Before writing about the List of Prepositions, we have to know about the prepositions.
What is Preposition?
The preposition is a word that correlates between two different words or phrases, usually about the time or position. It places before the noun or a pronoun in a sentence that relates to the rest of the sentence and makes it meaningful by telling us what is exactly happening in the sentence.
In the English Language, there are various prepositional words, and each of these is used according to their use in a sentence.
There are certain varieties of the preposition, based on their use like,
Basic examples of prepositions
A] One-word Prepositions:
- Common Prepositions
- Seldom used Prepositions
B] Complex Prepositions:
- Prepositional Phrases
- Prepositions with verbs
- Prepositions with Idioms.
One word Common prepositions:
Common prepositions are those prepositional words that are used mostly in sentences.
Here is the list of some common prepositional words,
- About, above, across, after, against, among, around, at
- Before, behind, below, beside, between, by
- Down, during
- For, from
- In, inside, into
- Near
- Of, off, on, out, over
- Through, towards, to
- Under, up
- With
Examples
- About:
- What about your health
- We are about to reach our destination.
- Above:
- An eagle is flying above the clouds.
- The water level goes above the marking line due to heavy rainfall.
- Across:
- There is a huge mountain across the river.
- A baby is going across the road
- After:
- We went home after the party was over.
- I will go to sleep after 10 o’clock.
- Against:
- What do you have against me?
- The man is running against the train.
- Among:
- He is the eldest son among all.
- He is not comfortable sitting among us.
- Around:
- We all are sitting around the table.
- Her age was around 80.
- At:
- We are at the party.
- Come to my home at 8 o’clock.
- Before:
- He came before any other.
- The train was left before its time
- Behind:
- He is doing something behind my house.
- She is coming from behind.
- Below:
- He is swimming below the surface.
- I will not decrease its price below the cost price.
- Beside:
- She lives beside this colony.
- He was sitting beside my aunt.
- Between:
- I will catch you between 1 to 4 PM.
- He overtakes his bike between two trucks.
- By :
- She was murdered by any sharp metal object.
- We will provide you with the rest part by this evening.
- Down:
- He fell down on the ground.
- You go straight, then step down the hill and continue your walk.
- During
- Nobody is allowed to go out during the lecture.
- He was sleeping during the day.
- For:
- Let us go out for a trek.
- Smoking is bad for your health.
- From:
- I wish her a happy new year from my side too.
- He bought this shirt from supermart.
- In:
- He is working in this location.
- We are in the zoo now.
- Inside:
- The puppy is sitting inside the box.
- I have some cash inside my pocket.
- Into:
- Water turns into ice at 0-degree celsius.
- Jayson cut the eraser into two and gave them one each.
- Near:
- His office is just near my school.
- She stands near the statue.
- Of:
- She came to meet me at the end of the month.
- I am in the middle of something.
- Off:
- This shop is giving a 30% off sale on clothes.
- Please take off your shirt.
- On:
- We started our project on that site.
- He is sitting on the table.
- Out:
- He scored 79 marks out of 100 marks.
- She is out of the world.
- Over:
- That airplane is flying over the buildings.
- The village is situated just over the mountain.
- Through:
- The bullet is passing through this hole.
- We had gone through bad situations.
- Towards:
- She is looking towards me for the last hour.
- He has some responsibilities towards his family.
- To:
- You are coming to London.
- This little girl waited for a long time to wish you personally.
- Under:
- He knows how to swim under-water.
- He escaped from the cops on a boat under the bridge.
- Up:
- Jack and Jill both went up the hill.
- He strikes a ball up the sky.
- With:
- Are you coming with us?
- I pulled her out with the help of this rope.
Seldom used Prepositions:
Seldom used prepositions are those prepositional words that are rarely used in sentences.
Here is the list of some seldom-used prepositional words,
Examples:
- Aboard:
- She climbed aboard the ship.
- Welcome aboard this flight to Mumbai.
- Along:
- We traveled along with the boat in the Arabian Sea.
- The bedroom is along with the kitchen.
- Amid:
- She hadn’t listened to her amid the voice.
- We were lost amidst the world cup this year.
- As:
- My brother is working as a manager at this hotel.
- Sugarcane is as sweet as sugar.
- Astride:
- He sat astride the Terries.
- She slept astride on the sofa.
- Alongside:
- Their car is standing alongside our car.
- My roll number is alongside my friend in the exam hall.
- Beneath:
- She hides beneath the bed.
- He stands beneath the building.
- Beyond:
- This difficult stunt is beyond my limits.
- Nobody can break the record beyond him.
- But:
- Everyone was present, but my friend didn’t.
- He agreed to work here, but he has certain conditions.
- Bar:
- She stood on the table bar her friend did not.
- I will come to the bar after 8 o’clock.
- Concerning:
- Your parents came to my house, and they discussed with us concerning your sister’s marriage.
- I want to make some changes because I am concerned about you.
- Considering:
- Considering the demand, I will increase production.
- This race is finished, considering the rules.
- Counting:
- If we start counting now, it will take 2 hours to finish.
- The net cash is only $20k after counting.
- Cum:
- He invented a bicycle-cum-bike.
- His mind is so sharp that he can sleep-cum-talk at the same time.
- Despite:
- We went on a picnic despite any arrangement.
- He finished the race despite filling petrol in it.
- Except:
- You can purchase any other cell phone except Vivo. That is out of stock.
- I will go anywhere for dinner except for this restaurant.
- Exclude:
- The total amount is 470$, excluded taxes.
- He attends every seminar excluding Sundays.
- Following:
- The red t-shirt guy is following me.
- Write down the following sentences.
- Given:
- She has given all her money to the kidnapper already.
- All students will have to finish their paper at a given time.
- Gone:
- Let us go now; some of them have already gone away.
- Your turn is gone earlier; now, it is my turn.
- Including:
- We provide you with special treatment in our hotel, including VIP services.
- Like:
- His behavior is like his brother.
- I want a refreshing juice like Lemon soda.
- Less:
- Its qualities are less than the previous one.
- 100 less 20 equals 80.
- Minus:
- Today’s temperature is minus 12 degrees Celsius.
- Eighty minus ten equals’ seventy.
- Next:
- The next candidate is absent.
- Call the cops standing next to you.
- Notwithstanding:
- Notwithstanding the quality, I refuse to buy it.
- The hot iron is notwithstanding the strokes of the hammer.
- Onto:
- He jumped onto the trampoline from Terries.
- The dog jumped onto the fence.
- Opposite:
- Opposite poles of a magnet repel each other.
- She sat opposite my seat on the bus.
- Outside:
- He has not escaped outside the city.
- The hot lava came outside from volcanoes.
- Past:
- The time half-past ten.
- After an accident, I forgot my past memories.
- Per:
- His vehicle runs at a speed of 120 miles per hour.
- She charges $50 per photo.
- Plus:
- Twenty-five plus seven equals thirty-two.
- We won the match, and this is our plus point for qualifying for the finals.
- Pro:
- This phone is a pro version of my old phone.
- We are playing a pro league match in this tournament.
- Pending:
- My payment is still pending.
- She had completed all her pending works on this holiday.
- Regarding:
- I will discuss this with the management regarding your promotion.
- Regarding this situation, I purchased a new machine for our work.
- Round:
- He stands outside the 30 yards round.
- The bullet motions round, not straight.
- Respecting:
- I am talking too politely with you respecting your age.
- Are you still respecting your teachers?
- Save:
- We all present here because he saves all of us at that moment.
