In this Article
- Select Entire Rows or Columns
- Select Single Row
- Select Single Column
- Select Multiple Rows or Columns
- Select ActiveCell Row or Column
- Select Rows and Columns on Other Worksheets
- Is Selecting Rows and Columns Necessary?
- Methods and Properties of Rows & Columns
- Delete Entire Rows or Columns
- Insert Rows or Columns
- Copy & Paste Entire Rows or Columns
- Hide / Unhide Rows and Columns
- Group / UnGroup Rows and Columns
- Set Row Height or Column Width
- Autofit Row Height / Column Width
- Rows and Columns on Other Worksheets or Workbooks
- Get Active Row or Column
This tutorial will demonstrate how to select and work with entire rows or columns in VBA.
First we will cover how to select entire rows and columns, then we will demonstrate how to manipulate rows and columns.
Select Entire Rows or Columns
Select Single Row
You can select an entire row with the Rows Object like this:
Rows(5).SelectOr you can use EntireRow along with the Range or Cells Objects:
Range("B5").EntireRow.Selector
Cells(5,1).EntireRow.SelectYou can also use the Range Object to refer specifically to a Row:
Range("5:5").SelectSelect Single Column
Instead of the Rows Object, use the Columns Object to select columns. Here you can reference the column number 3:
Columns(3).Selector letter “C”, surrounded by quotations:
Columns("C").SelectInstead of EntireRow, use EntireColumn along with the Range or Cells Objects to select entire columns:
Range("C5").EntireColumn.Selector
Cells(5,3).EntireColumn.SelectYou can also use the Range Object to refer specifically to a column:
Range("B:B").SelectSelect Multiple Rows or Columns
Selecting multiple rows or columns works exactly the same when using EntireRow or EntireColumn:
Range("B5:D10").EntireRow.Selector
Range("B5:B10").EntireColumn.SelectHowever, when you use the Rows or Columns Objects, you must enter the row numbers or column letters in quotations:
Rows("1:3").Selector
Columns("B:C").SelectSelect ActiveCell Row or Column
To select the ActiveCell Row or Column, you can use one of these lines of code:
ActiveCell.EntireRow.Selector
ActiveCell.EntireColumn.SelectSelect Rows and Columns on Other Worksheets
In order to select Rows or Columns on other worksheets, you must first select the worksheet.
Sheets("Sheet2").Select
Rows(3).SelectThe same goes for when selecting rows or columns in other workbooks.
Workbooks("Book6.xlsm").Activate
Sheets("Sheet2").Select
Rows(3).SelectNote: You must Activate the desired workbook. Unlike the Sheets Object, the Workbook Object does not have a Select Method.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Is Selecting Rows and Columns Necessary?
However, it’s (almost?) never necessary to actually select Rows or Columns. You don’t need to select a Row or Column in order to interact with them. Instead, you can apply Methods or Properties directly to the Rows or Columns. The next several sections will demonstrate different Methods and Properties that can be applied.
You can use any method listed above to refer to Rows or Columns.
Methods and Properties of Rows & Columns
Delete Entire Rows or Columns
To delete rows or columns, use the Delete Method:
Rows("1:4").Deleteor:
Columns("A:D").DeleteVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Insert Rows or Columns
Use the Insert Method to insert rows or columns:
Rows("1:4").Insertor:
Columns("A:D").InsertCopy & Paste Entire Rows or Columns
Paste Into Existing Row or Column
When copying and pasting entire rows or columns you need to decide if you want to paste over an existing row / column or if you want to insert a new row / column to paste your data.
These first examples will copy and paste over an existing row or column:
Range("1:1").Copy Range("5:5")or
Range("C:C").Copy Range("E:E")Insert & Paste
These next examples will paste into a newly inserted row or column.
This will copy row 1 and insert it into row 5, shifting the existing rows down:
Range("1:1").Copy
Range("5:5").InsertThis will copy column C and insert it into column E, shifting the existing columns to the right:
