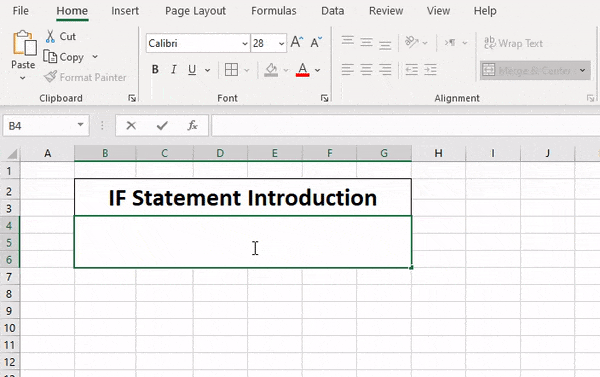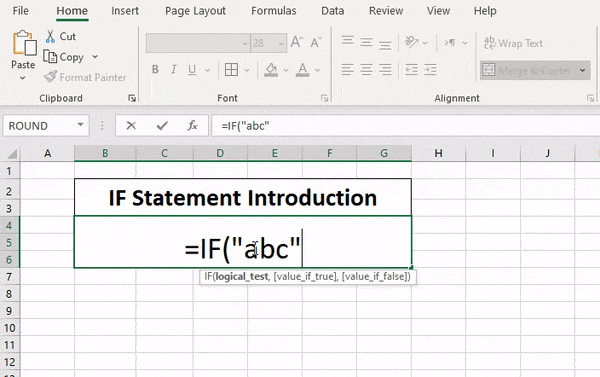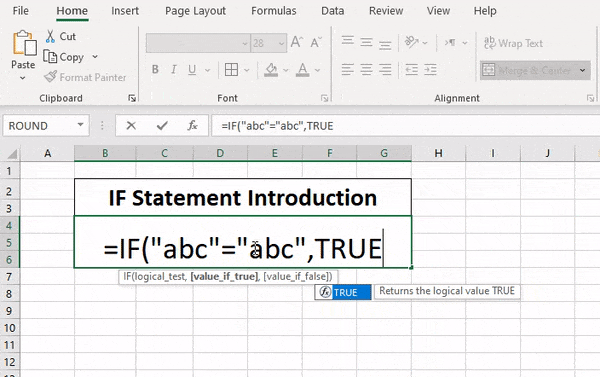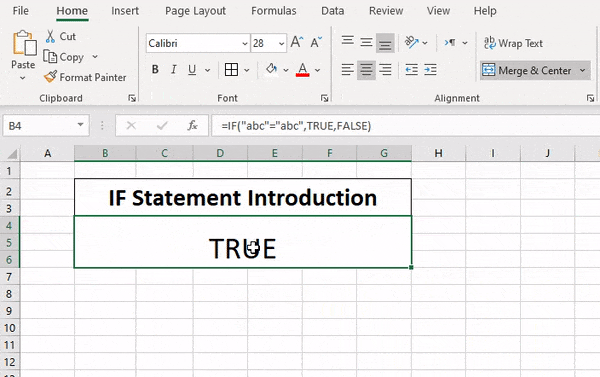
IF function
The IF function is one of the most popular functions in Excel, and it allows you to make logical comparisons between a value and what you expect.
So an IF statement can have two results. The first result is if your comparison is True, the second if your comparison is False.
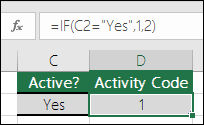
For example, =IF(C2=”Yes”,1,2) says IF(C2 = Yes, then return a 1, otherwise return a 2).
Use the IF function, one of the logical functions, to return one value if a condition is true and another value if it’s false.
IF(logical_test, value_if_true, [value_if_false])
For example:
-
=IF(A2>B2,»Over Budget»,»OK»)
-
=IF(A2=B2,B4-A4,»»)
|
Argument name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
logical_test (required) |
The condition you want to test. |
|
value_if_true (required) |
The value that you want returned if the result of logical_test is TRUE. |
|
value_if_false (optional) |
The value that you want returned if the result of logical_test is FALSE. |
Simple IF examples
-
=IF(C2=”Yes”,1,2)
In the above example, cell D2 says: IF(C2 = Yes, then return a 1, otherwise return a 2)
-
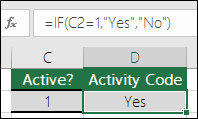
=IF(C2=1,”Yes”,”No”)
In this example, the formula in cell D2 says: IF(C2 = 1, then return Yes, otherwise return No)As you see, the IF function can be used to evaluate both text and values. It can also be used to evaluate errors. You are not limited to only checking if one thing is equal to another and returning a single result, you can also use mathematical operators and perform additional calculations depending on your criteria. You can also nest multiple IF functions together in order to perform multiple comparisons.
-
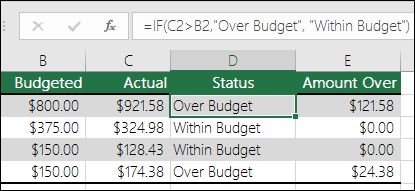
=IF(C2>B2,”Over Budget”,”Within Budget”)
In the above example, the IF function in D2 is saying IF(C2 Is Greater Than B2, then return “Over Budget”, otherwise return “Within Budget”)
-
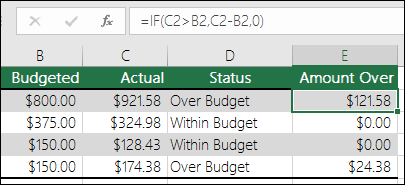
=IF(C2>B2,C2-B2,0)
In the above illustration, instead of returning a text result, we are going to return a mathematical calculation. So the formula in E2 is saying IF(Actual is Greater than Budgeted, then Subtract the Budgeted amount from the Actual amount, otherwise return nothing).
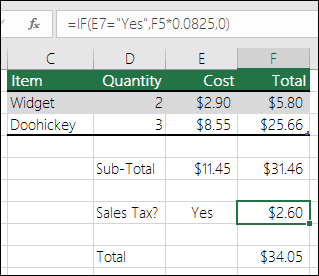
-
=IF(E7=”Yes”,F5*0.0825,0)
In this example, the formula in F7 is saying IF(E7 = “Yes”, then calculate the Total Amount in F5 * 8.25%, otherwise no Sales Tax is due so return 0)
Note: If you are going to use text in formulas, you need to wrap the text in quotes (e.g. “Text”). The only exception to that is using TRUE or FALSE, which Excel automatically understands.
Common problems
|
Problem |
What went wrong |
|---|---|
|
0 (zero) in cell |
There was no argument for either value_if_true or value_if_False arguments. To see the right value returned, add argument text to the two arguments, or add TRUE or FALSE to the argument. |
|
#NAME? in cell |
This usually means that the formula is misspelled. |
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.

See Also
IF function — nested formulas and avoiding pitfalls
IFS function
Using IF with AND, OR and NOT functions
COUNTIF function
How to avoid broken formulas
Overview of formulas in Excel
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
The goal of this example is to verify input before calculating a result. The key point to understand is that any valid formula can be substituted. The SUM function is used only as an example. The logic can also be adjusted in many ways to suit the situation.
In the example shown, we are using the IF function together with the COUNT function. The criteria is an expression based on the COUNT function, which only counts numeric values:
COUNT(C5:C7)=3 // returns TRUE or FALSE
As long as the range contains three numbers (i.e. all 3 cells are not blank) the result is TRUE and IF will run the SUM function. If not, result is FALSE and IF returns an empty string («»). Since C7 has no value in the screen above, the formula shows no result.
There are many ways to check for blank cells, and several options are explained below.
With COUNTBLANK
The COUNTBLANK function counts empty cells in a range, so we can write a slightly more compact formula like this:
=IF(COUNTBLANK(C5:C7),"",SUM(C5:C7))
If COUNTBLANK returns any number except zero, the IF function will evaluate as TRUE, and return nothing («»). If COUNTBLANK returns zero, IF evaluates as FALSE and returns the sum.
With ISBLANK
In the example shown, input cells are all in the same contiguous range. In cases where cells are not together, you can a formula like this:
=IF(OR(ISBLANK(C5),ISBLANK(C6),ISBLANK(C7)),"",SUM(C5:C7))
This example takes a literal approach with the ISBLANK function. Because we want to check all three cells at the same time, we need to use ISBLANK three times inside the OR function. This is the logical test inside IF:
OR(ISBLANK(C5),ISBLANK(C6),ISBLANK(C7)
When OR returns TRUE (at least one cell is empty), IF returns an empty string («»). When OR returns FALSE (no cells are blank), IF runs the SUM function and returns the result:
SUM(C5:C7)
With logical operators
The ISBLANK function can be replaced with standard logical operators like this:
=IF(OR(C5="",C6="",C7=""),"",SUM(C5:C7))
Alternately, we can combine the not equal to operator (<>) with AND function like this:
=IF(AND(C5<>"",C6<>"",C7<>""),SUM(C5:C7),"")
Notice the SUM function has been moved to the TRUE result. It will run only if C5 and C6 and C5 are not empty.
With COUNTA
Finally, you can use the COUNTA function to check for numeric or text input:
=IF(COUNTA(C5:C7)=3,SUM(C5:C7),"")
As long as the range C5:C5 contains three values (numbers or text), the result will be TRUE and the SUM function will run. This doesn’t really make sense for the example shown (which requires numeric input) but it can be used in other situations.
Функция ЕСЛИ в Excel — это отличный инструмент для проверки условий на ИСТИНУ или ЛОЖЬ. Если значения ваших расчетов равны заданным параметрам функции как ИСТИНА, то она возвращает одно значение, если ЛОЖЬ, то другое.
