Хитрости »
28 Май 2011 644966 просмотров
Как удалить строки по условию?
Предположу, что почти каждый сталкивался с ситуацией, когда необходимо удалить только определенные строки: имеется большая таблица и необходимо удалить из неё только те строки, которые содержат какое-то слово (цифру, фразу). Для выполнения подобной задачи можно воспользоваться несколькими способами.
Способ первый:
Использовать встроенное средство Excel — фильтр. Сначала его необходимо «установить» на листе:
- Выделяем таблицу с данными, включая заголовки. Если их нет — то выделяем с самой первой строки таблицы, в которой необходимо удалить данные
- устанавливаем фильтр:
- для Excel 2003: Данные—Фильтр—Автофильтр
- для Excel 2007-2010: вкладка Данные(Data) —Фильтр(Filter)(или вкладка Главная(Home) —Сортировка и фильтр(Sort&Filter) —Фильтр(Filter))
Теперь выбираем условие для фильтра:
- в Excel 2003 надо выбрать Условие и в появившейся форме выбрать непосредственно условие(«равно», «содержит», «начинается с» и т.д.), а напротив значение в соответствии с условием.
- Для 2007-2010 Excel нужно выбрать Текстовые фильтры(Text Filters) и либо сразу выбрать одно из предлагаемых условий, либо нажать Настраиваемый фильтр(Custom Filter) и ввести значения для отбора в форме
После этого удалить отфильтрованные строки. В 2007 Excel могут возникнуть проблемы с удалением отфильтрованных строк, поэтому рекомендую сначала так же прочитать статью: Excel удаляет вместо отфильтрованных строк — все?! Как избежать.
Способ второй:
применить код VBA, который потребует только указания значения, которое необходимо найти в строке и номер столбца, в котором искать значение.
Sub Del_SubStr() Dim sSubStr As String 'искомое слово или фраза(может быть указанием на ячейку) Dim lCol As Long 'номер столбца с просматриваемыми значениями Dim lLastRow As Long, li As Long Dim lMet As Long Dim arr sSubStr = InputBox("Укажите значение, которое необходимо найти в строке", "www.excel-vba.ru", "") If sSubStr = "" Then lMet = 0 Else lMet = 1 lCol = Val(InputBox("Укажите номер столбца, в котором искать указанное значение", "www.excel-vba.ru", 1)) If lCol = 0 Then Exit Sub lLastRow = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Row - 1 + ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count arr = Cells(1, lCol).Resize(lLastRow).Value Application.ScreenUpdating = 0 Dim rr As Range For li = 1 To lLastRow 'цикл с первой строки до конца If -(InStr(arr(li, 1), sSubStr) > 0) = lMet Then If rr Is Nothing Then Set rr = Cells(li, 1) Else Set rr = Union(rr, Cells(li, 1)) End If End If Next li If Not rr Is Nothing Then rr.EntireRow.Delete Application.ScreenUpdating = 1 End Sub
Если значение sSubStr не будет указано, то будут удалены строки, ячейки указанного столбца которых, пустые.
Данный код необходимо поместить в стандартный модуль. Вызвать с листа его можно нажатием клавиш Alt+F8, после чего выбрать Del_SubStr и нажать Выполнить. Если в данном коде в строке
If -(InStr(Cells(li, 1), sSubStr) > 0) = lMet Then
вместо = lMet указать <> lMet, то удаляться будут строки, не содержащие указанное для поиска значение. Иногда тоже удобно.
Но. Данный код просматривает строки на предмет частичного совпадения указанного значения. Например, если Вы укажете текст для поиска «отчет», то будут удалены все строки, в которых встречается это слово(«квартальный отчет», «отчет за месяц» и т.д.). Это не всегда нужно. Поэтому ниже приведен код, который будет удалять только строки, указанные ячейки которых равны конкретно указанному значению:
Sub Del_SubStr() Dim sSubStr As String 'искомое слово или фраза(может быть указанием на ячейку) Dim lCol As Long 'номер столбца с просматриваемыми значениями Dim lLastRow As Long, li As Long Dim arr sSubStr = InputBox("Укажите значение, которое необходимо найти в строке", "www.excel-vba.ru", "") lCol = Val(InputBox("Укажите номер столбца, в котором искать указанное значение", "www.excel-vba.ru", 1)) If lCol = 0 Then Exit Sub lLastRow = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Row - 1 + ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count arr = Cells(1, lCol).Resize(lLastRow).Value Application.ScreenUpdating = 0 Dim rr As Range For li = 1 To lLastRow 'цикл с первой строки до конца If CStr(arr(li, 1)) = sSubStr Then If rr Is Nothing Then Set rr = Cells(li, 1) Else Set rr = Union(rr, Cells(li, 1)) End If End If Next li If Not rr Is Nothing Then rr.EntireRow.Delete Application.ScreenUpdating = 1 End Sub
Здесь так же, как и в случае с предыдущим кодом можно заменить оператор сравнения(Cells(li, lCol) = sSubStr) с равно на неравенство(Cells(li, lCol) <> sSubStr) и тогда удаляться будут строки, значения ячеек которых не равно указанному.
