| Java Games: Flashcards, matching, concentration, and word search. | ||
Tools
- Copy this to my account
- E-mail to a friend
- Find other activities
- Start over
- Help
Many science words are combinations of two or more word parts. Scientists combine root words when they need a new word. Therefore, knowing the meaning of the roots will make it easier for you to read and understand science.
| A | B |
|---|---|
| ager | field |
| anti | against, oppostie |
| astro | star |
| auto | self |
| bi | two |
| carn | flesh |
| chrom | color |
| chron | time |
| derm | skin |
| eco | environment |
| geo | earth |
| graph, gram | write |
| hemi | half |
| hydro | water |
| ism | manner or state |
| itis | inflammation of |
| logy | science of, study of |
| meter | measure |
| meteor | sky phenomenon |
| micro | small |
| mono | one, single |
| morph | form, shape |
| nomy | sum of knowledge |
| photo | light |
| pod | foot |
| poly | many |
| protos | early, first |
| pseudo | false |
| psych | mind |
| retro | backward |
| scop | see |
| techno | art, craft |
| tele | far |
| thermo | heat |
| ultra | beyond |
| vorous | feeding on, eating |
| zoion | animal |
| bio | life |
| This activity was created by a Quia Web subscriber. Learn more about Quia |
Create your own activities |
Science Terms! The following is a list of common Science Terms in English.
Science Terms
Science Vocabulary Word List
Words That Start With A
astronomy
astrophysics
atom
Words That Start With B
beaker
biochemistry
biology
botany
Bunsen burner
burette
Words That Start With C
cell
chemical
chemistry
climate
climatologist
control
cuvette
Words That Start With D
data
datum
Words That Start With E
electricity
electrochemist
element
energy
entomology
evolution
experiment
Words That Start With F
fact
flask
fossil
funnel
Words That Start With G
genetics
geology
geophysics
glassware
graduated cylinder
gravity
Words That Start With H
herpetology
hypothesis
Words That Start With I
ichthyology
immunology
Words That Start With L
lab
laboratory
laws
lepidoptery
Words That Start With M
magnetism
mass
matter
measure
meteorologist
meteorology
microbiologist
microbiology
microscope
mineral
mineralogy
molecule
motion
Words That Start With O
observatory
observe
organism
ornithology
Words That Start With P
paleontology
particle
Petri dish
phase
physical science
physics
pipette
Words That Start With Q
quantum mechanics
Words That Start With R
radiology
research
retort
Words That Start With S
scale
science
scientist
seismology
Words That Start With T
telescope
temperature
test tube
theory
thermometer
tissue
Words That Start With V
variable
virologist
volcanology
volume
volumetric flask
Words That Start With W
watch glass
weather
weigh
Words That Start With Z
zoology
List of Science words with Examples
- astronomy
EX: Physics and astronomy are cognate sciences.
- astrophysics
EX: I am an astrophysics student for the University of TX.
- atom
EX: The nucleus of an atom consists of neutrons, protons and other particles.
- beaker
EX: The next days when the researchers flipped the beaker, the silicone oil began to form fat mounds.
- biochemistry
EX: Her specialty is biochemistry.
- biology
EX: The course will encompass physics, chemistry and biology.
- botany
EX: The life sciences include biology and botany.
- Bunsen burner
EX: You will learn how to use scientific apparatus such as test tubes, beakers and Bunsen burners.
- burette
EX: The burette is placed in water and the air pressure equalised by opening and closing the tap.
- cell
EX: DNA is stored in the nucleus of a cell.
- chemical
EX: Physical therapy alternates with chemical.
- chemistry
EX: The course will encompass physics, chemistry and biology.
- climate
EX: We need to assess the impact on climate change.
- climatologist
EX: A climatologist is greatly concerned with the time constants of the energy reservoirs of the world.
- control
EX: How do you operate the remote control unit?
- cuvette
EX: A new cuvette which is able to contain plastic centrifuge tube for fluorescence spectrophotometry is described.
- data
EX: The retention of data in a storage device.
- datum
EX: The crucial datum is this: the rate of gypsy-moth spread is now much more rapid than before.
- electricity
EX: Electricity companies pay a premium for renewable energy.
- element
EX: He was the discoverer of the element radium.
- energy
EX: It wastes energy to run the dishwasher half empty.
- entomology
EX: He decided to specialize in entomology after graduation.
- evolution
EX: In the course of evolution, some birds have lost the power of flight.
- experiment
EX: They are absorbed in the experiment.
- fossil
EX: This fossil may be over 2 million years old.
- funnel
EX: I need a funnel to pour petrol into the tank.
- genetics
EX: Knowledge in the field of genetics has been developing very rapidly.
- geology
EX: It is a problem that relates to geology.
- geophysics
EX: Developing seismoelectric exploration is the leading edge in geophysics.
- graduated cylinder
EX: Place 100 mL of pyridine in a 250-mL graduated cylinder , and, keeping the pyridine cold in an ice bath, pass in dry sulfur dioxide until the volume reaches 200 mL.
- gravity
EX: Gravity is a natural phenomenon.
- laboratory
EX: The laboratory was well insulated against all outside noise.
- microscope
EX: An object was magnified 200 times by the microscope.
- telescope
EX: The telescope was pointing in the wrong direction.
- temperature
EX: In hot weather the temperature gets very high.
- test tube
EX: The test tube was then put in an ultrasound bath for 5 minutes.
- thermometer
EX:Use a thermometer to gauge the temperature.
- tissue
EX: The virus remains dormant in nerve tissue until activated.
- variable
EX: The variable weather is a great trial to me.
- virologist
EX: The veterinary virologist and the clinician are naturally interested in effectively combating a viral infection.
- weigh
EX: The scales can be used to weigh other items such as parcels.
