Download Article
Download Article
If you’re looking for a great way to visualize data in Microsoft Excel, you can create a graph or chart. Whether you’re using Windows or macOS, creating a graph from your Excel data is quick and easy, and you can even customize the graph to look exactly how you want. This wikiHow tutorial will walk you through making a graph in Excel.
Steps
-
1
Open Microsoft Excel. Its app icon resembles a green box with a white «X» on it.
-
2
Click Blank workbook. It’s a white box in the upper-left side of the window.
Advertisement
-
3
Consider the type of graph you want to make. There are three basic types of graph that you can create in Excel, each of which works best for certain types of data:[1]
- Bar — Displays one or more sets of data using vertical bars. Best for listing differences in data over time or comparing two similar sets of data.
- Line — Displays one or more sets of data using horizontal lines. Best for showing growth or decline in data over time.
- Pie — Displays one set of data as fractions of a whole. Best for showing a visual distribution of data.
-
4
Add your graph’s headers. The headers, which determine the labels for individual sections of data, should go in the top row of the spreadsheet, starting with cell B1 and moving right from there.
- For example, to create a set of data called «Number of Lights» and another set called «Power Bill», you would type Number of Lights into cell B1 and Power Bill into C1
- Always leave cell A1 blank.
-
5
Add your graph’s labels. The labels that separate rows of data go in the A column (starting in cell A2). Things like time (e.g., «Day 1», «Day 2», etc.) are usually used as labels.
- For example, if you’re comparing your budget with your friend’s budget in a bar graph, you might label each column by week or month.
- You should add a label for each row of data.
-
6
Enter your graph’s data. Starting in the cell immediately below your first header and immediately to the right of your first label (most likely B2), enter the numbers that you want to use for your graph.
- You can press the Tab ↹ key once you’re done typing in one cell to enter the data and jump one cell to the right if you’re filling in multiple cells in a row.
-
7
Select your data. Click and drag your mouse from the top-left corner of the data group (e.g., cell A1) to the bottom-right corner, making sure to select the headers and labels as well.
-
8
Click the Insert tab. It’s near the top of the Excel window. Doing so will open a toolbar below the Insert tab.
-
9
Select a graph type. In the «Charts» section of the Insert toolbar, click the visual representation of the type of graph that you want to use. A drop-down menu with different options will appear.
- A bar graph resembles a series of vertical bars.
- A line graph resembles two or more squiggly lines.
- A pie graph resembles a sectioned-off circle.
-
10
Select a graph format. In your selected graph’s drop-down menu, click a version of the graph (e.g., 3D) that you want to use in your Excel document. The graph will be created in your document.
- You can also hover over a format to see a preview of what it will look like when using your data.
-
11
Add a title to the graph. Double-click the «Chart Title» text at the top of the chart, then delete the «Chart Title» text, replace it with your own, and click a blank space on the graph.
- On a Mac, you’ll instead click the Design tab, click Add Chart Element, select Chart Title, click a location, and type in the graph’s title.[2]
- On a Mac, you’ll instead click the Design tab, click Add Chart Element, select Chart Title, click a location, and type in the graph’s title.[2]
-
12
Save your document. To do so:
- Windows — Click File, click Save As, double-click This PC, click a save location on the left side of the window, type the document’s name into the «File name» text box, and click Save.
- Mac — Click File, click Save As…, enter the document’s name in the «Save As» field, select a save location by clicking the «Where» box and clicking a folder, and click Save.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
How do I change the horizontal axis to a vertical axis in Excel?
Click «Edit» and then press «Move.» If this doesn’t work, double click the axis and use the dots to move it.
-
Question
How do I print a graph only in Excel?
Type control p on your laptop or go to print on the page font of your screen?
-
Question
How do I label a Series?
Jayna Akanova
Community Answer
Right-click the chart with the data series you want to rename, and click Select Data. In the Select Data Source dialog box, under Legend Entries (Series), select the data series, and click Edit. In the Series name box, type the name you want to use.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
-
You can change the graph’s visual appearance on the Design tab.
-
If you don’t want to select a specific type of graph, you can click Recommended Charts and then select a graph from Excel’s recommendation window.
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
-
Some graph formats won’t include all of your data, or will display it in a confusing manner. It’s important to choose a graph format that works with your data.
Advertisement
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Enter the graph’s headers.
2. Add the graph’s labels.
3. Enter the graph’s data.
4. Select all data including headers and labels.
5. Click Insert.
6. Select a graph type.
7. Select a graph format.
8. Add a title to the graph.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 1,722,650 times.
Is this article up to date?
Over the past years, one of the things we’ve learned is that Microsoft Excel is like a Hallmark movie.
Some of us can’t get enough of them and others just can’t stand it. 💔😬
Regardless of your preference, if you’re a manager or business owner, you’ll probably have to rely on Excel for business insights.
Tools like Microsoft Excel graphs are helpful for data analysis and tracking.
And wayyy better than endless spreadsheets that can easily trigger a migraine.
Then why not turn your boring Excel spreadsheet into something interesting?
In this article, we’ll learn what an Excel graph is, how to make a graph in Excel, and its drawbacks. We’ll also suggest an alternative to create effortless graphs.
Let’s graph away!
What are Graphs & Charts in Microsoft Excel?
Graphs in Excel are graphical representations of variations in values of data points over a given period.
In other words, it’s a diagram that represents changes in comparison to one or more variables.
Too technical? 👀
Take a look at the image for clarity:

Wondering if graphs and charts in Excel are the same?
Graphs are mostly numerical representations of data as it shows how one variable is affecting or changing another.
On the other hand, charts are visual representations where variables may or may not be associated. They’re also considered more aesthetically pleasing than graphs. For example, a pie chart. 🥧
However, if you’re wondering how to make a chart in Excel, it isn’t very different from making a graph.
But for now, let’s focus on the main plot: graphs!✨
Steps To Make a Graph in Excel
The first (and obvious step) is to open a new Excel file or a blank Excel worksheet.
Done?
Then let’s learn how to create a graph in Excel.
⭐️ Step 1: fill the Excel sheet with data
Start by populating your Excel spreadsheet with the data you need.
You may import this data from different software, insert it manually, or copy and paste it.
For our example, let’s say you’re an owner of a movie theater in a small town, and you often screen older movies. You probably want to track the sales of your tickets to see which movie is a hit so you can screen it frequently.
Let’s do that by comparing the ticket sales in January and February.
Here’s what your data might look like:

Column A contains the movie names.
Column B contains tickets sold in January.
And column C contains tickets sold in February.
You can bold headings and center align your text for better readability.
Done? Okay, get ready to pick a graph.
⭐️ Step 2: determine the Excel graph type you want
The type of graph you pick will depend on the data you have and the number of different parameters you want to track.
You’ll find the different graph types under the Excel Insert tab, in the Excel Ribbon, arranged close to one another like this:

Note: The Excel Ribbon is where you can find the Home, Insert, and Draw tabs.
Here are some of the different Excel graph or chart type options you can choose from:
- Line graph
- Column graph or bar graph
- Pie graph or chart
- Combo chart
- Area chart
- Scatter plot chart
➡️ Fun fact: Excel can help you decide the graph or chart type with the Recommended Charts (formerly known as Chart Wizard) option.
If you want to take notes of trends (increase or decrease) over time, then a line graph is perfect.
But for a long time frame and more data, a bar graph is the best option.
We’ll use these two graphs for the purpose of this Excel tutorial.
How To Create a Line Graph in Excel – 3 Steps
A line graph in Excel typically has two axes (horizontal and vertical) to function.
You need to enter the data in two columns.
Lucky for us, we’ve already done this when creating the ticket sales data table.
⭐️ Step 1: select data to turn into a line graph
Click and drag from the top-left cell (A1) in your ticket sales data to the bottom-right cell (C7) to select. Don’t forget to include column headers.
This will highlight all the data you want to display in your line graph.

⭐️ Step 2: insert line graph
Now that you’ve selected your data, it’s time to add the line graph.
Look for the line graph icon under the Insert tab.

With the data selected, go to Insert > Line. Click on the icon, and a dropdown menu will appear to select the type of line chart you want.
For this example, we’ll choose the fourth 2-D line graph (Line with Markers).
Excel will add your line graph representing your selected data series.

You’ll then notice the names of the movies appear on the horizontal axis and the number of tickets sold on the vertical axis.
⭐️ Step 3: customize your line graph
After adding the line graph, you’ll notice a new tab called Chart Design on your Excel Ribbon.
Select the Design tab to make the line graph your own by choosing the chart style you prefer.
