It’s
a process of creating new words from material available in the
language after a certain structural and semantic formulas and
pattern, forming words by combining root & affix morphemes.
2 Types of word formation:
1)
Compounding (словосложение)
2)
Word – derivation
Within
the types further distinction may be made between the ways of forming
words. The basic way of forming words is word-derivation affixation
and conversion apart from this shortening and a number of minor ways
of formal words such as back-forming, blending, sound imitation are
traditionally referred to formation.
Different types of word
formation:
Affixation
is
the formation of new words by means of suffixes and prefixes to
stemsbasis.
Affixes may be grouped
1) according to their
linguistic origin. We distinguish affixes of Germanic origin (full,
less), of Romanic origin (ion), of Greek origin (ise, izm);
2) according to the parts of
speech. We distinguish noun forming, adj. forming and verb forming
affixes;
3)
according to semantic functions. They may denote persons, quality,
negation. Many suffixes originated from separate words: hood
originated for the noun hood, which meant state or condition; full –
полный
(adj. In O.E) now it is suffix. Suffixes may change the part of
speech: critic (al).
All
suffixes are divided into lexical
and grammatical.
Lexical
suffixes build new word. Productive
affixes. For
ex: read-readable, happy-happiness, act-actor.
Grammatical
suffixes change the grammatical form of a word. Often used to create
neologisms and nonce-words (I
don’t like Sunday evenings: I feel so mondayish).
For ex: finish-finished, say-says, rose-roses.
Some
productive suffixes:
Noun
forming – er,
ing, is, ist, ance
Adj
– forming – y,
ish, ed, able, less
Adv
– forming – ly
Verb – forming — Ize, /ise,
ate
Prefixies
—
Un, die, re
Conversion
(zero derivation) it is one of the major ways of enriching EV &
referrers to the numerous cases of phonetic identity of word forms of
2 words belonging to different part of speech.. The new word has a
meaning which differs from that of original one though it can ><
be associated with it. nurse
(noun) to nurse – to feed
A certain stem is used for the
formation of a categorically different word without a derivative
element being added.
Bag
– to bag, Back – to back , Bottle – to bottle This
specific pattern is very productive in English
The
most popular types are noun →verb or verb→noun To
take off – a take off
Conversion
can be total
or partial.
Partial: the then
president (тогдашний).
An adverb is used as an adjective, only in this particular context.
Total: work
– to work
Conversion
may be the result of shading of English endings. The historical
changes may be briefly outlined as follows: in O.E. a verb and a noun
of the same root were distinguished by their endings. For ex: the
verb ‘to love’ had a form (Old Eng.) ‘lufian’. This verb had
personal conjunctions. The noun ‘love’ had the form ‘lufu’
with different case endings. But in the course of time, the personal
and case endings were lost. There are numerous pairs of words (e. g.
love, n. — to love, v.; work, n. — to work, v.; drink, n. — to
drink, v., etc.) which did, not occur due to conversion but coincided
as a result of certain historical processes (dropping of endings,
simplification of stems) when before that they had different forms
(e. g. O. E. lufu, n. — lufian, v.).
The
two categories of parts of speech especially affected by conversion
are nouns and verbs. Verbs made from nouns are the most numerous
amongst the words produced by conversion: e. g. to
hand, to back, to face, to eye, to mouth, to nose, to dog, to wolf,
to monkey, to can, to coal, to stage, to screen, to room, to floor,
to blackmail, to blacklist, to honeymoon,
and very many others.
Nouns
are frequently made from verbs: do (e. g. This
is the queerest do I»ve ever come across.
Do — event, incident), go (e. g. He
has still plenty of go at his age.
Go — energy), make,
run, find, catch, cut, walk, worry, show, move,
etc. Verbs can also be made from adjectives: to
pale, to yellow, to cool, to grey, to rough
(e. g. We
decided to rough it in the tents as the weather was warm),
etc.
Other
parts of speech are not entirely unsusceptible to conversion as the
following examples show: to
down, to out (as in a newspaper heading Diplomatist Outed from
Budapest), the ups and downs, the ins and outs, like, n, (as in the
like of me and the like of you).
Compounding
& word comparison. Compound
words are made of 2 derivational stems. The types of structure of CW:
neutral,
morphological &syntactic.
In
neutral
compound
the process is released without any linking elements sunflower.
There
are three types of neutral compounds simple compounds went a compound
consist of a simple affixes stems.
Derivate/
derivational compound
— has affixes babysitter.
Contracted
–
has a shorten stems. TV-set
Morphological
C –
few
in number. This type is non productive. Represented by words, where 2
stems are combined by a linking vowel/ consonant Anglo-Saxon,
statesman, craftsmanship.
Syntactic
C
– formed of segments of speech preserving articles, prepositions,
adverbs. Mother-in-law
Reduplication.
New
word are made by stem ether without any phonetic changes Bye-Bye
or variation of a root vowel or consonant ping-pong
Shortening.
There
are 2 ways of producing them:
1.
The word is formed from the syllable of the original word which in
term may loose its beginning –phone,
its ending vac
(vacation) or
both
fridge.
2.
The word is formed from the initial letter of a word group BB,
bf – boyfriend. Acronyms are
shorten words but read as one UNO
[ju:nou]
TYPES OF WF
Sound
imitation – words
are made by imitating different links of sounds that may be produced
by animals, birds…bark
– лаять,
mew – мяукать…some
names of animals, birds & insects are made by SI coo-coo
– кукушка,
crow – ворона.
To
glide, to slip are
supposed to convey the very sound of the smooth easy movement over a
slippery surface.
Back
formation a
verb is produced from a noun by subtraction (вычитание)
bagger
– to bag, babysitter – to babysit
Blending
— Is
blending part of two words to form one word (merging into one word),
combining letters/sounds they have in common as a connecting element.
Smoke
+ fog = smog, Breakfast + lunch = brunch, Smoke + haze = smaze
(дымка)
—
addictive type: they are transformable into a phrase consisting of
two words combined by a conjunction “and” smog
→ smoke & fog
—
blending of restrictive type: transformable into an attributive
phrase, where the first element serves as modifier of a second.
Positron
– positive electron,
Medicare
– medical care
Borrowings.
Contemporary
English is a unique mixture of Germanic & Romanic elements. This
mixing has resulted in the international character of the vocabulary.
In the comparison with other languages English possesses great
richness of vocabulary.
All languages are mixtures to
a greater or lesser extent, but the present day English vocabulary is
unique in this respect.
A brief look on various
historical strata of the English vocabulary:
1) through cultural contacts
with Romans partly already on the continent and all through the
influence of Christianity a very early stratum of Latin-Greek words
entered the language.
