Had better (I’d better/you’d better etc.)
I’d better do something = It is advisable to do it. If I don’t, there will be a problem or a danger:
* I have to meet Ann in ten minutes. I’d better go now or I’ll be late.
* ‘Shall I take an umbrella?’ ‘Yes, you’d better. It might rain.’
* We’d better stop for petrol soon. The tank is almost empty.
The negative is I’d better not (= I had better not):
* A: Are you going out tonight?
B: I’d better not. I’ve got a lot of work to do.
* You don’t look very well. You’d better not go to work today.
You can use had better when you warn somebody that they must do something:
* You’d better be on time./You’d better not be late. (or I’ll be very angry)
The form is ‘had better’ (usually ‘I’d better/you’d better’ etc. in spoken English):
* I’d better phone Carol, hadn’t I?
Had is a past form, but in this expression the meaning is present or future, not past: * I’d better go to the bank now/tomorrow.
We say ‘I’d better do…’ (not ‘to do’):
* It might rain. We’d better take an umbrella. (not ‘we’d better to take’)
Had better and should
Had better is similar to should but not exactly the same.
We use had better only for a particular situation (not for things in general).
You can use should in all types of situation to give an opinion or to give advice:
* It’s cold today. You’d better wear a coat when you go out. (a particular situation)
* I think all drivers should wear seat belts. (in general — not ‘had better wear’)
Also, with had better, there is always a danger or a problem if you don’t follow the advice.
Should only means ‘it is a good thing to do’. Compare.
* It’s a great film. You should go and see it. (but no danger, no problem if you don’t)
* The film starts at 8.30. You’d better go now or you’ll be late.
It’s time …
You can say ‘It’s time (for somebody) to do something’:
* It’s time to go home./It’s time for us to go home.
You can also say:
* It’s late. It’s time we went home.
Here we use the past (went) but the meaning is present or future, not past:
* It’s 10 o’clock and he’s still in bed. It’s time he got up. (not ‘It’s time he gets up’)
It’s time you did something = ‘you should have done it already or started it’. We often use this structure to criticise or to complain:
* It’s time the children were in bed. It’s long after their bedtime.
* The windows are very dirty. I think it’s time we cleaned them.
You can also say: It’s about time…/It’s high time… . This makes the criticism stronger:
* Jack is a great talker. But it’s about time he did something instead of )’just talking.
* You’re very selfish. It’s high time you realised that you’re not the most important person in the world.
EXERCISES
35.1 Complete the sentences. Sometimes you need only one word, sometimes two.
1. a I need some money. I’d better _go_ to the bank.
b John is expecting you to phone him. You — better do it now.
c ‘Shall I leave the window open?’ ‘No, you’d better — it.’
d We’d better leave as soon as possible, — we?
2. a It’s time the government — something about the problem.
b It’s time something — about the problem.
c I think it’s about time you — about me instead of only thinking about yourself.
35.2 Read the situations and write sentences with had better. Use the words in brackets.
1. You’re going out for a walk with Tom. It might rain. You say to Tom:
(an umbrella) We’d better take an umbrella.
2. Jack has just cut himself. It’s quite a bad cut. You say to him:
(a plaster) —
3. You and Ann plan to go to a restaurant this evening. It’s a very popular restaurant. You say to Ann: (reserve) We —
4. Jill doesn’t look very well — not well enough to go to work. You say to her:
(work) —
5. You received your phone bill four weeks ago but you haven’t paid it yet. If you don’t pay very soon, you could be in trouble. You say to yourself: (pay) —
6. You want to go out but you’re expecting an important phone call. You say to your friend: (go out) I —
7. You and Fiona are going to the theatre. You’ve missed the bus and you don’t want to be late.
You say to Fiona: (a taxi) —
35.3 Put in had better or should. Sometimes either is possible.
1. I have an appointment in ten minutes. _I’d better_ go now or I’ll be late.
2. It’s a great film. You _should_ go and see it. You’ll really like it.
3. I — get up early tomorrow. I’ve got a lot to do.
4. When people are driving, they — keep their eyes on the road.
5. Thank you for coming to see us. You — come more often.
6. She’ll be upset if we don’t invite her to the wedding, so we — invite her.
7. These biscuits are delicious. You — try one.
8. I think everybody — learn a foreign language.
35.4 Read the situations and write sentences with It’s time (somebody did something).
1. You think the children should be in bed. It’s already 11 o’clock.
_It’s time the children were in bed._
2. You haven’t had a holiday for a very long time. You need one now.
It’s time I —
3. You’re waiting for Mary. She is late. Why isn’t she here yet?
It’s time she —
4. You’re sitting on a train waiting for it to leave the station. It’s already five minutes late.
5. You enjoy having parties. You haven’t had one for a long time.
6. The company you work for is badly run. You think there should be some changes.
35.1
1 b. had or ‘d
c. close or shut
d. hadn’t
2 a. did
b. was done
c. thought
35.2
2 You’d better put a plaster on it.
3 We’d better reserve a table./We’d better phone to reserve …
4 You’d better not go to work.
5 I’d better pay the phone bill. or … pay my phone bill.
6 I’d better not go out.
7 We’d better take a taxi. or … get a taxi
35. 3
3 had better/’d better or should
4 should
5 should
6 had better/’d better
7 should
8 should
35.4
2 had a holiday.
