How do I search and replace text in a file using Python 3?
Here is my code:
import os
import sys
import fileinput
print ("Text to search for:")
textToSearch = input( "> " )
print ("Text to replace it with:")
textToReplace = input( "> " )
print ("File to perform Search-Replace on:")
fileToSearch = input( "> " )
#fileToSearch = 'D:dummy1.txt'
tempFile = open( fileToSearch, 'r+' )
for line in fileinput.input( fileToSearch ):
if textToSearch in line :
print('Match Found')
else:
print('Match Not Found!!')
tempFile.write( line.replace( textToSearch, textToReplace ) )
tempFile.close()
input( 'nn Press Enter to exit...' )
Input file:
hi this is abcd hi this is abcd
This is dummy text file.
This is how search and replace works abcd
When I search and replace ‘ram’ by ‘abcd’ in above input file, it works as a charm. But when I do it vice-versa i.e. replacing ‘abcd’ by ‘ram’, some junk characters are left at the end.
Replacing ‘abcd’ by ‘ram’
hi this is ram hi this is ram
This is dummy text file.
This is how search and replace works rambcd
pppery
3,66620 gold badges31 silver badges44 bronze badges
asked Jun 17, 2013 at 5:24
4
As pointed out by michaelb958, you cannot replace in place with data of a different length because this will put the rest of the sections out of place. I disagree with the other posters suggesting you read from one file and write to another. Instead, I would read the file into memory, fix the data up, and then write it out to the same file in a separate step.
# Read in the file
with open('file.txt', 'r') as file :
filedata = file.read()
# Replace the target string
filedata = filedata.replace('abcd', 'ram')
# Write the file out again
with open('file.txt', 'w') as file:
file.write(filedata)
Unless you’ve got a massive file to work with which is too big to load into memory in one go, or you are concerned about potential data loss if the process is interrupted during the second step in which you write data to the file.
mkrieger1
17.7k4 gold badges54 silver badges62 bronze badges
answered Jun 17, 2013 at 6:29
Jack AidleyJack Aidley
19.2k7 gold badges42 silver badges70 bronze badges
14
fileinput already supports inplace editing. It redirects stdout to the file in this case:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import fileinput
with fileinput.FileInput(filename, inplace=True, backup='.bak') as file:
for line in file:
print(line.replace(text_to_search, replacement_text), end='')
Jacktose
6897 silver badges21 bronze badges
answered Dec 15, 2013 at 10:47
jfsjfs
394k191 gold badges973 silver badges1658 bronze badges
24
As Jack Aidley had posted and J.F. Sebastian pointed out, this code will not work:
# Read in the file
filedata = None
with file = open('file.txt', 'r') :
filedata = file.read()
# Replace the target string
filedata.replace('ram', 'abcd')
# Write the file out again
with file = open('file.txt', 'w') :
file.write(filedata)`
But this code WILL work (I’ve tested it):
f = open(filein,'r')
filedata = f.read()
f.close()
newdata = filedata.replace("old data","new data")
f = open(fileout,'w')
f.write(newdata)
f.close()
Using this method, filein and fileout can be the same file, because Python 3.3 will overwrite the file upon opening for write.
answered Apr 5, 2014 at 5:19
NeamerjellNeamerjell
8156 silver badges7 bronze badges
4
You can do the replacement like this
f1 = open('file1.txt', 'r')
f2 = open('file2.txt', 'w')
for line in f1:
f2.write(line.replace('old_text', 'new_text'))
f1.close()
f2.close()
answered Jun 17, 2013 at 5:32
JayramJayram
18.7k6 gold badges51 silver badges68 bronze badges
0
You can also use pathlib.
from pathlib2 import Path
path = Path(file_to_search)
text = path.read_text()
text = text.replace(text_to_search, replacement_text)
path.write_text(text)
Georgy
11.9k7 gold badges68 silver badges72 bronze badges
answered Feb 8, 2019 at 2:24
1
(pip install python-util)
from pyutil import filereplace
filereplace("somefile.txt","abcd","ram")
Will replace all occurences of «abcd» with «ram».
