VBA Code to Send Emails From Excel
In VBA, to send emails from Excel, we can automatically automate our mailing feature to send emails to multiple users at a time. However, to do so, we need to remember that we may do it by outlook, another product of outlook, so we need to enable outlook scripting in VBA. Once done, we use the .Application method to use outlook features.
VBA’s versatility is just amazing. VBA coders love Excel because by using VBA, we not only can work within Excel. Rather, we can also access other Microsoft tools. For example, we can access PowerPoint, Word, and Outlook by using VBAMicrosoft Outlook has a VBA reference that can be used to control Outlook. This makes it easy to automate repetitive activities in Outlook. To use VBA in Outlook, you’ll need to enable the developer feature, just like in Excel.read more. So I was impressed when I heard of sending emails from Excel. Yes, it is true. We can send emails from excel. This article will show you how to send emails from Excel with attachments using VBA CodingVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more.
Table of contents
- VBA Code to Send Emails From Excel
- Set Reference to Microsoft Office Library
- 13 Easy Steps to Send Emails from Excel
- Step #1
- Step #2
- Step #3
- Step #4
- Step #5
- Step #6
- Step #7
- Step #8
- Step #9
- Step #10
- Step #11
- Step #12
- Step #13
- Recommended Articles
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA Send Email from Excel (wallstreetmojo.com)
Set Reference to Microsoft Office Library
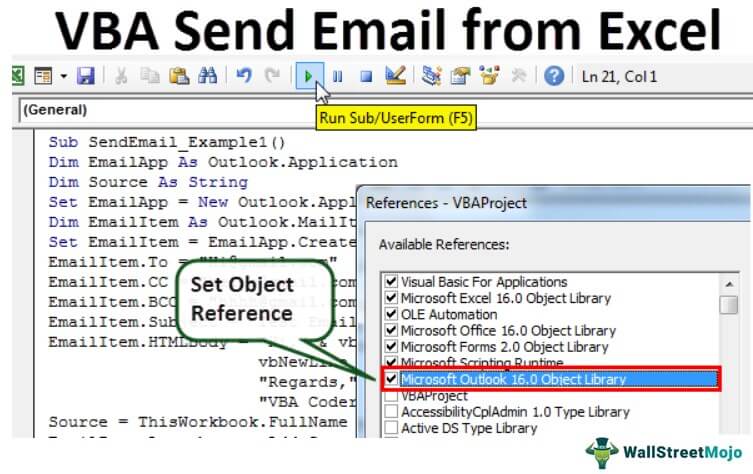
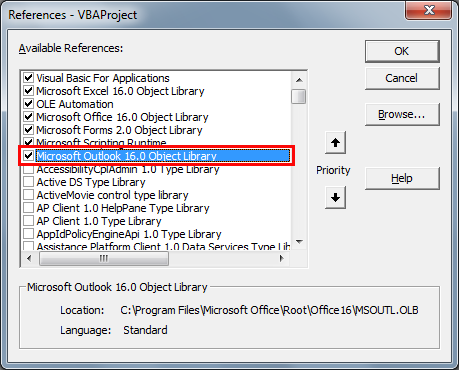
We need to send emails from Outlook. Since Outlook is an external objec, we first need object reference to “Microsoft Outlook 16.0 Object Library.”
- 1. In VBA, Go to Tools > References.
- Now, we will see the object reference library. In this window, we need to set the reference to “Microsoft Outlook 16.0 Object Library.”
- After setting the object reference, click on “OK.”
Now, we can access Outlook objects in VBA coding.
13 Easy Steps to Send Emails from Excel
Writing the code to send an email with an attachment from Excel is quite complicated but worth spending some time.
You can download this VBA Send Email Excel Template here – VBA Send Email Excel Template
Follow the below steps to write your first email excel macroA macro in excel is a series of instructions in the form of code that helps automate manual tasks, thereby saving time. Excel executes those instructions in a step-by-step manner on the given data. For example, it can be used to automate repetitive tasks such as summation, cell formatting, information copying, etc. thereby rapidly replacing repetitious operations with a few clicks.
read more.
Step #1
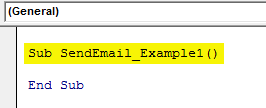
Start the sub procedure in VBASUB in VBA is a procedure which contains all the code which automatically gives the statement of end sub and the middle portion is used for coding. Sub statement can be both public and private and the name of the subprocedure is mandatory in VBA.read more.
Code:
Sub SendEmail_Example1() End Sub
Step #2
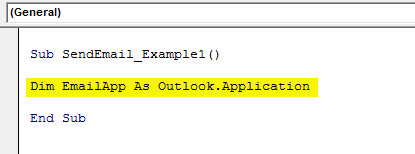
Declare the variable Outlook.Application
Code:
Dim EmailApp As Outlook.Application 'To refer to outlook application
Step #3
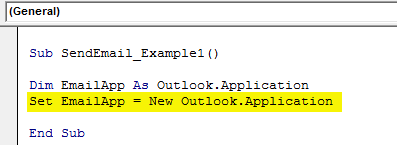
The above variable is an object variable. Therefore, we need to create an instance of a new object separately. Below is the code to create a new instance of the external object.
Code:
Set EmailApp = New Outlook.Application 'To launch outlook application
Step #4
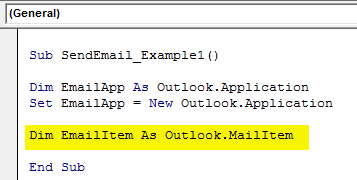
Now, to write the email, we declare one more variable as “Outlook.MailItem”.
Code:
Dim EmailItem As Outlook.MailItem 'To refer new outlook email
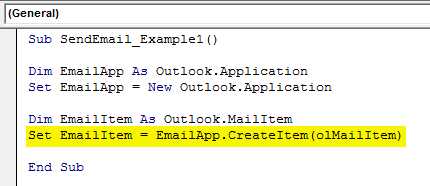
Step #5
To launch a new email, we need to set the reference to our previous variable as “CreateItem.”
Code:
Set EmailItem = EmailApp.CreateItem(olMailItem) 'To launch new outlook email
Now, the variable “EmailApp” will launch outlook. In the variable “EmailItem,” we can start writing the email.
Step #6
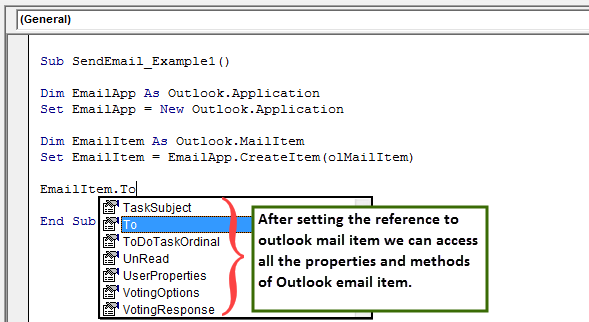
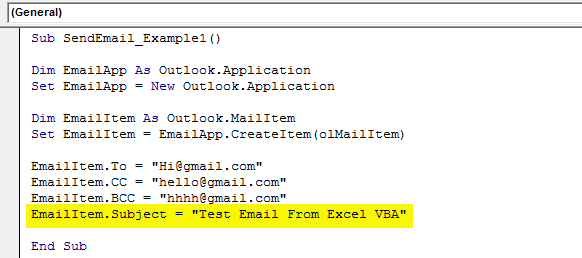
We need to be aware of our items while writing an email. First, we need to decide to whom we are sending the email. So for this, we need to access the “TO” property.
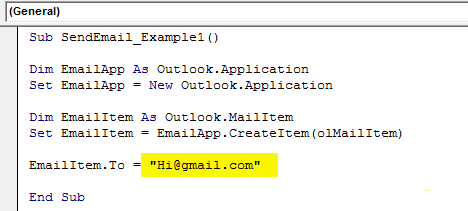
Step #7
Enter the email ID of the receiver in double quotes.
Code:
EmailItem.To = "[email protected]"
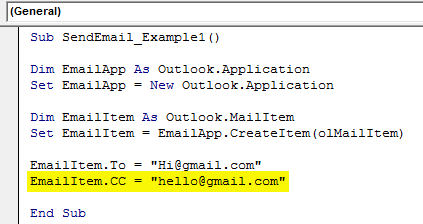
Step #8
After addressing the main receiver, if you would like to CC anyone in the email, we can use the “CC” property.
Code:
EmailItem.CC = "[email protected]"
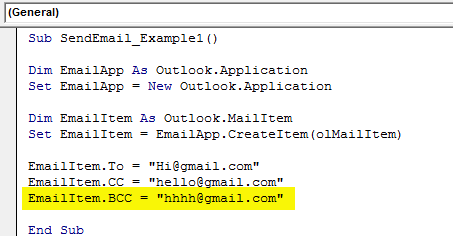
Step #9
After the CC, we can set the BCC email ID as well.
Code:
EmailItem.BCC = "[email protected]"
Step #10
We need to include the subject of the email we are sending.
