For many English learners, articles are one of the most difficult things to remember! Articles are confusing because it’s not always necessary to use an article in English.
This lesson is about when NOT to use the definite article the. Sometimes it’s easier to remember when NOT to use something instead of trying to memorize when to use something!
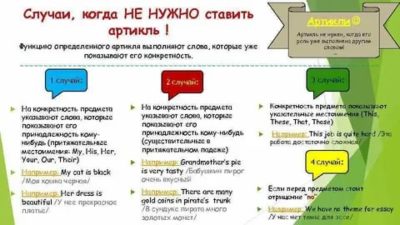
Here are some situations in which you don’t need to use the.
1. Things in general
You don’t need an article when you talk about things in general.
The does NOT = all.
Use plural count nouns:
Cats are great pets!
You’re not talking about one specific cat or one specific pet. You’re talking about all cats and all pets in general.I love reading books.
Women love it when men send them flowers!
Houses are expensive in that neighbourhood.
Americans drive big cars.
Use non-count nouns:
I love listening to music.
You enjoy music in general, not any specific song or kind of music.She’s afraid of heights, so we couldn’t go to the top of the Eiffel Tower.
I love chocolate!
Have you eaten lunch yet?
She’s a vegetarian. She doesn’t eat meat.
NOTE: Count nouns (or countable nouns) are nouns that have a singular and plural form because you can count them, for example one cat, two cats, three cats. Non-count (or uncountable nouns) are nouns that do not have a plural form. You cannot count non-count nouns. For example, you can’t say one music, two musics, three musics.
LEARN MORE: When to use “a” and “the” to talk about one of something
2. Names
Names of holidays, countries, companies, languages, etc. are all proper nouns. You don’t need to use an article with a proper noun.
a. Holidays
I got a beautiful new dress for Christmas.
I got my mom a necklace for Mother’s Day.
Everybody wears green on St. Patrick’s Day.
What are you doing on Valentine’s Day?
b. Geography
Articles are not used before countries, states, cities, towns, continents, single lakes, or single mountains.
I live in Canada.
Mt. Rosa is part of the Alps mountain range.
Mt. Rosa is one mountain. The Alps describe a group of mountains.I’m going to Europe next month on vacation.
Lake Ontario and Lake Huron are 2 of the Great Lakes.
The Great Lakes are a group of lakes on the border between Canada and the US.Mt. Fuji is the highest mountain in Japan.
NOTE: There is an exception to every rule in English. The is part of the names of these countries:
the United States
the Czech Republic
the Philippines
c. Companies
I use Twitter and Facebook every day.
Bill Gates founded Microsoft.
Wal-Mart is the largest employer in the U.S.
McDonald’s has restaurants in 119 countries.
d. Universities
Her son graduated from Harvard.
She goes to Oxford.
He applied to Cambridge, Yale, and Stanford.
However, if the name of the university begins with University, then you must use the:
He has a master’s degree from the University of Toronto.
e. Languages
I am studying Russian.
I speak French.
In Brazil people speak Portuguese.
I teach people how to speak English.
3. Places, locations, streets
Streets, some locations, and some places do not need an article:
I left my book at home.
I have to go to work early tomorrow.
He was found guilty of murder and sent to jail for life.
My office is located on Main Street.
I usually go to church on Sundays.
Good night everyone! I’m going to bed.
Did you go to school today?
When I was in high school, everyone had to study French.
She’s studying business at university.
NOTE: You don’t need an article for subjects you study at school: math, geography, business, history, science.
Places where you DO need to use an article:
I need to go to the bank.
Let’s go to the movies.
My dad is in the hospital.
She works at the post office.
What time do you have to be at the airport?
Please drop me off at the bus stop.
She doesn’t like to go to the doctor or the dentist.
4. Sports
Sports and other physical activities do not need an article:
I love to go skiing in the winter.
I play football every day after school.
He loves watching hockey on TV.
She does yoga 3 times a week.
My daughter really enjoys dancing.
LEARN MORE:
Play, do, or go? Verbs used to talk about sports
Gerunds used for sports
5. Noun + number
He’s staying at the Hilton hotel in room 221.
The train to Paris leaves from platform 2.
My English class is in room 6 on the first floor.
First is an adjective in this sentence. It describes the floor.
6. Acronyms
An acronym is an abbreviation (a short form) of a name. It uses the first letter of each word to form a new word.
a. If the acronym is pronounced as a word, don’t use the.
NATO ambassadors met to discuss the situation.
NATO is the acronym used for the North Atlantic Treaty Organization. NATO is pronounced as one word, /’neɪtoʊ/.UNESCO was formed in 1946.
UNESCO is the acronym used for the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. UNESCO is pronounced as one word, /ju’nɛskoʊ/.
You need to use the before acronyms when the letters are pronounced individually, not as a word.
The UN was created after the Second World War.
UN is used to represent the United Nations. UN is pronounced you-N /ju’ɛn/. It is not pronounced un /ʌn/, like in the word under.
Other acronyms that need the:
the EU
the US
the CIA
the FBI
b. The is not used before university acronyms:
John Smith got his MBA at UCLA.
She has a Ph.D. from MIT.
A, an, the: how not to confuse articles in English
Let’s remember how many articles are in English. There are three of them: a, an, the. If we turn to linguistics, then you can easily remember: the definite article is used when we have the clearest idea of the subject.
As the most remarkable puzzle in the English language, it raises a lot of questions and difficulties to remember. There are no articles in the Russian language, so it is difficult for us to understand how the British use them to separate old information from new, and also very important from just important.
Also, with their help, we find out how many subjects we are talking about — one or more.
So when is the article used in English? It is placed before a noun to define the context of a given noun in a sentence.
Articles are certain и undefined, and perform an orientation function. Thanks to the chosen article, we clearly understand the meaning of the statement.
The definite article the originated from the word «that», it is used with countable and uncountable nouns, both in the singular and plural.
- We have the same feelings towards you. — We have the same feelings for you.
- Is this the same book as ever it was? — Is this the same book as always?
Indefinite article a / an comes from «one», so it can only be used with singular nouns.
- She is a teacher. — She is a teacher.
- A friend in need is a friend indeed. — Friend is known in trouble.
The article is not used in a variety of cases; below we will analyze these cases. For now, a couple of examples:
- I am going to have dinner. — I’m going to dinner.
- He claims total memory loss. — He has a complete memory loss.
Articles in English: Are the Rules That Simple?
Of course not. On the appropriate forums, students are in full swing discussing the specifics of using articles and lamenting how to remember them all. In this article, we analyze only the most basic rules that you most often face when learning English.