The function also supports regex by specifying regex=True
from pyutil import filereplace
filereplace("somefile.txt","\w+","ram",regex=True)
Disclaimer: I’m the author (https://github.com/MisterL2/python-util)
answered Aug 23, 2019 at 13:43
MisterL2MisterL2
1613 silver badges7 bronze badges
3
Open the file in read mode. Read the file in string format. Replace the text as intended. Close the file. Again open the file in write mode. Finally, write the replaced text to the same file.
try:
with open("file_name", "r+") as text_file:
texts = text_file.read()
texts = texts.replace("to_replace", "replace_string")
with open(file_name, "w") as text_file:
text_file.write(texts)
except FileNotFoundError as f:
print("Could not find the file you are trying to read.")
mkrieger1
17.7k4 gold badges54 silver badges62 bronze badges
answered Apr 16, 2021 at 17:40
SanzvSanzv
911 silver badge2 bronze badges
Late answer, but this is what I use to find and replace inside a text file:
with open("test.txt") as r:
text = r.read().replace("THIS", "THAT")
with open("test.txt", "w") as w:
w.write(text)
DEMO
answered Aug 22, 2020 at 3:35
Pedro LobitoPedro Lobito
92.1k30 gold badges246 silver badges265 bronze badges
2
With a single with block, you can search and replace your text:
with open('file.txt','r+') as f:
filedata = f.read()
filedata = filedata.replace('abc','xyz')
f.truncate(0)
f.write(filedata)
answered Jun 14, 2019 at 13:00
1
Your problem stems from reading from and writing to the same file. Rather than opening fileToSearch for writing, open an actual temporary file and then after you’re done and have closed tempFile, use os.rename to move the new file over fileToSearch.
answered Jun 17, 2013 at 5:43
icktoofayicktoofay
125k21 gold badges248 silver badges230 bronze badges
1
My variant, one word at a time on the entire file.
I read it into memory.
def replace_word(infile,old_word,new_word):
if not os.path.isfile(infile):
print ("Error on replace_word, not a regular file: "+infile)
sys.exit(1)
f1=open(infile,'r').read()
f2=open(infile,'w')
m=f1.replace(old_word,new_word)
f2.write(m)
answered Dec 15, 2013 at 10:19
LiPiLiPi
1791 silver badge5 bronze badges
Using re.subn it is possible to have more control on the substitution process, such as word splitted over two lines, case-(in)sensitive match. Further, it returns the amount of matches which can be used to avoid waste of resources if the string is not found.
import re
file = # path to file
# they can be also raw string and regex
textToSearch = r'Ha.*O' # here an example with a regex
textToReplace = 'hallo'
# read and replace
with open(file, 'r') as fd:
# sample case-insensitive find-and-replace
text, counter = re.subn(textToSearch, textToReplace, fd.read(), re.I)
# check if there is at least a match
if counter > 0:
# edit the file
with open(file, 'w') as fd:
fd.write(text)
# summary result
print(f'{counter} occurence of "{textToSearch}" were replaced with "{textToReplace}".')
Some regex:
- add the
re.Iflag, short form ofre.IGNORECASE, for a case-insensitive match - for multi-line replacement
re.subn(r'n*'.join(textToSearch), textToReplace, fd.read()), depending on the data also'n{,1}'. Notice that for this casetextToSearchmust be a pure string, not a regex!
answered Aug 6, 2022 at 22:47
cardscards
3,7391 gold badge6 silver badges24 bronze badges
Besides the answers already mentioned, here is an explanation of why you have some random characters at the end:
You are opening the file in r+ mode, not w mode. The key difference is that w mode clears the contents of the file as soon as you open it, whereas r+ doesn’t.
This means that if your file content is «123456789» and you write «www» to it, you get «www456789». It overwrites the characters with the new input, but leaves any remaining input untouched.
You can clear a section of the file contents by using truncate(<startPosition>), but you are probably best off saving the updated file content to a string first, then doing truncate(0) and writing it all at once.
