The C# programming language includes capabilities that make working with Microsoft Office API objects easier. With the advent of named and optional arguments, introduction of the dynamic type in .NET, and the ability to pass arguments to the reference parameters in COM methods, C# 4.0 quickly became the language of choice for working with COM and Interop objects.
This article talks about office interop objects in C# and how you can use them to interact with Microsoft Word and Microsoft Excel. Code examples are also provided to illustrate the concepts covered.
Prerequisites for working with Interop Objects
Visual Studio 2019 or Visual Studio 2022 must be installed on your computer to work with the code samples demonstrated in this C# tutorial. In this example, we will be using Visual Studio 2022. If you don’t have it installed in your computer, you can download it from here.
As of this writing, Visual Studio 2022 RC 2 has been released. You should also have Microsoft Office Excel 2007 or Microsoft Office Word 2007 (or their later versions) installed on your computer.
Read: Code Refactoring Tips for C#.
How to Create a New Console Application in Visual Studio
In this section we will examine how we can create a new console application project in Visual Studio 2022. Assuming Visual Studio 2022 is installed on your system, adhere to the steps given below to create a new Console Application project:
- Start the Visual Studio 2022 IDE.
- Click on “Create new project.”
- In the “Create new project” page, select C# in the language drop down list, Windows from the Platforms list and Console from the “Project types” list.
- Select Console App (.NET Framework) from the project templates displayed.
- Click Next.
- In the “Configure your new project” screen, specify the project’s name and the location where you would want the project to be created.
- Before you move on to the next screen, you can optionally select the “Place solution and project in the same directory” checkbox.
- Click Next.
- In the Additional Information screen, specify the Framework version you would like to use. We will use .NET Framework 4.8 in this example.
- Click Create to complete the process.
This will create a new .NET Framework Console application project in Visual Studio 2022. We will use this project in the sections that follow.
Install NuGet Packages
Install the following libraries from NuGet using the NuGet Package Manager or from the NuGet Package Manager Console:
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel
Read: Working with C# Math Operators.
How to Program Office Interop Objects in C#
In this section we will examine how to work with Office Interop objects and use them to connect to Microsoft Word and Excel and read/write data.
You must add the following using directives in your program for working with Word and Excel respectively when using Office interop objects:
using Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel; using Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word;
Working with Excel Interop Objects in C#
To begin, create a new Excel document named Test.xslx as a sample Excel file present in the root directory of the D:> drive. We will use this file in the following example.
You should create an instance of the Application class pertaining to the Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel library for communicating with Excel. To do this, write the following C# code:
Application excelApplication = new Application();
The next step is to create an instance of the Workbook class to access a Workbook in Excel. You can create an instance of Workbook using the following code:
Workbook excelWorkBook = excel.Workbooks.Open(@"D:Test.xslx");
To read the name of the workbook, you can use the Name property of the workbook instance as shown in the code snippet given below:
string workbookName = excelWorkBook.Name;
The following code listing illustrates how you can display the value of the first cell of the first worksheet of the Excel document:
int worksheetcount = excelWorkBook.Worksheets.Count;
if (worksheetcount > 0) {
Worksheet worksheet = (Worksheet) excelWorkBook.Worksheets[1];
string worksheetName = worksheet.Name;
var data = ((Range) worksheet.Cells[row, column]).Value;
Console.WriteLine(data);
} else {
Console.WriteLine("No worksheets available");
}
Here’s the complete code listing for your reference:
using Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel;
using Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word;
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace OfficeInteropDemoApp
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string filename = @"D:Test.xlsx";
DisplayExcelCellValue(filename, 1, 1);
Console.Read();
}
static void DisplayExcelCellValue(string filename,
int row, int column)
{
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application
excelApplication = null;
try
{
excelApplication = new
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application();
Workbook excelWorkBook =
excelApplication.Workbooks.Open(filename);
string workbookName = excelWorkBook.Name;
int worksheetcount = excelWorkBook.Worksheets.Count;
if (worksheetcount > 0)
{
Worksheet worksheet =
(Worksheet)excelWorkBook.Worksheets[1];
string firstworksheetname = worksheet.Name;
var data = ((Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Range)
worksheet.Cells[row, column]).Value;
Console.WriteLine(data);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("No worksheets available");
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
finally
{
if (excelApplication != null)
{
excelApplication.Quit();
Marshal.FinalReleaseComObject(excelApplication);
}
}
}
}
}
Refer to the code listing given above. Note, the finally block of the DisplayExcelCellValue method. The Quit method is called on the Excel application instance to stop the application. Finally, a call to Marshall.FinalReleaseComObject sets the reference counter of the Excel application instance to 0.
The following code listing illustrates how you can create a new Excel document using Office Interop in C#. Note how a new workbook has been created:
static void CreateExcelDocument()
{
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application excelApplication = null;
try {
excelApplication = new
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application();
Workbook excelWorkBook = excelApplication.Workbooks.Add();
Worksheet worksheet = (Worksheet) excelWorkBook.Worksheets[1];
worksheet.Cells[1, 1] = "Product Id";
worksheet.Cells[1, 2] = "Product Name";
worksheet.Cells[2, 1] = "1";
worksheet.Cells[2, 2] = "Lenovo Laptop";
worksheet.Cells[3, 1] = "2";
worksheet.Cells[3, 2] = "DELL Laptop";
excelWorkBook.SaveAs(@"D:Test.xls");
}
catch(Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
finally {
if (excelApplication != null) {
excelApplication.Quit();
Marshal.FinalReleaseComObject(excelApplication);
}
}
}
When you run this code, a new Excel document will be created at the path specified with the following content inside:
Read: Working with Strings in C#.
Working with Word Interop Objects in C#
To work with Microsoft Word, you would need to create an instance of Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application. Like Excel, this instance would be used to communicate with a Word document.
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application wordApplication = new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application();
The next step is to create a document instance using the Documents property of the Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application instance we just created, as shown in the C# code snippet given below:
wordApplication.Documents.Add();
Next, you can create a paragraph and add some text to it using the as shown in the code snippet shown below:
var paragraph = document.Paragraphs.Add(); paragraph.Range.Text = "This is a sample text to demonstrate how Interop works...";
Then you can save the Word document using this code:
wordApplication.ActiveDocument.SaveAs(@"D:Test.doc", WdSaveFormat.wdFormatDocument);
Here is the complete code listing showing how to work with Microsoft Word Interop Objects in C# for your reference:
using Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel;
using Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word;
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace OfficeInteropDemoApp
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string filename = @"D:Test.doc";
CreateWordDocument(filename);
Console.Read();
}
static void CreateWordDocument(string filename)
{
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application
wordApplication = null;
try
{
wordApplication = new
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application();
var document = wordApplication.Documents.Add();
var paragraph = document.Paragraphs.Add();
paragraph.Range.Text = "This is a sample text to
demonstrate how Interop works...";
wordApplication.ActiveDocument.SaveAs(filename,
WdSaveFormat.wdFormatDocument);
document.Close();
}
finally
{
if (wordApplication != null)
{
wordApplication.Quit();
Marshal.FinalReleaseComObject(wordApplication);
}
}
}
}
}
To read a Word document and display each word of the document you can use the following C# code:
static void ReadWordDocument(string filename)
{
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application
wordApplication = null;
try
{
wordApplication = new
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application();
Document document =
wordApplication.Documents.Open(filename);
int count = document.Words.Count;
for (int i = 1; i <= count; i++)
{
string text = document.Words[i].Text;
Console.WriteLine(text);
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
Console.Write(ex.Message);
}
finally
{
if (wordApplication != null)
{
wordApplication.Quit();
Marshal.FinalReleaseComObject(wordApplication);
}
}
}
Note how the Words property of the Word application instance has been used to retrieve the words contained in the document.
C# Interop Objects Tutorial
In this article we have examined how we can access Microsoft Office Interop objects using C#. Since there is still no support for working with Interop objects in .NET Core, we have created a .NET Framework Console Application in this example.
<< Back to C-SHARP
Use Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word. Open a DOC file and read the text in it.
Microsoft Word can be used with C# code. You have a Microsoft Word document (.doc) and want to read it in your C# program. With the Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word assembly, we get the contents and formatting from the document.