Basic rules for articles a and an:
Usage rules Examples
| We are talking about something general, not specific | She is a journalist. She is a journalist |
| Generalizing concept for the entire group of subjects | If you want to be a doctor, you should know a lot. If you want to become a doctor, you have to know a lot. |
| The article in its first meaning «one» | Would you a cup of tea? — Would you like (one) cup of tea? |
| First mention of the item | I bought aa carton of milk. The carton is in the fridge. I bought a carton of milk. A bag in a (specific) refrigerator |
| If there is a repeatable action | She drinks coffee twice a day. She drinks coffee twice a day |
| Before adjectives | Have you bought a small flat? — Have you bought a small apartment? |
| With units | She works part-time, only 4 hours a day. — She works part-time, only 4 hours a day. |
So we have named some rules for articles a and an in English.
It is important to remember that the a / an setting depends on the first sound, not the letter in the word. So, in the words hour — hour and honor — honor, the first sounds are vowels, so we put an, and in the words hooligan — a bully and yacht — a yacht, the first sounds are consonants, so we put a.
We now turn to the definite article.
Basic rules for the article the:
Usage rules Examples
| The article in its first meaning «this» (ie the specifics of the subject) |
Source: https://www.bkc.ru/blog/about-language/grammar/a-an-the-kak-ne-putat-artikli-v-angliyskom-yazyke/
LESSON 17 English
Abstract of the 17th lesson in PDF format can be viewed, printed and downloaded at this link
Do you know what is the most frequently used word in English? This is the article the! There is also an article a/an, and in some cases the article should not be used at all.
The topic of the correct arrangement of articles, despite its apparent simplicity, remains one of the «stumbling blocks» even for those who have been studying English for a long time.
In this lesson we will try to understand why this interesting part of speech is needed, in which cases it is necessary to use articles and how to do it correctly.
The meaning and use of articles
In English before everyone noun, as a rule, the article is put. Of course, there are cases when the article is not used (the so-called Article zero). But in general, the rule remains in force — this part of speech goes along with the noun «in conjunction». If a noun is used with adjective, the article is placed before the adjective, and all article placement rules remain in effect.
This topic seems difficult to us because in the Russian language there is no such part of speech as the article. However, we still have words that seem to play his role. Let’s look at how the definite and indefinite articles differ, and with what words they can be replaced in Russian.
Use of the indefinite article ‘a / an’
Article a/an in English comes from the word one — «one«. The analogue of this article in Russian will be the word “one”, But not in the meaning of quantity, but in the meaning of“ one of many ”. For example: “I knew one doctor «.
If the article is followed by a word that begins with a consonant, we put the article a, if with a vowel — use an… If a noun is used with an adjective, the rule applies to the adjective preceded by the article. For example: to book (book), an actress (actress), a nice girl, an interesting film (interesting film).
Pay attention! This rule is determined by phonetics (pronunciation), not spelling. For example, the word an hour [auə] («Hour») begins with a consonant, but with a vowel, so we put the article an. The words a university
Source: http://en1632.com/f/lesson32_17_synopsis.html
A, AN, THE — all about articles in English. Navit for Rivnya Advanced!
Frankly, would you like to remember everything about articles in English once and for all? And we admit that we really want to help you with this! In this article, we have collected all the rules for using A, AN and THE in English — from the Beginner level to the most advanced. We do not promise that it will be easy, but very useful. Save to bookmarks so you don’t get lost!
A / AN or THE — basic rule
A and AN are indefinite articles. We use them when:
- We are talking about something in general, and not about a specific thing:
— I need a vocabulary. — Not a specific dictionary, but in general. - We are talking about something new or unknown:
— Jane is a DJ. — New information for the listener. - For the first time, we tell the listener something:
— I have a bicycle. — This is the first time we are talking about a bicycle. - We ask about the presence / existence of something:
— Do you have a power bank? — Not specific, but any. - We describe something (which, as a rule, we are talking about for the first time) or ask about the characteristics:
— This is an excellent album.
— Do you live in a big house?
! A rule that everyone should know. We never use A / AN with plural and uncountable nouns, because these articles indicate the singular and mean «one» or «singular.»
THE article is definite. We use it when:
- We speak or ask about something that is already known to the listener, has been mentioned, introduced or discussed before:
— There is a book in my table. The book is very old. — After the first mention of the book with the article A, it becomes definite and used with the article THE.
— Don’t you know where I left the keys? — We ask about specific keys, not keys in general. - We speak or ask about something that is described by defining phrases:
— Did you listen to the song which I sent you?
— I the movie that we watched yesterday.
Important! Not all descriptions make the subject matter specific. Some simply describe its qualities (as in clause 5 on the use of A / AN articles). It all depends on the context and you need to be careful:
- She bought a phone with 2 cameras. — When we just say that she bought some kind of phone with two cameras.
- She bought the phone with 2 cameras. — When she was choosing among specific phones (and the listener knew about it), she chose the one with two cameras.
The singular and plural rule. THE article can be used with both singular and plural nouns.
All English verbs followed by an infinitive
A or AN before consonants and vowels
Of course, everyone knows that A and AN are interchangeable articles. A is used before nouns (or adjectives describing nouns) that begin with a consonant, and AN is used before consonants:
- She is a doctor.
- He is an actor.
- She is an excellent doctor.
- He is a brilliant actor.
Important! An English consonant at the beginning of a word is not always a consonant.
The article AN is used before words that begin with vowels, although the letter is a consonant. For example, «hour». This also applies to the names of the letters «F», «L», «M», «N», «R», «S», «X».
And one more catch. Some words, such as «herb» or «hospital», are pronounced differently in British and American English. For example, in the UK the «h» in the word «herb» is pronounced, but in the American it is not.
In the word «hospital», on the contrary, the «h» is pronounced by the Americans and not by the British. Accordingly, the articles for the two accents will be different. What to do? Don’t worry too much.
Just remember this funny exception and use the articles in accordance with how you personally pronounce these words.
English articles with tense nouns: A, AN, THE or nothing?
Moving on to a more complex level of grammar of English articles. This topic is rightfully considered one of the most difficult, along with the next one — articles with geographical names and other designations of places. So.
The article THE is used in such time expressions:
- in the morning
- in the afternoon
- in the evening
- during the night
- during the day
- the day before yesterday
- the day after tomorrow
- the fall, the summer, the winter, the spring
examples:
- We’ll meet in the evening
- I love to travel in the summer.
Articles are not used before the names of the days of the week, months, holidays and in such expressions:
- at night, at noon, at midnight
- all day, all night
- all year, all month, all week
- every month, every year
- last night, last day, last week, last mont, last year
- yesterday, today, tomorrow
examples:
- Did you sleep well last night?