Range("C:C").Copy
Range("E:E").InsertHide / Unhide Rows and Columns
To hide rows or columns set their Hidden Properties to True. Use False to hide the rows or columns:
'Hide Rows
Rows("2:3").EntireRow.Hidden = True
'Unhide Rows
Rows("2:3").EntireRow.Hidden = Falseor
'Hide Columns
Columns("B:C").EntireColumn.Hidden = True
'Unhide Columns
Columns("B:C").EntireColumn.Hidden = FalseGroup / UnGroup Rows and Columns
If you want to Group rows (or columns) use code like this:
'Group Rows
Rows("3:5").Group
'Group Columns
Columns("C:D").GroupTo remove the grouping use this code:
'Ungroup Rows
Rows("3:5").Ungroup
'Ungroup Columns
Columns("C:D").UngroupThis will expand all “grouped” outline levels:
ActiveSheet.Outline.ShowLevels RowLevels:=8, ColumnLevels:=8and this will collapse all outline levels:
ActiveSheet.Outline.ShowLevels RowLevels:=1, ColumnLevels:=1Set Row Height or Column Width
To set the column width use this line of code:
Columns("A:E").ColumnWidth = 30To set the row height use this line of code:
Rows("1:1").RowHeight = 30AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Autofit Row Height / Column Width
To Autofit a column:
Columns("A:B").AutofitTo Autofit a row:
Rows("1:2").AutofitRows and Columns on Other Worksheets or Workbooks
To interact with rows and columns on other worksheets, you must define the Sheets Object:
Sheets("Sheet2").Rows(3).InsertSimilarly, to interact with rows and columns in other workbooks, you must also define the Workbook Object:
Workbooks("book1.xlsm").Sheets("Sheet2").Rows(3).InsertGet Active Row or Column
To get the active row or column, you can use the Row and Column Properties of the ActiveCell Object.
MsgBox ActiveCell.Rowor
MsgBox ActiveCell.ColumnThis also works with the Range Object:
MsgBox Range("B3").ColumnThis example teaches you how to select entire rows and columns in Excel VBA. Are you ready?
Place a command button on your worksheet and add the following code lines:
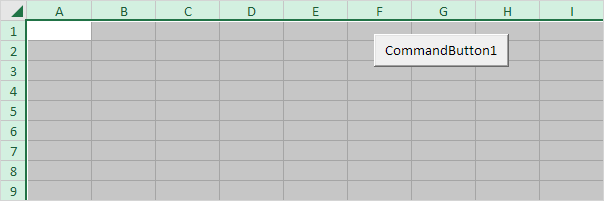
1. The following code line selects the entire sheet.
Cells.Select
Note: because we placed our command button on the first worksheet, this code line selects the entire first sheet. To select cells on another worksheet, you have to activate this sheet first. For example, the following code lines select the entire second worksheet.
Worksheets(2).Activate
Worksheets(2).Cells.Select
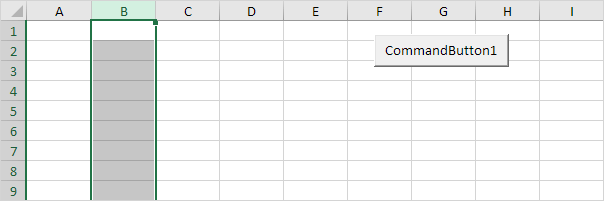
2. The following code line selects the second column.
Columns(2).Select
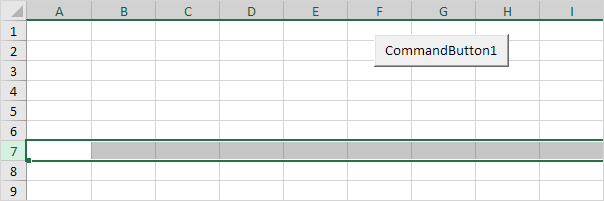
3. The following code line selects the seventh row.
Rows(7).Select
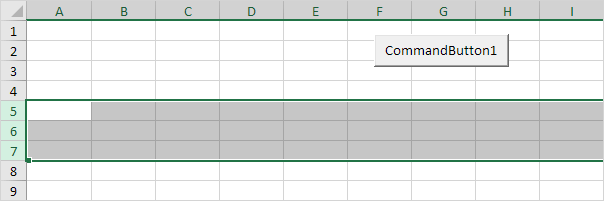
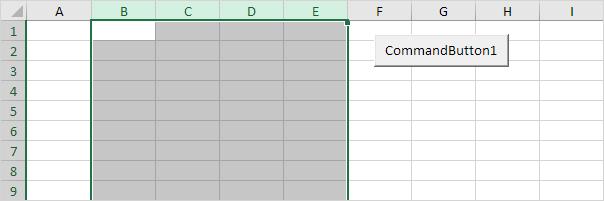
4. To select multiple rows, add a code line like this:
Rows(«5:7»).Select
5. To select multiple columns, add a code line like this:
Columns(«B:E»).Select
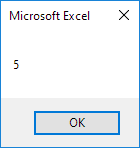
6. Be careful not to mix up the Rows and Columns properties with the Row and Column properties. The Rows and Columns properties return a Range object. The Row and Column properties return a single value.
Code line:
MsgBox Cells(5, 2).Row
Result:
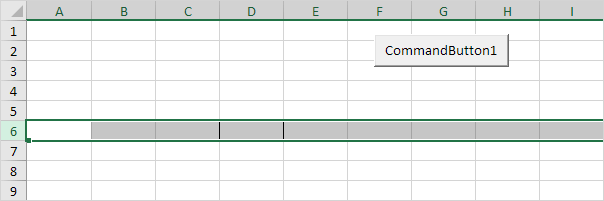
7. Select cell D6. The following code line selects the entire row of the active cell.
ActiveCell.EntireRow.Select
Note: border for illustration only.
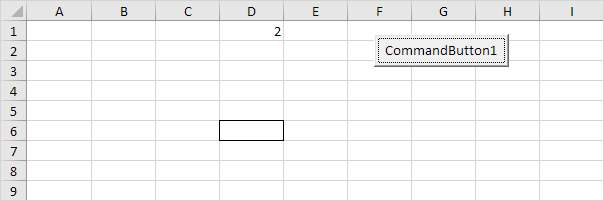
8. Select cell D6. The following code line enters the value 2 into the first cell of the column that contains the active cell.
ActiveCell.EntireColumn.Cells(1).Value = 2
Note: border for illustration only.
9. Select cell D6. The following code line enters the value 3 into the first cell of the row below the row that contains the active cell.
ActiveCell.EntireRow.Offset(1, 0).Cells(1).Value = 3
Note: border for illustration only.
VBA Select
It is very common to find the .Select methods in saved macro recorder code, next to a Range object.
.Select is used to select one or more elements of Excel (as can be done by using the mouse) allowing further manipulation of them.
Selecting cells with the mouse:

