Preposition
other than a new jacket, I bought no special clothes for the wedding
Recent Examples on the Web
Otherwise very little changed from Thursday’s practice other than cornerback Jalil Tucker returning after being absent.
—
Outside, the three-acre property has many diversions to offer other than just its guest house and four-car garage.
—
Politicians, especially candidates for the presidency, are judged on matters other than their political views and the grievousness of their sins.
—
Samsung doesn’t have much explanation for the drop other than a weakening economy and lowered demand for chips.
—
Counting federal funds and income from sources other than state taxes, House Bill 1 as passed out by the Appropriations Committee last month would spend $302.7 billion.
—
The legal documents claim that West was spending $10,000 every week on sushi for Donda students, and that they weren’t allowed to bring in any outside food or drink other than water.
—
Anything other than those four exact results and the Nets get No. 6 ahead of the Heat.
—
The term encompasses financial firms, other than banks, that provide all manner of financial services, including lending to households and businesses.
—
Not a lot has changed other than maybe a few paintings on the wall and a few decorations around the Oval Office and White House that each president sort of comes in with.
—
Most of the program’s expenditure goes to relatively affluent seniors and has little effect other than to push up taxes, reduce incentives …
—
That’s because the CDC separates the rate in New York City from the rate in New York other than the city.
—
And on one of those nights, after a beating from her father, Paula runs all the way to the police station and begs to be given somewhere to live other than home.
—
But those who reach Canadian soil somewhere other than a port of entry are allowed to stay and request protection.
—
Among other provisions, companies would have to provide an annual reminder to consumers enrolled in negative-option programs involving anything other than physical goods before they are automatically renewed.
—
Rabbit Hole has no clue how seriously to take his mental illness other than references to an apparent breakdown eight years earlier, so how could the actor?
—
But those who reach Canadian soil somewhere other than a port of entry are allowed to stay and request protection.
—
See More
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word ‘other than.’ Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Certain features require a modern browser to function.
Please use a different browser, like Firefox, Chrome, or Safari
Published March 25, 2021. Updated August 6, 2021.
Differences between other than and other then
Below is a quick overview of the differences between the words.
| OTHER THAN | OTHER THEN | |
| PART OF SPEECH: | Preposition or Conjunction | None |
| DEFINITION: | Means “with the exception of” or “except” | This word is a misspelling |
| USE WHEN: | You are talking about someone or something that stands apart. | – |
Defining other than
This word means “with the exception of” or “except.”
Part of speech: Preposition or Conjunction
Example sentences:
Other than the lone restaurant, there was no eatery open.
There was no living thing on the darkened road other than a decrepit dog.
In the first sentence, no eatery was open except one. The second sentence shows that, with the exception of a dog, there was no living thing on the road.
Defining other then
Other then is a common (and understandable) misspelling of the word other than. It’s not a real word that is used in the English language.
Worried about your writing? Submit your paper for a Chegg Writing grammar check, or for an Expert Check proofreading. Both can help you find and fix potential writing issues.

What’s included with a Chegg Writing subscription
- Unlimited number of paper scans
- Plagiarism detection: Check against billions of sources
- Expert proofreading for papers on any subject
- Grammar scans for 200+ types of common errors
- Automatically create & save citations in 7,000+ styles
- Cancel subscription anytime, no obligation
The words ‘Except’ and ‘Other than’ convey that something is excluded from a general sentence. Both words sound similar in meaning because one is a synonym for the other.
Key Takeaways
- Except is a preposition or conjunction used to indicate exclusion or exception; other than is a preposition that means different from, distinct, or beside.
- Except emphasizes the exclusion or exception of a specific item or group, other than highlighting a difference or distinction between items or groups.
- Both except and other than convey contrast, but except focuses on exclusion or exception, while other than emphasizes difference or distinction.
The difference between Except and Other than is in grammatical usage. The sentence formation matters, and when both ‘Except’ and ‘Other than’ are in conjunction, their meaning changes slightly. The placement of the words within the sentence varies too.
Want to save this article for later? Click the heart in the bottom right corner to save to your own articles box!
‘Except’ can be used to ‘not include a particular object or person’. You can also use it in a sentence when differentiating between two objects.
‘Other than’ is a derivative of except and is defined as “providing an exception”. ‘Other than’ is also used to emphasise an object beside the others already mentioned in the sentence.
