These examples may contain rude words based on your search.
These examples may contain colloquial words based on your search.
Suggestions
Then, that computer of yours must have an amazing predictive algorithm.
Alors, votre ordinateur doit avoir un incroyable algorithme prédictif.
This helps to maintain the computer‘s reliability and performance.
Cela permet de préserver la fiabilité et l’efficacité de l’ordinateur.
The temperature regulator is capable of connecting to a computer.
Le régulateur de température est capable d’être connecté à un ordinateur.
A processor of a computer converts the vibrations into electrical pulses.
Le processeur d’un ordinateur convertit les vibrations en impulsions électriques.
Your computer can get infected with a trojan by multiple ways.
Votre ordinateur peut être infecté par un trojan de plusieurs façons.
Verify that all the appropriate drives are connected to the computer.
Vérifiez que tous les lecteurs appropriés sont connectés à l’ordinateur.
The only problem with your computer right now is the adware.
Le seul problème avec votre ordinateur dès maintenant est l’adware.
I then transfer the collection of harvested images to the computer.
Je transfère alors l’ensemble des images récoltées dans l’ordinateur.
The signal is collected also at computer audio headphone output.
Le signal est recueilli également à l’ordinateur casque audio de sortie.
Your own dive computer is set up according to your personal preferences.
Votre ordinateur de plongée personnel est configuré selon vos préférences.
Open the application and insert the code generated on your computer.
Ouvrir l’application et introduire le code généré sur l’ordinateur.
Click on the edited document to download it onto your computer.
Cliquez sur le document édité pour le télécharger vers votre ordinateur.
Protects your computer against intruders and controls the network traffic.
Protège votre ordinateur contre les intrus et contrôle le trafic du réseau.
Transform your computer into a super television with just a few clicks.
Transformer votre ordinateur en télévision superbe avec juste quelques clics.
Include audio generated by computer or microphone in the captures.
Inclusion du son sur les captures générées par ordinateur ou par micro.
Your hardware could be what is bogging down performance on your computer.
Ces pièces maîtresses pourraient améliorer la performance de votre ordinateur.
Test to determine if the issue is resolved by restarting your computer.
Redémarrez l’ordinateur pour vérifier si le problème est résolu.
This will establish a stable connection between your device and computer.
Cela établira une connexion stable entre votre appareil et votre ordinateur.
Connect your flash disk to the computer and launch the application.
Connectez votre disque flash à l’ordinateur et lancez l’application.
The current computer is the third generation used with the sonar.
L’ordinateur actuel est la troisième génération utilisée avec le sonar.
Suggestions that contain computer
Results: 355078. Exact: 355078. Elapsed time: 310 ms.
New technologies comme (like) the Internet and computers need new words to describe them. Those new words either comes from adaptations of older words or are completely new inventions. One such word is computer in French: ordinateur.
Le nom (the noun) computer comes from le verbe (the verb) to compute, which originally comes from the French word compter, which then comes from Latin: computare.
Computare → Compter → To Compute → Computer
The original meaning of to compute has the same meaning as the modern French word compter: to count or add up.
In English, le mot (the word) computer was used to describe people who performed calculations more than any machine for most of son histoire (its history). With the new inventions of the 20th century le mot began to take on a new meaning as new electronic machines began making complicated calculations more than computers.
IBM 650 Photo by Cushing Memorial Library and Archives, Texas A&M. Licnensed under CC BY 2.0.
In 1955, l’entreprise (the company) IBM brought a new computer and le mot ordinateur to France. They needed a word for the device and l’entreprise could have simply used the English word, especially since the word compter is already un mot français, but they decided to create something new instead.
François Girard, le responsable du service publicité (the head of the advertising department) at IBM France, thought that computer was too similar to calculatrice (calculator) and wanted to find a better name for « la nouvelle machine électronique destinée au traitement de l’information (the new electronic machine intended for information processing) » .
In an effort to find un bon nom français (a good french name), François Girard asked son ancien professeur de lettres (his old humanities professor), Jacques Perret, for advice.
Monsieur Perret had a suggestion based on a rare word, ordonnateur: someone who puts things in order. Le mot comes from le verbe ordonner, meaning to put in order, to order, to arrange, which comes from le mot latin: ordinare.
Monsieur Perret’s idea was more cumbersome than the final word: ordinatrice électronique.
Eventually, IBM settled on ordinateur as le mot for the new product. Au début (at first), l’entreprise wanted to keep le mot ordinateur as a trademark, but l’ordinateur became too popular and entered la langue française as a normal word.
Ordinare → Ordonner → Ordonnateur → Ordinateur
L’histoire behind l’ordinateur gives us an interesting look into how new words are developed. It can be a bit confusing at times, but I find seeing l’etymologie (the etymology) makes it easier to remember du vocabulaire. If I know l’histoire and can arrange everything in my head it’s like remembering a thrilling story instead of a vocabulary list!