3 was here.
4 It’s time the train left.
5 It’s time I had a party.
6 It’s time some changes were made./It’s time there were some changes.
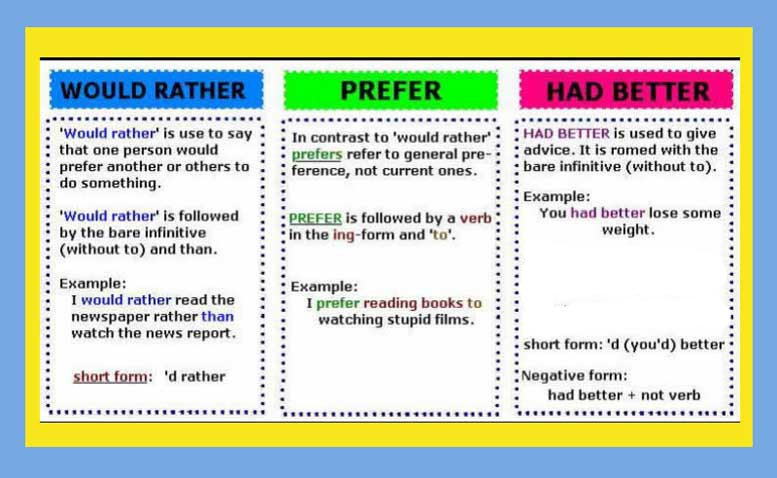
Иногда употребление выражений had better и would rather, а также глагола prefer вызывает затруднения, поэтому давайте разбираться. Если коротко, то разница заключается в следующем:
Мы используем выражение had better, когда выражаем свое мнение о том, что другой человек должен сделать, как другой должен поступить. Такие предложения иногда похожи на совет.
You had better go and look with a candle. – Лучше иди и поищи со свечкой.
You had better apply to Lambert! – Лучше тебе обратиться к Ламберту.
Также зачастую в предложении говорится о том, что может случится, если человек поступит не так, как вы говорите:
She’d better get here soon or she’ll miss the opening ceremony. — Ей лучше поторопиться, иначе она опоздает на церемонию открытия.
Had better также можно использовать применимо к себе в выражениях ‘уж лучше бы мне’ или ‘уж лучше бы нам’:
I thought I had better come myself. – Я подумал, лучше мне прийти самому.
I think we had better change the subject before you get yourself overexcited. – Думаю, лучше сменить тему, пока вы не перенервничали.
Обратите внимание: мы используем had better, чтобы говорить о настоящем и будущем без изменения формы.
It’s six o’clock. I’d better go now. – Уже шесть часов, лучше я уйду сейчас. (Настоящее время)
You had better not be here tomorrow. – Уж лучше вам убраться отсюда до завтра! (Будущее)
Для образования отрицания с had better необходимо добавить not после данного выражения:
I’d better not leave my bag there. – Лучше не оставлять здесь рюкзак.
Для образования вопросительного предложения Had выносится перед подлежащим.
Had I better speak to Jillian first? – Быть может, лучше я сначала поговорю с Джиллиан?
Синонимом фразы had better являются модальные глаголы should и ought to.
Иногда в разговорной речи вместо had better можно услышать had best:
You’d best come on Monday. There’s no one in the office now. – Лучше Вам прийти в понедельник. Сейчас в офисе никого нет.
Употребление фразы WOULD RATHER.
Мы будем употреблять would rather для выражения предпочтения:
I’d rather have tea than coffee – Я бы лучше выпил чаю, нежели кофе.
I would rather leave. – Я бы предпочла уйти.
Вместо would rather можно употреблять would sooner (would rather=would sooner)
I would sooner come with you. I feel I must come with you. – Я бы предпочла пойти с Вами. Я чувствую, что должна пойти с Вами.
Would rather чаще употребляется после I и WE. (Мы говорим о своих предпочтениях same subject)
Если при помощи would rather вы хотите выразить предпочтение, которое касается другого человека (different subject) , то нужно использовать следующие паттерны:
Would rather + person + past tense (для настоящего или будущего)
She would rather you didn’t tell anyone about our plans. – Она бы хотела, чтобы ты никому не говорила о наших планах.
Would rather + person + past perfect (для прошлого)
I would rather you hadn’t spent so much money last month – Как жаль, что ты истратил так много денег в прошлом месяце. (Я бы предпочла, чтобы ты их не тратил)
Употребление глагола PREFER
Глагол prefer синонимичен выражению would rather, однако следует запомнить, как употреблять его правильно.
Prefer smth. to smth.
I prefer tea to coffee.
Prefer doing something to doing something
I prefer drinking tea to drinking coffee.
Prefer to do rather than (do)
I prefer to drink tea rather than (drink) coffee
Закрепите правило еще раз и начнем выполнять упражнения.
Упражнения на had better // would rather // prefer
Упражнение 1. Complete the following sentences using HAD BETTER/´D BETTER and HAD BETTER NOT and an appropriate expression from the following list.
take a sandwich, do that again, ask his friends if they know where he is, go to the doctor, book a table, leave now.