- zoology
EX: The library didn’t stock zoology textbooks.
Science Terms | Pictures
Students must learn new specific terminology if they are to develop their understanding of scientific concepts.
Beck, McKeown and Kucan (2013) categorise vocabulary into three tiers:
- Tier 1: everyday words (e.g. word, number)
- Tier 2: words that are useful across multiple subject areas (e.g. analysis, argument)
- Tier 3: subject-specific words or technical terminology (e.g. electromagnetism, photovoltaic).
Within Science, explicitly teaching Tier 2 and 3 words will allow students to access and communicate scientific content knowledge.
Leno and Dougherty (2007) argue that methods of teaching vocabulary that focus on students copying definitions from a textbook are problematic for three reasons:
- definitions in isolation can be too broad or too narrow, having no direct link to the topic being taught
- students may copy definitions absentmindedly, rather than reading and understanding the definition
- identifying definitions within a passage of text may lead to incomplete or incorrect definitions.
Introducing new vocabulary in contextually rich and cognitively demanding ways benefits all students, whether students identify as English-speaking, English as an additional language (EAL), or as having a disability or additional needs.
Four strategies that teachers can use to introduce new vocabulary to students are:
- Teaching base words and words parts (morphemes)
- Joint construction of definitions
- Naming processes (nominalisation)
-
Everyday vs scientific words (register)
Teaching base words and word parts (morphemes)
Morphemes are the smallest units of meaning represented in written and spoken language. There are different types of morphemes, including bases and affixes (prefixes and suffixes). Words, for example, can be deconstructed into more than one morpheme as in the word electric consisting of two morphemes: [electr] + [-ic]. New words can also be created by attaching additional morphemes. For example, adding the noun forming suffix [-ity] to the adjective [electric], creates the noun, electricity.
Rather than memorising words, students can learn about morphemes as a way to look ‘inside’ unfamiliar technical terms to find meaningful parts.
Understanding how scientific terminology is structured using common Greek and Latin morphemes, and how morphemes connect words in meaningful ways, offers students portable knowledge about form-function-meaning relationships in words to support vocabulary development with potential flow-on benefits to writing and reading comprehension (Herrington & Macken-Horarik, 2015; Nunes & Bryant, 2006).
Literacy in Practice Video: Biology — Morphemes
In this video, Catherine Walkear introduces students to morphemes. In the video, Catherine uses the parts card strategy in a Year 7 science class learning about taxonomy. She also uses morphological matrices in a Year 8 Biology class learning about diseases and disorders.
Teacher prompts
- What do you think the value is in teaching students about morphemes in Science?
- How might you introduce your students to morphemes in Science
Student prompts
- Do you think knowing more about morphemes would help you better learn new vocabulary in Science?
Read the
in-depth notes for this video.
Parts card strategy for introducing vocabulary
Stants’s (2013) parts card strategy is one way for teachers to introduce students to new vocabulary. The parts card strategy requires students to dissect new vocabulary, generate meaning, and then draw a diagram to demonstrate their understanding. Zoski et al. (2018) have modified Stants’s parts card strategy to emphasise the language modes.
See an example of a
parts card work sample for Year 7 or Year 8 (VCSSU092,
VCSSU095)
Morphological matrix
Bowers and Cooke’s (2012) morphological matrix is another tool teachers and students can use to develop new vocabulary. Morphological matrices list the various prefixes and suffixes that can be combined to base words to generate new words. The two worked examples below show how the matrix can be used from Year 7 to Year 10, depending on the vocabulary and context.
hyper + tonic = hypotonic
iso + tonic = isotonic
hypo + tonic = hypotonic
Curriculum links for the above example:
VCSSU095,
VCSSU117
| endo | therm | al |
| exo | ||
| geo | ||
| hydro | ic | |
| meso | ||
| iso |
endo + therm + al = endothermal
endo + therm + ic = endothermic
therm + al = thermal
exo + therm + al = exothermal
exo + therm + ic = exothermic
geo + therm + al = geothermal
geo + therm + ic = geothermic
hydro + therm + al = hydrothermal
hydro + therm + ic = hydrothermic
meso + therm + ic = mesothermic
meso + therm + al = mesothermal
iso + therm + al = isothermal
iso + therm + ic = isothermic
Curriculum links for the above example:
VCSSU091,
VCSSU100,
VCSSU098,
VCSSU117,
VCSSU126,
VCSSU127
Joint construction of definitions
Joint construction is a collaborative process that involves the teacher and students working together to construct understanding. It is a reciprocal process in which the students’ responses and behaviours influence the teacher’s responses and behaviours, and vice versa (van Vondel et al., 2017).
Joint construction can be used to develop students’ understanding of new scientific terminology and definitions as outlined below:
- The teacher introduces a technical term within context, for example, read a definition from a textbook, watching an informative video
- Students talk out the term with a partner
- Individually or in pairs, students write a definition for the term in their own words
- The teacher asks students to share their definitions, writing one of them on the board
- Through dialogue, the teacher and students refine the definition on the board
- Students compare and correct their own definitions in relation to the jointly constructed definition.
