Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 More…Less
This article describes the formula syntax and usage of the SHEETS
function in Microsoft Excel.
Description
Returns the number of sheets in a reference.
Syntax
SHEETS(reference)
The SHEETS function syntax has the following arguments.
-
Reference Optional. Reference is a reference for which you want to know the number of sheets it contains. If Reference is omitted, SHEETS returns the number of sheets in the workbook that contains the function.
Remarks
-
SHEETS includes all worksheets (visible, hidden, or very hidden) in addition to all other sheet types (macro, chart, or dialog sheets).
-
If reference is not a valid value, SHEETS returns the #REF! error value.
-
SHEETS is not available in the Object Model (OM) because the Object Model already includes similar functionality.
Example
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
|
Formula |
Description |
Result |
|
=SHEETS() |
Because there is no Reference argument specified, the total number of sheets in the workbook is returned (3). |
3 |
|
=SHEETS(My3DRef) |
Returns the number of sheets in a 3D reference with the defined name My3DRef, which includes Sheet2 and Sheet3 (2). |
2 |
Top of Page
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
SHEET function in Excel returns a numeric value corresponding to the sheet number referenced by the link passed to the function as a parameter.
SHEET and SHEETS functions in Excel: description of arguments and syntax
SHEETS function in Excel returns a numeric value that corresponds to the number of sheets referenced.
Notes:
- Both functions are useful for use in documents containing a large number of sheets.
- A sheet in Excel is a table of all the cells that are displayed on the screen and are outside of it (a total of 1,048,576 rows and 16,384 columns). When sending a sheet to print, it can be divided into several pages. Therefore, the terms “sheet” and “page” should not be confused.
- The number of sheets in the book is limited only by the amount of PC RAM.
Function has only 1 argument in its syntax and is optional for: =SHEET(value).
- value is an optional function argument that contains text data with the name of the sheet or a link for which you want to set the sheet number. If this parameter is not specified, the function will return the number of the sheet in one of the cells of which it was written.
Notes:
- When the sheet works, all sheets that are visible, hidden and very hidden are taken into account. Exceptions are dialogs, macros, and diagrams.
- If the function argument is a text value that does not match the name of any of the sheets contained in the book, the error #NA will be returned.
- If an invalid value was passed as an argument to the function, the result of its calculation will be the error #REF!.
- Within the object model (the hierarchy of objects in VBA, in which Application is the main object and Workbook, WorkSheet, etc., are child objects), the SHEET function is not available because it contains a similar function.
The function has the following syntax: =SHEETS(reference).
- reference — an object of reference type for which you want to determine the number of sheets. This argument is optional. If this parameter is not specified, the function will return the number of sheets contained in the book where it was written.
Notes:
- This function counts the number of all hidden, very hidden and visible sheets, with the exception of charts, macros and dialogs.
- If an invalid reference was passed as a parameter, the result of the calculation is the error code #REF!.
- This function is not available in the object model due to the presence of a similar function there.
How to get sheet name by formula in Excel
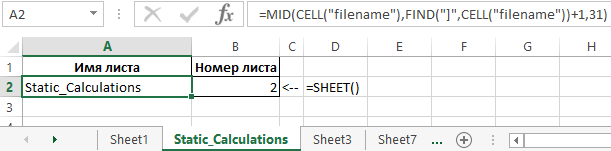
Example 1. In carrying out the calculated work the student used the Excel program, in which he created a book of several sheets. For his own convenience, the student decided to display in the cells A2 and B2 of each sheet data on the name of the sheet and its serial number, respectively. For this, he used the following formulas:
Description of arguments for the MID function:
- =CELL(«filename») is a function that returns text in which the MID function searches for a specified number of characters. In this case, the value “C:UserssoulpDesktop[Workbook.xlsx] Static_Calculations” will return, where after the “]” symbol is the required text — the name.
- =FIND(«]»,CELL(«filename»))+1 is a function that returns the position number of the character «]», one is added so that the MID function does not take into account the character].
- 31 — the maximum number of characters in the name.
=SHEET() — this function without parameter returns the number of the current sheet. As a result of its calculation, we get the number of sheets in the current book.
Examples of using the SHEET function and SHEETS
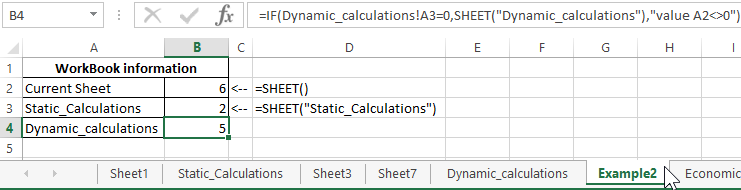
Example 2. The Excel workbook contains several sheets. It is necessary:
- Return the current sheet number.