Code:
EmailItem.Subject = "Test Email From Excel VBA"
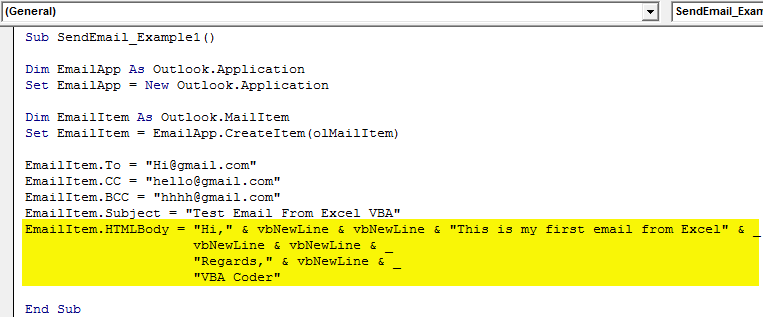
Step #11
We need to write the email body using HTML body type.
Code:
EmailItem.HTMLBody = "Hi," & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & "This is my first email from Excel" & _
vbNewLine & vbNewLine & _
"Regards," & vbNewLine & _
"VBA Coder" 'VbNewLine is the VBA Constant to insert a new line
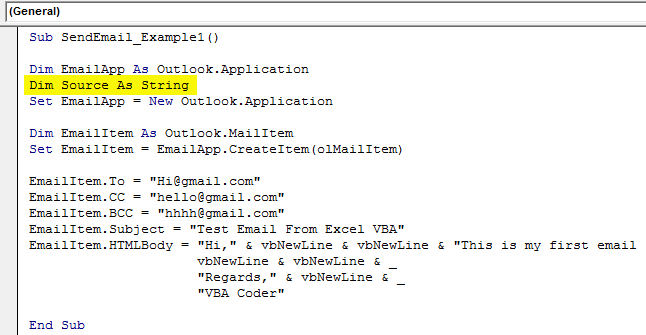
Step #12
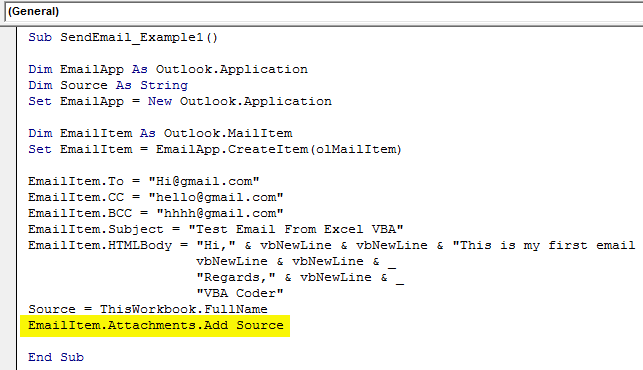
We are working on if we want to add an attachment to the current workbook. Then, we need to use the attachments property. First, declare a variable source as a string.
Code:
Dim Source As String
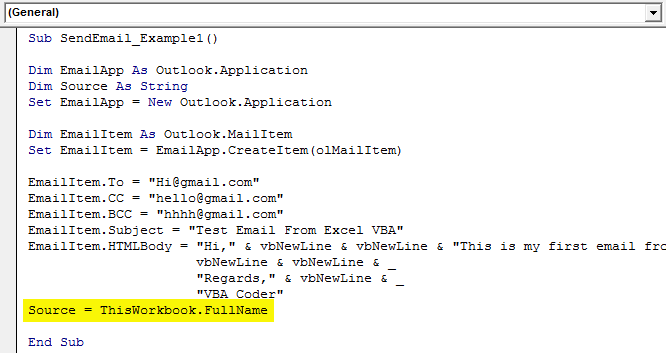
Then in this variable, write ThisWorkbook.FullName after Email body.
Code:
Source = ThisWorkbook.FullName
In this VBA Code, ThisWorkbook is used for the current workbook and .FullName is used to get the full name of the worksheet.
Then, write the following code to attach the file.
Code:
EmailItem.Attachments.Add Source
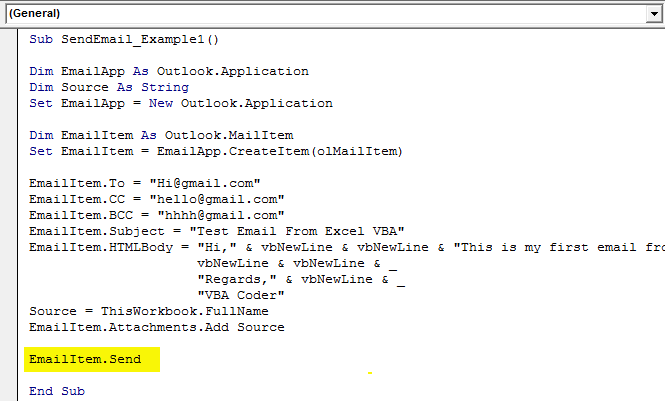
Step #13
Finally, we need to send the email to the mentioned email IDs. We can do this by using the “Send” method.
Code:
EmailItem.Send
We have completed the coding part.
Code:
Sub SendEmail_Example1() Dim EmailApp As Outlook.Application Dim Source As String Set EmailApp = New Outlook.Application Dim EmailItem As Outlook.MailItem Set EmailItem = EmailApp.CreateItem(olMailItem) EmailItem.To = "[email protected]" EmailItem.CC = "[email protected]" EmailItem.BCC = "[email protected]" EmailItem.Subject = "Test Email From Excel VBA" EmailItem.HTMLBody = "Hi," & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & "This is my first email from Excel" & _ vbNewLine & vbNewLine & _ "Regards," & vbNewLine & _ "VBA Coder" Source = ThisWorkbook.FullName EmailItem.Attachments.Add Source EmailItem.Send End Sub
Run the above code. It will send the email with the mentioned body with the current workbook as the attachment.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA Send Email from Excel. Here, we learn how to write VBA code to send emails from Excel with attachments along with an example and downloadable Excel template. You can learn more about VBA from the following articles: –
- VBA TimeValue Function
- Dictionary in VBA
- Create Progress Bar in VBA
- GetOpenFilename VBA
Excel позволяет создавать диаграммы высокого качества, работать с огромным количеством данных, обрабатывать картинки, блок-схемы и многое другое. И даже если вам и этого не достаточно, можно использовать Excel для автоматической отправки писем с помощью встроенного VBA редактора.
Данная статья описывает три способа отправки писем с помощью VBA в Excel. Вы можете скачать файл с примером отправки email с помощью VBA в Excel.
Отправить письмо в Excel с помощью VBA
Один из самых простых способов для автоматизации отправки почты с Excel заключается в вызове функции Create («ObjectOutlook.Application»). Данная функция возвращающает ссылку на ActiveX объект (в данном случает приложение Outlook), которое затем используется для создания и отправки электронной почты.
Чтобы проверить данный способ в работе, скопируйте и вставьте код ниже в VB редактор.
|
1 |
Sub Send_Email_Using_VBA() |
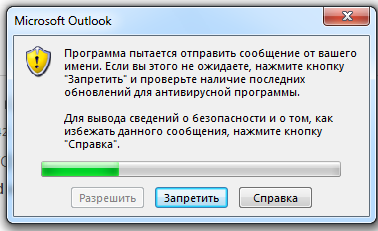
В качестве напоминания: Когда вы пытаетесь отправить письмо вышеуказанным способом, система безопасности будет выдавать каждый раз предупреждающее окно, в котором будет говориться о том, что Программа пытается отправить сообщение от вашего имени… и возможности обойти этот шаг нет.
К счастью, существует еще два способа, с помощью которых данный вопрос может быть решен: первый – через использование CDO, второй – имитирующий использование событий нажатий клавиш клавиатуры.
Отправить письмо в Excel с помощью CDO
Что такое CDO? CDO является библиотекой объектов, которая предоставляет интерфейс Messaging Application Programming Interface (MAPI). CDO позволяет манипулировать обменом данных, и отправлять и получать сообщения.
Использование CDO может быть предпочтительно в случаях, когда вы хотите предотвратить появление вплывающих окон безопасности Программа пытается отправить сообщение от вашего имени… и следовательно, предотвратить задержку отправки сообщения.
В нашем примере мы используем функцию CreateObject («CDO.Message»). Важно отметить, что необходимо правильно установить конфигурацию SMTP сервера, чтобы не допустить появления ошибок Run-time error 2147220973(80040213) или sendUsing configuration value is invalid. Пример ниже настроен на отправку сообщений через почту Google (Gmail). Для других почтовых серверов, вам потребуется ввести свои значения SMTP-сервера и SMTP-порта.
|
1 |
Sub CDO_Mail_Small_Text_2() |
Обратите внимание, чтобы воспользоваться данным методом вам необходимо подключить библиотеку CDO в редакторе макросов Tool –> References.
