Motivation is the reason for which humans and other animals initiate, continue, or terminate a behavior at a given time. Motivational states are commonly understood as forces acting within the agent that create a disposition to engage in goal-directed behavior. It is often held that different mental states compete with each other and that only the strongest state determines behavior.[1] This means that we can be motivated to do something without actually doing it. The paradigmatic mental state providing motivation is desire. But various other states, such as beliefs about what one ought to do or intentions, may also provide motivation. Motivation is derived from the word ‘motive’, which denotes a person’s needs, desires, wants, or urges. It is the process of motivating individuals to take action in order to achieve a goal. The psychological elements fueling people’s behavior in the context of job goals might include a desire for money.
Various competing theories have been proposed concerning the content of motivational states. They are known as content theories and aim to describe what goals usually or always motivate people. Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs and the ERG theory, for example, posit that humans have certain needs, which are responsible for motivation. Some of these needs, like for food and water, are more basic than other needs, such as for respect from others. On this view, the higher needs can only provide motivation once the lower needs have been fulfilled.[2] Behaviorist theories try to explain behavior solely in terms of the relation between the situation and external, observable behavior without explicit reference to conscious mental states.
Motivation may be either intrinsic, if the activity is desired because it is inherently interesting or enjoyable, or extrinsic, if the agent’s goal is an external reward distinct from the activity itself.[3][4] It has been argued that intrinsic motivation has more beneficial outcomes than extrinsic motivation.[4] Motivational states can also be categorized according to whether the agent is fully aware of why he acts the way he does or not, referred to as conscious and unconscious motivation. Motivation is closely related to practical rationality. A central idea in this field is that we should be motivated to perform an action if we believe that we should perform it. Failing to fulfill this requirement results in cases of irrationality, known as akrasia or weakness of the will, in which there is a discrepancy between our beliefs about what we should do and our actions.
Research on motivation has been employed in various fields. In the field of business, a central question concerns work motivation, for example, what measures an employer can use to ensure that his employees are motivated. Motivation is also of particular interest to educational psychologists because of its crucial role in student learning. Specific interest has been given to the effects of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation in this field.
Definition[edit]
The term «motivation» is commonly defined as what explains why people or animals initiate, continue or terminate a certain behavior at a particular time.[5][6][7][8] Motivational states can be expressed in various degrees of strength, where the higher the degree, the more likely it is that the state exerts an influence on behavior.[9] This is often linked to forces acting from within the agent that result in goal-directed behavior.[6][10]
One problem with defining motivation in terms of internal forces is that it is very difficult to measure them, which is why empirically-minded theorists often prefer definitions that are more closely linked to observable behavior.[11][10] One approach is to define motivation in terms of the flexibility of the animal’s behavior. This flexibility involves goal-directed behavior that changes as the animal learns through new experiences.[12] Rats, for example, can learn to traverse through complicated mazes in order to satisfy their hunger. The feeding behavior of flies, on the other hand, is not flexible in this sense. On this view, we are justified to ascribe motivational states to rats but not to flies.[12]
However, it could also be argued that there are cases of motivation without flexible behavior. A totally paralyzed person, for example, could still have motivation despite being unable to engage in physical behavior. This means that flexibility may still be a sufficient but not a necessary mark of motivation.[12] Some definitions stress the continuity between human and animal motivation but others draw a clear distinction between the two. This is often emphasized by the idea that human agents act for reasons and commit themselves to the intentions they form while animals just follow their strongest desire.[13][10] Causalist definitions stress the causal relation between motivation and the resulting behavior. Non-causalist definitions, on the other hand, hold that motivation explains behavior in a non-causal way.[9][12][14]
Motivation and mental states[edit]
Behaviorists have tried to explain motivation solely in terms of the relation between the situation and external, observable behavior. But the same entity often behaves differently despite being in the same situation as before. This suggests that explanation needs to make reference to internal states of the entity that mediate the link between stimulus and response.[12][15] Among these internal states, psychologists and philosophers are most interested in mental states. The paradigmatic mental state providing motivation is desire. But it has been argued that various other states, such as beliefs about what one ought to do or intentions, can also provide motivation.[15][13] The absence of motivation might result in mental diseases like depression.
An important distinction is between states that provide motivation whenever they are present, sometimes referred to as «essentially motivation-constituting attitudes», while other states provide motivation contingent on certain circumstances or other states.[15][16] It has been argued that a desire to perform an action, a so-called action-desire, always provides motivation.[15][16] This is even the case if the agent decides against performing the action because there are other more pressing issues.[12] An instrumental belief about how to reach a certain goal, on the other hand, provides motivation contingent on the agent currently having this goal. We can desire many things besides actions, like that our favorite soccer team wins their next match or that world peace is established.[15] Whether these desires provide motivation depends, among other things, on whether the agent has the ability to contribute to their realization. While some theorists accept the idea that desire is essential to motivation, others have argued that we can act even without desires.[15][16] The motivation may instead be based, for example, on rational deliberation. On this view, attending a painful root canal treatment is in most cases motivated by deliberation and not by a desire to do so.[17] So desire may not be essential to motivation.[16] But it is open to opponents of the thesis that there is motivation without desires to reject the analysis of such examples. Instead, they may argue that attending the root canal treatment is desired in some sense, even if there is also a very vivid desire present against doing so.[17][15]
Another important distinction is between occurrent and standing desires. Occurrent desires are either conscious or otherwise causally active, in contrast to standing desires, which exist somewhere in the back of one’s mind. If Dhanvi is busy convincing her friend to go hiking this weekend, for example, then her desire to go hiking is occurrent. But many of her other desires, like to sell her old car or to talk with her boss about a promotion, are merely standing during this conversation. Only occurrent desires can act as sources of motivation.[17][18][19] But not all occurrent desires are conscious. This leaves open the possibility of unconscious motivation.[20][19]
Some psychological theories claim that motivation exists purely within the individual, but socio-cultural theories express motivation as an outcome of participation in actions and activities within the cultural context of social groups.[21]
Strength of desire and action[edit]
Some theorists, often from a Humean tradition, deny that states other than desires can motivate us.[13] When such a view is combined with the idea that desires come in degrees, it can naturally lead to the thesis that we always follow our strongest desire.[22][11] This theory can be modified in the way that we always follow the course of action with the highest net force of motivation. This accounts for cases where several weaker desires all recommend the same course of action and together trump the strongest desire.[23][11] Various types of objections have been raised against this thesis. Some base their arguments on the assumption that we have free will, meaning that it is up to the agent what we do. From this position, it is natural to reject a point of view that lets behavior be determined by desires and not by the agent.[11][24] Others point to counterexamples, like when the agent acts out of a sense of duty even though he has a much stronger desire to do something else.[25] One line of argumentation holds that there is an important difference between the motivation based on a desire and an intention to act: an intention involves some kind of commitment to or identification with the intended course of action.[13] This happens on the side of the agent and is not present in regular desires. This approach can be combined with the view that desires somehow contribute to the formation of intentions based on their strength.[11] It has been argued that this distinction is important for the difference between human agency and animal behavior. On this view, animals automatically follow their strongest desire while human agents act according to their intention which may or may not coincide with their strongest desire.[13]
Content theories[edit]
Theories articulating the content of motivation: what kinds of things people find motivating are among the earliest theories in motivation research history. Because content theories focus on which categories of goal (needs) motivate people, content theories are related to need theories.
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs[edit]
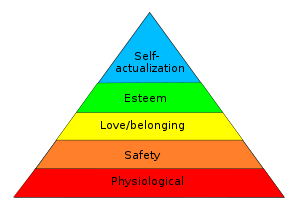
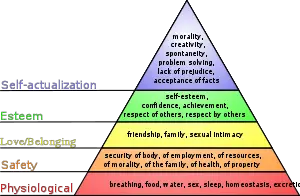
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs (1943, 1954) is represented as a pyramid with the more basic needs at the bottom
Content theory of human motivation includes both Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs and Herzberg’s two-factor theory. Maslow’s thesis is based on the idea that we are driven by our basic human needs. Maslow’s theory is one of the most widely discussed theories of motivation. Furthermore, if some of our most basic requirements are not addressed, we may be unable to advance and meet our other needs. Abraham Maslow believed that man is inherently good and argued that individuals possess a constantly growing inner drive that has great potential. The needs hierarchy system is a commonly used scheme for classifying human motives.[26] Maslow’s hierarchy of needs emphasizes certain characteristics like family and community that involve the needs to be met.[27] The basic needs, safety, love and belonging, and esteem have to be met first in order for the individual to actually reach self-actualization. The needs can overlap within the pyramid, but the lower needs have to be met first in order to move up. Some basic needs can include food and shelter. The need of safety has to do with receiving protection.[27] For the individual to feel love and belonging, they have to feel some type of attachment by giving and receiving love. Having competence and control in personal life has to do with meeting the need of esteem. Not being able to meet the lower and higher needs can have a detrimental effect on mental health.[27] This could lead to symptoms of depression, and lower self-esteem during adolescent years.[27] If safety needs are not met during adolescence, then the individual will have less confidence. A study found that just having support from the community, friends can lead to decreased emotional challenges. It is important to satisfy these needs in order to reduce emotional and mental challenges over time.[27]
Maslow (1954) developed the hierarchy of needs consisting of five hierarchic classes. According to Maslow, people are motivated by unsatisfied needs. The needs, listed from basic (lowest-earliest) to most complex (highest-latest), are as follows:[28]
- Physiology (hunger, thirst, sleep, etc.)
- Safety/Security/Shelter/Health
- Social/Love/Friendship
- Self-esteem/Recognition/Achievement
- Self-actualization/achievement of full potential
The basic requirements build upon the first step in the pyramid: physiology. If there are deficits on this level, all behavior will be oriented to satisfy this deficit. Essentially, if someone has not slept or eaten adequately, they would not be interested in their self-esteem desires. Subsequently, people that have the second level, awakens a need for security and so on and so forth. After securing those two levels, the motives shift to the social sphere, the third level. Psychological requirements comprise the fourth level, while the top of the hierarchy consists of self-realization and self-actualization.
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory can be summarized as follows:
- Human beings have wants and desires which, when unsatisfied, may influence behavior.
- Differing levels of importance to human life are reflected in a hierarchical structure of needs.
- Needs at higher levels in the hierarchy are held in abeyance until lower-level needs are at least minimally satisfied.
- Needs at higher levels of the hierarchy are associated with individuality, humanness, and psychological health.
Herzberg’s two-factor theory[edit]
Frederick Herzberg’s two-factor theory concludes that certain factors in the workplace result in job satisfaction (motivators), while others (hygiene factors), if absent, lead to dissatisfaction but are not related to satisfaction. The name hygiene factors are used because, like hygiene, the presence will not improve health, but absence can cause health deterioration.
The factors that motivate people can change over their lifetime. Some claimed motivating factors (satisfiers) were: Achievement, recognition, work itself, responsibility, advancement, and growth. Some hygiene factors (dissatisfiers) were: company policy, supervision, working conditions, interpersonal relations, salary, status, job security, and personal life.[26]
Alderfer’s ERG theory[edit]
Alderfer, building on Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, posited that needs identified by Maslow exist in three groups of core needs—existence, relatedness, and growth, hence the label: ERG theory. The existence group is concerned with providing our basic material existence requirements. They include the items that Maslow considered to be physiological and safety needs. The second group of needs is relatedness—the desire we have to maintain important personal relationships. These social and status desires require interaction with others if they are to be satisfied, and they align with Maslow’s social need and the external component of Maslow’s esteem classification. Finally, Alderfer isolates growth needs as an intrinsic desire for personal development. All these needs should be fulfilled to greater wholeness as a human being.[29]
Self-determination theory[edit]
Self-determination theory is an approach to human motivation and personality that uses traditional empirical methods while employing an organismic metatheory that highlights the importance of humans’ evolved inner resources for personality development and behavioral self-regulation (Ryan, Kuhn, & Deci, 1997). It takes a look into people’s psychological needs and growth tendencies that reveal their personality and level of self-determination. Competence, relatedness, and autonomy are important conditions that play a huge part in one’s motivation and engagement in activities, because it determines a person’s well-being.[30] The social environment, with the correct amount of support, can help fulfill basic psychological needs. These basic psychological needs are autonomy, competence, and relatedness. These basic needs can create behaviors that result from personal support which leads to being engaged in a certain environment and provides relationships that are important.[30] Two types of motivation found in the self-determination theory are called amotivation and autonomous motivation.[30] These types of motivations can lead to intrinsic and extrinsic actions. The amotivation can derive from feelings of inadequacy which leads to having a lack of motivation. The person feels their environment is controlled through monitoring and rewards.[30] The person only feels motivation because of external rewards or to avoid punishment. On the other hand, autonomous motivation comes from the person’s own lifestyle and engaging in a task is done innately. Having a supportive social environment can help bring out behaviors from autonomous motivations.[30]
Classical and operant conditioning[edit]
In classical (or respondent) conditioning, behaviour is understood as responses triggered by certain environmental or physical stimuli. They can be unconditioned, such as in-born reflexes, or learned through the pairing of an unconditioned stimulus with a different stimulus, which then becomes a conditioned stimulus. In relation to motivation, classical conditioning might be seen as one explanation as to why an individual performs certain responses and behaviors in certain situations.[31][32] For instance, a dentist might wonder why a patient does not seem motivated to show up for an appointment, with the explanation being that the patient has associated the dentist (conditioned stimulus) with the pain (unconditioned stimulus) that elicits a fear response (conditioned response), leading to the patient being reluctant to visit the dentist.
In operant conditioning, the type and frequency of behaviour are determined mainly by its consequences. If a certain behaviour, in the presence of a certain stimulus, is followed by a desirable consequence (a reinforcer), the emitted behaviour will increase in frequency in the future, in the presence of the stimulus that preceded the behaviour (or a similar one). Conversely, if the behaviour is followed by something undesirable (a punisher), the behaviour is less likely to occur in the presence of the stimulus. In a similar manner, the removal of a stimulus directly following the behaviour might either increase or decrease the frequency of that behaviour in the future (negative reinforcement or punishment).[31][32] For instance, a student that gained praise and a good grade after turning in a paper might seem more motivated in writing papers in the future (positive reinforcement); if the same student put in a lot of work on a task without getting any praise for it, he or she might seem less motivated to do school work in the future (negative punishment). If a student who causes trouble in class gets punished with something he or she dislikes, such as detention (positive punishment), that behaviour would decrease in the future. The student might seem more motivated to behave in class, presumably in order to avoid further detention (negative reinforcement).
The strength of reinforcement or punishment is dependent on schedule and timing. A reinforcer or punisher affects the future frequency of a behaviour most strongly if it occurs within seconds of the behaviour. A behaviour that is reinforced intermittently, at unpredictable intervals, will be more robust and persistent compared to one that is reinforced every time the behaviour is performed.[31][32] For example, if the misbehaving student in the above example was punished a week after the troublesome behaviour, that might not affect future behaviour.
In addition to these basic principles, environmental stimuli also affect behavior. Behaviour is punished or reinforced in the context of whatever stimuli were present just before the behaviour was performed, which means that a particular behaviour might not be affected in every environmental context, or situation, after it is punished or reinforced in one specific context.[31][32] A lack of praise for school-related behaviour might, for instance, not decrease after-school sports-related behaviour that is usually reinforced by praise.
