Содержание
- How to Create a Report in Excel
- In This Article
- What to Know
- Creating Basic Charts and Tables for an Excel Report
- Using PivotTables to Generate a Report From an Excel Spreadsheet
- How to Print Your Excel Report
- Create a Project report
- Work with your report
- Change the data in a report
- Example
- Change how a report looks
- Example
- Make your own report
- Share a report
- Make a new report available for future projects
- More ways to report project info
- Create a visual report by using a template
- Edit an existing visual report template
- Create a new visual report template
- Export report data
- Excel
- More about Excel Report options
- Power BI Desktop
- Licensing
How to Create a Report in Excel
Using charts, graphs, and pivot tables makes it easy
In This Article
Jump to a Section
What to Know
- Create a report using charts: Select Insert >Recommended Charts, then choose the one you want to add to the report sheet.
- Create a report with pivot tables: Select Insert >PivotTable. Select the data range you want to analyze in the Table/Range field.
- Print: Go to File >Print, change the orientation to Landscape, scaling to Fit All Columns on One Page, and select Print Entire Workbook.
This article explains how to create a report in Microsoft Excel using key skills like creating basic charts and tables, creating pivot tables, and printing the report. The information in this article applies to Excel 2019, Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2010, and Excel for Mac.
Creating Basic Charts and Tables for an Excel Report
Creating reports usually means collecting information and presenting it all in a single sheet that serves as the report sheet for all of the information. These report sheets should be formatted in a way that’s easy to print as well.
One of the most common tools people use in Excel to create reports is the chart and table tools. To create a chart in an Excel report sheet:
Select Insert from the menu, and in the charts group, select the type of chart you want to add to the report sheet.
In the Chart Design menu, in the Data group, select Select Data.
Select the sheet with the data and select all cells containing the data you want to chart (include headers).
The chart will update in your report sheet with the data. The headers will be used to populate the labels in the two axis.
Repeat the above steps to create new charts and graphs that appropriately represent the data you want to show in your report. When you need to create a new report, you can just paste the new data into the data sheets, and the charts and graphs update automatically.
There are different ways to lay out a report using Excel. You can include graphs and charts on the same page as tabular (numeric) data, or you can create multiple sheets so visual reporting is on one sheet, tabular data is on another sheet, and so on.
Using PivotTables to Generate a Report From an Excel Spreadsheet
Pivot tables are another powerful tool for creating reports in Excel. Pivot tables help with digging more deeply into data.
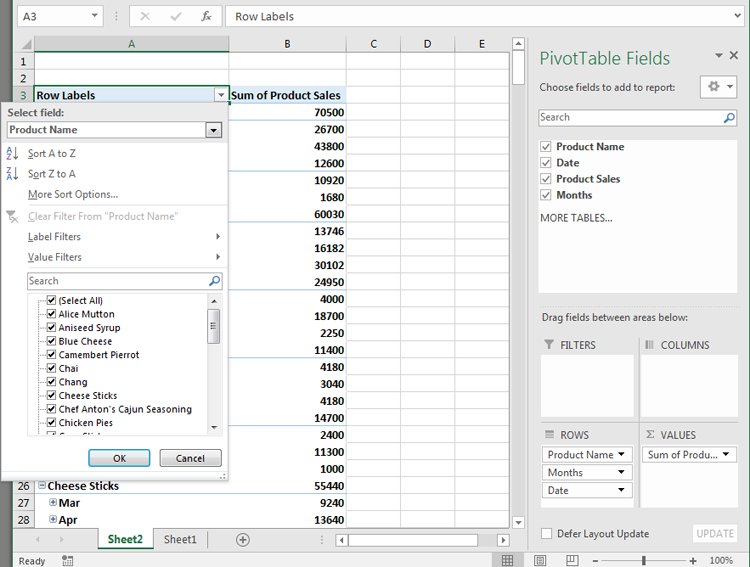
Select the sheet with the data you want to analyze. Select Insert > PivotTable.
In the Create PivotTable dialogue, in the Table/Range field, select the range of data you want to analyze. In the Location field, select the first cell of the worksheet where you want the analysis to go. Select OK to finish.
This will launch the pivot table creation process in the new sheet. In the PivotTable Fields area, the first field you select will be the reference field.
In this example, this pivot table will show website traffic information by month. So, first, you’d select Month.
Next, drag the data fields you want to show data for into the values area of the PivotTable fields pane. You’ll see the data imported from the source sheet into your pivot table.
The pivot table collates all of the data for multiple items by adding them (by default). In this example, you can see which months had the most page views. If you want a different analysis, just select the drop-down arrow next to the item in the Values pane, then select Value Field Settings.
In the Value Field Settings dialog box, change the calculation type to whichever you prefer.
This will update the data in the pivot table accordingly. Using this approach, you can perform any analysis you like on source data, and create pivot charts that display the information in your report in the way you need.
How to Print Your Excel Report
You can generate a printed report from all the sheets you created, but first you need to add page headers.
Select Insert > Text > Header & Footer.
Type the title for the report page, then format it to use larger than normal text. Repeat this process for each report sheet you plan to print.
Next, hide the sheets you don’t want included in the report. To do this, right-click the sheet tab and select Hide.
To print your report, select File > Print. Change orientation to Landscape, and scaling to Fit All Columns on One Page.
Select Print Entire Workbook. Now when you print your report, only the report sheets you created will print as individual pages.
You can either print your report out on paper, or print it as a PDF and send it out as an email attachment.
Open an Excel spreadsheet, turn off gridlines, and enter your basic expense report information, such as a title, time period, and employee name. Add data columns for Date and Description, and then add columns for expense specifics, such as Hotel, Meals, and Phone. Enter your information and create an Excel table.
To use Excel’s scenario manager function, select the cells with the information you’re exploring, and then go to the ribbon and select Data. Select What-If Analysis > Scenario Manager. In the Scenario Manager dialog box, select Add. Name the scenario and change your data to see various outcomes.
