Скачать материал

Скачать материал






- Сейчас обучается 268 человек из 64 регионов


Описание презентации по отдельным слайдам:
-
1 слайд
Word-building in Modern English
-
2 слайд
By word-building are understood processes of producing new words from the resources of this particular language. Together with borrowing, word-building provides for enlarging and enriching the vocabulary of the language.
-
3 слайд
Morpheme is the smallest recurrent unit of language directly related to meaning
-
4 слайд
All morphemes are subdivided into two large classes: roots (or radicals) and affixes. The latter, in their turn, fall into prefixes which precede the root in the structure of the word (as in re-read, mispronounce, unwell) and suffixes which follow the root (as in teach-er, cur-able, diet-ate).
-
5 слайд
We can distinguish words due to a morphological structure
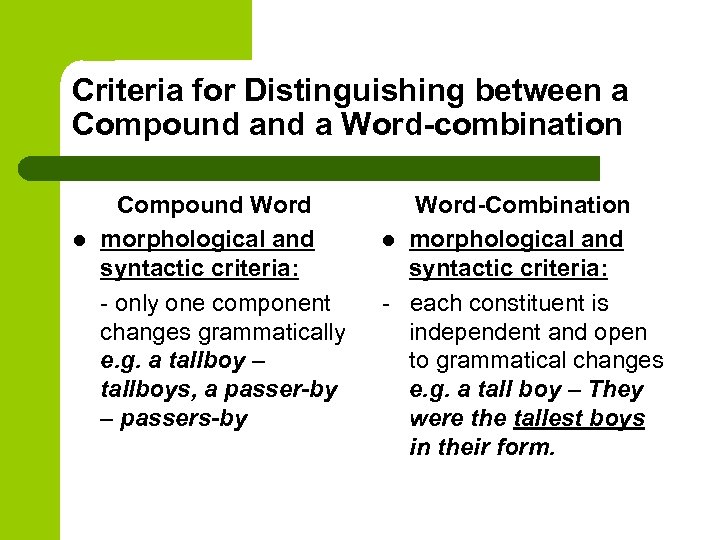
Words which consist of a root are called root words:
house, room, book, work, port, street, table, etc. -
6 слайд
We can distinguish words due to a morphological structure
Words which consist of a root and an affix (or several affixes) are called derived words or derivatives and are produced by the process of word-building known as affixation (or derivation):
re-read, mis-pronounce, un-well, teach-er. -
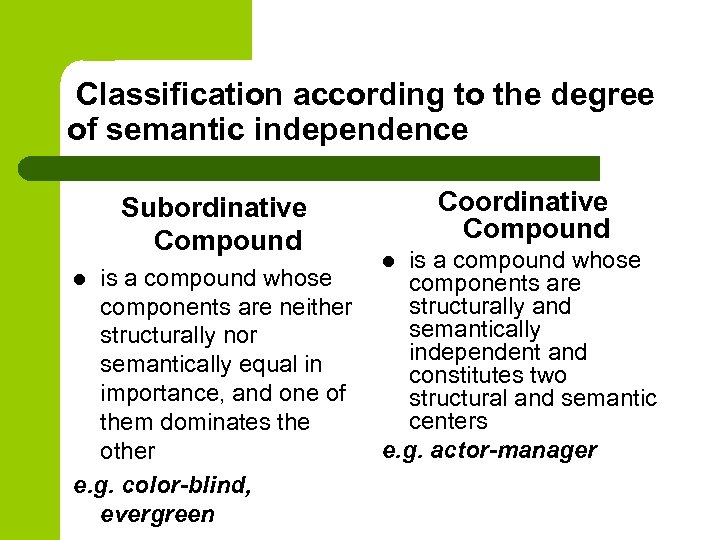
7 слайд
We can distinguish words due to a morphological structure
A compound word is made when two words are joined to form a new word:
dining-room, bluebell (колокольчик), mother-in-law, good-for-nothing(бездельник) -
8 слайд
We can distinguish words due to a morphological structure
Сompound-derivatives are words in which the structural integrity of the two free stems is ensured by a suffix referring to the combination as a whole, not to one of its elements:
kind-hearted, old-timer, schoolboyishness, teenager. -
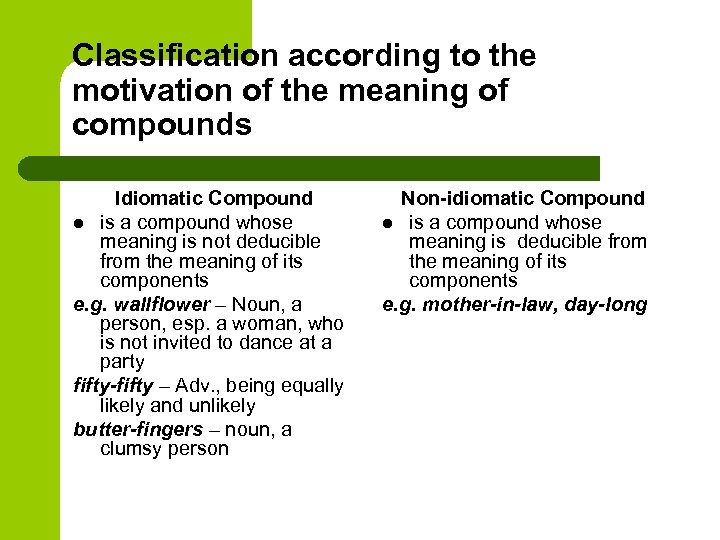
9 слайд
There are the following ways of word-building:
Affixation
Composition
Conversion
Shortening (Contraction)
Non-productive types of word-building:
A) Sound-Imitation
B) Reduplication
C) Back-Formation (Reversion) -
10 слайд
Affixation
The process of affixation consists in coining a new word by adding an affix or several affixes to some root morpheme.
-
11 слайд
The role of the affix in this procedure is very important and therefore it is necessary to consider certain facts about the main types of affixes. From the etymological point of view affixes are classified into the same two large groups as words: native and borrowed.
-
-
-
-
15 слайд
An affix of foreign origin can be regarded as borrowed only after it has begun an independent and active life in the recipient language and it is taking part in the word-making processes of that language. This can only occur when the total of words with this affix is so great in the recipient language as to affect the native speakers’ subconscious to the extent that they no longer realize its foreign flavour and accept it as their own.
-
16 слайд
By productive affixes we mean the ones, which take part in deriving new words in this particular period of language development. The best way to identify productive affixes is to look for them among neologisms and so-called nonce-words.
The adjectives thinnish (жидковатый) and baldish (лысоватый) bring to mind dozens of other adjectives made with the same suffix: oldish (староватый), youngish (моложавый), mannish (мужеподобная), girlish (женоподобный), longish (длинноватый), yellowish (желтоватый), etc.The same is well illustrated by the following popular statement: «/ don’t like Sunday evenings: I feel so Mondayish». (Чу́вствующий лень по́сле воскре́сного о́тдыха)
-
17 слайд
One should not confuse the productivity of affixes with their frequency of occurrence. There are quite a number of high-frequency affixes which, nevertheless, are no longer used in word-derivation
e. g. the adjective-forming native suffixes -ful, -ly; the adjective-forming suffixes of Latin origin -ant, -ent, -al which are quite frequent
-
-
19 слайд
Some Non-Productive Affixes
-
20 слайд
Composition
Composition is a type of word-building, in which new words are produced by combining two or more stems
-
21 слайд
Compounds are not homogeneous in structure. Traditionally three types are distinguished:
neutral
morphological
syntactic -
22 слайд
Neutral
In neutral compounds the process of compounding is realised without any linking elements, by a mere juxtaposition of two stems, as in
blackbird(дрозд)
shopwindow(витрина) sunflower(подсолнух) bedroom(спальня) etc. -
23 слайд
There are three subtypes of neutral compounds depending on the structure of the constituent stems.
The examples: shopwindow(витрина), sunflower(подсолнух), bedroom(спальня) represent the subtype which may be described as simple neutral compounds: they consist of simple affixless stems.
-
24 слайд
Compounds which have affixes in their structure are called derived or derivational compounds.
E.g. blue-eyed(голубоглазый),
broad-shouldered(широкоплечий) -
25 слайд
The third subtype of neutral compounds is called contracted compounds. These words have a shortened (contracted) stem in their structure:
V-day (день победы) (Victory day), G-man (агент ФБР) (Government man «FBI agent»), H-bag (сумочка) (handbag), T-shirt(футболка), etc. -
26 слайд
Morphological
Morphological compounds are few in number. This type is non-productive. It is represented by words in which two compounding stems are combined by a linking vowel or consonant:
e. g. Anglo-Saxon, Franko-Prussian, handiwork(изделие ручной работы), statesman (политический деятель/политик) -
27 слайд
Syntactic
These words are formed from segments of speech, preserving in their structure numerous traces of syntagmatic relations typical of speech: articles, prepositions, adverbs.
e.g. father-in-law, mother-in-law etc. -
28 слайд
Conversion
Conversion consists in making a new word from some existing word by changing the category of a part of speech, the morphemic shape of the original word remaining unchanged.
-
29 слайд
It has also a new paradigm peculiar to its new category as a part of speech. Conversion is a convenient and «easy» way of enriching the vocabulary with new words. The two categories of parts of speech especially affected by conversion are nouns and verbs.
-
30 слайд
Verbs made from nouns are the most numerous amongst the words produced by conversion:
e. g. to hand(передавать)
to back(поддерживать)
to face(стоять лицом к кому-либо)
to eye(рассматривать)
to nose(разнюхивать)
to dog(выслеживать) -
31 слайд
Nouns are frequently made from verbs:
e.g. make(марка)
run(бег)
find(находка)
walk(прогулка)
worry(тревога)
show(демонстрация)
move(движение) -
32 слайд
Verbs can also be made from adjectives:
e. g. to pale(побледнеть)
to yellow(желтеть)
to cool(охлаждать)Other parts of speech are not entirely unsusceptible to conversion.
-
33 слайд
Shortening (Contraction)
This comparatively new way of word-building has achieved a high degree of productivity nowadays, especially in American English.
Shortenings (or contracted words) are produced in two different ways. -
34 слайд
The first way
The first is to make a new word from a syllable (rarer, two) of the original word.