Содержание
- Что возвращает функция
- Синтаксис
- Аргументы функции
- Дополнительная информация
- Функция Если в Excel примеры с несколькими условиями
- Пример 1. Проверяем простое числовое условие с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ)
- Пример 2. Использование вложенной функции IF (ЕСЛИ) для проверки условия выражения
- Пример 3. Вычисляем сумму комиссии с продаж с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ) в Excel
- Пример 4. Используем логические операторы (AND/OR) (И/ИЛИ) в функции IF (ЕСЛИ) в Excel
- Пример 5. Преобразуем ошибки в значения “0” с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ)
Что возвращает функция
Заданное вами значение при выполнении двух условий ИСТИНА или ЛОЖЬ.
Синтаксис
=IF(logical_test, [value_if_true], [value_if_false]) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИ(лог_выражение; [значение_если_истина]; [значение_если_ложь]) — русская версия
Аргументы функции
- logical_test (лог_выражение) — это условие, которое вы хотите протестировать. Этот аргумент функции должен быть логичным и определяемым как ЛОЖЬ или ИСТИНА. Аргументом может быть как статичное значение, так и результат функции, вычисления;
- [value_if_true] ([значение_если_истина]) — (не обязательно) — это то значение, которое возвращает функция. Оно будет отображено в случае, если значение которое вы тестируете соответствует условию ИСТИНА;
- [value_if_false] ([значение_если_ложь]) — (не обязательно) — это то значение, которое возвращает функция. Оно будет отображено в случае, если условие, которое вы тестируете соответствует условию ЛОЖЬ.
Дополнительная информация
- В функции ЕСЛИ может быть протестировано 64 условий за один раз;
- Если какой-либо из аргументов функции является массивом — оценивается каждый элемент массива;
- Если вы не укажете условие аргумента FALSE (ЛОЖЬ) value_if_false (значение_если_ложь) в функции, т.е. после аргумента value_if_true (значение_если_истина) есть только запятая (точка с запятой), функция вернет значение “0”, если результат вычисления функции будет равен FALSE (ЛОЖЬ).
На примере ниже, формула =IF(A1> 20,”Разрешить”) или =ЕСЛИ(A1>20;»Разрешить») , где value_if_false (значение_если_ложь) не указано, однако аргумент value_if_true (значение_если_истина) по-прежнему следует через запятую. Функция вернет “0” всякий раз, когда проверяемое условие не будет соответствовать условиям TRUE (ИСТИНА).
|
- Если вы не укажете условие аргумента TRUE(ИСТИНА) (value_if_true (значение_если_истина)) в функции, т.е. условие указано только для аргумента value_if_false (значение_если_ложь), то формула вернет значение “0”, если результат вычисления функции будет равен TRUE (ИСТИНА);
На примере ниже формула равна =IF (A1>20;«Отказать») или =ЕСЛИ(A1>20;»Отказать»), где аргумент value_if_true (значение_если_истина) не указан, формула будет возвращать “0” всякий раз, когда условие соответствует TRUE (ИСТИНА).
Функция Если в Excel примеры с несколькими условиями
Пример 1. Проверяем простое числовое условие с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ)
При использовании функции ЕСЛИ в Excel, вы можете использовать различные операторы для проверки состояния. Вот список операторов, которые вы можете использовать:
Ниже приведен простой пример использования функции при расчете оценок студентов. Если сумма баллов больше или равна «35», то формула возвращает “Сдал”, иначе возвращается “Не сдал”.
Пример 2. Использование вложенной функции IF (ЕСЛИ) для проверки условия выражения
Функция может принимать до 64 условий одновременно. Несмотря на то, что создавать длинные вложенные функции нецелесообразно, то в редких случаях вы можете создать формулу, которая множество условий последовательно.
В приведенном ниже примере мы проверяем два условия.
- Первое условие проверяет, сумму баллов не меньше ли она чем 35 баллов. Если это ИСТИНА, то функция вернет “Не сдал”;
- В случае, если первое условие — ЛОЖЬ, и сумма баллов больше 35, то функция проверяет второе условие. В случае если сумма баллов больше или равна 75. Если это правда, то функция возвращает значение “Отлично”, в других случаях функция возвращает “Сдал”.
Пример 3. Вычисляем сумму комиссии с продаж с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ) в Excel
Функция позволяет выполнять вычисления с числами. Хороший пример использования — расчет комиссии продаж для торгового представителя.
В приведенном ниже примере, торговый представитель по продажам:
- не получает комиссионных, если объем продаж меньше 50 тыс;
- получает комиссию в размере 2%, если продажи между 50-100 тыс
- получает 4% комиссионных, если объем продаж превышает 100 тыс.
Рассчитать размер комиссионных для торгового агента можно по следующей формуле:
=IF(B2<50,0,IF(B2<100,B2*2%,B2*4%)) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИ(B2<50;0;ЕСЛИ(B2<100;B2*2%;B2*4%)) — русская версия
В формуле, использованной в примере выше, вычисление суммы комиссионных выполняется в самой функции ЕСЛИ. Если объем продаж находится между 50-100K, то формула возвращает B2 * 2%, что составляет 2% комиссии в зависимости от объема продажи.

Пример 4. Используем логические операторы (AND/OR) (И/ИЛИ) в функции IF (ЕСЛИ) в Excel
Вы можете использовать логические операторы (AND/OR) (И/ИЛИ) внутри функции для одновременного тестирования нескольких условий.
Например, предположим, что вы должны выбрать студентов для стипендий, основываясь на оценках и посещаемости. В приведенном ниже примере учащийся имеет право на участие только в том случае, если он набрал более 80 баллов и имеет посещаемость более 80%.
Вы можете использовать функцию AND (И) вместе с функцией IF (ЕСЛИ), чтобы сначала проверить, выполняются ли оба эти условия или нет. Если условия соблюдены, функция возвращает “Имеет право”, в противном случае она возвращает “Не имеет право”.
Формула для этого расчета:
=IF(AND(B2>80,C2>80%),”Да”,”Нет”) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИ(И(B2>80;C2>80%);»Да»;»Нет») — русская версия
Пример 5. Преобразуем ошибки в значения “0” с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ)
С помощью этой функции вы также можете убирать ячейки содержащие ошибки. Вы можете преобразовать значения ошибок в пробелы или нули или любое другое значение.
Формула для преобразования ошибок в ячейках следующая:
=IF(ISERROR(A1),0,A1) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИ(ЕОШИБКА(A1);0;A1) — русская версия
Формула возвращает “0”, в случае если в ячейке есть ошибка, иначе она возвращает значение ячейки.
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ. Если вы используете Excel 2007 или версии после него, вы также можете использовать функцию IFERROR для этого.
Точно так же вы можете обрабатывать пустые ячейки. В случае пустых ячеек используйте функцию ISBLANK, на примере ниже:
=IF(ISBLANK(A1),0,A1) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИ(ЕПУСТО(A1);0;A1) — русская версия
This post will guide you how to use Excel IF function with syntax and examples in Microsoft excel.
- Excel IF function Description
- Excel IF function Syntax
- Nested IF statements
- Excel Logical operators
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Related Functions
- Excel IF Formula Examples
Table of Contents
- Description
- Syntax
- Nested IF statements
- Excel Logical operators
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Related Functions
- More Excel IF Formula Examples
Description
The Excel IF function perform a logical test to return one value if the condition is TRUE and return another value if the condition is FALSE.
The IF function is a build-in function in Microsoft Excel and it is categorized as a Logical Function.
The IF function is available in Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2010, Excel 2007, Excel 2003, Excel XP, Excel 2000, Excel 2011 for Mac.
Syntax
The syntax of the IF function is as below:
= IF (condition, [true_value], [false_value])
Where the IF function arguments are:
Condition -This is a required argument. A user-defined condition that is to be tested.
True_value – This is an optional argument. The value that is returned if condition evaluates to TRUE.
False_value – This is an optional argument. The value that is returned if condition evaluates to FALSE.
The below examples will show you how to use Excel IF Function to return one value if the condition is TRUE or FALSE.
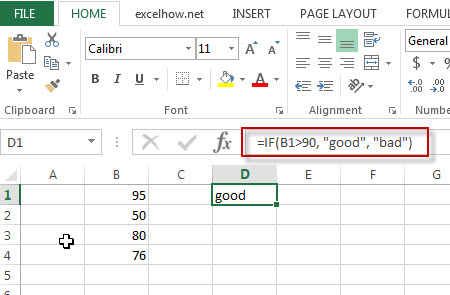
=IF(B1>90, good, bad)
Note: the above excel formula will test a condition “b1>90”, if the condition is true, then “good” will return or “bad” will return.
Nested IF statements
The excel if function just only test one condition and if you want to deal with more than one condition and return different actions depending on the result of the tests, then you need to include several IF statements (functions) in one excel IF formula, these multiple IF statements are also called Excel Nested IF formula(Nested IFs).
For example:
=IF(A1>=80, "excellent", IF(A1>=60, "good", IF(A1>0, "bad", "no valid score")))
More reading: Excel Nexted IF Functions (Statements) Tutorial
Excel Logical operators
When you are writing an If statement, you may need to use any of the following excel logical operators:
| Operator | Meaning | Example | Description |
| = | Equal To | A1=B1 | Returns True if a value in cell A1 is equal to the values in cell B1; FALSE if they are not. |
| > | Greater Than | A1>B1 | Returns True if a value in cell A1 is greater than the values in cell B1; FALSE if they are not. |
| >= | Greater Than or Equal to | A1>=B1 | Returns True if a value in cell A1 is greater than or equal to the values in cell B1; FALSE if they are not. |
| < | Less Than | A1<B1 | Returns True if a value in cell A1 is less than the values in cell B1; FALSE if they are not. |
| <= | Less Than or Equal to | A1<=B1 | Returns True if a value in cell A1 is less than or equal to the values in cell B1; FALSE if they are not. |
| <> | Not Equal to | A1<>B1 | Returns True if a value in cell A1 is not equal to the values in cell B1; FALSE if they are not. |
Let’s see some examples for logical operators in Excel formula:
=(A1>B1) Output: TRUE =(A1<B1) Output: FALSE =(A1>=B1) Output: TRUE =(A1<>8) Output: FALSE =(A1<>B1) Output: TRUE =(IF A1>3, “TRUE”, “FALSE”) Output: TRUE
Frequently Asked Questions
Question1: I want to write an IF Formula based on the below test criteria in the Microsoft excel.