- We’ll meet tomorrow.
Any articles, both THE and A / AN, can be used in these expressions:
- a / the whole day
- a / the whole month
- an / the entire year
- an / the entire decade
examples:
- Mike spent a whole year in London.
- Last Monday I went to the doctor and spent the whole day in his office.
All English verbs followed by a gerund
English articles with place names and directions
Names of countries and cities in English — with or without the article?
Countries, cities, states and provinces are usually not preceded by an article. Exceptions with the article THE:
- Countries, states, cities and provinces with the words States, Kingdom, Republic, Emirates, Union, Coast, Territory in their names: the United States, the Northwest Territories
- Island States: the Philippines, the Maldives, the Bahamas
- The Netherlands
In the not too distant past, the Sudan, the Gambia and the Congo were also exceptions, but more and more often they appear without an article. So now it is 1 point easier for us to understand the rules of English articles.
Geographical (and astronomical) names with the article THE
In English, the article THE uses the following names:
- oceans, seas, rivers, swamps: the Black Sea, the River Thames
- groups of lakes: the Great Lakes
- coasts: the Florida Suncoast, the Emerald Coast
- archipelagos: the Berlengas, the Canary Islands
Source: https://grade.ua/ru/blog/a-an-the-articles-in-english/
The article the in English is a total analysis!
Hello my wonderful readers!
You can probably guess what is the most frequently used word in English, right? Of course it is the article «the»… And today we will analyze where its use in English is appropriate and where it is not. We will study the rules for its use, look at numerous examples, analyze a table with stable expressions, which you can always have at hand. And then you can move on to the exercises and the online quiz to reinforce what you’ve learned here.
Go ahead, friends!
A little grammar
If the article «a» (about it in detail here!) Is used only with nouns that can be counted, then «the» is used with all nouns: both in the singular and in the plural; with both countable and uncountable objects.
By the way, the pronunciation of the article also changes depending on which letter the next word begins with. If the word begins with a consonant, then the article is pronounced like [ðə], for example the banana — banana. But if the object begins with a vowel, then it is pronounced like [ði], for example, the apple is an apple.
When used
- If in speech or writing already mentioned the subject, then in the future you can put this article with it.
I received an e-mail from my friends. The letter told me that they would visit me on the weekend. — I received a letter from my friends. The letter said that they would visit me on the weekend.
- With unique items that are one of a kind, we also use the — the sun, the moon, the Earth.
The moon today is extremely beautiful. — The moon is incredibly beautiful today.
- The article has a very special relationship with place names. With titles rivers, deserts, oceans, island groups and mountain ranges we can confidently use the article, but we must not forget about the exceptions. I talk about them in great detail separately.
The Atlantic Ocean is the most beautiful ocean on the planet. — The Atlantic Ocean is the most beautiful ocean on the planet.
The Comoro Islands attract lots of tourists every year. — The Comoros attracts many tourists every year.
- With titles hotels, cinemas, ships, museums, galleries and newspapers we also use the definite article most often.
The Hilton hotel is about to open in our city. — The Hilton Hotel is about to open in our city.
The Louvre is the most attended museum in Europe. — The Louvre is the most visited museum in Europe.
- With adjectives of the highest degree of comparisons: the most, the best, the worst.
The most beautiful place I’ve ever been is Japan in spring. — The most beautiful place I’ve ever seen is Japan in the spring.
The best books I’ve ever read were about Harry Potter. — The best books I’ve read are Harry Potter.
- With musical instruments and titles dancing.
The violin is my most beloved musical instrument. — The violin is my favorite musical instrument.
The contemporary has become very popular among dancers some years ago. — Contempo became very popular among dancers a few years ago.
When not used
It is extremely important to know when the definite article is used, but it is equally important to know when it is not used up.
- With plural nouns that cannot be countedwhen we tell something common.
Trees produce oxygen. — Trees produce oxygen. (Any trees in general)
- With names own and before names we never use it.
Jinny is very talented. She can play 3 different musical instruments. — Ginny is very talented. She can play three different instruments.
- With titles countries, cities, streets, parks, mountains, lakes, bridges and islands we try to avoid it.
Source: https://lizasenglish.ru/grammatika/artikly-the.html
Articles in English — definite and indefinite
The indefinite and definite articles, although they seem small and insignificant, actually play a very important role in the language. Their use is so important that when dealing with foreigners, you run the risk of driving yourself into a dead end if you don’t know how to use the article. In order not to get confused when to use them and in what form, let’s figure it out once and for all in simple, but very important rules.
What is an article?
Due to the fact that there is no such thing as an «article» in Russian, articles cause a stupor in many English language learners.
Where? What for? And most importantly, how do you use articles in English? And, although not everyone is able to cope with them right away, first you need to remember: articles are placed in front of almost ALL nouns in English.
In colloquial speech, and sometimes in the English-language media, articles can be omitted, but this does not mean that they should be forgotten as a nightmare and never used.
The use of articles in English is necessary to clarify what is being discussed. Are you talking about an abstract subject or a concrete one? Therefore, there are only two options — the definite and indefinite article. But more about the rules for using articles in English — further.
Rules of Use
Actually, the rules for using articles in English are already laid down in the name itself.
Definite article used in cases where the speaker clearly understands what is at stake.
Indefinite article — if we are talking about an object from a set, about one of, some — in other words, not specific.
If during speech you can point to something and say «this», then, most likely, you will need a definite article, if not, then an indefinite one. It’s simple.
| Table of common uses of articles in English: | |||
| units number — countable nouns | pl. number of countable, uncountable nouns | ||
| uncertain | before consonant sound | a | no article |
| before vowel sound | an | no article | |
| certain | the | the |
Let’s give an example.
There’s a girl waiting for you on the first floor. — Some girl is waiting for you on the first floor.
The speaker is not familiar with the girl, the article can be easily replaced with «some» or «one».
The girl that we were talking about is waiting for you on the first floor. — The same girl we talked about is waiting for you on the first floor.
The speaker knows this girl and refers to the moment in the previous speech so that the interlocutor understands which girl is being discussed.
From the two examples, it is obvious that if a conversation about an object comes up for the first time, and it is not yet entirely clear what it is, it is necessary to use the indefinite article.
Once lived a young girl, who loved catching butterflies. — Once there was a girl who loved to catch butterflies.
But, if we continue to talk about the subject, we already perfectly understand who we are talking about, and must use the definite article. If another object appears in speech, it is the same again.