The latter may lose its beginning (as in phone made from telephone, fence from defence), its ending (as in hols from holidays, vac from vacation, props from properties, ad from advertisement) or both the beginning and ending (as in flu from influenza, fridge from refrigerator) -
35 слайд
The second way
The second way of shortening is to make a new word from the initial letters of a word group:
U.N.O. from the United Nations Organisation, B.B.C. from the British Broadcasting Corporation, M.P. from Member of Parliament. This type is called initial shortenings. -
36 слайд
Both types of shortenings are characteristic of informal speech in general and of uncultivated speech particularly:
E. g. Movie (from moving-picture), gent (from gentleman), specs (from spectacles), circs (from circumstances, e. g. under the circs), I. O. Y. (from I owe you), lib (from liberty), cert (from certainty), exhibish (from exhibition), posish (from position) -
37 слайд
Non-productive types of word-building
Sound-Imitation
Words coined by this interesting type of word-building are made by imitating different kinds of sounds that may be produced by
human beings: to whisper (шептать), to whistle (свистеть), to sneeze (чихать), to giggle (хихикать); -
38 слайд
animals, birds, insects: to hiss (шипеть), to buzz (жужжать), to bark (лаять), to moo (мычать);
inanimate objects: to boom (гудеть), to ding-dong (звенеть), to splash (брызгать); -
39 слайд
Reduplication
In reduplication new words are made by doubling a stem, either without any phonetic changes as in bye-bye (coll, for good-bye)
or with a variation of the root-vowel or consonant as in ping-pong, chit-chat (this second type is called gradational reduplication). -
40 слайд
This type of word-building is greatly facilitated in Modern English by the vast number of monosyllables. Stylistically speaking, most words made by reduplication represent informal groups: colloquialisms and slang. E. g. walkie-talkie («a portable radio»), riff-raff («the worthless or disreputable element of society»; «the dregs of society»), chi-chi (sl. for chic as in a chi-chi girl)
-
41 слайд
In a modern novel an angry father accuses his teenager son of doing nothing but dilly-dallying all over the town. (dilly-dallying — wasting time, doing nothing)
-
42 слайд
Another example of a word made by reduplication may be found in the following quotation from “The Importance of Being Earnest” by O. Wilde:
Lady Bracknell: I think it is high time that Mr. Bunbury made up his mind whether he was going to live or to die. This shilly-shallying with the question is absurd. (shilly-shallying — irresolution, indecision) -
43 слайд
Back-formation
Forming the allegedly original stem from a supposed derivative on the analogy of the existing pairs, i. e. the singling-out of a stem from a word which is wrongly regarded as a derivative.
-
44 слайд
The earliest examples of this type of word-building are the verb to beg (попрошайничать) that was made from the French borrowing beggar (нищий, бедняк), to burgle (незаконно проникать в помещение) from burglar (вор-домушник).
In all these cases the verb was made from the noun by subtracting what was mistakenly associated with the English suffix -er. -
45 слайд
Later examples of back-formation are to blood-transfuse (делать переливание крови) from blood-transfuing, to force-land (совершать вынужденную посадку) from forced landing, to baby-sit (присматривать за ребенком) from baby-sitter.
Найдите материал к любому уроку, указав свой предмет (категорию), класс, учебник и тему:
6 209 950 материалов в базе
- Выберите категорию:
- Выберите учебник и тему
- Выберите класс:
-
Тип материала:
-
Все материалы
-
Статьи
-
Научные работы
-
Видеоуроки
-
Презентации
-
Конспекты
-
Тесты
-
Рабочие программы
-
Другие методич. материалы
-
Найти материалы
Другие материалы
- 22.12.2020
- 161
- 0
- 21.12.2020
- 503
- 1
- 04.12.2020
- 135
- 0
- 19.11.2020
- 358
- 4
- 21.10.2020
- 267
- 0
- 15.10.2020
- 259
- 2
- 08.10.2020
- 182
- 0
- 03.09.2020
- 154
- 1
Вам будут интересны эти курсы:
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Клиническая психология: организация реабилитационной работы в социальной сфере»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Экономика и право: налоги и налогообложение»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Организация практики студентов в соответствии с требованиями ФГОС педагогических направлений подготовки»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Логистика: теория и методика преподавания в образовательной организации»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Маркетинг в организации как средство привлечения новых клиентов»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Разработка бизнес-плана и анализ инвестиционных проектов»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Основы менеджмента в туризме»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Управление ресурсами информационных технологий»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Разработка эффективной стратегии развития современного вуза»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Деятельность по хранению музейных предметов и музейных коллекций в музеях всех видов»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Риск-менеджмент организации: организация эффективной работы системы управления рисками»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Организация системы менеджмента транспортных услуг в туризме»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Финансовые инструменты»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Информационная этика и право»
Word-building in
English, major means of WB in English:
a) affixation;
b) conversion;
c) composition; types
of compounds.
WB
is the process of creating new words in a language with the help of
its inner sources.
Two
types of WB proper :
-
Word derivation when 1 stem undergoes different changes;
-
Word composition when 2 or more stems are put together.
The most important means of word derivation are:
a) affixation;
b) conversion;
c) composition; types of compounds.
Affixation,
conversion, composition are the most productive or major means of WB
in modern English.
Shortening
occupies the intermediate position between major & “minor” or
less productive & unproductive means of WB.
Minor
means of word-building are:
-
Back formation = reversion;
-
Blending = telescoping;
-
Reduplication = doubling the stem;
-
Sound immitation;
-
Sound interchange;
-
Shift of stress, etc.
Affixation is the most productive means of word-building in English.
Affixation is the formation of new words by adding a derivational
affix to a derivational base.
Affixation is subdivided into:
-
Suffixation
-
Prefixation.
The essential differences between suffixes &
preffixes is that preffixes as a rule only modify the lexical meaning
of a word without changing the part of speech to which the word
belongs
e.g. to tie – to untie
However, some preffixes form new words in a
different part of speech:
e.g. friend – N., to be friend-V., adj.- little., V.-
to be little.
Suffixes do not only modify the lexical meaning of a word but also
form a word belonging to a different part of speech.
Suffixes are usually classified according to the part of speech they
form:
-
Noun-forming suffixes ( to read – reader, dark – darkness);
-
Adjective-forming (power-powerful);
-
Verb-forming ( to organize, to purify);
-
Adverbal-forming (quick-quickly).
Prefixes are usually classified according to their meaning:
-
Negative prefixes (-un; -non; -in; -dis…);
-
Reversative = privative (-un; -de; -dis..);
-
Pejorative (уничижительные)
(mis-; mal- (maltreat-дурно
обращаться); pseudo-); -
Preffixes of time & order (fore-(foretell); pre-(prewar); post-;
ex-(ex-wife); -
Prefixes of repetition (re- rewrite);
-
Locative prefixes (super-; sub-subway; into-; trans –atlantic))
The 2 main criteria, according to which all the affixes are
subdivided are:
1)
origin;
2) productivity.
As to their origin (etymology) affixes are:
-
Native;
-
Borrowed.
Borrowed affixes may be classified according to the source of
borrowing (Greek, Latin, etc.) According to their productivity, i.e.
the ability to build new words at the present time, English affixes
are:
-
Productive or living affixes, used to build new words now;
-
Non-productive = unproductive affixes, not used in the word-building
now, or used very rarely.
Productivity shouldn’t be confused with frequency. What is frequent
may turn out to be non-productive (-some (adj.)-handsome is very
frequent, but not productive).
Some native prefixes still productive in English
are: — fore; -out (grow); over (estimate); -un (able); -up
(bringing); -under, -mis, etc.
Productive foreign prefixes are: -dis (like); -en (close); -re(call);
-super (natural); -pre (war); -non (drinking); -anti (noise).
Native noun-forming suffixes in modern English are: -er (writer);
-ster (youngster), -ness(brightness), etc.
Adjective-forming native suffixes (productive in English) are: -y
(rocky); -ish (Turkish), ful; -ed (cultured); -less (useless), etc.
Foreign productive noun-forming suffixes are: -ee
(employee); -tion (revolution); -ism(Gr., realism); -ist, etc.
Borrowed productive verb-forming suffixes of
Romanic origin are: -ise,ize (organize), -fy, ify (signify).
Prefixation is more typical of adjectives & verbs. Suffixation is
approximately evenly used in all parts of speech.
There are 2 types of semantic relations between affixes:
-
Homonymy;
-
Synonymy.
Homonymous prefixes are: -in: inactive, to inform.
Homonymous suffixes are: -ful1
(adjective-forming), -ful2
(noun-forming-spoonful), -ly1
(adj.-forming-friendly), -ly2
(adverb-forming-quickly).
Some affixes make a chain of synonyms: the native
suffix –er denoting an agent, is synonymous to suffix –ist
(Gr.)-socialist & to suffix –eer – also denoting an agent
(engineer) but often having a derrogatory force (`sonneteer-
стихоплёт, profiteer –
спекулянт, etc.)
Some affixes are polysemantic: the noun-forming suffix –er has
several meanings:
-
An agent or doer of the action –giver, etc.
-
An instrument –boiler, trailer
-
A profession, occupation –driver;
-
An inhabitant of some place –londoner.
b)
Conversion
is one of the most productive word-building means in English. Words,
formed by means of conversion have identical phonetic & graphic
initial forms but belong to different parts of speech (noun –
doctor; verb –to doctor). Conversion
is a process of coining (создание)
a new word in a different part of speech & with different
distribution characteristic but without adding any derivative
elements, so that the basic form of the original & the basic form
of the derived words are homonymous (identical). (Arnold)
The
main reason for the widespread conversion in English is its
analytical character, absence of scarcity of inflections. Conversion
is treated differently in linguistic literature. Some linguists
define conversion as a non-affixal way of word-building (Marchened
defines conversion as the formation of new words with the help of a
zero morpheme, hence the term zero derivation)
Some
American & English linguists define conversioon as a functional
shift from one part of speech to another, viewing conversion as a
purely syntactical process. Accoding to this point of view, a word
may function as 2 or more different parts of speech at the same time,
which is impossible. Professor Smernitsky treats conversion as a
morphological way of word-building. According to him conversion is
the formation of a new word through the changes in its paradigm.
Some
other linguists regard conversion as a morphological syntactical way
of word-building, as it involves both a change of the paradigm &
the alterration of the syntactic function of the word.
