Excel for Microsoft 365 Outlook for Microsoft 365 PowerPoint for Microsoft 365 Excel 2021 Outlook 2021 PowerPoint 2021 Excel 2019 Outlook 2019 PowerPoint 2019 Excel 2016 Outlook 2016 PowerPoint 2016 Excel 2013 Outlook 2013 PowerPoint 2013 Project Professional 2013 Project Standard 2013 Excel 2010 Outlook 2010 PowerPoint 2010 More…Less
When you add pictures, shapes, or other objects to your Office documents, they automatically stack in individual layers as you add them. You can move individual shapes or other objects or groups of objects in a stack. For example, you can move objects up or down within a stack one layer at a time, or you can move them to the top or bottom of a stack in one move. You can overlap objects when you draw to create different effects.
Notes:
-
For information on aligning objects, see Align or arrange a picture, shape, text box, or WordArt.
-
For information about grouping objects, see Group or ungroup shapes, pictures, or other objects.
Move a picture, shape, text box, or WordArt
-
Click the border of the WordArt, text box, or shape that you want to move.
To move multiple text boxes or shapes, press and hold Ctrl while you click the borders.
-
When the cursor changes to the four headed arrow, drag it to the new location.
To move in small increments, press and hold Ctrl while pressing an arrow key. And to move the object horizontally or vertically only, press and hold Shift while you drag it.
Note: The incremental, or nudge, distance is a 1 pixel increment. What 1 screen pixel represents relative to the document area depends on the zoom percentage. When your document is zoomed in to 400%, 1 screen pixel is a relatively small nudge distance on the document. When your document is zoomed out to 25%, 1 screen pixel is a relatively large nudge distance on the document.
Depending on how far you’re moving the WordArt, shape, or text box, it might be easier to cut and paste it. Right-click the object, and then click Cut (or, press Ctrl+X). Press Ctrl+V to paste it. You can also cut and paste it into a different document, or between programs, such as from a PowerPoint slide to an Excel worksheet.
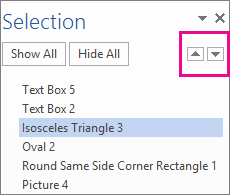
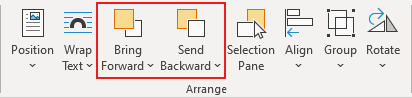
Move a text box, WordArt, or shape forward or backward in a stack
-
Click the WordArt, shape, or text box that you want to move up or down in the stack.
-
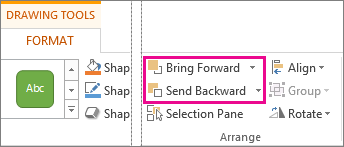
On the Drawing Tools Format tab, click either Bring Forward or Send Backward.
You’ll have the choice of moving the object up one layer (Bring Forward) or to the top of the stack (Bring to Front). Send Backward has similar options: down one layer (Send Backward) or to the bottom of the pile (Send to Back).
Tips:
-
In Office 2016 and Office 2013, if you have a lot of WordArt, shapes, text boxes, or other objects, it may be easier to use up and down arrows in the Selection Pane to move objects. The Selection Pane is not available in Project or in Office 2010.
-
-
See also
-
Align or arrange a picture, shape, text box, or WordArt
-
Group or ungroup shapes, pictures, or other objects
Need more help?
Move a picture, shape, text box, or WordArt
- Click the border of the WordArt, text box, or shape that you want to move. To move multiple text boxes or shapes, press and hold Ctrl while you click the borders.
- When the cursor changes to the four headed arrow, drag it to the new location.
Contents
- 1 How do I move a text box in Word using the keyboard?
- 2 How do you adjust text boxes in Word?
- 3 Why can’t I move textbox in Word?
- 4 How do you move objects freely in Word?
- 5 How do I resize a text box?
- 6 How do I stretch a text box in Word?
- 7 How do I fix the size of a text box in Word?
- 8 How do I move a text box anywhere in Word?
- 9 How do I move a text box outside the margin?
- 10 How do I move a text box horizontally in Word?
- 11 Why can’t I move images in Word?
- 12 How do I move objects in small increments in Word for Mac?
- 13 How do I remove a text box but keep the text in Word?