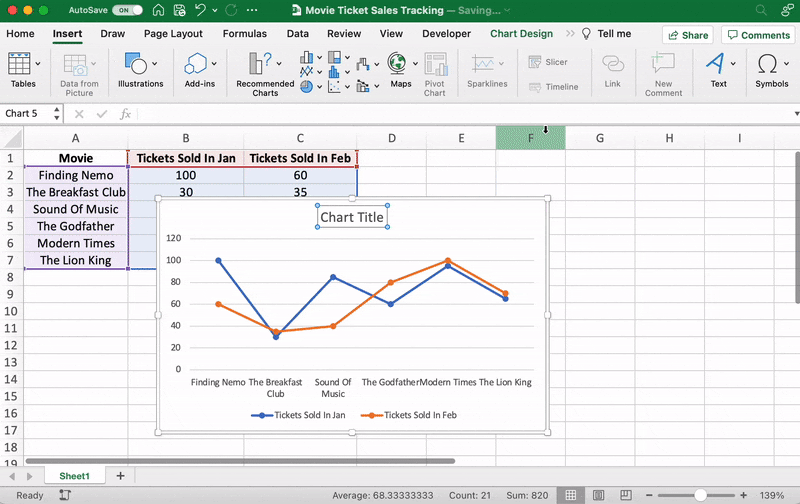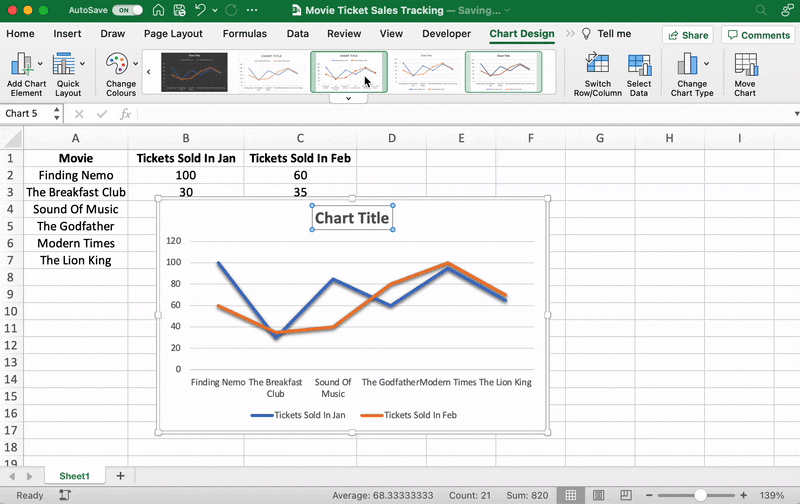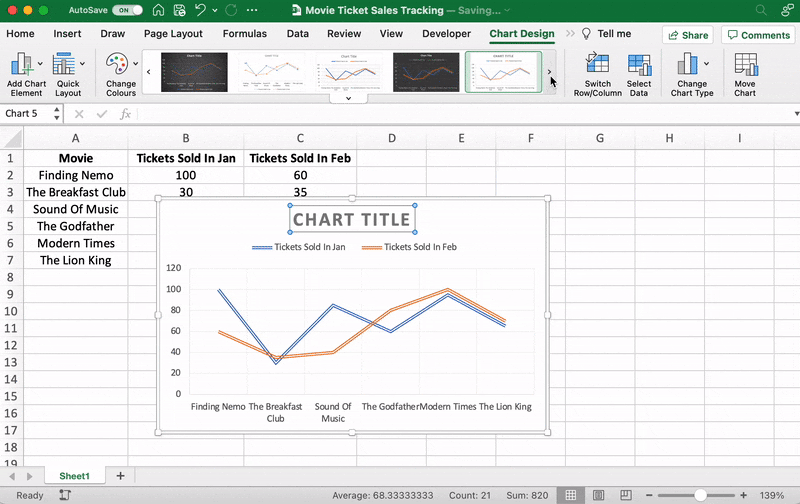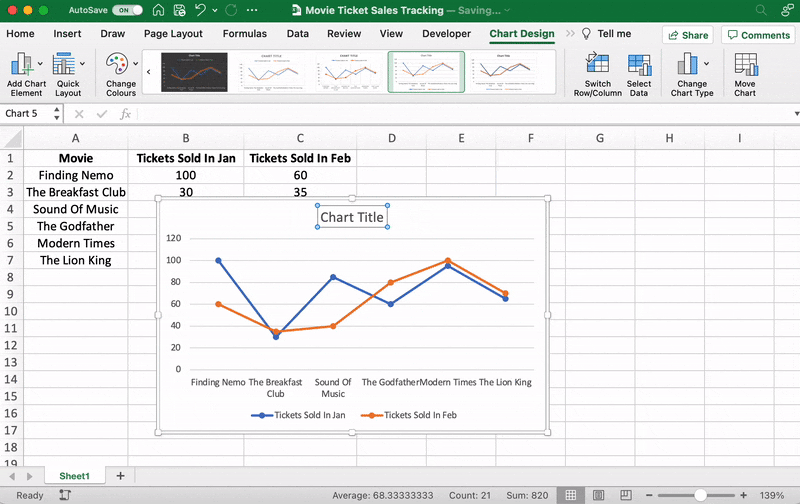
You can also change the graph’s title.
Select the Chart Title > double click to name > type in the name you wish to call it. To save it, simply click anywhere outside the graph’s title box or chart area.
We’ll name our graph “Movie Ticket Sales.”
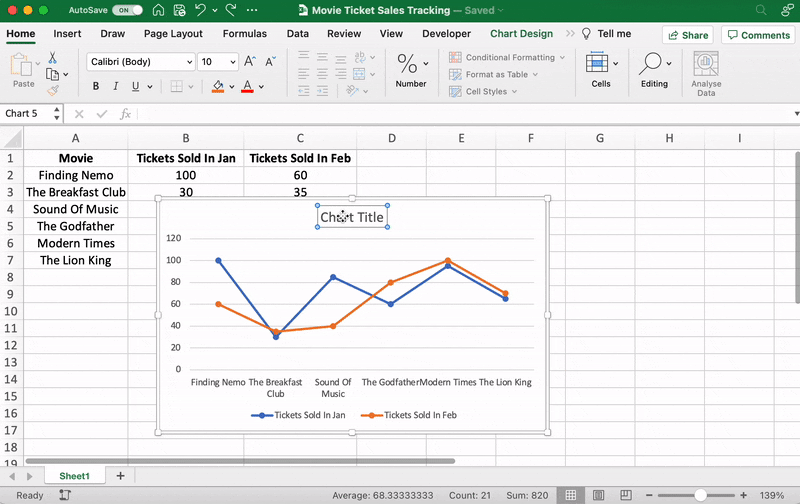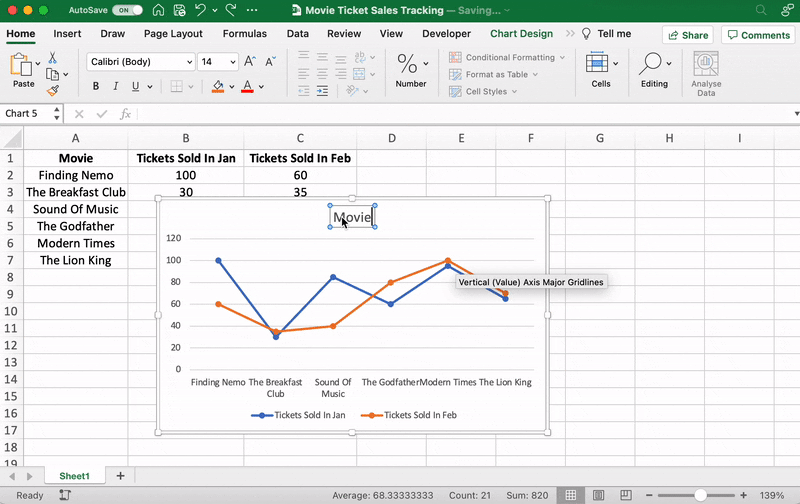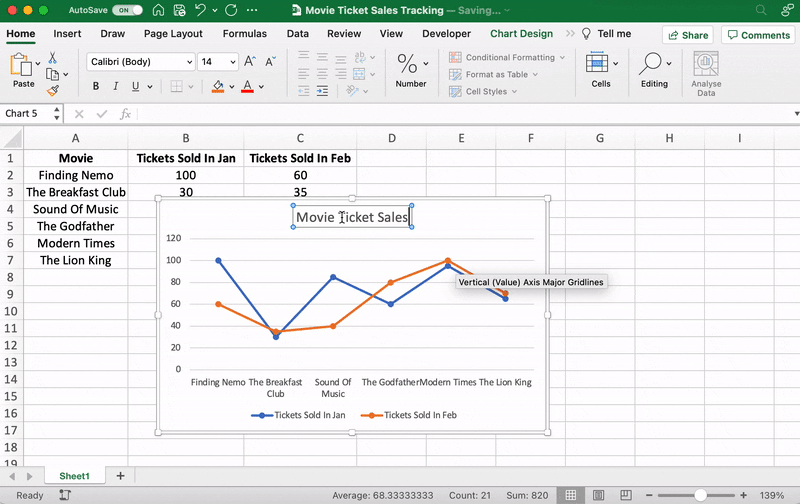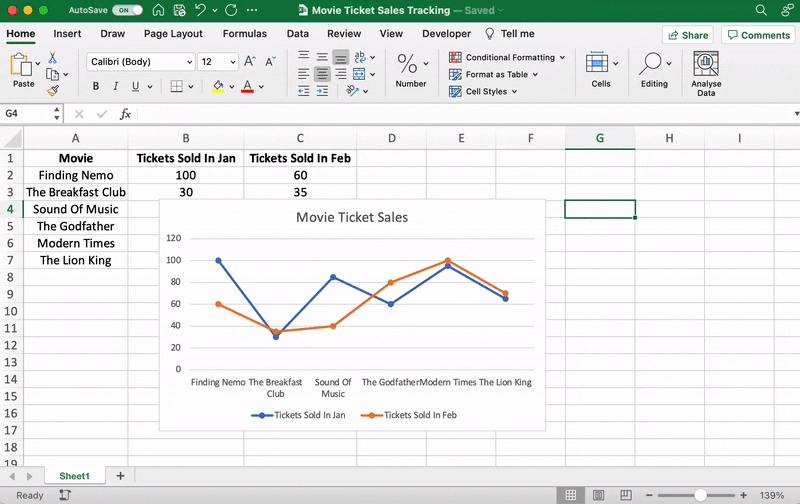
Anything else you need to tweak?
If you spot anything, now is the time to make those edits!
For example, here you can see The Godfather and Modern Times are smooshed together.
Let’s give them some space.
How?
Just drag any corner of the graph until it’s how you desire.

These are just some examples. You can customize every chart element if you like including the Axis Labels (the color of the lines that represent each data point, etc.)