But
we shouldn’t overlook the semantic change, in the process of
conversion. All the morphological & syntactical changes, only
accompany the semantic process in conversion. Thus, conversion may be
treated as a semantico-morphologico-syntactical process.
As a word within the conversion pair is
semantically derived from the other there are certain semantic
relationswithin a conversion pair.
De-nominal words (от
глагола) make up the largest group &
display the following semantic relations with the nouns:
-
action characteristic of the thing: -a butcher; to butcher
-
instrumental use of the thing: -a whip; to wheep
-
acquisition of a thing: a coat; to coat
-
deprivation of a thing: skin – to skin.
Deverbal substantives (отглаг.сущ)they
may denote:
-
instance of the action: to move – a move;
-
agent of the action: to switch – a switch;
-
place of the action: to walk- a walk;
-
object or result of the action: to find – a find.
The English vocabulary abounds mostly in verbs,
converted from nouns( or denominal verbs) & nouns, converted from
verbs (deverbal substances): pin –to pin; honeymoon-to honeymoon.
There are also some other cases of conversion: batter-to batter, up –
to up, etc.
c)
Composition is one of the most productive word-building
means in modern English. Composition is the production of a new word
by means of uniting 2 or more stems which occur in the language as
free forms (bluebells, ice-cream).
According
to the type of composition & the linking element, there are
following types of compounds:
-
neutral compounds; (1)
-
morphological compounds; (2)
-
syntactical compounds. (3)
(1)
Compounds built by means of stem junction (juxt – opposition)
without any morpheme as a link, are called neutral compounds. The
subtypes of neutral compounds according to the structure of immediate
constituents:
a)
simple neutral compounds (neutral compounds proper) consisting of 2
elements (2 simple stems): sky –blue;film-star.
b) derived compounds (derivational compounds) –
include at least one derived stem: looking-glass, music-lover,
film-goer, mill-owner derived compounds or derivational should be
distinguished from compound derivatives, formed by means of a suffix,
which reffers to the combination of stems as a whole. Compound
derivatives (сложно-произв.слова)
are the result of 2 acts of word-building composition &
derivation. ( golden-haired, broad-shouldered, honey-mooner,
first-nighter).
c)
contracted compounds which have a shortened stem or a simple stem in
their structure, as “V-day” (victory), G-man (goverment), H-bag
(hand-bag).
d)
compounds, in which at least 1 stem is compound (waterpaper(comp)
–basket(simple))
(2)
Compounds with a specific morpheme as a link (comp-s with a linking
element = morphological compounds). E.g. Anglo-Saxon, Franko-German,
speedometer, statesman, tradespeople, handicraft, handiwork.
(3)
Compounds formed from segments of speech by way of isolating speech
sintagmas are sometimes called syntactic compounds, or compounds with
the linking element(s) represented as a rule by the stems of
form-words (brother-in-law, forget-me-not, good-in-nothing).
II.
Compounds may be classified according to a part of speech they belong
& within each part of speech according to their structural
pattern (structural types of compound-nouns):
-
compounds nouns formed of an adjectival stem + a noun stem A+N.
e.g.blackberry, gold fish
-
compound nouns formed of a noun-stem +a noun stem N+N
e.g. waterfall, backbone, homestead, calhurd
III.
Semantically compounds may be: idiomatic (non-motivated),
non-idiomatic
(motivated).
The compounds whose meanings can be derived from the meanings of
their component stems, are called non-idiomatic, e.g. classroom,
handcuff, handbag, smoking-car.
The
compounds whose meanings cannot be derived from the meanings of their
component stems are called idiomatic, e.g. lady-bird, man of war,
mother-of-pearls.
The
critiria applied for distinguishing compounds from word combinations
are:
-
graphic;
-
phonetic;
-
grammatical (morphological, syntactic);
-
semantic.
The graphic criteria can be relied on when
compounds are spelled either sollidly, or with or with a hyphen, but
it fails when the compound is spelled as 2 separate words,
e.g.
blood(-)vessel
(крово-сосудистый)
The phonetic criterium is applied to comp-s which
have either a high stress on the first component as in “hothead”
(буйная голова),
or a double stress “ `washing-ma`chine”, but it’s useless when
a compound has a level stress on both components, as in “
`arm-chair, `ice-cream” etc.
If we apply morphological & syntactical
criterium, we’ll see that compounds consisting of stems, possess
their structural integrity. The components of a compound are
grammatically invariable. No word can be inserted between the
components, while the components of a word-group, being independant
words, have the opposite features (tall-boy(высокий
комод), tall boy (taller&
cleverer,tallest)).
One of the most reliable criteria is the semantic
one. Compounds generally possess the higher degree of semantic
cohesion (слияние) of its elements
than word-groups. Compounds usually convey (передавать)
1 concep. (compare: a tall boy – 2 concepts, & a tallboy – 1
concept). In most cases only a combination of different criteria can
serve to distinguish a compound word from a word combination.
Для знания иностранного языка богатство словарного запаса ничуть не менее важно, чем понимание грамматики. Чем большим количеством слов владеет человек, тем свободнее он себя чувствует в иноязычной среде.
Многообразие лексики во многом определяется богатством словообразования в английском языке. Построение новых слов основано на общих принципах. И тот, кто знает эти принципы, чувствует себя среди незнакомой лексики гораздо увереннее.
Структура слова и ее изменение
Новые слова усваиваются постепенно. Чаще всего, сначала мы только понимаем их в текстах или чужой речи, а уже потом начинаем активно использовать в своей. Поэтому освоение новой лексики – процесс длительный и требует от ученика терпения, активной практики чтения, слушания и работы со словарем.
Один из методов быстро расширить свой словарный запас – освоить способы словообразования в английском языке. Поняв принципы, по которым строятся слова, можно из уже известного слова вывести значения его однокоренных слов.
Строительный материал для каждого слова – это корень, приставки и суффиксы. Корень – это та часть слова, которая несет основной смысл. Слово без корня не может существовать. Тогда как приставки и суффиксы – необязательная часть, однако прибавляясь к корню, именно они помогают образовать новые слова. Поэтому, описывая словообразование в английском, мы будем разделять приставочные и суффиксальные способы.
Все приставки и суффиксы обладают собственным значением. Обычно оно довольно размыто и служит для изменения основного значения слова. Когда к корню добавляется приставка или суффикс (или же оба элемента), то их значение прибавляется к значению корня. Так получается новое слово.
Образование новых слов может приводить не только к изменению значения, но и менять части речи. В этой функции чаще выступают суффиксы. Прибавляясь к корню, они переводят слово из одной части речи в другую, например, делают прилагательное из глагола или глагол из существительного.
Так, от одного корня может образоваться целая группа, все элементы которой связаны между собой. Поэтому словообразование помогает изучающим английский видеть смысловые отношения между словами и лучше ориентироваться в многообразии лексики.
Получить новое слово можно не только за счет приставок и суффиксов. Еще один способ – это словосложение, при котором в одно слово объединяются два корня, образуя новый смысл. Кроме того, к словообразованию относится сокращение слов и создание аббревиатур.
Приставки как способ словообразования в английском
Приставка (также употребляется термин «префикс») – элемент слова, который ставится перед корнем. Приставочное словообразование английский язык редко использует для смены частей речи (в качестве исключения можно назвать префикс «en-» / «em-» для образования глаголов). Зато приставки активно используются для изменения значения слова. Сами префиксы могут иметь различные значения, но среди них выделяется большая группа приставок со схожей функцией: менять смысл слова на противоположный.
1. Приставки с отрицательным значением:
- un-: unpredictable (непредсказуемый), unable (неспособный)
- dis-: disapproval (неодобрение), disconnection (отделение от)
- im-, in-, il -,ir-: inactive (неактивный), impossible (невозможный), irregular (нерегулярный), illogical (нелогичный). То, какая из этих приставок будет присоединяться к слову, зависит от следующего за ней звука. «Im-» ставится только перед согласными «b», «p», «m» (impatient — нетерпеливый). «Il-» возможно только перед буквой «l» (illegal — незаконный), «ir-» – только перед «r» (irresponsible — безответственный). Во всех остальных случаях употребляется приставка «in-» (inconvenient – неудобный, стесняющий).
- mis-: misfortune (несчастье, беда). Приставка «mis-» может использоваться не только для образования прямых антонимов, но и иметь более общее значение отрицательного воздействия (misinform — дезинформировать, вводить в заблуждение, misunderstand — неправильно понять).
2. Другие приставочные значения
- re-: rebuild (отстроить заново, реконструировать). Приставка описывает повторные действия (rethink — переосмыслить) или указывает на обратное направление (return — возвращаться).
- co-: cooperate (сотрудничать). Описывает совместную деятельность (co-author – соавтор).
- over-: oversleep (проспать). Значение префикса — избыточность, излишнее наполнение (overweight — избыточный вес) или прохождение определенной черты (overcome — преодолеть).
- under-: underact (недоигрывать). Приставку можно назвать антонимом к приставке «over-», она указывает на недостаточную степень действия (underestimate — недооценивать). Кроме того, приставка используется и в изначальном значении слова «under» — «под» (underwear — нижнее белье, underground — подземка, метро).
- pre-: prehistoric (доисторический). Приставка несет в себе идею предшествования (pre-production — предварительная стадия производства).
- post-: post-modern (постмодернизм). В отличие от предыдущего случая, приставка указывает на следование действия (postnatal – послеродовой).
- en-, em-: encode (кодировать). Префикс служит для образования глагола и имеет значение воплощения определенного качества или состояния (enclose — окружать). Перед звуками «b», «p», «m» приставка имеет вид «em-» (empoison — подмешивать яд), в остальных случаях – «en-» (encourage — ободрять).
- ex-: ex-champion (бывший чемпион). Используется для обозначения бывшего статуса или должности (ex-minister — бывший министр).
Образование новых слов при помощи суффиксов
Суффиксы занимают позицию после корня. За ними может также следовать окончание (например, показатель множественного числа «-s»). Но в отличие от суффикса окончание не образует слова с новым значением, а только меняет его грамматическую форму (boy – мальчик, boys – мальчики).