- 14 Can I stretch text in Word?
- 15 How do I fit text to page width in Word?
- 16 How do I make my font taller?
How do I move a text box in Word using the keyboard?
To move in small increments, press and hold Ctrl while pressing an arrow key. And to move the object horizontally or vertically only, press and hold Shift while you drag it. Depending on how far you’re moving the WordArt, shape, or text box, it might be easier to cut and paste it.
How do you adjust text boxes in Word?
Adjust the text box margins
- Click the outer edge of the text box to select it.
- On the Shape Format tab, click Format Pane.
- Click the Shape Options tab if it isn’t already selected.
- Click the text box icon. , and then click Text Box.
- You can adjust the left, right, top, and bottom margins.
Why can’t I move textbox in Word?
If the text box is In Line With Text, it’s constrained by the margins. With any other text wrapping, you should be able to drag it anywhere. But it may be that all you need to do is change the internal margin of the text box: Right-click on the edge of the text box and choose Format Shape…
How do you move objects freely in Word?
First, confirm that the object is not set to In Line with Text: With the object selected click the Arrange button on the Shape Format contextual tab. From the Wrap Text choices select the method you prefer. You then should be able to freely drag the object to any location.
How do I resize a text box?
To change the size of an existing text box, follow these steps:
- Click once on the information within the text box.
- Use the mouse to point to one of the handles.
- Drag the handle to resize the text box.
- Release the mouse button when the text box is the size you want.
How do I stretch a text box in Word?
Stretch Text Horizontally
- Highlight the text you want to stretch.
- Select the “Home” tab, then click the small arrow in the Font section to open the Font dialog box.
- Select the “Advanced” tab.
- Increase the percentage value in the “Scale” field.
- Highlight the text you want to stretch.
How do I fix the size of a text box in Word?
Follow these general steps.
- Place the text box in your document.
- Adjust the width of your text box to reflect what you need.
- Right-click the text box and choose Format Text Box from the resulting Context menu.
- Make sure the Text Box tab is displayed.
- Make sure the Resize AutoShape to Fit Text check box is selected.
How do I move a text box anywhere in Word?
To move a text box:
- Click the text box you want to move.
- Hover the mouse over one of the edges of the text box. The mouse will change into a cross with arrows.
- Click and drag the text box to the desired location.
How do I move a text box outside the margin?
RECOMMENDED FOR YOU
- Click the Insert menu and Click Text Box in the Text group.
- Use the mouse to drag and drop a text box of the approximate size in the margin.
- Enter the text “Use Quick Styles.”
- On the Contextual Format ribbon, choose Middle from the Align Text dropdown in the Text group.
How do I move a text box horizontally in Word?
Enter the text in the shape or text box or table cell, and then select the text. Ctrl+Click the selected text, and then select Format Shape. On the Text Box tab in the dialog box, choose a direction from the Text Direction box.
Why can’t I move images in Word?
You must set the layout to something other than ‘in-line‘ before you can drag it around. You can only move them around if their layout property is set to something other than in-line, otherwise you can cut and paste to a new position, just like a font character.
How do I move objects in small increments in Word for Mac?
To move an object up, down, or sideways in small increments, click the object, hold down OPTION, and then press an arrow key.
How do I remove a text box but keep the text in Word?
Follow these steps:
- In your document, press Ctrl+A.
- Press Ctrl+C.
- Open a new, blank document.
- Make sure the Home tab of the ribbon is displayed.
- Click the down-arrow under the Paste tool (at the left side of the ribbon) and choose Paste Special.
- In the list of formats, choose Unformatted Text.
- Click on OK.
Can I stretch text in Word?
Stretch or scale the text horizontally
On the Home tab, click the Font Dialog Box Launcher, and then click the Advanced tab. Note: If you’re using Word 2007 the tab is called Character Spacing. In the Scale box, enter the percentage that you want. Percentages above 100 percent stretch the text.
How do I fit text to page width in Word?
To fit the columns to the text (or page margins if cells are empty), click [AutoFit] > select “AutoFit Contents.” To fit the table to the text, click [AutoFit] > select “AutoFit Window.” To keep Word from automatically adjusting your column size, click [AutoFit] > select “Fixed Column Width.”
How do I make my font taller?
