The basic features of word-groups are the lexical
valency and the grammatical valency. Words are used in certain
lexical context, i.e. in combinations with other words. E.g. the noun
“question” is often combined with such adjectives as vital,
pressing, urgent, etc. this noun is a component of other word-groups.
E.g. to raise a question (not to lift a question of the hour). The
aptness (готовность) of a word to
appear in various combinations is described as its lexical
valency. The range of the lexical
valency of words is delimited by the inner structure of the E. words.
Thus “to raise” and “to lift” are synonyms but only the
former is collocated with the noun. Words habitually collocative in
speech tend to form a cliché. The lexical valency in different
languages is not identical because it depends on the inner stricture
of the vocabulary. E.g. both the E. “flower” and the R. “цветок”
may be combined with a number of similar words (garden flowers / hot
house flowers – садовые
цветы/оранжерейные
цветы). But “pot flowers” –
“комнатные цветы”.
The aptness of a word to appear in specific
grammatical (or other syntactical structures) is called grammatical
valency. E.g. the adjective “heavy”
can be followed by a known: heavy food, heavy storm, heavy box, but
we can not say heavy to lift, to carry. The gr. valency of words may
be different. It is delimited by the part of speech the word belongs
to. E.g no E. adjective can be followed by a finite form of a verb.
The gr. val-cy is also delimited by the inner structure of the
language. E.g. “to suggest” – “to propose”. Both can be
followed by a noun but only “to propose” can be followed by the
infinitive – “to propose to do smth”.
Structure of word-groups
The
word-groups may be classified:
-
according
to their head-words:
nominal group (red flower), adjective group (kind to people), verbal
group (to speak well).
-
according
to their syntactical pattern:
-
predicative (such word-groups as “he went” that have a
syntactic structure similar to that of a sentence), -
non-predicative (all others).
Non-predicative
word-groups depending on the type of syntactic relations between the
components are divided into:
-
Subordinative
(“a red flower”, “red” is dependent word) -
Coordinative
(“day and night”, “do and die”)
Meaning of word-groups
The
lexical meaning of the word-group may be defined as the combined
lexical meaning of the component members. But the term combined
lexical meaning doesn’t imply that the meaning of a word-group is
always a simple additive result of all the lexical meanings of the
component words. As a rule, the meanings of the component words are
mutually dependent and the meaning of the word-group naturally
predominance of the lexical meaning of the components. The
interdependence is well-seen in word-groups made up of polysemantic
words. In the phrases “the blind man” and “the blind type”
the words blind have different meanings.
Motivation in word-groups
Word-groups
may be called lexically motivated if the combined lexical meaning of
the group is deducible from the meaning of the components. All types
of phrases are completely motivated. Non-motivated word-groups are
called phraseological units, or idioms.
Criteria
of stability and lack of motivation (idiomaticity).
Phraseological units
are defined as non-motivated word-groups that can not be freely made
up in speech but are reproduced as ready-made units. The other
essential feature of phraseological units is stability of the lexical
components and grammatical structure.
General
class-ion of phras. unitswas suggested by academician Vinogradov
mainly according to the degree of idiomaticity:
-
Phraseological fusions (сращения).
Completely non-motivated word-groups. The meaning of the components
has no connection with the meaning of the whole group.
Idiomaticallycombined with complete stability of the lexical
components and the grammatical structure of the fusion. E.g. to kick
the bucket (умереть), to seeze an
elephant (узнать жизнь). -
Phraseological unities. Practically non-motivated
word-groups as their meaning can be understood through the
metaphoric meaning of the whole phraseological unit. E.g. to skate
on thin ice (рисковать), as busy
as a bee. They are marked by a comparatively high degree of
stability of the lexical components and grammatical structure. -
Phraseological collocations (словосочетания).
Are (partially) motivated but they are made up of words having
special lexical valency, which is marked by a certain degree of
stability. They differ from the phraseological unities by the fact
that one of the components is used in its direct meaning, the other
in indirect meaning and the meaning of the whole group dominates on
the meaning of its components. E.g. to pay a visit, to pay
attention, to break a rule, to break a silence, to meet demands.
Соседние файлы в папке Gosy
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
LECTURE 12.
WORD-GROUPS AND PHRASEOLOGICAL UNITS
1. Lexical and Grammatical Valency
2. Structure and Classification of Word-Groups
3. Types of Meaning of Word-Groups
4. Motivation in Word-Groups
1. Lexical and grammatical valency
The aptness of a word to appear in various combinations is described as its lexical valency or collocability. The noun job, for example, is often combined with such adjectives as backbreaking, difficult, hard; full-time, part-time, summer, cushy, easy; demanding; menial, etc. The noun myth may be a component of a number of word-groups, e.g. to create a myth, to dispel a myth, to explode a myth, myths and legends, etc. Lexical valency acquires special importance in case of polysemy as through the lexical valency different meanings of a polysemantic word can be distinguished, for instance, cf.: heavy table (safe, luggage); heavy snow (rain, storm); heavy drinker (eater); heavy sleep (sorrow, disappointment); heavy industry (tanks).
The range of the lexical valency of words is linguistically restricted by the inner structure of the English word-stock. Though the verbs lift and raise are usually treated as synonyms, it is only the latter that is collocated with the noun question.
The restrictions of lexical valency of words may also manifest themselves in the lexical meanings of the polysemantic members of word groups. For example, the adjective heavy in the meaning ‘rich and difficult to digest’ is combined with the words food, meals, supper. But it cannot be used with the words cheese or sausage (the words with more or less the same component of meaning) implying that the cheese or the sausage is difficult to digest.
Words habitually collocated in speech tend to constitute a cliche, for instance, the noun arms and the noun race. Thus, arms race is a cliche.
The lexical valency of correlated words in different languages is different, cf.: in English pot flowers – in Russian комнатные цветы.
Grammatical valency is the aptness of a word to appear in specific grammatical (or rather syntactic) structures. The minimal grammatical context in which words are used when brought together to form word-groups is usually described as the pattern of the word-groups. For instance, the verb to offer can be followed by the infinitive (to offer to do smth.) and the noun (to offer a cup of tea). The verb to suggest can be followed by the gerund (to suggest doing smth.) and the noun (to suggest an idea). The grammatical valency of these verbs is different.