For example, students in Year 8 (VCSSU090,
VCSSU094) could:
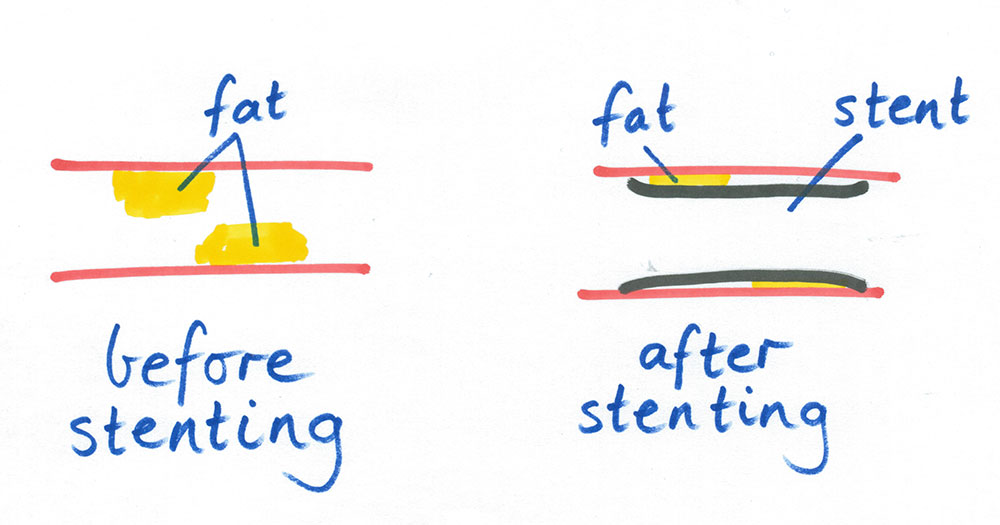
- watch an informative video on stenting (e.g. “Coronary angioplasty, balloons and stents”)
- talk out what stenting means
- draw and write a definition.
Student definition: «Stenting is when a stent (tube) is placed in an artery to unblock it.»
Naming processes (nominalisation)
Nominalisation is the process of forming nouns from other word groups. Nominalisation is one of the most distinctive linguistic features of scientific writing (Banks, 2008; Halliday, 2004). This is because scientific texts are often highly condensed and frequently contain abstract ideas and concepts.
In Science, verbs are often nominalised to create the names of processes. This can be done by:
- creating a gerund (by adding the [-ing] suffix). For example, weather can be nominalised to weathering (e.g. chemical weathering)
- adding noun forming suffixes such as [-al], [-ce], [-ion] and [-ment]. For example, when [-ion] is added to the end of the verb, stagnate, the nominalised form is produced: stagnation
- Adding a noun forming prefix such as [ante-], [fore-], [macro-], [maxi-], [micro-], [mid-], [mini-], [pre-] and [post-]. For example, when [sur-] meaning ‘extra’ is attached to the front of the verb charge, the noun surcharge is formed.
Similarly, adjectives can be nominalised by adding noun suffixes. For example, noun density is formed by adding the morpheme [-ity] to the adjective, dense.
Educating students about regular noun forming suffixes (morphemes) is one way to introduce students to nominalisation. The tables below show how verbs and adjectives are nominalised in Science using a selection of regular noun suffixes.
| Verb | Noun forming suffix | Noun |
|---|---|---|
| diffuse | -ion | diffusion |
| mix | -ure | mixture |
| measure | -ment | measurement |
| analyse | -is | analysis |
| survive | -al | survival |
| resist | -ance | resistance |
| insulate | -or | insulator |
| Adjective | Noun forming suffix | Noun |
|---|---|---|
| soluble | -ity | solubility |
| frequent | -cy | frequency |
| soft | -ness | softness |
An unintended consequence of using nominalisation is the introduction of abstraction (Halliday, 2004). Explicitly teaching the word parts of nominalised terms helps students to identify embedded meaning.
Knowing how to construct and deconstruct nominalised terms also helps students to better interpret and create texts, and to write in a more sophisticated and scientific manner.
One way to teach Year 9 and 10 students to use nominalisation in their writing is outlined below, along with an example of what a student’s work may look like. The example supports the teaching of the following curriculum links:
VCSSU124,
VCSSU125,
VCSIS140
| Step | Student example |
|---|---|
| 1. Student writes a conclusion for an experiment | The chemicals reacted and bubbles formed. |
| 2. Student highlights verbs in their writing | The chemicals reacted and bubbles formed. |
| 3. Student converts the verbs to nouns | reacted becomes reaction formed becomes formation |
| 4. Student rewrites the conclusion using the newly created nouns (nominalised verbs) | The chemical reaction resulted in the formation of bubbles. |
When reading, reversing the strategy above can help students to unpack the meaning of dense nouns, particularly those relating to scientific or experimental processes. Compound nouns ([noun + noun] or [adjective + noun]) may also be underlined. Again, the example supports the teaching of the following curriculum links:
VCSSU124,
VCSSU125,
VCSIS140
| Step | Student example |
|---|---|
| 1. Student reads a passage from a text | A combustion reaction is an example of an exothermic reaction. Combustion occurs when a substance reacts with oxygen gas to produce heat, usually in the form of an explosion or burning. Combustion reactions are also a type of oxidation reaction because oxygen is a reactant. |
| 2. Student highlights nouns in the passage, looking for noun-forming suffixes or compound nouns | A combustion reaction is an example of an exothermic reaction. Combustion occurs when a substance reacts with oxygen gas to produce heat, usually in the form of an explosion or burning. Combustion reactions are also a type of oxidation reaction because oxygen is a reactant |
| 3. Student converts the selected nouns to verbs | “combustion» becomes “to combust” “combustion reaction” becomes “to react and combust” “exothermic reaction” becomes “react and produce heat” “explosion” becomes “to explode” “burning” becomes “to burn” “oxidation reaction” becomes “to react with oxygen.” |
| 4. Student writes or orates a definition for the noun | Combustion is a chemical reaction with oxygen that results in an explosion or burning. |
Everyday vs scientific words (register)
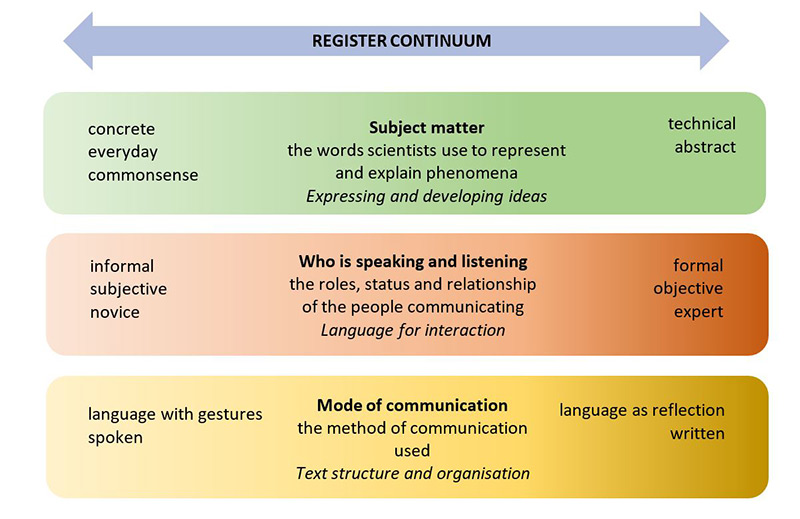
Scientists speak and write differently depending on the audience, the context and the purpose. The different styles or formalities of speaking and writing are known as ‘register’ and can be placed along a continuum. The register continuum below emphasises the links between scientific communication and the
F–10 Victorian Curriculum: English sub-strands.