Отправить письмо в Excel с помощью Send Keys
Другой способ отправки email с помощью Excel – использование команды ShellExecute, которая выполняет любую программу в VBA. Команда ShellExecute используется для загрузки документа с соответствующей программой. По сути, вы создаете объект String (текстовые данные) и передаете его в качестве параметра для функции ShellExecute. Остальная часть операций выполняется в окнах. Автоматически определяется, какая программа связана с данным типом документа и используется для загрузки документа. Вы можете использовать функцию ShellExecute, чтобы открыть Internet Explorer, Word, Paint и множество других приложений. В коде ниже используется задержка в три секунды, чтобы убедиться, что отправляемое письмо корректно и для возможности предотвратить отправку, если вы вдруг нашли какие-нибудь недочеты.
|
1 |
Sub Send_Email_Using_Keys() |
Cкачать файл с примером отправки email с помощью VBA в Excel
This tutorial introduces how to send email from Excel using VBA and VBScript.
It also demonstrates SSL, HTML Email, Email Queue and Exchange Web Service (EWS) usage.
Sections:
- Send email from MS Excel using VBA and SMTP protocol
- Common SMTP Transport Error
- TLS 1.2
- Where can I get my SMTP email server address, user and password?
- Gmail, Hotmail, Outlook.COM, Office365 and Yahoo SMTP Server Settings
- Email Address Syntax and Multiple Recipients
- From, ReplyTo, Sender and Return-Path
- Mail Priority
- Troubleshooting
- 32bit/x64 ActiveX DLL
- Distribution
Send email from MS Excel using VBA and SMTP protocol¶
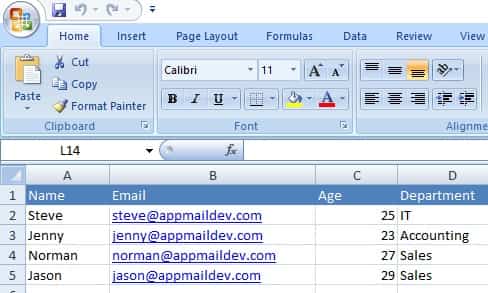
To better demonstrate how to send email using SMTP protocol in Excel + VBA, let’s open MS Excel and input the data like this:
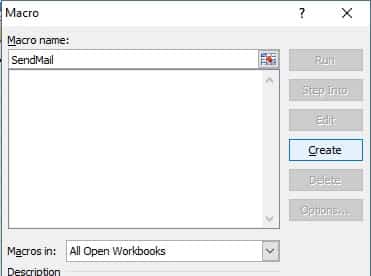
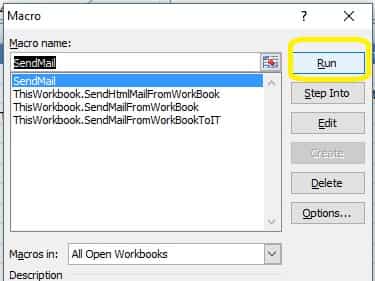
After you input the data, press Alt+F8, open the Macro dialog box, input SendMail and click Create
Input the following codes in Module1
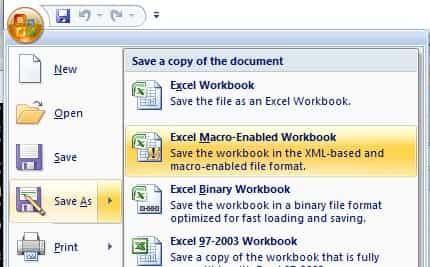
Then you can close the VBA IDE and back to Excel and click File -> Save As -> select Excel Macro Enabled Workbook and save it as Sample.xlsm.
Installation¶
EASendMail is a SMTP component which supports all operations of SMTP/ESMTP protocols
(RFC 821, RFC 822, RFC 2554). Before you can use the following example codes,
you should download the EASendMail Installer and install it on your machine at first.
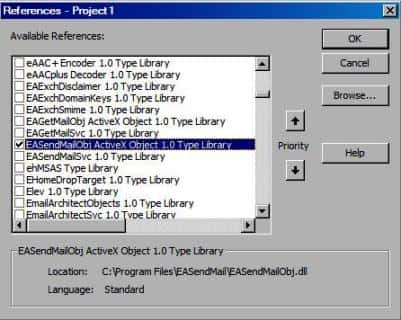
Add Reference¶
To use EASendMail SMTP ActiveX Object in VBA project, the first step is “Add reference
of EASendMail to your project”. Open VBA IDE by press Alt+F11, Please select menu -> Tools -> References ->
and select EASendMailObj ActiveX Object, click OK, the reference will be added
to current VBA project, and you can start to use it to send email in your project.
[Excel + VBA — Send Email — Example]¶
After the reference is added, click ThisWorkBook and input the following codes:
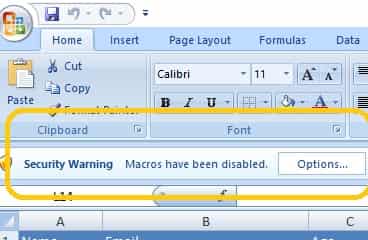
Please enable Macro if you closed and re-opened this file, otherwise the codes cannot be executed.
Important
You need to access the Trust Center in the Excel Options dialog box. Click the Microsoft Office Button, and then click Excel Options.
In the Trust Center category, click Trust Center Settings, and then click the Macro Settings category.
' To use the following codes, please download and install ' https://www.emailarchitect.net/webapp/download/easendmail.exe on your machine Option Explicit Private WithEvents oSmtp As EASendMailObjLib.Mail Private CurrentEmailIsFinished As Boolean Private HasErrorWithEmail As Boolean Private ErrorDescription As String Private Sub InitVariables() CurrentEmailIsFinished = True HasErrorWithEmail = False ErrorDescription = "" End Sub Private Sub oSmtp_OnAuthenticated() Application.StatusBar = "Authenticated" End Sub Private Sub oSmtp_OnClosed() CurrentEmailIsFinished = True End Sub Private Sub oSmtp_OnConnected() Application.StatusBar = "Connected" End Sub Private Sub oSmtp_OnError(ByVal lError As Long, ByVal ErrDescription As String) HasErrorWithEmail = True CurrentEmailIsFinished = True ErrorDescription = ErrDescription End Sub Private Sub oSmtp_OnSending(ByVal lSent As Long, ByVal lTotal As Long) Application.StatusBar = "Sending " & lSent & "/" & lTotal & " ..." End Sub Public Sub SendMailFromWorkBook() Dim oSheet Set oSheet = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(1) Dim i, rows rows = oSheet.UsedRange.rows.Count Dim sender, name, address, subject, bodyTemplate, body, bodyFormat bodyFormat = 0 'Text body format ' Please change sender address to yours sender = "test@emailarchitect.net" subject = "Test email from Excel and VBA" ' Use a body template to build body text based on recipient's name bodyTemplate = "Dear {name}," & Chr(13) & Chr(10) & Chr(13) & Chr(10) & _ "This is a test email from Excel using VBA, do not reply." Dim emailSent emailSent = 0 ' enumerate all email addresses in sheet1 For i = 2 To rows name = Trim(oSheet.Cells(i, 1)) address = Trim(oSheet.Cells(i, 2)) body = Replace(bodyTemplate, "{name}", name) If Not SendMailTo(sender, name, address, subject, body, bodyFormat) Then Exit Sub End If emailSent = emailSent + 1 Next Application.StatusBar = "Total " & emailSent & " email(s) sent." End Sub Function SendMailTo(sender, name, address, subject, body, bodyFormat) Set oSmtp = New EASendMailObjLib.Mail oSmtp.LicenseCode = "TryIt" ' Please change server address, user, password to yours oSmtp.ServerAddr = "mail.emailarchitect.net" oSmtp.UserName = "test@emailarchitect.net" oSmtp.Password = "yourpassword" ' Set server port, if 25 port doesn't work, try to use 587 port oSmtp.ServerPort = 25 ' Using TryTLS, ' If smtp server supports TLS, then TLS connection is used; otherwise, normal TCP connection is used. ' https://www.emailarchitect.net/easendmail/sdk/?ct=connecttype oSmtp.ConnectType = 4 ' If your server is Exchange 2007 or later version, you can use EWS protocol. ' https://www.emailarchitect.net/easendmail/sdk/?ct=protocol ' Set Exchange Web Service Protocol - EWS - Exchange 2007/2010/2013/2016 ' oSmtp.Protocol = 1 oSmtp.FromAddr = sender oSmtp.AddRecipient name, address, 0 oSmtp.subject = subject oSmtp.bodyFormat = bodyFormat oSmtp.BodyText = body ' You can add attachment like this: ' Add attachment from local disk ' If oSmtp.AddAttachment("d:test.jpg") <> 0 Then ' Application.StatusBar = "Failed to add attachment with error:" & oSmtp.GetLastErrDescription() ' SendMailTo = False ' Exit Function 'End If Application.DisplayStatusBar = True Application.StatusBar = "Connecting " & oSmtp.ServerAddr & " ..." oSmtp.Asynchronous = 1 InitVariables CurrentEmailIsFinished = False oSmtp.SendMail Do While Not CurrentEmailIsFinished ' Wait for the email sending, you can do other thing here DoEvents Loop If HasErrorWithEmail Then Application.StatusBar = "Failed to send email to " & address & "; " & ErrorDescription SendMailTo = False Else Application.StatusBar = "Message to " & address & " has been submitted to server." SendMailTo = True End If Set oSmtp = Nothing End Function
and click Module1 and change the codes to:
ThisWorkbook.SendMailFromWorkBook
Close VBA IDE and back to Excel, press Alt+F8 to open Macro dialog box, select SendMail and click Run.