In Salesforce, go to Reports and find the report you want to export. Select Export and choose an export view (Formatted Report or Details Only). Formatted Report will export in .xlsx format, while Details Only gives you other choices. Select Export when ready.
Источник
Create a Project report
With Project, you can create and customize striking graphical reports of whatever project data you want, without having to rely on any other software. As you work on the project, the reports change to reflect the latest info — no manual updates required! See a list of all reports and how you can use them.
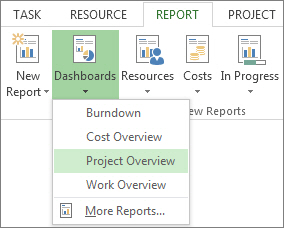
Click the Report tab.
In the View Reports group, click the type of report you want and then pick a specific report.
For example, to open the Project Overview report, click Report > Dashboards > Project Overview.
The Project Overview report combines graphs and tables to show where each phase of the project stands, upcoming milestones, and tasks that are past their due dates.
Project provides dozens of reports you can use right away, but you don’t have to let that limit your choices. You can customize the content and the look of any of the reports, or build a new one from scratch.
Work with your report
Change the data in a report
You can choose the data that Project shows in any part of a report.
Click the table or chart you want to change.
Use the Field list pane on the right of the screen to pick fields to show and filter information.
Tip: When you click a chart, three buttons also pop up directly to the right of the chart. Use the Chart Elements 

Example
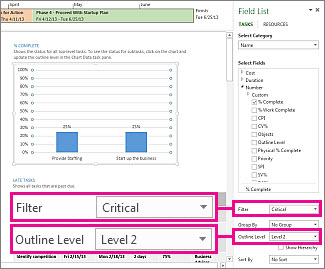
In the Project Overview report, you could change the % Complete chart to show critical subtasks instead of top-level summary tasks:
Click anywhere in the % Complete chart.
In the Field List pane, go to the Filter box and pick Critical.
In the Outline Level box, pick Level 2. For this example, this is the first level of the outline that has subtasks instead of summary tasks.
The chart changes as you make your selections.
Change how a report looks
With Project, you control the look of your reports, from no-nonsense black and white to explosions of colors and effects.
Tip: You can make a report part of a split view so you can see the report change in real time as you work on project data. To learn more, see Split a view.
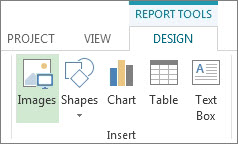
Click anywhere in the report and then click Report Tools Design to see the options for changing the look of the whole report. From this tab, you can change the font, color, or theme of the whole report. You can also add new images (including photos), shapes, charts, or tables here.
When you click individual elements (charts, tables, and so on) of a report, new tabs appear at the top of the screen with options for formatting that part.
Drawing Tools Format tab. Format shapes and text boxes.
Table Tools Design and Table Tools Layout tabs. Configure and tweak tables, like you would in other Office programs.
Chart Tools Design and Chart Tools Format tabs. Configure and tweak charts.
Tip: When you click a chart, three buttons also pop up directly to the right of the chart. Click the Chart Styles button 
Example
Say you decide that the % Complete chart in the Project Overview report needs a facelift.
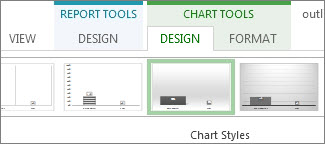
Click anywhere in the % Complete chart, and then click Chart Tools Design.
Pick a new style from the Chart Styles group. This style removes the lines and adds shadows to the columns.
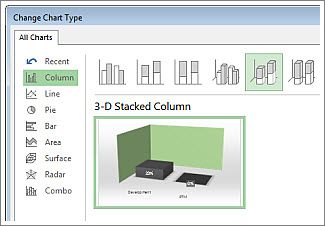
Give the chart some depth. Click Chart Tools Design > Change Chart Type.
Click Column > 3-D Stacked Column.
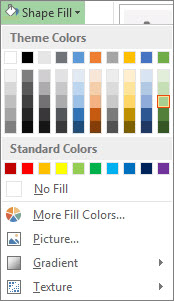
Add a background color. Click Chart Tools Format > Shape Fill, and pick a new color.
Change the bar colors. Click the bars to select them, then click Chart Tools Format > Shape Fill, and pick a new color.
Move the numbers off the bars. Click the numbers to select them, and then drag them upward.
Just a few clicks make a big difference. And we only scratched the surface of the formatting options.
Make your own report
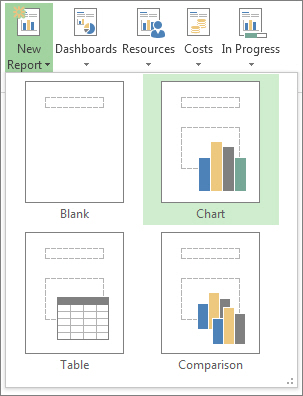
Click Report > New Report.
Pick one of the four options, and then click Select.
Give your report a name and start adding information to it.
Blank Creates a blank canvas. Use the Report Tools Design tab to add charts, tables, text, and images.
Chart Project creates a chart comparing Actual Work, Remaining Work, and Work by default. Use the Field List pane to pick different fields to compare, and use the controls to change the color and format of the chart.
Table Use the Field List pane to choose what fields to display in the table (Name, Start, Finish, and % Complete appear by default). The Outline level box lets you select how many levels in the project outline the table should show. You can change the look of the table on the Table Tools Design and Table Tools Layout tabs.
Comparison Sets two charts side-by-side. The charts have the same data at first. Click one chart and pick the data you want in the Field List pane to begin differentiating them.
Any of the charts you create from scratch are fully customizable. You can add and delete elements and change the data to meet your needs.