Once the girl met a boy, who loved butterflies too. The boy told her they should be friends. — Once this girl met a boy who also loved to collect butterflies. This boy told her that they should be friends.
Further in the text, both the girl and the boy come with definite articles. If a butterfly appears in the text that asks them to stop catching butterflies, it will also first have an indefinite article in front of it, and then a definite article.
Или:
I want to buy a coat. — I want to buy myself some kind of coat.
The speaker has not yet gone shopping, did not find out the prices, he simply says that it would not hurt him to buy a new coat — for example, because the old one is completely leaky.
I want to buy the coat. — I want to buy that / this coat.
The speaker stands right in front of the window, points to the coat that matches his preference.
If a noun is preceded by an adjective in addition to the article, it is placed after the article.
A young man and an old woman crossed the road. — A young man and an elderly woman crossed the road.
The clever students made the task all by themselves. — Smart students coped with the task on their own.
Definite article also used in cases:
- when it comes to something that is one of a kind: the Sun (sun), the Earth (planet Earth);
- before place names with additional nouns: the Black Sea, the Volga river, the Ural Mountains, BUT: Russia (Russia), America (America), the United Stated (USA);
- in front of the cardinal points: the Northern Europe, the East wind;
- before ordinal numbers: the first room (first room), the third place (third place);
- before the classes of animals / plants: the whale (whales), the roses (roses);
- before titles / ranks, one of a kind: the Queen (Queen), the president of Russia (president of Russia);
- before the superlative: the best swimmer, the highest mountain;
- before the words «most of», «one of», «some of»: most of the days (most of the days), one of the books (one of the books);
- before the family name in the plural: the Smiths, the Browns.
Indefinite article in English can be replaced with the words «one» («one»), «some» («some», «some»). So if you can put these words, and the meaning does not change, then you really need the indefinite article.
It is also used for:
- profession name: She’s a nurse. — She is a nurse;
- before the words «such», «rather», «quite»: He’s rather a good guy. — He’s a pretty nice guy;
- before nouns denoting time, meaning «one»: back in a minute — I’ll be back in a minute; phone you in an hour — I’ll call you in an hour.
There are also cases when the article is not used at all — in this case, they speak of using the «zero article».
Using the zero article
First of all, it should be remembered that the zero article in English is placed before most of the proper names. That is, calling someone by name, you cannot put anything in front of him, and if you say «The Peter», you will definitely be considered illiterate. Why does Peter need a definite article, if he is alone in your environment, and so it is clear what it is about?
Peter left his keys. — Peter left his keys.
In addition, the plural does not require the zero article when it comes to the subject for the first time. «A / an» always displays the item in the SINGLE number.
He left keys in my room. He said the keys were yellow. He always forgets his keys at my place. — He left some keys in my room. He said these keys were yellow.
Yes, if the noun is preceded by a possessive pronoun, the article is also not needed. The same goes for numerals: if the number is in front of the noun, the article is not put:
I’ve spent ten dollars. — I spent 10 dollars.
If the noun is abstract, that is, it has no concrete meaning and cannot be counted, the article is not put:
I need money. — I need money.
I need information. — I need information.
If a noun is used as a definition, the article is also not needed:
He s punk-rock music. — He likes punk rock music.
Source: https://www.lovelylanguage.ru/grammar/rules/179-articles-in-english
When «the» is written, when «a», «an». The definite and indefinite articles of the English language
Articles are absent in Russian, but are present in English and are
Articles are absent in Russian, but are present in English and are determinants of a noun. Articles are of two types: classifying (a or an) and individualizing (the).
A и an are called the indefinite article (the Indefinite Article). The is called the Definite Article. Articles are not stressed.
Indefinite article form а used before words starting with a consonant: a table table, a balso book. Second form of the indefinite articlean used before words starting with
vowel sound: anauthor author, anarm arm, an old manсtarik.
Notes:
Words beginning with the letter u are preceded by the article аwhen u reads [ju:] because the first sound in such words is a consonant, and an article when u reads [a]: a union union, an umbrella umbrella.
Words starting with the letter h are preceded by the article anwhen h is unreadable, since the first sound in such words is a vowel, and the article аwhen h is read: an hour hour, a hunter hunter.
This article was formed from the numeral one — one, so it can only be used with countable nouns in the singular.
The definite article has one form –the. It was formed from the word that — that. You can use this article with both singular and plural countable nouns and uncountable nouns.
Example:
The book — book
The songs — songs
As already mentioned, we use articles in front of nouns, but it is necessary to remember that if there are definitions in front of a noun, then the article is placed in front of them.
Use
The most important and important thing: «a», because in the soul it is still one, is used only with countable nouns, that is, with those nouns that can be counted through 1, 2, 3 (of course, 2, 3 and more only are implied).
The article «a» is used when we communicate something for the first time.
This is a table.
“The” indicates to us that this something has already been discussed and known to the speakers. The table is made of wood.
Further, the articles perform different functions.
«A» is placed where the subject is given a description:
This is a nice film. We saw a very large building.
“The” is used when there is a clarification, additional information about the subject, and the clarification is after this word.
This is the house I live in. This was the man I definitelty knew before. The girl, standing by the window, is my sister.
This is brief and basic information.
| A | The |
| Uncertainone, some, some, any, any of many, no matter what | Certainthis one, specific; that, which |
| A plate — plates (no article in plural) | The plate plates |
| Here is a house. | The house is broken. |
| It was an old dusty clock. (description) | This is the clock that wakes me up every morning (clarification) |
Null article
The article is not used if there are already words in front of the noun that somehow identify it.
*some, any, no, each, every
* (whose) my, your, his, our, their, her, its, Tom’s, etc.
* this, that, these, those
* (how many) 2, 3, 4 many, much, few, little
In the bulk, the article is not put in cases, if it is about it at all, with uncountable nouns. (more details next time)
* liquids: water, oil, juice, jam, milk
* bulk: sand, sugar, salt, serials
* chipping objects: marble, chalk
* chemical elements
* abstract concepts (mainly feelings and emotions): love, friendship, grief
Source: https://engrammar.ru/grammar/kogda-pishetsya-the-kogda-a-an-opredelennyj-i-neopredelennyj-artikli-anglijskogo-yazyka/
When to use the article a and the, or the basics of the English language
People have a lot of controversy when it comes to the most popular word in the English language. Some are sure that this is some kind of famous event, for example, «Christmas». Others are convinced that it is about God (God). But both are wrong in the end.
Have you already guessed what this is about? Of course, about the. By the way, «a» is used a little less than it. As you already understood, today we will focus on them.