Changing the Height of a Font
- Select the text you want to affect.
- Enlarge the font size to 15 points. (12 times 1.25 is 15.)
- Display the Advanced tab of the Font dialog box.
- Using the Scale control, specify a scaling of 80%.
Lesson 21: Text Boxes
/en/word2016/shapes/content/
Introduction
Text boxes can be useful for drawing attention to specific text. They can also be helpful when you need to move text around in your document. Word allows you to format text boxes and the text within them with a variety of styles and effects.
Optional: Download our practice document.
Watch the video below to learn more about text boxes in Word.
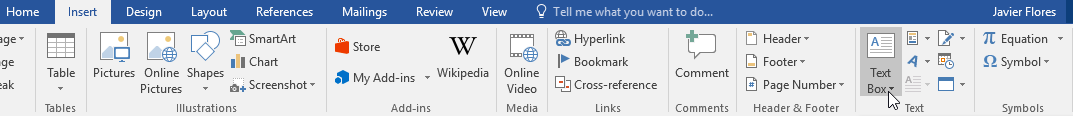
To insert a text box:
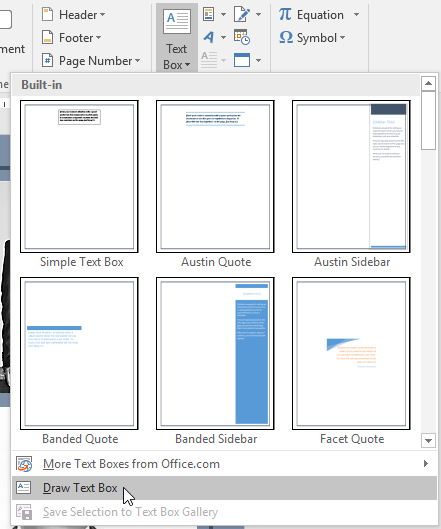
- Select the Insert tab, then click the Text Box command in the Text group.
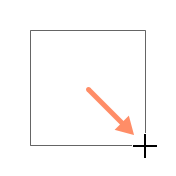
- A drop-down menu will appear. Select Draw Text Box.
- Click and drag anywhere on the document to create the text box.
- The insertion point will appear inside the text box. You can now type to create text inside the text box.
- If you want, you can select the text and then change the font, color, and size by using the commands on the Format and Home tabs. To learn more about using these formatting commands, see our Formatting Text lesson.
- Click anywhere outside the text box to return to your document.
You can also select one of the built-in text boxes that have predefined colors, fonts, positions, and sizes. If you choose this option, the text box will appear automatically, so you will not need to draw it.
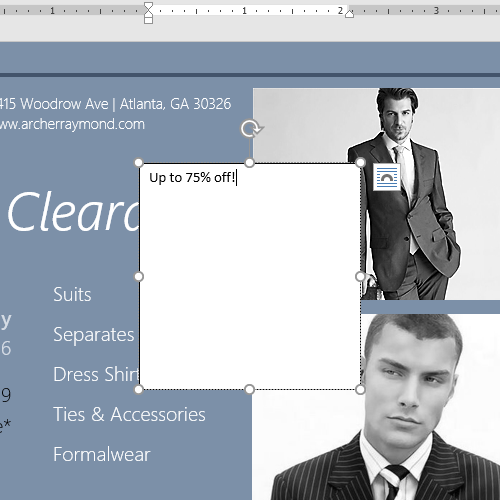
To move a text box:
- Click the text box you want to move.
- Hover the mouse over one of the edges of the text box. The mouse will change into a cross with arrows.
- Click and drag the text box to the desired location.
To resize a text box:
- Click the text box you want to resize.
- Click and drag any of the sizing handles on the corners or sides of the text box until it is the desired size.
Modifying text boxes
Word offers several options for changing the way text boxes appear in your document. You can change the shape, style, and color of text boxes or add various effects.
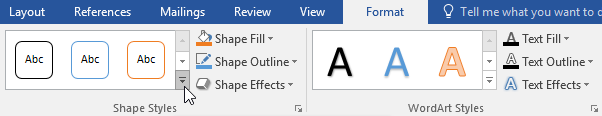
To change the shape style:
Choosing a shape style allows you to apply preset colors and effects to quickly change the appearance of your text box.