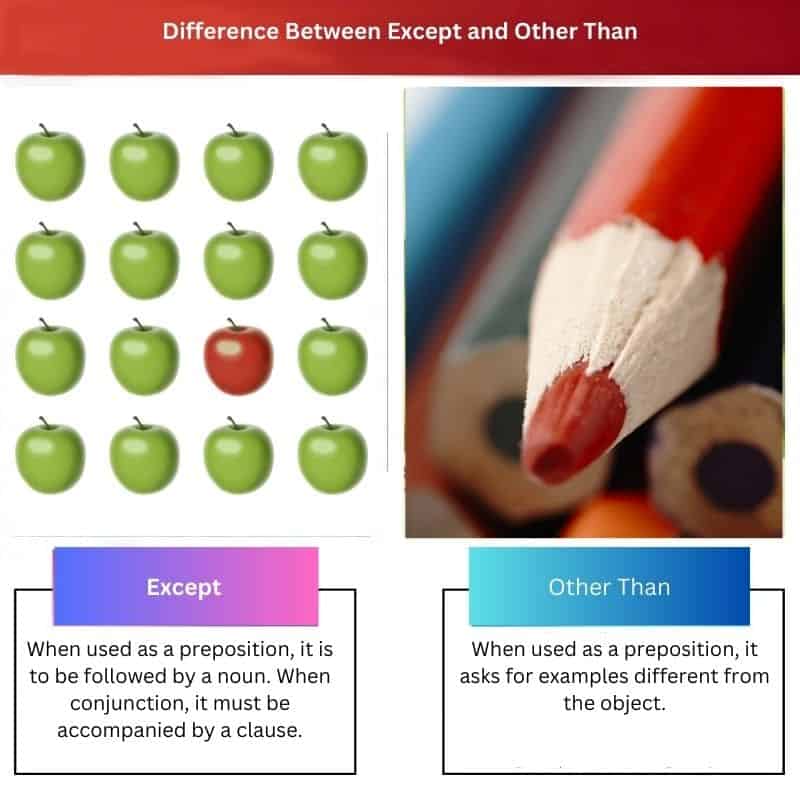
Comparison Table
| Parameters of comparison | Except | Other than |
|---|---|---|
| Form | It exists in 3 states – Conjunction, preposition, and as verbs. | It exists in 2 different forms – Conjunction and preposition. |
| Grammatical usage (1) | When used as a preposition, it is to be followed by a noun. When conjunction, it must be accompanied by a clause. | When used as a preposition, it asks for examples different from the object. |
| Grammatical usage (2) | ‘Except’ is a conjunction used to differentiate between objects of a sentence. ‘Except’ is a verb; it is used not to include the thing from the sentence. | When ‘Other than’ is a conjunction, one can use it to provide one option, besides which no other option is accepted. |
| Example | “Henry and John are brothers, except Henry is the older of the two.” | “Nothing can help you pass your exams other than studying hard from the beginning.” |
| Synonyms | Excluding, omitting, passing over. | Besides, apart from, but. |
What is meant by Except?
The word ‘Except’ is present in grammatical nature in three different forms, namely –
- Preposition
- Conjunction
- Verb
When used as a preposition, ‘Except’ must be followed by a noun instead of a phrase. It keeps the exact meaning of ‘not to include something or someone’ or ‘but not’, but the way it is used changes with the structure of the sentence.
Here, the synonyms are ‘apart from’, ‘but’, and ‘Other than’. This is where the meaning of ‘Other than’ is derived from.
Example –
- “Do you sell any juices except mango?”
- “Everyone arrived for the meeting except Mike.”
The form of the word used depends on how the general flow of the structure. Sometimes, when ‘Except’ is a conjunction, it can mean to ‘differentiate between two given objects in a sentence.’
Here, the synonyms of ‘Except’ in the conjunctive form are ‘aside from’, besides etc. Also, as a conjunction, it must be accompanied by a phrase.
Example –
- “The newborns were twins, except one was a boy, and one was a girl.”
- “Both the assignments looked precisely the same, except one was the original and the other a copy.’
When except is a verb, it is plain and means to ‘not include someone or something’. It is not commonly found in this form as it was primarily used in old English.
Example – “ After my mishap in the project, I was excepted for receiving the promotion.”
What is meant by Other Than?