If the number in Cell B1 is greater than 30, then I want it to return A
If the number in cell B1 is between 20 and 30, then I want it to return B
If the number in Cell B1 is below 20, then I want it to return C
The below formula is what I currently write:
=IF(B1>30,"A",IF(B1<30,B1>20,"B","C"))
When I entered the above formula in the Cell C1, and it will return an Error.
Answer: You can use IF function in combination with AND function to reflect the above logic. So you can do it using the following formula:
=IF(B1>30,"A",IF(AND(B1>=20,B1<=30),"B","C"))
Or you can use another IF formula without AND function as follows:
=IF(B1>30,"A",IF(B1<20,"C","B"))
Question 2: I want to write a excel Formula for sales rep, If the sales are less than 10K, then the member will get no commission. If the sales are between 10 and 50K, then the member will get a 3% commission. If the sales are more than 50k, then the member will get 5% commission. Could you help me?
Answer: Based on the above description, we can use the following excel IF formula:
=IF(B1<10,0,IF(B1<50,B1*3%,B1*5%))
Question 3: I want to select students for the scholarship in school, and based on the student’s scores and attendance value, if the student scores more than 85 and has the attendance of more than 85%, then he/she will get the scholarship. Please help me how to write this formula based on my test criteria.
Answer: you can use the IF function with the AND function to check whether both of two conditions are met or not. If the test are met, then return “Yes”, otherwise returns “No”.
So you can use the following IF formula in Excel:
=IF(AND(B1>85, C1>85%),"Yes","No")
Question 4: I am trying to write an excel formula based on the following logic:
I want to enter a formula in Cell C1 that will Add B1, B2 and B3 or multiply B1 by 1, multiply B2 by 2, multiply B2 by 3, which action will be taken based on what you put in Cell D1.
Appreciated for any help. Thanks
Answer: Based on the above logic description, you need to use SUM function to count the sum of B1, B2 and B3. We can use the following IF formula:
=IF(D1="Add”,SUM(B1,B2,B3),IF(D1="Multiply",B1*B2*B3,"ERROR"))
Question 5: I am trying to write a formula in excel to check the employee number field and returns the relevant band of employee. I already have one IF formula, but I always return the first value of “A”. Could you help?
=IF(B1>=10,"A",IF(B1>=20,"B",IF(B1>=50,"C")))
Answer: when you write an IF nested formula, you need to start with the largest number first or start the smallest number first with less than or equal to operator.
1# start with the largest number first, we can write down the below formula:
=IF(B1>=50,"C",IF(B1>=20,"B",IF(B1>=10,"A")))
2# start with the smallest number first, you need to change the >= to <= , just see the below formula:
=IF(B1<=10,"A",IF(B1<=20,"B",IF(B1<=50,"C")))
Question 6: I want to write a Formula in excel to return “bad” if the cell B1 is either <100 or >500, otherwise, it should be returned the value of cell B1.
Answer: For the above logic test, we should use the OR function in the IF condition, so we can write down the below IF formula:
=IF(OR(B1>500,B1<100),"good",B1)
Question 7: I want to write a formula in excel using IF function to check if the cell B1 >10 and B1<20. If TRUE, returns “good”, If FALSE, returns “bad”
Answer: You can use IF function in combination with AND function to check the value of Cell B1, if cell B1 is greater than 10 and cell B1 is less than 20, then returns “good”, otherwise, it will return “bad”.
=IF(AND(B1>10,B1<20),"good","bad")
Question 8: I need to write a nested IF statement in excel 2013 to check the following logic:
If Cell B1 is less than 5, then multiply it by 5.
If Cell B1 is greater than or equal to 5 but less than 10, then multiply it by 10.
If cell B1 is greater than 10, then multiply it by 15.
Answer: This is a generic nested IF formula in excel, we can write the below nested IF statement to reflect the logic.
=IF(B1<5, B1*5, IF(B1<10, B1*10, B1*15))
Question 9: I want to write a formula to match the following logic in MS Excel 2013:
If A1*B1 <=10, then returns A
If A1*B1 >10 but A1*B1 <=20, then returns B
If A1*B1 >20 but A1*B1 <=30, then returns C
If A1*B1>30, then returns D
Answer: You can use IF function to build a Nested IF statement in combination with AND function to achieve it. Let’s write down the following IF formula:
=IF(A1*B1<=10,"A", IF(AND(A1*B1>10,A1*B1<=20),"B", IF(AND(A1*B1>20,a1*B1<=30,"C","D"))))
Question 10: I want to write an IF function to check if the value in cell B1 is blank or Text string or Numeric value, if the cell B1 is empty, then return “blank”, if the cell B1 is a text string, then return “Text”, if the value in cell B1 is a numeric value, then return “number”. Any help for this formula, thanks.
Answer: Based on the description, you need to use ISBLANK function to check if the value in cell b1 is blank or not. And need to use ISTEXT function to check if the value in cell B1 is a text string or not and need to use ISNUMBER function to check if the value in cell B1 is a number or not. So you can write a nested IF statements in combination with ISBLANK, ISTEXT and ISNUMBER functions in Excel as follows:
=IF(ISBLANK(B1),"blank", IF(ISTEXT(B1),"Text", IF(ISNUMBER(B1),"number")))
Question 11: I want to write a formula in excel to calculate the bonus for employees in company, if the employee salary is greater than or equal to $2000, then the bonus will be 10% of the salary , otherwise, the bonus will be 5% of the employee salary.
Answer: we need to check if the salary in Cell B1 (it’s the salary of the first employee) is greater than or equal to 2000. It the condition test is TRUE, then returns B1*10%, otherwise returns b1*5%. So we can write down the following IF formula in excel:
=IF(B1>=2000, B1*10%, B1*5%)
Question 12: In Microsoft Excel 2013, I want to create an IF function to check if any employee who have at least 10 years of experience and whose salary is greater than $5000, If TRUE, then the bonus will be 20% of salary.
Answer: you can use IF function in combination with AND function to check if the value in cell B1 is greater than or equal to 10 and the value in Cell C1 is greater than 5000. If both of two conditions are TRUE, then returns C1*20%, otherwise returns “No Bonus”.
Let’s write down the following IF statement as follows:
=IF(AND(B1>=10,C1>5000),C1*20%, "No Bonus")
Question 13: I want to create an IF formula in Excel 2013 to check the following text logic:
If B1<10, then multiply B1 by 1%, but the returned value is not less than 50.
If B1>10, then multiply B1 by 2%, but the returned value is not greater than 100.
Answer: To reflect the first test condition, you need to use MAX function to match the condition. To reflect the second test condition, you need to use MIN function to match that the returned value should not be greater than 100. So we can use the following excel IF formula:
=IF(B1<10, MAX(50,B1*1%), IF(B1>10, MIN(100,B1*5%)))
Question 14: I want to use IF function to check if B1 is greater than 10 and B2 is greater than 20 and B3 is less than 30, if TRUE, then returns “good”, otherwise, it should be returned “bad”. So How to create the IF formula based on the above test criteria to check three conditions at the same time.
Answer: you need to use AND function within the IF function in excel to create an IF formula as follows:
=IF(AND(B1>10,B2>20,B3<30),"good","bad")
Question 15: I have an IF formula that might cause a division by zero error, I don’t know how to avoid this kind of errors in Excel formula.
Answer: You can use ISERROR function to catch this kind of errors then use the IF function to check the returned values from ISERROR function to avoid an error. So we can write an IF function in combination with ISERROR function in excel. For example, we can use the following IF formula:
=IF(ISERROR(B1/C1),0, B1/C1)
The ISERROR function will return TRUE when trying to divide B1 by 0.
Question 16: I need to create a formula in Excel 2013 to reflect the following logic:
If B1=Excel, then return E
If B1=word, then return W
If B1=access, then return A
Answer: You can use IF function to create a nested IF statements as follows:
=IF(B1="Excel","E",IF(B1="word","W",IF(B1="access","A")))
Question 17: I have a worksheet that containing cells that are formatted as date format. I want to write an IF formula to check the first value in Cell (month part). So I am trying to create the following IF formula:
=IF(LEFT(B1,1)=8, "August","Null")
The returned results are always “Null”.
Answer: As the dates are not recognized as string, so you cannot use the LEFT function to exact the first value in the dates. At this moment, you need to use Month function to convert the date to its month number in Excel. So we can write down the below IF formula in combination with Month function:
=IF(MONTH(B1)=8, "August","Null")
Question18: I am trying to create an IF formula to check if the time value in cells are greater than 10.00h for the following date format: 08/11/2018 09:43.50. Appreciative of any help.