You will see the status and result at Excel status bar.
Common SMTP Transport Error¶
When you execute above example code, if it returned an error about “Networking connection/Socket”
or “No such host”, it is likely that your SMTP server address is not correct.
If it threw an exception about “5xx Relay denied”, it is likely that you did not
set user authentication. Another common error is “5xx Must issue a STARTTLS command
first” or “No supported authentication marshal found!”, that is because
your SMTP server requires user authentication under SSL connection. You can set
the SSL connection to solve this problem. You can learn more detail in Troubleshooting section.
TLS 1.2¶
TLS is the successor of SSL, more and more SMTP servers require TLS 1.2 encryption now.
If your operating system is Windows XP/Vista/Windows 7/Windows 2003/2008/2008 R2/2012/2012 R2,
and you got connection error with SSL/TLS connection,
you need to enable TLS 1.2 protocol in your operating system like this:
Enable TLS 1.2 on Windows XP/Vista/7/10/Windows 2008/2008 R2/2012
Where can I get my SMTP email server address, user and password?¶
Because each email account provider has different server address, so you should
query your SMTP server address from your email account provider. To prevent spreading
email from the server, most SMTP servers also require user authentication. User
name is your email address or your email address without domain part, it depends
on your email provider setting.
Finally, if you have already set your account in your email client such as Outlook
or Window Mail, you can query your SMTP server address, user in your email client.
For example, you can choose menu -> “Tools” — > — “Accounts” — > “Your email
account” — > “Properties” — > “Servers” in Outlook express or Windows Mail
to get your SMTP server, user. Using EASendMail to send email does not require you
have email client installed on your machine or MAPI, however you can query your
exist email accounts in your email client.
Email Address Syntax and Multiple Recipients¶
The following example codes demonstrates how to specify display name and email address by different syntax.
' For single email address (From, ReplyTo, ReturnPath), the syntax can be: ' ["][display name]["]<email address>. ' For example: "Tester, T" <test@adminsystem.com> Tester <test@adminsystem.com> <test@adminsystem.com> test@adminsystem.com ' For mulitple email address (To, CC, Bcc), the syntax can be: ' [single email],[single email]... ' (,;rn) can be used to separate multiple email addresses. ' For example: "Tester, T" <test1@adminsystem.com>, Tester2 <test2@adminsystem.com>, <test3@adminsystem.com>, test4@adminsystem.com
[VBA — Email Syntax — Example]¶
Here are some examples:
oSmtp.FromAddr = "Tester<test@adminsystem.com>" oSmtp.FromAddr = "test@adminsystem.com" oSmtp.FromAddr = "<test@adminsystem.com>" ' Using AddRecipientEx to add To, Cc and Bcc in VB 6.0/Visual Basic 6.0 ' Multiple addresses are separated with (,) ' The syntax is like this: "test@adminsystem.com, test1@adminsystem.com" oSmtp.AddRecipientEx "test1@adminsystem.com, test2@adminsystem.com", 0 oSmtp.AddRecipientEx "Test1<test@adminsystem.com>, Test2<test2@adminsystem.com>", 0 ' You can also add carbon copy (CC) or blind carbon copy (BCC) in the email. oSmtp.AddRecipientEx "CC recipient<cc@adminsystem.com>", 1 oSmtp.AddRecipientEx "Bcc recipient<bcc@adminsystem.com>", 2
From, ReplyTo, Sender and Return-Path¶
From, Reply-To, Sender and Return-Path are common email headers in email message.
You should always set From property at first, it is a MUST to identify the email sender.
The following table lists the header and corresponding properties:
| Header | Property |
| From | Mail.FromAddr |
| Reply-To | Mail.ReplyTo |
| Sender | Mail.Sender |
| Return-Path | Mail.ReturnPath |
-
From
This property indicates the original email sender. This is what you see as the “FROM” in most mail clients.
-
Reply-To
This property indicates the reply address. Basically, when the user clicks “reply” in mail client, the Reply-To value should be used as the recpient address of the replied email. If you don’t set this property, the Reply address is same as From address.
-
Sender
This property indicates the who submit/send the email. When the user received the email, the email client displays:
From: “sender address” on behalf of “from address”.
If you don’t set this property, the Sender address is same as From address. Sender property is common used by mail listing provider. This property also takes effect to DKIM/DomainKeys signature, if Sender is different with From address, then you should sign DKIM/DomainKeys based on Sender domain instead of From address domain. -
Return-Path
This property indicates the delivery notification report address. If you don’t set this property, the Return-Path address is same as From address. This property also takes effect to SPF record, if Return-Path is different with From address, then remote SMTP server checkes SPF record of Return-Path instead of From address.
[VBA — From, ReplyTo, Sender and Return-Path in Email — Example]¶
The following example codes demonstrate how to specify From, Reply-To, Sender and Return-Path in Email. With the following example codes:
- If the email couldn’t be delivered to recipient, a non-delivery report will be sent
toreport@emailarchitect.net. - If the user received the email, the email client will display:
sender@emailarchitect.net
on behalf offrom@adminsystem.com. - If the user click “reply”, the replied email will be sent to
reply@adminsystem.com.
' [VB, VBA - From, ReplyTo, Sender and Return-Path] Dim oSmtp As New EASendMailObjLib.Mail oSmtp.LicenseCode = "TryIt" oSmtp.FromAddr = "from@adminsystem.com" oSmtp.ReplyTo = "reply@adminsystem.com" oSmtp.Sender = "sender@emailarchitect.net" oSmtp.ReturnPath = "report@emailarchitect.net" '[VBScript, ASP - From, ReplyTo, Sender and Return-Path] Dim oSmtp Set oSmtp = Server.CreateObject("EASendMailObj.Mail") oSmtp.LicenseCode = "TryIt" oSmtp.FromAddr = "from@adminsystem.com" oSmtp.ReplyTo = "reply@adminsystem.com" oSmtp.Sender = "sender@emailarchitect.net" oSmtp.ReturnPath = "report@emailarchitect.net"
Mail Priority¶
If you want to set Higher or Lower priority to your email, you can use Priority prority
' Set high priority oSmtp.Priority = 1 'High priority
Troubleshooting¶
When you send email in above simple VB project, if it returned an error, please have a look at the following tips:
“No Such Host” Error¶
This error means DNS server cannot resolve SMTP server, you should check if you input correct server address. If your server address is correct, you should check if your DNS server setting is correct.
Common “Socket/Networking Connection” Error¶
This error means there is a problem with networking connection to SMTP server. You can use Windows built-in Telnet command to detect the networking connection.
Using Telnet to detect networking connection to SMTP server¶
Note
Notice: in Windows 2008/Windows 8 or later version, Telnet Client is not installed
by default, you should enable this command in Control Panel -> Programs and ->
FeaturesTurn Windows feature on or off -> have Telnet Client checked.
Under DOS command prompt, input “telnet [serveraddress] [port]”:
telnet mail.emailarchitect.net 25 press enter.
If the networking connection to your SMTP server is good, it should return a message
like 220 .... If it returns Could not open connection to ..., that means the
networking connection to SMTP server is bad, or outbound 25 port is blocked by anti-virus
software, firewall or ISP. Please have a look at the following screenshot:
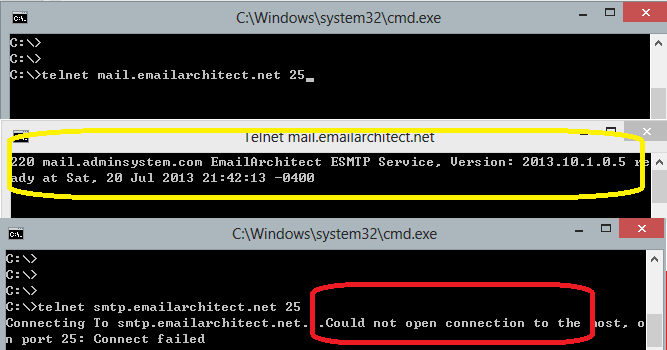
SMTP 25, 587, 465 port¶
25 port is the default SMTP server port to receive email. However, some ISP block outbound 25 port to prevent user to send email directly to other SMTP server. Therefore, many email providers also provide an alternative port 587 to receive email from such users. 465 port is the common port used to receive email over implicit SSL connection. If you use telnet to test 465 port, it doesn’t return the “220…”, because it requires SSL hand shake. But if the connection is ok, telnet returns a flash cursor.
“5xx … IP address block or on black list or bad reputation” Exception¶
This error means SMTP server blocks your IP address or email content. You can try to set user/password in your codes to do user authentication and try it again. If email client set user authentication, most SMTP servers do not check client source IP address in black list.
“5xx user authenticaton” Error¶
TThis error means user authentication is failed, you should check whether you input correct user/password. Password is always case-sensitive.
“5xx relay denied” Error¶
For anti-spam policy, most SMTP servers do not accept the email to outbound domain without user authentication. You should set user/password in the codes and try it again.
