English is a beautiful language, and one of its many perks is the one-word sentences. One-word sentences — as the name suggests is a sentence with a single word, and which makes total sense.
One word sentences can be used in different forms. It could be in form of a question such as “Why?” It could be in form of a command such as “Stop!” Furthermore, it could be used as a declarative such as “Me.” Also, a one-word sentence could be used to show location, for example, “here.” It could also be used as nominatives e.g. “David.”
Actually, most of the words in English can be turned into one-word sentences. All that matters is the context in which they are used. In a sentence, there is usually a noun, and a verb. In a one-word sentence, the subject and the action of the sentence is implied in the single word, and this is why to understand one-word sentences, one has to understand the context in which the word is being used.
Saying only a little at all times is a skill most people want to learn; knowing when to use one-word sentences can help tremendously. However, you cannot use one-word sentences all the time so as robotic or come off as rude.
 Here are common one-word sentences, and their meanings:
Here are common one-word sentences, and their meanings:
- Help: This signifies a call for help.
- Hurry: Used to ask someone to do something faster
- Begin: Used to signify the beginning of a planned event.
Basically, the 5 Wh-question words — where, when, why, who and what? can also stand as one-word sentences.
By Bizhan Romani
Dr. Bizhan Romani has a PhD in medical virology. When it comes to writing an article about science and research, he is one of our best writers. He is also an expert in blogging about writing styles, proofreading methods, and literature.

What does a conjunction do?Where is a conjunction used?What is a conjunction? Here we have answers to all these questions! Conjunctions, one of the English parts of speech, act as linkers to join different parts of a sentence. Without conjunctions, the expression of the complex ideas will seem odd as you will have to use…

Introduction An adverb is a word that modifies a sentence, verb, or adjective. An adverb can be a word or simply an expression that can even change prepositions, and clauses. An adverb usually ends only- but some are the same as their adjectives counterparts. Adverbs express the time, place, frequency, and level of certainty. The…

What is a noun?What are all types of nouns?How is a noun used in a sentence? A noun is referred to any word that names something. This could be a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns play different roles in sentences. A noun could be a subject, direct object, indirect object, subject complement, object complement,…

What is a pronoun?How is a pronoun used in a sentence?What are all types of pronouns? A pronoun is classified as a transition word and a subcategory of a noun that functions in every capacity that a noun will function. They can function as both subjects and objects in a sentence. Let’s see the origin…

In the English language, sentence construction is quite imperative to understanding. A sentence can be a sequence, set or conglomerate of words that is complete in itself as it typically contains a subject, verb, object and predicate. However, this sentence regardless of its intent, would be chaotic if not constructed properly. Proper sentence construction helps…
Image by Ozzy Delaney on Flickr.com licensed under CC BY 2.0.
Here I’m going to highlight some of the simplest sentences in English. All of these sentences are only ONE word long! Sit back, relax, and enjoy; these are going to be some of the easiest English sentences you’ve ever learned. (It is about time something in English was easy, right?!)
One-word sentences in English come in a few different forms:
interrogatives or questions (example: Who?)
imperatives or commands (example: Stop!)
declaratives (example: Me.)
locatives (example: Here.)
nominatives (example: Jesse.)
In fact a lot of words in English can be one-word sentences, it all depends on the context.
A complete sentence, even a one-word sentence, needs to have a noun and a verb. In one-word sentences the subject (noun) or the action (verb) of the sentence is implied. That means it is understood in the context of the sentence (or the sentences around it) so that the subject and/or verb do not need to be stated explicitly.
Being brief and saying as much as you can in as few words as possible is something a lot of people want to do. Be careful though, sometimes you can sound robotic or rude if you use too many one-word sentences.
Here is a list of some common one-word sentences. I’m sure you already use some of these. Along side the one-word sentences I have written out what you could say, with more words, to mean the same thing.
Hi. (Hi there.)
Wait. (Please wait.)
Begin. (You may begin.)
Stop. (You need to stop.)