- I have to be at school in ten minutes. __________
- You don’t look very well. You ________________
- I’m worried. Tom should have been here by now. I____________________________
- The restaurant is usually crowded. We________________________
- I won’t have time to go out for lunch. I ____________________________
- I was very angry with you. You ______________________
Упражнение 2. Дополните диалоги, используя WOULD RATHER (´d rather) or WOULD RATHER NOT (‘d rather not) и следующие фразы.
have some hot chocolate, go to Italy, watch a film on TV, go by train, go to school today, say
Frank: Let’s go to London by car.
Dan: _______________________________________ (1)
Mikel: Do you prefer to go to Italy or France this summer?
Rachel: _______________________________________ (2)
Ron: What did Alice tell you?
Gil: _______________________________________ (3)
Liz: Do you feel like going to the movies this evening?
Rina: No, ____________________________________ (4)
Nora: What’s the matter?
Sheila: I don’t feel very well. _________________________ (5)
Vera: Would you like some coffee?
Simon: ________________________________________ (6)
Упражнение 3. Перепишите следующие предложения, используя had better или would rather
- I don’t want to play chess. Let’s play poker.
- It isn’t a good idea to invite him.
- I don’t want to go to a restaurant. I want to eat at home.
- Your nails are too long. You should trim them.
- If I were in your shoes, I would paint that wall yellow.
Упражнение 4. Choose the correct answer.
1.You ………………………………… so much yesterday.
a) would rather I didn’t drink b) had better haven’t drunk
c) would rather drunk d) had better not drink
2. ‘Are the children sleepy?’ ‘Yes, they ………………………………………… to bed.
a) would rather went b) have rather go
c) had better go d) would rather have gone
3. You’d better …………………………………. talk to that man.
a) not to talk b) don’t talk
c) not talk d) didn’t talk
4. She’d rather ……………………………… than go to university.
a) work b) worked
c) to work d) have worked
5. I’d rather you ………………………… than went to university.
a) work b) to work
c) worked d) working
I’d rather you ………………………………… alone. It was a mistake.
a) lived b) live
c) have lived d) had lived
Ответы к упражнениям.
Exercise 1.
- I’d better leave now.
- You had better go to the doctor.
- I had better ask his friends if they know where he is.
- We had better book a table in advance.
- Had better take a sandwich.
- You had better not do that again.
Exercise 2.
- I would rather go by train.
- I would rather go to Italy.
- I would rather not say.
- I would rather watch a film on TV.
- I would rather not go to school today.
- I would rather have some hot chocolate.
Exercise 3.
- I would rather play poker.
- We had better not invite them
- I would rather eat at home.
- You had better trim your nails.
- You had better paint that wall yellow.
Exercise 4. 1 d, 2 c, 3 c, 4 a, 5 c, 6 d
Понравилось? Сохраните на будущее и поделитесь с друзьями!
ENGLISH GRAMMAR IN USE FOR INTERMEDIATE
35. Had better
It’s time …….
|
A |
Had better (I’d I’d better do something= it is · · · The negative is I’d better not(= I had · · Remember that: The form is ‘had better’ (usually · Had is normally · We say ‘I’d better do’ (not · |
|
B |
Had better and should Had better is similar to should, · · Also, with had better, there · · |
|
C |
It’s time … You can say It’s time (for · But you can also say: · When we use it’s time+ past · It’s time somebody did · · You can also say It’s about time · |
EXERCISES
|
35.1 |
Read the situations
|
||||||||||||||||
|
35.2 |
Put in had better where suitable. If had better is not suitable, use should.
|
||||||||||||||||
|
35.3 |
Complete the
|
||||||||||||||||
|
35.4 |
Read the
|
ANSWER
KEY
35.1
2 You’d better put a plaster on it.
3 We’d better reserve a table.
4 You’d better not go to work (this morning).
5 I’d better pay my phone bill (soon). /I’d
better pay it (soon).
6 I’d better not disturb him.
35.2
3 ‘d better
4 should
5 should
6 ‘d better
7 should
8 should
35.3
1 b ‘d/had
c close/shut
d hadn’t
2 a did
b was done
c thought
35.4
2 it’s time I had a holiday.
3 it’s time the train left.
4 it’s time 1/we had a party.
5 it’s time some changes were made. /it’s
time the company made some changes.
6 it’s time he tried something else.
В английском языке есть две похожие конструкции: had better и would rather. Они близки по значению, но у каждой из них свои особенности употребления. Сегодня разберем, в чем же между had better / would rather разница и посмотрим на примеры.
Had better
Значение конструкции had better — выразить строгий совет. Она используется, чтобы сказать, что нужно сделать, дать рекомендацию. На русский словосочетание часто переводится как «лучше сделать… / стоит…». Had better выражает мнение о том, что если не совершить действие, произойдут негативные последствия.
I had better talk to Mary right now — Мне лучше поговорить с Мэри прямо сейчас.
You had better stop arguing before your boss gets really angry — Хватит спорить, пока твой начальник не рассердился всерьез.
После конструкции had better употребляется глагол в форме инфинитива без частицы to. Часто используется сокращенная форма — ’d better, особенно в разговорной речи.
