MORPHEMIC STRUCTURE OF THE
WORD
The
morphological system of language reveals its properties through the
morphemic structure of the word. Morphology as part of the
grammatical theory faces the two segmental units: the morpheme and
the word. The morpheme is identified as part of the word, the
functions of the morpheme are effected only as the corresponding
constituent functions of the word as a whole. For instance, the form
of the verbal past tense is built up by means of the dental
grammatical suffix: train-ed
[-d]; publish-ed
[-t], meditate-ed
[-id].
The
morpheme is
a meaningful segmental component of the word; the morpheme is formed
by phonemes; as a meaningful component of the word it is elementary
(i.e. indivisible into smaller segments as regards its significative
function).
The
word is
a nominative unit of language; it is formed by morphemes; it enters
the lexicon of language as its elementary component (i.e. a component
indivisible into smaller segments as regards its nominative
function). Together with other nominative units the word is used for
the formation of the sentence – a unit of information in the
communication process.
In
traditional grammar the study of the morphemic structure of the word
was conducted in the light of the
two basic criteria: positional criterion
(the location of the marginal morphemes in relation to the central
ones) and
semantic or functional criterion
(the correlative contribution of the morphemes to the general meaning
of the word). The combination of these two criteria in an integral
description has led to the rational classification of morphemes that
is widely used both in research linguistic work and in practical
language teaching.
In accord with the
traditional classification, morphemes are divided into root-morphemes
(roots) and affixal morphemes (affixes). The roots express the
concrete, “material” part of the meaning of the word, while the
affixes express the specificational part of the meaning of the word;
the specifications being of lexico-semantic and grammatico-semantic
character.
The roots of notional words
are classical lexical morphemes.
The affixal morphemes include
prefixes, affixes, and inflexions. Of these, prefixes and lexical
suffixes have word-building functions, together with the root they
form the stem of the word; inflexions (grammatical suffixes) express
different morphological categories.
The root is obligatory for
any word, while affixes are not obligatory. Therefore one and the
same morphemic segment of functional status, depending on various
morphemic environment, can be used now as an affix, now as a root,
e.g.:
Out
– a root-word (preposition, adverb, verbal postposition, adjective,
noun, verb);
Throughout
–
a composite word in which
–out serves
as one of the roots;
Outing –
a two-morpheme word in which
out- is
a root, and –ing
is a suffix;
Outlook,
outline –
words in which out-
serves
as a prefix;
Look-out,
time-out –
words in which
–out serves
as a suffix.
As
a result of the distributional analysis
(the analysis of the environment of a unit), different types of
morphemes have been discriminated.
On the
basis of the degree
of self-dependence,
“free” morphemes and “bound” morphemes are distinguished.
Bound morphemes cannot form words by themselves, they are identified
only as component segmental parts of words. As different from this,
free morphemes can build up words by themselves, i.e. can be used
“freely”. For instance, in the word handful
the root hand
is
a free morpheme, while the suffix –ful
is a bound morpheme.
On the
basis of formal
presentation, “overt”
morphemes and “covert” morphemes are distinguished. Overt
morphemes are genuine, explicit morphemes building up words; the
covert morpheme is identified as a contrastive absence of morpheme
expressing a certain function. The notion of covert morpheme
coincides with the notion of zero morpheme in the oppositional
description of grammatical categories. For instance, the word-form
clocks
consists
of two overt morphemes: one lexical (root) and one grammatical
expressing the plural. The one- morpheme word-form clock,
since it expresses the singular, is also considered as consisting of
two morphemes, i.e. of the overt root and the covert (implicit)
grammatical suffix of the singular. The usual symbol for the covert
morpheme employed by linguists is the sign of the empty set: Ø.
On the
basis of segmental
relation, “segmental”
morphemes and “supra-segmental” morphemes are distinguished.
Interpreted as supra-segmental morphemes are intonation contours,
accents, pauses.
On the
basis of grammatical
alternation, “additive”
morphemes and “replacive” morphemes are distinguished.
Interpreted as additive morphemes are outer grammatical suffixes,
since, as a rule, they are opposed to the absence of morphemes in
grammatical alternation, e.g. look + ed, small + er, etc. In
distinction to these, the root phonemes pf grammatical interchange
are considered as replacive morphemes, since they replace one another
in the paradigmatic forms, e.g. dr-i-ve – dr-o-ve – dr-i-ven;
m-a-n – m-e-n, etc.
On the
basis of linear
characteristic, “continuous”
(or “linear”) morphemes and “discontinuous” morphemes are
distinguished. By the discontinuous morpheme, opposed to the common,
i.e. uninterruptedly expressed, continuous morpheme, a two-element
grammatical unit is meant which is identified in the analytical
grammatical form comprising an auxiliary word and a grammatical
suffix. These two elements, as it were, embed the notional stem;
hence, they are symbolically represented as follows:
Be …
ing –
for the continuous verb forms (e.g. is going);
Have …
en –
for the perfect verb forms (e.g. has gone);
Be …
en –
for the passive verb forms (e.g. is taken).
It is easy to see that the
notion of morpheme applied to the analytical form of the word
violates the principle of the identification of morpheme as an
elementary meaningful segment: the analytical “framing” consists
of two meaningful segments, i.e. of two different morphemes. On the
other hand, the general notion “discontinuous constituent” (or
unit) is quite rational and can be helpfully used in linguistic
description in its proper place.
3
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Lecture №3. Productive and Non-productive Ways of Word-formation in Modern English
Productivity is the ability to form new words after existing patterns which are readily understood by the speakers of language. The most important and the most productive ways of word-formation are affixation, conversion, word-composition and abbreviation (contraction). In the course of time the productivity of this or that way of word-formation may change. Sound interchange or gradation (blood-to bleed, to abide-abode, to strike-stroke) was a productive way of word building in old English and is important for a diachronic study of the English language. It has lost its productivity in Modern English and no new word can be coined by means of sound gradation. Affixation on the contrary was productive in Old English and is still one of the most productive ways of word building in Modern English.
WORDBUILDING
Word-building is one of the main ways of enriching vocabulary. There are four main ways of word-building in modern English: affixation, composition, conversion, abbreviation. There are also secondary ways of word-building: sound interchange, stress interchange, sound imitation, blends, back formation.
AFFIXATION
Affixation is one of the most productive ways of word-building throughout the history of English. It consists in adding an affix to the stem of a definite part of speech. Affixation is divided into suffixation and prefixation.
Suffixation
The main function of suffixes in Modern English is to form one part of speech from another, the secondary function is to change the lexical meaning of the same part of speech. (e.g. «educate» is a verb, «educator» is a noun, and music» is a noun, «musical» is also a noun or an adjective). There are different classifications of suffixes :
1. Part-of-speech classification. Suffixes which can form different parts of speech are given here :
a) noun-forming suffixes, such as: —er (criticizer), —dom (officialdom), —ism (ageism),
b) adjective-forming suffixes, such as: —able (breathable), less (symptomless), —ous (prestigious),
c) verb-forming suffixes, such as —ize (computerize) , —ify (minify),
d) adverb-forming suffixes , such as : —ly (singly), —ward (tableward),
e) numeral-forming suffixes, such as —teen (sixteen), —ty (seventy).
2. Semantic classification. Suffixes changing the lexical meaning of the stem can be subdivided into groups, e.g. noun-forming suffixes can denote:
a) the agent of the action, e.g. —er (experimenter), —ist (taxist), -ent (student),
b) nationality, e.g. —ian (Russian), —ese (Japanese), —ish (English),
c) collectivity, e.g. —dom (moviedom), —ry (peasantry, —ship (readership), —ati (literati),
d) diminutiveness, e.g. —ie (horsie), —let (booklet), —ling (gooseling), —ette (kitchenette),
e) quality, e.g. —ness (copelessness), —ity (answerability).
3. Lexico—grammatical character of the stem. Suffixes which can be added to certain groups of stems are subdivided into:
a) suffixes added to verbal stems, such as: —er (commuter), —ing (suffering), — able (flyable), —ment (involvement), —ation (computerization),
b) suffixes added to noun stems, such as: —less (smogless), —ful (roomful), —ism (adventurism), —ster (pollster), —nik (filmnik), —ish (childish),
c) suffixes added to adjective stems, such as: —en (weaken), —ly (pinkly), —ish (longish), —ness (clannishness).
4. Origin of suffixes. Here we can point out the following groups:
a) native (Germanic), such as —er,-ful, —less, —ly.
b) Romanic, such as : —tion, —ment, —able, —eer.
c) Greek, such as : —ist, —ism, -ize.
d) Russian, such as —nik.
5. Productivity. Here we can point out the following groups:
a) productive, such as: —er, —ize, —ly, —ness.
b) semi-productive, such as: —eer, —ette, —ward.
c) non-productive , such as: —ard (drunkard), —th (length).
Suffixes can be polysemantic, such as: —er can form nouns with the following meanings: agent, doer of the action expressed by the stem (speaker), profession, occupation (teacher), a device, a tool (transmitter). While speaking about suffixes we should also mention compound suffixes which are added to the stem at the same time, such as —ably, —ibly, (terribly, reasonably), —ation (adaptation from adapt). There are also disputable cases whether we have a suffix or a root morpheme in the structure of a word, in such cases we call such morphemes semi-suffixes, and words with such suffixes can be classified either as derived words or as compound words, e.g. —gate (Irangate), —burger (cheeseburger), —aholic (workaholic) etc.