‘Other than’ is a derivative of ‘Except’ and can mean ‘to provide an exception for the object in focus’. The term is present in grammatical nature in two different forms, namely –
- Preposition
- Conjunction
When the word is in preposition form when used in a sentence, firstly, it must be followed by a noun. Secondly, its meaning changes to ‘aside from or beside something’.
This form of ‘Other than’ is a synonym of ‘except’ and is derived from it.
Example –
- “Other than reading books all day, Harry doesn’t do much else with his free time.”
- When going through his old things, he hoped to find anything valuable besides dust.”
When the word is used with the sentence, it means to ‘not include something or someone along with the general statement.”
Example –
- “Nothing can help you pass your exams other than studying hard from the beginning.”
- “There will never be a cure to the common cold other than taking your medicines and waiting for seven days.”
Main Differences Between Except and Other Than
- ‘Except’ can be used in three forms, preposition, conjunction and verb, while ‘Other than’ can only be used as a preposition or a meeting.
- ‘Except’ can convey that something is ‘not included’. ‘Other than’ is a derivative of except and hence can be defined as providing an exception.
- ‘Except’, when used as a conjunction, can allow differentiating particular sentence objects. ‘Other than’ just means to exclude something from the general statement.
- One can use ‘Other than’ to ask for different options in a sentence as a preposition, while ‘Except’ cannot be used in that manner.
- The synonyms of except ( Excluding, omitting, pass over.) show us that except purely means to exclude. The ‘Other than’ synonyms are besides, apart from, but, etc.
References
- https://www.macmillandictionary.com/dictionary/british/other-than
- https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/except
Emma Smith holds an MA degree in English from Irvine Valley College. She has been a Journalist since 2002, writing articles on the English language, Sports, and Law. Read more about me on her bio page.
-
#1
other than / rather than
1. use fuel other than gasoline
2. use diesel rather than gasoline
Does 1 make sense? If it does, what does it really mean?
3. the presence of elements other than iron
4. the presence of elements rather than iron
Do they mean the same thing?
5. facebook is the most hyped thing this year other than the iPhone
6. facebook is the most hyped thing this year rather than the iPhone.
Would there be any difference between the two?
Many many thanks in advance.
-
#2
«Other than» means except while «rather than» means instead of.
For example, these two are very different.
facebook is the most hyped thing this year other than the iPhone
This means that facebooks is the second most hyped-up thing this year (while the iPhone is the first).
facebook is the most hyped thing this year rather than the iPhone.
This means that facebooks is the most hyped-up thing this year instead of the iPhone.
I hope this helps.
-
#3
Thank you very much.
«Other than» means except
Yes. But other than has another meaning: besides/in addition to, so I still feel puzzled with Sentence1, Sentence3. Do they can only be understood in a certain context? Do they have double meanings without a context?
-
#4
According to dictionary.com
other than
prep. With the exception of; except for; besides: Other than one sister, she has no close relatives.
adverbin another and different manner; «very soon you will know differently»; «she thought otherwise»; «there is no way out other than the fire escape»; [syn: differently]
rather than
conj. And not: «Gibson guitars—with their carved tops and necks that are fitted and glued to the body, rather than bolted on—are expensive to make» (Joshua Rosenbaum).
prep. Instead of: «diseases in which the immune system plays the villain rather than the protector» (Sandra Blakeslee).
If you wish to say «Use fuel but not gasoline», I would suggest «rather than«.
If you wish to say «the presence of elements besides iron», I would suggest «other than«.
-
#5
To make things clear, what’s your opinion about the other than in «use fuel other than gasoline» ? Do you think it is used correctly? I think other than may possibly mean including,for we can’t say …use fuel except gasoline, considering gasoline is a kind of fuel.
-
#6
To make things clear, what’s your opinion about the other than in «use fuel other than gasoline» ? Do you think it is used correctly? I think other than may possibly mean including,for we can’t say …use fuel except gasoline, considering gasoline is a kind of fuel.
Aha! This is starting to sound like a trick question
«Use fuels other than gasoline» or «Use other fuels (rather) than gasoline» are probably better………
-
#7
1. use fuel other than gasoline
2. use diesel rather than gasoline
Does 1 make sense? If it does, what does it really mean?3. the presence of elements other than iron
4. the presence of elements rather than iron
Do they mean the same thing?5. facebook is the most hyped thing this year other than the iPhone
6. facebook is the most hyped thing this year rather than the iPhone.