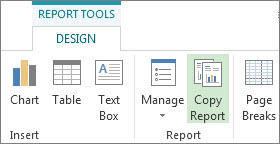
Click anywhere in the report.
Click Report Tools Design > Copy Report.
Paste the report into any program that displays graphics.
Tip: You might need to resize and line up the report when you paste it into its new home.
You can also print the report to share it the old-fashioned way.
Make a new report available for future projects
More ways to report project info
See a list of all reports and how you can use them.
Compare actual work against your estimates with burndown reports.
Create a timeline of key tasks and milestones.
Set the status date for project reporting.
Visual reports allow you to view Project information graphically using enhanced PivotTables in Excel 2010. Once Project information has been exported to Excel, you can customize the reports further with Excel 2010 enhanced PivotTable features, such as filter slicers, searching within PivotTables, sparklines within PivotTables to show trends instantly, and OLAP write-back improvements.
The report templates in Project 2010 are divided into six categories in the Visual Reports — Create Report dialog box, which you can access by clicking Visual Reports in the Reports group of the Project tab. The following sections provide descriptions of the visual reports in each category.
You can also create your own custom reports. Custom reports will appear in the category for the type of data used.
Task Usage category
The following table describes the visual reports in the Task Usage category. These reports are based on timephased task data.
Note: Timephased assignment data is available in reports in the Assignment Usage category.
Cash Flow Report
Use this report to view a bar graph with cost and cumulative cost amounts illustrated over time.
Earned Value Over Time Report
Use this report to view a chart that plots AC (actual cost of work performed), planned value (budgeted cost of work scheduled), and earned value (budgeted cost of work performed) over time.
Resource Usage category
The following table describes the visual reports in the Resource Usage category. These reports are based on the timephased resource data.
Note: Timephased assignment data is available in reports in the Assignment Usage category.
Cash Flow Report
Use this report to view a diagram that shows planned and actual costs for your project over time. Costs are broken down by resource type (work, material, and cost). An indicator shows if planned costs exceed baseline costs.
Resource Availability Report
Use this report to view a diagram that shows the work and remaining availability for your project’s resources, broken down by resource type (work, material, and cost). A red flag is displayed next to each resource that is overallocated.
Resource Cost Summary Report
Use this report to view a pie chart that illustrates the division of resource cost between the three resource types: cost, material, and work.
Resource Work Availability Report
Use this report to view a bar graph with total capacity, work, and remaining availability for work resources illustrated over time.
Resource Work Summary Report
Use this report to view a bar graph with total resource capacity, work, remaining availability, and actual work illustrated in work units.
Assignment Usage category
The following table describes the visual reports in the Assignment Usage category. These reports are based on the timephased data, similar to the data found in the Task Usage and Resource Usage views.
Baseline Cost Report
Use this report to view a bar graph with baseline cost, planned cost, and actual cost for your project illustrated across tasks.
Use this report to view a diagram of your project broken down by quarter, then by task. This report compares planned work and cost to baseline work and cost. Indicators are used to show when planned work exceeds baseline work, and when planned cost exceeds baseline cost.
Baseline Work Report
Use this report to view a bar graph with baseline work, planned work, and actual work for your project illustrated across tasks.
Budget Cost Report
Use this report to view a bar graph with budget cost, baseline cost, planned cost, and actual cost illustrated over time.
Budget Work Report
Use this report to view a bar graph with budget work, baseline work, planned work, and actual work illustrated over time.
Earned Value Over Time Report
Use this report to view a chart that plots AC (actual cost of work performed), planned value (budgeted cost of work scheduled), and earned value (budgeted cost of work performed) over time.
Task, Resource, and Assignment Summary categories
The following table describes the visual reports in the Task Summary, Resource Summary, and Assignment Summary categories. Summary reports do not include timephased data.
Critical Tasks Status Report
Use this report to view a diagram showing the work and remaining work for both critical and non-critical tasks. The data bar indicates the percent of work complete.
Task Status Report
Use this report to view a diagram of the work and percent of work complete for tasks in your project, with symbols indicating when baseline work exceeds work, when baseline work equals work, and when work exceeds baseline work. The data bar indicates the percent of work complete.
Resource Remaining Work Report
Use this report to view a bar graph with remaining work and actual work for each work resource, illustrated in work units.
Resource Status Report
Use this report to view a diagram of the work and cost values for each of your project’s resources. The percent of work complete is indicated by the shading in each of the boxes on the diagram. The shading gets darker as the resource nears completion of the assigned work.
Create a visual report by using a template
On the Project tab, in the Reports group, click Visual Reports.
In the Visual Reports dialog box, on the All tab, click the report that you want to create.
If the report that you want to create is not listed, select the Include report templates from check box, and then click Modify to browse to the location that contains your report.
Tip: If you know which category contains the report, you can click that category’s tab to view a shorter list of reports. If you only want to list reports that open in either Excel or Visio, select or clear the Microsoft Excel or Microsoft Visio check box.
To change the level of usage data included in the report, select Years, Quarters, Months, Weeks, or Days from the Select level of usage data to include in the report list.
Note: By default, Project sets the level of usage data to what it recommends for your project’s size. For most projects, this will be weeks. If you choose to include data at a more detailed level, report performance may be decreased. For best performance, if you are viewing multiple reports for the same project at one time, refrain from changing the data level. If you change the data level, the temporary reporting database stored locally must be recreated. If you don’t need to include usage data in your reports, set the data level to Years for best performance.
Click View to generate the report and open it in Excel or Visio.
Edit an existing visual report template
On the Project tab, in the Reports group, click Visual Reports.
In the Visual Reports dialog box, on the All tab, click the report that you want to edit.
Tip: If you know which category contains the report, you can click that category’s tab to view a shorter list of reports. If you only want to list reports that open in either Excel or Visio, select or clear the Microsoft Excel or Microsoft Visio check boxes.
Click Edit Template.