In Science, students need to be explicitly taught how to write and speak in more formal registers. Teacher modelling (HITS Strategy 3) and ongoing feedback (HITS Strategy 
VCSSU095 and
VCSIS113.
- The students are asked to design an experiment to show how impurities affect the melting and/or boiling points of a substance.
- The teacher revises the scientific content and knowledge students require, introducing and explaining technical terms, making explicit links between concrete verbs and more abstract nouns (e.g. melting/liquify and liquefaction; boiling/evaporate and evaporation).
- The teacher writes the words on the board, organised in a table like the one below.
Everyday word Everyday word and scientific word Scientific word bubbles
turns to waterboils
meltsvapourise
liquifies - Students work in small groups to design the experiment.
- The teacher moves around the groups, questioning and assisting students to use more technical terms in their small group discussions.
- So when you say ___, that means ___.
- Do you remember the technical term we use?
- Each group presents their experiment to the class.
- Again, the teacher questions and assists the students to use more formal and technical language. The teacher may also model or scaffold how to do this.
- How would the textbook describe that process?
- That’s an everyday term; can you remember the scientific name for it?
Classroom discussions and questioning
Questioning (HITS Strategy 7) provides students with opportunities to talk about, argue and express opinions and differing points of view (DET, 2017). Effective questioning is fundamental to fostering productive discussion (or classroom talk) (Fisher, Frey and Hattie, 2016). During conversations, teachers can ask a number of questions to promote deeper thinking and to increase the level of rigour of classroom talk.
The following two strategies have been adapted from
Accountable Talk® Sourcebook (Michaels et al., 2010) for the Science classroom. Teachers can find other strategies to promote effective discussions in the online resource.
Fishbowl
- A research question or hypothesis is shared with the whole class (either teacher- or student-generated).
- A small, focal group of students (the “fish”) are selected to discuss and determine a methodology for the given investigation. The focal group should:
- select appropriate equipment
- identify controlled and independent variables
- propose an appropriate procedure
- explain how data will be recorded.
- The focal group is positioned so that the rest of the class (the “researchers”) can observe their conversation. The researchers are critical observers, assessing the talk of the focal group.
- At different points during the conversation, the teacher interrupts the focal group and asks the researchers to discuss the focal students’ talk, process, or reasoning.
- The teacher should not intervene or comment on each student’s contribution
- At strategic moments, the teacher refocuses the observers and guides the group discussion to determine a final methodology for the investigation.
- The investigation is conducted by the entire class in the following lesson.
Curriculum links for the above example:
VCSIS108,
VCSIS109,
VCSIS135
Pressing for accuracy and evidence
The questions below can support students to develop their understanding of the use and importance of evidence in scientific conversations. Teachers can ask these questions during class discussions, with small groups, or individually with a student.
- Where can we find that in the textbook?
- What did you observe to make you think/say that?
- What evidence do you have to support what you have just said?
- How could we check what you have just said?
- Is there more data to support that inference?
- How could we collect more data to support your claim?
When necessary, teachers can model to students how to use evidence to answer such questions.
References
- Banks, D. (2008). The Development of Scientific Writing. Linguistic features and historical context (p. 221). Equinox.
- Beck, I.L., McKeown, M.G., & Kucan, L. (2013). Bringing words to life: Robust vocabulary instruction. Guilford Press.
- Bowers, P.N., & Cooke, G. (2012). Morphology and the common core building students’ understanding of the written word. Perspectives on Language and Literacy, 38(4), 31-35
- Derewianka, B., & Jones, P. (2016). Teaching language in context. Oxford University Press. 198 Madison Avenue, New York, NY 10016.
- Department of Education and Training (DET). (2017). High impact teaching strategies: Excellence in teaching and learning. Melbourne: DET.
- Fisher, D., Frey, N., & Hattie, J. (2016). Visible learning for literacy, grades K-12: Implementing the practices that work best to accelerate student learning. Corwin Press.
- Halliday, M.A.K. (2004). The language of science. London: Continuum.
- Herrington, M.H., & Macken-Horarik, M. (2015). Linguistically informed teaching of spelling: Toward a relational approach. Australian Journal of Language and Literacy, The, 38(2), 61-71.
- Leno, L.C., & Dougherty, L. A. (2007). Using direct instruction to teach content vocabulary. Science Scope, 31(1), 63-66.
- Michaels, S., O’Connor, M.C., Hall, M.W., & Resnick, L.B. (2010).