Prefixation
Prefixation is the formation of words by means of adding a prefix to the stem. In English it is characteristic for forming verbs. Prefixes are more independent than suffixes. Prefixes can be classified according to the nature of words in which they are used: prefixes used in notional words and prefixes used in functional words. Prefixes used in notional words are proper prefixes which are bound morphemes, e.g. un— (unhappy). Prefixes used in functional words are semi-bound morphemes because they are met in the language as words, e.g. over— (overhead) (cf. over the table). The main function of prefixes in English is to change the lexical meaning of the same part of speech. But the recent research showed that about twenty-five prefixes in Modern English form one part of speech from another (bebutton, interfamily, postcollege etc).
Prefixes can be classified according to different principles:
1. Semantic classification:
a) prefixes of negative meaning, such as: in— (invaluable), non— (nonformals), un— (unfree) etc,
b) prefixes denoting repetition or reversal actions, such as: de— (decolonize), re— (revegetation), dis— (disconnect),
c) prefixes denoting time, space, degree relations, such as: inter— (interplanetary) , hyper— (hypertension), ex— (ex-student), pre— (pre-election), over— (overdrugging) etc.
2. Origin of prefixes:
a) native (Germanic), such as: un-, over-, under— etc.
b) Romanic, such as: in-, de-, ex-, re— etc.
c) Greek, such as: sym-, hyper— etc.
When we analyze such words as adverb, accompany where we can find the root of the word (verb, company) we may treat ad-, ac— as prefixes though they were never used as prefixes to form new words in English and were borrowed from Romanic languages together with words. In such cases we can treat them as derived words. But some scientists treat them as simple words. Another group of words with a disputable structure are such as: contain, retain, detain and conceive, receive, deceive where we can see that re-, de-, con— act as prefixes and —tain, —ceive can be understood as roots. But in English these combinations of sounds have no lexical meaning and are called pseudo-morphemes. Some scientists treat such words as simple words, others as derived ones. There are some prefixes which can be treated as root morphemes by some scientists, e.g. after— in the word afternoon. American lexicographers working on Webster dictionaries treat such words as compound words. British lexicographers treat such words as derived ones.
COMPOSITION
Composition is the way of word building when a word is formed by joining two or more stems to form one word. The structural unity of a compound word depends upon: a) the unity of stress, b) solid or hyphеnated spelling, c) semantic unity, d) unity of morphological and syntactical functioning. These are characteristic features of compound words in all languages. For English compounds some of these factors are not very reliable. As a rule English compounds have one uniting stress (usually on the first component), e.g. hard-cover, best—seller. We can also have a double stress in an English compound, with the main stress on the first component and with a secondary stress on the second component, e.g. blood—vessel. The third pattern of stresses is two level stresses, e.g. snow—white, sky—blue. The third pattern is easily mixed up with word-groups unless they have solid or hyphеnated spelling.
Spelling in English compounds is not very reliable as well because they can have different spelling even in the same text, e.g. war—ship, blood—vessel can be spelt through a hyphen and also with a break, insofar, underfoot can be spelt solidly and with a break. All the more so that there has appeared in Modern English a special type of compound words which are called block compounds, they have one uniting stress but are spelt with a break, e.g. air piracy, cargo module, coin change, penguin suit etc. The semantic unity of a compound word is often very strong. In such cases we have idiomatic compounds where the meaning of the whole is not a sum of meanings of its components, e.g. to ghostwrite, skinhead, brain—drain etc. In nonidiomatic compounds semantic unity is not strong, e. g., airbus, to bloodtransfuse, astrodynamics etc.
English compounds have the unity of morphological and syntactical functioning. They are used in a sentence as one part of it and only one component changes grammatically, e.g. These girls are chatter-boxes. «Chatter-boxes» is a predicative in the sentence and only the second component changes grammatically. There are two characteristic features of English compounds:
a) Both components in an English compound are free stems, that is they can be used as words with a distinctive meaning of their own. The sound pattern will be the same except for the stresses, e.g. «a green-house» and «a green house». Whereas for example in Russian compounds the stems are bound morphemes, as a rule.
b) English compounds have a two-stem pattern, with the exception of compound words which have form-word stems in their structure, e.g. middle-of-the-road, off—the—record, up—and—doing etc. The two-stem pattern distinguishes English compounds from German ones.
WAYS OF FORMING COMPOUND WORDS
Compound words in English can be formed not only by means of composition but also by means of:
a) reduplication, e.g. too—too, and also by means of reduplication combined with sound interchange , e.g. rope-ripe,
b) conversion from word-groups, e.g. to micky—mouse, can—do, makeup etc,
c) back formation from compound nouns or word-groups, e.g. to bloodtransfuse, to fingerprint etc ,
d) analogy, e.g. lie—in (on the analogy with sit-in) and also phone—in, brawn—drain (on the analogy with brain—drain) etc.
CLASSIFICATIONS OF ENGLISH COMPOUNDS
1. According to the parts of speech compounds are subdivided into:
a) nouns, such as: baby-moon, globe-trotter,
b) adjectives, such as : free-for-all, power-happy,
c) verbs, such as : to honey-moon, to baby-sit, to henpeck,
d) adverbs, such as: downdeep, headfirst,
e) prepositions, such as: into, within,
f) numerals, such as : fifty—five.
2. According to the way components are joined together compounds are divided into: a) neutral, which are formed by joining together two stems without any joining morpheme, e.g. ball—point, to windowshop,
b) morphological where components are joined by a linking element: vowels «o» or «i» or the consonant «s», e.g. («astrospace», «handicraft», «sportsman»),
c) syntactical where the components are joined by means of form-word stems, e.g. here-and-now, free-for-all, do-or-die.
3. According to their structure compounds are subdivided into:
a) compound words proper which consist of two stems, e.g. to job-hunt, train-sick, go-go, tip-top,
b) derivational compounds, where besides the stems we have affixes, e.g. ear—minded, hydro-skimmer,
c) compound words consisting of three or more stems, e.g. cornflower—blue, eggshell—thin, singer—songwriter,
d) compound-shortened words, e.g. boatel, VJ—day, motocross, intervision, Eurodollar, Camford.
4. According to the relations between the components compound words are subdivided into:
a) subordinative compounds where one of the components is the semantic and the structural centre and the second component is subordinate; these subordinative relations can be different: with comparative relations, e.g. honey—sweet, eggshell—thin, with limiting relations, e.g. breast—high, knee—deep, with emphatic relations, e.g. dog—cheap, with objective relations, e.g. gold—rich, with cause relations, e.g. love—sick, with space relations, e.g. top—heavy, with time relations, e.g. spring—fresh, with subjective relations, e.g. foot—sore etc
b) coordinative compounds where both components are semantically independent. Here belong such compounds when one person (object) has two functions, e.g. secretary-stenographer, woman-doctor, Oxbridge etc. Such compounds are called additive. This group includes also compounds formed by means of reduplication, e.g. fifty-fifty, no-no, and also compounds formed with the help of rhythmic stems (reduplication combined with sound interchange) e.g. criss-cross, walkie-talkie.
5. According to the order of the components compounds are divided into compounds with direct order, e.g. kill—joy, and compounds with indirect order, e.g. nuclear—free, rope—ripe.
CONVERSION
Conversion is a characteristic feature of the English word-building system. It is also called affixless derivation or zero-suffixation. The term «conversion» first appeared in the book by Henry Sweet «New English Grammar» in 1891. Conversion is treated differently by different scientists, e.g. prof. A.I. Smirntitsky treats conversion as a morphological way of forming words when one part of speech is formed from another part of speech by changing its paradigm, e.g. to form the verb «to dial» from the noun «dial» we change the paradigm of the noun (a dial, dials) for the paradigm of a regular verb (I dial, he dials, dialed, dialing). A. Marchand in his book «The Categories and Types of Present-day English» treats conversion as a morphological-syntactical word-building because we have not only the change of the paradigm, but also the change of the syntactic function, e.g. I need some good paper for my room. (The noun «paper» is an object in the sentence). I paper my room every year. (The verb «paper» is the predicate in the sentence). Conversion is the main way of forming verbs in Modern English. Verbs can be formed from nouns of different semantic groups and have different meanings because of that, e.g.:
a) verbs have instrumental meaning if they are formed from nouns denoting parts of a human body e.g. to eye, to finger, to elbow, to shoulder etc. They have instrumental meaning if they are formed from nouns denoting tools, machines, instruments, weapons, e.g. to hammer, to machine-gun, to rifle, to nail,
b) verbs can denote an action characteristic of the living being denoted by the noun from which they have been converted, e.g. to crowd, to wolf, to ape,
c) verbs can denote acquisition, addition or deprivation if they are formed from nouns denoting an object, e.g. to fish, to dust, to peel, to paper,
d) verbs can denote an action performed at the place denoted by the noun from which they have been converted, e.g. to park, to garage, to bottle, to corner, to pocket,
e) verbs can denote an action performed at the time denoted by the noun from which they have been converted e.g. to winter, to week-end.
Verbs can be also converted from adjectives, in such cases they denote the change of the state, e.g. to tame (to become or make tame), to clean, to slim etc.