УДАЛЕНИЕ СТРОК НА ОСНОВАНИИ СПИСКА ЗНАЧЕНИЙ(МНОЖЕСТВЕННЫЕ КРИТЕРИИ)
Иногда бывают ситуации, когда необходимо удалить строки не по одному значению, а по нескольким. Например, если строка содержит или Итог или Отчет. Ниже приведен код, при помощи которого можно удалить строки, указав в качестве критерия диапазон значений.
Значения, которые необходимо найти и удалить перечисляются на листе с именем «Лист2». Т.е. указав на «Лист2» в столбце А(начиная с первой строки) несколько значений — они все будут удалены. Если лист называется иначе(скажем «Соответствия») в коде необходимо будет «Лист2» заменить на «Соответствия». Удаление строк происходит на активном в момент запуска кода листе. Это значит, что перед запуском кода надо перейти на тот лист, строки в котором необходимо удалить.
Sub Del_Array_SubStr() Dim sSubStr As String 'искомое слово или фраза Dim lCol As Long 'номер столбца с просматриваемыми значениями Dim lLastRow As Long, li As Long Dim avArr, lr As Long Dim arr lCol = Val(InputBox("Укажите номер столбца, в котором искать указанное значение", "www.excel-vba.ru", 1)) If lCol = 0 Then Exit Sub Application.ScreenUpdating = 0 lLastRow = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Row - 1 + ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count 'заносим в массив значения листа, в котором необходимо удалить строки arr = Cells(1, lCol).Resize(lLastRow).Value 'Получаем с Лист2 значения, которые надо удалить в активном листе With Sheets("Лист2") 'Имя листа с диапазоном значений на удаление avArr = .Range(.Cells(1, 1), .Cells(.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp)) End With 'удаляем Dim rr As Range For lr = 1 To UBound(avArr, 1) sSubStr = avArr(lr, 1) For li = 1 To lLastRow 'цикл с первой строки до конца If CStr(arr(li, 1)) = sSubStr Then If rr Is Nothing Then Set rr = Cells(li, 1) Else Set rr = Union(rr, Cells(li, 1)) End If End If DoEvents Next li DoEvents Next lr If Not rr Is Nothing Then rr.EntireRow.Delete Application.ScreenUpdating = 1 End Sub
Чтобы код выше удалял строки не по точному совпадению слов, а по частичному(например, в ячейке записано «Привет, как дела?», а в списке есть слово «привет» — надо удалить, т.к. есть слово «привет»), то надо строку:
If CStr(arr(li, 1)) = sSubStr Then
заменить на такую:
If InStr(1, arr(li, 1), sSubStr, 1) > 0 Then
УДАЛЕНИЕ ИЗ ЛИСТА СТРОК, КОТОРЫХ НЕТ В СПИСКЕ ЗНАЧЕНИЙ(МНОЖЕСТВЕННЫЕ КРИТЕРИИ)
Т.к. в последнее время стало поступать все больше и больше вопросов как не удалять значения по списку, а наоборот — оставить в таблице только те значения, которые перечислены в списке — решил дополнить статью и таким кодом.
Значения, которые необходимо оставить перечисляются на листе с именем «Лист2». Т.е. указав на «Лист2» в столбце А(начиная с первой строки) несколько значений — после работы кода на листе будут оставлены только те строки, в которых присутствует хоть одно из перечисленных в списке значений. Если лист называется иначе(скажем «Соответствия») в коде необходимо будет «Лист2» заменить на «Соответствия». Удаление строк происходит на активном в момент запуска кода листе. Это значит, что перед запуском кода надо перейти на тот лист, строки в котором необходимо удалить.