По суффиксу часто можно определить, к какой части речи принадлежит слово. Среди суффиксов существуют и такие, которые выступают только как средство образования другой части речи (например, «-ly» для образования наречий). Поэтому рассматривать эти элементы слова мы будем в зависимости от того, какую часть речи они характеризуют.
Словообразование существительных в английском языке
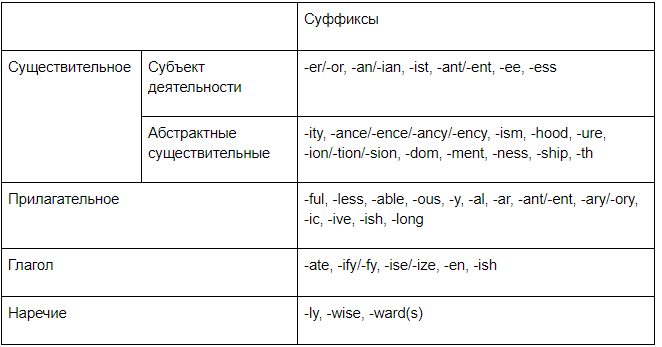
Среди суффиксов существительных можно выделить группу, обозначающую субъектов деятельности и группу абстрактных значений.
1. Субъект деятельности
- -er, -or: performer (исполнитель). Такие суффиксы описывают род занятий (doctor — доктор, farmer — фермер) или временные роли (speaker — оратор, visitor — посетитель). Могут использоваться и в качестве характеристики человека (doer — человек дела, dreamer — мечтатель).
- -an, -ian: magician (волшебник). Суффикс может участвовать в образовании названия профессии (musician — музыкант) или указывать на национальность (Belgian — бельгийский / бельгиец).
- -ist: pacifist (пацифист). Этот суффикс описывает принадлежность к определенному роду деятельности (alpinist – альпинист) или к социальному течению, направлению в искусстве (realist — реалист).
- -ant, -ent: accountant (бухгалтер), student (студент).
- -ee: employee (служащий), conferee (участник конференции).
- -ess : princess (принцесса). Суффикс используется для обозначения женского рода (waitress – официантка).
2. Абстрактные существительные
Основа этой группы значений – обозначение качества или состояния. Дополнительным значением может выступать объединение группы людей и обозначение определенной совокупности.
- -ity: activity (деятельность), lability (изменчивость).
- -ance, -ence, -ancy, -ency: importance (важность), dependence (зависимость), brilliancy (великолепие), efficiency (эффективность).
- -ion, -tion, -sion: revision (пересмотр, исправление), exception (исключение), admission (допущение), information (информация).
- -ism: realism (реализм). В отличие от суффикса «-ist» обозначает не представителя некоторого течения, а само течение (modernism — модернизм) или род занятий (alpinism — альпинизм).
- -hood: childhood (детство). Может относиться не только к состоянию, но и описывать группу людей, форму отношений: brotherhood (братство).
- -ure: pleasure (удовольствие), pressure (давление).
- -dom: wisdom (мудрость). Также используется при обозначении группы людей, объединения по некоторому признаку: kingdom (королевство).
- -ment: announcement (объявление), improvement (улучшение).
- -ness: darkness (темнота), kindness (доброта).
- -ship: friendship (дружба). К дополнительным значениям относится указание на титул (lordship — светлость), умение (airmanship — лётное мастерство) или на объединение круга людей определенными отношениями (membership — круг членов, partnership — партнерство).
- -th: truth (правда), length (длина).
Словообразование прилагательных в английском языке
- -ful: helpful (полезный). Указывает на обладание определенным качеством (joyful — радостный, beautiful — красивый).
- -less: countless (бессчетный). Значение суффикса близко к отрицанию и характеризует отсутствие определенного качества, свойства (careless — беззаботный). Этот суффикс можно определить как антоним для «-ful» (hopeless — безнадежный, а hopeful — надеющийся).
- -able: comfortable (комфортный). «Able» (способный) существует и как самостоятельное прилагательное. Оно определяет значение суффикса – возможный для выполнения, доступный к осуществлению (acceptable – приемлемый, допустимый, detectable – тот, который можно обнаружить).
- -ous: famous (знаменитый), dangerous (опасный).
- -y: windy (ветреный), rusty (ржавый).
- -al: accidental (случайный), additional (добавочный).
- -ar: molecular (молекулярный), vernacular (народный).
- -ant, -ent: defiant (дерзкий), evident (очевидный).
- -ary, -ory: secondary (второстепенный), obligatory (обязательный).
- -ic: democratic (демократический), historic (исторический).
- -ive: creative (творческий), impressive (впечатляющий).
- -ish: childish (детский, ребяческий). Суффикс описывает характерный признак с негативной оценкой (liquorish – развратный) или с ослабленной степенью качества (reddish — красноватый). Кроме того, суффикс может отсылать к национальности (Danish — датский).
- -long: livelong (целый, вечный). Такой суффикс обозначает длительность (lifelong — пожизненный) или направление (sidelong — косой, вкось) и может принадлежать не только прилагательному, но и наречию.
Словообразование глаголов
Для глагольных суффиксов сложно определить конкретные значения. Основная функция таких суффиксов — перевод в другую часть речи, то есть само образование глагола.
- -ate: activate (активизировать), decorate (украшать).
- -ify, -fy: notify (уведомлять), verify (проверять).
- -ise, -ize: summarize (суммировать), hypnotize (гипнотизировать).
- -en: weaken (ослабевать), lengthen (удлинять).
- -ish: demolish (разрушать), embellish (украшать).
Словообразование наречий
- -ly: occasionally (случайно).
- -wise: otherwise (иначе). Обозначает способ действия (archwise — дугообразно).
- -ward(s): skyward/skywards (к небу). Обозначает направление движения (northward — на север, shoreward — по направлению к берегу).
Суффиксы: таблица словообразования по частям речи
Приведенный список суффиксов – это далеко не все возможности английского языка. Мы описали наиболее распространенные и интересные случаи. Для того чтобы разобраться в этом множестве вариантов и лучше усвоить образование слов в английском языке, таблица резюмирует, для каких частей речи какие суффиксы характерны.
Поскольку суффиксальное преобразование слов в английском языке различается по частям речи, таблица разбита на соответствующие группы. Одни и те же суффиксы могут добавляться к разным частям речи, но в результате они определяют, к какой части речи принадлежит новое слово.
Объединение суффиксов и приставок
Важная характеристика словообразования – это его продуктивность. От одного корня можно образовать целую группу слов, добавляя разные приставки и суффиксы. Приведем несколько примеров.
- Для possible словообразование может выглядеть следующим образом: possible (возможный) — possibility (возможность) — impossibility (невозможность).
- Цепочка переходов для слова occasion: occasion (случай) — occasional (случайный) — occasionally (случайно).
- Для слова agree словообразование можно выстроить в цепочки с приставкой и без приставки: agree (соглашаться) — agreeable (приемлемый / приятный) — agreeably (приятно) — agreement (соглашение, согласие).
agree (соглашаться) — disagree (противоречить, расходиться в мнениях) — disagreeable (неприятный) — disagreeably (неприятно) — disagreement (разногласие).
Словосложение и сокращение слов
Словосложение — еще один способ образовать новое слово, хотя и менее распространенный. Он основан на соединении двух корней (toothbrush — зубная щетка, well-educated — хорошо образованный). В русском языке такое словообразование тоже встречается, например, «кресло-качалка».
Если корень активно используется в словосложении, то он может перейти в категорию суффиксов. В таком случае сложно определить, к какому типу – суффиксам или словосложению – отнести некоторые примеры:
- -man: fireman (пожарный), spiderman (человек-паук)
- -free: sugar-free (без сахара), alcohol-free (безалкогольный)
- -proof: fireproof (огнестойкий), soundproof (звукоизолирующий)
Помимо объединения нескольких корней, возможно также сокращение слов и создание аббревиатур: science fiction — sci-fi (научная фантастика), United States of America – USA (Соединенные Штаты Америки, США).
Новые слова без внешних изменений
К особенности словообразования в английском языке относится и то, что слова могут выступать в разных частях речи без изменения внешнего вида. Это явление называется конверсией:
I hope you won’t be angry with me — Надеюсь, ты не будешь на меня злиться (hope – глагол «надеяться»).
I always had a hope to return to that city — У меня всегда оставалась надежда вернуться в этот город (hope – существительное «надежда»).
The sea is so calm today — Море так спокойно сегодня (calm – прилагательное «спокойный»).
With a calm she realized that her life was probably at its end — Со спокойствием она осознала, что ее жизнь, вероятно, подходила к концу (calm – существительное «спокойствие, невозмутимость»).
I beg you to calm down — Я умоляю тебя успокоиться (calm – глагол «успокоиться»).
Lecture №3. Productive and Non-productive Ways of Word-formation in Modern English
Productivity is the ability to form new words after existing patterns which are readily understood by the speakers of language. The most important and the most productive ways of word-formation are affixation, conversion, word-composition and abbreviation (contraction). In the course of time the productivity of this or that way of word-formation may change. Sound interchange or gradation (blood-to bleed, to abide-abode, to strike-stroke) was a productive way of word building in old English and is important for a diachronic study of the English language. It has lost its productivity in Modern English and no new word can be coined by means of sound gradation. Affixation on the contrary was productive in Old English and is still one of the most productive ways of word building in Modern English.
WORDBUILDING
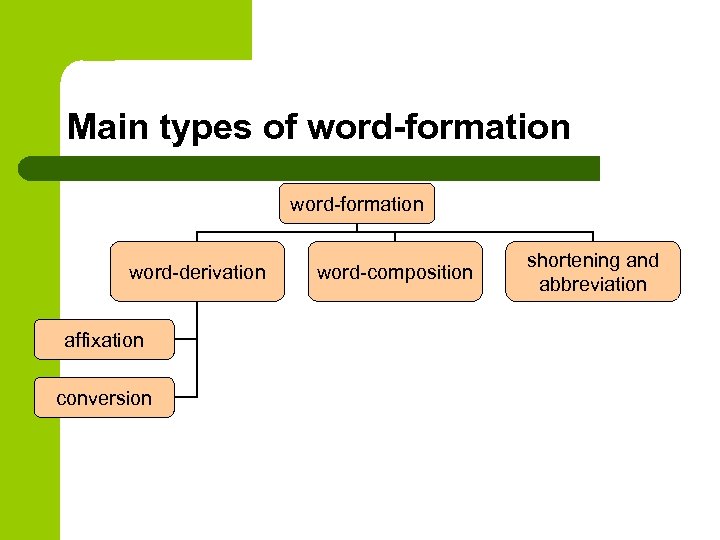
Word-building is one of the main ways of enriching vocabulary. There are four main ways of word-building in modern English: affixation, composition, conversion, abbreviation. There are also secondary ways of word-building: sound interchange, stress interchange, sound imitation, blends, back formation.