Their origin is no longer felt
by the normal speaker today in such word: pound, mint, mustard,
school, dish, chin, cleric, cheese, devil, pepper, street, gospel,
bishop.
The
same can be said about some Scandinavian words (from about the 10th
century) that today belong to the central core of the vocabulary.
It
means that their frequency is very high. They,
their, them, sky, skin, skill, skirt, ill, dies, take… They
partly supersede the number of OE words OE
heofon – heaven (sky) Niman – take
Steorfan – die
A
more radical change & profound influence on the English
vocabulary occurred on 1066 (Norman Conquest). Until the 15th
cent., a great number of French words were adopted. They belong to
the areas of court,
church, law, state.
Virtue, religion,
parliament, justice, noble, beauty, preach, honour…
The
influx of the words was the strongest up to the 15th
cent., but continued up to the 17th
cent.
Many French borrowings
retained their original pronunciation & stress
Champagne,
ballet, machine, garage…
Separate, attitude,
constitute, introduce…
Adjectives in English –
arrogant, important, patient
Sometimes with their
derivatives:
Demonstrative –
demonstration
Separate – separation
17-18 cc. due to the
establishing of cultural, trade relations many words were borrowed
from Italian, Spanish, Dutch, French.
Italian:
libretto,
violin, opera
Spanish:
hurricane, tomato, tobacco
Dutch:
yacht,
dog, landscape
French:
bouquet,
buffet
From the point of view of
their etymology formal words are normally of classical Romanic
origin, informal – Anglo-Saxon.
Nowadays many Americanisms
become familiar due to the increase of transatlantic travel & the
influence of broadcast media.
Even
in London (Heathrow airport) “baggage”
instead of “luggage”
The present day English
vocabulary is from being homogeneous.
6.
Neologisms new
word expressions are created for new things irrespective of their
scale of importance. They may be all important and concern some
social relationships (new form/ state)
People’s republic. Or
smth threatening the very existence of humanity nuclear
war
or the thing may be short lived. N
is
a newly coined word, phrase/ a new meaning for an existing word / a
word borrowed from another language.
The
development of science and industry technology: black
hole, internet, supermarket.
The
adaptive lexical system isn’t only adding new units but readjust
the ways & means of word formation radio
detection and ranging – RADAR
The
lex. System may adopt itself by combining several word-building
processes face-out
(noun) – the radioactive dust descending through the air after an
anatomic explosion. This
word was coined by composition/ compounding & conversion.
Teach
–in (n) –a student conference/ series of seminars on some burning
issue of the day, meaning some demonstration on protest. This
pattern is very frequent lis–in
, due-in
means protest demonstration when fluking traffic. Bionies
– the
combination of bio & electron.
Back
formation:
air-condion
– air-conditioner – air-conditioning
Semi-affixes
(могут
быть
как
самостоятельные
слова)
chairman
used
to be not numerous and might be treated as exceptions now, evolving
into separate set.
Some
N abscessed with smth and containing the elements mad
& happy: powermad, moneymad, auto-happy.
Conversion, composition,
semantic change are in constant use when coining N
The
change of meaning rather an introduction of a new additional meaning
may be illustrated by the word NETWORK
– stations for simultaneous broadcast of the same program.
Once
accepted N may become a basis for further word formation. ZIP
– to zip – zipper –
zippy.
The
lex. System is unadaptive system, developing for many centuries and
reflecting the changing needs, servicing only in special context.
Archaism
& historisms.
Archaism
–
once common but are now replaced by synonyms. Mostly they are poetic:
morn
– arch, morning – new word, hapless – arch, unlucky – modern.
Historism
– when
the causes of the word’s disappearance are extralinguistic, eg. The
thing named is no longer used. They are very numerous as names for
social relations, institutions, objects of material culture of the
past, eg. many types of sailing craft belong to the past: caravels,
galleons.A
great many of
H
denotes various types of weapons in historical novels: blunderbuss
— мушкетер,
breastplate. Many
of them are in Voc in some figurative meaning: shiel
– щит,
sword. – меч.
7.
Homonymy.
Different
in meaning, but identical in sound or spelling form
Sources:
1.
The result of split of polysemy capital
– столица,
заглавная
буква
Homonymy
differs from polysemy because there is no semantic bond (связь)
between homonyms; it has been lost & doesn’t exist.
2.
as the result of leveling of grammar in flections, when different
parts of speech become identical in their forms. Care
(in OE) — caru(n), care (OE) – carian (v)
3.
By conversion
slim – to slim, water – to water
4.
With the help of the same suffix fro the same stem. Reader
– the person who reads/a book for reading.
5.
Accidentally. Native words can coincide in their form beran
– to bear, bera (animal) – to bear
6.
Shortening of different words. Cab
(cabriolet, cabbage, cabin)
Homonyms can be of 3 kinds:
1.
Homonyms proper (the sound & the spelling are identical)
bat – bat
— flying
animal (летучая
мышь)
— cricket bat (бита,
back — part of body, away from the front, go to back
2.
Homophones (the same sound form but different spelling)
flower – flour, sole – soul, rain – reign, bye-by-buy
3.
Homographs (the same spelling)
tear [iə] – tear [εə, lead [i:] – lead [e]
Homonyms in English are very
numerous. Oxford English Dictionary registers 2540 homonyms, of which
89% are monosyllabic words and 9,1% are two-syllable words.
So,
most homonyms are monosyllabic words. The trend towards
monosyllabism, greatly increased by the loss of inflections and
shortening, must have contributed much toward increasing the number
of homonyms in English.
Among the other ways of
creating homonyms the following processes must be mentioned:
From
the viewpoint of their origin homonyms are sometimes divided into
historical and etymological. Historical
homonyms are those which result from the breaking up of polysemy;
then one polysemantic word will split up into two or more separate
words. Etymo1ogiсal
homonyms are words of different origin which come to be alike in
sound or in spelling (and may be both written and pronounced alike).
Borrowed
and native words can coincide in form, thus producing homonyms (as in
the above given examples). In other cases homonyms are a result of
borrowing when several different words become identical in sound or
spelling. E.g. the Latin vitim — «wrong», «an immoral
habit» has given the English vice — вада
«evil conduct»; the Latin vitis -«spiral» has
given the English »vice» — тиски
«apparatus with strong jaws in which things can be hold
tightly»; the Latin vice — «instead of», «in
place of» will be found in vice — president.
8.
Synonymy.