On the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, click the fields that you want to add or remove from the report, and then click Add, Remove, or Remove All to move fields between the Available Fields and Selected Fields boxes, or between the Available Custom Fields and Selected Custom Fields boxes.
Fields in the Selected Fields and Selected Custom Fields boxes are included in the report.
Click Edit Template to create the report with the modified list of fields.
On the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, some fields are identified as dimensions. It is important to select fewer than six dimensions for your report. If you select more than six dimensions, report performance is significantly decreased.
Not all fields are available in all reports. Some fields are only available in Visio reports, but not in Excel reports.
If you are unable to locate the field you want to include on the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, it may be stored in a different category of data. For example, many fields that you might think of as Task Summary fields are actually Assignment Summary fields.
Create a new visual report template
On the Project tab, in the Reports group, click Visual Reports.
In the Visual Reports dialog box, click New Template.
In the Select Application section, click Excel to create an Excel template, or click Visio (Metric) to create a Visio template.
In the Select Data Type section, select the type of data that you want to use in the report.
To include timephased data, select Task Usage, Resource Usage, or Assignment Usage from the list in the Select Data Type section.
Click Field Picker.
On the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, hold CTRL and click the default Project fields that you want to add to the report in the Available Fields box.
Click Add to move them to the Selected Fields box.
Hold CTRL and click the custom fields that you want to add to the report in the Available Custom Fields box.
Click Add to move them to the Selected Custom Fields box.
If you have the English version of Office Project 2007 installed, you have the option to create a Visio template that uses U.S. units.
To remove a field from the report, on the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, click the field in the Selected Fields or Selected Custom Fields box, and then click Remove. To remove all default or custom fields from the report, click Remove All in the Select Fields or Select Custom Fields section.
Not all fields are available in all reports. Some fields are only available in Visio reports, and not in Excel reports.
If you are unable to locate the field you want to include on the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, it may be stored in a different category of data. For example, many fields that you might think of as Task Summary fields are actually Assignment Summary fields.
On the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, some fields are identified as dimensions. It is important to select fewer than six dimensions for your report. If you select more than six dimensions, report performance is significantly decreased.
When you have finished creating your visual report, you can choose to save it to the default template location (c:Program FilesMicrosoft OfficeTemplates) or to another location on your computer or your network. Templates saved in the default template location automatically appear on the Visual Reports — Create Report dialog box.
If you begin using a different language pack after saving a custom visual report template, the template remains available but is not populated. The original field names are not recognized in the new language and are not included in the report.
Export report data
You can select specific data to export within a category (OLAP cube), or you can export all project data as a reporting database.
Export data as an OLAP cube
On the Project tab, in the Reports group, click Visual Reports.
In the Visual Reports dialog box, click Save Data.
In the Save Reporting Cube section, select the category that contains the type of data that you want to save.
Click Field Picker to modify the fields included in the list of data to export.
On the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, click the fields that you want to add or remove from the list of data to export, and then click Add, Remove, or Remove All to move fields between the Available Fields and Selected Fields boxes, or between the Available Custom Fields and Selected Custom Fields boxes.
Fields in the Selected Fields and Selected Custom Fields boxes are included in the exported data.
Click OK on the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, and then click Save Cube.
Browse to the location where you want to save the cube data, and then click Save.
Cube data is saved as a .cub file.
When accessing cube data with Visio, the .cub file cannot be stored on a network share.
Export data as a reporting database
On the Project tab, in the Reports group, click Visual Reports.
In the Visual Reports dialog box, click Save Data.
Click Save Database.
Browse to the location where you want to save the database, and then click Save.
The data is saved as a Microsoft Office Access database (.mdb) file.
Project for the web offers two main options for reporting: Excel and Power BI Desktop. Excel reporting comes with Microsoft 365, while Power BI Desktop is licensed separately.
Excel
When managing a project in Project for the web, export your project to Excel allows you to:
Create reports and visuals
Send a file containing project details to external stakeholders
Archive copies of your project data for audit and compliance
Print copies of your project
Here’s how to export your project:
Go to project.microsoft.com and open the project you want to export to Excel.
In the top right corner, select the three dots ( . ), then select Export to Excel.
When you see the message » All done! We’ve exported [your project name].» at the bottom of the screen, you can look for your new Excel file where you store your downloads.
When you open the Excel file containing your project, you’ll see a worksheet named «Project tasks» that contains a summary of project-wide information at the top, including its name, project manager, and the start and finish dates, duration, and percent complete for the whole project. You’ll also see what date it was exported. Under that, you’ll see a table of all the information for your project.
More about Excel Report options
Power BI Desktop
Important: You’ll need a Power BI subscription (and a Project subscription in many cases) to use this reporting tool. See the following section for details.
Licensing
To use Power BI reports on Project for the web data, you need to be a licensed user of Power BI Desktop or Power BI Pro. See Power BI Pricing for more information.
To build or customize Power BI reports on Project for the web data, you’ll also need Project Plan 3 (formerly Project Online Professional) or Project Plan 5 (formerly Project Online Premium).
Источник
37
37 people found this article helpful
How to Create a Report in Excel
Using charts, graphs, and pivot tables makes it easy
Updated on September 25, 2022
What to Know
- Create a report using charts: Select Insert > Recommended Charts, then choose the one you want to add to the report sheet.
- Create a report with pivot tables: Select Insert > PivotTable. Select the data range you want to analyze in the Table/Range field.
- Print: Go to File > Print, change the orientation to Landscape, scaling to Fit All Columns on One Page, and select Print Entire Workbook.
This article explains how to create a report in Microsoft Excel using key skills like creating basic charts and tables, creating pivot tables, and printing the report. The information in this article applies to Excel 2019, Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2010, and Excel for Mac.
Creating Basic Charts and Tables for an Excel Report
Creating reports usually means collecting information and presenting it all in a single sheet that serves as the report sheet for all of the information. These report sheets should be formatted in a way that’s easy to print as well.