Or you can use my library 
answered Dec 15, 2020 at 1:18
MisterL2MisterL2
1613 silver badges7 bronze badges
I got the same issue. The problem is that when you load a .txt in a variable you use it like an array of string while it’s an array of character.
swapString = []
with open(filepath) as f:
s = f.read()
for each in s:
swapString.append(str(each).replace('this','that'))
s = swapString
print(s)
answered Feb 26, 2021 at 13:07
I tried this and used readlines instead of read
with open('dummy.txt','r') as file:
list = file.readlines()
print(f'before removal {list}')
for i in list[:]:
list.remove(i)
print(f'After removal {list}')
with open('dummy.txt','w+') as f:
for i in list:
f.write(i)
answered Mar 2, 2021 at 10:44
you can use sed or awk or grep in python (with some restrictions). Here is a very simple example. It changes banana to bananatoothpaste in the file. You can edit and use it. ( I tested it worked…note: if you are testing under windows you should install «sed» command and set the path first)
import os
file="a.txt"
oldtext="Banana"
newtext=" BananaToothpaste"
os.system('sed -i "s/{}/{}/g" {}'.format(oldtext,newtext,file))
#print(f'sed -i "s/{oldtext}/{newtext}/g" {file}')
print('This command was applied: sed -i "s/{}/{}/g" {}'.format(oldtext,newtext,file))
if you want to see results on the file directly apply: «type» for windows/ «cat» for linux:
####FOR WINDOWS:
os.popen("type " + file).read()
####FOR LINUX:
os.popen("cat " + file).read()
answered Apr 3, 2022 at 15:27
BARIS KURTBARIS KURT
4473 silver badges15 bronze badges
I have done this:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import fileinput
import os
Dir = input ("Source directory: ")
os.chdir(Dir)
Filelist = os.listdir()
print('File list: ',Filelist)
NomeFile = input ("Insert file name: ")
CarOr = input ("Text to search: ")
CarNew = input ("New text: ")
with fileinput.FileInput(NomeFile, inplace=True, backup='.bak') as file:
for line in file:
print(line.replace(CarOr, CarNew), end='')
file.close ()
answered Feb 16, 2017 at 21:26
1
I modified Jayram Singh’s post slightly in order to replace every instance of a ‘!’ character to a number which I wanted to increment with each instance. Thought it might be helpful to someone who wanted to modify a character that occurred more than once per line and wanted to iterate. Hope that helps someone. PS- I’m very new at coding so apologies if my post is inappropriate in any way, but this worked for me.
f1 = open('file1.txt', 'r')
f2 = open('file2.txt', 'w')
n = 1
# if word=='!'replace w/ [n] & increment n; else append same word to
# file2
for line in f1:
for word in line:
if word == '!':
f2.write(word.replace('!', f'[{n}]'))
n += 1
else:
f2.write(word)
f1.close()
f2.close()
answered Sep 24, 2017 at 16:57
def word_replace(filename,old,new):
c=0
with open(filename,'r+',encoding ='utf-8') as f:
a=f.read()
b=a.split()
for i in range(0,len(b)):
if b[i]==old:
c=c+1
old=old.center(len(old)+2)
new=new.center(len(new)+2)
d=a.replace(old,new,c)
f.truncate(0)
f.seek(0)
f.write(d)
print('All words have been replaced!!!')
answered Jan 23, 2018 at 18:45
1
I have worked this out as an exercise of a course: open file, find and replace string and write to a new file.