- The superhero is always ready to save the world.
- Since:
- We have been friends since 1980.
- The museum had been closed since 1800 AD.
- Than:
- My brother is stronger than his brother.
- I have an expensive toy car than anyone.
- Till:
- The shop will open till Saturday.
- Throughout:
- We have done nothing throughout the day.
- Touching:
- He still starts his morning touching his parents’ feet.
- Your voice is touching my soul.
- Underneath:
- The money is hidden underneath the cushion.
- The transformer is fixed underneath the poles.
- Upon:
- The spaceship needs extra force to go upon the earth.
- An author has started writing a book upon his struggle.
- Until:
- You have to wait until I come.
- The match will be continued until one loses.
- Unlike:
- You have so many, unlike characteristics.
- He is working hard, unlike his younger brother.
- Versus:
- The match of David versus Jayul will start on time.
- You have to select Range Rover versus Land Rover.
- Via:
- This ship travels to South Africa via Cambodia.
- The International flight to Dubai ready to take off from Chennai, taking a route via Delhi.
- Within:
- Accessories also come within the box.
- We are taking off our jet within two minutes.
- Without:
- I wore this blazer without a waistcoat inside.
- Please do not leave without eating food.
- Worth
- I bought an Apple iPhone X worth USD 2565$ only.
- Your good behavior is worth it.
Complex Prepositions or Prepositional phrases:
A complex preposition is a combination of two words. It may be a combination of
- a preposition and a phrase, Prepositional Phrases:
- A preposition and a verb, Prepositions with verbs:
- preposition with an idiom, Prepositions with Idioms, respectively.
Examples
Here is a list of complex prepositions,
- According to:
- According to my father, I don’t know how to eat.
- Ahead of:
- She was seated ahead of my seat on the bus.
- Along with:
- Have some biscuits or snacks along with Tea.
- Apart from:
- He has parked his car apart from his house.
- As for:
- As for me, this one is outstanding.
- Aside from:
- We have another day aside from this evening.
- As per:
- The exam will start on time as per the rules.
- As well as:
- He read as well as writing at the same time.
- Away from:
- The thief ran away from the cops and escaped.
- Because of:
- We failed to enjoy it because of the poor weather.
- But for:
- Usually, I refused to work with him, but for you, I agreed.
- By means of:
- You can climb the mountain by means of ropes.
- Close to:
- Your vehicle stands very close to my car.
- Contrary to:
- Contrary to desires, he failed the competitive exam.
- Depending on:
- We will go for a picnic by bus, depending on the strength.
- Due to:
- Due to the rain, the match was delayed.
- Except for:
- All are present at the party except for Shong,
- Forward of:
- He is driving his vehicle just forward of our vehicle.
- Further to:
- Further to this topic, I have to talk with your guardian.
- In addition to:
- There are a total of twelve players in addition to me in the team.
- In the face of:
- He looks at me like a stranger in the face of a big question mark for him.
- In favor of:
- All members are in favor of this decision.
- In between:
- His bike is in between the two-sport cars.
- In front of:
- No one will stand in front of the door.
- In spite of:
- We chose these curtains in spite of those ones.
- Instead of:
- He went on the road by walking instead of a car.
- In view of:
- In view of the celebration, we have decided to stay here.
- Irrespective of:
- Don’t try to judge me irrespective of my behavior.
- Near to:
- There is a workshop near to my school.
- Next to:
- His roll number is next to my seat in the hall.
- On account of:
- We are going to announce a holiday on account of the boss’s wedding celebration.
- On behalf of:
- You are appointed here on behalf of your colleague.
- On top of:
- We are sitting on top of the building.
- Opposite to:
- Your friend is standing opposite to the music system.
- Other than:
- You can order anything other than Tequila.
- Out of:
- Pick one cloth out of these ones.
- Outside of:
- Throw the ball outside of the stadium.
- Owing to:
- We can afford one AC owing to the monthly income.
- Preparatory to:
- We made a presentation preparatory to the seminar.
- Prior to:
- He never dares to go to the basement prior to living in the hostel.
- Regardless of:
- I won’t help you, regardless of our relationship, even if you pay for help.
- Save for:
- This is money that I have saved for a long time.
- Thanks to:
- We are in good condition, thanks to our Manager for his kindness.
- Together with:
- He would like to have some water together with the whiskey.
- Up against:
- China is fighting back up against the powerful nation of America.
- Up to:
- I will work in this building for up to ten years.
- Up until:
- We played up until they lost the game.
- With regard to:
- We would like to speak about your father with regard to his bravery in the Army.
- With reference to:
- With reference to your mail, I’m sending you the details of our company.

Have you ever thought about the different things that a frog could do to a log? The frog could be on the log, on top of the log, below or under the log, beside the log, between two logs, or any other infinite number of possibilities.
When I was younger, my teacher used the silly image of frogs and logs to help us remember what prepositions are.
While this is a very simply explanation of the different prepositions, it does serve as a remind of what they are for: describing how different parts of a sentence are in relation to each other.
👉 Preposition Definition
A preposition is a word that tells you how words are related in a sentence. It could often follow a verb, but it does not always. The example of the frog and a log can tell you a lot of them, but those are only one of two categories of prepositions.
In fact, there are two types of prepositions: ones that tell about place and ones that tell about time and time order.
Regardless of which preposition you use, you can change the meaning of a sentence. Be careful about saying that you are coming in, coming from, coming after, coming before, or coming at something!
Each of these prepositions, when they come after the right verb, changes the relationship of the two nouns that would complete that sentence.
👉 List of Common Prepositions
Prepositions of Place
- On
- Under
- Below
- From
- In
- Beside
- Next to
- Between
- To
- At
- With
- Behind
- Up over
- Into
- For
- Concerning
- Despite
- Except
- Along
- Against
- Unlike
- Because of
- Beyond
Prepositions of Time
- After
- Before
- Since
- Until
- From
- During
- In
- On
- Beyond
- At
👉 Prepositions Example
Many of these prepositions can be in phrases, both for prepositions of space and time. These are typically known as prepositional phrases. This includes any descriptor of the space or time that something is in.
For example:
- Under the table
- Along the fence
- Beyond the meadow
- Unlike her peers
- Except for Taylor
- After the show
- Since 2017
- During the game
- In October
- On Monday
👉 What is a prepositional phrase?
These prepositional phrases serve to show the reader or listener where or when something happened.
Some phrases that have prepositions actually function as subordinate conjunctions. This means that the words that follow the preposition have both a subject and a verb.
The prepositions that can form these subordinate clauses are after, as, before, since, and until.
For example:
- After she realized she want to eat cake, she decided to stop by the bakery.
- I walked in the door just as my mom was getting ready to head out.
- Since I decided that medicine was not for me, I had been looking for different careers that might be interesting and fit my personality.
- Until the visa process is easier to navigate, I will not travel to those countries.
Note that, if you take away the preposition in each of these subordinate clauses, you end up with a complete sentence. If you add them in, you need to connect the clause to another independent clause that is related in some way.
Prepositional Phrase Examples
👉 Prepositional Phrase BY

👉 Prepositional Phrase FOR
- I haven’t been abroad for ages. I hope I can go to the seaside for a holiday this year.
- I’m not hungry, I ate a lot for breakfast.
- I know for certain I put my car key in my bag, but I can’t find it.
- I don’t want to work here forever. I’ll quit, as soon as I get a better job.
- Not everybody likes cats. For example, I prefer dogs.