The adjectives clever and intelligent are seen to possess different grammatical valency as clever can be used in word-groups having the pattern: adjective + preposition ‘at’ + noun (clever at mathematics), whereas intelligent can never be found in exactly the same word-group pattern.
The grammatical valency of correlated words in different languages is not identical, cf.: in English to influence a person, a decision, a choice (verb + noun) — in Russian влиять на человека, на решение, на выбор (verb + preposition + noun).
2. Structure and classification of word groups
The term ‘syntactic structure (formula)’ implies the description of the order and arrangement of member-words in word-groups as parts of speech. For instance, the syntactic structure of the word-groups a clever man, a red flower may be described as made up of an adjective and a noun, i.e. A + N; of the word-groups to take books, to build houses — as a verb and a noun, i.e. V + N.
The structure of word-groups may also be described in relation to the head-word. In this case it is usual to speak of the pattern but not of formulas. For example, the patterns of the verbal groups to take books, to build houses are to take + N, to build + N. The term ‘syntactic pattern’ implies the description of the structure of the word-group in which a given word is used as its head.
According to the syntactic pattern word-groups may be classified into predicative and non-predicative. Predicative word-groups have a syntactic structure similar to that of a sentence, e.g. he went, John works. All other word-groups are called non-predicative. Non-predicative word-groups may be subdivided into subordinative (e.g. red flower, a man of wisdom) and coordinative (e.g. women and children, do or die).
Structurally, all word-groups can be classified by the criterion of distribution into two extensive classes: endocentric and exocentric.
Endocentric word-groups are those that have one central member functionally equivalent to the whole word-group, i.e. the distribution
The meaning of word-groups can be divided into: 1) lexical and 2) structural (grammatical) components of the whole word-group and the distribution of its central member are identical. For instance, in the word-groups red flower, kind to people, the head-words are the noun flower and the adjective kind correspondingly. These word-groups are distributionally identical with their central components. According to their central members word-groups may be classified into: nominal groups or phrases (e.g. redflower), adjectival groups (e.g. kind to people), verbal groups (e.g. to speak well), etc.
Exocentric word-groups are those that have no central component and the distribution of the whole word-group is different from either of its members. For instance, the distribution of the word-group side by side is not identical with the distribution of its component-members, i.e. the component-members are not syntactically substitutable for the whole word-group.
3. Types of meaning of word-groups
The meaning of word-groups can be divided into: 1) lexical and 2) structural (grammatical) components).
1. The lexical meaning of the word-group may be defined as the combined lexical meaning of the component words. Thus, the lexical meaning of the word-group red flower may be described denotationally as the combined meaning of the words red and flower. However, the term ‘combined lexical meaning’ is not to imply that the meaning of the word-group is a mere additive result of all the lexical meanings of the component members. The lexical meaning of the word-group predominates over the lexical meanings of its constituents.
2. The structural meaning of the word-group is the meaning conveyed mainly by the pattern of arrangement of its constituents. For example, such word-groups as school grammar (школьная грамматика) and grammar school (грамматическая школа) are semantically different because of the difference in the pattern of arrangement of the component words. The structural meaning is the meaning expressed by the pattern of the word-group but not either by the word school or the word grammar. It follows that it is necessary to distinguish between the structural meaning of a given type of a word-group as such and the lexical meaning of its constituents.
The lexical and structural components of meaning in word-groups are interdependent and inseparable. For instance, the structural pattern of the word-groups all day long, all night long, all week long in ordinary usage and the word-group all the sun long is identical. The generalized meaning of the pattern may be described as ‘a unit of time’. Replacing day, night, week by another noun – the sun the structural meaning of the pattern does not change. The group all the sun long functions semantically as a unit of time. But the noun sun included in the group, continues to carry the semantic value, i.e. the lexical meaning that it has in word-groups of other structural patterns, e.g. the sun rays, African sun.
Thus, the meaning of the word-group is derived from the combined lexical meanings of its constituents and is inseparable from the meaning of the pattern of their arrangement.
4. Motivation in word-groups
Semantically all word-groups can be classified into motivated and non-motivated.
A word-group is lexically motivated if the combined lexical meaning of the group is deducible from the meanings of its components, e.g. red flower, heavy weight, teach a lesson.
If the combined lexical meaning of a word-group is not deducible from the lexical meanings of its constituent components, such a word-group is lexically non-motivated, e.g. red tape (‘official bureaucratic methods’), take place (‘occur’).
The degree of motivation can be different. Between the extremes о complete motivation and lack of motivation there are innumerable intermediate cases. For example, the degree of lexical motivation in the nominal group black market is higher than in black death, but lower than in black dress, though none of the groups can be considered completely non-motivated. This is also true of other words-groups, e.g old man and old boy both of which may be regarded as lexically motivated though the degree of motivation in old man is noticeably higher.
It should be noted that seemingly identical word-groups are sometimes found to be motivated or non-motivated depending on their semantic interpretation. Thus, apple sauce is lexically motivated where it means ‘a sauce made of apples’ but when used to denote ‘nonsense’ it is clearly non-motivated.
Completely non-motivated or partially motivated word-groups are described as phraseological units or idioms.
Изображение слайда
2
Слайд 2: Word-groups vs. phraseological units
Words put together to form lexical units make phrases or word-groups.
The largest two-facet lexical unit comprising more than one word is the word-group observed on the syntagmatic level of analysis. The degree of structural and semantic cohesion of word-groups may vary.
Functionally and semantically inseparable word-groups like at least, point of view, by means of, take place are phraseological units.
Semantically and structurally more independent word-groups a week ago, man of wisdom, take lessons, kind to people are defined as free or variable word-groups or phrases
Изображение слайда
3
Слайд 3: Valency of words
The two main linguistic factors to be considered in uniting words into word-groups are:
1) the lexical valency of words
2) the syntactic valency of words.
Изображение слайда
4
Слайд 4: Lexical valency
Words are used in certain lexical contexts, i.e. in combination with other words.
The noun question is often combined with such adjectives as vital, pressing, urgent, disputable, delicate, etc.
This noun is a component of a number of other word-groups, e.g. to raise a question, a question of great importance, a question of the agenda, a question of the day, and many others.