- Select the text box you want to change.
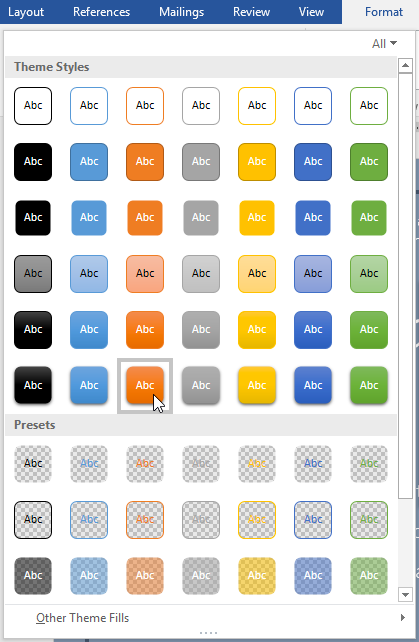
- On the Format tab, click the More drop-down arrow in the Shape Styles group.
- A drop-down menu of styles will appear. Select the style you want to use.
- The text box will appear in the selected style.
If you want to have more control over text box formatting, you can use any of the shape formatting options such as Shape Fill and Shape Outline. To learn more, see our Shapes lesson.
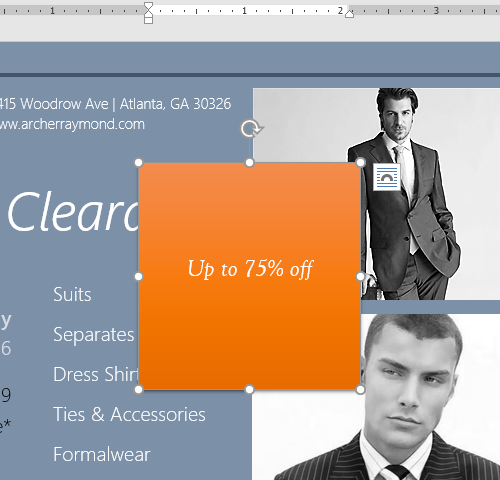
To change the text box shape:
Changing the shape of a text box can be a useful option for creating an interesting look in your document.
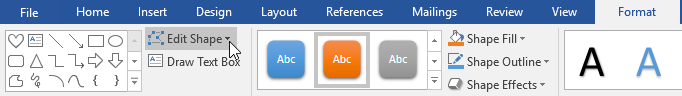
- Select the text box you want to change. The Format tab will appear.
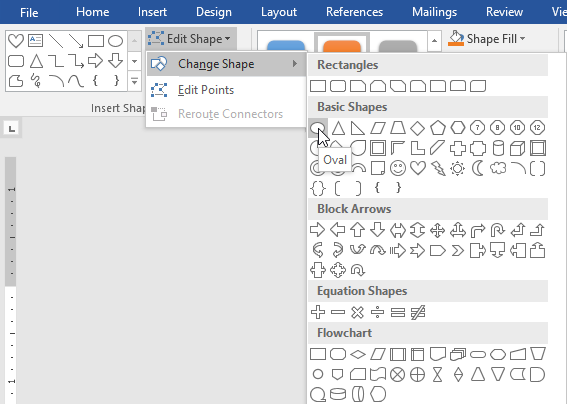
- From the Format tab, click the Edit Shape command.
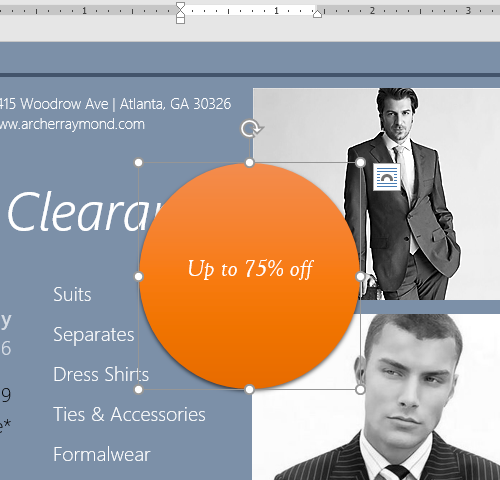
- Hover the mouse over Change Shape, then select the desired shape from the menu that appears.