You’d better hurry up — Тебе лучше поторопиться.
По форме глагола had можно подумать, что он стоит в прошедшем времени. Но у словосочетаний типа you had better грамматика заключается в другом. Это специальная форма — сослагательное наклонение в английском. Глагол здесь выражает не прошедшее время, а нереальность ситуации. Поставить had в данном случае в другие формы (например, have или has) — невозможно.
Несмотря на то, что в этой конструкции есть слово better (лучше), в значении не подразумевается сравнение с какой-либо другой ситуацией. Had better означает определенный совет, рекомендацию к действию.
You had better ask for help, the work should be done by next Tuesday — Тебе лучше попросить помощи, работа должна быть готова к следующему четвергу.
Форма had better не меняется при различных подлежащих: существительное может стоять в любом числе и в любом лице. Здесь не действует правило, при котором глаголы с местоимениями he / she / it получают окончание -s:
He had better listen to what I’m saying — Он лучше бы послушал, что я говорю.
Чтобы построить вопросительное предложение, не нужно добавлять во фразу вспомогательный глагол. Достаточно перенести had на первое место:
Had I better talk to Mary right now? — Мне лучше поговорить с Мэри прямо сейчас?
Отрицание в грамматике you had better выражается непривычным для английского образом. Обычно негативная частица not добавляется непосредственно к вспомогательному глаголу. Здесь же частица ставится после слова better — had better not.
You had better not take the responsibility — Ты бы лучше не брал на себя ответственность.
Хотя построить отрицательное предложение через форму hadn’t возможно, но такая фраза менее употребляема:
Hadn’t we better tell him the truth? — Не лучше ли сказать ему правду?
Had better может выступать отдельным предложением в качестве ответа на вопрос или в качестве ответного мнения:
Shall I wake you up when I return? — You’d better not. Разбудить тебя, когда я вернусь? — Лучше не стоит.
He promised he would pay the debt next week. — He’d better! Он обещал, что отдаст долг на следующей неделе. — И ему лучше так и сделать!
Как видно из предыдущих примеров, на русский эта конструкция может переводиться разными способами. Главное, предложение должно выражать идею совета, необходимости выполнить определенное действие.
Had better выражает строгую форму совета (и в этом заключается одно из различий would rather / had better). Когда конструкция употребляется по отношению к собеседнику, она, скорее, обозначает строгое наставление или приказ, чем просьбу. В вежливых просьбах используется не had better, а could:
Could you give me that letter from the shelf? — Можешь дать мне то письмо с полки? (Вежливая просьба).
You’d better give me that letter. Anyway, I’ll know what’s going on — Лучше тебе дать мне то письмо. В любом случае, я узнаю, что происходит. (Приказ / угроза).
Had better наиболее близко по значению к модальному глаголу should («следует»):
I had better talk to Mary right now — Мне лучше поговорить с Мэри прямо сейчас.
I should talk to Mary right now — Мне стоит поговорить с Мэри прямо сейчас.
Хотя между ними существует определенное различие. Словосочетание had better относится к непосредственному будущему, выражает определенное и более срочное действие. Тогда как should может использоваться и для самых общих ситуаций:
You should be persistent if you want to be successful — Нужно быть настойчивым, если хочешь быть успешным.
You’d better be persistent if you want to get this job — Тебе лучше проявить настойчивость, если хочешь получить эту работу.
You should go by train — Тебе нужно ехать поездом.
You’d better go by train, it’s more comfortable — Лучше тебе поехать поездом, так удобнее.
Другое отличие had better и should: первый случай подразумевает некоторую опасность или негативный исход событий, если пожелание не будет выполнено. Тогда как should такого значения не несет:
You should ask Mr Brown, he can give you good advice — Тебе стоит спросить мистера Брауна, он может дать хороший совет (но не случится ничего страшного, если не спросишь).
You had better ask Mr Brown, he is the only one who can solve this problem — Тебе лучше спросить мистера Брауна, он единственный, кто знает, как решить эту проблему (если не сделать этого, проблема не будет решена).
Would rather
Конструкция would rather имеет другое значение, она синонимична фразе would prefer to (предпочесть что-то сделать).
I would rather stay home today — Я лучше останусь сегодня дома.
После конструкции would rather также следует инфинитив глагола без частицы to. Как и had better, грамматика would rather не позволяет изменять форму по временам, она не зависит от лица и числа подлежащего, не присоединяет показатель -s:
- I would rather go now — Я, пожалуй, уйду сейчас.
- He would rather go now — Он бы предпочел уйти сейчас.
- They would rather go now — Они бы лучше ушли сейчас.
Сокращенная форма выглядит как ’d rather:
I’d rather stay here = I would rather stay here — Я лучше останусь здесь.
В значении конструкции would rather присутствует предпочтение определенного события, выбор одного, а не другого действия. Предпочтение может только подразумеваться, а может быть явно выражено в предложении:
I would rather stay home today instead of going to that party — Я лучше останусь сегодня дома вместо того, чтобы идти на ту вечеринку.