Tip: Add the Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word assembly to your project. Go to Project -> Add Reference.
Example. First, we show the file we will read. It contains three paragraphs containing one word each. The program first instantiates an Application instance and then we call Documents.Open on that variable.
Next: We loop through the Words collection and read the Text property on each element. We then display and call Quit.
Word document: word.doc
One
Two
three
C# program that uses Microsoft Word interop
using System;
using Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// Open a doc file.
Application application = new Application();
Document document = application.Documents.Open(«C:\word.doc»);
// Loop through all words in the document.
int count = document.Words.Count;
for (int i = 1; i <= count; i++)
{
// Write the word.
string text = document.Words[i].Text;
Console.WriteLine(«Word {0} = {1}», i, text);
}
// Close word.
application.Quit();
}
}
Output
Word 1 = One
Word 2 =
Word 3 = Two
Word 4 =
Word 5 = three
Word 6 =
Empty paragraphs. We see that Word 2, Word 4, and Word 6 are empty. The empty paragraphs in the input file are considered words. If you have multiple words in a paragraph, they will each be separate in the Words collection.
So: In Interop.Word, a paragraph is made up of a collection of one or more words.
Quit. Why is the application.Quit statement important? If you don’t include this, the WINWORD.EXE application will remain in the process list. Then, when this program is run again, a new one will be started. This wastes memory.
Note: It is important to iterate on Words from 1 to Count inclusive. Correction suggested by Robert Ford.
Summary. We looked at the Microsoft.Office Interop.Word assembly and learned how to read in data from a Word document. This can be useful when you have DOC or DOCX files and want to programmatically read in data from your C# program.
Related Links:
- C# ContainsValue Method (Value Exists in Dictionary)
- C# ContextMenuStrip Example
- C# Normalize, IsNormalized Methods
- C# continue Keyword
- C# Control: Windows Forms
- C# File.Open Examples
- C# Null String Example
- C# null Keyword
- C# Windows Forms Controls
- C# File.ReadAllBytes, Get Byte Array From File
- C# Nullable Examples
- C# NullReferenceException and Null Parameter
- C# File.ReadAllLines, Get String Array From File
- C# Object Array
- C# Color Table
- C# Convert Char Array to String
- C# File.ReadAllText, Get String From File
- C# Obsolete Attribute
- C# Color Examples: FromKnownColor, FromName
- C# ColorDialog Example
- C# Comment: Single Line and Multiline
- C# Concat Extension: Combine Lists and Arrays
- C# Conditional Attribute
- C# Console Color, Text and BackgroundColor
- C# String Clone() method
- C# Convert Char to String
- C# Convert Days to Months
- C# File.ReadLines, Use foreach Over Strings
- C# File.Replace Method
- C# FileInfo Length, Get File Size
- C# FileInfo Examples
- C# StreamReader ReadLine, ReadLineAsync Examples
- C# readonly Keyword
- C# Aggregate: Use Lambda to Accumulate Value
- C# AggressiveInlining: MethodImpl Attribute
- C# Multidimensional Array
- C# MultiMap Class (Dictionary of Lists)
- C# Anagram Method
- C# Recursion Example
- C# And Bitwise Operator
- C# Regex, Read and Match File Lines
- C# Regex Groups, Named Group Example
- C# Anonymous Function (Delegate With No Name)
- C# Any Method, Returns True If Match Exists
- C# Regex.Matches Quote Example
- C# StringBuilder Append and AppendLine
- C# Optimization
- C# StringBuilder AppendFormat
- ASP.NET appSettings Example
- C# ArgumentException: Invalid Arguments
- C# Regex.Matches Method: foreach Match, Capture
- C# File Handling
- C# Filename With Date Example (DateTime.Now)
- C# FileNotFoundException (catch Example)
- C# FileStream Length, Get Byte Count From File
- C# Convert String to Byte Array
- C# FileStream Example, File.Create
- C# FileSystemWatcher Tutorial (Changed, e.Name)
- C# finally Keyword
- C# String Format
- C# String Replace() method
- C# Sum Method: Add up All Numbers
- C# Switch Char, Test Chars With Cases
- C# Switch Enum
- C# String Split() method
- C# String StartsWith() method
- C# String SubString() method
- C# System (using System namespace)
- C# Partial Types
- C# Tag Property: Windows Forms
- C# Iterators
- C# TextInfo Examples
- C# TextReader, Returned by File.OpenText
- C# Delegate Covariance
- C# Delegate Inference
- C# Array.ConvertAll, Change Type of Elements
- HelpProvider Control Use
- C# SplitContainer: Windows Forms
- C# SqlClient Tutorial: SqlConnection, SqlCommand
- C# SqlCommand Example: SELECT TOP, ORDER BY
- C# SqlCommandBuilder Example: GetInsertCommand
- C# SqlConnection Example: Using, SqlCommand
- C# SqlDataAdapter Example
- C# SqlDataReader: GetInt32, GetString
- C# SqlParameter Example: Constructor, Add
- C# Array.Copy Examples
- C# Array.CreateInstance Method
- C# HTML and XML Handling
- C# HtmlEncode and HtmlDecode
- C# HtmlTextWriter Example
- C# Array and Dictionary Test, Integer Lookups
- C# HttpUtility.HtmlEncode Methods
- C# HybridDictionary
- C# String ToCharArray() method
- C# Array.Exists Method, Search Arrays
- C# default Operator
- C# Func Object (Lambda That Returns a Value)
- C# GC.Collect Examples: CollectionCount, GetTotalMemory
- C# Path.GetDirectoryName (Remove File From Path)
- C# goto Examples
- C# Array.Find Examples, Search Array With Lambda
- C# Array.ForEach: Use Lambda on Every Element
- C# DefaultIfEmpty Method
- C# HttpClient Example: System.Net.Http
- C# Array Versus List Memory Usage
- C# Define and Undef Directives
- ASP.NET HttpContext Request Property
- C# Stack Collection: Push, Pop
- C# Static List: Global List Variable
- C# Static Regex
- C# Array Property, Return Empty Array
- C# Destructor
- C# Constructor Examples
- C# Contains Extension Method
- C# String GetTypeCode() method
- C# String ToLowerInvariant() method
- C# Customized Dialog Box
- C# DataColumn Example: Columns.Add
- C# DataGridView Add Rows
- DataGridView Columns, Edit Columns Dialog
- C# DataGridView Row Colors (Alternating)
- C# DataGridView Tutorial
- C# DataGridView
- C# DataRow Examples
- C# DataSet Examples
- C# DataSource Example
- C# DataTable Compare Rows
- C# DataTable foreach Loop
- C# DataTable RowChanged Example: AcceptChanges
- C# DataTable Select Example
- C# DataTable Examples
- C# DataView Examples
- C# OfType Examples
- C# OpenFileDialog Example
- C# operator Keyword
- C# Odd and Even Numbers
- C# BaseStream Property
- C# Console.Beep Example
- C# Bitwise Or
- C# orderby Query Keyword
- C# Benchmark
- C# String ToUpperInvariant() method
- C# String Trim() method
- C# out Parameter
- C# BinaryReader Example (Use ReadInt32)
- C# OutOfMemoryException
- C# BinaryWriter Type
- C# BitArray Examples
- C# BitConverter Examples
- C# Bitcount Examples
- C# OverflowException
- C# Overload Method
- C# Static String
- C# First Sentence
- C# Regex.Replace, Matching End of String
- C# Regex.Replace, Remove Numbers From String
- C# Anonymous Types
- C# FirstOrDefault (Get First Element If It Exists)
- C# Fisher Yates Shuffle: Generic Method
- C# fixed Keyword (unsafe)
- C# Flatten Array (Convert 2D to 1D)
- C# Regex.Replace, Merge Multiple Spaces
- C# Regex.Replace Examples: MatchEvaluator
- C# Extension Methods
- C# Query Expression
- C# First Words in String
- C# First (Get Matching Element With Lambda)
- C# Regex.Split, Get Numbers From String
- C# Partial Method
- C# ContainsKey Method (Key Exists in Dictionary)
- C# Regex.Split Examples
- C# Regex Trim, Remove Start and End Spaces