Looking up l’origine (the origin) of les mots is also much less embarrassing than not knowing how to say something au magasin!
программируемый логический контроллер
ПЛК
—
[Интент]
контроллер
Управляющее устройство, осуществляющее автоматическое управление посредством программной реализации алгоритмов управления.
[Сборник рекомендуемых терминов. Выпуск 107. Теория управления.
Академия наук СССР. Комитет научно-технической терминологии. 1984 г.]
EN
storage-programmable logic controller
computer-aided control equipment or system whose logic sequence can be varied via a directly or remote-control connected programming device, for example a control panel, a host computer or a portable terminal
[IEV ref 351-32-34]
FR
automate programmable à mémoire
équipement ou système de commande assisté par ordinateur dont la séquence logique peut être modifiée directement ou par l’intermédiaire d’un dispositif de programmation relié à une télécommande, par exemple un panneau de commande, un ordinateur hôte ou un terminal de données portatif
[IEV ref 351-32-34]
См. также:
— архитектура контроллера;
— производительность контроллера;
— время реакции контроллера;
КЛАССИФИКАЦИЯ
Основным показателем ПЛК является количество каналов ввода-вывода. По этому признаку ПЛК делятся на следующие группы:
- нано— ПЛК (менее 16 каналов);
- микро-ПЛК (более 16, до 100 каналов);
- средние (более 100, до 500 каналов);
- большие (более 500 каналов).
По расположению модулей ввода-вывода ПЛК бывают:
- моноблочными — в которых устройство ввода-вывода не может быть удалено из контроллера или заменено на другое. Конструктивно контроллер представляет собой единое целое с устройствами ввода-вывода (например, одноплатный контроллер). Моноблочный контроллер может иметь, например, 16 каналов дискретного ввода и 8 каналов релейного вывода;
- модульные — состоящие из общей корзины (шасси), в которой располагаются модуль центрального процессора и сменные модули ввода-вывода. Состав модулей выбирается пользователем в зависимости от решаемой задачи. Типовое количество слотов для сменных модулей — от 8 до 32;
- распределенные (с удаленными модулями ввода-вывода) — в которых модули ввода-вывода выполнены в отдельных корпусах, соединяются с модулем контроллера по сети (обычно на основе интерфейса RS-485) и могут быть расположены на расстоянии до 1,2 км от процессорного модуля.
Часто перечисленные конструктивные типы контроллеров комбинируются, например, моноблочный контроллер может иметь несколько съемных плат; моноблочный и модульный контроллеры могут быть дополнены удаленными модулями ввода-вывода, чтобы увеличить общее количество каналов.
Многие контроллеры имеют набор сменных процессорных плат разной производительности. Это позволяет расширить круг потенциальных пользователей системы без изменения ее конструктива.
По конструктивному исполнению и способу крепления контроллеры делятся на:
- панельные (для монтажа на панель или дверцу шкафа);
- для монтажа на DIN-рейку внутри шкафа;
- для крепления на стене;
- стоечные — для монтажа в стойке;
- бескорпусные (обычно одноплатные) для применения в специализированных конструктивах производителей оборудования (OEM — «Original Equipment Manufact urer»).
По области применения контроллеры делятся на следующие типы:
- универсальные общепромышленные;
- для управления роботами;
- для управления позиционированием и перемещением;
- коммуникационные;
- ПИД-контроллеры;
- специализированные.
По способу программирования контроллеры бывают:
- программируемые с лицевой панели контроллера;
- программируемые переносным программатором;
- программируемые с помощью дисплея, мыши и клавиатуры;
- программируемые с помощью персонального компьютера.
Контроллеры могут программироваться на следующих языках:
- на классических алгоритмических языках (C, С#, Visual Basic);
- на языках МЭК 61131-3.
Контроллеры могут содержать в своем составе модули ввода-вывода или не содержать их. Примерами контроллеров без модулей ввода-вывода являются коммуникационные контроллеры, которые выполняют функцию межсетевого шлюза, или контроллеры, получающие данные от контроллеров нижнего уровня иерархии АСУ ТП.
Контроллеры для систем автоматизации
Слово «контроллер» произошло от английского «control» (управление), а не от русского «контроль» (учет, проверка). Контроллером в системах автоматизации называют устройство, выполняющее управление физическими процессами по записанному в него алгоритму, с использованием информации, получаемой от датчиков и выводимой в исполнительные устройства.