- I don’t go to zoos for fear of huge animals.
- Don’t be mad, I did it for fun.
- We broke up for good. I won’t let him back even if he begs me.
- He will definitely help you. Take it for granted.
- For instance, she prefers tea instead of coffee.
- I bought you a necklace. Take it with you to the exam for luck.
- Being a mother is a job for life.
- I love this job, but the salary is low. I can’t do it for love.
- Could you hold my glass for a moment? I need to find something in my bag.
- I can’t believe he fired me. I worked so hard for nothing.
- I love this place so much. I can imagine I live here for the rest of my life.
- We moved to the seaside for Joe’s sake, because he is suffering from asthma in the city.
- Is it for sale? No, I don’t want to sell it.
- I don’t live here. I came for a visit.
- I go for a walk with my dogs every morning.
- I haven’t visited her for a while.
- I will go for a walk every day from now on.
- I have a headache from time to time, and I don’t know why.
👉 Prepositional Phrase IN
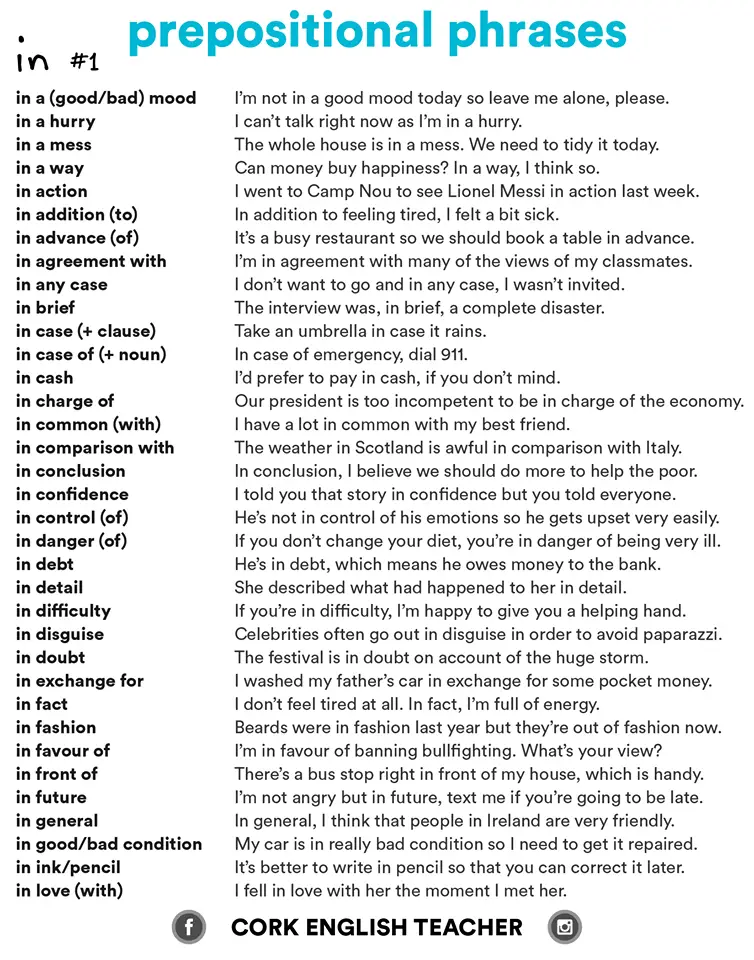

👉 Prepositional Phrase OF and more

👉 OF Preposition Examples
We normally use the preposition OF when we want to connect things to one another, for example:
- The highlight of the holiday was the walking tour of the ancient city.
- The new movie was excellent, but some parts of the movie were very violent.
- The pictures of earth taken from space are incredible.
We can also use OF to show an amount, for example:
- Studies show that 7 hours of sleep per night is the recommended amount of sleep an adult requires.
- Dieticians recommend 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight.
- To pass the driving test a score of 35 out of 40 is required in the theory part of the test.
👉 TO Preposition Examples
The preposition TO is often used when talking about movement. For example:
- Every evening, the children run to their parents when they get home from work.
- The CEO is flying to Hong Kong this week to visit the new office there.
- The letter was sent to the wrong address.
TO is very often used to indicate a time period. For example:
- From January to July there will be training days every second Friday.
- Most employees work from 9 am to 5 pm, Monday to Friday.
- The English course is from 10 am to 1 pm every day for three months.
👉 There are about 150 prepositions in English
Most common ones are here
- with
- against
- above
- over
- on/ upon
- around
- across
- to
- to the left
- to the right
- outside
- into
- through
- near
- far
- at
- beside
- under
- below
- behind
- backward
- forward
- away
- out
- among
- between
- in front (of)
- far
👉 Use of AT IN ON in English Grammar (Time)

A preposition is a word that connects a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase to some other parts of sentences.
Prepositions can be confusing and difficult for English learners because there is no definite rule or formula for choosing the right preposition!
In the early stages of learning English, you should just try to identify a preposition when you’re reading or listening in English and recognize how it is used.
- to the supermarket
- at the dinner table
- on the sofa
- in an hour
- about myself
A preposition is used to show direction, location, time, or to introduce an object.
Some more examples are listed above!
AT
- at 9 o’clock
- at Christmas
- at noon
- at night
- at the weekend
- at dinner
- at the moment
IN
- in the evening
- in the Christmas holiday
- in the summer
- in 2014
- in August
- in 3 hours
ON
- on Mondays
- on that day
- on June 17th
👉 Difference Between the Prepositions IN and ON!

If my keys are IN my bag, you can’t see them. You have to open my bag first and look inside to see them.
If my bag is ON the table, you can see it- it’s on the surface. You look at the table and see my bag ON the top.
If my husband is IN the house, you can’t see him from outside. He is behind the walls. He may be IN the kitchen.
If he’s ON the roof, he’s fixing our satellite dish. You can see him from the street. You look up and there he is, ON the top.
Cats love sitting ON our roof. They never come IN the house.
When you’ve ironed your shirts, you put them IN the wardrobe. You close the doors and you can’t see the shirts anymore.
I have a box of old photographs that I like to keep ON the wardrobe. You can see this box when you enter my bedroom- it’s ON the top.
IN my wardrobe, there are my clothes. ON the wardrobe there is this box. And some dust.
👉 Prepositions IN / ON / AT with words like Playground / Field / Beach
1. Use ‘IN’ when talking about enclosed places.
So, if it is a playground (with swings and slides) enclosed by a fence:
- We spent all morning IN the playground.
The same goes for field: if it is an enclosed one, you can say IN the field, However,
2. ON the playground and ON the field are both correct
when talking about the SURFACE:
- I found this watch on the playground.
or
when the places are OPEN (not enclosed/defined):
- The kids were running on the playground.
3. AT means something like ‘very near’ or ‘next to’:
- Let’s meet AT the playground.
(You don’t have to go inside, but have to be there, very near, so that I can see you if I look at the playground from a distance)
Regarding the BEACH, because it’s an open area, we never say in the beach. It’s not enclosed, we are on its surface, so the correct form is: ON the beach.
👉 Prepositions Phrases: 14 Nouns plus a Preposition
Nouns are often followed by prepositions in English. They form something similar to a phrase that is used over and over again by native speakers. Here is a sampling of popular nouns followed by a preposition.
1. Credit for
this refers to the person who will get the benefit or the praise for something positive being accomplished.
- I didn’t think it was fair that she got all of the credit for the entire team’s hard work.
2. Belief in
refers to someone trusting in or having faith that another person, entity, or organization exist or will do what they say they will do.