What is it, why are they needed, and, most importantly, when is the article a and the put in English? Let’s figure it out together. So let’s get started.
The article
By itself, the word article is that part of speech that is always placed before a noun. In English, there are three of them: a, an and the. In fact, it all depends on the noun to which they are attached. That is why we are figuring out how to put articles in English.
There are a number of rules here, following which you will always use this part of speech correctly. In fact, this topic is, on the one hand, the most beloved, on the other, the most confusing among people who start learning a foreign language. Many are confused by the question when the articles a and the are put in English.
However, thanks to our article, you will be able to better understand what is at stake and will no longer doubt the choice of this part of speech.
First, let’s take a look at how to use articles in English. We have already mentioned that they are used together with nouns. But when should you use which one? The fact is that nouns in English can be of only two types:
- Countable;
- Uncountable.
In the first case, we are talking about such items that you and I can count. These are newspapers, days, children and so on. The second option refers to more global and stable concepts. Like water, air, oxygen. Agree, we will not count them individually. When the article a, an, the is put in English depends on which noun is in front of us. We’ll go into more detail on this below.
Not unimportant in the case of the article is the number of the noun. As in Russian, it can be singular and plural. And this affects when the article a, the and an is put. «How?» — you ask.
The fact is that with nouns in the plural of a countable form, the or the zero article is always used, we will talk about it later. The same is the case with the uncountable type of this part of speech. When are the articles a and an used? Also, together with «the» they are placed before the countable noun, in the singular.
A bit confusing, isn’t it? For you, we have compiled a small table so that it becomes clear when the articles a and the are put in English.
| Nouns | |||
| Countable | Uncountable | ||
| Singular | Plural | the | |
| a / an | the | the |
Thus, we hope, due to the visual form, it will be easier for you to understand when the article the is put in English, and when a. And we are moving on.
The definite article the
Now we would like to tell you in which cases the article the is used. But first of all, it is worth recalling that this article is definite. This means that we are talking about something specific, definite. Another variant of the definition when the article the is put in English is the translation of the phrase into Russian.
If in this case it is possible to put a demonstrative pronoun instead of it, then it is definitely needed in this text. We have already mentioned where the article the is put. Before nouns, both countable and uncountable, in any number. Below we will tell you in detail about when we put the article the, and when not.
Let’s get started.
When a noun is preceded by the article the in English:
- In the case when the word has already been used in the context. This fact allows this article to be used unmistakably. For example: I got correspondence this morning. The newspaper was useful. Which means: I received the correspondence this morning. The newspaper was helpful.
- This article is also placed before nouns that are known in the singular gender.
For example: the sun, the God, and so on.
- When geographical names are used in the text, the article «the» is used, as, for example, in the following cases: the Atlantic Ocean, The Comoro Islands.
- In the case when it comes to the names of cinemas, hotels, firms and others, the definite article is used. For example, The Hilton hotel, the Louvre.
- Also, this article is used with adjectives of the highest degree of comparison. That is, we are talking about expressions such as: the best, the most beautiful.
- And also when mentioning musical instruments and the names of famous dance styles. For example, the ballet, the piano.
Next, we will talk about when the article the is not put.
This is important because, given this criterion, you can always understand where the article is put and where it is not. So let’s get started.
The article the is not used:
- In the case when plural nouns are used and we are talking about something in common. For example: Flowers bloomed in the spring. In this case, we are talking about all flowers, we are not specifying, which means that the article the is not put.
- It is not used before names, as well as before proper names. For example: Anne came home.
- Before the names of cities, countries, rivers, lakes, parks and islands. New-York, Spain, Russia.
- The article is not used with the names of various sports, activities, colors, days, months and drinks. For example: May, green, Sunday.
- In the event that the text contains the pronouns those, that and this, we do not put the the. And also before possessive pronouns. This house is beautiful.
- There are certain situations when you can put or not put this article in front of certain words.
It all depends on the specific meaning. For example: I go to school — I go to school. My mother went to the school for a meeting. That is, in the case when we are talking about attending a particular school for a specific purpose, the use of the article is possible.
- Another option with an exception is the name of the diseases. You can use the at your discretion.
We have examined where the article the is put, and where the «a» is put — we will find out below.
Article «a»
Here we will talk about when the article «a» is put in English. First of all, it should be noted that we are talking about two options. That is, in fact, we will talk about when the article a and an are put in English. If you are wondering what this is related to, read on.
This happens because some nouns begin with vowels, and, accordingly, it is impossible to use the article a, and we put an. Very similar to the situation in the Russian language — o / v. Now let’s talk in more detail about when the article «a» is put in English.
- It is generally accepted that this article can be translated as «some». That is, if you do not know when to put the article a, just try to attach this translation to a noun. If the meaning of the phrase is unchanged, then this is the case when the article a / an is put.
- When a subject is mentioned for the first time, «a» is put. We have already considered the option when the item was declared several times — we put the.
- As a substitute for the word «per». For example: 5 hours per week can be replaced with 5 hours a week.
We have already considered when the article «a» is put in English. Now it’s time to talk about the times when it is best to avoid it.
- We have already said that this article is not placed before plural nouns, as well as before uncountable ones.
- You should never use it with pronouns. You yourself choose the use of one or the other.
- There are also fixed expressions in which the use of articles is just worth learning. We will talk about them below. There are also exceptions when «a» is not used despite the rules.
Now you and I know exactly where the articles the and a are placed. We will be able to calmly communicate with foreigners, as well as ourselves to tell others when the article «a» is put in English, and when «an» is used. But this is far from all the information on a given topic. Below we will talk about how articles are put in English, as well as about those very fixed expressions that you just need to learn. Well, let’s get started.
A little about is and are
To begin with, when a preposition is used, «the» is not used in English. Another thing is the article «a». It is used with the verb is. This happens in cases where any professions are mentioned: She is a doctor. In addition, «a» is always used after expressions with «this is», «that is», «it is». For example: This is a table.
Thus, we have learned a little more about when the article «a» is put in English. The article is not used with the verb are.
Combinations to Learn
How the articles are put in English, we figured it out a bit. However, as we stated earlier, there are a number of specific exceptions. We will talk about them further.
Despite the rules about when to use an article in English, there are some specific variations worth remembering.
You need to use the article a or an:
- With diseases: a headache (headache);
- With professions: a doctor (doctor);
- With the verb to have: to have a look;
- In stable terms: as a rule, as a result, as a matter of fact, a lot of, a few, it is a pity, to tell a lie, to go for a walk.