Hurry. (Hurry up please.)
Catch. (Catch this.)
Here. (Here you go.)
Go! (Get going now!)
Help! (I need help!)
Eat. (Go ahead and eat.)
Yes. (Yes, that would be great.)
No. (No, thank you.)
Thank you. (Thank you, I really appreciate it.)
The wh-question words: Who? What? Where? When? Why? How?
A lot of swear words: Sh*t., F*ck., etc.
Do you have a favorite one-word sentence? Add to this list by posting a comment below! Thank you.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A sentence word (also called a one-word sentence) is a single word that forms a full sentence.
Henry Sweet described sentence words as ‘an area under one’s control’ and gave words such as «Come!», «John!», «Alas!», «Yes.» and «No.» as examples of sentence words.[1] The Dutch linguist J. M. Hoogvliet described sentence words as «volzinwoorden».[2] They were also noted in 1891 by Georg von der Gabelentz, whose observations were extensively elaborated by Hoogvliet in 1903; he does not list «Yes.» and «No.» as sentence words. Wegener called sentence words «Wortsätze».[3]
Single-word utterances and child language acquisition[edit]
One of the predominant questions concerning children and language acquisition deals with the relation between the perception and the production of a child’s word usage. It is difficult to understand what a child understands about the words that they are using and what the desired outcome or goal of the utterance should be.[4]
Holophrases are defined as a «single-word utterance which is used by a child to express more than one meaning usually attributed to that single word by adults.»[5] The holophrastic hypothesis argues that children use single words to refer to different meanings in the same way an adult would represent those meanings by using an entire sentence or phrase. There are two opposing hypotheses as to whether holophrases are structural or functional in children. The two hypotheses are outlined below.
Structural holophrastic hypothesis[edit]
The structural version argues that children’s “single word utterances are implicit expressions of syntactic and semantic structural relations.” There are three arguments used to account for the structural version of the holophrastic hypothesis: The comprehension argument, the temporal proximity argument, and the progressive acquisition argument.[5]
- The comprehension argument is based on the idea that comprehension in children is more advanced than production throughout language acquisition. Structuralists believe that children have knowledge of sentence structure but they are unable to express it due to a limited lexicon. For example, saying “Ball!” could mean “Throw me the ball” which would have the structural relation of the subject of the verb. However, studies attempting to show the extent to which children understand syntactic structural relation, particularly during the one-word stage, end up showing that children “are capable of extracting the lexical information from a multi-word command,” and that they “can respond correctly to a multi-word command if that command is unambiguous at the lexical level.”[5] This argument therefore does not provide evidence needed to prove the structural version of the holophrastic hypothesis because it fails to prove that children in the single-word stage understand structural relations such as the subject of a sentence and the object of a verb.[5]
- The temporal proximity argument is based on the observation that children produce utterances referring to the same thing, close to each other. Even the utterances aren’t connected, it is argued that children know about the linguistic relationships between the words, but cannot connect them yet.[5] An example is laid out below:
→ Child: «Daddy» (holding pair of fathers pants)
- → Child
-
-
- «Bai» (‘bai’ is the term the child uses for any item of clothing)
-
The usage of ‘Daddy’ and ‘Bai’ used in close proximity are seen to represent a child’s knowledge of linguistic relations; in this case the relation is the ‘possessive’.[6] This argument is seen as having insufficient evidence as it is possible that the child is only switching from one way to conceptualize pants to another. It is also pointed out that if the child had knowledge of linguistic relationships between words, then the child would combine the words together, instead of using them separately.[5]
- Finally, the last argument in support of structuralism is the progressive acquisition argument. This argument states that children progressively gain new structural relations throughout the holophrastic stage. This is also unsupported by the research.[5]
Functional holophrastic hypothesis[edit]
Functionalists doubt whether children really have structural knowledge, and argue that children rely on gestures to carry meaning (such as declarative, interrogative, exclamative or vocative). There are three arguments used to account for the functional version of the holophrastic hypothesis: The intonation argument, the gesture argument, and the predication argument.[5]
- The intonation argument suggests that children use intonation in a contrastive way. Researchers have established through longitudinal studies that children have knowledge of intonation and can use it to communicate a specific function across utterances.[7][8][9] Compare the two examples below:
→ Child: «Ball.» (flat intonation) — Can mean «That is a ball.»