Selecting cells with VBA:
'Range([cell1],[cell2])
Range(Cells(1, 1), Cells(9, 5)).Select
Range("A1", "E9").Select
Range("A1:E9").Select
Each of the above lines select the range from «A1» to «E9».

VBA Select CurrentRegion
If a region is populated by data with no empty cells, an option for an automatic selection is the CurrentRegion property alongside the .Select method.
CurrentRegion.Select will select, starting from a Range, all the area populated with data.
Range("A1").CurrentRegion.Select

Make sure there are no gaps between values, as CurrentRegion will map the region through adjoining cells (horizontal, vertical and diagonal).
Range("A1").CurrentRegion.SelectWith all the adjacent data

Not all adjacent data

«C4» is not selected because it is not immediately adjacent to any filled cells.
VBA ActiveCell
The ActiveCell property brings up the active cell of the worksheet.
In the case of a selection, it is the only cell that stays white.
A worksheet has only one active cell.
Range("B2:C4").Select
ActiveCell.Value = "Active"

Usually the ActiveCell property is assigned to the first cell (top left) of a Range, although it can be different when the selection is made manually by the user (without macros).

The AtiveCell property can be used with other commands, such as Resize.
VBA Selection
After selecting the desired cells, we can use Selection to refer to it and thus make changes:
Range("A1:D7").Select
Selection = 7

Selection also accepts methods and properties (which vary according to what was selected).
Selection.ClearContents 'Deletes only the contents of the selection
Selection.Interior.Color = RGB(255, 255, 0) 'Adds background color to the selection

As in this case a cell range has been selected, the Selection will behave similarly to a Range. Therefore, Selection should also accept the .Interior.Color property.
RGB (Red Green Blue) is a color system used in a number of applications and languages. The input values for each color, in the example case, ranges from 0 to 255.
Selection FillDown
If there is a need to replicate a formula to an entire selection, you can use the .FillDown method
Selection.FillDown
Before the FillDown