Would there be any difference between the two?
«Other than» = «but not». «Other» excludes part.
«Rather than» = «(and) not». «Rather» opposes exclusively.
In other words, the difference is in an underlying assumption. The underlying assumptions in your sentences are:
1. Gasoline
is
a fuel.
2. Gasoline is
not
diesel.
3. Iron
is
an (atomic or chemical) element.
4. «Elements» refers to something that iron is
not
. Sentence 4 does not make sense if «elements» refers to atomic or chemical elements.
5. The iPhone
is
a thing. It is possibly a hyped thing.
6. The iPhone is
not
the most hyped thing this year.
-
#8
«Other than» means «of a kind, type, or class that is different from the item that is named».
If you use a fuel other than gasoline, you may use kerosene, or wood, or coal, or solar energy.
If I asked you to name a city in Japan other than Tokyo, you could name Osaka, or Kyoto, or Yokahama.
If you were told that the price for a hotel applied in months other than July and August, you would be able to stay for the price given in September, or January, or May.
-
#9
Thank you very much.
Yes. But other than has another meaning: besides/in addition to, so I still feel puzzled with Sentence1, Sentence3. Do they can only be understood in a certain context? Do they have double meanings without a context?
“Other than” can usually be replaced with “except for”, but sometimes “in addition to” fits as well. “Other than” never distinguishes between these two meanings. I would not say it has a double meaning, but it has a more general meaning than “except for” or “in addition to”. It does, however, always distinguish itself from “rather than”.
“Besides” is also general in meaning but happens to be used more often in places where “in addition to” would fit.
Examples:
- Sign on gas cap: “Use fuel other than gasoline.” [most probably not “in addition to”]
- “These cars allow you to use fuel other than gasoline.” [probably “in addition to”]
- “The presence of elements other than iron has been detected on some asteroids.” [probably “in addition to”]
- “Facebook is the most hyped thing this year other than the iPhone.” [possibly “in addition to”, but does it matter?]
The difference between “other than” and “rather than” is similar to the difference between restrictive and non-restrictive modifiers. “Other than” is restrictive; “rather than” is non-restrictive.
For example, in (1) we restrict “fuel” with “other than gasoline”: if we didn’t say “other than gasoline”, “fuel” would include gasoline because gasoline is a fuel. But in (2) “rather than gasoline” does not restrict “diesel” because diesel and gasoline are mutually exclusive.
1. “use fuel other than gasoline” = “use fuel that is not gasoline” [does not = “use fuel”, because gasoline is a fuel and is only excluded if we say so]
2. “use diesel rather than gasoline” = “use diesel, which is not gasoline” [= “use diesel” because gasoline is not diesel and so is automatically excluded]
3. “the presence of elements other than iron” = “the presence of elements that are not iron” [does not = “the presence of elements”, because iron is an element]
4. “the presence of elements rather than iron” [= “the presence of elements”. In this speaker’s mind, iron is not an element]
-
#11
After reading your comments I want to know if I got it right.
I read in an English learning text «I think I’ll have a cold drink other than coffee». Is it correct to assume they made a mistake and should have used «rather than», unless they are talking about iced coffee?
- I think I’ll have a cold drink other than coffee.(implying that it’s iced coffee)
- I think I’ll have a cold drink rather than coffee. (implying that it’s hot)
-
#12
After reading your comments I want to know if I got it right.
I read in an English learning text «I think I’ll have a cold drink other than coffee». Is it correct to assume they made a mistake and should have used «rather than», unless they are talking about iced coffee?
- I think I’ll have a cold drink other than coffee.(implying that it’s iced coffee)
- I think I’ll have a cold drink rather than coffee. (implying that it’s hot)
Exactly.
-
#13
After reading your comments I want to know if I got it right.
I read in an English learning text «I think I’ll have a cold drink other than coffee». Is it correct to assume they made a mistake and should have used «rather than», unless they are talking about iced coffee?
- I think I’ll have a cold drink other than coffee.(implying that it’s iced coffee)
- I think I’ll have a cold drink rather than coffee. (implying that it’s hot)
Sort of.
«I want a cold drink other than coffee» could mean that the speaker wants a drink that is not coffee and the speaker wants that drink cold. It is not about whether coffee is iced or not, but it assumes coffee is a drink.