List of fixed expressions with the article the:
- By the way (by the way);
- On the one hand (on the one hand);
Source: https://tutskill.ru/grammatika/kogda-stavitsya-artikl-a-i-the-ili-osnovy-anglijskogo
The definite article in English: rules and examples
Having difficulty with articles? Can’t remember more than a few rules? We promise to tell you everything you need to know about articles in English. Read about how to correctly apply the definite article in English in our article!
Introductory article
Articles are one of the riches of the English language and a big problem for those who speak other languages where there are no articles. The majority of Russian-speaking students learning English find it difficult to understand the category of certainty-uncertainty, which is used by native speakers of English. We need a real restructuring of the mind, a readjustment of logic.
But English long ago got rid of the complex system of cases and categories of grammatical gender, which are preserved in Russian and so scare everyone who wants to master it. And perhaps it was this transformation from a synthetic language to a predominantly analytical language that helped the English language achieve a truly unique worldwide recognition.
Despite all the simplifications, the rules for the use of articles in English for a number of reasons are difficult for speakers of other European languages.
For comparison, take a sentence in German: “Da er_Botaniker ist, liebt er die Natur” (“Being a botanist, he loves nature”) — and the corresponding sentence in English: “Being a botanist, he is fond of nature”.
As you can see, in the English version there is an indefinite article in front of the name of the profession, in German it is not. Conversely, English does not place articles in front of nouns such as “nature,” while German requires a definite article in the same position.
Even between British and American English in this case, there are discrepancies. For example, Americans usually speak of someone in a hospital as “in the hospital”; in the same way he could be in the bank, “at the bank,” or in the park, “in the park”.
For a Briton, this means that there is only one hospital in the city, or an American talks about a specific hospital that he constantly visits. The British will say that the patient is “in hospital”, the child is “at school”, and the criminal is “in prison”. In their understanding, it is more about the profile of these institutions, and not about the buildings in which they are located.
But if you just walked into a hospital, school or prison building, then you are at the hospital, at the school or at the prison — here the British are in solidarity with the Americans.
These examples are intended to show that articles in English are a more significant part of the language than meets the eye. They are precise instruments that help to express all the subtle nuances of meaning in English in a delicate way. In the vast majority of cases, the use of the article has a clear rationale. Understanding this can help disguise non-native English and improve communication with native speakers.
Differences between the article The and A
Let’s remember a little from theory. A (year) — this is an indefinite article, it indicates an indefinite subject, and emphasizes that the subject is one. THE — the definite article, it is used when something is mentioned that is already known to the speaker.
Consider this example:
— My father bought me UN Chien.
— Great! What color is the dog?
— The dog is black. And my mother bought me a book.
The first sentence applies article A, since the dog is mentioned for the first time, and the interlocutor does not know anything about it yet. Further used article THE, since it became clear to both speakers what kind of dog they were talking about. In the last sentence, the word book also used with the indefinite article, since it is mentioned for the first time, the person has not yet determined what kind of book it is.
Some more examples:
Yesterday I got a letter. The letter was from my friend. — Yesterday I received a letter. The letter was from a friend of mine.
I am reading a newspaper… I bought the newspaper from the newsagent. — I am reading a newspaper. I bought a newspaper from a periodicals seller.
Remember the rule: If in front of you is a countable noun in the singular, then use A if this subject is mentioned for the first time or if it is indefinite, irrelevant. THE is used if the subject has already been mentioned before and is known to the interlocutors.
Sometimes, despite the fact that something is mentioned for the first time, we can understand from the context what it is about: when additional information about the subject is given, an explanation, or when it is clear from the situation itself. Let’s look at examples with explanations:
I was at a party yesterday. — I was at a party yesterday.
(I mean some kind of party that we don’t know anything about yet)
I was at the party organized by my friend. — I was at a party organized by a friend of mine.
(We understand what kind of party we are talking about)
He saw a woman in the corridor. — He saw (some) woman in the hallway.
(No additional information is given about the woman)
He saw the woman who lived next door to him. — He saw a woman who lived next door.
(We understand what kind of woman she is)
He entered a by… — He entered the door.
(He entered one of the doors, we do not know which one).
He entered the door nearest to the stairs. He entered the door closest to the stairs.
(Specifies which door)
The definite article The
The main rule of thumb for using the definite article in English is this: if we use the, then we are talking about something concrete, specific, about something that is familiar to both us and our interlocutor. A synonym for the definite article can be considered words such as this, That.
In general rules, we told the main use cases for the article the, now we will consider many special cases:
The definite article the is used with one-of-a-kind, exceptional objects: the sun, the environment, the internet.
The superlative adjective will help make objects unique: the tallest building (the tallest building), the best singer (the best singer), the most expensive car (the most expensive car).
And thanks to the words only (unique), same (same), first (first) objects also become unique: the same exam (the same exam), the only person (only person), the first time (first time).
Yuri Gagarin was the first person in space. — Yuri Gagarin was first person in space.
To describe or indicate a group of objects, a class as a whole, use the construction «the + countable noun in the singular».
The cheetah is the fastest animal in the world. — Cheetah Is the fastest animal in the world. (we are not talking about one cheetah, but about the type of animals)
i play the piano… — I play on pianist.
I consider the telephone to be the most important invention. — I think that phone Is the most important invention.
Also, when talking about a group of people, use the + adjective. Please note that the verb in this case will be plural.
For example: the young, the poor, the homeless.
The young always argue with their parents. — The youth always argues with his parents.
The same construction is used with adjectives that end in -сh, -sh, -ese, if all representatives of any nation are meant.
For example: the French, the English, the Chinese.
The french are charming. — French people adorable.
The Vietnamese are very hard-working. — Vietnamese very hardworking.
When referring to all family members as a group, use the definite article the and the plural surname: the Joneses.
Often the definite article the is used with names:
- buildings (hotels, cinemas, theaters, museums, galleries, restaurants, pubs) — the Plaza hotel, the Odeon, the Kremlin, the Red Lion pub a lion»);
- newspapers (the article is part of the name and is written with a capital letter) — The Times (the Times newspaper), The Guardian (the Guardian newspaper);
- sporting events — the FIFA World Cup;
- historical periods and events — the Bronze Age (Bronze Age), the Vietnam War (Vietnam War);
- famous ships and trains — the Mayflower (ship «Mayflower»);
- organizations, political parties, institutions — the Red Cross, the Democratic Party;
Source: https://englishfull.ru/grammatika/artikl-the.html
Article in English
Zolotareva T.P., teacher, secondary school № 100, Krasnodar
Terms of use of the article in English
ARTICLE
indefinite article «a «(«an «) the definite article»the »
Indefinite article in english
- If you can put the words in front of a noun: any, everyone, everyone.