The various mechanisms of operant conditioning may be used to understand the motivation for various behaviours by examining what happens just after the behaviour (the consequence), in what context the behaviour is performed or not performed (the antecedent), and under what circumstances (motivating operators).[31][32]
Incentive motivation[edit]
Incentive theory is a specific theory of motivation, derived partly from behaviorist principles of reinforcement, which concerns an incentive or motive to do something. The most common incentive would be a compensation. Compensation can be tangible or intangible; it helps in motivating the employees in their corporate lives, students in academics, and inspires people to do more and more to achieve profitability in every field. Studies show that if the person receives the reward immediately, the effect is greater, and decreases as delay lengthens.[33] Repetitive action-reward combination can cause the action to become a habit[33]
«Reinforcers and reinforcement principles of behaviour differ from the hypothetical construct of reward.» A reinforcer is anything that follows an action, with the intention that the action will now occur more frequently. From this perspective, the concept of distinguishing between intrinsic and extrinsic forces is irrelevant.
Incentive theory in psychology treats motivation and behaviour of the individual as they are influenced by beliefs, such as engaging in activities that are expected to be profitable. Incentive theory is promoted by behavioral psychologists, such as B.F. Skinner. Incentive theory is especially supported by Skinner in his philosophy of Radical behaviorism, meaning that a person’s actions always have social ramifications: and if actions are positively received people are more likely to act in this manner, or if negatively received people are less likely to act in this manner.
Incentive theory distinguishes itself from other motivation theories, such as drive theory, in the direction of the motivation. In incentive theory, stimuli «attract» a person towards them, and push them towards the stimulus. In terms of behaviorism, incentive theory involves positive reinforcement: the reinforcing stimulus has been conditioned to make the person happier. As opposed to in drive theory, which involves negative reinforcement: a stimulus has been associated with the removal of the punishment—the lack of homeostasis in the body. For example, a person has come to know that if they eat when hungry, it will eliminate that negative feeling of hunger, or if they drink when thirsty, it will eliminate that negative feeling of thirst.[34]
Motivating operations[edit]
Motivating operations, MOs, relate to the field of motivation in that they help improve understanding aspects of behavior that are not covered by operant conditioning. In operant conditioning, the function of the reinforcer is to influence future behavior. The presence of a stimulus believed to function as a reinforcer does not according to this terminology explain the current behavior of an organism – only previous instances of reinforcement of that behavior (in the same or similar situations) do. Through the behavior-altering effect of MOs, it is possible to affect the current behavior of an individual, giving another piece of the puzzle of motivation.
Motivating operations are factors that affect learned behavior in a certain context. MOs have two effects: a value-altering effect, which increases or decreases the efficiency of a reinforcer, and a behavior-altering effect, which modifies learned behavior that has previously been punished or reinforced by a particular stimulus.[31]
When a motivating operation causes an increase in the effectiveness of a reinforcer or amplifies a learned behaviour in some way (such as increasing frequency, intensity, duration, or speed of the behavior), it functions as an establishing operation, EO. A common example of this would be food deprivation, which functions as an EO in relation to food: the food-deprived organism will perform behaviors previously related to the acquisition of food more intensely, frequently, longer, or faster in the presence of food, and those behaviours would be especially strongly reinforced.[31] For instance, a fast-food worker earning a minimal wage, forced to work more than one job to make ends meet, would be highly motivated by a pay raise, because of the current deprivation of money (a conditioned establishing operation). The worker would work hard to try to achieve the raise, and getting the raise would function as an especially strong reinforcer of work behavior.
Conversely, a motivating operation that causes a decrease in the effectiveness of a reinforcer, or diminishes a learned behavior related to the reinforcer, functions as an abolishing operation, AO. Again using the example of food, satiation of food prior to the presentation of a food stimulus would produce a decrease on food-related behaviors, and diminish or completely abolish the reinforcing effect of acquiring and ingesting the food.[31] Consider the board of a large investment bank, concerned with a too-small profit margin, deciding to give the CEO a new incentive package in order to motivate him to increase firm profits. If the CEO already has a lot of money, the incentive package might not be a very good way to motivate him, because he would be satiated on the money. Getting even more money wouldn’t be a strong reinforcer for profit-increasing behavior, and wouldn’t elicit increased intensity, frequency, or duration of profit-increasing behavior.
William McDougall’s purposive psychology[edit]
Purposive psychology, also known as hormic psychology, emphasizes that actions by people are done for a purpose or with specific intent. This is a behaviorist theory that states behavior is a reflex because of internal or intrinsic motivation.[35]
Drives[edit]
A drive or desire can be described as an urge that activates behavior that is aimed at a goal or an incentive.[36] These drives are thought to originate within the individual and may not require external stimuli to encourage the behavior. Basic drives could be sparked by urges such as hunger, which motivates a person to seek food whereas more subtle drives might be the desire for praise and approval, which motivates a person to behave in a manner pleasing to others.
Another basic drive is the sexual drive which, like food, motivates us because it is essential to our survival.[37] The desire for sex is wired deep into the brain of all human beings as glands secrete hormones that travel through the blood to the brain and stimulates the onset of sexual desire.[37] The hormone involved in the initial onset of sexual desire is called dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA).[37] The hormonal basis of both men and women’s sex drives is testosterone.[37][need quotation to verify]
Types of motivation[edit]
Intrinsic and extrinsic[edit]
Intrinsic[edit]
Intrinsic motivation exists within the individual and is driven by satisfying internal rewards rather than relying on external pressures or extrinsic rewards. It involves an interest in or enjoyment of the activity itself. For example, an athlete may enjoy playing football for the experience, rather than for an award.[3] Activities involving their own inherent reward provide motivation that is not dependent on external rewards.[38] Pursuing challenges and goals comes easier and is more enjoyable when one is intrinsically motivated to complete a certain objective; for example, because the individual is more interested in learning, rather than achieving the goal.[3] It has been argued that intrinsic motivation is associated with increased subjective well-being[39] and that it is important for cognitive, social, and physical development.[40] It can also be observed in animal behaviour, for example, when organisms engage in playful and curiosity-driven behaviours in the absence of reward. Studies have shown that intrinsically motivated individuals (compared those who are externally motivated) have more interest, excitement, and confidence, which leads to enhanced performance, persistence, and creativity.[41]
According to some theorists, the two necessary elements for intrinsic motivation are self-determination or autonomy and competence.[42] On this view, the cause of the behaviour must be internal, and the individual who engages in the behaviour must perceive that the task increases their competence.[40] Social-contextual events like feedback and reinforcement can cause feelings of competence and therefore contribute to intrinsic motivation. However, feelings of competence will not increase intrinsic motivation if there is no sense of autonomy. In situations where choices, feelings, and opportunities are present, intrinsic motivation is increased because people feel a greater sense of autonomy.[3][42] Some studies suggest that there is a negative correlation between external rewards and intrinsic motivation, i.e. that by providing high external rewards for an activity, the intrinsic motivation for engaging in it tends to be lower.[43][44]
Various studies have focused on the intrinsic motivation of students.[45] They suggest that intrinsically motivated students are more likely to engage in the task willingly as well as work to improve their skills, which tends to increase their capabilities.[46] Students are likely to be intrinsically motivated if they…
- attribute their educational results to factors under their own control, also known as autonomy or locus of control
- believe they have the skills to be effective agents in reaching their desired goals, also known as self-efficacy beliefs
- are interested in mastering a topic, not just in achieving good grades
Traditionally, researchers thought of motivations to use computer systems to be primarily driven by extrinsic purposes; however, many modern systems have their use driven primarily by intrinsic motivations.[47] Examples of such systems used primarily to fulfill users’ intrinsic motivations include online gaming, virtual worlds, online shopping,[48] learning/education, online dating, digital music repositories, social networking, online pornography, gamified systems, and general gamification.
Intrinsic motivation tends to be more long-lasting, self-sustaining, and satisfying than extrinsic motivation.[3] For this reason, many efforts in education aim to modify intrinsic motivation with the goal of promoting student learning performance and creativity.[3] But various studies suggest that intrinsic motivation is hard to modify or inspire. Attempts to recruit existing intrinsic motivators require an individualized approach: they involve identifying and making relevant the different motivators needed to motivate different students.[3] This usually requires additional skills from the instructor.[49] Mindfulness has been found to be an intraindividual factor that supports autonomous motivation and thereby contributes to intrinsic motivation.[50]
Extrinsic[edit]
Extrinsic motivation occurs when an individual is driven by external influences.[3] These can be either rewarding (money, good grades, fame, etc.) or punishing (threat of punishment, pain, etc.). The distinction between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation lies within the driving force behind the action. When someone is intrinsically motivated, they engage in an activity because it is inherently interesting, enjoyable, or satisfying. With extrinsic motivation, the agent’s goal is a desired outcome distinct from the activity itself.[3] The agent can have both intrinsic and extrinsic motives for the same activity, but usually one type of motivation outweighs the other.[51] Playing tennis to receive an award is an example of extrinsic motivation, while playing because one enjoys the game involves intrinsic motivation.[3][52]
Some studies indicate that extrinsic rewards can lead to overjustification and a subsequent reduction in intrinsic motivation. In one study demonstrating this effect, children who expected to be (and were) rewarded with a ribbon and a gold star for drawing pictures spent less time playing with the drawing materials in subsequent observations than children who were assigned to an unexpected reward condition.[53] This indicates that there is a tendency to care less about the activity itself if a reward is expected.[3] However, other studies suggest that positive or negative extrinsic rewards can also increase intrinsic motivation.[54] This leads us to the assumption that the effects of extrinsic motivation on intrinsic motivation may depend on the type of reward.[55]
According to the article «Self-Determination Theory and the Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development and Well-Being»,[56] a lot of what we do after childhood is not inspired by intrinsic motivation because we are not solely doing things anymore to satisfy our intrinsic motivations, but is instead done more to satisfy our extrinsic motivations since we must adhere to social pressures which force us to do things that are not intrinsically motivating.[57]
One advantage of extrinsic motivation is that it can be used relatively easily to motivate other people to work towards goal completion.[3] One disadvantage is that the quality of work may need to be monitored since the agent might otherwise not be motivated to do a good job.[3] Extrinsic motivation fueling engagement in the activity soon ceases once external rewards are removed. It has also been suggested that extrinsic motivators may diminish in value over time, making it more difficult to motivate the same person in the future.[3]
Johnmarshall Reeve distinguishes between four types of extrinsic motivation that involve different degrees of autonomy: external regulation, introjected regulation, identified regulation, and integrated regulation. External regulation is the least autonomous form of extrinsic motivation. In it, only the consequence of an action counts for the agent. For example, if a student wants a good grade, they are motivated to study for that grade.[58] Introjected regulation arises from the agent’s impression of what they should do. For instance, a student knows that they «should» study and does not want to feel the guilt that comes with not studying, so they do.[58] Identified regulation comes from what the agent believes is personally important. In the example of the student, they may have an understanding that studying is important to their success and will pursue their studies for that reason. Integrated regulation is the most autonomous form of extrinsic motivation and occurs when motivation arises from the impression of personal identity. This type of extrinsic motivation is very close to intrinsic motivation, but is not quite there yet. This is because the individual is motivated to engage in an activity by how well it expresses their values instead of by pure interest and enjoyment. In this case, a student studies because doing so expresses their core values and reflects how they see themselves as a person.[58] A student intrinsically motivated to study would do so purely because they thought studying was interesting and fun.
Unconscious and conscious[edit]
Conscious motivation involves motives of which the agent is aware. In the case of unconscious motivation, on the other hand, the agent may be partially or fully unaware of why they act the way they do.[59]
Unconscious[edit]
The conscious–unconscious distinction plays an important role in Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalytical theories.[60] According to him, the unconscious contains various repressed parts of the mind, like anxiety-inducing thoughts and socially unacceptable ideas. He identifies censorship as a force that keeps the repressed parts from entering consciousness. But unconscious instinctual impulses can nonetheless have a great influence on behavior in the form of unconscious motivation.[61] When these instincts serve as a motive, the person is only aware of the goal of the motive, and not its actual source. Freud divides these instincts into sexual instincts, death instincts, and ego or self-preservation instincts. Sexual instincts are those that motivate humans to stay alive and ensure the continuation of mankind. On the other hand, Freud also maintains that humans have an inherent drive for self-destruction: the death instinct. Similar to the devil and angel that everyone has on their shoulder, the sexual instinct and death instinct are constantly battling each other to both be satisfied. The death instinct can be closely related to Freud’s other concept, the id, which is our need to experience pleasure immediately, regardless of the consequences. The last type of instinct that contributes to motivation is the ego or self-preservation instinct. This instinct is geared towards assuring that a person feels validated in whatever behavior or thought they have. The mental censor, or door between the unconscious and preconscious, helps satisfy this instinct. For example, one may be sexually attracted to a person, due to their sexual instinct, but the self-preservation instinct prevents them to act on this urge until that person finds that it is socially acceptable to do so. Quite similarly to his psychic theory that deals with the id, ego, and superego, Freud’s theory of instincts highlights the interdependence of these three instincts. All three serve as checks and balances system to control what instincts are acted on and what behaviors are used to satisfy as many of them at once.
Priming is another source of unconscious motivation. It is a phenomenon whereby exposure to one stimulus influences a response to a subsequent stimulus, without conscious guidance or intention.[62][63][64] For example, when someone is exposed to the word «cancer», they are afterward less likely to smoke a cigarette offered to them.[65] There are various forms of priming, but visual and semantic priming are the most relevant for motivation.[65] Because of this link to external stimuli, priming is closely related to exposure theory, which states that people tend to like things that they have been exposed to before. This is used by advertising companies to get people to buy their products. In product placements in movies and TV shows, for example, we see a product in our favorite movie, which makes us more inclined to buy that product when we see it again.[66] Another example comes from former drug users, who are more tempted to relapse when exposed to stimuli associated with the drug.[67]
Conscious[edit]
|
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (May 2021) |
Freud relied heavily upon the theories of unconscious motivation as explained above. This approach has been criticized by Gordan Allport, who holds that conscious motives are the main source of motivation.[59][68]
Neuroscience[edit]
Two parts usually define motivation as a desire to act: the directional (such as directed towards a positive stimulus or away from a negative one) and the activated «seeking phase» and consummatory «liking phase». This type of motivation has neurobiological roots in the basal ganglia and mesolimbic (dopaminergic) pathways. Activated «seeking» behaviour, such as locomotor activity, is influenced by dopaminergic drugs, and microdialysis experiments reveal that dopamine is released during the anticipation of a reward.[69] The «wanting behaviour» associated with a rewarding stimulus can be increased by microinjections of dopamine and dopaminergic drugs in the dorsorostral nucleus accumbens and posterior ventral pallidum. Opioid injections in this area produce pleasure; however, outside of these hedonic hotspots, they create an increased desire.[70] Furthermore, depletion or inhibition of dopamine in neurons of the nucleus accumbens decreases appetitive but not consummatory behaviour. Dopamine, further implicated in motivation as administration of amphetamine, increases the breakpoint in a progressive ratio self-reinforcement schedule; subjects will be willing to go to greater lengths (e.g. press a lever more times) to obtain a reward.[71]
In situations where memory influences the motivational state, the hippocampus is activated. This can be apparent in circumstances where contextual details are needed to achieve the desired goals.[72]
Motivational reasons and rationality[edit]
Motivational reasons are practical reasons an agent has for favoring a certain course of action. They are contrasted with normative reasons, which determine what the agent should do from an impartial point of view.[73] For example, Jane suffers from high blood pressure, which is a normative reason not to have a big piece of chocolate cake. Its deliciousness, on the other hand, is Jane’s motivating reason to have a serving anyway. We can have normative reasons without being aware of them, which is not the case for motivating reasons.[13] It is possible for unconscious states to affect our behavior in various ways. But these states and their contents are not considered motivating reasons in such cases.[13] Taken in the widest sense, there are forms of motivation that do not involve motivating reasons.[20] A second difference is that normative reasons are factive while motivating reasons may deceive the agent.[73][13] So having high blood pressure can only be a normative reason for Jane if she actually has high blood pressure. But the cake’s deliciousness can be a motivating reason even if the cake is not delicious at all. In this case, the motivation is based on a false belief.[73] But ideally, motivational reasons and normative reasons coincide: the agent is motivated by facts determining what he should do.
