Pin
Pin
- HAS: We use ‘has’ to show possession or ownership for singular objects.
- HAVE: We use ‘have’ to show possession or ownership for plural objects.
- HAD: ‘Had’ is used to show possession or ownership of something in the past.
Has Have Had use in sentences
Sentences using “has”
- He has a sharp knife.
- The horse has four hoofs.
- She has had a beautiful cat.
- Tom has completed his assignment before the target date.
- Bob has a variety of coins.
- The old man has no stick.
- The fruit seller has no apples.
- The passenger has a lot of luggage.
- Has the cow two horns?
- The girl has the keys to the door.
- The poor man has no bicycle.
- The dog has a beautiful collar on its neck.
- Julia has no ornaments.
- Has the carpenter made this unique chair?
- This parrot has a red peak.
- He has worked here for five years.
- It has rained heavily this morning.
- She has a plan to spend her holidays in Austria.
- Rosina has prepared the meal for her children.
- Tom has no interest in marketing.
Read also: 27 Figures of Speech with Examples
Sentences using “have”
- They have many books.
- Have you a dog in the house?
- I have a 50-megapixel camera.
- Tom and Bob are brothers. They have an ordinary residence.
- They have raised the issue of clean water at the conference.
- I have applied for the American visa lottery.
- They have not helped him in his illegal activities.
- I have tried a lot for a job but in vain.
- I have opened a bank account to save money for the future.
- Have you a precious watch?
- I have nothing in my wallet except my ID card.
- Do you have a pen in your pocket?
- I have an older brother.
- We have done some extra work for the project
- I have met Antonia several times before.
- We have made appointments in advance.
Sentences using “had”
- Our garden had a hedge around it.
- How many cars has this rich man had?
- I had a beautiful picture which is no more with me.
- He had no dog in the house.
- My brother had worked there in 2005.
- Had the king crown on his head?
- The farmer had two bullocks.
- How long a piece of cloth had the girl?
- Had the horse bridle and saddle.
- This city had a clock tower in its middle.
- The mechanic had fixed my car before I reached there.
- He had a precious watch that was lost.
- She had won a gold medal in swimming in 1994.
- Jacob had no job in 2017.
- She had a great time on her vacation.
Read also: 11 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement with Examples

To express a statement, question, request, command, or exclamation, sentences are used to drive a meaningful message through it, and that sentence uses words.
A sentence is nothing but a compound of phrases which can be a verb phrase or a noun phrase along with a clause. These clauses can be either single or more than one.
A verb is a word that conveys a message of action or can convey a state of being, and that is what a verb phrase is made of. Now that phrase should be agreeing with the subject or the object used in the same sentence.
Key Takeaways
- “Has” serves as the present tense third-person singular form of “have,” whereas “had” is the past tense of both “have” and “has.”
- Use “has” to describe a present situation, action, or possession and “had” for past occurrences.
- “Has” combines with present participles to create present perfect verb forms, while “had” forms past perfect verb constructions.
Has is a verb that means to possess, own, or hold, and it is the third person present of the word ‘have.’ It also means to undergo or experience. Had is the past tense or past participle of the word ‘have’ that means to own, hold, possess, or experience. It is sometimes used instead of ‘if.’
Want to save this article for later? Click the heart in the bottom right corner to save to your own articles box!
Has while using requires a direct subject along with one or even more than one object, and that is why it is one of the transitive verbs. Has is used while mentioning a third person in a sentence. Verbs that have only one subject in a sentence are called intransitive.
Had is also a transitive verb for the same reason, but the difference here is that it is used only while mentioning something that is in the past. Had is also used for referring to a third person.
Had can be used in place of the word ‘taken’ as they both are synonymous with each other. They both mean ‘deceived’.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of comparison | Has | Had |
|---|---|---|
| Tense | Has is used for referring to the third person but in the singular present tense of the verb. | Had is used for referring to the third person but in singular past tense and past participle of the verb. |
| Meaning | Has is a helping verb that is referred to as occupying stuff. | Had is a helping verb that is referred to as taking stuff. |
| Referred person | Has is used while referring to a third person. | Had is also used while referring to a third person. |
| Synonym | Own, possess, occupy are synonyms of has. | Taken is the synonym of had. |
| Past/present | Has is used while talking about something in the present. | Had is used while mentioning something that happed in the past. |
What is Has?