- The text box will appear formatted as the shape.
Challenge!
- Open our practice document.
- Insert a Simple Text Box.
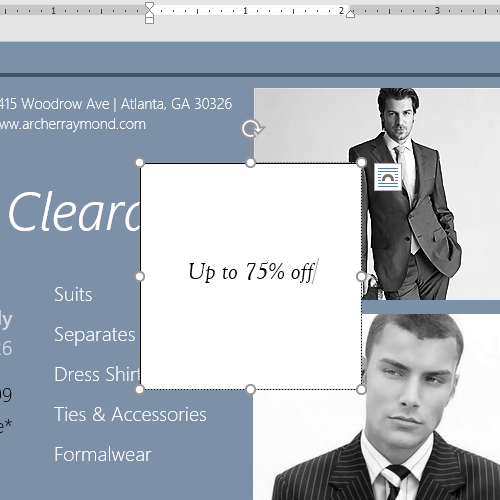
- In the text box, type Get an additional 25% off when you mention this ad!
- Change the font to Gadugi, 20 pt, Center Align.
- Change the shape of the text box to Double Wave from the Stars and Banners group.
- Change the text box style by selecting any style in the Intense Effect row.
- Drag the text box to the space below Buy 1, Get 1 Free* and Formalwear.
- When you’re finished, your document should look something like this:
/en/word2016/aligning-ordering-and-grouping-objects/content/
Achieve more control and flexibility with your documents
Updated on September 11, 2022
What to Know
- Select Insert > Text Box > choose a text box template. Select and drag box to the position you want.
- To resize text, select and drag circles around the edge. To rotate text, select and drag the circular arrow.
- Place the cursor inside the text box and type the information you want to appear.
This article explains how to use text boxes in Microsoft Word. Instructions apply to Word for Microsoft 365, Word 2019, Word 2016, and Word 2013.
How to Insert a Text Box in Word
Start by opening the document you want to add a text box to. Then follow the steps below.
-
On the ribbon, select Insert.
-
In the Text group, select Text Box, then choose a text box template.
-
The new text box appears in the middle of the text, and the Shape Format tab is automatically selected.
-
Select and drag the box to the position you want. To resize the text box, select and drag the circles around the edge. To rotate the text box, select and drag the circular arrow at the top of the box.
-
Place the cursor inside the text box and type the information you want to appear there.
Why Use Text Boxes?
When you type text in Microsoft Word, you have options for making it look a particular way on the page (such as changing the page margins), but those options are limited. Text boxes expand your formatting repertoire by offering additional control and flexibility for how your text appears. You can place a text box anywhere within a document and format it with different colors and fonts. This feature is especially helpful for creating a blockquote or a sidebar.
Customize a Text Box
After you create a text box, you can customize it in a number of ways.
-
To bring up options, place the cursor inside the text box and right-click. Choose an option and follow the screen prompts to add a border, change the style, or adjust the way the text box interacts with the other text on the page.
Alternatively, use the controls on the Shape Format tab.
-
To go directly to the Layout Options menu, select the text box, then select the Layout Options icon (it looks like a horseshoe and is located to the right of the text box).
-
Change the text, make more adjustments, or move the box to another location at any time. To delete a text box, select its border, then press Delete on the keyboard.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
Word offers many useful features for working with various objects, such as images, photographs, text boxes, shapes, WordArt objects. All visual objects, excluding tables and equations, are figures in Microsoft Word. One of the most challenging steps in formatting objects is placing them with the text content. The Layout dialog box controls the positioning of figures.
Position images, text boxes, shapes on the page
Word attaches the figure to the paragraph at the current cursor position when you insert a figure. However, you can move the visual object independently of the text and place it anywhere on the page.