- I have a strong belief in the system. Everything will work out the way it is supposed to.
3. Anxiety about
refers to someone being nervous or anxious that something will or won’t happen. When someone has anxiety about something, the situation is making them uncomfortable.
- I have a lot of anxiety about tomorrow’s math test, even though I’ve been studying all week.
4. Addiction to
refers to someone not being able to be without a person, object, or a substance. When someone has an addiction it is usually unhealthy. This is often used to speak about an addiction to alcohol, drugs, food, or some other health issue. While one can have an addiction to something positive, it’s not discussed as often.
- I have an addiction to chocolate, once I start eating one piece, I eat entire bags full every day.
5. Advantage of
refers to someone having a leg up or benefit over someone else. If someone has an advantage they have something extra to help them succeed. The advantage can be anything including physical appearance, money, or connections.
- He had the advantage of height over all of the other players, considering he was five inches taller than all of them.
6. Talent for
means that someone has the potential to be good at something. Someone who has a talent for something may already be established in that thing, or it may be something that they’ve only tried one time.
- He has a newly discovered talent for playing the piano.
7. Responsibility for/ Responsibility to
refers to someone having a duty or obligation to do something. Someone may be being told that they have an obligation to do something or someone may feel like doing something is their obligation.
- You have to take responsibility for your actions.
- It’s not your responsibility to justify his actions.
8. Regret for
means that someone wished something had not happened, or that they did not do something.
- The man had so much regret for his actions, he knew it would be a long time before he would be forgiven.
9. Reason for
refers to why someone is doing something or why something has happened. It doesn’t matter if the reason is good or bad, and it doesn’t matter if the action is positive or negative.
- You better have a good reason for letting the dog in the house right after he played in the mud.
10. Love of / Love for
means that someone really likes something. Someone can have a love for or love of anything. When someone does have a love for something or someone they are really passionate about it.
- He has such a strong love for her, and it’s so beautiful to see.
- The love of money has lead to the downfall of many.
11. Reaction to
refers to someone having a certain feeling or doing a certain action because of something that happened. It can be a physical or emotional reaction.
- He had a reaction to peanuts that caused him to go to the hospital.
- Her squeals of joy were in reaction to seeing her dad after such a long period of time.
12. Ability to
refers to someone or something being able to do something. A person can have an ability to do something, or a machine can have the ability to do something.
- Does this copier have the ability to make copies in color?
13. Memory of / Memory from
refers to remembering something from the past.
- I have so many memories of us playing together as kids.
- I don’t have a lot of memories from that night.
14. Chance of / Chance to
refers to there being a likelihood of something happening or of someone being able to do something. When there is a chance it means something might happen, there isn’t a guarantee that it will happen.
- Is there any chance of us being able to meet tomorrow afternoon.
- Will we have a chance to see each other while you’re on vacation?
Question: Why is the preposition IN used instead of FOR?
Could you please help me? I read this sentence in a grammar book ” Last week, I encountered a friend I hadn’t seen IN five years”.
I got confused about the usage of the preposition. My question is: why the preposition IN is used instead of FOR? Which one is correct? In 5 years OR for 5 years?
Thank you very much in advance!
Answer:
IN is correct, of course, when referring to a period of time. It’s not so frequent as FOR in perfect tenses, but it’s correct.
Look at this slight change: ‘I haven’t seen him in the past five years.’ Doesn’t it sound better?
On the other hand, IN is often used with future forms:
- Talk to you IN 5 days!
- I’ll be back IN an hour.
- I have to find a new job in a month.
IN means NOT LATER THAN in these examples.
Question: Is AT a preposition?
Answer: Yes, AT is a preposition.
What is a preposition?
A preposition is a word used to link nouns, pronouns, or phrases to other words within a sentence. They act to connect the people, objects, time and locations of a sentence. Prepositions are usually short words, and they are normally placed directly in front of nouns. In some cases, you’ll find prepositions in front of gerund verbs.
A nice way to think about prepositions is as the words that help glue a sentence together. They do this by expressing position and movement, possession, time and how an action is completed.
Indeed, several of the most frequently used words in all of English, such as of, to, for, with, on and at, are prepositions. Explaining prepositions can seem complicated, but they are a common part of language and most of us use them naturally without even thinking about it.
In fact, it’s interesting to note that prepositions are regarded as a ‘closed class’ of words in the English language. This means, unlike verbs and nouns, no new words are added to this group over time. In a way, it reflects their role as the functional workhorse of the sentence. They are unassuming and subtle, yet vitally important to the meaning of language.
There are two very important rules to remember when using prepositions. Because they are somewhat vague, learning about prepositions and using them correctly in sentences takes practice. Because 1:1 translation is often impossible when dealing with prepositions, even the most advanced English students have some difficulty at first.
- The first rule is that to make sentences clear, specific prepositions are needed. For example, the preposition in means one thing and the preposition on cannot substitute for it in all cases. Some prepositions are interchangeable but not always. The correct preposition means one particular thing and using a different proposition will give the sentence a very different meaning. I want to see you in the house now, Bill! means something very different from I want to see you on the house now, Bill! In the house means Bill should go through the door, walk inside, and stand in the hall or living room. On the house means Bill would need to get a ladder and climb to the roof where he would be on top of the house.
- The second rule for using prepositions is that prepositions are generally followed by nouns or pronouns. There was a time in the past when teachers held strictly to this rule, but it made for some clunky sentences. I am seeking someone I can depend on ends with the preposition on, so people who insisted that sentences shouldn’t end with a preposition would be forced to use convoluted and unnatural phrasing. To avoid ending that sentence above with a preposition, you’d have to say, someone I can depend on is whom I am seeking.
- There are more than 100 prepositions in the English language. In addition, there are endless possibilities for creating prepositional phrases, phrases that begin with a preposition and end with a noun or pronoun. In the following sections, you will find examples of prepositions, types of prepositions, a comprehensive list of prepositions, and some helpful preposition exercises. As you read the examples and study the list, remember that prepositions usually convey concepts such as comparison, direction, place, purpose, source possession, and time.
In the following sentences, examples of prepositions have been italicized. As you read, consider how using different prepositions or even different types of prepositions in place of the examples might change the relationship between the rest of the words in the sentence.
- I prefer to read in the library.
- He climbed up the ladder to get onto the roof.
- Please sign your name on the dotted line after you read the contract.
- Go down the stairs and through the door.
- He swam across the pool.
- Take your brother with you.
Types of Prepositions
There are three types of prepositions, including time prepositions, place prepositions, and direction prepositions.
Time prepositions are those such as before, after, during, and until; place prepositions are those indicating position, such as around, between, and against; and direction prepositions are those indicative of direction, such as across, up, and down. Each type of preposition is important.
Type of Prepositions
Prepositions of Time
Basic examples of time prepositions include: at, on, in, before and after. They are used to help indicate when something happened, happens or will happen. It can get a little confusing though, as many different prepositions can be used.
Prepositions of time examples in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
For example:
- I was born on July 4th, 1982.
- I was born in 1982.
- I was born at exactly 2am.
- I was born two minutes before my twin brother.
- I was born after the Great War ended.
The above makes it seem quite difficult, with five different prepositions used to indicate when something happened. However, there is a set of guidelines that can help decide which preposition to use:
For years, months, seasons, centuries and times of day, use the preposition in:
- I first met John in 1987.
- It’s always cold in January
- Easter falls in spring each year.