В отличие от приведенных выше кодов, данный код ориентирован на то, что значения в списке указаны не полностью. Т.е. если необходимо оставить только те ячейки, в которых встречается слово «активы», то в списке надо указать только это слово. В этом случае если в ячейке будет записана фраза «Нематериальные активы» или «Активы сторонние» — эти ячейки не будут удалены, т.к. в них встречается слово «активы». Регистр букв при этом неважен.
'процедура оставляет в листе только те значения, которые перечислены в списке Sub LeaveOnlyFoundInArray() Dim sSubStr As String 'искомое слово или фраза Dim lCol As Long 'номер столбца с просматриваемыми значениями Dim lLastRow As Long, li As Long Dim avArr, lr As Long Dim arr Dim IsFind As Boolean lCol = Val(InputBox("Укажите номер столбца, в котором искать указанное значение", "www.excel-vba.ru", 1)) If lCol = 0 Then Exit Sub Application.ScreenUpdating = 0 lLastRow = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Row - 1 + ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count 'заносим в массив значения листа, в котором необходимо удалить строки arr = Cells(1, lCol).Resize(lLastRow).Value 'Получаем с Лист2 значения, которые надо удалить в активном листе With Sheets("Лист2") 'Имя листа с диапазоном значений на удаление avArr = .Range(.Cells(1, 1), .Cells(.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp)) End With 'удаляем Dim rr As Range For li = 1 To lLastRow 'цикл с первой строки таблицы до конца IsFind = False For lr = 1 To UBound(avArr, 1) 'цикл по списку значений на удаление sSubStr = avArr(lr, 1) If InStr(1, arr(li, 1), sSubStr, 1) > 0 Then IsFind = True End If DoEvents Next lr 'если значение таблицы не найдено в списке - удаляем строку If Not IsFind Then If rr Is Nothing Then Set rr = Cells(li, 1) Else Set rr = Union(rr, Cells(li, 1)) End If End If DoEvents Next li If Not rr Is Nothing Then rr.EntireRow.Delete Application.ScreenUpdating = 1 End Sub
Чтобы код выше сравнивал значения таблицы со значениями списка по точному совпадению слов, а не по частичному, то надо строку:
If InStr(1, arr(li, 1), sSubStr, 1) > 0 Then
заменить на такую:
If CStr(arr(li, 1)) = sSubStr Then
Для всех приведенных кодов можно строки не удалять, а скрывать. Для этого надо строку:
If Not rr Is Nothing Then rr.EntireRow.Delete
заменить на такую:
If Not rr Is Nothing Then rr.EntireRow.Hidden = True
По умолчанию все коды начинают просмотр строк с первой по последнюю заполненную на листе. И если необходимо удалять строки не с первой или не по последнюю, то надо внести корректировки в эту строку:
For li = 1 To lLastRow 'цикл с первой строки до конца
1 — это первая строка; lLastRow — определяется автоматически кодом и равна номеру последней заполненной строки на листе. Если надо начать удалять строки только с 7-ой строки(например, в первых 6-ти шапка), то код будет выглядеть так:
For li = 7 To lLastRow 'цикл с седьмой строки до конца
А если надо удалять только с 3-ей по 300-ю, то код будет выглядеть так:
For li = 3 To 300 'цикл с третьей строки до трехсотой
Так же см.:
Что такое макрос и где его искать?
Что такое модуль? Какие бывают модули?
Как создать кнопку для вызова макроса на листе
Удаление всех пустых строк в таблице
Удаление пустых столбцов на листе
Установить Быстрый фильтр
Фильтр
Статья помогла? Поделись ссылкой с друзьями!
