Помогаю со студенческими работами здесь
Для какой строки массива сумма элементов максимальная?
Добрый вечер всем, кто не спит. Задали задачу в универе, но решить никак ее не могу: дан…
Сумма элементов массива, расположенных после последнего отрицательного элемента
Помогите, пожалуйста, сделать код для по счета Суммы элементов массива, расположенных после…
Выяснить, является ли сумма элементов одномерного массива четным числом
Ребята, подскажите.
Задача:
Для целочисленного массива A выяснить, является ли сумма его…
Сумма элементов массива, которые без остатка делятся на заданное число
Найти сумму всех элементов массива (массив динамический, одномерный) которые без остатка деляться…
Искать еще темы с ответами
Или воспользуйтесь поиском по форуму:
2
Добрый день! Впервые столкнулась с проблемой массивов.
написала код, все работало. Все было отлично, скопировала код, после перестало все работать, сумма элементов массива выдает всегда ноль, может кто знает в чем проблема, при том что на этом коде все считалось. По заданию дан массив В(10) нужно найти сумму и количество отрицательных элементов. Нигде не могу найти ответ. Файл с кодом в приложении.
| Код |
|---|
Sub test()
Dim i As Integer, sum As Integer, o As Integer, ch As Integer
Dim B() As Integer
summ = 0
o = 0
n = InputBox("n=")
ReDim B(n)
For i = 0 To n
If B(i) < 0 Then
o = o + 1
sum = sum + B(i)
End If
Next i
'ch = sum / o
MsgBox "Êîëè÷åñòâî îòðèöàòåëüíûõ ýëåìåíòîâ â ìàññèâå: " & o & vbNewLine & "Èõ ñóììà ðàâíà=" & sum
'ch = Format(ch, "###0.0")
'MsgBox "×àñòíîå =" & ch
End Sub
|
I want to do a sumif from an array but i am not sure how to reference a full column in an array. For instance i have the following data in excel (in columns A and B) and code that works fine,
RR TT
1 J
2 K
3 J
4 K
5 J
5 K
6 J
7 K
8 J
9 K
Sub test()
Dim s As Range
Dim s2 As Range
Set s = Range("A2:A11")
Set s2 = Range("B2:B11")
e = WorksheetFunction.SumIfs(s, s2, "J")
MsgBox e
End Sub
This sums the RR column where the TT column equals «J» and the answer is 23. But in the code i assign each column to a seperate Range in VBA. I would like to assign both columns to an array and do the sumifs from the array. The first part of the code would then look as follows,
Dim s() As Variant
ReDim s(1 To 10, 1 To 2)
s = Range("A2:B11")
How do i then reference the columns of the array in the sumifs function? (the first two entries in the sumifs function)
e = WorksheetFunction.SumIfs(?, ?, "J")
I will at the end work with a much bigger dataset and if it is possible i would like not create a ton of seperate Ranges but just one array.
-
If you would like to post, please check out the MrExcel Message Board FAQ and register here. If you forgot your password, you can reset your password.
-
Thread starter
Lokai
-
Start date
Mar 29, 2004
-
#1
What is the best way to sum values in an array()?
I can get a more complicated NPV like this x=npv(.1/12,arrayX()) but can I do a simple sum without looping thru the array?
Copy PDF to Excel
Select data in PDF. Paste to Microsoft Word. Copy from Word and paste to Excel.
DRJ
MrExcel MVP
-
#2
So you have an array called MyArray then
Application.WorksheetFunction.Sum(MyArray) will sum the array.
-
#3
Hi Lokai,
Simply use the Excel SUM() worksheet function, e.g.:
Xsum = WorksheetFunction.Sum(arrayX)
-
#4
Thank you both, I didn’t realize that a worksheet function would work on a VBA generated array. Blinded by the not so obvious.
DRJ
MrExcel MVP
- Threads
- 1,192,700
- Messages
- 5,993,951
- Members
- 440,523
- Latest member
- yuliuyan07
In this Article
- Sum WorksheetFunction
- Assigning a Sum result to a Variable
- Sum a Range Object
- Sum Multiple Range Objects
- Sum Entire Column or Row
- Sum an Array
- Using the SumIf Function
- Sum Formula
- Formula Method
- FormulaR1C1 Method
This tutorial will show you how to use the Excel Sum function in VBA
The sum function is one of the most widely used Excel functions, and probably the first one that Excel users learn to use. VBA does not actually have an equivalent – a user has to use the built-in Excel function in VBA using the WorkSheetFunction object.