- The Second World War occurred in the 20th century.
- We eat breakfast in the morning.
For days, dates and specific holiday days, use the preposition on.
- We go to school on Mondays, but not on Sunday
- Christmas is on December 25th.
- Buy me a present on my birthday.
For times, indicators of exception and festivals, use the preposition at:
- Families often argue at Christmas time.
- I work faster at night.
- Her shift finished at 7pm.
Before and after should be much easier to understand than the other examples of prepositions of time. Both are used to explain when something happened, happens or will happen, but specifically in relation to another thing.
- Before I discovered this bar, I used to go straight home after work.
- We will not leave before 3pm.
- David comes before Bryan in the line, but after Louise.
Other prepositions of time could include: During, about, around, until and throughout.
- The concert will be staged throughout the month of May.
- I learned how to ski during the holidays.
- He usually arrives around 3pm.
- It was about six in the morning when we made it to bed.
- The store is open until midnight.
Prepositions of Place
To confuse matters a bit, the most common prepositions to indicate time – on, at, in – are also the most common prepositions to indicate position. However, the rules are a little clearer as place prepositions are a more rigid concept than time prepositions.
Prepositions of place examples in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
- The cat is on the table.
- The dogs are in the kennel.
- We can meet at the crossroads.
The guidelines can be broken down as follows:
On is used when referring to something with a surface:
- The sculpture hangs on the wall.
- The images are on the page.
- The specials are on the menu, which is on the table.
In is used when referring to something that is inside or within confined boundaries. This could be anything, even a country:
- Jim is in France, visiting his aunt in the hospital.
- The whiskey is in the jar in the fridge.
- The girls play in the garden.
At is used when referring to something at a specific point:
- The boys are at the entrance at the movie theater.
- He stood at the bus stop at the corner of Water and High streets.
- We will meet at the airport.
Lot’s of other prepositions of place, such as under, over, inside, outside, above and below are used in English. There is, however, a lot less confusion as they refer to rigid positions rather than abstract ones.
- The cat is under the table.
- Put the sandwich over there.
- The key is locked inside the car.
- They stepped outside the house.
- Major is ranked above corporal.
- He is waving at you from below the stairs.
Prepositions of Movement
Prepositions of movement are quite easy to understand as they are less abstract than prepositions of place and time. Essentially, they describe how something or someone moves from one place to another. The most commonly used preposition of movement is to, which usually serves to highlight that there is movement towards a specific destination.
Prepositions of movement examples in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
- He has gone on vacation to France.
- She went to the bowling alley every Friday last summer.
- I will go to bed when I am tired.
- They will go to the zoo if they finish their errands.
Other more specific prepositions of movement include: through, across, off, down and into. These prepositions can sometimes get mixed up with others. While they are similar, they have individual meanings that add context to the movement.
Across refers to moving from one side to another.
- Mike travelled across America on his motorcycle.
- Rebecca and Judi are swimming across the lake.
Through refers to moving directly inside something and out the other end.
- The bullet Ben shot went through the window.
- The train passes through the tunnel.
Into refers to entering or looking inside something.
- James went into the room.
- They stare into the darkness.
Up, over, down, past and around indicate directions of movement:
- Jack went up the hill.
- Jill came tumbling down after.
- We will travel over rough terrain on our way to Grandma’s house.
- The horse runs around the track all morning.
- A car zoomed past a truck on the highway
How to Recognize a Preposition?
Recognizing prepositions can be challenging as they do not always follow a consistent pattern in terms of their position in a sentence, nor do they have a discernible structure or spelling. We do know, however, that prepositions are almost always short words, with the majority having less than six letters. One technique people use to identify a preposition is to think of a preposition as anywhere a mouse can go. Above, below, next to, between, beyond, through, by, with…It won’t cover them all, but it can be a useful question to ask when trying to identify and recognize a preposition. While there are over 100 prepositions, there are around 500,00-700,000 nouns in English! It is unlikely anyone will learn so many nouns, but recognizing and then mastering prepositions might be a worthwhile and attainable goal.
Prepositions with Nouns
There are lots of different nouns that carry specific prepositions to consolidate their meaning. These are called dependent prepositions. Again, there isn’t a set rule that says a particular type of noun will take a dependent preposition, although they normally follow the noun. Moreover, there are many possible combinations. Essentially, it’s case of familiarizing yourself with the different possibilities of nouns and dependent prepositions. Examples:
- He displayed cruelty towards his dog.
- She had knowledge of physics.
- The trouble with Jack.
- 21 is the age at which you are allowed to drink.
- Bolt made another attempt at the world record.
- The police held an inquiry into the murder.
Prepositions with Verbs
Prepositional verbs – the phrasal combinations of verbs and prepositions – are important parts of speech. The prepositions again act as links between the verb and noun or gerund, giving extra meaning to the sentence. The prepositions most commonly used with verbs are: to, for, about, of, in, at and from. The good news is that these will always come after the verb in the sentence. However, it should also be noted that the prepositional verbs can have slightly different meaning compared to the original verb. For example, to relate a story simply means to tell a story, to relate to a story means you identify with it, find some personally meaning in that story.
Verb + to:
- He admitted to the charge.
- I go to Vancouver on vacation twice a year.
- William can relate to the character in the play.
Verb + for:
- He must apologize for his actions.
- We searched for ages before we found the perfect apartment.
- I provide for my family by working two jobs.
Verb + with:
- I don’t agree with your claim.
- The lawyer said he will meet with your representatives.
- They began with a quick warm-up.
Verb + of:
- I dream of a better life.
- Have you heard of Shakespeare?
- The bread consists of dough, raisins and a little honey.
Verb + in:
- Does Rick believe in miracles?
- Fallon lives in New York.
- The bus accident resulted in my being late to work.
Verb + at
- We arrived at our destination.
- Ilene excels at singing.
- Will the baby smile at her mother?
Verb + on:
- We should really concentrate on our studies now.
- Helen insisted on Brenda’s company.
- Morris experimented on some canvas.
Verb + from:
- Since turning 80, she suffers from lapses in concentration.
- Dad retired from the navy in the 1970s.
- Billy Bob, please refrain from doing that.
Prepositions with Adjectives
Prepositions can form phrases with adjectives to give further context to the action, emotion or thing the adjective is describing. Like verbs and nouns, adjectives can be followed by: to, about, In, for, with, at and by.
- I am happily married to David.
- Ellie is crazy about this movie.
- Michelle is interested in politics.
- We are sorry for your loss.
- Jane will be delighted with her results.
- Is he still angry at the world?
- The entire room was astonished by the election results.
There can sometimes be a pattern in deciding which prepositions go with adjectives, for example, when adjectives have the same or very similar meaning to each other, they might take the same preposition:
- Frightened of, afraid of, scared of, terrified of
Indeed, when adjectives have opposite meaning they might also take the same preposition:
- Good at, great at, superb at, wonderful at
- Bad at, terrible at, woeful at, inept at
There are always many exceptions to the above, but it can help that there seems to be some
consistency when adjectives have the same meaning or opposite meaning.
Nevertheless, perhaps a more general rule is that English speakers simply need to learn which prepositions go with which adjectives, as meaning can change significantly by using a different preposition.
- I am good at sports means I have some athletic talent.
- The nurse was good to my mother means she took care of her and was nice, kind, and helpful.
- I am good with animals means I get along with them and handle them well.
- Swimming is good for your health.
- That was good of you to come means you were begin nice and good to visit.