Accountable talk sourcebook: For classroom conversation that works. Pittsburgh, PA: University of Pittsburgh Institute for Learning. Retrieved from - Nunes, T., & Bryant, P. (2006). Improving literacy by teaching morphemes. Routledge.
- Stants, N. (2013). Parts cards: Using morphemes to teach science vocabulary. Science Scope, 36(5), 58-63.
- van Vondel, S., Steenbeek, H., van Dijk, M., & van Geert, P. (2017). Ask, don’t tell; A complex dynamic systems approach to improving science education by focusing on the co-construction of scientific understanding. Teaching and Teacher Education, 63, 243-253.
- Yore, L.D., Bisanz, G.L, & Hand, B.M. (2003). Examining the literacy component of science literacy: 25 years of language arts and science research. International Journal of Science Education, 25(6), 689–725.
- Zoski, J.L., Nellenbach, K.M., & Erickson, K.A. (2018). Using morphological strategies to help adolescents decode, spell, and comprehend big words in science. Communication Disorders Quarterly, 40(1), 57–64.
Science Words : Physics Vocabulary
Previous PageScience Words : Physics Vocabulary :
As per the Oxford Dictionary, the term VOCABULARY means
1. The stock of words used by or known to a particular people or group of persons
2. A List or collection of the words or phrases of a language, technical field, etc., usually arranged in alphabetical order and defined
3. The words of a language
We have collected almost all the words related to Science and listed them here for your reference. Although the list is exhausting, we have added all that we have and keep on out steps to collect more and more words. We humbly request YOU all to share the collection of words that you may have in your library with us so that we will add those list of words in this page and that will ultimately benefit our visitors like YOU.
Here is The Complete Lists.
- Aberration
- Absolute
- Absorptive Power
- Acceleration
- Accelerator
- Accelerometer
- Accessory
- Accommodation
- Action
- Adhesion
- Adiabatic
- Advantage
- Aerial
- Aeroplane
- Aileron
- Air Brake
- Air Pump
- Alternating Current
- Alternation
- Alternator
- Altimeter
- Amplifier
- Amplitude
- Analogy
- Analysis (Of Light)
- Angle of Contact
- Angle of Deviation
- Angle of Emergence
- Angle of Incidence
- Angle of Projection
- Angle of Reflection
- Angular Moment
- Angular Velocity
- Anode
- Anticlockwise
- Apparatus
- Apparent
- Apparent Expansion
- Arrestment
- Astigmatism
- Astronomical
- Astronomy
- Atmosphere
- Atom
- Atomic Number
- Automatic
- Auxiliary
- Axis of Mirror
- Balance Wheel
- Balancing Point
- Bar Magnet
- Barograph
- Baroscope
- Baroscopic
- Base
- Battery
- Beaker
- Beam of Balance
- Beam of Light
- Beats
- Bell Jar
- Belt (For Driving)
- Biconvex Lens
- Binding Energy
- Biding Screw
- Bioscope
- Black Body
- Block (Pulling)
- Bob
- Boiler
- Boiling Point
- Brake
- Brush
- Bulb
- Buoy
- Buoyancy
- Calibration
- Calliper
- Cam
- Capacitance
- Capillarity
- Carrier Waves
- Cathode
- Centre of Buoyancy
- Centre of Curvature
- Centre of Gravity
- Centre of Oscillation
- Centre of Pressure
- Centre of Suspension
- Centrifugal
- Centripetal
- Chromatic Aberration
- Chromo Sphere
- Chronometer
- Circulation
- Clamp
- Clip
- Clockwise
- Code
- Coefficient
- Cohesion
- Collination
- Collinator
- Collision
- Colour Blindness
- Commutator
- Compass
- Compass Needle
- Compass Points
- Compensated
- Components (Of Forces)
- Composition of Forces
- Compressibility
- Computer
- Concave
- Concave Lens
- Concave Mirror
- Concavo-Convex Lens
- Concurrent
- Condenser
- Conductance
- Conduction
- Conductor
- Conjugated Foci
- Connection in Parallel
- Constant
- Continuous Current
- Convection
- Convergent (Pencil)
- Convex Lens
- Convex Mirror
- Core
- Counter Clockwise
- Couple
- Couple Forces
- Coupling
- Crank
- Crests and Troughs
- Critical Angle
- Cross Section
- Cross Wire
- Cubical Expansion
- Declination
- Definition
- Deflection
- Demagnetization
- Density
- Depolarisation
- Depolariser
- Depression
- Detector
- Developer
- Deviation
- Dew-point
- Diagram
- Diaphragm
- Diatomic scale
- Dielectric
- Diffraction
- Direct current
- Directive property
- Disc
- Discord
- Displacement
- Divergent
- Divisibility
- Down stroke
- Ductility
- Ebullition
- Eccentric
- Efficiency
- Effort
- Elastic Fatigue
- Elasticity
- Electric Circuit
- Electric Charge
- Electric Current
- Electric Discharge
- Electric Field
- Electric Induction
- Electric Resistance
- Electric Shock
- Electrification
- Electrode
- Electro Motive Force
- Electrolysis
- Electrolyte
- Electron
- Electronics
- Electroplating
- Electroscope
- Elevator
- Elongation
- Emergent Ray
- Energy
- Equilibrant
- Equilibrium
- Exhaustion
- Expansion
- Eye Lens
- Eye Piece
- Fathometer
- Fatigue
- Film
- Fixed Point
- Fixing
- Flask
- Flexibility
- Flotation
- Flow
- Fluid
- Focal Length
- Focus
- Fog
- Force Pump
- Formula
- Freezing Mixture
- Freezing Point
- Frequency
- Friction
- Frictional Resistance
- Frost
- Fulcrum
- Fundamental
- Fuse
- Gaseous State
- Gauge
- Generator
- Graduation
- Grating
- Gravitation
- Gravity
- Grid
- Ground Glass
- Hail
- Hardness
- Harmony
- Heating effect
- Hinge
- Horse power
- Humidity
- Hydraulic brake