A
synonym – a word of similar or identical meaning to one or more
words in the same language. All languages contain synonyms but in
English they exist in superabundance. There no two absolutely
identical words because connotations, ways of usage, frequency of an
occurrence are different. Senses of synonyms are identical in respect
of central semantic trades (denotational meaning) but differ in
respect of minor semantic trades (connotational). In each group of S
there’s a word with the most general meaning, with can substitute
any word of the group. TO
LOOK AT — to glance – to stare
Classification:
Weather the different in
denotational/ connotational component
1.
Ideographic
synonyms. They
bear the same idea but not identical in their referential content,
different shades of meaning or degree. BEAUTIFUL
– fine, handsome – pretty,
to
ascent – to mount – to climb.
2.
Stylistic
synonyms. Different
in emotive and stylistic sphere.
|
child girl happiness |
Infant maid
bliss |
Kid |
|
neutral |
elevated |
colloquial |
|
To |
To |
Eat
— Devour (degradation),
Face
— muzzle
(морда)
Synonymic condensation is
typical of the English language.
It
refers to situations when writers or speakers bring together several
words with one & the same meaning to add more conviction, to
description more vivid. Ex.:
Lord & master, First & foremost, Safe & secure,
Stress & strain, by force & violence
Among
synonyms there’s a special group of words –
euphemism used
to substitute some unpleasant or offensive words. Drunk
– marry
According to interchangability
context S are classified
3.
Total
synonyms
An extremely rare occurrence. Ulman: “a luxury that language
can hardly afford.” M. Breal spoke about a law of distribution in
the language (words should be synonyms, were synonyms in the past
usually acquire different meanings and are no longer
interchangeable). Ex.: fatherland
— motherland
4.
Contextual
synonyms.
Context can emphasize some certain semantic trades & suppress
other semantic trades; words with different meaning can become
synonyms in a certain context. Ex.: tasteless
– dull, Active – curious, Curious – responsive
Synonyms can reflect social
conventions.
Ex.:
|
clever |
bright |
brainy |
intelligent |
Dever-clever |
|
neutral |
Only speaking about younger |
Is not used by the higher |
Positive connotation |
Stylistically remarked |
5.
Dialectical
synonyms.
Ex.:
lift – elevator, Queue – line, autumn – fall
6.
Relative
some
authors classify group like:
like – love – adore, famous- celebrated – eminentthey
denote different degree of the same notion or different shades of
meanings and can be substituted only in some context.
Antonymy.
Words
belonging to the same part of speech identical in speech expressing
contrary or contradictory notion.
Комиссаров
В.Н.
classify them into absolute/
root (late/early)they
have different roots
,
derivational (to
please-to
displease) the
same root but different affixes. In most cases “-“ prefixes from
antonyms an,
dis, non.
Sometimes they are formed by suffixes full
& less.
But they do not always substitute each other selfless
– selfish, successful – unsuccessful .the
same with “-“ prefixes
to appoint – to disappoint.
The
difference is not only in structure but in semantic. The DA
express
contradictory notions, one of then excludes the other active
– inactive. The
AA
express
contrary notion: ugly
–
plain – good-looking – pretty –
beautiful
Antonimy
is
distinguished from complementarily
by being based on different logical relationshipd for pairs of
antonyms like
good – bad, big – small.
He
is good (not bad). He is not good (doesn’t imply he is bad).
The negation (отрицание)
of one term doesn’t implies the assertion of the other.
John
Lines suggests proper
hot-warm
– tapped – cold &
complementary antonyms only
2 words negative and assertion not
male — female.
There’s
also one type of semantic opposition conversives
words
denote one reference as viewed from different points of view that of
the subject & that of the object.
Bye
– sell, give — receive
Conversness
is
minor image relations of functions husband
– wife, pupil – teacher, above – below, before — after
9.
Phraseology.
Phrasiological units/ idioms – motivated word group. They are
reproduced as readymade units. Express a singe notion, used in
sentence as one part of it.
Idiomaticy
—
PU when the meaning of the whole
is
not deducible from the sum of the meanings of the parts. Stability
of PU implies that it exist as a readymade linguistic unit, which
doesn’t allow of any variability of its lexical component of gr.
Structure.
In
ling. literature the term
Phraseology is
used for the expressions where the meaning of one element is depended
on the other. Vinogradov: “irrespective of structure and properties
of the units”. Smernitsky: “it denotes only such set expressions
which do not possess expressiveness or emotional coloring”. Arnold:
“it says that only denotes such set expressions that are
imaginative, expressive and emotional”. Ammosova call them fixed
context units – we
can’t substitute an element without changing the meaning of the
whole. Ahmanova insists on the semantic intearity of such phrases:
“prevailing over the structural separates of their element”.
Kuning lays stress on the structural separatness of the elements in
the PU on the change of meaning in the whole as compared with its
elements taken separately with its elements and on a certain minimum
stability.
Phraseology
(Webster’s
dictionary) mode of expression peculiarities of diction. That is
choice and arrangement of words and phrases characteristic of some
author.there are difficult terms. Idioms word equivalents & these
difficult units or terminology reflects certain differences in the
main criteria used to distinguish.
The
features: 1.
lack of semantic motivation 2. Lexical & grammatical stability
Semantic
classification:2
criteria: 1). The degree of semantic isolation 2). The degree of
disinformation
1.
Opaque in meaning (трудный
для
понимания)
the meaning of the individual words can’t be summed together to
produce the meaning of the whole.to
kick the bucket = to die It
contains no clue to the idiomatic meaning of this expression.The
degree of semantic isolation is the highest.
The 3 typesof PU:
1.
Phraseological fusions. The degree of motivation is very low. one
component preserves its direct meaning Ex.:
to pass the buck = to pass responsibility – свалить
ответственность,
2.
Phraseological unities. Clearly motivated. Transparent both
components in their direct meaning but the combination acquires
figurative sense to
see the light = to understand, old salt — морской
волк
3.
Phraseological combinations. There is a component used in its
direct meaning. There are lots of idioms (proverbs, saying). To
be good at smth.:
Curiosity
killed the cat, but satisfaction brought it back
Idioms institutionalized formulas of politeness:How
do you do?Good-bye (God be with you) How about a drink?
Structural classification
of PU
Prof. A.I. Smirnitsky worked
out structural classification of phraseological units, comparing them
with words. He points out one-top units which he compares with
derived words because derived words have only one root morpheme. He
points out two-top units which he compares with compound words
because in compound words we usually have two root morphemes.
