Recent Examples on the Web
Compared to a full reveal of the 2024 Toyota Tacoma, this teaser is a bit of a snooze.
—
There was a bit of a double standard to some discussion of Reese, with some commentators criticizing the gesture, even though Clark had done the exact same thing while having a particularly strong game against Louisville previously.
—
But while the plot remains a mystery, the characters give us a bit more insight on where the film could go.
—
The time since has been a bit of a blur.
—
San Antonio’s median home price may be $310,000, but those in the market for something a bit more expensive and expansive have plenty of options in and around the Alamo City.
—
With a short commute to and from work, Grimes has a bit more time to focus on his country music career.
—
Wrestler of the Year Coleman Nogle, Mount Saint Joseph, senior, 126 pounds To say that Coleman Nogle made the most of his senior year might be a bit of an understatement.
—
It’s been a bit of an odd offseason for Bill Belichick, who had to walk back an uncharacteristic remark at the annual league meeting to emphasize the team was not resting on its laurels.
—
The Aztecs could and probably should have taken the lead several times, but free throws — that old bugaboo — bit them at the most inopportune time.
—
The octopus fell out of the shell and bit the woman twice on her stomach, according to a Facebook post by New South Wales Ambulance, which responded to an emergency call on March 16.
—
That design stores bits in a conducting layer.
—
Of course, viewers already know the true culprit who bit Ni’jah.
—
The ‘who bit Beyonce?’ drama comes back to the spotlight in ‘Swarm’ | Credit: amazon studios; Kevin Mazur/Getty Swarm has a lot of fun with this moment.
—
Deputies in Pickaway County shot and killed a zebra after attacked a man and bit off his arm on Sunday https://t.co/Wg6vYnsLhl #10TV — 10TV (@10TV) March 13, 2023 No other injuries to humans or animals were reported.
—
Police wrote in the affidavit that one of the dogs bit someone in December, causing the victim to need several stitches on one of her fingers.
—
The dogs also injured one of the relatives and bit a first responder who tried to pull the animals off the couple, authorities said.
—
See More
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word ‘bit.’ Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
English[edit]
snaffle bit (1)
drill bit (2)
key bit (15)
Pronunciation[edit]
- enPR: bĭt, IPA(key): /bɪt/
- Rhymes: -ɪt
Etymology 1[edit]
From Middle English bitte, bite, from Old English bita (“bit; fragment; morsel”) and bite (“a bite; cut”), from Proto-Germanic *bitô and *bitiz; both from Proto-Indo-European *bʰeyd- (“to split”). More at bite.
Noun[edit]
bit (plural bits)
- A piece of metal placed in a horse’s mouth and connected to the reins to direct the animal.
-
A horse hates having a bit put in its mouth.
-
- A rotary cutting tool fitted to a drill, used to bore holes.
- (dated, Britain) A coin of a specified value.
-
a threepenny bit
-
- (obsolete, Canada) A ten-cent piece, dime.
- 1941, Emily Carr, Klee Wyck, Chapter 10, [3]
- The smallest coin we had in Canada in early days was a dime, worth ten cents. The Indians called this coin «a Bit«. Our next coin, double in buying power and in size, was a twenty-five cent piece and this the Indians called «Two Bits».
- 1941, Emily Carr, Klee Wyck, Chapter 10, [3]
- (now US) A unit of currency or coin in the Americas worth a fraction of a Spanish dollar; now specifically, an eighth of a US dollar.
-
A quarter is two bits.
- 1789, Olaudah Equiano, The Interesting Narrative, vol. I, ch. 6:
- I trusted to the Lord to be with me; and at one of our trips to St. Eustatia, a Dutch island, I bought a glass tumbler with my half bit, and when I came to Montserrat I sold it for a bit, or sixpence.
-
- (historical, US) In the southern and southwestern states, a small silver coin (such as the real) formerly current; commonly, one worth about 12½ cents; also, the sum of 12½ cents.
- A small amount of something.
-
There were bits of paper all over the floor.
-
Does your leg still hurt? —Just a bit now.
-
I’ve done my bit; I expect you to do yours.
-
- (informal) Specifically, a small amount of time.
-
I’ll be there in a bit; I need to take care of something first.
-
He was here just a bit ago, but it looks like he’s stepped out.
-
- (in the plural, informal, sports) Fractions of a second.
-
The 400 metres race was won in 47 seconds and bits.
-
- A portion of something.
-
I’d like a big bit of cake, please.
-
2013 July-August, Catherine Clabby, “Focus on Everything”, in American Scientist:
-
Not long ago, it was difficult to produce photographs of tiny creatures with every part in focus. […] A photo processing technique called focus stacking has changed that. Developed as a tool to electronically combine the sharpest bits of multiple digital images, focus stacking is a boon to biologists seeking full focus on a micron scale.
-
-
- Somewhat; something, but not very great; also used like jot and whit to express the smallest degree. See also a bit.
-
Am I bored? Not a bit of it!
- T. Hook
- My young companion was a bit of a poet.
-
- (slang) A prison sentence, especially a short one.
-
1904, The Anamosa prison press, volume 7, Iowa. Colony of Detention at Anamosa:
-
Had it not been for the influence of Mrs. Booth and Hope Hall I should still be grafting or doing a bit in some stir
-
-
1916, Thomas Mott Osborne. Warden, Sing Sing Prison, N. Y., “Prison Reform”, in The Journal of sociologic medicine, volume 17, page 407:
-
Before doing that I am going to tell you what was the result of my own incarceration, because I presume it may not be a secret to you, that I have done a «bit» myself, not the «bit» which the prosecuting attorney was so anxious to have me do.
-
-
1994, Odie Hawkins, Lost Angeles, page 158:
-
Chino didn’t make me think of Dachau or that notorious joint in Angola, Louisiana, where a brother who had done a bit there told me how they used to cut the grass on the front lawn with their fingernails.
-
-
2001, Andrew H. Vachss, Pain management:
-
Not counting the days—that’s okay for a county-time slap, but it’ll make you crazy if you’ve got years to go on a felony bit.
-
-
- An excerpt of material making up part of a show, comedy routine, etc.
-
His bit about video games was not nearly as entertaining as the other segments of his show.
-
- Short for bit part.
-
She acted her bit in the opening scene.
-
- The part of a key which enters the lock and acts upon the bolt and tumblers[1].
- The cutting iron of a plane[2].
- The bevelled front edge of an axehead along which the cutting edge runs.
- (BDSM) A gag of a style similar to a bridle.
- (MLE) A gun.
-
-
2013 December 23, Stephen Reynolds; Stephen Reynolds, director, Vendetta, spoken by Jimmy Vickers (Danny Dyer), 46:53 from the start:
-
JIMMY: I need to get my hands on some bits. If you’re still in the business. RONNIE (played by Nick Nevern): Oi! TROJAN (played by Jean-Paul Van Cauwelaert): Ronnie. {…} TROJAN: Now that is a SIG Sauer P226.
-
-
-
Synonyms[edit]
- (coin): coin, piece
- (small piece): morsel (of food), piece, scrap
- (portion): portion, share, segment
- (horse equipment): snaffle, pelham, kimberwicke
- (prison sentence): bid
Derived terms[edit]
- a bit
- a fair bit
- a little bit
- a little bit of bread and no cheese
- a lot of bit
- behind the bit
- bergy bit
- bit and bit
- bit array
- bit banging
- bit between one’s teeth
- bit bucket
- bit by bit
- bit crusher
- bit decay
- bit depth
- bit interval
- bit lifter
- bit map
- bit nibbler
- bit of all right
- bit of alright
- bit of crumpet
- bit of fluff
- bit of muslin
- bit of rough
- bit of skirt
- bit of stuff
- bit on the side
- bit part
- bit plane
- bit player
- bit rate
- bit role
- bit rot
- bit shank
- bit shift
- bit slice
- bit string
- bit stuffing
- bit-banger
- bit-bucket
- bit-compressed
- bit-count integrity
- bit-map
- bits and bobs
- bits and pieces
- bitty
- blind bit
- blown to bits
- brace and bit
- bucky bit
- cannon bit
- canon bit
- centre-bit
- chafe at the bit
- champ at the bit
- chicken bit
- chomp at the bit
- curb bit
- curb-bit
- devil’s bit
- do one’s bit
- drag bit
- every bit
- every little bit helps
- fall to bits
- fippenny bit
- Forstner bit
- German bit
- gouge bit
- hair of the dog that bit one
- high bit
- high order bit
- itty-bitty
- key bit
- lip bit
- long bit
- modesty bit
- naughty bit
- nose bit
- not a bit of it
- not a bit, not one bit
- parity bit
- pod bit
- quantum bit
- quill bit
- quite a bit
- rearing bit
- roller cone bit
- roller-cone bit
- rollercone bit
- rose bit
- sheep’s-bit
- short bit
- sign bit
- sticky bit
- the biter bit
- threepenny bit
- threepenny-bit
- tit bit
- tongue-lolling bit
- two-bit
- wait-a-bit
- weather-bit
[edit]
- bits (“genitals”)
Translations[edit]
coin of a specified value — see coin
ten-cent piece — see dime
coin worth about 12½ cents; sum of 12½ cents
small amount of something — See also translations at a little
- Armenian: կտոր (hy) (ktor)
- Bulgarian: късче (bg) n (kǎsče), частица (bg) (častica)
- Burmese: please add this translation if you can
- Catalan: mica (ca) f, poquet m
- Chamicuro: naspejka
- Chinese:
- Mandarin: please add this translation if you can
- Czech: kousek (cs) m, troška f
- Dutch: beetje (nl), hapje (nl) (of food)
- Esperanto: peco, iometa
- Estonian: please add this translation if you can
- Finnish: pala (fi), palanen (fi); osa (fi), osuus (fi) (small amount of work)
- French: petit morceau m, peu (fr) m
- German: Bisschen (de) n, Wenig n, Stück (de) n, Stückchen (de) n, Happen (de) m (of food)
- Irish: ruainne m
- Italian: poco (it) m, poca (it) f, pezzetto (it) m, pezzettino m
- Japanese: ちょっと (ja) (chotto), 少々 (ja) (しょうしょう, shōshō), 少し (ja) (すこし, sukoshi)
- Khmer: please add this translation if you can
- Korean: 작은 조각 (jageun jogak), 도막 (ko) (domak)
- Lao: please add this translation if you can
- Latin: frustum n, morsum n, pauxillum n, tantillum n
- Macedonian: парче n (parče), парченце n (parčence), трошка f (troška)
- Maori: pīhi, maramara
- Norman: morcé m (Jersey, Guernsey)
- Norwegian: bit (no) m
- Plautdietsch: Tips m, Bät n
- Polish: kawałek (pl) m inan
- Portuguese: bocado (pt) m, pedaço (pt) m, porção (pt) f, pitada (pt)
- Romanian: bucată (ro)
- Russian: кусо́к (ru) m (kusók)
- Scottish Gaelic: bìdeag f, criomag f, mìr m, car (gd) m
- Slovak: kúsok, úlomok, časť (sk)
- Slovene: košček m
- Swahili: charaza (sw)
- Swedish: bit (sv) c
- Telugu: ముక్క (te) (mukka), తుంపు (te) (tumpu), తునక (te) (tunaka)
- Thai: please add this translation if you can
- Tibetan: ཅུང་ཙམ (cung tsam), ཅུང་ཟད (cung zad), ཅུང་ཟད་ཙམ (cung zad tsam)
- Turkish: azıcık (tr), biraz (tr), gıdım (tr), parça (tr), parçacık (tr), zerre (tr)
- Vietnamese: tí (vi)
sports: fraction of a second
- Finnish: osa (fi)
portion
- Bulgarian: парче (bg) n (parče)
- Chinese:
- Mandarin: please add this translation if you can
- Czech: kousek (cs) m, dílek (cs) m
- Dutch: stuk (nl) n
- Finnish: pala (fi), palanen (fi); annos (fi)
- French: part (fr) f
- Hindi: टुकड़ा m (ṭukṛā)
- Italian: parte (it) f, porzione (it) f
- Khmer: please add this translation if you can
- Korean: 조금 (ko) (jogeum), 약간 (ko) (yakgan)
- Lao: please add this translation if you can
- Macedonian: парче n (parče)
- Maori: inati, pīhi, tiri
- Norwegian: bit (no) m
- Polish: kawałek (pl) m inan, porcja (pl) f
- Portuguese: bocado (pt) m, pedaço (pt) m, porção (pt) f
- Russian: кусо́к (ru) m (kusók)
- Scottish Gaelic: bìdeag f, criomag f, mìr m
- Slovak: kúsok, časť (sk)
- Spanish: porción (es)
- Swahili: charaza (sw)
- Swedish: bit (sv) c, lite (sv)
- Thai: please add this translation if you can
- Turkish: parça (tr)
- Vietnamese: phần (vi)
somewhat; something, but not very great — See also translations at a bit
Translations to be checked
- Breton: (please verify) gweskenn (br) f (1), (please verify) un tammig (4)
- Indonesian: (please verify) sedikit (id) (4)
- Interlingua: (please verify) morso (1), (please verify) puncta (2), (please verify) pauco, (please verify) poco, (please verify) morsello (4)
Verb[edit]
bit (third-person singular simple present bits, present participle bitting, simple past and past participle bitted)
- (transitive) To put a bridle upon; to put the bit in the mouth of (a horse).
References[edit]
- ^ 1874, Edward H. Knight, American Mechanical Dictionary
- ^ 1874, Edward H. Knight, American Mechanical Dictionary
Etymology 2[edit]
See bite
Verb[edit]
bit
- simple past tense of bite
- Your dog bit me!
- (informal in US, archaic in UK) past participle of bite, bitten
- I have been bit by your dog!
Adjective[edit]
bit (not comparable)
- (chiefly in combination) Having been bitten.
-
Even though he’s bit, of course the zombies would still chase him.
-
1984, Field & Stream, volume 89, number July, page 24:
-
Fortunately, someone who gets skeeter-bit this much may develop an immunity to the skeeter’s saliva
-
-
1992, Robert Lewis Taylor, The Travels of Jaimie McPheeters:
-
Only the year before, the conjure man had brought in the Jackson County madstone, from way over in Illinois, for a white peddler that had been dog-bit, and the man went ahead and died just the same
-
-
1998, Adele Griffin, Rainy Season, page 121:
-
He will not — he’ll tell you not to be loco, climbing up trees late at night when you’ll get bug-bit to death plus you can’t see anything
-
-
Etymology 3[edit]
Coined by John Tukey in 1946 as an abbreviation of binary digit, probably influenced by connotations of “small portion”.[1][2] First used in print 1948 by Claude Shannon.[3] Compare byte and nybble, with similar food associations.
Noun[edit]
bit (plural bits)
- (mathematics, computing) A binary digit, generally represented as a 1 or 0.
- (computing) The smallest unit of storage in a digital computer, consisting of a binary digit.
- Synonym: b
- (information theory, cryptography) Any datum that may take on one of exactly two values.
-
status bits on IRC
-
permission bits in a file system
-
- (information theory) A unit of measure for information entropy.
-
2011 May 17, Lisa Grossman, “Entropy Is Universal Rule of Language”, in Wired Science[4], retrieved 2012-09-26:
- The researchers found that the original texts spanned a variety of entropy values in different languages, reflecting differences in grammar and structure.