There are two kinds of verbs, as said before, intransitive and transitive. Has is the transitive one. This is because it requires a subject while using plus one object or more than just one.
It is used in the singular form of the past tense while mentioning a third person in a sentence.
This can be understood better with some examples- Sarah has pimples, here pimples are the objects that we talked about, and Sarah is the third person we are referring to.
Here has is used to complete the sentence and make it meaningful. The word has originated from middle English, in which there was a word called ‘haven’ or ‘Habben’s.
The word Habben was from the old form of the English language, which is related to the word ‘heave’.
What is Had?
Had is another transitive verb that is used for referring to a third person in a sentence. It is used as the past participle and past tense of the verb ‘have’.
The word ‘taken’ can be used as the substitute for had as they are synonymous with each other, plus they both mean the same, which is ‘deceived’.
Let’s understand it with some examples- “john had his dinner early today”, here john is the subject, and the dinner referred to here is the object, while the verb had is used to complete the sentence and to give it a meaning.
“She had a nice car”, here, the car is the object talking about while ‘she’ is the third person.
Main Differences Between Has and Had
- The main difference between has and had is the tense they are used in Has is used for referring to the third person but in the singular present tense of the verb, while Had is used for referring to the third person but in singular past tense and past participle of the verb.
- Both of them are transitive verbs which means both of them requires a subject and objects while being implemented, Has is a helping verb that is referred to as occupying stuff, and Had is too a helping verb, as mentioned before that is referred to as taking stuff.
- Both of them are used for mentioning another person or something, and that is why Has is used while referring to a third person in the same way Had is also used while referring to a third person.
- Well, they both have substitutes too- Own, possess, occupy are synonyms of has, while Taken is the synonym of had.
- Has is used while talking about something in the present, but Had is used while mentioning something that happed in the past.
- ‘Sarah has bike’ is an example of the verb ‘has’ while ‘John had a glass of juice’ is an example of the verb ‘had’.
References
- https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/mono/10.4324/9781315835464/meaning-english-verb-geoffrey-leech
- https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-child-language/article/children-use-syntax-to-learn-verb-meanings/4E19981CDD2D247CBB37D32A45BAFE31
Emma Smith holds an MA degree in English from Irvine Valley College. She has been a Journalist since 2002, writing articles on the English language, Sports, and Law. Read more about me on her bio page.
Have and has are different forms of the verb to have. Even though they come from the same word, there are slight differences in the way they’re used.
While the verb to have has many different meanings, its primary meaning is “to possess, own, hold for use, or contain.” Have and has indicate possession in the present tense (describing events that are currently happening).
Have is used with the pronouns I, you, we, and they, while has is used with he, she, and it.
How do you use have?
Have is the conjugation of to have that’s used when:
- speaking in the first person (I, we)
- speaking in the second person (you)
- speaking in the third person plural (they)
Take, for example, the following sentence: “They have two dogs.” Here, have is the correct choice because the subject (they) is a third person plural pronoun.
How do you use has?
Has is the conjugation of to have that’s used when:
- speaking in the third person singular (he, she, and it).
This example from And the Mountains Echoed by Khaled Hosseini shows has used with a third person singular pronoun (he): “He has a slender nose, a narrow mouth, and tight blond curls.”
As noted, this use of have and has only really applies when you’re speaking in the present tense.
How do you use have and has with other verbs?
Indicating possibility
Now that you’ve mastered the basics of have and has, it’s time to talk about how to use them in combination with other verbs. For every sentence that simply indicates possession (I have a cat), there’s going to be another that uses to have in a more complex way. For example, if you say I have to groom the cat, that’s definitely more complicated of an issue … in more ways than one!
One way have and has combine with other verbs is to describe what could happen (but hasn’t yet):
- You have to call me tonight.
- He has to do his homework before dinner.