“5xx Must issue a STARTTLS command first”¶
This error means SMTP server requires SSL/TLS connection. You should enable SSL/TLS connection like this:
' If your smtp server requires TLS connection, please add this line oSmtp.ConnectType = 1
“No supported authentication marshal found!”¶
This error means SMTP server doesn’t support user authentication or it requires user authentication over SSL/TLS connection. You can try to remove user/password in your codes and try it again.
Other error returned by SMTP server¶
If SMTP server returns an error, it usually returns description about this error. Some descriptions also include a HTTP link, you can go to this linked web page to learn more detail. You can also use the following codes to generate a log file to learn all SMTP session between client and server.
[VBA — Using log file to detect SMTP server response — Example]
oSmtp.LogFileName = "d:smtp.txt"
32bit/x64 ActiveX DLL¶
Seperate builds of run-time dll for 32 and x64 platform
| File | Platform |
| Installation PathLibnativex86EASendMailObj.dll | 32 bit |
| Installation PathLibnativex64EASendMailObj.dll | 64 bit |
Distribution¶
-
Standard EXE
For VB6, C++, Delphi or other standard exe application, you can distribute EASendMailObj.dll with your application to target machine without COM-registration and installer.
To learn more detail, please have a look at Registration-free COM with Manifest File. -
Script
For ASP, VBScript, VBA, MS SQL Stored Procedure, you need to install EASendMail on target machine by EASendMail installer, both 32bit/x64 DLL are installed and registered.
Next Section
In this section, I introduced how to send text email in Excel VBA project using SMTP protocol.
At next section I will introduce how to send HTML email to specified recipients based on Excel data.
To send emails from Microsoft Excel only requires a few simple scripts. Add this functionality to your spreadsheets, and you can accomplish much more in Excel.
Excel macros can do many of the same things VBA scripts can, without the need for as much programming knowledge. VBA lets you implement more advanced routines, like creating a spreadsheet report with all of your PC information.
Prefer to watch this tutorial as a video? We’ve got you covered!
Why Send Email From Excel?
There are a lot of reasons why you might want to send an email from inside Microsoft Excel.
Maybe you have staff who update documents or spreadsheets every week, and you’d like to receive an email notification when they do. Or you might have a spreadsheet of contacts, and you want to send one email to all of them at once.
You’re probably thinking that scripting an email broadcast from Excel is going to be complicated. That’s not the case at all. The technique in this article makes use of a feature that’s been available in Excel VBA for a long time, Collaboration Data Objects (CDO).
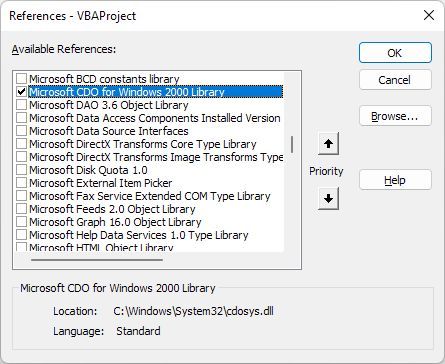
CDO is a messaging component used in Windows since very early generations of the OS. It used to be called CDONTS, and then with the advent of Windows 2000 and XP, was replaced with «CDO for Windows 2000.» This component is already included in your VBA installation within Microsoft Word or Excel and is ready for use.
Using the component makes sending emails from within Windows products with VBA extremely easy. In this example, you’ll use the CDO component in Excel to send out an email that will deliver the results from a specific Excel cell.
Step 1: Prepare Your Gmail Account
To send email from Microsoft Excel, we’ll be using Gmail, though you can customize the macro below to work with other email clients. Note that Gmail no longer permits third-party app access, meaning you’ll first have to enable Gmail’s 2-step authentication.
From your Google account’s Security page, under Signing in to Google, click App passwords. On the App passwords screen, find the Select app drop-down menu and select Mail. From Select device, select Windows Computer. Then click GENERATE.
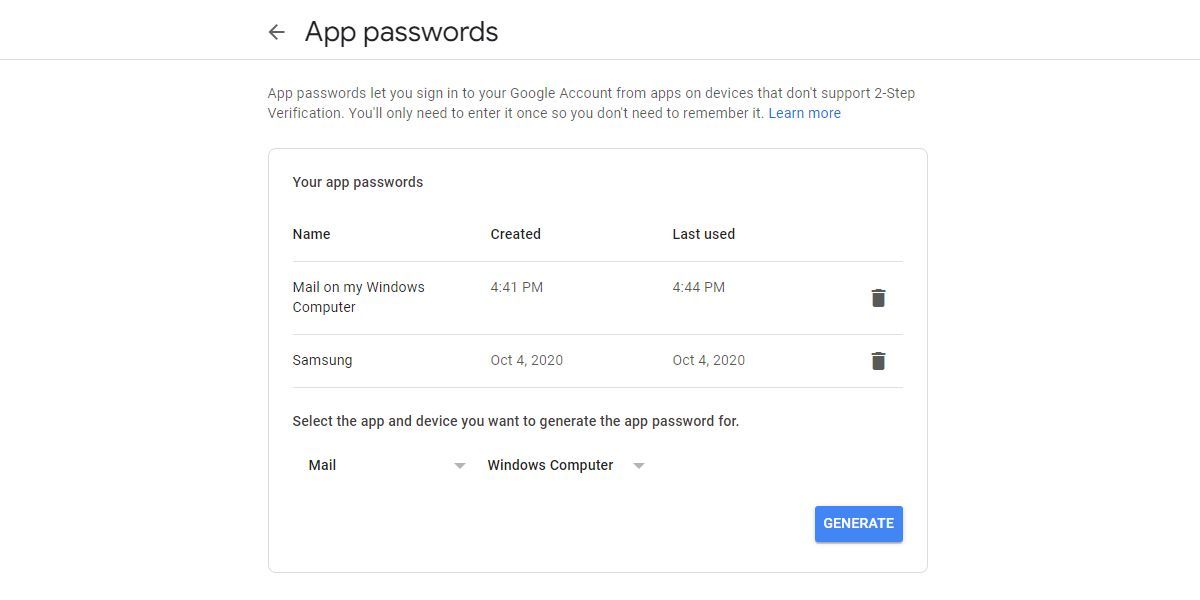
Jot down the 16-character app password; you’ll need it when you configure the macro.
Step 2: Create a VBA Macro
Tip: Before you start, save the Excel file you’ll be working with as a Macro-Enabled Workbook, i.e. in the XLSM format.
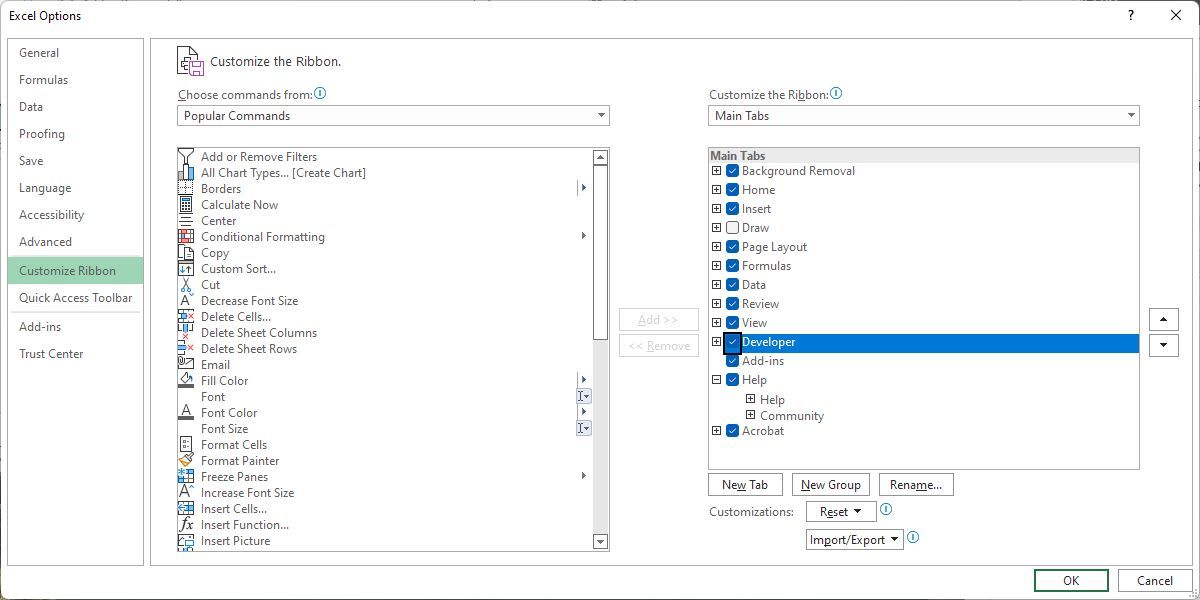
First, we’ll need the Excel Developer tab. If you don’t see it, here’s how to enable it:
- Go to File > Options.
- Under Customize the Ribbon > Main Tabs, check the Developer option.
- Click OK to save your changes.
Inside Excel’s Developer tab, click on Insert in the Controls box, and then select a command button.