But strangely, the difference in entropy between the original, ordered text and the randomly scrambled text was constant across languages. This difference is a way to measure the amount of information encoded in word order, Montemurro says. The amount of information lost when they scrambled the text was about 3.5 bits per word.
- The researchers found that the original texts spanned a variety of entropy values in different languages, reflecting differences in grammar and structure.
-
- A microbitcoin, or a millionth of a bitcoin (0.000001 BTC).
Hyponyms[edit]
- hidden bit
- high-order bit
- least significant bit
- most significant bit
- qubit
Derived terms[edit]
- 128-bit
- 16-bit
- 32-bit
- 64-bit
- 7-bit
- 8-bit
- bit-depth
- biter
- bitstream
- bitwise
Translations[edit]
math: binary digit
- Bulgarian: бит (bg) m (bit)
- Czech: bit (cs) m
- Dutch: bit (nl) m
- Esperanto: bito
- Finnish: bitti (fi)
- French: bit (fr) m
- German: Bit (de) n
- Greek: δυφίο (el) n (dyfío)
- Gujarati: દ્વયંક (dvayaṅk)
- Hebrew: ביט (he) m
- Hindi: द्वयंक (dvayaṅk)
- Hungarian: bit (hu)
- Icelandic: biti, tvíundatölustafur
- Ido: bico (io)
- Irish: giotán
- Japanese: ビット (ja) (bitto)
- Latvian: bits m
- Lithuanian: bitas (lt) m
- Macedonian: бит m (bit)
- Marathi: द्वयंक (dvayaṅka)
- Nepali: द्वयंक (dvayaṅka)
- Portuguese: bit (pt) m
- Russian: бит (ru) m (bit)
- Slovak: bit m
- Slovene: bit m
- Spanish: binio m
- Swahili: charaza (sw)
- Swedish: bit (sv) c
- Turkish: bit (tr)
- Ukrainian: біт m (bit)
computing: smallest unit of storage
- Arabic: please add this translation if you can
- Armenian: բիթ (hy) (bitʿ)
- Bulgarian: бит (bg) m (bit)
- Chinese:
- Cantonese: 位元 (wai6 jyun4), 二進制位/二进制位 (ji6 zeon3 zai3 wai6-2), 二進制位元/二进制位元 (ji6 zeon3 zai3 wai6 jyun4)
- Mandarin: 位 (zh) (wèi), 比特 (zh) (bǐtè), 位元 (zh) (wèiyuán), 二進位元/二进位元 (èrjìn wèiyuán) (Taiwan), 二進制位元/二进制位元 (èrjìnzhì wèiyuán) (Taiwan), 二進制數字/二进制数字 (èrjìnzhì shùzì), 二進制位/二进制位 (èrjìnzhì wèi)
- Min Nan: 位元 (zh-min-nan) (ūi-gôan)
- Czech: bit (cs) m
- Dutch: bit (nl) m
- Esperanto: bito, duumo
- Estonian: please add this translation if you can
- Finnish: bitti (fi)
- Georgian: ბიტი (biṭi)
- German: Bit (de) n
- Greek: μπιτ (el) n (bit), δυφίο (el) n (dyfío), δυαδικό ψηφίο (el) n (dyadikó psifío)
- Hebrew: ביט (he) m (bit)
- Hungarian: bit (hu)
- Icelandic: biti, tvíundatölustafur
- Japanese: ビット (ja) (bitto)
- Korean: 비트 (biteu)
- Latvian: bits m
- Lithuanian: bitas (lt) m
- Macedonian: бит m (bit)
- Polish: bit (pl) m
- Portuguese: bit (pt) m
- Romanian: bit (ro) m
- Russian: бит (ru) m (bit)
- Slovak: bit
- Slovene: bit m
- Spanish: binio m
- Swahili: charaza (sw)
- Swedish: bit (sv) c
- Thai: please add this translation if you can
- Turkish: bit (tr)
- Vietnamese: bit (vi)
information theory: unit of measure for information entropy
- Esperanto: bito
Translations to be checked
- Indonesian: (please verify) bit (id) (5,6)
- Interlingua: (please verify) bit (5,6)
See also[edit]
- ban, nat, qubit
References[edit]
- ^ “Six Receive Honorary Degrees at Princeton Commencement”, in (please provide the title of the work)[1], (please provide a date or year), archived from the original on 2002-02-09
- ^ (please provide the title of the work)[2], accessed 23 March 2007, archived from the original on 2007-03-03
- ^ Claude Shannon (July 1948), “A Mathematical Theory of Communication”, in The Bell System Technical Journal, →DOI
Anagrams[edit]
- Bti, ITB, TBI, TiB, tib
Azerbaijani[edit]
| Cyrillic | бит |
|---|---|
| Perso-Arabic | بیت |
Etymology[edit]
From Proto-Turkic *bït (“louse”).
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): [bit]
Noun[edit]
bit (definite accusative biti, plural bitlər)
- louse
Declension[edit]
| Declension of bit | ||
|---|---|---|
| singular | plural | |
| nominative | bit | bitlər |
| definite accusative | biti | bitləri |
| dative | bitə | bitlərə |
| locative | bitdə | bitlərdə |
| ablative | bitdən | bitlərdən |
| definite genitive | bitin | bitlərin |
| Possessive forms of bit | ||
|---|---|---|
| nominative | ||
| singular | plural | |
| mənim (“my”) | bitim | bitlərim |
| sənin (“your”) | bitin | bitlərin |
| onun (“his/her/its”) | biti | bitləri |
| bizim (“our”) | bitimiz | bitlərimiz |
| sizin (“your”) | bitiniz | bitləriniz |
| onların (“their”) | biti or bitləri | bitləri |
| accusative | ||
| singular | plural | |
| mənim (“my”) | bitimi | bitlərimi |
| sənin (“your”) | bitini | bitlərini |
| onun (“his/her/its”) | bitini | bitlərini |
| bizim (“our”) | bitimizi | bitlərimizi |
| sizin (“your”) | bitinizi | bitlərinizi |
| onların (“their”) | bitini or bitlərini | bitlərini |
| dative | ||
| singular | plural | |
| mənim (“my”) | bitimə | bitlərimə |
| sənin (“your”) | bitinə | bitlərinə |
| onun (“his/her/its”) | bitinə | bitlərinə |
| bizim (“our”) | bitimizə | bitlərimizə |
| sizin (“your”) | bitinizə | bitlərinizə |
| onların (“their”) | bitinə or bitlərinə | bitlərinə |
| locative | ||
| singular | plural | |
| mənim (“my”) | bitimdə | bitlərimdə |
| sənin (“your”) | bitində | bitlərində |
| onun (“his/her/its”) | bitində | bitlərində |
| bizim (“our”) | bitimizdə | bitlərimizdə |
| sizin (“your”) | bitinizdə | bitlərinizdə |
| onların (“their”) | bitində or bitlərində | bitlərində |
| ablative | ||
| singular | plural | |
| mənim (“my”) | bitimdən | bitlərimdən |
| sənin (“your”) | bitindən | bitlərindən |
| onun (“his/her/its”) | bitindən | bitlərindən |
| bizim (“our”) | bitimizdən | bitlərimizdən |
| sizin (“your”) | bitinizdən | bitlərinizdən |
| onların (“their”) | bitindən or bitlərindən | bitlərindən |
| genitive | ||
| singular | plural | |
| mənim (“my”) | bitimin | bitlərimin |
| sənin (“your”) | bitinin | bitlərinin |
| onun (“his/her/its”) | bitinin | bitlərinin |
| bizim (“our”) | bitimizin | bitlərimizin |
| sizin (“your”) | bitinizin | bitlərinizin |
| onların (“their”) | bitinin or bitlərinin | bitlərinin |
Catalan[edit]
Pronunciation[edit]
- (Balearic, Central, Valencian) IPA(key): /ˈbit/
- Rhymes: -it
Noun[edit]
bit m (plural bits)
- (computing) bit
Czech[edit]
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): [ˈbɪt]
- Rhymes: -ɪt
- Homophone: byt
Etymology 1[edit]
Borrowed from English bit, from binary digit.
Noun[edit]
bit m
- (computing) bit
Declension[edit]
Derived terms[edit]
- bitový
- gigabit
- kilobit
- megabit
- osmibitový
- šestnáctibitový
- terabit
Etymology 2[edit]
See the etymology of the corresponding lemma form.
Verb[edit]
bit
- masculine singular passive participle of bít
Further reading[edit]
- bit in Kartotéka Novočeského lexikálního archivu
- bit in Slovník spisovného jazyka českého, 1960–1971, 1989
- bit in Akademický slovník cizích slov, 1995, at prirucka.ujc.cas.cz
Dutch[edit]
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): /bɪt/
- Hyphenation: bit
- Rhymes: -ɪt
Etymology 1[edit]
Ablaut of bijten.
Noun[edit]
bit n (plural bitten, diminutive bitje n)
- bit (for a working animal)
- bit (rotary cutting tool)
- mouthguard
Etymology 2[edit]
From English bit.
Noun[edit]
bit m (plural bits, diminutive bitje n)
- bit (binary digit)
- bit (unit of storage)
- bit (datum with two possible values)
French[edit]
Etymology[edit]
From English.
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): /bit/
Noun[edit]
bit m (plural bits)
- (computing) bit
Derived terms[edit]
- bit le moins significatif
- bit le plus significatif
Further reading[edit]
- “bit”, in Trésor de la langue française informatisé [Digitized Treasury of the French Language], 2012.
Hungarian[edit]
Etymology[edit]
From English bit.[1]
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): [ˈbit]
- Hyphenation: bit
- Rhymes: -it
Noun[edit]
bit (plural bitek)
- (computing) bit (binary digit)
Declension[edit]
| Inflection (stem in -e-, front unrounded harmony) | ||
|---|---|---|
| singular | plural | |
| nominative | bit | bitek |
| accusative | bitet | biteket |
| dative | bitnek | biteknek |
| instrumental | bittel | bitekkel |
| causal-final | bitért | bitekért |
| translative | bitté | bitekké |
| terminative | bitig | bitekig |
| essive-formal | bitként | bitekként |
| essive-modal | — | — |
| inessive | bitben | bitekben |
| superessive | biten | biteken |
| adessive | bitnél | biteknél |
| illative | bitbe | bitekbe |
| sublative | bitre | bitekre |
| allative | bithez | bitekhez |
| elative | bitből | bitekből |
| delative | bitről | bitekről |
| ablative | bittől | bitektől |
| non-attributive possessive — singular |
bité | biteké |
| non-attributive possessive — plural |
bitéi | bitekéi |
| Possessive forms of bit | ||
|---|---|---|
| possessor | single possession | multiple possessions |
| 1st person sing. | bitem | bitjeim |
| 2nd person sing. | bited | bitjeid |
| 3rd person sing. | bitje | bitjei |
| 1st person plural | bitünk | bitjeink |
| 2nd person plural | bitetek | bitjeitek |
| 3rd person plural | bitjük | bitjeik |
Derived terms[edit]
- jelzőbit
References[edit]
- ^ Tótfalusi, István. Idegenszó-tár: Idegen szavak értelmező és etimológiai szótára (’A Storehouse of Foreign Words: an explanatory and etymological dictionary of foreign words’). Budapest: Tinta Könyvkiadó, 2005. →ISBN
Indonesian[edit]
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): [ˈbɪt]
- Hyphenation: bit
Etymology 1[edit]
From English bit (“binary digit”), from Middle English bitte, bite, from Old English bita (“bit; fragment; morsel”) and bite (“a bite; cut”), from Proto-Germanic *bitô and *bitiz; both from Proto-Indo-European *bʰeyd- (“to split”).
Noun[edit]
bit (first-person possessive bitku, second-person possessive bitmu, third-person possessive bitnya)
- (computing) bit, smallest unit of storage.
Etymology 2[edit]
From Dutch biet, from Middle Dutch bete, from Latin bēta.
Noun[edit]
bit (first-person possessive bitku, second-person possessive bitmu, third-person possessive bitnya)
- Beta vulgaris, common beet, beetroot, sugar beet, and chard.
Further reading[edit]
- “bit” in Kamus Besar Bahasa Indonesia, Jakarta: Language Development and Fostering Agency — Ministry of Education, Culture, Research, and Technology of the Republic Indonesia, 2016.
Lashi[edit]
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): /bit/
Noun[edit]
bit
- sun
References[edit]
- Hkaw Luk (2017) A grammatical sketch of Lacid[5], Chiang Mai: Payap University (master thesis)
Lower Sorbian[edit]
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): /bʲit/
Verb[edit]
bit
- supine of biś
Nigerian Pidgin[edit]
Etymology[edit]
From English beat.
Verb[edit]
bit
- beat
Norwegian Bokmål[edit]
Etymology 1[edit]
From Old Norse biti.
Noun[edit]
bit m (definite singular biten, indefinite plural biter, definite plural bitene)
- a bit, piece (of something)
- a bite, mouthful (of food)
Derived terms[edit]
- isbit
- smakebit
Etymology 2[edit]
From English bit (binary digit).
Noun[edit]
bit m (definite singular biten, indefinite plural bit or biter, definite plural bitene)
- a bit (binary digit)
References[edit]
- “bit” in The Bokmål Dictionary.
Norwegian Nynorsk[edit]
Etymology 1[edit]
From Old Norse.
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): /biːt/
Noun[edit]
bit m (definite singular biten, indefinite plural bitar, definite plural bitane)
- a bit, piece (of something)
Derived terms[edit]
- isbit
- smakebit
Etymology 2[edit]
From English bit (binary digit).
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): /bɪtː/
Noun[edit]
bit m (definite singular biten, indefinite plural bit or bitar, definit plural bitane)
- a bit (binary digit)
Etymology 3[edit]
From Old Norse bit.
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): /biːt/
Noun[edit]
bit n (definite singular bitet, indefinite plural bit, definite plural bita)
- a bite (e.g. insect bite, dog bite)
- a bite, mouthful (of food)
Etymology 4[edit]
From the first person singular present indicative of Old Norse bíta, and from the second person singular imperative Old Norse bíta.
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): /biːt/
Verb[edit]
bit
- inflection of bite:
- present
- imperative
References[edit]
- “bit” in The Nynorsk Dictionary.
Old Irish[edit]
Verb[edit]
bit
- third-person plural future of is
Polish[edit]
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): /bit/
- Rhymes: -it
- Syllabification: bit
- Homophone: bid
Etymology 1[edit]
Borrowed from English bit.
Noun[edit]
bit m inan
- (mathematics, computing) bit (binary digit, generally represented as a 1 or 0)
- bit informacji ― a bit of information
- bit po bicie ― bit by bit
Declension[edit]
The genitive singular form bita is overall less common.
Derived terms[edit]
- bitowy
[edit]
- bitmapowy
- bitmapa
Etymology 2[edit]
Borrowed from English beat.
Noun[edit]
bit m inan
- beat (instrumental portion of a piece of hip-hop music)
- (music) beat (rhythm signalled by a conductor or other musician to the members of a group of musicians)
Declension[edit]
Alternative forms[edit]
- beat
Etymology 3[edit]
Borrowed from English drill bit.