These actions have not occurred yet. As before, have is used with the pronouns I, you, we, and they, while has is used with he, she, and it.
Indicating completed action
Have or has can be used to communicate that the action of a verb was completed prior to the present. To do that, you will create what’s called the present perfect tense, which involves more complex time relationships, and combines a verb with has, have, or had:
- We have waited for hours in this line.
- You have finished the job on time.
- She has learned an important lesson.
In the sentence “She has played banjo for four years,” for example, has is an auxiliary verb (a helping verb used in the construction of verb forms), and played is a past participle. As in the examples mentioned before, has is used with a third person singular pronoun.
Get that essay, email, or letter to Nana over the finish line with a little writing help from Grammar Coach™. Get grammar check, spelling help and more free!
This is complex stuff, so don’t feel bad for not memorizing all of these rules. What’s important to remember is that together, has and a past participle like played form the present perfect tense.
Another example of the present perfect tense is seen in this sentence from The Night Circus by Erin Morgenstern: “‘I have invited you all here for a reason,’ Chandresh says, ‘as I’m sure you have surmised by now.’”
In the first part of the sentence, have is used because there is a first person subject (I). In the second part of the sentence, have is used again because there is a second person subject (you).
Here’s a recap
Have is used with the pronouns I, you, we, and they. Has is used with he, she, and it.
- Have and has can indicate possession.
- Have and has can combine with other verbs to indicate more complex relationships with time.
Want to possess an even better grasp on grammar? Then you have to check out this article on the difference between who and whom.

By
Last updated:
December 15, 2022
As an English learner, you probably see the English words “has” and “have” frequently.
If you’re a beginner English speaker, you might be confused about how to use them. In that case, you’ve come to the right post.
We’re going to crack the code and solve the mystery of “has” vs. “have.”
Contents
- What Are “Has” and “Have”?
-
- “Has” and “Have” to Mean Possession
- “Has” and “Have” as Auxiliary Verbs
- “Has” vs. “Have”: What’s the Difference?
-
- Points of View in English
- “Has” vs. “Have” in the Present Tense
-
- Using “Has” in the Present Tense
- Using “Have” in the Present Tense
- “Has” vs. “Have” in the Present Perfect Tense
-
- Using “Has” in the Present Perfect Tense
- Using “Have” in the Present Perfect Tense
- Summary: “Has” vs. “Have”
- How to Practice “Has” and “Have”
Download:
This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you
can take anywhere.
Click here to get a copy. (Download)
What Are “Has” and “Have”?
“Has” and “have” are both verbs.
Verbs are used to indicate action. Along with nouns, adjectives, pronouns and prepositions, they’re one of the basic parts of speech in English.
“Has” and “Have” to Mean Possession
When we talk about possessing (owning) something, we use the verb “to have.”
“To have” is the infinitive, or original, form of the verb.
Here are some conjugations of the verb “to have”:
| Tense | Conjugation |
|---|---|
| Present | has, have |
| Present progressive | is / are having |
| Past | had |
“Has” and “have” are both conjugations in the English present tense.
For example, look at the following sentences:
She has the book.
I have the book.
In both sentences, the verb “to have” is conjugated in the present tense.
“Has” and “Have” as Auxiliary Verbs
The verb “to have” has another use. It’s also an auxiliary verb.
An auxiliary verb is combined with another verb to complete the meaning of a sentence. Because of this, it’s also called a helping verb. For example:
She has eaten dinner already.
I have seen that movie.
These sentences both use the perfect tense. Here, “has” and “have” don’t indicate possession. Instead, adding “has” or “have” to another verb creates that verb’s perfect tense form.
In general, the verb “to have” is important as an auxiliary verb because it creates the past perfect and present perfect tenses for other verbs.
“Has” vs. “Have”: What’s the Difference?
Really, the difference between “has” and “have” is all about English points of view:
Points of View in English
In English, anything we read or speak is coming from a particular point of view. The point of view tells you who is speaking, and who is being spoken about.