Первые контроллеры появились на рубеже 60-х и 70-х годов в автомобильной промышленности, где использовались для автоматизации сборочных линий. В то время компьютеры стоили чрезвычайно дорого, поэтому контроллеры строились на жесткой логике (программировались аппаратно), что было гораздо дешевле. Однако перенастройка с одной технологической линии на другую требовала фактически изготовления нового контроллера. Поэтому появились контроллеры, алгоритм работы которых мог быть изменен несколько проще — с помощью схемы соединений реле. Такие контроллеры получили название программируемых логических контроллеров (ПЛК), и этот термин сохранился до настоящего времени. Везде ниже термины «контроллер» и «ПЛК» мы будем употреблять как синонимы.
Немного позже появились ПЛК, которые можно было программировать на машинно-ориентированном языке, что было проще конструктивно, но требовало участия специально обученного программиста для внесения даже незначительных изменений в алгоритм управления. С этого момента началась борьба за упрощение процесса программирования ПЛК, которая привела сначала к созданию языков высокого уровня, затем — специализированных языков визуального программирования, похожих на язык релейной логики. В настоящее время этот процесс завершился созданием международного стандарта IEC (МЭК) 1131-3, который позже был переименован в МЭК 61131-3. Стандарт МЭК 61131-3 поддерживает пять языков технологического программирования, что исключает необходимость привлечения профессиональных программистов при построении систем с контроллерами, оставляя для них решение нестандартных задач.
В связи с тем, что способ программирования является наиболее существенным классифицирующим признаком контроллера, понятие «ПЛК» все реже используется для обозначения управляющих контроллеров, которые не поддерживают технологические языки программирования.
Жесткие ограничения на стоимость и огромное разнообразие целей автоматизации привели к невозможности создания универсального ПЛК, как это случилось с офисными компьютерами. Область автоматизации выдвигает множество задач, в соответствии с которыми развивается и рынок, содержащий сотни непохожих друг на друга контроллеров, различающихся десятками параметров.
Выбор оптимального для конкретной задачи контроллера основывается обычно на соответствии функциональных характеристик контроллера решаемой задаче при условии минимальной его стоимости. Учитываются также другие важные характеристики (температурный диапазон, надежность, бренд изготовителя, наличие разрешений Ростехнадзора, сертификатов и т. п.).
Несмотря на огромное разнообразие контроллеров, в их развитии заметны следующие общие тенденции:
- уменьшение габаритов;
- расширение функциональных возможностей;
- увеличение количества поддерживаемых интерфейсов и сетей;
- использование идеологии «открытых систем»;
- использование языков программирования стандарта МЭК 61131-3;
- снижение цены.
Еще одной тенденцией является появление в контроллерах признаков компьютера (наличие мыши, клавиатуры, монитора, ОС Windows, возможности подключения жесткого диска), а в компьютерах — признаков контроллера (расширенный температурный диапазон, электронный диск, защита от пыли и влаги, крепление на DIN-рейку, наличие сторожевого таймера, увеличенное количество коммуникационных портов, использование ОС жесткого реального времени, функции самотестирования и диагностики, контроль целостности прикладной программы). Появились компьютеры в конструктивах для жестких условий эксплуатации. Аппаратные различия между компьютером и контроллером постепенно исчезают. Основными отличительными признаками контроллера остаются его назначение и наличие технологического языка программирования.
[ http://bookasutp.ru/Chapter6_1.aspx]
Программируемый логический контроллер (ПЛК, PLC) – микропроцессорное устройство, предназначенное для управления технологическим процессом и другими сложными технологическими объектами.
Принцип работы контроллера состоит в выполнение следующего цикла операций:
1. Сбор сигналов с датчиков;
2. Обработка сигналов согласно прикладному алгоритму управления;
3. Выдача управляющих воздействий на исполнительные устройства.
В нормальном режиме работы контроллер непрерывно выполняет этот цикл с частотой от 50 раз в секунду. Время, затрачиваемое контроллером на выполнение полного цикла, часто называют временем (или периодом) сканирования; в большинстве современных ПЛК сканирование может настраиваться пользователем в диапазоне от 20 до 30000 миллисекунд. Для быстрых технологических процессов, где критична скорость реакции системы и требуется оперативное регулирование, время сканирования может составлять 20 мс, однако для большинства непрерывных процессов период 100 мс считается вполне приемлемым.