Nouns can also be formed by means of conversion from verbs. Converted nouns can denote: a) instant of an action e.g. a jump, a move,
b) process or state e.g. sleep, walk,
c) agent of the action expressed by the verb from which the noun has been converted, e.g. a help, a flirt, a scold,
d) object or result of the action expressed by the verb from which the noun has been converted, e.g. a burn, a find, a purchase,
e) place of the action expressed by the verb from which the noun has been converted, e.g. a drive, a stop, a walk.
Many nouns converted from verbs can be used only in the Singular form and denote momentaneous actions. In such cases we have partial conversion. Such deverbal nouns are often used with such verbs as: to have, to get, to take etc., e.g. to have a try, to give a push, to take a swim.
CRITERIA OF SEMANTIC DERIVATION
In cases of conversion the problem of criteria of semantic derivation arises: which of the converted pair is primary and which is converted from it. The problem was first analized by prof. A.I. Smirnitsky. Later on P.A. Soboleva developed his idea and worked out the following criteria:
1. If the lexical meaning of the root morpheme and the lexico-grammatical meaning of the stem coincide the word is primary, e.g. in cases pen — to pen, father — to father the nouns are names of an object and a living being. Therefore in the nouns «pen» and «father» the lexical meaning of the root and the lexico-grammatical meaning of the stem coincide. The verbs «to pen» and «to father» denote an action, a process therefore the lexico-grammatical meanings of the stems do not coincide with the lexical meanings of the roots. The verbs have a complex semantic structure and they were converted from nouns.
2. If we compare a converted pair with a synonymic word pair which was formed by means of suffixation we can find out which of the pair is primary. This criterion can be applied only to nouns converted from verbs, e.g. «chat» n. and «chat» v. can be compared with «conversation» – «converse».
3. The criterion based on derivational relations is of more universal character. In this case we must take a word-cluster of relative words to which the converted pair belongs. If the root stem of the word-cluster has suffixes added to a noun stem the noun is primary in the converted pair and vica versa, e.g. in the word-cluster: hand n., hand v., handy, handful the derived words have suffixes added to a noun stem, that is why the noun is primary and the verb is converted from it. In the word-cluster: dance n., dance v., dancer, dancing we see that the primary word is a verb and the noun is converted from it.
SUBSTANTIVIZATION OF ADJECTIVES
Some scientists (Yespersen, Kruisinga) refer substantivization of adjectives to conversion. But most scientists disagree with them because in cases of substantivization of adjectives we have quite different changes in the language. Substantivization is the result of ellipsis (syntactical shortening) when a word combination with a semantically strong attribute loses its semantically weak noun (man, person etc), e.g. «a grown-up person» is shortened to «a grown-up». In cases of perfect substantivization the attribute takes the paradigm of a countable noun, e.g. a criminal, criminals, a criminal’s (mistake), criminals’ (mistakes). Such words are used in a sentence in the same function as nouns, e.g. I am fond of musicals. (musical comedies). There are also two types of partly substantivized adjectives: 1) those which have only the plural form and have the meaning of collective nouns, such as: sweets, news, finals, greens; 2) those which have only the singular form and are used with the definite article. They also have the meaning of collective nouns and denote a class, a nationality, a group of people, e.g. the rich, the English, the dead.
«STONE WALL» COMBINATIONS
The problem whether adjectives can be formed by means of conversion from nouns is the subject of many discussions. In Modern English there are a lot of word combinations of the type, e.g. price rise, wage freeze, steel helmet, sand castle etc. If the first component of such units is an adjective converted from a noun, combinations of this type are free word-groups typical of English (adjective + noun). This point of view is proved by O. Yespersen by the following facts:
1. «Stone» denotes some quality of the noun «wall».
2. «Stone» stands before the word it modifies, as adjectives in the function of an attribute do in English.
3. «Stone» is used in the Singular though its meaning in most cases is plural, and adjectives in English have no plural form.
4. There are some cases when the first component is used in the Comparative or the Superlative degree, e.g. the bottomest end of the scale.
5. The first component can have an adverb which characterizes it, and adjectives are characterized by adverbs, e.g. a purely family gathering.
6. The first component can be used in the same syntactical function with a proper adjective to characterize the same noun, e.g. lonely bare stone houses.
7. After the first component the pronoun «one» can be used instead of a noun, e.g. I shall not put on a silk dress, I shall put on a cotton one.
However Henry Sweet and some other scientists say that these criteria are not characteristic of the majority of such units. They consider the first component of such units to be a noun in the function of an attribute because in Modern English almost all parts of speech and even word-groups and sentences can be used in the function of an attribute, e.g. the then president (an adverb), out-of-the-way villages (a word-group), a devil-may-care speed (a sentence). There are different semantic relations between the components of «stone wall» combinations. E.I. Chapnik classified them into the following groups:
1. time relations, e.g. evening paper,
2. space relations, e.g. top floor,
3. relations between the object and the material of which it is made, e.g. steel helmet,
4. cause relations, e.g. war orphan,
5. relations between a part and the whole, e.g. a crew member,
6. relations between the object and an action, e.g. arms production,
7. relations between the agent and an action e.g. government threat, price rise,
8. relations between the object and its designation, e.g. reception hall,
9. the first component denotes the head, organizer of the characterized object, e.g. Clinton government, Forsyte family,
10. the first component denotes the field of activity of the second component, e.g. language teacher, psychiatry doctor,
11. comparative relations, e.g. moon face,
12. qualitative relations, e.g. winter apples.
ABBREVIATION
In the process of communication words and word-groups can be shortened. The causes of shortening can be linguistic and extra-linguistic. By extra-linguistic causes changes in the life of people are meant. In Modern English many new abbreviations, acronyms, initials, blends are formed because the tempo of life is increasing and it becomes necessary to give more and more information in the shortest possible time. There are also linguistic causes of abbreviating words and word-groups, such as the demand of rhythm, which is satisfied in English by monosyllabic words. When borrowings from other languages are assimilated in English they are shortened. Here we have modification of form on the basis of analogy, e.g. the Latin borrowing «fanaticus» is shortened to «fan» on the analogy with native words: man, pan, tan etc. There are two main types of shortenings: graphical and lexical.
Graphical abbreviations
Graphical abbreviations are the result of shortening of words and word-groups only in written speech while orally the corresponding full forms are used. They are used for the economy of space and effort in writing. The oldest group of graphical abbreviations in English is of Latin origin. In Russian this type of abbreviation is not typical. In these abbreviations in the spelling Latin words are shortened, while orally the corresponding English equivalents are pronounced in the full form, e.g. for example (Latin exampli gratia), a.m. – in the morning (ante meridiem), No – number (numero), p.a. – a year (per annum), d – penny (dinarius), lb – pound (libra), i. e. – that is (id est) etc.
Some graphical abbreviations of Latin origin have different English equivalents in different contexts, e.g. p.m. can be pronounced «in the afternoon» (post meridiem) and «after death» (post mortem). There are also graphical abbreviations of native origin, where in the spelling we have abbreviations of words and word-groups of the corresponding English equivalents in the full form. We have several semantic groups of them: a) days of the week, e.g. Mon – Monday, Tue – Tuesday etc
b) names of months, e.g. Apr – April, Aug – August etc.
c) names of counties in UK, e.g. Yorks – Yorkshire, Berks – Berkshire etc
d) names of states in USA, e.g. Ala – Alabama, Alas – Alaska etc.
e) names of address, e.g. Mr., Mrs., Ms., Dr. etc.
f) military ranks, e.g. capt. – captain, col. – colonel, sgt – sergeant etc.
g) scientific degrees, e.g. B.A. – Bachelor of Arts, D.M. – Doctor of Medicine. (Sometimes in scientific degrees we have abbreviations of Latin origin, e.g., M.B. – Medicinae Baccalaurus).
h) units of time, length, weight, e.g. f./ft – foot/feet, sec. – second, in. – inch, mg. – milligram etc.
The reading of some graphical abbreviations depends on the context, e.g. «m» can be read as: male, married, masculine, metre, mile, million, minute, «l.p.» can be read as long-playing, low pressure.
Initial abbreviations
Initialisms are the bordering case between graphical and lexical abbreviations. When they appear in the language, as a rule, to denote some new offices they are closer to graphical abbreviations because orally full forms are used, e.g. J.V. – joint venture. When they are used for some duration of time they acquire the shortened form of pronouncing and become closer to lexical abbreviations, e.g. BBC is as a rule pronounced in the shortened form. In some cases the translation of initialisms is next to impossible without using special dictionaries. Initialisms are denoted in different ways. Very often they are expressed in the way they are pronounced in the language of their origin, e.g. ANZUS (Australia, New Zealand, United States) is given in Russian as АНЗУС, SALT (Strategic Arms Limitation Talks) was for a long time used in Russian as СОЛТ, now a translation variant is used (ОСВ – Договор об ограничении стратегических вооружений). This type of initialisms borrowed into other languages is preferable, e.g. UFO – НЛО, CП – JV etc. There are three types of initialisms in English:
a) initialisms with alphabetical reading, such as UK, BUP, CND etc
b) initialisms which are read as if they are words, e.g. UNESCO, UNO, NATO etc.
c) initialisms which coincide with English words in their sound form, such initialisms are called acronyms, e.g. CLASS (Computor-based Laboratory for Automated School System). Some scientists unite groups b) and c) into one group which they call acronyms. Some initialisms can form new words in which they act as root morphemes by different ways of wordbuilding:
a) affixation, e.g. AVALism, ex- POW, AIDSophobia etc.
b) conversion, e.g. to raff, to fly IFR (Instrument Flight Rules),
c) composition, e.g. STOLport, USAFman etc.
d) there are also compound-shortened words where the first component is an initial abbreviation with the alphabetical reading and the second one is a complete word, e.g. A-bomb, U-pronunciation, V -day etc. In some cases the first component is a complete word and the second component is an initial abbreviation with the alphabetical pronunciation, e.g. Three -Ds (Three dimensions) – стереофильм.