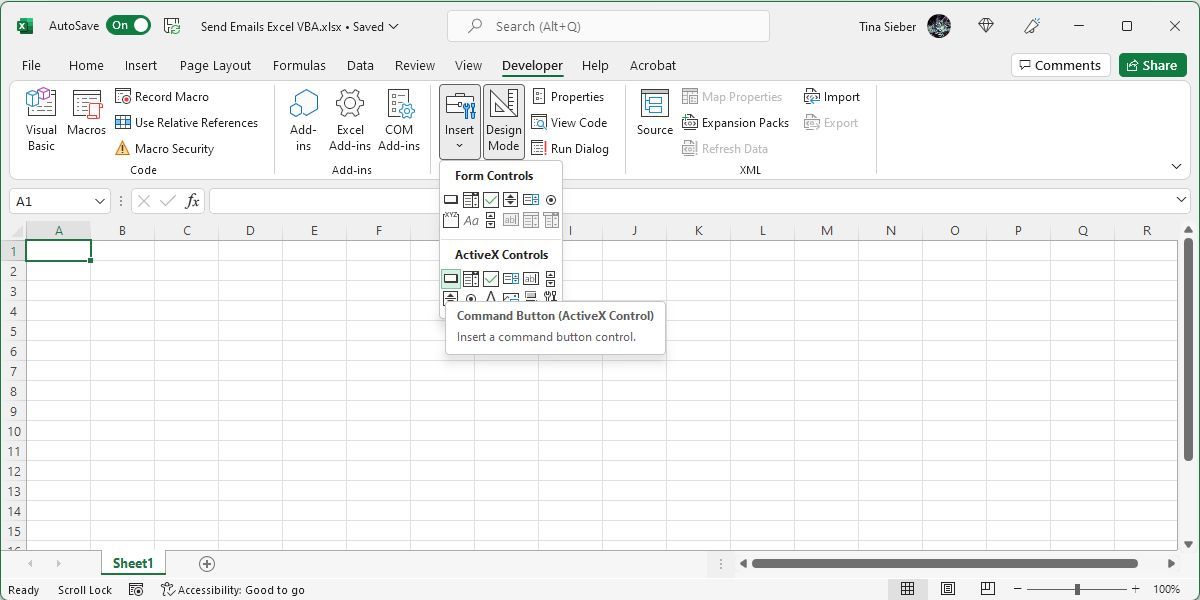
Draw it into the sheet and then create a new macro for it by clicking on Macros in the Developer ribbon.
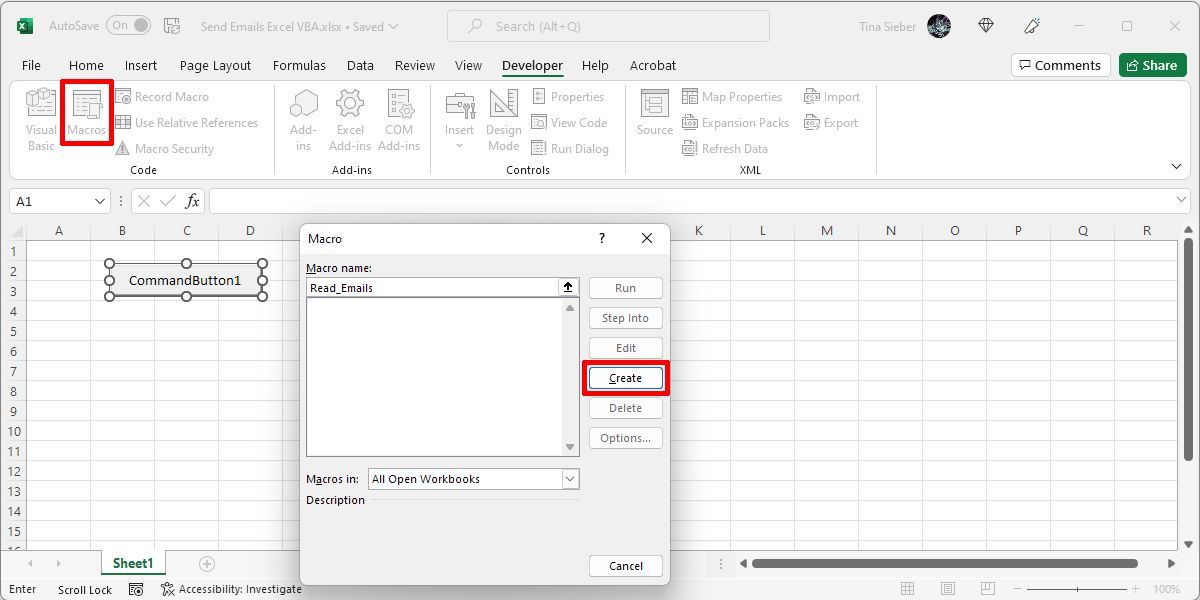
When you click the Create button, it’ll open the VBA editor.
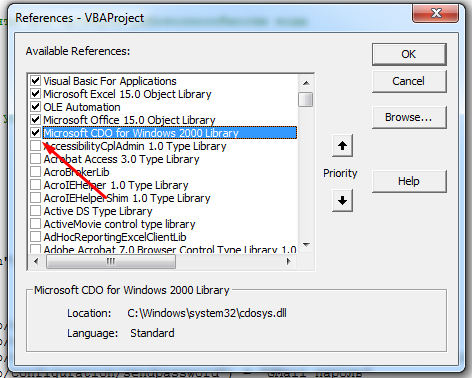
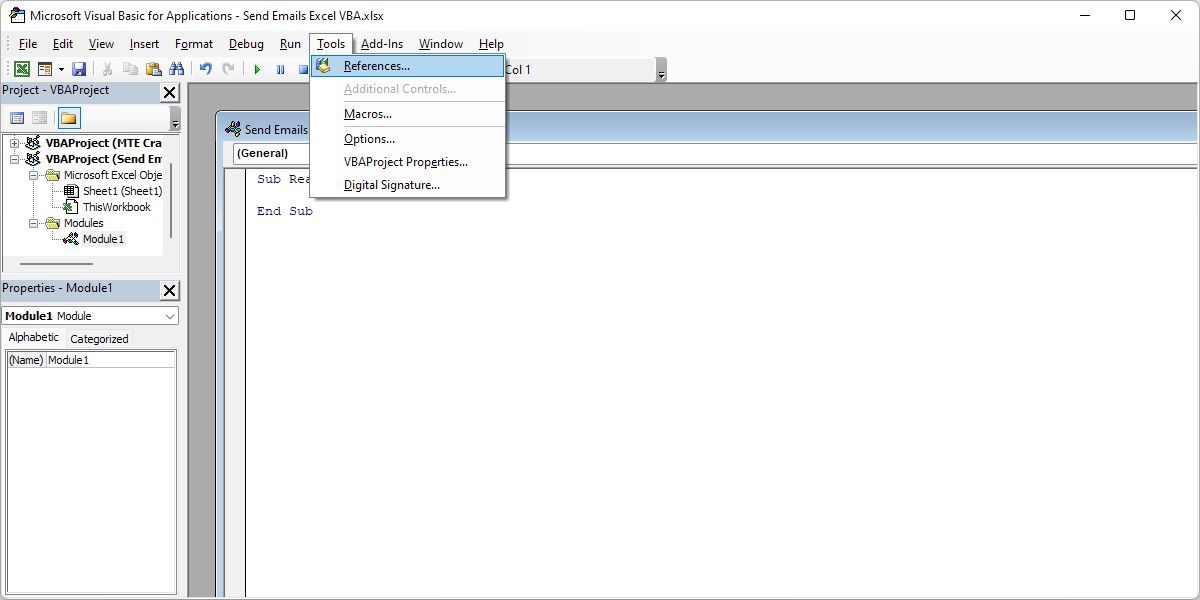
Add the reference to the CDO library by navigating to Tools > References in the editor.
Scroll down the list until you find Microsoft CDO for Windows 2000 Library. Mark the checkbox and click OK.
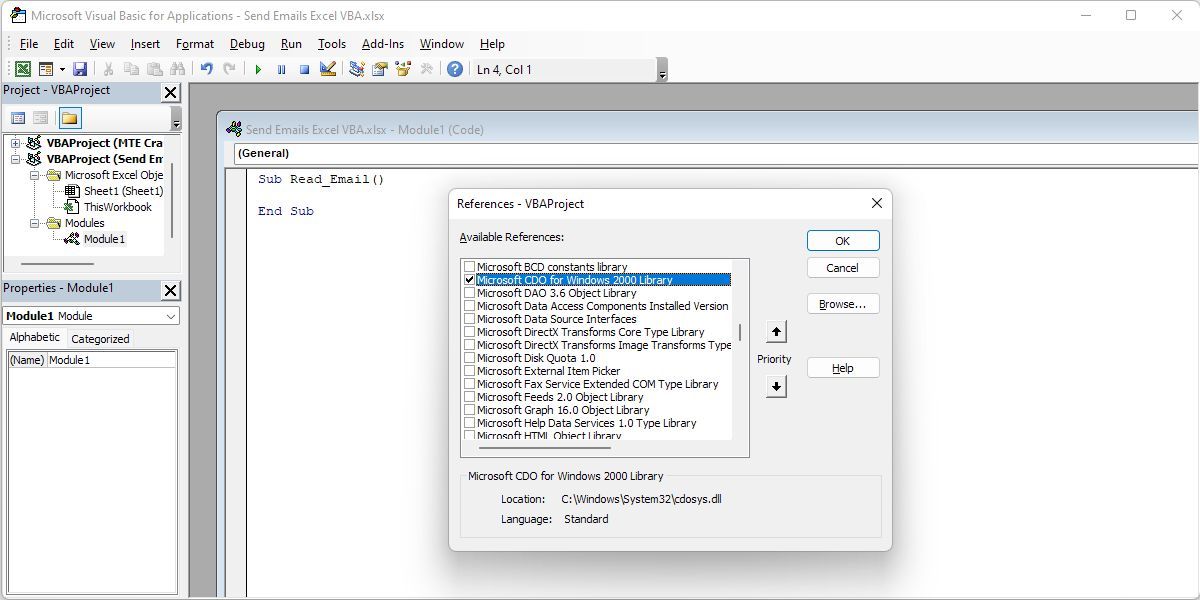
When you click OK, make note of the name of the function where you’re pasting the script. You’ll need it later.