class Letter:
def __init__(self):
with open("./Input/Names/invited_names.txt", "r") as file:
# read the list of names
list_names = [line.rstrip() for line in file]
with open("./Input/Letters/starting_letter.docx", "r") as f:
# read letter
file_source = f.read()
for name in list_names:
with open(f"./Output/ReadyToSend/LetterTo{name}.docx", "w") as f:
# replace [name] with name of the list in the file
replace_string = file_source.replace('[name]', name)
# write to a new file
f.write(replace_string)
brief = Letter()
Ruli
2,54212 gold badges31 silver badges38 bronze badges
answered Feb 15, 2021 at 16:52
Like so:
def find_and_replace(file, word, replacement):
with open(file, 'r+') as f:
text = f.read()
f.write(text.replace(word, replacement))
answered Jan 17, 2020 at 7:08
2
def findReplace(find, replace):
import os
src = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), os.pardir)
for path, dirs, files in os.walk(os.path.abspath(src)):
for name in files:
if name.endswith('.py'):
filepath = os.path.join(path, name)
with open(filepath) as f:
s = f.read()
s = s.replace(find, replace)
with open(filepath, "w") as f:
f.write(s)
answered Jun 20, 2018 at 10:06
Deepak GDeepak G
6097 silver badges10 bronze badges
In this article, we will learn how we can replace text in a file using python.
Method 1: Searching and replacing text without using any external module
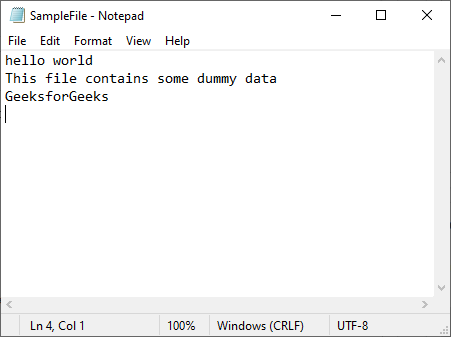
Let see how we can search and replace text in a text file. First, we create a text file in which we want to search and replace text. Let this file be SampleFile.txt with the following contents:
To replace text in a file we are going to open the file in read-only using the open() function. Then we will t=read and replace the content in the text file using the read() and replace() functions.
Syntax: open(file, mode=’r’)
Parameters:
- file : Location of the file
- mode : Mode in which you want toopen the file.
Then we will open the same file in write mode to write the replaced content.
Python3
search_text = "dummy"
replace_text = "replaced"
with open(r'SampleFile.txt', 'r') as file:
data = file.read()
data = data.replace(search_text, replace_text)
with open(r'SampleFile.txt', 'w') as file:
file.write(data)
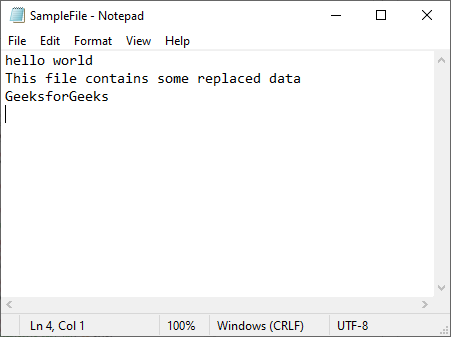
print("Text replaced")
Output:
Text replaced
Method 2: Searching and replacing text using the pathlib2 module
Let see how we can search and replace text using the pathlib2 module. First, we create a Text file in which we want to search and replace text. Let this file be SampleFile.txt with the following contents:
Install pathlib2 module using the below command:
pip install pathlib2
This module offers classes representing filesystem paths with semantics appropriate for different operating systems. To replace the text using pathlib2 module we will use the Path method of pathlib2 module.
Syntax: Path(file)
Parameters:
- file: Location of the file you want to open
In the below code we are replacing “dummy” with “replaced” in our text file. using the pathlib2 module.