Abbreviations of words
Abbreviation of words consists in clipping a part of a word. As a result we get a new lexical unit where either the lexical meaning or the style is different form the full form of the word. In such cases as «fantasy» and «fancy», «fence» and «defence» we have different lexical meanings. In such cases as «laboratory» and «lab», we have different styles. Abbreviation does not change the part-of-speech meaning, as we have it in the case of conversion or affixation, it produces words belonging to the same part of speech as the primary word, e.g. prof. is a noun and professor is also a noun. Mostly nouns undergo abbreviation, but we can also meet abbreviation of verbs, such as to rev. from to revolve, to tab from to tabulate etc. But mostly abbreviated forms of verbs are formed by means of conversion from abbreviated nouns, e.g. to taxi, to vac etc. Adjectives can be abbreviated but they are mostly used in school slang and are combined with suffixation, e.g. comfy, dilly etc. As a rule pronouns, numerals, interjections. conjunctions are not abbreviated. The exceptions are: fif (fifteen), teen-ager, in one’s teens (apheresis from numerals from 13 to 19). Lexical abbreviations are classified according to the part of the word which is clipped. Mostly the end of the word is clipped, because the beginning of the word in most cases is the root and expresses the lexical meaning of the word. This type of abbreviation is called apocope. Here we can mention a group of words ending in «o», such as disco (dicotheque), expo (exposition), intro (introduction) and many others. On the analogy with these words there developed in Modern English a number of words where «o» is added as a kind of a suffix to the shortened form of the word, e.g. combo (combination) – небольшой эстрадный ансамбль, Afro (African) – прическа под африканца etc. In other cases the beginning of the word is clipped. In such cases we have apheresis, e.g. chute (parachute), varsity (university), copter (helicopter), thuse (enthuse) etc. Sometimes the middle of the word is clipped, e.g. mart (market), fanzine (fan magazine) maths (mathematics). Such abbreviations are called syncope. Sometimes we have a combination of apocope with apheresis, when the beginning and the end of the word are clipped, e.g. tec (detective), van (vanguard) etc. Sometimes shortening influences the spelling of the word, e.g. «c» can be substituted by «k» before «e» to preserve pronunciation, e.g. mike (microphone), Coke (coca-cola) etc. The same rule is observed in the following cases: fax (facsimile), teck (technical college), trank (tranquilizer) etc. The final consonants in the shortened forms are substituded by letters characteristic of native English words.
NON-PRODUCTIVE WAYS OF WORDBUILDING
SOUND INTERCHANGE
Sound interchange is the way of word-building when some sounds are changed to form a new word. It is non-productive in Modern English, it was productive in Old English and can be met in other Indo-European languages. The causes of sound interchange can be different. It can be the result of Ancient Ablaut which cannot be explained by the phonetic laws during the period of the language development known to scientists, e.g. to strike – stroke, to sing – song etc. It can be also the result of Ancient Umlaut or vowel mutation which is the result of palatalizing the root vowel because of the front vowel in the syllable coming after the root (regressive assimilation), e.g. hot — to heat (hotian), blood — to bleed (blodian) etc. In many cases we have vowel and consonant interchange. In nouns we have voiceless consonants and in verbs we have corresponding voiced consonants because in Old English these consonants in nouns were at the end of the word and in verbs in the intervocalic position, e.g. bath – to bathe, life – to live, breath – to breathe etc.
STRESS INTERCHANGE
Stress interchange can be mostly met in verbs and nouns of Romanic origin: nouns have the stress on the first syllable and verbs on the last syllable, e.g. `accent — to ac`cent. This phenomenon is explained in the following way: French verbs and nouns had different structure when they were borrowed into English, verbs had one syllable more than the corresponding nouns. When these borrowings were assimilated in English the stress in them was shifted to the previous syllable (the second from the end). Later on the last unstressed syllable in verbs borrowed from French was dropped (the same as in native verbs) and after that the stress in verbs was on the last syllable while in nouns it was on the first syllable. As a result of it we have such pairs in English as: to af«fix -`affix, to con`flict- `conflict, to ex`port -`export, to ex`tract — `extract etc. As a result of stress interchange we have also vowel interchange in such words because vowels are pronounced differently in stressed and unstressed positions.
SOUND IMITATION
It is the way of word-building when a word is formed by imitating different sounds. There are some semantic groups of words formed by means of sound imitation:
a) sounds produced by human beings, such as : to whisper, to giggle, to mumble, to sneeze, to whistle etc.
b) sounds produced by animals, birds, insects, such as: to hiss, to buzz, to bark, to moo, to twitter etc.
c) sounds produced by nature and objects, such as: to splash, to rustle, to clatter, to bubble, to ding-dong, to tinkle etc.
The corresponding nouns are formed by means of conversion, e.g. clang (of a bell), chatter (of children) etc.
BLENDS
Blends are words formed from a word-group or two synonyms. In blends two ways of word-building are combined: abbreviation and composition. To form a blend we clip the end of the first component (apocope) and the beginning of the second component (apheresis) . As a result we have a compound- shortened word. One of the first blends in English was the word «smog» from two synonyms: smoke and fog which means smoke mixed with fog. From the first component the beginning is taken, from the second one the end, «o» is common for both of them. Blends formed from two synonyms are: slanguage, to hustle, gasohol etc. Mostly blends are formed from a word-group, such as: acromania (acronym mania), cinemaddict (cinema adict), chunnel (channel, canal), dramedy (drama comedy), detectifiction (detective fiction), faction (fact fiction) (fiction based on real facts), informecial (information commercial), Medicare (medical care), magalog (magazine catalogue) slimnastics (slimming gymnastics), sociolite (social elite), slanguist (slang linguist) etc.
BACK FORMATION
It is the way of word-building when a word is formed by dropping the final morpheme to form a new word. It is opposite to suffixation, that is why it is called back formation. At first it appeared in the language as a result of misunderstanding the structure of a borrowed word. Prof. Yartseva explains this mistake by the influence of the whole system of the language on separate words. E.g. it is typical of English to form nouns denoting the agent of the action by adding the suffix -er to a verb stem (speak- speaker). So when the French word «beggar» was borrowed into English the final syllable «ar» was pronounced in the same way as the English —er and Englishmen formed the verb «to beg» by dropping the end of the noun. Other examples of back formation are: to accreditate (from accreditation), to bach (from bachelor), to collocate (from collocation), to enthuse (from enthusiasm), to compute (from computer), to emote (from emotion), to televise (from television) etc.
As we can notice in cases of back formation the part-of-speech meaning of the primary word is changed, verbs are formed from nouns.
23
WORD FORMATION • Compounding/composition – Criteria of compounds. – Classification of compounds. • Secondary ways of word formation.
Recommended literature: • Антрушина, Г. Б. , Афанасьева, О. В. , Морозова, Н. Н. Лексикология английского языка: Учеб. пособие для студентов. – 3 -е изд. , стереотип. – M. : Дрофа, 2001. — С. 104 -120. • Arnold I. V. The English word. – M. : Высш. школа, 1986. – С. 108 -133, 134 -152. • Харитончик З. А. Лексикология английского языка: Учеб. пособие. –Мн. : Выш. шк. , 1992. – С. 177 — 187, 188 -191. • Дубенец Э. М. Лексикология современного английского языка: лекции и семинары. Пособие для студентов гуманитарных вузов. – М. : «Глосса. Пресс» , 2002. – С. 37 -45, 58 -70.
Compounding/Composition is the way of word building when a word is formed by joining two or more stems to form one word. • I. V. Arnold: Compounds are words consisting of at least 2 stems, which are characterized by semantic integrity and structural cohesion.
• R. S. Ginsburg distinguishes between 2 levels of analysis: derivational and morphemic. • E. g. to nickname, to baby-sit, to honeymoon • On the morphemic level these are compound words, • On the derivational level these are words created by either conversion (to nickname, to honeymoon) or by back formation (to babysit) => they are derivatives.
Compound words are characterized • by semantic integrity and structural cohesion. • Structurally compounds are characterized by the specific order of arrangement in which stems follow one another.
The lexical meaning of a compound • may be a sum of meanings of its constituents, i. e. they may be motivated, e. g. tablecloth, shoemaker, bookshelf; • the lexical meanings of the constituents may be fused together to create a new additive meaning, i. e. partially motivated, e. g. handbag – a bag to be carried in the hand -> additive meaning: a women’s bag to keep money and other stuff; flowerbed), • the meaning of a compound has nothing to do with the meanings of its constituents, i. e. nonmotivated or idiomatic, e. g. a sweet tooth, a chatter box.
Main features of compounds • The unity of stress; • Solid or hyphenated spelling; • Semantic unity; • Unity of morphological and syntactic functioning.