A closely related issue concerns the relation between what we believe we ought to do, so-called ought-beliefs, and what we are motivated to do or actually intend to do.[13][9][74] Philosopher John Broome holds that this relation is at the core of enkratic rationality: «Rationality requires of you that, if you believe you ought to F, then you intend to F». He thinks that the process of reasoning is responsible for getting our intentions in line with our ought-beliefs.[74][75][76] The requirements of rationality are not always fulfilled, resulting in cases of irrationality. A person is said to suffer from akrasia or weakness of the will if they fail to satisfy the enkratic requirement, i.e. if they do something different from what they believe they should do.[77][78] An author who believes he ought to work on his new book but ends up watching TV instead is an example of a case of akrasia. Accidie is a closely related phenomenon in which the agent believes that there is something important to be done but lacks any motivation to engage in this action due to listlessness.[13][79]
Practical applications[edit]
The control of motivation is only understood to a limited extent. There are many different approaches to motivation training, but many of these are considered pseudoscientific by critics.[which?] To understand how to control motivation it is first necessary to understand why many people lack motivation.[original research?]
Like any theory, motivational theory makes predictions about what will work in practice. For instance, Douglas McGregor’s Theory Y makes the assumption that the average person not only accepts, but also seeks out responsibility, enjoys doing work and, therefore, is more satisfied when they have a wider range of work to do.[80] The practical implication is that, as a firm gives individuals greater responsibilities, they will feel a greater sense of satisfaction and, subsequently, more commitment to the organization. Likewise, allocating more work is predicted to increase engagement. Additionally, Malone argues that the delegation of responsibility encourages motivation because employees have creative control over their work and increase productivity as many people can work collaboratively to solve a problem rather than just one manager tackling it alone.[81] Others have argued that participation in decision making boosts morale and commitment to the organization, subsequently increasing productivity.[82][83] Likewise, if teams and membership increase motivation (as reported in the classic Hawthorn Western Electric Company studies)[84] incorporating teams make provide incentives to work. In general, motivation theory is often applied to employee motivation.[85]
Applications in business[edit]
Within Maslow’s hierarchy of needs (first proposed in 1943), at lower levels (such as physiological needs) money functions as a motivator; however, it tends to have a motivating effect on staff that lasts only for a short period (in accordance with Herzberg’s two-factor model of motivation of 1959). At higher levels of the hierarchy, praise, respect, recognition, empowerment, and a sense of belonging are far more powerful motivators than money, as both Abraham Maslow’s theory of motivation and Douglas McGregor’s theory X and theory Y (originating in the 1950s and pertaining to the theory of leadership) suggest.
According to Maslow, people are motivated by unsatisfied needs.[86] The lower-level needs (such as physiological and safety needs) must be satisfied before addressing higher-level needs. One can relate to Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs theory with employee motivation. For example, if managers attempt to motivate their employees by satisfying their needs, according to Maslow, they should try to satisfy the lower-level needs before trying to satisfy the upper-level needs – otherwise the employees will not become motivated. Managers should also remember that not everyone will be satisfied with the same needs. A good manager will try to figure out which levels of needs are relevant to a given individual or employee.
Maslow places money at the lowest level of the hierarchy and postulates other needs as better motivators to staff. McGregor places money in his Theory X category and regards it as a poor motivator. Praise and recognition (placed in the Theory Y category) are considered stronger motivators than money.
- Motivated employees always look for better ways to do a job.
- Motivated employees are more quality-oriented.
- Motivated workers are more productive.[87]
The average workplace lies about midway between the extremes of high threat and high opportunity. Motivation by threat is a dead-end strategy, and naturally, staff are more attracted to the opportunity side of the motivation curve than the threat side. Lawrence Steinmetz (1983) sees motivation as a powerful tool in the work environment that can lead to employees working at their most efficient levels of production.[88] Nonetheless, Steinmetz also discusses three common character-types of subordinates—ascendant, indifferent, and ambivalent—who all react and interact uniquely, and must be treated, managed, and motivated accordingly. An effective leader must understand how to manage all characters, and more importantly, the manager must utilize avenues that allow room for employees to work, grow, and find answers independently.[88][need quotation to verify]
A classic study at Vauxhall Motors’ UK manufacturing plant challenged the assumptions of Maslow and Herzberg were by.[89] Goldthorpe et al. (1968) introduced the concept of orientation to work and distinguished three main orientations:[89]
- instrumental (with work seen as a means to an end)
- bureaucratic (where work serves as a source of status, security, and immediate reward)
- solidaristic (which prioritizes group loyalty)
Other theories expanded and extended those of Maslow and Herzberg. These included the 1930s force-field analysis of Kurt Lewin, Edwin A. Locke’s goal-setting theory (mid-1960s onwards) and Victor Vroom’s expectancy theory of 1964. These tend to stress cultural differences and the fact that different factors tend to motivate individuals at different times.[90][need quotation to verify]
According to the system of scientific management developed by Frederick Winslow Taylor (1856–1915), pay alone determines a worker’s motivation, and therefore management need not consider psychological or social aspects of work. In essence, scientific management bases human motivation wholly on extrinsic rewards and discards the idea of intrinsic rewards.
In contrast, David McClelland (1917–1998) believed that workers could not be motivated by the mere need for money—in fact, extrinsic motivation (e.g., money) could extinguish intrinsic motivation such as achievement motivation, though money could be used as an indicator of success for various motives, e.g., keeping score. In keeping with this view, his consulting firm, McBer & Company (1965–1989), had as its first motto «To make everyone productive, happy, and free». For McClelland, satisfaction lay in aligning peoples’ lives with their fundamental motivations.
Elton Mayo (1880–1949) discovered the importance of the social contacts a worker has at the workplace and found that boredom and repetitiveness of tasks lead to reduced motivation. Mayo believed that workers could be motivated by acknowledging their social needs and making them feel important. As a result, employees were given the freedom to make decisions on-the-job and greater attention was paid to informal work-groups.
Mayo named his model the Hawthorne effect.[91] His model has been judged[by whom?] as placing undue reliance on social contacts within work situations for motivating employees.[92][need quotation to verify]
In 1981 William Ouchi introduced Theory Z, a hybrid management approach consisting of both Japanese and American philosophies and cultures.[93][need quotation to verify] Its Japanese segment is much like the clan culture where organizations focus on a standardized structure with a heavy emphasis on socialization of its members. All underlying goals are consistent across the organization. Its American segment retains formality and authority amongst members and the organization. Ultimately, Theory Z promotes common structure and commitment to the organization, as well as constant improvement of work efficacy.
In Essentials of Organizational Behavior (2007), Robbins and Judge examine recognition programs as motivators, and identify five principles that contribute to the success of an employee incentive program:[94]
- recognition of employees’ individual differences, and clear identification of behavior deemed worthy of recognition
- allowing employees to participate
- linking rewards to performance
- rewarding of nominators
- visibility of the recognition process
Modern organizations which adopt non-monetary employee motivation methods rather than tying it with tangible rewards. When the reward is aimed at fulfilling employee contribution, participation, and individual satisfaction, it boosts their morale.[95]
- Provide a positive work environment[96]
- Encourage team contribution and rewards[97]
- Feedback[98]
- Give challenging roles[99]
Job characteristics model[edit]
The Job characteristics Model (JCM), as designed by Hackman and Oldham attempts to use job design to improve employee motivation. They suggest that any job can be described in terms of five key job characteristics:[100][101]
- Skill variety – the degree to which the job requires the use of different skills and talents
- Task identity – the degree to which the job has contributed to a clearly identifiable larger project
- Task significance – the degree to which the job affects the lives or work of other people
- Autonomy – the degree to which the worker has independence, freedom and discretion in carrying out the job
- Task feedback – the degree to which the worker is provided with clear, specific, detailed, actionable information about the effectiveness of his or her job performance
The JCM links the core job dimensions listed above to critical psychological states which results in desired personal and work outcomes. This forms the basis of this ’employee growth-need strength.» The core dimensions listed above can be combined into a single predictive index, called the motivating potential score (MPS). The MPS can be calculated, using the core dimensions discussed above, as follows:
Jobs high in motivating potential must be high on both autonomy and feedback, and also must be high on at least one of the three factors that lead to experienced meaningfulness.[102] If a job has a high MPS, the job characteristics model predicts motivation, performance, and job satisfaction will be positively affected and the likelihood of negative outcomes, such as absenteeism and turnover, will be reduced.[102]
Employee recognition programs[edit]
Employee recognition is not only about gifts and points. It is about changing the corporate culture in order to meet goals and initiatives and most importantly to connect employees to the company’s core values and beliefs. Strategic employee recognition is seen as the most important program not only to improve employee retention and motivation but also to positively influence the financial situation.[103] The difference between the traditional approach (gifts and points) and strategic recognition is the ability to serve as a serious business influencer that can advance a company’s strategic objectives in a measurable way. «The vast majority of companies want to be innovative, coming up with new products, business models, and better ways of doing things. However, innovation is not so easy to achieve. A CEO cannot just order it, and so it will be. You have to carefully manage an organization so that, over time, innovations will emerge.»[104]
Applications in education[edit]
Motivation is of particular interest to educational psychologists because of the crucial role it plays in student learning. However, the specific kind of motivation that is studied in the specialized setting of education differs qualitatively from the more general forms of motivation studied by psychologists in other fields.
Motivation in education can have several effects on how students learn and how they behave towards the subject matter. It can:[105]
- Direct behavior toward particular goals
- Lead to increased effort and energy
- Increase initiation of, and persistence in, activities
- Enhance cognitive processing
- Determine what consequences are reinforcing
- Lead to improved performance.
Because students are not always internally motivated, they sometimes need situated motivation, which is found in environmental conditions that the teacher creates.
If teachers decided to extrinsically reward productive student behaviors, they may find it difficult to extricate themselves from that path. Consequently, student dependency on extrinsic rewards represents one of the greatest detractors from their use in the classroom.[106]
The majority of new student orientation leaders at colleges and universities recognize that the distinctive needs of students should be considered in regard to orientation information provided at the beginning of the higher education experience. Research done by Whyte in 1986 raised the awareness of counselors and educators in this regard. In 2007, the National Orientation Directors Association reprinted Cassandra B. Whyte’s research report allowing readers to ascertain improvements made in addressing specific needs of students over a quarter of a century later to help with academic success.[107]
Generally, motivation is conceptualized as either intrinsic, actions driven by internal rewards, or extrinsic, actions driven by external rewards. Classically, these categories are regarded as distinct.[3] Today, these concepts are less likely to be used as distinct categories, but instead as two ideal types that define a continuum:[108]
- Intrinsic motivation occurs when people are internally motivated to do something because it either brings them pleasure, they think it is important, or they feel that what they are learning is significant. It has been shown that intrinsic motivation for education drops from grades 3–9, though the exact cause cannot be ascertained.[109] Also, in younger students it has been shown that contextualizing material that would otherwise be presented in an abstract manner increases the intrinsic motivation of these students.[110]
- Extrinsic motivation comes into play when a student is compelled to do something or act a certain way because of factors external to him or her (like meeting a goal, making more money or earning good grades). Extrinsic motivation can be increased by goal setting.[111]
Whyte researched and reported about the importance of locus of control and academic achievement. Students tending toward a more internal locus of control are more academically successful, thus encouraging curriculum and activity development with consideration of motivation theories.[112][113]
Academic motivation orientation may also be tied with one’s ability to detect and process errors. Fisher, Nanayakkara, and Marshall conducted neuroscience research on children’s motivation orientation, neurological indicators of error monitoring (the process of detecting an error), and academic achievement. Their research suggests that students with high intrinsic motivation attribute performance to personal control and that their error-monitoring system is more strongly engaged by performance errors. They also found that motivation orientation and academic achievement were related to the strength in which their error-monitoring system was engaged.[114]
Motivation has been found to be an important element in the concept of andragogy (what motivates the adult learner), and in treating Autism Spectrum Disorders, as in pivotal response treatment.
Motivation has also been found critical in adolescents compliance to health suggestions, since «commitment requires belief in potentially negative and serious consequences of not acting.»[115]
Doyle and Moeyn have noted that traditional methods tended to use anxiety as negative motivation (e.g. use of bad grades by teachers) as a method of getting students to work. However, they have found that progressive approaches with focus on positive motivation over punishment has produced greater effectiveness with learning, since anxiety interferes with performance of complex tasks.[116]
Symer et al. attempted to better define those in medical training programs who may have a «surgical personality». They evaluated a group of 801 first-year surgical interns to compare motivational traits amongst those who did and did not complete surgical training. There was no difference noted between the 80.5% who completed training when comparing their responses to the 19.5% who did not complete training using the validated Behavior Inhibitory System/Behavior Approach System. They concluded based on this that resident physician motivation is not associated with completion of a surgical training program.[117]
It may appear that the reason some students are more engaged and perform better in class activities relative to other students is because some are more motivated than others. However, current research suggests that motivation is «dynamic, context sensitive, and changeable.»[118] Thus, students have the flexibility to alter their motivation for engaging in an activity or learning, even if they were not intrinsically motivated in the first place.[119] While having this type of flexibility is important, research reveals that a teacher’s teaching style and the school environment may play a factor in student motivation.[120][118][121]
According to Sansone and Morgan, when students are already motivated to engage in an activity for their own personal pleasure and then a teacher provides the student with feedback, the type of feedback given can change the way that student views the activity and can even undermine their intrinsic motivation.[119][122] Maclellan also looked at the relationship between tutors and students and in particular, and the type of feedback the tutor would give to the student. Maclellan’s results showed that praise or criticism directed towards the student-generated a feeling of «fixed intelligence» while praise and criticism directed towards the effort and strategy used by the student generated a feeling of «malleable intelligence».[118] In other words, feedback concerning effort and strategy leaves students knowing that there is room for growth. This is important because when students believe their intelligence is «fixed», their mindset can prevent skill development because students will believe that they only have a «certain amount» of understanding on a particular subject matter and might not even try. Therefore, it’s crucial that a teacher is aware of how the feedback they give to their students can both positively and negatively impact the student’s engagement and motivation.[118][120]
In a correlational study, Katz and Shahar used a series of questionnaires and Likert-style scales and gave them to 100 teachers to see what makes a motivating teacher. Their results indicate that teachers who are intrinsically motivated to teach and believe that students should be taught in an autonomous style are the types of teachers that promote intrinsic motivation in the classroom.[120] Deci, Sheinman, and Nezlek also found that when teachers adapted to an autonomous teaching style, students were positively affected and became more intrinsically motivated to achieve in the classroom. However, while the students were quick to adapt to the new teaching style, the impact was short-lived.[123] Thus, teachers are limited in the way they teach by pressure to act, teach, and provide feedback in a certain way from the school district, administration, and guardians.[123][121] Furthermore, even if students do have a teacher that promotes an autonomous teaching style, their overall school environment is also a factor because it can be extrinsically motivating. Examples of this would be posters around school promoting pizza parties for the highest grade point average or longer recess times for the classroom that brings more canned food donations.