- Hydraulic press
- Hydro meter
- Hygrometer
- Hygrometric state
- Ignition
- Illuminative Power
- Impact
- Impulse
- Incandescence
- Incident Ray
- Inclination
- Inclined Plane
- Incompressibility
- Indestructibility
- Index
- Indigo
- Indivisibility
- Induced Magnetization
- Induction
- Induction Coil
- Inertia
- Inference
- Inflator
- Insulation
- Intensity
- Interaction
- Interference
- Interval
- Inverse Proportion
- Inverse Square Law
- Invisible Rays
- Ion
- Ionization
- Iridescence
- Isothermal
- Jet
- Jet Propulsion
- Joule
- Kelvin
- Kepler
- Key
- Kilogram
- Kilowatt Hour
- Kinematics
- Kinetic Energy
- Kinetic Theory
- Lactometer
- Laser
- Latent Heat
- Lateral Displacement
- Lateral Inversion
- Lathe
- Law of Conservation Of Energy
- Law of Inertia
- Law of Reflection
- Law of Universal Gravitation
- Lepton
- Lever
- Lifebuoys
- Light Emitting Diode
- Like Charges
- Like Poles
- Linear Accelerator
- Linear Expansion
- Liquefaction
- Liquid
- Liquid Crystal Diode
- Load Distance
- Load Force
- Loadstone
- Local Action
- Longitudinal Wave
- Loudness
- Lubricant
- Lumen
- Luminous Flux
- Lunar Eclipse
- Lux
- Magic Lantern
- Magnetic Field
- Magnetic Force
- Magnetic Induction
- Magnifying Power
- Magnitude
- Malleability
- Manometer
- Mass
- Matter
- Mechanical Advantage
- Medium
- Melody
- Melting Point
- Meniscus
- Microscope
- Minimum Deviation
- Mirage
- Mist
- Momentum
- Musical Note
- Myopia
- Natural Frequency
- Net Force
- Neutrino
- Neutron
- Newton
- Newton-Meter
- Newton’s First Law Of Motion
- Newton’s Second Law Of Motion
- Newton’s Third Law Of Motion
- Nodal Lines
- Node
- Non-Metal
- Normal
- Nuclear
- Nuclear Chain Reaction
- Nuclear Decay Series
- Nuclear Energy
- Nuclear Fission
- Nuclear Fusion
- Nuclear Radiation
- Nucleons
- Nucleus
- Nuclide
- Objective
- Observation
- Octave
- Opaque
- Open Circuit
- Operational Definitions
- Optic Centre
- Optical Fibre
- Optics
- Orbital Motion
- Ordinary Hydrogen
- Organizing Data
- Ort Circuit
- Oscillation
- Oscillator
- Oton Bean
- Out’s Hypothesis
- Overtones
- Parallax
- Partial Eclipse
- Particle
- Pendulum
- Penumbra
- Photometer
- Pitch of The Screw
- Pivot
- Plane
- Plane Mirror
- Pointer
- Polarisation
- Pole
- Porosity
- Positive Electricity
- Potential Energy
- Potentiality
- Power
- Pressure
- Principal Axis
- Pulley
- Pyknometer
- Quantized
- Quantum
- Quantum Mechanics
- Quantum Number
- Quantum of Light
- Quantum Theory
- Quarks
- Radiation
- Rain Gauge
- Reaction
- Reading
- Real Image
- Receiver
- Recoil
- Rectifier
- Reflection
- Refraction
- Refractive Index
- Refractometer
- Refrigerant
- Regulation
- Relative Density
- Relative Expansion
- Relative Humidity
- Relay
- Repulsion
- Reservoir
- Resistance
- Resolution of Forces
- Resonance
- Resting Point
- Resultant
- Retardation
- Rigidity
- Rim
- Rocket
- Rotatory Compressor
- Rudder
- Safety Fuse
- Satellite
- Saturation
- Screen
- Screw Thread
- Secondary Axis
- Sensitized
- Shaft
- Simple Pendulum
- Siphon
- Slide Valve
- Slit
- Snow
- Solenoid
- Solidify
- Solidity
- Sonometer
- Space
- Specific Gravity
- Specific Heat
- Spectrometer
- Spectroscope
- Spectrum
- Speed
- Spherometer
- Spiral Spring
- Statics
- Stopcock
- Stop Watch
- Suction Pump
- Suction Tube
- Surface
- Surface Tension
- Swing
- Sympathetic Vibration
- Synthesis of Light
- Tachometer
- Telescope
- Temperature
- Tension
- Terminal
- Theory
- Thermal capacity
- Thermal couple
- Thermodynamics
- Thermoscope
- Thermostat
- Thickness
- Thrust
- Tone
- Torsion
- Total internal reflection
- Transformer
- Translucent
- Transmitter
- Transparent
- Transverse vibration
- Turbine
- Tuning fork
- Turning point
- Ultimate Stress
- Ultrasonic
- Ultrasonic Cleaners
- Ultrasonic Waves
- Ultrasound
- Ultraviolet
- Ultraviolet Radiation
- Ultraviolet Rays
- Umbra
- Unbalanced Force
- Uncertainty Principle
- Unit
- Universal Gravitation
- Unsaturated
- Up Quarks
- UV
- Vacuum
- Vacuum Brake
- Vacuum Tube
- Valence Electrons
- Valve
- Vaporization
- Vapour Pressure
- Vector
- Vector Addition
- Vector Resolution
- Velocity
- Velocity of Sound
- Vertical Motion
- Vibration
- Virtual Image
- Viscosity
- Visible Light
- Visible Radiation
- Visible Spectrum
- Vocal Chord
- Vocal Cords
- Volatile
- Volta Meter
- Voltmeter
- Volume
- Volume of A Cylinder
- Volume of Sphere
- Water Equivalent
- Water Level
- Water Wheel
- Wave Front
- Wave Length
- Wave Theory
- Wheel And Axle
- Winding and Axle
- Winding
- Wound
- Watt
- Watts
- Wave
- Wavelength
- Weak Force
- Weight
- White
- Work Function
- X Rays
- Xwell’s Law of Induction
- Zero Error
- Zener DiodeVocabulary Index
From Science Words to HOME PAGE
101 ACT® Science Vocabulary Words You Should Know
-
The Albert Team -
Last Updated On: March 1, 2022

ACT® Science Vocabulary Words
ACT® Science is all about getting the maximum number of questions right in a relatively short period. Having a strong vocabulary helps a lot in improving your understanding of the questions and reducing the time it would take for you to understand the question. This article will help you improve your ACT® score by compiling a list of commonly used words in the ACT® Science vocabulary along with their meanings.