Sum WorksheetFunction
The WorksheetFunction object can be used to call most of the Excel functions that are available within the Insert Function dialog box in Excel. The SUM function is one of them.
Sub TestFunction
Range("D33") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Sum("D1:D32")
End SubYou are able to have up to 30 arguments in the SUM function. Each of the arguments can also refer to a range of cells.
This example below will add up cells D1 to D9
Sub TestSum()
Range("D10") = Application.WorksheetFunction.SUM("D1:D9")
End SubThe example below will add up a range in column D and a range in column F. If you do not type the Application object, it will be assumed.
Sub TestSum()
Range("D25") = WorksheetFunction.SUM (Range("D1:D24"), Range("F1:F24"))
End SubNotice for a single range of cells you do not have to specify the word ‘Range’ in the formula in front of the cells, it is assumed by the code. However, if you are using multiple arguments, you do need to do so.
Assigning a Sum result to a Variable
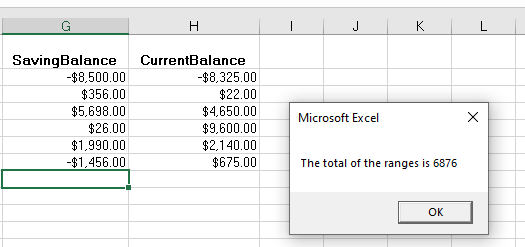
You may want to use the result of your formula elsewhere in code rather than writing it directly back to and Excel Range. If this is the case, you can assign the result to a variable to use later in your code.
Sub AssignSumVariable()
Dim result as Double
'Assign the variable
result = WorksheetFunction.SUM(Range("G2:G7"), Range("H2:H7"))
'Show the result
MsgBox "The total of the ranges is " & result
End SubSum a Range Object
You can assign a group of cells to the Range object, and then use that Range object with the WorksheetFunction object.
Sub TestSumRange()
Dim rng As Range
'assign the range of cells
Set rng = Range("D2:E10")
'use the range in the formula
Range("E11") = WorksheetFunction.SUM(rng)
'release the range object
Set rng = Nothing
End SubSum Multiple Range Objects
Similarly, you can sum multiple Range Objects.
Sub TestSumMultipleRanges()
Dim rngA As Range
Dim rngB as Range
'assign the range of cells
Set rngA = Range("D2:D10")
Set rngB = Range("E2:E10")
'use the range in the formula
Range("E11") = WorksheetFunction.SUM(rngA, rngB)
'release the range object
Set rngA = Nothing
Set rngB = Nothing
End SubSum Entire Column or Row
You can also use the Sum function to add up an entire column or an entire row
This procedure below will add up all the numeric cells in column D.
Sub TestSum()
Range("F1") = WorksheetFunction.SUM(Range("D:D")
End SubWhile this procedure below will add up all the numeric cells in Row 9.
Sub TestSum()
Range("F2") = WorksheetFunction.SUM(Range("9:9")
End SubVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Sum an Array
You can also use the WorksheetFunction.Sum to add up values in an array.
Sub TestArray()
Dim intA(1 To 5) As Integer
Dim SumArray As Integer
'populate the array
intA(1) = 15
intA(2) = 20
intA(3) = 25
intA(4) = 30
intA(5) = 40
'add up the array and show the result
MsgBox WorksheetFunction.SUM(intA)
End SubUsing the SumIf Function
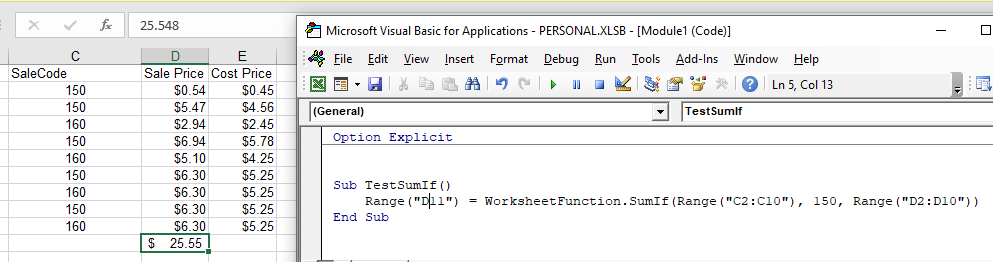
Another worksheet function that can be used is the SUMIF function.