«I want a cold drink, rather than coffee» means the speaker wants a cold drink as opposed to (or instead of) coffee. It is not about the temperature of coffee, but it does assume coffee is not a «cold drink». Sometimes «a cold drink» means a drink that is cold, but where I live, it can also be a synonym for «soft drink» or «fizzy drink».
-
#14
Sort of.
«I want a cold drink other than coffee» could mean that the speaker wants a drink that is not coffee and the speaker wants that drink cold. It is not about whether coffee is iced or not, but it assumes coffee is a drink.
«I want a cold drink, rather than coffee» means the speaker wants a cold drink as opposed to (or instead of) coffee. It is not about the temperature of coffee, but it does assume coffee is not a «cold drink». Sometimes «a cold drink» means a drink that is cold, but where I live, it can also be a synonym for «soft drink» or «fizzy drink».
Thank you. I didn’t know it could be interpreted that way.
-
#15
«Other than» means «of a kind, type, or class that is different from the item that is named».
Does «to be other than what we are» in the following context mean «to be different to what we are»?
Like Descartes, most of us begin these inquiries as thinkers, condemned by the terms of our subjectivity to maneuver in a world that appears to be other than what we are. Descartes accentuated this dichotomy by declaring that two substances were to be found in God’s universe; matter and spirit.
-Sam Harris’ The End of Faith
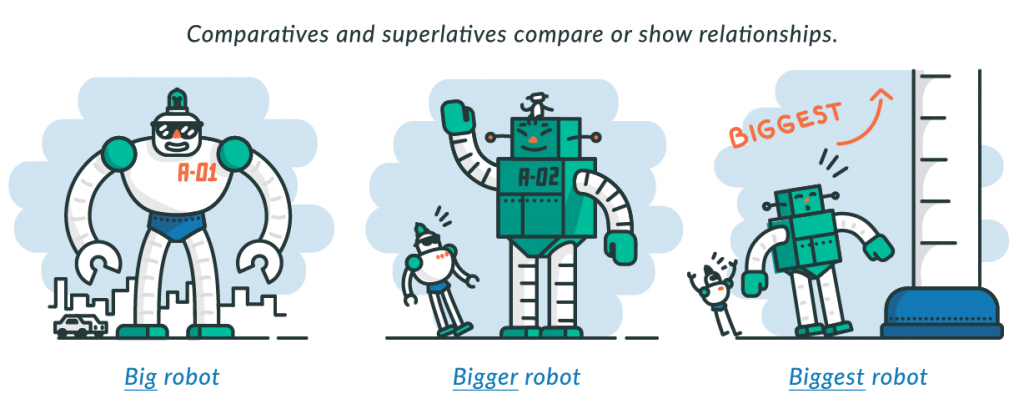
Comparatives and superlatives are special types of adjectives used when comparing two or more things. The trickiest thing when using comparatives and superlatives is making sure we are writing them the correct way, but with a little practice, comparatives and superlatives can quickly be mastered.
In this post we’ll review what comparatives and superlatives are, the rules for how to form these adjectives the correct way, and how to use them effectively in a sentence.
After reviewing the information below, test yourself with a post-assessment quiz and practice with our high quality, standards-aligned questions here.
The Basics of Comparatives and Superlatives

What is a Comparative?
Comparative Adjectives are words used to describe a noun by comparing it to another noun. We usually think of ‘er’ words like bigger or smaller, but they can be a little trickier than that.
The way we form comparative adjectives is based on the number of syllables in the adjective and whether or not the adjective ends with the letter ‘y’.
What is a Superlative?
Superlative Adjectives are words used to describe a noun when comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree. Think: big, bigger, biggest, or small, smaller, smallest.
Like with comparative adjectives, it’s not always as simple as adding ‘est’. The number of syllables and whether or not the adjective ends with the letter ‘y’ also help us determine how to form a superlative adjective.
One Syllable Adjectives
Let’s look at a chart showing the comparative and superlative forms of the word for the most basic one syllable adjectives, where we add ‘er’ for the comparative and ‘est’ for the superlative. *Note: when the adjective follows the CVC, or consonant, vowel, consonant spelling, the final consonant is doubled.
|
ADJECTIVE |
COMPARATIVE |
SUPERLATIVE |
|
Big |
Bigger |
Biggest |
|
Tall |
Taller |
Tallest |
|
Small |
Smaller |
Smallest |
|
Hot |
Hotter |
Hottest |
Comparative Adjectives:
- I am faster than my friend.