Indigenous education and learning[edit]
For many indigenous students (such as Native American children), motivation may be derived from social organization; an important factor educators should account for in addition to variations in sociolinguistics and cognition.[124] While poor academic performance among Native American students is often attributed to low levels of motivation, top-down classroom organization is often found to be ineffective for children of many cultures who depend on a sense of community, purpose, and competence in order to engage.[125] Horizontally structured, community-based learning strategies often provide a more structurally supportive environment for motivating indigenous children, who tend to be driven by «social/affective emphasis, harmony, holistic perspectives, expressive creativity, and nonverbal communication.»[126] This drive is also traceable to a cultural tradition of community-wide expectations of participation in the activities and goals of the greater group, rather than individualized aspirations of success or triumph.[127]
Also, in some indigenous communities, young children can often portray a sense of community-based motivation through their parent-like interactions with siblings.[128] Furthermore, it is commonplace for children to assist and demonstrate for their younger counterparts without being prompted by authority figures. Observation techniques and integration methods are demonstrated in such examples as weaving in Chiapas, Mexico, where it is commonplace for children to learn from «a more skilled other» within the community.[129] The child’s real responsibility within the Mayan community can be seen in, for example, weaving apprenticeships; often, when the «more skilled other» is tasked with multiple obligations, an older child will step in and guide the learner.[129] Sibling guidance is supported from early youth, where learning through play encourages horizontally structured environments through alternative educational models such as «Intent Community Participation.»[130] Research also suggests that formal Westernized schooling can actually reshape the traditionally collaborative nature of social life in indigenous communities.[131] This research is supported cross-culturally, with variations in motivation and learning often reported higher between indigenous groups and their national Westernized counterparts than between indigenous groups across international continental divides.[132]
Also, in some indigenous communities in the Americas, motivation is a driving force for learning. Children are incorporated and welcomed to participate in daily activities and thus feel motivated to participate due to them seeking a sense of belonging in their families and communities.[133]
Children’s participation is encouraged and their learning is supported by their community and family, furthering their motivation. Children are also trusted to be active contributors. Their active participation allows them to learn and gain skills that are valuable and useful in their communities.[134]
As children transition from early childhood to middle childhood, their motivation to participate changes. In both the Indigenous communities of Quechua people and Rioja in Peru, children often experience a transition in which they become more included in their family’s and community’s endeavors. This changes their position and role in their families to more responsible ones and leads to an increase in their eagerness to participate and belong. As children go through this transition, they often develop a sense of identity within their family and community.[135]
The transition from childhood to adolescence can be seen in the number of work children partake in as this changes over time. For example, Yucatec Mayan children’s play time decreases from childhood to adolescence and as the child gets older, is replaced for time spent working. In childhood, the work is initiated by others, whereas in adolescence it is self-initiated. The shift in the initiation and the change in time spent working versus playing shows the children’s motivation to participate in order to learn.[136]
This transition between childhood and adolescence increases motivation because children gain social responsibility within their families. In some Mexican communities of Indigenous heritage, the contributions that children make within their community is essential to being social beings, establishes their developing roles, and also helps with developing their relationship with their family and community.[137]
As children gain more roles and responsibilities within their families, their eagerness to participate also increases. For example, young Mayan children of San Pedro, Guatemala learn to work in the fields and family run businesses because they are motivated to contribute to their family. Many San Pedro women learned to weave by watching their mothers sew when they were children, sometimes earning their own wool through doing small tasks such as watching young children of busy mothers. Eager to learn and contribute, these young girls helped other members of their community in order to help their mothers with their weaving businesses or through other tasks such as helping carry water while young boys helped with tasks such as carrying firewood alongside their fathers.[138]
Children’s motivation to learn is not solely influenced by their desire to belong but also their eagerness to see their community succeed. Children from Navajo communities were shown to have higher levels of social concern than Anglo-American children in their schools. By having high levels of social concern the indigenous children are showing concern for not only their learning but also their peers, which serves as an example of their instilled sense of responsibility for their community. They wish to succeed as a united group rather than just themselves.[139]
In order to be knowledgeable contributors, children must be aware of their surroundings and the community’s goals. Children’s learning in Indigenous-heritage communities is mainly based upon observing and helping out others in their community. Through this type of participation within their community, they gain purpose and motivation for the activity that they are doing within their community and become active participants because they know they are doing it for their community.[140]
Applications in game design[edit]
Motivational models are central to game design, because without motivation, a player will not be interested in progressing further within a game.[141] Several models for gameplay motivations have been proposed, including Richard Bartle’s. Jon Radoff has proposed a four-quadrant model of gameplay motivation that includes cooperation, competition, immersion and achievement.[142] The motivational structure of games is central to the gamification trend, which seeks to apply game-based motivation to business applications.[143] In the end, game designers must know the needs and desires of their customers for their companies to flourish.
There have been various studies on the connection between motivation and games. One particular study was on Taiwanese adolescents and their drive of addiction to games. Two studies by the same people were conducted. The first study revealed that addicted players showed higher intrinsic than extrinsic motivation and more intrinsic motivation than the non-addicted players.[144] It can then be said that addicted players, according to the studies’ findings, are more internally motivated to play games. They enjoy the reward of playing. There are studies that also show that motivation gives these players more to look for in the future such as long-lasting experience that they may keep later on in life.[145]
Applications in legal compliance[edit]
The findings on intrinsic motivation can be used to achieve legal compliance more effectively. Indeed, while the deterrence theory assumes that punishment will decrease the behavior, some empirical findings suggest a different view.[146] This is based on the idea that fining a behavior puts a price on the violation and provides certainty as to the specific consequences of the violation. At the same time, the crowding out effect has been observed in whistleblowing practices, with the reward discouraging reports among highly internally motivated subjects.[147] These findings indicate that an effective policy should make more use of tools such as advocacy and promoting compliance rather than relying exclusively on deterrence. For instance, corporate compliance programs can be a tool to build a stronger ethical culture within the company, thus increasing intrinsic motivation. However, rewarding them with fine reductions might have crowding-out effects.
See also[edit]
- Adaptive performance
- Addiction
- Amotivational syndrome
- Effects of hormones on sexual motivation
- Employee engagement
- Enthusiasm
- Equity theory
- Frustration
- Happiness at work
- Health action process approach
- Hedonic motivation
- Humanistic psychology
- I-Change Model
- Incentives
- Learned industriousness
- Motivation crowding theory
- Motivational intensity
- Positive education
- Positive psychology in the workplace
- Regulatory focus theory
- Rubicon model (psychology)
- Work engagement
- Work motivation
References[edit]
- ^ Wasserman T, Wasserman L (2020). «Motivation: State, Trait, or Both». Motivation, Effort, and the Neural Network Model. pp. 93–101. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-58724-6_8. ISBN 978-3-030-58724-6. S2CID 229258237.
- ^ Caulton JR (2012). «The development and use of the theory of ERG: A literature review». Emerging Leadership Journeys. Regent University School of Global Leadership & Entrepreneurship. 5 (1): 2–8. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.1071.4400.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Ryan RM, Deci EL (January 2000). «Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being». The American Psychologist. 55 (1): 68–78. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.529.4370. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.55.1.68. PMID 11392867.
- ^ a b Radel R, Pjevac D, Davranche K, d’Arripe-Longueville F, Colson SS, Lapole T, Gruet M (November 2016). «Does intrinsic motivation enhance motor cortex excitability?». Psychophysiology. 53 (11): 1732–1738. doi:10.1111/psyp.12732. PMID 27479318.
- ^ Kazdin AE, ed. (2000). «Motivation: an overview». Encyclopedia of Psychology. American Psychological Association. ISBN 978-1-55798-187-5.
- ^ a b «Motivation and Motivation Theory». Encyclopedia of Management.
- ^ Graham S. «Motivation». Encyclopedia of Education.
- ^ Filipp SH. «Motivation». Encyclopedia of Aging.
- ^ a b c Mele AR (2005). «Motivation and Agency: Precis». Philosophical Studies. 123 (3): 243–247. doi:10.1007/s11098-004-4903-0. S2CID 143586904.
- ^ a b c «Motivation». Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ^ a b c d e Mele AR (2003). «7. Motivational Strength». Motivation and Agency. Oxford University Press.
- ^ a b c d e f Mele AR (2003). «Introduction». Motivation and Agency. Oxford University Press.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Miller C (2008). «Motivation in Agents». Noûs. 42 (2): 222–266. doi:10.1111/j.1468-0068.2008.00679.x.
- ^ Wilson G, Shpall S, Piñeros Glasscock JS (2016). «Action». The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University.
- ^ a b c d e f g Mele AR (1995). «Motivation: Essentially Motivation-Constituting Attitudes». Philosophical Review. 104 (3): 387–423. doi:10.2307/2185634. JSTOR 2185634.
- ^ a b c d Framarin CG (2008). «Motivation-Encompassing Attitudes». Philosophical Explorations. 11 (2): 121–130. doi:10.1080/13869790802015676. S2CID 143542576.
- ^ a b c Mele AR (2003). «7. Motivation and Desire». Motivation and Agency. Oxford University Press.
- ^ Strandberg C (2012). «Expressivism and Dispositional Desires: 2. a distinction in mind». American Philosophical Quarterly. 49 (1): 81–91.
- ^ a b Bartlett G (2018). «Occurrent States». Canadian Journal of Philosophy. 48 (1): 1–17. doi:10.1080/00455091.2017.1323531. S2CID 220316213.
- ^ a b «Unconscious Motivation». Gale Encyclopedia of Psychology.
- ^ Rueda R, Moll LC (1994). «Chapter 7: A Sociocultural Perspective on Motivation». In O’Neill Jr HF, Drillings M (eds.). Motivation: Theory and Research. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. ISBN 978-0-8058-1286-2.
- ^ McCann H (1995). «Intention and Motivational Strength». Journal of Philosophical Research. 20: 571–583. doi:10.5840/jpr_1995_19.
- ^ Broome J (2009). «Motivation». Theoria. 75 (2): 79–99. doi:10.1111/j.1755-2567.2009.01034.x.
- ^ O’Connor T, Franklin C (2021). «Free Will». The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ^ Ewing AC (1934). «Can We Act Against Our Strongest Desire?». The Monist. 44 (1): 126–143. doi:10.5840/monist19344415. ISSN 0026-9662. JSTOR 27901421.
- ^ a b Pardee RL (1990). A literature review of selected theories dealing with job satisfaction and motivation. Motivation Theories of Maslow, Herzberg, McGregor & McClelland (PDF) (Report). pp. 6–7.
The basic concept behind the hierarchy system is that it’s like a food pyramid. Everybody starts at the bottom of the pyramid and is motivated to satisfy each level in ascending order to work our way to the top of the pyramid, and those levels (needs) are categorized into two main groups with five different sections which are explained below.
- ^ a b c d e Crandall A, Powell EA, Bradford GC, Magnusson BM, Hanson CL, Barnes MD, Novilla ML, Bean RA (February 1, 2020). «Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs as a Framework for Understanding Adolescent Depressive Symptoms Over Time». Journal of Child and Family Studies. 29 (2): 273–281. doi:10.1007/s10826-019-01577-4. ISSN 1062-1024. S2CID 204353035.
- ^ «The Content Theories of Motivation». module 9791F Leading Organisations. New South Wales, Australia: Technical and Further Education (TAFE). Archived from the original on 2018-03-15. Retrieved 2014-10-21.
- ^ Schneider B, Alderfer CP (1973). «Three Studies of Measures of Need Satisfaction in Organizations». Administrative Science Quarterly. 18 (4): 489–505. doi:10.2307/2392201. JSTOR 2392201.
- ^ a b c d e Otundo JO, Garn A (2020-05-28). «Testing an Integrated Model of Interest Theory and Self-Determination Theory in University Physical Activity Classes». The Physical Educator. 77 (3). doi:10.18666/TPE-2020-V77-I3-9571. S2CID 219756118.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Cooper JO (2007). Applied Behavior Analysis. Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA: Pearson Education. ISBN 978-0-13-129327-4.
- ^ a b c d e Donahoe JW (2004). Learning and Complex Behavior. Richmond, MA, USA: Ledgetop Publishing. ISBN 978-0-9762371-0-5.
- ^ a b «Drive Theories», The Concept of Motivation, Routledge, pp. 95–129, 2015-08-11, doi:10.4324/9781315712833-4, ISBN 978-1-315-71283-3, retrieved 2021-07-13
- ^ Killeen PR (1982). «Incentive theory». Nebraska Symposium on Motivation. Nebraska Symposium on Motivation. 29: 169–216. PMID 7050739.
- ^ Wertheimer M, Puente E (2020). A Brief History of Psychology (Sixth ed.). New York: Routledge. pp. 88–89. ISBN 978-1-138-28473-9.
- ^ «Drive». Dictionary.com. Retrieved 22 March 2013.
- ^ a b c d Schacter DL, Gilbert DL, Wegner DM (2009). Psychology (2nd ed.). New York: Worth.
- ^ Deci EL, Koestner R, Ryan RM (November 1999). «A meta-analytic review of experiments examining the effects of extrinsic rewards on intrinsic motivation». Psychological Bulletin. 125 (6): 627–68, discussion 692–700. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.125.6.627. PMID 10589297.
- ^ Tak HJ, Curlin FA, Yoon JD (July 2017). «Association of Intrinsic Motivating Factors and Markers of Physician Well-Being: A National Physician Survey». Journal of General Internal Medicine. 32 (7): 739–746. doi:10.1007/s11606-017-3997-y. PMC 5481224. PMID 28168540.
- ^ a b Ryan RM, Deci EL (January 2000). «Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivations: Classic Definitions and New Directions». Contemporary Educational Psychology. 25 (1): 54–67. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.318.808. doi:10.1006/ceps.1999.1020. PMID 10620381.
- ^ Ryan, Richard M.; Deci, Edward L. (January 2000). «Self-Determination Theory and the Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development, and Well-Being». American Psychologist. 55 (1): 68–78.
- ^ a b Deci EL, Ryan RM (2013-06-29). Intrinsic motivation and self-determination in human behavior. New York. ISBN 978-1-4899-2271-7. OCLC 861705534.
- ^ Deci EL (1971). «Effects of externally mediated rewards on intrinsic motivation». Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 18 (1): 105–115. doi:10.1037/h0030644.
- ^ Deci EL (1972). «Intrinsic motivation, extrinsic reinforcement, and inequity». Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 22 (1): 113–120. doi:10.1037/h0032355.
- ^ Graham S. «Motivation». Encyclopedia of Education.
- ^ Wigfield A, Guthrie JT, Tonks S, Perencevich KC (2004). «Children’s motivation for reading: Domain specificity and instructional influences». Journal of Educational Research. 97 (6): 299–309. doi:10.3200/joer.97.6.299-310. S2CID 145301292.
- ^ Lowry PB, Gaskin J, Twyman NW, Hammer B, Roberts TL (2013). «Taking ‘fun and games’ seriously: Proposing the hedonic-motivation system adoption model (HMSAM)». Journal of the Association for Information Systems. 14 (11): 617–671. doi:10.17705/1jais.00347. S2CID 2810596. SSRN 2177442.
- ^ Parker CJ, Wang H (2016). «Examining hedonic and utilitarian motivations for m-commerce fashion retail app engagement». Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management. 20 (4): 487–506. doi:10.1108/JFMM-02-2016-0015.