- C# Implicitly Typed Local Variable
- C# Object and Collection Initializer
- C# RegexOptions.Compiled
- C# Auto Implemented Properties
- C# Dynamic Binding
- C# Named and Optional Arguments
- C# Asynchronous Methods
- C# Convert ArrayList to Array (Use ToArray)
- C# RegexOptions.IgnoreCase Example
- C# New Features | C# Version Features
- C# Programs
- C# Caller Info Attributes
- C# Convert ArrayList to List
- C# Convert Bool to Int
- C# RegexOptions.Multiline
- C# Using Static Directive
- C# Convert Bytes to Megabytes
- C# Region and endregion
- C# Remove Char From String at Index
- C# Exception Filters
- C# DialogResult: Windows Forms
- C# Dictionary, Read and Write Binary File
- C# Array Examples, String Arrays
- C# ArrayList Examples
- C# ArraySegment: Get Array Range, Offset and Count
- C# break Statement
- C# Buffer BlockCopy Example
- C# BufferedStream: Optimize Read and Write
- IL Disassembler Tutorial
- C# Intermediate Language (IL)
- C# new Keyword
- C# NotifyIcon: Windows Forms
- C# NotImplementedException
- C# Null Array
- C# static Keyword
- C# StatusStrip Example: Windows Forms
- C# Dictionary Memory
- C# Dictionary Optimization, Increase Capacity
- 404 Not Found
- C# 24 Hour Time Formats
- C# Dictionary Optimization, Test With ContainsKey
- C# String Chars (Get Char at Index)
- C# DictionaryEntry Example (Hashtable)
- C# Directives
- C# String GetType() method
- C# Directory.CreateDirectory, Create New Folder
- C# Directory.GetFiles Example (Get List of Files)
- C# DivideByZeroException
- C# DllImport Attribute
- C# Do While Loop Example
- C# CharEnumerator
- C# Chart, Windows Forms (Series and Points)
- C# CheckBox: Windows Forms
- C# Await in Catch Finally Blocks
- C# Increment String That Contains a Number
- C# Increment, Preincrement and Decrement Ints
- C# String ToString() method
- C# String ToUpper() method
- C# class Examples
- Dot Net Perls
- C# Indexer Examples (This Keyword, get and set)
- C# Default Values for Getter Only Properties
- C# Digit Separator
- C# Clear Dictionary: Remove All Keys
- C# Clone Examples: ICloneable Interface
- C# Closest Date (Find Dates Nearest in Time)
- C# Expression Bodied Members
- C# DateTime.MinValue (Null DateTime)
- C# DateTime.Month Property
- C# Combine Arrays: List, Array.Copy and Buffer.BlockCopy
- C# Combine Dictionary Keys
- C# ComboBox: Windows Forms
- C# IndexOutOfRangeException
- C# Inheritance
- C# Null Propagator
- C# CompareTo Int Method
- C# Comparison Object, Used With Array.Sort
- C# Insert String Examples
- C# int Array
- C# String Interpolation
- C# nameof operator
- C# DateTime.Parse: Convert String to DateTime
- C# DateTime Subtract Method
- C# Compress Data: GZIP
- C# Interface Examples
- C# Interlocked Examples: Add, CompareExchange
- C# Dictionary Initializer
- C# 2D Array Examples
- 7 Zip Command Line Examples
- C# 7 Zip Executable (Process.Start)
- C# Decompress GZIP
- C# Remove Duplicates From List
- C# dynamic Keyword
- C# Null Coalescing and Null Conditional Operators
- C# Null List (NullReferenceException)
- C# DayOfWeek
- C# Remove Element
- C# Pattern Matching
- C# Tuples
- C# Enum.Format Method (typeof Enum)
- C# Enum.GetName, GetNames: Get String Array From Enum
- C# Enum.Parse, TryParse: Convert String to Enum
- C# stackalloc Operator
- C# Deconstruction
- C# Remove HTML Tags
- C# Local Functions
- C# ElementAt, ElementAtOrDefault Use
- C# Error and Warning Directives
- C# ErrorProvider Control: Windows Forms
- C# Remove String
- C# StackOverflowException
- C# Program to swap numbers without third variable
- C# Binary Literals
- C# event Examples
- C# Program to convert Decimal to Binary
- C# Ref Returns and Locals
- C# Encapsulate Field
- C# Enum Array Example, Use Enum as Array Index
- C# enum Flags Attribute Examples
- C# IndexOf Examples
- C# IndexOfAny Examples
- C# Initialize Array
- C# Get Every Nth Element From List (Modulo)
- C# Excel Interop Example
- C# StartsWith and EndsWith String Methods
- C# Static Array
- C# Program to Convert Number in Characters
- C# Expression Bodied Constructors and Finalizers
- C# Initialize List
- C# InitializeComponent Method: Windows Forms
- C# Numeric Casts
- C# NumericUpDown Control: Windows Forms
- C# object.ReferenceEquals Method
- C# Object Examples
- C# Optional Parameters
- C# Except (Remove Elements From Collection)
- C# Static Dictionary
- C# Program to Print Alphabet Triangle
- C# Expression Bodied Getters and Setters
- C# Prime Number
- C# Reserved Filenames
- C# Program to print Number Triangle
- C# Async Main
- C# Default Expression
- C# Inline Optimization
- C# Override Method
- C# Enum ToString: Convert Enum to String
- C# enum Examples
- C# Enumerable.Range, Repeat and Empty
- C# Dictionary Equals: If Contents Are the Same
- C# Dictionary Versus List Loop
- C# Dictionary Order, Use Keys Added Last
- C# Dictionary Size and Performance
- C# Dictionary Versus List Lookup Time
- C# Dictionary Examples
- C# Get Directory Size (Total Bytes in All Files)
- C# Directory Type
- C# Distinct Method, Get Unique Elements Only
- C# Divide by Powers of Two (Bitwise Shift)
- C# Divide Numbers (Cast Ints)
- C# DomainUpDown Control Example
- C# Double Type: double.MaxValue, double.Parse
- C# Environment Type
- C# Main args Examples
- C# All Method: All Elements Match a Condition
- C# Alphabetize String
- C# Alphanumeric Sorting
- C# EventLog Example
- C# PadRight and PadLeft: String Columns
- C# Arithmetic Expression Optimization
- C# Array.AsReadOnly Method (ObjectModel)
- C# Array.BinarySearch Method
- C# Map Example
- ASP.NET MapPath: Virtual and Physical Paths
- C# Get Paragraph From HTML With Regex
- C# Array.Clear Examples
- C# Exception Handling
- C# explicit and implicit Keywords
- C# Factory Design Pattern
- C# File.Copy Examples
- C# typeof and nameof Operators
- C# string.Concat Examples
- C# String Interpolation Examples
- C# string.Join Examples
- C# String Performance, Memory Usage Info
- C# String Property
- C# String Slice, Get Substring Between Indexes
- C# String Switch Examples
- C# String
- C# StringBuilder Append Performance
- C# Mask Optimization
- C# MaskedTextBox Example
- C# Parallel.For Example (Benchmark)
- C# StringBuilder Cache
- C# Math.Abs: Absolute Value
- C# Parallel.Invoke: Run Methods on Separate Threads
- C# Array.IndexOf, LastIndexOf: Search Arrays
- C# Remove Duplicate Chars
- C# IEqualityComparer
- C# If Preprocessing Directive: Elif and Endif
- C# If Versus Switch Performance
- C# if Statement
- C# Parameter Optimization
- C# Parameter Passing, ref and out
- C# params Keyword
- C# int.Parse: Convert Strings to Integers
- C# TextWriter, Returned by File.CreateText
- C# this Keyword
- C# ThreadPool
- C# OrderBy, OrderByDescending Examples
- C# Process Examples (Process.Start)
- C# Thread Join Method (Join Array of Threads)
- C# ThreadPool.SetMinThreads Method
- C# TimeZone Examples
- Panel, Windows Forms (Create Group of Controls)
- C# Path Examples
- C# Get Percentage From Number With Format String
- ASP.NET PhysicalApplicationPath
- C# PictureBox: Windows Forms
- C# PNG Optimization
- C# Position Windows: Use WorkingArea and Location
- Visual Studio Post Build, Pre Build Macros
- C# Get Title From HTML With Regex
- C# ToArray Extension Method
- C# ProfileOptimization
- C# ProgressBar Example
- C# ToCharArray: Convert String to Array
- C# ToDictionary Method
- C# Bool Methods, Return True and False
- C# bool Sort Examples (True to False)
- C# Stopwatch Examples
- C# Stream
- C# StreamReader ReadToEnd Example (Read Entire File)
- C# StreamReader ReadToEndAsync Example (Performance)