Among
one-top units he
points out three structural types;
a)
units of the type «to give up» (verb + postposition type), e.g. to
art up, to back up, to drop out, to nose out, to buy into, to
sandwich in etc.;
b)
units of the type «to be tired» . Some of these units remind the
Passive Voice in their structure but they have different prepositions
with them, while in the Passive Voice we can have only prepositions
«by» or «with», e.g. to
be tired of, to be interested in, to be surprised at etc.
There are also units in this type which remind free word-groups of
the type «to be young», e.g. to be akin to, to be aware of etc.
The difference between them is that the adjective «young» can be
used as an attribute and as a predicative in a sentence, while the
nominal component in such units can act only as a predicative. In
these units the verb is the grammar centre and the second component
is the semantic centre;
c)
Prepositional- nominal phraseological units. These units are
equivalents of unchangeable words: prepositions, conjunctions,
adverbs, that is why they have no grammar centre, their semantic
centre is the nominal part, e.g.
On the doorstep (quite near), on the nose (exactly), in the course
of, on the stroke of, in time, on the point of
etc. In the course of time such units can become words, e.g.
tomorrow,
instead etc.
Among
two-top units
A.I. Smirnitsky points out the following structural types:
a) attributive-nominal such
as: a month of Sundays, grey matter, a millstone round one’s neck
and many others. Units of this type are noun equivalents and can be
partly or perfectly idiomatic. In partly idiomatic units (phrasisms)
sometimes the first component is idiomatic, e.g. high road, in other
cases the second component is idiomatic, e.g. first night. In many
cases both components are idiomatic, e.g. red tape, blind alley, bed
of nail, shot in the arm and many others.
b) verb-nominal phraseological
units, e.g. to read between the lines , to speak BBC, to sweep under
the carpet etc. The grammar centre of such units is the verb, the
semantic centre in many cases is the nominal component, e.g. to fall
in love. In some units the verb is both the grammar and the semantic
centre, e.g. not to know the ropes. These units can be perfectly
idiomatic as well, e.g. to burn one’s boats,to vote with one’s
feet, to take to the cleaners’ etc.
Very close to such units are
word-groups of the type to have a glance, to have a smoke. These
units are not idiomatic and are treated in grammar as a special
syntactical combination, a kind of aspect.
c) phraseological repetitions,
such as : now or never, part and parcel , country and western etc.
Such units can be built on antonyms, e.g. ups and downs , back and
forth; often they are formed by means of alliteration, e.g cakes and
ale, as busy as a bee. Components in repetitions are joined by means
of conjunctions. These units are equivalents of adverbs or adjectives
and have no grammar centre. They can also be partly or perfectly
idiomatic, e.g. cool as a cucumber (partly), bread and butter
(perfectly).
Phraseological units the same
as compound words can have more than two tops (stems in compound
words), e.g. to take a back seat, a peg to hang a thing on, lock,
stock and barrel, to be a shaddow of one’s own self, at one’s own
sweet will.
Syntactical classification
of PU
Phraseological
units can be classified as parts of speech. This classification was
suggested by I.V. Arnold. Here we have the following groups:
a) noun phraseologisms
denoting an object, a person, a living being, e.g. bullet train,
latchkey child, redbrick university, Green Berets,
b) verb phraseologisms
denoting an action, a state, a feeling, e.g. to break the log-jam, to
get on somebody’s coattails, to be on the beam, to nose out , to
make headlines,
c) adjective phraseologisms
denoting a quality, e.g. loose as a goose, dull as lead ,
d) adverb phraseological
units, such as : with a bump, in the soup, like a dream , like a dog
with two tails,
e) preposition phraseological
units, e.g. in the course of, on the stroke of ,
f) interjection phraseological
units, e.g. «Catch me!», «Well, I never!» etc.
In I.V.Arnold’s
classification there are also sentence equivalents, proverbs, sayings
and quatations, e.g. «The sky is the limit», «What makes him
tick», » I am easy». Proverbs are usually metaphorical, e.g. «Too
many cooks spoil the broth», while sayings are as a rule
non-metaphorical, e.g. «Where there is a will there is a way».
Definition
Word Formation Process (also called Morphological Process) is a means by which new words are produced either by modification of existing words or by complete innovation, which in turn become a part of the language.
Types of Word Formation Processes
Different types of word formation processes are employed to create new words. However, all word formation processes basically bring either inflectional or derivational changes. Therefore, inflection (also called inflexion) and derivation are the two core processes of word formation. Inflection differs from derivation to the following extent:
| Inflection | Derivation |
| Produces grammatical variants of the same word. | Produces a new word on the basis of an existing word. |
| Modifies a word to express different grammatical categories such as tense, mood, voice, aspect, person, number, gender and case. | Changes the word class (also called parts of speech; form class; lexical class; syntactic category). |
| Does not change the meaning of a word. For example: determine→ determines, determining, determined. | Modifies the meaning of the root. For example: modern → modernize (to make modern). |
The major word formation processes include but are not limited to the following:
Affixation
It is a word formation process wherein an affix is attached to a root (also called stem; base) to form a new word. A root is a free morpheme (also called unbound morpheme) that can appear alone. On the other hand, an Affix is a bound morpheme which never occurs by itself, but is always attached to some free morpheme and can be either inflectional or derivational. An Inflectional affix modifies the form/grammatical category of a word, i.e., tense, person, number, gender, case, etc. For example: rat → rats. Contrariwise, a derivational affix modifies the parts of speech of the root, while leaving the grammatical category unchanged. In this way, there is a change of meaning of the root. For example: write → writer.
In English there are two types of affixations:
- Prefixation: In this morphological process words are formed by adding an affix to the front of a root. The type of affix used in this process is referred to as prefix. For example: un + tidy → untidy
- Suffixation: In this morphological process words are formed by adding an affix to the end of a root. The type of affix used in this process is referred to as suffix. For example: fear + less → fearless
Conversion
This refers to the change of function or parts of speech of a word without adding an affix. Conversion is also called zero derivation or null derivation since the functional change is brought about by supplementing an invisible affix. Sometimes it is also called functional shift. Typically conversion is made from “noun to verb” and from “verb to noun”. Less frequently, conversion is also done from “adjective to verb” and “adjective to noun”. For instance:
Noun to Verb:
- access
- film
- name
- shape
Verb to Noun:
- attack
- alert
- hope
- increase
- visit
- cover
Adjective to Verb:
- brown
- black
- slow
Adjective to Noun:
- crazy
- nasty
Back-formation
Back-formation is a morphological process in which new word is created by extracting affixes from another word. In this way, it is the reverse of affixation, in which affixes are added. Back-formation is also different from clipping since it brings a change in the parts of speech or the word’s meaning. For example: the noun insertion has been back-formed into verb insert by removing the suffix ion.