Часто would rather используется в противопоставлении другому действию:
How about going to the cinema this evening? — I would rather stay home. Как насчет похода в кино сегодня вечером? — Я бы предпочел остаться дом.
Словосочетание would rather не нужно путать с would like to. Они имеют разные значения: первое отражает предпочтение одного из вариантов, второе — вежливая форма глагола want (хотеть). Кроме того, отличается и грамматика would rather: за ним следует ставить глагол без частицы to, а после would like — c частицей:
Would you like to have a cup of tea? — I would rather have a coffee. Вы хотели бы выпить чашку чая? — Я бы лучше выпил кофе.
Помимо инфинитива без частицы to после would rather может стоять и целое предложение. В таком случае появляется другой участник действия — подлежащее придаточного предложения: например, I’d rather you… Так можно выразить не только чье-то мнение (I would rather talk to you – Я лучше поговорю с тобой), но и пожелание к другому лицу. Глагол в придаточном предложении ставится в прошедшее время:
I’d rather you talked to Mr Phillips — Я бы предпочел, чтобы ты поговорил с мистером Филлипсом.
Несмотря на то, что глагол придаточного предложения стоит в прошедшем времени, фраза относится к пожеланию на будущее:
My father would rather we didn’t talk about it anymore — Мой отец хотел бы, чтобы мы больше не говорили об этом (действие в придаточном предложении относится к будущему).
Чтобы сказать о прошедшем действии, глагол в придаточном предложении необходимо поставить в форму Past Perfect (had + глагол в третьей форме):
My father would rather we hadn’t talked about it yesterday — Мой отец хотел бы, чтобы мы не стали вчера это обсуждать (действие в придаточном относится к плану прошлого).
Хотя в таком значении более типично использовать глагол wish вместо would rather:
My father wishes we hadn’t talked about it at all — Мой отец хотел бы, чтобы мы вообще об этом не стали говорить.
Сравнение had better и would rather
Часто конструкции had better и would rather путают в их сокращенных формах. Глаголы had и would оба сокращаются до формы ’d:
I’d rather stay here = I would rather stay here — Я лучше останусь здесь (Я предпочитаю остаться здесь).
I’d better stay here = I had better stay here — Лучше мне остаться здесь (Будет правильно, если я останусь здесь).
Хотя оба варианта часто переводятся как «лучше…», они несут в себе разные значения. Различие would rather / had better в том, что в первом случае подразумевается сравнение с каким-то другим действием, тогда как во втором случае — нет.
I don’t want to spend all evening standing here, I would rather dance — Я не хочу простоять здесь весь вечер, я лучше потанцую.
You had better accept this proposal, it’s can be the last — Тебе стоит принять это предложение, оно может быть последним.
Упражнения на had better // would rather // prefer
Упражнение 1. Complete the following sentences using HAD BETTER/´D BETTER and
HAD BETTER NOT and an appropriate expression from the following list.
take a sandwich, do that again,
ask his friends if they know where he is, go to the doctor,
book a table, leave now.
I have to be at school in ten minutes. __________
You don’t look very well. You
________________
I’m worried. Tom should have been here by now. I____________________________
The restaurant is usually crowded. We________________________
I won’t have time to go out for lunch. I ____________________________
I was very angry with you. You
______________________
Упражнение 2. Дополните
диалоги, используя WOULD RATHER (´d rather) or WOULD RATHER NOT (‘d rather not)
и следующие фразы.
have some hot chocolate, go to Italy, watch a film on TV, go by
train, go to school today, say
Frank: Let’s go to London by car.
Dan: _______________________________________ (1)
Mikel: Do you prefer to go to Italy or France this summer?
Rachel: _______________________________________ (2)
Ron: What did Alice tell you?
Gil:
_______________________________________ (3)
Liz: Do you feel
like going to the movies this evening?
Rina: No, ____________________________________
(4)
Nora: What’s the matter?
Sheila: I don’t feel very well.
_________________________ (5)
Vera: Would you like some coffee?
Simon: ________________________________________ (6)
Упражнение 3. Перепишите следующие предложения, используя had better или would
rather
I don’t want to play chess. Let’s play
poker.
It isn’t a good idea to invite him.
I don’t want to go to a restaurant. I want to eat at home.
Your nails are too long. You should
trim them.
If I were in your shoes, I would paint that wall yellow.
Упражнение 4. Choose
the correct answer.
1.You ………………………………… so much yesterday.
a) would rather I didn’t drink b) had
better haven’t drunk
c) would rather drunk d)
had better not drink
2. ‘Are the children sleepy?’ ‘Yes, they ………………………………………… to
bed.
a) would rather went b) have rather go
c) had better go d) would rather have gone
3. You’d better …………………………………. talk to that man.
a) not to talk b) don’t talk
c) not talk d) didn’t
talk
4. She’d rather ……………………………… than go to university.
a) work b) worked
c) to work d) have worked
5. I’d rather you ………………………… than went to university.
a) work b) to work
c) worked d) working
I’d rather you ………………………………… alone. It was a mistake.
a) lived b) live
c) have lived d) had
lived
Ответы к упражнениям.
Exercise 1.
I’d better leave now.
You had better go to the doctor.
I had better ask his friends if they know where he is.
We had better book a table in advance.