-
-
- → Child: «Ball?» (rising inflection) — Can mean «Where is the ball?»
-
- However, it has been noted by Lois Bloom that there is no evidence that a child intends for intonation to be contrastive, it is only that adults are able to interpret it as such.[10] Martyn Barrett contrasts this with a longitudinal study performed by him, where he illustrated the acquisition of a rising inflection by a girl who was a year and a half old. Although she started out using intonation randomly, upon acquisition of the term «What’s that» she began to use rising intonation exclusively for questions, suggesting knowledge of its contrastive usage.[11]
- The gesture argument establishes that some children use gesture instead of intonation contrastively. Compare the two examples laid out below:
→ Child: «Milk.» (points at milk jug) — could mean “That is milk.”
-
-
- → Child: «Milk.» (open-handed gesture while reaching for a glass of milk) — could mean “I want milk.”
-
- Each use of the word ‘milk’ in the examples above could have no use of intonation, or a random use of intonation, and so meaning is reliant on gesture. Anne Carter observed, however, that in the early stages of word acquisition children use gestures primarily to communicate, with words merely serving to intensify the message.[12] As children move onto multi-word speech, content and context are also used alongside gesture.
- The predication argument suggests that there are three distinct functions of single word utterances, ‘Conative’, which is used to direct the behaviour of oneself or others; ‘Expressive’, which is used to express emotion; and referential, which is used to refer to things.[13] The idea is that holophrases are predications, which is defined as the relationship between a subject and a predicate. Although McNeill originally intended this argument to support the structural hypothesis, Barrett believes that it more accurately supports the functional hypothesis, as McNeill fails to provide evidence that predication is expressed in holophrases.[5]
Single-word utterances and adult usage[edit]
While children use sentence words as a default strategy due to lack of syntax and lexicon, adults tend to use sentence words in a more specialized way, generally in a specific context or to convey a certain meaning. Because of this distinction, single word utterances in children are called ‘holophrases’, while in adults, they are called ‘sentence words’. In both the child and adult use of sentence words, context is very important and relative to the word chosen, and the intended meaning.
Sentence word formation[edit]
Many sentence words have formed from the process of devaluation and semantic erosion. Various phrases in various languages have devolved into the words for «yes» and «no» (which can be found discussed in detail in yes and no), and these include expletive sentence words such as «Well!» and the French word «Ben!» (a parallel to «Bien!»).[14]
However, not all word sentences suffer from this loss of lexical meaning. A subset of sentence words, which Fonagy calls «nominal phrases», exist that retain their lexical meaning. These exist in Uralic languages, and are the remainders of an archaic syntax wherein there were no explicit markers for nouns and verbs. An example of this is the Hungarian language «Fecske!», which transliterates as «Swallow!», but which has to be idiomatically translated with multiple words «Look! A swallow!» for rendering the proper meaning of the original, which to a native Hungarian speaker is neither elliptical nor emphatic. Such nominal phrase word sentences occur in English as well, particularly in telegraphese or as the rote questions that are posed to fill in form data (e.g. «Name?», «Age?»).[14]
Sentence word syntax[edit]
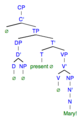
A sentence word involves invisible covert syntax and visible overt syntax. The invisible section or «covert» is the syntax that is removed in order to form a one word sentence. The visible section or «overt» is the syntax that still remains in a sentence word.[15] Within sentence word syntax there are 4 different clause-types: Declarative (making a declaration), exclamative (making an exclamation), vocative (relating to a noun), and imperative (a command).
| Overt | Covert | |
|---|---|---|
| Declarative | ‘That is excellent!’
|
‘Excellent!’
|
| Exclamative | ‘That was rude!’
|
‘Rude!’
|
| Vocative | ‘There is Mary!’
|
‘Mary!’
|
| Imperative | ‘You should leave!’
|
‘Leave!’
|
| Locative | ‘The chair is here.’
|
‘Here.’
|
| Interrogative | ‘Where is it?’
|
‘Where?’
|
The words in bold above demonstrate that in the overt syntax structures, there are words that can be omitted in order to form a covert sentence word.