Criteria of compounds • Eugene Nider: Criteria for determining the word units in a language are of 3 types: phonological, morphological, and syntactic. • Charles Bally suggested the graphic criterion, • Otto Jesperson – the semantic criterion.
The phonological criterion • compound words are, as a rule, characterised by 1 main primary stress (and a secondary stress) in compound, while in free word combinations both components are stressed: • /blackboard — /black /board; • /laughing gas — /laughing /boys.
The morphological criterion • the structural integrity of compounds enables compounds to function as an inseparable unit and has 1 paradigm.
The syntactic criterion • The components of compounds can t have modifiers. E. g. compare: sky – blue (adj. ), but: blue sky -> very blue sky. • The semantic criterion • A combination of words refers to the number of concepts/notions = the number of words, a compound refers to 1 concept : Its colour; kind of colour.
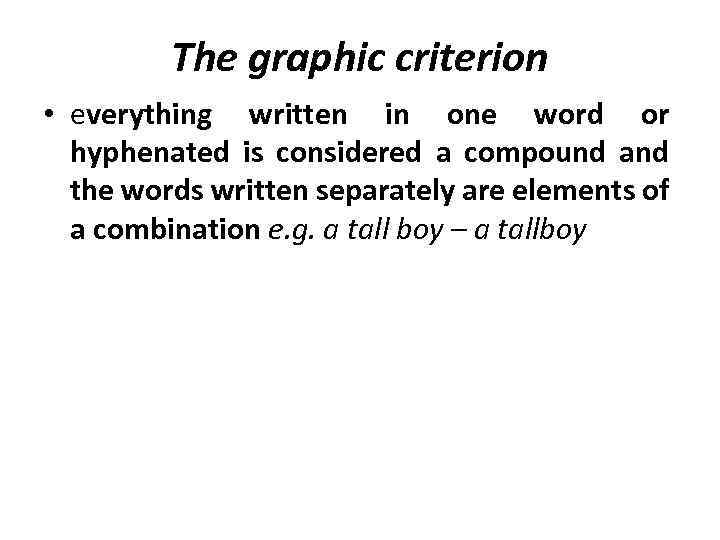
The graphic criterion • everything written in one word or hyphenated is considered a compound and the words written separately are elements of a combination e. g. a tall boy – a tallboy
Classifications of compounds • Compounds may be classified in accordance with different principles: • -part of speech reference: Noun honeymoon, Verb to babysit, Adjective power-happy; • -the way components are joined: • neutral compounds (without a linking element) to window-shop; • morphological compounds (with a linking element) handicraft; • syntactical compounds free-for-all, do-or-die, here-and-now;
— the syntactic relations between the stems (coordination or subordination) • compounds fall into coordinative and subordinative. • In coordinative compounds the constituents are semantically and structurally equal. The coordinative compounds may be subdivided into • 1. additive actor – manager, secretary –stenographer • 2. reduplicative tic-tic, hash-hash • 3. words with varied rhythmic form of the same stem: willy- nilly, tic-toc, drip – drop.
• In subordinative compounds the components are neither semantically nor structurally equal. • Their relation is based on the domination of 1 component over the other. The 2 nd component is usually a structural and semantic center of a compound, e. g. ship – wreck, inn – keeper, tooth – brush
-the order of components: syntactic compounds in which the components are put in the same order as in a free word group (direct word order): sun -rise <= the sun rises, blackbird <= a black bird, long-tailed <= long tail, killjoy<= to kill joy; • asyntactic compounds in which the order of the components is not the same as in a free word-group (indirect word order): sky-blue <= blue sky, lamp-lit <= to lit a lamp, well-dressed <= to dress well, mud-stained <= stained with mud. •
-structure: • compounds proper (2 root stems): to job-hunt; • compound-affixed words: videoplayer; • compounds of 3 or more stems: cornflower-blue, singer-songwriter; • compound-shortened words: V-day, motocross, AIDSphobia, motel;
Semi-affixes • The words with such elements as -man, -land, -like, –proof, -worthy stand between compounds and derived words because the mentioned elements • 1) have all the features of a stem and preserve the semantic associations with the free form and • 2) their meaning has become so generalized that it is close to the meaning of an affix: • • • Sportsman, policeman, seaman, countryman (man = -er, -or); Ireland, Scotland, motherland, wonderland; Businesslike, ladylike, starlike; kissproof, fireproof, foolproof, bulletproof; Trustworthy, praiseworthy, seaworthy.
Secondary ways of word formation • Shortening/clipping can be of different types: • initial clipping – the initial part of a word is clipped: phone <= telephone, bus<= omnibus • final clipping — the final part of a word is clipped: vac <= vacations, cab<= cabriolet, lab <= laboratory; • initial and final clipping – frige <= refrigerator; • Acronyms are words made of initial letters of a word group: UNO, BBC, MP, PM, NATO, USA, EU, etc.
Blending • is a way to combine elements of two words to create one, so it includes 2 word building processes: clipping and composition: smog<= smoke + fog, brunch<= breakfast + lunch, Oxbridge<= Oxford + Cambridge; edutainment <= education + entertainment, slanguage <= slang +language, • medicare <= medical care; • •
Back-formation/reversion • is such a way of word building when a new word is produces not by adding an affix to a stem but by subtracting an affix. • It is normally used to create a verb from a noun: • beggar => to beg, • burglar => to burgle, • baby-sitter => to baby-sit, • television =>to televise.
Stress and sound interchange: • import- to import, export – to export, conduct –to conduct; • sing-song, bleed-blood, feed – food. • Lexicalization • is a process of turning a word form into a separate lexical unit: Customs, arms, irons, glasses.
Sound imitation/onomatopoeia • is a way of coining a word by imitating different sounds produced in nature by animals: bark, croak, miaow; people: giggle, gargle, groan; things: crack, etc; • Reduplication – • doubling a stem, either without phonetic changes: bye-bye, or with variation of a root sound: ping-pong, riff-raff (the disreputable elements of society), dilly -dally (wasting time)
• -structure: compounds proper (2 root stems): to job-hunt; • compound-affixed words: videoplayer; • compounds of 3 or more stems: cornflowerblue, singer-songwriter; • compound-shortened words: V-day, motocross, AIDSphobia, motel;
Lecture 3. Word-building: affixation, conversion, composition, abbreviation. THE WORD-BUILDING SYSTEM OF ENGLISH 1. Word-derivation 2. Affixation 3. Conversion 4. Word-composition 5. Shortening 6. Blending 7. Acronymy 8. Sound interchange 9. Sound imitation 10. Distinctive stress 11. Back-formation Word-formation is a branch of Lexicology which studies the process of building new words, derivative structures and patterns of existing words. Two principle types of wordformation are distinguished: word-derivation and word-composition. It is evident that wordformation proper can deal only with words which can be analyzed both structurally and semantically. Simple words are closely connected with word-formation because they serve as the foundation of derived and compound words. Therefore, words like writer, displease, sugar free, etc. make the subject matter of study in word-formation, but words like to write, to please, atom, free are irrelevant to it. WORD-FORMATION WORD-DERIVATION AFFIXATION WORD-COMPOSITION CONVERSION 1. Word-derivation. Speaking about word-derivation we deal with the derivational structure of words which basic elementary units are derivational bases, derivational affixes and derivational patterns. A derivational base is the part of the word which establishes connection with the lexical unit that motivates the derivative and determines its individual lexical meaning describing the difference between words in one and the same derivative set. For example, the individual lexical meaning of the words singer, writer, teacher which denote active doers of the action is signaled by the lexical meaning of the derivational bases: sing-, write-, teach-. Structurally derivational bases fall into 3 classes: 1. Bases that coincide with morphological stems of different degrees оf complexity, i.e., with words functioning independently in modern English e.g., dutiful, day-dreamer. Bases are functionally and semantically distinct from morphological stems. Functionally the morphological stem is a part of the word which is the starting point for its forms: heart – hearts; it is the part which presents the entire grammatical paradigm. The stem remains unchanged throughout all word-forms; it keeps them together preserving the identity of the word. A derivational base is the starting point for different words (heart – heartless – hearty) and its derivational potential outlines the type and scope of existing words and new creations. Semantically the stem stands for the whole semantic structure of the word; it represents all its lexical meanings. A base represents, as a rule, only one meaning of the source word. 2. Bases that coincide with word-forms, e.g., unsmiling, unknown. The base is usually represented by verbal forms: the present and the past participles. 3. Bases that coincide with word-groups of different degrees of stability, e.g., blue-eyed, empty-handed. Bases of this class allow a rather limited range of collocability, they are most active with derivational affixes in the class of adjectives and nouns (long-fingered, blue-eyed). Derivational affixes are Immediate Constituents of derived words in all parts of speech. Affixation is generally defined as the formation of words by adding derivational affixes to different types of bases. Affixation is subdivided into suffixation and prefixation. In Modern English suffixation is mostly characteristic of nouns and adjectives coining, while prefixation is mostly typical of verb formation. A derivational pattern is a regular meaningful arrangement, a structure that imposes rigid rules on the order and the nature of the derivational base and affixes that may be brought together to make up a word. Derivational patterns are studied with the help of distributional analysis at different levels. Patterns are usually represented in a generalized way in terms of conventional symbols: small letters v, n, a, d which stand for the bases coinciding with the stems of the respective parts of speech: verbs, etc. Derivational patterns may represent derivative structure at different levels of generalization: - at the level of structural types. The patterns of this type are known as structural formulas, all words may be classified into 4 classes: suffixal derivatives (friendship) n + -sf → N, prefixal derivatives (rewrite), conversions (a cut, to parrot) v → N, compound words (musiclover). - at the level of structural patterns. Structural patterns specify the base classes and individual affixes thus indicating the lexical-grammatical and lexical classes of derivatives within certain structural classes of words. The suffixes refer derivatives to specific parts of speech and lexical subsets. V + -er = N (a semantic set of active agents, denoting both animate and inanimate objects - reader, singer); n + -er = N (agents denoting residents or occupations Londoner, gardener). We distinguish a structural semantic derivationa1 pattern. - at the level of structural-semantic patterns. Derivational patterns may specify semantic features of bases and individual meaning of affixes: N + -y = A (nominal bases denoting living beings are collocated with the suffix meaning "resemblance" - birdy, catty; but nominal bases denoting material, parts of the body attract another meaning "considerable amount" - grassy, leggy). The basic ways of forming new words in word-derivation are affixation and conversion. Affixation is the formation of a new word with the help of affixes (heartless, overdo). Conversion is the formation of a new word by bringing a stem of this word into a different paradigm (a fall from to fall). 