Just double click on any chart element to open a sidebar for formatting like this:
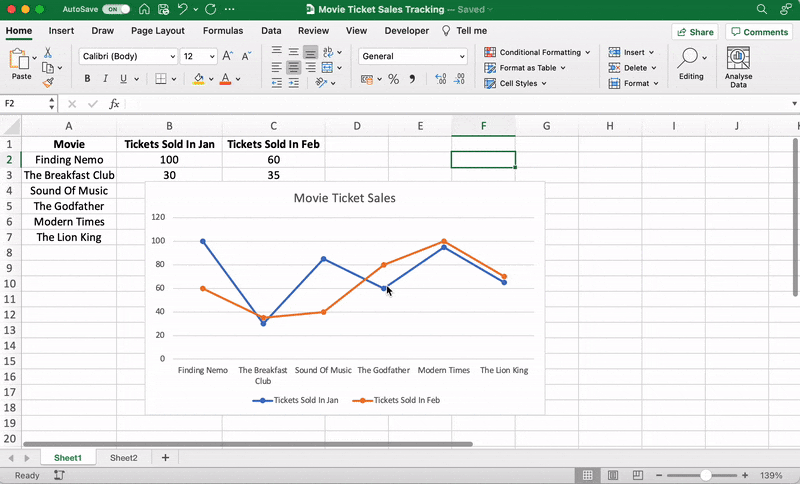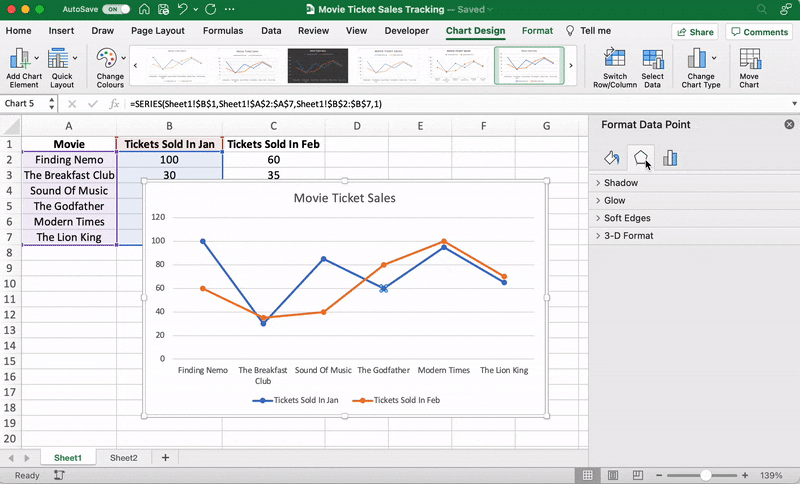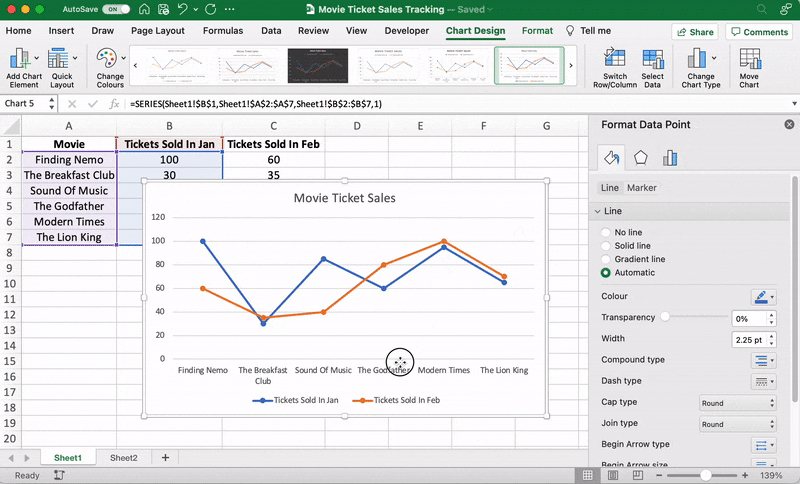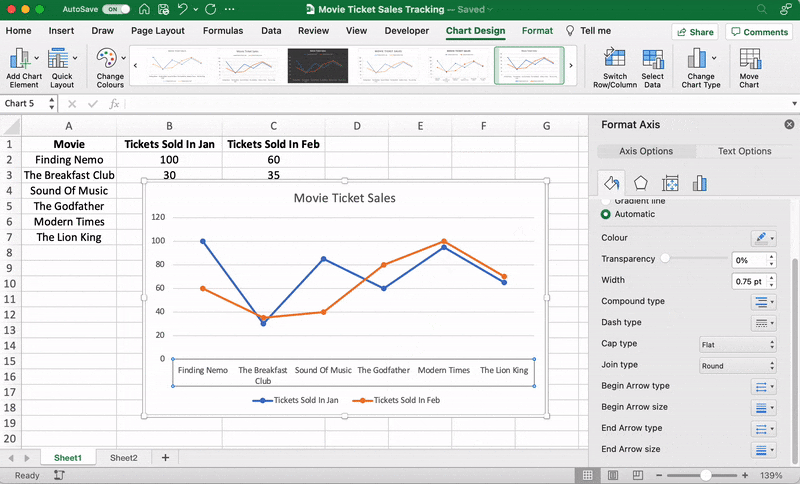
That’s it! You’ve successfully created a line graph in Excel!
Now, let’s learn how to make a bar graph. 📊
3 Steps To Create a Bar Graph in Excel
Any Excel graph or Excel chart begins with a populated sheet.
We’ve already done this, so copy and paste the movie ticket sales data to a new sheet tab in the same Excel workbook.
⭐️ Step 1: select data to turn into a bar graph
Like step 1 for the line graph, you need to select the data you wish to turn into a bar graph.
Drag from cell A1 to C7 to highlight the data.
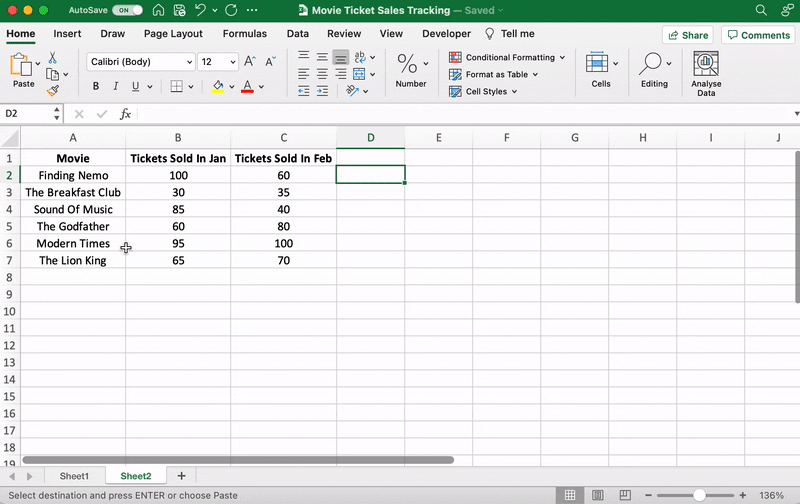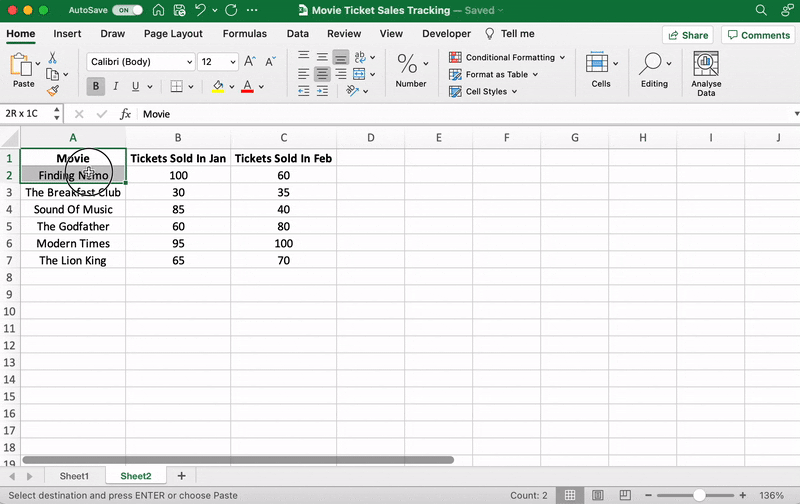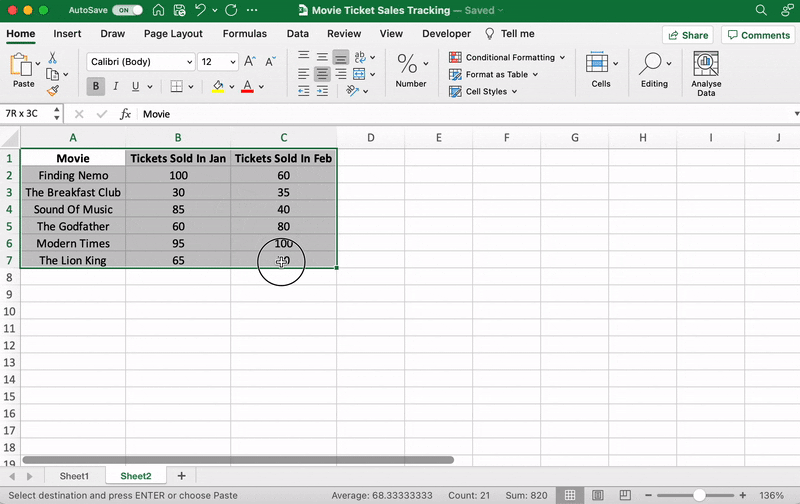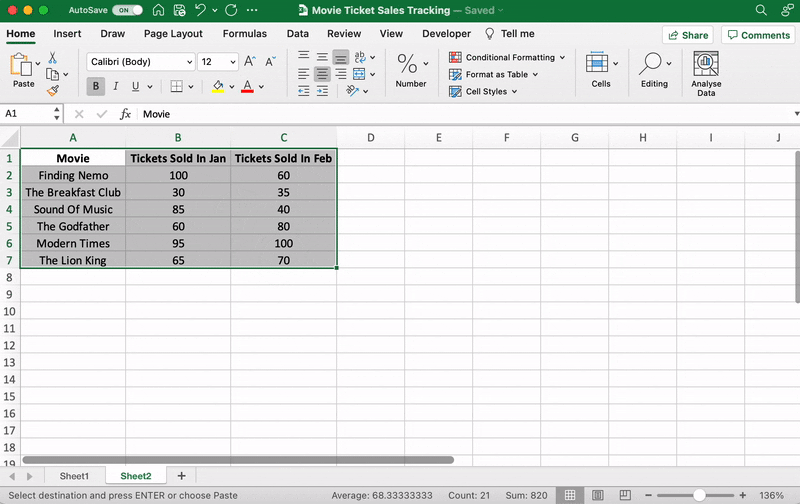
⭐️ Step 2: insert bar graph
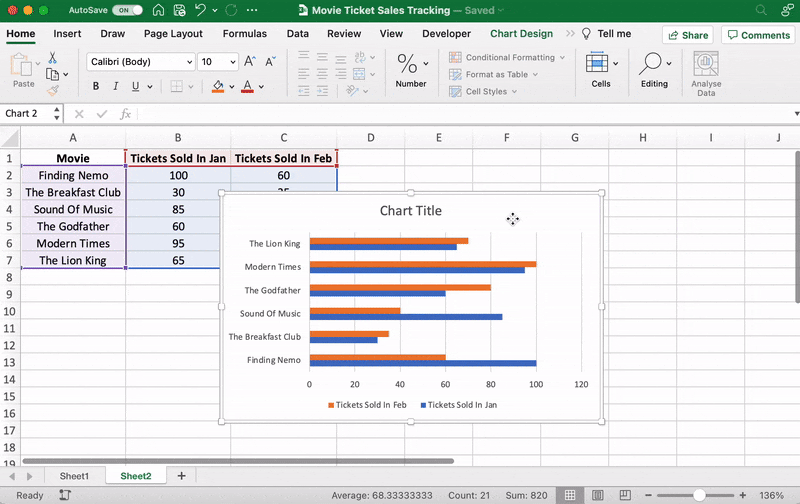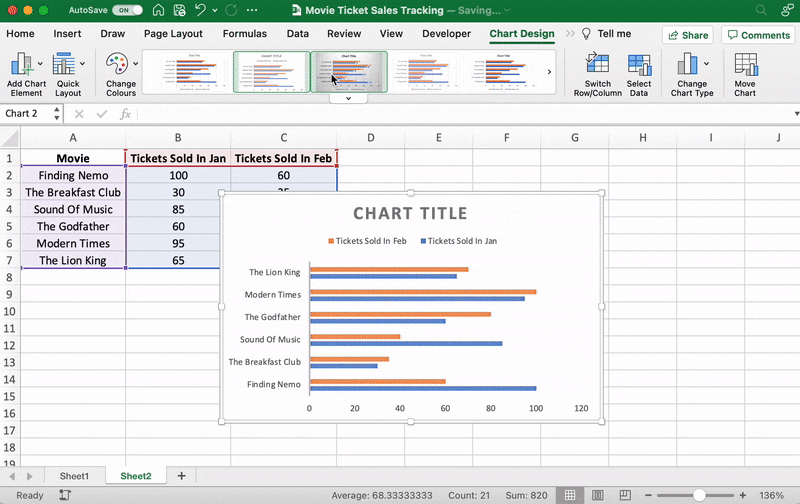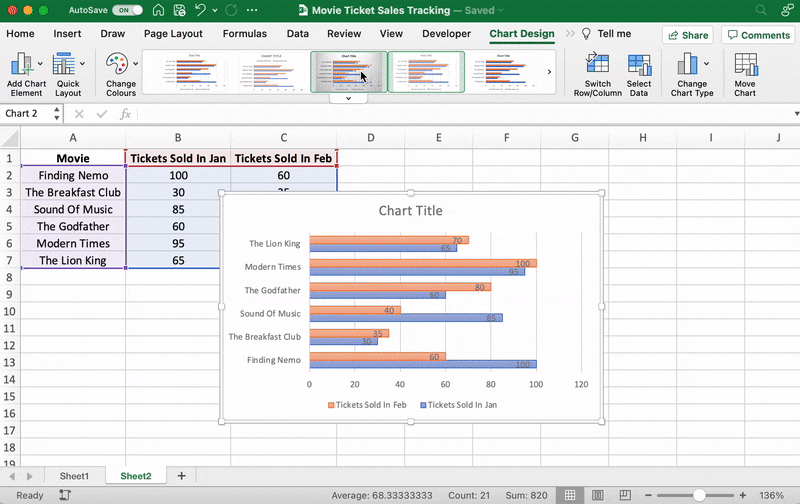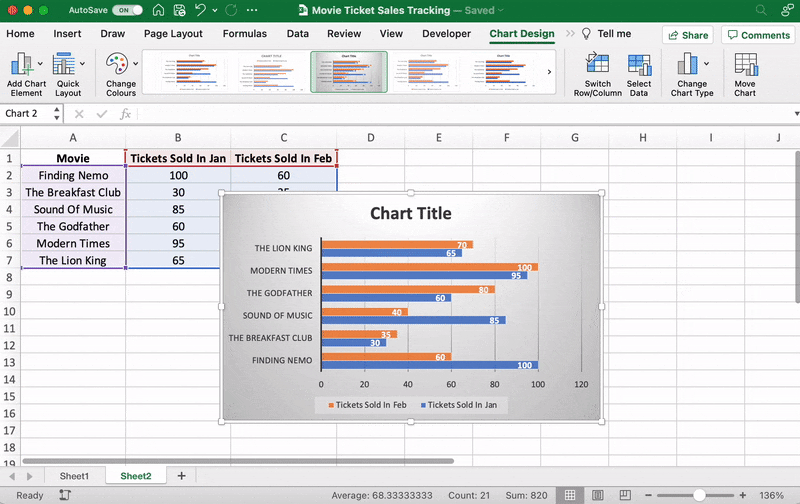
Highlight your data, go to the Insert tab, and click on the Column chart or graph icon. A dropdown menu should appear.
Select Clustered Bar under the 2-D bar options.
Note: you can choose a different type of bar chart option like a 3D clustered column or 2D stacked bar, etc.
As soon as you click on the bar graph option, it’ll be added to your Excel sheet.

⭐️ Step 3: customize your Excel bar graph
Now, you can go to the Chart Design tab in the Excel Ribbon to personalize it.
Click on the Design tab to apply a bar style you prefer from the many options.
You know the next step! Change the bar graph’s title.
Select the Excel Chart Title > double click on the title box > type in “Movie Ticket Sales.”
Then click anywhere on the excel sheet to save it.

Note: you can also add other graph elements such as Axis Title, Data Label, Data Table, etc., with the Add Chart Element option. You’ll find it under the Chart Design tab.
And that’s a wrap. 🎬
You’ve successfully created a bar graph in Excel!
Well, that was fun.
But the question is, do you have the time for graphs in your busy work schedule?