Distribution cross-linguistically[edit]
Other languages use sentence words as well.
- In Japanese, a holophrastic or single-word sentence is meant to carry the least amount of information as syntactically possible, while intonation becomes the primary carrier of meaning.[16] For example, a person saying the Japanese word e.g. «はい» (/haɪ/) = ‘yes’ on a high level pitch would command attention. Pronouncing the same word using a mid tone, could represent an answer to a roll-call. Finally, pronouncing this word with a low pitch could signify acquiescence: acceptance of something reluctantly.[16]
| High tone pitch | Mid tone pitch | Low tone pitch |
|---|---|---|
| Command attention | Represent an answer to roll-call | Signify acquiescence acceptance of something reluctantly |
- Modern Hebrew also exhibits examples of sentence words in its language, e.g. «.חַם» (/χam/) = «It is hot.» or «.קַר» (/kar/) = «It is cold.».
References[edit]
- ^ Henry Sweet (1900). «Adverbs». A New English Grammar. Oxford: Clarendon Press. pp. 127. ISBN 978-1-4021-5375-4.
- ^ Jan Noordegraaf (2001). «J. M. Hoogvliet as a teacher and theoretician». In Marcel Bax; C. Jan-Wouter Zwart; A. J. van Essen (eds.). Reflections on Language and Language Learning. John Benjamins B.V. p. 24. ISBN 978-90-272-2584-9.
- ^ Giorgio Graffi (2001). 200 Years of Syntax. John Benjamins B.V. p. 121. ISBN 978-1-58811-052-7.
- ^ Hoff, Erika (2009). Language Development. Wadsworth, Cengage Learning. p. 167.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Barrett, Martyn, D. (1982). «The holophrastic hypothesis: Conceptual and empirical issues». Cognition. 11: 47–76. doi:10.1016/0010-0277(82)90004-x.
- ^ Rodgon, M.M. (1976). Single word usage, cognitive development and the beginnings of combinatorial speech. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Dore, J. (1975). «Holophrases, speech acts and language universals». Journal of Child Language. 2: 21–40. doi:10.1017/s0305000900000878.
- ^ Leopold, W.F. (1939). Speech Development of a Bilingual Child: A Linguist’s Record. Volume 1: Vocabulary growth in the first two years. Evanston, ill: Northwestern University Press.
- ^ Von Raffler Engel, W. (1973). «The development from sound to phoneme in child language». Studies of Child Language Development.
- ^ Bloom, Lois (1973). One word at a time: The use of single word utterances before syntax. The Hague: Mouton.
- ^ Barrett, M.D (1979). Semantic Development during the Single-Word Stage of Language Acquisition (Unpublished doctoral thesis).
- ^ Carter, Anne :L. (1979). «Prespeech meaning relations an outline of one infant’s sensorimotor morpheme development». Language Acquisition: 71–92.
- ^ David, McNeill (1970). The Acquisition of Language: The Study of Developmental Psycholinguistics.
- ^ a b Ivan Fonagy (2001). Languages Within Language. John Benjamins B.V. p. 66. ISBN 978-0-927232-82-1.
- ^ Carnie, Andrew (2012). Syntax: a generative introduction. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 496.
- ^ a b Hirst, D. (1998). Intonation systems: a survey of twenty languages. Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press. p. 372.
A sentence is a group of words that expresses a complete thought and contains a subject and a predicate. The most basic sentence structure consists of only one clause. However, many sentences have one main clause and one or more subordinate clauses.