- Return the sheet number with the name «Static_calculations».
- Return the number of the sheet «Dynamic_calculations», if its cell A3 contains the value 0.
Enter the data in the table:
Next, we write the formulas for all 4 conditions:
- For condition # 1, use the following formula: =SHEET()
- For condition # 2, enter the formula: =SHEET(«Static_calculations»)
- For condition number 3 we write the formula:
The IF function checks whether the value stored in the A3 cell of the Dynamic_ calculations is equal to zero or null.
As a result, we get:
Processing information about the sheets of the book on the formula Excel
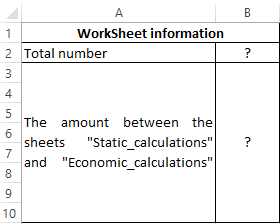
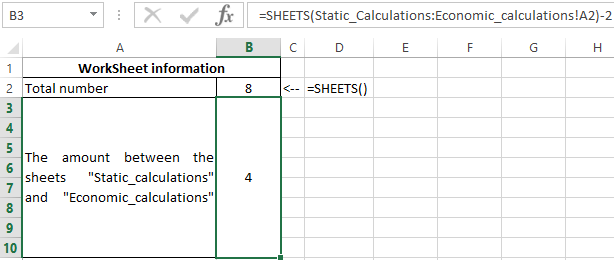
Example 3. To determine the contains several sheets. It is necessary to determine the total number of sheets, as well as the number contained between the “Static_calculations” and “Economic_calculations”.
The source table is:
The total number of sheets is calculated by the formula:
To determine the number contained between these two sheets, we write the formula:
- Static_calculations: Economic_calculations!A2 — A reference to cell A2 of the range of sheets between «Static_calculations» and «Economic_calculations» including these sheets.
- To get the desired value, 2 was subtracted.
As a result, we get the following:
Download examples SHEET and SHEETS functions in Excel formulas
The formula displays detailed information on the data on the sheets in a certain range of their location in the Excel workbook.
In this article, we will learn about how to use the SHEET function in Excel.
What is the SHEET function?
SHEET function in excel is a built-in reference function. This function returns a number, reference to the input sheet indicated. SHEET function can be used for the following purposes in Excel.
- The function returns the total number of sheets in the current worksheet.
- The function returns the sheet number of the reference sheet cell.
- The function returns the sheet number for the reference table in the worksheet.
What is the SHEET function?
SHEET function in excel returns SHEET number for the reference value.
Syntax of SHEET function:
= SHEET ( value )
value : value be given using cell reference
Example:
All of these might be confusing to understand. So, let’s test this formula via running it on the example shown below. Here we have some random data values to test the SHEET function in Excel.
Here we have some different uses of SHEET function and we need to get the Sheet number in number format .using the below formula
Use the formula:
=SHEET()
Or
=SHEET(table1)
Where table1 is name given to the table using the named range in Excel.
As you can see the formula returns error if the table name is not defined.
Here are some observational notes shown below.
Notes:
- The formula returns the sheet number of the input reference cell.
- If the sheet array is given as cell reference, the formula returns the first sheet number.
- Use the SHEETS function to count the number of sheet if the range of sheet is given as input.
Hope this article about How to use the SHEET function in Excel is explanatory. Find more articles on the SHEETS function here. If you liked our blogs, share it with your fristarts on Facebook. And also you can follow us on Twitter and Facebook. We would love to hear from you, do let us know how we can improve, complement or innovate our work and make it better for you. Write to us at T@exceltip.com.
Related Articles
How to use the CELL function in Excel : returns Information about a cell in a worksheet using the CELL function.
How to use the TYPE Function in Excel : returns numeric code representing the TYPE of data using TYPE function in Excel.
How to use the SHEETS function in Excel : returns a number, reference to input sheet indicated using the SHEETS function.
How to Use ISNUMBER Function in Excel : ISNUMBER function returns TRUE if number or FALSE if not in Excel.
Popular Articles:
50 Excel Shortcuts to Increase Your Productivity | Get faster at your task. These 50 shortcuts will make you work even faster on Excel.
The VLOOKUP Function in Excel | This is one of the most used and popular functions of excel that is used to lookup value from different ranges and sheets.