And that’s just the teaser when it comes to Excel graph drawbacks.
Read on to watch the full movie. 👀
Bonus: Check out these Excel Alternatives!
Create Effortless Graphs With ClickUp
If ClickUp were a Hallmark movie, graphs and this project management tool would be the perfect match.
A forever kind-of-love. ❤️
Whether you want to create graphs to monitor time, projects, people, ticket sales… you name it because we can do it all within a few clicks.
All without the drawbacks of using Excel!
Excel can be:
- Time-consuming and manual
- Complex and pricey
- Error-prone
The best part?
Most of those functions are automated without manual data entry. Phew.
1. Line Chart Widgets
The Line Chart Widget is a Custom Widget on our Dashboard. Use this ClickUp production to visualize literally anything in the form of a line graph.
It can be tracking profits, total daily sales, or how many movies you’ve watched in a month.
Like we said, a-n-y-t-h-i-n-g!

Visualize any set of values as a line graph with the Line Chart Widget on ClickUp’s Dashboard!
And that’s not it. You can visualize your data in many different ways too.
Just use any of these Custom Widgets:
- Calculations
- Bar charts
- Battery chart
- Pie chart
- And more

Present your data visually as a pie chart with Custome Widgets in ClickUp!
2. Gantt Chart view
Just like it’s difficult to love just one movie genre, we totally get that graphs alone don’t work.
And that’s why we have charts too!
Specifically, ClickUp’s Gantt chart, an interactive chart with live updates and progress tracking that can help you:
- Plan projects
- Assign tasks and assignees
- Schedule a timeline
- Manage dependencies
- And more

Drawing a relationship from one task to a future task in ClickUp’s Gantt Chart view!
3. Table view
If you’re a fan of the Excel grids, ClickUp has your back.
Starring… ClickUp Table view!
This view lets you visualize your tasks in the spreadsheet style.
It’s super fast and allows easy navigation between fields, bulk edits, and data export.
➡️ Fun fact: you can quickly copy and paste your table’s data into other programs, like MS Excel. Just click and drag to highlight the cells you want to copy.