You can know the point of view by looking at which pronouns are used. Let’s quickly review:
| Point of View | Meaning | Singular Pronoun | Plural Pronoun |
|---|---|---|---|
| First Person | The speaker is talking about himself or herself (with other people included if plural). | I | We |
| Second Person | The speaker is talking directly to somebody else. | You | You |
| Third Person | The speaker is talking about somebody or something else. | He (men) She (women) It (non-living things) |
They (people or things) |
Got it? Great! Now that you understand points of view, using “has” and “have” becomes very easy.
“Has” vs. “Have” in the Present Tense
“Has” and “have” can both be used in the present tense as a main verb to mean possession.
Here’s the difference:
| Type of Sentence | Has | Have |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative Statement | ✓ (he, she, it, singular nouns) | ✓ (I, we, you, plural nouns) |
| Negative Statement | 𐄂 | ✓ |
| Question | 𐄂 | ✓ |
Using “Has” in the Present Tense
There are two points you have to remember:
1. In the present tense, “has” is used with the third-person singular point of view.
That means you’ll use it with “he,” “she,” “it,” a name or a singular noun.
It’s also used with singular pronouns like “everybody,” “anybody,” or “nobody”:
Everybody has a copy of the book.
Nobody has the answer.
I don’t think anybody has coffee.
2. “Has” is only used with affirmative (non-negative) statements.
If you’re asking a question or if you’re talking in the negative (using the word “not”), you won’t use “has.”
He has brown eyes.
She has the answer to your question.
That book has 400 pages.
Japan has amazing food.
Meena has 45 pencils.
Using “Have” in the Present Tense
1. In the present tense, use “have” in the first- and second-person points of view, and in the third-person plural point of view.
In other words, use “have” with the subjects “I,” “you,” “we” or “they”:
I have a headache.
You have a new laptop.
They have three cats.
We have a big house.
Also, use “have” with plural nouns or when talking about multiple people or things at the same time:
Those dresses have stripes.
Roger and I have a red car.
My dog and Patricia’s cat have brown fur.
2. If you’re asking a question or making a negative statement, then always use “have,” regardless of the point of view.
Here are some questions in the present tense, all using “have”:
Does anybody have the answer to the question?
Do you have the book?
Does she have a house?
Does Meena have a best friend?
Do I have your attention?
The same is true for negative statements in the present tense:
She does not have a room.
I do not have a brother.
They do not have time to see you.
The movie does not have a good plot.
We do not have a dog.
To repeat: with a negative statement or a question, use “have” even if the subject is “he,” “she,” “it,” a name or a singular noun.
“Has” vs. “Have” in the Present Perfect Tense
“Has” and “have” can also be auxiliary verbs that help create the present perfect tense, in combination with other verbs.
The rules for using them as auxiliary verbs are actually simpler. It just depends on the subject:
| Subject | Has | Have |
|---|---|---|
| Pronoun | He, she, it | I, you, we, they |
| Noun | Singular | Plural |
Using “Has” in the Present Perfect Tense
Whatever kind of statement you’re making, whether it’s an affirmative or negative statement or even a question, you’ll use “has” as long as the subject is third-person singular: “he,” “she,” “it,” a name or a singular noun.
John has gone to California four times. (Affirmative statement)
The dog has not eaten today. (Negative statement)
Has she received the letter? (Question)
Has he not told you about this? (Question)
Using “Have” in the Present Perfect Tense
Similarly, with “have,” you use it in the present perfect tense with subjects “I,” “you,” “we” or “they,” as well as plural nouns.
I have watched “Game of Thrones” four times.
You have helped me a lot.
They have asked many questions.
We have thought about this all day.
This is true for any kind of statement or question too:
My friends have not watched “Game of Thrones.” (Negative statement)
You have not helped me at all. (Negative statement)
Have they asked too many questions? (Question)
Have we thought about this enough? (Question)
Summary: “Has” vs. “Have”
Here’s a quick summary of what we’ve learned:
- “To have” is the verb associated with possession or ownership.
- “Have” and “has” are both conjugations of “to have” in the present tense.
- “Have” and “has” are also used as auxiliary (helping) verbs in the present perfect tense
In the present tense…
- Use “has” with the subjects “he,” “she,” “it,” a name or a singular noun.