2. Affixation Affixation is generally defined as the formation of words by adding derivational affixes to different types of bases. Affixation includes suffixation and prefixation. Distinction between suffixal and prefixal derivates is made according to the last stage of derivation, for example, from the point of view of derivational analysis the word unreasonable – un + (reason- + -able) is qualified as a prefixal derivate, while the word discouragement – (dis- + -courage) + -ment is defined as a suffixal derivative. Suffixation is the formation of words with the help of suffixes. Suffixes usually modify the lexical meaning of the base and transfer words to a different part of speech. Suffixes can be classified into different types in accordance with different principles. According to the lexico-grammatical character suffixes may be: deverbal suffixes, e.d., those added to the verbal base (agreement); denominal (endless); deadjectival (widen, brightness). According to the part of speech formed suffixes fall into several groups: noun-forming suffixes (assistance), adjective-forming suffixes (unbearable), numeral-forming suffixes (fourteen), verb-forming suffixes (facilitate), adverb-forming suffixes (quickly, likewise). Semantically suffixes may be monosemantic, e.g. the suffix –ess has only one meaning “female” – goddess, heiress; polysemantic, e.g. the suffix –hood has two meanings “condition or quality” falsehood and “collection or group” brotherhood. According to their generalizing denotational meaning suffixes may fall into several groups: the agent of the action (baker, assistant); collectivity (peasantry); appurtenance (Victorian, Chinese); diminutiveness (booklet). Prefixation is the formation of words with the help of prefixes. Two types of prefixes can be distinguished: 1) those not correlated with any independent word (un-, post-, dis-); 2) those correlated with functional words (prepositions or preposition-like adverbs: out-, up-, under-). Diachronically distinction is made between prefixes of native and foreign origin. Prefixes can be classified according to different principles. According to the lexico-grammatical character of the base prefixes are usually added to, they may be: deverbal prefixes, e.d., those added to the verbal base (overdo); denominal (unbutton); deadjectival (biannual). According to the part of speech formed prefixes fall into several groups: noun-forming prefixes (ex-husband), adjective-forming prefixes (unfair), verb-forming prefixes (dethrone), adverb-forming prefixes (uphill). Semantically prefixes may be monosemantic, e.g. the prefix –ex has only one meaning “former” – ex-boxer; polysemantic, e.g. the prefix –dis has four meanings “not” disadvantage and “removal of” to disbrunch. According to their generalizing denotational meaning prefixes may fall into several groups: negative prefixes – un, non, dis, a, in (ungrateful, nonpolitical, disloyal, amoral, incorrect); reversative prefixes - un, de, dis (untie, decentralize, disconnect); pejorative prefixes – mis, mal, pseudo (mispronounce, maltreat, pseudo-scientific); prefix of repetition (redo), locative prefixes – super, sub, inter, trans (superstructure, subway, intercontinental, transatlantic). 3. Conversion Conversion is a process which allows us to create additional lexical terms out of those that already exist, e.g., to saw, to spy, to snoop, to flirt. This process is not limited to one syllable words, e.g., to bottle, to butter, nor is the process limited to the creation of verbs from nouns, e.g., to up the prices. Converted words are extremely colloquial: "I'll microwave the chicken", "Let's flee our dog", "We will of course quiche and perrier you". Conversion came into being in the early Middle English period as a result of the leveling and further loss of endings. In Modern English conversion is a highly-productive type of word-building. Conversion is a specifically English type of word formation which is determined by its analytical character, by its scarcity of inflections and abundance of mono-and-de-syllabic words in different parts of speech. Conversion is coining new words in a different part of speech and with a different distribution but without adding any derivative elements, so that the original and the converted words are homonyms. Structural Characteristics of Conversion: Mostly monosyllabic words are converted, e.g., to horn, to box, to eye. In Modern English there is a marked tendency to convert polysyllabic words of a complex morphological structure, e.g., to e-mail, to X-ray. Most converted words are verbs which may be formed from different parts of speech from nouns, adjectives, adverbs, interjections. Nouns from verbs - a try, a go, a find, a loss From adjectives - a daily, a periodical From adverbs - up and down From conjunctions - but me no buts From interjection - to encore Semantic Associations / Relations of Conversion: The noun is the name of a tool or implement, the verb denotes an action performed by the tool, e.g., to nail, to pin, to comb, to brush, to pencil; The noun is the name of an animal, the verb denotes an action or aspect of behavior considered typical of this animal, e.g., to monkey, to rat, to dog, to fox; When the noun is the name of a part of a human body, the verb denotes an action performed by it, e.g., to hand, to nose, to eye; When the noun is the name of a profession or occupation, the verb denotes the activity typical of it, e.g., to cook, to maid, to nurse; When the noun is the name of a place, the verb will denote the process of occupying the place or by putting something into it, e.g., to room, to house, to cage; When the word is the name of a container, the verb will denote the act of putting something within the container, e.g., to can, to pocket, to bottle; When the word is the name of a meal, the verb means the process of taking it, e.g., to lunch, to supper, to dine, to wine; If an adjective is converted into a verb, the verb may have a generalized meaning "to be in a state", e.g., to yellow; When nouns are converted from verbs, they denote an act or a process, or the result, e.g., a try, a go, a find, a catch. 4. Word-composition Compound words are words consisting of at least two stems which occur in the language as free forms. Most compounds in English have the primary stress on the first syllable. For example, income tax has the primary stress on the in of income, not on the tax. Compounds have a rather simple, regular set of properties. First, they are binary in structure. They always consist of two or more constituent lexemes. A compound which has three or more constituents must have them in pairs, e.g., washingmachine manufacturer consists of washingmachine and manufacturer, while washingmachine in turn consists of washing and machine. Compound words also usually have a head constituent. By a head constituent we mean one which determines the syntactic properties of the whole lexeme, e.g., the compound lexeme longboat consists of an adjective, long and a noun, boat. The compound lexeme longboat is a noun, and it is а noun because boat is a noun, that is, boat is the head constituent of longboat. Compound words can belong to all the major syntactic categories: • Nouns: signpost, sunlight, bluebird, redwood, swearword, outhouse; • Verbs: window shop, stargaze, outlive, undertake; • Adjectives: ice-cold, hell-bent, undersized; • Prepositions: into, onto, upon. From the morphological point of view compound words are classified according to the structure of immediate constituents: • Compounds consisting of simple stems - heartache, blackbird; • Compounds where at least one of the constituents is a derived stem -chainsmoker, maid-servant, mill-owner, shop-assistant; • Compounds where one of the constituents is a clipped stem - V-day, A-bomb, Xmas, H-bag; • Compounds where one of the constituents is a compound stem - wastes paper basket, postmaster general. Compounds are the commonest among nouns and adjectives. Compound verbs are few in number, as they are mostly the result of conversion, e.g., to blackmail, to honeymoon, to nickname, to safeguard, to whitewash. The 20th century created some more converted verbs, e.g., to weekend, to streamline,, to spotlight. Such converted compounds are particularly common in colloquial speech of American English. Converted verbs can be also the result of backformation. Among the earliest coinages are to backbite, to browbeat, to illtreat, to housekeep. The 20th century gave more examples to hitch-hike, to proof-read, to mass-produce, to vacuumclean. One more structural characteristic of compound words is classification of compounds according to the type of composition. According to this principle two groups can be singled out: words which are formed by a mere juxtaposition without any connecting elements, e.g., classroom, schoolboy, heartbreak, sunshine; composition with a vowel or a consonant placed between the two stems. e.g., salesman, handicraft. Semantically compounds may be idiomatic and non-idiomatic. Compound words may be motivated morphologically and in this case they are non-idiomatic. Sunshine - the meaning here is a mere meaning of the elements of a compound word (the meaning of each component is retained). When the compound word is not motivated morphologically, it is idiomatic. In idiomatic compounds the meaning of each component is either lost or weakened. Idiomatic compounds have a transferred meaning. Chatterbox - is not a box, it is a person who talks a great deal without saying anything important; the combination is used only figuratively. The same metaphorical character is observed in the compound slowcoach - a person who acts and thinks slowly. The components of compounds may have different semantic relations. From this point of view we can roughly classify compounds into endocentric and exocentric. In endocentric compounds the semantic centre is found within the compound and the first element determines the other as in the words filmstar, bedroom, writing-table. Here the semantic centres are star, room, table. These stems serve as a generic name of the object and the determinants film, bed, writing give some specific, additional information about the objects. In exocentric compound there is no semantic centre. It is placed outside the word