Noun[edit]
bit m inan
- drill bit
Declension[edit]
Etymology 4[edit]
Borrowed from English big beat.
Alternative forms[edit]
- beat
Noun[edit]
bit m inan
- big beat (form of pop music having distorted breakbeats at a moderate tempo)
- Synonym: big-beat
- polski bit ― Polish big beat
Declension[edit]
Further reading[edit]
- bit in Wielki słownik języka polskiego, Instytut Języka Polskiego PAN
- bit in Polish dictionaries at PWN
Portuguese[edit]
Etymology[edit]
Unadapted borrowing from English bit.
Pronunciation[edit]
- (Brazil) IPA(key): /ˈbi.t͡ʃi/
- (Southern Brazil) IPA(key): /ˈbi.te/
- (Portugal) IPA(key): /ˈbi.t(ɨ)/
Noun[edit]
bit m (plural bits)
- (mathematics, computing) bit (binary digit)
Synonyms[edit]
- Abbreviations: b
Coordinate terms[edit]
- Multiples: kilobit, megabit, gigabit, terabit, petabit, exabit, zettabit, yottabit
[edit]
- byte (unit equivalent to 8 bits)
Romanian[edit]
Etymology[edit]
From English bit or French bit.
Noun[edit]
bit m (plural biți)
- (computing) bit
Declension[edit]
Declension of bit
| singular | plural | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| indefinite articulation | definite articulation | indefinite articulation | definite articulation | |
| nominative/accusative | (un) bit | bitul | (niște) biți | biții |
| genitive/dative | (unui) bit | bitului | (unor) biți | biților |
| vocative | bitule | biților |
Saterland Frisian[edit]
Etymology[edit]
Related to German bis.
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): /bɪt/
- Hyphenation: bit
- Rhymes: -ɪt
Conjunction[edit]
bit
- until
Preposition[edit]
bit
- until, to
Derived terms[edit]
- bit tou
References[edit]
- Marron C. Fort (2015), “bit”, in Saterfriesisches Wörterbuch mit einer phonologischen und grammatischen Übersicht, Buske, →ISBN
Scots[edit]
Adjective[edit]
bit
- Little.
- 1889, Jessup Whitehead, The Steward’s Handbook and Guide to Party Catering (page 439)
- A bit wee lambie
- 1902, John Buchan, The Outgoing of the Tide
- He laid a hundred guineas with the laird of Slofferfield that he would drive four horses through the Slofferfield loch, and in the prank he had his bit chariot dung to pieces and a good mare killed.
- 1889, Jessup Whitehead, The Steward’s Handbook and Guide to Party Catering (page 439)
Serbo-Croatian[edit]
Etymology 1[edit]
From bȉti (“to be”).
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): /bîːt/
Noun[edit]
bȋt f (Cyrillic spelling би̑т)
- essence
- point, meaning
Declension[edit]
Etymology 2[edit]
From English bit.
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): /bît/
Noun[edit]
bȉt m (Cyrillic spelling би̏т)
- (computing) bit
Declension[edit]
Slavomolisano[edit]
Etymology[edit]
From Serbo-Croatian biti, from Proto-Slavic *byti, from Proto-Balto-Slavic *bū́ˀtei, from Proto-Indo-European *bʰuH-.
Verb[edit]
bit pf or impf
- to be
References[edit]
- Walter Breu and Giovanni Piccoli (2000), Dizionario croato molisano di Acquaviva Collecroce: Dizionario plurilingue della lingua slava della minoranza di provenienza dalmata di Acquaviva Collecroce in Provincia di Campobasso (Parte grammaticale)., pp. 409–412
Spanish[edit]
Etymology[edit]
From English bit.
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): /ˈbit/ [ˈbit̪]
- Rhymes: -it
- Syllabification: bit
Noun[edit]
bit m (plural bits)
- bit (binary digit)
Further reading[edit]
- “bit”, in Diccionario de la lengua española, Vigésima tercera edición, Real Academia Española, 2014
Swedish[edit]
Etymology[edit]
From Old Norse biti, noun definitions 2 and 4: From English bit, from binary digit.
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): /biːt/ (1–4)
- IPA(key): /bɪt/ (3–4)
Noun[edit]
bit c
- bit, a piece (small piece)
- bit (portion)
- bit (binary digit)
- bit (unit of storage)
- bit, a tune (piece of music)
Declension[edit]
| Declension of bit | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | Plural | |||
| Indefinite | Definite | Indefinite | Definite | |
| Nominative | bit | biten | bitar | bitarna |
| Genitive | bits | bitens | bitars | bitarnas |
Derived terms[edit]
- bitsocker (“sugar in the form of sugar cubes, lump sugar”)
- pusselbit (“puzzle piece”)
- sockerbit (“sugar cube”)
Verb[edit]
bit
- imperative of bita.
Turkish[edit]
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): /ˈbit/
Etymology 1[edit]
From Ottoman Turkish بیت, بت, from Proto-Turkic *bït (“louse”).
Noun[edit]
bit (definite accusative biti, plural bitler)
- (zoology) louse
Declension[edit]
| Inflection | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative | bit | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Definite accusative | biti | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Singular | Plural | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nominative | bit | bitler | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Definite accusative | biti | bitleri | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dative | bite | bitlere | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locative | bitte | bitlerde | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ablative | bitten | bitlerden | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Genitive | bitin | bitlerin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Derived terms[edit]
- bit yeniği (fishy)
- bitli (lousy)
See also[edit]
- pire (flea)
Etymology 2[edit]
Borrowed from English bit, abbreviation of binary digit.
Noun[edit]
bit (definite accusative biti, plural bitler)
- (computing) bit
Declension[edit]
| Inflection | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative | bit | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Definite accusative | biti | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Singular | Plural | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nominative | bit | bitler | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Definite accusative | biti | bitleri | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dative | bite | bitlere | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locative | bitte | bitlerde | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ablative | bitten | bitlerden | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Genitive | bitin | bitlerin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Etymology 3[edit]
Verb[edit]
bit
- second-person singular imperative of bitmek
Turkmen[edit]
Etymology[edit]
From Proto-Turkic *bït (“louse”). Cognate with Old Turkic [script needed] (bit), Turkish bit (“louse”), etc.
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): /bit̪/
Noun[edit]
bit (definite accusative bidi, plural bitler)
- (zoology) louse
Declension[edit]
Vietnamese[edit]
Pronunciation[edit]
- (Hà Nội) IPA(key): [ʔɓit̚˧˧]
- (Huế) IPA(key): [ʔɓit̚˧˧]
- (Hồ Chí Minh City) IPA(key): [ʔɓɨt̚˧˧]
-
Audio (Ho Chi Minh City) (file)
Noun[edit]
bit
- (computing) bit
Zhuang[edit]
Pronunciation[edit]
- (Standard Zhuang) IPA(key): /pit˥/
- Tone numbers: bit7
- Hyphenation: bit
Etymology 1[edit]
From Proto-Tai *pitᴰ (“duck”). Cognate with Thai เป็ด (bpèt), Lao ເປັດ (pet), Lü ᦵᦔᧆ (ṗed), Tai Dam ꪹꪜꪸꪒ, Shan ပဵတ်း (páet), Ahom 𑜆𑜢𑜄𑜫 (pit), Bouyei bidt, Saek ปิ๊ด. Compare Old Chinese 鴄 (OC *pʰid).
Noun[edit]
bit (classifier duz, Sawndip forms 鴓 or 𱈶 or ⿰品鳥, 1957–1982 spelling bit)
- duck
Derived terms[edit]
- roegbit
Etymology 2[edit]
From Chinese 筆 (MC pˠiɪt̚).
Noun[edit]
bit (classifier gaiq, Sawndip forms 𣭈 or 𰚎, 1957–1982 spelling bit)
- pen; pencil; writing implement
Classifier[edit]
bit (1957–1982 spelling bit)
- Classifier for sums of money and deals.
Etymology 3[edit]
From Chinese 匹 (MC pʰiɪt̚).
Classifier[edit]
bit (1957–1982 spelling bit)
- Classifier for cloth: bolt of
| Word | BIT |
| Character | 3 |
| Hyphenation | bit |
| Pronunciations | /bɪt/ |
Sorry, your browser does not support the audio element!
What do we mean by bit?
The sharp part of a tool, such as the cutting edge of a knife or ax. noun
A pointed and threaded tool for drilling and boring that is secured in a brace, bitstock, or drill press. noun
The part of a key that enters the lock and engages the bolt and tumblers. noun
The tip of the mouthpiece on a pipe or a cigarette or cigar holder. noun
The metal mouthpiece of a bridle, serving to control, curb, and direct an animal. noun
Something that controls, guides, or curbs. noun
To place a bit in the mouth of (a horse, for example). transitive verb
To check or control with or as if with a bit. transitive verb
To make or grind a bit on (a key). transitive verb
(have/take) To be uncontrollable; cast off restraint. idiom
A binary digit, having either the value 0 or 1, used to store or represent data. noun
A small portion, degree, or amount. noun
A brief amount of time; a moment. noun
A short scene or episode in a theatrical performance. noun
A bit part. noun
An entertainment routine given regularly by a performer; an act. noun
A particular kind of action, situation, or behavior. noun
A piece of metal placed in a horse’s mouth and connected to the reins to direct the animal.
A rotary cutting tool fitted to a drill, used to bore holes.
A coin of a specified value.
A ten-cent piece, dime.
A unit of currency or coin in the Americas worth a fraction of a Spanish dollar; now specifically, an eighth of a US dollar.
In the southern and southwestern states, a small silver coin (such as the real) formerly current; commonly, one worth about 12½ cents; also, the sum of 12½ cents.
A small amount of something.
Specifically, a small amount of time.
(plural) Fractions of a second.
A portion of something.
Somewhat; something, but not very great; also used like jot and whit to express the smallest degree. See also a bit.
A prison sentence, especially a short one.
An excerpt of material making up part of a show, comedy routine, etc.
A small part or role, sometimes with spoken lines, in a theatrical performance.
The part of a key which enters the lock and acts upon the bolt and tumblers.
The cutting iron of a plane.
The bevelled front edge of an axehead along which the cutting edge runs.
A routine or section of a routine during a stand-up comedy show of approximately 1-4 jokes in length. Urban Dictionary
When someone bullshits you and you bullshit them back, sometimes continuing until someone cracks/laughs Urban Dictionary
Binary digIT — the least amount of information there is, i.e. yes or no, true or false, on or off. Eight bits make a byte Urban Dictionary
An unspecified short amount of time (usually less than an hour).
Can be used to indicate that events will follow a normal timescale, or otherwise be used to postpone an event for a time.
A ‘bit’ usually refers to the expected or average amount of time that should be taken to complete the task in question.
When postponing an event, however, a ‘bit’ can be considerably longer.
Eg, If you are due to visit a friend who lives a 15 minute drive away, to be round ‘in a bit’ could indicate that you will be there in about 1/2 hour, 15 minutes preparation to leave and 15 minutes driving.
The expression ‘in a bit’ is often used in Midland dialect as a farewell, similar to laters.
‘A bit’ should not however be confused with ‘Quite a bit’, which always indicates an unusually large amount of time (or something else), and is analogous to a ‘while’. Urban Dictionary
Prison lingo for a usually short prison sentence. Urban Dictionary
A word that is short for the term «bittie» Urban Dictionary
In the Western States after the War with Mexico U.S. coins were not commonly circulated; however the peso ( Mexican, Spanish) was common. The exchange rate (circa 1849) was one peso to one dollar. To convert small change the peso was cut in eighths. One eighth was one bit of a peso, or 12 and one half cents. Two bits was 25 cents and so on. The expression two bits or four bits or six bits is still used in this manner in the Far West, especially in Northern California. Urban Dictionary
BInary digiT. The smallest unit of information on a computer/machine. A single bit can only hold one of 2 values, either 0 or 1. Urban Dictionary
A hot girl. Only used to describe girls you want to fuck. You can’t say, for instance, your friend’s mom is a bit. Unless she really is, in which case go for it, you fuckin dog.
Shortening of biddy. Urban Dictionary
French word to tell a dick Urban Dictionary
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about the unit of information. For other uses, see Bit (disambiguation).
«Qbit (quettabit)» redirects here. For quantum bits, see Qubit.
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communications. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit.[1] The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represented as either «1» or «0«, but other representations such as true/false, yes/no, on/off, or +/− are also commonly used.
The relation between these values and the physical states of the underlying storage or device is a matter of convention, and different assignments may be used even within the same device or program. It may be physically implemented with a two-state device.
A contiguous group of binary digits is commonly called a bit string, a bit vector, or a single-dimensional (or multi-dimensional) bit array.
A group of eight bits is called one byte, but historically the size of the byte is not strictly defined.[2] Frequently, half, full, double and quadruple words consist of a number of bytes which is a low power of two. A string of four bits is a nibble.
In information theory, one bit is the information entropy of a random binary variable that is 0 or 1 with equal probability,[3] or the information that is gained when the value of such a variable becomes known.[4][5] As a unit of information, the bit is also known as a shannon,[6] named after Claude E. Shannon.
The symbol for the binary digit is either «bit» as per the IEC 80000-13:2008 standard, or the lowercase character «b», as per the IEEE 1541-2002 standard. Use of the latter may create confusion with the capital «B» which is used for the byte.
History[edit]
The encoding of data by discrete bits was used in the punched cards invented by Basile Bouchon and Jean-Baptiste Falcon (1732), developed by Joseph Marie Jacquard (1804), and later adopted by Semyon Korsakov, Charles Babbage, Hermann Hollerith, and early computer manufacturers like IBM. A variant of that idea was the perforated paper tape. In all those systems, the medium (card or tape) conceptually carried an array of hole positions; each position could be either punched through or not, thus carrying one bit of information. The encoding of text by bits was also used in Morse code (1844) and early digital communications machines such as teletypes and stock ticker machines (1870).
Ralph Hartley suggested the use of a logarithmic measure of information in 1928.[7] Claude E. Shannon first used the word «bit» in his seminal 1948 paper «A Mathematical Theory of Communication».[8][9][10] He attributed its origin to John W. Tukey, who had written a Bell Labs memo on 9 January 1947 in which he contracted «binary information digit» to simply «bit».[8] Vannevar Bush had written in 1936 of «bits of information» that could be stored on the punched cards used in the mechanical computers of that time.[11] The first programmable computer, built by Konrad Zuse, used binary notation for numbers.
Physical representation[edit]
A bit can be stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in either of two possible distinct states. These may be the two stable states of a flip-flop, two positions of an electrical switch, two distinct voltage or current levels allowed by a circuit, two distinct levels of light intensity, two directions of magnetization or polarization, the orientation of reversible double stranded DNA, etc.
Bits can be implemented in several forms. In most modern computing devices, a bit is usually represented by an electrical voltage or current pulse, or by the electrical state of a flip-flop circuit.
For devices using positive logic, a digit value of 1 (or a logical value of true) is represented by a more positive voltage relative to the representation of 0. Different logic families require different voltages, and variations are allowed to account for component aging and noise immunity. For example, in transistor–transistor logic (TTL) and compatible circuits, digit values 0 and 1 at the output of a device are represented by no higher than 0.4 volts and no lower than 2.6 volts, respectively; while TTL inputs are specified to recognize 0.8 volts or below as 0 and 2.2 volts or above as 1.