- ^ Yarborough C, Fedesco H (2020). «Motivating Students». Vanderbilt University Center for Teaching. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- ^ Donald JN, Bradshaw EL, Ryan RM, Basarkod G, Ciarrochi J, Duineveld JJ, Guo J, Sahdra BK (July 2020). «Mindfulness and Its Association With Varied Types of Motivation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Using Self-Determination Theory». Personality & Social Psychology Bulletin. 46 (7): 1121–1138. doi:10.1177/0146167219896136. PMID 31884892. S2CID 209510306.
- ^ Schroeder T (2020). «Desire». The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 22 May 2021.
- ^ Dewani V (2013-01-12). «Motivation». slideshare. Retrieved 22 March 2013.
- ^ Lepper MR, Greene D, Nisbet R (1973). «Undermining Children’s Intrinsic Interest with Extrinsic Reward; A Test of ‘Overjustification’ Hypothesis». Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 28: 129–37. doi:10.1037/h0035519.
- ^ Marinak BA, Gambrell LB (2008). «Intrinsic Motivation and Rewards: What Sustains Young Children’s Engagement with Text?». Literacy Research and Instruction. 47: 9–26. doi:10.1080/19388070701749546. S2CID 145209271.
- ^ Wilson TD, Lassiter GD (1982). «Increasing intrinsic interest with superfluous extrinsic constraints». Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 42 (5): 811–819. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.42.5.811.
- ^ Ryan & Deci p 71, 2000
- ^ Ryan & La Guardia, in press
- ^ a b c Reeve, Johnmarshall (2018). Understanding motivation and emotion. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 131–135. ISBN 978-1119367604.
- ^ a b McClelland DC (1988). «1. Conscious and Unconscious Motives». Human Motivation. Cambridge University Press. pp. 3–30. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139878289.003. ISBN 978-0-521-36951-0.
- ^ Freud S (2012). A General Introduction to Psychoanalysis. Renaissance Classics. ISBN 9781484156803.
- ^ Deckers L (2018). Motivation: Biological, Psychological, and Environmental. Routledge. pp. 39–41. ISBN 9781138036338.
- ^ Weingarten E, Chen Q, McAdams M, Yi J, Hepler J, Albarracín D (May 2016). «From primed concepts to action: A meta-analysis of the behavioral effects of incidentally presented words». Psychological Bulletin. 142 (5): 472–97. doi:10.1037/bul0000030. PMC 5783538. PMID 26689090.
- ^ Bargh JA, Chartrand TL (2000). «Studying the Mind in the Middle: A Practical Guide to Priming and Automaticity Research». In Reis H, Judd C (eds.). Handbook of Research Methods in Social Psychology. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. pp. 1–39.
- ^ «Priming». Encyclopedia of Psychology. 2016-06-17. Retrieved 2018-10-13.
- ^ a b Elgendi M, Kumar P, Barbic S, Howard N, Abbott D, Cichocki A (May 2018). «Subliminal Priming-State of the Art and Future Perspectives». Behavioral Sciences. 8 (6): 54. doi:10.3390/bs8060054. PMC 6027235. PMID 29849006.
- ^ «Mere Exposure Effect». Encyclopedia of Psychology. 2016-06-17. Retrieved 2018-10-13.
- ^ Deckers L (2018). Motivation Biological, Psychological, and Environmental (5th ed.). New York: Routledge. pp. 30–38, 71–75. ISBN 9781138036321.
- ^ «Gordon W. Allport». psychology.fas.harvard.edu. Retrieved 2019-12-10.
- ^ Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (April 1996). «Neurobehavioural mechanisms of reward and motivation». Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 6 (2): 228–36. doi:10.1016/S0959-4388(96)80077-8. PMID 8725965. S2CID 16313742.
- ^ Berridge KC, Kringelbach ML (June 2013). «Neuroscience of affect: brain mechanisms of pleasure and displeasure». Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 23 (3): 294–303. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2013.01.017. PMC 3644539. PMID 23375169.
- ^ Salamone JD, Correa M (November 2012). «The mysterious motivational functions of mesolimbic dopamine». Neuron. 76 (3): 470–85. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2012.10.021. PMC 4450094. PMID 23141060.
- ^ Kennedy PJ, Shapiro ML (June 2009). «Motivational states activate distinct hippocampal representations to guide goal-directed behaviors». Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 106 (26): 10805–10. Bibcode:2009PNAS..10610805K. doi:10.1073/pnas.0903259106. PMC 2705558. PMID 19528659.
- ^ a b c Alvarez M (2017). «Reasons for Action: Justification, Motivation, Explanation». The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ^ a b Southwood N (2016). «The Motivation Question». Philosophical Studies. 173 (12): 3413–3430. doi:10.1007/s11098-016-0719-y. S2CID 171181144.
- ^ Broome J (2013). Rationality Through Reasoning. Wiley-Blackwell.
- ^ McHugh C, Way J (2015). «Broome on Reasoning». Teorema: Revista Internacional de Filosofía. 34 (2): 131–140. ISSN 0210-1602. JSTOR 43694673.
- ^ Lee W (2020). «Enkratic Rationality Is Instrumental Rationality». Philosophical Perspectives. 34 (1): 164–183. doi:10.1111/phpe.12136. ISSN 1520-8583.
- ^ Steward H. «Akrasia — Routledge Encyclopedia of Philosophy». www.rep.routledge.com. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ^ Tenenbaum S (2010). «Akrasia and Irrationality». In O’Connor T, Sandis C (eds.). A Companion to the Philosophy of Action. Blackwell Companions to Philosophy. Blackwell. pp. 274–282. doi:10.1002/9781444323528.ch35. ISBN 9781444323528.
- ^ McGregor D (1960). The Human Side of Enterprise. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- ^ Malone T (1997). «Is ‘Empowerment’ Just a Fad? Control, Decision-Making, and Information Technology». Sloan Management Review. 23 (38).
- ^ Markowitz L (1996). «Employee Participation at the Workplace: Capitalist Control or Worker Freedom?». Critical Sociology. 22 (2): 89–103. doi:10.1177/089692059602200205. S2CID 143788356.
- ^ Denison DR (1990). Corporate Culture and Organizational Effectiveness. New York: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9780471800217.
- ^ Mayo E (1949). «Hawthorne and the Western Electric Company.». In Pugh DS (ed.). Organization Theory: Selected Readings (Second ed.). New York: Penguin. pp. 279–292.
- ^ Miner JB (September 2003). «The rated importance, scientific validity, and practical usefulness of organizational behavior theories: A quantitative review». Academy of Management Learning & Education. 2 (3): 250–68. doi:10.5465/amle.2003.10932132.
- ^ Pisello T (2 March 2004). «Managing IT According To A Hierarchy Of Needs». WebProNews. Archived from the original on 27 November 2018.
The well-traveled theory by Abraham Maslow asserts that people are motivated by unsatisfied needs […].
- ^ «The benefits of a motivated workforce — Motivation». Eduqas — GCSE Business Revision — Eduqas. BBC Bitesize. Retrieved 2020-10-09.
- ^ a b Steinmetz L (1983). Nice Guys Finish Last: Management Myths and Reality. Boulder, CO: Horizon Publications Inc. pp. 43–44. ISBN 978-0-8159-6316-5.
- ^ a b Goldthorpe JH, Lockwood D, Bechhofer F, Platt J (1968). The affluent worker: Industrial attitudes and behaviour. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Weightman J (2008). The Employee Motivation Audit. Cambridge Strategy Publications.
- ^ Kenton W. «What Is the Hawthorne Effect?». Investopedia. Retrieved 2020-10-09.
- ^ Graham HT, Bennett R (1993). Human Resources Management. M+E Handbooks. ISBN 0-7121-0844-0.
- ^ Barnett T, Droege SB (2006). «Theory Z». In Helms MM (ed.). Encyclopedia of Management. Gale Virtual Reference Library (5th ed.). Detroit: Gale Cengage Learning. pp. 914–916.
- ^ Robbins SP, Judge TA (2007). Essentials of Organizational Behavior (9th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. Archived from the original on 2009-06-14.
- ^ Mann AM (28 June 2016). «Employee Recognition: Low Cost, High Impact». Gallup. Gallup. Retrieved 25 September 2019.
- ^ Vroom V, Lee D (1964). Work and Motivation.
- ^ «Description of a Positive Workplace». Small Business — Chron.com. Retrieved 2020-10-09.
- ^ Burgers C, Eden A, Van Engelenburg MD, Buningh S (2015-07-01). «How feedback boosts motivation and play in a brain-training game». Computers in Human Behavior. 48: 94–103. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2015.01.038. ISSN 0747-5632.
- ^ Bragg T (2 September 2002). «Motivate your employees by offering more interesting, challenging job experiences». Louisville Business First. Retrieved 2020-10-09.
- ^ Hackman JR, Oldham GR (1980). Work Redesign. Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Pearson Education, Inc. pp. 78–80.
- ^ Katz R (2015). «Motivating Technical Professionals Today». Research-Technology Management. 48 (6): 19–27. doi:10.1080/08956308.2005.11657344. S2CID 218756298.
- ^ a b Steel P (2012). Motivation: Theory and Applied. Boston, MA: Pearson Learning Solutions. p. 49.
- ^ Pfeil M (11 January 2013). «How Employee Recognition Programmes Improve Retention». CFO Insight Magazine. Archived from the original on 2013-01-16.
- ^ Vermeulen F (May 2011). «Five mistaken beliefs business leaders have about innovation». Forbes.
- ^ Ormrod JE (2003). Educational Psychology: Developing Learners. Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Merrill/Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-088716-0. OCLC 49626269.
- ^ Williams RL, Stockdale SL (2004). «Classroom motivation strategies for prospective teachers». The Teacher Educator. 39 (3): 212–230. doi:10.1080/08878730409555342. S2CID 144007655.
- ^ Whyte CB (2007). «An Additional Look at Orientation Programs Nationally- (reprint of 1986 article in same journal)». National Orientation Directors Association Journal. 15 (1): 71–77.
- ^ Vallerand RJ, Pelletier LG, Blais MR, Brière NM, Senecal C, Vallières ÉF (2016). «The Academic Motivation Scale: A Measure of Intrinsic, Extrinsic, and Amotivation in Education». Educational and Psychological Measurement. 52 (4): 1003–1017. doi:10.1177/0013164492052004025. S2CID 145465675.
- ^ Harter S (1981). «A new self-report scale of intrinsic versus extrinsic orientation in the classroom: Motivational and informational components». Developmental Psychology. 17 (3): 300–312. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.17.3.300.
- ^ Cordova DI, Lepper MR (1996). «Intrinsic motivation and the process of learning: Beneficial effects of contextualization, personalization, and choice». Journal of Educational Psychology. 88 (4): 715–730. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.88.4.715.
- ^ Ordóñez, Lisa; Schweitzer, Maurice; Galinsky, Adam; Bazerman, Max (2020-03-25), «Goals Gone Wild», Organizational Collaboration, Routledge, pp. 21–34, doi:10.4324/9781315881201-5, ISBN 978-1-315-88120-1, S2CID 216306833, retrieved 2023-01-27
- ^ Whyte CB (2018). «Effective Counseling Methods for High-Risk College Freshmen». Measurement and Evaluation in Guidance. 10 (4): 198–200. doi:10.1080/00256307.1978.12022132.
- ^ Lauridsen K, Whyte CB, eds. (1980). An Integrated counseling and Learning Assistance Center. New Directions Sourcebook. Jossey-Bass.
- ^ Fisher K, Marshall M, Nanayakkara A (2009). «Motivational orientation, error monitoring, and academic performance in middle childhood: A behavioral and electrophysiological investigation». Mind, Brain, and Education. 3: 56–63. doi:10.1111/j.1751-228x.2008.01053.x.
- ^ O’Donohue WT, Benuto LT, Tolle LW, eds. (2013). Handbook of Adolescent Health Psychology. Springer. p. 376. ISBN 978-1-4614-6632-1.
- ^ Moen R, Doyle KO (1978). «Measures of Academic Motivation: A Conceptual Review». Research in Higher Education. 8 (1): 1–23. doi:10.1007/BF00985853. JSTOR 40195071. S2CID 143695767.
- ^ Symer MM, Abelson JS, Yeo HL, Sosa JA, Rosenthal MZ (May 2018). «The Surgical Personality: Does Surgery Resident Motivation Predict Attrition?». Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 226 (5): 777–783. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2018.02.007. PMID 29510202.
- ^ a b c d Maclellan E (2005). «Academic achievement:The role of praise in motivating students». Active Learning in Higher Education. 6 (3). doi:10.1177/1469787405057750. S2CID 146571882.
- ^ a b Sansone C, Morgan C (1992). «Intrinsic motivation and education: Competence in context». Motivation and Emotion. 16 (3): 249–270. doi:10.1007/bf00991654. S2CID 144370965.
- ^ a b c Katz I, Shahar BH (2015). «What makes a motivating teacher? Teacher’s motivation and beliefs as predictors of their autonomy-supportive style». School Psychology International. 36 (6): 575–588. doi:10.1177/0143034315609969. S2CID 146836262.
- ^ a b Reeve JM (2009). «Why teachers adopt a controlling motivating style toward students and how they can become more autonomy supportive». Educational Psychologist. 44 (3): 159–175. doi:10.1080/00461520903028990. S2CID 29543108.
- ^ Deci EL, Koestner R, Ryan RM (2001). «Extrinsic rewards and intrinsic motivation in education: Reconsidered once again». Review of Educational Research. 71 (1): 1–27. doi:10.3102/00346543071001001. S2CID 11589745.
- ^ a b Deci EL, Sheinman L, Nezlek JB (1981). «Characteristics of the rewardee and intrinsic motivation of the rewardee». Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 40 (1): 1–10. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.40.1.1.
- ^ Tharp R, Yamauchi L (2000). «Instructional Conversations in Native American Classrooms. Rural, Urban and Minority Education». Journal of Early Education and Family Review. 7 (5): 33–37.
- ^ McInerney DM, Swisher KG (April 1995). «Exploring Navajo Motivation in School Settings». Journal of American Indian Education. 34: 3.
- ^ Pewewardy C (January 2002). «Learning Styles of American Indian/Alaska Native Students: A Review of the Literature and Implications for Practice». Journal of American Indian Education. 41 (3): 22–56. JSTOR 24398583.
- ^ Pelletier W (1969). Childhood in an Indian Village. Toronto etc.: Institute for Indian Studies. Neewin Publishing.
- ^ Maynard AE (2004). «Cultures of teaching in childhood: formal schooling and Maya sibling teaching at home». Cognitive Development. 19 (4): 517–535. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.492.6959. doi:10.1016/j.cogdev.2004.09.005.
- ^ a b Greenfield PM, Maynard AE, Childs CP (2000). «History, culture, learning, and development». Cross-Cultural Research. 34 (4): 351–374. doi:10.1177/106939710003400404. S2CID 55190308.
- ^ Rogoff B (2011). Developing Destinies: A Mayan Midwife and Town. Cambridge: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-971780-4.
- ^ Chavajay P, Rogoff B (January 2002). «Schooling and traditional collaborative social organization of problem solving by Mayan mothers and children». Developmental Psychology. 38 (1): 55–66. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.38.1.55. PMID 11806702.
- ^ Lillemyr OF, Søbstad F, Marder K, Flowerday T (June 2010). «Indigenous and non-Indigenous primary school students’ attitudes on play, humour, learning and self-concept: a comparative perspective». European Early Childhood Education Research Journal. 18 (2): 243–267. doi:10.1080/13502931003784396. S2CID 145281027.