Answer: In excel, you can use HOUR, MINUTE, SECOND functions to compare the date or time value. so if you want to compare the value in Cell B1 if it is greater than 10h, then you can use HOUR function within IF function, just like this: HOUR(B1)>10, so we can write down the below formula:
=IF(HOUR(B1)>10, "greater","less")
Question 19: I want to create an IF function and need to combine with another RAND function. The formula just works find for the first IF_VALUE_TRUE statement, but the formula works not good for IF_VALUE_FALSE statement. Here is the IF formula I have got:
=IF(ISBLANK(B1),"","=rand()")
In the above IF function, it will return empty string when the value in cell B1 is blank. Otherwise, it should add a random function, the problem is that the cell doesn’t run the RAND function. So how can I fix it? Thanks
Answer: when you write an IF formula, if you want to enclose others function, you need not to add quotes around the RAND () function, so just remove the quotes and equal sign in your IF function. Just like the below IF formula:
=IF(ISBLANK(B1),"",RAND())
Question 20: I am trying to write an IF formula in Excel 2013 to reflect the following logic:
If B1 is greater than or equal to 50 and C1 is 0
OR
If B1 is greater than or equal to 30 and C1 is greater than or equal to 1
OR
If B1 is greater than or equal to 20 and C1 is 2
Then take the following action: D2/E2
Otherwise, return FALSE
I have wrote the following IF formula, but it doesn’t work at all.
=IF(AND(B1>=50,C1>=0),OR(AND(B1>=30,C1>=1)),OR(AND(B1>=20,C1>=2)),D2/E2,"FALSE")
Answer: you need to nest your different AND function within an OR function in the IF formula. So you can try the below IF formula:
=IF(OR(AND(B1>=50,C1>=0),AND(B1>=30,C1>=1),AND(B1>=20,C1>=2)), D2/E2,"FALSE")
Question 21: I want to create an IF function in combination with MID function in excel 2013. it need to check if the value in one specified cell is TRUE, then return the first six characters from another cell. Otherwise return empty value.
Answer: you just need to add MID function within IF function in excel, and do not add any quotes around MID function. So you can use the following IF formula to achieve your request:
=IF(B1=TRUE, MID(C1,1,5), "")
Question 22: I have a excel worksheet as below:
A B
——
20 O
30 V
10 T
50 T
I want to create an IF formula to reflect the following logic:
IF cell A1 is less than or equal to 30 and Cell B1 is equal to “O” or “V”, if TRUE, then returns 300, otherwise returns 400.
IF Cell A1 is greater than 30 and Cell B1 is equal to “O” or “V”, then returns 500, otherwise returns 600.
I have wrote the below tow IF formulas for the above two conditions as follows:
=IF(AND(A1<=30,OR(B1="O",B1="V")),300,400)
=IF(AND(A1>30,OR(B1="O",B1="V")),500,600)
I am able to check the above two IF formula and the returned results is OK… But I am not able to combine the above two IF formula into a single IF formula. So anybody can help? Many thanks
Answer: Based on the above logic, you can use the below IF formula to combine with above two IF formulas:
=IF(A1<=30,IF(OR(B1="O",B1="V"),300,400),IF(OR(B1="O",B1="V"),500,600))
Question 23: I am trying to write an IF function to prevent zero and negative values in cells. What I would like is that if the value in cell B1 is less than or equal to 0, then it should be returned “Null” otherwise, it should return the calculation of Cells value, like as:B2*(C2-D2)*E2.
The below IF formula is what I have:
=IF(B1<=0,"Null","B2*(C2-D2)*E2")
When I run the formula above, it only returns my calculation string and do not take the actual calculation.
Answer: In excel, the double quotes make any values in between be recognized as Text string. So if you want to take calculation for your IF formula, just remove the double quotes. Let’s see the modified IF formula as follows:
=IF(B1<=0,"Null",B2*(C2-D2)*E2)
Question 24: I want to create an new IF function to check if the value in cells is Saturday or Sunday, If TRUE, returns “yes”, otherwise, returns “No”. And I am using the following IF formula, but I get an error, so what’s wrong for this formula?
=IF((OR($B1="Saturday","$B1="Sunday"),"yes","no"))
Answer: you need to use the WEEKDAY function within IF function to handle the dates if they are in date format, like as: 11/8/2018.
So you can use the below IF function to achieve your logic:
=IF(WEEKDAY($B$1,2)>5,"yes","no")
You can also use TEXT function within the IF function to achieve the same results, just like the below IF formula:
=IF(LEFT(TEXT($B$1,"ddd"))="S","yes","no")
Question 25: I want to write an IF function in excel to check if the first character in one Cell is equal to 5, then the returned value should be the five rightmost characters of that cell, otherwise, the returned value should be the four rightmost characters. I wrote one IF formula as follows, but it doesn’t work.
=IF(LEFT(B1,1)=5, RIGHT(B1,5),RIGHT(B1,4))
In the above IF function, it always return the rightmost four characters even though the first character in Cell B1 starts with “S”. Please help me to fix it.
Answer: you should know the returned value of the LEFT function firstly in excel. As the LEFT function will return a Text value, so you also need to provide a string for comparison, so adding quotes to enclose it. Just like the below IF function:
=IF(LEFT(B1,1)="5", RIGHT(B1,5),RIGHT(B1,4))
There is another way to achieve the same results, you can use NUMBERVALUE function to convert the result of LEFT function to a numeric value, like the below IF function:
=IF(NUMBERVALUE(LEFT(B1,1))=5,RIGHT(B1,5),RIGHT(B1,4))
Question 26: I have 2 columns contain date and time or just only contain time. And I want to check if the times of column A is greater than the times of column B. the key issue may be that column A has the date and time. I wrote the following IF formula to run it in Cell C1, but it returned the inaccurate results.
=IF(A1>B1,"yes","no")
Any help would be appreciated… Many thanks!
Answer: the date part of the value in column A is the integer, while the time is the decimal. You can use the following IF formula:
=IF(A1-INT(A1)>B2),"yes","no")
Question 27: The below are the results that I expected, and I want cell B1 to B4 can detect the string from A1 to A4 automatically and return the same string value plus the severity level when the test match. For example, If A1 is equal to “critical”, then it should be returned “critical severity 1” in the cell B1. Etc.
And I am using the following IF formula, but it does not work at all. Please help to fix it. Thanks
=IF(A1="Critical","Critical Severity 1",""),IF(A1="High","High Severity 2",""),IF(A1="Medium","Medium Severity 3",""),IF(A1="Low","Low Severity 4","")
| A | B |
| critical | critical severity 1 |
| high | high severity 2 |
| medium | Medium severity 3 |
| low | low severity 4 |
Answer: you can try to run the following IF formula in excel:
=IF(A1="critical","critical Severity 1",IF(A1="high","high Severity 2",IF(A1="medium","medium Severity 3",IF(A1="low","low Severity 4",""))))
Question 28: I am working on an excel file and want to create a new IF formula to reflect the following logic:
If the value in Cell A1 is equal to the value in Cell A2, then check if the minus of B1 and B2 is equal to a special value, and if the condition is TRUE, returns “yes”, otherwise, returns “no”. Here is the IF formula I have:
=if(A1=A2,B1-B2=5 or B1-B2=-5 or B1-B2=20 or B1-B2=-20, "yes", "no")
Any help is appreciated…Thanks
Answer: you need to use OR function with IF function to create a nested IF statement to achieve your request. So you can try the following Excel IF formula in your excel file.
=IF(A1=A2,IF(OR(B1-B2=5,B1-B2=-5,B1-B2=20,B1-B2=-20),"yes","no"),"no")
Question 29: I want to create an IF formula to check the range of cells in excel. I have scores of different subject for a student, and want to check if any one of scores is less than 60, If TRUE, then return “BAD”. Can this logic be done with the IF statements in excel 2013?
Answer: you can use COUNTIF function within IF function to create a generic IF formula as follows:
=IF(COUNTIF(B:B,"<60")>0,"BAD","Good")
Question 30: I am trying to create a new IF statement so that when the formula is looking at Row A and Row B, the returned values should be shown in the Row C. the following logic need to be checked:
IF the value in the Row A is equal to “NA” And the value in the Row B is equal to “NA”, then return “NA” value in Row C.
IF the value in the Row A is equal to “NA”, and the value in the Row B is equal to “denied”, then return “denied” value in Row C.
IF the value in the Row A is equal to “allowed” and the value in the Row B is equal to “NA”, then return “allowed” value in Row C.
Here is my formula:
=IF(AND(A1 = "NA", B1 = "NA"),"NA",IF(OR(A1="denied",B1 ="denied"),"denied", "NA"))
I don’t know how to include “allowed” in the IF formula above, anyone can help this, many thanks.