Transmission and processing[edit]
Bits are transmitted one at a time in serial transmission, and by a multiple number of bits in parallel transmission. A bitwise operation optionally processes bits one at a time. Data transfer rates are usually measured in decimal SI multiples of the unit bit per second (bit/s), such as kbit/s.
Storage[edit]
In the earliest non-electronic information processing devices, such as Jacquard’s loom or Babbage’s Analytical Engine, a bit was often stored as the position of a mechanical lever or gear, or the presence or absence of a hole at a specific point of a paper card or tape. The first electrical devices for discrete logic (such as elevator and traffic light control circuits, telephone switches, and Konrad Zuse’s computer) represented bits as the states of electrical relays which could be either «open» or «closed». When relays were replaced by vacuum tubes, starting in the 1940s, computer builders experimented with a variety of storage methods, such as pressure pulses traveling down a mercury delay line, charges stored on the inside surface of a cathode-ray tube, or opaque spots printed on glass discs by photolithographic techniques.
In the 1950s and 1960s, these methods were largely supplanted by magnetic storage devices such as magnetic-core memory, magnetic tapes, drums, and disks, where a bit was represented by the polarity of magnetization of a certain area of a ferromagnetic film, or by a change in polarity from one direction to the other. The same principle was later used in the magnetic bubble memory developed in the 1980s, and is still found in various magnetic strip items such as metro tickets and some credit cards.
In modern semiconductor memory, such as dynamic random-access memory, the two values of a bit may be represented by two levels of electric charge stored in a capacitor. In certain types of programmable logic arrays and read-only memory, a bit may be represented by the presence or absence of a conducting path at a certain point of a circuit. In optical discs, a bit is encoded as the presence or absence of a microscopic pit on a reflective surface. In one-dimensional bar codes, bits are encoded as the thickness of alternating black and white lines.
Unit and symbol[edit]
The bit is not defined in the International System of Units (SI). However, the International Electrotechnical Commission issued standard IEC 60027, which specifies that the symbol for binary digit should be ‘bit’, and this should be used in all multiples, such as ‘kbit’, for kilobit.[12] However, the lower-case letter ‘b’ is widely used as well and was recommended by the IEEE 1541 Standard (2002). In contrast, the upper case letter ‘B’ is the standard and customary symbol for byte.
|
Multiple-bit units
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Orders of magnitude of data |
Multiple bits[edit]
Multiple bits may be expressed and represented in several ways. For convenience of representing commonly reoccurring groups of bits in information technology, several units of information have traditionally been used. The most common is the unit byte, coined by Werner Buchholz in June 1956, which historically was used to represent the group of bits used to encode a single character of text (until UTF-8 multibyte encoding took over) in a computer[2][13][14][15][16] and for this reason it was used as the basic addressable element in many computer architectures. The trend in hardware design converged on the most common implementation of using eight bits per byte, as it is widely used today. However, because of the ambiguity of relying on the underlying hardware design, the unit octet was defined to explicitly denote a sequence of eight bits.
Computers usually manipulate bits in groups of a fixed size, conventionally named «words». Like the byte, the number of bits in a word also varies with the hardware design, and is typically between 8 and 80 bits, or even more in some specialized computers. In the 21st century, retail personal or server computers have a word size of 32 or 64 bits.
The International System of Units defines a series of decimal prefixes for multiples of standardized units which are commonly also used with the bit and the byte. The prefixes kilo (103) through yotta (1024) increment by multiples of one thousand, and the corresponding units are the kilobit (kbit) through the yottabit (Ybit).
Information capacity and information compression[edit]
|
|
This article needs to be updated. The reason given is: it cites a fact about global information content in computers from 2007. Please help update this section to reflect recent events or newly available information. (October 2018) |
When the information capacity of a storage system or a communication channel is presented in bits or bits per second, this often refers to binary digits, which is a computer hardware capacity to store binary data (0 or 1, up or down, current or not, etc.).[17] Information capacity of a storage system is only an upper bound to the quantity of information stored therein. If the two possible values of one bit of storage are not equally likely, that bit of storage contains less than one bit of information. If the value is completely predictable, then the reading of that value provides no information at all (zero entropic bits, because no resolution of uncertainty occurs and therefore no information is available). If a computer file that uses n bits of storage contains only m < n bits of information, then that information can in principle be encoded in about m bits, at least on the average. This principle is the basis of data compression technology. Using an analogy, the hardware binary digits refer to the amount of storage space available (like the number of buckets available to store things), and the information content the filling, which comes in different levels of granularity (fine or coarse, that is, compressed or uncompressed information). When the granularity is finer—when information is more compressed—the same bucket can hold more.
For example, it is estimated that the combined technological capacity of the world to store information provides 1,300 exabytes of hardware digits. However, when this storage space is filled and the corresponding content is optimally compressed, this only represents 295 exabytes of information.[18] When optimally compressed, the resulting carrying capacity approaches Shannon information or information entropy.[17]
Bit-based computing[edit]
Certain bitwise computer processor instructions (such as bit set) operate at the level of manipulating bits rather than manipulating data interpreted as an aggregate of bits.
In the 1980s, when bitmapped computer displays became popular, some computers provided specialized bit block transfer instructions to set or copy the bits that corresponded to a given rectangular area on the screen.
In most computers and programming languages, when a bit within a group of bits, such as a byte or word, is referred to, it is usually specified by a number from 0 upwards corresponding to its position within the byte or word. However, 0 can refer to either the most or least significant bit depending on the context.
Other information units[edit]
Similar to torque and energy in physics; information-theoretic information and data storage size have the same dimensionality of units of measurement, but there is in general no meaning to adding, subtracting or otherwise combining the units mathematically, although one may act as a bound on the other.
Units of information used in information theory include the shannon (Sh), the natural unit of information (nat) and the hartley (Hart). One shannon is the maximum amount of information needed to specify the state of one bit of storage. These are related by 1 Sh ≈ 0.693 nat ≈ 0.301 Hart.
Some authors also define a binit as an arbitrary information unit equivalent to some fixed but unspecified number of bits.[19]
See also[edit]
- Byte
- Integer (computer science)
- Primitive data type
- Trit (Trinary digit)
- Qubit (quantum bit)
- Bitstream
- Entropy (information theory)
- Bit rate and baud rate
- Binary numeral system
- Ternary numeral system
- Shannon (unit)
- Nibble
References[edit]
- ^ Mackenzie, Charles E. (1980). Coded Character Sets, History and Development. The Systems Programming Series (1 ed.). Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc. p. x. ISBN 978-0-201-14460-4. LCCN 77-90165. Archived from the original on 2016-11-18. Retrieved 2016-05-22. [1]
- ^ a b Bemer, Robert William (2000-08-08). «Why is a byte 8 bits? Or is it?». Computer History Vignettes. Archived from the original on 2017-04-03. Retrieved 2017-04-03.
[…] With IBM’s STRETCH computer as background, handling 64-character words divisible into groups of 8 (I designed the character set for it, under the guidance of Dr. Werner Buchholz, the man who DID coin the term «byte» for an 8-bit grouping). […] The IBM 360 used 8-bit characters, although not ASCII directly. Thus Buchholz’s «byte» caught on everywhere. I myself did not like the name for many reasons. […]
- ^ Anderson, John B.; Johnnesson, Rolf (2006), Understanding Information Transmission
- ^ Haykin, Simon (2006), Digital Communications
- ^ IEEE Std 260.1-2004
- ^ «Units: B». Archived from the original on 2016-05-04.
- ^ Abramson, Norman (1963). Information theory and coding. McGraw-Hill.
- ^ a b Shannon, Claude Elwood (July 1948). «A Mathematical Theory of Communication» (PDF). Bell System Technical Journal. 27 (3): 379–423. doi:10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb01338.x. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-002C-4314-2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1998-07-15.
The choice of a logarithmic base corresponds to the choice of a unit for measuring information. If the base 2 is used the resulting units may be called binary digits, or more briefly bits, a word suggested by J. W. Tukey.
- ^ Shannon, Claude Elwood (October 1948). «A Mathematical Theory of Communication». Bell System Technical Journal. 27 (4): 623–666. doi:10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb00917.x. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-002C-4314-2.
- ^ Shannon, Claude Elwood; Weaver, Warren (1949). A Mathematical Theory of Communication (PDF). University of Illinois Press. ISBN 0-252-72548-4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1998-07-15.
- ^ Bush, Vannevar (1936). «Instrumental analysis». Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society. 42 (10): 649–669. doi:10.1090/S0002-9904-1936-06390-1. Archived from the original on 2014-10-06.
- ^ National Institute of Standards and Technology (2008), Guide for the Use of the International System of Units. Online version. Archived 3 June 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Buchholz, Werner (1956-06-11). «7. The Shift Matrix» (PDF). The Link System. IBM. pp. 5–6. Stretch Memo No. 39G. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-04-04. Retrieved 2016-04-04.
[…] Most important, from the point of view of editing, will be the ability to handle any characters or digits, from 1 to 6 bits long […] the Shift Matrix to be used to convert a 60-bit word, coming from Memory in parallel, into characters, or «bytes» as we have called them, to be sent to the Adder serially. The 60 bits are dumped into magnetic cores on six different levels. Thus, if a 1 comes out of position 9, it appears in all six cores underneath. […] The Adder may accept all or only some of the bits. […] Assume that it is desired to operate on 4 bit decimal digits, starting at the right. The 0-diagonal is pulsed first, sending out the six bits 0 to 5, of which the Adder accepts only the first four (0-3). Bits 4 and 5 are ignored. Next, the 4 diagonal is pulsed. This sends out bits 4 to 9, of which the last two are again ignored, and so on. […] It is just as easy to use all six bits in alphanumeric work, or to handle bytes of only one bit for logical analysis, or to offset the bytes by any number of bits. […]
- ^ Buchholz, Werner (February 1977). «The Word «Byte» Comes of Age…» Byte Magazine. 2 (2): 144.
[…] The first reference found in the files was contained in an internal memo written in June 1956 during the early days of developing Stretch. A byte was described as consisting of any number of parallel bits from one to six. Thus a byte was assumed to have a length appropriate for the occasion. Its first use was in the context of the input-output equipment of the 1950s, which handled six bits at a time. The possibility of going to 8 bit bytes was considered in August 1956 and incorporated in the design of Stretch shortly thereafter. The first published reference to the term occurred in 1959 in a paper «Processing Data in Bits and Pieces» by G A Blaauw, F P Brooks Jr and W Buchholz in the IRE Transactions on Electronic Computers, June 1959, page 121. The notions of that paper were elaborated in Chapter 4 of Planning a Computer System (Project Stretch), edited by W Buchholz, McGraw-Hill Book Company (1962). The rationale for coining the term was explained there on page 40 as follows:
Byte denotes a group of bits used to encode a character, or the number of bits transmitted in parallel to and from input-output units. A term other than character is used here because a given character may be represented in different applications by more than one code, and different codes may use different numbers of bits (ie, different byte sizes). In input-output transmission the grouping of bits may be completely arbitrary and have no relation to actual characters. (The term is coined from bite, but respelled to avoid accidental mutation to bit.)
System/360 took over many of the Stretch concepts, including the basic byte and word sizes, which are powers of 2. For economy, however, the byte size was fixed at the 8 bit maximum, and addressing at the bit level was replaced by byte addressing. […] - ^ Blaauw, Gerrit Anne; Brooks, Jr., Frederick Phillips; Buchholz, Werner (1962), «Chapter 4: Natural Data Units» (PDF), in Buchholz, Werner (ed.), Planning a Computer System – Project Stretch, McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc. / The Maple Press Company, York, PA., pp. 39–40, LCCN 61-10466, archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-04-03, retrieved 2017-04-03
- ^ Bemer, Robert William (1959). «A proposal for a generalized card code of 256 characters». Communications of the ACM. 2 (9): 19–23. doi:10.1145/368424.368435. S2CID 36115735.
- ^ a b Information in small bits Information in Small Bits is a book produced as part of a non-profit outreach project of the IEEE Information Theory Society.
The book introduces Claude Shannon and basic concepts of Information Theory to children 8 and older using relatable cartoon stories and problem-solving activities. - ^ «The World’s Technological Capacity to Store, Communicate, and Compute Information» Archived 2013-07-27 at the Wayback Machine, especially Supporting online material Archived 2011-05-31 at the Wayback Machine, Martin Hilbert and Priscila López (2011), Science, 332(6025), 60-65; free access to the article through here: martinhilbert.net/WorldInfoCapacity.html
- ^ Bhattacharya, Amitabha (2005). Digital Communication. Tata McGraw-Hill Education. ISBN 978-0-07059117-2. Archived from the original on 2017-03-27.
External links[edit]
Look up bit in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
- Bit Calculator – a tool providing conversions between bit, byte, kilobit, kilobyte, megabit, megabyte, gigabit, gigabyte
- BitXByteConverter – a tool for computing file sizes, storage capacity, and digital information in various units
Meaning bit
What does bit mean? Here you find 192 meanings of the word bit. You can also add a definition of bit yourself
1 |
1 The tool used to crush or cut rock. Everything on a drilling rig directly or indirectly assists the bit in crushing or cutting the rock. The bit is on the bottom of the drillstring and must be changed [..]
|
2 |
1 bitRelationships Related Term: byte character set n. ~ 1. A b(inary dig)it. — 2. The smallest unit of information in a binary system. Notes: A string of bits can be used to represent a number using o [..]
|
3 |
0 bitThe smallest unit of information storage; a contraction of the term "binary digit;" one of two symbolsÑ"0" (zero) and "1" (one) — that are used t [..]
|
4 |
0 bitSee Binary digit.
|
5 |
0 bitFrom binary digit, is a basic unit of data storage, and has a value of either 0 or 1. Eight bits = one byte (See «Byte» below)
|
6 |
0 bitA bit (binary digit) is the smallest unit of digital information. Eight bits equals one byte. Digital images are often described by the number of bits used to represent each pixel, i.e., a 1-bit image [..]
|
7 |
0 bitcomputerese word, 1948 abbreviation coined by U.S. computer pioneer John W. Tukey (1915-2000) of binary digit, probably chosen for its identity with bit (n.1).
|
8 |
0 bitpast tense of bite.
|
9 |
0 bit«small piece,» c. 1200; related Old English bite «act of biting,» and bita «piece bitten off,» probably are the source of the modern words meaning «boring-piece of a [..]
|
10 |
0 bitThe smallest piece of computer information, either the number 0 or 1. In short they are called binary digits.
|
11 |
0 bitA binary digit (either 0 or 1); it is the most basic unit of data that can be recognized and processed by a computer.
|
12 |
0 bitA ‘bit’ is a basic unit of information in computing, essentially a ‘1’ or ‘0’. Bits per second (bps) is a common measure for data transmission speed. The speed in bps is [..]
|
13 |
0 bitA unit of measurement indicating the information capacity of one binary digit.
|
14 |
0 bitThe hardened and strengthened device at the end of a drill rod that transmits the energy of breakage to the rock. The size of the bit determines the size of the hole. A bit may be either detachable fr [..]
