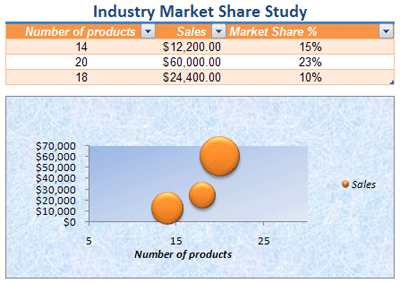
Application examples of formatting Excel data of various types for computationally intensive calculations.
Changing of cells format in data tables
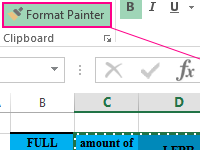
Multiple copies of table cell formats on multiple sheets using the Format Painter tool. Copying the width of columns and rows of a sheet.
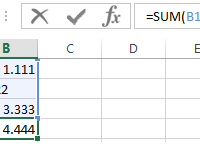
The possible errors in the summation, where there is a comma instead of a dot. Quick search of incorrect fractional numbers. Automatic assignment of the cell formats with the SUMM function.
You can transfer table data within one sheet, as well as to another sheet or to another file. In this case, you can copy either the entire table, or its individual values, properties or parameters.
Formatting
Excel has many ways to format and style a spreadsheet.
Why format and style your spreadsheet?
- Make it easier to read and understand
- Make it more delicate
Styling is about changing the looks of cells, such as changing colors, font, font sizes, borders, number formats, and so on.
The most used styling functions are:
- Colors
- Fonts
- Borders
- Number formats
- Grids
There are two ways to access the styling commands in Excel:
- The Ribbon
- Formatting menu, by right clicking cells
Read more about the Ribbon in the Excel overview chapter.
Styling Commands in Ribbon
The Ribbon can be expanded by clicking the arrow/caret-down icon on the right side. This gives access to more commands:
Styling Commands, Right Clicking Cells
You can also right-click on any cell to style it:
Styling commands can be accessed from both views.
Chapter summary
Formatting is used to make spreadsheets more readable. There are many ways to add styles. The most common ones are; Color, Font, Number format and Grids.
Formatting in Excel (2016, 2013 & 2010 and Others)
Formatting in Excel is a neat trick used to change the appearance of the data represented in the worksheet. We can do formatting in multiple ways, such as we can format the font of the cells or format the table by using the “Styles” and “Format” tabs available in the “Home” tab.
Table of contents
- Formatting in Excel (2016, 2013 & 2010 and Others)
- How to Format Data in Excel? (Step by Step)
- Shortcut Keys to Format Data in Excel
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
How to Format Data in Excel? (Step by Step)