Clipping
As the name suggests, clipping is the word formation process in which a word is reduced to a shorter form. With a sharp contrast to back-formation, clipping keeps the original word meaning intact. These words are very common in everyday speech. For instance: lab is the clipped form of laboratory. . There are four types of clippings:
- Back clipping: (also called final clipping; apocope) it involves the truncation of end of a word as in ad from advertisement.
- Fore-clipping: (also called initial clipping; apheresis) it is the removal of the beginning of a word as in phone from telephone.
- Middle clipping: (also medial clipping; syncope) it is the extraction of the beginning and end of a word as in flu from influenza.
- Complex clipping: is removing multiple parts from multiple words as in cablegram from cabletelegram.
Compounding
Also called composition, by this process two or more than two words are combined together to create a single word, having a single idea and function. In English, there are compound nouns, compound adjectives, and compound verbs. Customarily compound words are spelt as a single word, or as two or more hyphenated words, and even as two or more separate words. For example:
- life + style → lifestyle
- mother + in + law → mother-in-law
- shopping + mall → shopping mall
There are no specific rules for hyphenated compounds. Generally, some new and original compound nouns are hyphenated, but the hyphen is ignored when they become more familiar. However, there are some compound adjectives that are always hyphenated. For instance: state-of-the-art. The hyphen is often retained when two vowels come together, such as: Co-operation. Hyphens are often used to tell the ages of people and things, for example: 10-year-old. The general rule is that words are combined with hyphens to avoid confusion.
Borrowing
This refers to the words adopted from other languages. There are two types of borrowings:
- Loan-word: By this process, a word is borrowed from another language without translating it into the target language. For example: the phrase tour-de-force is borrowed directly from French, which means a masterly or brilliant feat.
- Loan-translation: Also known as calque, a morphological process wherein a word or phrase from another language is borrowed by literally translating it into the target language. For example: the phrase point of view has been translated into English from the French phrase point de vue.
Coinage
Also called invention, is a morphological process by which new words are invented. Sometimes popular trademark names of various products are adopted by people so extensively that they ultimately become the everyday words of language. For example:
- Heroin
- Aspirin
- Escalator
- Xerox
- Kerosene
- Nylon
- Band-Aid
- Vaseline
- Margarine
- Videotape
Again, some words are being invented due to rapid cultural changes and the spread of information technology, mass media, internet, etc. For example:
- Blog
- Hotspot
- Netbook
- Tablet
- Tweet
- Emoticon
- Smartphone
Blending
Blending (also called portmanteau) is a morphological process in which the parts of two or more words are combined together to form a new word. Usually, the parts consist of the beginning of one word and the end of the other word(s). Typically, the meaning of the blended word reverberates with the meanings of the original words. For example:
- breakfast + lunch → brunch
- motor+hotel → motel
However, blending should not be confused with compounding, which combines two words without truncation of parts of the roots of the blended words.
Acronyms
These words are formed with the initial letters or each of the major parts of a word or a longer phrase. With a few exceptions, acronyms are usually capitalized. Some linguists confuse acronyms with initialisms, which are also abbreviations formed in the similar manner as the former. In essence, there is a sharp difference between the two. In language, an acronym is pronounced as a single word rather than just a sequence of individual letters, which is characteristic of initialisms. For example:
Acronyms:
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization → UNESCO
- Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation → Laser
- International Criminal Police Organization → Interpol
Initialisms:
- Personal Computer → PC
- Asian Development Bank → ADB
- Liquid Crystal Display → LCD
Reduplication
Reduplication (also called cloning; doubling; duplication; repetition; tautonym) is a word formation process in which a new word is created by repeating all or part of a root or a stem, often with a change of vowel or initial consonant. Reduplication is not a major means of creating lexemes in English, but it is perhaps the most unusual one. Based on their usage, the techniques of reduplication could be classified in the following manner:
- Repetition without Change: bye-bye, tick-tick
- Rhyming Reduplication: ding-dong, super-duper, bow-wow
- Repetition with Change of Vowel: tiptop, chitchat, flip-flop, ping-pong, dilly-dally, wishy-washy
- Repetition with Change of Initial Consonant: teeny-weeny
References
“English Word Formation Processes.” Really Learn English. 2016. Really-Learn-English.com.
14 July 2016 <http://www.really-learn-english.com/word-formation-processes.html>.
“Inflection.” Wikipedia. 2016. Wikimedia Foundation Inc. 14 July 2016
<http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inflection>.
“Morphological Derivation.” Wikipedia. 2016. Wikimedia Foundation Inc. 14 July 2016
<http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Morphological_derivation>.
Yule, George. The Study of Language. 2nd ed. Cambridge: CUP, 1996.
“Word Formation.” Wikipedia. 2016. Wikimedia Foundation Inc. 14 July 2016
<https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Word_formation>.
10.1. The morphological structure of English words.
10.2. Definition of word-formation. Synchronic and diachronic approaches to word formation.
10.3. Main units of word-formation. Derivational analysis.
10.4. Ways of word-formation.
10.5. Functional approach to word-formation.
10.6. The communicative aspect of word-formation.
10.1. Structurally, words are divisible into smaller units which are called morphemes. Morphemes are the smallest indivisible two-facet (significant) units. A morpheme exists only as a constituent part of the word.
One morpheme may have different phonemic shapes, i.e. it is represented by allomorphs (its variants),
e.g. in please, pleasure, pleasant [pli: z], [ple3-], [plez-] are allomorphs of one morpheme.
Semantically, all morphemes are classified into roots and affixes. The root is the lexical centre of the word, its basic part; it has an individual lexical meaning,
e.g. in help, helper, helpful, helpless, helping, unhelpful — help- is the root.
Affixes are used to build stems; they are classified into prefixes and suffixes; there are also infixes. A prefix precedes the root, a suffix follows it; an infix is inserted in the body of the word,
e.g. prefixes: re -think, mis -take, dis -cover, over -eat, ex -wife;
suffixes: danger- ous, familiar- ize, kind- ness, swea- ty etc.
Structurally, morphemes fall into: free morphemes, bound morphemes, semi-bound (semi-free) morphemes.
A free morpheme is one that coincides with a stem or a word-form. A great many root-morphemes are free,
e.g. in friendship the root -friend — is free as it coincides with a word-form of the noun friend.
A bound morpheme occurs only as a part of a word. All affixes are bound morphemes because they always make part of a word,
e.g. in friendship the suffix -ship is a bound morpheme.
Some root morphemes are also bound as they always occur in combination with other roots and/or affixes,
e.g. in conceive, receive, perceive — ceive — is a bound root.