|
15 |
0 bitBit [N]the curb put into the mouths of horses to restrain them. The Hebrew word (metheg) so rendered in Psalms 32:9 is elsewhere translated «bridle» ( 2 Kings 19:28 ; Proverbs 26:3 ; Isaiah [..]
|
16 |
0 bitA binary unit of information. A small piece of sea ice; a single fragment of brash.
|
17 |
0 bithorse’s bit placed in between teeth to attach rein.
|
18 |
0 bitThe smallest unit of information in a computer, with a value of either 0 or 1.
|
19 |
0 bitBInary digiT. A 1 or a 0. The basic element of digital communication.
|
20 |
0 bit(Binary DigIT) A single digit number in base-2, in other words, either a 1 or a zero. The smallest unit of computerized data. Bandwidthis usually measured in bits-per-second. See also: Bandwidth, Bit, [..]
|
21 |
0 bitBit is a single digit in the binary numbering system (base 2). For example: 1 is a bit or 0 is a bit.
|
22 |
0 bitThe basic unit of data representation in digital computers. a memory location that can have one of two values.
|
23 |
0 bitShort for binary digit (0 or 1). Lower case b is used in abbreviations to distinguish it from bytes. For example, KBps (thousand bytes per second) is 8 times as great as Kbps (thousand bits per second [..]
|
24 |
0 bitAbbreviation for binary digit. Used in all digital communications. A bit is a binary unit, represented by either a «0» or a «1».
|
25 |
0 bitElementary unit of information/data stored as a choice between two mutually exclusive possibilities, such as 1 or 0 in binary notation.
|
26 |
0 bitspot: a small piece or quantity of something; &quot;a spot of tea&quot;; &quot;a bit of paper&quot;; &quot;a bit of lint&quot;; &quot;I gave him [..]
|
27 |
0 bitBilateral investment treaty
|
28 |
0 bitA binary digit, either a 0 or 1. In the U. S. , 8 bits make up one byte; in Europe, byte equals one word.
|
29 |
0 bitA contraction of the term binary digit. The bit is the basic unit of digital data. It may be in one of two states, logic 1 or logic 0. It may be thought of as a switch which is either on or off. Bits [..]
|
30 |
0 bitA base-level unit of information for content storage and transport, a bit can have either 0 or 1 as its value, which also refer to on/off or yes/no. Eight bits equal a byte. Various levels of bytes (k [..]
|
31 |
0 bitA bit is a single digit number that is in base of 2 (either a zero or one). Bandwidth usage is measured in bits per second.
|
32 |
0 bita small piece of something
|
33 |
0 bitAbbreviation for binary digit. 1. A character used to represent one of the two digits in the numeration system with a base of two, and only two, possible states of a physical entity or system. 2. In binary notation either of the characters 0 or 1. 3. A unit of information equal to one binary decision or the designation of one of two possible and eq [..]
|
34 |
0 bitthe smallest unit of computer memory storage capacity.
|
35 |
0 bit[from the mainstream meaning and `Binary digIT’] n. 1. [techspeak] The unit of information; the amount of information obtained by asking a yes-or-no question for which the two outcomes are equall [..]
|
36 |
0 bitA bit (an acronym standing for Binary digIT) was a unit of information stored in a computer. It was commonly represented as a zero (0) or one (1).
|
37 |
0 bitWebGuest Dictionary The smallest unit of computerized data. A bit is either "on" or "off" and is represented by "1" or "0".
|
38 |
0 bitBit is Binary Digit. It refers to a digit number, either a 0 or a 1. The binary digit is used to represent computerized data.
|
39 |
0 bitis the smallest unit of data. There are 8 bits to a byte.
|
40 |
0 bitBinary digIT. A single digit number in base-2 (binary), in other words, either a one or a zero. The smallest unit of computerized data. The term ‘bit’ was coined by early computer scientist [..]
|
41 |
0 bitthe curb put into the mouths of horses to restrain them. The Hebrew word (metheg) so rendered in Ps. 32:9 is elsewhere translated «bridle» (2 Kings 19:28; Prov. 26:3; Isa. 37:29). Bits were [..]
|
42 |
0 bitA bit (short for binary digit) is the smallest unit of measurement in computing. 8 bits make up 1 byte.
|
43 |
0 bitA measure of quantity of data. A bit is one binary digit, a 0 or a 1.
|
44 |
0 bitA Bit is an individual binary digit. A Byte is a collection of 8 bits.
|
45 |
0 bitShort for binary digit, the smallest unit of information on a machine. The term was first used in 1946 by John Tukey, a leading statistician and adviser to five presidents. A single bit can hold only [..]
|
46 |
0 bitBinary digIT — A bit is the smallest unit of computerised data. A bit is represented by a 0 or a 1. Eight bits typically make up a byte.
|
47 |
0 bitbisl or bisel
|
48 |
0 bitThe smallest unit of information in the binary system of notation.
|
49 |
0 bitA contraction of binary digit, either of the two values (0 and 1) used in the binary number system and as the smallest unit of storage in digital computers. In personal computers, data is stored and p [..]
|
50 |
0 bitAn abbreviation for binary digit. A single character in a binary number. A single pulse in a group of pulses. A unit of information capacity of a storage device.
|
51 |
0 bitNoun. A woman. Abb. of ‘bit of fluff’ or ‘bit of skirt’, generally a person viewed sexually. Derog.
|
52 |
0 bitA bit is the smallest measure of data. It is a compilation of letter from Binary digIT. See byte; it takes 8 bits to make a byte. Don’t know your KB from your MB? You can see the conversion of bit flow rate units in our Data Rate Converter. If you are seeking byte conversion, please use our Memory and Storage Converter. For sample download tim [..]
|
53 |
0 bitShort for binary digit, the smallest unit of information on a machine. A single bit can hold only one of two values: 0 or 1.
|
54 |
0 bitThe number of bits used to represent a character. For personal computers a byte is usually 8 bits.
|
55 |
0 bitA binary digit that is 1 or 0. A string of bit’s makes a byte (see below)
|
56 |
0 bitA unit of measurement that represents one figure or character of data. A bit is the smallest unit of storage in a computer. Since computers actually read 0s and 1s, each is measured as a bit. The letter A consists of 8 bits which amounts to one byte. Bits are often used to measure the capability of a microprocessor to process data, such as 16-bit o [..]
|
57 |
0 bit(Binary DigIT) — A bit is the smallest unit of computerized data, comprised of either a 0 (off) or a 1 (on). Bandwidth is usually measured in bits-per-second. See Also: Bandwidth, Bps, Byte
|
58 |
0 bitA minor acting role in which an actor may only speak a few lines.
|
59 |
0 bitContraction of binary digit. A bit is the smallest measurement unit of computer memory or data transmission speed, e.g. via a Modem. See the entry on Measurement Units. See Byte, Kilobit, Kilobyte, Me [..]
|
60 |
0 bitA single piece of computer information — either 0 or 1 (off or on).
|
61 |
0 bitA bit is the smallest unit of information on a computer. This is rarely referred to as the more common unit is the byte, which is a groupof 8 bits.
|
62 |
0 bitIn computers, the basic unit of digital information; contraction of Binary digit.
|
63 |
0 bitShort for «Binary Digit». The smallest piece if binary digital data and is represented by either a «1» or a «0». Numbers of bits are used in digital video as a representation of signal quality (i.e. an 8-bit signal can have 256 levels from black to white while a 10-bit signal can have 1024 levels).
|
64 |
0 bitBinary digit. The basic unit of all digital communications. A bit is a «1» or «0» in a binary language.
|
65 |
0 bitIn information theory, a single bit
|
66 |
0 bitA bit is the smallest unit of information that a computer can work with. Each bit is either a «1» or a «0». Often computers work with groups of bits rather than one bit at a time; [..]
|
67 |
0 bitA stainless steel, rubber or aluminum bar, attached to the bridle, which fits in the horse’s mouth and is one of the means by which a jockey exerts guidance and control. The most common racing bi [..]
|
68 |
0 bitThe most basic unit of information on a computer. In accordance with binary code, each bit is designated as either a 1 or a 0; all other information stored on the computer is composed of combinations [..]
|
69 |
0 bitThe smallest unit of information in a binary system, consisting of a “0” or a “1” (formed from Binary Digit).
|
70 |
0 bitA single numeric character. Each bit of a binary number can either be 0 or 1. Physically, a memory cell within the computer and the smallest unit of information in a computer. The value of a bit represents a simple two-way choice, such as yes or no, on or off, positive or negative, something or nothing. The small unit of information (usually either [..]
|
71 |
0 bitUnit of measurement used for computing and telecommunication purposes. See Byte.
|
72 |
0 bitcontraction of the term Binary Digit. The smallest unit of information a computer can process, representing one of two states (usually indicated by “1” or “0”).
|
73 |
0 bitA hardened steel bar or plate that is shaped according to the operation to be performed and the material to be machined.
|
74 |
0 bitA parallel or taper shank drill tool
|
75 |
0 bitA bit is the smallest unit of information that a computer can work with. Each bit is either a one or a zero. Often computers work with chunks of bits rather than one bit at a time; the smallest chunk [..]
|
76 |
0 bitA binary digit. The smallest unit of information represented by one of two states (usually 0 or 1). It is often denoted by a lower case ‘b’ as in Mbs (mega-bits per second). Or the amount of info [..]
|
77 |
0 bitShort for binary digit. A number expressed in binary notation utilizes the digits 1 and 0, and these are called bits. Any number can be expressed with combinations of them.
|
78 |
0 bitThe smallest element of computerized data. A full text page in English is about 16,000 bits. (See also “Byte”)
|
79 |
0 bitThe base unit of information in computing. For our purposes, also the base unit of measuring network speeds. 1 bit is a single piece of information. Network speeds tend to be measured by bits per seco [..]
|
80 |
0 bitOne binary digit, in base 2. The basic unit for electronically stored or transmitted data. See also: Byte.
|
81 |
0 bitBinary Digit. The basic units of computer data – either a one or a zero.
|
82 |
0 bitThe smallest unit of storage in a computer, this represents a single letter or character.
|
83 |
0 bitA basic storage unit used in computers; a bit can only be one of two values ‘1’ or’0′.Data is stored in a computer as a combination of bits (eight together are referred to as a byte).
|
84 |
0 bit(Binary DigIT)
|
85 |
0 bitThe unit of measure which represents a single character of data. The smallest unit of storage on a computer.
|
86 |
0 bitIn a computer, all digital data is made up of bits and bytes. When computers talk or write to each other, they represent all of the information in ‘ones and zeros’-known as binary codes (1’s and 0’s).
|
87 |
0 bitA single piece of data. A bit has a numerical value of either «1» or «0».
|
88 |
0 bitShort for binary digit. The smallest form of computer memory, a bit is either on or off (ie — 1 or 0). 8 bits form a byte.
|
89 |
0 bitBIT (Binary digit). Modems send information in a serial stream of zeros and ones. Each of these zeros or ones is called a bit. Eight bits is enough to encode one ASCII (American Standard Code for Info [..]
|
90 |
0 bitA binary unit.
|
91 |
0 bit(Binary DigIT) — A single digit number in base-2, in other words, either a 1 or a zero. The smallest unit of computerized data. Bandwidth is usually measured in bits-per-second. See Also: Bandwidth
|
92 |
0 bitthe tiniest unit of data, represented by a 0 or 1
|
93 |
0 bitA reduction in binary unit, a bit is a unit of information that is conveyed in either a 1 or a 0.
|
94 |
0 bitBits are the elements of digital data. All letters, documents, sound, images or other information held in digital format is stored and processed as a stream of ones and zeroes. Each individual 0 or 1 [..]
|
95 |
0 bitA bit can either be on or off; one or zero. All computer data can ultimately be reduced to a series of bits. The term is also used as a (very rough) measure of sound quality, color quality, and even p [..]
|
96 |
0 bitA single digit number in base-2. In other words, either a 1 or a 0. The smallest unit of computerized data.
|
97 |
0 bitA single digit number in base-2, in other words, either a 1 or a zero. The smallest unit of computerized data. Bandwidth is usually measured in bits-per-second.
|
98 |
0 bitThis is the smallest unit of digital information with which computers operate.
|
99 |
0 bitThe smallest element of computer storage, a bit is a single digit in a binary number (0 or 1). A computer uses 8 bits to store one text character.
|
100 |
0 bitBinary DigIT-a single-digit number in base-2; in other words, either a 1 or a 0; the smallest unit of computerized data. Bandwidth is usually measured in bits per second. See also: bandwidth, bps, byte, kilobyte, megabyte
|
101 |
0 bitThe smallest piece of digital information understood by computers.
|
102 |
0 bitA contraction of binary digit, a bit is the smallest unit of information that a computer can hold. The speed at which bits are transmitted or bit rate is usually expressed as bits per second or bps. � [..]
|
103 |
0 bitThe basic unit of information in a computer. A bit is one binary digit, either a "1" or a "0".
|
104 |
0 bit(n) a small piece or quantity of something(n) a small fragment of something broken off from the whole(n) an indefinitely short time(n) an instance of some kind(n) piece of metal held in horse [..]
|
105 |
0 bitA bit (binary digit) is the smallest unit of digital information. A bit can have only two values (0 or 1). Originally the name «bigit» was used. The term was probably introduced by a scienti [..]
|
106 |
0 bitStands for binary digit. A bit is either on or off and is represented by «1» or «0». A collection of bits are put together to form a byte.
|
107 |
0 bitThe smallest unit of information in a computer, can either equal 0 or 1. Eight bits equal one byte.
|
108 |
0 bitThe smallest unit of information in a computer, can either equal 0 or 1. Eight bits equal one byte.
|
109 |
0 bitÁ piece.
|
110 |
0 bitTo take the bit in (or between) his teeth. To be obstinately self-willed; to make up one’s mind not to yield. When a horse has a mind to run away, he catches the bit “between his tee [..]
|
111 |
0 bitMoney. The word is used in the West Indies for a half pistareen (fivepence). In Jamaica, a bit is worth sixpence, English; in America, 12 1/2 cents; in Ireland, tenpence.
|
112 |
0 bitAn acronym for BInary digiT. It is the basic unit of information in the computer world. A bit is a digit in binary form and carries one of two values, 0 or 1.
|
113 |
0 bitA single on/off binary position. If the position is set to 1 the bit is «on.» If the position is off the bit would be set to 0. 8 bits make a byte. (Now that makes me hungry!)
|
114 |
0 bitA numeric quantity with precisely two values, such as 0 and 1, false and true, up or down, and so forth. Key point: In many contexts, each additional bit means «twice as much». 8 extra [..]
|
115 |
0 bita binary digit, 0 or 1. Computers process all information digitally in the form of bits. Eight bits make a byte, 1,024 bytes make a kilobyte, 1,024 kilobytes make a megabyte, etc. See byte.
|
116 |
0 bitA stainless steel, rubber or aluminum bar that is attached to the bridle, which fits in the horse’s mouth and is one of the means by which a jockey exerts guidance and control. The most common ra [..]
|
117 |
0 bitA star or chisel pointed tip forged or screwed (detachable) to the end of a drill steel.
|
118 |
0 bitA single binary digit, can be either a 0 or 1.