- C# StreamReader Examples
- C# StreamWriter Examples
- C# String Append (Add Strings)
- C# Caesar Cipher
- C# String Compare and CompareTo Methods
- C# Cast Extension: System.Linq
- C# Cast to Int (Convert Double to Int)
- C# Cast Examples
- C# catch Examples
- C# String Constructor (new string)
- C# Math.Ceiling Usage
- C# return Keyword
- C# Math.Floor Method
- C# Program to generate Fibonacci Triangle
- C# String TrimEnd() method
- C# Math.Max and Math.Min Examples
- C# String Compare() method
- C# var Examples
- C# virtual Keyword
- C# void Method, Return No Value
- C# volatile Example
- C# WebBrowser Control (Navigate Method)
- C# WebClient: DownloadData, Headers
- C# Where Method and Keyword
- C# Math.Pow Method, Exponents
- C# String CompareOrdinal() method
- C# String TrimStart() method
- C# Math.Round Examples: MidpointRounding
- C# String CompareTo() method
- C# Math Type
- C# Reverse String
- C# String Concat() method
- C# Max and Min: Get Highest or Lowest Element
- C# Reverse Words
- C# Reverse Extension Method
- C# RichTextBox Example
- C# String Contains() method
- C# MemoryFailPoint and InsufficientMemoryException
- C# String CopyTo() method
- C# partial Keyword
- C# ToBase64String (Data URI Image)
- C# Path.ChangeExtension
- C# Struct Versus Class
- C# struct Examples
- C# Path Exists Example
- C# Path.GetExtension: File Extension
- C# Path.GetRandomFileName Method
- C# Pragma Directive
- C# Predicate (Lambda That Returns True or False)
- C# Pretty Date Format (Hours or Minutes Ago)
- C# PreviewKeyDown Event
- C# Substring Examples
- C# Numeric Suffix Examples
- C# switch Examples
- C# Convert Degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit
- C# Convert Dictionary to List
- C# Convert Dictionary to String (Write to File)
- C# Convert List to Array
- C# Convert List to DataTable (DataGridView)
- C# Convert List to String
- C# Convert Miles to Kilometers
- C# Convert Milliseconds, Seconds, Minutes
- C# Convert Nanoseconds, Microseconds, Milliseconds
- C# Console.Read Method
- C# Console.ReadKey Example
- C# Console.ReadLine Example (While Loop)
- C# Console.SetOut and Console.SetIn
- C# Intersect: Get Common Elements
- C# InvalidCastException
- C# InvalidOperationException: Collection Was Modified
- C# Console.WindowHeight
- C# DriveInfo Examples
- C# IOException Type: File, Directory Not Found
- C# Right String Part
- C# RNGCryptoServiceProvider Example
- C# Property Examples
- C# PropertyGrid: Windows Forms
- C# Protected and internal Keywords
- C# Public and private Methods
- C# Console.Write, Append With No Newline
- C# Console.WriteLine (Print)
- C# DropDownItems Control
- C# IOrderedEnumerable (Query Expression With orderby)
- C# is: Cast Examples
- C# Remove Punctuation From String
- C# Query Windows Forms (Controls.OfType)
- C# Queryable: IQueryable Interface and AsQueryable
- ASP.NET QueryString Examples
- C# Queue Collection: Enqueue
- C# const Example
- C# Constraint Puzzle Solver
- C# IComparable Example, CompareTo: Sort Objects
- C# RadioButton Use: Windows Forms
- C# ReadOnlyCollection Use (ObjectModel)
- C# Recursion Optimization
- C# Recursive File List: GetFiles With AllDirectories
- C# ref Keyword
- C# Reflection Examples
- C# Regex.Escape and Unescape Methods
- C# Count Characters in String
- C# Count, Dictionary (Get Number of Keys)
- C# IDictionary Generic Interface
- C# IEnumerable Examples
- C# IsFixedSize, IsReadOnly and IsSynchronized Arrays
- C# Count Letter Frequencies
- C# IList Generic Interface: List and Array
- C# string.IsNullOrEmpty, IsNullOrWhiteSpace
- C# IsSorted Method: If Array Is Already Sorted
- C# ROT13 Method, Char Lookup Table
- C# StringBuilder Examples
- C# StringComparison and StringComparer
- C# StringReader Class (Get Parts of Strings)
- C# Count Extension Method: Use Lambda to Count
- C# Image Type
- C# ImageList Use: Windows Forms
- C# string.Copy Method
- C# CopyTo String Method: Put Chars in Array
- C# value Keyword
- C# Empty String Examples
- C# ValueTuple Examples (System.ValueTuple, ToTuple)
- C# ValueType Examples
- C# String Equals Examples
- C# String For Loop, Count Spaces in String
- C# string.Intern and IsInterned
- C# Variable Initializer for Class Field
- C# String IsUpper, IsLower
- C# String Length Property: Get Character Count
- C# Token
- C# String EndsWith() method
- C# ToList Extension Method
- C# String Equals() method
- C# String IsNormalized() method
- C# ToLookup Method (Get ILookup)
- C# String Format() method
- C# ToLower and ToUpper: Uppercase and Lowercase Strings
- C# String IndexOf() method
- C# TabControl: Windows Forms
- TableLayoutPanel: Windows Forms
- ToolStripContainer Control: Dock, Properties
- C# ToolTip: Windows Forms
- C# ToString Integer Optimization
- C# String Insert() method
- C# Take and TakeWhile Examples
- C# Task Examples (Task.Run, ContinueWith and Wait)
- C# Ternary Operator
- C# Text Property: Windows Forms
- C# TextBox.AppendText Method
- C# TextBox Example
- C# TextChanged Event
- C# TextFieldParser Examples: Read CSV
- C# ToString: Get String From Object
- C# String Intern(String str) method
- C# String IsInterned() method
- C# ToTitleCase Method
- C# TrackBar: Windows Forms
- C# Tree and Nodes Example: Directed Acyclic Word Graph
- C# TreeView Tutorial
- C# String Normalize() method
- C# Convert String Array to String
- C# Jagged Array Examples
- C# MemoryStream: Use Stream on Byte Array
- C# MenuStrip: Windows Forms
- C# int.MaxValue, MinValue (Get Lowest Number)
- C# Program to reverse number
- C# Modulo Operator: Get Remainder From Division
- C# MonthCalendar Control: Windows Forms
- C# Int and uint Types
- C# Integer Append Optimization
- C# Keywords
- C# Label Example: Windows Forms
- C# Lambda Expressions
- C# LastIndexOf Examples
- C# Last, LastOrDefault Methods
- C# Convert TimeSpan to Long
- C# Convert Types
- C# join Examples (LINQ)
- C# Multiple Return Values
- C# Multiply Numbers
- C# Mutex Example (OpenExisting)
- C# Named Parameters
- C# String GetEnumerator() method
- C# String GetHashCode() method
- C# KeyCode Property and KeyDown
- C# namespace Keyword
- C# NameValueCollection Usage
- C# Nested Lists: Create 2D List or Jagged List
- C# Nested Switch Statement
- C# Copy Dictionary
- C# KeyNotFoundException: Key Not Present in Dictionary
- C# KeyValuePair Examples
- C# Environment.NewLine
- C# Let Keyword (Use Variable in Query Expression)
- C# Levenshtein Distance
- C# Regex Versus Loop: Use For Loop Instead of Regex
- C# Regex.Match Examples: Regular Expressions
- C# RemoveAll: Use Lambda to Delete From List
- C# Replace String Examples
- ASP.NET Response.BinaryWrite
- ASP.NET Response.Write
- C# Return Optimization: out Performance
- C# Count Elements in Array and List
- C# SelectMany Example: LINQ
- C# Sentinel Optimization
- C# SequenceEqual Method (If Two Arrays Are Equal)
- C# Shift Operators (Bitwise)
- C# Short and ushort Types
- C# Single Method: Get Element If Only One Matches
- C# SingleOrDefault
- C# Singleton Pattern Versus Static Class
- C# Singleton Class
- C# sizeof Keyword
- C# Skip and SkipWhile Examples
- C# Sleep Method (Pause)
- C# Sort Dictionary: Keys and Values
- C# String Literal: Newline and Quote Examples
- C# LinkLabel Example: Windows Forms
- C# LINQ
- C# List Add Method, Append Element to List
- C# List AddRange, InsertRange (Append Array to List)
- C# List Clear Example
- C# List Contains Method
- C# List Remove Examples
- C# List Examples
- C# ListBox Tutorial (DataSource, SelectedIndex)
- C# ListView Tutorial: Windows Forms
- C# SaveFileDialog: Use ShowDialog and FileName