- My little brother is good inside (his body) means even though you can’t see how he thinks and feels, he is good. Even if his behavior is bad.
- The blueberry jam will be good on toast.
Prepositions Exercises
The following exercises will help you gain greater understanding about how prepositions work. Choose the best answer to complete each sentence.
1. The bone was _______ the dog.
a. About
b. For
c. After
d. Considering
Answer: b. The bone was for the dog.
2. We are going on vacation _______ August.
a. On
b. At
c. In
d. Since
Answer: c. We are going on vacation in August.
3. Please put the vase ________ the table.
a. In
b. On
c. For
d. Over
Answer: b. Please put the vase on the table.
4. I received a present ________ Janet.
a. From
b. Of
c. By
d. About
Answer: a. I received a present from Janet.
5. School begins ________ Monday.
a. In
b. On
c. From
d. Since
Answer: b. School begins on Monday.
List of Prepositions
While there are only about 150 prepositions in the English language, these words are among the most important. Without them, the sentences we speak, read, and write would be difficult to understand. The following list of prepositions is not a complete one, however it is among the most comprehensive lists of prepositions available anywhere.
Aboard
About
Above
Absent
Across
After
Against
Along
Alongside
Amid
Among
Amongst
Anti
Around
As
At
Before
Behind
Below
Beneath
Beside
Besides
Between
Beyond
But
By
Circa
Concerning
Considering
Despite
Down
During
Except
Excepting
Excluding
Failing
Following
For
From
Given
In
Inside
Into
Like
Minus
Near
Of
Off
On
Onto
Opposite
Outside
Over
Past
Per
Plus
Regarding
Round
Save
Since
Than
Through
To
Toward
Towards
Under
Underneath
Unlike
Until
Up
Upon
Versus
Via
With
Within
Without
Worth
What is a preposition?
We use a preposition to relate a noun or a pronoun to some other word in the sentence. For example, in the sentence, “The water in the glass is cold.”
The preposition “in” shows the relationship between ‘water’ and ‘glass’.
Preposition Meaning: ‘Preposition‘ is a word used to show the relationship between a noun or a pronoun and some other word in the sentence.
The relationship includes direction, place, time, cause, manner and amount.
Preposition Examples
Prepositions are short words such as ‘in’, ‘at’, ‘on’ etc. that usually stand in front of nouns (sometimes also in front of gerund verbs). Some examples of preposition sentences are given below. Each sentence will show you the type of relationship.
- In the sentence, She went to the store, “To” is a preposition which shows direction.
- In the sentence, He came by bus, “By” is a preposition which shows manner.
- In the sentence, They will be here at three o’clock, “At” is a preposition which shows time.
- In the sentence, It is under the table, “Under” is a preposition which shows place.
Now, we look at some more examples
Example of Preposition + Noun
I gave a book to Julia.
Example of Preposition + Pronoun
I gave a book to him
Example of Preposition + Gerund
I devote my time to reading.
A preposition is always used with a noun or a pronoun. The noun or pronoun it is used with is called the object of the preposition.
For example, “You may go with your brother.”
Here the preposition ‘with’ relates its object ‘brother’ to ‘may go’.
When you find a word that you think is a preposition, look for the object. Say the preposition and then say, ‘what?’. If there is a ‘what’ or ‘when’ you have a preposition. For example, “He jumped in.” In what? there is no answer; therefore, ‘in’ is not a preposition.
Now, look at the following sentence.
He jumped in the water.
Now when we say, ‘in what?’ there is an answer, ‘water”, so ‘in’ here is a preposition.
See also: In, On, At – Preposition of Time and Place Exercises
Types of Prepositions
There are following types of prepositions.
1. Simple Preposition
When a preposition consists of one word is called single or simple preposition.
Simple Preposition Examples: in, at, on, to for, of, from, up, after, over, under, with, till, etc.
2. Double Preposition
When a preposition consists of more than one word, it is called double preposition.
Double Preposition Examples: into, within, upto etc.
3. Compound Preposition
Compound preposition consists of two or more words.
Compound Preposition Examples: on behalf of, according to, in front of, from accross etc.
4. Participle Preposition
Participle preposition consists of words that end in “ing”.
Participle Examples: regarding, barring, concerning, considering, etc.
5. Disguised Prepositions
Disguised Preposition Examples: ‘by’ can be changed into ‘be’, ‘on’ into ‘a’, and ‘of’ can be changed into ‘o’ for example, 5 O’ clock.
6. Phrase Prepositions
Group of words used with the force of a single preposition is called phrase preposition.
Phrase Preposition Examples: according to, by means of, owing to, with a view to, in place of, in front of, in spite of, instead of, in order to, by virtue of, by way of, etc.
Read also: Preposition of Place, Preposition of Time
Prepositions List
Here is an alphabetically organized list of common prepositions.
- Abide by a promise
- Ability for in some work
- Abound in or with fish
- Absolved of a charge
- Absorbed in thoughts
- Abstain from wine
- Abundance of food
- Accede to a request
- Acceptable to a person
- Access to a person or a place
- Accomplice with a person in some crime
- Accountable to a person for a thing
- Accustomed to hearing abuses
- Acquaintance with a person or a thing
- Accuse of some misdeed
- Acquitted of a charge
- Adhere to a plan
- Adjacent to a place
- Admit to an excuse
- Adverse to his interests
- Affection for a person
- Affectionate to a person
- Affinity with something between two things
- Afraid of death
- Agree to a proposal
- Agree with a person
- Aim at a mark
- Alarmed at a bad news
- Alight from a carriage
- Allegiance to a person
- Alliance with a person or state
- Allot to a person
- Allusion to something
- Alternative to a plan
- Amazed at anything
- Ambition for something
- Amused at a joke
- Animosity against a person
- Angry at a thing with a person
- Answer to a person
- Answer for conduct
- Anxious for his safety about the results
- Apology for some fault to a person
- Appeal to a person for redress or help against
- Appetite for food
- Applicable to a case
- Apply to a person for a thing
- Appoint to a situation
- Apprise of a fact
- Appropriate to an occasion
- Approve of an action
- Aptitude for science etc
- Arrive at a place in a country
- Ashamed of his ignorance
- Ask for a thing from a person
- Astonished at her behavior
- Astonishing to a person
- Assent to an opinion
- Associate with a person or thing
- Attack on a place
- Attain to a high place
- Attend to a speaker
- Attend on a person
- Attention to study
- Avail oneself of an offer
- Avenge oneself on a person
- Aversion to a person or thing
- Aware of his intentions
- Bark at a person or thing
- Beat against a rock
- Believe in one’s honesty
- Belong to a person
- Bestow a thing on a person
- Beware of pick-pockets
- Blessed with health
- Blind to his own fault
- Blush at one’s own fault
- Boast of one’s wealth
- Born of rich parents
- Break into a house
- Break with a person
- Burst into a rage
- Busy with his lessons
- Call on a person at a place
- Call for punishment
- Canvass for votes
- Capable of improvement
- Care for a person
- Careful of his money about his dress
- Charge man with a crime
- Cling to a person or thing
- Close to a person or thing
- Clothed in blue
- Commence with a thing
- Comment on a matter
- Common to sever persons or things
- Compete with a person
- Competent for certain work
- Complain against a person
- Complaint about a thing
- Comply with someone’s orders
- Composed of a material
- Conceal facts from anyone
- Concede to some demand
- Condole with a person
- Conducive to success
- Confer a thing on anyone
- Confidence in a person
- Confident of success
- Conform to rule with one’s views
- Congratulate a man on his success
- Connive at other men’s fault
- Consent to some proposal
- Conscious of her beauty
- Consist of material in facts or results
- Consult with a person on or about some matter
- Contempt for a person or thing
- Contend with or against a person
- Contend for or about a thing
- Contented with a little
- Contrary to rules
- Contrast to a person or thing
- Contribute to a fund