- Arizona is hotter than Alaska.
Superlative Adjectives:
- She is the tallest student.
- That was the shortest movie in the series.
Notice the other words around the comparative and superlative adjectives. Most comparatives are followed by ‘than’, and most superlatives follow the word ‘the’.
Two Syllable Adjectives
Now let’s look at a chart showing the comparative and superlative forms of the word for adjectives with two syllables. Comparative adjectives with two syllables can be formed by making the ‘er’ ending or by adding the words ‘more’ or ‘less’ before the adjective.
For superlative adjectives, you make the ‘est’ ending but use the word ‘most’ or ‘least’ instead of ‘more’ or ‘less’.
|
ADJECTIVE |
COMPARATIVE |
SUPERLATIVE |
|
Happy |
Happier |
Happiest |
|
Crazy |
Crazier |
Craziest |
|
Nervous |
More/Less Nervous |
Most/Least Nervous |
|
Massive |
More/Less Massive |
Most/Least Massive |
|
Quiet |
Quieter or More/Less Quiet |
Quietest or Most/Least Quiet |
*Note: In many cases, either form of the comparative or superlative can be used, but there is generally a ‘most common’ usage. Additionally, the adjective does not need to end in ‘y’ in order to use the ‘er’ or ‘est’ usage, as the last example in the table shows. Your ear will often be able to recognize what sounds best.
Comparative Adjectives:
- She tends to be less passive than her brother.
- This quiz is simpler than the last one.
Superlative Adjectives:
- Fall is the busiest shopping season.
- This is the most rapid method of delivery.
Notice again how the comparative adjectives are followed by ‘than’, and superlative adjectives follow the word ‘the’.
Three or More Syllable Adjectives
The chart below shows the comparative and superlative forms of the word for adjectives that are three or more syllables long. In these cases, we always add ‘more’ or ‘less’ before a comparative adjective and ‘most’ or ‘least’ before a superlative adjective.
|
ADJECTIVE |
COMPARATIVE |
SUPERLATIVE |
|
Mysterious |
More/Less Mysterious |
Most/Least Mysterious |
|
Complicated |
More/Less Complicated |
Most/Least Complicated |
|
Wonderful |
More/Less Wonderful |
Most/Least Wonderful |
Comparative Adjectives:
- I tend to be more reluctant than my friends when trying new things.
- The noise at the pool was less bothersome than the noise on the beach.
Superlative Adjectives:
- Her second compilation was the most exceptional of them all.
- Those were the least comfortable couches I have ever sat on.
Irregular Adjectives
When using comparative and superlative adjectives, it is important to note that there are a handful of irregular adjectives that don’t follow the rules above. The chart below shows these irregular adjectives along with their comparative and superlative forms.
|
ADJECTIVE |
COMPARATIVE |
SUPERLATIVE |
|
Good |
Better |
Best |
|
Bad or Ill |
Worse |
Worst |
|
Little (Amount) |
Less |
Least |
|
Far (Distance) |
Farther |
Farthest |
|
Far (Extent) |
Further |
Furthest |
|
Many or Much |
More |
Most |
Comparative Adjectives:
- I did better than the rest of my class on the final.
- She ran farther in this race than she did in the last one.
Superlative Adjectives:
- That was the best birthday present ever!
- I bought the least expensive souvenir that I could find.
Return to the Table of Contents
2 Tips for Recognizing and Using Comparative & Superlative Adjectives
Tip #1: Rearrange your sentence to use different forms of the adjective
We can use different forms of the adjective if we adjust our sentence to fit the adjective.
Here are some examples we used for one syllable adjectives:
Comparative Example:
- I ran faster than my friend.
Now, let’s rearrange the sentence in a way that allows us to use the superlative form of the adjective.
- Between my friend and I, I ran the fastest.
Here, the comparison is still being made between two people; however, when we limit the nouns that we are comparing, we can use the superlative form of the adjective. Notice this sentence follows the other superlative characteristic of using the word ‘the’ before the adjective.
Superlative Example:
- That was the shortest movie in the series.