Видеоуроки
Поиск по меткам
Access
apple watch
Multex
Power Query и Power BI
VBA управление кодами
Бесплатные надстройки
Дата и время
Записки
ИП
Надстройки
Печать
Политика Конфиденциальности
Почта
Программы
Работа с приложениями
Разработка приложений
Росстат
Тренинги и вебинары
Финансовые
Форматирование
Функции Excel
акции MulTEx
ссылки
статистика
|
sashgera Пользователь Сообщений: 83 |
#1 16.04.2014 00:28:25 Здравствуйте
Помогите, пожалуйста, изменить код макроса, что бы строки удалялись, начиная со строки ‘B2’ и до последней активной ячейки этого столбца (строки в таблице добавляются/удаляются). Прикрепленные файлы
|
||
|
Scripter Пользователь Сообщений: 255 |
#2 16.04.2014 02:06:57 просто изменить For i = .Rows.Count To 1 Step -1 на To2 но ваш код будет выдавать ошибку в случае конвертации пустой ячейки в Cnlg,
либо еще проще
Изменено: Scripter — 16.04.2014 02:29:27 |
||||
|
sashgera Пользователь Сообщений: 83 |
Scripter, Изменено: sashgera — 16.04.2014 02:30:56 |
|
Scripter Пользователь Сообщений: 255 |
#4 16.04.2014 02:30:32
Изменено: Scripter — 16.04.2014 08:56:06 |
||||
|
sashgera Пользователь Сообщений: 83 |
Scripter, большое спасибо, все отлично работает! |
|
sashgera Пользователь Сообщений: 83 |
#6 16.04.2014 03:13:19 Scripter, только что заметил, не удаляются пустые ячейки,
[USER=11992][/USER] |
||
|
Scripter Пользователь Сообщений: 255 |
#7 16.04.2014 03:38:25
добавил проверку на пустые ячейки
проверка на пустые может быть выполнена разными вариантами: Cells(i, 2).Value = «» |
||||
|
sashgera Пользователь Сообщений: 83 |
|
|
sashgera Пользователь Сообщений: 83 |
#9 17.04.2014 01:32:16 Scripter, я немного изменил макрос, все работает УДАЛЯЕМ строку если в ячейке столбца «B» есть число: от 0 до 399
не получается сделать аналогичный макрос
если можно, пожалуйста, помогите Прикрепленные файлы
Изменено: sashgera — 17.04.2014 01:39:50 |
||||
|
Scripter Пользователь Сообщений: 255 |
#10 17.04.2014 04:38:28 так
|
||
|
sashgera Пользователь Сообщений: 83 |
#11 17.04.2014 09:26:13 Scripter, спасибо! |
макрос удалит на листе все строки, в которых содержится искомый текст:
(пример — во вложении ConditionalRowsDeleting.xls)
Sub УдалениеСтрокПоУсловию() Dim ra As Range, delra As Range, ТекстДляПоиска As String Application.ScreenUpdating = False ' отключаем обновление экрана ТекстДляПоиска = "Наименование ценности" ' удаляем строки с таким текстом ' перебираем все строки в используемом диапазоне листа For Each ra In ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows ' если в строке найден искомый текст If Not ra.Find(ТекстДляПоиска, , xlValues, xlPart) Is Nothing Then ' добавляем строку в диапазон для удаления If delra Is Nothing Then Set delra = ra Else Set delra = Union(delra, ra) End If Next ' если подходящие строки найдены - удаляем их If Not delra Is Nothing Then delra.EntireRow.Delete End Sub
Чтобы вместо удаления просто скрыть такие строки, замените строку
If Not delra Is Nothing Then delra.EntireRow.Delete
на
If Not delra Is Nothing Then delra.EntireRow.Hidden=TRUE
Расширенная версия этого макроса — с использованием UserForm для ввода искомого значения
Function ПоискСтрокПоУсловию(ByVal ТекстДляПоиска As String, Optional HideOnly As Boolean) As Long ' функция получает в качестве параметра ТекстДляПоиска (можно использовать символы * и ?) ' Если HideOnly = TRUE, то строки, содержащие в ячейках ТекстДляПоиска, скрываются, ' иначе (HideOnly = FALSE - по умолчанию) - удаляются ' Функция возвращает количество удалённых строк Dim ra As Range, delra As Range Application.ScreenUpdating = False ' отключаем обновление экрана ' перебираем все строки в используемом диапазоне листа For Each ra In ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows ' если в строке найден искомый текст If Not ra.Find(ТекстДляПоиска, , xlValues, xlPart) Is Nothing Then ' добавляем строку в диапазон для удаления If delra Is Nothing Then Set delra = ra Else Set delra = Union(delra, ra) End If Next On Error Resume Next: ПоискСтрокПоУсловию = delra.Areas.Count ' количество найденных строк If Not delra Is Nothing Then ' если подходящие строки найдены - скрываем или удаляем их If HideOnly Then delra.EntireRow.Hidden = True Else delra.EntireRow.Delete End If End Function
Ещё один вариант кода, позволяющего выполнять поиск (с последующим удалением или скрытием строк) сразу по нескольким условиям:
Sub УдалениеСтрокПоНесколькимУсловиям() Dim ra As Range, delra As Range Application.ScreenUpdating = False ' отключаем обновление экрана ' ищем и удаляем строки, содержащие заданный текст ' (можно указать сколько угодно значений, и использовать подстановочные знаки) УдалятьСтрокиСТекстом = Array("Наименование *", "Количество", _ "текст?", "цен*сти", "*78*") ' перебираем все строки в используемом диапазоне листа For Each ra In ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows ' перебираем все фразы в массиве For Each word In УдалятьСтрокиСТекстом ' если в очередной строке листа найден искомый текст If Not ra.Find(word, , xlValues, xlPart) Is Nothing Then ' добавляем строку в диапазон для удаления If delra Is Nothing Then Set delra = ra Else Set delra = Union(delra, ra) End If Next word Next ' если подходящие строки найдены, то: (оставьте одну из 2 следующих строк) If Not delra Is Nothing Then delra.EntireRow.Hidden = True ' скрываем их If Not delra Is Nothing Then delra.EntireRow.Delete ' удаляем их End Sub
First, let me say categorically that there is nothing wrong with loops — they certainly have their place!