- Control over a person or thing
- Converse to a point
- Converse with a person about a thing
- Convince a person of a fact
- Cope with a person
- Correspond to something
- Count on a thing
- Cure a man of a disease
- Deaf to his advice
- Deal in clothes(trade)
- Deal with a person
- Deficient in energy
- Delight to see you
- Depend on a person or thing
- Deprive a person of a thing
- Desire for wealth
- Desirous of success
- Despair of success
- Detrimental to health
- Devoid of happiness
- Die of a disease
- Die from some cause as overwork
- Die by violence
- Differ with a person on a subject
- Disagree with a person or thing
- Disappointed with a person in a thing
- Disapprove of anything
- Disgrace to a person
- Dispense with a man’s services
- Displeased with a person
- Dispose of property
- Dispute with a person about anything
- Disqualified for a post
- Dissent from an opinion
- Dissuade from an action
- Distinguish one thing from another
- Distinguish between two things
- Dream of strange things
- Duty to a person
- Dwell on a subject
- Eat into iron
- Elicit from a person
- Eligible for employment
- Embark on board ship
- Embark in business
- Eminent for his poetry
- Employed in gardening
- Encroach on one’s authority
- Endow a person or thing with something
- Engaged to some person in some business
- Enmity with a person
- Entitled to some facility
- Entrust anyone with a thing
- Entrust a thing to anyone
- Envy at another’s success
- Envious of another’ success
- Equal to the occasion
- Escape from jail
- Excuse for a fault
- Exempt a person from a rule
- Exonerate a person from blame
- Experience in doing something
- Explain to a person
- Exult in a victory over a rival
- Faith in a person or a thing
- Faithful to a master
- Familiar to a person or thing with a language
- Famous for his learning
- Fatal to his health
- Feed on grass
- Feed a cow with grass
- Fit for a position fond of music
- Forbearance for some weakness
- Fraught with danger
- Gifted with abilities
- Glance at a person to a thing
- Grapple with difficulties
- Grieve at or for or about an event
- Grieve for a person
- Guard against a bad habit
- Guess at something
- Hanker after wealth
- Harmony with anything
- Hatred of or for a person of a thing
- Heal of a disease
- Heir to some property
- Hint at an intention
- Hope for something
- Hopeful of success
- Hostile to my efforts
- Ignorant of English
- Ill with fever
- Impart a thing to a person
- Impose on a person
- Incite a person to some action
- Inclined to laziness
- Incumbent on a person
- Indebted to a person for some kindness
- Indicative of his motives
- Indifference to a person or thing
- Indulge in gambling
- Infected with smallpox
- Infer one fact from another
- Infested with rats
- Inflict punishment on a man
- Influence over a person on a man’s action
- Informed of a fact
- Infringe on a man’s rights
- Innocent of a charge
- Inquire into a matter of a person about some matter
- Insist on something being done
- Instill a thing into the mind
- Interest in music with a person about some matter
- Interfere with a person in some matter
- Intimate with a person
- Introduce a man to someone into a place or sect
- Invite a man to dinner
- Involve a man in debt
- Irrelevant to a question
- Irrespective of color and creed
- Jeer at person
- Jealous of his reputation
- Jest at a person
- Jump at a person
- Jump to a conclusion into the river
- Lame of one leg
- Lament for the dead
- Laugh at a person or thing
- Lean against a wall
- Liable to an error of payment
- Limited to a certain area
- Live on a small income
- Long for or after some business
- Long at a person or thing
- Long into a matter
- Long for something lost
- Loyal to the government
- Lust after/for riches
- Mad with hunger
- Malice against a person
- Marry one person to another
- Meddle with other man’s affairs
- Merge into anything
- Moved to tears
- Moved with pity
- Moved at the sight
- Moved by request
- Negligent of duty
- Necessity for a thing
- Need for assistance
- Nomination of a person to a post
- Notorious for his misdeeds
- Obedience to a person or order
- Object to some proposal
- Obliged to a person
- Oblivious of the past
- Occupied with some work
- Operate on/upon a patient
- Opposed to facts
- Opposite to a place
- Overcome with sorrow
- Overwhelm with emotions
- Painful to one’s feelings
- Parallel to or with anything
- Part with a person or thing
- Persevere in an effort
- Persist in doing something
- Pertain to question
- Play at cards
- Play upon the guitar
- Play tricks with a person
- Plot against a man
- Plunge into a river
- Ponder on or over a subject
- Popular with students
- Pounce on a thing
- Prefer one thing to another
- Prejudice against a person
- Present anyone with a book
- Preside at or over a meeting
- Prevent from going
- Previous to some event
- Proficient in mathematics
- Prohibit from doing something
- Prone to laziness
- Protect from harm
- Protest against injustice
- Proud of his wealth
- Provide for one’s children
- Provide with something
- Purged of evil thoughts
- Qualification for office
- Quarrel with someone over or about something
- Quick at mathematics
- Recover from an illness
- Reduced to poverty
- Related to a person
- Refer to a subject
- Refrain from some action
- Regard for a man’s feeling
- Rejoice at the success of another in one’s own success
- Relieve of or from pain
- Rely on a person or thing
- Remedy for or against a snake bite
- Remind a person of a thing
- Repent for a sin
- Repentance for sin
- Result from a cause
- Result in a consequence
- Revenge me on someone for some injury
- Revolt against a government
- Reward a man with something for some service done
- Rob a person for something
- Rule over a country
- Run after new fashions
- Run at a cat
- Run into debt
- Sacred to a person
- Satiated with pleasure
- Satisfied with income
- Search for something lost
- Send for a doctor
- Shocked at your behavior
- Short of money
- Shudder at cruelty
- Sick of waiting
- Similar to a person or thing
- Slow at accounts
- Sorry for your sufferings
- Stand against an enemy
- Stand by a friend
- Stand to one’s opinion
- Stare at a person
- Startled at a sight
- Steeped in evils
- Stoop to greediness
- Strange to a person
- Struggle against difficulties
- Subject to authority
- Submit to authority
- Subordinate to a person
- Subscribe to a fund
- Succeed to a property
- Succeed in doing something
- Succumb to difficulties
- Sue for peace
- Sufficient for a purpose
- Suitable to the occasion
- Suitable for his income
- Supplement to a book
- Supply a thing to a person
- Supply a person with a thing
- Sure of success
- Surrender to the enemy
- Suspicious of his meaning
- Sympathize with a person in trouble
- Synonymous with another word
- Take after her mother
- Take a person for a thief
- Take to gambling
- Take upon oneself to do a thing
- Talk to or with a person
- Thankful for some favor
- Throw a stone at any one
- Tired of doing nothing
- Tired with his exertions
- Traitor to his country
- Tremble at a snake with fear
- True to his words
- Trust in a person
- Trust a man with money
- Vested in a person
- Vexed with a person
- Vexed at a thing
- Victorious over difficulties
- View with another person
- Vote for anything
- Vote against a thing
- Wait for a person or thing
- Wait on a person
- Warn a person of danger against a fault
- Want of money
- Weary of doing nothing
- Welcome to my house
- Wish for anything
- Witness of or to an event
- Wonder at something
- Worthy of praise
- Yearn for love
- Yield for pedestrians
- Zeal for a cause
- Zealous for improvement
- Zest for enjoyment
Practice Exercise: Mixed Preposition Exercises with Answers
A list of prepositions contains fewer than 200 words. That’s not many considering English contains at least a couple hundred thousand words. It’s amazing that the list of all prepositions is so short considering they are used to demonstrate how words and phrases connect in nearly every single sentence. In fact, most sentences contain more than one connecting word. That means you’ll use words from a prepositions list more often than you will nouns, verbs, and most parts of speech. Now that you know how important these connecting words are, let’s take a look at a preposition list and all of its functions including a prepositional phrase list.