Answer: This is a typical nested if statement, you can use OR function within IF function in excel. We can write down this nested IF formula as follows:
=IF(OR(A1="denied", B1="denied"), "denied", IF(OR(A1="allowed", B1="allowed"), "allowed", "NA"))
- Excel AND function
The Excel AND function returns TRUE if all of arguments are TRUE, and it returns FALSE if any of arguments are FALSE.The syntax of the AND function is as below:= AND (condition1,[condition2],…) … - Excel ISBLANK function
The Excel ISBLANK function returns TRUE if the value is blank or null.The syntax of the ISBLANK function is as below:= ISBLANK (value)… - Excel COUNTIF function
The Excel COUNTIF function will count the number of cells in a range that meet a given criteria.= COUNTIF (range, criteria) … - Excel ISERROR function
The Excel ISERROR function returns TRUE if the value is any error value except #N/A. The ISERROR function is a build-in function in Microsoft Excel and it is categorized as an Information Function. The syntax of the ISERROR function is as below: = ISERROR (value) … - Excel LEFT function
The Excel LEFT function returns a substring (a specified number of the characters) from a text string, starting from the leftmost character.The syntax of the LEFT function is as below:= LEFT(text,[num_chars])… - Excel MID function
The Excel MID function returns a substring from a text string at the position that you specify. The MID function is a build-in function in Microsoft Excel and it is categorized as a Text Function. The syntax of the MID function is as below: = MID (text, start_num, num_chars) … - Excel TEXT function
The Excel TEXT function converts a numeric value into text string with a specified format. The syntax of the TEXT function is as below:= TEXT (value, Format code)… - Excel RIGHT function
The Excel RIGHT function returns a substring (a specified number of the characters) from a text string, starting from the rightmost character…
More Excel IF Formula Examples
- Excel nested if function
The nested IF function is formed by multiple if statements within one Excel if function. This excel nested if statement makes it possible for a single formula to take multiple actions… - Excel IF formula with Equal to logical operators
The “Equal to” logical operator can be used to compare the below data types, such as: text string, numbers, dates, Booleans. This section will guide you how to use equal to logical operator in excel IF formula with text string value and dates value… - Excel IF formula with greater than logical operators
How to use if function with greater than, greater than or equal to, less than and less than or equal to logical operators in excel. Let’s see the below generic if formula with greater than operator: =IF(A1>10,”excelhow.net”,”google”) … - Excel IF formula with AND logical function
You can use the IF function combining with AND function to construct a condition statement. If the test is FALSE, then take another action. The syntax of AND function in excel is as follow: =AND(condition1,[condition2],…)… - Excel IF function with OR logical function
If you want to check if one of several conditions is met in your excel workbook, if the test is TRUE, then you can take certain action. You can use the IF function combining with OR function to construct a condition statement… - Excel IF function with “NOT” logical function
If you want to check several test conditions in an excel formula, then take different actions. You can use NOT function in combination with the AND or OR logical function in excel IF function… - Excel IF formula with AND & OR logical functions
If you want to test the result of cells based on several sets of multiple test conditions, you can use the IF function with the AND and OR functions at a time… - Excel IF Function With Numbers
If you want to check if a cell values is between two values or checking for the range of numbers or multiple values in cells, at this time, we need to use AND or OR logical function in combination with the logical operator and IF function… - Excel IF function with text values
If you want to write an IF formula for text values in combining with the below two logical operators in excel, such as: “equal to” or “not equal to”… - Excel IF function with Dates
If you have a list of dates and then want to compare to these dates with a specified date to check if those dates is greater than or less than that specified date. … - Excel IF function check if the cell is blank or not-blank
If you want to check the value in one cell if it is blank or empty cell, then you can use IF function in combination with ISBLANK function or logical operator (equal to) in excel… -
Excel nested if statements with ranges
Many people usually asked that how to write an excel nested if statements based on multiple ranges of cells to return different values in a cell? How to nested if statement using date ranges? How to use nested if statement between different values in excel 2013 or 2016… - Count Cells That Contain Specific Text
This post will discuss that how to count the number of cells that contain specific text or certain text in a specified cells of range in Excel. How to get the total number of cells that contain certain text.…… - Sum Values by Group
Assuming that you have a table that contain the product name and its sales result. And you have group by those values based on the product name, then you want to sum values based one each product name. You can create a new Excel formula based on the IF function and SUMIF function.… - Get nth Largest Value with Duplicates
If you want to get the largest unique value in a data set with duplicates, you can create a new excel array formula based on the MAX function and the IF function..… - Find the Largest Value Based on Multiple Criteria
Assuming that you have a list of data that you want to find the largest value based on the product “excel” and the sales region “east”. You can create a new excel formula based on the SUMPRODUCT function and the LARGE function..…… - Create a Five Star Rating System
How do I change the five points system to five star rating in excel. How to use the conditional formatting function to create a five star rating system in excel….. - Rank values in a column based a specific value in another column
Assuming that you have a list of data contains two columns and the first column is product list and another is Sales number. You want to rank the sales number of a specified product name. You can try to write a complex formula based on the IF function and the COUNTIFS function to achieve the result..… - Comparing Columns Using Conditional Formatting Icon Sets
how to compare the adjacent cells in the different columns using Conditional Formatting Icon Sets in Excel. How to compare Columns or rows using Conditional Formatting Icon Sets to show increase or decrease status in your current worksheet..… - Show Only Positive Values
You can create a formula based on the IF function, and the SUM function to sum all values in the range A1:C5 and just show only positive values… - Count Unique Values Using Pivot Table
You can insert a 3rd or helper column with a formula to check if the value is unique in the selected range of cells, and the create pivot table based on the 1st and 3rd column to count unique values..… - Compare Dates
Assuming that you have a list of data that contain date values in Excel, you can use the IF function to create a formula to achieve it. If the date is greater that the given date value, then return True. Otherwise, it returns False…. - Excel Vlookup Return True or False
you can use the VLOOKUP function to look for a value in a column in a table and then returns TRUE from a given column in that table if it finds something. If it doesn’t, it returns FALSE … - VLOOKUP Return Multiple Values Horizontally
You can create a complex array formula based on the INDEX function, the SMALL function, the IF function, the ROW function and the COLUMN function to vlookup a value and then return multiple corresponding values horizontally in Excel.… - Copy and Paste Only Non-blank Cells
If you want only copy non-blank cells in a range in Excel, you need to select the non-blank cells firstly, then press Ctrl +C keys to copy the selected cells. So how to only select all non-blank cells in the selected range in your worksheet..… - Changing Negative Number to Zero in Excel
If you want to change all negative numbers to zero value from a cell in Excel, you can use a formula based on the MAX function or IF function.… - Count Dates in Given Year/Month/Day in Excel
You can create a formula based on the SUMPRODUCT function and the YEAR function to count dates by a give year…. - Generate All Possible Combinations of Two Lists
You can use a formula based on the IF function, the ROW function, the COUNTA function, The INDEX function and the MOD function to get a list of all possible combinations from those two list…. - Find Missing Numbers in a Sequence in Excel
You can use an excel array formula based on the SMALL function, the IF function, the ISNA function, the MATCH function, and the ROW function to find missing numbers in a sequence…
IF function is undoubtedly one of the most important functions in excel. In general, IF statements give the desired intelligence to a program so that it can make decisions based on given criteria and, most importantly, decide the program flow.
In Microsoft Excel terminology, IF statements are also called «Excel IF-Then statements». IF function evaluates a boolean/logical expression and returns one value if the expression evaluates to ‘TRUE’ and another value if the expression evaluates to ‘FALSE’.
Definition of Excel IF Function
According to Microsoft Excel, IF function is defined as a formula which «checks whether a condition is met, returns one value if true and another value if false».
Syntax
Syntax of IF function in Excel is as follows:
=IF(logic_test, [value_if_true], [value_if_false])
'logic_test' (required argument) – Refers to the boolean expression or logical expression that needs to be evaluated.'value_if_true' (optional argument) – Refers to the value that will be returned by the IF function if the 'logic_test' evaluates to TRUE.'value_if_false' (optional argument) – Refers to the value that will be returned by the IF function if the 'logic_test' evaluates to FALSE.
Important Characteristics of IF Function in Excel
- To use the IF function, you need to provide the
'logic_test'or conditional statement mandatorily. - The arguments
'value_if_true'and'value_if_false'are optional, but you need to provide at least one of them. - The result of the IF statement can only be any one of the two given values (either it will be
'value_if_true'or'value_if_false'). Both values cannot be returned at the same time. - IF function throws a ‘#Name?’ error if the
'logic_test'or boolean expression you are trying to evaluate is invalid. - Nesting of IF statements is possible, but Excel only allows this to 64 levels. Nesting of IF statement means using one if statement within another.
Comparison Operators That Can Be Used With IF Statements
Following comparison operators can be used within the 'logic_test' argument of the IF function:
- = (equal to)
- <> (not equal to)
- < (less than)
- > (greater than)
- >= (greater than or equal to)
- <= (less than or equal to)
- Apart from these, you can also use any other function that returns a boolean result (either ‘true’ or ‘false’). For example – ISBLANK, ISERROR, ISEVEN, ISODD, etc
Now, let’s see some simple examples to use these comparison operators within the IF Function:
Simple Examples of Excel IF Statement
Now, let’s try to see a simple example of the Excel IF function:
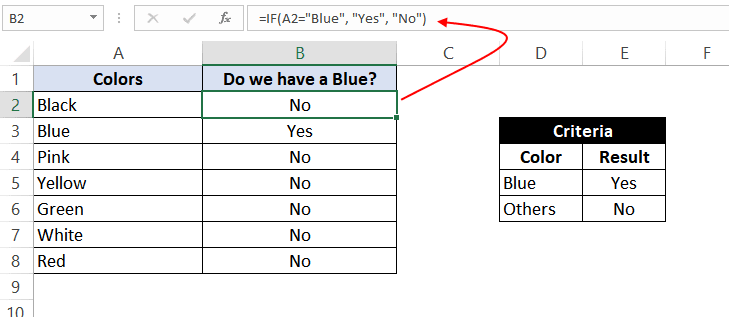
Example 1: Using ‘equal to’ comparison operator within the IF function
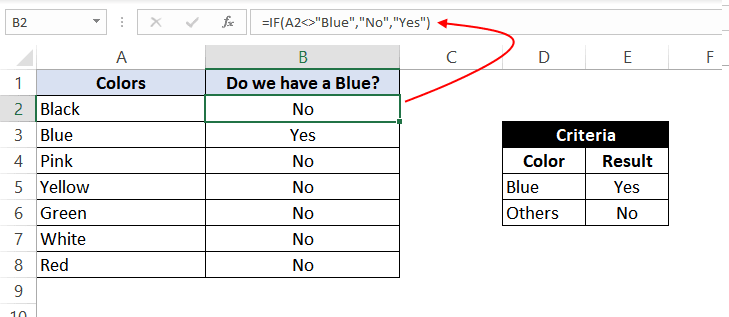
In this example, we have a list of colors, and we aim to find the ‘Blue’ color. If we are able to find the ‘Blue’ color, then in the adjacent cell, we need to assign a ‘Yes’; otherwise, assign a ‘No’.