- C# Scraping HTML Links
- C# sealed Keyword
- C# Seek File Examples: ReadBytes
- C# select new Example: LINQ
- C# ThreadStart and ParameterizedThreadStart
- C# Extension Method
- C# StringBuilder Capacity
- C# extern alias Example
- C# StringBuilder Clear (Set Length to Zero)
- C# StringBuilder Data Types
- C# StringBuilder Performance
- C# Select Method (Use Lambda to Modify Elements)
- C# StringBuilder Equals (If Chars Are Equal)
- C# StringBuilder Memory
- C# Convert Feet, Inches
- C# StringBuilder ToString: Get String From StringBuilder
- C# Serialize List (Write to File With BinaryFormatter)
- C# Maze Pathfinding Algorithm
- C# Memoization
- C# Memory Usage for Arrays of Objects
- C# MessageBox.Show Examples
- C# Method Call Depth Performance
- C# Method Parameter Performance
- C# Method Size Optimization
- C# throw Keyword Examples
- C# Timer Examples
- C# TimeSpan Examples
- C# StringWriter Class
- C# async, await Examples
- C# Attribute Examples
- C# Average Method
- C# BackgroundWorker
- C# base Keyword
- C# String Between, Before, After
- C# Binary Representation int (Convert, toBase 2)
- C# BinarySearch List
- C# bool Array (Memory Usage, One Byte Per Element)
- C# bool.Parse, TryParse: Convert String to Bool
- C# bool Type
- C# Change Characters in String (ToCharArray, For Loop)
- C# FromOADate and Excel Dates
- C# Char Combine: Get String From Chars
- C# Generic Class, Generic Method Examples
- C# char.IsDigit (If Char Is Between 0 and 9)
- C# CSV Methods (Parse and Segment)
- C# GetEnumerator: While MoveNext, Get Current
- C# GetHashCode (String Method)
- C# Thumbnail Image With GetThumbnailImage
- C# char.IsLower and IsUpper
- C# Character Literal (const char)
- C# DataRow Field Method: Cast DataTable Cell
- C# GetType Method
- C# Global Variable Examples (Public Static Property)
- ASP.NET Global Variables Example
- C# Char Lowercase Optimization
- C# Char Test (If Char in String Equals a Value)
- C# char.ToLower and ToUpper
- C# Get Day Count Elapsed From DateTime
- C# DateTime Format
- C# Group By Operator: LINQ
- GroupBox: Windows Forms
- C# char Examples
- C# DateTime.Now (Current Time)
- C# GroupBy Method: LINQ
- C# GroupJoin Method
- C# Array Length Property, Get Size of Array
- C# GZipStream Example (DeflateStream)
- C# abstract Keyword
- C# Action Object (Lambda That Returns Void)
- C# DateTime.Today (Current Day With Zero Time)
- C# DateTime.TryParse and TryParseExact
- C# DateTime Examples
- C# DateTimePicker Example
- C# Debug.Write Examples
- C# Visual Studio Debugging Tutorial
- C# decimal Examples
- C# HashSet Examples
- C# Hashtable Examples
- C# delegate Keyword
- C# descending, ascending Keywords
- C# while Loop Examples
- C# Whitespace Methods: Convert UNIX, Windows Newlines
- C# XmlReader, Parse XML File
- C# XmlTextReader
- C# XmlTextWriter
- C# XmlWriter, Create XML File
- C# XOR Operator (Bitwise)
- C# yield Example
- C# File.Delete
- C# File Equals: Compare Files
- C# File.Exists Method
- C# TrimEnd and TrimStart
- C# True and False
- C# Truncate String
- C# String ToLower() method
- C# History
- C# Features
- C# Variables
- C# Data Types
- C# float Numbers
- C# Settings.settings in Visual Studio
- C# Shuffle Array: KeyValuePair and List
- C# Single and Double Types
- C# try Keyword
- C# TryGetValue (Get Value From Dictionary)
- C# Tuple Examples
- C# Trim Strings
- C# String IsNullOrEmpty() method
- C# Type Class: Returned by typeof, GetType
- C# Word Count
- C# Thread Methods
- C# String IsNullOrWhiteSpace() method
- C# Single Instance Windows Form
- C# TypeInitializationException
- C# String Join() method
- C# Word Interop: Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word
- C# String LastIndexOf() method
- FlowLayoutPanel Control
- C# Focused Property
- C# FolderBrowserDialog Control
- C# Font Type: FontFamily and FontStyle
- C# FontDialog Example
- C# for Loop Examples
- C# foreach Loop Examples
- ForeColor, BackColor: Windows Forms
- C# Form: Event Handlers
- C# Contains String Method
- C# Union: Combine and Remove Duplicate Elements
- C# XElement Example (XElement.Load, XName)
- C# String LastIndexOfAny() method
- C# Snippet Examples
- C# Sort DateTime List
- C# Sort List With Lambda, Comparison Method
- C# Sort Number Strings
- C# Sort Examples: Arrays and Lists
- C# SortedDictionary
- C# SortedList
- C# SortedSet Examples
- C# Unreachable Code Detected
- C# Unsafe Keyword: Fixed, Pointers
- C# Uppercase First Letter
- C# Uri and UriBuilder Classes
- C# String PadLeft() method
- C# Split String Examples
- C# Zip Method (Use Lambda on Two Collections)
- C# String PadRight() method
- C# Nullable
- C# String Copy() method
- C# Using Alias Example
- C# using Statement: Dispose and IDisposable
- C# File.Move Method, Rename File
- C# String Remove() method
- C# Array.Resize Examples
- C# Array.Sort: Keys, Values and Ranges
- C# Operators
- C# Keywords
- C# Button Example
- C# Byte Array: Memory Usage, Read All Bytes
- C# Byte and sbyte Types
- C# Capacity for List, Dictionary
- C# Case Insensitive Dictionary
- C# case Example (Switch Case)
- C# Char Array
- C# Array.Reverse Example
- C# Random Lowercase Letter
- C# Random Paragraphs and Sentences
- C# Array Slice, Get Elements Between Indexes
- C# Array.TrueForAll: Use Lambda to Test All Elements
- C# Random String
- C# Checked and Unchecked Keywords
- C# ArrayTypeMismatchException
- C# as: Cast Examples
- C# Random Number Examples
- C# Assign Variables Optimization
- C# ASCII Table
- C# ASCII Transformation, Convert Char to Index
- C# CheckedListBox: Windows Forms
- C# AsEnumerable Method
- C# AsParallel Example
- ASP.NET AspLiteral
- C# Line Count for File
- C# Sort by File Size
- C# Line Directive
- C# Sort, Ignore Leading Chars
- C# Sort KeyValuePair List: CompareTo
- C# LinkedList
- C# Sort Strings by Length
- C# List CopyTo (Copy List Elements to Array)
- C# List Equals (If Elements Are the Same)
- C# List Find and Exists Examples
- C# List Insert Performance
- C# Thread.SpinWait Example
- ASP.NET LiteralControl Example
- C# Locality Optimizations (Memory Hierarchy)
- C# lock Keyword
- C# Long and ulong Types
- C# Loop Over String Chars: Foreach, For
- C# Loop Over String Array
- C# Math.Sqrt Method
Related Links
Adjectives
Ado
Ai
Android
Angular
Antonyms
Apache
Articles
Asp
Autocad
Automata
Aws
Azure
Basic
Binary
Bitcoin
Blockchain
C
Cassandra
Change
Coa
Computer
Control
Cpp
Create
Creating
C-Sharp
Cyber
Daa
Data
Dbms
Deletion
Devops
Difference
Discrete
Es6
Ethical
Examples
Features
Firebase
Flutter
Fs
Git
Go
Hbase
History
Hive
Hiveql
How
Html
Idioms
Insertion
Installing
Ios
Java
Joomla
Js
Kafka
Kali
Laravel
Logical
Machine
Matlab
Matrix
Mongodb
Mysql
One
Opencv
Oracle
Ordering
Os
Pandas
Php
Pig
Pl
Postgresql
Powershell
Prepositions
Program
Python
React
Ruby
Scala
Selecting
Selenium
Sentence
Seo
Sharepoint
Software
Spellings
Spotting
Spring
Sql
Sqlite
Sqoop
Svn
Swift
Synonyms
Talend
Testng
Types
Uml
Unity
Vbnet
Verbal
Webdriver
What
Wpf
Table of Contents
- Introducing Interop.Word
- Working with the Document
- Find and Replace Text
- Find and replace Bookmarks
- Convert a DOC / DOCX file to PDF
- Export a DOC / DOCX file into a PDF
- From a Byte Array
If you’re working with ASP.NET C# and you need to open, edit or otherwise access a Microsoft Word DOC or DOCX file, you can easily do that using the Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word library package. This post explains how to do so: you might find it useful in case you need to perform such task or whenever you want to read some insights regarding the process.