To this group belong so-called combining forms, root morphemes of Greek and Latin origin,
e.g. tele -, mega, — logy, micro -, — phone: telephone, microphone, telegraph, etc.
Semi-bound morphemes are those that can function both as a free root morpheme and as an affix (sometimes with a change of sound form and/or meaning),
e.g. proof, a. » giving or having protection against smth harmful or unwanted» (a free root morpheme): proof against weather;
-proof (in adjectives) » treated or made so as not to be harmed by or so as to give protection against» (a semi-bound morpheme): bulletproof, ovenproof, dustproof, etc.
Morphemic analysis aims at determining the morphemic (morphological) structure of a word, i.e. the aim is to split the word into morphemes and state their number, types and the pattern of arrangement. The basic unit of morphemic analysis is the morpheme.
In segmenting words into morphemes, we use the method of Immediate and Unltimate Constituents. At each stage of the analysis, a word is broken down into two meaningful parts (ICs, i.e. Immediate Constituents). At the next stage, each IC is broken down into two smaller meaningful elements. The analysis is completed when we get indivisible constituents, i.e. Ultimate Constituents, or morphs, which represent morphemes in concrete words,
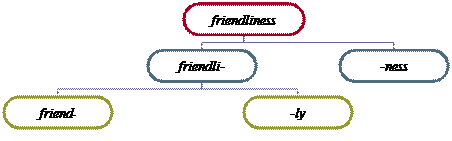
e.g.
Friend-, -ly, -ness are indivisible into smaller meaningful units, so they are Ultimate Constituents (morphs) and the word friendliness consists of 3 morphemes: friend-+-li+-ness.
There are two structural types of words at the morphemic level of analysis: monomorphic (non-segmentable, indivisible) and polymorphic words (segmentable, divisible). The former consist only of a root morpheme, e.g. cat, give, soon, blue, oh, three. The latter consist of two or more morphemes, e.g. disagreeableness is a polymorphic word which consists of four morphemes, one root and three affixes: dis- + -agree- + -able + -ness. The morphemic structure is Pr + R + Sf1 + Sf2.
10.2. Word-Formation (W-F) is building words from available linguistic material after certain structural and semantic patterns. It is also a branch of lexicology that studies the process of building words as well as the derivative structure of words, the patterns on which they are built and derivational relations between words.
Synchronically, linguists study the system of W-F at a given time; diachronically, they are concerned with the history of W-F, and the history of building concrete words. The results of the synchronic and the diachronic analysis may not always coincide,
e.g. historically, to beg was derived from beggar, but synchronically the noun beggar is considered derived from the verb after the pattern v + -er/-ar → N, as the noun is structurally and semantically more complex. Cf. also: peddle- ← -pedlar/peddler, lie ← liar.
10.3. The aim of derivational analysis is to determine the derivational structure of a word, i.e. to state the derivational pattern after which it is built and the derivational base (the source of derivation).
Traditionally, the basic units of derivational analysis are: the derived word (the derivative), the derivational base, the derivational pattern, the derivational affix.
The derivational base is the source of a derived word, i.e. a stem, a word-form, a word-group (sometimes even a sentence) which motivates the derivative semantically and on which the latter is based structurally,
e.g. in dutifully the base is dutiful-, which is a stem;
in unsmiling it is the word-form smiling (participle I);
in blue-eyed it is the word-group blue eye.
In affixation, derivational affixes are added to derivational bases to build new words, i.e. derivatives. They repattern the bases, changing them structurally and semantically. They also mark derivational relations between words,
e.g. in encouragement en- and -ment are derivational affixes: a prefix and a suffix; they are used to build the word encouragement: (en- + courage) + -ment.
They also mark the derivational relations between courage and encourage, encourage and encouragement.
A derivational pattern is a scheme (a formula) describing the structure of derived words already existing in the language and after which new words may be built,
e.g. the pattern of friendliness is a+ -ness- → N, i.e. an adjective stem + the noun-forming suffix -ness.
Derivationally, all words fall into two classes: simple (non-derived) words and derivatives. Simple words are those that are non-motivated semantically and independent of other linguistic units structurally, e.g. boy, run, quiet, receive, etc. Derived words are motivated structurally and semantically by other linguistic units, e.g. to spam, spamming, spammer, anti-spamming are motivated by spam.
Each derived word is characterized by a certain derivational structure. In traditional linguistics, the derivational structure is viewed as a binary entity, reflecting the relationship between derivational bases and derivatives and consisting of a stem and a derivational affix,
e.g. the structure of nationalization is nationaliz- + -ation
(described by the formula, or pattern v + -ation → N).
But there is a different point of view. In modern W-F, the derivational structure of a word is defined as a finite set of derivational steps necessary to produce (build) the derived word,
e.g. [(nation + -al) + — ize ] + -ation.
To describe derivational structures and derivational relations, it is convenient to use the relator language and a system of oriented graphs. In this language, a word is generated by joining relators to the amorphous root O. Thus, R1O describes the structure of a simple verb (cut, permiate); R2O shows the structure of a simple noun (friend, nation); R3O is a simple adjective (small, gregarious) and R4O is a simple adverb (then, late).
e.g. The derivational structure of nationalization is described by the R-formula R2R1R3R2O; the R-formula of unemployment is R2R2R1O (employ → employment → unemployment).
In oriented graphs, a branch slanting left and down » /» correspond to R1; a vertical branch » I» corresponds to R2; a branch slanting right and down » » to R3, and a horizontal right branch to R4.

and dutifulness like this:
Words whose derivational structures can be described by one R-formula are called monostructural, e.g. dutifulness, encouragement; words whose derivational structures can be described by two (or more) R-formulas are polystructural,
e.g. disagreement R2R2R1O / R2R1R1O
(agree → disagree → disagreement R2R1R1O or
agree → agreement → disagreement R2R2R1O)
There are complex units of word-formation. They are derivational clusters and derivational sets.