So, the formula would be:
=IF(A2="Blue", "No", "Yes")
This suggests that if the value present in cell A2 is ‘Blue’, then return a ‘Yes’; otherwise, return a ‘No’.
If we drag this formula down to all the rows, we will find that it returns ‘Yes’ for the cells with the value ‘Blue’ for all others; it would result in ‘No’.
Example 2: Using ‘not equal to’ comparison operator within the IF function.
Let’s take example 1, and understand how we can reverse the logic and use a ‘not equal to’ operator to construct the formula so that it still results in ‘Yes’ for ‘Blue’ color and ‘No’ for any other text.
So the formula would be:
=IF(A2<>"Blue", "No", "Yes")
This suggests that if the value at A2 is not equal to ‘Blue’, then return a ‘No’; otherwise, return a ‘Yes’.
When dragged down to all the below rows, this formula would find all the cells (from A2 to A8) where the value is not ‘Blue’ and marks a ‘No’ against them. Otherwise, it marks a ‘Yes’ in the adjacent cells.
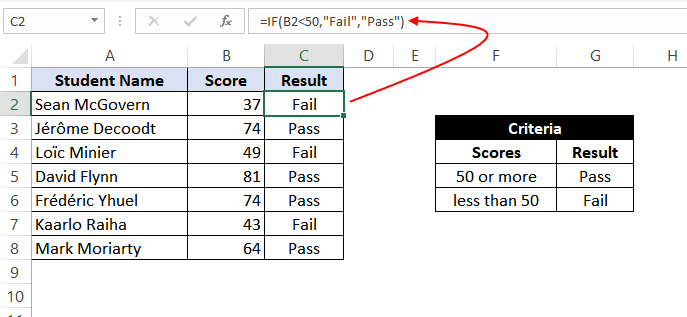
Example 3: Using ‘less than’ operator within the IF function.
In this example, we have scores of some students, along with their names. We want to assign either «Pass» or «Fail» against each student in the result column.
Based on our criteria, the passing score is 50 or more.
For this, we can use the IF function as:
=IF(B2<50,"Fail","Pass")
This suggests that if the value at B2, i.e., 37, is less than 50, then return «Fail»; otherwise, return «Pass».
As 37 is less than 50 so the result will be «Fail».
We can drag the above-given formula for the rest of the cells below and the result would be correct.
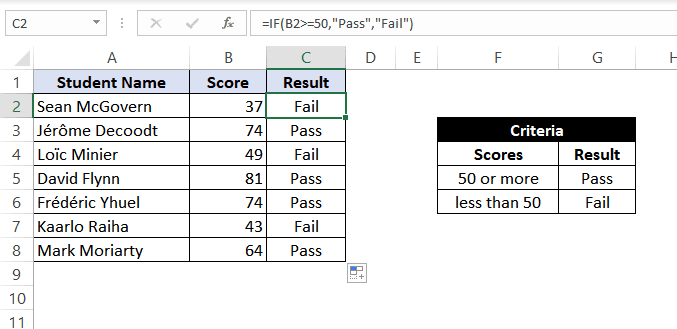
Example 4: Using ‘greater than or equal to’ operator within the IF statement.
Let’s take example 3 and see how we can reverse the logic and use a ‘greater than or equal to’ operator to construct the formula so that it still results in ‘Pass’ for scores of 50 or more and ‘Fail’ for all the other scores.
For this, we can use the Excel IF function as:
=IF(B2>=50,"Pass","Fail")
This suggests that if the value at B2, i.e., 37 is greater than or equal to 50, then return «Pass»; otherwise, return «Fail».
As 37 not greater than or equal to 50 so the result will be «Fail».
When dragged down for the rest of the cells below, this formula would assign the correct result in the adjacent rows.
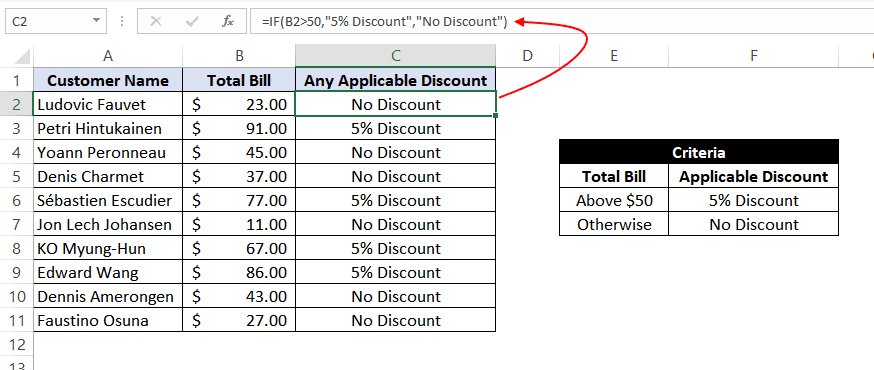
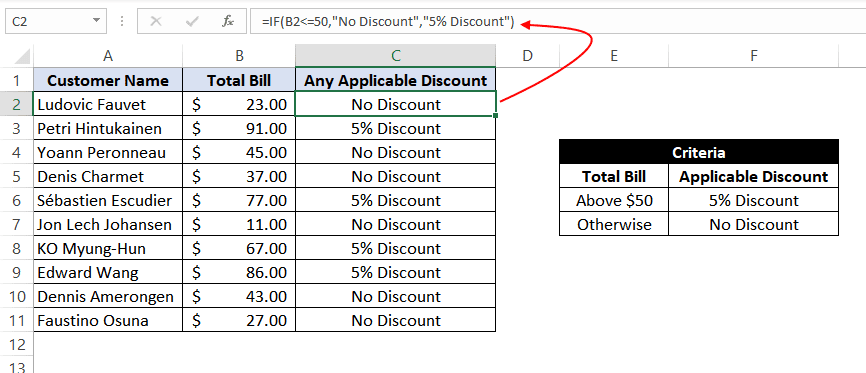
Example 5: Using ‘greater than’ operator within the IF statement.
In this example, we have a small online store that gives a discount to its customers based on the amount they spend. If a customer spends $50 or more, he is applicable for a 5% discount; otherwise, no discounts are offered.
To find whether a discount is offered or not, we can use the following excel formula:
=IF(B2>50,"5% Discount","No Discount")
This translates to – If the value at B2 cell is greater than 50, assign a text «5% Discount» otherwise, assign a text «No Discount» against the customer.
In the first case, as 23 is not greater than 50, the output will be «No Discount».
We can drag the above-given formula for the rest of the cells below are the result would be correct.
Example 6: Using ‘less than or equal to’ operator within the IF statement.
Let’s take example 5 and see how we can reverse the logic and use a ‘less than or equal to’ operator to construct the formula so that it still results in a ‘5% Discount’ for all customers whose total spend exceeds $50 and ‘No Discount’ for all the other customers.
For this, we can use the IF-then statement as:
=IF(B2<=50,"No Discount","5% Discount")
This means that if the value at B2, i.e., 23, is less than or equal to 50, then return «No Discount»; otherwise, return «5% Discount».
As 23 is less than or equal to 50 so the result will be «No Discount».
When dragged down for the rest of the cells below, this formula would assign the correct result in the adjacent rows.
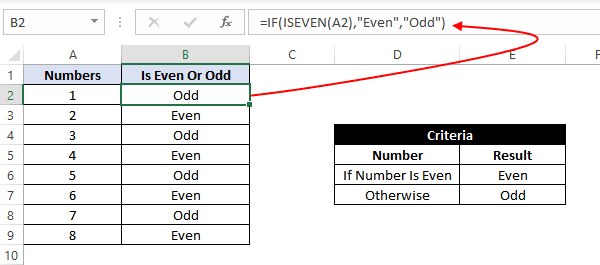
Example 7: Using an Excel Logical Function within the IF formula in Excel.
In this example, let’s suppose we have a list of numbers, and we have to mark Even and Odd numbers. We can do this using the IF condition and the ISEVEN or ISODD inbuilt functions provided by Microsoft Excel.
ISEVEN function returns ‘true’ if the number passed to it is even; otherwise, it returns a ‘false’. Similarly, ISODD function return ‘true’ if the number passed to it is odd; otherwise, it returns a ‘false’.
For this, we can use the IF-then statement as:
=IF(ISEVEN(A2),"Even","Odd")
This means that – If the value at A2 cell is an even number, then the result would be «Even»; otherwise, the result would be «Odd».
Alternatively, the above logic can also be written using the ISODD function along with the IF statement as:
=IF(ISODD(A2),"Odd","Even")
This means that – If the value at A2 cell is an odd number, then the result would be «Odd»; otherwise, the result would be «Even».
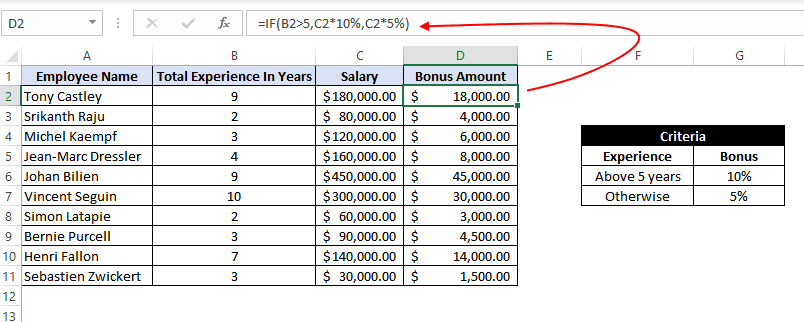
Example 8: Using the Excel IF function to return another formula a result.
In this example, we have Employee Data from a company. The company comes up with a simple way to reward its loyal employees. They decide to give the employees an annual bonus based on the years spent by the employee within the organization.
Employees with experience of more than 5 years are given 10% of annual salary as a bonus whereas everyone else gets a 5% of annual salary as a bonus.