Introducing Interop.Word
To access the namespace from your ASP.NET project you have two main choices:
- Install the official Microsoft Office primary interop assemblies (PIAs) package on your machine by downloading and executing the runtime installer, then manually add a Reference to the Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.dll file.
- Install the appropriate NuGet package within Visual Studio using the Package Manager Console.
Needless to say, you should really go for the second option, but we’ll leave that to you.
Working with the Document
As soon as you have the namespace available, you can do the following:
|
// NS alias to avoid writing the required namespace all the time using word = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word; // […] Application app = new word.Application(); Document doc = app.Documents.Open(filePath); |
Once you have the app and the doc objects you can perform a lot of editing task, such as:
Find and Replace Text
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
var textToFind = «any source text»; var textToReplace = «any replacement text»; var matchCase = true; var matchWholeWord = true; var matchWildcards = false; var matchSoundsLike = false; var matchAllWordForms = false; var forward = true; var wrap = 1; var format = false; var replace = 2; app.Selection.Find.Execute( textToFind, matchCase, matchWholeWord, matchWildcards, matchSoundsLike, matchAllWordForms, forward, wrap, format, textToReplace, replace); |
Find and replace Bookmarks
|
var bookmarkName = «anyName»; var bookmarkNewValue = «anyValue»; if (doc.Bookmarks.Exists(bookmarkName)) { doc.Bookmarks[bookmarkName].Select(); app.Selection.TypeText(bookmarkNewValue); } |
Convert a DOC / DOCX file to PDF
Surprisingly enough, we can even do that with an one-liner thanks to the native «Save As PDF…» feature introduced with Office 2010.
|
doc.SaveAs2(«path-to-pdf-file.pdf», word.WdSaveFormat.wdFormatPDF); |
Export a DOC / DOCX file into a PDF
This one is almost identical to the previous one in terms of results.
|
doc.ExportAsFixedFormat(tmpFile, WdExportFormat.wdExportFormatPDF); |
… and so on.
For additional info regarding word-to-pdf conversion, you can also read this dedicated post: otherwise, keep reading.
What if you have the DOC or DOCX file stored outside the FileSystem, such as in blob-format within a Database? If that’s the case you need to use a temporary file, because most Office Interop methods do not support working with byte arrays, streams and so on.
Here’s a decent workaround you can use:
|
// byte[] fileBytes = getFileBytesFromDB(); var tmpFile = Path.GetTempFileName(); File.WriteAllBytes(tmpFile, fileBytes); Application app = new word.Application(); Document doc = app.Documents.Open(filePath); // .. do your stuff here … doc.Close(); app.Quit(); byte[] newFileBytes = File.ReadAllBytes(tmpFile); File.Delete(tmpFile); |
You might notice that we used the
Close()
method in order to close (and thus save) the file. In case you wan’t to save your changes to the DOC / DOCX file you opened, you need to explicitly say it by adding the
WdSaveOptions.wdDoNotSaveChanges
object parameter in the following way:
|
doc.Close(word.WdSaveOptions.wdDoNotSaveChanges); |
IMPORTANT: Do not underestimate the call to
app.Quit()
! If you don’t do that, the MS Word instance will be left open on your server (see this thread on StackOverflow for more info on that issue). If you want to be sure to avoid such dreadful scenario entirely you should strengthen the given implementation adding a try/catch fallback strategy such as the follow:
|
Application app = null; Document doc = null; try { app = new word.Application(); doc = Document doc = app.Documents.Open(filePath); // .. do your stuff here … doc.Close(); app.Quit(); } catch (Exception e) { if (doc != null) doc.Close(); if (app != null) app.Quit(); } |
Unfortunately these objects don’t implement IDisposable, otherwise it would’ve been even easier.
That’s pretty much it: happy coding!
“
Продолжаем работу над приложением и сегодня изучим способы его взаимодействия с Word. Разберем основные методы программной работы с документами такого типа и попробуем применить их на практике.
Для успешного освоения материала рекомендуем вам изучить следующие понятия:
DB (Database), БД. Организованная структура, предназначенная для хранения, изменения и обработки взаимосвязанной информации, преимущественно больших объемов
Windows Presentation Foundation. Аналог WinForms, система для построения клиентских приложений Windows с визуально привлекательными возможностями взаимодействия с пользователем, графическая (презентационная) подсистема в составе .NET Framework (начиная с версии 3.0), использующая язык XAML
Демонстрация работы с документами Word в WPF
На данном занятии будет реализована возможность экспорта данных из приложения для визуализации расходов пользователей в документ Word. Расходы каждого пользователя будут экспортироваться на отдельную страницу, названием которой будет ФИО пользователя. Расходы будут просуммированы по категориям и представлены в виде таблицы. Под таблицей будет размещена информация о максимальном и минимальном платежах данного пользователя. Основные шаги построения приложения:
- Подготовительный этап
- Реализация экспорта в документ Word
- Завершение оформления документа Word
1. Подключаем библиотеку для работы с Word
Важно
Для экспорта данных в Word используется библиотека InteropWord (Object Library), расположенная во вкладке COM
2. Добавляем кнопку экспорта
Важно
Экспорт данных в Word будет осуществляться с помощью кнопки «Экспорт в Word»
3. Подключаем пространство имен для работы с Word
Важно
Требуемое пространство имен подключается с помощью директивы using
Реализация экспорта в документ Word
1. Получаем список пользователей и категорий
Важно
Список пользователей и категорий выгружается из базы данных
2. Создаем новый документ Word
Важно
После создания экземпляра Word в приложение добавляется новый документ, с которым далее происходит работа
3. Создаем параграф для хранения названий страниц
Важно
Основной структурной единицей текста является параграф, представленный объектом Paragraph. Все абзацы объединяются в коллекцию Paragraphs, причем новые параграфы добавляются с помощью метода Add. Доступ к тексту предоставляет объект Range, являющийся свойством Paragraph, а текстовое содержание абзаца доступно через Range.Text. В данном случае для хранения ФИО каждого пользователя создается новый параграф
4. Добавляем названия страниц
Важно
В качестве названия выбирается имя пользователя, к которому применяется стиль «Title», после чего добавляется новый параграф для таблицы с платежами
5. Добавляем и форматируем таблицу для хранения информации о платежах
Важно
После создания параграфа для таблицы и получения его Range, добавляется таблица с указанием числа строк (по количеству категорий + 1) и столбцов. Последние две строчки касаются указания границ (внутренних и внешних) и выравнивания ячеек (по центру и по вертикали)
6. Добавляем названия колонок и их форматирование
Важно
Таблица состоит из трех колонок с названиями «Иконка», «Категория» и «Сумма расходов». Названия колонок выделяются жирным шрифтом и выравниваются по центру
7. Заполняем первую колонку таблицы
Важно
Положение ячейки заносится в переменную cellRange. Метод AddPicture() класса InlineShape позволяет добавить изображение в ячейку. Иконки категорий размещаются в новой папке Assets, основные шаги создания которой изображены на скриншоте
8. Форматируем первую колонку таблицы
Важно
Для первой колонки устанавливаются длина, ширина, а также горизонтальное выравнивание по центру
9. Заполняем вторую и третью колонки
Важно
Сумма платежей приводится к нужному формату с указанием единиц измерения (руб.) непосредственно в коде
Завершение оформления документа Word
1. Добавляем максимальную величину платежа
Важно
Для поиска максимального платежа сначала платежи сортируются по стоимости. В случае, если такой платеж найден, добавляется новый параграф. Получается диапазон и выводится текст с информацией о наименовании платежа, его стоимости и дате совершения. В заключение устанавливается стиль и цвет текста (красный)
2. Добавляем минимальную величину платежа
Важно
Аналогично среди всех платежей данного пользователя определяется наименьший платеж и отображается шрифтом зеленого цвета
3. Делаем заключительные шаги
Важно
По завершении работы с данными пользователя добавляется разрыв страницы. Далее, разрешается отображение таблицы по завершении экспорта. Наконец, документ сохраняется в формате .docx и .pdf
“
Вы познакомились с основными программными методами работы с документами Word в WPF. Теперь давайте перейдем от теории к практике!