Lexical valency is the possibility of lexical-semantic connections of a word with other words.
Lexical collocability is the realisation in speech of the potential connections of a word with other words.
Изображение слайда
Lexical valency acquires special importance in case of polysemy as through the lexical valency different meanings of a polysemantic word can be distinguished, e.g.
heavy weight (safe, table, etc.),
heavy snow (storm, rain, etc.),
heavy drinker (eater, etc.),
heavy sleep (disappointment, sorrow, etc.),
heavy industry (tanks, etc.), and so on.
These word-groups are called collocations or such combinations of words which condition the realization of a certain meaning
Изображение слайда
The range of the lexical valency of words is linguistically restricted by the inner structure of the English word-stock.
Though the verbs lift and raise are treated as synonyms, only raise is collocated with the noun question.
The verb take may be interpreted as ‘grasp’, ’seize’, ‘catch’, etc. but only take is found in collocations with the nouns examination, measures, precautions, etc.,
only catch in catch smb. napping
and grasp in grasp the truth.
Изображение слайда
The restrictions of lexical valency of words may manifest themselves in the lexical meanings of the polysemantic members of word-groups.
The adjective heavy, e.g., is combined with the words food, meals, supper, etc. in the meaning ‘rich and difficult to digest’.
But not all the words with the same component of meaning can be combined with this adjective *heavy cheese or *heavy sausage.
The lexical valency of correlated words in different languages is different: pot flowers – комнатные цветы
Изображение слайда
8
Слайд 8: Syntactic valency —
the aptness of a word to appear in different syntactic structures.
The minimal syntactic context in which words are used when brought together to form word-groups is described as the pattern of the word-groups.
E.g., the verb to offer can be followed by the infinitive ( to offer to do smth ) and the noun ( to offer a cup of tea ).
The verb to suggest can be followed by the gerund ( to suggest doing smth ) and the noun ( to suggest an idea ). The syntactic valency of these verbs is different.
Изображение слайда
The adjectives clever and intelligent are seen to possess different syntactic valency as clever can be used in word-groups having the pattern:
Adjective-Preposition at+Noun : clever at mathematics, whereas intelligent can never be found in exactly the same word-group pattern.
The syntactic valency of correlated words in different languages is not identical, in English to influence a person, a decision, a choice ( verb +noun ) — in Russian влиять на человека, на решение, на выбор ( verb+ preposition+noun ).
Изображение слайда
T he individual meanings of a polysemantic word may be described through its syntactic valency:
Keen + N: keen sight, hearing, etc.
Keen + on + N : keen on sports, tennis, etc.
Keen + V( inf ): keen to know, to find out, etc.
Thus word-groups may be regarded as minimal syntactic (or syntagmatic) structures that operate as distinguishing clues for different meanings of a polysemantic word.
Изображение слайда
11
Слайд 11: INTERDEPENDENCE OF STRUCTURE AND MEANING IN WORD-GROUPS
Syntactic structure and pattern of word-groups is the description of the order and arrangement of member-words in word-groups as parts of speech.
The syntactic structure of the word-group an old woman, a blue dress, clever man, red flower is an adjective and a noun, i.e. A+N ;
The syntactic structure of the word-groups wash a car, read books, take books, build houses – as a verb and a noun, i.e. V+N.
The syntactic structure of the word-groups a touch of the sun, a matter of importance — as a preposition and a noun, i.e. N+prp+N.
Изображение слайда
12
Слайд 12: Structural formulas:
V+N: ( to build houses ),
V+prp+N: ( to rely on somebody ),
V+N+prp+N: ( to hold something against somebody ),
V+N+V(inf.): ( to make somebody work ),
V+ V(inf.): ( to get to know ), and so on.
Изображение слайда
13
Слайд 13: Syntactic structure of word-groups
Word-groups may be described through the order and arrangement of the component members:
To see sth – verbal-nominal group;
To see to sth – ( If you see to something that needs attention, you deal with it ) verbal-prepositional-nominal, etc.
Изображение слайда
Word-groups may be classified according to their headwords into:
Nominal: red flower ;
Adjectival: kind to people ;
Verbal: to speak well, etc.
The head is not necessarily the component that occurs first in the word-group: great bravery, bravery in the struggle the noun bravery is the head whether followed or preceded by other words.
Изображение слайда
Thus the structure of word-groups may also be described in relation to the head-word.
In this case it is usual to speak of the pattern but not of formulas.
E.g., the patterns of the verbal groups to read a book, to wash a car are to read + N, to wash + N ; to rely on somebod y – to rely+on+N.
Syntactic pattern implies the description of the structure of the word-group in which a given word is used as its head.
Изображение слайда
16
Слайд 16: The interdependence of the pattern and meaning of head-words can be easily perceived by comparing word-groups of different patterns in which the same head-word is used
Three patterns with the verb ‘get’ as the head-word represent three different meanings of this verb:
get+ N ( get a letter, information, money, etc.);
get+ to +N ( get to Moscow, to the Institute, etc.);
get+N+V (inf.) ( get somebody to come, to do the work, etc.).
Изображение слайда
Notional member-words are habitually represented in conventional symbols whereas prepositions and other form-words are given in their usual graphic form. This is accounted for by the fact that individual form-words may modify or change the meaning of the word with which it is combined, as in, e.g.:
anxious+for+ N ( anxious for news ), anxious+about+ N ( anxious about his health ).
the difference in the meaning of the head-word is conditioned by a difference in the pattern of the word-group in which this word is used
Изображение слайда
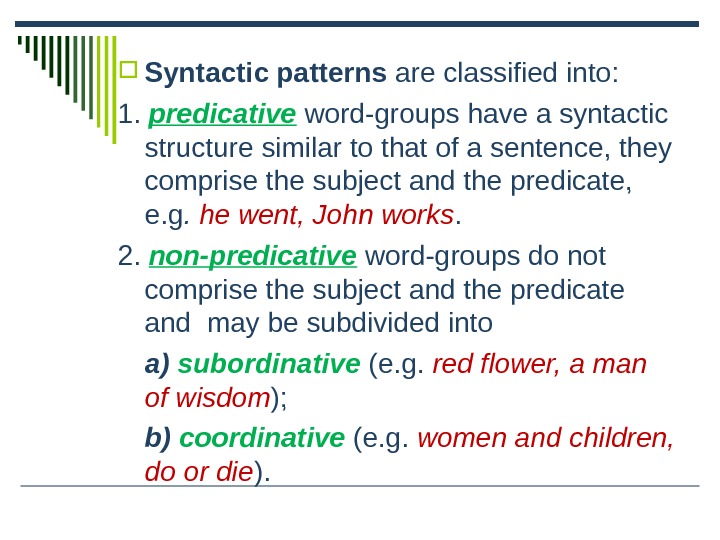
Syntactic patterns are classified into:
1. predicative word-groups have a syntactic structure similar to that of a sentence, they comprise the subject and the predicate, e.g. he went, John works.