- Use “have” with the subjects “I,” “you,” “they,” “we,” a plural noun or multiple subjects.
- But, use “have” for any questions or any negative statements—no matter the “point of view.”
In the present perfect tense…
- Use “has” any time you use the subjects “he,” “she,” “it,” a name or a singular noun.
- Use “have” any time you use the subjects “I,” “you,” “they,” “we,” a plural noun or multiple subjects.
How to Practice “Has” and “Have”
Practicing English grammar doesn’t need to be hard or boring. There are many amazing resources available on the internet, plus other fun ways to practice.
Take Online Quizzes
You can test your progress by taking free online quizzes.
If you’re curious as to whether you’ve understood the differences between “has” and “have,” try this quiz on EnglishGrammar and this one on EnglishExcercises.
For on-the-go practice, check out this worksheet from Study.com that you can download and print.
Watch Authentic Videos
Think of something you’re interested in, and find English videos about it.
Whether you want to watch vehicle rescues or follow American sports, there’s something out there for you.
Action-packed themes like these often describe people and their qualities/attributes, so you’ll be able to hear the difference between “has” and “have” quite frequently.
You could also use a virtual immersion platform.
FluentU, for example, has a large library of culturally relevant short videos for different learner levels, along with annotated subtitles. These can make it easier to notice the context that “has” and “have” are used in:
Immersing yourself in English helps you learn and remember grammar rules like the difference between “has” and “have.”
If you listen to enough English, you’ll be able to know which word to use just by knowing what “sounds right.”
Write from Multiple Points of View
If you’re keen to improve both your grammar and writing skills, try this writing exercise. Write a short paragraph about yourself. Be sure to use the verb “have” as many times as you can.
Then, rewrite the paragraph as though it’s about somebody else. As we’ll see below, this will force you to practice the difference between “has” and “have.”
As a warm-up exercise, you can also try changing the pronouns in the example sentences we’ve provided in this article. Once you’ve changed the pronouns, change the verb to match.
Now, it’s time to use these important words.
Study all the examples closely. Use “has” and “have” in your daily conversations, and don’t be afraid of making mistakes!
Download:
This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you
can take anywhere.
Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Cлайд 1
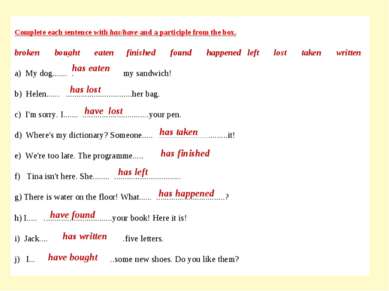
Complete each sentence with has/have and a participle from the box. broken bought eaten finished found happened left lost taken written a) My dog………. my sandwich! b) Helen………………………………….her bag. c) I’m sorry. I………………………………….your pen. d) Where’s my dictionary? Someone………………………………….it! e) We’re too late. The programme………………………………….. f) Tina isn’t here. She………………………………….. g) There is water on the floor! What………………………………….? h) I………………………………….your book! Here it is! i) Jack………………………………….five letters. j) I………………………………….some new shoes. Do you like them? has eaten has lost have lost has taken has finished has left has happened have found has written have bought
Cлайд 2
Change the verbs in brackets into the present perfect. a) Harry (do)…… ……………….the housework. b) Kate and Bill (find)………………………………….a new flat. c) Nick (send)………………………………….an email. d) I (try)………………………………….to learn Japanese. e) Sam and Dave (eat)………………………………….all the sandwiches. f) Carlos (buy)………………………………….a dog. g) Maria and Helen (start)………………………………….at a new school. h) Frances (break)………………………………….her cup. i) I (lose)………………………………….my umbrella. j) Max (take)………………………………….the dog for a walk.