A derivational cluster is a group of words that have the same root and are derivationally related. The structure of a cluster can be shown with the help of a graph,
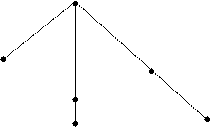
reread read
misreadreaderreadable
reading
readership ∙ unreadable
A derivational set is a group of words that are built after the same derivational pattern,
e.g. n + -ish → A: mulish, dollish, apish, bookish, wolfish, etc,
Table TWO TYPES OF STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS
| MORPHEMIC ANALYSIS | DERIVATIONAL ANALYSIS | |
| AIM | to find out the morphemic structure (composition) | to determine the derivational structure |
| BASIC UNITS | morphemes (roots and affixes) | derived word, derivational pattern, derivational base, derivational step, derivational means (e.g. affix) |
| RESULTS: CLASSES OF WORDS | monomorphic (non-segmentable) and polymorphic (segmentable) words | simple and derived words |
| EXAMPLES | 1. cut, v. and cut, n. are monomorphic (root) words | 1. cut, v. is a simple word (R1O); cut, n. is derived from it (R2R1O) |
| 2. encouragement, unemployment consist of three morphemes and have the same morphemic composition: Pr + R + Sf | 2. encouragement and unemployment have different derivational structures: v + -ment → N (R2R1R2O) and un- + n → N (R2R2R1O) |
10.4. Traditionally, the following ways of W-F are distinguished:
affixation, compounding, conversion, shortening, blending, back-formation. Sound interchange, sound imitation, distinctive stress, lexicalization, coinage certainly do not belong to word-formation as no derivational patterns are used.
Affixation is formation of words by adding derivational affixes to derivational bases. Affixation is devided into prefixation and suffixation,
e.g. the following prefixes and suffixes are used to build words with negative or opposite meanings: un-, non-, a-, contra-, counter-, de-, dis-, in-, mis-, -less, e.g. non-toxic.
Compounding is building words by combining two (or more) derivational bases (stems or word-forms),
e.g. big -ticket (= expensive), fifty-fifty, laid-back, statesman.
Among compounds, we distinguish derivational compounds, formed by adding a derivational affix (usu. a suffix) to a word group,
e.g. heart-shaped (= shaped like a heart), stone-cutter (= one who cuts stone).
Conversion consists in making a word from some existing word by transferring it into another part of speech. The new word acquires a new paradigm; the sound form and the morphimic composition remain unchanged. The most productive conversion patterns are n → V (i.e. formation of verbs from noun-stems), v → N (formation of nouns from verb stems), a → V (formation of verbs from adjective stems),
e.g. a drink, a do, a go, a swim: Have another try.
to face, to nose, to paper, to mother, to ape;
to cool, to pale, to rough, to black, to yellow, etc.
Nouns and verbs can be converted from other parts of speech, too, for example, adverbs: to down, to out, to up; ifs and buts.
Shortening consists in substituting a part for a whole. Shortening may result in building new lexical items (i.e. lexical shortenings) and so-called graphic abbreviations, which are not words but signs representing words in written speech; in reading, they are substituted by the words they stand for,
e.g. Dr = doctor, St = street, saint, Oct = 0ctober, etc.
Lexical shortenings are produced in two ways:
(1) clipping, i.e. a new word is made from a syllable (or two syllables) of the original word,
e.g. back-clippings: pro ← professional, chimp ← chimpanzee,
fore-clippings: copter ← helicopter, gator ← alligator,
fore-and-aft clippings: duct ← deduction, tec ← detective,
(2) abbreviation, i.e. a new word is made from the initial letters of the original word or word-group. Abbreviations are devided into letter-based initialisms (FBI ← the Federal Bureau of Investigation) and acronyms pronounced as root words (AIDS, NATO).
Blending is building new words, called blends, fusions, telescopic words, or portmanteau words, by merging (usu.irregular) fragments of two existing words,
e.g. biopic ← biography + picture, alcoholiday ← alcohol + holiday.
Back-formation is derivation of new words by subtracting a real or supposed affix (usu. a suffix) from existing words (on analogy with existing derivational pairs),
e.g. to enthuse ← enthusiasm, to intuit ← intuition.
Sound interchange and distinctive stress are not ways of word-formation. They are ways of distinguishing words or word forms,
e.g. food -feed, speech — speak, life — live;
‘ insult, n. — in ‘ sult, v., ‘ perfect, a. — per ‘ fect, v.
Sound interchange may be combined with affixation and/or the shift of stress,
e.g. strong — strength, wide — width.
10.5. Productivity and activity of derivational ways and means.
Productivity and activity in W-F are close but not identical. By productivity of derivational ways/types/patterns/means we mean ability to derive new words,
e.g. The suffix -er/ the pattern v + -er → N is highly productive.
By activity we mean the number of words derived with the help of a certain derivational means or after a derivational pattern,
e.g. — er is found in hundreds of words so it is active.
Sometimes productivity and activity go together, but they may not always do.
| DERIVATIONAL MEANS | EXAMPLE | PRODUCTIVITY | ACTIVITY |
| -ly | nicely | + | + |
| -ous | dangerous | _ | + |
| -th | breadth | _ | _ |
In modern English, the most productive way of W-P is affixation (suffixation more so than prefixation), then comes compounding, shortening takes third place, with conversion coming fourth.
Productivity may change historically. Some derivational means / patterns may be non-productive for centuries or decades, then become productive, then decline again,
e.g. In the late 19th c. US -ine was a popular feminine suffix on the analogy of heroine, forming such words as actorine, doctorine, speakerine. It is not productive or active now.
|
Шрифт зодчего Шрифт зодчего состоит из прописных (заглавных), строчных букв и цифр… |
Картограммы и картодиаграммы Картограммы и картодиаграммы применяются для изображения географической характеристики изучаемых явлений… |
Практические расчеты на срез и смятие При изучении темы обратите внимание на основные расчетные предпосылки и условности расчета… |
Функция спроса населения на данный товар Функция спроса населения на данный товар: Qd=7-Р. Функция предложения: Qs= -5+2Р,где… |
The vocabulary of any language is constantlyExpanding at the expense of new lexical units. Word formation is the main way to replenish it. This process has its own characteristics and types. The basic ways of word formation are individual for each specific language. It depends on the structure, characteristics and compatibility of parts of speech.
The concept of
By word formation is understood the emergence of newlexical units by means of suffixation, prefixation, and also other methods. A person who knows the ways of word formation in languages can quickly replenish his lexical stock, and also read and understand phrases without having to use a dictionary.
There are several classifications of methodsword formation. Some linguists use the concept of synchrony and diachrony to typologize, but the most common variant is the distribution of this process to morphemic and non-morphogenic subspecies. Classification also depends on the language where word formation takes place. The table below illustrates the features of this process for the Russian language.
|
Morphemic |
Nemorfemny |
|
Affixation Suffixing Prefixing Prefix-suffix and its combinations Abbreviation Addition |
Morphological-syntactic Lexico-syntactic Lexico-Semantic |
Each subspecies has its own characteristics and characteristics.
Word formation with the help of morphemes
Morphemic way is characterized by the fact that newwords in the language appear due to the use of already existing lexical units and specific affixes. This type has its own basic ways of word formation:
- The suffix.
- Prefix.