Remember that this word list is not a substitute for the concepts themselves. It serves as a summary of commonly used words with which you need to be familiar. However, if you do not understand a word or the associated concept, it is necessary that you study that concept from a recommended textbook.
A Few Tips to Help You Remember the Words and Concepts
Some students understandably have a hard time memorizing a given list of words or phrases. Here are a few tips which might help you if you feel like you’re getting stuck and are unable to remember the words or concepts:
- Use flashcards as a tool for improving your learning.
- Do not try to study and remember all of them at once. ACT® Science vocabulary is not something you can read once and then remember. Break them down into sets of 10 – 20 words and then study them. Once you feel confident with one set, move onto the next set until you are done.
- If you are unable to understand the underlying concept, try looking it up in your textbook or online. It is always easier to remember something you understand rather than simply memorizing it.
- You can also use the list as a tool for a quick review before your ACT® exam.
The 101 Words
Here is a list of words which have commonly been a part of the ACT® Science vocabulary. However, keep in mind that this list is not exhaustive and would not contain all the possible words and concepts you would need to know.
- Absolute zero: the lowest possible temperature. It is 0 Kelvin or approximately -273 degrees Celsius.
- Abundant: something which is plentiful or exists in large quantities.
- Acceleration: rate of change of velocity, often expressed in m/s2.
- Acid: a molecule capable of donating a positively-charged hydrogen ion, or capable of forming a covalent bond by donating an electron pair.
- Adhere: to stick completely on a surface.
- Aerobic respiration: the process of glucose breakdown in the body of an animal for supplying muscles with oxygen.
- Altitude: the vertical distance between an object and the ground or sea level; any object on the ground or sea level is said to have 0 altitude.
- Analyze: to examine something in detail (such as phenomena, the result of an experiment, data collected from a survey, etc.).
- Anecdote: a story told by someone based on his/her past experiences.
- Anticipate: to predict an event or a result based on current events or past experiences.
- Assert: to state a fact or belief with authority and confidence; to make others believe in one’s authority.
- Burgeon: for something to grow or increase rapidly.
- Attribute: a feature or property which is regarded as a part of something or someone.
- Characteristic: something which is commonly a feature or a quality of a person, place, or a thing.
- Carbohydrate: an organic compound containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen at a ratio of 1:2:1. For example, sugars and starches are the main sources of energy for living beings.
- Catalyst: a substance which speeds up a chemical reaction but does not change the outcomes of the reaction.
- Chlorophyll: the green pigment present in plants which captures light energy for photosynthesis.
- Coherent: logical and consistent with the preceding arguments, theories, or policies.
- Correspond: to agree or correlate with; to communicate by exchanging messages.
- Combustion: a high-temperature reaction involving a fuel and an oxidant (usually oxygen), commonly associated with the process of burning.
- Compose: to be a part of or to make up something; to write or create a work of literature, art, science, etc.
- Compressibility: a measure of the amount of effort it would take to reduce the volume of the matter by applying pressure. Lower compressibility would indicate more effort is required to reduce the volume.
- Conduction and conductivity: conduction is the transmission of energy like heat or electricity. Conductivity is an attribute of a material specifying its efficiency in transferring that energy.
- Conductor: a material which offers minimum resistance to the flow of heat or electricity.
- Contour: the outline which represents the bounding shape of an object or form; to mold something into a specific shape.
- Consecutive: something which is followed in an unbroken or continuous sequence.
- Contradict: to assert the opposite or to deny the truth of a statement.
- Correlate: to have a mutual relationship or connection between two or more things.
- Critical: expressing harsh or disapproving comments or judgments about something; analyzing a work of science, literature, music, etc.; describing a situation or a problem which can be potentially disastrous.
- Decelerate: to slow down, or to reduce the speed (or velocity) of a moving body.
- Deposition: a substance that is naturally deposited somewhere.
- Determine: to find the exact cause and explanation of an event, phenomena, result (in an experiment), etc.
- Diffusion time: the amount of time it takes for molecules or atoms of a material to spread from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration.
- Distinguish: to treat something or recognize it as different.
- Dissoluble: something which can be dissolved into another liquid or aqueous solution.
- Ecology: the field of science which is concerned with relationships between organisms and their environments.
- Efficient: to be able to accomplish a task or a purpose without wasting resources (such as time, energy, money, etc.).
- Electron: a fundamental part of an atom. It is negatively charged.
- Emit: to discharge, generally used in the context of heat, light, radiation, etc.
- Emerge: to become obvious, more prominent, or important.