Cлайд 3
Complete each sentence with the present perfect form of a verb from the box. arrive copy have make miss phone read see spend wash a) Oh no! That’s the last bus, and we …… …………………… it. b) ( you)………….„………………any James Bond books? They’re really good. c) I haven’t got any more money. I………………………….. .all of it! d) I……………………………an idea! Let’s go to Big Burger’s! e) I won’t lose this information now. I…………………………… the disk. f) Your hair looks terrible! (you)…………………………………………it? g) Hurry up, Carol. Your taxi……………………………. It’s waiting outside. h) I’m sorry I (not)…………………………… the travel agent. I’ve been very busy. i) ( you)……………………………Harry Potter? It’s my favourite film. j) Read this again. You………………………….. . some mistakes.
Cлайд 4
Underline the correct verb form in each sentence. a) Can I have another book? I’ve read/read this one. b) I’m not ready. I didn’t finish/haven’t finished my homework. c) I can’t find my wallet. I think I’ve lost/lost it. d) Did you eat/Have you eaten spaghetti last night? e) Harry left/has left at 10.30. f) Hurry up, Jim! You didn’t start/haven’t started! g) Did you see/Have you seen this film last year?
Cлайд 5
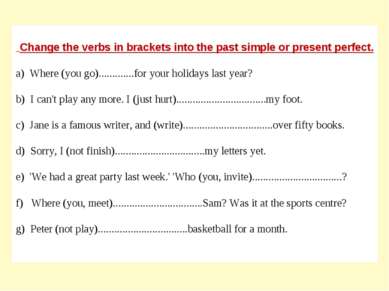
Change the verbs in brackets into the past simple or present perfect. a) Where (you go)………….for your holidays last year? b) I can’t play any more. I (just hurt)……………………………my foot. c) Jane is a famous writer, and (write)……………………………over fifty books. d) Sorry, I (not finish)……………………………my letters yet. e) ‘We had a great party last week.’ ‘Who (you, invite)……………………………? f) Where (you, meet)……………………………Sam? Was it at the sports centre? g) Peter (not play)……………………………basketball for a month.
Cлайд 6
Underline the correct word in each sentence. a) Have you ever/yet visited Slovenia? b) Tim has for/just come back from the USA. c) I’m not hungry. I’ve already/since eaten. d) Jane lived in Greece since/for fifteen years. e) Brian and Claire got married ten years ago/since ten years. f) I can’t come out. I haven’t done my homework already/yet. g) Mark has worked in Turkey ago/since 1998.
Cлайд 7
Complete each sentence with a time word from the box. already ever for just never since yet a) Sue has been on the beach………… an hour, but she hasn’t had a swim yet: b) I don’t want to see this film. I’ve…………….. .seen it. c) Have you………………been to the Greek islands? d) Can you wait a moment? I haven’t finished…………………. e) Ouch! An insect has………………bitten me! f) George has………………eaten Chinese food, so this is the first time for him! g) Rick has lived in Japan………………1998. for already ever yet just never since
Cлайд 8
Complete each sentence. Use one word in each space. a) Kate has… twenty photos of the children so far. b) Have you ever………………this book? It’s really good. c) Have you ever………………to Egypt? d) The dog’s not hungry. It hasn’t………………its dinner. e) I’m going to bed. I think I’ve………………a cold. f) Oh no! I’ve………………my bag on the bus. g) Jim has just………………a new mountain bike. It was very expensive. h) The washing machine doesn’t work. I think I’ve ……………..it.
Cлайд 9
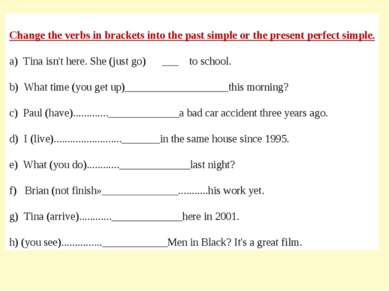
Change the verbs in brackets into the past simple or the present perfect simple. a) Tina isn’t here. She (just go) ___ to school. b) What time (you get up)___________________this morning? c) Paul (have)…………._____________a bad car accident three years ago. d) I (live)……………………._______in the same house since 1995. e) What (you do)…………_____________last night? f) Brian (not finish»______________………..his work yet. g) Tina (arrive)…………_____________here in 2001. h) (you see)……………____________Men in Black? It’s a great film.