Recently we were presented with the below situation:
400000 | Smith, John| 2.4 | 5.66| =C1+D1
400001 | Q, Suzy | 4.6 | 5.47| =C2+D2
400002 | Schmoe, Joe| 3.8 | 0.14| =C3+D3
Blank | | | | #VALUE
Blank | | | | #VALUE
The OP wanted to delete rows where Column A is blank, but there is a value in Column E.
I suggest that this is an example where we could make use of SpecialCells and a temporary Error Column to identify the rows to be deleted.
Consider that you might add a column H to try and identify those rows; in that row you could use a formula like below:
=IF(AND(A:A="",E:E<>""),"DELETE THIS ROW","LEAVE THIS ROW")
now, it is possible get that formula to put an error in the rows where I test returns True. The reason we would do this is a feature of Excel called SpecialCells.
In Excel select any empty cell, and in the formula bar type
=NA()
Next, hit F5 or CTRL+G (Go to… on the Edit menu) then click the Special button to show the SpecialCells dialog.
In that dialog, click the radio next to ‘Formulas’ and underneath, clear the checkboxes so that only Errors is selected. Now click OK
Excel should have selected all the cells in the worksheet with an Error (#N/A) in them.
The code below takes advantage of this trick by creating a formula in column H that will put an #N/A in all the rows you want to delete, then calling SpecialCells to find the rows, and clear (delete) them…
Sub clearCells()
'
Dim sFormula As String
'
' this formula put's an error if the test returns true,
' so we can use SpecialCells function to highlight the
' rows to be deleted!
Create a formula that will return #NA when the formula returns TRUE
sFormula = "=IF(AND(A:A="""",E:E<>""""),NA(),"""")"
Put that formula in Column H, to find the rows that are to be deleted…
Range("H5:H" & Range("E65536").End(xlUp).Row).Formula = sFormula
Now use SpecialCells to highlight the rows to be deleted:
Range("H5:H" & Range("E65536").End(xlUp).Row).SpecialCells(xlCellTypeFormulas, xlErrors).entirerow.select
This line of code would highlight just Column A by using OFFSET in case instead of deleting the entire row, you wanted to put some text in, or clear it
Range("H5:H" & Range("E65536").End(xlUp).Row).SpecialCells(xlCellTypeFormulas, xlErrors).Offset(0, -7).select
and the below line of code will delete thhe entire row because we can 
Range("H5:H" & Range("E65536").End(xlUp).Row).SpecialCells(xlCellTypeFormulas, xlErrors).EntireRow.Delete shift:=xlup
' clean up the formula
Range("H5:H" & Range("E65536").End(xlUp).Row).Clear
'
End Sub
BTW, it’s also possible WITH A LOOP if you really want one 
One more thing, before Excel 2010 there was a limit of 8192 rows (I think because this feature went all the way back to 8-bit versions of Excel maybe)
The VBA legend Ron de Bruin (on whose website I first picked up this technique, among others) has something to say about this
Philip
Bottom Line: Learn how to use VBA macros to delete rows based on cell values or conditions. Includes video tutorial and sample code.
Skill Level: Intermediate
Video Tutorial
Download the Excel File
Here is the file I use in the video above that contains the VBA macro code examples.
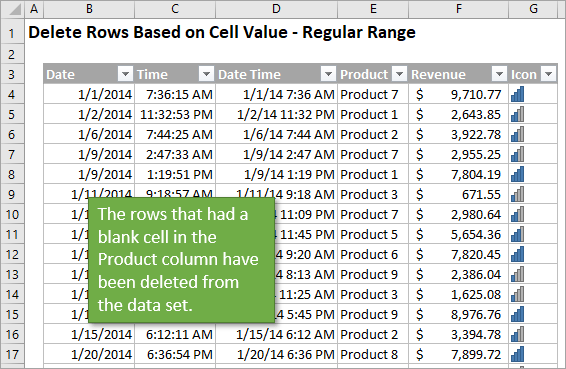
Does your data preparation process include deleting the same rows based on a condition? If so, you can use a macro to instantly delete any rows that have a particular value, date, or even blank cells.