One of the most common tools people use in Excel to create reports is the chart and table tools. To create a chart in an Excel report sheet:
-
Select Insert from the menu, and in the charts group, select the type of chart you want to add to the report sheet.
-
In the Chart Design menu, in the Data group, select Select Data.
-
Select the sheet with the data and select all cells containing the data you want to chart (include headers).
-
The chart will update in your report sheet with the data. The headers will be used to populate the labels in the two axis.
-
Repeat the above steps to create new charts and graphs that appropriately represent the data you want to show in your report. When you need to create a new report, you can just paste the new data into the data sheets, and the charts and graphs update automatically.
There are different ways to lay out a report using Excel. You can include graphs and charts on the same page as tabular (numeric) data, or you can create multiple sheets so visual reporting is on one sheet, tabular data is on another sheet, and so on.
Using PivotTables to Generate a Report From an Excel Spreadsheet
Pivot tables are another powerful tool for creating reports in Excel. Pivot tables help with digging more deeply into data.
-
Select the sheet with the data you want to analyze. Select Insert > PivotTable.
-
In the Create PivotTable dialogue, in the Table/Range field, select the range of data you want to analyze. In the Location field, select the first cell of the worksheet where you want the analysis to go. Select OK to finish.
-
This will launch the pivot table creation process in the new sheet. In the PivotTable Fields area, the first field you select will be the reference field.
In this example, this pivot table will show website traffic information by month. So, first, you’d select Month.
-
Next, drag the data fields you want to show data for into the values area of the PivotTable fields pane. You’ll see the data imported from the source sheet into your pivot table.
-
The pivot table collates all of the data for multiple items by adding them (by default). In this example, you can see which months had the most page views. If you want a different analysis, just select the drop-down arrow next to the item in the Values pane, then select Value Field Settings.
-
In the Value Field Settings dialog box, change the calculation type to whichever you prefer.
-
This will update the data in the pivot table accordingly. Using this approach, you can perform any analysis you like on source data, and create pivot charts that display the information in your report in the way you need.
How to Print Your Excel Report
You can generate a printed report from all the sheets you created, but first you need to add page headers.
-
Select Insert > Text > Header & Footer.
-
Type the title for the report page, then format it to use larger than normal text. Repeat this process for each report sheet you plan to print.
-
Next, hide the sheets you don’t want included in the report. To do this, right-click the sheet tab and select Hide.
-
To print your report, select File > Print. Change orientation to Landscape, and scaling to Fit All Columns on One Page.
-
Select Print Entire Workbook. Now when you print your report, only the report sheets you created will print as individual pages.
You can either print your report out on paper, or print it as a PDF and send it out as an email attachment.
FAQ
-
How do I create an expense report in Excel?
Open an Excel spreadsheet, turn off gridlines, and enter your basic expense report information, such as a title, time period, and employee name. Add data columns for Date and Description, and then add columns for expense specifics, such as Hotel, Meals, and Phone. Enter your information and create an Excel table.
-
How do I create a scenario summary report in Excel?
To use Excel’s scenario manager function, select the cells with the information you’re exploring, and then go to the ribbon and select Data. Select What-If Analysis > Scenario Manager. In the Scenario Manager dialog box, select Add. Name the scenario and change your data to see various outcomes.
-
How do I export a Salesforce report to Excel?
In Salesforce, go to Reports and find the report you want to export. Select Export and choose an export view (Formatted Report or Details Only). Formatted Report will export in .xlsx format, while Details Only gives you other choices. Select Export when ready.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
Constructing of financial analyses for evaluation of business activity and investment projects. Forming reports and documents forms in Excel for accounts department, marketing department, warehouse facilities, and other structures of the company.
Forming of reports analyses with examples
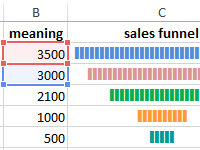
How to make the sales funnel in Excel using formulas, the SmartArt drawing and the Charts tool. The description of different methods with step-by-step instructions and illustrations.
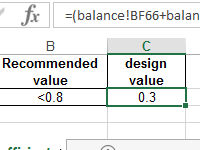
The coefficient of the financial activity shows how much the enterprise depends on borrowed funds. It characterizes financial stability and profitability. How to calculate the indicator by the formula?
The financial and statistical analysis in Excel: automation of calculations. How to analyze the time series and forecast sales, taking into account the trend component and seasonality?
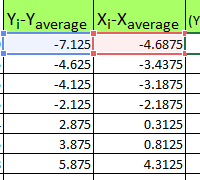
The correlation coefficient (the paired correlation coefficient) allows us to discover the interconnection between the series of values. How to calculate the coefficient of pair correlation? The construction of the correlation matrix.
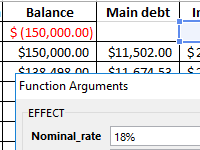
Calculation of the effective interest rate on the loan, leasing and government bonds is performed using the functions EFFECT, IRR, XIRR, FV, etc. Let’s look at examples of how real interest is considered.
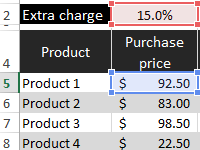
Template for planning the budget of the trading company with the calculation of providing customers discounts. The main advantage is the ability to create loyalty programs with control over the company’s profit. Management of discounts, their impact on margin.
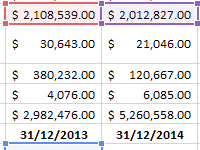
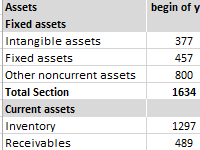
The factor of turnover of receivables shows the rate of conversion of goods sold into the money supply. Formula by balance, calculation of the indicator in days.