For this, the excel formula would be:
=IF(B2>5,C2*10%,C2*5%)
This means that – if the value at B2 (experience column) is greater than 5, then return a result by calculating 10% of C2 (annual salary column). However, if the logic test is evaluated to false, then return the result by calculating 5% of C2 (annual salary column)
Use Of AND & OR Functions or Logical Operators with Excel IF Statement
Excel IF Statement can also be used along with the other functions like AND, OR, NOT for analyzing complex logic. These functions (AND, OR & NOT) are called logical operators as they are used for connecting two or more logical expressions.
AND Function– AND function returns true when all the conditions inside the AND function evaluate to true. The syntax of AND Function in Excel is:
=AND(Logic1, Logic2, logic_n)
OR Function– OR function returns true when any one of the conditions inside the OR function evaluates to true. The syntax of OR Function in Excel is:
=OR(Logic1, Logic2, logic_n)
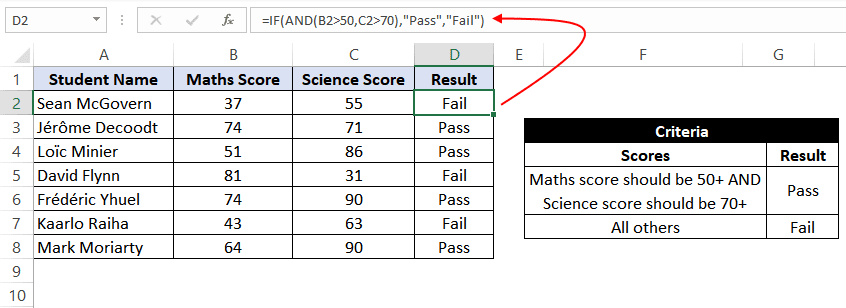
Example 9: Using the IF function along with AND Function.
In this example, we have Math and science test scores of some students, and we want to assign a ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ value against the students based on their scores.
Passing criteria: Students have to get more than 50 marks in Math and more than 70 marks in science to pass the test.
Based on the above conditions, the formula would be:
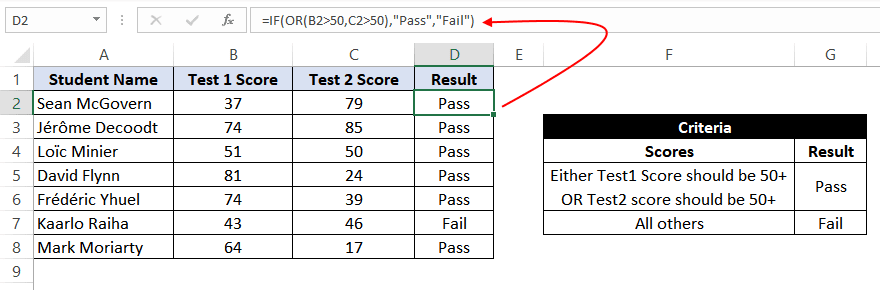
=IF(AND(B2>50,C2>70),"Pass","Fail")
The formula translates to – if the value at B2 (Math score) is greater than 50 and the value at C2 (Science Score) is greater than 70, then assign the value «Pass»; otherwise, assign the value «Fail».
Example 10: Using the IF function along with OR Function.
In this example, we have two test scores of some students, and we want to assign a ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ value against the students based on their scores.
Passing criteria: Students have to clear either one of the two tests with more than 50 marks.
Based on the above conditions, the formula would be:
=IF(OR(B2>50,C2>50),"Pass","Fail")
The formula translates to – if either the value at B2 (Test 1 score) is greater than 50, OR the value at C2 (Test 2 Score) is greater than 50, then assign the value «Pass»; otherwise, assign the value «Fail».
Recommended Reading: Excel NOT Function
Nested IF Statements
When used alone, IF formula can only result in two outcomes, i.e., True or False. But there are many cases when we want to test multiple outcomes with IF statement.
In such cases, nesting two or more IF Then statements one inside another can be convenient in writing formulas.
Syntax:
The syntax of the Nested IF Then statements is as follows:
=IF(condition_1,value_if_true_1,IF(condition_2,value_if_true_2,value_if_false_2))
'condition_1' – Refers to the first logical test or conditional expression that needs to be evaluated by the outer IF function.'value_if_true_1' – Refers to the value that will be returned by the outer IF function if the 'condition_1' evaluates to TRUE.'condition_2' – Refers to the second logical test or conditional expression that needs to be evaluated by the inner IF function.'value_if_true_2' – Refers to the value that will be returned by the inner IF function if the 'condition_2' evaluates to TRUE.'value_if_false_2' – Refers to the value that will be returned by the inner IF function if the 'condition_2' evaluates to FALSE.
The above syntax translates to this:
IF Condition1 = true THEN value_if_true1 'If Condition1 is true
ELSE IF Condition2 = true THEN value_if_true2 'Elseif Clause Condition2 is true
ELSE value_if_false2 'If both conditions are false
END IF 'End of IF Statement
As we can see, Nested formulas can quickly become complicated so, let’s try to understand how nesting of the IF statement works with an example.
Recommended Reading: VBA Select Case Statement
Example 11: Nested IF Statements
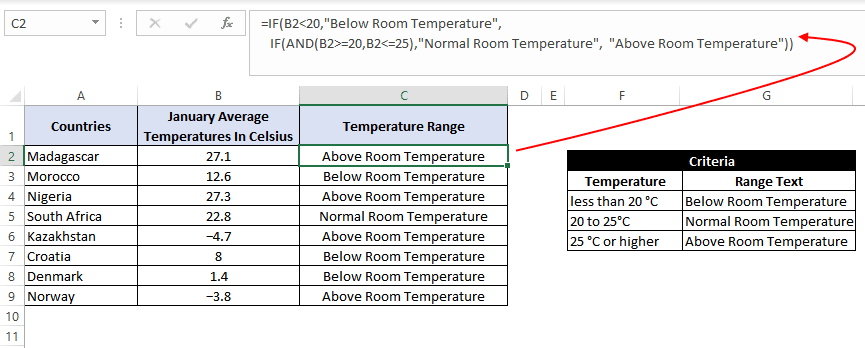
In this example, we have a list of countries and their average temperatures in degree Celsius for the month of January. Our goal is to categorize the country based on the temperature range as follows:
Criteria: Temperatures below 20 °C should be marked as «Below Room Temperature», temperatures between 20°C to 25°C should be classified as «Normal Room Temperature», whereas any temperature over 25°C should be marked as «Above Room Temperature».
Based on the above conditions, the formula would be:
=IF(B2<20,"Below Room Temperature",IF(AND(B2>=20,B2<=25),"Normal Room Temperature", "Above Room Temperature"))
The formula translates to – if the value at B2 is less than 20, then the text «Below Room Temperature» is returned from the outer IF block. However, if the value at B2 is greater than or equal to 20, then the inner IF block is evaluated.
Inside the inner IF block, the value at B2 is checked. If the value at B2 is greater than or equal to 20 and less than or equal to 25. Then the inner IF block returns the text «Normal Room Temperature».
However, if the condition inside the inner IF block also evaluates to ‘false’ that means the value at B2 is greater than 25, so the result will be «Above Room Temperature».
Recommended Reading: SWITCH Function in Excel
Partial Matching or Wildcards with IF Function
Although IF function itself doesn’t accept any wildcard characters like (* or ?) while performing the logic test, thankfully, there are ways to perform partial matching and wildcard searches with the IF function.
To perform partial matching inside the IF function, we can use the FIND (case sensitive) or SEARCH (case insensitive) functions.
Let’s have a look at this with some examples.
Example 12: Using FIND and SEARCH functions inside the IF statement
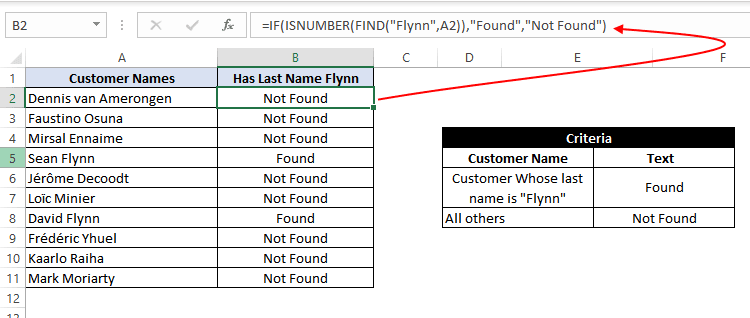
In this example, we have a list of customers, and we need to find all the customers whose last name is «Flynn». If the customer name contains the text «Flynn», then we need to assign a text «Found» against their names. Otherwise, we need to assign a text «Not Found».
For this, we can make use of the FIND function within the IF function as:
=IF(ISNUMBER(FIND("Flynn",A2)),"Found","Not Found")
Using the FIND function, we perform a case-sensitive search of the text «Flynn» within the customer name column. If the FIND function is able to find the text «Flynn», it returns a number signifying the position where it found the text.
If the number returned by the FIND function is valid, the ISNUMBER Function returns a value true. Else, it returns false. Based on the ISNUMBER function’s output, the logic test is performed and the appropriate value «Found» or «Not Found» is assigned.
Note: It should be noted that the FIND function performs a case-sensitive search.
This means in the above example if the customer name is entered in lower case (like «sean flynn» then the above function would return not found against them.
To perform a case-insensitive search, we can replace the find function with the search function, and the rest of the formula would be the same.