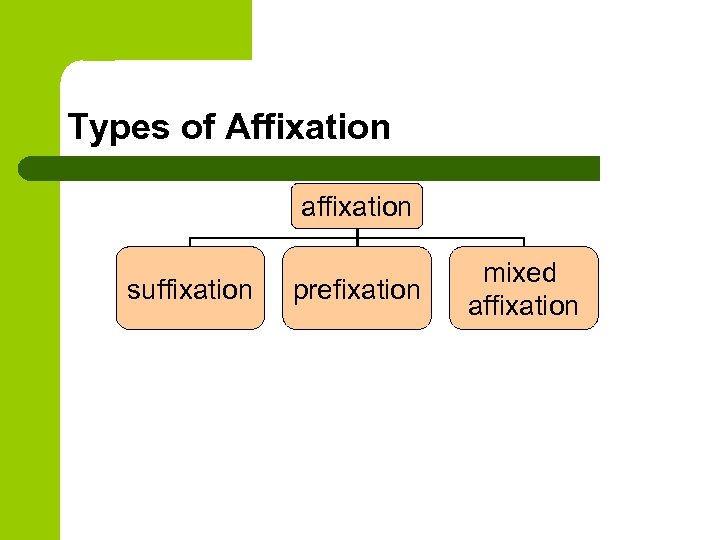
AFFIXATION
Affixation is one of the most productive ways of word-building throughout the history of English. It consists in adding an affix to the stem of a definite part of speech. Affixation is divided into suffixation and prefixation.
Suffixation
The main function of suffixes in Modern English is to form one part of speech from another, the secondary function is to change the lexical meaning of the same part of speech. (e.g. «educate» is a verb, «educator» is a noun, and music» is a noun, «musical» is also a noun or an adjective). There are different classifications of suffixes :
1. Part-of-speech classification. Suffixes which can form different parts of speech are given here :
a) noun-forming suffixes, such as: —er (criticizer), —dom (officialdom), —ism (ageism),
b) adjective-forming suffixes, such as: —able (breathable), less (symptomless), —ous (prestigious),
c) verb-forming suffixes, such as —ize (computerize) , —ify (minify),
d) adverb-forming suffixes , such as : —ly (singly), —ward (tableward),
e) numeral-forming suffixes, such as —teen (sixteen), —ty (seventy).
2. Semantic classification. Suffixes changing the lexical meaning of the stem can be subdivided into groups, e.g. noun-forming suffixes can denote:
a) the agent of the action, e.g. —er (experimenter), —ist (taxist), -ent (student),
b) nationality, e.g. —ian (Russian), —ese (Japanese), —ish (English),
c) collectivity, e.g. —dom (moviedom), —ry (peasantry, —ship (readership), —ati (literati),
d) diminutiveness, e.g. —ie (horsie), —let (booklet), —ling (gooseling), —ette (kitchenette),
e) quality, e.g. —ness (copelessness), —ity (answerability).
3. Lexico—grammatical character of the stem. Suffixes which can be added to certain groups of stems are subdivided into:
a) suffixes added to verbal stems, such as: —er (commuter), —ing (suffering), — able (flyable), —ment (involvement), —ation (computerization),
b) suffixes added to noun stems, such as: —less (smogless), —ful (roomful), —ism (adventurism), —ster (pollster), —nik (filmnik), —ish (childish),
c) suffixes added to adjective stems, such as: —en (weaken), —ly (pinkly), —ish (longish), —ness (clannishness).
4. Origin of suffixes. Here we can point out the following groups:
a) native (Germanic), such as —er,-ful, —less, —ly.
b) Romanic, such as : —tion, —ment, —able, —eer.
c) Greek, such as : —ist, —ism, -ize.
d) Russian, such as —nik.
5. Productivity. Here we can point out the following groups:
a) productive, such as: —er, —ize, —ly, —ness.
b) semi-productive, such as: —eer, —ette, —ward.
c) non-productive , such as: —ard (drunkard), —th (length).
Suffixes can be polysemantic, such as: —er can form nouns with the following meanings: agent, doer of the action expressed by the stem (speaker), profession, occupation (teacher), a device, a tool (transmitter). While speaking about suffixes we should also mention compound suffixes which are added to the stem at the same time, such as —ably, —ibly, (terribly, reasonably), —ation (adaptation from adapt). There are also disputable cases whether we have a suffix or a root morpheme in the structure of a word, in such cases we call such morphemes semi-suffixes, and words with such suffixes can be classified either as derived words or as compound words, e.g. —gate (Irangate), —burger (cheeseburger), —aholic (workaholic) etc.
Prefixation
Prefixation is the formation of words by means of adding a prefix to the stem. In English it is characteristic for forming verbs. Prefixes are more independent than suffixes. Prefixes can be classified according to the nature of words in which they are used: prefixes used in notional words and prefixes used in functional words. Prefixes used in notional words are proper prefixes which are bound morphemes, e.g. un— (unhappy). Prefixes used in functional words are semi-bound morphemes because they are met in the language as words, e.g. over— (overhead) (cf. over the table). The main function of prefixes in English is to change the lexical meaning of the same part of speech. But the recent research showed that about twenty-five prefixes in Modern English form one part of speech from another (bebutton, interfamily, postcollege etc).
Prefixes can be classified according to different principles:
1. Semantic classification:
a) prefixes of negative meaning, such as: in— (invaluable), non— (nonformals), un— (unfree) etc,
b) prefixes denoting repetition or reversal actions, such as: de— (decolonize), re— (revegetation), dis— (disconnect),
c) prefixes denoting time, space, degree relations, such as: inter— (interplanetary) , hyper— (hypertension), ex— (ex-student), pre— (pre-election), over— (overdrugging) etc.
2. Origin of prefixes:
a) native (Germanic), such as: un-, over-, under— etc.
b) Romanic, such as: in-, de-, ex-, re— etc.
c) Greek, such as: sym-, hyper— etc.
When we analyze such words as adverb, accompany where we can find the root of the word (verb, company) we may treat ad-, ac— as prefixes though they were never used as prefixes to form new words in English and were borrowed from Romanic languages together with words. In such cases we can treat them as derived words. But some scientists treat them as simple words. Another group of words with a disputable structure are such as: contain, retain, detain and conceive, receive, deceive where we can see that re-, de-, con— act as prefixes and —tain, —ceive can be understood as roots. But in English these combinations of sounds have no lexical meaning and are called pseudo-morphemes. Some scientists treat such words as simple words, others as derived ones. There are some prefixes which can be treated as root morphemes by some scientists, e.g. after— in the word afternoon. American lexicographers working on Webster dictionaries treat such words as compound words. British lexicographers treat such words as derived ones.
COMPOSITION
Composition is the way of word building when a word is formed by joining two or more stems to form one word. The structural unity of a compound word depends upon: a) the unity of stress, b) solid or hyphеnated spelling, c) semantic unity, d) unity of morphological and syntactical functioning. These are characteristic features of compound words in all languages. For English compounds some of these factors are not very reliable. As a rule English compounds have one uniting stress (usually on the first component), e.g. hard-cover, best—seller. We can also have a double stress in an English compound, with the main stress on the first component and with a secondary stress on the second component, e.g. blood—vessel. The third pattern of stresses is two level stresses, e.g. snow—white, sky—blue. The third pattern is easily mixed up with word-groups unless they have solid or hyphеnated spelling.
Spelling in English compounds is not very reliable as well because they can have different spelling even in the same text, e.g. war—ship, blood—vessel can be spelt through a hyphen and also with a break, insofar, underfoot can be spelt solidly and with a break. All the more so that there has appeared in Modern English a special type of compound words which are called block compounds, they have one uniting stress but are spelt with a break, e.g. air piracy, cargo module, coin change, penguin suit etc. The semantic unity of a compound word is often very strong. In such cases we have idiomatic compounds where the meaning of the whole is not a sum of meanings of its components, e.g. to ghostwrite, skinhead, brain—drain etc. In nonidiomatic compounds semantic unity is not strong, e. g., airbus, to bloodtransfuse, astrodynamics etc.
English compounds have the unity of morphological and syntactical functioning. They are used in a sentence as one part of it and only one component changes grammatically, e.g. These girls are chatter-boxes. «Chatter-boxes» is a predicative in the sentence and only the second component changes grammatically. There are two characteristic features of English compounds:
a) Both components in an English compound are free stems, that is they can be used as words with a distinctive meaning of their own. The sound pattern will be the same except for the stresses, e.g. «a green-house» and «a green house». Whereas for example in Russian compounds the stems are bound morphemes, as a rule.
b) English compounds have a two-stem pattern, with the exception of compound words which have form-word stems in their structure, e.g. middle-of-the-road, off—the—record, up—and—doing etc. The two-stem pattern distinguishes English compounds from German ones.
WAYS OF FORMING COMPOUND WORDS
Compound words in English can be formed not only by means of composition but also by means of:
a) reduplication, e.g. too—too, and also by means of reduplication combined with sound interchange , e.g. rope-ripe,
b) conversion from word-groups, e.g. to micky—mouse, can—do, makeup etc,
c) back formation from compound nouns or word-groups, e.g. to bloodtransfuse, to fingerprint etc ,
d) analogy, e.g. lie—in (on the analogy with sit-in) and also phone—in, brawn—drain (on the analogy with brain—drain) etc.
CLASSIFICATIONS OF ENGLISH COMPOUNDS
1. According to the parts of speech compounds are subdivided into:
a) nouns, such as: baby-moon, globe-trotter,
b) adjectives, such as : free-for-all, power-happy,
c) verbs, such as : to honey-moon, to baby-sit, to henpeck,
d) adverbs, such as: downdeep, headfirst,
e) prepositions, such as: into, within,
f) numerals, such as : fifty—five.