Code:
Python3
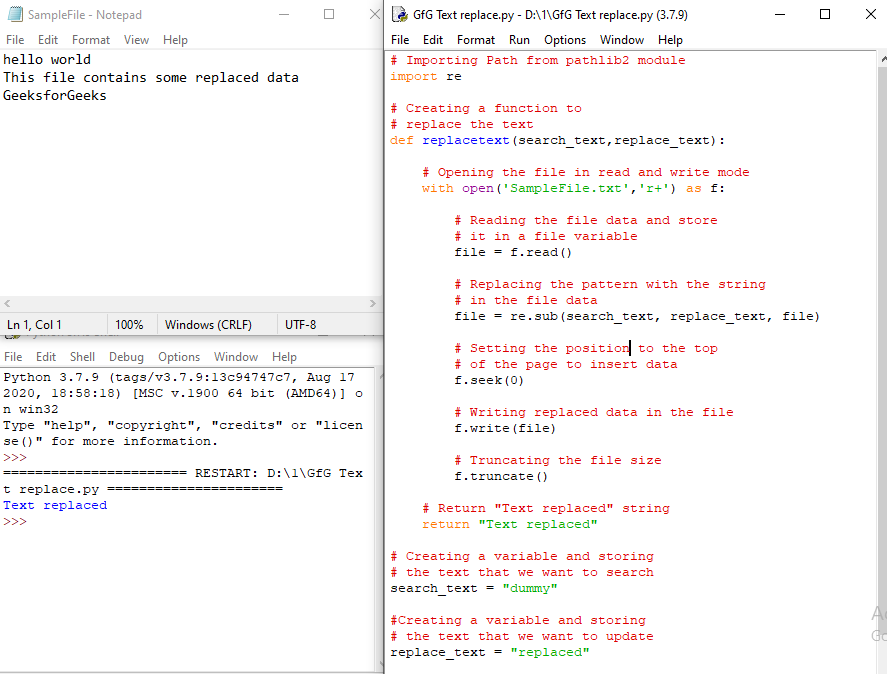
from pathlib2 import Path
def replacetext(search_text, replace_text):
file = Path(r"SampleFile.txt")
data = file.read_text()
data = data.replace(search_text, replace_text)
file.write_text(data)
return "Text replaced"
search_text = "dummy"
replace_text = "replaced"
print(replacetext(search_text, replace_text))
Output:
Text replaced
Method 3: Searching and replacing text using the regex module
Let see how we can search and replace text using the regex module. We are going to use the re.sub( ) method to replace the text.
Syntax: re.sub(pattern, repl, string, count=0, flags=0)
Parameters:
- repl : Text you want to add
- string : Text you want to replace
Code:
Python3
import re
def replacetext(search_text,replace_text):
with open('SampleFile.txt','r+') as f:
file = f.read()
file = re.sub(search_text, replace_text, file)
f.seek(0)
f.write(file)
f.truncate()
return "Text replaced"
search_text = "dummy"
replace_text = "replaced"
print(replacetext(search_text,replace_text))
Output:
Text replaced
Method 4: Using fileinput
Let see how we can search and replace text using the fileinput module. For this, we will use FileInput() method to iterate over the data of the file and replace the text.
Syntax: FileInput(files=None, inplace=False, backup=”, *, mode=’r’)
Parameters:
- files : Location of the text file
- mode : Mode in which you want toopen the file
- inplace : If value is True then the file is moved to a backup file and
- standard output is directed to the input file
- backup : Extension for the backup file
Code:
Python3
from fileinput import FileInput
def replacetext(search_text, replace_text):
with FileInput("SampleFile.txt", inplace=True,
backup='.bak') as f:
for line in f:
print(line.replace(search_text,
replace_text), end='')
return "Text replaced"
search_text = "dummy"
replace_text = "replaced"
print(replacetext(search_text, replace_text))
Output:
Text replaced
In this article, we will learn to search and replace a text of a file in Python. We will use some built-in functions and some custom codes as well. We will replace text, or strings within a file using mentioned ways.
Python provides multiple built-in functions to perform file handling operations. Instead of creating a new modified file, we will search a text from a file and replace it with some other text in the same file. This modifies the file with new data. This will replace all the matching texts within a file and decreases the overhead of changing each word. Let us discuss some of the mentioned ways to search and replace text in a file in Python.
Sample Text File
We will use the below review.text file to modify the contents.