COUNTIF in Excel 2016 | Count values with conditions using this amazing function. You don’t need to filter your data to count specific values. Countif function is essential to prepare your dashboard.
How to Use SUMIF Function in Excel | This is another dashboard essential function. This helps you sum up values on specific conditions.
Функция ЛИСТ возвращает номер листа, на значения которого ссылается функция. Впервые функция была представлена в Excel 2013.
Описание функции ЛИСТ
Возвращает номер листа, на значения которого ссылается функция.
Синтаксис
=ЛИСТ(значение)Аргументы
значение
Необязательный аргумент. Значение — это название листа или ссылка, для которой необходимо установить номер листа. Если опустить значение, функция ЛИСТ вернет номер листа, который содержит функцию.
Замечания
- Функция ЛИСТ включает в себя все листы (видимые, скрытые или очень скрытые), кроме всех остальных типов листов (макросов, диаграмм или диалогов).
- Если аргумент значения не является действительным значением, функция ЛИСТ возвращает значение ошибки #ССЫЛКА!. Например, =ЛИСТ(Лист1!#ССЫЛКА) вернет значение ошибки #ССЫЛКА!.
- Если аргумент значения является названием недействительного листа, функция ЛИСТ вернет значение ошибки #НД. Например, =ЛИСТ(«badЛИСТName») вернет значение ошибки #НД.
- Функция ЛИСТ недоступна в объектной модели (OM), поскольку там уже содержится похожая функция.
Пример
Видео работы функции
Использование ЛИСТ и ЛИСТЫ (англ.)
The Excel SHEET function, new in Excel 2013, returns the sheet number of the referenced sheet based on its position in the file. It can return the sheet number of any worksheet including visible, hidden or very hidden as well as macro, chart and dialog sheets.
SHEET function syntax:
=SHEET(value)
Where value is the name of the sheet or reference you want the sheet number of. The value can include cell references, named ranges or Table names.
You can see it in action in the table below:
Tip: If you enter the SHEET function without a reference e.g. =SHEET() it will return the position of the current sheet.
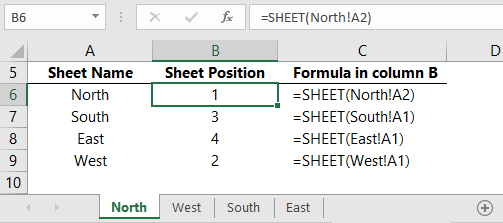
Use SHEET Function to Return a Sheet Index
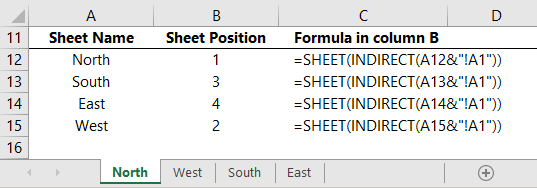
Let’s say you have a list of your sheet names in column A and you want to find their position in the workbook. We can use the INDIRECT function to populate the ‘value’ argument by returning the sheet name from column A and appending it to cell reference A1, as shown below:
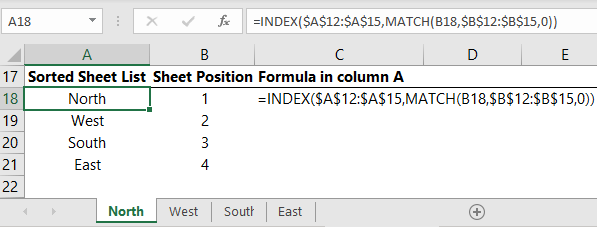
Sort Sheet Index with INDEX & MATCH Functions
We can then use INDEX & MATCH to return a sorted list of the sheets listed in cells A12:A15 based on their sheet position in cells B12:B15:
If any changes are made to the sheet order, the table above will automatically update.
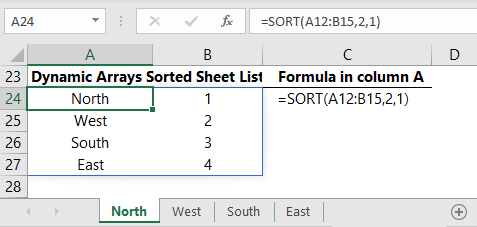
Sort Sheet Index with SORT Function
Or if you have Office 365 and the new Dynamic Array formulas you can use the SORT function:
Download the Excel Example File
Enter your email address below to download the sample workbook.
By submitting your email address you agree that we can email you our Excel newsletter.
Excel Sheet Function Related Lessons
Automatically generate a list of sheet names