Step 3: Configure Your Macro
Now you’re ready to create the mail objects and set up all the fields necessary to send an email. Keep in mind that while many of the fields are optional, the From and To fields are required. Paste all the code snippets below into your Module1 (Code) window.
This is what the complete code looks like:
Sub Send_Emails()
Dim NewMail As CDO.Message
Dim mailConfig As CDO.Configuration
Dim fields As Variant
Dim msConfigURL As String
On Error GoTo Err: 'early binding
Set NewMail = New CDO.Message
Set mailConfig = New CDO.Configuration
'load all default configurations
mailConfig.Load -1
Set fields = mailConfig.fields
'Set All Email Properties
With NewMail
.From = "username@gmail.com"
.To = "username@gmail.com"
.CC = ""
.BCC = ""
.Subject = "Send Email From an Excel Spreadsheet"
.TextBody = "This is the body of your email. And here is some added data:" & Str(Sheet1.Cells(2, 1))
.Addattachment "c:dataemail.xlsx" 'Optional file attachment; remove if not needed.
.Addattachment "c:dataemail.pdf" 'Duplicate the line for a second attachment.
End With
msConfigURL = "http://schemas.microsoft.com/cdo/configuration"
With fields
.Item(msConfigURL & "/smtpusessl") = True 'Enable SSL Authentication
.Item(msConfigURL & "/smtpauthenticate") = 1 'SMTP authentication Enabled
.Item(msConfigURL & "/smtpserver") = "smtp.gmail.com" 'Set the SMTP server details
.Item(msConfigURL & "/smtpserverport") = 465 'Set the SMTP port Details
.Item(msConfigURL & "/sendusing") = 2 'Send using default setting
.Item(msConfigURL & "/sendusername") = "username@gmail.com" 'Your gmail address
.Item(msConfigURL & "/sendpassword") = "password" 'Your password or App Password
.Update 'Update the configuration fields
End With
NewMail.Configuration = mailConfig
NewMail.Send
MsgBox "Your email has been sent", vbInformation
Exit_Err:
'Release object memory
Set NewMail = Nothing
Set mailConfig = Nothing
End
Err:
Select Case Err.Number
Case -2147220973 'Could be because of Internet Connection
MsgBox "Check your internet connection." & vbNewLine & Err.Number & ": " & Err.Description
Case -2147220975 'Incorrect credentials User ID or password
MsgBox "Check your login credentials and try again." & vbNewLine & Err.Number & ": " & Err.Description
Case Else 'Report other errors
MsgBox "Error encountered while sending email." & vbNewLine & Err.Number & ": " & Err.Description
End Select
Resume Exit_Err
End Sub
And these are the sections and fields you need to customize:
- With NewMail: This section contains all the parameters for sending your email, including the body of your email. The .From field needs to contain your Gmail address, but you’re free to set the other fields however you want. For the body, you can piece together components of the message by using the & string to insert data from any of the Microsoft Excel sheets right into the email message, just like shown above. You can also attach one or more files.
- With fields: This is where you configure your SMTP settings for your Gmail account. Leave the smtpserver and smtpserverport fields as is when copying the code. Enter your Gmail username and the 16-digit app password into the respective fields.
Step 4: Test Your Macro
In the VBA editor, go to Run > Run Sub/User Form or press F5 to test the macro. If your email fails to go through, you should see an error message. Otherwise, you’ll see a confirmation that your email was sent successfully.
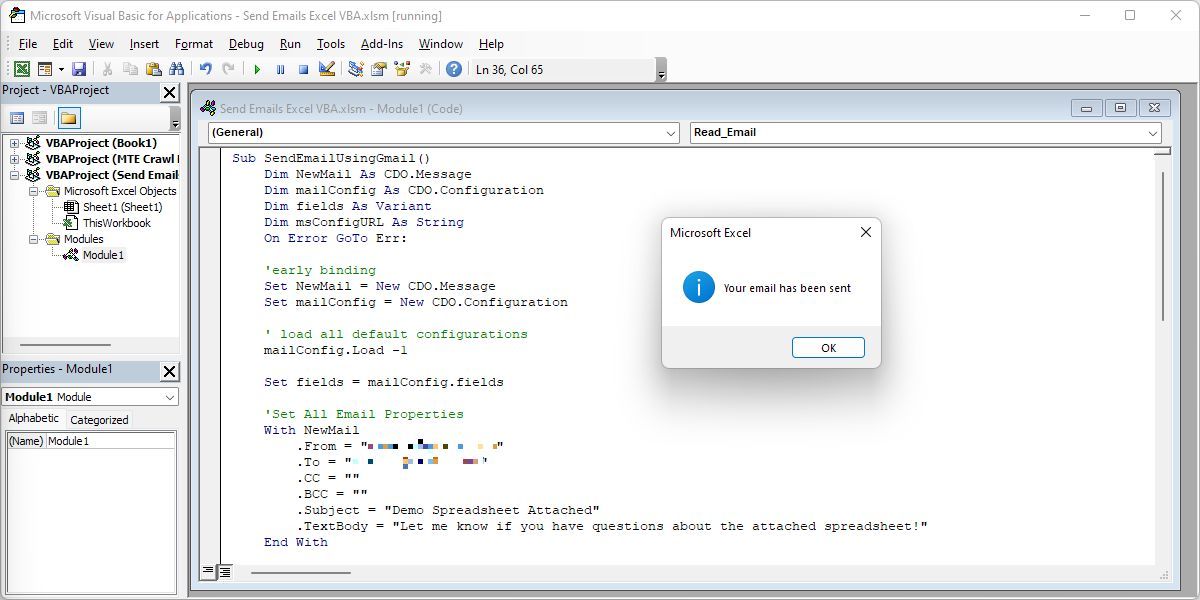
If you receive an error that reads The transport failed to connect to the server, make sure you’ve entered the correct username, password, SMTP server, and port number in the lines of code listed underneath With fields.
Step 5: Connect the Command Button to Your Script
To connect your command button to this script, go into the code editor and double-click on Sheet1 to view the VBA code for that worksheet. Select your button, e.g. CommandButton1, from the drop-down on the left and define the action on the right; Click works. Then type the name of the function where you pasted the script above; in our example it’s Send_Emails.
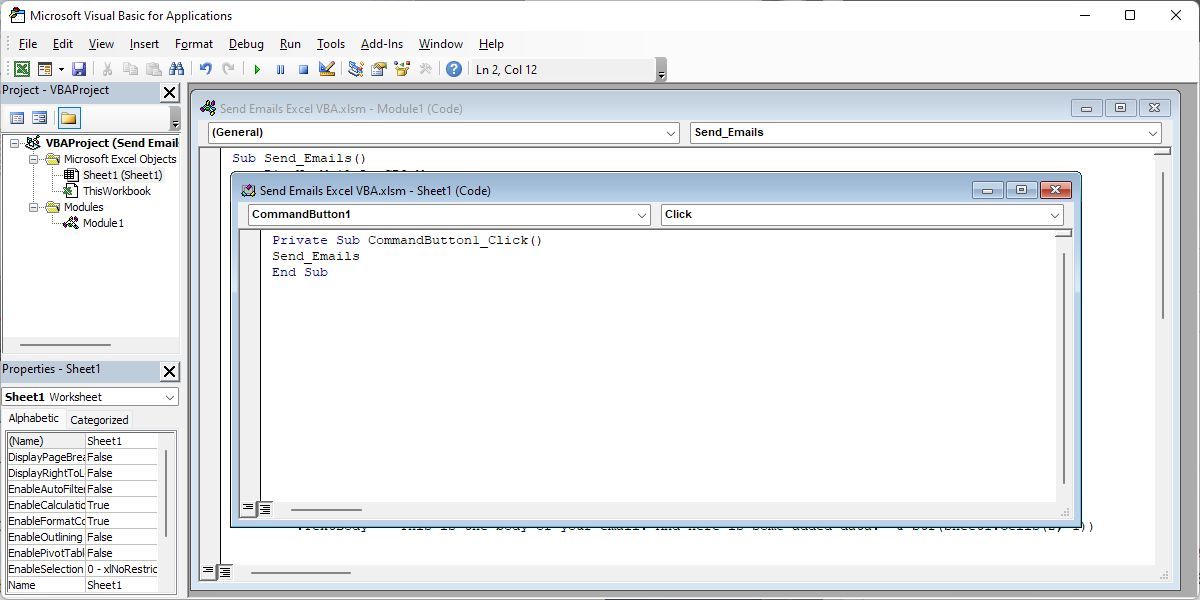
When you go back to your sheet now, click the button to send the email.