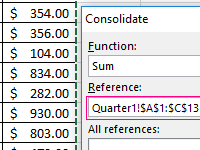
Let’s look at the example of practical work how to do data consolidation. Combining the ranges on different sheets and in different books. Consolidated report using formulas.

In Excel 2016, users will find that they have numerous ways of organizing and visualizing their records. Making use of these options will allow you to put tables and charts together to create reports worthy of praise.
- Basic chart and table creation
- How to create PivotTables
- How to create a Dashboard
- Timelines and Slicers
Basic chart and table creation
Before you can impress your team with an in-depth report, you need to learn how to generate charts, tables, and other visual elements. Here are a few types to get you started.
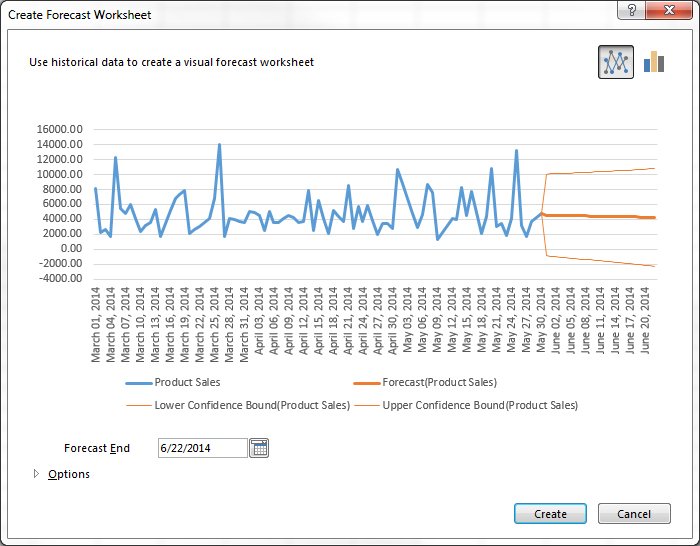
How to create a basic forecast report
- Load a workbook into Excel
- Select the top-left cell in the source data
- Click on Data tab in the navigation ribbon
- Click on Forecast Sheet under the Forecast section to display the Create Forecast Worksheet dialog box
- Choose between a line graph or bar graph
- Choose Forecast end date
- Click Options for customization
- Select Forecast start date
Forecast reports are useful for calculating projections for sales, growth or revenue.
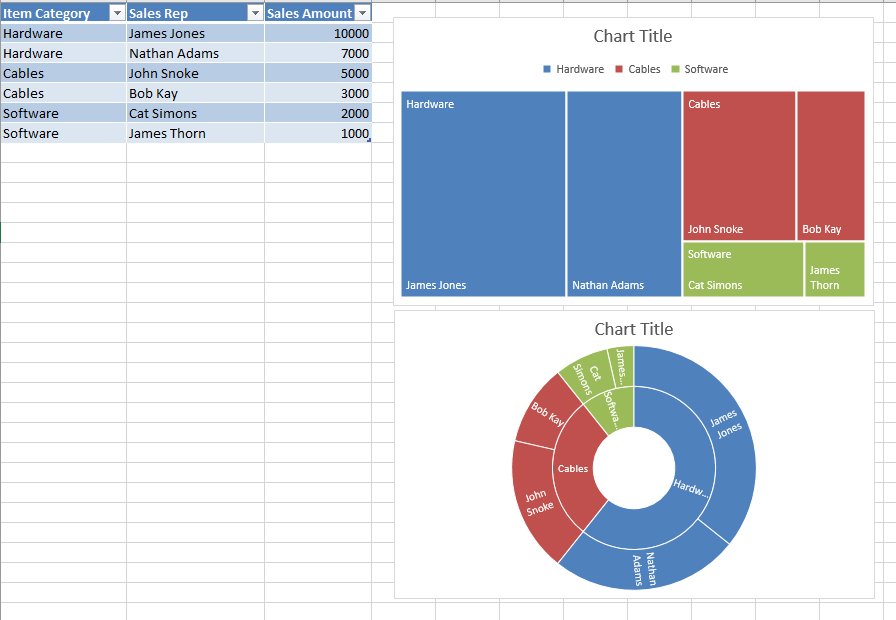
How to create hierarchal charts
- Select a cell inside of the data table
- Click on Insert in the ribbon
- Click Insert Hierarchy Chart under the Charts group
- Select between TreeMap or Sunburst chart
- Click on the + (plus) sign to add or remove chart elements such as title, data labels, and legend
- Click on the right arrow for each element to customize the appearance or behavior
The Charts group itself is an effective way to find the chart that best suits your data. In fact, Excel 2016 has a Recommended Charts option, which allows you to scroll through shortlisted charts or through all available charts.
How to create PivotTables
A PivotTables enable users to sort through and reorganize data in columns and rows in order to find the most effective view. It’s especially useful when you are working with vast amounts of data.
How to create a recommended P{ivotTable
- Select a cell within the table range or source data
- Navigate to the Tables section in the Insert ribbon tab
- Select Recommended PivotTable
- Browse through the presented types of PivotTables
- Click on the PivotTable you want
- Click OK to generate
- Select Seasonality options
- Modify timeline and value ranges
- Select to fill any missing points by zeros or by interpolation
- Select criteria to aggregate duplicates by
- Select Create to finish
How to create your own PivotTable
- Click on a cell within the source data or table range
- Click on the Insert tab in the navigation ribbon
- Select PivotTable in the Tables section to generate the Create PivotTable dialog box
- Decide on the data source in the Choose the data that you want to analyze section, in case you don’t want to use the selected source
- Select New or Existing Worksheet under the Choose where you want the PivotTable to be placed section
- Click Add this data to the Data Model to incorporate additional data sources in the PivotTable
- Click on fields to include in the report in the PivotTable Fields
- Click and drag fields to reside in either Filters, Columns, Rows, and Values
Once you have decided on the layout and contents of your PivotTable fields, you can use it as the foundation for other Pivot Tables.