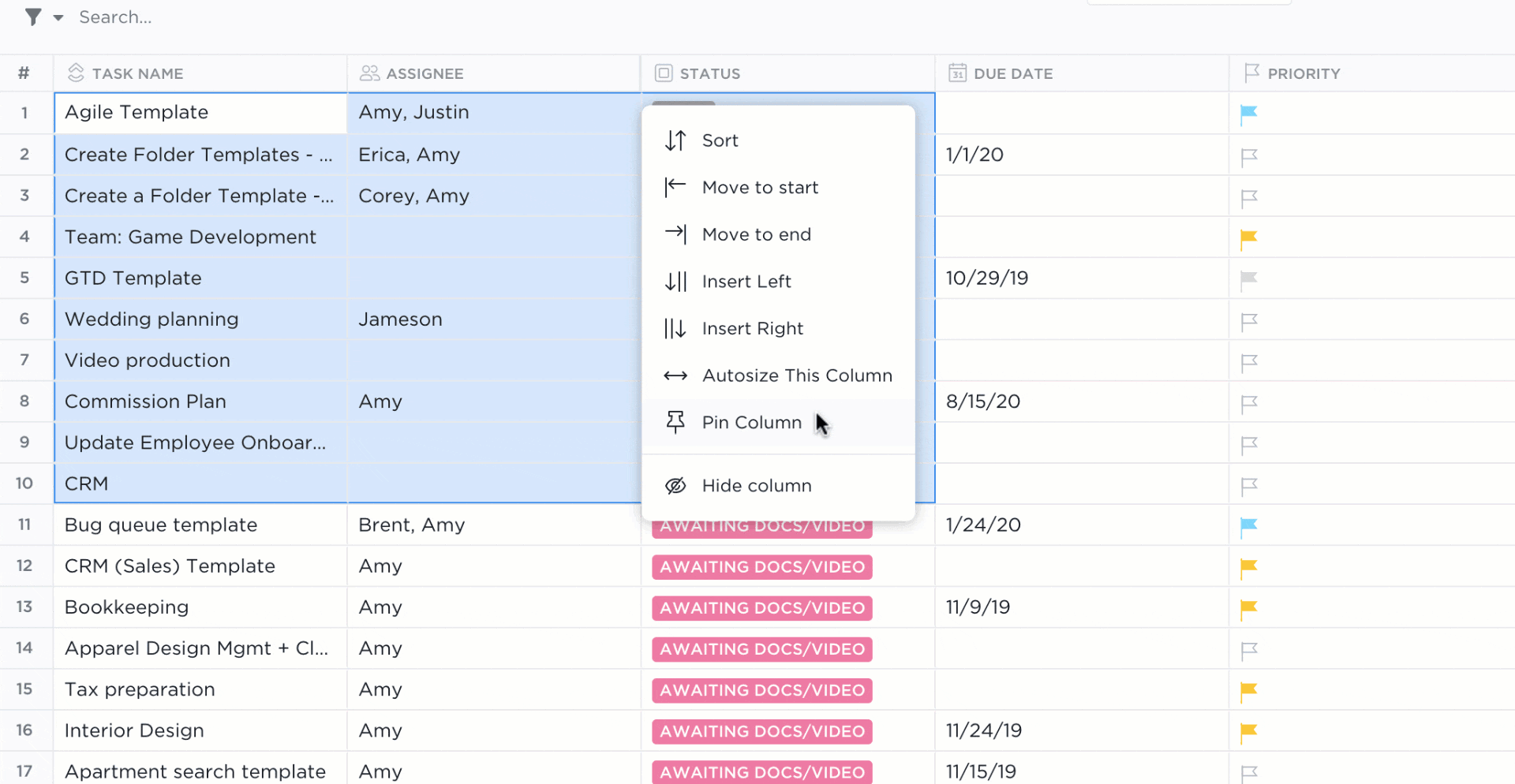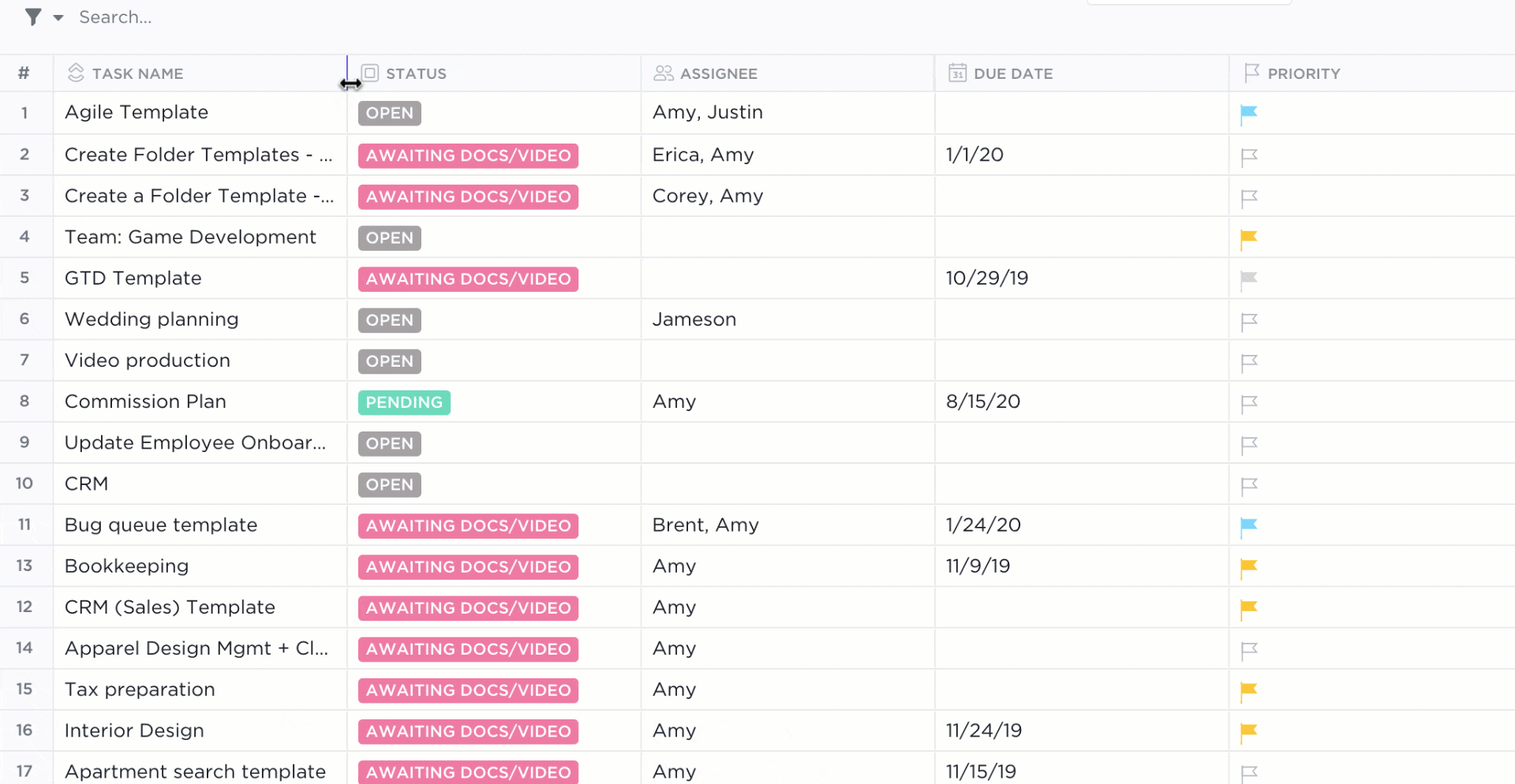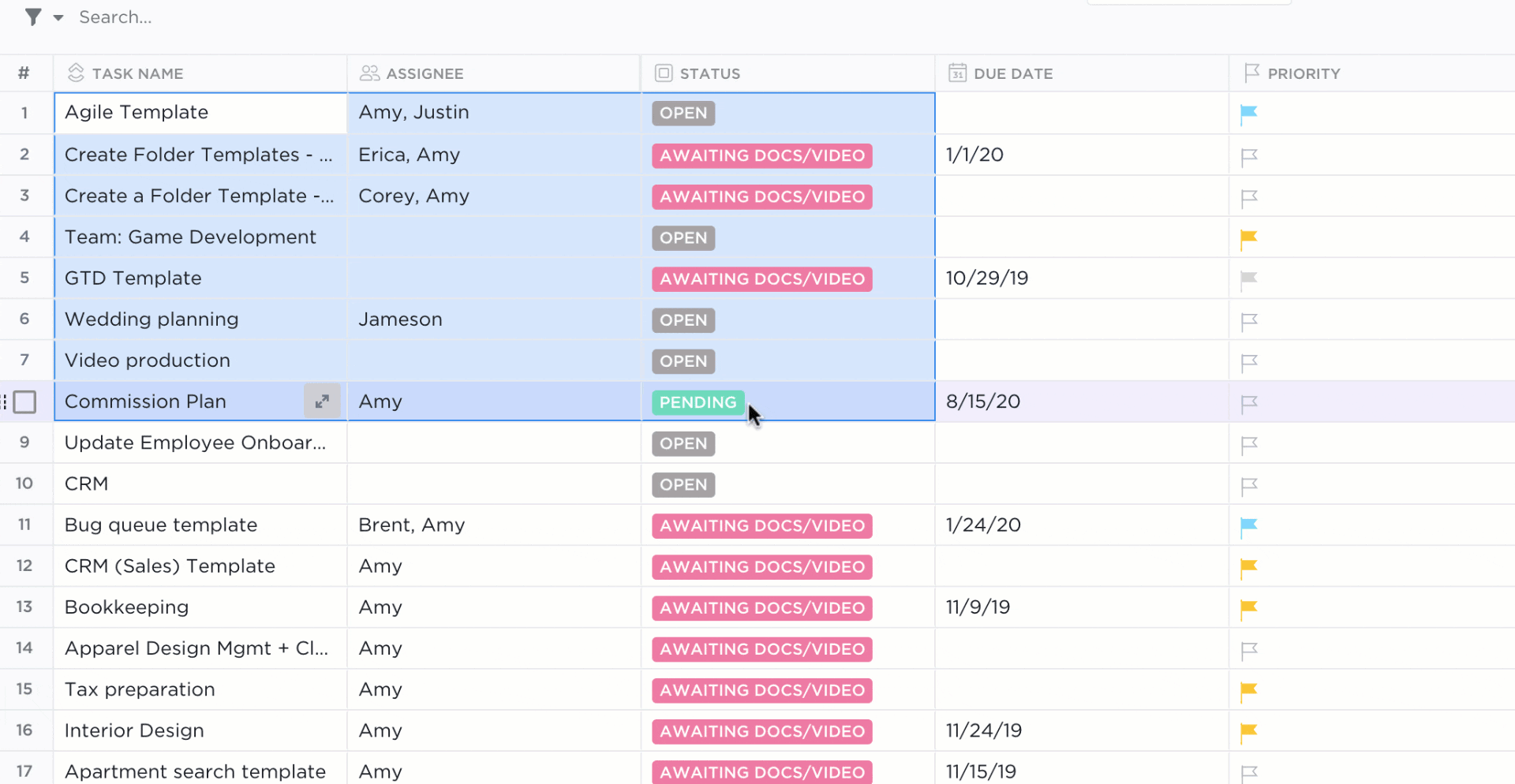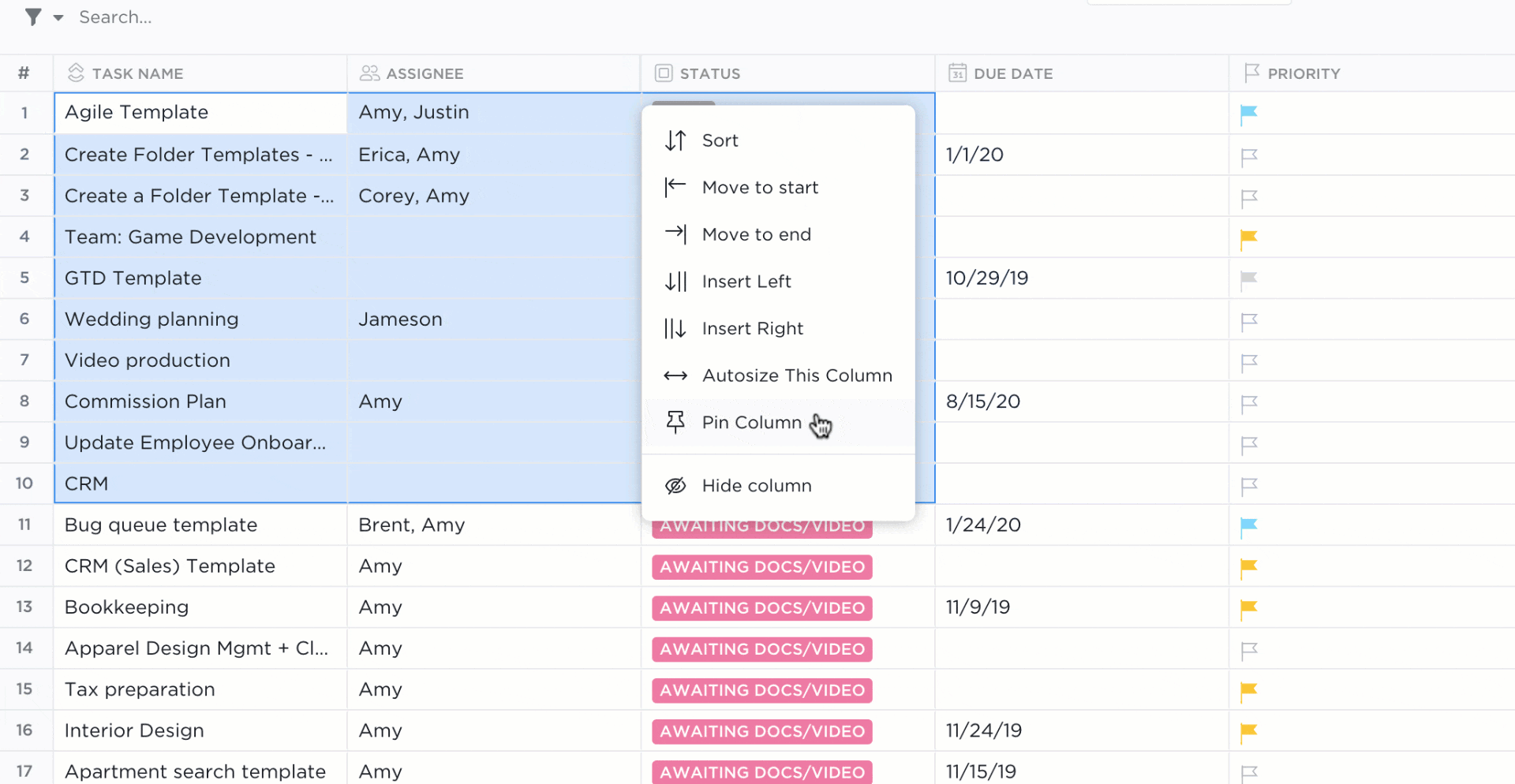
Highlight data from your table in ClickUp to copy and paste into other programs!
And that was just the trailer for you. 📽️
Here are some more powerful ClickUp features in store for:
- Send and receive emails right from your project management tool with Email in ClickUp
- Work even when the wifi acts up with Offline Mode
- Work how you like with multiple ClickUp Views, including Calendar, Mind Maps, Chat, etc.
- Reduce your workload with ClickUp Automations
- Track time spent on tasks with ClickUp’s Native Time Tracker
- Share Table view or Dashboards with clients and external users using Public Sharing and Permissions
- View all graphs and charts on the go with ClickUp mobile apps
Now Showing: ClickUp 🎥🍿
You can surely make tons of graphs in Excel.
No doubt there.
But does that make it a smart choice?
I mean, if you have to Google how to make a graph in Excel, maybe that’s your red flag. 🚩
Tools are supposed to make your life easier.
Take ClickUp, for instance.
Our project management tool can be your graph maker, chart creator, spreadsheet builder, time tracker, workload manager…
It’s a hallmark for a quality tool that can be your all-in-one solution.
Get your ClickUp ticket for free today and enjoy watching your graphs come to life in minutes!
Related readings:
- How to create Gantt charts in Excel
- How to create a Kanban board in Excel
- How to create a burndown chart in Excel
- How to create a flowchart in Excel
- How to show dependencies in Excel
- How to create a KPI dashboard in Excel
- How to create a dashboard in Excel