2. non-predicative word-groups do not comprise the subject and the predicate and may be subdivided into
a) subordinat ive (e.g. red flower, a man of wisdom );
b) coordinative (e.g. women and children, do or die ).
Изображение слайда
19
Слайд 19: Classification of word-groups
ENDOCENTRIC WORD-GROUPS
have one central member functionally equivalent to the whole word-group.
In the word-group blue dress, friendly to people, the head-words are the noun dress and the adjective friendly correspondingly.
According to their central members
word-groups may be classified into:
a) nominal groups or phrases ( blue dress ),
b) adjectival groups ( friendly to people ),
c) verbal groups ( to sing well ), etc.
Изображение слайда
2. EXOCENTRIC WORD-GROUPS
have no central component and the distribution of the whole word-group is different from either of its members.
For instance, the distribution of the word-groups side by side, at first, grow smaller is not identical with the distribution of their component-members, i.e. the component-members are not syntactically substitutable for the whole word-group.
Изображение слайда
21
Слайд 21: TYPES OF MEANING OF WORD-GROUPS
The lexical meaning –
the combined lexical meaning of the component words, e.g. a blind man may be described denotationally as the combined meaning of the words blind and man.
In most cases the lexical meanings of the word-group predominates over the lexical meanings of its components, e.g. blind alley, blind date.
Polysemantic words are used in word-groups only in one of their meanings. These meanings of the component words in such word-groups are mutually interdependent and inseparable. Semantic inseparability of word-groups treats them as self-contained lexical units.
Изображение слайда
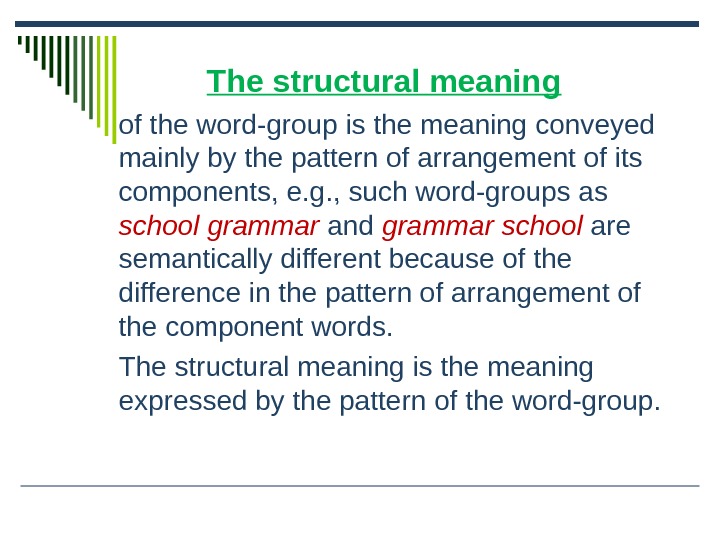
The structural meaning
of the word-group is the meaning conveyed mainly by the pattern of arrangement of its components, e.g., such word-groups as school grammar and grammar school are semantically different because of the difference in the pattern of arrangement of the component words.
The structural meaning is the meaning expressed by the pattern of the word-group.
Изображение слайда
Interrelation of lexical and structural meaning in word-groups
The lexical and structural components of meaning in word-groups are interdependent and inseparable. The structural pattern in all the day long, all the night long, all the week long in ordinary usage and the word-group all the sun long is identical. The generalised meaning of the pattern ‘a unit of time’.
Replacing day, night, week by another noun the sun structural meaning of the pattern does not change. The group all the sun long functions semantically as a unit of time. But the noun sun included in the group continues to carry the semantic value or the lexical meaning that it has in word-groups of other structural patterns (cf. the sun rays, African sun, etc.).
Изображение слайда
It follows that the meaning of the word-group is derived from the combined lexical meanings of its constituents and is inseparable from the meaning of the pattern of their arrangement.
a factory hand − ‘ a factory worker’
a hand bag − ‘ a bag carried in the hand’.
Though the word hand makes part of both its lexical meaning and the role it plays in the structure of word-groups is different which accounts for the difference in the lexical and structural meaning of the word-groups under discussion.
Thus, the meaning of the word-group is derived from the combined lexical meanings of its constituents and is inseparable from the meaning of the pattern of their arrangement.
Изображение слайда
25
Слайд 25: Polysemantic and monosemantic patterns
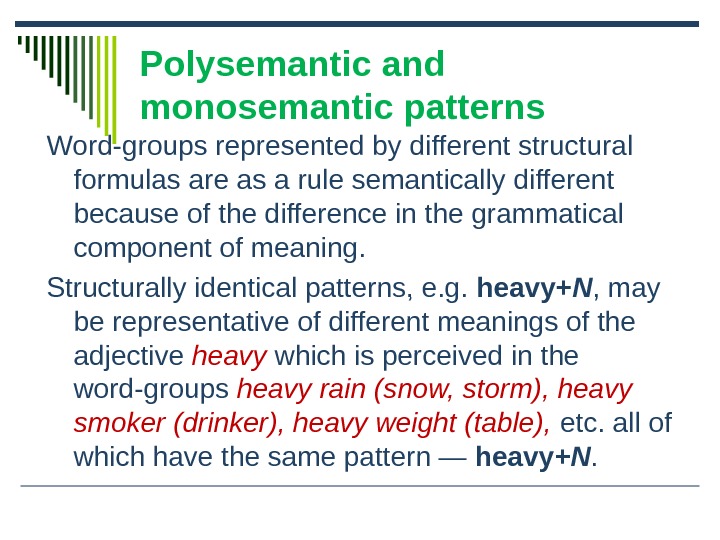
Word-groups represented by different structural formulas are as a rule semantically different because of the difference in the grammatical component of meaning.