The overall process is two simple steps:
- The first step is to filter the rows based on filter criteria for the values to be deleted.
- Then the macro deletes the visible cells in the range.
The Process Explained
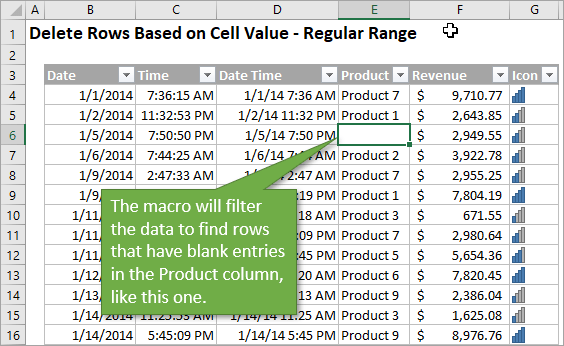
Below is an image of a data set that has some blank cells in column E (Product). You can see one of those blank cells is E6.
To remove the rows that have blank cells like this one, the macro first applies a filter to the product column.
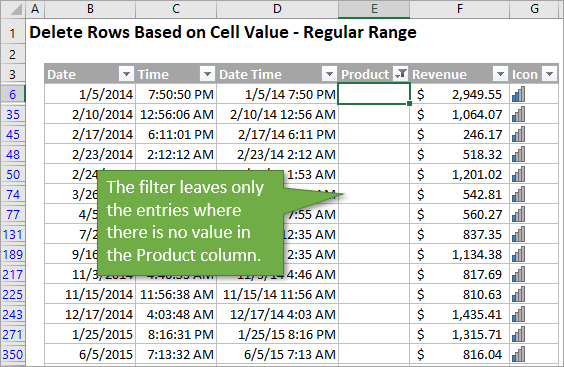
Next, the macro simply deletes all of the visible rows that have been left by the filter. It uses the SpecialCells method to create a reference to the visible cells.
This is the same as using the Go To Special menu (keyboard shortcut Alt+;) to select blanks. Checkout my article and video on how to copy & paste visible cells to learn more.
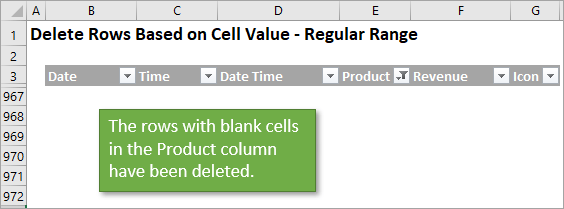
Finally, the macro can also clear the filters so that you are left viewing the entire data range, minus the rows you’ve deleted.
It’s a simple 2 or 3 step macro that will save time from doing this process manually.
Important Note: I added a step to clear all filters in the range or Table at the beginning of the macro. This ensures that there are no filters applied to other columns that could cause additional rows to be filtered out.
A big thanks to Hoang for pointing this out on the YouTube video!
The VBA Macro Code
The VBA code below can be copy/pasted to the VB Editor. The code is also included in the Excel file in the Download section above.
Sub Delete_Rows_Based_On_Value()
'Apply a filter to a Range and delete visible rows
'Source: https://www.excelcampus.com/vba/delete-rows-cell-values/Dim ws As Worksheet
'Set reference to the sheet in the workbook.
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Regular Range")
ws.Activate 'not required but allows user to view sheet if warning message appears
'Clear any existing filters
On Error Resume Next
ws.ShowAllData
On Error GoTo 0
'1. Apply Filter
ws.Range("B3:G1000").AutoFilter Field:=4, Criteria1:=""
'2. Delete Rows
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
ws.Range("B4:G1000").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeVisible).Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
'3. Clear Filter
On Error Resume Next
ws.ShowAllData
On Error GoTo 0
End Sub
You will just need to update the Worksheet and Range references for your specific file.
Avoiding the Pop-up Warning
When you run the macro you will receive a pop-up warning message that says “Delete entire sheet row?”
If you want to run the macro without having that pop-up box interrupting, you can simply remove the apostrophes before the two lines of code that begin with Application.DisplayAlerts.