|
119 |
0 bitThe smallest amount of information that can be transmitted. In binary digital transmission, a bit has one of two values: 0 or 1. A combination of bits can indicate an alp [..]
|
120 |
0 bitAbbreviated with small «b». Binary Digit. The smallest unit of data in a computer.
|
121 |
0 bitThe smallest unit for measuring data.
|
122 |
0 bitIn computer science, a single character of a language having just two characters, as either of the binary digits 0 or 1; a unit of information equivalent to the choice of either of two equally likely alternatives; a unit of information storage capacity, as of memory.
|
123 |
0 bitThe smallest unit of data in a computer. A bit has a single binary value of either 0 or 1. There are eight bits in a byte.
|
124 |
0 bitThe smallest unit of memory. The word comes from binary
|
125 |
0 bitA binary digit. The values of a bit are either «0» or «1». Eight bits form a byte.
|
126 |
0 bitA binary digit, the smallest piece of data a computer can manipulate.
|
127 |
0 bit
|
128 |
0 bitA single unit of information. Often referred to as a 1 or 0 in the binary system and as an «on» or «off» state in computer operations.
|
129 |
0 bitBit is short for ‘binary’ digit — the smallest unit of data in digital systems; it can have a value of ‘1’ or ‘0’. A group of 8-bits compose what is referred to as a byte.
|
130 |
0 bitA shortened name for binary digit 0 or 1. This is the smallest unit of digital information used by a computer or digital camera.
|
131 |
0 bitBinary digit, the smallest unit of digital information a computer can work with.
|
132 |
0 bitA contraction of "binary digit", representing the number 1 or 0 in the base 2 number system that computers work with.
|
133 |
0 bitShort for ‘binary digit’, a bit is the smallest piece of information that can be handled by a computer and has a value of 0 or 1.
|
134 |
0 bitThis is a Binary Digit and can either be one of two states — 0 or 1. Bitmap
|
135 |
0 bitA unit of measurement indicating the information capacity of one binary digit.
|
136 |
0 bitAbbreviation for binary digit; the smallest unit of information a computer can use. A bit is either one or zero (a high or low voltage state).
|
137 |
0 bitShort for "Binary Digit". The smallest piece if binary digital data and is represented by either a "1" or a "0". Numbers of bits are used in digit [..]
|
138 |
0 bitThe smallest unit of storage used in computing; a digit in the binary numeral system it can be 1 or 0.
|
139 |
0 bitA computing term referencing Binary digIT. A BIT is the smallest unit of data a computer can handle. BITs are represented by the binary number code (0 or 1).
|
140 |
0 bitThe smallest unit of digital information, eight bits is equal to one byte. An image can be described by the number of bits representing a single pixel. The more bits available, the greater range of color the image will have (i.e. 1-bit = monochrome; 8 bit= 256 colors or grayscale; 24 & 32 bit = even greater range).
|
141 |
0 bitMetal bar on a bridle that goes in the horses mouth and is used to control the horse while riding.
|
142 |
0 bitBuilt in Test
|
143 |
0 bitA bit, short for binary digit, is defined as the most basic unit of data in telecommunications and computing. Each bit is represented by either a 1 or a 0 and this can be executed in various systems t [..]
|
144 |
0 bitA single binary unit of information where the information is either a 1 or a 0 for notation. If you have 8-bits this is also referred to as a byte. If you have 16-bits this is also referred as two bytes or a word. However, some words can be 16, 32 or even 64-bits long.
|
145 |
0 bitCutting blade used in rodding (pipe clearing) operations. Cutting teeth on the auger head of a sewer boring tool.
|
146 |
0 bit, (1) sb. The bit of a key is the part that is cut to pass the wards of the lock. (2) sb. to ‘come to the bit,’ is to come to the point; to arrive at the last stage of a bargain.
|
147 |
0 bitAn integer in the range from 0 to 1, inclusive. The smallest possible unit of information storage. An eighth of a byte or of a dollar. (The term «Pieces of Eight» comes from being able to split the old Spanish dollar into 8 bits, each of which still counted for money. That’s why a 25-cent piece today is still «two bits».)
|
148 |
0 bitElementary unit of information/data stored as a choice between two mutually exclusive possibilities, such as 1 or 0 in binary notation.
|
149 |
0 bitPrison sentence
|
150 |
0 bitA contraction of Binary Digit, abbreviation ‘b’. A digital (as opposed to analogue) computer recognises only two states in the smallest item of information available to it — typically represented as 0 and 1. This smallest available item of information is called a Bit. Because digital computers can only recognise two states, they ca [..]
|
151 |
0 bitAbbreviation for binary digit. A bit is a unit of data that can have a value of 0 or 1. It is the smallest unit of data that can be stored in a computer.
|
152 |
0 bitAn integer in the range from 0 to 1, inclusive. The smallest possible unit of information storage. An eighth of a byte
|
153 |
0 bitOne binary digit. A bit can be either a 1 or 0, either on or off. This is the smallest piece of information in the PLC. Typically eight bits make a byte and 16 bits make a word. See also: Binary, Bina [..]
|
154 |
0 bitShort for “Binary Digit.” All values in computer memory ultimately reduce to binary digits: values that are either zero or one. Groups of bits may be interpreted differently—as integers, floatin [..]
|
155 |
0 bitA unit of information derived from a choice between two equally probable alternatives or ‘events’; such a unit stored electronically in a computer, e.g. 1 and 0.
|
156 |
0 bita unit of memory that can hold 0 or 1. An individual bit cannot be directly accessed in C++ (the unit of addressing is a byte), but a bit can be accessed through a bitfield or by using the bitwise [..]
|
157 |
0 bitBuilt-In Test or Binary Digit
|
158 |
0 bitWhen a defender falls for a fake, Example: “Ricky Manning bit on Deion Branch’s hitch and it was a big gainer for Branch.”
|
159 |
0 bitThe smallest unit that can carry information in a computer — this is a base 2 number, equaling either 0 or 1.
|
160 |
0 bitA binary digit. This is the smallest unit of information and is valued at either zero or one.
|
161 |
0 bitA basic unit of computer information; abbreviation of binary digit.
|
162 |
0 bita unit of the binary code that consists of either a single "1" or "O."
|
163 |
0 bitThe smallest unit of information (normally either a 0 or a 1) recognizable by a computer. A contraction of “binary digit”.
|
164 |
0 bita 1 or 0 used in binary code.
|
165 |
0 bitA measurement of data that is the smallest unit of data. A bit is either the «1» or «0» component of the binary code. A collection of bits is put together to form a byte.
|
166 |
0 bitA bit is the basic unit of information in computing. It can have only one of two values commonly represented as either a 0 or 1.The two values can be interpreted as any two-valued attribute (yes/no, on/off, etc).
|
167 |
0 bitA binary digit, taking a value of either 0 or 1. Binary digits are a basic unit of information storage and communication in digital computing and digital .
|
168 |
0 bitA drilling tool that cuts the hole. Bits are designed on two basic and different principles. The cable tool bit moves up and down to pulverize. The rotary bit revolves to grind.
|
169 |
0 bitA sophisticated cutting tool used in drilling. Two types are used — rock bits (roller cone) and diamond bits. Roller cone bits are the most commonly used. High performance diamond bits are selected wh [..]
|
170 |
0 bitThe tool attached to the lower end of the drillpipe; a heavy steel head equipped with various types of cutting or grinding teeth. Some are fixed; some turn on bearings. A hole in the bottom of the [..]
|
171 |
0 bitA bit used to start the borehole; a bit that is some variation of the fishtail or drag bit, one used in soft, unconsolidated, near-surface material.
|
172 |
0 bitsee drill bit.
|
173 |
0 bitA bit is the drilling tool that bores or cuts into the earth. There are two basic types: the cable tool bit which moves up and down the hole, striking the bottom, chipping away the rock, and the rotar [..]
|
174 |
0 bitThe cutting or boring element used in drilling oil and gas wells. The bit consists of a cutting element and a circulating element. The circulating element permits the passage of drilling fluid and uti [..]
|
175 |
0 bitThe cutting or boring element used in drilling oil and gas wells. The bit consists of a cutting element and a circulating element. The circulating element allows the passage of drilling fluid and employs the hydraulic force of the fluid stream to improve drilling rates. In rotary drilling, several drill collars are joined to the bottom end of the d [..]
|
176 |
0 bitA bit is a «binary digit,» that is, a single value that makes up a binary number. A bit can be either 1 or 0. See Binary.
|
177 |
0 bitBar in horse’s mouth which is used to guide or control horse.
|
178 |
0 bitA joke or, more often, a series of related jokes. “His bit about jogging killed, but the doctor’s office bit was too long—it definitely needs some more polishing.”
|
179 |
0 bitThe smallest unit of digital information representing a single “0” or 1.
|
180 |
0 bitA piece of metal placed in a horse’s mouth and connected to reins to direct the animal. (A horse hates having a bit put in its mouth.) A rotary cutting tool fitted to a drill, used to bore holes. [..]
|
181 |
0 bitbit eighth of a dollar (mathematics,computing) bit binary digit (computing) bit smallest unit of storage (information theory,cryptography) bit datum that may take on one of exactly two values
|
182 |
0 bitcontraction of the expression “binary digit”; smallest unit of data in a computer
|
183 |
0 bitThe bit (a portmanteau of binary digit) is a basic unit of information used in computing and digital communications. A binary digit can have only one of two values, and may be physically represented w [..]
|
184 |
0 bitA bit is a unit of information storage on a computer.
|
185 |
0 bitThe word bit is a colloquial expression referring to specific coins in various coinages throughout the world.
|
186 |
0 bitThe bit of a key is the part that actually engages the locking mechanism of a lock. (For example the tumblers in a pin tumbler lock.)
|
187 |
0 bitBIT was an information service, publisher, travel guide and social centre founded, in 1968, by John «Hoppy» Hopkins. It pre-dated the internet as a free service that would try to find any in [..]
|
188 |
0 bitA bit is a type of horse tack used in equestrian activities, usually made of metal or a synthetic material, and is placed in the mouth of a horse or other equid and assists a rider in communicating wi [..]
|
189 |
0 bit The smallest unit of memory storage.
|
190 |
0 bitThe smallest unit of information in a computer, with a value of either 0 or 1.
|
191 |
0 bitBinary digit, the smallest unit of digital information a computer can work with.
|
192 |
0 bitAbbreviation for “binary digit,” the most common unit computers use for representing data internally.
|
Dictionary.university is a dictionary written by people like you and me.
Please help and add a word. All sort of words are welcome!
Add meaning
Britannica Dictionary definition of BIT
1
[count]
:
a small piece of something
-
Put all the broken bits back together.
— often + of
-
He ate every last/single bit of the food. [=he ate all of the food]
-
He ate only a couple of tiny little bits of bread and cheese and drank a drop or two of wine.
-
We need to get all the bits of dirt out of the carpet.
-
There were broken bits of glass all over the floor.
—
see also bits and pieces (below)
2
[count]
a
chiefly British
:
a part of something (such as a book, play, etc.)
-
There are some good bits [=parts] near the end of the story: one is the bit where the hero and the heroine are nearly separated.
b
chiefly US
:
a brief comic performance or joke
-
The comedian did a funny bit about taking his daughter to the dentist.
-
a corny comedy bit
c
:
a very short performance in a movie, play, etc.
— usually used before another noun
-
a bit part/role
-
bit players
3
[singular]
informal
:
all the things that are connected to an activity, a process, etc.
-
He says he’s tired of his job, tired of driving to work every day, the whole bit. [=everything]
4
[count]
British
:
an old coin with a specified small value
-
a threepenny bit
—
see also two bits
a bit
1
:
a little
:
somewhat or rather
-
I let it bother me a bit. [=slightly]
-
His house is down the street a bit further.
-
There’s a bit too much sugar in the dessert, which makes it a bit too sweet.
-
I’m feeling a bit better today.
-
It’s a bit like driving a car.
-
This one is a bit bigger than that one.
-
At first, I was a bit confused.
2
:
a small amount or quantity
:
a little of something
-
They don’t understand much—but they do understand a bit.
-
They saved money a bit at a time.
-
“How much cake is left?” “Only a (very little) bit.”
-
“How old is your daughter?” “She’s two and a bit.” [=she’s slightly older than two]
— often + of
-
They understand only a bit of [=a little of] what is going on.
-
There’s a bit of both brown sugar and molasses in these cookies.
-
The job may cause you a bit of trouble.
-
His mind’s already made up. It won’t do you a bit of good to argue. [=it won’t do you any good to argue]
3
a
:
a short period of time
:
a while
-
Let’s wait a (little/wee) bit longer.
-
Repairs will begin in a bit more than a month.
-
He left but came back after a bit. [=he came back soon]
b
:
for a short period of time
-
Please stay here with me a bit.
— used to describe a person or thing that is regarded as annoying, excessive, or unfair
-
My mother thinks he’s funny, but I find him a bit much.
-
I find his constant joking a bit much.
-
It was a bit much to expect us to wait that long.
-
The hot weather is getting to be a bit much.
a bit of a/an
chiefly British
— used to make a statement or description less forceful or definite
-
I had a bit of a shock when I saw him. [=I was somewhat shocked when I saw him]
-
He’s a bit of a rascal. [=he’s something of a rascal]
-
We had a bit of a laugh about it afterwards.
a bit of all right
British, informal
:
someone or something very pleasing
especially
:
a sexually attractive person
-
His girlfriend’s a bit of all right.
bit by bit
:
by small steps or amounts
:
gradually
-
The situation improved bit by bit. [=little by little]
-
I got to know them bit by bit.
bits and pieces
1
:
small pieces
-
There were broken bits and pieces of glass all over the floor.
-
I finished the project in bits and pieces [=a little at a time] during my spare time.
2
or British
bits and bobs
:
things or objects of different kinds
-
There are just a few bits and pieces of furniture in the office.
-
No one knows exactly what happened. All we have is a few bits and pieces [=odds and ends] of information so far.
do your bit
chiefly British
:
to do your share of a job or task
-
We all have to do our bit [=do our part] to help out.
every bit
:
in every way
-
The end of the movie was every bit [=just] as good as the beginning.
-
This new project seems every bit as ambitious as the first one.
-
He is every bit the high-powered businessman.
-
You are every bit as deserving as she is.
not a/one bit
or
not (in) the least/smallest/slightest/tiniest bit
:
not at all
-
It didn’t interest me a bit. = It didn’t interest me one (single/little) bit.
-
I’m not a bit interested in this movie. = I’m not the least bit interested in this movie.
-
That joke was not a/one bit funny. [=was not funny at all]
-
We weren’t a bit tired. [=we weren’t tired at all]
not a bit of it
British, informal
— used to say that something expected or possible did not happen or is not true
-
Am I tired? Not a bit of it. [=I am not tired at all]
-
I thought she’d be angry, but not a bit of it. [=she wasn’t angry at all]
quite a bit
or chiefly British
a good/fair bit
:
a fairly large amount
:
a lot
-
He knows quite a bit [=quite a lot] more about it than I do.
-
The wait was quite a bit [=considerably] longer than I thought it would be.
-
She lost the race by quite a bit.
-
We’ve been seeing quite a bit of each other lately. [=we’ve been spending a lot of time together lately]
-
She’d already finished a good bit of the work before I returned.