- Emulsion: a state where one liquid is suspended in another but the two liquids would not dissolve in one another.
- Engage: to make someone or something involved in an event, conversation, or discussion; to participate or get involved in something; to keep someone’s interest.
- Equilibrium: a state where all the constituents of a system (such as reactants in a chemical reaction) are in balance.
- Erode or Erosion: the process of air or water flow removing soil, rock, or material from one location and transporting them to another location.
- Evolve: to develop something gradually; to develop something from a simpler form to more complex forms.
- Exhibit: to make property or a skill visible or apparent.
- Fermentation: the chemical process of breaking something down into simpler substances. For example, when sugar is fermented into alcohol.
- Friction: a force acting between two solid surfaces where the relative motion of the surfaces is resisted.
- Fuse: (verb) to join different objects together; (noun) a safety device used in electrical equipment which breaks the circuit in case more current than desired is drawn into the circuit.
- Gauge: (verb) to estimate or measure a property (such as volume, amount, etc.); (noun) a device which measures a certain property of something.
- Given: information which is specified or stated.
- Habitat: an area where an organism naturally lives in the ecosystem.
- Herbivore: an animal that survives by exclusively eating plants.
- Humidity: the measurement representing the amount of water vapor present in the air.
- Hypothesis: a tentative theory which has not been verified or proven, but tries to explain certain facts or phenomena.
- Imminent: an event which is close to happening; something which is about to happen in a short period.
- Incendiary: something which causes conflicting arguments; a device which is designed to cause and propagate fires.
- Incremental: a quantity which is gradually increasing with discrete additions regularly.
- Indigenous: something which naturally exists in a certain area or is native to that area.
- Infer: to deduce a conclusion not explicitly written in the given evidence and information.
- Infrared radiation: Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths longer than those of visible light (0.7 microns).
- Impervious: something which is immune to any change from another thing (specific or in general).
- Insoluble: something which cannot be dissolved into another liquid or aqueous solution.
- Insulator: the opposite of conductor, a substance which resists the transfer of heat or electricity through it.
- Interval: a deterministic period between two activities or instants.
- Ion: a molecule or an atom which has a positive or negative charge due to losing or gaining one or more electrons
- Kinetic energy: the energy of the motion of an object.
- Latter: the second statement stated of the two previous statements.
- Mass: a measure determined by the amount of matter or energy present in a body, it is the measure of a body’s resistance to acceleration.
- Neutron: a fundamental part of an atom which has no charge.
- Notion: a belief about something, an impulse, or desire.
- Obsolete: something which is no longer of any use, or has a viable replacement which is easier to obtain or function.
- Organic matter: carbon-based compounds found within natural environments and beings.
- Osmosis: the process of liquid moving through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated solution to a more concentrated solution.
- Omit: to exclude some information intentionally or forgetfully; to fail or neglect to do something.
- Precipitation: phenomena of any form of water falling to the ground (in the form of rain, mist, snow, etc.).
- Parasite: an organism which uses another organism as a host and feeds off the host for survival.
- pH: a scale from 1-14 which specifies the concentration of hydrogen ions in an aqueous solution. It represents the alkalinity or acidity of that solution. A pH value of 7 is neutral, lower is acidic, and higher is alkaline.
- Photosynthesis: a process used by plants to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, using energy from sunlight.
- Precede: an event which occurs before another event in time; something which comes before another thing regarding their positions.
- Principle: something which forms the foundation of a system or behavior.
- Proficient: to be well versed and skilled in using a tool or thing.
- Prolong: to increase the duration or the physical space of an event or object.
- Proportionality: the relationship between two distinct quantities or amounts. In “directly proportional” quantities, an increase of one quantity causes the increase of the other quantity. In “indirectly proportional” quantities, increase of one quantity causes the decrease of the other quantity.
- Protein: a compound made up of amino acids which plays several roles in forming the structural components of the body (such as muscles, hair, etc.) within an organism.
- Proton: a fundamental part of the atom which is positively charged.
- Radioactive decay: a naturally occurring process by which an atom spontaneously decays into another atom of a different element.
- Redundant: information which is no longer needed or is of use, usually because it has been stated or deduced earlier.
- Relevant: information which is related or appropriate to the subject or holds some value or interest to the subject being discussed.
- Residual: remaining parts after an activity has been done to an object, or something which was left over.
- Solution: a mixture of two or more substances which is homogeneous (has a uniform mixture and composition).
- Specific gravity: the ratio of the weight of one substance to the weight of a different substance.
- Starch: a complex carbohydrate which forms the energy supply within many vegetables.
- Substrate: a substance which is acted upon by an enzyme; a layer which is underneath another layer.
- Trial: testing the performance or result of an experiment.
- Uniform: something which always shows the same form or manner without variation.
- Variable: a factor which is meant to be changed in an experiment to determine the effects it has on the experiment.
- Vapor: liquid in gaseous state.
- Velocity: the speed and direction of an object’s motion.
- Viscosity: the tendency of a liquid to resist flow. More viscous liquids flow more slowly than less viscous ones.
- Wavelength: the distance between two successive crests of a wave, such as a sound wave or electromagnetic wave.
Looking for ACT® practice?
You can find thousands of practice questions on Albert.io. Albert.io lets you customize your learning experience to target practice where you need the most help. We’ll give you challenging practice questions to help you achieve mastery of the ACT®.
Start practicing here.
Are you a teacher or administrator interested in boosting ACT® student outcomes?
Learn more about our school licenses here.
Interested in a school license?
Bring Albert to your school and empower all teachers with the world’s best question bank for:
➜ SAT® & ACT®
➜ AP®
➜ ELA, Math, Science, & Social Studies
➜ State assessments
Options for teachers, schools, and districts.
Popular Posts