After the FillDown

.FillDown is a method applicable to Range. Since the Selection was done in a range of cells (equivalent to a Range), the method will be accepted.
.FillDown replicates the Range/Selection formula of the first line, regardless of which ActiveCell is selected.
.FillDown can be used at intervals greater than one column (E.g. Range(«B1:C2»).FillDown will replicate the formulas of B1 and C1 to B2 and C2 respectively).
VBA EntireRow and EntireColumn
You can select one or multiple rows or columns with VBA.
Range("B2").EntireRow.Select
Range("C3:D3").EntireColumn.Select

The selection will always refer to the last command executed with Select.
To insert a row use the Insert method.
Range("A7").EntireRow.Insert
'In this case, the content of the seventh row will be shifted downward
To delete a row use the Delete method.
Range("A7").EntireRow.Delete
'In this case, the content of the eighth row will be moved to the seventh
VBA Rows and Columns
Just like with the EntireRow and EntireColumn property, you can use Rows and Columns to select a row or column.
Columns(5).Select
Rows(3).Select

To hide rows:
Range("A1:C3").Rows.Hidden = True

In the above example, rows 1 to 3 of the worksheet were hidden.
VBA Row and Column
Row and Column are properties that are often used to obtain the numerical address of the first row or first column of a selection or a specific cell.
Range("A3:H30").Row 'Referring to the row; returns 3
Range("B3").Column 'Referring to the column; returns 2
The results of Row and Column are often used in loops or resizing.
Consolidating Your Learning
Suggested Exercise
SuperExcelVBA.com is learning website. Examples might be simplified to improve reading and basic understanding. Tutorials, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content. All Rights Reserved.
Excel ® is a registered trademark of the Microsoft Corporation.
© 2023 SuperExcelVBA | ABOUT

If the user selects multiple rows in Microsoft Excel, the selection can contain multiple areas. An area is a subselection of rows created when the user presses the Shift button while doing a multiselect. In VBA we need to handle each area independently to be able to retrieve all the selected rows.
' Example
Public Sub Test()
Dim objSelection As Range
Dim objSelectionArea As Range
Dim objCell As Range
Dim intRow As Integer
' Get the current selection
Set objSelection = Application.Selection
' Walk through the areas
For Each objSelectionArea In objSelection.Areas
' Walk through the rows
For intRow = 1 To objSelectionArea.Rows.Count Step 1
' Get the row reference
Set objCell = objSelectionArea.Rows(intRow)
' Get the actual row index (in the worksheet).
' The other row index is relative to the collection.
intActualRow = objCell.Row
' Get any cell value by using the actual row index
' Example:
strName = objNameRange(intActualRow, 1).value
Next
Next
End Sub
In the example we have not defined the variables strName and objNameRange. For your reference the variables are defined as follows:
Dim strName As String Dim objNameRange As Range
objNameRange can be any range in your selected worksheet.
Related
- Get Column Name from Column Index in Excel
- Get Microsoft Excel
Ulf Emsoy
Ulf Emsoy has long working experience in project management, software development and supply chain management.
Back To Top
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However, you may visit «Cookie Settings» to provide a controlled consent.
Sometimes you’ll want to select entire rows or columns, or even every cell in
a worksheet. Here’s how:
Selecting Columns
You can do this using the Columns collection. For
example:
Sub SelectColumns()
Columns(«B»).Select
Columns(«B:D»).Select
End Sub
The above macro would select column B, then columns
B through to D:
The result of running the above macro.
Note that you can select a single column by number too — for example,
Columns(2).Select — but this method doesn’t work for a range of
columns.
Selecting Rows
You can select rows in the same way, but using the Rows
collection:
Sub SelectRows()
Rows(«2»).Select
Rows(«2:4»).Select
End Sub
The above routine would leave rows 2 through to 4 selected:
The results of running the macro above.
Note that as for columns you can dispense with the quotation marks if you’re
selecting a single row. So Rows(2).Select would also
select the second row.
Selecting Every Cell in a Worksheet
In Excel you can select every single cell by clicking on the square at the
top left corner of a worksheet:
Click on the square shown to select every cell in a worksheet.
The VBA equivalent command to select every single cell in a sheet is:
Having seen how to select cells, rows and columns, it’s time to complete the
picture by showing some of the less commonly used selection commands.