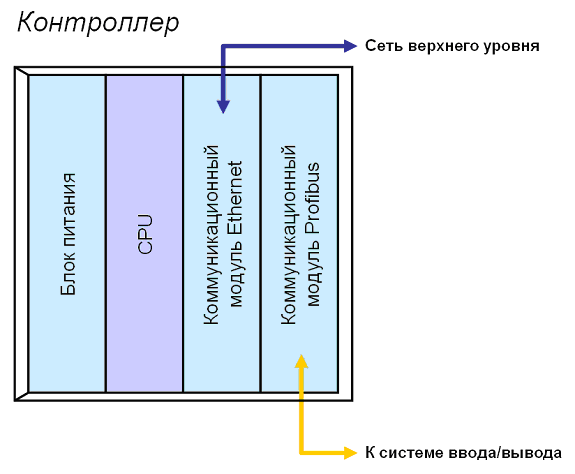
Аппаратно контроллеры имеют модульную архитектуру и могут состоять из следующих компонентов:
1. Базовая панель ( Baseplate). Она служит для размещения на ней других модулей системы, устанавливаемых в специально отведенные позиции (слоты). Внутри базовой панели проходят две шины: одна — для подачи питания на электронные модули, другая – для пересылки данных и информационного обмена между модулями.
2. Модуль центрального вычислительного устройства ( СPU). Это мозг системы. Собственно в нем и происходит математическая обработка данных. Для связи с другими устройствами CPU часто оснащается сетевым интерфейсом, поддерживающим тот или иной коммуникационный стандарт.
3. Дополнительные коммуникационные модули. Необходимы для добавления сетевых интерфейсов, неподдерживаемых напрямую самим CPU. Коммуникационные модули существенно расширяют возможности ПЛК по сетевому взаимодействию. C их помощью к контроллеру подключают узлы распределенного ввода/вывода, интеллектуальные полевые приборы и станции операторского уровня.
4. Блок питания. Нужен для запитки системы от 220 V. Однако многие ПЛК не имеют стандартного блока питания и запитываются от внешнего.
Рис.1. Контроллер РСУ с коммуникациями Profibus и Ethernet.
Иногда на базовую панель, помимо указанных выше, допускается устанавливать модули ввода/вывода полевых сигналов, которые образуют так называемый локальный ввод/вывод. Однако для большинства РСУ (DCS) характерно использование именно распределенного (удаленного) ввода/вывода.
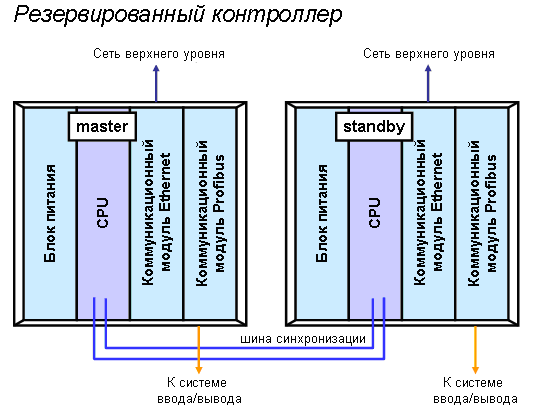
Отличительной особенностью контроллеров, применяемых в DCS, является возможность их резервирования. Резервирование нужно для повышения отказоустойчивости системы и заключается, как правило, в дублировании аппаратных модулей системы.
Рис. 2. Резервированный контроллер с коммуникациями Profibus и Ethernet.
Резервируемые модули работают параллельно и выполняют одни и те же функции. При этом один модуль находится в активном состоянии, а другой, являясь резервом, – в режиме “standby”. В случае отказа активного модуля, система автоматически переключается на резерв (это называется “горячий резерв”).
Обратите внимание, контроллеры связаны шиной синхронизации, по которой они мониторят состояние друг друга. Это решение позволяет разнести резервированные модули на значительное расстояние друг от друга (например, расположить их в разных шкафах или даже аппаратных).
Допустим, в данный момент активен левый контроллер, правый – находится в резерве. При этом, даже находясь в резерве, правый контроллер располагает всеми процессными данными и выполняет те же самые математические операции, что и левый. Контроллеры синхронизированы. Предположим, случается отказ левого контроллера, а именно модуля CPU. Управление автоматически передается резервному контроллеру, и теперь он становится главным. Здесь очень большое значение имеют время, которое система тратит на переключение на резерв (обычно меньше 0.5 с) и отсутствие возмущений (удара). Теперь система работает на резерве. Как только инженер заменит отказавший модуль CPU на исправный, система автоматически передаст ему управление и возвратится в исходное состояние.
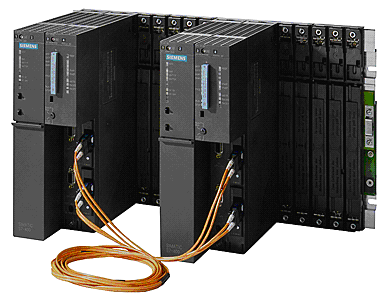
На рис. 3 изображен резервированный контроллер S7-400H производства Siemens. Данный контроллер входит в состав РСУ Simatic PCS7.
Рис. 3. Резервированный контроллер S7-400H.