- ^ Rogoff B, Paradise R, Arauz RM, Correa-Chavez M, Angelillo C (2003). «Firsthand learning through intent participation». Annual Review of Psychology. 54: 175–203. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.54.101601.145118. hdl:10400.12/5953. PMID 12499516.
- ^ Rogoff B (2012). «Learning without lessons: Opportunities to expand knowledge». Infancia y Aprendizaje. 35 (2): 233–252. doi:10.1174/021037012800217970. S2CID 144442624.
- ^ Ames P (2013). «Learning to be responsible: Young children transitions outside of school». Learning, Culture and Social Interaction. 2 (3): 143–154. doi:10.1016/j.lcsi.2013.04.002.
- ^ Gaskins S (2000). «Children’s daily activities in a Mayan village: A culturally grounded description». Cross-Cultural Research. 34 (4): 375–389. doi:10.1177/106939710003400405. S2CID 144751184.
- ^ Correa-Chávez M, Roberts AL, Pérez MM (2011). Cultural patterns in children’s learning through keen observation and participation in their communities. Advances in Child Development and Behavior. Vol. 40. pp. 209–41. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-386491-8.00006-2. ISBN 978-0-12-386491-8. PMID 21887963.
- ^ Mejía-Arauz R, Rogoff B, Dexter A, Najafi B (2007). «Cultural variation in children’s social organization». Child Development. 78 (3): 1001–14. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2007.01046.x. PMID 17517018.
- ^ Ali J, McInerney DM, Craven RG, Yeung AS, King RB (2013). «Socially Oriented Motivational Goals and Academic Achievement: Similarities Between Native and Anglo Americans». The Journal of Educational Research. 107 (2): 123–137. doi:10.1080/00220671.2013.788988. S2CID 144741545.
- ^ Paradise R, Rogoff B (2009). «Side by Side: Learning by Observing and Pitching In». Ethos. 37: 102–138. doi:10.1111/j.1548-1352.2009.01033.x.
- ^ Radoff J (April 2011). Game On: Energize Your Business with Social Games. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-470-93626-9.
- ^ Radoff J (May 2011). «Game Player Motivations». radoff.com. Archived from the original on 2011-05-21.
- ^ Popkin H (June 1, 2010). «FarmVille invades the real world». NBC News.
- ^ Wan CS, Chiou WB (2007). «The motivations of adolescents who are addicted to online games: a cognitive perspective». Adolescence. 42 (165): 179–97. PMID 17536482.
- ^ Ryan RM, Rigby CS, Przybylski A (2006). «The motivational pull of video games: A self-determination theory approach». Motivation and Emotion. 30 (4): 344–360. doi:10.1007/s11031-006-9051-8. S2CID 53574707.
- ^ Gneezy, Uri; Rustichini, Aldo (2000). «Pay Enough or Don’t Pay at All». The Quarterly Journal of Economics. 115 (3): 791–810. doi:10.1162/003355300554917. ISSN 0033-5533. JSTOR 2586896.
- ^ Feldman, Yuval; Lobel, Orly (7 June 2009). «The Incentives Matrix: The Comparative Effectiveness of Rewards, Liabilities, Duties and Protections for Reporting Illegality». Texas Law Review. 87. doi:10.2139/ssrn.1415663. SSRN 1415663.
Further reading[edit]
- Baumeister RF, Vohs KD (2004). Handbook of self-regulation: Research, theory, and applications. New York: Guilford Press. p. 574. ISBN 978-1-57230-991-3.
- Carver CS, Scheier MF (2001). On the self-regulation of behavior. New York: Cambridge University Press. p. 460. ISBN 978-0-521-00099-4.
- Cervone D, Shadel WG, Smith RE, Fiori M (2006). «Self-Regulation: Reminders and Suggestions from Personality Science». Applied Psychology: An International Review. 55 (3): 333–385. doi:10.1111/j.1464-0597.2006.00261.x. Archived from the original on 2013-01-05.
- Cofer CN, Appley MH (1967). Motivation: Theory and Research. New York, London, Sydney: John Wiley & Sons.
- Fishbein M, Ajzen I (1975). Belief, attitude, intention, and behavior: An introduction to theory and research. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
- Gollwitzer PM (1999). «Implementation intentions: Strong effects of simple plans» (PDF). American Psychologist. 54 (7): 493–503. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.54.7.493.
- Jones I (2008). The Human Factor: Inside the CIA’s Dysfunctional Intelligence Culture. New York: Encounter Books. ISBN 978-1-59403-382-7.
- Murphy J (2009). Inner Excellence. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-163504-2.
- Richard R (2019). The Oxford Handbook of Human Motivation. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780190666453.
Types
of word meaning (classifications):
According
to the aspect relation of a word to the components of the situation
where it is used:
Referential
meaning — determined by the relation of linguistic sign to the
referent in the material world
Significative
meaning — determined by the relation of a linguistic sign to its
user, the speaker’s intention
Differential
(systematic) meaning — determined by the relation of the given
linguistic sign to other signs in the language system of speech
Another
typology is based on the conception of word meaning as specific
structure:
Part-of-speech
meaning (functional)Grammatical — may be defined as the component
of meaning recurrent in identical sets of individual forms of
different words, as, e.g., the tense meaning in the word-forms of
verbs (asked, thought, walked, etc.) or the case meaning in the
word-forms of various nouns (girl’s, boy’s, night’s,
etc.)Lexical — may be described as the component of meaning proper
to the word as a linguistic unit, i.e. recurrent in all the forms of
this word. E.g. the word-forms go, goes, went, going, gone possess
different grammatical meanings of tense, person and so on, but in
each of these forms we find one and the same semantic component
denoting the process of movement.
DENOTATIONAL
(reference of a word or other lexical unit to individual object or
concept) REVEALED IN THE DICTIONARY DEFINITION
CONNOTATIONAL
(includes ideas or emotions)
Emotional
implications (personal, studied by pragmatics)
Emotive
charge (may be inherent in word meaning or created by prefixes and
suffixes)
Stylistic
reference (refers the word to a certain style register (neutral,
colloquial, literary) This may be best illustrated by comparing words
almost identical in their denotational meaning, e. g., ‘parent —
father — dad’. In comparison with the word father which is
stylistically neutral, dad stands out as colloquial and parent is
felt as bookish.
Motivation
is the suggestion of the meaning of the word by the lexical form of
the word.
Morphological
motivation implies a direct connection between the lexical meaning of
the component morphemes, the pattern of their arrangement and the
meaning of the word. The degree of morphological motivation may be
different varying from the extreme of complete motivation to lack of
motivation. (The words finger-ring and ring-finger, e.g., contain two
morphemes, the combined lexical meaning of which is the same; the
difference in the meaning of these words can be accounted for by the
difference in the arrangement of the component morphemes).
Phonetical
motivation implies a direct connection between the phonetic structure
of the word and its meaning. Phonetical motivation is not universally
recognised in modern linguistic science. It is argued that speech
sounds may suggest spatial and visual dimensions, shape, size, etc.
Experiments carried out by a group of linguists showed that back open
vowels are suggestive of big size, heavy weight, dark colour, etc.
Words
as swish, sizzle, boom, splash, etc. may be defined as phonetically
motivated because the soundclusters [swi∫, sizl, bum, splæ∫] are
a direct imitation of the sounds these words denote.
Semantic
motivation implies a direct connection between the central and
marginal meanings of the word. This connection may be regarded as a
metaphoric extension of the central meaning based on the similarity
of different classes of referents denoted by the word. (For example,
a woman who has given birth is called a mother; by extension, any act
that gives birth is associated with being a mother,Cf. also mother
country, a mother’s mark (=a birthmark), mother tongue, etc.)
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
The word ‘motivation’ has been derived from the word ‘motive’ which means any idea, need or emotion that prompts a man into action.
Meaning of Motivation
The word ‘motivation’ has been
derived from the word ‘motive’ which means any idea, need or emotion that
prompts a man into action. Whatever may be the behaviour of a man, there is
some stimulus behind it. Stimulus is dependent upon the motive of the person
concerned. Motive can be known by studying his needs and desires. Generally,
different motives operate at different times among different people and
influence their behaviour. The management should try to understand the motives
of individuals which cause different types of behaviour.
Dubin has defined motivation as “the complex of forces starting and keeping a person at work in an
organisation. Motivation is something that moves the person to action, and
continues him in the course of action already initiated”. Motivation refers
to the way a person in enthused at work
to intensify his desire and willingness to use his energy for the achievement
of organisational objectives.
According to Dalton E.McFarland, “Motivation refers to the way in which urges, drives, aspirations,
striving or needs direct, control or explain the behaviour of human beings”. Motivation
has close relationship with the
behaviour of human beings. It explains how and why human behaviour is caused.
Thus, motivation is a term which applies to the entire class of urges, derives,
desires, needs and similar forces.
Tags : Management Concepts & Organisational Behaviour — Motivation
Last 30 days 908 views
Motivation is the longing or willingness to do something due to the set of psychological forces or factors that compel you to act in service of a goal. It’s a vital component of human behavior in setting and accomplishing our goals. Psychologists define motivation as our overall readiness to accomplish something. Human beings do something due to a wide variety of motivating factors that are the combination of psychological powers that urge you to make a move.
It is one of the most integral factors behind human conduct, as it is closely related to connecting emotions with every action of an individual. Its absence can prompt psychological hindrances like discouragement, as people struggle to do something with full enthusiasm when they do not feel motivated. All in all, motivation incorporates the desire to keep endeavoring toward a goal, purpose, or meaning in professional or personal life.
Definition: Motivation is defined as a driving force that makes individuals act, put forth objectives, and accomplish them. As a psychophysiological process, motivation controls human behavior and because of this people tend to stay motivated to set directions, take action, and accomplish goals.
While understanding motivation, it is important to understand that various societies have their motivation drivers. Culture, conditioning, society, lifestyle, social environment, education, etc are the intrinsic as well as extrinsic motivators. Motivation is the pivotal component in setting and accomplishing our targets. It is one of the main impetuses behind the completion of our to-do list.
The word motivation is originated from the word ‘motive’ which means desires, needs, wants or drives inside the people. You may also understand it as the method involved with stimulating individuals to perform an activity due to internal or external rewards to achieve the objectives.
Motivation Definitions
1. As per the Encyclopedia of Management
Motivation refers to the degree of readiness of an organism to pursue some designated goal and implies the determination of the nature and locus of the forces, including the degree of readiness.
2. Robert Dubin defines it as
Something that moves the person to action and continues him in the course of action already initiated. It refers to the way a person is enthused at work to intensify his desire and willingness to use his potentiality for the achievement of organizational objectives.”
3. Koontz and O’Donnell Definition of Motivation
Motivation is a general term applying to the entire class of drives, desires, needs, wishes, and similar forces that induce an individual or a group of people to work.
4. According to Dalton E. McFarlan
Motivation refers to the way in which urges, drives, desires, aspirations, strivings, or needs direct, control, or explain the behavior of human beings.
5. In the words of Michael J. Jucious
Motivation is the act of stimulating someone or oneself to get a desired course of action, to push the right button to get the desired action.” It is nothing but an act of inducement.
Nature of Motivation
1. Continuous Process
Human wants are unending and with the fulfillment of one want, new wants might pop up. This is why motivation is a continuous process.
2. Psychological Concept
Motivation is associated with the psychological aspects of human inclinations, desires, goals, and behavioral conducts.
3. Every Individual is Motivated
Every individual in itself can be understood as an integrated and comprehensive system that has his or her own conditioning and belief system to stay motivated in some or another way.
4. Frustrated Individual Fails to get Motivated
When an individual is frustrated, he or she can not be motivated until they come out of their frustrations. It might also be due to the wide gap between their inspiration and rewards.
5. Goals Lead to Motivation
Goals are one of the most integral parts of the whole process of motivation. Accomplishing a goal helps a motivated individual be satisfied.
What is Motivation in a Workplace?
While understanding what is motivation in a workplace or work-goal setting, different psychological factors that can increase motivation are-
- Desire for money
- Recognition or acknowledgment
- Success
- Teamwork
- Job satisfaction, etc.
One of the main roles of workplace managers or leaders is to make willingness among the workers to perform with full enthusiasm. In this manner, a leader or manager’s job is to create interest in the heart and mind of the employee, so they can be intrinsically motivated.
In addition to this, external incentives also play a key role in motivating employees.
Different phases through which the process of motivation takes place are the felt drive or need, a stimulus to arouse the need or drive, and the fulfillment of objectives or needs being satisfied.
Why Motivation is Important
It is essential for the growth and success of an individual, plus, for a leader or manager, motivation is also important for guiding the team or employees towards an objective.
For a manager, leader, or administrator, having a team that offers genuine commitment is essential to optimize the success rate.
If you can motivate your team members, they will work with more enthusiasm and dedication to meet their goals.
Some of the reasons why motivation is important for an organization are-
- Putting human resources into action
- Promoting the willingness to work
- Improving the level of efficiency of employees
- Leading to the achievement of organizational goals
- Building friendly relationship
- Leading to the stability of the workforce
- Reducing absenteeism and turnover
- Channelizing a sense of belonging
History of Motivation- Theories of Motivation
Since the beginning of time, various theories are proposed by psychologists for explaining human behavior. Coming up next are a portion of some of those theories-
1. Instinct Theory of Motivation
It recommends that our instincts are crucial in motivating our behaviors. Our instincts are fixed and intrinsic examples of human behaviors.
A number of psychologists including McDougal, William James, Sigmund Freud, etc have proposed various essential human drives that motivate human behavioral patterns.
2. Drive and Needs theory of Motivation
A significant number of human practices like drinking water or eating foods etc are motivated by biological needs and drives.
As per drive theory and Maslow’s theory of hierarchy of needs proposes that individuals have essential biological drives and such behavioral patterns are motivated through the needs of fulfilling such drives.
3. Arousal Theory of Motivation
It proposes that individuals are motivated for taking part in different activities to reach the top level of arousal.
Therefore, an individual with low arousal needs would seek after some relaxing activities while those with high arousal needs may be motivated to participate in energizing as well as thrill-seeking practices.
Sources of Motivation
Human beings generally have various intentions and motives for incorporating different behavioral patterns. Human motivation can be maybe outward or extrinsic, by which an individual is influenced by outside factors.
Motivation can likewise be natural or intrinsic, by which the motivation comes from inside due to an internal desire to do something. Internal or intrinsic motivation will in general push individuals all the more strongly make the achievements really satisfying.
American psychologist Abraham Maslow in 1943 suggested one such framework to understand motivation named as a hierarchy of needs. He suggests that people are intrinsically persuaded to push toward doing something in their maximum capacity to fulfill their different degrees of needs ranging from safety and foods to belonging, love, and self-esteem.
In the end, Maslow stretched out the theory to incorporate a requirement for self-transcendence that lets people arrive at the zenith of development to accomplish the highest meaning in life by taking care of things past oneself.
Types of Human Motivation
Various sorts of inspiration are as often as possibly depicted as being either extraneous or characteristic:
1. Extrinsic Motivation
Such types of motivation emerge from outside of the individual. Extrinsic motivations generally include rewards and incentives like prizes, cash, social acknowledgment, praise, other forms of money, etc.
2. Intrinsic Motivation
The intrinsic motivation factors are those that emerge from the inside of an individual. Some of the examples can be playing tennis because it is fun or learning a new language because you like learning and experiencing new things.