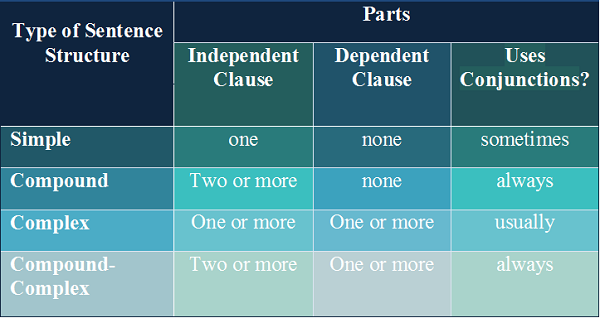
The standard order of words in an English sentence is subject + verb + object. While this sounds simple, it may be difficult to identify the subject(s), verb(s), and object(s), depending on the structure and complexity of the sentence. There are four types of sentence structure: (1) simple, (2) compound, (3) complex, and (4) compound-complex.
Types of sentence structures
| Sentence structure type | Sentence parts | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Sentence |
Independent clause |
I like animals. |
| Compound Sentence |
Independent clause + coordinating |
I like animals, |
| Complex Sentence |
Independent clause + |
I like animals |
|
Compound-Complex Sentence |
Independent clause + |
I like animals |
Sentence Structures in Academic Writing
Simple Sentence Structure
A simple sentence is the most basic sentence structure and consists of a single independent clause.
Types of clauses
An independent clause expresses a full thought. Only independent clauses can function as complete sentences.
- Example
- The proposed system has the advantage of a wide scope.
I went shopping last weekend.
The cat is sleeping by the window.
In contrast, a dependent clause does not express a full thought and cannot function as a complete sentence.
- Example
- which was developed over three months
even though I was tired
because the weather is sunny
A dependent clause starts with either a relative pronoun or subordinating conjunction.
Common subordinating conjunctions
because, since, once, although, if, until, unless, why, while, whether, than, that, in order to
Common relative pronouns
that, which, who, whom, whoever, whomever
Subject of a sentence
The subject is whatever is performing the action of the sentence. This is the first of the two basic components of a sentence.
- Example
- This study investigated the relationship between the personal traits and clinical parameters.
- Example
- Dolly made a cake for the party.
Predicate of a sentence
The predicate contains the verb (the action) and can include further clarifying information.
- Example
- This study investigated the relationship between the personal traits and clinical parameters.
- Example
- Mary gave her sheep a bath.
Direct and Indirect Objects
The direct object is the person, thing, or idea that receives an action.
- Example
- This study investigated the relationship between the personal traits and clinical parameters.
- Example
- Dolly made a cake.
The indirect object is the person, thing, or idea for which an action is being done.
- Example
- The national lab offered us an opportunity to work on an exciting new project.
- Example
- Mary gave her sheep a bath.
Transitive vs. Intransitive Verbs
A transitive verb is the action the subject takes on a direct object.
- Example
- We fabricated a composite.
Here, “we” is the subject, “fabricated” is the transitive verb, and “a composite” is the direct object.
An intransitive verb is a verb that does not have to be followed by an object. Intransitive verbs can function as predicates all on their own.
- Example
- We arrived.
We arrived early.
- Example
- I always eat.
I always eat before work.
“We” and “I” are the subjects; “arrived” and “eat” are intransitive verbs.
Subject Complement
A subject complement complements the subject by renaming or describing it. Subject complements always follow a linking verb, which is often a form of the verb “to be.”
- Example
- The material is a gold composite.
“Gold composite” renames the subject “the material.”
- Example
- Charlotte is very pretty.
“Pretty” describes the subject “Charlotte.”
Get professional proofreading and expert feedback on any document!
-
Academic papers
-
Admissions essays
-
CVs/resumes
-
Business reports
-
Blog and website content
-
Personal essays
Compound Sentence Structure
A compound sentence is composed of two or more independent clauses connected by a coordinating conjunction or semicolon. Note that US English conventions dictate that coordinating conjunctions must be used with a comma when joining independent clauses.