- Different combinations of prefix, suffix and postfix types.
- Addition.
- Abbreviation.
Each variant has distinctive characteristics, features and certain rules of education.
Suffix type
The basic way of word formation for Russianlanguage is the process of suffixation. In this case, new lexical units appear by adding to the basis of the word suffix of the word-formative type. For example, learn, teacher. Suffixation covers almost all parts of speech, but the most common word formation is nouns, adverbs and adjectives.
This process is accompanied by a variety of morphemic changes, which are divided into several subspecies:
- Alternation of morphemes: friend — to be friends (Ms).
- Truncation of the producing morpheme: high — height.
- The imposition of several morphemes: pink — pinkish.
- Change of stress: green — greens.
This is not a complete list of changes that word formation can lead to. The suffixes also affect other morphemic characteristics. The level of change depends on the specific language.
Prefix Type
If a new word is formed by addingto the basis of the corresponding prefix, then we are talking about the process of prefixation. Unlike the suffix, the prefix usually forms new lexical units within one part of the speech. For the Russian language, the word-formation of verbs is traditional with the help of this method. For example: cook — cook — prepare; write — sign — unsubscribe, etc.
Despite the sufficient prevalence of this type, most often prefixation is used in parallel with other types of word formation. Quite often this is suffixation, postfixation, etc.
The combination of suffixing, prefixing and postfixation
Modern word formation is characterized bypresence of words with simultaneous use of suffixation, prefixation and other similar options, as well as a variety of their combination. In Russian, the following methods are distinguished:
- Prefix-suffix. A new word is formed simultaneously with the help of a prefix and a suffix. For example, the road is plantain; border — foreign.
- Postfixical. The emergence of a new word by adding postfix: -sa, -or-, -tow, -a, etc. For example, who is — anyone — anyone.
- Prefix-postfix. In this case, a new word is formed using the prefix and the postfix at the same time. Most often, such a variant is present in the same part of the speech. Accordingly, in this way, the word formation of adjectives, nouns, verbs, etc. is possible. For example, to call — to call; sleep — get enough sleep, etc.
- Suffix-postfix. The word appears simultaneously with the help of the suffix and postfix. For example, fuss — fuss; the crowd is crowded. Word formation of verbs is the only sphere in the Russian language where this method is used.
- Prefix-suffix-postfix. This option is characterized by the formation of a new word with the help of simultaneous suffixation, prefixation and postfixation. For example, whispering — whispering; talk — talk.
These types of word formation are very active not only in Russian, but also in many other languages.
Addition
Quite common for the Russian languageis the presence of addition as a way of word formation. In this case, a new lexical unit appears as a result of combining two or more separate words into one whole. Depending on which words are combined and in which way, the following basic ways of word formation are distinguished by addition:
- The basis. New lexical units appear after the addition of two or more words with the application of the interfix. The main component is the last component of the combination. For example, fertilize, everyday, etc.
- Addition of two or more words, which is characterized by the presence of meaningful equality. For example, a sofa bed, a prime minister, etc.
Addition is actively used in Russian and other languages and is most often responsible for the word formation of nouns and verbs.
Abbreviation
The method of formation, which isthe construction of new tokens by splicing parts of other words is called an abbreviation. Depending on the method of combination and features of the parts of the word used, the following abbreviations are distinguished:
- Initsialnaya. In this case, new words appear by using separate sounds or letters. Accordingly, the initial abbreviation can be sound (for example, MKhAT, high school) or alphabetic (for example, UFO, CIS, etc.).
- Syllable. This type involves the use of separate parts of different words (for example, department store, trade union committee, etc.).
- Mixed. This type is a combination of the initial part of one lexical unit and the other unit completely (for example, salary, trade union, etc.).
The abbreviation is especially relevant in modern lexicology, as there is a worldwide trend towards ensuring maximum accuracy and shortness of the language.
Nemorfemnye word formation
As for the construction of new lexical units without the use of morphemes, the following basic ways of word formation are distinguished:
- Lexico-syntactic.
- Morphological-syntactic.
- Lexico-semantic.
In such cases new words appear due to the transition of one part of speech to another, the splicing or dismemberment of the lexical meaning of the word into separate components.
The lexico-syntactic method
This option is also called fusion,Since new words in this case are formed by merging a specific word combination. This leads to the fact that not only the lexical meaning of the word changes, but also its syntactic role. For example, forever green — evergreen: crazy — crazy, etc.
Most often a dependent lexical unitspeaks an adverb, and the fusion itself is often the word-formation of adjectives or participles. From synonyms, such lexical units differ in that they have an accent and a strict order of arrangement of all their parts.
Morphological-syntactic method
This option is characterized by the formation of new words by moving one part of the speech to another. There are the following subspecies of this method:
- Substantivization. The transition of one part of speech into a noun. For example, a leading specialist and host show, a wounded fighter and a silent wounded, etc.
- Adjectivation. The transition of parts of speech into an adjective. For example, a novice singer, a painted table, etc.
- Adverbialization. The transition of a noun into an adverb. For example, in the winter morning — come in the morning.
There are also other variants of the morphological-syntactic method. Each language has its own characteristics, variants of compatibility and distinctive features.
Lexical and semantic method
In this case, the new lexical unitsappear after a particular word splits its base value and receives additional ones. For example, the satellite — as a companion and as a heavenly body; titanium — a mythical giant and metal and many others. Thus, the composition of the vocabulary of the language varies due to the variation of the semantics of the word.
For word-formation in a similar way, certain conditions and the similarity of two phenomena or objects are necessary. This often requires a fairly large amount of time.
Word formation in English
Construction of new words in Englishis carried out in different ways. Traditionally, linguists distinguish composing and word-production as word formation in English. The table below illustrates this:
|
Synthesis |
Derivation |
|
Noun + noun (toothpaste) Adjective + noun (high way) Preposition + noun (underworld) Noun + verb (to babysit) Adverb + noun (to downgrade) |
Conversion Change stress Alternating sounds Affixation |
As for the composition, this methodis also characteristic of the Russian language. Similarly, in English almost any part of speech is formed. For example, to blackmail, girlfriend, dark-blue, somebody, etc. Word-production is characterized by the formation of some lexical units from others. This can be done by converting one part of the speech into another (answer-to answer), changing the place of stress (conflict-to conflict), alternating sounds (advice-to advise) or affixing using suffixes and prefixes. Combination and transition is the foundation that word formation in English has. This table demonstrates.
The main way to expand the dictionary is toword formation, which has its own types, as well as features, depending on the part of speech. The process of formation of new lexical units never stops and has its own distinctive features in different languages.
</ p>>