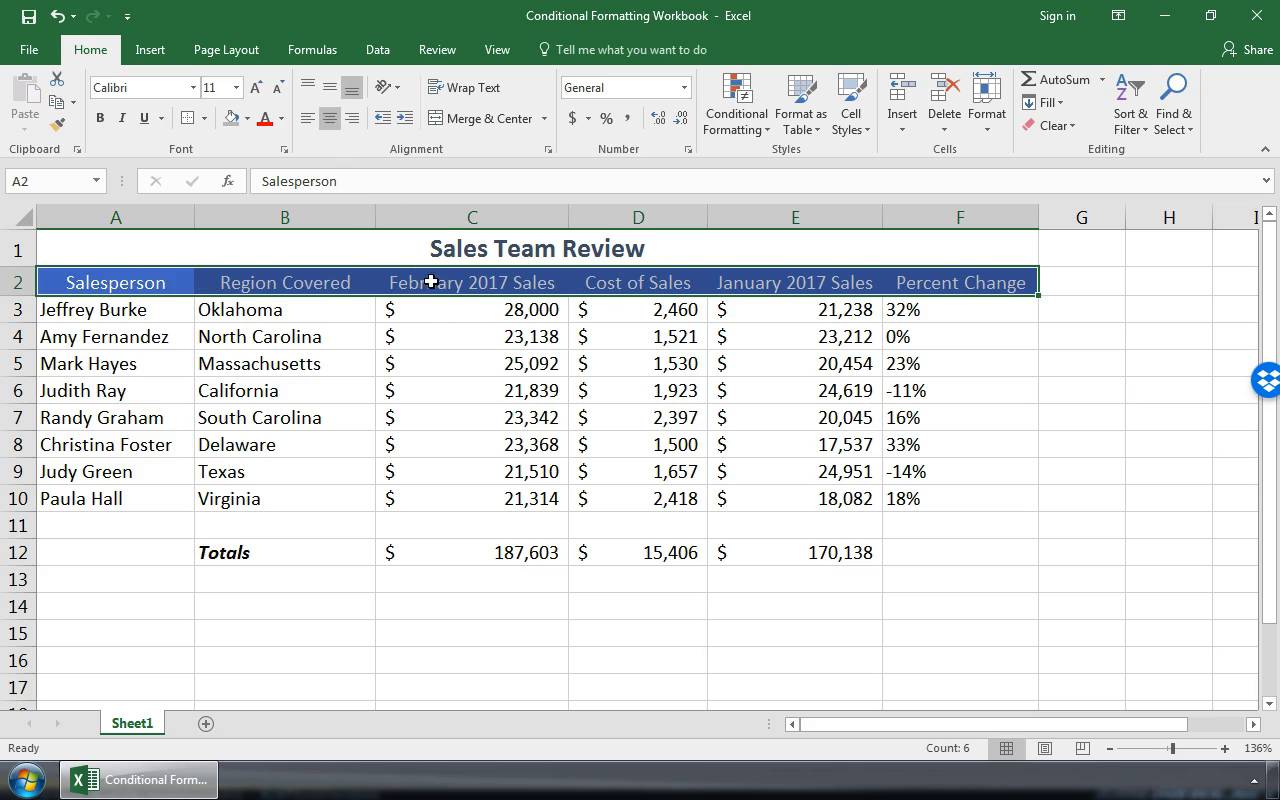
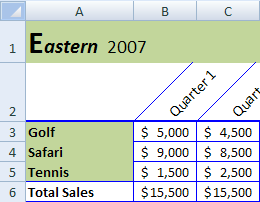
Let us understand the working of data formatting in Excel by simple examples. Now, suppose we have a simple report of sales for an organization as below:
You can download this Formatting Excel Template here – Formatting Excel Template
This report is not attractive to viewers. Therefore, we need to format the data.
Now, to format data in Excel, we must do the following:
- Bold the text of the column header.
- Make the font size larger.
- Adjust the column width using the shortcut key (Alt+H+O+I) after selecting the whole table (Ctrl+A).
- Align the data in the center.
- Apply the outline border by using (Alt+H+B+T)
- Apply background color using the “Fill Color” command available in the “Font” group on the “Home” tab
We will be applying the same format for the table’s last “Total” row by using the “Format Painter” command available in the “Clipboard” group on the “Home” tab.
As the amount collected is a currency, we should format the same as “Currency” using the command available in the “Number” group placed on the “Home” tab.
After selecting the cells we need to format as currency, we need to open the “Format Cells” dialog box by clicking the above arrow.
Choose “Currency” and click on “OK.“
We can also apply the outline border to the table.
We will be creating the label for the report by using “Shapes.” To make the shape above the table, we need to add two new rows. So, we will select the row by “Shift+Spacebar” and then insert two rows by pressing “Ctrl+’+” twice.
We must choose an appropriate shape from the “Shapes” command available in the “Illustration” group in the “Insert” tab to insert the shape.
Create the shape according to the requirement and with the same color as the heads of the column. Then, add the text on the shape by right-clicking on the shapes and choosing “Edit Text.”
We can also use the “Format” contextual tab for formatting the shape using various commands such as “Shape Outline,” “Shape Fill,” “Text Fill,” “Text Outline,” etc. We can also apply the excel formatting on textText formatting in Excel include changing the colour, font name, font size, alignment, font appearance in bold, underlining, italic, background colour of the font cell, and so on.read more using the commands available in the “Font” group placed on the “Home” tab.