Structure of a Compound Sentence: Independent clause + coordinating conjunction (or semicolon) + independent clause
List of coordinating conjunctions: and, but, yet, or, nor, for, so
- Example
- The material is a gold composite, and it was fabricated in clean room no. 45.
- Example
- Glenda usually eats before work, but today she could not.
- Example
- The proposed system has the advantage of a wide scope; it uses a novel algorithm that expands the range by a factor of ten.
Complex Sentence Structure
A complex sentence is composed of an independent clause and a dependent clause.
Structure of a Complex Sentence: Independent clause + subordinating conjunction (or relative pronoun) + dependent clause
- Example
- We built a new system because the previous model had to be narrowed in scope.
- Example
- Sarah will buy a train ticket if her flight is cancelled.
Compound-Complex Sentence Structure
A compound-complex sentence is composed of two or more independent clauses and one or more dependent clauses.
Structure of a Compound-Complex Sentence: Independent clause + subordinating conjunction + dependent clause + coordinating conjunction + independent clause
- Example
- The first method failed because it caused the wires to melt, but the second method succeeded in bending the wires without causing the same issue.
- Example
- Sarah’s flight took off before she started driving to the airport, so she drove to the train station instead.
1. What is Sentence Structure?
A sentence’s “structure” is the way its words are arranged.
In English, we have four main sentence structures: the simple sentence, the compound sentence, the complex sentence, and the compound-complex sentence. Each uses a specific combination of independent and dependent clauses to help make sure that our sentences are strong, informational, and most importantly, that they make sense!
2. Examples of Sentence Structures
In the examples, independent clauses are green, dependent clauses are purple, and conjunctions are orange. Here are examples of each type of sentence:
- The dog ran. Simple Sentence
- The dog ran and he ate popcorn. Compound sentence
- After the dog ran, he ate popcorn. Complex sentence
- After the dog ran, he ate popcorn and he drank a big soda. Compound-complex sentence
3. Parts of Sentence Structures
All forms of sentence structures have clauses (independent, dependent, or both), and some also have conjunctions to help join two or more clauses or whole sentences.
a. Independent Clause
Independent clauses are key parts of every sentence structure. An independent clause has a subject and a predicate and makes sense on its own as a complete sentence. Here are a few:
- The dog ate brownies.
- The dog jumped high.
- She ate waffles.
- He went to the library.
So, you can see that all of the clauses above are working sentences. What’s more, all sentences have an independent clause!
b. Dependent (Subordinate) Clause
A dependent clause is a major part of three of the four sentence structures (compound, complex, and compound-complex). It has a subject and a predicate; BUT, it can’t be a sentence. It provides extra details about the independent clause, and it doesn’t make sense on its own, like these:
- After he went to the party
- Though he ate hotdogs
- While he was at the dance
- If the dog eats chocolate
Each of the bullets above leaves an unanswered question. By itself, a dependent clause is just a fragment sentence (an incomplete sentence). So, it needs to be combined with an independent clause to be a sentence.
c. Conjunction
A conjunction is a word in a sentence that connects other words, phrases and clauses. Conjunctions are a big part of compound, complex, and compound-complex sentences. The most common conjunction that you know is “and.” Others are for, but, or, yet, and so. Conjunctions are important because they let us combine information, but still keep ideas separate so that they are easy to understand.
Here are two sentences, with and without conjunctions:
Incorrect: The girl ran to the ice cream truck then she ate ice cream.
Correct: The girl ran to the ice cream truck, and then she ate ice cream.
So, you can see that we need a conjunction for the sentence to be clear!
It is important to know that the word “then” is NOT a conjunction—it’s an adverb.
4. Types of Sentence Structures
As mentioned, there are four main types of sentence structures: simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex. To begin, here is a simple chart that outlines the patterns of each type.
a. Simple sentence
A simple sentence has only one subject and one predicate—one independent clause. In fact, an independent clause itself is a simple sentence. Here are some examples:
- She jumped.