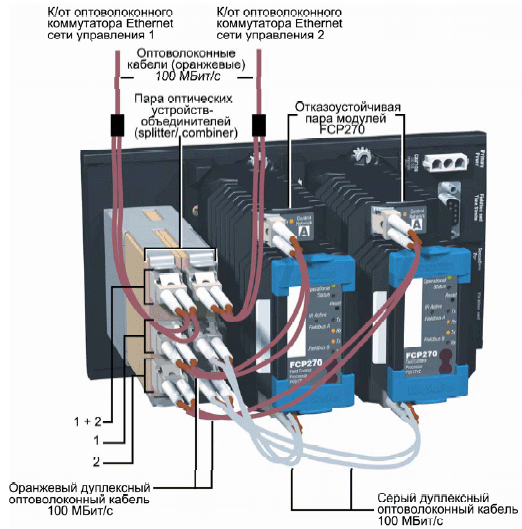
Несколько другое техническое решение показано на примере резервированного контроллера FCP270 производства Foxboro (рис. 4). Данный контроллер входит в состав системы управления Foxboro IA Series.
Рис. 4. Резервированный контроллер FCP270.
На базовой панели инсталлировано два процессорных модуля, работающих как резервированная пара, и коммуникационный модуль для сопряжения с оптическими сетями стандарта Ethernet. Взаимодействие между модулями происходит по внутренней шине (тоже резервированной), спрятанной непосредственно в базовую панель (ее не видно на рисунке).
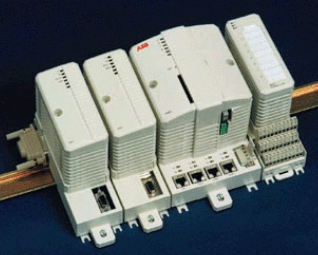
На рисунке ниже показан контроллер AC800M производства ABB (часть РСУ Extended Automation System 800xA).
Рис. 5. Контроллер AC800M.
Это не резервированный вариант. Контроллер состоит из двух коммуникационных модулей, одного СPU и одного локального модуля ввода/вывода. Кроме этого, к контроллеру можно подключить до 64 внешних модулей ввода/вывода.
При построении РСУ важно выбрать контроллер, удовлетворяющий всем техническим условиям и требованиям конкретного производства. Подбирая оптимальную конфигурацию, инженеры оперируют определенными техническими характеристиками промышленных контроллеров. Наиболее значимые перечислены ниже:
1. Возможность полного резервирования. Для задач, где отказоустойчивость критична (химия, нефтехимия, металлургия и т.д.), применение резервированных конфигураций вполне оправдано, тогда как для других менее ответственных производств резервирование зачастую оказывается избыточным решением.
2. Количество и тип поддерживаемых коммуникационных интерфейсов. Это определяет гибкость и масштабируемость системы управления в целом. Современные контроллеры способны поддерживать до 10 стандартов передачи данных одновременно, что во многом определяет их универсальность.
3. Быстродействие. Измеряется, как правило, в количестве выполняемых в секунду элементарных операций (до 200 млн.). Иногда быстродействие измеряется количеством обрабатываемых за секунду функциональных блоков (что такое функциональный блок – будет рассказано в следующей статье). Быстродействие зависит от типа центрального процессора (популярные производители — Intel, AMD, Motorola, Texas Instruments и т.д.)
4. Объем оперативной памяти. Во время работы контроллера в его оперативную память загружены запрограммированные пользователем алгоритмы автоматизированного управления, операционная система, библиотечные модули и т.д. Очевидно, чем больше оперативной памяти, тем сложнее и объемнее алгоритмы контроллер может выполнять, тем больше простора для творчества у программиста. Варьируется от 256 килобайт до 32 мегабайт.
5. Надежность. Наработка на отказ до 10-12 лет.
6. Наличие специализированных средств разработки и поддержка различных языков программирования. Очевидно, что существование специализированный среды разработки прикладных программ – это стандарт для современного контроллера АСУ ТП. Для удобства программиста реализуется поддержка сразу нескольких языков как визуального, так и текстового (процедурного) программирования (FBD, SFC, IL, LAD, ST; об этом в следующей статье).
7. Возможность изменения алгоритмов управления на “лету” (online changes), т.е. без остановки работы контроллера. Для большинства контроллеров, применяемых в РСУ, поддержка online changes жизненно необходима, так как позволяет тонко настраивать систему или расширять ее функционал прямо на работающем производстве.
8. Возможность локального ввода/вывода. Как видно из рис. 4 контроллер Foxboro FCP270 рассчитан на работу только с удаленной подсистемой ввода/вывода, подключаемой к нему по оптическим каналам. Simatic S7-400 может спокойно работать как с локальными модулями ввода/вывода (свободные слоты на базовой панели есть), так и удаленными узлами.