To change the position, on the Picture Format (Graphics Format, Shape Format) tab, in the Arrange group, click the Position button:
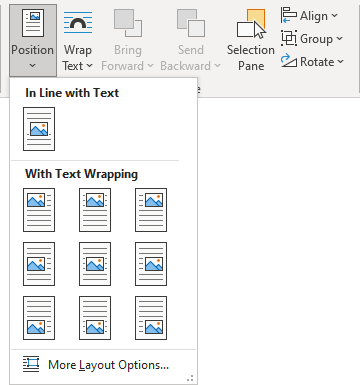
- In Line with Text places an object in the paragraph on the same line as the surrounding text
- Position in Top Left with Square Text Wrapping places a figure in the upper left corner of the document page
- Position in Top Center with Square Text Wrapping
- Position in Top Right with Square Text Wrapping
- Position in Middle Left with Square Text Wrapping
- Position in Middle Center with Square Text Wrapping places a picture in the center of the document page
- Position in Middle Right with Square Text Wrapping
- Position in Bottom Left with Square Text Wrapping
- Position in Bottom Center with Square Text Wrapping
- Position in Bottom Right with Square Text Wrapping places a picture in the lower right corner of the document page
Using these options, position the object in a specific location relative to the page margins.
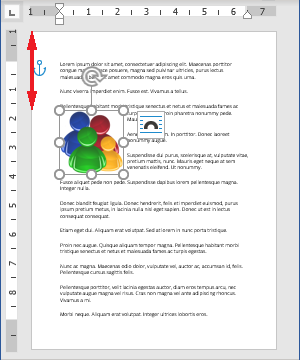
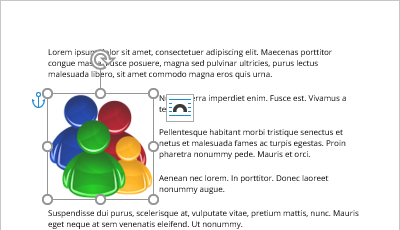
Use the anchor
When changing the text wrapping style from the In Line with Text to another one, Word adds an anchor to the object. In other words, all floating figures are anchored. Select the picture to see its anchor indicated by a small anchor icon (see how to display non-printing characters in a Word document).
Attention! The anchor and the figure are always on the same page but not in the same place on the page.
By default, the anchor is positioned at the beginning of the nearest paragraph above the upper-left corner of the figure. When you move the object across the page, the anchor moves, using the same logic to place the anchor.
Also, you can select the anchor and drag it to a new location on the page.
Change the layout
To choose additional options for positioning an object, choose More Layout Options… from the dropdown list:
In the Layout dialog box, on the Position tab:
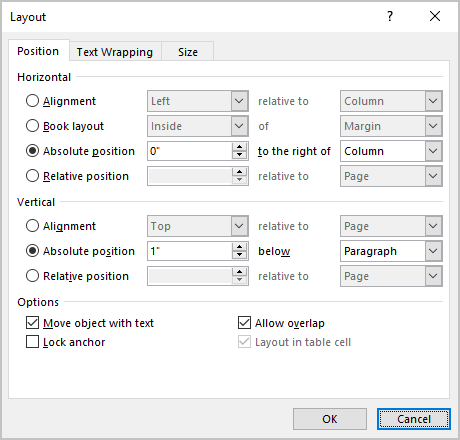
Note: The available positions vary based on the selected text-wrapping option.
- In the Horizontal section, specify that a figure is positioned horizontally:
- Alignment places the object to the Left, Center, or Right relative to:
- Margin
- Page
- Column
- Character
- Left Margin
- Right Margin
- Inside Margin
- Outside Margin
For example:
- Alignment to the Left relative to Margin:
- Alignment to the Left relative to Page:
- Book layout defines where the figure appears on odd (large left margin) or even (large right margin) pages. You can position figures relative to the Inside or Outside of the Margin or Page.
This option is useful if you use the Mirrored margins.
For example, Book layout Inside of Margin:
The odd page The even page - Absolute position specifies the exact distance to the right of:
- Margin
- Page
- Column
- Character
- Left Margin
- Right Margin
- Inside Margin
- Outside Margin
Measurements can be positive or negative. The figure will remain in the same position regardless of formatting changes.