-
There’s still a fair bit (of the cake) left.
take a bit of doing
—
see doing
to bits
1
:
to pieces
:
apart
-
The ball hit the window and smashed it to bits.
-
The bridge was blown to bits by the explosion.
-
(chiefly Brit) The pie was falling to bits [=falling apart] as I tried to serve it.
2
informal
:
to a very great degree
-
She was thrilled to bits. [=she was very thrilled]
Britannica Dictionary definition of BIT
[count]
1
:
the part of a tool (such as a drill) that is used for cutting, drilling, etc.
—
see picture at carpentry
2
:
a piece of metal that is put in the mouth of a horse and that is part of the device (called a bridle) that is used to control the horse
—
see picture at horse
champing/chomping at the bit
:
waiting in an impatient way to do something
-
We’ve all been champing at the bit to get started on the project.
get/take the bit between your teeth
:
to start doing something in a very enthusiastic and determined way
-
He can be lazy about doing his work, but when he gets the bit between his teeth there’s no stopping him.
Britannica Dictionary definition of BIT
:
a single unit of computer information that is represented as either 1 or 0
—
compare byte;
see also megabit
4
bit
Britannica Dictionary definition of BIT
Other forms: bits
Let me give you a bit of advice: Use bit when you’re talking about a small amount.
Bit is a small but useful word. Like drill bits, which fit on the end of a drill to change its function, the word bit has several uses. Usually, it means a little piece of something, even time. If you ask me when I’m arriving, I might say, «In a little bit.» A bit can also be a short theatrical entertainment, the metal piece a horse bites on, or digital information that’s 1/8 the size of a byte.
Definitions of bit
-
noun
a small piece or quantity of something
“a
bit of paper”“a
bit of lint”“I gave him a
bit of my mind”-
synonyms:
spot
-
noun
a small fragment of something broken off from the whole
“a
bit of rock caught him in the eye”-
synonyms:
chip, flake, fleck, scrap
-
noun
a small amount of solid food; a mouthful
“all they had left was a
bit of bread”-
synonyms:
bite, morsel
-
noun
an indefinitely short time
“in just a
bit”-
synonyms:
minute, mo, moment, second
-
noun
an instance of some kind
“he had a
bit of good luck”-
synonyms:
piece
-
noun
a short theatrical performance that is part of a longer program
-
noun
piece of metal held in horse’s mouth by reins and used to control the horse while riding
“the horse was not accustomed to a
bit” -
noun
the part of a key that enters a lock and lifts the tumblers
-
noun
the cutting part of a drill; usually pointed and threaded and is replaceable in a brace or bitstock or drill press
“he looked around for the right size
bit” -
noun
a unit of measurement of information (from binary + digit); the amount of information in a system having two equiprobable states
“there are 8
bits in a byte”see moresee less-
types:
-
check bit, parity, parity bit
(computer science) a bit that is used in an error detection procedure in which a 0 or 1 is added to each group of bits so that it will have either an odd number of 1’s or an even number of 1’s; e.g., if the parity is odd then any group of bits that arrives with an even number of 1’s must contain an error
-
type of:
-
unit, unit of measurement
any division of quantity accepted as a standard of measurement or exchange
-
check bit, parity, parity bit
DISCLAIMER: These example sentences appear in various news sources and books to reflect the usage of the word ‘bit’.
Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Vocabulary.com or its editors.
Send us feedback
EDITOR’S CHOICE
Look up bit for the last time
Close your vocabulary gaps with personalized learning that focuses on teaching the
words you need to know.
Sign up now (it’s free!)
Whether you’re a teacher or a learner, Vocabulary.com can put you or your class on the path to systematic vocabulary improvement.
Get started
бит, долото, кусочек, кусок, укушенный, взнуздать, взнуздывать
существительное ↓
- кусок; кусочек
small bits of sugar — кусочки сахара
small bits of plaster — куски штукатурки
every bit of — всё
he ate all the cake bit by bit — он по кусочку съел весь пирог
to go /to come/ to bits — разбиться на мелкие кусочки
- частица, доля
give me a bit — дай мне немного /часть/
- (a bit) небольшое количество, немного, чуть-чуть
a bit at a time — понемногу, не спеша, постепенно
wait a bit — подожди немного
I am a bit tired — я немного устал
he is a bit late — он слегка опоздал
not a bit — нисколько, ничуть
he is not a bit tired — он совсем не устал
he is a bit of a coward — он трусоват
- разг. мелкая монета
threepenny bit — монета в три пенса
short bit — амер. монета в 10 центов
long bit — амер. монета в 15 центов
two bits — амер. монета в 25 центов
- амер. сл. срок заключения
ещё 15 вариантов
глагол
- взнуздывать
- обуздывать, сдерживать
Мои примеры
Словосочетания
comedy bit — комический номер 
to give smb. a bit of one’s mind — высказаться напрямик, откровенно 
to have a bit of a do — устроить небольшую вечеринку 
a bit / stroke of luck — удача 
to take / eat a bit of mutton with smb. — обедать с кем-л. 
quite a bit / few / lot — значительное количество 
a bit rusty English — немного запущенный английский 
storage bit — бит памяти 
chopping drill bit — буровое долото ударного бурения 
six-point drill bit — шестиугольное буровое долото 
Примеры с переводом
That’s a bit odd. 
Это немного странно.
I feel a bit better now. 
Сейчас я чувствую себя немного лучше.
You’ll have to wait a bit. 
Вам придётся немного подождать.
He knows quite a bit about painting. 
Он довольно мало знает о живописи. / Он не много знает о живописи.
We sat around for a bit chatting. 
Мы немного посидели и поболтали.
She’s quite a bit older than you, isn’t she? 
Она немного старше вас, не так ли?
They’re worth quite a bit more than I thought. 
Они стоят немного больше, чем я думал.
ещё 23 примера свернуть
Примеры, ожидающие перевода
I used to act a bit when I was younger. 
He still likes to do a bit of gardening. 
‘Are you sorry to be leaving?’ ‘Yes, I am a bit.’ 
Для того чтобы добавить вариант перевода, кликните по иконке ☰, напротив примера.
Возможные однокоренные слова
biter — кусающееся животное, тот, кто кусает
biting — кусающий, резкий, едкий, хлесткий, кусачий, острый, грызущий, язвительный
bitten — укушенный, покусанный, искусанный
bitter — горький, ожесточенный, горько, жестоко, резко, очень, горечь, горькое пиво
bittern — выпь, маточный раствор, рапа
bitty — разношерстный, бессвязный, разрозненный, бессистемный
Формы слова
noun
ед. ч.(singular): bit
мн. ч.(plural): bits
bit 1
(bĭt)
n.
1. A small portion, degree, or amount: a bit of lint; a bit of luck.
2. A brief amount of time; a moment: Wait a bit.
3.
a. A short scene or episode in a theatrical performance.
b. A bit part.
4. An entertainment routine given regularly by a performer; an act.
5. Informal
a. A particular kind of action, situation, or behavior: got tired of the macho bit.
b. A matter being considered: What’s this bit about inflation?
6. Informal An amount equal to one eighth of a dollar: two bits.
7. Chiefly British A small coin: a threepenny bit.
Idioms:
a bit
To a small degree; somewhat: a bit warm.
bit by bit
Little by little; gradually.
do (one’s) bit
To do one’s part or contribute one’s share.
bit 2
(bĭt)
n.
1. The sharp part of a tool, such as the cutting edge of a knife or axe.
2. A pointed and threaded tool for drilling and boring that is secured in a brace, bitstock, or drill press.
3. The part of a key that enters the lock and engages the bolt and tumblers.
4. The tip of the mouthpiece on a pipe or a cigarette or cigar holder.
5. The metal mouthpiece of a bridle, serving to control, curb, and direct an animal.
6. Something that controls, guides, or curbs.
tr.v. bit·ted, bit·ting, bits
1. To place a bit in the mouth of (a horse, for example).
2. To check or control with or as if with a bit.
3. To make or grind a bit on (a key).
Idiom:
have/take the bit in one’s teeth
To be uncontrollable; cast off restraint.
bit 3
(bĭt)
n. Computers
A binary digit, having either the value 0 or 1, used to store or represent data.
bit 4
(bĭt)
v.
Past tense and a past participle of bite.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
bit
(bɪt)
n
1. a small piece, portion, or quantity
2. a short time or distance
3. informal US and Canadian the value of an eighth of a dollar: spoken of only in units of two: two bits.
4. any small coin
6. informal way of behaving, esp one intended to create a particular impression: she’s doing the prima donna bit.
7. a bit rather; somewhat: a bit dreary.
8. a bit of
a. rather: a bit of a dope.
b. a considerable amount: that must take quite a bit of courage.
9. a bit of all right a bit of crumpet a bit of stuff a bit of tail slang Brit a sexually attractive woman
10. bit by bit gradually
11. bit on the side informal an extramarital affair
12. do one’s bit to make one’s expected contribution
13. every bit (foll by as) to the same degree: she was every bit as clever as her brother.
14. not a bit not a bit of it not in the slightest; not at all
15. to bits completely apart: to fall to bits.
[Old English bite action of biting; see bite]
bit
(bɪt)
n
1. (Horse Training, Riding & Manège) a metal mouthpiece, for controlling a horse on a bridle
2. anything that restrains or curbs
3. take the bit in one’s teeth take the bit between one’s teeth have the bit in one’s teeth have the bit between one’s teeth
a. to undertake a task with determination
b. to rebel against control
4. (Mechanical Engineering) a cutting or drilling tool, part, or head in a brace, drill, etc
5. (Mechanical Engineering) the blade of a woodworking plane
6. (Tools) the part of a pair of pincers designed to grasp an object
7. (General Engineering) the copper end of a soldering iron
8. (Tools) the part of a key that engages the levers of a lock
vb (tr) , bits, bitting or bitted
9. (Horse Training, Riding & Manège) to put a bit in the mouth of (a horse)
10. to restrain; curb
[Old English bita; related to Old English bītan to bite]
bit
(bɪt)
vb
the past tense and (archaic) past participle of bite
bit
(bɪt)
n
1. (Mathematics) a single digit of binary notation, represented either by 0 or by 1
2. (Mathematics) the smallest unit of information, indicating the presence or absence of a single feature
3. (Mathematics) a unit of capacity of a computer, consisting of an element of its physical structure capable of being in either of two states, such as a switch with on and off positions, or a microscopic magnet capable of alignment in two directions
[C20: from abbreviation of binary digit]
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
bit1
(bɪt)
n., v. bit•ted, bit•ting. n.
1. the mouthpiece of a bridle, having fittings at each end to which the reins are fastened.
2. anything that curbs or restrains.
3. a removable drilling or boring tool for use in a brace, drill press, or the like.
4. the cutting part of an ax or hatchet.
5. the wide portion at the end of an ordinary key that moves the bolt.
v.t.
6. to put a bit in the mouth of (a horse).
7. to curb with or as if with a bit.
8. to grind a bit on (a key).
Idioms:
1. chafe or champ at the bit, to become impatient and restless because of delay.
2. take the bit in or between one’s teeth, to reject control; go one’s own way.
[before 900; Middle English bite, Old English: action of biting; c. Old High German biz. See bite]
bit2
(bɪt)
n.
1. a small piece or quantity of something.
2. a short time: Wait a bit.
3. a stereotypic set of behaviors, attitudes, or actions associated with a particular role, situation, etc.: the whole Wall Street bit.
5. Informal. an amount equivalent to 12½ cents (used only in even multiples): two bits.
Idioms:
1. a bit, somewhat; a little: a bit sleepy.
2. a bit much, somewhat overdone or beyond tolerability.
3. bit by bit, by degrees; gradually.
4. do one’s bit, to contribute one’s share to an effort.
5. every bit, quite; just: every bit as good.
6. quite a bit, a fairly large amount.
[before 1000; Middle English bite, Old English bita bit, morsel; c. Old High German bizzo, Old Norse biti. See bite]
bit3
(bɪt)
n.
a single, basic unit of computer information, valued at either 0 or 1 to signal binary alternatives.
[1945–50; bi (nary) + (digi) t]
bit4
(bɪt)
v.
pt. and a pp. of bite.
Random House Kernerman Webster’s College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
bit
(bĭt)
The smallest unit of computer memory. A bit holds one of two possible values, either of the binary digits 0 or 1. See Note at byte.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
bit
1. ‘bit’
A bit is a small amount or a small part of something.
There’s a bit of cake left.
He found a few bits of wood in the garage.
2. ‘a bit’
A bit means ‘to a small degree’.
She looks a bit like her mother.
He was a bit deaf.
Be Careful!
Don’t use ‘a bit’ with an adjective in front of a noun. Don’t say, for example, ‘He was a bit deaf man‘.
3. ‘a bit of’
In conversation and in less formal writing, you can use a bit of in front of a and a noun. You do this to make a statement seem less extreme.
Our room was a bit of a mess too.
His question came as a bit of a shock.
4. ‘a bit’ and ‘one bit’ with negatives
You can add a bit or one bit at the end of a negative statement to make it stronger.
I don’t like this one bit.
She hadn’t changed a bit.
5. ‘not a bit’
You can use not a bit in front of an adjective to emphasize that someone or something does not have a particular quality. For example, if you say you are not a bit hungry, you mean you are not hungry at all.
They’re not a bit interested.
I wasn’t a bit surprised by the news.
6. ‘for a bit’
For a bit means ‘for a short period of time’.
She was silent for a bit.
Why can’t we stay here for a bit?
Collins COBUILD English Usage © HarperCollins Publishers 1992, 2004, 2011, 2012
bit
Past participle: bitted
Gerund: bitting
| Imperative |
|---|
| bit |
| bit |
| Present |
|---|
| I bit |
| you bit |
| he/she/it bits |
| we bit |
| you bit |
| they bit |
| Preterite |
|---|
| I bitted |
| you bitted |
| he/she/it bitted |
| we bitted |
| you bitted |
| they bitted |
| Present Continuous |
|---|
| I am bitting |
| you are bitting |
| he/she/it is bitting |
| we are bitting |
| you are bitting |
| they are bitting |
| Present Perfect |
|---|
| I have bitted |
| you have bitted |
| he/she/it has bitted |
| we have bitted |
| you have bitted |
| they have bitted |
| Past Continuous |
|---|
| I was bitting |
| you were bitting |
| he/she/it was bitting |
| we were bitting |
| you were bitting |
| they were bitting |
| Past Perfect |
|---|
| I had bitted |
| you had bitted |
| he/she/it had bitted |
| we had bitted |
| you had bitted |
| they had bitted |
| Future |
|---|
| I will bit |
| you will bit |
| he/she/it will bit |
| we will bit |
| you will bit |
| they will bit |
| Future Perfect |
|---|
| I will have bitted |
| you will have bitted |
| he/she/it will have bitted |
| we will have bitted |
| you will have bitted |
| they will have bitted |
| Future Continuous |
|---|
| I will be bitting |
| you will be bitting |
| he/she/it will be bitting |
| we will be bitting |
| you will be bitting |
| they will be bitting |
| Present Perfect Continuous |
|---|
| I have been bitting |
| you have been bitting |
| he/she/it has been bitting |
| we have been bitting |
| you have been bitting |
| they have been bitting |
| Future Perfect Continuous |
|---|
| I will have been bitting |
| you will have been bitting |
| he/she/it will have been bitting |
| we will have been bitting |
| you will have been bitting |
| they will have been bitting |
| Past Perfect Continuous |
|---|
| I had been bitting |
| you had been bitting |
| he/she/it had been bitting |
| we had been bitting |
| you had been bitting |
| they had been bitting |
| Conditional |
|---|
| I would bit |
| you would bit |
| he/she/it would bit |
| we would bit |
| you would bit |
| they would bit |
| Past Conditional |
|---|
| I would have bitted |
| you would have bitted |
| he/she/it would have bitted |
| we would have bitted |
| you would have bitted |
| they would have bitted |
Collins English Verb Tables © HarperCollins Publishers 2011
bit
Short for binary digit, either 1 or 0.