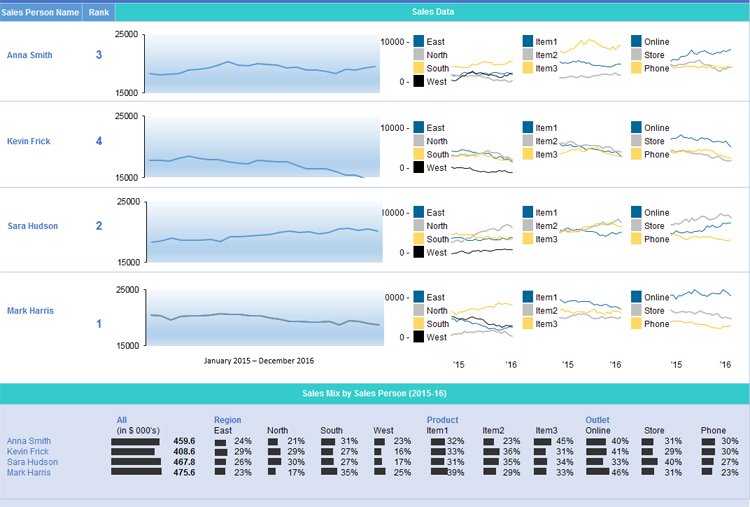
How to create a Dashboard
Once you have become comfortable enough to generate charts and tables using your provided data, it’s time to begin piecing the story together in a dashboard. The Dashboard is your chance to showcase your data in an attractive, informative and insightful hub view. It provides a top-level view of the data, allowing your audience to quickly see data and trends in order to view results and make decisions. This reporting tool is highly adaptable and can be used to report a plethora of results regardless of your line of business.
How to prepare your PivotTables for the Dashboard
- Select the original PivotTable that wish to use as your master or reference table
- Right-click on the selection
- Choose Copy
- Select another cell on your worksheet
- Right-click on the selected cell
- Choose Paste to duplicate
- Repeat steps No. 4 to No. 6 as needed
- Click on PivotTable Tools for each table
- Click Analyze
- Insert a name in the PivotTable Name box to identify the function of each table
How to generate PivotCharts from PivotTables
- Select the original PivotTable
- Click on PivotTable Tools
- Select Analyze
- Select PivotChart
- Choose the type of chart that you need
- Choose formatting options in the PivotChart Tools tab
- Click on Analyze under PivotChart Tools
- Enter a name in the Chart Name box
- Apply steps No. 1 to No. 8 as needed for all PivotTables in use
Timelines and Slicers
With your multiple PivotCharts and PivotTables created, you’ll need to be able to find specific information that supports the details you wish to share in the dashboard. Slicers and Timelines provide a way to filter through the data with ease. Timelines allow you to filter by time to locate a specific period. Slicers are essentially click-to-filter options for PivotTables. Not only do they apply a filter, they also indicate the filter currently in use.
How to add a Slicer
- From a PivotTable click on PivotTable Tools
- Select Analyze
- Select Filter
- Select Insert Slicer
- Select the items to be used as slicers
- Click Ok
- Select a Slicer
- Click on Slicer Tools
- Select Options
- Select Report Connections
- Choose the PivotTables that connect to the chosen Slicer
How to add a Timeline
- Click on a PivotTable
- Select Analyze
- Select Filter
- Select Insert Timeline
- Click on the items to use in the Timeline
- Click on the Timeline
- Select Tools
- Select Options
- Select Report Connections
- Select PivotTables to link the Timeline to
With each resulting chart, you can choose to copy and paste it on your dashboard. You can then decide how the dashboard should appear, what will tell the best story for your report.
This results in a dynamic dashboard that allows recipients to look over your presented data while allowing them to sort through the data to give them customization options pertinent to them. If you are creating a Dashboard to be used on a regular basis, you only need to update the source data to recreate the report with new information.
Wrapping Up
There isn’t one report to rule them all, but Excel has the tools to help you make the report you need. How often do you have to create reports in Excel? Which one are you most proud of? Let us know in the comments. And be sure to visit our Office 101 help hub for more related articles!
- Microsoft Office 101: Help, how-tos and tutorials
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
Download Article
Download Article
This wikiHow teaches you how to automate the reporting of data in Microsoft Excel. For external data, this wikiHow will teach you how to query and create reports from any external data source (MySQL, Postgres, Oracle, etc) from within your worksheet using Excel plugins that link your worksheet to external data sources.
For data already stored in an Excel worksheet, we will use macros to build reports and export them in a variety of file types with the press of one key. Luckily, Excel comes with a built-in step recorder which means you will not have to code the macros yourself.
-
1
If the data you need to report on is already stored, updated, and maintained in Excel, you can automate reporting workflows using Macros. Macros are a built in function that allow you to automate complex and repetitive tasks.
-
2
Open Excel. Double-click (or click if you’re on a Mac) the Excel app icon, which resembles a white «X» on a green background, then click Blank Workbook on the templates page.
- On a Mac, you may have to click File and then click New Blank Workbook in the resulting drop-down menu.
- If you already have an Excel report that you want to automate, you’ll instead double-click the report’s file to open it in Excel.
Advertisement
-
3
Enter your spreadsheet’s data if necessary. If you haven’t added the column labels and numbers for which you want to automate results, do so before proceeding.
-
4
Enable the Developer tab. By default, the Developer tab doesn’t show up at the top of the Excel window. You can enable it by doing the following depending on your operating system:
-
Windows — Click File, click Options, click Customize Ribbon on the left side of the window, check the «Developer» box in the lower-right side of the window (you may first have to scroll down), and click OK.[1]
-
Mac — Click Excel, click Preferences…, click Ribbon & Toolbar, check the «Developer» box in the «Main Tabs» list, and click Save.[2]
-
Windows — Click File, click Options, click Customize Ribbon on the left side of the window, check the «Developer» box in the lower-right side of the window (you may first have to scroll down), and click OK.[1]
-
5
Click Developer. This tab should now be at the top of the Excel window. Doing so brings up a toolbar at the top of the Excel window.