- How to create a database in Excel
- How to make a work breakdown structure in Excel
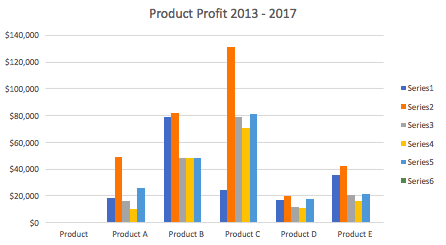
After you input your data and select the cell range, you’re ready to choose the chart type. In this example, we’ll create a clustered column chart from the data we used in the previous section.
Step 1: Select Chart Type
Once your data is highlighted in the Workbook, click the Insert tab on the top banner. About halfway across the toolbar is a section with several chart options. Excel provides Recommended Charts based on popularity, but you can click any of the dropdown menus to select a different template.
Step 2: Create Your Chart
- From the Insert tab, click the column chart icon and select Clustered Column.
- Excel will automatically create a clustered chart column from your selected data. The chart will appear in the center of your workbook.
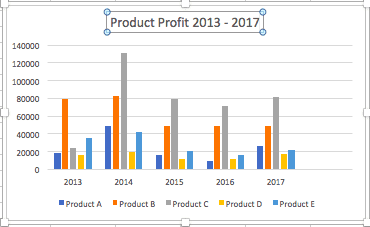
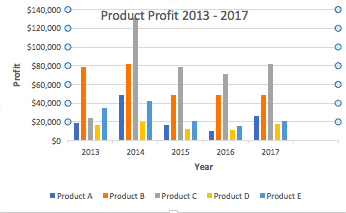
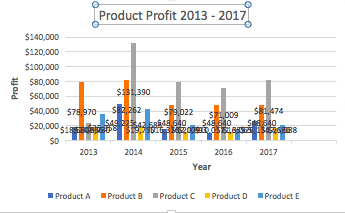
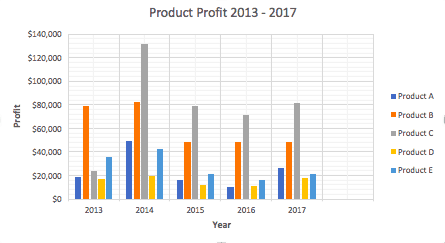
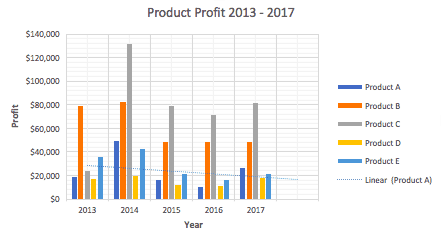
- To name your chart, double click the Chart Title text in the chart and type a title. We’ll call this chart “Product Profit 2013 — 2017.”
We’ll use this chart for the rest of the walkthrough. You can download this same chart to follow along.
Download Sample Column Chart Template
There are two tabs on the toolbar that you will use to make adjustments to your chart: Chart Design and Format. Excel automatically applies design, layout, and format presets to charts and graphs, but you can add customization by exploring the tabs. Next, we’ll walk you through all the available adjustments in Chart Design.