So that portion of the macro now looks like this:
'2. Delete Rows
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
ws.Range("B4:G1000").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeVisible).Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
The Application.DisplayAlerts property is a toggle to turn warning alerts on/off. Setting it to False will turn off the alerts. These are alerts you might see from Excel when deleting ranges, deleting sheets, closing without saving, etc.
Applying the Macro to Tables
If your data is in an Excel Table instead of just a range of cells, you can still delete rows based on cell contents using a macro. The code is almost the same, but tweaked slightly so that it applies to Tables. Here is the code you would use for a Table.
Sub Delete_Rows_Based_On_Value_Table()
'Apply a filter to a Table and delete visible rows
'Source: https://www.excelcampus.com/vba/delete-rows-cell-values/Dim lo As ListObject
'Set reference to the sheet and Table.
Set lo = Sheet3.ListObjects(1)
ws.Activate
'Clear any existing filters
lo.AutoFilter.ShowAllData
'1. Apply Filter
lo.Range.AutoFilter Field:=4, Criteria1:="Product 2"
'2. Delete Rows
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
lo.DataBodyRange.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeVisible).Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
'3. Clear Filter
lo.AutoFilter.ShowAllData
End Sub
Additional Macros
I’ve also included a few additional macros to help customize the process further.
Custom Warning Message
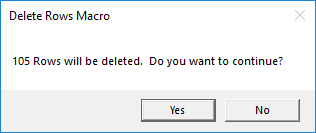
You can create a custom message box before deleting rows, instead of the default Excel warning to delete rows. The macro below also tells you the number of rows it is going to delete, and asks if you want to proceed.
Sub Delete_Rows_Based_On_Value_Table_Message()
'Display Yes/No message prompt before deleting rows
'Source: https://www.excelcampus.com/vba/delete-rows-cell-values/Dim lo As ListObject
Dim lRows As Long
Dim vbAnswer As VbMsgBoxResult
'Set reference to the sheet and Table.
Set lo = Sheet6.ListObjects(1)
lo.Parent.Activate 'Activate sheet that Table is on.
'Clear any existing filters
lo.AutoFilter.ShowAllData
'1. Apply Filter
lo.Range.AutoFilter Field:=4, Criteria1:="Product 2"
'Count Rows & display message
On Error Resume Next
lRows = WorksheetFunction.Subtotal(103, lo.ListColumns(1).DataBodyRange.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeVisible))
On Error GoTo 0
vbAnswer = MsgBox(lRows & " Rows will be deleted. Do you want to continue?", vbYesNo, "Delete Rows Macro")
If vbAnswer = vbYes Then
'Delete Rows
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
lo.DataBodyRange.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeVisible).Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
'Clear Filter
lo.AutoFilter.ShowAllData
End If
End Sub
This is what the custom pop-up box looks like:
This pop-up just serves as a check before deleting rows. It’s a great way to double check everything looks good before deleting. It also prevents you or your users from accidentally running the macro.
Checkout my video on how to add a Yes/No message box before the macro runs for details on this code. It’s part of my 4 part video series on the Personal Macro Workbook.
Deleting Rows Based on Multiple Criteria
You can also delete rows with a macro using more than one criteria. In the video above, I filter for rows that have both a blank Product field and a date before 1/1/2015.
Sub Delete_Rows_Based_On_Multiple_Values()
'Apply a filter to a Table and delete visible rows
'Source: https://www.excelcampus.com/vba/delete-rows-cell-values/Dim lo As ListObject
'Set reference to the sheet and Table.
Set lo = Sheet5.ListObjects(1)
lo.Parent.Activate 'Activate sheet that Table is on.
'Clear any existing filters
lo.AutoFilter.ShowAllData
'1. Apply Filter - Blanks in Product for before 2015 only
lo.Range.AutoFilter Field:=4, Criteria1:=""
lo.Range.AutoFilter Field:=1, Criteria1:="<1/1/2015"
'2. Delete Rows
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
lo.DataBodyRange.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeVisible).Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
'3. Clear Filter
lo.AutoFilter.ShowAllData
End Sub
This allows you to delete rows based on values in multiple columns. The filtering essentially uses AND logic between the columns and all conditions must be met.
If you want to use OR logic where any of the conditions are met, you can run multiple macros, or create a formula in a helper column with the logic.
Depending on the logic, it might be easiest to just create two separate macros. You can put the code all in one macro, or create another macro to call each macro. Here’s an example of what that macro might look like.