9. Вес, габаритные размеры, вид монтажа (на DIN-рейку, на монтажную панель или в стойку 19”). Важно учитывать при проектировании и сборке системных шкафов.
10. Условия эксплуатации (температура, влажность, механические нагрузки). Большинство промышленных контроллеров могут работать в нечеловеческих условиях от 0 до 65 °С и при влажности до 95-98%.
[ http://kazanets.narod.ru/PLC_PART1.htm]
Тематики
- ПЛК (программируемые логические контроллеры)
Синонимы
- контроллер
- ПЛК
EN
- PLC
- programmable controller
- Programmable Logic Controller
- storage-programmable logic controller
DE
- speicherprogrammierbare Steuerung, f
FR
- automate programmable à mémoire
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > automate programmable à mémoire
Technical skills system, computer, software.
TECHNIQUES(SYSTÈME, ORDINATEUR, LOGICIEL) 79% CAPACITÉ À ÉCOUTER.
Just connect it to your computer and it is ready to print.
Il suffit de le connecter à votre pc et voilà il est immédiatement prêt à imprimer.
Gauge wanted the computer, but he didn’t want a witness.
Gauge voulait le pc mais pas de témoins.
Every malfunctioning computer, including the original atms
Tous les pc défaillants, les distributeurs y compris,
Du-station is the link between your computer and your dualo du-touch.
dualo qui fait le lien entre votre pc et votre du-touch.
avec un laser, depuis un pc.
easy configuration of the Accessibility mode via iTunes on a computer.
Configuration rapide et facile du mode Accessibilité via iTunes sur pc.
ideas of how to use our computer monitoring software.
Voici plusieurs idées pour utiliser notre logiciel de surveillance pc.
C’est ce qu’on appelait un« ordinateur de loisir».
It’s what we pulled off the dead lawyer’s computer.
C’était dans le PC de l’avocat mort.
Host name of the computer in access IP-address.
The computer‘s recommended operating environment differs according to the DJ software.
L’environnement opérationnel recommandé pour l’ordinateur diffère selon le logiciel DJ utilisé.
Computer: i don’t understand which pyramid you mean.
SHRDLU: Je ne comprends pas de quelle pyramide vous parlez.
Computer: the blue pyramid and the blue block.
SHRDLU: La pyramide bleue et le bloc.
Computer Entertainment Suppliers Association CESA.
Computer cataloguing of the library’s collections began in the 1980s.
They are commonly used in small-configured computer systems.
Cela lui permet d’être utilisée par des ordinateurs dotés d’une configuration faible.
Peripherals connected to a bus in a computer system.
How does a quantum computer factor large numbers?
New jobs computer engineers and scientists, network experts, etc.
Abolish computer voting in the state where you live.
Abolissez les machines à voter dans chaque état où vous vivez.
Meulée avec des machines à contrôle numérique.
Plug the computer and this monitor into a different outlet so.
Brancher I’ordinateur et son moniteur dans une prise secteur.
The Polar Cycling Computer shows your performance indicators.
C’était le PC de
la
famille Miller.
The computer never loses its peripherals.
The entrance to the computer core should be up ahead.
L’entrée du serveur principal devrait être au bout.
Results: 73990,
Time: 0.0708
English
—
French
French
—
English
- Go to Preferences page and choose from different actions for taps or mouse clicks.
WordReference English-French Dictionary © 2023:
| Principales traductions | ||
| Anglais | Français | |
| computer n | (computing device) (informatique) | ordinateur nm |
| Tony has a powerful computer. | ||
| Tony a un ordinateur puissant. | ||
| computer n as adj | (of computer devices) | d’ordinateur loc adj |
| He stared at the computer screen. | ||
| Il regardait fixement l’écran d’ordinateur. |
| Traductions supplémentaires | ||
| Anglais | Français | |
| computer n | dated (person who computes) | personne qui calcule nf |
| The accountant is the computer of tax payments. | ||
| Le comptable est celui qui calcule les contributions. | ||
| computer n as adj | (of software) | informatique adj |
| Curtis works in the computer industry. | ||
| Curtis travaille dans le secteur informatique. | ||
| computers npl | (industry, job) (secteur d’activité) | informatique nf |
| Pete works in computers. | ||
| Pete travaille dans l’informatique. |
WordReference English-French Dictionary © 2023:
| Formes composées computer |
||
| Anglais | Français | |
| computer algorithm n | (computing: problem-solving steps) | algorithme informatique nm |
| computer animated, computer-animated adj |
(cartoon, film: digital) (film) | d’animation en images de synthèse loc adj |
| Note: hyphen used when the term is before a noun | ||
| computer animation n | (digitally made cartoons, etc.) | animation numérique nf |
| This film was made using computer animation. | ||
| computer art n | (artmaking: digital) | art infographique nm |
| (courant) | infographie nf | |
| computer art n | (artwork: digital) | image informatique nf |
| computer basics npl | (basic computer knowledge) | bases de l’informatique nfpl |