Now, let’s rearrange the sentence in a way that allows us to use the comparative form of the adjective.
- That was shorter than any other movie in the series.
Here, the comparison is still being made to two or more movies, and we are still describing it to the lowest degree. By adding ‘any other’ before ‘movie in the series’, we can use the comparative form of the adjective. Notice that this sentence also now follows the other comparative characteristic of using the word ‘than’ after the adjective.
Tip #2: Remember your spelling rules before making the comparative or superlative form of the adjective
Any time we change the ending of a word, we need to take into account how the word is normally spelled.
If the adjective already ends with an ‘e’, only add ‘r’ for the comparative and ‘st’ for the superlative.
- Wide becomes Wider or Widest.
- Brave becomes Braver or Bravest.

If the adjective ends with a consonant + short vowel + consonant (CVC), we typically double the last consonant.
- Big becomes Bigger or Biggest.
- Hot becomes Hotter or Hottest.
If the adjective ends with a ‘y’, we change the ‘y’ to and ‘i’.
- Early becomes Earlier or Earliest.
- Silly becomes Sillier or Silliest.
Return to the Table of Contents
Applying the Basics: Comparative and Superlative Adjective Review & Practice
Now that you understand what comparatives and superlatives are, and how to use them properly in a sentence, let’s practice identifying them and checking for proper usage.
Remember, comparative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to another noun. Superlative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree.
Comparative Adjectives Exercises & Review
Complete the quick exercise below to assess your mastery of comparative adjectives.
In the sentences below, select the option that accurately shows the comparative form of the adjective. Remember, a comparative adjective describes a noun by comparing it to another noun.
1. Lucas is (oldest/older) than Lily.
- older
2. Alaska is (colder/more cold) than Florida.
- colder
3. I am (more worried/worrieder) about this exam than the last one.
- more worried
4. This map is (more confusing/most confusing) than my calculus homework.
- more confusing
5. I ran (further/farther) than my best friend did yesterday.
- Farther
Superlative Adjectives Exercises & Review
Complete the quick exercise below to assess your mastery of superlative adjectives.
In the sentences below, select the option that accurately shows the superlative form of the adjective. Remember, a superlative adjective describes a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree.
1. Playing games with your family is the (funner/funnest) way to pass the time when you’re cooped up at home.
- funnest
2. My brother is the (most annoying/annoyingest) person to have around when looking for peace and quiet.
- most annoying
3. As soon as possible, we hope to go to the (beautifulest/most beautiful) tropical island.
- most beautiful
4. Reading a good book is the (most leisurely/more leisurely) way to relax.
- most leisurely
5. Multitasking is the (less efficient/least efficient) method of productivity.
- least efficient
Comparative & Superlative Exercises
Use your knowledge of both comparative and superlative adjectives in the exercise below.
Identify the comparative and superlative adjectives in the sentences below. There may be more than one in a sentence. Make sure you specify which are comparative and which are superlative.
1. I worked on the least complicated homework before starting the more challenging work.
- Comparative: more challenging
- Superlative: least complicated
2. She is taller than the other girls in her class, but she is not the tallest student in the class.
- Comparative: taller
- Superlative: tallest
3. I find direct instruction to be the most straightforward way learning new material.
- Superlative: most straightforward
4. I believe the most obvious answer is correct more often than not.
- Comparative: more often
- Superlative: most obvious
5. Finishing first in the finals was the most fulfilling accomplishment after a sectional performance that was harder than she expected.
- Comparative: harder
- Superlative: most fulfilling
For additional practice, check out the Comparative and Superlative content on Albert.
Return to the Table of Contents
Try for Yourself: Comparative and Superlative Adjectives Quiz
Feeling confident in your understanding of comparative and superlative adjectives?
Take this short quiz to see what you’ve learned:
1. Do comparative or superlative adjectives show the highest degree of a quality?
- Answer: Superlative Adjectives
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! Superlative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree. Comparative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to another noun.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. Remember, comparative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to another noun. Superlative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree.
2. Do comparative or superlative adjectives sometimes use the additional modifier ‘more’?
- Answer: Comparative Adjectives
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! Since comparative adjectives do not describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree, they can use modifiers such as ‘more’.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. Remember, superlative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree, so they would use modifiers such as ‘most’ or ‘least’. Comparative adjectives do not describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree, they can use modifiers such as ‘more’.