Structurally identical patterns, e.g. heavy+ N, may be representative of different meanings of the adjective heavy which is perceived in the word-groups heavy rain (snow, storm), heavy smoker (drinker), heavy weight (table), etc. all of which have the same pattern — heavy +N.
Изображение слайда
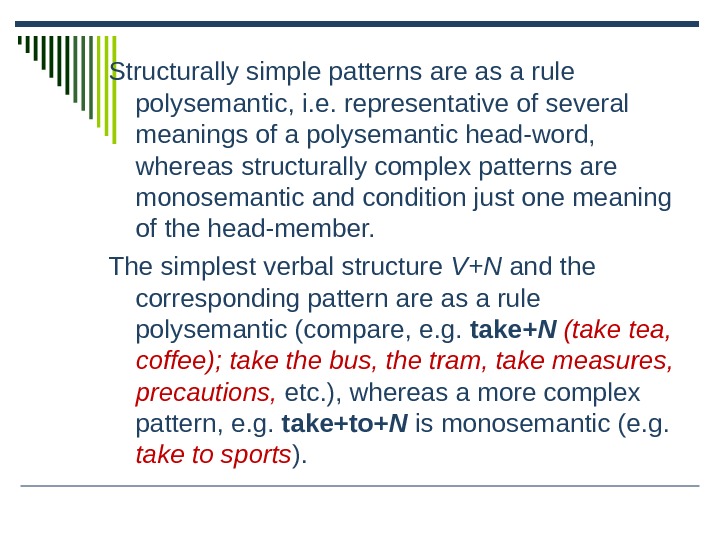
Structurally simple patterns are as a rule polysemantic, i.e. representative of several meanings of a polysemantic head-word, whereas structurally complex patterns are monosemantic and condition just one meaning of the head-member.
The simplest verbal structure V+N and the corresponding pattern are as a rule polysemantic (compare, e.g. take +N (take tea, coffee); take the bus, the tram, take measures, precautions, etc.), whereas a more complex pattern, e.g. take+to+ N is monosemantic (e.g. take to sports ).
Изображение слайда
27
Слайд 27: MOTIVATION IN WORD-GROUPS
A word-group is lexically-motivated if the combined lexical meaning of the group is deducible from the meaning of its components, e.g. red flower, heavy weight, take lessons.
If the combined lexical meaning of a word-group is not deducible from the lexical meanings of its constituent components, such a word-group is lexically non-motivated, e.g. red tape (official bureaucratic methods) take place (occur).
Изображение слайда
The degree of motivation can be different. Between the extremes of complete motivation and lack of motivation there are innumerable intermediate cases.
E.g., the degree of lexical motivation in the nominal group black market is higher than in black death, but lower than in black dress, though none of the groups can be considered completely non-motivated.
Изображение слайда
Completely motivated word-groups are correlated with certain structural types of compound words.
Verbal groups having the structure V+N, e.g. to read books, to love music, etc., are habitually correlated with the compounds of the pattern N+(V+er) (book-reader, music-lover);
adjectival groups such as A + prp+N (e.g. rich in oil, shy before girls ) are correlated with the compounds of the pattern N+A, e.g. oil-rich, girl-shy.
Изображение слайда
Seemingly identical word-groups are sometimes found to be motivated or non-motivated depending on their semantic interrelation. Thus, apple sauce is lexically motivated when it means ‘a sauce made of apples’ but when used to denote ‘nonsense’ it is clearly non-motivated.
Completely non-motivated or partially motivated word-groups are called phraseological units or idioms.
Изображение слайда
31
Слайд 31: Summary and Conclusions
1. Words put together to form lexical units make up phrases or word-groups. The main factors active in bringing words together are lexical and syntactic valency of the components of word-groups.
Изображение слайда
2. Lexical valency is the aptness of a word to appear in various collocations. All the words of the language possess a certain norm of lexical valency. Restrictions of lexical valency are to be accounted for by the inner structure of the vocabulary of the English language.
Изображение слайда
Lexical valency of polysemantic words is observed in various collocations in which these words are used. Different meanings of a polysemantic word may be described through its lexical valency.
Изображение слайда
Syntactic valency is the aptness of a word to appear in various syntactic structures. All words possess a certain norm of syntactic valency. Restrictions of syntactic valency are to be accounted for by the grammatical structure of the language. The range of syntactic valency of each individual word is essentially delimited by the part of speech the word belongs to and also by the specific norm of syntactic valency peculiar to individual words of Modern English.
Изображение слайда
The syntactic valency of a polysemantic word may be observed in the different structures in which the word is used. Individual meanings of a polysemantic word may be described through its syntactic valency.
Изображение слайда
Structurally, word-groups may be classified by the criterion of distribution into endocentric and exocentric.
Endocentric word-groups can be classified according to the head-word into nominal, adjectival, verbal and adverbial groups or phrases.
Изображение слайда
Semantically all word-groups may be classified into motivated and non-motivated. Non-motivated word-groups are usually described as phraseological units.
Изображение слайда
Зыкова И.В. Практический курс английской лексикологии. М.: Академия, 2006. – С. 121-124.
Гинзбург Р.З. Лексикология английского языка. М.: Высшая школа, 1979. – С. 64-74.
Антрушина Г.Б., Афанасьева О.В., Морозова Н.Н. Лексикология английского языка. М.: Дрофа, 2006. – С. 225- 256.
Изображение слайда
39
Последний слайд презентации: WORD-GROUPS Lecture 12: WORD-GROUPS
Изображение слайда
Free word groups and phraseological units
A word-group is the largest two-facet lexical unit comprising more than one word but expressing one global concept.
The lexical meaning of the word groups is the combined lexical meaning of the component words. The meaning of the word groups is motivated by the meanings of the component members and is supported by the structural pattern. But it’s not a mere sum total of all these meanings! Polysemantic words are used in word groups only in 1 of their meanings. These meanings of the component words in such word groups are mutually interdependent and inseparable (blind man – «a human being unable to see», blind type – «the copy isn’t readable).