-
6
Click Record Macro. It’s in the toolbar. A pop-up window will appear.
-
7
Enter a name for the macro. In the «Macro name» text box, type in the name for your macro. This will help you identify the macro later.
- For example, if you’re creating a macro that will make a chart out of your available data, you might name it «Chart1» or similar.
-
8
Create a shortcut key combination for the macro. Press the ⇧ Shift key along with another key (e.g., the T key) to create the keyboard shortcut. This is what you’ll use to run your macro later.
- On a Mac, the shortcut key combination will end up being ⌥ Option+⌘ Command and your key (e.g., ⌥ Option+⌘ Command+T).
-
9
Store the macro in the current Excel document. Click the «Store macro in» drop-down box, then click This Workbook to ensure that the macro will be available for anyone who opens the workbook.
- You’ll have to save the Excel file in a special format for the macro to be saved.
-
10
Click OK. It’s at the bottom of the window. Doing so will save your macro settings and place you in record mode. Any steps you take from now until you stop the recording will be recorded.
-
11
Perform the steps that you want to automate. Excel will track every click, keystroke, and formatting option you enter and add them to the macro’s list.
- For example, to select data and create a chart out of it, you would highlight your data, click Insert at the top of the Excel window, click a chart type, click the chart format that you want to use, and edit the chart as needed.
- If you wanted to use the macro to add values from cells A1 through A12, you would click an empty cell, type in =SUM(A1:A12), and press ↵ Enter.
-
12
Click Stop Recording. It’s in the Developer tab’s toolbar. This will stop your recording and save any steps you took during the recording as an individual macro.
-
13
Save your Excel sheet as a macro-enabled file. Click File, click Save As, and change the file format to xlsm instead of xls. You can then enter a file name, select a file location, and click Save.
- If you don’t do this, the macro won’t be saved as part of the spreadsheet, meaning that other people on different computers won’t be able to use your macro if you send the workbook to them.
-
14
Run your macro. Press the key combination which you created as part of the macro to do so. You should see your spreadsheet automate according to your macro’s steps.
- You can also run a macro by clicking Macros in the Developer tab, selecting your macro’s name, and clicking Run.
Advertisement
-
1
Download Kloudio’s Excel plugin from Microsoft AppSource. This will allow you to create a persistent connection between an external database or data source and your workbook. This plugin also works with Google Sheets.
-
2
Create a connection between your worksheet and your external data source by clicking the + button on the Kloudio portal. Type in the details of your database (database type, credentials) and select any security/encryption options if working with confidential or company data.
-
3
Once you’ve created a connection between your worksheet and your database, you will be able to query and build reports from external data without leaving Excel. Create your custom reports from the Kloudio portal and then select them from the drop-down menu in Excel. You can then apply any additional filters and choose the frequency that the report will refresh (so you can have your sales spreadsheet update automatically every week, day, or even hour.)
-
4
In addition, you can also input data into your connected worksheet and have the data update your external data source. Create an upload template from the Kloudio portal and you will be able to manually or automatically upload changes in your spreadsheet to your external data source.
Advertisement
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
-
Only download Excel plugins from Microsoft AppSource, unless you trust the third party provider.
-
Macros can be used for anything from simple tasks (e.g., adding values or creating a chart) to complex ones (e.g., calculating your cell’s values, creating a chart from the results, labeling the chart, and printing the result).
-
When opening a spreadsheet with your macro included, you may have to click Enable Content in a yellow banner at the top of the window before you can use the macro.
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
-
Macros can be used maliciously (e.g., to delete files on your computer). Don’t run macros from untrustworthy sources.
-
Macros will implement literally every step you make while recording. Make sure that you don’t accidentally enter the incorrect value, open a program you don’t want to use, or delete a file.
Advertisement
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Enable the Developer tab.
2. Click the Developer tab.
3. Click Record Macro.
4. Create a shortcut key.
5. Store the content in the current workbook.
6. Click OK.
7. Perform the steps you want to automate.
8. Click Stop Recording.
9. Use the shortcut key to run the same steps.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 543,932 times.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/001-how-to-create-a-report-in-excel-3384b6a8655f46d194f9a6c4e66f8267.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/002-how-to-create-a-report-in-excel-ae2e9c1538e84d9e979d564addf9ef8b.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/003-how-to-create-a-report-in-excel-fb008687c1694cca980abec23c313112.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-create-a-report-in-excel-4691111-4-23f0e5d9ab484e1caa2bd8f05c1e85e6.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-create-a-report-in-excel-4691111-5-db599f2149f54e4c87a2d2a0509c6b71.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/006-how-to-create-a-report-in-excel-e603cd4511e54819bf066fc05ab5301e.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/007-how-to-create-a-report-in-excel-50510dcd3ef44eef804b57df0404a1de.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/008-how-to-create-a-report-in-excel-193e2114b8944b0fb2f2a307f747dc70.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-create-a-report-in-excel-4691111-9-8f7a7e77198d4a14a5594546c0cafdcf.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/010-how-to-create-a-report-in-excel-9274c07370fd4061974b59fd7a5c9b19.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/011-how-to-create-a-report-in-excel-5c74ef47bcee4ed0bc3884e5064c430f.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/012-how-to-create-a-report-in-excel-889c9bba712140278816b0ec1668efdd.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/013-how-to-create-a-report-in-excel-011fb58b22d348dd83c9cbeaf5302440.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/014-how-to-create-a-report-in-excel-7cb2d864bfc44964ae580859bc0c2b76.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/015-how-to-create-a-report-in-excel-0fdfa4a1748a48f1a261ac07e9b9eb81.jpg)