Had better take a sandwich.
You had better not do that again.
Exercise 2.
I would rather go by train.
I would rather go to Italy.
I would rather not say.
I would rather watch a film on TV.
I would rather not go to school today.
I would rather have some hot chocolate.
Exercise 3.
I would rather play poker.
We had better not invite them
I would rather eat at home.
You had better trim your nails.
You had better paint that wall yellow.
Exercise 4. 1 d, 2 c, 3 c, 4 a, 5 c, 6
— Hello, guys! My name is James Wilson. This is my best friend Martin
Green.
— Welcome to our grammar lesson.
— Listen to the conversation between John and Dan and find out the theme
of our lesson today.
— John is at home, because he doesn’t feel well.
— Dan is in London at this moment.
— Hi, Dan! How is London?
— Hi, John! It’s so wonderful here! I’ve already visited many interesting
and amazing places!
— Oh, Dan! I’m so happy for you! When did you come to London?
— I came on Sunday and the airport was so overcrowded! I couldn’t even
take a taxi, so I went on foot to my hotel with all the bags.
— Really? It’s so awful! You had better not go to London at the weekends.
— Yes, you’re right! However, I would rather go to places, which are full
of people. It makes me feel safe.
— Oh, this is a strong reason! Especially if you are going somewhere
alone. Nevertheless, if I were you, I would rather go on Monday.
— Well, it’s your choice! What about you? Why didn’t you come with me? You
told me that you’ll explain me everything later!
— Yes. I’m so sorry. I just had a temperature and was so weak, so I
couldn’t talk at all.
— Oh, I see. How do you feel now?
— I have a sore throat and runny nose.
— You had better stay in bed and drink tea with lemon.
— I would rather take some medicine, because I feel so awful!
— Maybe, you’re right! John, I have to go now.
Get well and talk to you later!
— OK, thanks, Dan! Bye.
— Bye. John.
Now I think you understand
that in the lesson today we will:
·
talk about the word
combinations “would rather” and “had better”;
·
learn how to use them.
First of all, we will look closely at the word combination had
better.
Do you know when we can use
it?
Let me help you!
We use “had better”
when we talk about present or future. The meaning of this word combination is similar to the meaning of modal verb “should”.
Now we will find the answers
to the following questions: “What do “had better” and “should”
have in common?” and “What is the difference between them?”
1. What do had better
and should have in common?
We use both
of them, when we want to give somebody some piece of advice.
2. What is the difference between had better and should?
Modal verb “should” is used to give general advice and it’s not connected to a
particular situation. We can use “should”, when we want to share our
opinion with somebody about what needs to be done. If our opinion is not taken into account, nothing serious will happen.
Look at the example:
Dialogue 1
— Hey, Peter! How are you?
— Hi, Dan! I’m fine, thank you. And you?
— I’m fantastic, thanks. Do you know that
Alex will have a party next weekend?
— No, I don’t. That’s great! Let’s go
together!
— Peter, I think you shouldn’t go. Mark will
also be there. I know that you don’t really like him.
— Oh, please! I don’t have to talk to him!
We should go!
— Okay. I think it will be fun!
From this dialogue
we can see that nothing serious will happen if Peter goes to the party. He
might meet the person he can’t stand. However, if he does, there won’t be any
terrible consequences.
Word combination “had
better”, on the contrary, is used in certain situation. It’s a very strong
expression. When the speaker uses this construction, he’s hinting at the fact
that if you don’t follow the advice, something bad and awful can happen. For
instance, someone will get hurt or get sick.
Let’s look at the example:
Dialogue 2 Mike
and his dad are talking on the phone.
— Hi, daddy!
— Hi, Mike. Is something wrong?
— Yes. Could you, please, pick me up from
school right now? I have a high temperature.
— Oh, I knew this was going to happen. You
ate too much ice-cream yesterday! I’ll be there in 20 minutes.
— You had better go to your school nurse.
She will give you some pills or your temperature will go up.
— Okay, dad!
From this dialogue
we can see that if Mike doesn’t go to his school nurse, his temperature will go
up. This can lead to serious health problems.
— Now, do you know how we can form the
sentences, using this construction?
— Let’s find out!
Positive sentences:
1. Despite
the fact that we use “had better”, when we talk about present or future,
the verb form is “HAD,” not “HAVE”.
For example:
She had better take an
umbrella with her on Tuesday, because the forecast calls for rain.
2. If we talk in an informal
atmosphere, we usually use short form. It means that instead of “I HAD BETTER”
we use “I’D BETTER”.
For example:
We’d better go before she gets
furious.
3. After this construction, we
use infinitive without particle “to”.
For example:
You had better get some sleep,
because it will be very difficult for you to stay awake all night at work.
We don’t need particle to.
Negative sentences:
To form negative sentences, we
need to add adverb not after the construction “had better”.
REMEMBER! We don’t need
particle to before the verb.
For instance:
— Andy, you had better not
tell your parents about this awful situation!
— I know. They will
be mad at me.
Interrogative sentences:
To form this type of sentences
we need to put had in first place, subject in second, better in third,
infinitive (without particle to) in fourth. Than we
put the rest of the words.