Sub TestSumIf()
Range("D11") = WorksheetFunction.SUMIF(Range("C2:C10"), 150, Range("D2:D10"))
End SubThe procedure above will only add up the cells in Range(D2:D10) if the corresponding cell in column C = 150.
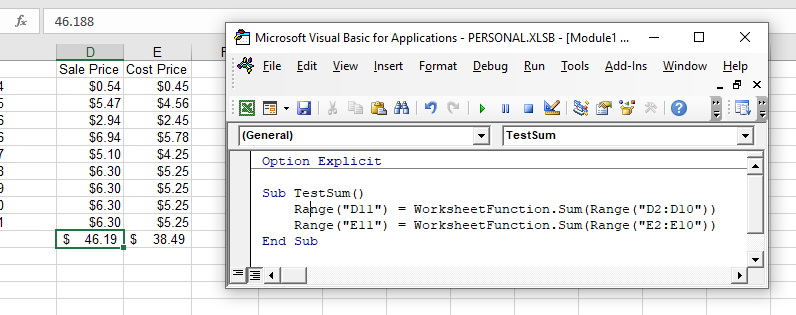
Sum Formula
When you use the WorksheetFunction.SUM to add a sum to a range in your worksheet, a static sum is returned, not a flexible formula. This means that when your figures in Excel change, the value that has been returned by the WorksheetFunction will not change.
In the example above, the procedure TestSum has added up Range(D2:D10) and the result has been put in D11. As you can see in the formula bar, this result is a figure and not a formula.
If any of the values change therefore in the Range(D2:D10), the result in D11 will NOT change.
Instead of using the WorksheetFunction.SUM, you can use VBA to apply a Sum Function to a cell using the Formula or FormulaR1C1 methods.
VBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
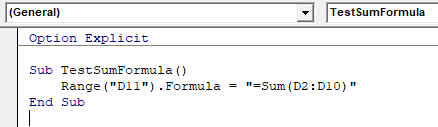
Formula Method
The formula method allows you to point specifically to a range of cells eg: D2:D10 as shown below.
Sub TestSumFormula
Range("D11").Formula = "=SUM(D2:D10)"
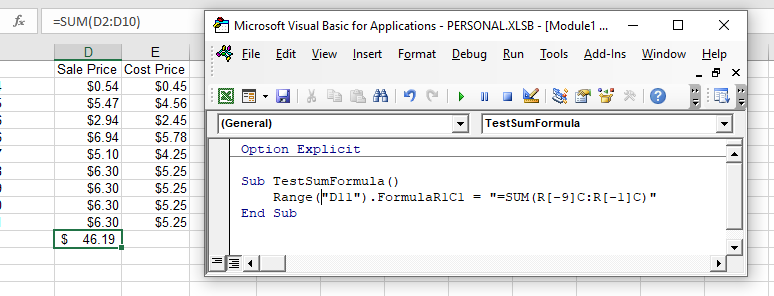
End SubFormulaR1C1 Method
The FromulaR1C1 method is more flexible in that it does not restrict you to a set range of cells. The example below will give us the same answer as the one above.
Sub TestSumFormula()
Range("D11").FormulaR1C1 = "=SUM(R[-9]C:R[-1]C)"
End SubHowever, to make the formula more flexible, we could amend the code to look like this:
Sub TestSumFormula()
ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = "=SUM(R[-9]C:R[-1]C)"
End SubWherever you are in your worksheet, the formula will then add up the 8 cells directly above it and place the answer into your ActiveCell. The Range inside the SUM function has to be referred to using the Row (R) and Column (C) syntax.
Both these methods enable you to use Dynamic Excel formulas within VBA.
There will now be a formula in D11 instead of a value.