Word groups possess not only the lexical meaning, but also the meaning conveyed mainly by the pattern of arrangement of their constituents. The structural pattern of word groups is the carrier of a certain semantic component not necessarily dependent on the actual lexical meaning of its members (school grammar – «grammar which is taught in school», grammar school – «a type of school»). We have to distinguish between the structural meaning of a given type of word groups as such and the lexical meaning of its constituents.
It is often argued that the meaning of word groups is also dependent on some extra-linguistic factors – on the situation in which word groups are habitually used by native speakers.
Words put together to form lexical units make phrases or word-groups. One must recall that lexicology deals with words, word-forming morphemes and word-groups.
The degree of structural and semantic cohesion of word-groups may vary. Some word-groups, e.g. at least, point of view, by means, to take place, etc. seem to be functionally and semantically inseparable. They are usually described as set phrases, word-equivalents or phraseological units and are studied by the branch of lexicology which is known as phraseology. In other word-groups such as to take lessons, kind to people, a week ago, the component-members seem to possess greater semantic and structural independence. Word-groups of this type are defined as free word-groups or phrases and are studied in syntax.
Before discussing phraseology it is necessary to outline the features common to various word-groups irrespective of the degree of structural and semantic cohesion of the component-words.
There are two factors which are important in uniting words into word-groups:
– the lexical valency of words;
– the grammatical valency of words.
Lexical valency
Words are used in certain lexical contexts, i.e. in combinations with other words. E.g. the noun question is often combined with such adjectives as vital, pressing, urgent, delicate, etc.
The aptness of a word to appear in various combinations is described as its lexical valency. The range of the lexical valency of words is delimited by the inner structure of the English words. Thus, to raise and to lift are synonyms, but only the former is collocated with the noun question. The verbs to take, to catch, to seize, to grasp are synonyms, but they are found in different collocations:
to take – exams, measures, precautions, etc.;
to grasp – the truth, the meaning.
Words habitually collocated in speech tend to form a cliche.
The lexical valency of correlated words in different languages is not identical, because as it was said before, it depends on the inner structure of the vocabulary of the language. Both the English flower and the Russian цветок may be combined with a number of similar words, e.g. garden flowers, hot house flowers (cf. the Russian – садовые цветы, оранжерейные цветы), but in English flower cannot be combined with the word room, while in Russian we say комнатные цветы (in English we say pot-flowers).
Words are also used in grammatical contexts. The minimal grammatical context in which the words are used to form word-groups is usually described as the pattern of the word-group. E.g., the adjective heavy can be followed by a noun (A+N) – heavy food, heavy storm, heavy box, heavy eater. But we cannot say «heavy cheese» or «heavy to lift, to carry», etc.
The aptness of a word to appear in specific grammatical (or rather syntactical) structures is termed grammatical valency.
The grammatical valency of words may be different. The grammatical valency is delimited by the part of speech the word belongs to. E.g., no English adjective can be followed by the finite form of a verb.
Then, the grammatical valency is also delimited by the inner structure of the language. E.g., to suggest, to propose are synonyms. Both can be followed by a noun, but only to propose can be followed by the infinitive of a verb – to propose to do something.
Clever and intelligent have the same grammatical valency, but only clever can be used in word-groups having the pattern A+prep+N – clever at maths.
Structurally word-groups can be considered in different ways. Word-groups may be described as for the order and arrangement of the component-members. E.g., the word-group to read a book can be classified as a verbal-nominal group, to look at smb. – as a verbal-prepositional-nominal group, etc.
By the criterion of distribution all word-groups may be divided into two big classes: according to their head-words and according to their syntactical patterns.
Word-groups may be classified according to their head-words into:
nominal groups – red flower;
adjective groups – kind to people;
verbal groups – to speak well.
The head is not necessarily the component that occurs first.
Word-groups are classified according to their syntactical pattern into predicative and non-predicative groups. Such word-groups as he went, Bob walks that have a syntactic structure similar to that of a sentence are termed as predicative, all others are non-predicative ones.
Non-predicative word-groups are divided into subordinative and coordinative depending on the type of syntactic relations between the components. E.g., a red flower, a man of freedom are subordinative non-predicative word-groups, red and freedom being dependent words, while day and night, do and die are coordinative non-predicative word-groups.
The lexical meaning of a word-group may be defined as the combined lexical meaning of the component members. But it should be pointed out, however, that the term «combined lexical meaning» does not imply that the meaning of the word-group is always a simple additive result of all the lexical meanings of the component words. As a rule, the meanings of the component words are mutually dependent and the meaning of the word-group naturally predominates over the lexical meaning of the components. The interdependence is well seen in word-groups made up of polysemantic words. E.g., in the phrases the blind man, the blind type the word blind has different meanings – unable to see and vague.
So we see that polysemantic words are used in word-groups only in one of their meanings.
The term motivation is used to denote the relationship existing between the phonemic or morphemic composition and structural pattern of the word on the one hand and its meaning on the other.
There are three main types of motivation:
1) phonetical
2) morphological
3) semantic
1. Phonetical motivation is used when there is a certain similarity between the sounds that make up the word. For example: buzz, cuckoo, gigle. The sounds of a word are imitative of sounds in nature, or smth that produces a characteristic sound. This type of motivation is determined by the phonological system of each language.
2. Morphological motivation – the relationship between morphemic structure and meaning. The main criterion in morphological motivation is the relationship between morphemes. One-morphemed words are non-motivated. Ex – means «former» when we talk about humans ex-wife, ex-president. Re – means «again»: rebuild, rewrite. In borowed words motivation is faded: «expect, export, recover (get better)». Morphological motivation is especially obvious in newly coined words, or in the words created in this century. In older words motivation is established etymologically.
The structure-pattern of the word is very important too: «finger-ring» and «ring-finger». Though combined lexical meaning is the same. The difference of meaning can be explained by the arrangement of the components.
Morphological motivation has some irregularities: «smoker» – si not «the one who smokes», it is «a railway car in which passenger may smoke».
The degree of motivation can be different:
«endless» is completely motivated
«cranberry» is partially motivated: morpheme «cran-» has no lexical meaning.