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("Flynn",A2)),"Found","Not Found")
Example 13: Using SEARCH function inside the Excel IF formula with wildcard operators
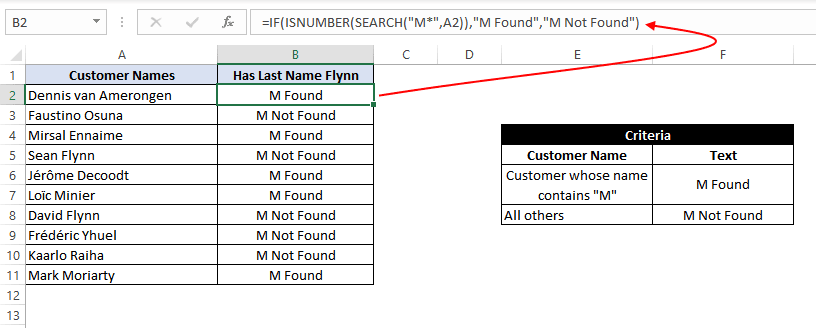
In this example, we have the same customer list from example 12, and we need to find all the customers whose name contains «M». If the customer name contains the alphabet «M», we need to assign a text «M Found» against their names. Otherwise, we need to assign a text «M Not Found».
For this, we can use the SEARCH function with a wildcard ‘*’ operator inside the IF function as:
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("M*",A2)),"M Found","M Not Found")
For more details on Search Function and wildcard, operators check out this article – Search Function In Excel
Some Practical Examples of using the IF function
Now, let’s have a look at some more practical examples of the Excel IF Function.
Example 14: Using Excel IF function with dates.
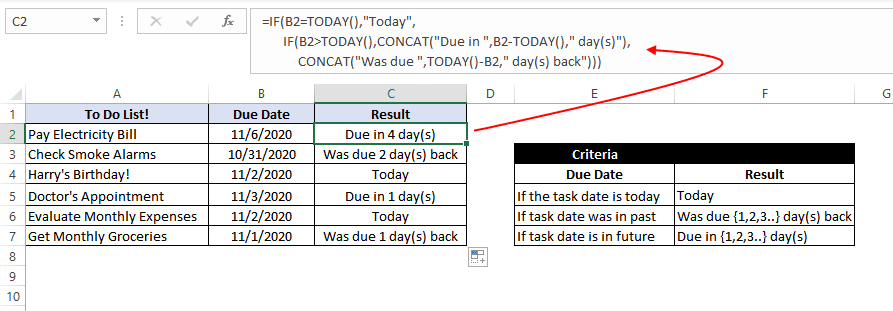
In this example, we have a task list along with the task due dates. Our goal is to show results based on the task due date.
If the task due date was in the past, we need to show «Was due {1,2,3..} day(s) back», if the task due date is today’s date, we need to show «Today» and similarly, if the task due date is in the future then we need to show «Due in {1,2,3..} day(s)»
In Microsoft Excel, we can do this with the help of the IF-then statement and TODAY function, as shown below:
=IF(B2=TODAY(),"Today", IF(B2>TODAY(),CONCAT("Due in ",B2-TODAY()," day(s)"), CONCAT("Was due ",TODAY()-B2," day(s) back")))
This means that – compare the date present in cell B2 if the date is equal to today’s date show the text «Today». If the date in cell B2 is not equal to today’s date, then the inner IF block checks if the date in B2 is greater than today’s date. If the date in cell B2 is greater than today’s date, that means the date is in the future, so show the text «Due in {1,2,3…} days».
However, if the date in cell B2 is not greater than today’s date, that means the date was in the past; in such a case, show the text «Was due {1,2,3..} day(s) back».
You can also go a step further and apply conditional formatting on the range and highlight all the cells with the text «Today!». This will help you to clearly see
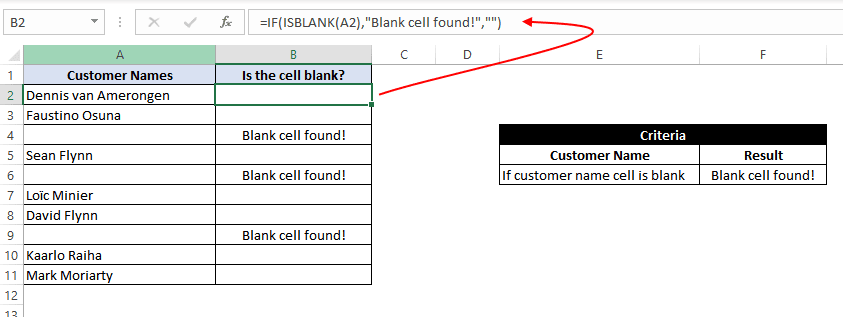
Example 15: Use an IF function-based formula to find blank cells in excel.
In this example, we will use the IF function to find the blank cells in Microsoft Excel. We have a list of customers, and in between the list, some of the cells are blank. We aim to find the blank cells and add the text «blank call found!» against them.
We can do this with the help of the IF function along with the ISBLANK function. The ISBLANK function returns a true if the cell reference passed to it is blank. Otherwise, the ISBLANK function returns false.
Let’s see the formula –
=IF(ISBLANK(A2), "Blank cell found!"," ")
This means that – If the cell at A2 is blank, then the resultant text should be «Blank cell found!», however, if the cell at A2 is not blank, then don’t show any text.
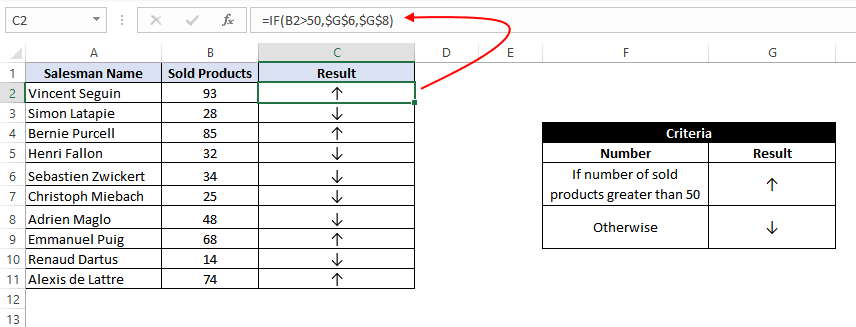
Example 16: Use the Excel IF statement to show symbolic results (instead of textual results).
In this example, we have a list of sales employees of a company along with the number of products sold by the employees in the current month. We want to show an upward arrow symbol (↑) if the employee has done more than 50 sales and a downward arrow symbol (↓) if the employee has made less than 50 sales.
To do this, we can use the formula:
=IF(B2>50,$G$6,$G$8)
This implies – If the value at B2 is greater than 50, then, as a result, show the content in cell G6 (cell containing upward arrow) and otherwise show the content at G8 (cell containing downward arrow)
If you wonder about the ‘$’ signs used in the formula, you can check out this post – Excel Absolute References. These ‘$’ symbols are used for making excel cell references absolute.
Recommended Reading: CHOOSE Function in Excel
IFS Function In Excel:
IFS Function in Microsoft Excel is a great alternative to nested IF Statements. It is very similar to a switch statement. The IFS function evaluates multiple conditions passed to it and returns the value corresponding to the first condition that evaluates to true.
IFS function is a lot simple to write and read than nested IF statements. IFS function is available in Office 2019 and higher versions.
Syntax for IFS function:
=IFS (test1, value1, [test2, value2], ...)
'test1' (required argument) – Refers to the first logical test that needs to be evaluated.
'value1' (required argument) – Refers to the result to be returned when 'test1'evaluates to TRUE.
'test2' (optional argument) – Refers to the second logical test that needs to be evaluated
'value2' (optional argument) – Refers to the result to be returned when 'test2'evaluates to TRUE.
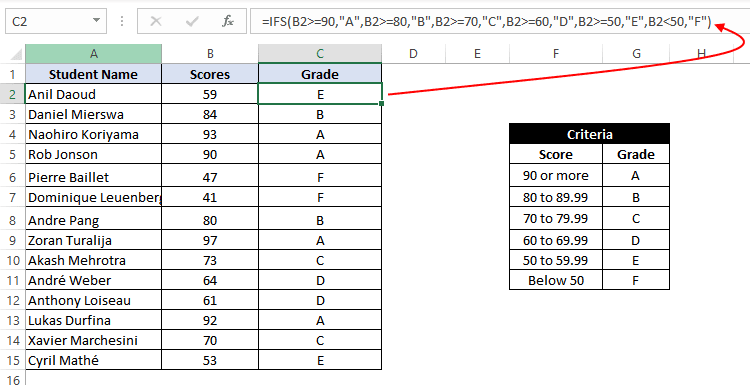
Example 17: Using IFS function in Excel
In this example, we have a list of students, along with their scores, and we need to assign a grade to the students based on the scores.
The grading criteria is as follows – Grade A for a score of 90 or more, Grade B for a score between 80 to 89.99, Grade C for a score between 70 to 79.99, Grade D for a score between 60 to 69.99, Grade E for a score between 60 to 59.99, Grade F for a score lower than 50.
Let’s see how easily write such a complicated formula with the IFS function:
=IFS(B2 >= 90,"A",B2 >= 80,"B",B2 >= 70,"C",B2 >= 60,"D",B2 >= 50,"E",B2 < 50,"F")
This implies that – If B2 is greater than or equal to 90, return A. Else if B2 is greater than or equal to 80, return B. Else if B2 is greater than or equal to 70, return C. Else if B2 is greater than or equal to 60, return D. Else if B2 is greater than or equal to 50, return E. Else if B2 is less than 50, return F.
If you would try to write the same formula using nested IF statements, see how long and complicated it becomes:
=IF(B2 >= 90,"A",IF(B2 >= 80, "B",IF(B2 >= 70, "C",IF(B2 >= 60, "D",IF(B2 >= 50, "E",IF(B2 < 50, "F"))))))
So, this was all about the IF function in excel. If you want to learn more about IF function, I would recommend you to go through this article – VBA IF Statement With Examples