For example:
- The Absolute position of -5 inches to the right of Right Margin:
- The Absolute position of 4 inches to the right of Page:
- Relative position specifies a percentage of the distance relative to:
- Margin
- Page
- Left Margin
- Right Margin
- Inside Margin
- Outside Margin
For example, Relative position of 20% relative to Margin:
Note: 8.5 inches page with 1-inch margins in each side = 6.5 inches * 20% = 1.3 inch
- Alignment places the object to the Left, Center, or Right relative to:
- In the Vertical section, specify that an object is positioned vertically:
- Alignment allows to set the object to the Top, Centered, Bottom, Inside, or Outside relative to:
- Margin
- Line
- Top Margin
- Bottom Margin
- Inside Margin
- Outside Margin
For example, Alignment to the Top relative to Margin:
- Absolute position specifies the exact distance to the right of:
- Margin
- Page
- Paragraph
- Line
- Top Margin
- Bottom Margin
- Inside Margin
- Outside Margin
Measurements can be positive or negative. The figure will remain in the same position regardless of formatting changes.
For example:
- The Absolute position of 3 inches to the right of Line:
- The Absolute position of -7 inches to the right of Bottom Margin:
- Relative position specifies a percentage of the distance relative to:
- Margin
- Page
- Top Margin
- Bottom Margin
- Inside Margin
- Outside Margin
For example, Relative position of 25% relative to Page:
Note: 11 inches page * 25% = 2.75 inches
- Alignment allows to set the object to the Top, Centered, Bottom, Inside, or Outside relative to:
Note: It is impossible to fix a figure on the page.
- In the Options section:
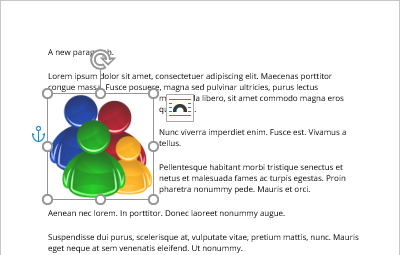
- Move object with text moves the figure along with the text in which it is located.
If this option is selected, the picture moves with a paragraph (anchored to a paragraph). When you delete or add any context before that paragraph, the figure will move with it.
If the Move object with text option is deselected, the picture is anchored to the page location. After deleting or adding context before the anchor, except when the paragraph moves to the next page — the figure moves and keeps its position relative to the page.
Note: This option works only for floating figures (see Text Wrapping for more details).
For example:
- Before moving:
- After moving with the selected Move object with text check box:
- After moving with the deselected Move object with text check box:
When you select this option, the horizontal and vertical alignment will change to Absolute positions relative to the margin (horizontal) and paragraph (vertical).
- Before moving:
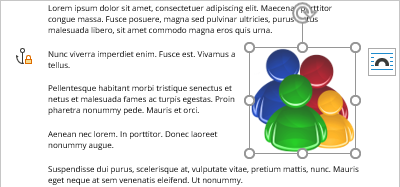
- Lock anchor keeps the anchor at the same place (at the paragraph) when the figure is removed. Word changes the anchor symbol to the locked anchor
.
The anchor symbol will remain to the left of the start of the anchored paragraph, regardless of the picture position.
For example:
- Before moving:
- After moving with the selected Lock anchor check box:
Note: An example is shown with hidden Headers and Footers.
However, if you select and drag a paragraph to another page, the picture shifts to another page.
- Before moving:
- Allow overlap allows to layer figures on top of each other.
For example:
To easily work with such figures, open the Selection pane. To change which figure in front or behind another one, use the Bring Forward or Send Backward buttons in the Arrange group on the Picture Format (Graphics Format, Shape Format) tab:
- Layout in table cell is the option from the older versions of Word and older file formats.
For example, in a *.doc file, you can’t put an image whose text wrapping style is set to Square inside a table cell unless the Layout in table cell option is selected:
- Move object with text moves the figure along with the text in which it is located.
To align a figure on the page simpler, see snap an object to the Grid or a Shape.
Main features of the anchor
- The anchor is related to the paragraph, not words, characters, or other objects.
- When you select the text where the figure is anchored, the figure also is highlighted.
- If you move or delete the text where the figure is anchored, the figure will also be moved or deleted.
- If the paragraph with the anchor is pushed to the next page, the anchored figure also jumps to the next page, even if the figure is located above the anchor.
Delete an anchor
The anchor cannot be deleted. An anchor is a feature of the floating figure.
If the anchor is visible, the figure is selected, and pressing the Delete key will delete the figure and anchor.
Select the figure and change the text wrapping style to the In Line with Text to remove the anchor. The figure will cease floating, and Word will stop showing its anchor when you select this figure.