3. Semantic motivation is based on the co-existence of direct and figurative meanings of the same word within the same synchronous system. «Mouth» denotes a part of the human face and at the same time it can be applied to any opening: «the mouth of a river». «Ermine» is not only the anme of a small animal, but also a fur. In their direct meaning «mouth» and «ermine» are not motivated.
In compound words it is morphological motivation when the meaning of the whole word is based on direct meanings of its components and semantic motivation is when combination of components is used figuratively. For example «headache» is «pain in the head» (morphological) and «smth. annoying» (sematic).
When the connection between the meaning of the word and its form is conventional (there is no perceptible reason for the word having this phonemic and morphemic composition) the word is non-motivated (for the present state of language development). Words that seem non-motivated now may have lost their motivation: «earn» is derived from «earnian – to harvest», but now this word is non-motivated.
As to compounds, their motivation is morphological if the meaning of the whole is based on the direct meaning of the components, and semantic if the combination is used figuratively: watchdog – a dog kept for watching property (morphologically motivated); – a watchful human guardian (semantically motivated).
Every vocabulary is in a state of constant development. Words that seem non-motivated at present may have lost their motivation. When some people recognize the motivation, whereas others do not, motivation is said to be faded.
Semantically all word-groups may be classified into motivated and non-motivated. Non-motivated word-groups are usually described as phraseological units or idioms.
Word-groups may be described as lexically motivated if the combined lexical meaning of the groups is based on the meaning of their components. Thus take lessons is motivated; take place – ‘occur’ is lexically non-motivated.
Word-groups are said to be structurally motivated if the meaning of the pattern is deduced from the order and arrangement of the member-words of the group. Red flower is motivated as the meaning of the pattern quality – substance can be deduced from the order and arrangement of the words red and flower, whereas the seemingly identical pattern red tape (‘official bureaucratic methods’) cannot be interpreted as quality – substance.
Seemingly identical word-groups are sometimes found to be motivated or non-motivated depending on their semantic interpretation. Thus apple sauce, e.g., is lexically and structurally motivated when it means ‘a sauce made of apples’ but when used to denote ‘nonsense’ it is clearly non-motivated
Word-groups like words may be also analyzed from the point of view of their motivation. Word-groups may be called as lexically motivated if the combined lexical meaning of the group is deducible from the meaning of the components. All free phrases are completely motivated.
It follows from the above discussion that word-groups may be also classified into motivated and non-motivated units. Non-motivated word-groups are habitually described as phraseological units or idioms.
Investigations of English phraseology began not long ago. English and American linguists as a rule are busy collecting different words, word-groups and sentences which are interesting from the point of view of their origin, style, usage or some other features. All these units are habitually described as «idioms», but no attempt has been made to describe these idioms as a separate class of linguistic units or a specific class of word-groups.
Difference in terminology («set-phrases», «idioms» and «word-equivalents») reflects certain differences in the main criteria used to distinguish types of phraseological units and free word-groups. The term «set phrase» implies that the basic criterion of differentiation is stability of the lexical components and grammatical structure of word-groups.
There is a certain divergence of opinion as to the essential features of phraseological units as distinguished from other word-groups and the nature of phrases that can be properly termed «phraseological units». The habitual terms «set-phrases», «idioms», «word-equivalents» are sometimes treated differently by different linguists. However these terms reflect to certain extend the main debatable points of phraseology which centre in the divergent views concerning the nature and essential features of phraseological units as distinguished from the so-called free word-groups.
The term «set expression» implies that the basic criterion of differentiation is stability of the lexical components and grammatical structure of word-groups.
The term «word-equivalent» stresses not only semantic but also functional inseparability of certain word-groups, their aptness to function in speech as single words.
The term «idioms» generally implies that the essential feature of the linguistic units under consideration is idiomaticity or lack of motivation. Uriel Weinreich expresses his view that an idiom is a complex phrase, the meaning of which cannot be derived from the meanings of its elements. He developed a more truthful supposition, claiming that an idiom is a subset of a phraseological unit. Ray Jackendoff and Charles Fillmore offered a fairly broad definition of the idiom, which, in Fillmore’s words, reads as follows: «…an idiomatic expression or construction is something a language user could fail to know while knowing everything else in the language». Chafe also lists four features of idioms that make them anomalies in the traditional language unit paradigm: non-compositionality, transformational defectiveness, ungrammaticality and frequency asymmetry.
Great work in this field has been done by the outstanding Russian linguist A. Shakhmatov in his work «Syntax». This work was continued by Acad. V.V. Vinogradov. Great investigations of English phraseology were done by Prof. A. Cunin, I. Arnold and others.
Phraseological units are habitually defined as non-motivated word-groups that cannot be freely made up in speech but are reproduced as ready-made units; the other essential feature of phraseological units is stability of the lexical components and grammatical structure.
Unlike components of free word-groups which may vary according to the needs of communication, member-words of phraseological units are always reproduced as single unchangeable collocations. E.g., in a red flower (a free phrase) the adjective red may be substituted by another adjective denoting colour, and the word-group will retain the meaning: «the flower of a certain colour».
In the phraseological unit red tape (bürokratik metodlar) no such substitution is possible, as a change of the adjective would cause a complete change in the meaning of the group: it would then mean «tape of a certain colour». It follows that the phraseological unit red tape is semantically non-motivated, i.e. its meaning cannot be deduced from the meaning of its components, and that it exists as a ready-made linguistic unit which does not allow any change of its lexical components and its grammatical structure.
Grammatical structure of phraseological units is to a certain degree also stable:
red tape – a phraseological unit;
red tapes – a free word-group;
to go to bed – a phraseological unit;
to go to the bed – a free word-group.
Still the basic criterion is comparative lack of motivation, or idiomaticity of the phraseological units. Semantic motivation is based on the coexistence of direct and figurative meaning.
Taking into consideration mainly the degree of idiomaticity phraseological units may be classified into three big groups. This classification was first suggested by Acad. V.V. Vinogradov. These groups are:
– phraseological fusions,
– phraseological unities,
– phraseological collocations, or habitual collocations.