2. According to the way components are joined together compounds are divided into: a) neutral, which are formed by joining together two stems without any joining morpheme, e.g. ball—point, to windowshop,
b) morphological where components are joined by a linking element: vowels «o» or «i» or the consonant «s», e.g. («astrospace», «handicraft», «sportsman»),
c) syntactical where the components are joined by means of form-word stems, e.g. here-and-now, free-for-all, do-or-die.
3. According to their structure compounds are subdivided into:
a) compound words proper which consist of two stems, e.g. to job-hunt, train-sick, go-go, tip-top,
b) derivational compounds, where besides the stems we have affixes, e.g. ear—minded, hydro-skimmer,
c) compound words consisting of three or more stems, e.g. cornflower—blue, eggshell—thin, singer—songwriter,
d) compound-shortened words, e.g. boatel, VJ—day, motocross, intervision, Eurodollar, Camford.
4. According to the relations between the components compound words are subdivided into:
a) subordinative compounds where one of the components is the semantic and the structural centre and the second component is subordinate; these subordinative relations can be different: with comparative relations, e.g. honey—sweet, eggshell—thin, with limiting relations, e.g. breast—high, knee—deep, with emphatic relations, e.g. dog—cheap, with objective relations, e.g. gold—rich, with cause relations, e.g. love—sick, with space relations, e.g. top—heavy, with time relations, e.g. spring—fresh, with subjective relations, e.g. foot—sore etc
b) coordinative compounds where both components are semantically independent. Here belong such compounds when one person (object) has two functions, e.g. secretary-stenographer, woman-doctor, Oxbridge etc. Such compounds are called additive. This group includes also compounds formed by means of reduplication, e.g. fifty-fifty, no-no, and also compounds formed with the help of rhythmic stems (reduplication combined with sound interchange) e.g. criss-cross, walkie-talkie.
5. According to the order of the components compounds are divided into compounds with direct order, e.g. kill—joy, and compounds with indirect order, e.g. nuclear—free, rope—ripe.
CONVERSION
Conversion is a characteristic feature of the English word-building system. It is also called affixless derivation or zero-suffixation. The term «conversion» first appeared in the book by Henry Sweet «New English Grammar» in 1891. Conversion is treated differently by different scientists, e.g. prof. A.I. Smirntitsky treats conversion as a morphological way of forming words when one part of speech is formed from another part of speech by changing its paradigm, e.g. to form the verb «to dial» from the noun «dial» we change the paradigm of the noun (a dial, dials) for the paradigm of a regular verb (I dial, he dials, dialed, dialing). A. Marchand in his book «The Categories and Types of Present-day English» treats conversion as a morphological-syntactical word-building because we have not only the change of the paradigm, but also the change of the syntactic function, e.g. I need some good paper for my room. (The noun «paper» is an object in the sentence). I paper my room every year. (The verb «paper» is the predicate in the sentence). Conversion is the main way of forming verbs in Modern English. Verbs can be formed from nouns of different semantic groups and have different meanings because of that, e.g.:
a) verbs have instrumental meaning if they are formed from nouns denoting parts of a human body e.g. to eye, to finger, to elbow, to shoulder etc. They have instrumental meaning if they are formed from nouns denoting tools, machines, instruments, weapons, e.g. to hammer, to machine-gun, to rifle, to nail,
b) verbs can denote an action characteristic of the living being denoted by the noun from which they have been converted, e.g. to crowd, to wolf, to ape,
c) verbs can denote acquisition, addition or deprivation if they are formed from nouns denoting an object, e.g. to fish, to dust, to peel, to paper,
d) verbs can denote an action performed at the place denoted by the noun from which they have been converted, e.g. to park, to garage, to bottle, to corner, to pocket,
e) verbs can denote an action performed at the time denoted by the noun from which they have been converted e.g. to winter, to week-end.
Verbs can be also converted from adjectives, in such cases they denote the change of the state, e.g. to tame (to become or make tame), to clean, to slim etc.
Nouns can also be formed by means of conversion from verbs. Converted nouns can denote: a) instant of an action e.g. a jump, a move,
b) process or state e.g. sleep, walk,
c) agent of the action expressed by the verb from which the noun has been converted, e.g. a help, a flirt, a scold,
d) object or result of the action expressed by the verb from which the noun has been converted, e.g. a burn, a find, a purchase,
e) place of the action expressed by the verb from which the noun has been converted, e.g. a drive, a stop, a walk.
Many nouns converted from verbs can be used only in the Singular form and denote momentaneous actions. In such cases we have partial conversion. Such deverbal nouns are often used with such verbs as: to have, to get, to take etc., e.g. to have a try, to give a push, to take a swim.
CRITERIA OF SEMANTIC DERIVATION
In cases of conversion the problem of criteria of semantic derivation arises: which of the converted pair is primary and which is converted from it. The problem was first analized by prof. A.I. Smirnitsky. Later on P.A. Soboleva developed his idea and worked out the following criteria:
1. If the lexical meaning of the root morpheme and the lexico-grammatical meaning of the stem coincide the word is primary, e.g. in cases pen — to pen, father — to father the nouns are names of an object and a living being. Therefore in the nouns «pen» and «father» the lexical meaning of the root and the lexico-grammatical meaning of the stem coincide. The verbs «to pen» and «to father» denote an action, a process therefore the lexico-grammatical meanings of the stems do not coincide with the lexical meanings of the roots. The verbs have a complex semantic structure and they were converted from nouns.
2. If we compare a converted pair with a synonymic word pair which was formed by means of suffixation we can find out which of the pair is primary. This criterion can be applied only to nouns converted from verbs, e.g. «chat» n. and «chat» v. can be compared with «conversation» – «converse».
3. The criterion based on derivational relations is of more universal character. In this case we must take a word-cluster of relative words to which the converted pair belongs. If the root stem of the word-cluster has suffixes added to a noun stem the noun is primary in the converted pair and vica versa, e.g. in the word-cluster: hand n., hand v., handy, handful the derived words have suffixes added to a noun stem, that is why the noun is primary and the verb is converted from it. In the word-cluster: dance n., dance v., dancer, dancing we see that the primary word is a verb and the noun is converted from it.
SUBSTANTIVIZATION OF ADJECTIVES
Some scientists (Yespersen, Kruisinga) refer substantivization of adjectives to conversion. But most scientists disagree with them because in cases of substantivization of adjectives we have quite different changes in the language. Substantivization is the result of ellipsis (syntactical shortening) when a word combination with a semantically strong attribute loses its semantically weak noun (man, person etc), e.g. «a grown-up person» is shortened to «a grown-up». In cases of perfect substantivization the attribute takes the paradigm of a countable noun, e.g. a criminal, criminals, a criminal’s (mistake), criminals’ (mistakes). Such words are used in a sentence in the same function as nouns, e.g. I am fond of musicals. (musical comedies). There are also two types of partly substantivized adjectives: 1) those which have only the plural form and have the meaning of collective nouns, such as: sweets, news, finals, greens; 2) those which have only the singular form and are used with the definite article. They also have the meaning of collective nouns and denote a class, a nationality, a group of people, e.g. the rich, the English, the dead.
«STONE WALL» COMBINATIONS
The problem whether adjectives can be formed by means of conversion from nouns is the subject of many discussions. In Modern English there are a lot of word combinations of the type, e.g. price rise, wage freeze, steel helmet, sand castle etc. If the first component of such units is an adjective converted from a noun, combinations of this type are free word-groups typical of English (adjective + noun). This point of view is proved by O. Yespersen by the following facts:
1. «Stone» denotes some quality of the noun «wall».
2. «Stone» stands before the word it modifies, as adjectives in the function of an attribute do in English.
3. «Stone» is used in the Singular though its meaning in most cases is plural, and adjectives in English have no plural form.
4. There are some cases when the first component is used in the Comparative or the Superlative degree, e.g. the bottomest end of the scale.
5. The first component can have an adverb which characterizes it, and adjectives are characterized by adverbs, e.g. a purely family gathering.
6. The first component can be used in the same syntactical function with a proper adjective to characterize the same noun, e.g. lonely bare stone houses.
7. After the first component the pronoun «one» can be used instead of a noun, e.g. I shall not put on a silk dress, I shall put on a cotton one.
However Henry Sweet and some other scientists say that these criteria are not characteristic of the majority of such units. They consider the first component of such units to be a noun in the function of an attribute because in Modern English almost all parts of speech and even word-groups and sentences can be used in the function of an attribute, e.g. the then president (an adverb), out-of-the-way villages (a word-group), a devil-may-care speed (a sentence). There are different semantic relations between the components of «stone wall» combinations. E.I. Chapnik classified them into the following groups:
1. time relations, e.g. evening paper,
2. space relations, e.g. top floor,
3. relations between the object and the material of which it is made, e.g. steel helmet,
4. cause relations, e.g. war orphan,
5. relations between a part and the whole, e.g. a crew member,
6. relations between the object and an action, e.g. arms production,
7. relations between the agent and an action e.g. government threat, price rise,
8. relations between the object and its designation, e.g. reception hall,
9. the first component denotes the head, organizer of the characterized object, e.g. Clinton government, Forsyte family,
10. the first component denotes the field of activity of the second component, e.g. language teacher, psychiatry doctor,
11. comparative relations, e.g. moon face,
12. qualitative relations, e.g. winter apples.
ABBREVIATION
In the process of communication words and word-groups can be shortened. The causes of shortening can be linguistic and extra-linguistic. By extra-linguistic causes changes in the life of people are meant. In Modern English many new abbreviations, acronyms, initials, blends are formed because the tempo of life is increasing and it becomes necessary to give more and more information in the shortest possible time. There are also linguistic causes of abbreviating words and word-groups, such as the demand of rhythm, which is satisfied in English by monosyllabic words. When borrowings from other languages are assimilated in English they are shortened. Here we have modification of form on the basis of analogy, e.g. the Latin borrowing «fanaticus» is shortened to «fan» on the analogy with native words: man, pan, tan etc. There are two main types of shortenings: graphical and lexical.
Graphical abbreviations
Graphical abbreviations are the result of shortening of words and word-groups only in written speech while orally the corresponding full forms are used. They are used for the economy of space and effort in writing. The oldest group of graphical abbreviations in English is of Latin origin. In Russian this type of abbreviation is not typical. In these abbreviations in the spelling Latin words are shortened, while orally the corresponding English equivalents are pronounced in the full form, e.g. for example (Latin exampli gratia), a.m. – in the morning (ante meridiem), No – number (numero), p.a. – a year (per annum), d – penny (dinarius), lb – pound (libra), i. e. – that is (id est) etc.