3. Positive Motivation
This type of motivation is also understood as incentive motivation that depends on external rewards. Employees, workers, or team members are offered a wide variety of incentives for accomplishing their objectives. Such motivations are also like extrinsic motivations. Such incentives might be promotion, increasing payments, recognition of work, etc.
4. Negative Motivation
Negative motivation is also understood as fear motivation that depends on fear or force. Due to fear, workers or team members act with a specific goal in mind. In the event that, they don’t act appropriately, they might be punished with downgrades or lay-offs.
In negative motivation, fear goes about as a pushing method. With such type of motivation, workers or team members don’t enthusiastically co-work or cooperate, rather they need to keep away from the punishment. Such forms of motivation cause outrage, frustration, and disappointment.
Financial Incentives of Motivation
- Pay and Allowances
- Bonus
- Retirement Benefits
- Profit-Sharing
- Co-Partnership
- Productivity-based Wage Incentives
- Prerequisites, etc.
Non-Financial Incentives of Motivation
- Status/Recognition
- Job Enrichment
- Organizational Climate
- Job Enrichment
- Opportunity for Growth
- Employees’ Empowerment
- Employee’s Reward
- Employees’ Participation
- Job Security, etc
Here is a video by Marketing91 on Motivation.
Uses of Motivation
Motivation has a wide variety of utilization. It fills in as a directing power as well as a driving force for human beings. Some of the key uses of motivation are-
- Improving the efficiency of employees, people, or team members
- Influencing or persuading people to take action
- Encouraging people toward health-oriented behaviors
- Guiding people to avoid unhealthy or maladaptive behaviors like addiction
- Enabling people to feel more in control of their lives
- Optimizing overall well-being and happiness
Components of Motivation
If you have had an objective, you must have understood that just wanting to achieve something isn’t sufficient.
Accomplishing a wide variety of objectives requires the capacity to persevere through different obstructions and perseverance for continuing onward regardless of hardships.
There are three significant parts of motivation that comes into play in such a situation-
1. Activation or Initiation
It includes the choice to start behavioral conduct, for example, signing up for a subscription blog
2. Determination or Persistence
It can be understood as a continuous effort toward an objective despite the presence of different hindrances. Being determined towards accomplishing something is one of the key components of motivation
3. Intensity
This component of motivation will be evident in the focus and energy that one has while accomplishing a goal.
Types of Motivation for different Activities
Knowing different types of motivation activities in different scenarios is important for overcoming the challenges of motivating different groups of people. Let us have a look at some of these types of emotions here and now
1. Motivation Types for Employees
For employees in the business world, they must be motivated internally as well as externally.
A few types of employee motivations that business leaders and managers can use are-
- Reward-based motivation
- Creative motivation
- Achievement motivation
- Attitude motivation
- Power motivation
- Competence motivation
- Fear-based motivation, etc.
2. Motivations Types for Managers
Managers might need to motivate groups of 1o, 100, or 1000 team members, plus they are also supposed to meet a wide variety of people.
Some of the best types of motivation important for managers are
- Reward-based motivation
- Competence motivation
- Attitude motivation
- Achievement motivation
- Power motivation, etc
3. Types of Motivation in Education
Different types of motivations that are crucial for the learners are
- Reward-based motivation
- Achievement motivation
- Fear-based motivation, etc
Conclusion!
You must have seen instances when a few managers get succeeded in the toughest of circumstances while others fail, and the reason behind this is successful managers know how to promote workplace motivation.
They constructively motivate their team members to coordinate with every member of the team to accomplish goals.
Successful leaders positively influence the motivational needs of their team members.
For effective workplace motivation, aligning organizational objectives with the individual needs, goals, and emotions of every member is crucial.
Creating a working ambiance that can foster their internal motivations will for sure be a big upside for running a motivated organization.
Now, on the concluding note, what is motivation according to you? How crucial do you consider motivation in accomplishing success in life?
Liked this post? Check out these detailed articles on Topic of Motivation
Alternatively, check out the Marketing91 Academy, which provides you access to 10+ marketing courses and 100s of Case studies.
What is the meaning of motivation?
Meaning of Motivation: – Motivation is a reason for actions, willingness, and goals. Motivation is derived from the word ‘motive’, or a need that requires satisfaction. These needs, wants or desires may be acquired through influence of culture, society, lifestyle, or may be generally innate.
Motivation is the process that initiates, guides, and maintains goal-oriented behaviors. Motivation is an important factor that encourages individuals to give their best performance and help them reach enterprise goals. A strong positive motivation will enable increased production of employees but a negative motivation will reduce their performance. A key element in personnel management is motivation.

Definitions of Motivation by various Jurist’s
- Berelson and Steiner: – “A motive is an inner state that energizes, activates, or moves and directs or channels behaviour goals.”
- Lillis: – “It is the stimulation of any emotion or desire operating upon one’s will and promoting or driving it to action.”
- The Encyclopedia of Management: – “Motivation refers to degree of readiness of an organism to pursue some designated goal and implies the determination of the nature and locus of the forces, including the degree of readiness.”
- Dubin: – “Motivation is the complex of forces starting and keeping a person at work in an organization.”
- Vance: – “Motivation implies any emotion or desire which so conditions one’s will that the individual is properly led into action.”
Motivation is a psychological phenomenon that occurs within a person. A person lacks some needs, which makes him satisfied that he works more. The need to satisfy the ego motivates a person to do better in general.
The following conclusions can be drawn from the definitions given earlier: –
- Motivation is an inner feeling that makes a person excited to do more work.
- A person’s feelings or desires motivate him to perform a particular task.
- A person has unsatisfying needs that impair his balance.
- A person proceeds to fulfill his dissatisfied needs by conditioning his energies.
- A person has passive energies that are activated by channeling in actions.
What are the Types of Motivation?
When a manager wants to take more work from his subordinates, he has to be motivated to improve his performance. They will either be offered incentives for more work, or they may be in place of rewards, better reports, recognition, etc., or they may instill fear in them or use force to achieve the desired task.
The following are the types of motivation: –
1. Positive Motivation: –
- Positive motivation is based on reward. Workers are offered incentives to achieve desired goals. Incentives may be in the form of higher salaries, promotions, recognition of work, etc. Employees are offered incentives and seek to improve their performance voluntarily.
- According to Peter Drucker, genuine and positive motivators are responsible for placement, high levels of performance, sufficient information for self-control, and worker involvement as a responsible citizen in the plant community. Positive motivation comes from the support of employees and they feel happy.
2. Negative Motivation: –
- Negative or fear is based on motivation or fear. Fear causes employees to act a certain way. In case, they do not act accordingly then they can be punished with demotion or take-off. Fear acts as a pushing mechanism. Employees do not cooperate voluntarily; instead they want to avoid punishment.
- Although employees work to a level where punishment is avoided, this type of motivation leads to anger and frustration. This type of motivation usually becomes the cause of industrial unrest. Despite the drawbacks of negative motivation, this method is commonly used to achieve desired results. There can hardly be any management who has not used negative motivation at one time or another.
Theories of motivation
1. Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory
It is probably safe to say that the most famous theory of motivation is Maslow’s requirement hierarchy theory. Maslow’s theory is based on human needs. Primarily based on their clinical experience, they categorized all human needs from lower to higher order.
In short, he believed that once the level of need given is satisfied, it does not work to motivate man. Then, the next higher level need to be activated to motivate the man. Maslow identified five levels in its need hierarchy.

These are now discussed one by one below: –
1. Physiological Needs: –
- These needs are basic to human life and, therefore, include food, clothing, shelter, air, water and life requirements. These are related to the existence and maintenance of human life.
- They have a tremendous impact on human behavior. These needs must be met at least partially before high levels of needs emerge. Once physical needs are met, they do not motivate the man.
2. Safety Needs: –
- After satisfying the physical requirements, the next needs to be felt are called the need for safety and security. These require expression in desires such as economic security and protection from material threats.
- To meet these needs more money is required and hence, the person is motivated to do more work. Like physical needs, they become inactive after being satisfied.
3. Social Needs: –
- Man is a social animal. Therefore, he is interested in social interaction, companionship, belonging, etc.
- It is because of this socialization and belonging that individuals like to work in groups and especially older people go to work.
4. Esteem Needs: –
- These refer to self-esteem and self-respect. They include requirements that indicate confidence, achievement, ability, knowledge, and independence.
- Meeting the requirements of respect creates confidence, strength and the ability to be useful in the organization. However, inability to meet these needs creates feelings of inferiority, weakness and helplessness.
5. Self-Actualization Needs: –
- This level represents the culmination of all lower, intermediate and higher needs of humans. In other words, the last step under the needs hierarchy model is self-realization. It refers to fulfillment.
- The term self-realization was coined by Kurt Goldstein and it means that what is probably good becomes real. In fact, self-realization is the motivation to change one’s perception of oneself in reality.
Criticism of this theory: –
- The needs may or may not follow a certain hierarchical order. So to say, needs can be overlapping in the hierarchy. For example, even if the need for security is not satisfied, social need can emerge.
- The requirement priority model may not be applicable to all locations at all times.
- Research suggests that human behavior at any given time is guided by a multiplicity of behaviors. Therefore, Maslow’s proposal that one satisfied at a time also has questionable validity.
- In the case of some people, the level of motivation may be permanently reduced. For example, a person suffering from chronic unemployment can remain satisfied for the rest of his life, if only he can get enough food.
Despite this, Maslow’s theory of hierarchy has received widespread recognition, especially among practicing managers.
2. Herzberg’s Motivation Hygiene Theory: –
Psychologist Friedrich Herzberg carried on Maslow’s work and introduced a new motivation theory known as Herzberg’s Motivation Hygiene (Two-Factor) theory. He conducted a widely reported motivational study on 200 accountants and engineers employed by firms in and around western Pennsylvania.
He asked these people to describe two important events in their jobs: –
- When did you feel good about your job and
- When did you feel exceptionally bad about your job? They used the critical event method of obtaining data.
When analyzed, responses were found to be quite interesting and quite consistent. Respondents when they felt good about their jobs were significantly different from the answers given when they felt bad. Reported good feelings are usually associated with job satisfaction, while bad feelings accompany job dissatisfaction.
Herzberg labeled the job-satisfying motivators, and he called the job unsatisfactory with hygiene or maintenance factors. Taken together, the motivators and hygiene factors are known as Herzberg’s two-factor theory of motivation.
According to Herzberg, dissatisfaction is not the opposite of satisfaction. The underlying reason, they say, is that removing dissatisfied characteristics from a job does not necessarily make the job satisfactory. He believes in the existence of a double continuum.
According to Herzberg, today’s motivators are the hygiene of tomorrow because the latter influences the behavior of individuals when they receive them. Accordingly, one hygiene may be the motivator of another.
Herzberg’s model is labeled with the following criticism: –
- When things go well, people usually start taking credit for it themselves. They blame failure on the external environment.
- The theory basically explains job satisfaction, not motivation.
- Even job satisfaction is not measured on an aggregate basis. It is unlikely that a person may dislike part of their job, yet they consider the work acceptable.
- This theory ignores situational variables to motivate the individual.
Due to its ubiquitous nature, pay usually appears as a motivator as well as clean.
Despite criticism, Herzberg’s ‘two-factor motivation theory’ has been widely read and some managers seem ineligible with his recommendations. The main use of their recommendations is in the planning and control of the work of employees.
3. McGregor’s Participation Theory: (X and Y theory)
Douglas McGregor formulated two different views of humans based on worker’s participation. The first basically negative, the label of Theory X, and the second basically positive, the enabling of Theory Y.
Theory X is based on the following assumptions: –
- People are indolent by nature. That is, they like to do as little work as possible.
- People lack ambition, dislike responsibility, and prefer to be guided by others.
- People are naturally self-centered and indifferent to organizational needs and goals.
- People are usually naive and not very sharp and bright.
On the contrary, theory Y assumes that: –
- They want to assume responsibility.
- They want their organization to succeed.
- People are able to direct their own behavior.
- They require achievement.
4. Urwick’s Theory Z
Following the propositions of theories X and Y by McGregor, three theorists Urvik, Rangnekar, and Auchi accepted the third theory as the Z theory.
The two propositions in Urwicks’s theory are that: –
- Everyone should know the organizational goals properly and the amount of contribution to these goals through their efforts.
- Everyone should also know that the relationship of organizational goals is positively satisfying their needs.
In Urwik’s view, both people above are willing to behave positively to meet both organizational and personal goals.
However, Ouchi’s Theory Z has attracted a lot of attention from management practitioners as well as researchers. It should be noted that Z does not stand for anything, only the last alphabet in the English language.
Theory Z is based on the following points: –
- Strong bond between organization and employees
- Employee participation and participation
- No formal organization structure
- Human Resource Development
Ouchi’s Theory Z represents the adoption of Japanese management practices (group decision making, social cohesion, job security, overall concern for employees, etc.) by American companies. In India, Maruti-Suzuki, Hero-Honda etc. apply the post-up of Principle Z.
In psychology, motivation refers to the initiation, direction, intensity, and persistence of behavior. Motivation is a temporal and dynamic state that should not be confused with personality or emotion. It involves having the desire and willingness to do something. A motivated person can be reaching for a long-term goal such as becoming a professional writer or a more short-term goal like learning how to spell a particular word. Personality invariably refers to more or less permanent characteristics of an individual’s state of being (such as shy, extrovert, conscientious). As opposed to motivation, emotion refers to temporal states that do not immediately link to behavior (such as anger, grief, or happiness).
Motivation can be categorized according to whether it is a basic, instinctive drive, unlearned and common to all people and also animals, or a learned motivation that can be unique. The former type of motivation involves satisfying the needs of the physical body, and include hunger, thirst, shelter or safety, sexual activity, and so forth. The latter type includes achievement of goals, whether they be in terms of gaining knowledge, power, self-development, or a loving relationship. This latter type can be seen as satisfying the desires of the mind and spirit. Motivation is complex since human nature is complex. Yet, to understand what motivates people to act in certain ways enables people to live and work peaceably with one another.
Definition
Motivation can be anything that arouses an organism toward action for a desired goal. Motivation can be the reason for the action or that which gives direction to an action.[1]
The word motivation most likely comes from the word «motive,» which stems from either the French motiver or the German motivieren. The word first appeared in English in 1904.[2]
Importance of motivation
Motivation is considered an essential element not only in learning, but also in the performance of learned responses. In other words, even when an organism (including a human being) has learned the appropriate response to a particular situation they will not necessarily produce this behavior. The incentive to produce the behavior is motivation.
Sources of Motivation
Sources of motivation can be broken into two main categories: intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic sources include physical, mental, and spiritual. Extrinsic sources include operant and social conditioning. Some examples of needs within these categories are listed below:
- Physical
- Avoidance of pain
- Seeking physical pleasure
- Hunger, fatigue, and so forth.
- Mental
- Cognitive: maintaining attention, developing interests, problem solving
- Affective: increase feeling good, decrease feeling bad, increasing security, becoming enthusiastic
- Conative: meeting goals, developing self efficacy, taking control of one’s life
- Spiritual
- Understanding the purpose of one’s life
- Connecting one’s life to deeper meanings.[3]
Theories of motivation
Theories of motivation are based on different criteria, and emphasize various needs as key drivers in our actions. Like needs, these theories are both internal and external.
Behavioral
Behaviorists believe that everything performed by organisms, including thinking, feeling, and acting, are behaviors. For Behaviorists there is no philosophical difference in describing externally visible things such as actions and internal things such as thoughts. Though there are nuanced theories of behaviorism, they generally state that behaviors can be traced to factors within a person’s life such as their past and present environments, the actions of others, and their present feelings. These forces act on one another and result in an action, effectively making them the motivation for action.