In the movie Ghost
the joke is built on a rock-solid boundation
the movie would still work played perfectly straight
The notion of a ghost-extermination squad taking on
the paramal hordes makes a compelling setup for a big-budget adventure of any stripe
Indeed, the film as it stands frequently allows time to pass without a gag
But then comes the punch line: the characters are funny
And because we’ve been hooked by the story, the humor the characters provide is all the richer.Example: Use replace() to Replace a Text within a File
The below example uses replace() function to modify a string within a file. We use the review.txt file to modify the contents. It searches for the string by using for loop and replaces the old string with a new string.
open(file,'r') — It opens the review.txt file for reading the contents of the file.
strip() — While iterating over the contents of the file, strip() function strips the end-line break.
replace(old,new) — It takes an old string and a new string to replace its arguments.
file.close() — After concatenating the new string and adding an end-line break, it closes the file.
open(file,'w') — It opens the file for writing and overwrites the old file content with new content.
reading_file = open("review.txt", "r")
new_file_content = ""
for line in reading_file:
stripped_line = line.strip()
new_line = stripped_line.replace("Ghost", "Ghostbusters")
new_file_content += new_line +"n"
reading_file.close()
writing_file = open("review.txt", "w")
writing_file.write(new_file_content)
writing_file.close()Output:
Example: Replace a Text using Regex Module
An alternative method to the above-mentioned methods is to use Python’s regex module. The below example imports regex module. It creates a function and passed a file, an old string, and a new string as arguments. Inside the function, we open the file in both read and write mode and read the contents of the file.
compile() — It is used to compile a regular expression pattern and convert it into a regular expression object which can then be used for matching.
escape() — It is used to escape special characters in a pattern.
sub() — It is used to replace a pattern with a string.
#importing the regex module
import re
#defining the replace method
def replace(filePath, text, subs, flags=0):
with open(file_path, "r+") as file:
#read the file contents
file_contents = file.read()
text_pattern = re.compile(re.escape(text), flags)
file_contents = text_pattern.sub(subs, file_contents)
file.seek(0)
file.truncate()
file.write(file_contents)
file_path="review.txt"
text="boundation"
subs="foundation"
#calling the replace method
replace(file_path, text, subs)Output:
FileInput in Python
FileInput is a useful feature of Python for performing various file-related operations. For using FileInput, fileinput module is imported. It is great for throwaway scripts. It is also used to replace the contents within a file. It performs searching, editing, and replacing in a text file. It does not create any new files or overheads.
Syntax-
FileInput(filename, inplace=True, backup='.bak')Parameters-
backup — The backup is an extension for the backup file created before editing.
Example: Search and Replace a Text using FileInput and replace() Function
The below function replaces a text using replace() function.
import fileinput
filename = "review.txt"
with fileinput.FileInput(filename, inplace = True, backup ='.bak') as f:
for line in f:
if("paramal" in line):
print(line.replace("paramal","paranormal"), end ='')
else:
print(line, end ='') Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we learned to search and replace a text, or a string in a file by using several built-in functions such as replace(), regex and FileInput module. We used some custom codes as well. We saw outputs too to differentiate between the examples. Therefore, to search and replace a string in Python user can load the entire file and then replaces the contents in the same file instead of creating a new file and then overwrite the file.
- Используйте функцию
replace(), когда входные и выходные файлы различаются - Используйте функцию
replace(), когда для ввода и вывода используется только один файл

Работа с файлами — важный аспект любого веб-приложения. Python, как и другие языки программирования, поддерживает обработку файлов. Это позволяет программистам иметь дело с файлами и, по сути, выполнять некоторые базовые операции, такие как чтение, запись и некоторые другие параметры обработки файлов для работы с файлами.
Функцию open() можно использовать для открытия файла в программе Python. Файл можно открыть в текстовом или двоичном режиме, который выбирает пользователь. Функция open() имеет несколько режимов, каждый из которых обеспечивает различные варианты доступа к открываемому файлу.
Термин String в Python можно описать как набор символов Unicode, заключенных в одинарные или двойные кавычки. Строки могут содержаться внутри текстовых файлов, которые должны открываться в коде Python.