Dictionary of Unfamiliar Words by Diagram Group Copyright © 2008 by Diagram Visual Information Limited
Bridle bit
A steel rod inserted in a horse’s mouth and held in place by the rest of the bridle. Horses are guided by means of reins (lines) attached to each side of the bit. While oxen could be guided from a ring in their nose, horses apparently did not respond well to that approach, and almost as soon as evidence of domestic horses first appeared in a region, the bit also appeared. Bits for riding bridles have always tended to be quite elaborate, but some of the basic workhorse bits looked just like those in the British Museum dating back almost a thousand years.
1001 Words and Phrases You Never Knew You Didn’t Know by W.R. Runyan Copyright © 2011 by W.R. Runyan
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
| Noun | 1. |  bit — a small piece or quantity of something; «a spot of tea»; «a bit of paper»; «a bit of lint»; «I gave him a bit of my mind» bit — a small piece or quantity of something; «a spot of tea»; «a bit of paper»; «a bit of lint»; «I gave him a bit of my mind»
spot small indefinite amount, small indefinite quantity — an indefinite quantity that is below average size or magnitude |
| 2. |  bit — a small fragment of something broken off from the whole; «a bit of rock caught him in the eye» bit — a small fragment of something broken off from the whole; «a bit of rock caught him in the eye»
chip, fleck, scrap, flake fragment — a piece broken off or cut off of something else; «a fragment of rock» matchwood — fragments of wood; «it was smashed into matchwood» exfoliation, scurf, scale — a thin flake of dead epidermis shed from the surface of the skin scurf — (botany) a covering that resembles scales or bran that covers some plant parts sliver, splinter — a small thin sharp bit or wood or glass or metal; «he got a splinter in his finger»; «it broke into slivers» |
|
| 3. |  bit — an indefinitely short time; «wait just a moment»; «in a mo»; «it only takes a minute»; «in just a bit» bit — an indefinitely short time; «wait just a moment»; «in a mo»; «it only takes a minute»; «in just a bit»
mo, moment, second, minute time — an indefinite period (usually marked by specific attributes or activities); «he waited a long time»; «the time of year for planting»; «he was a great actor in his time» instant, jiffy, New York minute, split second, trice, twinkling, wink, blink of an eye, heartbeat, flash — a very short time (as the time it takes the eye to blink or the heart to beat); «if I had the chance I’d do it in a flash» |
|
| 4. | bit — an instance of some kind; «it was a nice piece of work»; «he had a bit of good luck»
piece case, instance, example — an occurrence of something; «it was a case of bad judgment»; «another instance occurred yesterday»; «but there is always the famous example of the Smiths» |
|
| 5. |  bit — piece of metal held in horse’s mouth by reins and used to control the horse while riding; «the horse was not accustomed to a bit» bit — piece of metal held in horse’s mouth by reins and used to control the horse while riding; «the horse was not accustomed to a bit»
bar bit — a bit for horses that is a solid bar of metal bridle — headgear for a horse; includes a headstall and bit and reins to give the rider or driver control bridoon — a bit resembling a snaffle bit; used with a separate curb curb bit, curb — a horse’s bit with an attached chain or strap to check the horse Pelham — a bit with a bar mouthpiece that is designed to combine a curb and snaffle snaffle, snaffle bit — a simple jointed bit for a horse; without a curb saddlery, stable gear, tack — gear for a horse |
|
| 6. | bit — a unit of measurement of information (from binary + digit); the amount of information in a system having two equiprobable states; «there are 8 bits in a byte»
unit, unit of measurement — any division of quantity accepted as a standard of measurement or exchange; «the dollar is the United States unit of currency»; «a unit of wheat is a bushel»; «change per unit volume» check bit, parity bit, parity — (computer science) a bit that is used in an error detection procedure in which a 0 or 1 is added to each group of bits so that it will have either an odd number of 1’s or an even number of 1’s; e.g., if the parity is odd then any group of bits that arrives with an even number of 1’s must contain an error byte — a sequence of 8 bits (enough to represent one character of alphanumeric data) processed as a single unit of information |
|
| 7. | 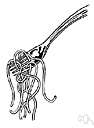 bit — a small amount of solid food; a mouthful; «all they had left was a bit of bread» bit — a small amount of solid food; a mouthful; «all they had left was a bit of bread»
bite, morsel mouthful, taste — a small amount eaten or drunk; «take a taste—you’ll like it» chaw, chew, cud, plug, quid, wad — a wad of something chewable as tobacco crumb — small piece of e.g. bread or cake sop, sops — piece of solid food for dipping in a liquid |
|
| 8. | bit — a small fragment; «overheard snatches of their conversation»
snatch fragment — an incomplete piece; «fragments of a play» |
|
| 9. |  bit — a short theatrical performance that is part of a longer program; «he did his act three times every evening»; «she had a catchy little routine»; «it was one of the best numbers he ever did» bit — a short theatrical performance that is part of a longer program; «he did his act three times every evening»; «she had a catchy little routine»; «it was one of the best numbers he ever did»
routine, number, act, turn performance, public presentation — a dramatic or musical entertainment; «they listened to ten different performances»; «the play ran for 100 performances»; «the frequent performances of the symphony testify to its popularity» showstopper, show-stopper, stopper — an act so striking or impressive that the show must be delayed until the audience quiets down |
|
| 10. | key — metal device shaped in such a way that when it is inserted into the appropriate lock the lock’s mechanism can be rotated part, portion — something less than the whole of a human artifact; «the rear part of the house»; «glue the two parts together» |
|
| 11. |  bit — the cutting part of a drill; usually pointed and threaded and is replaceable in a brace or bitstock or drill press; «he looked around for the right size bit» bit — the cutting part of a drill; usually pointed and threaded and is replaceable in a brace or bitstock or drill press; «he looked around for the right size bit»
bur, burr — small bit used in dentistry or surgery center bit, centre bit — a bit with a sharp center point for guidance and two side cutters chamfer bit — a bit that is used for beveling counterbore, countersink bit, countersink — a bit for enlarging the upper part of a hole cutting implement — a tool used for cutting or slicing drill — a tool with a sharp point and cutting edges for making holes in hard materials (usually rotating rapidly or by repeated blows) drill bit, drilling bit — a bit used in drilling for oil expansion bit, expansive bit — a bit with a cutting blade that can be adjusted to different sizes pilot bit — a small bit that drills a first hole to guide a larger drill shank — cylinder forming the part of a bit by which it is held in the drill spade bit — a thin bit with a center point and cutting edges on either side twist bit, twist drill — a bit or drill having deep helical grooves |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
bit
1
bit
2
Collins Thesaurus of the English Language – Complete and Unabridged 2nd Edition. 2002 © HarperCollins Publishers 1995, 2002
bit 1
noun
1. A tiny amount:
crumb, dab, dash, dot, dram, drop, fragment, grain, iota, jot, minim, mite, modicum, molecule, ort, ounce, particle, scrap, scruple, shred, smidgen, speck, tittle, trifle, whit.
Chiefly British: spot.
2. A small portion of food:
3. A usually brief detail of news or information:
4. A rather short period:
5. Informal. A particular kind of activity:
bit 2
noun
An instrument or means of restraining:
verb
To control, restrict, or arrest:
brake, bridle, check, constrain, curb, hold, hold back, hold down, hold in, inhibit, keep, keep back, pull in, rein (back, in, or up), restrain.
The American Heritage® Roget’s Thesaurus. Copyright © 2013, 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Translations
بت: أصغر وِحْدَةٌ في الذّاكِرَهجُزْءٌ أو قِطْعَطةٌ صَغيرَهجُزْء صَغِيرشَكيمَةُ اللِّجامفَقْرَةٌ قَصيرَه
kousekbitchvilkamalýtrocha
smulestykkebidbidselbit
palanenbittipala
komadić
bitill, mélbrotögn, svolítiîstundarkorn
小片
작은 조각
bitas
bitsdrusciņadruskugabaliņšlaužņi
bitzubadlo
koščekmalopostopoma
bitstycke
เล็กๆ น้อยๆ
miếng
Collins Spanish Dictionary — Complete and Unabridged 8th Edition 2005 © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1971, 1988 © HarperCollins Publishers 1992, 1993, 1996, 1997, 2000, 2003, 2005
bit
[ˈbɪt]
n
(= small piece) [bread, cheese, cake] → morceau m; [paper, string] → bout m
Would you like another bit? → Est-ce que tu en veux un autre morceau?
a bit of cake → un morceau de gâteau
to come to bits, to fall to bits (= break) → tomber en morceaux
to take sth to bits → démonter qch
to do one’s bit → y mettre du sien
quite a bit of (= quite a lot of) → pas mal de
bits and pieces, bits and bobs (= things) → trucs mpl
bits and pieces of (= small amounts of)
I did bits and pieces of translation work → J’ai fait un peu de traduction.
not a bit (mainly British) (= not at all) [surprised, disappointed] → pas du tout
not a bit of it! (British) → pas le moins du monde!
a bit, for a bit > (= British, for some time) → un certain temps
Let’s wait a bit
BUT Attendons un peu.
(= part) [programme, lesson] → partie f
[horse] → mors m
to get the bit between one’s teeth, to take the bit between one’s teeth → prendre le mors aux dents
to champ at the bit, to chomp at the bit → ronger son frein
Collins English/French Electronic Resource. © HarperCollins Publishers 2005
bit
:
bitmap
n (Comput)
no pl (= mode) → Bitmap nt
(also bitmapped image) → Bitmap-Abbildung f
bitmapped
adj (Comput) → Bitmap-, bit-mapped pred; bit graphics → Bitmapgrafik f
bit
1
n
(of key) → (Schlüssel)bart m
bit
2
n
(= piece) → Stück nt; (smaller) → Stückchen nt; (of glass also) → Scherbe f; (= section: of book, film, symphony) → Teil m; (part or place in book, drama, text, symphony etc) → Stelle f; a few bits of furniture → ein paar Möbelstücke; a bit of bread → ein Stück Brot; I gave my bit to my sister → ich habe meiner Schwester meinen Teil gegeben; this is the bit I hate, he said, taking out his wallet → das tue ich gar nicht gern, sagte er und zückte seine Brieftasche; a bit (= not much, small amount) → ein bisschen, etwas; would you like a bit of ice cream? → möchten Sie etwas or ein bisschen Eis?; there’s a bit of truth in what he says → daran ist schon etwas Wahres; a bit of advice/luck/news → ein Rat m → /ein Glück nt → /eine Neuigkeit; we had a bit of trouble/excitement → wir hatten ein wenig Ärger/Aufregung; I only read a bit of the novel → ich habe nur ein bisschen or Stückchen von dem Roman gelesen; don’t you feel the slightest bit of remorse? → hast du denn nicht die geringsten Gewissensbisse?; it did me a bit of good → das hat mir geholfen; it might be a bit of help → das könnte eine kleine Hilfe sein; it wasn’t a bit of help → das war überhaupt keine Hilfe; I’ve experienced quite a bit in my life → ich habe in meinem Leben schon (so) einiges erlebt; there’s quite a bit of work left to do/bread left → es ist noch eine ganze Menge Arbeit zu erledigen/Brot da; in bits and pieces (= broken) → in tausend Stücken; (lit, fig: = come apart) → in die Brüche gegangen; to do the work in bits and pieces → die Arbeit stückchenweise machen; the bits and pieces → die einzelnen Teile; (= broken bits) → die Scherben pl; bring all your bits and pieces → bring deine Siebensachen; to pick up the bits and pieces (fig) → retten, was zu retten ist; to come or fall to bits → kaputtgehen, aus dem Leim gehen; to pull or tear something to bits (lit) → etw in (tausend) Stücke reißen; (fig) → keinen guten Faden an etw (dat) → lassen; to go to bits (fig inf) → durchdrehen (inf) ? bob3 N e
to do one’s bit → sein(en) Teil tun; (= fair share also) → das seine or Seine tun; look, you’re not doing your bit → hör mal zu, du setzt dich nicht genügend ein
a bit of a crack/bruise etc → ein kleiner Riss/Fleck etc; he’s a bit of a rogue/an expert → er ist ein ziemlicher Schlingel/ein Fachmann; he’s a bit of a musician → er ist gar kein schlechter Musiker; she’s a bit of a connoisseur → sie versteht einiges davon; you’re a bit of an idiot, aren’t you? → du bist ganz schön dumm; he’s got a bit of a nerve! → der hat vielleicht Nerven!; it’s a bit of a nuisance → das ist schon etwas ärgerlich; now that’s a bit of an improvement → das ist schon besser
(= coin) (Brit) → Münze f; 2/4/6 bits (US) → 25/50/75 Cent(s)
(Brit, inf) → Tussi f (sl)
bit
3
n (Comput) → Bit nt
Collins German Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged 7th Edition 2005. © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1980 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1997, 1999, 2004, 2005, 2007
bit
1 [bɪt] n
c. (considerable sum) a good bit
quite a bit → un bel po’
d. (Am) (coin) → ottavo di dollaro
bit
2 [bɪt] n (tool) → punta; (of horse) → morso
bit
4 [bɪt] n (Comput) → bit m inv
Collins Italian Dictionary 1st Edition © HarperCollins Publishers 1995
bit1
(bit) noun
1. a small piece. a bit of bread.
2. a piece of any size. a bit of advice.
3. a short time. Wait a bit longer.
4. (computers) the smallest unit of memory.
ˈbitty (informal) adjective
made up of small, unrelated pieces. We had a very bitty conversation; His essay was rather bitty.
bit by bit
gradually. Move the pile of rocks bit by bit.
do one’s bit
to take one’s share in a task. Each of us will have to do his bit if we are to finish the job soon.
in, to bits
in(to) usually small pieces. The broken mirror lay in bits on the floor; He loves taking his car to bits.
bit3
(bit) noun
the part of a bridle which a horse holds in its mouth.
Kernerman English Multilingual Dictionary © 2006-2013 K Dictionaries Ltd.
bit
→ جُزْء صَغِير kousek smule Stückchen τεμάχιο pedazo palanen morceau komadić pezzo 小片 작은 조각 beetje stykke kawałek pedaço кусочек stycke เล็กๆ น้อยๆ parça miếng 小块
Multilingual Translator © HarperCollins Publishers 2009
- It’s a little too hot (US)
It’s a bit too hot (UK)
Collins Multilingual Translator © HarperCollins Publishers 2009