Some graphical abbreviations of Latin origin have different English equivalents in different contexts, e.g. p.m. can be pronounced «in the afternoon» (post meridiem) and «after death» (post mortem). There are also graphical abbreviations of native origin, where in the spelling we have abbreviations of words and word-groups of the corresponding English equivalents in the full form. We have several semantic groups of them: a) days of the week, e.g. Mon – Monday, Tue – Tuesday etc
b) names of months, e.g. Apr – April, Aug – August etc.
c) names of counties in UK, e.g. Yorks – Yorkshire, Berks – Berkshire etc
d) names of states in USA, e.g. Ala – Alabama, Alas – Alaska etc.
e) names of address, e.g. Mr., Mrs., Ms., Dr. etc.
f) military ranks, e.g. capt. – captain, col. – colonel, sgt – sergeant etc.
g) scientific degrees, e.g. B.A. – Bachelor of Arts, D.M. – Doctor of Medicine. (Sometimes in scientific degrees we have abbreviations of Latin origin, e.g., M.B. – Medicinae Baccalaurus).
h) units of time, length, weight, e.g. f./ft – foot/feet, sec. – second, in. – inch, mg. – milligram etc.
The reading of some graphical abbreviations depends on the context, e.g. «m» can be read as: male, married, masculine, metre, mile, million, minute, «l.p.» can be read as long-playing, low pressure.
Initial abbreviations
Initialisms are the bordering case between graphical and lexical abbreviations. When they appear in the language, as a rule, to denote some new offices they are closer to graphical abbreviations because orally full forms are used, e.g. J.V. – joint venture. When they are used for some duration of time they acquire the shortened form of pronouncing and become closer to lexical abbreviations, e.g. BBC is as a rule pronounced in the shortened form. In some cases the translation of initialisms is next to impossible without using special dictionaries. Initialisms are denoted in different ways. Very often they are expressed in the way they are pronounced in the language of their origin, e.g. ANZUS (Australia, New Zealand, United States) is given in Russian as АНЗУС, SALT (Strategic Arms Limitation Talks) was for a long time used in Russian as СОЛТ, now a translation variant is used (ОСВ – Договор об ограничении стратегических вооружений). This type of initialisms borrowed into other languages is preferable, e.g. UFO – НЛО, CП – JV etc. There are three types of initialisms in English:
a) initialisms with alphabetical reading, such as UK, BUP, CND etc
b) initialisms which are read as if they are words, e.g. UNESCO, UNO, NATO etc.
c) initialisms which coincide with English words in their sound form, such initialisms are called acronyms, e.g. CLASS (Computor-based Laboratory for Automated School System). Some scientists unite groups b) and c) into one group which they call acronyms. Some initialisms can form new words in which they act as root morphemes by different ways of wordbuilding:
a) affixation, e.g. AVALism, ex- POW, AIDSophobia etc.
b) conversion, e.g. to raff, to fly IFR (Instrument Flight Rules),
c) composition, e.g. STOLport, USAFman etc.
d) there are also compound-shortened words where the first component is an initial abbreviation with the alphabetical reading and the second one is a complete word, e.g. A-bomb, U-pronunciation, V -day etc. In some cases the first component is a complete word and the second component is an initial abbreviation with the alphabetical pronunciation, e.g. Three -Ds (Three dimensions) – стереофильм.
Abbreviations of words
Abbreviation of words consists in clipping a part of a word. As a result we get a new lexical unit where either the lexical meaning or the style is different form the full form of the word. In such cases as «fantasy» and «fancy», «fence» and «defence» we have different lexical meanings. In such cases as «laboratory» and «lab», we have different styles. Abbreviation does not change the part-of-speech meaning, as we have it in the case of conversion or affixation, it produces words belonging to the same part of speech as the primary word, e.g. prof. is a noun and professor is also a noun. Mostly nouns undergo abbreviation, but we can also meet abbreviation of verbs, such as to rev. from to revolve, to tab from to tabulate etc. But mostly abbreviated forms of verbs are formed by means of conversion from abbreviated nouns, e.g. to taxi, to vac etc. Adjectives can be abbreviated but they are mostly used in school slang and are combined with suffixation, e.g. comfy, dilly etc. As a rule pronouns, numerals, interjections. conjunctions are not abbreviated. The exceptions are: fif (fifteen), teen-ager, in one’s teens (apheresis from numerals from 13 to 19). Lexical abbreviations are classified according to the part of the word which is clipped. Mostly the end of the word is clipped, because the beginning of the word in most cases is the root and expresses the lexical meaning of the word. This type of abbreviation is called apocope. Here we can mention a group of words ending in «o», such as disco (dicotheque), expo (exposition), intro (introduction) and many others. On the analogy with these words there developed in Modern English a number of words where «o» is added as a kind of a suffix to the shortened form of the word, e.g. combo (combination) – небольшой эстрадный ансамбль, Afro (African) – прическа под африканца etc. In other cases the beginning of the word is clipped. In such cases we have apheresis, e.g. chute (parachute), varsity (university), copter (helicopter), thuse (enthuse) etc. Sometimes the middle of the word is clipped, e.g. mart (market), fanzine (fan magazine) maths (mathematics). Such abbreviations are called syncope. Sometimes we have a combination of apocope with apheresis, when the beginning and the end of the word are clipped, e.g. tec (detective), van (vanguard) etc. Sometimes shortening influences the spelling of the word, e.g. «c» can be substituted by «k» before «e» to preserve pronunciation, e.g. mike (microphone), Coke (coca-cola) etc. The same rule is observed in the following cases: fax (facsimile), teck (technical college), trank (tranquilizer) etc. The final consonants in the shortened forms are substituded by letters characteristic of native English words.
NON-PRODUCTIVE WAYS OF WORDBUILDING
SOUND INTERCHANGE
Sound interchange is the way of word-building when some sounds are changed to form a new word. It is non-productive in Modern English, it was productive in Old English and can be met in other Indo-European languages. The causes of sound interchange can be different. It can be the result of Ancient Ablaut which cannot be explained by the phonetic laws during the period of the language development known to scientists, e.g. to strike – stroke, to sing – song etc. It can be also the result of Ancient Umlaut or vowel mutation which is the result of palatalizing the root vowel because of the front vowel in the syllable coming after the root (regressive assimilation), e.g. hot — to heat (hotian), blood — to bleed (blodian) etc. In many cases we have vowel and consonant interchange. In nouns we have voiceless consonants and in verbs we have corresponding voiced consonants because in Old English these consonants in nouns were at the end of the word and in verbs in the intervocalic position, e.g. bath – to bathe, life – to live, breath – to breathe etc.
STRESS INTERCHANGE
Stress interchange can be mostly met in verbs and nouns of Romanic origin: nouns have the stress on the first syllable and verbs on the last syllable, e.g. `accent — to ac`cent. This phenomenon is explained in the following way: French verbs and nouns had different structure when they were borrowed into English, verbs had one syllable more than the corresponding nouns. When these borrowings were assimilated in English the stress in them was shifted to the previous syllable (the second from the end). Later on the last unstressed syllable in verbs borrowed from French was dropped (the same as in native verbs) and after that the stress in verbs was on the last syllable while in nouns it was on the first syllable. As a result of it we have such pairs in English as: to af«fix -`affix, to con`flict- `conflict, to ex`port -`export, to ex`tract — `extract etc. As a result of stress interchange we have also vowel interchange in such words because vowels are pronounced differently in stressed and unstressed positions.
SOUND IMITATION
It is the way of word-building when a word is formed by imitating different sounds. There are some semantic groups of words formed by means of sound imitation:
a) sounds produced by human beings, such as : to whisper, to giggle, to mumble, to sneeze, to whistle etc.
b) sounds produced by animals, birds, insects, such as: to hiss, to buzz, to bark, to moo, to twitter etc.
c) sounds produced by nature and objects, such as: to splash, to rustle, to clatter, to bubble, to ding-dong, to tinkle etc.
The corresponding nouns are formed by means of conversion, e.g. clang (of a bell), chatter (of children) etc.
BLENDS
Blends are words formed from a word-group or two synonyms. In blends two ways of word-building are combined: abbreviation and composition. To form a blend we clip the end of the first component (apocope) and the beginning of the second component (apheresis) . As a result we have a compound- shortened word. One of the first blends in English was the word «smog» from two synonyms: smoke and fog which means smoke mixed with fog. From the first component the beginning is taken, from the second one the end, «o» is common for both of them. Blends formed from two synonyms are: slanguage, to hustle, gasohol etc. Mostly blends are formed from a word-group, such as: acromania (acronym mania), cinemaddict (cinema adict), chunnel (channel, canal), dramedy (drama comedy), detectifiction (detective fiction), faction (fact fiction) (fiction based on real facts), informecial (information commercial), Medicare (medical care), magalog (magazine catalogue) slimnastics (slimming gymnastics), sociolite (social elite), slanguist (slang linguist) etc.
BACK FORMATION
It is the way of word-building when a word is formed by dropping the final morpheme to form a new word. It is opposite to suffixation, that is why it is called back formation. At first it appeared in the language as a result of misunderstanding the structure of a borrowed word. Prof. Yartseva explains this mistake by the influence of the whole system of the language on separate words. E.g. it is typical of English to form nouns denoting the agent of the action by adding the suffix -er to a verb stem (speak- speaker). So when the French word «beggar» was borrowed into English the final syllable «ar» was pronounced in the same way as the English —er and Englishmen formed the verb «to beg» by dropping the end of the noun. Other examples of back formation are: to accreditate (from accreditation), to bach (from bachelor), to collocate (from collocation), to enthuse (from enthusiasm), to compute (from computer), to emote (from emotion), to televise (from television) etc.
As we can notice in cases of back formation the part-of-speech meaning of the primary word is changed, verbs are formed from nouns.