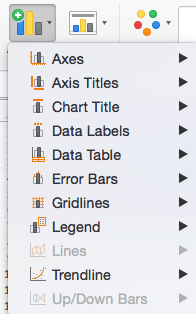
Step 3: Add Chart Elements
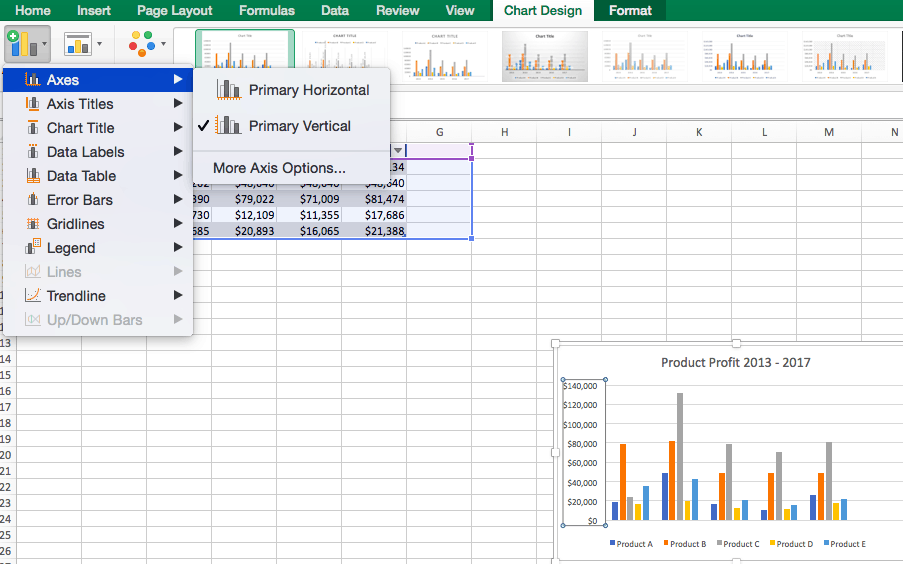
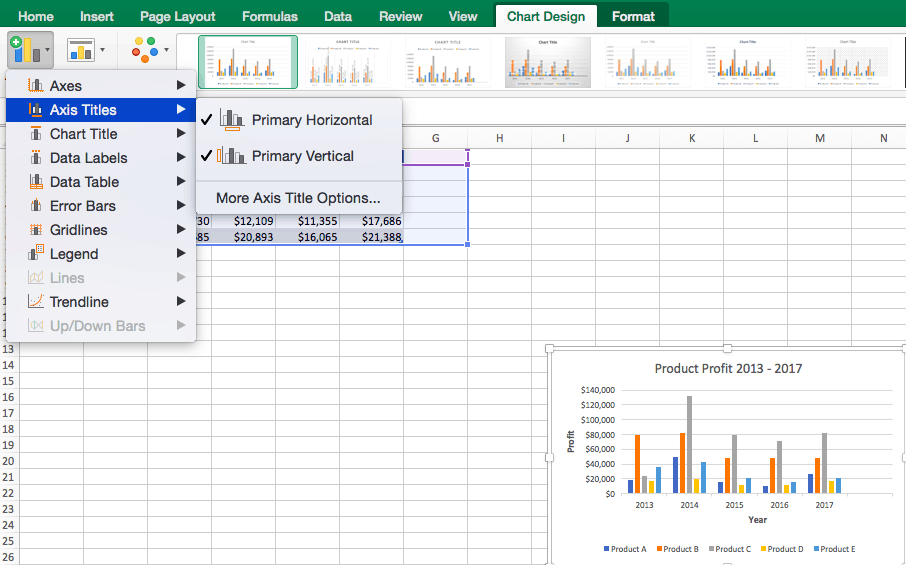
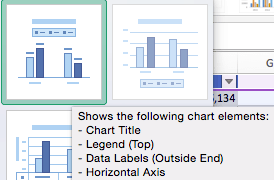
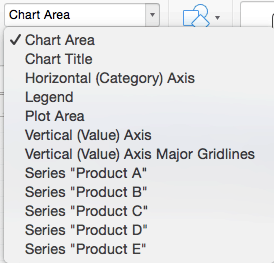
Adding chart elements to your chart or graph will enhance it by clarifying data or providing additional context. You can select a chart element by clicking on the Add Chart Element dropdown menu in the top left-hand corner (beneath the Home tab).
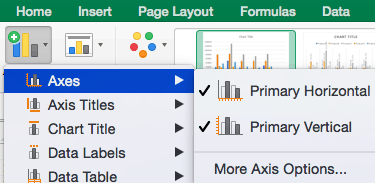
To Display or Hide Axes:
- Select Axes. Excel will automatically pull the column and row headers from your selected cell range to display both horizontal and vertical axes on your chart (Under Axes, there is a check mark next to Primary Horizontal and Primary Vertical.)
- Uncheck these options to remove the display axis on your chart. In this example, clicking Primary Horizontal will remove the year labels on the horizontal axis of your chart.
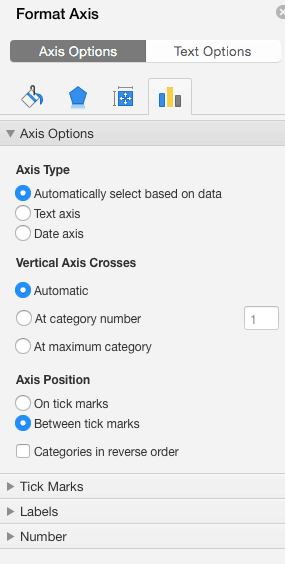
- Click More Axis Options… from the Axes dropdown menu to open a window with additional formatting and text options such as adding tick marks, labels, or numbers, or to change text color and size.
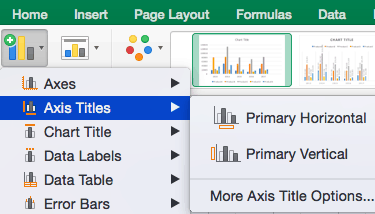
To Add Axis Titles:
- Click Add Chart Element and click Axis Titles from the dropdown menu. Excel will not automatically add axis titles to your chart; therefore, both Primary Horizontal and Primary Vertical will be unchecked.
- To create axis titles, click Primary Horizontal or Primary Vertical and a text box will appear on the chart. We clicked both in this example. Type your axis titles. In this example, the we added the titles “Year” (horizontal) and “Profit” (vertical).
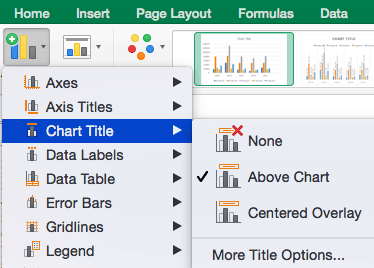
To Remove or Move Chart Title:
- Click Add Chart Element and click Chart Title. You will see four options: None, Above Chart, Centered Overlay, and More Title Options.
- Click None to remove chart title.
- Click Above Chart to place the title above the chart. If you create a chart title, Excel will automatically place it above the chart.
- Click Centered Overlay to place the title within the gridlines of the chart. Be careful with this option: you don’t want the title to cover any of your data or clutter your graph (as in the example below).
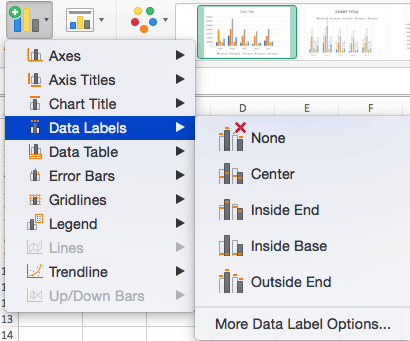
To Add Data Labels:
- Click Add Chart Element and click Data Labels. There are six options for data labels: None (default), Center, Inside End, Inside Base, Outside End, and More Data Label Title Options.
- The four placement options will add specific labels to each data point measured in your chart. Click the option you want. This customization can be helpful if you have a small amount of precise data, or if you have a lot of extra space in your chart. For a clustered column chart, however, adding data labels will likely look too cluttered. For example, here is what selecting Center data labels looks like:
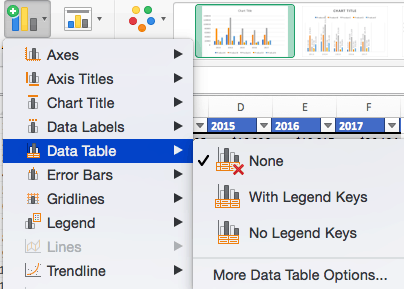
To Add a Data Table:
- Click Add Chart Element and click Data Table. There are three pre-formatted options along with an extended menu that can be found by clicking More Data Table Options:
Note: If you choose to include a data table, you’ll probably want to make your chart larger to accommodate the table. Simply click the corner of your chart and use drag-and-drop to resize your chart.
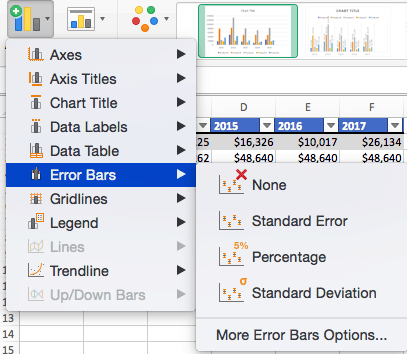
To Add Error Bars:
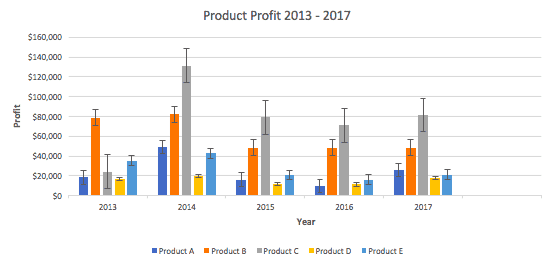
- Click Add Chart Element and click Error Bars. In addition to More Error Bars Options, there are four options: None (default), Standard Error, 5% (Percentage), and Standard Deviation. Adding error bars provide a visual representation of the potential error in the shown data, based on different standard equations for isolating error.