| I took an on-line tutorial to learn computer basics. | ||
| rudiments de l’informatique nmpl | ||
| connaissances, notions élémentaires en informatique nfpl | ||
| Mon père a les connaissances élémentaires en informatique. | ||
| computer break-in n | (computing: hack) | piratage informatique nm |
| The system is vulnerable to a break-in by hackers. | ||
| La société Duchmol a été la cible d’un piratage informatique. | ||
| exploitation d’une faille de sécurité nf | ||
| computer briefcase n | (bag for portable computer) | sacoche pour ordinateur, mallette pour ordinateur nf |
| computer code n | (instructions in a computer program) | code informatique nm |
| computer crash n | (computing: system failure) | panne informatique nf |
| (familier) | plantage nm | |
| My computer crash was caused by a bug in the operating system. | ||
| computer crime | (digital crime) (acte individuel) | délit informatique nm |
| (activité) | criminalité informatique nf | |
| computer data n | uncountable, colloquial (information on computer) | données informatiques nfpl |
| (Informatique) | données nfpl | |
| Note: «Data» is technically the plural form of «datum». However, in everyday usage, «data» is often treated as a mass noun, and therefore is used with a singular verb form | ||
| Computer data is a conceptual rather than physical thing. | ||
| Les données informatiques sont conceptuelles plutôt que physiques. | ||
| computer data npl | (information on computer) | données informatiques nfpl |
| (Informatique) | données nfpl | |
| Computer data is stored on the computer in the form of binary files. | ||
| computer desk n | (table for using a computer on) | bureau d’ordinateur, bureau multimédia nm |
| computer desktop n | (interface on a computer screen) (Informatique) | bureau nm |
| My computer desktop shows a picture of the African savannah. | ||
| Mon bureau est une photo de la savane africaine. | ||
| computer engineer n | (designer of computers) | ingénieur en informatique, ingénieure en informatique nm, nf |
| ingénieur informatique, ingénieure informatique nm, nf | ||
| The computer engineers are designing some new software. | ||
| computer file n | (stored data: document, image, etc.) (Informatique) | fichier nm |
| fichier informatique nm | ||
| computer game n | (interactive video game) | jeu vidéo nm |
| He’s busy playing his computer games again. | ||
| Il est encore occupé à jouer à son jeu vidéo. | ||
| computer geek n | slang (technology expert) | crack en informatique nm |
| My son is the family computer geek who handles all our computer problems. | ||
| as en informatique nm | ||
| (anglicisme, familier) | geek nm | |
| computer graphic n | (creation and use of digital images) (Informatique) | infographie nf |
| computer graphics n | (digital images) (Informatique) | graphisme nm |
| computer graphics n | (study of digital images) (domaine) | infographie nf |
| computer hardware n | (computer’s physical components) | matériel informatique nm |
| They sell computer hardware like keyboards and mice. | ||
| computer key n | (touch control on a keyboard) (Informatique) | touche, touche du clavier nf |
| J’ai appuyé sans faire exprès sur une touche, et depuis, mon ordinateur ne reconnaît plus aucun périphérique. | ||
| computer keyboard n | (typewriter part of a computer) | clavier d’ordinateur nm |
| It is hard to type in French on an American computer keyboard. | ||
| computer lab n | abbr (room with computers for use) | salle informatique nf |
| When I was in school I worked in the computer lab as part of my work-study program. | ||
| Quand j’étais à l’école, je travaillais dans la salle informatique dans la cadre de mon contrat en alternance. | ||
| computer language | (coding) | langage informatique nm |
| computer literacy n | (familiarity with computers) | compétences informatiques, connaissances informatiques nfpl |
| maîtrise de l’outil informatique nf | ||
| computer literate, computer-literate adj |
(able to use a computer) | capable de se servir d’un ordinateur loc adj |
| (familier, courant) | bon en informatique, bonne en informatique loc adj | |
| Note: hyphen used when term is an adj before a noun | ||
| I’m not very computer literate, I’m afraid. | ||
| Malheureusement, je ne suis pas très bon en informatique. | ||
| computer log n | (computing: record of user activity) (informatique) | historique d’activité nm |
| He was fired after management reviewed the on-line activities recorded on his computer log. | ||
| computer memory | (digital storage) | mémoire informatique nf |
| computer mouse, plural: computer mouses n |
(computing: pointing device) (Informatique) | souris nf |
| Use the computer mouse to click on the button. | ||
| Utilisez la souris pour cliquer sur le bouton. | ||
| computer network n | (linked computers) | réseau informatique nm |
| computer operator n | (person overseeing computer operations) (Informatique) | pupitreur, pupitreuse nm, nf |