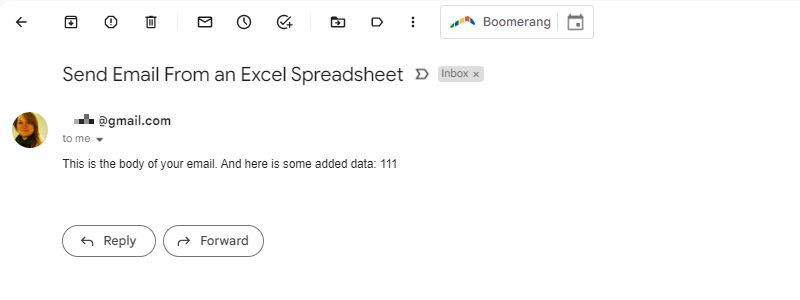
Here’s an example of what the message should look like in your inbox:
Take It Further and Automate the Whole Process
It’s all well and good to be able to send email from Excel at the touch of a button. However, you might want to use this functionality regularly, in which case it makes sense to automate the process. To do so, you’ll need to make a change to the macro. Head to the Visual Basic Editor and copy and paste the entirety of the code you’ve put together so far.
Next, double-click ThisWorkbook from the VBAProject hierarchy.
From the two dropdown fields at the top of the code window, select Workbook and select Open from the Methods dropdown.
Paste the email script above into Sub Workbook_Open().
This will run the macro whenever you open up the Excel file.
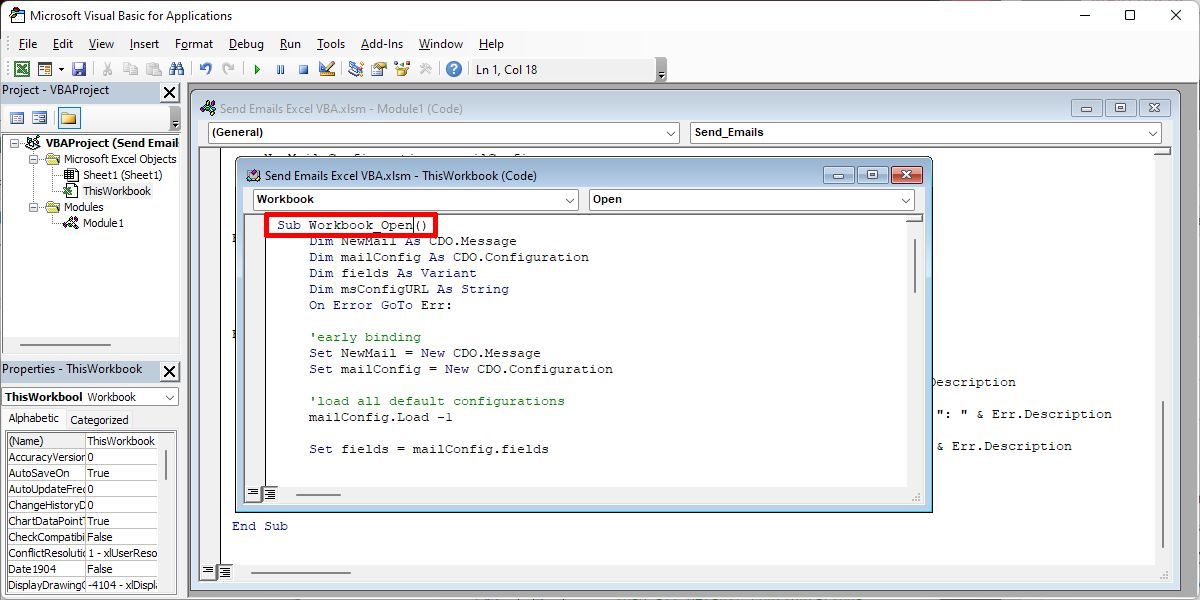
Next, open up Task Scheduler. You’re going to use this tool to ask Windows to open up the spreadsheet automatically at regular intervals, at which point your macro will run, sending the email.
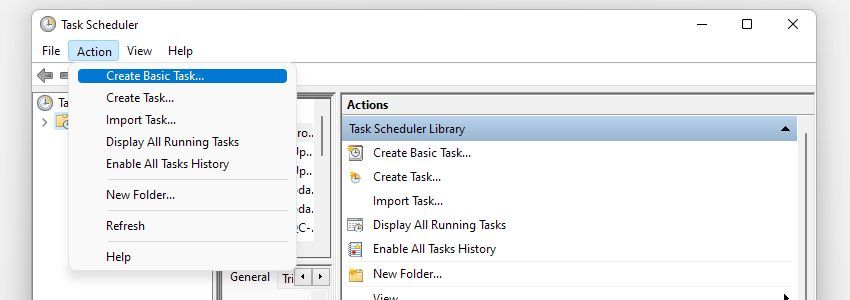
From the Action menu, select Create Basic Task… and work your way through the wizard until you reach the Action screen.
Select Start a program and click Next. Use the Browse button to find Microsoft Excel’s location on your computer, or copy and paste the path into the Program/script field. Then, enter the path to your Microsoft Excel document into the Add arguments field. Complete the wizard, and your scheduling will be in place.
It’s worth running a test by scheduling the action for a couple of minutes in the future, then amending the task once you can confirm that it’s working.
Note: You may have to adjust your Trust Center settings to ensure that the macro runs properly.
To do so, open the spreadsheet and navigate to File > Options > Trust Center. From here, click Trust Center Settings…, and on the next screen set the radio dial to Never show information about blocked content.
Make Microsoft Excel Work for You
Microsoft Excel is an incredibly powerful tool, but learning how to get the most out of it can be a little intimidating. If you want to truly master the software, you’ll need to be comfortable with VBA, and that’s no small task.
However, the results speak for themselves. With a little VBA experience under your belt, you’ll soon be able to make Microsoft Excel perform basic tasks automatically, giving you more time to concentrate on more pressing matters.
Hello Aakash Sehgal,
Sendmail()
Dim OutApp As Object
Dim OutMail As Object
Dim cell As Range
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Set OutApp = CreateObject("Outlook.Application")
On Error GoTo cleanup
For Each cell In Columns("B").Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeConstants)
If cell.Value Like "?*@?*.?*" And _
LCase(Cells(cell.Row, "C").Value) = "yes" Then
Set OutMail = OutApp.CreateItem(0)
On Error Resume Next
With OutMail
.To = cell.Value
.Subject = "Aakash Sehgal"
.Body = "Dear " & Cells(cell.Row, "A").Value _
& vbNewLine & vbNewLine & _
"Please contact us to discuss bringing " & _
"your account up to date"
'You can add files also by use:
'.Attachments.Add ("C:test.txt")
.Send 'Or use Display
End With
On Error GoTo 0
Set OutMail = Nothing
End If
Next cell
cleanup:
Set OutApp = Nothing
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
Make a list of following columns in ActiveSheet:
In column A : Names of the people
In column B : E-mail addresses
In column C : yes or no ( if the value is yes it will create a mail)
the macro loop through each row on the Activesheet and if there is a E-mail-address in column B
and «yes» in column C it will create a mail with a reminder like the one below for each person.
If you have duplicate addresses in the column check out this example.
this is one example how you can make it but if you instead want to add manually the smtp is that possible too take a look here:
Sub SMTP_Mail_SEND()
Dim iMsg As Object
Dim iConf As Object
Dim strbody As String
' Dim Flds As Variant
Set iMsg = CreateObject("CDO.Message")
Set iConf = CreateObject("CDO.Configuration")
' iConf.Load -1 ' CDO Source Defaults
' Set Flds = iConf.Fields
' With Flds
' .Item("http://schemas.microsoft.com/cdo/configuration/sendusing") = 2
' .Item("http://schemas.microsoft.com/cdo/configuration/smtpserver") _
' = "Fill in your SMTP server here"
' .Item("http://schemas.microsoft.com/cdo/configuration/smtpserverport") = 25
' .Update
' End With
strbody = "Hi there" & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & _
"This is line 1" & vbNewLine & _
"This is line 2" & vbNewLine & _
"This is line 3" & vbNewLine & _
"This is line 4"
With iMsg
Set .Configuration = iConf
.To = "test@test.com"
.CC = ""
.BCC = ""
.From = """daniel"" <daniel@test.com>"
.Subject = "This is a mail generated by use manually smtp mail"
.TextBody = strbody
.Send
End With
End Sub
Source:
http://www.rondebruin.nl/win/s1/cdo.htm
Cheers
XsiSec