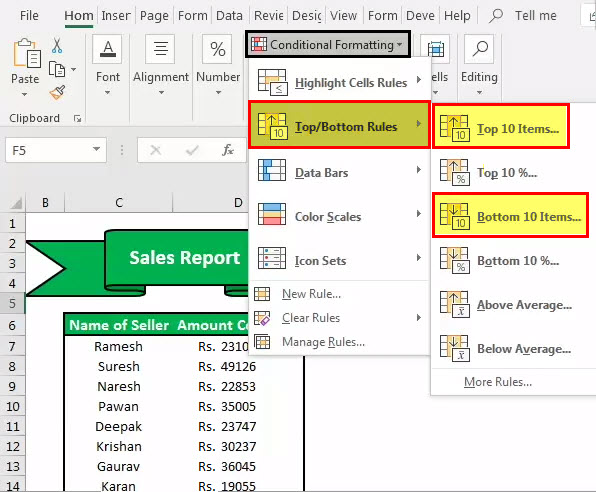
We can also use “Conditional Formatting” to take the viewers’ attention to the “Top 3” salesperson and “Bottom 3” salesperson.
Format the cells that rank in the “Top 3” with “Green Fill with Dark Green Text.”
Also, format the cells that rank in the “Bottom 3” with “Light Red with Dark Red Text.”
We can also apply another conditional formatting option, “Data Bars.”
We can also create a chart to display the data, part of “Data Formatting Excel.”
Shortcut Keys to Format Data in Excel
- To make the text bold: Ctrl+B or Ctrl+2
- To make the text italic: Ctrl+I or Ctrl+3
- To make the text underline: Ctrl+U or Ctrl+4
- To make the font size of the text larger: Alt+H, FG
- To make the font size of the text smaller: Alt+H, FK
- To open the ”Font” dialog box: Alt+H,FN
- To open the ”Alignment” dialog box: Alt+H, FA
- To center align cell contents: Alt+H, A, then C
- To add borders: Alt+H, B
- To open the ”Format Cells” dialog box: Ctrl+1
- To apply or remove strikethrough data formatting Excel: Ctrl+5
- To apply an outline border to the selected cells: Ctrl+Shift+Ampersand(&)
- To apply the “Percentage” format with no decimal places: Ctrl+Shift+Percent (%)
- To add a non-adjacent cell or range to a selection of cells using the arrow keys: Shift+F8
Things to Remember
- While data formatting in Excel, we must make the title stand out, good and bold, it ensures it conveys the content we are showing. Next, we should enlarge the column and row heads and put them in a second color. Readers may quickly scan the column and row headings to get a sense of how the information on the worksheet is organized. This way, it can help them view what is most important on the page and where they should begin.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to Formatting in Excel. We discuss formatting data in Excel, Excel examples, and downloadable Excel templates here. You may also look at these useful functions in Excel: –
- Conditional Formatting in the Pivot Table
- Filters in Excel
- Examples of Data Table in Excel
- Gantt Chart in Excel
Spreadsheets are often seen as boring and pure tools of utility. It’s true that they’re useful, but that doesn’t mean that we can’t bring some style and formatting to our spreadsheets.
Good formatting helps your user find meaning in the spreadsheet without going through each and every individual cell. Cells with formatting will draw the viewer’s attention to the important cells.
In this tutorial, we’re going to dive deep into Microsoft Excel spreadsheet formatting. I’ll show you some of the easiest ways to bring formatting to your spreadsheet with just a few clicks.
How to Format an Excel Spreadsheet (Watch & Learn)
If you want a guided walk through of using Excel formatting, check out the screencast below. I’ll show you many of my favorite tricks for bringing meaning to my spreadsheets. Adding style makes a spreadsheet easier to read and less prone to mistakes, and I’ll show you why in this screencast.