Example:A student must work hard.
Notes: Not used in the plural.
Example: Students must work hard.
- After revolutions: there is, there was.
Example:There is a pen on the table.
- After verbs am, have, is, has.
Example: I have a cat.
I am a worker.
- С sustainable combinations.
Example: to have a rest, to have a tooth ache, to make a mistake, to go for a walk, to catch a cold, to give a look. (Phrases must be remembered)
- In exclamation points after what, such.
Example: Such a good day!
- If the noun has a descriptive definition.
Example: It was night. — Was night.
It was a cold night. — Was cold night.
- When the subject is spoken about for the first time.
Example: I ate an egg for lunch.
8. The article «a «(«an «) is placed only before countable nouns !!!
The definite article in English
1. If the subject has already been discussed.
Example: I see a bird. The bird is big.
2. If the subject is known from the situation or context.
Example: The play was interesting.
3.
If before noun Yes limiting definitions, such as: only, main, central, same, right, left, next, last, final; or ordinal numerals: first, second.
Example: Give me the second cup of tea.
Notes:second, third — have the meaning «one more».
4. Before adjectives in superlative degree.
Example: The best, the nice.
5.
Before nouns unique in the world or in a given setting.
Example: The sky, the west, the cosmos.
6. Before nouns in the role of the circumstance of place, nouns have prepositions of place: in tea.
Example:in the garden.
7.
The noun is used in a generalized generic meaning and represents the entire class.
Example: The elephant is a strong animal.
8. Before nouns formed from adjectives and participles.
Example:Poor — poor the poors — the poor.
9. In a number of established phrases.
Example: in the morning, in the country, on the left, the day before yesterday, tell the truth.
Zero article in English
1. If there are other qualifiers before the noun (pronouns — possessive, demonstrative, interrogative, indefinite; noun in the possessive case)
Example: My room is large.
2. If the noun is preceded by a cardinal number.
Example: one man, two girls, three boys
3. Nouns denoting the names of substances are used, as a rule, without an article: water, milk, chalk, sugar, tea, snow, grass, wool, meat.
Example: He saw snow in the fields.
4. Uncountable abstract nouns (abstract concepts), as a rule, are used without an article: weather, music, power, knowledge, art, history, mathematics.
Example: I music.
5. Before a noun in the function of address (here a noun serving as an address is considered as a proper noun and is used without an article)
Example: Good morning, Captain!
| Name |
The |
Without article |
|
Parts of the world, continents |
If there are words States, Union, Federation; country in plural Number(The United States of America) |
Without article |
|
Oceans, seas, straits, lakes, rivers, waterfalls |
With article |
If there is a word lake in front of the name, etc. |
|
Deserts |
Only with the article |
An exception: Death Valley, Silicon Valley |
|
Mountain ranges |
With article |
Name of individual vertices without article |
| Name |
The |
Without article |
|
Streets, squares, parks |
Are written without an article |
|
|
Theaters, museums, galleries |
Only с article |
|
|
Cinemas, hotels, restaurants, cafes |
Only with the article |
Buckingham Palace (excluded) |
|
Famous works of art, books |
Only with the article |
|
|
Airports, stations, bridges |
Always without an article |
|
|
Schools, colleges, universities |
Remember: the Sorbonne, |
Always without an article |
|
Churches, cathedrals |
Always without article |
|
|
Ships, yachts, famous trains |
Only with the article |
|
|
Political institutions, historical events |
Only with the article |
Parliament, Congress, White hall (excl.) |
|
English, American newspapers and magazines |
Only with the article |
Russians — always without an article |
|
Sport events |
Only with the article |
Wimbledon (excl.) |
|
Music bands |
If the name is in plural. number, then with the article |
If in unit. number, then without article |
| Names |
the |
without article |
a |
|
Names, surnames |
If talking about all family members |
If in unit. number of |
One of the family members, some |
|
Personal names have become common nouns |
Always with article a only |
||
|
Appeals, titles |
Always without an article |
Source: https://ya-znau.ru/znaniya/zn/1
The definite article – the
The definite article the is the same for all genders in singular and in plural.
- the boy
- the girl
- the cat
- the computers
If the following word begins with a consonant, we speak [ðə], if the following word begins with a vowel, we speak [ði:].
| [ðə] | [ði:] |
|---|---|
the following word starts with a spoken consonant
|
the following word starts with a spoken vowel
|
| Compare the following words: | |
| Here [j] is pronounced at the beginning of the word → the unit | Here [ʌ] is pronounced at the beginning of the word → the uncle |
We have listed some examples in the following table. There you can see when we use the definite article and when we don’t.
| without the definite article | with the definite article – the |
|---|---|
general words (indefinite)
|
general words (definite)
|
names of persons on the singular, relatives
|
family names in the plural
|
public buildings, institutions, means of transport (indefinite)
|
public buildings, institutions, means of transport (definite)
|
names of countries in the singular, summits of mountains, continents, towns
|
names of countries in the plural, mountain ranges, regions
|
single islands
|
groups of islands
|
parks, lakes, streets
|
names with of-phrase, names in plural, well-known buildings, oceans, seas, rivers, musical instruments, newspapers
|
months, days of the week (indefinite)
|
months, days of the week (definite)
|
We use the seasons of the year (spring, summer, autumn, winter) with or without the definite article.
- in summer
- in the summer
The American English word fall is always used with the definite article the.
Sometimes we use the article and sometimes we do not. It often depends on the context. Watch the following example:
- The student goes to school.
- The mother is going to the school.
In the first sentence we do not use the definite article, in the second we do. The student goes to school for its primary purpose, so we do not use the article.
The mother might talk to a teacher, for example. She visits the school for a different reason. That’s why we use the definite article the in the second sentence.
Thanks to Erik.
The definite article The is an important part of the English language. It is used to indicate that a noun refers to a specific person, place, thing, or idea that has been previously mentioned or is already known to the listener or reader. The use of “the” implies that the listener or reader has some prior knowledge or understanding of the noun being referred to. It is also used to indicate that the noun is one of a kind or unique. Understanding when and how to use “the” is essential for clear and effective communication in English.
How to Use Definite Article THE
“The” can be used with both singular and plural nouns, with nouns of any gender, and with nouns that start with any letter. This is different from many other languages which have different articles for different genders and/or numbers.
For examples:
- the boy / the boys;
- the girl / the girls;
- the day / the days
The definite article the is used when the referent of the noun phrase is assumed to be unique or known from the context.
For example, in the sentence:
- The boy with glasses was looking at the moon. (it is assumed that in the context
the reference can only be to one boy and one moon.)