Cognitive
Cognitive theories center on the effects of the different ways people process information with motivation. Some key theories are listed below.
- Cognitive dissonance theory
The cognitive dissonance theory, first proposed by Leon Festinger, states that people need to maintain consistency among their beliefs, attitudes, and behavior. Contradicting cognitions serve as a driving force that compels the mind to acquire or invent new beliefs, or to modify existing beliefs, in order to reduce the amount of dissonance (conflict) between cognitions and bring them back into a consistent relationship.
- Attribution Theory
This theory posits that people explain success or failure with attributions. These attributions can be grouped as within or outside of a person’s control and then internal or external. People will say that an event that occurs that is both external and out of their control is unstoppable, but will pride themselves on events that occur because of an internal characteristic that is within their control.
- Expectancy Theory
Expectancy theory attempts to mathematize motivation. In this theory, expectancy (perceived probability of success), instrumentality (connection of success and reward), and value (value of obtaining goal) must all exist in order for a person to take action, according to the formula:
- Motivation = Expectancy * Instrumentality * Value
Pyschoanalytic theories
Sigmund Freud and his followers describe the unconscious mind as controlled by a person’s instinctual desires and needs. These instincts, however, come into conflict with the social demands of the conscious mind. Freud later divided the mind into three sections: the conscious mind, or ego, and two parts of the unconscious mind: the id, or instincts, and superego, the result of social conditioning.
Many of Freud’s students broke with his theories, emphasizing instead the importance of the social and spiritual on motivation.
Humanistic Theories
- Drive Reduction
Drive Reduction Theory grows out of the concept that we have certain biological needs, such as hunger. As time passes the strength of the drive increases as it is not satisfied. Then as we satisfy that drive by fulfilling its desire, such as eating, the drive’s strength is reduced. It is based on the theories of Freud and the idea of feedback control systems, such as a thermostat.
There are several problems, however, that leave the validity of the Drive Reduction Theory open for debate. The first problem is that it does not explain how Secondary Reinforcers reduce drive. For example, money does not satisfy any biological or psychological need but reduces drive on a regular basis through a pay check second-order conditioning. Secondly, if the drive reduction theory held true we would not be able to explain how a hungry human being can prepare a meal without eating the food before they finished cooking it.
However, when comparing this to a real life situation such as preparing food, one does become hungrier as the food is being made (drive increases), and after the food has been consumed the drive decreases. The reason that generally the food is not eaten before preparation is complete is the human element of restraint. Knowing that the food will be nicer (or simply edible as opposed to inedible when raw) after it is cooked enables the preparer to delay drive reduction.
- Maslow
Diagram of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs.
Abraham Maslow’s «hierarchy of human needs» theory is the most widely discussed theory of motivation. The theory can be summarized thus:
- Human beings have wants and desires which influence their behavior; only unsatisfied needs can influence behavior, satisfied needs cannot.
- Since needs are many, they are arranged in order of importance, from the basic to the complex.
- The person advances to the next level of needs only after the lower level need is at least minimally satisfied.
- The further the progress up the hierarchy, the more individuality, humanness and psychological health a person will show.
The hierarchy arranges needs from basic physiological (lowest, earliest), through safety, social, and self esteem to the most complex (highest, latest) need for self actualization.
- Alderfer
Created by Clayton Alderfer, Maslow’s hierarchy of needs was expanded, leading to his ERG theory (existence, relatedness and growth). Physiological and safety, the lower order needs, are placed in the existence category, Love and self esteem needs in the relatedness category. The growth category contained the self actualization and self esteem needs.
- Self-Determination Theory
Self-determination theory, developed by Edward Deci and Richard Ryan, focuses on the importance of intrinsic motivation in driving human behavior. Like Maslow’s hierarchical theory and others that built on it, SDT posits a natural tendency toward growth and development. Unlike these other theories, however, SDT does not include any sort of «autopilot» for achievement, but instead requires active encouragement from the environment. The primary factors that encourage motivation and development are autonomy, competence feedback, and relatedness.[4]
Social learning theories state that watching the actions of other can prove the most influential on the actions we take.
Social cognition theories elaborate on the three way relationship between personal qualities, behavior, and society. Theorists in this school write that all three can affect the other for good or bad.
Spiritual Theories
Spiritual theories attempt to find meaning in our lives and to develop the underlying spiritual goals towards which we act.
Achievement Motivation
Goal-setting theory is based on the notion that individuals sometimes have a drive to reach a clearly defined end state. Often, this end state is a reward in itself. A goal’s efficiency is affected by three features: proximity, difficulty and specificity. An ideal goal should present a situation where the time between the initiation of behavior and the end state is close in time. This explains why some children are more motivated to learn how to ride a bike than mastering algebra. A goal should be moderate, not too hard or too easy to complete. In both cases, most people are not optimally motivated, as many want a challenge (which assumes some kind of insecurity of success). At the same time people want to feel that there is a substantial probability that they will succeed. Specificity concerns the description of the goal. The goal should be objectively defined and intelligible for the individual. A classic example of a poorly specified goal is to get the highest possible grade. Most children have no idea how much effort they need to reach that goal.
Controlling motivation
The control of motivation is only understood to a limited extent. There are many different approaches of motivation training, but many of these are considered pseudoscientific by critics. To understand how to control motivation it is first necessary to understand why many people lack motivation.
Early programming
Modern imaging has provided solid empirical support for the psychological theory that emotional programming is largely defined in childhood. Harold Chugani, Medical Director of the PET Clinic at the Children’s Hospital of Michigan and professor of pediatrics, neurology and radiology at Wayne State University School of Medicine, has found that children’s brains are much more capable of consuming new information (linked to emotions) than those of adults. Brain activity in cortical regions is about twice as high in children as in adults from the third to the ninth year of life. After that period, it declines constantly to the low levels of adulthood. Brain volume, on the other hand, is already at about 95 percent of adult levels in the ninth year of life.
Organization
Besides the very direct approaches to motivation, beginning in early life, there are solutions which are more abstract but perhaps nevertheless more practical for self-motivation. Virtually every motivation guidebook includes at least one chapter about the proper organization of one’s tasks and goals. It is usually suggested that it is critical to maintain a list of tasks, with a distinction between those which are completed and those which are not, thereby moving some of the required motivation for their completion from the tasks themselves into a «meta-task,» namely the processing of the tasks in the task list, which can become a routine. The viewing of the list of completed tasks may also be considered motivating, as it can create a satisfying sense of accomplishment.
Most electronic to-do lists have this basic functionality, although the distinction between completed and non-completed tasks is not always clear (completed tasks are sometimes simply deleted, instead of kept in a separate list).
Other forms of information organization may also be motivational, such as the use of mind maps to organize one’s ideas, and thereby «train» the neural network that is the human brain to focus on the given task. Simpler forms of idea notation such as simple bullet-point style lists may also be sufficient, or even more useful to less visually oriented persons.
Drugs
Neurobiological evidence supports the idea that addictive drugs such as cocaine, nicotine, alcohol, and heroin act on brain systems underlying motivation for natural rewards, such as the mesolimbic dopamine system. Normally, these brain systems serve to guide us toward fitness-enhancing rewards (food, water, sex, etc.), but they can be co-opted by repeated use of drugs of abuse, causing addicts to excessively pursue drug rewards. Therefore, drugs can hijack brain systems underlying other motivations, causing the almost singular pursuit of drugs characteristic of addiction.[5]
Applications
Education
Motivation is of particular interest to Educational psychologists because of the crucial role it plays in student learning. However, the specific kind of motivation that is studied in the specialized setting of education differs qualitatively from the more general forms of motivation studied by psychologists in other fields.
Motivation in education can have several effects on how students learn and their behavior towards subject matter.[6] It can:
- Direct behavior toward particular goals
- Lead to increased effort and energy
- Increase initiation of, and persistence in, activities
- Enhance cognitive processing
- Determine what consequences are reinforcing
- Lead to improved performance.
Because students are not always internally motivated, they sometimes need situated motivation, which is found in environmental conditions that the teacher creates.
Business
The idea that money is a powerful motivator can be illustrated with numerous examples of theft or white-collar crime. However, Maslow and Herzberg both believed that money is not a very powerful motivator. At higher levels of the hierarchy, praise, respect, recognition, empowerment and a sense of belonging are far more powerful motivators than money, as both Abraham Maslow’s theory of motivation and Douglas McGregor argue. McGregor says of motivation:
- Motivated employees always look for better ways to do a job.
- Motivated employees are more quality oriented.
- Motivated workers are more productive.
Elton Mayo described workplace motivation in his Hawthorne studies, which revealed what has become known as the Hawthorne effect. His studies showed that workers are motivated to work harder when they perceive they are being studied. Mayo was originally intending to study the effects of lighting on employee productivity, but eventually isolated all variables and determined that by having workers believe they were being watched by their managers or others, they would in fact work harder.
Notes
- ↑ Motivation Dictionary.com. Retrieved March 6, 2008.
- ↑ Motivate Etymology Online. Retrieved March 6, 2008.
- ↑ Motivate Educational Psychology Interactive. Retrieved March 6, 2008.
- ↑ Edward Deci and Richard M. Ryan, Intrinsic motivation and self-determination in human behavior (New York, NY: Plenum, 1985, ISBN 0306420228).
- ↑ Cdk5 Modulates Cocaine Reward, Motivation, and Striatal Neuron Excitability Journal of Neuroscience. Retrieved March 6, 2008.
- ↑ Jeanne Ellis Ormrod, Educational Psychology: Developing Learners, (Prentice Hall, 2007, ISBN 0136127029).
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Bentham, J. An Introduction to the Principles of Morals and Legislation. Adamand Media, 2005. ISBN 1402185642
- Deci, Edward. Why We Do What We Do: Understanding Self-Motivation. Penguin, 1996. ISBN 0140255265
- Deci, Edward and Richard M. Ryan. Intrinsic Motivation and Self-determination in Human Behavior. New York, NY: Plenum, 1985. ISBN 0306420228
- Huitt, W. Motivation to Learn: An Overview Educational Psychology Interactive. Valdosta, GA: Valdosta State University, 2001. Retrieved March 6, 2008.
- Ormrod, Jeanne Ellis. Educational Psychology: Developing Learners. Prentice Hall, 2007. ISBN 0136127029
- Reeve, Johnmarshall. Understanding Motivation and Emotion. Wiley, 2004. ISBN 0471456195
- Schunk, Dale. Motivation in Education: Theory, Research, and Applications. Prentice Hall, 2007. ISBN 0132281554
- Thomas, Kenneth. Intrinsic Motivation at Work: Building Energy and Commitment. Berret-Koehler Publishers, 2002. ISBN 1576752380
External links
All links retrieved November 10, 2022.
- Helping People to Motivate Themselves and Others
- Daily Motivation Steps
- Motivating Your Staff
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article
in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
- Motivation history
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
- History of «Motivation»
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
Article shared by :
The term ‘motivation’ has been derived from the word ‘motive’. Motive may be defined as an inner state of our mind that activates and directs our behaviour. It makes us move to act. It is always internal to us and is externalized via our behaviour. Motivation is one’s willingness to exert efforts towards the accomplishment of his/her goal. Let us consider a few important definitions on motivation that will help us understand the meaning of motivation more clearly.
Fred Luthans defined motivation as a “process that starts with a physiological or psychological deficiency or need that activates behaviour or a drive that is aimed at a goal or incentive”.
According to Stephen P. Robbins “motivation is the willingness to exert high levels of efforts toward organisational goals, conditioned by the effort ability to satisfy some individual need”.
In the opinion of Gray and Starke “motivation is the result of processes, internal or external to the individual, that arouse enthusiasm and persistence to pursue a certain course of action”.
After going through the above definitions, motivation can be defined very simply as the willingness to exert towards the accomplishment of goal or need.
Motivation Cycle or Process:
As stated earlier, motivation is a process or cycle aimed at accomplishing some goals. The basic elements included in the process are motives, goals and behaviour. A brief mention of these follows:
Motives:
Almost all human behaviour is motivated. It requires no motivation to grow hair, but getting a hair cut does. Motives prompt people to action. Hence, these are at the very heart of motivational process. Motives provide an activating thrust towards reaching a goal. The examples of the needs for food and water are translated into the hunger and thrust drives or motives. Similarly, the need for friends becomes a motive for affiliation.
Goals:
Motives are generally directed towards goals. Motives generally create a state of physiological or psychological imbalance. Attaining goals restores balance. For example, a goal exists when the body of the man is deprived of food or water or one’s personality is deprived of friends or companions.
Behaviour:
Behaviour is a series of activities to be undertaken. Behaviour is directed to achieve a goal. For example, the man goes to saloon to cut his hair. Diagrammed simply, the cycle or process of motivation is presented in Figure 17.1 as follows:

Importance of motivation:
The need for and importance of motivation can be imbued with multiplicity of justifications as follows:
1. Organisations are run by people. Hence, mangers cannot afford to avoid a concern with human behaviour at work. This is because the motivated employees are more productive and quality- conscious than apathetic ones.
2. Motivation as a pervasive concept affects and is also affected by a host of factors in the organisational milieu. It enables managers to understand why people behave as they behave.
3. Organisational effectiveness becomes, to some extent, the question of management’s ability to motivate its employees. Hence, an appreciation of motivation helps the managers how to motivate their employees.
4. Machines become necessary in case of complex technology. However, these remain inefficient vehicles of effective and efficient operations without man to operate them. Therefore, organisations need to have employees with required capability and willingness to use the advanced complex technology to achieve the organisational goal.
5. With the realisation that organisations will run in more complex milieu in future, an increasing attention has been given to develop employees as future resources (a ‘talent bank’). This facilitates the managers to draw upon them as and when organisations grow and develop.
In sum and substance, the need for and significance of motivation for an organisation can be put as follows:
“If we compare management with driving, while the organisation is the vehicle, then motivation is the power or fuel that makes the vehicle moving”.


- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Geography & Travel
- Health & Medicine
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Literature
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- Science
- Sports & Recreation
- Technology
- Visual Arts
- World History
- On This Day in History
- Quizzes
- Podcasts
- Dictionary
- Biographies
- Summaries
- Top Questions
- Infographics
- Demystified
- Lists
- #WTFact
- Companions
- Image Galleries
- Spotlight
- The Forum
- One Good Fact
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Geography & Travel
- Health & Medicine
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Literature
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- Science
- Sports & Recreation
- Technology
- Visual Arts
- World History
- Britannica Explains
In these videos, Britannica explains a variety of topics and answers frequently asked questions. - Britannica Classics
Check out these retro videos from Encyclopedia Britannica’s archives. - Demystified Videos
In Demystified, Britannica has all the answers to your burning questions. - #WTFact Videos
In #WTFact Britannica shares some of the most bizarre facts we can find. - This Time in History
In these videos, find out what happened this month (or any month!) in history.
- Student Portal
Britannica is the ultimate student resource for key school subjects like history, government, literature, and more. - COVID-19 Portal
While this global health crisis continues to evolve, it can be useful to look to past pandemics to better understand how to respond today. - 100 Women
Britannica celebrates the centennial of the Nineteenth Amendment, highlighting suffragists and history-making politicians. - Saving Earth
Britannica Presents Earth’s To-Do List for the 21st Century. Learn about the major environmental problems facing our planet and what can be done about them! - SpaceNext50
Britannica presents SpaceNext50, From the race to the Moon to space stewardship, we explore a wide range of subjects that feed our curiosity about space!