- For example, when we click Standard Error from the options we get a chart that looks like the image below.
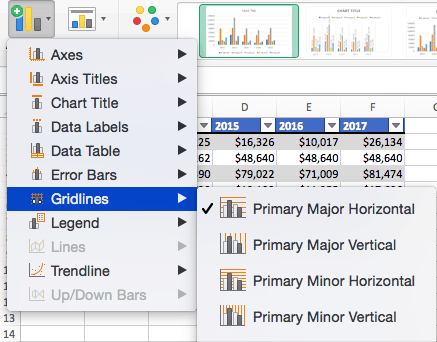
To Add Gridlines:
- Click Add Chart Element and click Gridlines. In addition to More Grid Line Options, there are four options: Primary Major Horizontal, Primary Major Vertical, Primary Minor Horizontal, and Primary Minor Vertical. For a column chart, Excel will add Primary Major Horizontal gridlines by default.
- You can select as many different gridlines as you want by clicking the options. For example, here is what our chart looks like when we click all four gridline options.
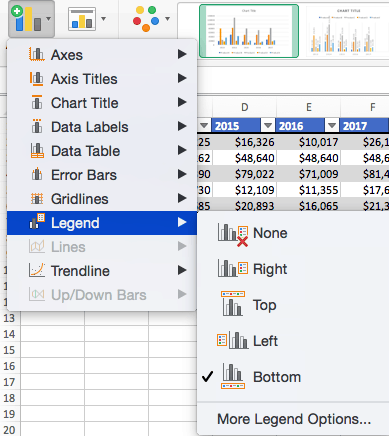
To Add a Legend:
- Click Add Chart Element and click Legend. In addition to More Legend Options, there are five options for legend placement: None, Right, Top, Left, and Bottom.
- Legend placement will depend on the style and format of your chart. Check the option that looks best on your chart. Here is our chart when we click the Right legend placement.
To Add Lines: Lines are not available for clustered column charts. However, in other chart types where you only compare two variables, you can add lines (e.g. target, average, reference, etc.) to your chart by checking the appropriate option.
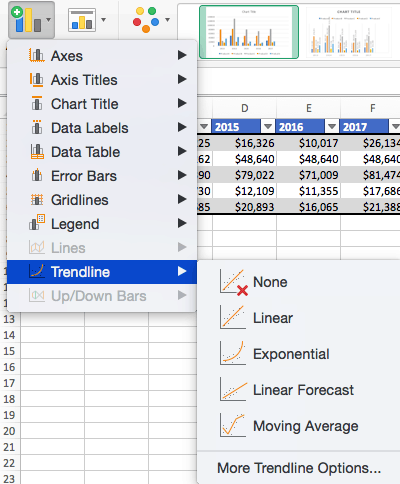
To Add a Trendline:
- Click Add Chart Element and click Trendline. In addition to More Trendline Options, there are five options: None (default), Linear, Exponential, Linear Forecast, and Moving Average. Check the appropriate option for your data set. In this example, we will click Linear.
- Because we are comparing five different products over time, Excel creates a trendline for each individual product. To create a linear trendline for Product A, click Product A and click the blue OK button.
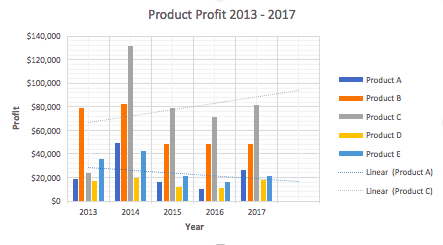
- The chart will now display a dotted trendline to represent the linear progression of Product A. Note that Excel has also added Linear (Product A) to the legend.
- To display the trendline equation on your chart, double click the trendline. A Format Trendline window will open on the right side of your screen. Click the box next to Display equation on chart at the bottom of the window. The equation now appears on your chart.
Note: You can create separate trendlines for as many variables in your chart as you like. For example, here is our chart with trendlines for Product A and Product C.
To Add Up/Down Bars: Up/Down Bars are not available for a column chart, but you can use them in a line chart to show increases and decreases among data points.
Step 4: Adjust Quick Layout
- The second dropdown menu on the toolbar is Quick Layout, which allows you to quickly change the layout of elements in your chart (titles, legend, clusters etc.).
- There are 11 quick layout options. Hover your cursor over the different options for an explanation and click the one you want to apply.
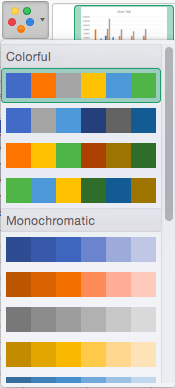
Step 5: Change Colors
The next dropdown menu in the toolbar is Change Colors. Click the icon and choose the color palette that fits your needs (these needs could be aesthetic, or to match your brand’s colors and style).
Step 6: Change Style
For cluster column charts, there are 14 chart styles available. Excel will default to Style 1, but you can select any of the other styles to change the chart appearance. Use the arrow on the right of the image bar to view other options.
Step 7: Switch Row/Column
- Click the Switch Row/Column on the toolbar to flip the axes. Note: It is not always intuitive to flip axes for every chart, for example, if you have more than two variables.
In this example, switching the row and column swaps the product and year (profit remains on the y-axis). The chart is now clustered by product (not year), and the color-coded legend refers to the year (not product). To avoid confusion here, click on the legend and change the titles from Series to Years.
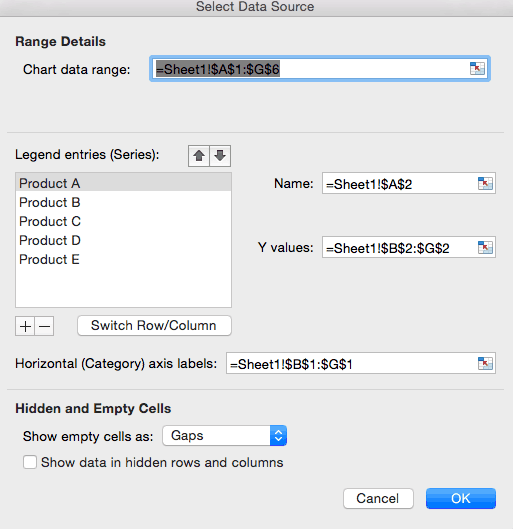
Step 8: Select Data
- Click the Select Data icon on the toolbar to change the range of your data.
- A window will open. Type the cell range you want and click the OK button. The chart will automatically update to reflect this new data range.
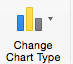
Step 9: Change Chart Type
- Click the Change Chart Type dropdown menu.
- Here you can change your chart type to any of the nine chart categories that Excel offers. Of course, make sure that your data is appropriate for the chart type you choose.
-
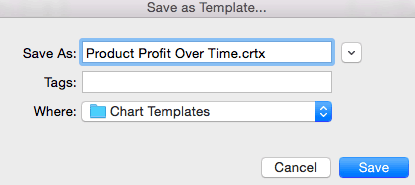
You can also save your chart as a template by clicking Save as Template…
- A dialogue box will open where you can name your template. Excel will automatically create a folder for your templates for easy organization. Click the blue Save button.
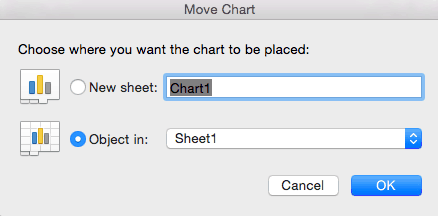
Step 10: Move Chart
- Click the Move Chart icon on the far right of the toolbar.
- A dialogue box appears where you can choose where to place your chart. You can either create a new sheet with this chart (New sheet) or place this chart as an object in another sheet (Object in). Click the blue OK button.
Step 11: Change Formatting
- The Format tab allows you to change formatting of all elements and text in the chart, including colors, size, shape, fill, and alignment, and the ability to insert shapes. Click the Format tab and use the shortcuts available to create a chart that reflects your organization’s brand (colors, images, etc.).
- Click the dropdown menu on the top left side of the toolbar and click the chart element you are editing.
Step 12: Delete a Chart
To delete a chart, simply click on it and click the Delete key on your keyboard.
Create a chart (graph) that is recommended for your data, almost as fast as using the chart wizard that is no longer available.
Create a chart
-
Select the data for which you want to create a chart.
-
Click INSERT > Recommended Charts.
-
On the Recommended Charts tab, scroll through the list of charts that Excel recommends for your data, and click any chart to see how your data will look.
If you don’t see a chart you like, click All Charts to see all the available chart types.
-
When you find the chart you like, click it > OK.
-
Use the Chart Elements, Chart Styles, and Chart Filters buttons, next to the upper-right corner of the chart to add chart elements like axis titles or data labels, customize the look of your chart, or change the data that is shown in the chart.
-
To access additional design and formatting features, click anywhere in the chart to add the CHART TOOLS to the ribbon, and then click the options you want on the DESIGN and FORMAT tabs.
Want more?
Copy an Excel chart to another Office program
Create a chart from start to finish
Charts provide a visual representation of your data, making it easier to analyze.
For example, I want to create a chart for Sales, to see if there is a pattern.
I select the cells that I want to use for the chart, click the Quick Analysis button, and click the CHARTS tab.
Excel displays recommended charts based on the data in the cells selected.
You can hover over each one to see what looks good for your data.
Clustered Column is great for comparing data, so I click it.
And now, I have an eye catching chart of the data.
It looks like the Summer months are slower and the Winter months are busier.
Up next, Create pie, bar, and line charts.