23
WORD-BUILDING IN ENGLISH
Word-formation l process of creating new words from resources of a particular language according to certain semantic and structural patterns existing in the language
Word-formation l branch of Lexicology l studies the patterns on which the English language builds words l may be studied synchronically and diachronically
Main types of word-formation word-derivation affixation conversion word-composition shortening and abbreviation
Minor types of word-formation sound- and stress interchange back formation sound imitation lexicalizatio of grammatical
Derivational Pattern is a meaningful combination of stems and affixes l regularly reproduced l indicates the grammatical part-of-speech meaning e. g. verbal stem + -ee = noun (‘one who is V-ed’) examine + -ee = examinee addressee, employee, divorcee l
Affixation l l formation of words by adding derivational affixes to stems one of the most productive ways of wordbuilding
Types of Affixation affixation suffixation prefixation mixed affixation
Affixation Suffixation l words are formed with the help of suffixes l changes a part-of-speech meaning (e. g. work – worker) l transfers a word into a different semantic group (e. g. child – childhood) l is characteristic of noun and adjective formation Prefixation l words are formed with the help of prefixes l does not change a part-ofspeech meaning (e. g. usual – unusual) l about 25 prefixes form one part of speech from another (e. g. head – to behead) l is characteristic of verb formation
Mixed Affixation l l l formation by both prefixation and suffixation semantic structure becomes more limited the more affixes added the less polysemantic the word becomes e. g. speak – unspeakable place – irreplaceable
Conversion l l process of creating a new word in a different part of speech with different distributional characteristic but without adding any affixes so that the basic form of the original and the basic form of a derived word are homonymous
Conversion A new word: l has a meaning different from the original one l has a new paradigm peculiar to its new category as a part of speech l the morphemic shape of the original word remains unchanged
Conversion l l face, noun -s, pl. -’s, poss. c. , sg -s’, poss. c. , pl a front part of the head from the forehead to the chin l l to face, verb -s, 3 rd p. sg. -ed, past ind. , past part. -ing, pres. part. , gerund to turn the face towards sb/smth
Reasons for the widespread development of conversion absence of morphological elements which mark the part of speech of the word e. g. back (noun) – If you use mirrors you can see the l back of your head to back – Their houses back onto the river. back (adverb) – Put the book back on the shelf. back (adjective) – a back garden, back teeth
Reasons for the widespread development of conversion l simplicity of paradigms of English parts of speech l a great number of one-syllable words that are mobile and flexible
Conversion in Present-Day English l l l typical of one-syllable words not common to affixed words (e. g. a commission – to commission) the predominant way of verb formation verbs are mainly formed from nouns and rarely from other parts of speech highly productive
Conversion in Different Parts of Speech l noun verb e. g. an eye – to eye, a bag – to bag, a room – to room l verb noun e. g. to jump – a jump, to do – a do l adjective verb e. g. pale – to pale l adjective noun e. g. private – a private, blind – the blind
Conversion in Different Parts of Speech form word noun e. g. He was familiar with ups and downs of life. I shan’t go into whys and wherefores. l affix noun e. g. Freudism, existentialism and all other ‘isms’ of l modern life. interjection verb e. g. pooh – to pooh-pooh l
Conversion and Other Types of Word. Formation l conversion and composition e. g. pin-point — to pin point, black-list – to blacklist l composition, conversion and shortening e. g. to drive in – a drive-in theater – a drive-in l conversion and composition in phrases and sentences e. g. Old man what-do-you-call-him’s book is on sale.
Traditional and Occasional Conversion Traditional Conversion l the use of a word is recorded in the dictionary e. g. to cook, to look, find, aim, etc. Occasional Conversion l the use of a word is not registered by the dictionary l occurs momentarily, through the immediate need of the situation, brings out the meaning more vividly e. g. If anybody oranges me again tonight, I’ll knock his face off!
Shortening l a way of word-formation when part of the original word or word group is taken away
Shortening A new word: l l l belongs to the same part of speech as a the original word (e. g. demo – demonstration) has the same lexical meaning as the original word capable of being used as a free form can take functional affixes (e. g. a bikes) mostly monosemantic
Shortening A new word: l may serve as basis for further word-formation by derivation and composition e. g. fancy (noun) fantasy (shortening) fancy (noun) to fancy (conversion) fancy (noun) fancier, fanciful (derivation) fancy (noun) fancy-ball, fancy-dress (composition)
Shortening A new word: l differs from the original word stylistically or emotionally, characteristic of colloquial speech e. g. Becky Rebecca (diminutive) Japs the Japanese examination (college slang) hanky handkerchief (nursery word) o’er over (bookish, poetic style)
Shortening in Different Parts of Speech l l nouns e. g. professor verbs e. g. to revolve adjectives (very few) e. g. dilly delightful (jargonism) interjection e. g. Shun! attention
Types of Shortening final clipping (apocope) — a word is shortened at the end e. g. ed editor, referee l initial clipping (apheresis) – a word is shortened at the beginning e. g. phone telephone, chute parachute l
Types of Shortening medial clipping (syncope) – some syllables or sounds are omitted from the middle of a word e. g. maths mathematics spectacles fancy fantasy l
Types of Shortening l a word is clipped both at the end at the beginning e. g. flu tec fridge influenza detective refridgerator
Abbreviation (graphical shortening) l l shortening of word or word-groups in written speech in speech the corresponding full forms are used e. g. lb — pound e. g. – for example i. e. – that is Dr. – Doctor Oct. — October
Composition l l is the way of word-building when a word is formed by joining two or more stems to form one word one of the most productive ways of wordbuilding in Modern English
Compound Words consist of at least two stems which occur in the language as free forms e. g. a brother-in-law, airbus, snow-white l
Criteria for Distinguishing between a Compound a Word-combination l l Compound Word graphic criterion: solid or hyphenated spelling e. g. sunbeam, warship semantic criterion: conveys one concept e. g. a green-house l l Word-Combination graphic criterion: spelling with a break e. g. a tall boy semantic criterion: conveys more than one concept e. g. a green house
Criteria for Distinguishing between a Compound a Word-combination Compound Word l phonetic criterion: a single uniting stress e. g. a ´greenhouse Word-Combination l phonetic criterion: each word in a group has a stress e. g. a ´green ´house
Criteria for Distinguishing between a Compound a Word-combination l Compound Word morphological and syntactic criteria: — only one component changes grammatically e. g. a tallboy – tallboys, a passer-by – passers-by Word-Combination l morphological and syntactic criteria: — each constituent is independent and open to grammatical changes e. g. a tall boy – They were the tallest boys in their form.
Criteria for Distinguishing between a Compound a Word-combination l Compound Word morphological and syntactic criteria: — no word can be inserted between the components Word-Combination l morphological and syntactic criteria: — other words may be inserted between the constituent parts e. g. a tall handsome boy
Classifications of Compounds l l l according to the parts of speech according to the joining element according to the structure of compounds according to the degree of semantic independence according to the order of components according to the motivation of the meaning of compounds
Classification of compounds according to the part of speech nouns and adjectives e. g. baby-sitter, power-hungry (энергоемкий) l adverbs and prepositions e. g. indoors, within, outside l verbs (formed by means of conversion or backformation) e. g. to handcuff hand-cuffs, to babysit baby-sitter l
Classification according to the joining element l neutral compounds are formed by joining two stems together without any joining morpheme e. g. classroom, dancing-hall l syntactical compounds – components are joined by means of form-word stems e. g. here-and-now, free-for-all
Classification according to the joining element l morphological compounds – components are joined by a linking element: — vowel “o”, “I” e. g. speedometer, handicraft — consonant “s” e. g. sportsman
Classification according to the structure of compounds l l compound words proper – formed by juxtaposition of two stems without any linking element e. g. top-notch (первоклассный), tiptop compound-affixed words – e. g. honeymooner
Classification according to the structure of compounds l l compound words consisting of three or more stems — e. g. eggshell-thin, cornflower-blue compound-shortened words – e. g. V-day, landsat
Classification according to the degree of semantic independence Subordinative Compound is a compound whose components are neither structurally nor semantically equal in importance, and one of them dominates the other e. g. color-blind, evergreen l Coordinative Compound is a compound whose components are structurally and semantically independent and constitutes two structural and semantic centers e. g. actor-manager l
Classification according to the order of components Syntactic Compound l is a compound that conforms to grammatical patterns current in the language e. g. northwest, for-free, maybe, killjoy, seashore Asyntactic Compound l is a compound that does not conform to grammatical patterns current in the language e. g. to babysit (to sit with a baby), rope-like (like a rope)
Classification according to the motivation of the meaning of compounds Idiomatic Compound l is a compound whose meaning is not deducible from the meaning of its components e. g. wallflower – Noun, a person, esp. a woman, who is not invited to dance at a party fifty-fifty – Adv. , being equally likely and unlikely butter-fingers – noun, a clumsy person Non-idiomatic Compound l is a compound whose meaning is deducible from the meaning of its components e. g. mother-in-law, day-long
Ways of forming compound words l l l reduplication – e. g. too-too, hush-hush partial conversion from word-groups e. g. can-do (исполнительный и энергичный) can do backformation from compound nouns and wordgroups e. g. to baby-sitter vowel interchange (ablaut compounds) e. g. chit-chat (сплетни), tip-top, riff-raff (сброд) rhyme compounds – e. g. willy-nilly (волей-неволей), hoity-toity(надменный)
Peculiarities of English Compounds l l l all components of compound words are free forms, can be used independently with a distinct meaning of their own e. g. motherland, day-off, everybody usually are two-stem compounds attributive compounds e. g. last-minute changes, four-year course
Sound Interchange l way of forming new words with the help of change of sounds within a word
Types of Sound Interchange l l l vowel change – e. g. full – to fill, blood – to bleed consonant interchange – e. g. to speakspeech, advice – to advise the combination of vowel and consonant change – e. g. life – to live, strong strength
Stress Interchange l e. g. ´import — to im´port, ´suspect – to sus´pect
Lexicalization of Grammatical Form l way of creating new words with the help of suffix “s” e. g. glass – glasses, custom – customs, colour — colours
Backformation l way of creating new words by subtracting a real or supposed suffix from the original word e. g. to beggar, to editor, to burgler
Sound Imitation (Onomatopoeia) l way of forming new words by imitating different kinds of sounds that may be produced by animals, birds, insects, human being and inanimate objects e. g. buzz, croak, moo, mew, purr, roar e. g. clink, whip, splash, bubble e. g. giggle, mutter, babble