- The cheetah ran.
- He ran to the gas station.
- He ate dinner.
Simple sentences don’t have many details and they don’t really combine multiple ideas—they are simple!
b. Compound sentence
A compound sentence has at least two independent clauses. It uses a conjunction like “and” to connect the ideas. Here are some examples:
- The dog ate pizza but the cat drank apple juice.
- The dog ate pizza but the cat drank apple juice and the fish had eggs.
As you can see, a compound sentence allows us to share a lot of information by combining two or more complete thoughts into one sentence.
c. Complex sentence
A complex sentence has one independent clause and one or more dependent clauses. It sometimes uses conjunctions and other words to combine all of the clauses together.
- When he was on the airplane, the man bought cookies.
- When he was on the airplane, the man bought cookies, but not brownies.
A great way to make a sentence more detailed is by adding dependent clauses (which couldn’t be sentences on their own). So, complex sentences let us add information to simple sentences.
d. Compound-complex sentence
A compound-complex sentence has two or more independent clauses and at least one dependent clause—so, it uses conjunction(s) to combine two complete sentences and at least one incomplete sentence. Here is an example:
The girl smelled cookies, which were baking at home, so, she ran all the way there.
The result of combining the three clauses and the conjunction is a compound-complex sentence that is both informational and easy to understand. The independent clauses give the main information, and the dependent clause(s) give the details.
5. How to Avoid Mistakes
When it comes to making sure your sentence is clear and complete, having the right sentence structure is very important. A couple of common mistakes can happen when you forget how to use clauses or conjunctions in the right way, like run-on sentences and fragment sentences.
a. Run-on sentences
In simple terms, a run-on sentence is a sentence that is too long. For instance, if a writer forgets to use conjunctions, a sentence seems like it “runs on” for too long. For example:
The fox really liked pancakes, he ate them every day for breakfast, he couldn’t eat them without syrup and butter.
But, with the right conjunctions, this can be a normal compound sentence:
The fox really liked pancakes, so, he ate them every day for breakfast; but, he couldn’t eat them without syrup and butter.
As you can see, the new sentence is much easier to read and makes more sense.
b. Fragment (incomplete) sentences
A “fragment” is a small piece of something. So, a fragment sentence is just a piece of a sentence: it is missing a subject, a predicate, or an independent clause. It’s simply an incomplete sentence. Fragment sentences can happen when you forget an independent clause.
For instance, by itself, a dependent clause is just a fragment. Let’s use a couple of the dependent clauses from above:
- While he was at the dance What happened?
- If he eats chocolate Then what?
As you can see, each leaves an unanswered question. So, let’s complete them:
- While he was at the dance, the dog drank fruit punch.
- The dog will get a stomachache if he eats chocolate.
Here, we completed the fragment sentences by adding independent clauses (underlined), which made them into complex sentences.
Test your Knowledge
1.
Which type of sentence combines two independent clauses?
a.Compound sentence
b.Simple sentence
c.None of the above
d.All of the above
2.
Which type of sentence can have two or more independent and dependent clauses?
a.Simple sentence
b.Compound-complex sentence
c.Compound sentence
d.None of the above
3.
Add a conjunction or conjunctions to make the following sentence clearer: The dog and the cat loved to eat ice cream, they liked going fishing, searching for clovers.
a.The dog and the cat loved to eat ice cream, they liked going fishing, and searching for clovers.
b.The dog and the cat loved to eat ice cream, so they liked going fishing, searching for clovers.
c.The dog and the cat loved to eat ice cream, and they liked going fishing, searching for clovers.
d.The dog and the cat loved to eat popcorn, and they liked going fishing and searching for clovers.
4.
Add an independent clause to complete the following sentence: If the rabbit goes to the dentist,
a.and
b.and gets a sticker.
c.he will get his teeth cleaned.
d.and his teeth cleaned.