| computer part n | (physical component of a computer) | pièce détachée d’ordinateur nf |
| Computer parts vary enormously in price. | ||
| computer printout n | ([sth] printed from computer) | sortie papier nf |
| We can get a computer printout of the calls he made in about two hours. | ||
| On peut obtenir une sortie papier des appels qu’il a passés en à peu près deux heures. | ||
| computer program n | (software) | logiciel nm |
| A computer program controls the operation of the equipment. | ||
| computer programmer n | ([sb]: writes software) (Informatique) | programmeur, programmeuse nm, nf |
| I’m a computer programmer but my job title is Chief Software Developer. | ||
| Je suis programmeur, mais mon intitulé de poste est développeur logiciel en chef. | ||
| computer room n | (room where computers are used) | salle informatique nf |
| Computer rooms are kept very cold to protect the computers from overheating. | ||
| computer scan n | (computing: virus check) | analyse d’un ordinateur nf |
| My anti-virus software carries out a regular computer scan. | ||
| recherche de virus nf | ||
| computer science n | (field of study) | informatique nf |
| Liz has a degree in computer science. | ||
| Liz a un diplôme en informatique. | ||
| computer scientist n | (expert in computing) | informaticien, informaticienne nm, nf |
| Computer scientists have developed new techniques for speech recognition. | ||
| computer skills npl | (ability to use computer) | compétences en informatique nfpl |
| I didn’t get the job because I didn’t have sufficient computer skills. | ||
| computer software n | (programs for use on a computer) | logiciel nm |
| Someone who writes computer software is known as a programmer or developer. | ||
| programme (informatique) nm | ||
| computer table n | (desk for a computer) | bureau d’ordinateur nm |
| Je vous propose ce bureau d’ordinateur à la fois très design et très fonctionnel, payable en trois fois sans frais. | ||
| meuble pour ordinateur nm | ||
| plan de travail pour ordinateur nm | ||
| computer technician n | (repairs computers) | technicien informatique, technicienne informatique nm, nf |
| I think we’re going to have to call a computer technician to help us out. | ||
| computer technician n | (supports computer use) | technicien informatique, technicienne informatique nm, nf |
| computer technology n | (computing) | technologie informatique nf |
| (plus courant) | informatique nf | |
| Computer technology has changed how people communicate with each other. | ||
| computer upgrading n | (installation of new features) | mise à jour d’un ordinateur nf |
| computer virus n | (computing: bug) | virus informatique nm |
| computer vision n | (robot visual processing) | vision par ordinateur, vision numérique, vision artificielle nf |
| computer vision, machine vision n |
(system for the blind) | vision par ordinateur, vision numérique, vision artificielle nf |
| computer-aided adj | (with assistance of a computer) | assisté par ordinateur loc adj |
| computer-aided design, Computer-Aided Design n |
(CAD: product designing using computers) | conception assistée par ordinateur nf |
| computer-aided drafting n | (use of 3D software in design) | dessin assisté par ordinateur nm |
| DAO nm inv | ||
| computer-assisted adj | (with aid of technology) | assisté par ordinateur loc adj |
| computer-controlled adj | (device, system) | commandé par ordinateur loc adj |
| computer-generated adj | (created with computers) | créé par ordinateur, conçu par ordinateur loc adj |
| computer-operated adj | (directed by a computer) | commandé par oridnateur loc adj |
| desktop computer n | (PC: not portable) | ordinateur de bureau nm |
| digital computer | (computing) | ordinateur numérique nm |
| display, computer display n |
(computer monitor) (Informatique) | affichage nm |
| You can adjust the colour and contrast of the computer display. | ||
| Tu peux régler la couleur et le contraste de l’affichage. | ||
| home computer | (computer used at home) | ordinateur personnel, ordinateur familial nm |
| host computer n | (network: main computer) | ordinateur hôte nm |
| mainframe, mainframe computer n |
(central computer) | ordinateur central nm |
| Important information is stored on the mainframe. | ||
| Les informations importantes sont stockées dans l’ordinateur central. | ||
| network computer n | (computer for accessing network) | ordinateur en réseau nm |
| notebook computer n | (laptop, portable) | ordinateur portable nm |
| portable nm | ||
| Note: Mais confusion possible avec portable = téléphone portable. | ||
| J’emmène toujours mon portable en vacances avec moi. | ||
| personal computer n | (PC: computer for home, office) | ordinateur personnel nm |
| (courant) | PC abr, nm inv | |
| theoretical computer science n | (computational mathematics) | informatique théorique nf |
| Joe is studying theoretical computer science at university. | ||
| wristop computer n | (gadget worn like a watch) | bracelet-ordinateur nm |