Read on to find out more about the tools that you can use to change the look and feel of an Excel spreadsheet.
Format Based on Cell Type
As you probably know, Excel spreadsheets can contain a variety of data ranging from simple text to complex formulas. These spreadsheets can become complex and used in important decisions.
Formatting Excel spreadsheets isn’t just about making them «pretty.» It’s about using the built-in styles to add meaning. A spreadsheet user should be able to glance at a cell and understand it without having to look at each and every formula.
Above all, styles should be applied consistently. One idea is to use yellow shading each time you’re using a calculation. This helps the user know that the cell’s value could change based upon other cells.
Let’s learn more about the tools you can use to add meaning to your spreadsheet.
How to Use Elements of Style
When you’re thinking about styling a spreadsheet, it helps to know the tools that you can use to add style. Basically, what tools change the look of a spreadsheet? Let’s walk through how to use some of the most popular styling tools.
1. Use Bold, Italic, and Underline
These are the most basic tweaks that you can use, and you’ve probably seen them in practically every app with text editing, like Microsoft Word or Apple Pages.
To apply any of these effects, simply highlight the cells that you want to apply the effects to, and then click on the icons on the Font section of the Home tab.
You probably already know what these three tools do, but how should you use them in a spreadsheet? Here are some ideas on how you can apply those styles:
- Bold. Draw attention to key cells using bold formatting. Apply bold to totals, key assumptions in your math, and conclusion cells.
- Italic. I like to use this style for notes or any text that should be less obvious, or build to a larger subtotal.
- Underline. Adding an underline is ideal for a summary cell, like a subtotal or conclusion.
In the example below, you can see a simple financial statement for a freelancer, before and after I apply basic formatting. The combination of bold, italic, and underline effects really make the information more readable.
2. Apply Borders
Borders help to segment your data and wall it off from other sections of data in your spreadsheet. Excel’s border tool can apply a variety of borders, but is a bit tricky to get started with.
First, start off by highlighting the cells that you want to apply a border to. Then, find the Borders dropdown menu and choose one of the built-in styles.
As you can see from the dropdown options, there are many options for applying borders. Simply click on one of these border options to apply it to cells.
One of my favorite border styles is the Top and Double Bottom Border style. This is ideal particularly for financial data when you’ve got a «grand total.»
Another option is to change the weight and color of the border. With the bordered cells selected, return to the Borders dropdown menu. The Line Color and Line Style settings can be used to tweak the style of borders.
Thick borders are ideal for setting a boundary for header columns, or the subtotal at the bottom of your data.
3. Use Shading
Shading, also often called fill, is simply a color that you apply to the background of a cell. To shade a cell, click and highlight any cells that you want to add shading too.
Then, click the arrow next to the paint bucket dropdown on the Font tab on the Home ribbon. You can pick from one of the many color thumbnails to apply it to a cell. I also will frequently use the More Colors option to open a fully-featured color selection tool. Light shades are best to keep text readable.
Again, you can highlight key data using shading. As I mentioned earlier, one idea is to use a consistent fill based on the contents of the cell, such as blue for any «input» fields where you manually type data.
Don’t overdo it with shading. With too many of these applied to your cells, it distracts from the content that’s stored inside the spreadsheet.
4. Change Alignment
Alignment refers to the way that the content in a cell is aligned to the edges. You can left align, center, or right align text. By default, content is left aligned in a cell. When you’ve got large data sets, you might want to tweak alignment to enhance readability.
One common tweak that I make is putting text on the left edge of a cell, while numeric amounts should be right-aligned. Also, column headers look great when they’re centered up at the top.
Change alignment using the three alignment buttons on the Alignment tab on Excel’s Home ribbon. You can also align content vertically, adjusting if the content aligns to the top, middle, or bottom of the cell.
How to Use Built-in Cell Styles
One of my favorite ways to style a spreadsheet rapidly is to use some of the built-in styles that Excel has. On the Home tab, click on the Cell Styles dropdown to apply one of the built-in styles to a cell.