and can be found only in the course of lexical transformation, e.g., pickpocket - a person who picks pockets of other people, scarecrow an object made to look like a person that a farmer puts in a field to frighten birds. The Criteria of Compounds As English compounds consist of free forms, it's difficult to distinguish them from phrases, because there are no reliable criteria for that. There exist three approaches to distinguish compounds from corresponding phrases: Formal unity implies the unity of spelling solid spelling, e.g., headmaster; with a hyphen, e.g., head-master; with a break between two components, e.g., head master. Different dictionaries and different authors give different spelling variants. Phonic principal of stress Many compounds in English have only one primary stress. All compound nouns are stressed according to this pattern, e.g., ice-cream, ice cream. The rule doesn't hold with adjectives. Compound adjectives are double-stressed, e.g., easy-going, new-born, sky-blue. Stress cannot help to distinguish compounds from phrases because word stress may depend on phrasal stress or upon the syntactic function of a compound. Semantic unity Semantic unity means that a compound word expresses one separate notion and phrases express more than one notion. Notions in their turn can't be measured. That's why it is hard to say whether one or more notions are expressed. The problem of distinguishing between compound words and phrases is still open to discussion. According to the type of bases that form compounds they can be of : 1. compounds proper – they are formed by joining together bases built on the stems or on the ford-forms with or without linking element, e.g., door-step; 2. derivational compounds – by joining affixes to the bases built on the word-groups or by converting the bases built on the word-groups into the other parts of speech, e.g., longlegged → (long legs) + -ed, a turnkey → (to turn key) + conversion. More examples: do-gooder, week-ender, first-nighter, house-keeping, baby-sitting, blue-eyed blond-haired, four-storied. The suffixes refer to both of the stems combined, but not to the final stem only. Such stems as nighter, gooder, eyed do not exist. Compound Neologisms In the last two decades the role of composition in the word-building system of English has increased. In the 60th and 70th composition was not so productive as affixation. In the 80th composition exceeded affixation and comprised 29.5 % of the total number of neologisms in English vocabulary. Among compound neologisms the two-component units prevail. The main patterns of coining the two-component neologisms are Noun stem + Noun stem = Noun; Adjective stem + Noun stem = Noun. There appeared a tendency to coin compound nouns where: The first component is a proper noun, e.g., Kirlian photograph - biological field of humans. The first component is a geographical place, e.g., Afro-rock. The two components are joined with the help of the linking vowel –o- e.g., bacteriophobia, suggestopedia. The number of derivational compounds increases. The main productive suffix to coin such compound is the suffix -er - e.g., baby-boomer, all nighter. Many compound words are formed according to the pattern Participle 2 + Adv = Adjective, e.g., laid-back, spaced-out, switched-off, tapped-out. The examples of verbs formed with the help of a post-positive -in -work-in, die-in, sleep-in, write-in. Many compounds formed by the word-building pattern Verb + postpositive are numerous in colloquial speech or slang, e.g., bliss out, fall about/horse around, pig-out. ATTENTION: Apart from the principle types there are some minor types of modern wordformation, i.d., shortening, blending, acronymy, sound interchange, sound imitation, distinctive stress, back-formation, and reduplicaton. 5. Shortening Shortening is the formation of a word by cutting off a part of the word. They can be coined in two different ways. The first is to cut off the initial/ middle/ final part: Aphaeresis – initial part of the word is clipped, e.g., history-story, telephone-phone; Syncope – the middle part of the word is clipped, e.g., madam- ma 'am; specs spectacles Apocope – the final part of the word is clipped, e.g., professor-prof, editored, vampirevamp; Both initial and final, e.g., influenza-flu, detective-tec. Polysemantic words are usually clipped in one meaning only, e.g., doc and doctor have the meaning "one who practices medicine", but doctor is also "the highest degree given by a university to a scholar or scientist". Among shortenings there are homonyms, so that one and the same sound and graphical complex may represent different words, e.g., vac - vacation/vacuum, prep — preparation/preparatory school, vet — veterinary surgeon/veteran. 6. Blending Blending is a particular type of shortening which combines the features of both clipping and composition, e.g., motel (motor + hotel), brunch (breakfast + lunch), smog (smoke + fog), telethon (television + marathon), modem , (modulator + demodulator), Spanglish (Spanish + English). There are several structural types of blends: Initial part of the word + final part of the word, e.g., electrocute (electricity + execute); initial part of the word + initial part of the word, e.g., lib-lab (liberal+labour); Initial part of the word + full word, e.g., paratroops (parachute+troops); Full word + final part of the word, e.g., slimnastics (slim+gymnastics). 7. Acronymy Acronyms are words formed from the initial letters of parts of a word or phrase, commonly the names of institutions and organizations. No full stops are placed between the letters. All acronyms are divided into two groups. The first group is composed of the acronyms which are often pronounced as series of letters: EEC (European Economic Community), ID (identity or identification card), UN (United Nations), VCR (videocassette recorder), FBI (Federal Bureau of Investigation), LA (Los Angeles), TV (television), PC (personal computer), GP (General Practitioner), ТВ (tuberculosis). The second group of acronyms is composed by the words which are pronounced according to the rules of reading in English: UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization), AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome), ASH (Action on Smoking and Health). Some of these pronounceable words are written without capital letters and therefore are no longer recognized as acronyms: laser (light amplification by stimulated emissions of radiation), radar (radio detection and ranging). Some abbreviations have become so common and normal as words that people do not think of them as abbreviations any longer. They are not written in capital letters, e.g., radar (radio detection and ranging), laser (light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation) yuppie, gruppie, sinbads, dinkies. Some abbreviations are only written forms but they are pronounced as full words, e.g., Mr, Mrs, Dr. Some abbreviations are from Latin. They are used as part of the language etc. - et cetera, e.g., (for example) — exampli gratia, that is - id est. Acromymy is widely used in the press, for the names of institutions, organizations, movements, countries. It is common to colloquial speech, too. Some acronyms turned into regular words, e.g., jeep -came from the expression general purpose car. There are a lot of homonyms among acronyms: MP - Member of Parliament/Military Police/Municipal Police PC - Personal Computer/Politically correct 8. Sound-interchange Sound-interchange is the formation of a new word due to an alteration in the phonemic composition of its root. Sound-interchange falls into two groups: 1) vowel-interchange, e.g., food – feed; in some cases vowel-interchange is combined with suffixation, e.g., strong – strength; 2) consonant-interchange e.g., advice – to advise. Consonant-interchange and vowel-interchange may be combined together, e.g., life – to live. This type of word-formation is greatly facilitated in Modern English by the vast number of monosyllabic words. Most words made by reduplication represent informal groups: colloquialisms and slang, hurdy-gurdy, walkie-talkie, riff-raff, chi-chi girl. In reduplication new words are coined by doubling a stem, either without any phonetic changes as in bye-bye or with a variation of the root-vowel or consonant as in ping-pong, chit-chat. 9. Sound imitation or (onomatopoeia) It is the naming of an action or a thing by more or less exact reproduction of the sound associated with it, cf.: cock-a-do-doodle-do – ку-ка-ре-ку. Semantically, according to the source sound, many onomatopoeic words fall into the following definitive groups: 1) words denoting sounds produced by human beings in the process of communication or expressing their feelings, e.g., chatter; 2) words denoting sounds produced by animals, birds, insects, e.g., moo, buzz; 3) words imitating the sounds of water, the noise of metallic things, movements, e.g., splash, whip, swing. 10. Distinctive stress Distinctive stress is the formation of a word by means of the shift of the stress in the source word, e.g., increase – increase. 11. Back-formation Backformation is coining new words by subtracting a real or supposed suffix, as a result of misinterpretation of the structure of the existing word. This type of word-formation is not highly productive in Modern English and it is built on the analogy, e.g., beggar-to beg, cobbler to cobble, blood transfusion — to blood transfuse, babysitter - to baby-sit.
Words in English public website
Ling 216
Rice University
Prof. S. Kemmer
Types of Word Formation Processes
Compounding
Compounding forms a word out of two or more root morphemes. The words
are called compounds or compound words.
In Linguistics, compounds can be either native or borrowed.
Native English roots are
typically free morphemes, so that means native compounds are made out of
independent words that can occur by themselves. Examples:
mailman (composed of free root mail and free root man)
mail carrier
dog house
fireplace
fireplug (a regional word for ‘fire hydrant’)
fire hydrant
dry run
cupcake
cup holder
email
e-ticket
pick-up truck
talking-to
Some compounds have a preposition as one of the component words as in the
last 2 examples.
In Greek and Latin, in contrast to English, roots do not typically stand
alone. So compounds are composed of bound roots. Compounds formed in
English from borrowed Latin and Greek morphemes preserve this
characteristic. Examples include photograph,
iatrogenic, and many thousands of other classical words.
Note that compounds are written in various ways in English:
with a space between the elements; with a hyphen between the
elements; or simply with the two roots run together with no separation.