For instance:
— Bobby, it seems to me that the earthquake is about to start.
— Had we better leave the town?
— I don’t think so!
From the example we can see
that in first place we used had, in second – subject “we”, in third – better,
in fourth – infinitive “to leave” without to.
Now we will talk about the
other construction “would rather”.
Do you know when we can use
it?
We can use the word
combination “would rather”, when we talk about present or future.
The meaning of this
construction is similar to the meaning of the verb “prefer”.
Let’s talk about the
similarity and difference between would rather and prefer!
One
What is the similarity between
“would rather” and “prefer”?
We use both
of them when we want to tell somebody what we want, discuss our
preferences. The construction “would rather” is also used to show that
we want somebody to do something.
Two
What is the difference?
The only difference between “prefer”
and “would rather” is that we use the first one in general situations
and the second in particular situations.
Let’s compare two examples!
I prefer to wear colorful
clothes rather than black clothes.
In this sentence we are
talking about general situation.
Next:
— Mike, what would you like to wear today?
— I would rather wear something colorful. It’s a very important day for
me!
Here we are talking about particular case. It’s a special day for Mike that’s why he
wants to wear colorful clothes.
Look at the following two
examples!
I prefer going to the cinema
to watching movies on TV or on the Internet.
This sentence describes the
general situation.
Next example:
— Steve, let’s watch the movie “Mission: Impossible – Fallout” on the Internet.
It’s of bad quality, but it doesn’t matter!
— Oh, no, Tony! I would rather go to the cinema and watch this movie in
HD.
This sentence describes the particular situation. Tony and Steve want to watch the
movie. Steve wants to watch it in the cinema, but not on the Internet.
Now we will talk about how to
form the sentences, using this construction.
Positive sentences:
1. We use “would rather”
instead of “will rather” and so on in spite of the fact that
this construction is used to talk about present or future.
For example:
I would rather call her and
try to find the truth myself.
2. If we want to use the short
variant of “I would rather”, we can say “I’d rather”.
For example:
She’d rather do her homework
now, because the girl has some plans for the evening.
3. After this construction, we
also use infinitive without particle “to”.
For example:
He would rather take a car to
drive his friend home.
We don’t need particle to.
Negative sentences:
When we form these sentences,
we put adverb not after would rather.
Look at the example:
— Kyle, I would rather not go to my sister’s dinner party! Let’s go home.
— As you wish, Brad!
Interrogative sentences:
When we form this type of
sentences, we put would in first place, subject in second, rather in third,
infinitive (without particle to) in fourth. Than we
use the rest of the words.
Look at the example:
— Charles, I know that you broke up with Kate, but you’d better go to the
party with me.
— No, Brian! I don’t want to go anywhere!
— Would you rather stay at home and do nothing? Kate will be at this
party!
— Really? Give me a second, please. I’ll get dressed.
From this example we see that
in first place we put would, in second – subject “you”, in third – rather, in
fourth – infinitive “to stay” without particle to.
Now I want to know whether you
understood the rule or not.
Complete the sentences. Use
the constructions from the box.
Let’s check the right answers.
1. Our boss would rather we
didn’t come to work at 9:30, because our working day starts at 9 o’clock.
2. Had we better invite him
for the dinner? His behavior is so awful!
3. I would rather stay thirsty
than have to drink this tasteless coffee. There is no
sugar in it.
4. Billy had better not call
Regina right now. She is teaching her pupils at this time.
5. Rachel had better eat more
fruits and vegetables. I think that she often gets sick, because her body needs
some vitamins.
The following sentences.
Let’s check.
6. Would your parents rather
spend their money on the trip to the USA or on buying a new car?
7. Peter would rather not see
his classmates, because he doesn’t like them at all. They played jokes on him
and bullied him all the time.
8. Wendy had better go to
Paris by bus or by car, because she gets airsick every time she goes by plane.
9. Kevin had better not eat
pizza all the time. It’s really bad for his health.
10. My sister would rather not
go to the doctor unless the case is very serious. She treats herself at home.
— Pupils often confuse these two constructions. We think that after our
lesson, you won’t have such problems.
— That’s all for today! We hope you liked the video. See you soon.
Complete the sentences with had better or would rather.
1) Which … you … do, go to the cinema or stay at home? 2) I think you … look the word up again: you don’t remember what it means. 3) If I had a choice, I … not say what I think. 4) Where … you … go − to Omsk or to Tomsk? 5) We … finish the work today as tomorrow evening we are leaving for Irkutsk. 6) My sister … eat porridge and fruit than meat and potatoes. I know her taste. 7) I think I … hurry up. The train leaves in ten minutes. 8) …n’t he … stay with us until he gets well? 9) You … put your warm coat on. It’s freezing outside. 10) We … not be late. Our parents will be worrying. 11) I … have five English lessons than one physics lesson. 12) She … change her job − it is too dangerous.
reshalka.com
ГДЗ Английский язык 10 класс Афанасьева. UNIT 1. Step 3. Номер №10
Решение
Перевод задания
Допишите предложения, используя лучше бы или предпочли бы.