Для закрепления полученных знаний пройдите тест
Выберите неверное утверждение относительно работы с документами Word:
Paragraph содержит все абзацы документа
Range предоставляет доступ к тексту абзаца
Обращение к ячейке начинается с указания номера строки
Range.Text и Paragraphs являются:
К сожалению, вы ответили неправильно
Прочитайте лекцию и посмотрите видео еще раз
Но можно лучше. Прочитайте лекцию и посмотрите видео еще раз
Вы отлично справились. Теперь можете ознакомиться с другими компетенциями
Большинству операций, выполняемых программным способом, есть эквиваленты в пользовательском интерфейсе (UI), доступные как команды в меню и на панелях инструментов. Также существует нижележащая архитектура, обеспечивающая поддержку команд, выбираемых из UI. Всякий раз, когда вы создаете новый документ Word, он базируется на каком-либо шаблоне; расширение файлов шаблонов «.dot», а файлы документов – «.doc». Шаблон Word может содержать текст, код, стили, панели инструментов, элементы автотекста, комбинации клавиш для быстрого доступа к командам. Новый документ связывается с шаблоном и получает полный доступ к его элементам. Если вы не указываете конкретный шаблон, новый документ создается на основе стандартного шаблона «Normal.dot», который устанавливается при установке Word).
Шаблон Normal.dot является глобальным, он доступен любому документу, который вы создаете. Вы могли бы при желании поместить весь свой код в Normal.dot и создавать все документы в своей среде на основе собственного шаблона Normal (Обычный). Но тогда его файл мог бы стать чрезмерно большим, поэтому более эффективное решение для многих разработчиков — создание собственных шаблонов для конкретных приложений. В документах, создаваемых на основе вашего шаблона, код из стандартного шаблона Normal по-прежнему будет доступен. При необходимости можно связывать документ с несколькими шаблонами в дополнение к шаблону Normal.
Для работы с приложением Microsoft Word в .NET, используется объект Application, который является предком всех остальных объектов. Получив на него ссылку, вы можете работать с его методами и свойствами. Этот объект предоставляет большой набор методов и свойств, позволяющих программным путем управлять Microsoft Word. Код инициализации нового объекта Application, представлен ниже.
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application winword = new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application();
Чтобы открыть существующий документ или создать новый, необходимо создать новый объект Document.
object missing = System.Reflection.Missing.Value;
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Document document =
winword.Documents.Add(ref missing, ref missing, ref missing, ref missing);
Выполняя какую-либо операцию в пользовательском интерфейсе Word (например, добавляя верхний колонтитул), вы выделяете соответствующую секцию, используя объект «Selection», определяющий текущую позицию «невидимого» курсора и применяете к ней новый параметр форматирования с использованием объекта «Range». Данный объект представляет область в документе и может включать в себя все что угодно — от пары символов, до таблиц, закладок и много другого. Вы не ограничены одним объектом «Range» — в одном документе можно определить сразу несколько таких объектов.
//Добавление верхнего колонтитула
foreach (Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Section section in document.Sections)
{
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Range headerRange =
section.Headers[Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdHeaderFooterIndex.wdHeaderFooterPrimary].Range;
headerRange.Fields.Add(headerRange, Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdFieldType.wdFieldPage);
headerRange.ParagraphFormat.Alignment =
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdParagraphAlignment.wdAlignParagraphCenter;
headerRange.Font.ColorIndex = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdColorIndex.wdBlue;
headerRange.Font.Size = 10;
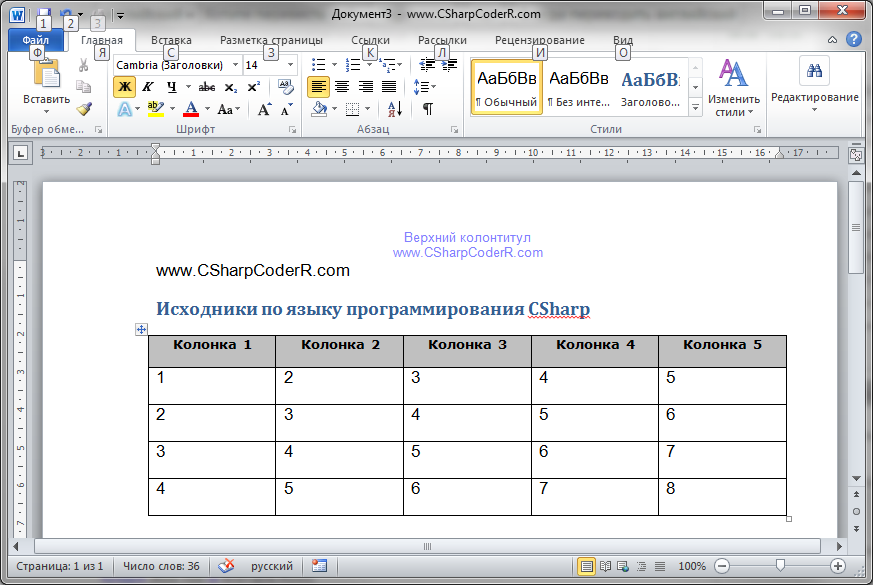
headerRange.Text = "Верхний колонтитул" + Environment.NewLine + "www.CSharpCoderR.com";
}
//Добавление нижнего колонтитула
foreach (Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Section wordSection in document.Sections)
{
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Range footerRange =
wordSection.Footers[Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdHeaderFooterIndex.wdHeaderFooterPrimary].Range;
footerRange.Font.ColorIndex = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdColorIndex.wdDarkRed;
footerRange.Font.Size = 10;
footerRange.ParagraphFormat.Alignment =
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdParagraphAlignment.wdAlignParagraphCenter;
footerRange.Text = "Нижний колонтитул" + Environment.NewLine + "www.CSharpCoderR.com";
}
Чтобы добавить текст в документ, необходимо указать позицию для вставки и сам текст.
//Добавление текста в документ document.Content.SetRange(0, 0); document.Content.Text = "www.CSharpCoderR.com" + Environment.NewLine;
Так же вы можете применить к тексту определенный стиль.
//Добавление текста со стилем Заголовок 1 Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Paragraph para1 = document.Content.Paragraphs.Add(ref missing); object styleHeading1 = "Заголовок 1"; para1.Range.set_Style(styleHeading1); para1.Range.Text = "Исходники по языку программирования CSharp"; para1.Range.InsertParagraphAfter();
В классе Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Document, присутствует коллекция «Tables», которая позволяет добавить таблицу в документ с использованием метода Add.