The way the word is written does not affect its status as a
compound. Over time, the convention for writing compounds can change,
usually in the direction from separate words (e.g. email used to be written with a hyphen.
In the 19th century, today and tomorrow were sometimes still written to-day and to-morrow. The to originally was the preposition to with an older meaning ‘at [a particular period of time]’.
Clock work changed
to clock-work and finally to one word with no break
(clockwork). If you read older literature you might see some
compound words that are now written as one word appearing
with unfamiliar spaces or hyphens between the components.
Another thing to note about compounds is that they can combine words
of different parts of speech. The list above shows mostly noun-noun
compounds, which is probably the most common part of speech
combination, but there are others, such as adjective-noun (dry
run, blackbird, hard drive), verb-noun (pick-pocket,
cut-purse, lick-spittle) and even verb-particle (where
‘particle’ means a word basically designating spatial expression that
functions to complete a literal or metaphorical path), as in
run-through, hold-over. Sometimes these compounds are
different in the part of speech of the whole compound vs. the part of
speech of its components. Note that the last two are actually nouns,
despite their components.
Some compounds have more than two component words. These are formed
by successively combining words into compounds, e.g. pick-up truck,
formed from pick-up and truck , where the first component,
pick-up is itself a compound formed from
pick and up. Other examples are ice-cream
cone, no-fault insurance and even more complex compounds like
top-rack dishwasher safe.
There are a number of subtypes of compounds that do not have to do
with part of speech, but rather the sound characteristics of the
words. These subtypes are not mutually exclusive.
Rhyming compounds (subtype of compounds)
These words are compounded from two rhyming words. Examples:
lovey-dovey
chiller-killer
There are words that are formally very similar to rhyming compounds,
but are not quite compounds in English because the second element is
not really a word—it is just a nonsense item added to a root word to
form a rhyme. Examples:
higgledy-piggledy
tootsie-wootsie
This formation
process is associated in English with child talk (and talk addressed
to children), technically called hypocoristic language. Examples:
bunnie-wunnie
Henny Penny
snuggly-wuggly
Georgie Porgie
Piggie-Wiggie
Another word type that looks a bit like rhyming compounds
comprises words that are formed of
two elements that almost match, but differ in their vowels.
Again, the second element is typically a nonsense form:
pitter-patter
zigzag
tick-tock
riffraff
flipflop
Derivation
Derivation is the creation of words by modification of a root without
the addition of other roots. Often the effect is a change in part of
speech.
Affixation (Subtype of Derivation)
The most common type of derivation is the addition of one or more affixes to a
root, as in the word derivation itself. This process is called
affixation, a term which covers both prefixation and suffixation.
Blending
Blending is one of the most beloved of word formation processes in
English. It is especially creative in that speakers take two words
and merge them based not on morpheme structure but on sound structure.
The resulting words are called blends.
Usually in word formation we combine roots or affixes along their
edges: one morpheme comes to an end before the next one starts. For example, we
form derivation out of the sequence of morphemes
de+riv+at(e)+ion. One morpheme follows the next and each one has
identifiable
boundaries. The morphemes do not overlap.
But in
blending, part of one word is stitched onto another word, without any
regard for where one morpheme ends and another begins. For example,
the word swooshtika ‘Nike swoosh as a logo symbolizing
corporate power and hegemony’
was formed from swoosh and swastika. The swoosh
part remains whole and recognizable in the blend, but the tika part is
not a morpheme, either in the word swastika or
in the blend. The blend is a perfect merger of form, and also of
content. The meaning contains an implicit analogy between the
swastika and the swoosh, and thus conceptually blends them into one
new kind of thing having properties of both, but also combined
properties of neither source. Other examples include glitterati (blending
glitter and literati) ‘Hollywood social set’, mockumentary (mock and
documentary) ‘spoof documentary’.
The earliest blends in English only go back to the 19th century, with
wordplay coinages by Lewis Carroll in Jabberwocky. For example, he
introduced to the language slithy, formed from lithe and
slimy, and galumph, (from gallop and
triumph. Interestingly galumph has survived as a word in
English, but it now seems to mean ‘walk in a stomping, ungainly way’.
Some blends that have been around for quite a while include brunch
(breakfast and lunch), motel (motor hotel), electrocute (electric and
execute), smog (smoke and
fog) and cheeseburger (cheese and hamburger).
These go back to the first half of the twentieth
century. Others, such as stagflation (stagnation and inflation),
spork (spoon and fork), and carjacking (car and hijacking) arose
since the 1970s.
Here are some more recent blends I have run across:
mocktail (mock and cocktail) ‘cocktail with no alcohol’
splog (spam and blog) ‘fake blog designed to attract hits and
raise Google-ranking’
Britpoperati (Britpop and literati) ‘those knowledgable about current British pop music’
Clipping
Clipping is a type of abbreviation of a word in which one part is
‘clipped’ off the rest, and the remaining word now means essentially the same
thing as what the whole word means or meant. For example, the word
rifle is a fairly modern clipping of an earlier compound
rifle gun, meaning a gun with a rifled barrel. (Rifled means
having a spiral groove causing the bullet to spin, and thus making it
more accurate.) Another clipping is burger, formed by clipping
off the beginning of the word hamburger. (This clipping could
only come about once hamburg+er was reanalyzed as ham+burger.)
Acronyms
Acronyms are formed by taking the initial letters of a phrase
and making a word out of it. Acronyms provide a way of turning a phrase into a word. The classical acronym is also
pronounced as a word. Scuba was formed
from self-contained underwater breathing apparatus. The
word snafu was originally WW2 army slang for Situation
Normal All Fucked Up. Acronyms were being used more and more by
military bureaucrats, and soldiers coined snafu in an
apparent parody of this overused device. Sometimes an acronym uses not just the first letter, but the first syllable of a component word, for example radar, RAdio Detection And Ranging and sonar, SOund Navigation and Ranging. Radar forms an analogical model for both sonar and lidar, a technology that measures distance to a target and and maps its surface by
bouncing a laser off it. There is some evidence that lidar was not coined as an acronym, but instead as a blend of light and radar. Based on the word itself, either etymology appears to work, so many speakers assume that lidar is an acronym rather than a blend.
A German example that strings together the initial syllables of the
words in the phrase, is Gestapo , from GEheime STAats POlizei
‘Sectret State Police’. Another is Stasi, from STAats
SIcherheit ‘State Security’.
Acronyms are a subtype of initialism. Initialisms also include words made from the initial letters of a Phrase but NOT pronounced as a normal word — it is instead pronounced as a string of letters. Organzation names aroften initialisms of his type. Examples:
NOW (National Organization of Women)
US or U.S., USA or U.S.A. (United States)
UN or U.N. (United Nations)
IMF (International Monetary Fund)
Some organizations ARE pronounced as a word:
UNICEF
MADD (Mothers Against Drunk Driving)
The last example incorporates a meaning into the word that fits the nature of the organization. Sometimes this type is called a Reverse Acronym or a Backronym.
These can be thought of as a special case of acronyms.
Memos, email, and text messaging (text-speak) are modes of communication
that give rise to both clippings and acronyms, since these
word formation methods are designed to abbreviate.
Some acronyms:
NB — Nota bene, literally ‘note well’. Used by scholars making notes
on texts. (A large number of other scholarly acronyms from Latin are
used, probably most invented in the medieval period or Renaissance,
not originally in Latin)
BRB — be right back (from 1980s, 90s)
FYI — for your information (from mid 20th century)
LOL — laughing
out loud (early 21st century) — now pronounced either /lol/ or /el o
el/; has spawned compounds like Lolcats).
ROFL — rolling on the floor laughing
ROFLMAO — rolling on the floor laughing my ass off
Reanalysis
Sometimes speakers unconsciously change the morphological boundaries of a word, creating a new morph or making an old one unrecognizable. This happened in hamburger, which was originally Hamburger steak ‘chopped and formed steak in the Hamburg style, then hamburger (hamburg + er), then ham + burger
Folk etymology
A popular idea of a word’s origin that is not in accordance with its real origin.
Many folk etymologies are cases of reanalysis in which the word is not only reanalysis but it changes under the influence of the new understanding of its morphemes. The result is that speakers think it has a different origin than it does.
Analogy
Sometimes speakers take an existing word as a model and form other words using some of its morphemes as a fixed part, and changing one of them to something new, with an analogically similar meaning. Cheeseburger was formed on the analogy of hamburger, replacing a perceived morpheme ham with cheese.
carjack and skyjack were also formed by analogy.
Novel creation
In novel creation, a speaker or writer forms a word without starting
from other morphemes. It is as if the word if formed out of ‘whole
cloth’, without reusing any parts.
Some examples of now-conventionalized words that were novel creations
include blimp, googol (the mathematical term),
bling, and possibly slang, which emerged in the last 200
years with no obvious etymology. Some novel creations seem to display
‘sound symbolism’, in which a word’s phonological form suggests its
meaning in some way. For example, the sound of the word bling
seems to evoke heavy jewelry making noise. Another novel creation whose sound seems
to relate to its meaning is badonkadonk, ‘female rear end’, a
reduplicated word which can remind English speakers of the repetitive
movement of the rear end while walking.
Creative respelling
Sometimes words are formed by simply changing the spelling of a word
that the speaker wants to relate to the new word. Product names
often involve creative respelling, such as Mr. Kleen.
© Suzanne Kemmer