1) Что бы Вы … : пойти в кино или остаться дома? 2) Я думаю, тебе … поискать это слово снова: ты не помнишь, что оно означает. 3) Если бы у меня был выбор, я … не говорить то, что думаю. 4) Куда … Вы … поехать: в Киев или Одессу? 5) Нам … закончить работу сейчас, потому что завтра вечером мы уезжаем в Иркутск. 6) Моя сестра … есть кашу и фрукты, а не мясо и картошку. Я знаю, что она любит. 7) Думаю, мне … поторопиться. Поезд отправляется через 10 минут. 8) Не … ли ему остаться с нами, пока он не почувствует себя лучше? 9) Тебе … надеть свое теплое пальто. На улице холодно. 10) Нам … не опаздывать. Наши родители будут волноваться. 11) Я … пять уроков английского, чем один урок физики. 12) Ей … найти новую работу – эта слишком опасная.
ОТВЕТ
1) Which would you rather do, go to the cinema or stay at home? 2) I think you had better look the word up again: you don’t remember what it means. 3) If I had a choice, I would rather not say what I think. 4) Where would you rather go − to Omsk or to Tomsk? 5) We had better finish the work today as tomorrow evening we are leaving for Irkutsk. 6) My sister would rather eat porridge and fruit than meat and potatoes. I know her taste. 7) I think I had better hurry up. The train leaves in ten minutes. 8) Hadn’t he better stay with us until he gets well? 9) You had better put your warm coat on. It’s freezing outside. 10) We had better not be late. Our parents will be worrying. 11) I would rather have five English lessons than one physics lesson. 12) She had better change her job − it is too dangerous.
Перевод ответа
1) Что бы вы предпочли: пойти в кино или остаться дома? 2) Думаю, вам лучше еще раз посмотреть это слово: вы не помните, что оно означает. 3) Если бы у меня был выбор, я бы предпочел не говорить то, что думаю. 4) Куда бы вы поехали − в Омск или в Томск? 5) Лучше закончить работу сегодня, так как завтра вечером мы уезжаем в Иркутск. 6) Моя сестра предпочла бы есть кашу и фрукты, чем мясо и картофель. Я знаю ее вкус. 7) Думаю, мне лучше поторопиться. Поезд отправляется через десять минут. 8) Не лучше ли ему остаться с нами, пока он не выздоровеет? 9) Тебе лучше надеть теплое пальто. На улице холодно. 10) Нам лучше не опаздывать. Наши родители будут волноваться. 11) Я бы предпочел пять уроков английского, чем один урок физики. 12) Ей лучше сменить работу − эта слишком опасна.
Had better: form and meaning
We use had better to refer to the present or the future, to talk about actions we think people should do or which are desirable in a specific situation. The verb form is always had, not have. We normally shorten it to ’d better in informal situations. It is followed by the infinitive without to:
It’s five o’clock. I’d better go now before the traffic gets too bad.
Not: I’d better to go now.
The democratic movement had better concentrate on the immediate issues of the economy and security. (more formal)
Had better is a strong expression. We use it if we think there will be negative results if someone does not do what is desired or suggested:
She’d better get here soon or she’ll miss the opening ceremony.
Spoken English:
Sometimes people say had best instead of had better, especially in informal speaking. This sounds slightly less strong and less direct:
You’d best leave it till Monday. There’s no one in the office today.
Had better: negative and question forms
The negative of had better is had better not (or ’d better not):
I’d better not leave my bag there. Someone might steal it.
You’d better not tell Elizabeth about the broken glass – she’ll go crazy!
The question form of had better is made by inverting the subject and had. This means the same as should, but is more formal:
Had I better speak to Joan first before I send this form off? What do you think?
Had we better leave a note for the delivery guy to take the parcel next door?
Negative questions with had better are more common than affirmative ones:
Hadn’t we better ring the school and tell them Liam is sick?
Hadn’t you better switch your computer off? It might overheat if you leave it on.
Had better or be better, be best?
We use had better to give advice in a specific situation. We use the phrase be better or be best + to-infinitive for more general suggestions:
It’s always better to be safe than sorry. (‘It’s better to be safe than sorry’ is a saying which means that you should be careful before taking any action.)
I think it would be best to speak to the people in the video shop to see what they recommend.
Had better or would rather, would prefer?
We don’t use had better when we talk about preferences. We use would rather or would prefer.
Compare
|
It is a good idea, better, or advisable to get a taxi. |
|
I prefer to get a taxi. |
Had better: typical errors
-
We use had better to give specific advice, not to talk about obligations or requirements; instead, we use have to, have got to or must:
You have to (or must) hold a full, valid driving licence to hire a car.
Not: You’d better hold a full, valid driving licence to hire a car.
-
We don’t use had better to talk about preferences; instead, we use would rather or would prefer:
They offered her a job in Warsaw, but she said she’d rather work in a smaller city. (or … she’d prefer to work …)
Not: … she’d better work …
-
We don’t use had better to make ordinary suggestions or recommendations:
Auckland is a great place to visit. I’d recommend you take a boat trip across the bay and see some of the islands. Then you can find a nice restaurant for lunch. There are plenty of them.
Not: You’d better take a boat trip across the bay and see some of the islands. Then you’d better find a nice restaurant for lunch.