//Создание таблицы 5х5
Table firstTable = document.Tables.Add(para1.Range, 5, 5, ref missing, ref missing);
firstTable.Borders.Enable = 1;
foreach (Row row in firstTable.Rows)
{
foreach (Cell cell in row.Cells)
{
//Заголовок таблицы
if (cell.RowIndex == 1)
{
cell.Range.Text = "Колонка " + cell.ColumnIndex.ToString();
cell.Range.Font.Bold = 1;
//Задаем шрифт и размер текста
cell.Range.Font.Name = "verdana";
cell.Range.Font.Size = 10;
cell.Shading.BackgroundPatternColor = WdColor.wdColorGray25;
//Выравнивание текста в заголовках столбцов по центру
cell.VerticalAlignment =
WdCellVerticalAlignment.wdCellAlignVerticalCenter;
cell.Range.ParagraphFormat.Alignment =
WdParagraphAlignment.wdAlignParagraphCenter;
}
//Значения ячеек
else
{
cell.Range.Text = (cell.RowIndex - 2 + cell.ColumnIndex).ToString();
}
}
}
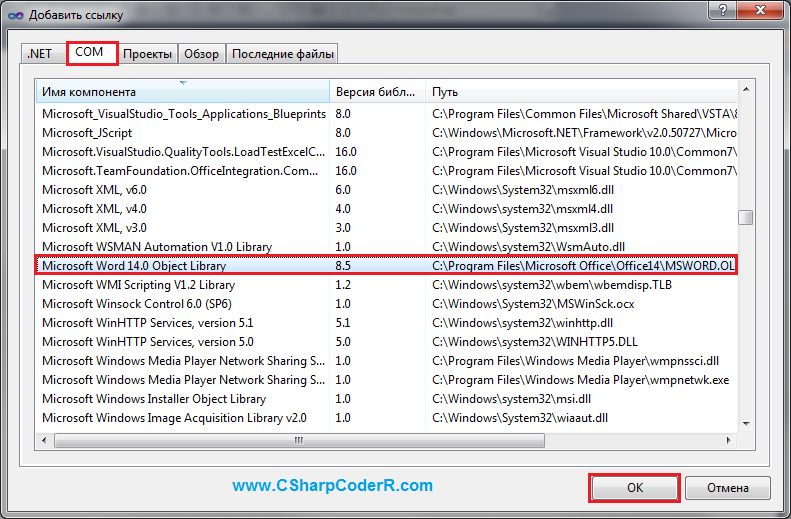
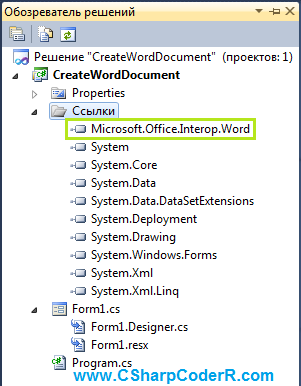
Для функционирования описанного выше кода, необходимо добавить к текущему проекту объектную библиотеку MS Word. Перейдите в меню «Проект» и выберете команду «Добавить ссылку» или в обозревателе решений, найдите пункт «Ссылки» и сделайте клик правой клавишей мыши по нему, из появившегося контекстного меню выберете соответствующий пункт.
В открывшемся окне «Добавить ссылку», перейдите на вкладку «COM» и выберете «Microsoft Word 14.0 Object Library» из предложенного списка библиотек.
В обозревателе решений у вас появится ссылка на данную библиотеку.
Перейдите в конструктор главной формы и добавьте из панели элементов, командную кнопку «Button». Данный элемент необходим для запуска процесса создания документа и вызов MS Word для отображения.
Сделайте двойной клик левой клавишей мыши по элементу «Button» и вы перейдете в автоматически созданный метод события «button1_Click». Добавьте в него приведенный ниже код.
try
{
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application winword =
new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application();
winword.Visible = false;
//Заголовок документа
winword.Documents.Application.Caption = "www.CSharpCoderR.com";
object missing = System.Reflection.Missing.Value;
//Создание нового документа
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Document document =
winword.Documents.Add(ref missing, ref missing, ref missing, ref missing);
//добавление новой страницы
//winword.Selection.InsertNewPage();
//Добавление верхнего колонтитула
foreach (Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Section section in document.Sections)
{
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Range headerRange = section.Headers[
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdHeaderFooterIndex.wdHeaderFooterPrimary].Range;
headerRange.Fields.Add(
headerRange, Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdFieldType.wdFieldPage);
headerRange.ParagraphFormat.Alignment =
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdParagraphAlignment.wdAlignParagraphCenter;
headerRange.Font.ColorIndex =
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdColorIndex.wdBlue;
headerRange.Font.Size = 10;
headerRange.Text = "Верхний колонтитул" + Environment.NewLine + "www.CSharpCoderR.com";
}
//Добавление нижнего колонтитула
foreach (Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Section wordSection in document.Sections)
{
//
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Range footerRange =
wordSection.Footers[Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdHeaderFooterIndex.wdHeaderFooterPrimary].Range;
//Установка цвета текста
footerRange.Font.ColorIndex = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdColorIndex.wdDarkRed;
//Размер
footerRange.Font.Size = 10;
//Установка расположения по центру
footerRange.ParagraphFormat.Alignment =
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdParagraphAlignment.wdAlignParagraphCenter;
//Установка текста для вывода в нижнем колонтитуле
footerRange.Text = "Нижний колонтитул" + Environment.NewLine + "www.CSharpCoderR.com";
}
//Добавление текста в документ
document.Content.SetRange(0, 0);
document.Content.Text = "www.CSharpCoderR.com" + Environment.NewLine;
//Добавление текста со стилем Заголовок 1
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Paragraph para1 = document.Content.Paragraphs.Add(ref missing);
object styleHeading1 = "Заголовок 1";
para1.Range.set_Style(styleHeading1);
para1.Range.Text = "Исходники по языку программирования CSharp";
para1.Range.InsertParagraphAfter();
//Создание таблицы 5х5
Table firstTable = document.Tables.Add(para1.Range, 5, 5, ref missing, ref missing);
firstTable.Borders.Enable = 1;
foreach (Row row in firstTable.Rows)
{
foreach (Cell cell in row.Cells)
{
//Заголовок таблицы
if (cell.RowIndex == 1)
{
cell.Range.Text = "Колонка " + cell.ColumnIndex.ToString();
cell.Range.Font.Bold = 1;
//Задаем шрифт и размер текста
cell.Range.Font.Name = "verdana";
cell.Range.Font.Size = 10;
cell.Shading.BackgroundPatternColor = WdColor.wdColorGray25;
//Выравнивание текста в заголовках столбцов по центру
cell.VerticalAlignment =
WdCellVerticalAlignment.wdCellAlignVerticalCenter;
cell.Range.ParagraphFormat.Alignment =
WdParagraphAlignment.wdAlignParagraphCenter;
}
//Значения ячеек
else
{
cell.Range.Text = (cell.RowIndex - 2 + cell.ColumnIndex).ToString();
}
}
}
winword.Visible = true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
Запустите ваш проект, нажав на клавиатуре, клавишу «F5». Нажмите на единственную кнопку, расположенную на главной форме вашего проекта. У вас автоматически откроется документ Microsoft Word с заполненным верхним и нижним колонтитулом, обычным и с применением стиля текстом, а так же заполненной таблицей.
Для сохранения документа в определенной директории, добавьте приведенный ниже код, после строки «winword.Visible = true;».
//Сохранение документа object filename = @"d:temp1.docx"; document.SaveAs(ref filename); //Закрытие текущего документа document.Close(ref missing, ref missing, ref missing); document = null; //Закрытие приложения Word winword.Quit(ref missing, ref missing, ref missing); winword = null;
При работе с приложением Word в памяти компьютера создается отдельный процесс, если его не закрыть или не вывести созданный документ на экран, то он будет работать до выключения компьютера. Так же при постоянной работе с такими документами, их процессы будут накапливаться незаметно для пользователя, что может привести к зависанию компьютера или другим последствиям.