3. Does the following sentence use a comparative or superlative adjective?
People from Chicago often agree that deep dish pizza is better than thin crust pizza.
- Answer: Comparative Adjective
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! In this sentence, deep dish pizza is being compared to thin crust pizza. The word ‘better’ is a comparative adjective since it is comparing one type of pizza to another.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. Remember, superlative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree. In this sentence, deep dish pizza is being compared to thin crust pizza. The word ‘better’ is a comparative adjective since it is comparing one type of pizza to another.
4. Is the underlined section of the sentence below a comparative or superlative adjective?
The tree in front of my house is the tallest tree in the neighborhood.
- Answer: Superlative Adjective
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! Superlative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree. The word ‘tallest’ describes the tree to the highest degree compared to the other trees in the neighborhood.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. Remember, Remember, comparative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to another noun. Superlative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree. The word ‘tallest’ describes the tree to the highest degree compared to the other trees in the neighborhood.
5. Which of the following sentences correctly uses a comparative adjective?
A. I thought your portion was the biggest than mine.
B. I thought your portion was bigger than mine.
- Answer: B
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! Comparative adjectives usually end with the letters ‘er’ because they are describing a comparison with one other noun.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. Superlative adjectives usually end with the letters ‘est’ because they are describing a comparison with two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree. Additionally, superlative adjectives are not typically followed by the word ‘than’. Comparative adjectives usually end with the letters ‘er’ because they are describing a comparison with one other noun.
6. Which of the following sentences correctly uses a superlative adjective?
A. That was the least memorable movie I’ve seen in a long time.
B. That was the less memorable movie I’ve seen in a long time.
- Answer: A
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! Superlative adjectives with three syllables use the words ‘least’ or ‘most’ because they are describing a comparison with two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. Comparative adjectives with three syllables use the words ‘more’ or ‘less’ because they are describing a comparison with one other noun. Superlative adjectives with three syllables use the words ‘least’ or ‘most’ because they are describing a comparison with two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree.
For additional practice with comparative and superlative adjectives, check out our practice on Albert.io: Comparatives and Superlatives.
Return to the Table of Contents
Teacher’s Corner for Comparatives and Superlatives
While it’s true that comparative and superlative adjectives are a foundational grammar skill, the Common Core English Language Progressive Skills Chart shows that even elementary-level skills “require continued attention in higher grades as they are applied to increasingly sophisticated writing and speaking.”
For specific standards addressing comparative and superlative adjectives, check out the Common Core State Standards site!
Albert’s Comparative and Superlative practice can be used for much more than homework!
Our assessments can be used as pre-and post-tests to measure student progress. Our pre-made quizzes can be used as bell-ringers, exit tickets, and more!
In addition to our pre-made assessments, you can also use our assignments feature to create your own quizzes and assessments.
Return to the Table of Contents
Summary on Comparative Adjectives and Superlative Adjectives
A Comparative Adjective is a word that describes a noun by comparing it to another noun. Comparative adjectives typically end in ‘er’ and are followed by the word ‘than’.
A Superlative Adjective is a word that describes a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree. Superlative adjectives typically end in ‘est’ and are preceded by the word ‘the’.
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives are words we often see and use in our writing. Make sure you are structuring your comparative and superlative adjectives appropriately for the number of syllables in the adjective.
Practice makes perfect! Use our Comparative and Superlative practice on Albert’s grammar course!
Need help preparing for your Grammar exam?
Albert has hundreds of grammar practice questions with detailed explanations to help you master concepts.
Click on the arrows to change the translation direction.
Bilingual Dictionaries
-
English–Dutch
Dutch–English -
English–French
French–English -
English–German
German–English -
English–Indonesian
Indonesian–English -
English–Italian
Italian–English -
English–Japanese
Japanese–English -
English–Norwegian
Norwegian–English -
English–Polish
Polish–English -
English–Portuguese
Portuguese–English -
English–Spanish
Spanish–English
Semi-bilingual Dictionaries
English–Arabic
English–Catalan
English–Chinese (Simplified)
English–Chinese (Traditional)
English–Czech
English–Danish
English–Hindi
English–Korean
English–Malay
English–Russian
English–Thai
English–Turkish
English–Ukrainian
English–Vietnamese