The word “the” is also used with comparatives.
For example, in phrases like:
- the sooner the better
- we were all the happier for it.
(this form of the definite article has a somewhat different etymology from other uses of the definite article).
The definite article is not used:
- with generic nouns (plural or uncountable): cars have accelerators, happiness is contagious referring to cars in general and happiness in general (compare the happiness I felt yesterday – specifying particular happiness);
- with many proper names: John, France, London, etc.
An area in which the use or non-use of the is sometimes problematic is with geographic names.
- Names of rivers, seas, mountain ranges, deserts, island groups and the like are generally used with the definite article (the Rhine, the North Sea, the Alps, the Sahara, the Hebrides).
- Names of continents, islands, countries, regions, administrative units, cities and towns mostly do not take the article (Europe, Skye, Germany, Scandinavia, Yorkshire, Madrid).
However, there are certain exceptions:
- Countries and regions whose names are modified common nouns, or are derived from island groups, take the article: the United States, the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, the Czech Republic, the Middle East, the Philippines, the Seychelles. Note also the Netherlands.
- Certain countries whose names derive from mountain ranges, rivers, deserts, etc. are sometimes used with an article (the Lebanon, the Sudan), but this usage is declining, although the Gambia is the recommended name of that country. Since the independence of Ukraine (formerly sometimes called the Ukraine), most style guides have advised dropping the article (in some other languages there is a similar issue involving prepositions). Use of the Argentine for Argentina is now old-fashioned.
- Some names include an article for historical reasons, such as The Bronx, or to reproduce the native name (The Hague).
- Names beginning with a common noun followed by of take the article, as in the Isle of Wight (compare Christmas Island). The same applies to names of institutions: Cambridge University, but the University of Cambridge.
How to Use Definite Article THE | Image
The Definite Article THE
Omission of the Definite Article THE
English Level: Upper-Intermediate, Advanced
Language Focus: A review of when to use the definite article with the names of places
Worksheet Download: definite-article-geography-worksheet.docx (scroll down to study the exercises online)
Jump to: Exercises
A proper noun is the unique name of a person, place, or thing that starts with a capital letter, for example, ‘John’, ‘Sweden’, ‘Google’. Before proper nouns, we generally do not use an article. For example,
- Matthew is a man.
- He lives in Canada.
- He worked for IBM.
However, sometimes you can find the definite article ‘the‘ before proper nouns.
- Carver lives in the United States.
- He lives near the Pacific Ocean.
Why? Well, it’s hard to give a reason. However, there are some rules we can follow. Please read below and do the exercises to practice.
Boats on the Pacific Ocean
Rule #1: Use the Definite Article ‘The’ with Countries that are States, Unions, Republics, etc.
We use ‘the’ before countries that contain a word like ‘Union’, ‘Emirates’, ‘Kingdom.’ These words mean that the country is a group of smaller states.
- the United States
- the Republic of Ireland
- the Czech Republic
- the United Arab Emirates
We also use ‘the’ before countries that end in a plural ‘s’.
- the Philippines (= the full name is The Republic of the Philippines)
- the Bahamas (= the full name is The Republic of the Bahamas)
- the Netherlands
Rule #2: Use the Definite Article ‘The’ with Names of Rivers, Seas, Oceans, etc.
We say the following:
- the Nile / the Nile River
- the Caspian Sea
- the Pacific / the Pacific Ocean
- the Mediterranean / the Mediterranean Sea
- the Panama Canal
Rule #3: Use the Definite Article ‘The’ with Deserts
- the Sahara / the Sahara Desert
Rule #4: Do Not Use ‘the’ with Lakes or Mounts
- I live by Lake Ontario.
- I swam in Lake Superior.
- He can see Mount Fuji.
- She can see Mount Rushmore.
Rule #5 — Use the Definite Article ‘The’ with Mountain Ranges
Just like how we add ‘the’ to countries that end with a plural ‘s’ (the Philippines), we add ‘the’ before mountain ranges (which also end in a plural noun).
- the Rockies / the Rocky Mountains
- the Himalayas / the Himalayan Mountains
Rule #6 — Use the Definite Article ‘The’ with Building Names
We usually use ‘the’ before the names of buildings.
- the Emperor’s Palace
- the Tower of Pisa
- the Louvre
- the Pentagon
- The Marriott / The Marriott Hotel
This is not true, however, in some cases:
- The names of stations: Grand Central Station, Main Station
- The names of airports: Pearson Airport, Gatwick Airport
- The names of universities (without ‘of’): Columbia University, Santa Monica College
General Rule: Use the Definite Article ‘The’ with Names that Have the Preposition ‘Of’
- the Island of Lesbos
- the University of Toronto
- the Republic of Congo
- the Gulf of Mexico
To summarize, use ‘the’ before the following:
- proper nouns that contain a word that means they are a group (unions, republics, etc.)
- deserts (the Mojave)
- rivers, seas, oceans, etc. (but not lakes!)
- mountain ranges (the Rockies)
- building names (the Pentagon)
- proper nouns that include ‘of’ (the University of Michigan)
Do not use ‘the’ for everything else, which includes
- lake names (Lake Superior)
- mounts (Mount Everest)
- street names (Main Street)
- airports (JFK Airport)
- stations (Broadway Station)
After reviewing the above rules, try the practice exercises below.
Exercises: Using Articles with Names of Places
Instructions: Add the definite article `the’ if necessary.
- Prague is the capital of Czech Republic.
- When I was in England, I visited Tower of London.
- Rhine is a river that goes through Netherlands.
- On my trip in Asia, I had a chance to visit Mount Aso and Yangtze River in China.
- I left Hong Kong via Hong Kong International Airport.
- Mohave Desert is located in United States.
- Appalachian Mountains are in North America.
- When I was in New York, I visited Empire State Building and Seneca Lake.
- Sea of Japan is located between Japan and South Korea. It is part of Pacific Ocean.
- MET Museum is located on Fifth Avenue.
- I met a man from New Zealand when I was skiing in Swiss Alps.
- On my trip around the world, I visited Jamaica, Bahamas, Australia, and Republic of Congo.
- John lives on Fraser Street in Sydney.
- Poland is part of European Union.
- The tourist arrived at Manaus Airport and then took a tour of Amazon River.
I hope these general rules about article use will be helpful. If you find a mistake or have any questions, please leave a comment below.
Best of luck in your English studies.
— Created by Matthew Barton (copyright) of Englishcurrent.com
Related Lessons:
- Article Practice Exercises (All Levels)
- Help Understanding Articles (Beginner)
- The Indefinite Article & Word Sounds (Advanced)