В этом руководстве будут рассмотрены различные методы замены строки в файле на Python.
Используйте функцию replace(), когда входные и выходные файлы различаются
Метод replace() в Python используется для поиска подстроки и замены ее другой подстрокой.
Функция replace() имеет три параметра, а именно newvalue, oldvalue и count. И oldvalue, и newvalue являются обязательными значениями, и предоставление функции с параметром count необязательно.
В следующем коде используется функция replace() для замены строки в Python, когда входные и выходные файлы различаются.
# the input file
fin = open("f1.txt", "rt")
# the output file which stores result
fout = open("f2.txt", "wt")
# iteration for each line in the input file
for line in fin:
# replacing the string and write to output file
fout.write(line.replace('gode', 'God'))
#closing the input and output files
fin.close()
fout.close()
В выводе приведенного выше кода строка gode в файле будет заменена словом God.
В приведенном выше коде мы одновременно работаем с двумя разными файлами: f1.txt и f2.txt. f1.txt открывается в режиме чтения текста rt и ссылается на end. f2.txt открывается в режиме записи текста wt и ссылается на fout. Затем цикл for повторяется, и при каждом появлении в файле строки gode она заменяется словом God. Затем оба файла закрываются после необходимых операций с помощью функции close().
Используйте функцию replace(), когда для ввода и вывода используется только один файл
В этом методе один и тот же файл используется как для ввода, так и для вывода.
Здесь мы используем оператор with вместе с функцией replace(). Менеджер контекста with выполняет фундаментальную функцию: делает программу короче и читабельнее.
Когда мы используем оператор with с обработкой файлов, файл, который мы открыли в коде Python, не нужно закрывать вручную; он автоматически закрывается после завершения блока with.
Следующий код использует функцию replace() для замены строки в Python, когда входной и выходной файл совпадают.
with open("file1.txt", "rt") as file:
x = file.read()
with open("file1.txt", "wt") as file:
x = x.replace("gode","God")
fin.write(x)
Следующий код принимает file1 как входной и выходной файл. Сначала файл открывается в режиме чтения текста rt, а содержимое файла считывается и сохраняется в переменной. Затем файл закрывается и открывается снова, но уже в режиме записи текста wt. Строка заменяется, и данные записываются в этом режиме, а затем файл закрывается.
Preface
I’m a Network Engineer learning Python, and these are purely my notes. I’m not an expert by any means. Feel free to use any of these examples and improve upon them. Feel free to call me out where things can be done better.
Onward
A common task I need to do is replace words in a file with something else. For example:
hostname $hostname
interface Gig0/1
ip address $ip 255.255.255.252
Where $hostname and $ip should be variables that needs replacing. This post looks at how to accomplish this on the Python interpretor, and via a script file using a Python function.
To keep things relatively simple, I’m only going to perform the replacement on a single file, using a single set of attributes.
Interpretor
Hop into Python
$ python Python 2.7.9 (default, Dec 15 2014, 10:01:34) [GCC 4.2.1 Compatible Apple LLVM 6.0 (clang-600.0.56)] on darwin Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>>
First, I’ll open a text file as ‘t‘ and read it into a string called ‘tempstr‘
>>> t = open('example_template.txt', 'r')
>>> tempstr = t.read()
>>> t.close()
Let’s take a look at this string:
>>> print tempstr Your hostname is: $hostname Your IP address is: $ip Did this work? $answer
The goal is to replace the words starting with a dollar sign ($) with something else. Note that I’m using dollar signs because it makes it easy when doing a find replace. This is not required.
Next I’ll create a dictionary of key/value pairs to be used when replacing variables. We’ll call this dictionary “device_values“
>>> device_values = {
... '$hostname': 'overlaid-router',
... '$ip': '169.254.66.6',
... '$answer': 'yes',
... }
You can see the keys are specified with a dollar sign ($) in front of them. Remember, this has nothing to do with Python, this is simply how I chose to name these keys so they line up with the words I’ll be replacing in my template file.