Sub Delete_Rows() Call Delete_Blank_Rows
Call Delete_Before_2015
End Sub
This method also allows you to run each macro individually.
Delete Rows Based on Criteria Specified by User
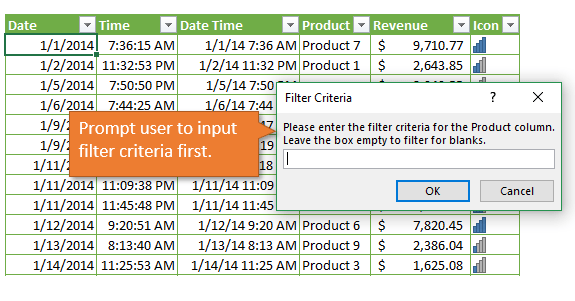
Daniel and Bob asked a great question in the comments below. They want the user of the file to be able to specify the filter criteria, instead of having it hard-coded in the macro.
We can use the Application.InputBox method to ask the user to input the criteria.
The InputBox method creates a pop-up message box that allows the user to type in the text box. The value in the text box is passed back to the macro and stored in a variable.
Here is the VBA code. I also added it to the sample file in the downloads section above.
Sub Delete_Rows_User_Input()
'Display Yes/No message prompt before deleting rows
'Source: https://www.excelcampus.com/vba/delete-rows-cell-values/Dim lo As ListObject
Dim lRows As Long
Dim vbAnswer As VbMsgBoxResult
Dim sCriteria As Variant
'Set reference to the sheet and Table.
Set lo = Sheet9.ListObjects(1)
lo.Parent.Activate 'Activate sheet that Table is on.
'Clear any existing filters
lo.AutoFilter.ShowAllData
'Ask user for input
sCriteria = Application.InputBox(Prompt:="Please enter the filter criteria for the Product column." _
& vbNewLine & "Leave the box empty to filter for blanks.", _
Title:="Filter Criteria", _
Type:=2)
'Exit if user presses Cancel button
If sCriteria = False Then Exit Sub
'1. Apply Filter
lo.Range.AutoFilter Field:=4, Criteria1:=sCriteria
'Count Rows & display message
On Error Resume Next
lRows = WorksheetFunction.Subtotal(103, lo.ListColumns(1).DataBodyRange.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeVisible))
On Error GoTo 0
vbAnswer = MsgBox(lRows & " Rows will be deleted. Do you want to continue?", vbYesNo, "Delete Rows Macro")
If vbAnswer = vbYes Then
'Delete Rows
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
lo.DataBodyRange.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeVisible).Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
'Clear Filter
lo.AutoFilter.ShowAllData
End If
End Sub
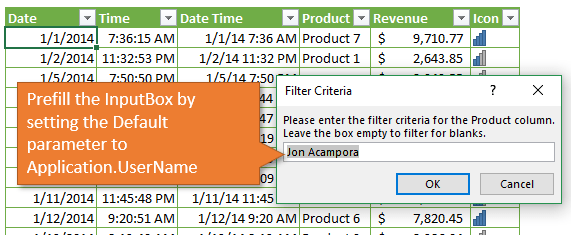
Pre-fill the User’s Name in the Input Box
Daniel also had a question about setting the filter criteria to the current user’s name. The Application.UserName property actually returns this value as long as the user has set it properly in Office/Excel.
We can use this as the Default parameter value in the input box.
sCriteria = Application.InputBox(Prompt:="Please enter the filter criteria for the Product column." _
& vbNewLine & "Leave the box empty to filter for blanks.", _
Title:="Filter Criteria", _
Default:=Application.UserName, _
Type:=2)
The user might still need to change the name if it does not match the value in the worksheet column you are filtering, but you can also get that synced up with the user to save them a lot of time.
Related Topics
Check out my posts on these similar topics as well.
- The Ultimate Guide to Filters with VBA Macros
- How to Copy and Paste Visible Cells Only
- 3 Ways to Delete Entire Blank Rows
- How to Create Your Personal Macro Workbook
Conclusion
Macros like this can be especially helpful if you are looking to clean up data and get rid of entries that you know you don’t need–maybe because they are too old or they are only partially complete.
There are a lot of ways to accomplish this task. Another common approach is to loop through cells and check their values individually.
However, I typically use this approach because it can be a lot faster to use the built in filters in Excel. It also allows us to preview the range before we delete it.
What will you use these macros for? Please leave a comment below with any suggestions and questions. Thank you! 🙂