Using these pre-built styles is a major time savings versus designing them from scratch. Use these as a way to take a shortcut to a more meaningful spreadsheet.
How to Achieve Faster Excel Formatting in Excel with Format Painter
Who wants to recreate Excel cell styles over and over again? Instead of recreating the wheel for each cell, you can use the Format Painter to pick up formatting and apply it to other cells.
Start off by clicking in the cell that has the format that you want to copy. Then, find the Format Painter tool on the Home tab on Excel’s ribbon. Click on the Format Painter, then click on the cell that you want to apply the same style to.
How to Turn Off Gridlines
As you probably already know, a spreadsheet is made up of rows and columns. Rows are ruled by horizontal lines and have numbers next to them. Columns are split with vertical lines and have letters at the top to refer to them.
Where rows and columns meet, cells are formed. Cells have names for which row and column they intersect. For example, where row 4 and column B meet is called B4.
Gridlines in Excel are one of the defining features of a spreadsheet. They make it easy to follow data across the screen into a cell. These lines are imaginary and only visible on screen. However, you might want to turn off gridlines for a stylistic effect.
Print with Gridlines
What if you wanted to show gridlines throughout the spreadsheet when you print it? Instead of having to manually add borders to each and every cell, you can simply print your workbook and include those gridlines.
To turn on gridlines when printing, start by going to the Print option. Then, click on Page Setup to open the settings.
On the Sheet tab, tick the box labeled Gridlines to include gridlines when you print your Excel workbook.
Keep in mind that this option will certainly use more ink when printing. However, it also might make it easier to read your printed spreadsheet.
How to Format Excel Data as Table
One of my favorite ways to style a dataset quickly is to use the Format as Table dropdown option. With just a couple of clicks, you can transform a few rows and columns into a structured data table.
This feature works best when you already have data in a set of rows and columns and want to apply a uniform style. It’s a combination of style and functionality, as tables add other features like automatic filtering buttons.
Learn more about why tables are a great feature in the tutorial below:
How to Use Conditional Formatting in Excel
What if the format for a cell could change based on the data that’s inside of it? This feature is built into Excel and is called Conditional Formatting. It’s easier to get started with than you may think.
Imagine using Conditional Formatting to highlight the top and bottom values in your cells. It makes it easy to visually scan your data and look for key indicators.
Conditional Formatting is best used with numerical data. To get started, simply highlight a column of data and make sure that you’re on the Home tab on Excel’s ribbon.
There are a number of styles that you can choose from the Conditional Formatting dropdown menu. Each of these applies a different style of Excel formatting to your cells, but each will adapt based on the cells that you’ve highlighted.
Recap & Keep Learning
Spreadsheets are often seen as boring and pure tools of utility. Sure, they’re very useful for organizing data or making calculations. That doesn’t mean that we can’t bring some style and Excel formatting to our spreadsheets.
When we do formatting the right way, it adds a second layer of meaning to a spreadsheet. Formatting isn’t a random exercise; it’s a way of using targeted styles to signal what type of data is in a cell.
Check out these other tutorials if you want to level up your Microsoft Excel skills and master spreadsheets:
What are your favorite Excel formatting tips? How do you make sure that the right cells stand out to your user? Let me know in the comments section below.
Did you find this post useful?
I believe that life is too short to do just one thing. In college, I studied Accounting and Finance but continue to scratch my creative itch with my work for Envato Tuts+ and other clients. By day, I enjoy my career in corporate finance, using data and analysis to make decisions.
I cover a variety of topics for Tuts+, including photo editing software like Adobe Lightroom, PowerPoint, Keynote, and more. What I enjoy most is teaching people to use software to solve everyday problems, excel in their career, and complete work efficiently. Feel free to reach out to me on my website.

 .
.
 > Excel Options > Advanced > Extend date range and formulas (under Editing options)).
> Excel Options > Advanced > Extend date range and formulas (under Editing options)).