Now we need to search our string ‘tempstr‘ for the keys found in device_values and replace them with the corresponding values. To accomplish this, we’ll iterate through our dictionary and use the .replace method.
Our current string:
>>> print tempstr Your hostname is: $hostname Your IP address is: $ip Did this work? $answer
Look at each key/value pair in the dictionary and update the tempstr string with the matching key/values
>>> for key,val in device_values.items(): ... tempstr = tempstr.replace(key,val) ...
Our new string:
>>> print tempstr Your hostname is: overlaid-router Your IP address is: 169.254.66.6 Did this work? yes
Perfect!
What is .items?
In case you’re curious, the .items method above returns a list of the dictionaries key/value pairs. Actually, they’re tuples, not dictionaries, but in this case serve the same purpose. Tuples cannot be changed, unlike dictionaries, but we’re not doing any changing here, just reading.
This is required when iterating through a dictionary. You can see the difference here between a simple print of the dictionary and a print of the dictionary items. Notice {} for the dictionary and [()] for the list [] of tuples ().
>>> device_values
{'$ip': '169.254.66.6', '$answer': 'yes', '$hostname': 'overlaid-router'}
>>> device_values.items()
[('$ip', '169.254.66.6'), ('$answer', 'yes'), ('$hostname', 'overlaid-router')]
Python Function to Replace Words
This function will take in two variables: base_text string and device_values dictionary. It will iterate through the dictionary just like the example above and replace words (keys) found in the base_text with corresponding words (values) from the dictionary.
def replace_words(base_text, device_values): for key, val in device_values.items(): base_text = base_text.replace(key, val) return base_text
The dictionary and string are derived via the same means as the first example.
t = open('example_template.txt', 'r')
tempstr = t.read()
t.close()
device_values = {
'$hostname': 'overlaid-router',
'$ip': '169.254.66.6',
'$answer': 'yes',
}
The only difference is how we send these to our function for processing. tempstr will go in as the base_text argument and device will go in as the device_values argument.
>>> output = replace_words(tempstr, device) >>> print output Your hostname is: overlaid-router Your IP address is: 169.254.66.6 Did this work? yes
As a Python script
The .py script below will ask you for three variables. It will open a template file and perform a find and replace, saving a new file called output.txt to your directory.
#!/usr/bin/env python
# This is a simple Python function that will open a text file and perform a find/replace, and save to a new text file.
def replace_words(base_text, device_values):
for key, val in device_values.items():
base_text = base_text.replace(key, val)
return base_text
# Here I'll create an empty dictionary, and prompt the user to enter in the values
device = {}
device["$hostname"] = raw_input("nHostname: ")
device["$ip"] = raw_input("nIP Address: ")
device["$answer"] = raw_input("nDo you like Python? ")
# Open your desired file as 't' and read the lines into string 'tempstr'
t = open('example_template.txt', 'r')
tempstr = t.read()
t.close()
# Using the "replace_words" function, we'll pass in our tempstr to be used as the base,
# and our device_values to be used as replacement.
output = replace_words(tempstr, device)
# Write out the new config file
fout = open('output.txt', 'w')
fout.write(output)
fout.close()
Let’s try it out. Notice I only have 2 files in this directory – my script and the example template
$ ls -l total 16 -rw-r--r--@ 1 vosx staff 87B Jan 28 17:28 example_template.txt -rw-r--r--@ 1 vosx staff 958B Jan 28 19:04 replace_words.py
Run the replace_words script
$ python replace_words.py Hostname: overlaid-router IP Address: 1.1.1.1 Do you like Python? yep
I now have a new file
$ ls -l
total 24
-rw-r--r--@ 1 vosx staff 87B Jan 28 17:28 example_template.txt
-rw-r--r--@ 1 vosx staff 93B Jan 28 19:06 output.txt
-rw-r--r--@ 1 vosx staff 958B Jan 28 19:04 replace_words.py
Let’s take a look
$ more output.txt
Your hostname is: overlaid-router
Your IP address is: 1.1.1.1
Did this work? yep