Phraseological fusions are completely non-motivated word-groups. Themeaning of the components has no connection at least synchronically with the meaning of the whole group. Idiomaticity is combined with complete stability of the lexical components and the grammatical structure of the fusion.
Phraseological unities are partially non-motivated word-groups as their meaning can usually be understood through (deduced from) the metaphoric meaning of the whole phraseological unit.
Phraseological unities are usually marked by a comparatively high degree of stability of the lexical components and grammatical structure. Phraseological unities can have homonymous free phrases, used in direct meanings.
§ to skate on thin ice – to skate on thin ice (to risk);
§ to wash one’s hands off dirt – to wash one’s hands off (to withdraw from participance);
§ to play the first role in the theatre – to play the first role (to dominate).
There must be not less than two notional wordsin metaphorical meanings.
Phraseological collocations are partially motivated but they are made up of words having special lexical valency which is marked by a certain degree of stability in such word-groups. In phraseological collocations variability of components is strictly limited. They differ from phraseological unities by the fact that one of the components in them is used in its direct meaning, the other – in indirect meaning, and the meaning of the whole group dominates over the meaning of its components. As figurativeness is expressed only in one component of the phrase it is hardly felt.
§ to pay a visit, tribute, attention, respect;
§ to break a promise, a rule, news, silence;
§ to meet demands, requirement, necessity;
§ to set free; to set at liberty;
§ to make money, journey;
§ to fall ill.
The structure V + N (дополнение) is the largest group of phraseological collocations.
Phraseological units may be defined as specific word-groups functioning as word-equivalents; they are equivalent to definite classes of words. The part-of-speech meaning of phraseological units is felt as belonging to the word-group as a whole irrespective of the part-of-speech meaning of component words. Comparing a free word-group, e.g. a long day and a phraseological unit, e.g. in the long run, we observe that in the free word-group the noun day and the adjective long preserve the part-of-speech meaning proper to these words taken in isolation. The whole group is viewed as composed of two independent units (A + N). In the phraseological unit in the long run the part-of-speech meaning belongs to the group as a single whole. In the long run is grammatically equivalent to single adverbs, e.g. finally, firstly, etc.
So, phraseological units are included into the system of parts of speech.
Phraseological units are created from free word-groups. But in the course of time some words – constituents of phraseological units may drop out of the language; the situation in which the phraseological unit was formed can be forgotten, motivation can be lost and these phrases become phraseological fusions.
The vocabulary of a language is enriched not only by words, but also by phraseological units. Phraseological units are word-groups that cannot be made in the process of speech, they exist in the language as ready-made units. They are compiled in special dictionaries. The same as words phraseological units express a single notion and are used in a sentence as one part of it. American and British lexicographers call such units «idioms». We can mention such dictionaries as: L. Smith «Words and Idioms», V. Collins «A Book of English Idioms» etc. In these dictionaries we can find words, peculiar in their semantics (idiomatic), side by side with word-groups and sentences. In these dictionaries they are arranged, as a rule, into different semantic groups.
Phraseological units can be classified according to the ways they are formed, according to the degree of the motivation of their meaning, according to their structure and according to their part-of-speech meaning.
A.V. Koonin classified phraseological units according to the way they are formed. He pointed out primary and secondary ways of forming phraseological units.
Among two-top units A.I. Smirnitsky points out the following structural types:
a) attributive-nominal such as: a month of Sundays, grey matter, a millstone round one’s neck and many others. Units of this type are noun equivalents and can be partly or perfectly idiomatic. In partly idiomatic units (phrasisms) sometimes the first component is idiomatic, e.g. high road, in other cases the second component is idiomatic, e.g. first night. In many cases both components are idiomatic, e.g. red tape, blind alley, bed of nail, shot in the arm and many others.
b) verb-nominal phraseological units, e.g. to read between the lines, to speak BBC, to sweep under the carpet etc. The grammar centre of such units is the verb, the semantic centre in many cases is the nominal component, e.g. to fall in love. In some units the verb is both the grammar and the semantic centre, e.g. not to know the ropes. These units can be perfectly idiomatic as well, e.g. to burn one’s boats, to vote with one’s feet, to take to the cleaners’ etc.
Very close to such units are word-groups of the type to have a glance, to have a smoke. These units are not idiomatic and are treated in grammar as a special syntactical combination, a kind of aspect.
c) phraseological repetitions, such as: now or never, part and parcel, country and western etc. Such units can be built on antonyms, e.g. ups and downs, back and forth; often they are formed by means of alliteration, e.g cakes and ale, as busy as a bee. Components in repetitions are joined by means of conjunctions. These units are equivalents of adverbs or adjectives and have no grammar centre. They can also be partly or perfectly idiomatic, e.g. cool as a cucumber (partly), bread and butter (perfectly).
Phraseological units the same as compound words can have more than two tops (stems in compound words), e.g. to take a back seat, a peg to hang a thing on, lock, stock and barrel, to be a shadow of one’s own self, at one’s own sweet will.
Phraseological units can be classified as parts of speech. This classification was suggested by I.V. Arnold. Here we have the following groups:
a) noun phraseologisms denoting an object, a person, a living being, e.g. bullet train, latchkey child, redbrick university, Green Berets,
b) verb phraseologisms denoting an action, a state, a feeling, e.g. to break the log-jam, to get on somebody’s coattails, to be on the beam, to nose out, to make headlines,
c) adjective phraseologisms denoting a quality, e.g. loose as a goose, dull as lead
d) adverb phraseological units, such as: with a bump, in the soup, like a dream, like a dog with two tails,
e) preposition phraseological units, e.g. in the course of, on the stroke of,
f) interjection phraseological units, e.g. «Catch me!», «Well, I never!» etc.
In I.V. Arnold’s classification there are also sentence equivalents, proverbs, sayings and quotations, e.g. «The sky is the limit», «What makes him tick», «I am easy». Proverbs are usually metaphorical, e.g. «Too many cooks spoil the broth», while sayings are as a rule non-metaphorical, e.g. «Where there is a will there is a way».
Теги:
Free word groups. Phraseological units
Контрольная работа
Английский
Просмотров: 27350
Найти в Wikkipedia статьи с фразой: Free word groups. Phraseological units
- Размер: 211 Кб
- Количество слайдов: 39