A Preposition List: Categories of Connecting Words
Instead of creating a single list of prepositions, let’s discuss the different groups that exist. You can organize these words in two ways. First, by words you use to create connectors. Second, by function.
Certain ones help describe different kinds of information in a sentence, therefore it makes sense to organize these words into groups. Let’s go over the words that comprise each group, so you understand how each category is different. It’ll give you a good start to creating you own list of all prepositions.
Prepositions List: Connecting Words by Word Group
1. A Simple Preposition List
Nearly half of the prepositions you use in the English language are “simple” words. Simple words mainly have one or two syllables and connect words in a sentence. Here’s a list of common prepositions:
| About | Above | Across | After | Ago |
| At | Below | By | Down | During |
| For | From | In | Into | Off |
| On | Over | Past | Since | Through |
| To | Under | Until | Up | With |
It’s said that it’s grammatically incorrect to have a preposition end a sentence. This is not always true. Though it does not follow the traditional rules of connecting a subject to a noun or verb, it can be done when you use a casual tone. For your papers and more formal writing, stick to keeping these words away from the end of a sentence.
Though the above is not a complete prepositions list, it does cover many of the more common words you’ll encounter. Reading ahead, you’ll find there are numerous words that fall under a complete list of all prepositions. However, to get there you will have to memorize and be able to differentiate between every single one.
Need a break from learning connecting words? Try something new! Learn about academic writing using MLA format and more citation styles. These two topics will help improve your writing skills and impress your English teacher.
2. A Double Preposition List
Now that you’ve seen the prepositions list above and know what a single preposition (or connecting word) is, you can move on to double prepositions. Basically, they are a combination of two simple connecting words. For instance, onto, inside, and without are all examples of double connecting words.
These words are very similar to compound prepositions (which will be covered in the next section), and they’re easy to mix up. That’s because compound connecting words also contain two individual words which take on one meaning. But there are some subtle, and more noticeable differences between double and compound prepositions.
The most noticeable difference is that instead of forming their own individual words (like compound connecting words do), double words combine into one. Let’s take a look at some examples:
A List of Prepositions: Double Words
| Amid | Atop | Inside | Into | Onto |
| Outside | Throughout | Upon | Within | Without |
3. A Compound Preposition List
As you can see, double words enjoy being together. Compound words on the other hand, prefer their own space. Words like regardless of, as for, and prior to are examples of compound connecting words.
Compound connecting words are also made up of two words, just like double words. But instead of coming together, they retain their individuality. They are two words with one joint meaning. Here is a list of prepositions for compound words found in English:
List of Prepositions With to:
- According to
- Close to
- Due to
- Near to
- Owing to
- Prior to
- Relative to
- Subsequent to
- Thanks to
List of Prepositions With of:
- Ahead of
- Because of
- Inside of
- Instead of
- Out of
- Outside of
- Right of
List of Prepositions With for or from:
- Apart for
- Apart from
- As for
- Aside from
- Except for
- Out from
Other examples:
- As per
- Rather than
- Where as
The second way you can tell compounds apart from doubles is from the actual words that make up a group of compound connecting words. If only one of the two words in the pair is a simple word, then you’re dealing with a compound phrase. A double word always uses two simple words and never just one.
The prepositional phrases list also has more than one word in each listing, but they differ from compound and double words. We will explore this more in section “5. A Prepositional Phrase List.”
Now that you know the differences, you’ll never mix the two up again. Here’s an informative site that explains this in greater detail.
4. The Participle List of Prepositions
Some gerunds, or -ing forms of verbs, can act as connecting words. There aren’t too many that function this way, so there aren’t too many participle prepositions to remember. Here’s the participle preposition list:
- Considering
- Concerning
- During
- Excluding
- Following
- Including
- Regarding
5. A Prepositional Phrase List
A prepositional phrase list includes groups (known as phrases) of different words that together act as a connecting word. The group/phrase can contain verbs, adverbs, and other parts of speech.
Remember, do not confuse these with compound or double words. All of the groups on this list of prepositional phrases have at least three words and are phrases instead of a pairing of words. Here is a list of prepositional phrases you should be aware of:
Prepositional Phrases List
- As far as
- As long as
- As soon as
- As well as
- In addition to
- In regard to
- In spite of
- On top of
- With regard to
- With the exception of
This list of prepositional phrases were sorted based on the words that made up each connecting word or group.
Aside from the above prepositional phrase list, are you generally concerned with grammar in your writing? If yes, take a look at this paper checker from Citation Machine Plus! It’ll spot grammar errors in your paper and check for accidental plagiarism. Citation Machine Plus also has services to help you create citations in APA format and other formats.
Connecting Words by Function
1. The Time List of Prepositions
There aren’t many connecting words that describe time, however, the words that do actually play a large role in the English language. With these words, you can describe when something will or did happen. The following prepositions list shows connecting words used to describe time:
List of Common Prepositions for Time
- After
- Ago
- At
- Before
- By
- During
- For
- From
- In
- On
- Past
- Since
- To
- Until
2. Place Prepositions List
The list of place words is very similar to the list of time words. In fact, they share much of the same language.
List of Common Prepositions for Place
- Above
- At
- Below
- Beside
- By
- Down
- In
- Off
- On
- Over
- Under
- Up
So, how can you tell whether a sentence includes a place or a time connecting word? When you can’t determine based on the connecting word alone—you must look at the context. Place words mostly describe physical location, whereas time words describe when something takes place.
Time:
- My birthday party is on Monday.
Place:
- Drew is currently on a cruise ship.
Do you need a little bit more help telling these two apart from each other? Click site for some helpful tips.
3. List of Prepositions for Agent
Connecting words that explain agent, help your audience understand the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in a sentence. Each sentence with an agent connecting word will explain how someone affects someone or something else. There are three words that show an agent connection. These words are by, without,and with. Agent words are the same words that you’ll find on a list of prepositions for instruments.
- This painting was designed by Warhol, but painted by his staff.
- You can’t unlock a computer without the password.
- Warhol also worked on this painting with his friend Basquiat.
Review Questions & Exercises
Compared to other parts of speech, a list of all prepositions is a short one, but is important nonetheless. Becoming familiar with each prepositions list above will help you further your understanding of English grammar.
Feel like you’ve absorbed everything above? Do you know what double prepositions are? Do you remember what words are on the list of prepositional phrases ? Flex your knowledge using the questions and exercises below.
- What is the difference between a double and a compound preposition?
- Look at the prepositional phrases list. Create 3 example sentences using the phrases on the prepositional phrases list.
- Find a short online article or post that you like and copy and paste it into a document. Highlight every preposition in the article that is also on the list of common prepositions for time and place.
- Review this guide and make your own preposition list of words you’re not familiar with. Make it your goal to memorize them and make an example sentence using each word.




